mirror of
https://github.com/huggingface/trl.git
synced 2025-11-06 06:14:29 +08:00
Compare commits
74 Commits
ci-test-de
...
docs/unify
| Author | SHA1 | Date | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 9bf8db4887 | |||
| 5dfb2db0c1 | |||
| c34de94903 | |||
| 0d5711040e | |||
| 4995b24b24 | |||
| 1cb0161ce7 | |||
| 91e7cdc3b8 | |||
| 800a4d928a | |||
| 6f906d5087 | |||
| 4677cf293e | |||
| 7a9592bc8c | |||
| 7f15a7f629 | |||
| 8b0a3ce7c7 | |||
| d9f9e2b1a9 | |||
| 4e138ab922 | |||
| 43253b2ae4 | |||
| 6f41b18e49 | |||
| 8d64144a23 | |||
| 91e540ce09 | |||
| 7347a10f1d | |||
| 6eb8d46a38 | |||
| 2a6408020b | |||
| bb057d15d9 | |||
| 580c6bb951 | |||
| 41c8ca1ad3 | |||
| 5cefb39fe2 | |||
| 50b96e25a8 | |||
| 3d718df9a9 | |||
| 77e4cd3420 | |||
| 6f8121e477 | |||
| 414cb7dd6d | |||
| ad9d9c927b | |||
| 095544e7a3 | |||
| 06c059bab8 | |||
| f6834206a8 | |||
| 0aef77b4a5 | |||
| 519cdf36eb | |||
| b3bf53f957 | |||
| c26b375ca3 | |||
| a8f70b02e1 | |||
| 1c2322eb7d | |||
| 242de1ee1e | |||
| caaf656271 | |||
| 9925469170 | |||
| 4e9ab9fa6e | |||
| b82a8f401e | |||
| 29fb69f033 | |||
| ac6cea80a3 | |||
| 1e39eb6c5a | |||
| 97830a3cc2 | |||
| d2754185db | |||
| 61bf96cd22 | |||
| b8f23ef3bd | |||
| f8073cba7d | |||
| 55854c8db5 | |||
| 4352074093 | |||
| 928f589746 | |||
| b0889d2188 | |||
| a9d33d052b | |||
| 34fdb6154b | |||
| a23e91c868 | |||
| 5e691d1bf8 | |||
| fa644b1bdf | |||
| fda88c642e | |||
| 2a138c7363 | |||
| 05a1feb050 | |||
| d8543c02b0 | |||
| 23c0062449 | |||
| 47b1aa7757 | |||
| a4872d97a8 | |||
| 3f66564804 | |||
| 9b80e336b3 | |||
| 2819a8f812 | |||
| e1c87e3589 |
70
.github/workflows/tests-experimental.yml
vendored
Normal file
70
.github/workflows/tests-experimental.yml
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,70 @@
|
||||
name: Tests (experimental)
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
pull_request:
|
||||
paths:
|
||||
# Run only when relevant files are modified
|
||||
- "trl/experimental/**"
|
||||
- "tests/experimental/**"
|
||||
|
||||
env:
|
||||
TQDM_DISABLE: 1
|
||||
PYTORCH_CUDA_ALLOC_CONF: "expandable_segments:True"
|
||||
TRL_EXPERIMENTAL_SILENCE: 1
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
check_code_quality:
|
||||
name: Check code quality
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
if: github.event.pull_request.draft == false
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
- name: Set up Python 3.13
|
||||
uses: actions/setup-python@v5
|
||||
with:
|
||||
python-version: 3.13
|
||||
- uses: pre-commit/action@v3.0.1
|
||||
with:
|
||||
extra_args: --all-files
|
||||
|
||||
tests:
|
||||
name: Tests (experimental)
|
||||
runs-on:
|
||||
group: aws-g4dn-2xlarge
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: pytorch/pytorch:2.8.0-cuda12.8-cudnn9-devel
|
||||
options: --gpus all
|
||||
defaults:
|
||||
run:
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Git checkout
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Set up Python 3.13
|
||||
uses: actions/setup-python@v5
|
||||
with:
|
||||
python-version: 3.13
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Install Make and Git
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
apt-get update && apt-get install -y make git curl
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Install uv
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
curl -LsSf https://astral.sh/uv/install.sh | sh
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Create Python virtual environment
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
uv venv
|
||||
uv pip install --upgrade setuptools wheel
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Install dependencies
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
source .venv/bin/activate
|
||||
uv pip install ".[dev]"
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Test with pytest
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
source .venv/bin/activate
|
||||
make test_experimental
|
||||
355
.github/workflows/tests.yml
vendored
355
.github/workflows/tests.yml
vendored
@ -2,6 +2,7 @@ name: Tests
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
push:
|
||||
branches: [ main ]
|
||||
pull_request:
|
||||
paths:
|
||||
# Run only when relevant files are modified
|
||||
@ -11,83 +12,85 @@ on:
|
||||
- "tests/**.py"
|
||||
- "trl/**.py"
|
||||
- "pyproject.toml"
|
||||
# Exclude if only experimental code/tests
|
||||
- "!trl/experimental/**"
|
||||
- "!tests/experimental/**"
|
||||
|
||||
env:
|
||||
TQDM_DISABLE: 1
|
||||
CI_SLACK_CHANNEL: ${{ secrets.CI_PUSH_MAIN_CHANNEL }}
|
||||
PYTORCH_CUDA_ALLOC_CONF: "expandable_segments:True"
|
||||
TRL_EXPERIMENTAL_SILENCE: 1
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
# check_code_quality:
|
||||
# name: Check code quality
|
||||
# runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
# if: github.event.pull_request.draft == false
|
||||
# steps:
|
||||
# - uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
# - name: Set up Python 3.12
|
||||
# uses: actions/setup-python@v5
|
||||
# with:
|
||||
# python-version: 3.12
|
||||
# - uses: pre-commit/action@v3.0.1
|
||||
# with:
|
||||
# extra_args: --all-files
|
||||
#
|
||||
# tests:
|
||||
# name: Tests
|
||||
# strategy:
|
||||
# matrix:
|
||||
# python-version: ['3.9', '3.10', '3.11', '3.12', '3.13']
|
||||
# fail-fast: false
|
||||
# runs-on:
|
||||
# group: aws-g4dn-2xlarge
|
||||
# container:
|
||||
# image: pytorch/pytorch:2.8.0-cuda12.8-cudnn9-devel
|
||||
# options: --gpus all
|
||||
# defaults:
|
||||
# run:
|
||||
# shell: bash
|
||||
# if: github.event.pull_request.draft == false
|
||||
# steps:
|
||||
# - name: Git checkout
|
||||
# uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
#
|
||||
# - name: Set up Python ${{ matrix.python-version }}
|
||||
# uses: actions/setup-python@v5
|
||||
# with:
|
||||
# python-version: ${{ matrix.python-version }}
|
||||
#
|
||||
# - name: Install Make and Git
|
||||
# run: |
|
||||
# apt-get update && apt-get install -y make git curl
|
||||
#
|
||||
# - name: Install uv
|
||||
# run: |
|
||||
# curl -LsSf https://astral.sh/uv/install.sh | sh
|
||||
#
|
||||
# - name: Create Python virtual environment
|
||||
# run: |
|
||||
# uv venv
|
||||
# uv pip install --upgrade setuptools wheel
|
||||
#
|
||||
# - name: Install dependencies
|
||||
# run: |
|
||||
# source .venv/bin/activate
|
||||
# uv pip install ".[dev]"
|
||||
#
|
||||
# - name: Test with pytest
|
||||
# run: |
|
||||
# source .venv/bin/activate
|
||||
# make test
|
||||
#
|
||||
# - name: Post to Slack
|
||||
# if: github.ref == 'refs/heads/main' && always() # Check if the branch is main
|
||||
# uses: huggingface/hf-workflows/.github/actions/post-slack@main
|
||||
# with:
|
||||
# slack_channel: ${{ env.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL }}
|
||||
# title: Results with Python ${{ matrix.python-version }} and latest dependencies
|
||||
# status: ${{ job.status }}
|
||||
# slack_token: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
check_code_quality:
|
||||
name: Check code quality
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
if: github.event.pull_request.draft == false
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
- name: Set up Python 3.12
|
||||
uses: actions/setup-python@v5
|
||||
with:
|
||||
python-version: 3.12
|
||||
- uses: pre-commit/action@v3.0.1
|
||||
with:
|
||||
extra_args: --all-files
|
||||
|
||||
tests:
|
||||
name: Tests
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
python-version: ['3.10', '3.11', '3.12', '3.13']
|
||||
fail-fast: false
|
||||
runs-on:
|
||||
group: aws-g4dn-2xlarge
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: pytorch/pytorch:2.8.0-cuda12.8-cudnn9-devel
|
||||
options: --gpus all
|
||||
defaults:
|
||||
run:
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
if: github.event.pull_request.draft == false
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Git checkout
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Set up Python ${{ matrix.python-version }}
|
||||
uses: actions/setup-python@v5
|
||||
with:
|
||||
python-version: ${{ matrix.python-version }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Install Make and Git
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
apt-get update && apt-get install -y make git curl
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Install uv
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
curl -LsSf https://astral.sh/uv/install.sh | sh
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Create Python virtual environment
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
uv venv
|
||||
uv pip install --upgrade setuptools wheel
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Install dependencies
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
source .venv/bin/activate
|
||||
uv pip install ".[dev]"
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Test with pytest
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
source .venv/bin/activate
|
||||
make test
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Post to Slack
|
||||
if: github.ref == 'refs/heads/main' && always() # Check if the branch is main
|
||||
uses: huggingface/hf-workflows/.github/actions/post-slack@main
|
||||
with:
|
||||
slack_channel: ${{ env.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL }}
|
||||
title: Results with Python ${{ matrix.python-version }} and latest dependencies
|
||||
status: ${{ job.status }}
|
||||
slack_token: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
|
||||
tests_dev:
|
||||
name: Tests with dev dependencies
|
||||
@ -145,109 +148,109 @@ jobs:
|
||||
status: ${{ job.status }}
|
||||
slack_token: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
|
||||
# tests_wo_optional_deps:
|
||||
# name: Tests without optional dependencies
|
||||
# runs-on:
|
||||
# group: aws-g4dn-2xlarge
|
||||
# container:
|
||||
# image: pytorch/pytorch:2.8.0-cuda12.8-cudnn9-devel
|
||||
# options: --gpus all
|
||||
# defaults:
|
||||
# run:
|
||||
# shell: bash
|
||||
# if: github.event.pull_request.draft == false
|
||||
# steps:
|
||||
# - name: Git checkout
|
||||
# uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
#
|
||||
# - name: Set up Python 3.12
|
||||
# uses: actions/setup-python@v5
|
||||
# with:
|
||||
# python-version: '3.12'
|
||||
#
|
||||
# - name: Install Make and Git
|
||||
# run: |
|
||||
# apt-get update && apt-get install -y make git curl
|
||||
#
|
||||
# - name: Install uv
|
||||
# run: |
|
||||
# curl -LsSf https://astral.sh/uv/install.sh | sh
|
||||
#
|
||||
# - name: Create Python virtual environment
|
||||
# run: |
|
||||
# uv venv
|
||||
# uv pip install --upgrade setuptools wheel
|
||||
#
|
||||
# - name: Install dependencies
|
||||
# run: |
|
||||
# source .venv/bin/activate
|
||||
# uv pip install ".[test]"
|
||||
#
|
||||
# - name: Test with pytest
|
||||
# run: |
|
||||
# source .venv/bin/activate
|
||||
# make test
|
||||
#
|
||||
# - name: Post to Slack
|
||||
# if: github.ref == 'refs/heads/main' && always() # Check if the branch is main
|
||||
# uses: huggingface/hf-workflows/.github/actions/post-slack@main
|
||||
# with:
|
||||
# slack_channel: ${{ env.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL }}
|
||||
# title: Results with Python 3.12 without optional dependencies
|
||||
# status: ${{ job.status }}
|
||||
# slack_token: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
#
|
||||
# tests_min_versions:
|
||||
# name: Tests with minimum versions
|
||||
# runs-on:
|
||||
# group: aws-g4dn-2xlarge
|
||||
# container:
|
||||
# image: pytorch/pytorch:2.8.0-cuda12.8-cudnn9-devel
|
||||
# options: --gpus all
|
||||
# defaults:
|
||||
# run:
|
||||
# shell: bash
|
||||
# if: github.event.pull_request.draft == false
|
||||
# steps:
|
||||
# - name: Git checkout
|
||||
# uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
#
|
||||
# - name: Set up Python 3.12
|
||||
# uses: actions/setup-python@v5
|
||||
# with:
|
||||
# python-version: '3.12'
|
||||
#
|
||||
# - name: Install Make and Git
|
||||
# run: |
|
||||
# apt-get update && apt-get install -y make git curl
|
||||
#
|
||||
# - name: Install uv
|
||||
# run: |
|
||||
# curl -LsSf https://astral.sh/uv/install.sh | sh
|
||||
#
|
||||
# - name: Create Python virtual environment
|
||||
# run: |
|
||||
# uv venv
|
||||
# uv pip install --upgrade setuptools wheel
|
||||
#
|
||||
# - name: Install dependencies
|
||||
# run: |
|
||||
# source .venv/bin/activate
|
||||
# uv pip install ".[dev]"
|
||||
# uv pip install accelerate==1.4.0
|
||||
# uv pip install datasets==3.0.0
|
||||
# uv pip install transformers==4.56.1
|
||||
#
|
||||
# - name: Test with pytest
|
||||
# run: |
|
||||
# source .venv/bin/activate
|
||||
# make test
|
||||
#
|
||||
# - name: Post to Slack
|
||||
# if: github.ref == 'refs/heads/main' && always() # Check if the branch is main
|
||||
# uses: huggingface/hf-workflows/.github/actions/post-slack@main
|
||||
# with:
|
||||
# slack_channel: ${{ env.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL }}
|
||||
# title: Results with Python 3.12 and minimum dependencies versions
|
||||
# status: ${{ job.status }}
|
||||
# slack_token: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
tests_wo_optional_deps:
|
||||
name: Tests without optional dependencies
|
||||
runs-on:
|
||||
group: aws-g4dn-2xlarge
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: pytorch/pytorch:2.8.0-cuda12.8-cudnn9-devel
|
||||
options: --gpus all
|
||||
defaults:
|
||||
run:
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
if: github.event.pull_request.draft == false
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Git checkout
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Set up Python 3.12
|
||||
uses: actions/setup-python@v5
|
||||
with:
|
||||
python-version: '3.12'
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Install Make and Git
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
apt-get update && apt-get install -y make git curl
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Install uv
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
curl -LsSf https://astral.sh/uv/install.sh | sh
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Create Python virtual environment
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
uv venv
|
||||
uv pip install --upgrade setuptools wheel
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Install dependencies
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
source .venv/bin/activate
|
||||
uv pip install ".[test]"
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Test with pytest
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
source .venv/bin/activate
|
||||
make test
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Post to Slack
|
||||
if: github.ref == 'refs/heads/main' && always() # Check if the branch is main
|
||||
uses: huggingface/hf-workflows/.github/actions/post-slack@main
|
||||
with:
|
||||
slack_channel: ${{ env.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL }}
|
||||
title: Results with Python 3.12 without optional dependencies
|
||||
status: ${{ job.status }}
|
||||
slack_token: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
|
||||
tests_min_versions:
|
||||
name: Tests with minimum versions
|
||||
runs-on:
|
||||
group: aws-g4dn-2xlarge
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: pytorch/pytorch:2.8.0-cuda12.8-cudnn9-devel
|
||||
options: --gpus all
|
||||
defaults:
|
||||
run:
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
if: github.event.pull_request.draft == false
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Git checkout
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Set up Python 3.12
|
||||
uses: actions/setup-python@v5
|
||||
with:
|
||||
python-version: '3.12'
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Install Make and Git
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
apt-get update && apt-get install -y make git curl
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Install uv
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
curl -LsSf https://astral.sh/uv/install.sh | sh
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Create Python virtual environment
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
uv venv
|
||||
uv pip install --upgrade setuptools wheel
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Install dependencies
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
source .venv/bin/activate
|
||||
uv pip install ".[dev]"
|
||||
uv pip install accelerate==1.4.0
|
||||
uv pip install datasets==3.0.0
|
||||
uv pip install transformers==4.56.1
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Test with pytest
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
source .venv/bin/activate
|
||||
make test
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Post to Slack
|
||||
if: github.ref == 'refs/heads/main' && always() # Check if the branch is main
|
||||
uses: huggingface/hf-workflows/.github/actions/post-slack@main
|
||||
with:
|
||||
slack_channel: ${{ env.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL }}
|
||||
title: Results with Python 3.12 and minimum dependencies versions
|
||||
status: ${{ job.status }}
|
||||
slack_token: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
|
||||
repos:
|
||||
- repo: https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff-pre-commit
|
||||
rev: v0.11.10
|
||||
rev: v0.13.3
|
||||
hooks:
|
||||
- id: ruff-check
|
||||
types_or: [ python, pyi ]
|
||||
|
||||
@ -285,24 +285,6 @@ def replicate_str(string: str, n: int, sep: str = " ") -> str:
|
||||
* **Definite Articles:** Removed definite articles where possible to streamline language. (Eg: Changed "The string to replicate" to "String to replicate")
|
||||
* **Type Annotations:**
|
||||
* Always include type definitions, indicating if a parameter is optional and specifying the default value.
|
||||
* Note that `Optional` means that the value can be `None`, and `*optional*` means that it is not required for the user to pass a value.
|
||||
E.g., for arguments that can't be `None` and aren't required:
|
||||
|
||||
```txt
|
||||
foo (`int`, *optional*, defaults to `4`):
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For arguments that can be `None` and are required:
|
||||
|
||||
```txt
|
||||
foo (`Optional[int]`):
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
for arguments that can be `None` and aren't required (in this case, if the default value is `None`, you can omit it):
|
||||
|
||||
```txt
|
||||
foo (`Optional[int]`, *optional*):
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* **String Defaults:**
|
||||
* Ensured that default string values are wrapped in double quotes:
|
||||
|
||||
2
Makefile
2
Makefile
@ -16,4 +16,4 @@ slow_tests:
|
||||
pytest -m "slow" tests/ $(if $(IS_GITHUB_CI),--report-log "slow_tests.log",)
|
||||
|
||||
test_experimental:
|
||||
pytest -k "experimental"
|
||||
pytest -k "experimental" -n auto -s -v
|
||||
10
README.md
10
README.md
@ -19,11 +19,9 @@
|
||||
|
||||
## 🎉 What's New
|
||||
|
||||
> **✨ OpenAI GPT OSS Support**: TRL now fully supports fine-tuning the latest [OpenAI GPT OSS models](https://huggingface.co/collections/openai/gpt-oss-68911959590a1634ba11c7a4)! Check out the:
|
||||
>
|
||||
> - [OpenAI Cookbook](https://cookbook.openai.com/articles/gpt-oss/fine-tune-transfomers)
|
||||
> - [GPT OSS recipes](https://github.com/huggingface/gpt-oss-recipes)
|
||||
> - [Our example script](https://github.com/huggingface/trl/blob/main/examples/scripts/sft_gpt_oss.py)
|
||||
**OpenEnv Integration:** TRL now supports **[OpenEnv](https://huggingface.co/blog/openenv)**, the open-source framework from Meta for defining, deploying, and interacting with environments in reinforcement learning and agentic workflows.
|
||||
|
||||
Explore how to seamlessly integrate TRL with OpenEnv in our [dedicated documentation](openenv).
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
@ -190,7 +188,7 @@ Example:
|
||||
from trl.experimental.new_trainer import NewTrainer
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Read more in the [Experimental docs](https://huggingface.co/docs/trl/experimental).
|
||||
Read more in the [Experimental docs](https://huggingface.co/docs/trl/experimental_overview).
|
||||
|
||||
## Citation
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -11,8 +11,6 @@
|
||||
title: Dataset Formats
|
||||
- local: paper_index
|
||||
title: Paper Index
|
||||
- local: experimental
|
||||
title: Experimental
|
||||
title: Conceptual Guides
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: clis
|
||||
@ -39,6 +37,8 @@
|
||||
title: Liger Kernel
|
||||
- local: peft_integration
|
||||
title: PEFT
|
||||
- local: rapidfire_integration
|
||||
title: RapidFire AI
|
||||
- local: trackio_integration
|
||||
title: Trackio
|
||||
- local: unsloth_integration
|
||||
@ -53,10 +53,6 @@
|
||||
title: Community Tutorials
|
||||
- local: lora_without_regret
|
||||
title: LoRA Without Regret
|
||||
- local: sentiment_tuning
|
||||
title: Sentiment Tuning
|
||||
- local: multi_adapter_rl
|
||||
title: Multi Adapter RLHF
|
||||
title: Examples
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- sections: # Sorted alphabetically
|
||||
@ -107,6 +103,22 @@
|
||||
title: Others
|
||||
title: API
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: experimental_overview
|
||||
title: Experimental Overview
|
||||
- local: bema_for_reference_model # Sorted alphabetically
|
||||
title: BEMA for Reference Model
|
||||
- local: bco_trainer
|
||||
title: BCO
|
||||
- local: gfpo
|
||||
title: GFPO
|
||||
- local: gold_trainer
|
||||
title: GOLD
|
||||
- local: grpo_with_replay_buffer
|
||||
title: GRPO With Replay Buffer
|
||||
- local: gspo_token
|
||||
title: GSPO-token
|
||||
- local: papo_trainer
|
||||
title: PAPO
|
||||
- local: openenv
|
||||
title: OpenEnv Integration
|
||||
title: Experimental
|
||||
31
docs/source/bema_for_reference_model.md
Normal file
31
docs/source/bema_for_reference_model.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
|
||||
# BEMA for Reference Model
|
||||
|
||||
This feature implements the BEMA algorithm to update the reference model during DPO training.
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from trl.experimental.bema_for_ref_model import BEMACallback, DPOTrainer
|
||||
from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
pref_dataset = load_dataset("trl-internal-testing/zen", "standard_preference", split="train")
|
||||
ref_model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("trl-internal-testing/tiny-Qwen2ForCausalLM-2.5")
|
||||
|
||||
bema_callback = BEMACallback(update_ref_model=True)
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("trl-internal-testing/tiny-Qwen2ForCausalLM-2.5")
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("trl-internal-testing/tiny-Qwen2ForCausalLM-2.5")
|
||||
tokenizer.pad_token = tokenizer.eos_token
|
||||
|
||||
trainer = DPOTrainer(
|
||||
model=model,
|
||||
ref_model=ref_model,
|
||||
train_dataset=pref_dataset,
|
||||
processing_class=tokenizer,
|
||||
callbacks=[bema_callback],
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
trainer.train()
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -132,8 +132,6 @@ preference_example = {
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Conversational datasets are useful for training chat models, but must be converted into a standard format before being used with TRL trainers. This is typically done using chat templates specific to the model being used. For more information, refer to the [Working with conversational datasets in TRL](#working-with-conversational-datasets-in-trl) section.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Tool Calling
|
||||
|
||||
Some chat templates support *tool calling*, which allows the model to interact with external functions—referred to as **tools**—during generation. This extends the conversational capabilities of the model by enabling it to output a `"tool_calls"` field instead of a standard `"content"` message whenever it decides to invoke a tool.
|
||||
@ -405,76 +403,6 @@ Choosing the right dataset type depends on the task you are working on and the s
|
||||
| [`SFTTrainer`] | [Language modeling](#language-modeling) or [Prompt-completion](#prompt-completion) |
|
||||
| [`XPOTrainer`] | [Prompt-only](#prompt-only) |
|
||||
|
||||
> [!TIP]
|
||||
> TRL trainers only support standard dataset formats, [for now](https://github.com/huggingface/trl/issues/2071). If you have a conversational dataset, you must first convert it into a standard format.
|
||||
> For more information on how to work with conversational datasets, refer to the [Working with conversational datasets in TRL](#working-with-conversational-datasets-in-trl) section.
|
||||
|
||||
## Working with conversational datasets in TRL
|
||||
|
||||
Conversational datasets are increasingly common, especially for training chat models. However, some TRL trainers don't support conversational datasets in their raw format. (For more information, see [issue #2071](https://github.com/huggingface/trl/issues/2071).) These datasets must first be converted into a standard format.
|
||||
Fortunately, TRL offers tools to easily handle this conversion, which are detailed below.
|
||||
|
||||
### Converting a conversational dataset into a standard dataset
|
||||
|
||||
To convert a conversational dataset into a standard dataset, you need to *apply a chat template* to the dataset. A chat template is a predefined structure that typically includes placeholders for user and assistant messages. This template is provided by the tokenizer of the model you use.
|
||||
|
||||
For detailed instructions on using chat templating, refer to the [Chat templating section in the `transformers` documentation](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/en/chat_templating).
|
||||
|
||||
In TRL, the method you apply to convert the dataset will vary depending on the task. Fortunately, TRL provides a helper function called [`apply_chat_template`] to simplify this process. Here's an example of how to use it:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import AutoTokenizer
|
||||
from trl import apply_chat_template
|
||||
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("microsoft/Phi-3-mini-128k-instruct")
|
||||
|
||||
example = {
|
||||
"prompt": [{"role": "user", "content": "What color is the sky?"}],
|
||||
"completion": [{"role": "assistant", "content": "It is blue."}]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
apply_chat_template(example, tokenizer)
|
||||
# Output:
|
||||
# {'prompt': '<|user|>\nWhat color is the sky?<|end|>\n<|assistant|>\n', 'completion': 'It is blue.<|end|>\n<|endoftext|>'}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Alternatively, you can use the [`~datasets.Dataset.map`] method to apply the template across an entire dataset:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from datasets import Dataset
|
||||
from trl import apply_chat_template
|
||||
|
||||
dataset_dict = {
|
||||
"prompt": [[{"role": "user", "content": "What color is the sky?"}],
|
||||
[{"role": "user", "content": "Where is the sun?"}]],
|
||||
"completion": [[{"role": "assistant", "content": "It is blue."}],
|
||||
[{"role": "assistant", "content": "In the sky."}]]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
dataset = Dataset.from_dict(dataset_dict)
|
||||
dataset = dataset.map(apply_chat_template, fn_kwargs={"tokenizer": tokenizer})
|
||||
# Output:
|
||||
# {'prompt': ['<|user|>\nWhat color is the sky?<|end|>\n<|assistant|>\n',
|
||||
# '<|user|>\nWhere is the sun?<|end|>\n<|assistant|>\n'],
|
||||
# 'completion': ['It is blue.<|end|>\n<|endoftext|>', 'In the sky.<|end|>\n<|endoftext|>']}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> [!WARNING]
|
||||
> We recommend using the [`apply_chat_template`] function instead of calling `tokenizer.apply_chat_template` directly. Handling chat templates for non-language modeling datasets can be tricky and may result in errors, such as mistakenly placing a system prompt in the middle of a conversation.
|
||||
> For additional examples, see [#1930 (comment)](https://github.com/huggingface/trl/pull/1930#issuecomment-2292908614). The [`apply_chat_template`] is designed to handle these intricacies and ensure the correct application of chat templates for various tasks.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!WARNING]
|
||||
> It's important to note that chat templates are model-specific. For example, if you use the chat template from [meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct](https://huggingface.co/meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct) with the above example, you get a different output:
|
||||
>
|
||||
> ```python
|
||||
> apply_chat_template(example, AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct"))
|
||||
> # Output:
|
||||
> # {'prompt': '<|im_start|>system\nYou are a helpful assistant.<|im_end|>\n<|im_start|>user\nWhat color is the sky?<|im_end|>\n<|im_start|>assistant\n',
|
||||
> # 'completion': 'It is blue.<|im_end|>\n'}
|
||||
> ```
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Always use the chat template associated with the model you're working with. Using the wrong template can lead to inaccurate or unexpected results.
|
||||
|
||||
## Using any dataset with TRL: preprocessing and conversion
|
||||
|
||||
Many datasets come in formats tailored to specific tasks, which might not be directly compatible with TRL. To use such datasets with TRL, you may need to preprocess and convert them into the required format.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -33,12 +33,6 @@ These notebooks are easier to run and are designed for quick experimentation wit
|
||||
| [`sft_qwen_vl.ipynb`](https://github.com/huggingface/trl/tree/main/examples/notebooks/sft_qwen_vl.ipynb) | Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) Qwen3-VL with QLoRA using TRL on free Colab | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/trl/blob/main/examples/notebooks/sft_qwen_vl.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [`grpo_qwen3_vl.ipynb`](https://github.com/huggingface/trl/tree/main/examples/notebooks/grpo_qwen3_vl.ipynb) | GRPO Qwen3-VL with QLoRA using TRL on free Colab | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/trl/blob/main/examples/notebooks/grpo_qwen3_vl.ipynb) |
|
||||
|
||||
Legacy / Older Notebooks
|
||||
|
||||
- [`best_of_n.ipynb`](https://github.com/huggingface/trl/tree/main/examples/notebooks/best_of_n.ipynb): This notebook demonstrates how to use the "Best of N" sampling strategy using TRL when fine-tuning your model with PPO.
|
||||
- [`gpt2-sentiment.ipynb`](https://github.com/huggingface/trl/tree/main/examples/notebooks/gpt2-sentiment.ipynb): This notebook demonstrates how to reproduce the GPT2 imdb sentiment tuning example on a jupyter notebook.
|
||||
- [`gpt2-sentiment-control.ipynb`](https://github.com/huggingface/trl/tree/main/examples/notebooks/gpt2-sentiment-control.ipynb): This notebook demonstrates how to reproduce the GPT2 sentiment control example on a jupyter notebook.
|
||||
|
||||
## Scripts
|
||||
|
||||
Scripts are maintained in the [`trl/scripts`](https://github.com/huggingface/trl/blob/main/trl/scripts) and [`examples/scripts`](https://github.com/huggingface/trl/blob/main/examples/scripts) directories. They show how to use different trainers such as `SFTTrainer`, `PPOTrainer`, `DPOTrainer`, `GRPOTrainer`, and more.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,163 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Experimental Features
|
||||
|
||||
The `trl.experimental` namespace provides a minimal, clearly separated space for fast iteration on new ideas.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!WARNING]
|
||||
> **Stability contract:** Anything under `trl.experimental` may change or be removed in *any* release (including patch versions) without prior deprecation. Do not rely on these APIs for production workloads.
|
||||
|
||||
## Current Experimental Features
|
||||
|
||||
The following modules are currently available under [`trl.experimental`](https://github.com/huggingface/trl/tree/main/trl/experimental).
|
||||
This list is not exhaustive and may change at any time.
|
||||
|
||||
### BEMA for Reference Model
|
||||
|
||||
This feature implements the BEMA algorithm to update the reference model during DPO training.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from trl.experimental.bema_for_ref_model import BEMACallback, DPOTrainer
|
||||
from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
pref_dataset = load_dataset("trl-internal-testing/zen", "standard_preference", split="train")
|
||||
ref_model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("trl-internal-testing/tiny-Qwen2ForCausalLM-2.5")
|
||||
|
||||
bema_callback = BEMACallback(update_ref_model=True)
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("trl-internal-testing/tiny-Qwen2ForCausalLM-2.5")
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("trl-internal-testing/tiny-Qwen2ForCausalLM-2.5")
|
||||
tokenizer.pad_token = tokenizer.eos_token
|
||||
|
||||
trainer = DPOTrainer(
|
||||
model=model,
|
||||
ref_model=ref_model,
|
||||
train_dataset=pref_dataset,
|
||||
processing_class=tokenizer,
|
||||
callbacks=[bema_callback],
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
trainer.train()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### GFPO
|
||||
|
||||
This feature implements the GFPO algorithm to enforce concise reasoning in the model's output generation, as proposed in the paper [Sample More to Think Less: Group Filtered Policy Optimization for Concise Reasoning](https://huggingface.co/papers/2508.09726).
|
||||
|
||||
To activate GFPO in [`GFPOTrainer`]:
|
||||
|
||||
- set `num_remains_in_group` in [`GFPOConfig`]
|
||||
- define a group filter function and set it to `group_filter_func` in [`GFPOTrainer`]. `group_filter_func` will score the `num_generations` completions and The GFPOTrainer filters groups according to their scores to get top `num_remains_in_group` completions as a new group. Model will be trained on the filtered group.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# train_gfpo.py
|
||||
from trl.experimental.gfpo import GFPOConfig, GFPOTrainer
|
||||
|
||||
# dummy group filter to scores the completions based on its indice in group
|
||||
class GroupFilter:
|
||||
def __call__(self, group_completions, group_rewards, **kwargs):
|
||||
group_scores = []
|
||||
for completions, rewards in zip(group_completions, group_rewards):
|
||||
scores = [float(i) for i in range(len(completions))]
|
||||
group_scores.append(scores)
|
||||
return group_scores
|
||||
|
||||
training_args = GFPOConfig(
|
||||
output_dir="Qwen3-0.6B-GFPO",
|
||||
per_device_train_batch_size=4,
|
||||
num_remains_in_group=2,
|
||||
bf16=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
trainer = GFPOTrainer(
|
||||
model="Qwen/Qwen3-0.6B",
|
||||
reward_funcs=...,
|
||||
train_dataset=...,
|
||||
args=training_args,
|
||||
group_filter_func=GroupFilter(),
|
||||
)
|
||||
trainer.train()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### GSPO-token
|
||||
|
||||
In the paper [Group Sequence Policy Optimization](https://huggingface.co/papers/2507.18071), the authors propose a token-level objective variant to GSPO, called GSPO-token. To use GSPO-token, you can use the `GRPOTrainer` class in `trl.experimental.gspo_token`.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from trl.experimental.gspo_token import GRPOTrainer
|
||||
from trl import GRPOConfig
|
||||
|
||||
training_args = GRPOConfig(
|
||||
importance_sampling_level="sequence_token",
|
||||
...
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> [!WARNING]
|
||||
> To leverage GSPO-token, the user will need to provide the per-token advantage \\( \hat{A_{i,t}} \\) for each token \\( t \\) in the sequence \\( i \\) (i.e., make \\( \hat{A_{i,t}} \\) varies with \\( t \\)—which isn't the case here, \\( \hat{A_{i,t}}=\hat{A_{i}} \\)). Otherwise, GSPO-Token gradient is just equivalent to the original GSPO implementation.
|
||||
|
||||
### GRPO With Replay Buffer
|
||||
|
||||
This experimental trainer, trains a model with GRPO but replaces groups (and corresponding completions) that have 0 standard deviation with groups with high rewards and standard deviation that've been used to train a model in prior batches.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Usage
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from trl.experimental.grpo_with_replay_buffer import GRPOWithReplayBufferTrainer
|
||||
from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
|
||||
dataset = load_dataset("trl-internal-testing/zen", "standard_prompt_only", split="train")
|
||||
|
||||
# Guarantee that some rewards have 0 std
|
||||
def custom_reward_func(completions, **kwargs):
|
||||
if torch.rand(1).item() < 0.25:
|
||||
return [0] * len(completions) # simulate some None rewards
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return torch.rand(len(completions)).tolist()
|
||||
|
||||
training_args = GRPOWithReplayBufferConfig(
|
||||
output_dir=self.tmp_dir,
|
||||
learning_rate=1e-4,
|
||||
per_device_train_batch_size=4,
|
||||
num_generations=4,
|
||||
max_completion_length=8,
|
||||
replay_buffer_size=8,
|
||||
report_to="none",
|
||||
)
|
||||
trainer = GRPOTrainer(
|
||||
model="trl-internal-testing/tiny-Qwen2ForCausalLM-2.5",
|
||||
reward_funcs=[custom_reward_func],
|
||||
args=training_args,
|
||||
train_dataset=dataset,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
previous_trainable_params = {n: param.clone() for n, param in trainer.model.named_parameters()}
|
||||
|
||||
trainer.train()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To silence the runtime notice:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
export TRL_EXPERIMENTAL_SILENCE=1
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Promotion Path (Simple)
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Prototype outside the main repo:** Start development in your own fork or a separate repository to iterate quickly.
|
||||
2. **Experimental inclusion:** Once it’s ready for early users, move the idea into `trl.experimental.<feature>`.
|
||||
3. **Improve:** Add tests, a short doc/example, and demonstrate the usage.
|
||||
4. **Promote:** Once the API proves stable and there is clear interest or adoption from the community, move it into `trl.<feature>` (stable module).
|
||||
|
||||
## FAQ
|
||||
|
||||
**Why not just use branches?**
|
||||
Because branches are not shipped to users; experimental code inside the package lets early adopters try things and give feedback.
|
||||
|
||||
**Can these APIs change or vanish without warning?**
|
||||
Yes. Anything inside `trl.experimental` can change or disappear in *any* release.
|
||||
|
||||
**Should I use this in production?**
|
||||
Only if you are fine with updating your code quickly when things change.
|
||||
|
||||
**Will maintainers promptly fix issues in `trl.experimental`?**
|
||||
Not necessarily. The experimental module is a playground for new ideas, and maintainers may not prioritize bug fixes or feature requests there. Issues may remain unresolved until (or unless) the feature graduates to the stable API.
|
||||
31
docs/source/experimental_overview.md
Normal file
31
docs/source/experimental_overview.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
|
||||
# Experimental
|
||||
|
||||
This directory contains a minimal, clearly separated space for fast iteration on new ideas.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!WARNING]
|
||||
> **Stability contract:** Anything under `trl.experimental` may change or be removed in *any* release (including patch versions) without prior deprecation. Do not rely on these APIs for production workloads.
|
||||
|
||||
## Promotion Path (Simple)
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Prototype outside the main repo:** Start development in your own fork or a separate repository to iterate quickly.
|
||||
2. **Experimental inclusion:** Once it’s ready for early users, move the idea into `trl.experimental.<feature>`.
|
||||
3. **Improve:** Add tests, a short doc/example, and demonstrate the usage.
|
||||
4. **Promote:** Once the API proves stable and there is clear interest or adoption from the community, move it into `trl.<feature>` (stable module).
|
||||
|
||||
## FAQ
|
||||
|
||||
**Why not just use branches?**
|
||||
Because branches are not shipped to users; experimental code inside the package lets early adopters try things and give feedback.
|
||||
|
||||
**Can these APIs change or vanish without warning?**
|
||||
Yes. Anything inside `trl.experimental` can change or disappear in *any* release.
|
||||
|
||||
**Should I use this in production?**
|
||||
Only if you are fine with updating your code quickly when things change.
|
||||
|
||||
**Will maintainers promptly fix issues in `trl.experimental`?**
|
||||
Not necessarily. The experimental module is a playground for new ideas, and maintainers may not prioritize bug fixes or feature requests there. Issues may remain unresolved until (or unless) the feature graduates to the stable API.
|
||||
|
||||
**How to silence the runtime notice?**
|
||||
|
||||
Use: `export TRL_EXPERIMENTAL_SILENCE=1`.
|
||||
39
docs/source/gfpo.md
Normal file
39
docs/source/gfpo.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,39 @@
|
||||
# GFPO
|
||||
|
||||
This feature implements the GFPO algorithm to enforce concise reasoning in the model's output generation, as proposed in the paper [Sample More to Think Less: Group Filtered Policy Optimization for Concise Reasoning](https://huggingface.co/papers/2508.09726).
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage
|
||||
|
||||
To activate GFPO in [`GFPOTrainer`]:
|
||||
|
||||
- set `num_remains_in_group` in [`GFPOConfig`]
|
||||
- define a group filter function and set it to `group_filter_func` in [`GFPOTrainer`]. `group_filter_func` will score the `num_generations` completions and The GFPOTrainer filters groups according to their scores to get top `num_remains_in_group` completions as a new group. Model will be trained on the filtered group.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# train_gfpo.py
|
||||
from trl.experimental.gfpo import GFPOConfig, GFPOTrainer
|
||||
|
||||
# dummy group filter to scores the completions based on its indice in group
|
||||
class GroupFilter:
|
||||
def __call__(self, group_completions, group_rewards, **kwargs):
|
||||
group_scores = []
|
||||
for completions, rewards in zip(group_completions, group_rewards):
|
||||
scores = [float(i) for i in range(len(completions))]
|
||||
group_scores.append(scores)
|
||||
return group_scores
|
||||
|
||||
training_args = GFPOConfig(
|
||||
output_dir="Qwen3-0.6B-GFPO",
|
||||
per_device_train_batch_size=4,
|
||||
num_remains_in_group=2,
|
||||
bf16=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
trainer = GFPOTrainer(
|
||||
model="Qwen/Qwen3-0.6B",
|
||||
reward_funcs=...,
|
||||
train_dataset=...,
|
||||
args=training_args,
|
||||
group_filter_func=GroupFilter(),
|
||||
)
|
||||
trainer.train()
|
||||
```
|
||||
120
docs/source/gold_trainer.md
Normal file
120
docs/source/gold_trainer.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,120 @@
|
||||
# General Online Logit Distillation (GOLD) Trainer
|
||||
|
||||
[](https://huggingface.co/models?other=sft,gold)
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
General Online Logit Distillation (GOLD) is an extension of Universal Logit Distillation (ULD) that supports
|
||||
student/teacher pairs with different tokenizers. It aligns the textual spans produced by both tokenizers and merges the
|
||||
associated logits so no completion tokens are dropped. This enables cross-tokenizer knowledge distillation, including
|
||||
mixed model families (for example, LLaMA students with Qwen teachers).
|
||||
|
||||
Key capabilities:
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Cross-tokenizer alignment** – GOLD incrementally decodes the student and teacher tokens, groups passages with the same visible text, and merges probabilities inside each group. This guarantees loss terms are computed over the full completion even when token boundaries differ.
|
||||
2. **Hybrid ULD loss** – when `uld_use_hybrid_loss` is enabled, GOLD compares exact vocabulary matches directly and falls back to the original sorted-probability ULD loss for unmatched tokens. This improves stability for students whose vocabularies only partially overlap with the teacher.
|
||||
3. **Seamless integration with GKD** – GOLD inherits the on-policy vs. off-policy scheduling from the [`GKDTrainer`](./gkd_trainer.md), so you can combine sequence-level KD, generalized JSD, and cross-tokenizer distillation in a single training run.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!NOTE]
|
||||
> GOLD is currently part of the `trl.experimental` namespace. APIs may change without notice while the feature is iterated on.
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage tips
|
||||
|
||||
The [`GOLDTrainer`] subclasses [`SFTTrainer`] and accepts the same datasets as other TRL trainers (lists of ChatML style
|
||||
messages). Important configuration flags on [`GOLDConfig`] include:
|
||||
|
||||
* `use_uld_loss` – toggles Universal Logit Distillation. Set this to `True` for cross-tokenizer setups.
|
||||
* `teacher_tokenizer_name_or_path` – required when `use_uld_loss=True`; GOLD uses the teacher tokenizer to align tokens.
|
||||
* `uld_use_hybrid_loss`, `uld_hybrid_matched_weight`, `uld_hybrid_unmatched_weight` – enables and weights the hybrid
|
||||
matched/unmatched loss.
|
||||
* `beta`, `lmbda`, `seq_kd` – inherited from `GKDConfig`, controlling the generalized JSD interpolation and on-policy
|
||||
sampling ratio.
|
||||
|
||||
A minimal end-to-end example:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
from trl.experimental.gold import GOLDConfig, GOLDTrainer
|
||||
|
||||
train_dataset = load_dataset(
|
||||
"HuggingFaceTB/OpenR1-Math-220k-default-verified",
|
||||
"all",
|
||||
split="train[:1024]",
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
trainer = GOLDTrainer(
|
||||
model="meta-llama/Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct",
|
||||
teacher_model="Qwen/Qwen2.5-0.5B-Instruct",
|
||||
args=GOLDConfig(output_dir="gold-model", use_uld_loss=True, teacher_tokenizer_name_or_path="Qwen/Qwen2.5-0.5B-Instruct"),
|
||||
train_dataset=train_dataset,
|
||||
)
|
||||
trainer.train()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For quick-start workflows you can rely on string identifiers as shown above—the trainer will load the model and tokenizer for you. Explicitly instantiating `AutoModelForCausalLM`, `AutoTokenizer`, or populating `GOLDConfig` is recommended only for advanced use cases where you need fine-grained control over initialization.
|
||||
|
||||
A more explicit setup might look like this when you need to customise model loading, tokenizer settings, or training arguments:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
from trl import GOLDConfig, GOLDTrainer
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
student_name = "meta-llama/Llama-3.2-1B-Instruct"
|
||||
teacher_name = "Qwen/Qwen2.5-0.5B-Instruct"
|
||||
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(student_name)
|
||||
if tokenizer.pad_token is None:
|
||||
tokenizer.pad_token = tokenizer.eos_token
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(student_name)
|
||||
teacher_model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(teacher_name)
|
||||
|
||||
train_dataset = load_dataset(
|
||||
"HuggingFaceTB/Countdown-Task-GOLD",
|
||||
"verified_Qwen2.5-0.5B-Instruct",
|
||||
split="train",
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
training_args = GOLDConfig(
|
||||
output_dir="gold-model",
|
||||
per_device_train_batch_size=1,
|
||||
teacher_model=teacher_name,
|
||||
teacher_tokenizer_name_or_path=teacher_name,
|
||||
use_uld_loss=True,
|
||||
uld_use_hybrid_loss=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
trainer = GOLDTrainer(
|
||||
model=model,
|
||||
teacher_model=teacher_model,
|
||||
args=training_args,
|
||||
processing_class=tokenizer,
|
||||
train_dataset=train_dataset,
|
||||
)
|
||||
trainer.train()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Expected dataset type
|
||||
|
||||
GOLD requires a [conversational](dataset_formats#conversational) [language modeling](dataset_formats#language_modeling) dataset, e.g.:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
{"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "What color is the sky?"},
|
||||
{"role": "assistant", "content": "It is blue."}]}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
`GOLDTrainer` keeps the raw messages so the ChatML collator can construct prompts and completions with the correct
|
||||
boundaries.
|
||||
|
||||
## GOLDTrainer
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] experimental.gold.GOLDTrainer
|
||||
- train
|
||||
- generate_on_policy_outputs
|
||||
- save_model
|
||||
- push_to_hub
|
||||
|
||||
## GOLDConfig
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] experimental.gold.GOLDConfig
|
||||
@ -80,7 +80,7 @@ This approach gives the method its name: **Group Relative Policy Optimization (G
|
||||
> It was shown in the paper [Understanding R1-Zero-Like Training: A Critical Perspective](https://huggingface.co/papers/2503.20783) that scaling by \\( \text{std}(\mathbf{r}) \\) may cause a question-level difficulty bias. You can disable this scaling by setting `scale_rewards=False` in [`GRPOConfig`].
|
||||
|
||||
> [!TIP]
|
||||
> [Part I: Tricks or Traps? A Deep Dive into RL for LLM Reasoning (Lite PPO)](https://huggingface.co/papers/2508.08221) showed that calculating the mean at the local (group) level and the standard deviation at the global (batch) level enables more robust reward shaping. You can use this scaling strategy by setting `scale_rewards="batch"` in [`GRPOConfig`].
|
||||
> As shown in [Part I: Tricks or Traps? A Deep Dive into RL for LLM Reasoning (Lite PPO)](https://huggingface.co/papers/2508.08221), calculating the mean at the local (group) level and the standard deviation at the global (batch) level enables more robust reward shaping. You can use this scaling strategy by setting `scale_rewards="batch"` in [`GRPOConfig`].
|
||||
|
||||
### Estimating the KL divergence
|
||||
|
||||
@ -563,8 +563,14 @@ accelerate launch \
|
||||
|
||||
### Configuration Tips
|
||||
|
||||
> [!WARNING]
|
||||
> VLM training may fail if image tokens are truncated. We highly recommend disabling truncation by setting `max_prompt_length` to `None`.
|
||||
> [!TIP]
|
||||
> For VLMs, truncating may remove image tokens, leading to errors during training. To avoid this, set `max_prompt_length=None` in the [`GRPOConfig`]. This allows the model to process the full sequence length without truncating image tokens.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> ```python
|
||||
> GRPOConfig(max_prompt_length=None, ...)
|
||||
> ```
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Only use `max_prompt_length` when you've verified that truncation won't remove image tokens for the entire dataset.
|
||||
|
||||
- Use LoRA on vision-language projection layers
|
||||
- Enable 4-bit quantization to reduce memory usage
|
||||
|
||||
39
docs/source/grpo_with_replay_buffer.md
Normal file
39
docs/source/grpo_with_replay_buffer.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,39 @@
|
||||
# GRPO With Replay Buffer
|
||||
|
||||
This experimental trainer, trains a model with GRPO but replaces groups (and corresponding completions) that have 0 standard deviation with groups with high rewards and standard deviation that've been used to train a model in prior batches.
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from trl.experimental.grpo_with_replay_buffer import GRPOWithReplayBufferTrainer
|
||||
from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
|
||||
dataset = load_dataset("trl-internal-testing/zen", "standard_prompt_only", split="train")
|
||||
|
||||
# Guarantee that some rewards have 0 std
|
||||
def custom_reward_func(completions, **kwargs):
|
||||
if torch.rand(1).item() < 0.25:
|
||||
return [0] * len(completions) # simulate some None rewards
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return torch.rand(len(completions)).tolist()
|
||||
|
||||
training_args = GRPOWithReplayBufferConfig(
|
||||
output_dir=self.tmp_dir,
|
||||
learning_rate=1e-4,
|
||||
per_device_train_batch_size=4,
|
||||
num_generations=4,
|
||||
max_completion_length=8,
|
||||
replay_buffer_size=8,
|
||||
report_to="none",
|
||||
)
|
||||
trainer = GRPOTrainer(
|
||||
model="trl-internal-testing/tiny-Qwen2ForCausalLM-2.5",
|
||||
reward_funcs=[custom_reward_func],
|
||||
args=training_args,
|
||||
train_dataset=dataset,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
previous_trainable_params = {n: param.clone() for n, param in trainer.model.named_parameters()}
|
||||
|
||||
trainer.train()
|
||||
```
|
||||
18
docs/source/gspo_token.md
Normal file
18
docs/source/gspo_token.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,18 @@
|
||||
# GSPO-token
|
||||
|
||||
In the paper [Group Sequence Policy Optimization](https://huggingface.co/papers/2507.18071), the authors propose a token-level objective variant to GSPO, called GSPO-token. To use GSPO-token, you can use the `GRPOTrainer` class in `trl.experimental.gspo_token`.
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from trl.experimental.gspo_token import GRPOTrainer
|
||||
from trl import GRPOConfig
|
||||
|
||||
training_args = GRPOConfig(
|
||||
importance_sampling_level="sequence_token",
|
||||
...
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> [!WARNING]
|
||||
> To leverage GSPO-token, the user will need to provide the per-token advantage \\( \hat{A_{i,t}} \\) for each token \\( t \\) in the sequence \\( i \\) (i.e., make \\( \hat{A_{i,t}} \\) varies with \\( t \\)—which isn't the case here, \\( \hat{A_{i,t}}=\hat{A_{i}} \\)). Otherwise, GSPO-Token gradient is just equivalent to the original GSPO implementation.
|
||||
@ -7,10 +7,16 @@
|
||||
TRL is a full stack library where we provide a set of tools to train transformer language models with methods like Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT), Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO), Direct Preference Optimization (DPO), Reward Modeling, and more.
|
||||
The library is integrated with 🤗 [transformers](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers).
|
||||
|
||||
Below is the current list of TRL trainers, organized by method type (⚡️ = vLLM support; 🧪 = experimental).
|
||||
## 🎉 What's New
|
||||
|
||||
**OpenEnv Integration:** TRL now supports **[OpenEnv](https://huggingface.co/blog/openenv)**, the open-source framework from Meta for defining, deploying, and interacting with environments in reinforcement learning and agentic workflows.
|
||||
|
||||
Explore how to seamlessly integrate TRL with OpenEnv in our [dedicated documentation](openenv).
|
||||
|
||||
## Taxonomy
|
||||
|
||||
Below is the current list of TRL trainers, organized by method type (⚡️ = vLLM support; 🧪 = experimental).
|
||||
|
||||
<div style="display: flex; justify-content: space-between; width: 100%; gap: 2rem;">
|
||||
<div style="flex: 1; min-width: 0;">
|
||||
|
||||
@ -47,14 +53,6 @@ Below is the current list of TRL trainers, organized by method type (⚡️ = vL
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
## 🎉 What's New
|
||||
|
||||
**✨ OpenAI GPT OSS Support**: TRL now fully supports fine-tuning the latest [OpenAI GPT OSS models](https://huggingface.co/collections/openai/gpt-oss-68911959590a1634ba11c7a4)! Check out the:
|
||||
|
||||
- [OpenAI Cookbook](https://cookbook.openai.com/articles/gpt-oss/fine-tune-transfomers)
|
||||
- [GPT OSS recipes](https://github.com/huggingface/gpt-oss-recipes)
|
||||
- [Our example script](https://github.com/huggingface/trl/blob/main/examples/scripts/sft_gpt_oss.py)
|
||||
|
||||
You can also explore TRL-related models, datasets, and demos in the [TRL Hugging Face organization](https://huggingface.co/trl-lib).
|
||||
|
||||
## Learn
|
||||
@ -76,6 +74,11 @@ The documentation is organized into the following sections:
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="mt-10">
|
||||
<div class="w-full flex flex-col space-y-4 md:space-y-0 md:grid md:grid-cols-2 md:gap-y-4 md:gap-x-5">
|
||||
<a class="!no-underline border dark:border-gray-700 p-5 rounded-lg shadow hover:shadow-lg" href="https://huggingface.co/blog/trl-vlm-alignment">
|
||||
<img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/huggingface/blog/main/assets/openenv/thumbnail.png" alt="thumbnail" class="mt-0">
|
||||
<p class="text-gray-500 text-sm">Published October 23, 2025</p>
|
||||
<p class="text-gray-700">Building the Open Agent Ecosystem Together: Introducing OpenEnv</p>
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a class="!no-underline border dark:border-gray-700 p-5 rounded-lg shadow hover:shadow-lg" href="https://huggingface.co/blog/trl-vlm-alignment">
|
||||
<img src="https://raw.githubusercontent.com/huggingface/blog/main/assets/trl_vlm/thumbnail.png" alt="thumbnail" class="mt-0">
|
||||
<p class="text-gray-500 text-sm">Published on August 7, 2025</p>
|
||||
@ -133,3 +136,15 @@ The documentation is organized into the following sections:
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
## Talks
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="mt-10">
|
||||
<div class="w-full flex flex-col space-y-4 md:space-y-0 md:grid md:grid-cols-2 md:gap-y-4 md:gap-x-5">
|
||||
<a class="!no-underline border dark:border-gray-700 p-5 rounded-lg shadow hover:shadow-lg" href="https://huggingface.co/datasets/trl-lib/documentation-images/resolve/main/Fine%20tuning%20with%20TRL%20(Oct%2025).pdf">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/trl-lib/documentation-images/resolve/main/Fine%20tuning%20with%20TRL%20(Oct%2025).png" alt="thumbnail" class="mt-0">
|
||||
<p class="text-gray-500 text-sm">Talk given on October 30, 2025</p>
|
||||
<p class="text-gray-700">Fine tuning with TRL</p>
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,8 +1,5 @@
|
||||
# Liger Kernel Integration
|
||||
|
||||
> [!WARNING]
|
||||
> Section under construction. Feel free to contribute!
|
||||
|
||||
[Liger Kernel](https://github.com/linkedin/Liger-Kernel) is a collection of Triton kernels designed specifically for LLM training. It can effectively increase multi-GPU training throughput by 20% and reduce memory usage by 60%. That way, we can **4x** our context length, as described in the benchmark below. They have implemented Hugging Face compatible `RMSNorm`, `RoPE`, `SwiGLU`, `CrossEntropy`, `FusedLinearCrossEntropy`, with more to come. The kernel works out of the box with [FlashAttention](https://github.com/Dao-AILab/flash-attention), [PyTorch FSDP](https://pytorch.org/tutorials/intermediate/FSDP_tutorial.html), and [Microsoft DeepSpeed](https://github.com/microsoft/DeepSpeed).
|
||||
|
||||
With this memory reduction, you can potentially turn off `cpu_offloading` or gradient checkpointing to further boost the performance.
|
||||
@ -11,19 +8,71 @@ With this memory reduction, you can potentially turn off `cpu_offloading` or gra
|
||||
| --- | --- |
|
||||
| 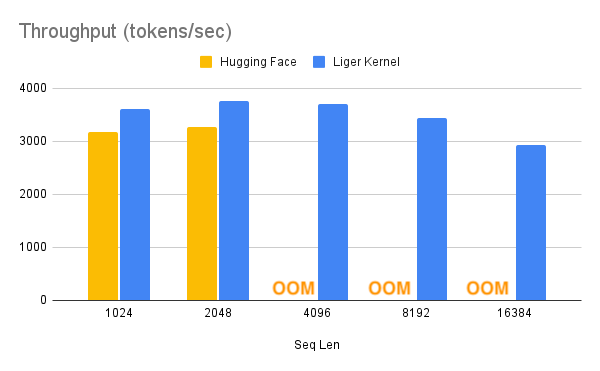 | 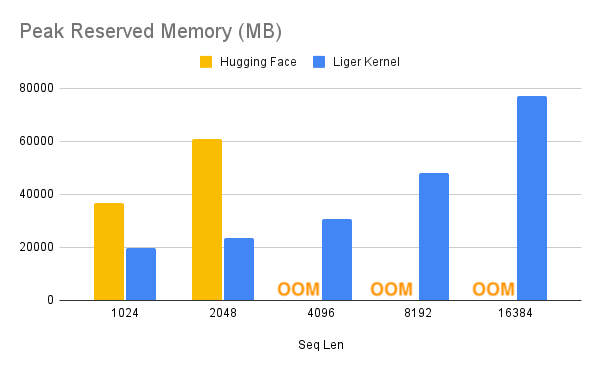 |
|
||||
|
||||
1. To use Liger-Kernel in [`SFTTrainer`], first install it by:
|
||||
|
||||
## Supported Trainers
|
||||
|
||||
Liger Kernel is supported in the following TRL trainers:
|
||||
- **SFT** (Supervised Fine-Tuning)
|
||||
- **DPO** (Direct Preference Optimization)
|
||||
- **GRPO** (Group Relative Policy Optimization)
|
||||
- **KTO** (Kahneman-Tversky Optimization)
|
||||
- **GKD** (Generalized Knowledge Distillation)
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage
|
||||
|
||||
1. First, install Liger Kernel:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install liger-kernel
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. Once installed, set `use_liger_kernel` in [`SFTConfig`]. No other changes are needed!
|
||||
2. Once installed, set `use_liger_kernel=True` in your trainer config. No other changes are needed!
|
||||
|
||||
<hfoptions id="liger">
|
||||
<hfoption id="SFT">
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
training_args = SFTConfig(
|
||||
use_liger_kernel=True,
|
||||
...
|
||||
)
|
||||
from trl import SFTConfig
|
||||
|
||||
training_args = SFTConfig(..., use_liger_kernel=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="DPO">
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from trl import DPOConfig
|
||||
|
||||
training_args = DPOConfig(..., use_liger_kernel=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="GRPO">
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from trl import GRPOConfig
|
||||
|
||||
training_args = GRPOConfig(..., use_liger_kernel=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="KTO">
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from trl import KTOConfig
|
||||
|
||||
training_args = KTOConfig(..., use_liger_kernel=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="GKD">
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from trl import GKDConfig
|
||||
|
||||
training_args = GKDConfig(..., use_liger_kernel=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
</hfoptions>
|
||||
|
||||
To learn more about Liger-Kernel, visit their [official repository](https://github.com/linkedin/Liger-Kernel/).
|
||||
|
||||
@ -141,7 +141,7 @@ For reinforcement learning, the blog uses a math reasoning task that we can repr
|
||||
```python
|
||||
def strip_reasoning_accuracy_reward(
|
||||
completions: list[list[dict[str, str]]], solution: list[str], **kwargs
|
||||
) -> list[Optional[float]]:
|
||||
) -> list[float | None]:
|
||||
"""Reward function that strips reasoning tags and checks mathematical accuracy.
|
||||
|
||||
This function:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,102 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Multi Adapter RL (MARL) - a single base model for everything
|
||||
|
||||
Here we present an approach that uses a single base model for the entire PPO algorithm - which includes retrieving the reference logits, computing the active logits and the rewards. This feature is experimental as we did not test the convergence of the approach. We encourage the community to let us know if they potentially face issues.
|
||||
|
||||
## Requirements
|
||||
|
||||
You just need to install `peft` and optionally install `bitsandbytes` as well if you want to go for 8bit base models, for more memory efficient finetuning.
|
||||
|
||||
## Summary
|
||||
|
||||
You need to address this approach in three stages that we summarize as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
1- Train a base model on the target domain (e.g. [IMDB dataset](https://huggingface.co/datasets/stanfordnlp/imdb)) - this is the Supervised Fine Tuning stage - it can leverage the `SFTTrainer` from TRL.
|
||||
2- Train a reward model using `peft`. This is required in order to re-use the adapter during the RL optimisation process (step 3 below). We show an example of leveraging the `RewardTrainer` from TRL in [this example](https://github.com/huggingface/trl/tree/main/examples/scripts/reward_modeling.py)
|
||||
3- Fine tune new adapters on the base model using PPO and the reward adapter. ("0 abstraction RL")
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to use the same model (i.e. same architecture and same weights) for the stages 2 & 3.
|
||||
|
||||
## Quickstart
|
||||
|
||||
Let us assume you have trained your reward adapter on `llama-7b` model using `RewardTrainer` and pushed the weights on the hub under `trl-lib/llama-7b-hh-rm-adapter`.
|
||||
When doing PPO, before passing the model to `PPOTrainer` create your model as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
model_name = "huggyllama/llama-7b"
|
||||
rm_adapter_id = "trl-lib/llama-7b-hh-rm-adapter"
|
||||
|
||||
# PPO adapter
|
||||
lora_config = LoraConfig(
|
||||
r=16,
|
||||
lora_alpha=32,
|
||||
lora_dropout=0.05,
|
||||
bias="none",
|
||||
task_type="CAUSAL_LM",
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLMWithValueHead.from_pretrained(
|
||||
model_name,
|
||||
peft_config=lora_config,
|
||||
reward_adapter=rm_adapter_id,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
...
|
||||
trainer = PPOTrainer(
|
||||
model=model,
|
||||
...
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then inside your PPO training loop, call the `compute_reward_score` method by accessing the `model` attribute from `PPOTrainer`.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
rewards = trainer.model.compute_reward_score(**inputs)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Advanced usage
|
||||
|
||||
### Control on the adapter name
|
||||
|
||||
If you are familiar with the `peft` library, you know that you can use multiple adapters inside the same model. What you can do is train multiple adapters on the same base model to fine-tune on different policies.
|
||||
In this case, you want to be able to control the adapter name you want to activate back, after retrieving the reward. For that, simply pass the appropriate `adapter_name` to `ppo_adapter_name` argument when calling `compute_reward_score`.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
adapter_name_policy_1 = "policy_1"
|
||||
rewards = trainer.model.compute_reward_score(**inputs, ppo_adapter_name=adapter_name_policy_1)
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Using 4-bit and 8-bit base models
|
||||
|
||||
For more memory efficient fine-tuning, you can load your base model in 8-bit or 4-bit while keeping the adapters in the default precision (float32).
|
||||
Just pass the appropriate arguments (i.e. `load_in_8bit=True` or `load_in_4bit=True`) to `AutoModelForCausalLMWithValueHead.from_pretrained` as follows (assuming you have installed `bitsandbytes`):
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
model_name = "llama-7b"
|
||||
rm_adapter_id = "trl-lib/llama-7b-hh-rm-adapter"
|
||||
|
||||
# PPO adapter
|
||||
lora_config = LoraConfig(
|
||||
r=16,
|
||||
lora_alpha=32,
|
||||
lora_dropout=0.05,
|
||||
bias="none",
|
||||
task_type="CAUSAL_LM",
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLMWithValueHead.from_pretrained(
|
||||
model_name,
|
||||
peft_config=lora_config,
|
||||
reward_adapter=rm_adapter_id,
|
||||
quantization_config=BitsAndBytesConfig(load_in_8bit=True),
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
...
|
||||
trainer = PPOTrainer(
|
||||
model=model,
|
||||
...
|
||||
)
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
373
docs/source/openenv.md
Normal file
373
docs/source/openenv.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,373 @@
|
||||
# OpenEnv Integration for Training LLMs with Environments
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
[OpenEnv](https://github.com/meta-pytorch/OpenEnv) is an open-source framework from Meta's PyTorch team for defining, deploying, and interacting with environments in reinforcement learning (RL) and agentic workflows. It offers [Gymnasium-style APIs](https://gymnasium.farama.org) (e.g., `reset()` and `step()`) to interface with environments in a standard manner, and supports running these environments as backend servers (for example via HTTP or containerised execution). You can find a collection of ready-to-use OpenEnv environments on the [Hugging Face Hub](https://huggingface.co/collections/openenv/environment-hub).
|
||||
|
||||
In this guide, we’ll focus on **how to integrate OpenEnv with TRL**, but feel free to explore the links above to dive deeper into OpenEnv itself.
|
||||
|
||||
## Installation
|
||||
|
||||
To use OpenEnv with TRL, install the framework:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install openenv-core
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Using `rollout_func` with OpenEnv environments
|
||||
|
||||
TRL's [`GRPOTrainer`] supports _custom rollout logic_ through the `rollout_func` argument. This lets you override the trainer's default text-generation loop and directly interact with OpenEnv environments — for instance, to compute environment-driven rewards instead of relying solely on model-based signals.
|
||||
|
||||
### Rollout Function Signature
|
||||
|
||||
A rollout function must have the following signature:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
def rollout_func(
|
||||
prompts: list[str],
|
||||
args: GRPOConfig,
|
||||
processing_class
|
||||
) -> dict[str, list]:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Custom rollout function for generation and reward computation.
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
prompts: List of prompts to generate from
|
||||
args: GRPOConfig containing sampling parameters (temperature, top_p, etc.)
|
||||
processing_class: Tokenizer/processor for encoding/decoding
|
||||
|
||||
Returns:
|
||||
Dictionary containing:
|
||||
- prompt_ids: List of token IDs for each prompt
|
||||
- completion_ids: List of token IDs for each completion
|
||||
- logprobs: List of log probabilities for each token
|
||||
- Any additional fields are forwarded to reward functions as kwargs
|
||||
"""
|
||||
pass
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> [!NOTE]
|
||||
> Any extra fields in the returned dictionary (beyond the required three) are automatically forwarded to your reward functions. This makes it easy to propagate signals such as environment rewards or auxiliary metrics from the rollout step.
|
||||
|
||||
### Integration pattern
|
||||
|
||||
The typical pattern when combining OpenEnv with TRL looks like this:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Start or connect to an OpenEnv environment (e.g., an HTTP endpoint or Dockerized env).
|
||||
2. Generate completions from your model — for example, via a vLLM inference server (`use_vllm=True`, `vllm_mode="server"`).
|
||||
3. Step through the environment using each completion to compute rewards or metrics.
|
||||
4. Add environment results (e.g., `env_reward`) to the rollout result dict.
|
||||
5. Access those rewards inside your reward function via `**kwargs`.
|
||||
|
||||
By using OpenEnv in this loop, you can:
|
||||
|
||||
* Train with realistic or interactive feedback (not just static reward functions).
|
||||
* Plug in custom simulators, web APIs, or evaluators as environments.
|
||||
* Pass structured reward signals back into RL training seamlessly.
|
||||
|
||||
## A simple example
|
||||
|
||||
The [echo.py](https://github.com/huggingface/trl/blob/main/examples/scripts/openenv/echo.py) script demonstrates a minimal, end-to-end integration between TRL and OpenEnv. In this example, the Echo environment rewards completions based on their text length, encouraging the model to generate longer outputs. This pattern can be extended to any custom environment that provides structured feedback or task-based rewards:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from envs.echo_env import EchoEnv, EchoAction
|
||||
from trl import GRPOConfig, GRPOTrainer
|
||||
|
||||
# Create HTTP client for Echo Environment
|
||||
client = EchoEnv.from_docker_image("echo-env:latest")
|
||||
|
||||
def rollout_func(prompts, args, processing_class):
|
||||
# 1. Generate completions via vLLM inference server (running on port 8000)
|
||||
payload = {
|
||||
"prompts": prompts,
|
||||
"n": args.num_generations,
|
||||
"temperature": args.temperature,
|
||||
"max_tokens": args.max_completion_length,
|
||||
}
|
||||
response = requests.post("http://0.0.0.0:8000/generate/", json=payload)
|
||||
result = response.json()
|
||||
|
||||
completions_text = processing_class.batch_decode(
|
||||
result["completion_ids"],
|
||||
skip_special_tokens=True
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# 2. Step through the environment to get rewards
|
||||
client.reset()
|
||||
env_rewards = []
|
||||
for msg in completions_text:
|
||||
env_result = client.step(EchoAction(message=msg))
|
||||
env_rewards.append(env_result.reward)
|
||||
|
||||
# 3. Add environment rewards as extra field
|
||||
result["env_reward"] = env_rewards
|
||||
return result
|
||||
|
||||
def reward_from_env(completions, **kwargs):
|
||||
"""Extract environment rewards passed via rollout_func kwargs."""
|
||||
env_rewards = kwargs.get("env_reward", [])
|
||||
return [float(reward) for reward in env_rewards] if env_rewards else [0.0] * len(completions)
|
||||
|
||||
dataset = Dataset.from_dict({"prompt": ["You are an AI that interacts with an *Echo* environment. Word to echo:"] * 64})
|
||||
|
||||
# Setup trainer with custom rollout
|
||||
trainer = GRPOTrainer(
|
||||
model="Qwen/Qwen2.5-0.5B-Instruct",
|
||||
reward_funcs=reward_from_env,
|
||||
train_dataset=dataset,
|
||||
rollout_func=rollout_func, # Use custom rollout
|
||||
args=GRPOConfig(
|
||||
vllm_mode="server",
|
||||
use_vllm=True,
|
||||
num_train_epochs=1,
|
||||
num_generations=8,
|
||||
max_completion_length=2048,
|
||||
per_device_train_batch_size=8,
|
||||
gradient_accumulation_steps=4,
|
||||
),
|
||||
)
|
||||
trainer.train()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
That's it! Now that you’ve seen the full example, let’s unpack how the main pieces fit together.
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Environment Client:** `EchoEnv` implements an HTTP interface to interact with the environment server.
|
||||
2. **Custom rollout:** The `rollout_func` generates completions and steps through the environment to collect rewards.
|
||||
3. **Extra fields:** The rollout adds `env_reward` to the result dictionary, which is automatically passed to reward functions.
|
||||
4. **Reward function:** Extracts `env_reward` from `kwargs` to apply environment-computed rewards during training.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!WARNING]
|
||||
> The `rollout_func` is currently only supported when using vLLM in server mode (`use_vllm=True`, `vllm_mode="server"`).
|
||||
|
||||
### Running the Example
|
||||
|
||||
The example requires two GPUs:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# Terminal 1: Start vLLM inference server
|
||||
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 trl vllm-serve --model Qwen/Qwen2.5-0.5B-Instruct --host 0.0.0.0 --port 8000
|
||||
|
||||
# Terminal 2: Run GRPO training with OpenEnv
|
||||
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=1 python examples/scripts/openenv/echo.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Below is the reward curve from training:
|
||||
|
||||
<iframe src="https://trl-lib-trackio.hf.space?project=openenv&metrics=train/rewards/reward_from_env/mean&runs=qgallouedec-1761202871&sidebar=hidden&navbar=hidden" style="width:600px; height:500px; border:0;"></iframe>
|
||||
|
||||
To learn more about how to create custom environments, see the [OpenEnv documentation](https://github.com/meta-pytorch/OpenEnv/blob/main/src/envs/README.md).
|
||||
|
||||
## Advanced Example
|
||||
|
||||
Let's level this up a bit by training a model to interact with a more complex environment. We'll use the game word guessing game [wordle](https://www.nytimes.com/games/wordle/index.html) from the `textarena` environment.
|
||||
|
||||
### The TextArena Environment
|
||||
|
||||
[TextArena](https://huggingface.co/papers/2504.11442) is an open-source collection of competitive text-based games designed to evaluate reasoning skills in LLMs using textual games like Wordle, Snake, Tic-Tac-Toe, and more. Research has shown that such games improve model performance on reasoning tasks.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
We will use the `textarena` environment to train a model to play Wordle. The environment is a simple text based response environment that allows the model to interact with the game by making guesses and receive feedback on them.
|
||||
|
||||
### Wordle
|
||||
|
||||
Wordle is a useful game to train a model on because it requires the model to reason about the word and the feedback provided by the environment. Also, it is a purely language based game that requires no external tools or knowledge. Furthermore, we found that models from 1 billion parameters and up are able to improve on wordle and only require 8 tokens to generate a guess, which makes the game a good benchmark to experiment with Reinforcement Learning environments without significant compute requirements.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!NOTE] How does Wordle work?
|
||||
> Wordle is a word guessing game where the player has to guess a 5-letter word. The player can make 6 guesses, and for each guess, the environment will provide feedback on the correctness of the guess. The player wins if they guess the word in 6 guesses or less. It challenges the model to generate words that are likely to be correct, and to learn from the feedback provided by the environment.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> For example, if the wordle environment returns the following feedback:
|
||||
>
|
||||
> ```
|
||||
> G U E S S
|
||||
> X G Y X X
|
||||
> ```
|
||||
> The model has guessed the word "GUESS" and the environment has provided feedback as the letters X, G, and Y. Referring to colors in the original game blank, green, and yellow. From this feedback, the model should learn that the word is "GUESS" is incorrect. The letter "E" is in the word, but in the wrong position. The letter "U" is correct and in the correct position.
|
||||
|
||||
In the TextArena environment, reward is only given when the model wins the game. The reward is 1.0 if the model wins, and 0.0 otherwise. This is not a very efficient reward signal for the model, so we have added a number of custom reward functions to the script to help the model learn to play the game. The extensible nature of `reward_funcs` and `rollout_func` allows you to add any custom reward function you want to the script.
|
||||
|
||||
### Rollout Function
|
||||
|
||||
The rollout function runs one full Wordle episode, prompting the model for a guess each turn and capturing both environment rewards and auxiliary signals such as letter coverage and repetition penalties.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
def rollout_once(
|
||||
env: TextArenaEnv,
|
||||
tokenizer: AutoTokenizer,
|
||||
args: GRPOConfig,
|
||||
dataset_prompt: str,
|
||||
cli_args: argparse.Namespace,
|
||||
system_prompt: str,
|
||||
) -> dict[str, list]:
|
||||
result = env.reset()
|
||||
observation = result.observation
|
||||
|
||||
prompt_ids: list[int] = []
|
||||
completion_ids: list[int] = []
|
||||
logprobs: list[float] = []
|
||||
raw_rewards: list[float] = []
|
||||
green_scores: list[float] = []
|
||||
yellow_scores: list[float] = []
|
||||
repetition_scores: list[float] = []
|
||||
correct_scores: list[float] = []
|
||||
guess_counts: dict[str, int] = {}
|
||||
|
||||
for _turn in range(cli_args.max_turns):
|
||||
# when the game is over the environment will return a done=True
|
||||
if result.done:
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
# set up the prompt for the model
|
||||
base_prompt = observation.prompt or dataset_prompt
|
||||
user_prompt = make_user_prompt(base_prompt, observation.messages)
|
||||
messages = [
|
||||
{"role": "system", "content": system_prompt},
|
||||
{"role": "user", "content": user_prompt},
|
||||
]
|
||||
prompt_text = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
|
||||
messages,
|
||||
add_generation_prompt=True,
|
||||
tokenize=False,
|
||||
enable_thinking=False,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# generate the completion from the model using vLLM
|
||||
vllm_result = request_vllm_completion(
|
||||
prompt_text,
|
||||
args,
|
||||
endpoint=cli_args.vllm_endpoint,
|
||||
timeout=cli_args.request_timeout,
|
||||
fallback=cli_args,
|
||||
)
|
||||
prompt_ids.extend(vllm_result["prompt_ids"])
|
||||
completion_ids.extend(vllm_result["completion_ids"])
|
||||
logprobs.extend(vllm_result["logprobs"])
|
||||
completion_text = vllm_result.get("text") or tokenizer.decode(
|
||||
vllm_result["completion_ids"], skip_special_tokens=True
|
||||
)
|
||||
# extract the guess from the completion
|
||||
guess = extract_guess(completion_text)
|
||||
|
||||
# step the environment with the guess
|
||||
result = env.step(TextArenaAction(message=guess))
|
||||
raw_rewards.append(float(result.reward or 0.0))
|
||||
observation = result.observation
|
||||
correct_score = float(result.reward or 0.0)
|
||||
feedback = extract_wordle_feedback(observation)
|
||||
|
||||
# Update guess counts
|
||||
previous_occurrences = guess_counts[guess]
|
||||
repetition_score = scale_repetition_score(previous_occurrences, len(guess_counts))
|
||||
guess_counts[guess] += 1
|
||||
|
||||
# calculate custom reward signals from the feedback
|
||||
if not feedback:
|
||||
green_score = 0.0
|
||||
yellow_score = 0.0
|
||||
else:
|
||||
green_count, yellow_count = extract_feedback_counts(feedback)
|
||||
green_score = green_count / 5.0
|
||||
yellow_score = yellow_count / 5.0
|
||||
|
||||
repetition_scores.append(repetition_score)
|
||||
green_scores.append(green_score)
|
||||
yellow_scores.append(yellow_score)
|
||||
correct_scores.append(correct_score)
|
||||
|
||||
correct_reward_value = correct_scores[-1] if correct_scores else (raw_rewards[-1] if raw_rewards else 0.0)
|
||||
|
||||
return {
|
||||
"prompt_ids": prompt_ids,
|
||||
"completion_ids": completion_ids,
|
||||
"logprobs": logprobs,
|
||||
"raw_rewards": raw_rewards,
|
||||
"correct_reward": correct_reward_value,
|
||||
"green_reward": green_scores[-1] if green_scores else 0.0,
|
||||
"yellow_reward": yellow_scores[-1] if yellow_scores else 0.0,
|
||||
"repetition_reward": repetition_scores[-1] if repetition_scores else 0.0,
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The environment has a reward signal based on the completion of the game. We found that most models struggle to ever win the game, so we have added a number of custom reward functions to the script to help the model learn to play the game more iteratively. At first, the model will learn to cover new letters and avoid repeating guesses. As it improves, it will learn to win the game.
|
||||
|
||||
### Reward Functions
|
||||
|
||||
We log four reward streams that encourage the model to solve the puzzle, cover new letters, and avoid repeating guesses:
|
||||
|
||||
- `reward_correct`: final win/loss signal from the environment.
|
||||
- `reward_greens`: density of green letters in the last feedback.
|
||||
- `reward_yellows`: density of yellow letters in the last feedback.
|
||||
- `reward_repetition`: penalty for guessing the same token multiple times.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
def reward_correct(completions: List[str], **kwargs: Optional[Dict]) -> List[float]:
|
||||
rewards = kwargs.get("correct_reward") if kwargs else None
|
||||
return [float(r) for r in rewards] if rewards is not None else [0.0] * len(completions)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def reward_greens(completions: List[str], **kwargs: Optional[Dict]) -> List[float]:
|
||||
rewards = kwargs.get("green_reward") if kwargs else None
|
||||
return [float(r) for r in rewards] if rewards is not None else [0.0] * len(completions)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def reward_yellows(completions: List[str], **kwargs: Optional[Dict]) -> List[float]:
|
||||
rewards = kwargs.get("yellow_reward") if kwargs else None
|
||||
return [float(r) for r in rewards] if rewards is not None else [0.0] * len(completions)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def reward_repetition(completions: List[str], **kwargs: Optional[Dict]) -> List[float]:
|
||||
rewards = kwargs.get("repetition_reward") if kwargs else None
|
||||
return [float(r) for r in rewards] if rewards is not None else [0.0] * len(completions)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Training the Model
|
||||
|
||||
The training script wires the custom rollout and rewards into `GRPOTrainer`. The CLI exposes the configuration used during development as defaults, so you can override endpoints or hyperparameters at launch time.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
|
||||
# ... add CLI arguments with sensible defaults ...
|
||||
cli_args = parser.parse_args()
|
||||
|
||||
trainer = GRPOTrainer(
|
||||
model=cli_args.model_id,
|
||||
processing_class=tokenizer,
|
||||
reward_funcs=[
|
||||
reward_correct,
|
||||
reward_greens,
|
||||
reward_yellows,
|
||||
reward_repetition,
|
||||
],
|
||||
train_dataset=dataset,
|
||||
args=grpo_config,
|
||||
rollout_func=lambda prompts, args, processing_class: rollout_func(
|
||||
env=env,
|
||||
tokenizer=tokenizer,
|
||||
prompts=prompts,
|
||||
args=args,
|
||||
cli_args=cli_args,
|
||||
system_prompt=system_prompt,
|
||||
),
|
||||
)
|
||||
trainer.train()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Running the Example
|
||||
|
||||
The example requires two GPUs:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# Terminal 1: Start vLLM inference server
|
||||
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 trl vllm-serve --model Qwen/Qwen2.5-0.5B-Instruct --host 0.0.0.0 --port 8000
|
||||
|
||||
# Terminal 2: Run GRPO training with OpenEnv
|
||||
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=1 python examples/scripts/openenv/wordle.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Results
|
||||
|
||||
The resulting model improves it's performance on the game, both by reducing the number of repetitions and by increasing the number of correct guesses. However, the the Qwen3-1.7B model we trained is not able to consistently win the game. The following reward curve shows the coverage of the model's guesses and the coverage of correct Y and G letters.
|
||||
|
||||
<iframe src="https://burtenshaw-wordle-grpo.hf.space/?project=group-Qwen-Qwen3-17B&metrics=train/rewards/reward_coverage/mean&runs=run-2025-10-26_09-39-49&sidebar=hidden&navbar=hidden" style="width:600px; height:500px; border:0;"></iframe>
|
||||
|
||||
We experimented larger models like `gpt-oss-20b` and found that model was able to consistently win the game. However, this requires a lot of compute to train and the model. Why not try this out yourself?
|
||||
@ -207,6 +207,31 @@ training_args = GRPOConfig(
|
||||
|
||||
See [Experimental - GFPO](experimental#gfpo).
|
||||
|
||||
### Perception-Aware Policy Optimization for Multimodal Reasoning
|
||||
|
||||
**📜 Paper**: https://huggingface.co/papers/2507.06448
|
||||
|
||||
A novel policy gradient algorithm that encourages VLMs to learn to perceive while learning to reason. This is a TRL adaptation. The TRL implementation is not the official one provided by the authors.
|
||||
This is a TRL adaptation of PAPO. Note that this is not the official implementation. The official code can be found in [MikeWangWZHL/PAPO](https://github.com/MikeWangWZHL/PAPO).
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from trl.experimental.papo import PAPOConfig, PAPOTrainer
|
||||
|
||||
training_args = PAPOConfig(
|
||||
# PAPO-specific params
|
||||
perception_loss_weight=0.01, # Weight for perception loss
|
||||
mask_ratio=0.6, # 40% of image will be masked
|
||||
mask_type="random", # Use patch masking (recommended)
|
||||
der_loss_weight1=0.02,
|
||||
der_loss_weight2=0.02,
|
||||
# ...other GRPO params...
|
||||
)
|
||||
trainer = PAPOTrainer(
|
||||
args=training_args,
|
||||
...
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Direct Policy Optimization
|
||||
|
||||
Papers relating to the [`DPOTrainer`]
|
||||
@ -266,7 +291,7 @@ These parameters only appear in the [published version](https://openreview.net/p
|
||||
|
||||
### Towards Efficient and Exact Optimization of Language Model Alignment
|
||||
|
||||
**📜 Paper**: https://huggingface.co/papers/2305.10425
|
||||
**📜 Paper**: https://huggingface.co/papers/2402.00856
|
||||
|
||||
Efficient exact optimization (EXO) method is proposed to align language models with human preferences, providing a guaranteed and efficient alternative to reinforcement learning and direct preference optimization. To reproduce the paper's setting, use this configuration:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -580,3 +605,47 @@ def add_margin(example):
|
||||
|
||||
dataset = dataset.map(add_margin)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Distillation
|
||||
Papers relating to training a student model with the help of a teacher model.
|
||||
|
||||
### On-Policy Distillation
|
||||
**📰 Blog**: https://thinkingmachines.ai/blog/on-policy-distillation/
|
||||
|
||||
On-Policy Distillation involves a student model generating rollouts for each batch of training data. We subsequently obtain the probability distributions for each token of the rollouts from both the student and teacher models. The student model is then optimized to minimize the negative Kullback-Leibler (KL) divergence between its own token distributions and those of the teacher model.
|
||||
|
||||
| Method | Sampling | Reward signal |
|
||||
|-------------------------|------------|---------------|
|
||||
| Supervised finetuning | off-policy | dense |
|
||||
| Reinforcement learning | on-policy | sparse |
|
||||
| On-policy distillation | on-policy | dense |
|
||||
|
||||
On-Policy Distillation has been shown to outperform SFT, GRPO and can be used to restore generalization capabilities lost during SFT.
|
||||
|
||||
Additionally on-policy distillation is more compute efficient and is less prone to overfitting when trained with limited data.
|
||||
|
||||
To train a model with on-policy distillation using TRL, you can use the following configuration, with the [`GKDTrainer`] and [`GKDConfig`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from trl import GKDConfig
|
||||
|
||||
config = GKDConfig(
|
||||
lmbda=1.0, # student produces rollouts for all batches
|
||||
beta=1.0, # to ensure reverse-kl as the loss function
|
||||
teacher_model_name_or_path="teacher-model", # specify the teacher model
|
||||
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Alternatively, you can use the [`GOLDTrainer`] and [`GOLDConfig`] to perform on-policy distillation with a similar configuration:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from trl.experimental import GOLDConfig
|
||||
|
||||
config = GOLDConfig(
|
||||
lmbda=1.0, # student produces rollouts for all batches
|
||||
beta=1.0, # to ensure reverse-kl as the loss function
|
||||
teacher_model_name_or_path="teacher-model", # specify the teacher model
|
||||
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
20
docs/source/papo_trainer.md
Normal file
20
docs/source/papo_trainer.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,20 @@
|
||||
# PAPO Trainer
|
||||
|
||||
[](https://huggingface.co/models?other=papo,trl)
|
||||
|
||||
TRL supports the Perception-Aware Policy Optimization (PAPO) as described in the paper [Perception-Aware Policy Optimization for Multimodal Reasoning](https://huggingface.co/papers/2507.06448) by [Zhenhailong Wang](https://huggingface.co/mikewang), Xuehang Guo, Sofia Stoica, [Haiyang Xu](https://huggingface.co/xhyandwyy), Hongru Wang, Hyeonjeong Ha, Xiusi Chen, Yangyi Chen, Ming Yan, Fei Huang, Heng Ji
|
||||
|
||||
The abstract from the paper is the following:
|
||||
|
||||
> Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR) has proven to be a highly effective strategy for endowing Large Language Models (LLMs) with robust multi-step reasoning abilities. However, its design and optimizations remain tailored to purely textual domains, resulting in suboptimal performance when applied to multimodal reasoning tasks. In particular, we observe that a major source of error in current multimodal reasoning lies in the perception of visual inputs. To address this bottleneck, we propose Perception-Aware Policy Optimization (PAPO), a simple yet effective extension of GRPO that encourages the model to learn to perceive while learning to reason, entirely from internal supervision signals. Notably, PAPO does not rely on additional data curation, external reward models, or proprietary models. Specifically, we introduce the Implicit Perception Loss in the form of a KL divergence term to the GRPO objective, which, despite its simplicity, yields significant overall improvements (4.4%) on diverse multimodal benchmarks. The improvements are more pronounced, approaching 8.0%, on tasks with high vision dependency. We also observe a substantial reduction (30.5%) in perception errors, indicating improved perceptual capabilities with PAPO. We conduct comprehensive analysis of PAPO and identify a unique loss hacking issue, which we rigorously analyze and mitigate through a Double Entropy Loss. Overall, our work introduces a deeper integration of perception-aware supervision into RLVR learning objectives and lays the groundwork for a new RL framework that encourages visually grounded reasoning. Project page: https://mikewangwzhl.github.io/PAPO.
|
||||
|
||||
## PAPOTrainer
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] experimental.papo.PAPOTrainer
|
||||
- train
|
||||
- save_model
|
||||
- push_to_hub
|
||||
|
||||
## PAPOConfig
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] experimental.papo.PAPOConfig
|
||||
@ -114,6 +114,94 @@ pretrained_model = AutoModelForCausalLMWithValueHead.from_pretrained(
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, make sure that the rewards are computed on correct device as well, for that you can use `ppo_trainer.model.current_device`.
|
||||
|
||||
## Multi-Adapter RL Training
|
||||
|
||||
You can use a single base model with multiple PEFT adapters for the entire PPO algorithm - including retrieving reference logits, computing active logits, and calculating rewards. This approach is useful for memory-efficient RL training.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!WARNING]
|
||||
> This feature is experimental and convergence has not been extensively tested. We encourage the community to share feedback and report any issues.
|
||||
|
||||
### Requirements
|
||||
|
||||
Install PEFT and optionally bitsandbytes for 8-bit models:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install peft bitsandbytes
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Training Workflow
|
||||
|
||||
The multi-adapter approach requires three stages:
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT)**: Train a base model on your target domain (e.g., IMDB dataset) using `SFTTrainer`
|
||||
2. **Reward Model Training**: Train a reward model adapter using PEFT and `RewardTrainer` (see [reward modeling example](https://github.com/huggingface/trl/tree/main/examples/scripts/reward_modeling.py))
|
||||
3. **PPO Training**: Fine-tune new adapters using PPO with the reward adapter
|
||||
|
||||
> [!IMPORTANT]
|
||||
> Use the same base model (architecture and weights) for stages 2 & 3.
|
||||
|
||||
### Basic Usage
|
||||
|
||||
After training your reward adapter and pushing it to the Hub:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from peft import LoraConfig
|
||||
from trl import AutoModelForCausalLMWithValueHead, PPOTrainer
|
||||
|
||||
model_name = "huggyllama/llama-7b"
|
||||
rm_adapter_id = "trl-lib/llama-7b-hh-rm-adapter"
|
||||
|
||||
# Configure PPO adapter
|
||||
lora_config = LoraConfig(
|
||||
r=16,
|
||||
lora_alpha=32,
|
||||
lora_dropout=0.05,
|
||||
bias="none",
|
||||
task_type="CAUSAL_LM",
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Load model with reward adapter
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLMWithValueHead.from_pretrained(
|
||||
model_name,
|
||||
peft_config=lora_config,
|
||||
reward_adapter=rm_adapter_id,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
trainer = PPOTrainer(model=model, ...)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In your training loop, compute rewards using:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
rewards = trainer.model.compute_reward_score(**inputs)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Advanced Features
|
||||
|
||||
#### Multiple Policy Adapters
|
||||
|
||||
You can train multiple adapters on the same base model for different policies. Control which adapter to activate using the `ppo_adapter_name` argument:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
adapter_name_policy_1 = "policy_1"
|
||||
rewards = trainer.model.compute_reward_score(**inputs, ppo_adapter_name=adapter_name_policy_1)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Quantized Base Models
|
||||
|
||||
For memory-efficient training, load the base model in 8-bit or 4-bit while keeping adapters in float32:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import BitsAndBytesConfig
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLMWithValueHead.from_pretrained(
|
||||
model_name,
|
||||
peft_config=lora_config,
|
||||
reward_adapter=rm_adapter_id,
|
||||
quantization_config=BitsAndBytesConfig(load_in_8bit=True),
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Naive pipeline parallelism (NPP) for large models (>60B models)
|
||||
|
||||
The `trl` library also supports naive pipeline parallelism (NPP) for large models (>60B models). This is a simple way to parallelize the model across multiple GPUs.
|
||||
|
||||
390
docs/source/rapidfire_integration.md
Normal file
390
docs/source/rapidfire_integration.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,390 @@
|
||||
# RapidFire AI Integration
|
||||
|
||||
RapidFire AI is an open-source experiment execution framework that enables concurrent training of multiple TRL configurations on the same GPU(s) through intelligent chunk-based scheduling.
|
||||
|
||||
## Key Features
|
||||
|
||||
- **16-24× higher experimentation throughput** compared to sequential training.
|
||||
- **Almost no code changes** - drop-in configuration wrappers around TRL's and PEFT's existing configs.
|
||||
- **Interactive Control Operations** - real-time control to stop, resume, clone, and modify training runs in flight
|
||||
- **Automatic multi-GPU orchestration** with intelligent scheduling
|
||||
- **Full compatibility** with transformers, PEFT, SFTTrainer, DPOTrainer, and GRPOTrainer
|
||||
- **Full MLflow Integration**: Automatic experiment tracking and visualization
|
||||
- **Production-Ready**: Already used in production environments with complete working examples.
|
||||
|
||||
### Problem It Solves
|
||||
|
||||
When fine-tuning or post-training with TRL, AI developers often need to:
|
||||
- Try different hyperparameter configurations
|
||||
- Compare different LoRA settings
|
||||
- Test different prompt schemes
|
||||
- Run ablation studies
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**Current approach**: Train each config one after another → slow and inefficient process
|
||||
|
||||
**With RapidFire AI**: Train all configs in one go even on a single GPU → 16-24× faster process
|
||||
|
||||
### How It Works
|
||||
|
||||
RapidFire AI employs **adaptive chunk-based scheduling**:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
GPU Timeline (Single GPU):
|
||||
Chunk 1: [Config A] → [Config B] → [Config C] → [Config D]
|
||||
Chunk 2: [Config A] → [Config B] → [Config C] → [Config D]
|
||||
Chunk 3: [Config A] → [Config B] → [Config C] → [Config D]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This enables:
|
||||
- Early comparison of configurations on same data subsets incrementally
|
||||
- Efficient GPU utilization and minimizing idle times
|
||||
- Real-time and automated experiment metrics tracking
|
||||
- Dynamic control over runs in flight to incentivize more experimentation
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Installation
|
||||
|
||||
### Prerequisites
|
||||
|
||||
- Python 3.12.x
|
||||
- NVIDIA GPU with Compute Capability 7.x or 8.x
|
||||
- CUDA Toolkit 11.8+
|
||||
- PyTorch 2.7.1+
|
||||
|
||||
### pip install
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install rapidfireai
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Once installed, authenticate with Hugging Face and initialize RapidFire AI:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# Authenticate with Hugging Face
|
||||
huggingface-cli login --token YOUR_TOKEN
|
||||
|
||||
# Workaround for current issue: https://github.com/huggingface/xet-core/issues/527
|
||||
pip uninstall -y hf-xet
|
||||
|
||||
# Initialize RapidFire AI
|
||||
rapidfireai init
|
||||
|
||||
# Start the RapidFire AI server
|
||||
rapidfireai start
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The dashboard will be available at `http://0.0.0.0:3000` where you can monitor and control experiments in real-time.
|
||||
|
||||
## Quick Start: SFT Training with Multiple Configs
|
||||
|
||||
Here's a complete example showing how to train multiple SFT configurations concurrently:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from rapidfireai import Experiment
|
||||
from rapidfireai.automl import List, RFGridSearch, RFModelConfig, RFLoraConfig, RFSFTConfig
|
||||
from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
# Load dataset
|
||||
dataset = load_dataset("bitext/Bitext-customer-support-llm-chatbot-training-dataset")
|
||||
train_dataset = dataset["train"].select(range(128)).shuffle(seed=42)
|
||||
eval_dataset = dataset["train"].select(range(100, 124)).shuffle(seed=42)
|
||||
|
||||
# Define data formatting function
|
||||
def formatting_function(row):
|
||||
return {
|
||||
"prompt": [
|
||||
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful customer support assistant."},
|
||||
{"role": "user", "content": row["instruction"]},
|
||||
],
|
||||
"completion": [
|
||||
{"role": "assistant", "content": row["response"]}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# Initialize experiment
|
||||
experiment = Experiment(experiment_name="sft-customer-support")
|
||||
|
||||
# Define multiple LoRA configurations to compare
|
||||
peft_configs = List([
|
||||
RFLoraConfig(r=8, lora_alpha=16, lora_dropout=0.1,
|
||||
target_modules=["q_proj", "v_proj"], bias="none"),
|
||||
RFLoraConfig(r=32, lora_alpha=64, lora_dropout=0.1,
|
||||
target_modules=["q_proj", "k_proj", "v_proj", "o_proj"], bias="none")
|
||||
])
|
||||
|
||||
# Define multiple training configurations
|
||||
# 2 base configs × 2 PEFT configs = 4 total training runs
|
||||
config_set = List([
|
||||
RFModelConfig(
|
||||
model_name="TinyLlama/TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0",
|
||||
peft_config=peft_configs,
|
||||
training_args=RFSFTConfig( # Wraps TRL's SFTConfig
|
||||
learning_rate=1e-3,
|
||||
per_device_train_batch_size=4,
|
||||
max_steps=128,
|
||||
fp16=True,
|
||||
),
|
||||
model_type="causal_lm",
|
||||
model_kwargs={"device_map": "auto", "torch_dtype": "auto", "use_cache": False},
|
||||
formatting_func=formatting_function,
|
||||
),
|
||||
RFModelConfig(
|
||||
model_name="TinyLlama/TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0",
|
||||
peft_config=peft_configs,
|
||||
training_args=RFSFTConfig(
|
||||
learning_rate=1e-4, # Different learning rate
|
||||
per_device_train_batch_size=4,
|
||||
max_steps=128,
|
||||
fp16=True,
|
||||
),
|
||||
model_type="causal_lm",
|
||||
model_kwargs={"device_map": "auto", "torch_dtype": "auto", "use_cache": False},
|
||||
formatting_func=formatting_function,
|
||||
)
|
||||
])
|
||||
|
||||
# Define model creation function
|
||||
def create_model(model_config):
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
|
||||
model_config["model_name"],
|
||||
**model_config["model_kwargs"]
|
||||
)
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_config["model_name"])
|
||||
return (model, tokenizer)
|
||||
|
||||
# Create grid search over all configurations
|
||||
config_group = RFGridSearch(configs=config_set, trainer_type="SFT")
|
||||
|
||||
# Run all 4 configurations concurrently with chunk-based scheduling
|
||||
experiment.run_fit(config_group, create_model, train_dataset, eval_dataset,
|
||||
num_chunks=4, seed=42)
|
||||
|
||||
# End experiment
|
||||
experiment.end()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### What Happens During Execution
|
||||
|
||||
When you run this example:
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Config Expansion**: 2 base configurations × 2 PEFT configs = 4 total training runs
|
||||
2. **Chunk-based Scheduling**: Training data is divided into chunks, and all 4 configs train concurrently
|
||||
3. **GPU Swapping**: Models are swapped in/out of GPU memory based on chunk boundaries
|
||||
4. **Real-time Tracking**: All metrics visible in the dashboard at `http://localhost:3000`
|
||||
5. **Interactive Control**: Stop, resume, or clone any configuration from the dashboard
|
||||
|
||||
This delivers **16-24× higher throughput** compared to training each configuration sequentially!
|
||||
|
||||
## Supported TRL Trainers
|
||||
|
||||
### SFTTrainer
|
||||
|
||||
Use `RFSFTConfig` as a drop-in replacement for `SFTConfig`:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from rapidfireai.automl import RFSFTConfig
|
||||
|
||||
training_args = RFSFTConfig(
|
||||
learning_rate=5e-5,
|
||||
per_device_train_batch_size=4,
|
||||
num_train_epochs=3,
|
||||
max_length = 512,
|
||||
# ... all other SFTConfig parameters supported
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Example Notebook**: [SFT for Customer Support](https://github.com/RapidFireAI/rapidfireai/blob/main/tutorial_notebooks/rf-tutorial-sft-chatqa-lite.ipynb)
|
||||
|
||||
### DPOTrainer
|
||||
|
||||
Use `RFDPOConfig` as a drop-in replacement for `DPOConfig`:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from rapidfireai.automl import RFDPOConfig
|
||||
|
||||
training_args = RFDPOConfig(
|
||||
beta=0.1,
|
||||
loss_type="sigmoid",
|
||||
max_prompt_length=512,
|
||||
max_completion_length=512,
|
||||
learning_rate=5e-4,
|
||||
# ... all other DPOConfig parameters supported
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Example Notebook**: [DPO for Preference Alignment](https://github.com/RapidFireAI/rapidfireai/blob/main/tutorial_notebooks/rf-tutorial-dpo-alignment-lite.ipynb)
|
||||
|
||||
### GRPOTrainer
|
||||
|
||||
Use `RFGRPOConfig` as a drop-in replacement for `GRPOConfig`:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from rapidfireai.automl import RFGRPOConfig
|
||||
|
||||
training_args = RFGRPOConfig(
|
||||
learning_rate=5e-6,
|
||||
num_generations=8,
|
||||
max_prompt_length=256,
|
||||
max_completion_length=256,
|
||||
# ... all other GRPOConfig parameters supported
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Example Notebook**: [GRPO for Math Reasoning](https://github.com/RapidFireAI/rapidfireai/blob/main/tutorial_notebooks/rf-tutorial-grpo-mathreasoning-lite.ipynb)
|
||||
|
||||
## Core Concepts
|
||||
|
||||
### Chunk-Based Concurrent Training
|
||||
|
||||
RapidFire AI divides training data into chunks and alternates between configurations:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
GPU Timeline (Single GPU):
|
||||
Chunk 1: [Config A] → [Config B] → [Config C] → [Config D]
|
||||
Chunk 2: [Config A] → [Config B] → [Config C] → [Config D]
|
||||
Chunk 3: [Config A] → [Config B] → [Config C] → [Config D]
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This approach maximizes GPU utilization and enables early comparison of configurations while maintaining training stability through automatic checkpointing.
|
||||
|
||||
### Interactive Control Operations (IC Ops)
|
||||
|
||||
Through the RapidFire AI dashboard, you can dynamically control running experiments:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Stop**: Pause a configuration (checkpointed automatically)
|
||||
- **Resume**: Continue from last checkpoint
|
||||
- **Clone**: Duplicate a configuration with modifications
|
||||
- **Clone & Warm Start**: Clone and initialize from parent's weights
|
||||
- **Delete**: Remove failed or unwanted runs
|
||||
|
||||
This enables adaptive experimentation where you can stop underperforming configs early and clone promising ones with tweaked hyperparameters.
|
||||
|
||||
### Multi-Config Experimentation
|
||||
|
||||
Use `RFGridSearch` or `RFRandomSearch` to automatically generate configuration combinations:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# Grid search: tests all combinations
|
||||
config_group = RFGridSearch(configs=config_list, trainer_type="SFT")
|
||||
|
||||
# Random search: samples N configurations
|
||||
config_group = RFRandomSearch(configs=config_list, trainer_type="DPO", num_samples=10)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Advanced Features
|
||||
|
||||
### PEFT/LoRA Integration
|
||||
|
||||
Full support for parameter-efficient fine-tuning:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from rapidfireai.automl import RFLoraConfig
|
||||
from peft import TaskType
|
||||
|
||||
lora_config = RFLoraConfig(
|
||||
task_type=TaskType.CAUSAL_LM,
|
||||
r=64,
|
||||
lora_alpha=64,
|
||||
lora_dropout=0.1,
|
||||
target_modules=["q_proj", "k_proj", "v_proj", "o_proj"],
|
||||
bias="none"
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Custom Reward Functions (GRPO)
|
||||
|
||||
Define multiple reward functions for GRPO training:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
def correctness_reward(prompts, completions, answer, **kwargs):
|
||||
"""Reward for correct answers"""
|
||||
responses = [completion[0]['content'] for completion in completions]
|
||||
extracted = [extract_answer(r) for r in responses]
|
||||
return [2.0 if r == a else 0.0 for r, a in zip(extracted, answer)]
|
||||
|
||||
def format_reward(completions, **kwargs):
|
||||
"""Reward for proper formatting"""
|
||||
import re
|
||||
pattern = r"<reasoning>.*?</reasoning>\s*<answer>.*?</answer>"
|
||||
responses = [completion[0]["content"] for completion in completions]
|
||||
matches = [re.match(pattern, r) for r in responses]
|
||||
return [0.5 if match else 0.0 for match in matches]
|
||||
|
||||
# Use in model config
|
||||
config = RFModelConfig(
|
||||
reward_funcs=[correctness_reward, format_reward],
|
||||
# ... other parameters
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Multi-GPU Support
|
||||
|
||||
RapidFire AI automatically detects and utilizes all available GPUs. No special configuration needed - the scheduler automatically distributes configurations across GPUs.
|
||||
|
||||
## Best Practices
|
||||
|
||||
### Tuning Chunk Granularity
|
||||
|
||||
The `num_chunks` parameter controls swap frequency:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# Fewer chunks = less overhead, less frequent comparison
|
||||
experiment.run_fit(..., num_chunks=2)
|
||||
|
||||
# More chunks = more overhead, more frequent comparison
|
||||
experiment.run_fit(..., num_chunks=16)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Rule of thumb**: Start with `num_chunks=4` and adjust based on dataset size and number of configurations.
|
||||
|
||||
### Memory Management
|
||||
|
||||
For large models, use quantization:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import BitsAndBytesConfig
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
bnb_config = BitsAndBytesConfig(
|
||||
load_in_4bit=True,
|
||||
bnb_4bit_compute_dtype=torch.bfloat16,
|
||||
bnb_4bit_use_double_quant=True,
|
||||
bnb_4bit_quant_type="nf4",
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
model_kwargs = {
|
||||
"quantization_config": bnb_config,
|
||||
"device_map": "auto",
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Performance Benchmarks
|
||||
|
||||
Based on internal benchmarks comparing sequential vs. RapidFire AI concurrent training:
|
||||
|
||||
| Scenario | Sequential Time | RapidFire AI Time | Speedup |
|
||||
|----------|----------------|-------------------|---------|
|
||||
| 4 configs, 1 GPU | 120 min | 7.5 min | 16× |
|
||||
| 8 configs, 1 GPU | 240 min | 12 min | 20× |
|
||||
| 4 configs, 2 GPUs | 60 min | 4 min | 15× |
|
||||
| 8 configs, 4 GPUs | 60 min | 3 min | 20× |
|
||||
|
||||
*Benchmarks performed on NVIDIA A100 40GB with TinyLlama-1.1B and Llama-3.2-1B models*
|
||||
|
||||
## Troubleshooting
|
||||
|
||||
For troubleshooting guidance, see the [RapidFire AI Troubleshooting Guide](https://oss-docs.rapidfire.ai/en/latest/troubleshooting.html).
|
||||
|
||||
## Additional Resources
|
||||
- **Colab Notebook**: [RapidFire AI in Google Colab](http://tinyurl.com/rapidfireai-colab)
|
||||
- **Documentation**: [oss-docs.rapidfire.ai](https://oss-docs.rapidfire.ai)
|
||||
- **GitHub**: [RapidFireAI/rapidfireai](https://github.com/RapidFireAI/rapidfireai)
|
||||
- **PyPI**: [pypi.org/project/rapidfireai](https://pypi.org/project/rapidfireai/)
|
||||
- **Discord**: [Join our Discord](https://discord.gg/6vSTtncKNN)
|
||||
- **Tutorial Notebooks**: [GitHub Repository](https://github.com/RapidFireAI/rapidfireai/tree/main/tutorial_notebooks)
|
||||
|
||||
Learn more about RapidFire AI in their [official repository](https://github.com/RapidFireAI/rapidfireai) and [documentation](https://oss-docs.rapidfire.ai).
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,7 +1,12 @@
|
||||
# Reducing Memory Usage
|
||||
|
||||
> [!WARNING]
|
||||
> Section under construction. Feel free to contribute!
|
||||
Training workflows can often be optimized to **reduce memory consumption**, and TRL provides several built-in features to help achieve this.
|
||||
|
||||
Below, we outline these techniques and recommend experimenting with different combinations to figure out which configuration works best for your specific setup.
|
||||
|
||||
Each method includes examples for the supported trainers. If you're unsure whether a technique is compatible with your trainer, please take a look at the corresponding trainer documentation.
|
||||
|
||||
For additional strategies, such as **gradient checkpointing**, which is supported across all trainers, see the [`transformers` performance guide](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/perf_train_gpu_one#gradient-checkpointing).
|
||||
|
||||
## Truncation
|
||||
|
||||
@ -54,7 +59,7 @@ training_args = SFTConfig(..., max_length=...)
|
||||
|
||||
### How to choose the `max_length` value?
|
||||
|
||||
If `max_length` is too small, a significant portion of your tokens will be discarded and won't contribute to training. If it's too large, memory usage can spike, potentially leading to OOM (Out-Of-Memory) errors. Without packing or padding-free, a large `max_length` may also result in inefficient training, as many tokens will be padding.
|
||||
If `max_length` is too small, a significant portion of your tokens will be discarded and won't contribute to training. If it's too large, memory usage can spike, potentially leading to out-of-memory (OOM) errors. Without packing or padding-free, a large `max_length` may also result in inefficient training, as many tokens will be padding.
|
||||
|
||||
To help you choose an appropriate value, we provide a utility to visualize the sequence length distribution in your dataset.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -63,7 +68,7 @@ To help you choose an appropriate value, we provide a utility to visualize the s
|
||||
## Packing
|
||||
|
||||
> [!TIP]
|
||||
> This technique applies only to SFT.
|
||||
> This technique is available only for **SFT** training and setups that use **FlashAttention** (or its variants).
|
||||
|
||||
[Truncation](#truncation) has several drawbacks:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -85,46 +90,57 @@ from trl import SFTConfig
|
||||
training_args = SFTConfig(..., packing=True, max_length=512)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> [!WARNING]
|
||||
> Packing may cause batch contamination, where adjacent sequences influence one another. This can be problematic for some applications. For more details, see [#1230](https://github.com/huggingface/trl/issues/1230).
|
||||
|
||||
## Liger for reducing peak memory usage
|
||||
|
||||
> [Liger Kernel](https://github.com/linkedin/Liger-Kernel) is a collection of Triton kernels designed specifically for LLM training. It can effectively increase multi-GPU training throughput by 20% and reduces memory usage by 60%.
|
||||
> [Liger Kernel](https://github.com/linkedin/Liger-Kernel) is a collection of Triton kernels designed specifically for LLM training. It can effectively increase multi-GPU training throughput by 20% and reduce memory usage by 60%.
|
||||
|
||||
For more information, see [Liger Kernel Integration](liger_kernel_integration)
|
||||
|
||||
<hfoptions id="liger">
|
||||
<hfoption id="DPO">
|
||||
For more information, see [Liger Kernel Integration](liger_kernel_integration).
|
||||
|
||||
To use Liger for reducing peak memory usage, use the following code snippet:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<hfoptions id="liger">
|
||||
<hfoption id="SFT">
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from trl import SFTConfig
|
||||
|
||||
training_args = SFTConfig(..., use_liger_kernel=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="DPO">
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from trl import DPOConfig
|
||||
|
||||
training_args = DPOConfig(..., use_liger_loss=True)
|
||||
training_args = DPOConfig(..., use_liger_kernel=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="GRPO">
|
||||
|
||||
To use Liger for reducing peak memory usage, use the following code snippet:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from trl import GRPOConfig
|
||||
|
||||
training_args = GRPOConfig(..., use_liger_loss=True)
|
||||
training_args = GRPOConfig(..., use_liger_kernel=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="KTO">
|
||||
|
||||
To use Liger for reducing peak memory usage, use the following code snippet:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from trl import KTOConfig
|
||||
|
||||
training_args = KTOConfig(..., use_liger_loss=True)
|
||||
training_args = KTOConfig(..., use_liger_kernel=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="GKD">
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from trl import GKDConfig
|
||||
|
||||
training_args = GKDConfig(..., use_liger_kernel=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
@ -172,25 +188,40 @@ from trl import SFTConfig
|
||||
training_args = SFTConfig(..., activation_offloading=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> [!WARNING]
|
||||
> When using activation offloading with models that use Liger kernels, you must disable Liger cross entropy due to compatibility issues. The issue occurs specifically with `use_liger_kernel=True` because Liger cross entropy performs in-place operations which conflict with activation offloading. The default setting (`use_liger_kernel=False`) works:
|
||||
>
|
||||
> ```python
|
||||
> # When using activation offloading with a model that uses Liger kernels:
|
||||
> from trl import SFTConfig
|
||||
>
|
||||
> training_args = SFTConfig(
|
||||
> activation_offloading=True,
|
||||
> use_liger_kernel=False, # Disable Liger cross entropy
|
||||
> # Other parameters...
|
||||
> )
|
||||
> ```
|
||||
Under the hood, activation offloading implements PyTorch's [`saved_tensors_hooks`](https://pytorch.org/tutorials/intermediate/autograd_saved_tensors_hooks_tutorial.html#hooks-for-autograd-saved-tensors) to intercept activations during the forward pass. It intelligently manages which tensors to offload based on size and context, avoiding offloading output tensors that would be inefficient. For performance optimization, it can, via a flag (which is true by default), use CUDA streams to overlap computation with CPU-GPU transfers.
|
||||
|
||||
Under the hood, activation offloading implements PyTorch's [`saved_tensors_hooks`](https://pytorch.org/tutorials/intermediate/autograd_saved_tensors_hooks_tutorial.html#hooks-for-autograd-saved-tensors) to intercept activations during the forward pass. It intelligently manages which tensors to offload based on size and context, avoiding offloading output tensors which would be inefficient. For performance optimization, it can optionally use CUDA streams to overlap computation with CPU-GPU transfers.
|
||||
## Padding Sequences to a Multiple
|
||||
|
||||
> [!TIP]
|
||||
> This technique is supported for **SFT** and **Reward** trainers currently.
|
||||
|
||||
When enabled, this option ensures that all sequences are **padded to a multiple** of the specified value.
|
||||
This can improve computational efficiency on some hardware by aligning sequence lengths to memory-friendly boundaries.
|
||||
|
||||
<hfoptions id="pad_to_multiple_of">
|
||||
<hfoption id="SFT">
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from trl import SFTConfig
|
||||
|
||||
training_args = SFTConfig(..., pad_to_multiple_of=2048)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="Reward">
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from trl import RewardConfig
|
||||
|
||||
training_args = RewardConfig(..., pad_to_multiple_of=2048)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
</hfoptions>
|
||||
|
||||
## Disabling model gathering for generation in online methods
|
||||
|
||||
When using DeepSpeed ZeRO-3, model weights are sharded across multiple GPUs. Online methods involve generating completions from the model as part of the training process. During this step, the model weights are temporarily gathered on a single GPU for generation. For very large models, this gathering can lead to out-of-memory (OOM) errors, as described in this issue: [#2250](https://github.com/huggingface/trl/issues/2250#issue-2598304204).
|
||||
When using DeepSpeed ZeRO-3, model weights are sharded across multiple GPUs. Online methods involve generating completions from the model as part of the training process. During this step, the model weights are temporarily gathered on a single GPU for generation. For very large models, this gathering can lead to OOM errors, as described in this issue: [#2250](https://github.com/huggingface/trl/issues/2250#issue-2598304204).
|
||||
|
||||
If you encounter this issue, you can disable the gathering of model weights for generation by setting the following parameter:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -237,7 +268,7 @@ This adjustment prevents model weights from being gathered, avoiding OOM errors,
|
||||
|
||||
## vLLM sleep mode
|
||||
|
||||
When using vLLM as the generation backend, you can enable _sleep mode_ to offload vLLM parameters and cache to CPU RAM during the optimization step and reload them back to GPU VRAM when needed for weight synchronization and generation.
|
||||
When using **vLLM** as the generation backend for online training methods, you can enable _sleep mode_ to offload vLLM parameters and cache to CPU RAM during the optimization step and reload them back to GPU VRAM when needed for weight synchronization and generation.
|
||||
|
||||
<hfoptions id="vllm_sleep">
|
||||
<hfoption id="GRPO">
|
||||
|
||||
@ -545,8 +545,14 @@ accelerate launch \
|
||||
|
||||
### Configuration Tips
|
||||
|
||||
> [!WARNING]
|
||||
> VLM training may fail if image tokens are truncated. We highly recommend disabling truncation by setting `max_prompt_length` to `None`.
|
||||
> [!TIP]
|
||||
> For VLMs, truncating may remove image tokens, leading to errors during training. To avoid this, set `max_prompt_length=None` in the [`RLOOConfig`]. This allows the model to process the full sequence length without truncating image tokens.
|
||||
>
|
||||
> ```python
|
||||
> RLOOConfig(max_prompt_length=None, ...)
|
||||
> ```
|
||||
>
|
||||
> Only use `max_prompt_length` when you've verified that truncation won't remove image tokens for the entire dataset.
|
||||
|
||||
- Use LoRA on vision-language projection layers
|
||||
- Enable 4-bit quantization to reduce memory usage
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,31 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Sentiment Tuning Examples
|
||||
|
||||
The notebooks and scripts in these examples show how to fine-tune a model with a sentiment classifier (such as `lvwerra/distilbert-imdb`).
|
||||
|
||||
Here's an overview of the notebooks and scripts in the [trl repository](https://github.com/huggingface/trl/tree/main/examples):
|
||||
|
||||
| File | Description |
|
||||
| --- |--- |
|
||||
| [`examples/scripts/ppo.py`](https://github.com/huggingface/trl/blob/main/examples/scripts/ppo.py) [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/trl/blob/main/examples/sentiment/notebooks/gpt2-sentiment.ipynb) | This script shows how to use the `PPOTrainer` to fine-tune a sentiment analysis model using IMDB dataset |
|
||||
| [`examples/notebooks/gpt2-sentiment.ipynb`](https://github.com/huggingface/trl/tree/main/examples/notebooks/gpt2-sentiment.ipynb) | This notebook demonstrates how to reproduce the GPT2 imdb sentiment tuning example on a jupyter notebook. |
|
||||
| [`examples/notebooks/gpt2-control.ipynb`](https://github.com/huggingface/trl/tree/main/examples/notebooks/gpt2-control.ipynb) [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/trl/blob/main/examples/sentiment/notebooks/gpt2-sentiment-control.ipynb) | This notebook demonstrates how to reproduce the GPT2 sentiment control example on a jupyter notebook. |
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# 1. run directly
|
||||
python examples/scripts/ppo.py
|
||||
# 2. run via `accelerate` (recommended), enabling more features (e.g., multiple GPUs, deepspeed)
|
||||
accelerate config # will prompt you to define the training configuration
|
||||
accelerate launch examples/scripts/ppo.py # launches training
|
||||
# 3. get help text and documentation
|
||||
python examples/scripts/ppo.py --help
|
||||
# 4. configure logging with wandb and, say, mini_batch_size=1 and gradient_accumulation_steps=16
|
||||
python examples/scripts/ppo.py --log_with wandb --mini_batch_size 1 --gradient_accumulation_steps 16
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Note: if you don't want to log with `wandb` remove `log_with="wandb"` in the scripts/notebooks. You can also replace it with your favourite experiment tracker that's [supported by `accelerate`](https://huggingface.co/docs/accelerate/usage_guides/tracking).
|
||||
|
||||
## Few notes on multi-GPU
|
||||
|
||||
To run in multi-GPU setup with DDP (distributed Data Parallel) change the `device_map` value to `device_map={"": Accelerator().process_index}` and make sure to run your script with `accelerate launch yourscript.py`. If you want to apply naive pipeline parallelism you can use `device_map="auto"`.
|
||||
@ -106,7 +106,7 @@ $$
|
||||
where \\( y_t \\) is the target token at timestep \\( t \\), and the model is trained to predict the next token given the previous ones. In practice, padding tokens are masked out during loss computation.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!TIP]
|
||||
> [On the Generalization of SFT: A Reinforcement Learning Perspective with Reward Rectification](https://huggingface.co/papers/2508.05629) proposes an alternative loss function, called **Dynamic Fine-Tuning (DFT)**, which aims to improve generalization by rectifying the reward signal. This method can be enabled by setting `loss_type="dft"` in the [`SFTConfig`]. For more details, see [Paper Index - Dynamic Fine-Tuning](paper_index#on-the-generalization-of-sft-a-reinforcement-learning-perspective-with-reward-rectification).
|
||||
> The paper [On the Generalization of SFT: A Reinforcement Learning Perspective with Reward Rectification](https://huggingface.co/papers/2508.05629) proposes an alternative loss function, called **Dynamic Fine-Tuning (DFT)**, which aims to improve generalization by rectifying the reward signal. This method can be enabled by setting `loss_type="dft"` in the [`SFTConfig`]. For more details, see [Paper Index - Dynamic Fine-Tuning](paper_index#on-the-generalization-of-sft-a-reinforcement-learning-perspective-with-reward-rectification).
|
||||
|
||||
### Label shifting and masking
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -9,7 +9,7 @@ If you have fine-tuned a model fully, meaning without the use of PEFT you can si
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM
|
||||
|
||||
model_name_or_path = "kashif/stack-llama-2" #path/to/your/model/or/name/on/hub
|
||||
model_name_or_path = "Qwen/Qwen3-0.6B" #path/to/your/model/or/name/on/hub
|
||||
device = "cpu" # or "cuda" if you have a GPU
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_name_or_path).to(device)
|
||||
@ -25,7 +25,7 @@ Alternatively you can also use the pipeline:
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
model_name_or_path = "kashif/stack-llama-2" #path/to/your/model/or/name/on/hub
|
||||
model_name_or_path = "Qwen/Qwen3-0.6B" #path/to/your/model/or/name/on/hub
|
||||
pipe = pipeline("text-generation", model=model_name_or_path)
|
||||
print(pipe("This movie was really")[0]["generated_text"])
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -36,7 +36,7 @@ print(pipe("This movie was really")[0]["generated_text"])
|
||||
from peft import PeftConfig, PeftModel
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
base_model_name = "kashif/stack-llama-2" #path/to/your/model/or/name/on/hub
|
||||
base_model_name = "Qwen/Qwen3-0.6B" #path/to/your/model/or/name/on/hub
|
||||
adapter_model_name = "path/to/my/adapter"
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(base_model_name)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -14,7 +14,6 @@
|
||||
|
||||
import re
|
||||
from dataclasses import dataclass, field
|
||||
from typing import Optional
|
||||
|
||||
from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
from huggingface_hub import ModelCard
|
||||
@ -42,7 +41,7 @@ class ScriptArguments:
|
||||
repo_id: str = field(
|
||||
default="trl-lib/hh-rlhf-helpful-base", metadata={"help": "Hugging Face repository ID to push the dataset to."}
|
||||
)
|
||||
dataset_num_proc: Optional[int] = field(
|
||||
dataset_num_proc: int | None = field(
|
||||
default=None, metadata={"help": "Number of workers to use for dataset processing."}
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -50,7 +49,7 @@ class ScriptArguments:
|
||||
def common_start(str1: str, str2: str) -> str:
|
||||
# Zip the two strings and iterate over them together
|
||||
common_chars = []
|
||||
for c1, c2 in zip(str1, str2):
|
||||
for c1, c2 in zip(str1, str2, strict=True):
|
||||
if c1 == c2:
|
||||
common_chars.append(c1)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -14,7 +14,6 @@
|
||||
|
||||
import ast
|
||||
from dataclasses import dataclass, field
|
||||
from typing import Optional
|
||||
|
||||
from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
from huggingface_hub import ModelCard
|
||||
@ -43,7 +42,7 @@ class ScriptArguments:
|
||||
default="trl-lib/llava-instruct-mix",
|
||||
metadata={"help": "Hugging Face repository ID to push the dataset to."},
|
||||
)
|
||||
dataset_num_proc: Optional[int] = field(
|
||||
dataset_num_proc: int | None = field(
|
||||
default=None,
|
||||
metadata={"help": "Number of workers to use for dataset processing."},
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -13,7 +13,6 @@
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
from dataclasses import dataclass, field
|
||||
from typing import Optional
|
||||
|
||||
from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
from huggingface_hub import ModelCard
|
||||
@ -42,7 +41,7 @@ class ScriptArguments:
|
||||
default="trl-lib/lm-human-preferences-descriptiveness",
|
||||
metadata={"help": "Hugging Face repository ID to push the dataset to."},
|
||||
)
|
||||
dataset_num_proc: Optional[int] = field(
|
||||
dataset_num_proc: int | None = field(
|
||||
default=None,
|
||||
metadata={"help": "Number of workers to use for dataset processing."},
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -13,7 +13,6 @@
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
from dataclasses import dataclass, field
|
||||
from typing import Optional
|
||||
|
||||
from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
from huggingface_hub import ModelCard
|
||||
@ -42,7 +41,7 @@ class ScriptArguments:
|
||||
default="trl-lib/lm-human-preferences-sentiment",
|
||||
metadata={"help": "Hugging Face repository ID to push the dataset to."},
|
||||
)
|
||||
dataset_num_proc: Optional[int] = field(
|
||||
dataset_num_proc: int | None = field(
|
||||
default=None,
|
||||
metadata={"help": "Number of workers to use for dataset processing."},
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -15,7 +15,6 @@
|
||||
import re
|
||||
from dataclasses import dataclass, field
|
||||
from itertools import chain
|
||||
from typing import Optional
|
||||
|
||||
from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
from huggingface_hub import ModelCard
|
||||
@ -44,7 +43,7 @@ class ScriptArguments:
|
||||
default="trl-lib/math_shepherd",
|
||||
metadata={"help": "Hugging Face repository ID to push the dataset to."},
|
||||
)
|
||||
dataset_num_proc: Optional[int] = field(
|
||||
dataset_num_proc: int | None = field(
|
||||
default=None,
|
||||
metadata={"help": "Number of workers to use for dataset processing."},
|
||||
)
|
||||
@ -64,7 +63,7 @@ def process_example(example):
|
||||
labels = [example["label"][idx] == "+" for idx in indexes]
|
||||
|
||||
# Split the inputs into steps (caution, the first step is missing here, it is the prompt)
|
||||
steps = [inputs[i:j] for i, j in zip(chain([0], indexes), chain(indexes, [None]))]
|
||||
steps = [inputs[i:j] for i, j in zip(chain([0], indexes), chain(indexes, [None]), strict=True)]
|
||||
|
||||
# Remove the last step (single ⶻ)
|
||||
steps = steps[:-1]
|
||||
|
||||
@ -13,7 +13,6 @@
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
from dataclasses import dataclass, field
|
||||
from typing import Optional
|
||||
|
||||
from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
from huggingface_hub import ModelCard
|
||||
@ -42,7 +41,7 @@ class ScriptArguments:
|
||||
default="trl-lib/prm800k",
|
||||
metadata={"help": "Hugging Face repository ID to push the dataset to."},
|
||||
)
|
||||
dataset_num_proc: Optional[int] = field(
|
||||
dataset_num_proc: int | None = field(
|
||||
default=None,
|
||||
metadata={"help": "Number of workers to use for dataset processing."},
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -13,7 +13,6 @@
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
from dataclasses import dataclass, field
|
||||
from typing import Optional
|
||||
|
||||
from datasets import features, load_dataset
|
||||
from huggingface_hub import ModelCard
|
||||
@ -42,7 +41,7 @@ class ScriptArguments:
|
||||
default="trl-lib/rlaif-v",
|
||||
metadata={"help": "Hugging Face repository ID to push the dataset to."},
|
||||
)
|
||||
dataset_num_proc: Optional[int] = field(
|
||||
dataset_num_proc: int | None = field(
|
||||
default=None,
|
||||
metadata={"help": "Number of workers to use for dataset processing."},
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -13,7 +13,6 @@
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
from dataclasses import dataclass, field
|
||||
from typing import Optional
|
||||
|
||||
from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
from huggingface_hub import ModelCard
|
||||
@ -42,7 +41,7 @@ class ScriptArguments:
|
||||
default="trl-lib/tldr",
|
||||
metadata={"help": "Hugging Face repository ID to push the dataset to."},
|
||||
)
|
||||
dataset_num_proc: Optional[int] = field(
|
||||
dataset_num_proc: int | None = field(
|
||||
default=None,
|
||||
metadata={"help": "Number of workers to use for dataset processing."},
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -13,7 +13,6 @@
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
from dataclasses import dataclass, field
|
||||
from typing import Optional
|
||||
|
||||
from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
from huggingface_hub import ModelCard
|
||||
@ -42,7 +41,7 @@ class ScriptArguments:
|
||||
default="trl-lib/tldr-preference",
|
||||
metadata={"help": "Hugging Face repository ID to push the dataset to."},
|
||||
)
|
||||
dataset_num_proc: Optional[int] = field(
|
||||
dataset_num_proc: int | None = field(
|
||||
default=None,
|
||||
metadata={"help": "Number of workers to use for dataset processing."},
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -13,7 +13,6 @@
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
from dataclasses import dataclass, field
|
||||
from typing import Optional
|
||||
|
||||
from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
from huggingface_hub import ModelCard
|
||||
@ -42,7 +41,7 @@ class ScriptArguments:
|
||||
default="trl-lib/ultrafeedback-prompt",
|
||||
metadata={"help": "Hugging Face repository ID to push the dataset to."},
|
||||
)
|
||||
dataset_num_proc: Optional[int] = field(
|
||||
dataset_num_proc: int | None = field(
|
||||
default=None,
|
||||
metadata={"help": "Number of workers to use for dataset processing."},
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -13,7 +13,6 @@
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
from dataclasses import dataclass, field
|
||||
from typing import Optional
|
||||
|
||||
from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
from huggingface_hub import ModelCard
|
||||
@ -79,7 +78,7 @@ class ScriptArguments:
|
||||
default="trl-lib/ultrafeedback-gpt-3.5-turbo-helpfulness",
|
||||
metadata={"help": "Hugging Face repository ID to push the dataset to."},
|
||||
)
|
||||
dataset_num_proc: Optional[int] = field(
|
||||
dataset_num_proc: int | None = field(
|
||||
default=None,
|
||||
metadata={"help": "Number of workers to use for dataset processing."},
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -2,16 +2,8 @@
|
||||
|
||||
This directory contains a collection of Jupyter notebooks that demonstrate how to use the TRL library in different applications.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
| Notebook | Description | Open in Colab |
|
||||
|----------|-------------|---------------|
|
||||
| --- | --- | --- |
|
||||
| [`sft_trl_lora_qlora.ipynb`](https://github.com/huggingface/trl/tree/main/examples/notebooks/sft_trl_lora_qlora.ipynb) | Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) using QLoRA on free Colab | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/trl/blob/main/examples/notebooks/sft_trl_lora_qlora.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [`sft_qwen_vl.ipynb`](https://github.com/huggingface/trl/tree/main/examples/notebooks/sft_qwen_vl.ipynb) | Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT) Qwen3-VL with QLoRA using TRL on free Colab | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/trl/blob/main/examples/notebooks/sft_qwen_vl.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [`grpo_qwen3_vl.ipynb`](https://github.com/huggingface/trl/tree/main/examples/notebooks/grpo_qwen3_vl.ipynb) | GRPO Qwen3-VL with QLoRA using TRL on free Colab | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/trl/blob/main/examples/notebooks/grpo_qwen3_vl.ipynb) |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Legacy / Older Notebooks
|
||||
|
||||
- [`best_of_n.ipynb`](https://github.com/huggingface/trl/tree/main/examples/notebooks/best_of_n.ipynb): This notebook demonstrates how to use the "Best of N" sampling strategy using TRL when fine-tuning your model with PPO.
|
||||
- [`gpt2-sentiment.ipynb`](https://github.com/huggingface/trl/tree/main/examples/notebooks/gpt2-sentiment.ipynb): This notebook demonstrates how to reproduce the GPT2 imdb sentiment tuning example on a jupyter notebook.
|
||||
- [`gpt2-sentiment-control.ipynb`](https://github.com/huggingface/trl/tree/main/examples/notebooks/gpt2-sentiment-control.ipynb): This notebook demonstrates how to reproduce the GPT2 sentiment control example on a jupyter notebook.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,609 +0,0 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cells": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"id": "WQpNapZNWuXP"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"**Best-of-n sampling as an alternative to RLHF**\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"This notebook compares reward-model scores of prompt based responses from \n",
|
||||
"1. a base model (`gpt2-imdb`)\n",
|
||||
"2. `RLHF` tuned model based on this base-model \n",
|
||||
"3. the base-model again from which we sample n responses to each prompt, score them and take the best scored one AKA the `best-of-n sampled` model\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Import dependencies"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"id": "vDA6qayz692w"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"%pip install transformers trl"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"id": "M1s_iNm773hM"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"import torch\n",
|
||||
"import pandas as pd\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"from transformers import pipeline, AutoTokenizer\n",
|
||||
"from datasets import load_dataset\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"from trl import AutoModelForCausalLMWithValueHead\n",
|
||||
"from trl.core import LengthSampler\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"device = torch.accelerator.current_accelerator().type if hasattr(torch, \"accelerator\") else \"cuda\"\n",
|
||||
"device = \"cpu\" if device is None else device"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"id": "Y7hyrIrO8tcY"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"Various constants"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 2,
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"id": "MqS3OM6Q8x6g"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"ref_model_name = \"lvwerra/gpt2-imdb\"\n",
|
||||
"model_name = \"lvwerra/gpt2-imdb-pos-v2\"\n",
|
||||
"reward_model = \"lvwerra/distilbert-imdb\"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"N_BEST_OF = 4"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"id": "c1YcXeElg6or"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"Models and tokenizers"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"id": "b855NrL181Hh"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"model = AutoModelForCausalLMWithValueHead.from_pretrained(model_name)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"ref_model = AutoModelForCausalLMWithValueHead.from_pretrained(ref_model_name)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"reward_pipe = pipeline(\"sentiment-analysis\", model=reward_model, device=device)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(ref_model_name)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"tokenizer.pad_token = tokenizer.eos_token\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# put models to accelerator\n",
|
||||
"model.to(device)\n",
|
||||
"ref_model.to(device)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"id": "Z1Cz0gCFhZYJ"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"Dataset building"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 4,
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"id": "LqLVEp5p_8XM"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"outputs": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "stderr",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"Generating train split: 100%|██████████| 25000/25000 [00:00<00:00, 113700.67 examples/s]\n",
|
||||
"Generating test split: 100%|██████████| 25000/25000 [00:00<00:00, 131049.39 examples/s]\n",
|
||||
"Generating unsupervised split: 100%|██████████| 50000/50000 [00:00<00:00, 126486.39 examples/s]\n",
|
||||
"Filter: 100%|██████████| 25000/25000 [00:00<00:00, 238843.61 examples/s]\n",
|
||||
"Map: 0%| | 0/24895 [00:00<?, ? examples/s]Token indices sequence length is longer than the specified maximum sequence length for this model (1168 > 1024). Running this sequence through the model will result in indexing errors\n",
|
||||
"Map: 100%|██████████| 24895/24895 [00:17<00:00, 1462.36 examples/s]\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"def build_dataset(\n",
|
||||
" tokenizer,\n",
|
||||
" dataset_name=\"stanfordnlp/imdb\",\n",
|
||||
" input_min_text_length=2,\n",
|
||||
" input_max_text_length=8,\n",
|
||||
"):\n",
|
||||
" # load imdb with datasets\n",
|
||||
" ds = load_dataset(dataset_name, split=\"train\")\n",
|
||||
" ds = ds.rename_columns({\"text\": \"review\"})\n",
|
||||
" ds = ds.filter(lambda x: len(x[\"review\"]) > 200, batched=False)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" input_size = LengthSampler(input_min_text_length, input_max_text_length)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" def tokenize(sample):\n",
|
||||
" sample[\"input_ids\"] = tokenizer.encode(sample[\"review\"])[: input_size()]\n",
|
||||
" sample[\"query\"] = tokenizer.decode(sample[\"input_ids\"])\n",
|
||||
" return sample\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" ds = ds.map(tokenize, batched=False)\n",
|
||||
" ds.set_format(type=\"torch\")\n",
|
||||
" return ds\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"dataset = build_dataset(tokenizer)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 5,
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"id": "AqA2McjMAxNw"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"gen_kwargs = {\n",
|
||||
" \"min_length\": -1,\n",
|
||||
" \"top_k\": 0.0,\n",
|
||||
" \"top_p\": 1.0,\n",
|
||||
" \"do_sample\": True,\n",
|
||||
" \"pad_token_id\": tokenizer.eos_token_id,\n",
|
||||
"}\n",
|
||||
"sent_kwargs = {\"top_k\": None, \"function_to_apply\": \"none\", \"batch_size\": 16}"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 6,
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"id": "L_q4qs35AxcR"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"output_min_length = 4\n",
|
||||
"output_max_length = 16\n",
|
||||
"output_length_sampler = LengthSampler(output_min_length, output_max_length)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"#### get a batch from the dataset\n",
|
||||
"bs = 16\n",
|
||||
"output_data = dict()\n",
|
||||
"dataset.set_format(\"pandas\")\n",
|
||||
"df_batch = dataset[:].sample(bs)\n",
|
||||
"output_data[\"query\"] = df_batch[\"query\"].tolist()\n",
|
||||
"query_tensors = df_batch[\"input_ids\"].tolist()\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# :: [Resp]\n",
|
||||
"response_tensors_ref, response_tensors = [], []\n",
|
||||
"# :: [[Resp]]\n",
|
||||
"response_tensors_best_of = []"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"id": "QVfpyHnZBLKY"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Generation using various models"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"id": "-imZ7uEFBNbw"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"for i in range(bs):\n",
|
||||
" gen_len = output_length_sampler()\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" query = torch.tensor(query_tensors[i])\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" output = ref_model.generate(\n",
|
||||
" query.unsqueeze(dim=0).to(device), max_new_tokens=gen_len, **gen_kwargs\n",
|
||||
" ).squeeze()\n",
|
||||
" response_tensors_ref.append(tokenizer.decode(output))\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" output = model.generate(\n",
|
||||
" query.unsqueeze(dim=0).to(device), max_new_tokens=gen_len, **gen_kwargs\n",
|
||||
" ).squeeze()\n",
|
||||
" response_tensors.append(tokenizer.decode(output))\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" # generating copies of the same query for the Best-of-n sampling\n",
|
||||
" queries = query.repeat((N_BEST_OF, 1))\n",
|
||||
" output = ref_model.generate(\n",
|
||||
" queries.to(device), max_new_tokens=gen_len, **gen_kwargs\n",
|
||||
" ).squeeze()\n",
|
||||
" response_tensors_best_of.append(tokenizer.batch_decode(output))"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"id": "Jp5FC0Y5h_Sf"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"Scoring"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 8,
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"id": "PyDbbAQ0F_h7"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"scores_ref = [\n",
|
||||
" output[0][\"score\"] for output in reward_pipe(response_tensors_ref, **sent_kwargs)\n",
|
||||
"]\n",
|
||||
"scores = [output[0][\"score\"] for output in reward_pipe(response_tensors, **sent_kwargs)]\n",
|
||||
"scores_best_of = []\n",
|
||||
"for i, response in enumerate(response_tensors_best_of):\n",
|
||||
" # base_score = scores_ref[i]\n",
|
||||
" scores_best_of.append(\n",
|
||||
" torch.tensor(\n",
|
||||
" [output[0][\"score\"] for output in reward_pipe(response, **sent_kwargs)]\n",
|
||||
" )\n",
|
||||
" )"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 9,
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"colab": {
|
||||
"base_uri": "https://localhost:8080/",
|
||||
"height": 682
|
||||
},
|
||||
"id": "nA1GDNJEiGm-",
|
||||
"outputId": "1389c686-0751-4304-dea2-b71fd68748e1"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"outputs": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"data": {
|
||||
"text/html": [
|
||||
"<div>\n",
|
||||
"<style scoped>\n",
|
||||
" .dataframe tbody tr th:only-of-type {\n",
|
||||
" vertical-align: middle;\n",
|
||||
" }\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" .dataframe tbody tr th {\n",
|
||||
" vertical-align: top;\n",
|
||||
" }\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" .dataframe thead th {\n",
|
||||
" text-align: right;\n",
|
||||
" }\n",
|
||||
"</style>\n",
|
||||
"<table border=\"1\" class=\"dataframe\">\n",
|
||||
" <thead>\n",
|
||||
" <tr style=\"text-align: right;\">\n",
|
||||
" <th></th>\n",
|
||||
" <th>query</th>\n",
|
||||
" <th>response (ref)</th>\n",
|
||||
" <th>scores (ref)</th>\n",
|
||||
" <th>response (RLHF)</th>\n",
|
||||
" <th>scores (RLHF)</th>\n",
|
||||
" <th>response (best_of)</th>\n",
|
||||
" <th>scores (best_of)</th>\n",
|
||||
" </tr>\n",
|
||||
" </thead>\n",
|
||||
" <tbody>\n",
|
||||
" <tr>\n",
|
||||
" <th>0</th>\n",
|
||||
" <td>This movie is one of</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>This movie is one of the most twisted films I</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>2.094254</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>This movie is one of the finest directors of the</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>2.726879</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>This movie is one of the best looking movies I</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>2.705925</td>\n",
|
||||
" </tr>\n",
|
||||
" <tr>\n",
|
||||
" <th>1</th>\n",
|
||||
" <td>one may</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>one may feel we are seeing more</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>1.478813</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>one may not have great assets,</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>0.420451</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>one may not be supported, terrible</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>2.043730</td>\n",
|
||||
" </tr>\n",
|
||||
" <tr>\n",
|
||||
" <th>2</th>\n",
|
||||
" <td>This is an amazing film,</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>This is an amazing film, one of our favorite g...</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>2.871389</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>This is an amazing film, with all thelike wond...</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>2.918770</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>This is an amazing film, very moving and this ...</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>2.871694</td>\n",
|
||||
" </tr>\n",
|
||||
" <tr>\n",
|
||||
" <th>3</th>\n",
|
||||
" <td>just below</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>just below)and makes it seem as</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>0.861618</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>just below the world capital is a man</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>0.238322</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>just below) in this beautiful comedy.</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>2.760033</td>\n",
|
||||
" </tr>\n",
|
||||
" <tr>\n",
|
||||
" <th>4</th>\n",
|
||||
" <td>Return To the</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>Return To the Museum. That film, called Bl</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>0.017376</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>Return To the East\" is a fascinating film,</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>2.648028</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>Return To the International: Miyazaki, by Ts</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>1.072344</td>\n",
|
||||
" </tr>\n",
|
||||
" <tr>\n",
|
||||
" <th>5</th>\n",
|
||||
" <td>Brando plays the ace jet</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>Brando plays the ace jet fighter pilot, who stops</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>0.565335</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>Brando plays the ace jet pilot, who's a</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>0.668954</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>Brando plays the ace jet pilot Charlie; his fo...</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>0.679582</td>\n",
|
||||
" </tr>\n",
|
||||
" <tr>\n",
|
||||
" <th>6</th>\n",
|
||||
" <td>And a rather U</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>And a rather Utopian horror movie and with good</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>2.245751</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>And a rather Utop Congressional Movie, with a 45</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>0.307100</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>And a rather U of A complete combination of wh...</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>2.209265</td>\n",
|
||||
" </tr>\n",
|
||||
" <tr>\n",
|
||||
" <th>7</th>\n",
|
||||
" <td>The plot of this movie hangs</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>The plot of this movie hangs in the balance as...</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>1.122540</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>The plot of this movie hangs out well. The who...</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>2.195263</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>The plot of this movie hangs together within t...</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>1.310783</td>\n",
|
||||
" </tr>\n",
|
||||
" <tr>\n",
|
||||
" <th>8</th>\n",
|
||||
" <td>This isn't</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>This isn't all that bad; as for my</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>0.623968</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>This isn't a good film because I loved it</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>1.694601</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>This isn't bad writing, powerful actors and sp...</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>1.835901</td>\n",
|
||||
" </tr>\n",
|
||||
" <tr>\n",
|
||||
" <th>9</th>\n",
|
||||
" <td>This movie was for a</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>This movie was for a good reason!' Uh, OK</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>0.437566</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>This movie was for a fun, and grand Robinson</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>2.531890</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>This movie was for a bastard.<br /><br</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>2.311337</td>\n",
|
||||
" </tr>\n",
|
||||
" <tr>\n",
|
||||
" <th>10</th>\n",
|
||||
" <td>witty. funny.</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>witty. funny.<|endoftext|></td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>1.636344</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>witty. funny. funnier. more funny. funnier. fu...</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>2.132353</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>witty. funny. In the first scene the comical n...</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>2.164077</td>\n",
|
||||
" </tr>\n",
|
||||
" <tr>\n",
|
||||
" <th>11</th>\n",
|
||||
" <td>It's very hard</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>It's very hard to believe that anyone would en...</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>1.003727</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>It's very hard to wrap your mind around what h...</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>0.778888</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>It's very hard to wrap this up, due to lack of...</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>1.598843</td>\n",
|
||||
" </tr>\n",
|
||||
" <tr>\n",
|
||||
" <th>12</th>\n",
|
||||
" <td>Absolutely fantastic trash....this one</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>Absolutely fantastic trash....this one was hav...</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>1.350834</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>Absolutely fantastic trash....this one is a pe...</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>2.177587</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>Absolutely fantastic trash....this one ruins i...</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>2.221997</td>\n",
|
||||
" </tr>\n",
|
||||
" <tr>\n",
|
||||
" <th>13</th>\n",
|
||||
" <td>Prior to</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>Prior to this action film,</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>0.242474</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>Prior to Christian Kane's star</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>0.297408</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>Prior to his restoration, Passion</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>1.655534</td>\n",
|
||||
" </tr>\n",
|
||||
" <tr>\n",
|
||||
" <th>14</th>\n",
|
||||
" <td>i,</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>i, Marty Rathbun, Damon Wayans, Mark Watney and</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>0.105734</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>i, perhaps the great movie the director should...</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>1.336116</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>i, Martin was a thrill of 70s---wow!lee and Heath</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>2.277638</td>\n",
|
||||
" </tr>\n",
|
||||
" <tr>\n",
|
||||
" <th>15</th>\n",
|
||||
" <td>The film</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>The film takes a very grim craggy look</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>0.069017</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>The film is one of the best of that era</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>2.737825</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>The film's ambition was almost so great that its</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>2.357480</td>\n",
|
||||
" </tr>\n",
|
||||
" </tbody>\n",
|
||||
"</table>\n",
|
||||
"</div>"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"text/plain": [
|
||||
" query \\\n",
|
||||
"0 This movie is one of \n",
|
||||
"1 one may \n",
|
||||
"2 This is an amazing film, \n",
|
||||
"3 just below \n",
|
||||
"4 Return To the \n",
|
||||
"5 Brando plays the ace jet \n",
|
||||
"6 And a rather U \n",
|
||||
"7 The plot of this movie hangs \n",
|
||||
"8 This isn't \n",
|
||||
"9 This movie was for a \n",
|
||||
"10 witty. funny. \n",
|
||||
"11 It's very hard \n",
|
||||
"12 Absolutely fantastic trash....this one \n",
|
||||
"13 Prior to \n",
|
||||
"14 i, \n",
|
||||
"15 The film \n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" response (ref) scores (ref) \\\n",
|
||||
"0 This movie is one of the most twisted films I 2.094254 \n",
|
||||
"1 one may feel we are seeing more 1.478813 \n",
|
||||
"2 This is an amazing film, one of our favorite g... 2.871389 \n",
|
||||
"3 just below)and makes it seem as 0.861618 \n",
|
||||
"4 Return To the Museum. That film, called Bl 0.017376 \n",
|
||||
"5 Brando plays the ace jet fighter pilot, who stops 0.565335 \n",
|
||||
"6 And a rather Utopian horror movie and with good 2.245751 \n",
|
||||
"7 The plot of this movie hangs in the balance as... 1.122540 \n",
|
||||
"8 This isn't all that bad; as for my 0.623968 \n",
|
||||
"9 This movie was for a good reason!' Uh, OK 0.437566 \n",
|
||||
"10 witty. funny.<|endoftext|> 1.636344 \n",
|
||||
"11 It's very hard to believe that anyone would en... 1.003727 \n",
|
||||
"12 Absolutely fantastic trash....this one was hav... 1.350834 \n",
|
||||
"13 Prior to this action film, 0.242474 \n",
|
||||
"14 i, Marty Rathbun, Damon Wayans, Mark Watney and 0.105734 \n",
|
||||
"15 The film takes a very grim craggy look 0.069017 \n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" response (RLHF) scores (RLHF) \\\n",
|
||||
"0 This movie is one of the finest directors of the 2.726879 \n",
|
||||
"1 one may not have great assets, 0.420451 \n",
|
||||
"2 This is an amazing film, with all thelike wond... 2.918770 \n",
|
||||
"3 just below the world capital is a man 0.238322 \n",
|
||||
"4 Return To the East\" is a fascinating film, 2.648028 \n",
|
||||
"5 Brando plays the ace jet pilot, who's a 0.668954 \n",
|
||||
"6 And a rather Utop Congressional Movie, with a 45 0.307100 \n",
|
||||
"7 The plot of this movie hangs out well. The who... 2.195263 \n",
|
||||
"8 This isn't a good film because I loved it 1.694601 \n",
|
||||
"9 This movie was for a fun, and grand Robinson 2.531890 \n",
|
||||
"10 witty. funny. funnier. more funny. funnier. fu... 2.132353 \n",
|
||||
"11 It's very hard to wrap your mind around what h... 0.778888 \n",
|
||||
"12 Absolutely fantastic trash....this one is a pe... 2.177587 \n",
|
||||
"13 Prior to Christian Kane's star 0.297408 \n",
|
||||
"14 i, perhaps the great movie the director should... 1.336116 \n",
|
||||
"15 The film is one of the best of that era 2.737825 \n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" response (best_of) scores (best_of) \n",
|
||||
"0 This movie is one of the best looking movies I 2.705925 \n",
|
||||
"1 one may not be supported, terrible 2.043730 \n",
|
||||
"2 This is an amazing film, very moving and this ... 2.871694 \n",
|
||||
"3 just below) in this beautiful comedy. 2.760033 \n",
|
||||
"4 Return To the International: Miyazaki, by Ts 1.072344 \n",
|
||||
"5 Brando plays the ace jet pilot Charlie; his fo... 0.679582 \n",
|
||||
"6 And a rather U of A complete combination of wh... 2.209265 \n",
|
||||
"7 The plot of this movie hangs together within t... 1.310783 \n",
|
||||
"8 This isn't bad writing, powerful actors and sp... 1.835901 \n",
|
||||
"9 This movie was for a bastard.<br /><br 2.311337 \n",
|
||||
"10 witty. funny. In the first scene the comical n... 2.164077 \n",
|
||||
"11 It's very hard to wrap this up, due to lack of... 1.598843 \n",
|
||||
"12 Absolutely fantastic trash....this one ruins i... 2.221997 \n",
|
||||
"13 Prior to his restoration, Passion 1.655534 \n",
|
||||
"14 i, Martin was a thrill of 70s---wow!lee and Heath 2.277638 \n",
|
||||
"15 The film's ambition was almost so great that its 2.357480 "
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
"execution_count": 9,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"output_type": "execute_result"
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"output_data[\"response (ref)\"] = response_tensors_ref\n",
|
||||
"output_data[\"scores (ref)\"] = scores_ref\n",
|
||||
"output_data[\"response (RLHF)\"] = response_tensors\n",
|
||||
"output_data[\"scores (RLHF)\"] = scores\n",
|
||||
"output_data[\"response (best_of)\"] = [\n",
|
||||
" response_tensors_best_of[i][a.argmax().item()] for i, a in enumerate(scores_best_of)\n",
|
||||
"]\n",
|
||||
"output_data[\"scores (best_of)\"] = [a.max().item() for a in scores_best_of]\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# store results in a dataframe\n",
|
||||
"df_results = pd.DataFrame(output_data)\n",
|
||||
"df_results"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"accelerator": "GPU",
|
||||
"colab": {
|
||||
"provenance": []
|
||||
},
|
||||
"gpuClass": "standard",
|
||||
"kernelspec": {
|
||||
"display_name": "Python 3",
|
||||
"language": "python",
|
||||
"name": "python3"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"language_info": {
|
||||
"codemirror_mode": {
|
||||
"name": "ipython",
|
||||
"version": 3
|
||||
},
|
||||
"file_extension": ".py",
|
||||
"mimetype": "text/x-python",
|
||||
"name": "python",
|
||||
"nbconvert_exporter": "python",
|
||||
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
|
||||
"version": "3.12.3"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"nbformat": 4,
|
||||
"nbformat_minor": 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
File diff suppressed because one or more lines are too long
@ -1,867 +0,0 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cells": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Tune GPT2 to generate positive reviews\n",
|
||||
"> Optimise GPT2 to produce positive IMDB movie reviews using a BERT sentiment classifier as a reward function."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"<div style=\"text-align: center\">\n",
|
||||
"<img src='https://huggingface.co/datasets/trl-lib/documentation-images/resolve/main/gpt2_bert_training.png' width='600'>\n",
|
||||
"<p style=\"text-align: center;\"> <b>Figure:</b> Experiment setup to tune GPT2. The yellow arrows are outside the scope of this notebook, but the trained models are available through Hugging Face. </p>\n",
|
||||
"</div>\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"In this notebook we fine-tune GPT2 (small) to generate positive movie reviews based on the IMDB dataset. The model gets the start of a real review and is tasked to produce positive continuations. To reward positive continuations we use a BERT classifier to analyse the sentiment of the produced sentences and use the classifier's outputs as rewards signals for PPO training."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Setup experiment"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Import dependencies"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"%load_ext autoreload\n",
|
||||
"%autoreload 2"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"%pip install transformers trl wandb"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"import torch\n",
|
||||
"from tqdm import tqdm\n",
|
||||
"import pandas as pd\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"tqdm.pandas()\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"from transformers import pipeline, AutoTokenizer\n",
|
||||
"from datasets import load_dataset\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"from trl import PPOTrainer, PPOConfig, AutoModelForCausalLMWithValueHead\n",
|
||||
"from trl.core import LengthSampler"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Configuration"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"config = PPOConfig(\n",
|
||||
" model_name=\"lvwerra/gpt2-imdb\",\n",
|
||||
" learning_rate=1.41e-5,\n",
|
||||
" log_with=\"wandb\",\n",
|
||||
")\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"sent_kwargs = {\"top_k\": None, \"function_to_apply\": \"none\", \"batch_size\": 16}"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"import wandb\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"wandb.init()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"You can see that we load a GPT2 model called `gpt2_imdb`. This model was additionally fine-tuned on the IMDB dataset for 1 epoch with the huggingface [script](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/examples/legacy/run_language_modeling.py) (no special settings). The other parameters are mostly taken from the original paper [\"Fine-Tuning Language Models from Human Preferences\"](\n",
|
||||
"https://huggingface.co/papers/1909.08593). This model as well as the BERT model is available in the Huggingface model zoo [here](https://huggingface.co/models). The following code should automatically download the models."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Load data and models"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"attachments": {},
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Load IMDB dataset\n",
|
||||
"The IMDB dataset contains 50k movie review annotated with \"positive\"/\"negative\" feedback indicating the sentiment. We load the IMDB dataset into a DataFrame and filter for comments that are at least 200 characters. Then we tokenize each text and cut it to random size with the `LengthSampler`."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"def build_dataset(\n",
|
||||
" config,\n",
|
||||
" dataset_name=\"stanfordnlp/imdb\",\n",
|
||||
" input_min_text_length=2,\n",
|
||||
" input_max_text_length=8,\n",
|
||||
"):\n",
|
||||
" \"\"\"\n",
|
||||
" Build dataset for training. This builds the dataset from `load_dataset`, one should\n",
|
||||
" customize this function to train the model on its own dataset.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" Args:\n",
|
||||
" config (`PPOConfig`):\n",
|
||||
" The configuration of the PPO training.\n",
|
||||
" dataset_name (`str`):\n",
|
||||
" The name of the dataset to be loaded.\n",
|
||||
" input_min_text_length (`int`, defaults to 5):\n",
|
||||
" The minimum length of the input text.\n",
|
||||
" input_max_text_length (`int`, defaults to 10):\n",
|
||||
" The maximum length of the input text.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" Returns:\n",
|
||||
" dataloader (`torch.utils.data.DataLoader`):\n",
|
||||
" The dataloader for the dataset.\n",
|
||||
" \"\"\"\n",
|
||||
" tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(config.model_name)\n",
|
||||
" tokenizer.pad_token = tokenizer.eos_token\n",
|
||||
" # load imdb with datasets\n",
|
||||
" ds = load_dataset(dataset_name, split=\"train\")\n",
|
||||
" ds = ds.rename_columns({\"text\": \"review\"})\n",
|
||||
" ds = ds.filter(lambda x: len(x[\"review\"]) > 200, batched=False)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" input_size = LengthSampler(input_min_text_length, input_max_text_length)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" def tokenize(sample):\n",
|
||||
" sample[\"input_ids\"] = tokenizer.encode(sample[\"review\"])[: input_size()]\n",
|
||||
" sample[\"query\"] = tokenizer.decode(sample[\"input_ids\"])\n",
|
||||
" return sample\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" ds = ds.map(tokenize, batched=False)\n",
|
||||
" ds.set_format(type=\"torch\")\n",
|
||||
" return ds"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"dataset = build_dataset(config)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"def collator(data):\n",
|
||||
" return dict((key, [d[key] for d in data]) for key in data[0])"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Load pre-trained GPT2 language models"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"We load the GPT2 model with a value head and the tokenizer. We load the model twice; the first model is optimized while the second model serves as a reference to calculate the KL-divergence from the starting point. This serves as an additional reward signal in the PPO training to make sure the optimized model does not deviate too much from the original language model."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"model = AutoModelForCausalLMWithValueHead.from_pretrained(config.model_name)\n",
|
||||
"ref_model = AutoModelForCausalLMWithValueHead.from_pretrained(config.model_name)\n",
|
||||
"tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(config.model_name)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"tokenizer.pad_token = tokenizer.eos_token"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"attachments": {},
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Initialize PPOTrainer\n",
|
||||
"The `PPOTrainer` takes care of device placement and optimization later on:"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"ppo_trainer = PPOTrainer(\n",
|
||||
" config, model, ref_model, tokenizer, dataset=dataset, data_collator=collator\n",
|
||||
")"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Load BERT classifier\n",
|
||||
"We load a BERT classifier fine-tuned on the IMDB dataset."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"device = ppo_trainer.accelerator.device\n",
|
||||
"if ppo_trainer.accelerator.num_processes == 1:\n",
|
||||
" device = 0 if torch.cuda.is_available() else \"cpu\" # to avoid a `pipeline` bug\n",
|
||||
"sentiment_pipe = pipeline(\n",
|
||||
" \"sentiment-analysis\", model=\"lvwerra/distilbert-imdb\", device=device\n",
|
||||
")"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"The model outputs are the logits for the negative and positive class. We will use the logits for positive class as a reward signal for the language model."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"data": {
|
||||
"text/plain": [
|
||||
"[{'label': 'NEGATIVE', 'score': 2.335048198699951},\n",
|
||||
" {'label': 'POSITIVE', 'score': -2.726576328277588}]"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"output_type": "execute_result"
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"text = \"this movie was really bad!!\"\n",
|
||||
"sentiment_pipe(text, **sent_kwargs)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"data": {
|
||||
"text/plain": [
|
||||
"[{'label': 'POSITIVE', 'score': 2.557040214538574},\n",
|
||||
" {'label': 'NEGATIVE', 'score': -2.294790267944336}]"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"output_type": "execute_result"
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"text = \"this movie was really good!!\"\n",
|
||||
"sentiment_pipe(text, **sent_kwargs)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Generation settings\n",
|
||||
"For the response generation we just use sampling and make sure top-k and nucleus sampling are turned off as well as a minimal length."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"gen_kwargs = {\n",
|
||||
" \"min_length\": -1,\n",
|
||||
" \"top_k\": 0.0,\n",
|
||||
" \"top_p\": 1.0,\n",
|
||||
" \"do_sample\": True,\n",
|
||||
" \"pad_token_id\": tokenizer.eos_token_id,\n",
|
||||
"}"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Optimize model"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Training loop"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"The training loop consists of the following main steps:\n",
|
||||
"1. Get the query responses from the policy network (GPT-2)\n",
|
||||
"2. Get sentiments for query/responses from BERT\n",
|
||||
"3. Optimize policy with PPO using the (query, response, reward) triplet\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"**Training time**\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"This step takes **~2h** on a V100 GPU with the above specified settings."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"output_min_length = 4\n",
|
||||
"output_max_length = 16\n",
|
||||
"output_length_sampler = LengthSampler(output_min_length, output_max_length)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"generation_kwargs = {\n",
|
||||
" \"min_length\": -1,\n",
|
||||
" \"top_k\": 0.0,\n",
|
||||
" \"top_p\": 1.0,\n",
|
||||
" \"do_sample\": True,\n",
|
||||
" \"pad_token_id\": tokenizer.eos_token_id,\n",
|
||||
"}\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"for epoch, batch in enumerate(tqdm(ppo_trainer.dataloader)):\n",
|
||||
" query_tensors = batch[\"input_ids\"]\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" #### Get response from gpt2\n",
|
||||
" response_tensors = []\n",
|
||||
" for query in query_tensors:\n",
|
||||
" gen_len = output_length_sampler()\n",
|
||||
" generation_kwargs[\"max_new_tokens\"] = gen_len\n",
|
||||
" query_response = ppo_trainer.generate(query, **generation_kwargs).squeeze()\n",
|
||||
" response_len = len(query_response) - len(query)\n",
|
||||
" response_tensors.append(query_response[-response_len:])\n",
|
||||
" batch[\"response\"] = [tokenizer.decode(r.squeeze()) for r in response_tensors]\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" #### Compute sentiment score\n",
|
||||
" texts = [q + r for q, r in zip(batch[\"query\"], batch[\"response\"])]\n",
|
||||
" pipe_outputs = sentiment_pipe(texts, **sent_kwargs)\n",
|
||||
" positive_scores = [\n",
|
||||
" item[\"score\"]\n",
|
||||
" for output in pipe_outputs\n",
|
||||
" for item in output\n",
|
||||
" if item[\"label\"] == \"POSITIVE\"\n",
|
||||
" ]\n",
|
||||
" rewards = [torch.tensor(score) for score in positive_scores]\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" #### Run PPO step\n",
|
||||
" stats = ppo_trainer.step(query_tensors, response_tensors, rewards)\n",
|
||||
" ppo_trainer.log_stats(stats, batch, rewards)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"### Training progress\n",
|
||||
"If you are tracking the training progress with Weights&Biases you should see a plot similar to the one below. Check out the interactive sample report on wandb.ai: [link](https://wandb.ai/huggingface/trl/runs/w9l3110g).\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"<div style=\"text-align: center\">\n",
|
||||
"<img src='https://huggingface.co/datasets/trl-internal-testing/example-images/resolve/main/images/gpt2_tuning_progress.png' width='800'>\n",
|
||||
"<p style=\"text-align: center;\"> <b>Figure:</b> Reward mean and distribution evolution during training. </p>\n",
|
||||
"</div>\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"One can observe how the model starts to generate more positive outputs after a few optimisation steps.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"> Note: Investigating the KL-divergence will probably show that at this point the model has not converged to the target KL-divergence, yet. To get there would require longer training or starting with a higher initial coefficient."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"attachments": {},
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Model inspection\n",
|
||||
"Let's inspect some examples from the IMDB dataset. We can use `ref_model` to compare the tuned model `model` against the model before optimisation."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"data": {
|
||||
"text/html": [
|
||||
"<div>\n",
|
||||
"<style scoped>\n",
|
||||
" .dataframe tbody tr th:only-of-type {\n",
|
||||
" vertical-align: middle;\n",
|
||||
" }\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" .dataframe tbody tr th {\n",
|
||||
" vertical-align: top;\n",
|
||||
" }\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" .dataframe thead th {\n",
|
||||
" text-align: right;\n",
|
||||
" }\n",
|
||||
"</style>\n",
|
||||
"<table border=\"1\" class=\"dataframe\">\n",
|
||||
" <thead>\n",
|
||||
" <tr style=\"text-align: right;\">\n",
|
||||
" <th></th>\n",
|
||||
" <th>query</th>\n",
|
||||
" <th>response (before)</th>\n",
|
||||
" <th>response (after)</th>\n",
|
||||
" <th>rewards (before)</th>\n",
|
||||
" <th>rewards (after)</th>\n",
|
||||
" </tr>\n",
|
||||
" </thead>\n",
|
||||
" <tbody>\n",
|
||||
" <tr>\n",
|
||||
" <th>0</th>\n",
|
||||
" <td>I rented Zero Day</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>4 for my sister. To my surprise, the Wii caug...</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>. It is a pleasure. It is a huge leap 68 years...</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>1.736068</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>2.423731</td>\n",
|
||||
" </tr>\n",
|
||||
" <tr>\n",
|
||||
" <th>1</th>\n",
|
||||
" <td>The only</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>distro of her</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>special compliments is the</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>0.150852</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>0.190159</td>\n",
|
||||
" </tr>\n",
|
||||
" <tr>\n",
|
||||
" <th>2</th>\n",
|
||||
" <td>I've read a few</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>news reports about Mr. Mueller's activities b...</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>novels and I never watch this. It has a reall...</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>-1.417962</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>2.831814</td>\n",
|
||||
" </tr>\n",
|
||||
" <tr>\n",
|
||||
" <th>3</th>\n",
|
||||
" <td>This is the second British Rank film</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>, and I wouldn't be surprised anymore if it</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>that I have enjoyed, achieving it in both the</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>0.835876</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>2.205628</td>\n",
|
||||
" </tr>\n",
|
||||
" <tr>\n",
|
||||
" <th>4</th>\n",
|
||||
" <td>A classic</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>classic.<br /><br />And only this one will ha...</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>. It's a movie with a fine cast. As the beginn...</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>2.113075</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>2.739168</td>\n",
|
||||
" </tr>\n",
|
||||
" <tr>\n",
|
||||
" <th>5</th>\n",
|
||||
" <td>This has to be one of the</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>worst with the differences being that for the</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>best thriller films I've seen in recent</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>-2.705339</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>2.730615</td>\n",
|
||||
" </tr>\n",
|
||||
" <tr>\n",
|
||||
" <th>6</th>\n",
|
||||
" <td>Happy Go Lovely is a waste</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>. Not only are extremely</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>of time, giving a</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>-2.429504</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>-2.934672</td>\n",
|
||||
" </tr>\n",
|
||||
" <tr>\n",
|
||||
" <th>7</th>\n",
|
||||
" <td>Wow, I just</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>can't make fun of it</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>feek it! This show</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>-2.201666</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>-0.106085</td>\n",
|
||||
" </tr>\n",
|
||||
" <tr>\n",
|
||||
" <th>8</th>\n",
|
||||
" <td>This movie makes several mistakes.</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>Despite being a great comedic diversion it es...</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>It's cool, wonderful - it held me into a very ...</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>-1.232380</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>2.707638</td>\n",
|
||||
" </tr>\n",
|
||||
" <tr>\n",
|
||||
" <th>9</th>\n",
|
||||
" <td>Branagh and Fish</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>burne, Drake is played</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>is a great show. Beautiful</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>0.776819</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>2.808996</td>\n",
|
||||
" </tr>\n",
|
||||
" <tr>\n",
|
||||
" <th>10</th>\n",
|
||||
" <td>I might have given this movie a</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>rating of *11 when I heard that!), but it was...</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>great performance. It was truly a great movie...</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>0.276380</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>2.743328</td>\n",
|
||||
" </tr>\n",
|
||||
" <tr>\n",
|
||||
" <th>11</th>\n",
|
||||
" <td>Really, really bad</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>with feel like there is no end to the</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>. This movie is incredibly good, with the</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>-2.639503</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>-1.568827</td>\n",
|
||||
" </tr>\n",
|
||||
" <tr>\n",
|
||||
" <th>12</th>\n",
|
||||
" <td>What another reviewer called lack of</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>judgment, connecting into her own harsh obser...</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>suspense. Rogers and Rooney rate this as exce...</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>-1.079707</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>2.696888</td>\n",
|
||||
" </tr>\n",
|
||||
" <tr>\n",
|
||||
" <th>13</th>\n",
|
||||
" <td>This is simply one</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>more problem of Steve</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>of the best choice</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>-1.445436</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>2.662699</td>\n",
|
||||
" </tr>\n",
|
||||
" <tr>\n",
|
||||
" <th>14</th>\n",
|
||||
" <td>\"Perhaps we can arrange a meet</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>-and-greet.<br /><br />Teleg</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>with spent, classic music and dance, and come...</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>0.258479</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>1.876662</td>\n",
|
||||
" </tr>\n",
|
||||
" <tr>\n",
|
||||
" <th>15</th>\n",
|
||||
" <td>Richard Willaims is</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>nice enough; the little black guy plays quite</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>beautifully hands on in his own spin, and</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>0.796508</td>\n",
|
||||
" <td>2.820259</td>\n",
|
||||
" </tr>\n",
|
||||
" </tbody>\n",
|
||||
"</table>\n",
|
||||
"</div>"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"text/plain": [
|
||||
" query \\\n",
|
||||
"0 I rented Zero Day \n",
|
||||
"1 The only \n",
|
||||
"2 I've read a few \n",
|
||||
"3 This is the second British Rank film \n",
|
||||
"4 A classic \n",
|
||||
"5 This has to be one of the \n",
|
||||
"6 Happy Go Lovely is a waste \n",
|
||||
"7 Wow, I just \n",
|
||||
"8 This movie makes several mistakes. \n",
|
||||
"9 Branagh and Fish \n",
|
||||
"10 I might have given this movie a \n",
|
||||
"11 Really, really bad \n",
|
||||
"12 What another reviewer called lack of \n",
|
||||
"13 This is simply one \n",
|
||||
"14 \"Perhaps we can arrange a meet \n",
|
||||
"15 Richard Willaims is \n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" response (before) \\\n",
|
||||
"0 4 for my sister. To my surprise, the Wii caug... \n",
|
||||
"1 distro of her \n",
|
||||
"2 news reports about Mr. Mueller's activities b... \n",
|
||||
"3 , and I wouldn't be surprised anymore if it \n",
|
||||
"4 classic.<br /><br />And only this one will ha... \n",
|
||||
"5 worst with the differences being that for the \n",
|
||||
"6 . Not only are extremely \n",
|
||||
"7 can't make fun of it \n",
|
||||
"8 Despite being a great comedic diversion it es... \n",
|
||||
"9 burne, Drake is played \n",
|
||||
"10 rating of *11 when I heard that!), but it was... \n",
|
||||
"11 with feel like there is no end to the \n",
|
||||
"12 judgment, connecting into her own harsh obser... \n",
|
||||
"13 more problem of Steve \n",
|
||||
"14 -and-greet.<br /><br />Teleg \n",
|
||||
"15 nice enough; the little black guy plays quite \n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" response (after) rewards (before) \\\n",
|
||||
"0 . It is a pleasure. It is a huge leap 68 years... 1.736068 \n",
|
||||
"1 special compliments is the 0.150852 \n",
|
||||
"2 novels and I never watch this. It has a reall... -1.417962 \n",
|
||||
"3 that I have enjoyed, achieving it in both the 0.835876 \n",
|
||||
"4 . It's a movie with a fine cast. As the beginn... 2.113075 \n",
|
||||
"5 best thriller films I've seen in recent -2.705339 \n",
|
||||
"6 of time, giving a -2.429504 \n",
|
||||
"7 feek it! This show -2.201666 \n",
|
||||
"8 It's cool, wonderful - it held me into a very ... -1.232380 \n",
|
||||
"9 is a great show. Beautiful 0.776819 \n",
|
||||
"10 great performance. It was truly a great movie... 0.276380 \n",
|
||||
"11 . This movie is incredibly good, with the -2.639503 \n",
|
||||
"12 suspense. Rogers and Rooney rate this as exce... -1.079707 \n",
|
||||
"13 of the best choice -1.445436 \n",
|
||||
"14 with spent, classic music and dance, and come... 0.258479 \n",
|
||||
"15 beautifully hands on in his own spin, and 0.796508 \n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" rewards (after) \n",
|
||||
"0 2.423731 \n",
|
||||
"1 0.190159 \n",
|
||||
"2 2.831814 \n",
|
||||
"3 2.205628 \n",
|
||||
"4 2.739168 \n",
|
||||
"5 2.730615 \n",
|
||||
"6 -2.934672 \n",
|
||||
"7 -0.106085 \n",
|
||||
"8 2.707638 \n",
|
||||
"9 2.808996 \n",
|
||||
"10 2.743328 \n",
|
||||
"11 -1.568827 \n",
|
||||
"12 2.696888 \n",
|
||||
"13 2.662699 \n",
|
||||
"14 1.876662 \n",
|
||||
"15 2.820259 "
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"output_type": "execute_result"
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#### get a batch from the dataset\n",
|
||||
"bs = 16\n",
|
||||
"game_data = dict()\n",
|
||||
"dataset.set_format(\"pandas\")\n",
|
||||
"df_batch = dataset[:].sample(bs)\n",
|
||||
"game_data[\"query\"] = df_batch[\"query\"].tolist()\n",
|
||||
"query_tensors = df_batch[\"input_ids\"].tolist()\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"response_tensors_ref, response_tensors = [], []\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"#### get response from gpt2 and gpt2_ref\n",
|
||||
"for i in range(bs):\n",
|
||||
" query = torch.tensor(query_tensors[i]).to(device)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" gen_len = output_length_sampler()\n",
|
||||
" query_response = ref_model.generate(\n",
|
||||
" query.unsqueeze(0), max_new_tokens=gen_len, **gen_kwargs\n",
|
||||
" ).squeeze()\n",
|
||||
" response_len = len(query_response) - len(query)\n",
|
||||
" response_tensors_ref.append(query_response[-response_len:])\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" query_response = model.generate(\n",
|
||||
" query.unsqueeze(0), max_new_tokens=gen_len, **gen_kwargs\n",
|
||||
" ).squeeze()\n",
|
||||
" response_len = len(query_response) - len(query)\n",
|
||||
" response_tensors.append(query_response[-response_len:])\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"#### decode responses\n",
|
||||
"game_data[\"response (before)\"] = [\n",
|
||||
" tokenizer.decode(response_tensors_ref[i]) for i in range(bs)\n",
|
||||
"]\n",
|
||||
"game_data[\"response (after)\"] = [\n",
|
||||
" tokenizer.decode(response_tensors[i]) for i in range(bs)\n",
|
||||
"]\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"#### sentiment analysis of query/response pairs before/after\n",
|
||||
"texts = [q + r for q, r in zip(game_data[\"query\"], game_data[\"response (before)\"])]\n",
|
||||
"pipe_outputs = sentiment_pipe(texts, **sent_kwargs)\n",
|
||||
"positive_scores = [\n",
|
||||
" item[\"score\"]\n",
|
||||
" for output in pipe_outputs\n",
|
||||
" for item in output\n",
|
||||
" if item[\"label\"] == \"POSITIVE\"\n",
|
||||
"]\n",
|
||||
"game_data[\"rewards (before)\"] = positive_scores\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"texts = [q + r for q, r in zip(game_data[\"query\"], game_data[\"response (after)\"])]\n",
|
||||
"pipe_outputs = sentiment_pipe(texts, **sent_kwargs)\n",
|
||||
"positive_scores = [\n",
|
||||
" item[\"score\"]\n",
|
||||
" for output in pipe_outputs\n",
|
||||
" for item in output\n",
|
||||
" if item[\"label\"] == \"POSITIVE\"\n",
|
||||
"]\n",
|
||||
"game_data[\"rewards (after)\"] = positive_scores\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# store results in a dataframe\n",
|
||||
"df_results = pd.DataFrame(game_data)\n",
|
||||
"df_results"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"Looking at the reward mean/median of the generated sequences we observe a significant difference."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "stdout",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"mean:\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"data": {
|
||||
"text/plain": [
|
||||
"rewards (before) -0.512965\n",
|
||||
"rewards (after) 1.676750\n",
|
||||
"dtype: float64"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"output_type": "display_data"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "stdout",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"median:\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"data": {
|
||||
"text/plain": [
|
||||
"rewards (before) -0.464427\n",
|
||||
"rewards (after) 2.679794\n",
|
||||
"dtype: float64"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"output_type": "display_data"
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"print(\"mean:\")\n",
|
||||
"display(df_results[[\"rewards (before)\", \"rewards (after)\"]].mean())\n",
|
||||
"print()\n",
|
||||
"print(\"median:\")\n",
|
||||
"display(df_results[[\"rewards (before)\", \"rewards (after)\"]].median())"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Save model\n",
|
||||
"Finally, we save the model and push it to the Hugging Face for later usage."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"data": {
|
||||
"text/plain": [
|
||||
"('gpt2-imdb-pos-v2/tokenizer_config.json',\n",
|
||||
" 'gpt2-imdb-pos-v2/special_tokens_map.json',\n",
|
||||
" 'gpt2-imdb-pos-v2/vocab.json',\n",
|
||||
" 'gpt2-imdb-pos-v2/merges.txt',\n",
|
||||
" 'gpt2-imdb-pos-v2/added_tokens.json',\n",
|
||||
" 'gpt2-imdb-pos-v2/tokenizer.json')"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"output_type": "execute_result"
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"model.save_pretrained(\"gpt2-imdb-pos-v2\", push_to_hub=True)\n",
|
||||
"tokenizer.save_pretrained(\"gpt2-imdb-pos-v2\", push_to_hub=True)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"kernelspec": {
|
||||
"display_name": "env",
|
||||
"language": "python",
|
||||
"name": "python3"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"language_info": {
|
||||
"codemirror_mode": {
|
||||
"name": "ipython",
|
||||
"version": 3
|
||||
},
|
||||
"file_extension": ".py",
|
||||
"mimetype": "text/x-python",
|
||||
"name": "python",
|
||||
"nbconvert_exporter": "python",
|
||||
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
|
||||
"version": "3.11.9"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"vscode": {
|
||||
"interpreter": {
|
||||
"hash": "4c8ff454cd947027f86954d72bf940c689a97dcc494eb53cfe4813862c6065fe"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"nbformat": 4,
|
||||
"nbformat_minor": 4
|
||||
}
|
||||
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
@ -64,7 +64,6 @@ from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer, HfArgumentParser
|
||||
|
||||
from trl import CPOConfig, CPOTrainer, ModelConfig, ScriptArguments, get_peft_config
|
||||
from trl.trainer.utils import SIMPLE_CHAT_TEMPLATE
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Enable logging in a Hugging Face Space
|
||||
@ -90,8 +89,6 @@ if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
# Dataset
|
||||
################
|
||||
dataset = load_dataset(script_args.dataset_name, name=script_args.dataset_config)
|
||||
if tokenizer.chat_template is None:
|
||||
tokenizer.chat_template = SIMPLE_CHAT_TEMPLATE
|
||||
|
||||
################
|
||||
# Training
|
||||
|
||||
@ -19,7 +19,6 @@
|
||||
# ///
|
||||
|
||||
from dataclasses import dataclass, field
|
||||
from typing import Optional
|
||||
|
||||
from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
from transformers import HfArgumentParser
|
||||
@ -74,7 +73,7 @@ class ScriptArguments:
|
||||
"'meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3-70B-Instruct'."
|
||||
},
|
||||
)
|
||||
num_examples: Optional[int] = field(default=None, metadata={"help": "Number of examples to evaluate."})
|
||||
num_examples: int | None = field(default=None, metadata={"help": "Number of examples to evaluate."})
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
@ -103,7 +102,7 @@ if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
else:
|
||||
judge = HfPairwiseJudge(script_args.judge_model)
|
||||
|
||||
completions = [[c0, c1] for c0, c1 in zip(reference_completions, model_completions)]
|
||||
completions = [[c0, c1] for c0, c1 in zip(reference_completions, model_completions, strict=True)]
|
||||
best_idxs = judge.judge(prompts, completions)
|
||||
model_win_rate = best_idxs.count(1) / len(best_idxs)
|
||||
print(f"Model win rate: {model_win_rate * 100:.2f}%")
|
||||
|
||||
@ -73,7 +73,6 @@ from trl import (
|
||||
get_kbit_device_map,
|
||||
get_quantization_config,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from trl.trainer.utils import SIMPLE_CHAT_TEMPLATE
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Enable logging in a Hugging Face Space
|
||||
@ -128,8 +127,6 @@ if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
)
|
||||
if tokenizer.pad_token is None:
|
||||
tokenizer.pad_token = tokenizer.eos_token
|
||||
if tokenizer.chat_template is None:
|
||||
tokenizer.chat_template = SIMPLE_CHAT_TEMPLATE
|
||||
|
||||
dataset = load_dataset(script_args.dataset_name, name=script_args.dataset_config)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -69,7 +69,6 @@ from trl import (
|
||||
get_peft_config,
|
||||
get_quantization_config,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from trl.trainer.utils import SIMPLE_CHAT_TEMPLATE
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Enable logging in a Hugging Face Space
|
||||
@ -131,8 +130,6 @@ if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
trust_remote_code=model_args.trust_remote_code,
|
||||
**model_kwargs,
|
||||
)
|
||||
if tokenizer.chat_template is None:
|
||||
tokenizer.chat_template = SIMPLE_CHAT_TEMPLATE
|
||||
if tokenizer.pad_token_id is None:
|
||||
tokenizer.pad_token = tokenizer.eos_token
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
251
examples/scripts/openenv/catch.py
Normal file
251
examples/scripts/openenv/catch.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,251 @@
|
||||
# Copyright 2020-2025 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
# ruff: noqa: T201
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import re
|
||||
import subprocess
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
import time
|
||||
from pathlib import Path
|
||||
|
||||
import requests
|
||||
from datasets import Dataset
|
||||
from envs.openspiel_env import OpenSpielEnv
|
||||
from envs.openspiel_env.models import OpenSpielAction
|
||||
|
||||
from trl import GRPOConfig, GRPOTrainer, RichProgressCallback, apply_chat_template
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Simple script to run GRPO training with OpenEnv's Catch environment (OpenSpiel) and a vLLM server. The reward function
|
||||
is based on the catch game where the agent tries to catch falling balls.
|
||||
|
||||
Setup:
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
uv pip install git+https://github.com/meta-pytorch/OpenEnv.git
|
||||
uv pip install open_spiel rich trackio
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Usage (2 GPUs required):
|
||||
|
||||
# Spin up vLLM server
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 trl vllm-serve --model Qwen/Qwen2.5-0.5B-Instruct --host 0.0.0.0 --port 8000
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
# Run training
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=1 python examples/scripts/openenv/catch.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
GEN_URL = "http://0.0.0.0:8000/generate/"
|
||||
ENV_URL = "http://0.0.0.0:8001"
|
||||
|
||||
BASE_PROMPT = """You are an AI agent playing the game **Catch**.
|
||||
|
||||
### Game Description
|
||||
- The game is played on a **10×5 grid**.
|
||||
- There is one **falling ball** and one **paddle** that you control at the bottom.
|
||||
- The objective is to **move the paddle left or right to catch the ball** as it falls.
|
||||
- The episode ends when the ball reaches the bottom row:
|
||||
- You get **+1 reward** if you catch it.
|
||||
- You get **–1 reward** if you miss it.
|
||||
|
||||
### Observation Format
|
||||
|
||||
- `observation`: a list of **50 numbers (floats)** representing the entire grid, flattened row by row.
|
||||
- Each cell contains `1.0` if it is occupied (either by the ball or the paddle), or `0.0` if it is empty.
|
||||
- The positions of the two `1.0` values indicate where the **ball** and **paddle** currently are.
|
||||
- `legal_actions`: a list of integers representing which actions are currently allowed.
|
||||
|
||||
### Actions Each action is a discrete integer:
|
||||
- `0` → Move paddle **left**
|
||||
- `1` → **Stay** (no movement)
|
||||
- `2` → Move paddle **right**
|
||||
|
||||
### Output Format Respond **only with one integer** representing your chosen action: `0`, `1`, or `2`.
|
||||
|
||||
### Current Observation
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
# Start the OpenSpiel server in background
|
||||
print("⚡ Starting FastAPI server for OpenSpiel Catch Environment...")
|
||||
|
||||
# Determine the correct path
|
||||
work_dir = str(Path.cwd().parent.absolute())
|
||||
|
||||
server_process = subprocess.Popen(
|
||||
[sys.executable, "-m", "uvicorn", "envs.openspiel_env.server.app:app", "--host", "0.0.0.0", "--port", "8001"],
|
||||
env={**os.environ, "PYTHONPATH": f"{work_dir}/src"},
|
||||
stdout=subprocess.PIPE,
|
||||
stderr=subprocess.PIPE,
|
||||
text=True,
|
||||
cwd=work_dir,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
print("⏳ Waiting for server to start...")
|
||||
time.sleep(5)
|
||||
|
||||
# Check if server is running
|
||||
try:
|
||||
response = requests.get(f"{ENV_URL}/health", timeout=2)
|
||||
print("\n✅ OpenSpiel Catch Environment server is running!")
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
print(f"\n❌ Server failed to start: {e}")
|
||||
print("\n📋 Checking error output...")
|
||||
server_process.poll()
|
||||
if server_process.stderr:
|
||||
stderr = server_process.stderr.read()
|
||||
if stderr:
|
||||
print(stderr)
|
||||
raise
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Create HTTP client for OpenSpiel Catch Environment
|
||||
client = OpenSpielEnv(base_url=f"{ENV_URL}")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def rollout_func(prompts: list[str], args: GRPOConfig, processing_class) -> dict[str, list]:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Custom rollout function that generates completions via vLLM server and computes environment rewards.
|
||||
|
||||
The catch game expects action IDs (integers). We'll parse the model's text output to extract action choices.
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
prompts: List of prompts to generate from
|
||||
args: GRPOConfig containing all sampling parameters
|
||||
processing_class: Tokenizer/processor for decoding completions
|
||||
|
||||
Returns:
|
||||
Dict containing prompt_ids, completion_ids, logprobs, and env_reward
|
||||
"""
|
||||
# Run full episodes for each generation to get episode rewards
|
||||
env_rewards = []
|
||||
all_prompt_ids = []
|
||||
all_completion_ids = []
|
||||
all_logprobs = []
|
||||
|
||||
for base_prompt in prompts:
|
||||
for _ in range(args.num_generations):
|
||||
# Run episode: Reset environment and loop until done
|
||||
env_result = client.reset()
|
||||
obs = env_result.observation
|
||||
total_reward = 0.0
|
||||
|
||||
episode_prompt_ids = []
|
||||
episode_completion_ids = []
|
||||
episode_logprobs = []
|
||||
|
||||
# TODO: parallelise!
|
||||
while not obs.done:
|
||||
# FIXME: handle the addition of observation to prompt more cleanly, ideally without a train_dataset
|
||||
episode_msg = {"prompt": [{"role": "user", "content": f"{base_prompt}\n\n{obs.info_state}\n"}]}
|
||||
episode_prompt = apply_chat_template(episode_msg, processing_class)
|
||||
|
||||
# Generate action from model
|
||||
gen_payload = {
|
||||
"prompts": [episode_prompt["prompt"]],
|
||||
"n": 1,
|
||||
"temperature": args.temperature,
|
||||
"top_p": args.top_p,
|
||||
"top_k": -1 if args.top_k is None else args.top_k,
|
||||
"min_p": 0.0 if args.min_p is None else args.min_p,
|
||||
"max_tokens": args.max_completion_length,
|
||||
"repetition_penalty": args.repetition_penalty,
|
||||
}
|
||||
gen_response = requests.post(GEN_URL, json=gen_payload)
|
||||
gen_response.raise_for_status()
|
||||
gen_result = gen_response.json()
|
||||
|
||||
# Collect prompt_ids, completion_ids, and logprobs from this step
|
||||
episode_prompt_ids.extend(gen_result["prompt_ids"][0])
|
||||
episode_completion_ids.extend(gen_result["completion_ids"][0])
|
||||
episode_logprobs.extend(gen_result["logprobs"][0])
|
||||
|
||||
completion_text = processing_class.batch_decode(
|
||||
gen_result["completion_ids"], skip_special_tokens=True
|
||||
)[0]
|
||||
|
||||
# Parse action from completion
|
||||
action_id = 0 # default
|
||||
numbers = re.findall(r"\b([0-2])\b", completion_text)
|
||||
if numbers:
|
||||
action_id = int(numbers[0])
|
||||
elif obs.legal_actions:
|
||||
action_id = obs.legal_actions[0]
|
||||
|
||||
# Take action in environment
|
||||
env_result = client.step(OpenSpielAction(action_id=action_id, game_name="catch"))
|
||||
reward = env_result.reward if env_result.reward is not None else 0.0
|
||||
total_reward += reward
|
||||
obs = env_result.observation
|
||||
|
||||
# Store episode results
|
||||
env_rewards.append(total_reward)
|
||||
all_prompt_ids.append(episode_prompt_ids)
|
||||
all_completion_ids.append(episode_completion_ids)
|
||||
all_logprobs.append(episode_logprobs)
|
||||
|
||||
return {
|
||||
"prompt_ids": all_prompt_ids,
|
||||
"completion_ids": all_completion_ids,
|
||||
"logprobs": all_logprobs,
|
||||
"env_reward": env_rewards,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
dataset = Dataset.from_dict({"prompt": [BASE_PROMPT] * 1000})
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def reward_from_env(completions, **kwargs):
|
||||
"""Reward function that uses the environment reward from the catch game."""
|
||||
# Extract environment rewards from kwargs (propagated via extra_fields)
|
||||
env_rewards = kwargs.get("env_reward", [])
|
||||
if env_rewards:
|
||||
return [float(reward) for reward in env_rewards]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
# Fallback if env_reward is not available
|
||||
return [0.0] * len(completions)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
training_args = GRPOConfig(
|
||||
output_dir="Qwen2.5-0.5B-GRPO-Catch",
|
||||
vllm_mode="server",
|
||||
use_vllm=True,
|
||||
logging_steps=1,
|
||||
report_to="trackio",
|
||||
num_train_epochs=1,
|
||||
max_completion_length=4,
|
||||
gradient_accumulation_steps=4,
|
||||
)
|
||||
trainer = GRPOTrainer(
|
||||
model="Qwen/Qwen2.5-0.5B-Instruct",
|
||||
reward_funcs=reward_from_env,
|
||||
args=training_args,
|
||||
train_dataset=dataset,
|
||||
rollout_func=rollout_func,
|
||||
callbacks=[RichProgressCallback()],
|
||||
)
|
||||
trainer.train()
|
||||
|
||||
# Give time for background threads to finish
|
||||
time.sleep(5)
|
||||
|
||||
print("🛑 Terminating environment server...")
|
||||
server_process.terminate()
|
||||
174
examples/scripts/openenv/echo.py
Normal file
174
examples/scripts/openenv/echo.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,174 @@
|
||||
# Copyright 2020-2025 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
# ruff: noqa: T201
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import subprocess
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
import time
|
||||
from pathlib import Path
|
||||
|
||||
import requests
|
||||
from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
from envs.echo_env import EchoEnv
|
||||
from envs.echo_env.models import EchoAction
|
||||
|
||||
from trl import GRPOConfig, GRPOTrainer, RichProgressCallback
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Simple script to run GRPO training with OpenEnv's Echo environment and a vLLM server. The reward function encourages
|
||||
longer completions.
|
||||
|
||||
Setup:
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
uv pip install git+https://github.com/meta-pytorch/OpenEnv.git
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Usage (2 GPUs required):
|
||||
|
||||
# Spin up server
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 trl vllm-serve --model Qwen/Qwen2.5-0.5B-Instruct --host 0.0.0.0 --port 8000
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
# Run training
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=1 python examples/scripts/openenv/echo.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
GEN_URL = "http://0.0.0.0:8000/generate/"
|
||||
ENV_URL = "http://0.0.0.0:8001"
|
||||
|
||||
print("⚡ Starting FastAPI server for Echo Environment...")
|
||||
# Workaround if you can't run the env with Docker
|
||||
work_dir = str(Path.cwd().parent.absolute())
|
||||
server_process = subprocess.Popen(
|
||||
[sys.executable, "-m", "uvicorn", "envs.echo_env.server.app:app", "--host", "0.0.0.0", "--port", "8001"],
|
||||
env={**os.environ, "PYTHONPATH": f"{work_dir}/src"},
|
||||
stdout=subprocess.PIPE,
|
||||
stderr=subprocess.PIPE,
|
||||
text=True,
|
||||
cwd=work_dir,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
print("⏳ Waiting for server to start...")
|
||||
time.sleep(5)
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
response = requests.get(f"{ENV_URL}/health", timeout=2)
|
||||
print("\n✅ Echo Environment server is running!")
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
print(f"\n❌ Server failed to start: {e}")
|
||||
print("\n📋 Checking error output...")
|
||||
server_process.poll()
|
||||
if server_process.stderr:
|
||||
stderr = server_process.stderr.read()
|
||||
if stderr:
|
||||
print(stderr)
|
||||
raise
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Create HTTP client for Echo Environment
|
||||
client = EchoEnv(base_url=f"{ENV_URL}")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def rollout_func(prompts: list[str], args: GRPOConfig, processing_class) -> dict[str, list]:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Custom rollout function that generates completions via vLLM server and computes environment rewards.
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
prompts: List of prompts to generate from
|
||||
args: GRPOConfig containing all sampling parameters
|
||||
processing_class: Tokenizer/processor for decoding completions
|
||||
|
||||
Returns:
|
||||
Dict containing prompt_ids, completion_ids, logprobs, and env_reward
|
||||
"""
|
||||
# 1. Generate completions via vLLM inference server (running on port 8000)
|
||||
payload = {
|
||||
"prompts": prompts,
|
||||
"n": args.num_generations,
|
||||
"temperature": args.temperature,
|
||||
"top_p": args.top_p,
|
||||
"top_k": -1 if args.top_k is None else args.top_k,
|
||||
"min_p": 0.0 if args.min_p is None else args.min_p,
|
||||
"max_tokens": args.max_completion_length,
|
||||
"repetition_penalty": args.repetition_penalty,
|
||||
}
|
||||
response = requests.post(GEN_URL, json=payload)
|
||||
|
||||
if response.status_code != 200:
|
||||
print(f"Error response: {response.text}")
|
||||
|
||||
response.raise_for_status()
|
||||
result = response.json()
|
||||
|
||||
completions_text = processing_class.batch_decode(result["completion_ids"], skip_special_tokens=True)
|
||||
|
||||
# 2. Step through the environment to get rewards
|
||||
env_result = client.reset()
|
||||
env_rewards = []
|
||||
for msg in completions_text:
|
||||
env_result = client.step(EchoAction(message=msg))
|
||||
env_rewards.append(env_result.reward)
|
||||
|
||||
# 3. Add environment rewards as extra field
|
||||
result["env_reward"] = env_rewards
|
||||
|
||||
return result
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def reward_from_env(completions, **kwargs):
|
||||
"""Reward function that uses the environment reward."""
|
||||
# Extract environment rewards from kwargs (propagated via extra_fields)
|
||||
env_rewards = kwargs.get("env_reward", [])
|
||||
if env_rewards:
|
||||
return [float(reward) for reward in env_rewards]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
# Fallback if env_reward is not available
|
||||
return [0.0] * len(completions)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
dataset = load_dataset("trl-lib/ultrafeedback-prompt", split="train[:1000]")
|
||||
|
||||
training_args = GRPOConfig(
|
||||
output_dir="Qwen2.5-0.5B-GRPO-Rollout",
|
||||
vllm_mode="server",
|
||||
use_vllm=True,
|
||||
logging_steps=1,
|
||||
report_to="trackio",
|
||||
num_train_epochs=1,
|
||||
max_completion_length=2048,
|
||||
gradient_accumulation_steps=4,
|
||||
)
|
||||
trainer = GRPOTrainer(
|
||||
model="Qwen/Qwen2.5-0.5B-Instruct",
|
||||
reward_funcs=reward_from_env,
|
||||
args=training_args,
|
||||
train_dataset=dataset,
|
||||
rollout_func=rollout_func,
|
||||
callbacks=[RichProgressCallback()],
|
||||
)
|
||||
trainer.train()
|
||||
|
||||
# Give time for background threads to finish
|
||||
time.sleep(5)
|
||||
|
||||
print("🛑 Terminating Echo Environment server...")
|
||||
server_process.terminate()
|
||||
574
examples/scripts/openenv/wordle.py
Normal file
574
examples/scripts/openenv/wordle.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,574 @@
|
||||
# Copyright 2020-2025 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
GRPO training for Wordle using TRL's `GRPOTrainer` and the TextArena OpenEnv environment.
|
||||
|
||||
Usage:
|
||||
# First, start the TextArena Wordle server (Docker or local):
|
||||
TEXTARENA_ENV_ID=Wordle-v0 TEXTARENA_NUM_PLAYERS=1 \
|
||||
python -m src.envs.textarena_env.server.app
|
||||
|
||||
# Start the vLLM server with your model
|
||||
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0 trl vllm-serve --model Qwen/Qwen2.5-0.5B-Instruct --host 0.0.0.0 --port 8000
|
||||
|
||||
# Then run this training script:
|
||||
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=1 python examples/scripts/openenv/wordle.py
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
from __future__ import annotations
|
||||
|
||||
import argparse
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
from collections.abc import Iterable
|
||||
from datetime import datetime
|
||||
from pathlib import Path
|
||||
|
||||
import requests
|
||||
from datasets import Dataset
|
||||
from transformers import AutoTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
from trl import GRPOConfig, GRPOTrainer
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Ensure src/ is on the path
|
||||
sys.path.insert(0, str(Path(__file__).parent / "src"))
|
||||
|
||||
from envs.textarena_env import TextArenaAction, TextArenaEnv
|
||||
from envs.textarena_env.models import TextArenaMessage
|
||||
from envs.textarena_env.rewards import (
|
||||
extract_feedback_counts,
|
||||
extract_guess,
|
||||
extract_wordle_feedback,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def parse_args() -> argparse.Namespace:
|
||||
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(
|
||||
description="Run GRPO training for Wordle using the TextArena OpenEnv environment."
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--tokenizer-id",
|
||||
default="Qwen/Qwen3-1.7B",
|
||||
help="Model identifier used to load the tokenizer.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--model-id",
|
||||
default="willcb/Qwen3-1.7B-Wordle",
|
||||
help="Model identifier passed to GRPOTrainer for fine-tuning.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--textarena-url",
|
||||
default="https://burtenshaw-textarena.hf.space",
|
||||
help="Base URL for the TextArena Wordle environment.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--system-prompt-path",
|
||||
default="wordle_prompt.txt",
|
||||
help="Path to the file containing the system prompt.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--dataset-prompt",
|
||||
default="Play Wordle like an expert.",
|
||||
help="Prompt text used to seed the training dataset.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--dataset-size",
|
||||
type=int,
|
||||
default=3000,
|
||||
help="Number of entries to include in the synthetic training dataset.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--max-turns",
|
||||
type=int,
|
||||
default=5,
|
||||
help="Maximum number of turns to play in the Wordle environment per episode.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--max-new-tokens",
|
||||
type=int,
|
||||
default=8,
|
||||
help="Maximum number of new tokens to request from vLLM for each guess.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--temperature",
|
||||
type=float,
|
||||
default=0.8,
|
||||
help="Sampling temperature used during rollout generation.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--top-k",
|
||||
type=int,
|
||||
default=10,
|
||||
help="Top-k sampling parameter forwarded to vLLM.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--top-p",
|
||||
type=float,
|
||||
default=None,
|
||||
help="Optional top-p sampling parameter forwarded to vLLM.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--learning-rate",
|
||||
type=float,
|
||||
default=5e-6,
|
||||
help="Learning rate for GRPO training.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--weight-decay",
|
||||
type=float,
|
||||
default=0.0,
|
||||
help="Weight decay applied during optimization.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--gradient-accumulation-steps",
|
||||
type=int,
|
||||
default=64,
|
||||
help="Gradient accumulation steps for GRPO training.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--warmup-steps",
|
||||
type=int,
|
||||
default=20,
|
||||
help="Warmup steps for the scheduler.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--per-device-batch-size",
|
||||
type=int,
|
||||
default=1,
|
||||
help="Per-device train batch size.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--num-generations",
|
||||
type=int,
|
||||
default=2,
|
||||
help="Number of rollout generations per dataset prompt.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--num-epochs",
|
||||
type=int,
|
||||
default=1,
|
||||
help="Number of training epochs.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--save-interval",
|
||||
type=int,
|
||||
default=10,
|
||||
help="Interval (in steps) between checkpoint saves.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--save-total-limit",
|
||||
type=int,
|
||||
default=None,
|
||||
help="Maximum number of checkpoints to keep.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--output-dir",
|
||||
default=None,
|
||||
help="Directory where training outputs and checkpoints are stored.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--run-name",
|
||||
default=None,
|
||||
help="Optional run name for logging systems.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--project",
|
||||
default=None,
|
||||
help="Optional project identifier for logging systems.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--trackio-space-id",
|
||||
default="Wordle-GRPO",
|
||||
help="TrackIO space identifier.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--vllm-endpoint",
|
||||
default=os.getenv("VLLM_ENDPOINT", "http://localhost:8000/generate/"),
|
||||
help="Endpoint for the vLLM server.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--request-timeout",
|
||||
type=int,
|
||||
default=60,
|
||||
help="Timeout (in seconds) for vLLM HTTP requests.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--logging-steps",
|
||||
type=int,
|
||||
default=1,
|
||||
help="Frequency of logging steps for GRPO training.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--debug",
|
||||
action="store_true",
|
||||
default=False,
|
||||
help="Enable verbose debugging output during rollouts.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
return parser.parse_args()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def resolve_system_prompt(path: str) -> str:
|
||||
prompt_path = Path(path)
|
||||
if not prompt_path.is_file():
|
||||
prompt_path = Path(__file__).parent / path
|
||||
return prompt_path.read_text()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def sanitize_name(name: str) -> str:
|
||||
return name.replace("/", "-")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
# Helpers
|
||||
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def format_history(messages: Iterable[TextArenaMessage]) -> str:
|
||||
lines: list[str] = []
|
||||
for message in messages:
|
||||
tag = message.category or "MESSAGE"
|
||||
content = message.content.strip()
|
||||
if not content:
|
||||
continue
|
||||
lines.append(f"[{tag}] {content}")
|
||||
return "\n".join(lines)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def make_user_prompt(prompt_text: str, messages: Iterable[TextArenaMessage]) -> str:
|
||||
history = format_history(messages)
|
||||
prompt_section = prompt_text.strip() if prompt_text.strip() else "Wordle-v0"
|
||||
history_section = history if history else "[PROMPT] Awaiting first feedback."
|
||||
return (
|
||||
f"Game prompt:\n{prompt_section}\n\n"
|
||||
f"Conversation so far:\n{history_section}\n\n"
|
||||
"Reply with your next guess enclosed in square brackets."
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def request_vllm_completion(
|
||||
prompt: str,
|
||||
trainer_args: GRPOConfig,
|
||||
endpoint: str,
|
||||
timeout: int,
|
||||
fallback: argparse.Namespace,
|
||||
) -> dict[str, list]:
|
||||
payload: dict[str, object] = {
|
||||
"prompts": [prompt],
|
||||
"n": 1,
|
||||
"temperature": getattr(trainer_args, "temperature", fallback.temperature),
|
||||
"max_tokens": getattr(trainer_args, "max_completion_length", fallback.max_new_tokens),
|
||||
"logprobs": True,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
top_k = getattr(trainer_args, "top_k", fallback.top_k)
|
||||
if top_k is not None:
|
||||
payload["top_k"] = top_k
|
||||
|
||||
top_p = getattr(trainer_args, "top_p", fallback.top_p)
|
||||
if top_p is not None:
|
||||
payload["top_p"] = top_p
|
||||
|
||||
min_p = getattr(trainer_args, "min_p", None)
|
||||
if min_p is not None:
|
||||
payload["min_p"] = min_p
|
||||
|
||||
repetition_penalty = getattr(trainer_args, "repetition_penalty", None)
|
||||
if repetition_penalty is not None:
|
||||
payload["repetition_penalty"] = repetition_penalty
|
||||
|
||||
response = requests.post(endpoint, json=payload, timeout=timeout)
|
||||
response.raise_for_status()
|
||||
data = response.json()
|
||||
|
||||
prompt_ids = data.get("prompt_ids") or data.get("prompt_token_ids") or [[]]
|
||||
completion_ids = data.get("completion_ids") or data.get("completion_token_ids") or [[]]
|
||||
logprobs = data.get("logprobs") or data.get("completion_logprobs") or [[]]
|
||||
texts = data.get("completions") or data.get("completion_texts") or data.get("texts")
|
||||
|
||||
return {
|
||||
"prompt_ids": prompt_ids[0] if prompt_ids else [],
|
||||
"completion_ids": completion_ids[0] if completion_ids else [],
|
||||
"logprobs": [float(lp) for lp in (logprobs[0] if logprobs else [])],
|
||||
"text": (texts[0] if texts else None),
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def scale_repetition_score(previous_occurrences: int, max_occurrences: int) -> float:
|
||||
"""Scale the repetition score based on the number of previous occurrences from 0 to 1"""
|
||||
if max_occurrences == 0:
|
||||
return 0.0
|
||||
return (max_occurrences - previous_occurrences) / max_occurrences
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def rollout_once(
|
||||
env: TextArenaEnv,
|
||||
tokenizer: AutoTokenizer,
|
||||
args: GRPOConfig,
|
||||
dataset_prompt: str,
|
||||
cli_args: argparse.Namespace,
|
||||
system_prompt: str,
|
||||
) -> dict[str, list]:
|
||||
result = env.reset()
|
||||
observation = result.observation
|
||||
|
||||
prompt_ids: list[int] = []
|
||||
completion_ids: list[int] = []
|
||||
logprobs: list[float] = []
|
||||
raw_rewards: list[float] = []
|
||||
green_scores: list[float] = []
|
||||
yellow_scores: list[float] = []
|
||||
repetition_scores: list[float] = []
|
||||
correct_scores: list[float] = []
|
||||
guess_counts: dict[str, int] = {}
|
||||
|
||||
for _turn in range(cli_args.max_turns):
|
||||
# when the game is over the environment will return a done=True
|
||||
if result.done:
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
# set up the prompt for the model
|
||||
base_prompt = observation.prompt or dataset_prompt
|
||||
user_prompt = make_user_prompt(base_prompt, observation.messages)
|
||||
messages = [
|
||||
{"role": "system", "content": system_prompt},
|
||||
{"role": "user", "content": user_prompt},
|
||||
]
|
||||
prompt_text = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
|
||||
messages,
|
||||
add_generation_prompt=True,
|
||||
tokenize=False,
|
||||
enable_thinking=False,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# generate the completion from the model using vLLM
|
||||
vllm_result = request_vllm_completion(
|
||||
prompt_text,
|
||||
args,
|
||||
endpoint=cli_args.vllm_endpoint,
|
||||
timeout=cli_args.request_timeout,
|
||||
fallback=cli_args,
|
||||
)
|
||||
prompt_ids.extend(vllm_result["prompt_ids"])
|
||||
completion_ids.extend(vllm_result["completion_ids"])
|
||||
logprobs.extend(vllm_result["logprobs"])
|
||||
completion_text = vllm_result.get("text") or tokenizer.decode(
|
||||
vllm_result["completion_ids"], skip_special_tokens=True
|
||||
)
|
||||
# extract the guess from the completion
|
||||
guess = extract_guess(completion_text)
|
||||
|
||||
# step the environment with the guess
|
||||
result = env.step(TextArenaAction(message=guess))
|
||||
raw_rewards.append(float(result.reward or 0.0))
|
||||
observation = result.observation
|
||||
correct_score = float(result.reward or 0.0)
|
||||
feedback = extract_wordle_feedback(observation)
|
||||
|
||||
# Update guess counts
|
||||
previous_occurrences = guess_counts[guess]
|
||||
repetition_score = scale_repetition_score(previous_occurrences, len(guess_counts))
|
||||
guess_counts[guess] += 1
|
||||
|
||||
# calculate custom reward signals from the feedback
|
||||
if not feedback:
|
||||
green_score = 0.0
|
||||
yellow_score = 0.0
|
||||
else:
|
||||
green_count, yellow_count = extract_feedback_counts(feedback)
|
||||
green_score = green_count / 5.0
|
||||
yellow_score = yellow_count / 5.0
|
||||
|
||||
repetition_scores.append(repetition_score)
|
||||
green_scores.append(green_score)
|
||||
yellow_scores.append(yellow_score)
|
||||
correct_scores.append(correct_score)
|
||||
|
||||
correct_reward_value = correct_scores[-1] if correct_scores else (raw_rewards[-1] if raw_rewards else 0.0)
|
||||
|
||||
return {
|
||||
"prompt_ids": prompt_ids,
|
||||
"completion_ids": completion_ids,
|
||||
"logprobs": logprobs,
|
||||
"raw_rewards": raw_rewards,
|
||||
"correct_reward": correct_reward_value,
|
||||
"green_reward": green_scores[-1] if green_scores else 0.0,
|
||||
"yellow_reward": yellow_scores[-1] if yellow_scores else 0.0,
|
||||
"repetition_reward": repetition_scores[-1] if repetition_scores else 0.0,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
# Rollout function
|
||||
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def rollout_func(
|
||||
env: TextArenaEnv,
|
||||
tokenizer: AutoTokenizer,
|
||||
prompts: list[str],
|
||||
args: GRPOConfig,
|
||||
cli_args: argparse.Namespace,
|
||||
system_prompt: str,
|
||||
) -> dict[str, list]:
|
||||
all_prompt_ids: list[list[int]] = []
|
||||
all_completion_ids: list[list[int]] = []
|
||||
all_logprobs: list[list[float]] = []
|
||||
correctness_rewards: list[float] = []
|
||||
green_rewards: list[float] = []
|
||||
yellow_rewards: list[float] = []
|
||||
repetition_rewards: list[float] = []
|
||||
num_generations = args.num_generations or cli_args.num_generations
|
||||
|
||||
for _ in range(num_generations):
|
||||
for prompt_text in prompts:
|
||||
rollout_stats = rollout_once(
|
||||
env=env,
|
||||
tokenizer=tokenizer,
|
||||
args=args,
|
||||
dataset_prompt=prompt_text,
|
||||
cli_args=cli_args,
|
||||
system_prompt=system_prompt,
|
||||
)
|
||||
all_prompt_ids.append(rollout_stats["prompt_ids"])
|
||||
all_completion_ids.append(rollout_stats["completion_ids"])
|
||||
all_logprobs.append(rollout_stats["logprobs"])
|
||||
correctness_rewards.append(rollout_stats["correct_reward"])
|
||||
green_rewards.append(rollout_stats["green_reward"])
|
||||
yellow_rewards.append(rollout_stats["yellow_reward"])
|
||||
repetition_rewards.append(rollout_stats["repetition_reward"])
|
||||
|
||||
return {
|
||||
"prompt_ids": all_prompt_ids,
|
||||
"completion_ids": all_completion_ids,
|
||||
"logprobs": all_logprobs,
|
||||
"correct_reward": correctness_rewards,
|
||||
"green_reward": green_rewards,
|
||||
"yellow_reward": yellow_rewards,
|
||||
"repetition_reward": repetition_rewards,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
# Rewards
|
||||
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def reward_correct(completions: list[str], **kwargs) -> list[float]:
|
||||
rewards = kwargs.get("correct_reward") if kwargs else None
|
||||
if rewards is None:
|
||||
return [0.0 for _ in completions]
|
||||
return [float(r) for r in rewards]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def reward_greens(completions: list[str], **kwargs) -> list[float]:
|
||||
rewards = kwargs.get("green_reward") if kwargs else None
|
||||
if rewards is None:
|
||||
return [0.0 for _ in completions]
|
||||
return [float(r) for r in rewards]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def reward_yellows(completions: list[str], **kwargs) -> list[float]:
|
||||
rewards = kwargs.get("yellow_reward") if kwargs else None
|
||||
if rewards is None:
|
||||
return [0.0 for _ in completions]
|
||||
return [float(r) for r in rewards]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def reward_repetition(completions: list[str], **kwargs) -> list[float]:
|
||||
rewards = kwargs.get("repetition_reward") if kwargs else None
|
||||
if rewards is None:
|
||||
return [0.0 for _ in completions]
|
||||
return [float(r) for r in rewards]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
# Main entrypoint
|
||||
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def main() -> None:
|
||||
cli_args = parse_args()
|
||||
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(cli_args.tokenizer_id)
|
||||
tokenizer.pad_token = tokenizer.eos_token
|
||||
|
||||
env = TextArenaEnv(base_url=cli_args.textarena_url)
|
||||
|
||||
system_prompt = resolve_system_prompt(cli_args.system_prompt_path)
|
||||
|
||||
dataset = Dataset.from_dict({"prompt": [cli_args.dataset_prompt] * cli_args.dataset_size})
|
||||
|
||||
timestamp = datetime.now().strftime("%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M-%S")
|
||||
default_output_dir = Path("outputs") / f"wordle-grpo-{sanitize_name(cli_args.model_id)}-{timestamp}"
|
||||
output_dir = Path(cli_args.output_dir or default_output_dir)
|
||||
|
||||
grpo_config = GRPOConfig(
|
||||
vllm_mode="server",
|
||||
use_vllm=True,
|
||||
output_dir=str(output_dir),
|
||||
num_train_epochs=cli_args.num_epochs,
|
||||
learning_rate=cli_args.learning_rate,
|
||||
weight_decay=cli_args.weight_decay,
|
||||
gradient_accumulation_steps=cli_args.gradient_accumulation_steps,
|
||||
per_device_train_batch_size=cli_args.per_device_batch_size,
|
||||
warmup_steps=cli_args.warmup_steps,
|
||||
num_generations=cli_args.num_generations,
|
||||
max_completion_length=cli_args.max_new_tokens,
|
||||
logging_steps=cli_args.logging_steps,
|
||||
save_strategy="steps",
|
||||
save_steps=cli_args.save_interval,
|
||||
save_total_limit=cli_args.save_total_limit,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
grpo_config.run_name = cli_args.run_name or f"run-{timestamp}"
|
||||
grpo_config.project = cli_args.project or f"group-{sanitize_name(cli_args.model_id)}"
|
||||
grpo_config.trackio_space_id = cli_args.trackio_space_id
|
||||
|
||||
def wrapped_rollout(prompts: list[str], args: GRPOConfig, processing_class) -> dict[str, list]:
|
||||
return rollout_func(
|
||||
env=env,
|
||||
tokenizer=tokenizer,
|
||||
prompts=prompts,
|
||||
args=args,
|
||||
cli_args=cli_args,
|
||||
system_prompt=system_prompt,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
trainer = GRPOTrainer(
|
||||
model=cli_args.model_id,
|
||||
processing_class=tokenizer,
|
||||
reward_funcs=[
|
||||
reward_correct,
|
||||
reward_greens,
|
||||
reward_yellows,
|
||||
reward_repetition,
|
||||
],
|
||||
train_dataset=dataset,
|
||||
args=grpo_config,
|
||||
rollout_func=wrapped_rollout,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
print("Starting GRPO training with Wordle environment...")
|
||||
print(f"Using {cli_args.num_generations} rollouts per dataset prompt")
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
trainer.train()
|
||||
finally:
|
||||
env.close()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
main()
|
||||
105
examples/scripts/openenv/wordle_prompt.txt
Normal file
105
examples/scripts/openenv/wordle_prompt.txt
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,105 @@
|
||||
You are an expert Wordle solver with deep knowledge of English vocabulary, letter frequency patterns, and optimal guessing strategies.
|
||||
|
||||
## GAME RULES
|
||||
|
||||
1. The target is a 5-letter English word
|
||||
2. You have 6 attempts to guess the correct word
|
||||
3. After each guess, you receive color-coded feedback:
|
||||
- GREEN: Letter is correct and in the correct position
|
||||
- YELLOW: Letter is in the word but in the wrong position
|
||||
- GRAY: Letter is not in the word at all
|
||||
4. All guesses must be valid 5-letter English words
|
||||
5. You cannot reuse a word you've already guessed
|
||||
|
||||
## RESPONSE FORMAT
|
||||
|
||||
Only respond with your next guess in square brackets, e.g., [crane].
|
||||
|
||||
Format:
|
||||
```
|
||||
[guess]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## STRATEGIC APPROACH
|
||||
|
||||
Do not repeat the same guess twice.
|
||||
|
||||
### Opening Strategy
|
||||
- Start with words rich in common vowels (A, E, I, O, U) and consonants (R, S, T, L, N)
|
||||
- Optimal starters: CRANE, SLATE, STARE, AROSE, IRATE
|
||||
- Prioritize words that test the most common letters in different positions
|
||||
|
||||
### Mid-Game Strategy
|
||||
- Use confirmed GREEN letters in their correct positions
|
||||
- Place YELLOW letters in different positions than where they appeared
|
||||
- Eliminate GRAY letters entirely from consideration
|
||||
- If multiple letters are unknown, prioritize common letter combinations (TH, CH, ST, ER, etc.)
|
||||
- Consider letter frequency: E is most common, followed by A, R, I, O, T, N, S
|
||||
|
||||
### Vowel Placement
|
||||
- Most 5-letter words have 2 vowels
|
||||
- Common patterns: vowel-consonant-vowel (like CRANE) or consonant-vowel-vowel-consonant-vowel (like QUEUE)
|
||||
- If you have 1-2 vowels confirmed, consider where the others might be
|
||||
|
||||
### Advanced Tactics
|
||||
- Use "sacrificial" guesses to test multiple new letters if you have attempts to spare
|
||||
- Avoid repeating letter patterns unless you're certain (e.g., SPEED has two E's)
|
||||
- Think about word endings: -ER, -LY, -ED, -ING are common but may not fit the 5-letter constraint
|
||||
- Consider less common letters (Q, X, Z, J) only when you've eliminated most common options
|
||||
|
||||
### Common Pitfalls to Avoid
|
||||
- Don't reuse X letters
|
||||
- Don't place Y letters in the same position they appeared
|
||||
- Don't ignore confirmed G letters
|
||||
- Don't guess words that contradict known information
|
||||
|
||||
## EXAMPLES
|
||||
|
||||
### Example 1: Opening Guess
|
||||
"Starting with a word that tests common vowels and consonants in varied positions."
|
||||
[crane]
|
||||
|
||||
### Example 2: After Receiving Feedback
|
||||
Previous guess: CRANE
|
||||
Feedback: C=gray, R=yellow, A=green, N=gray, E=yellow
|
||||
|
||||
"A is confirmed in position 2. R and E are in the word but need different positions. C and N are eliminated. I'll try a word with A in position 2, and test R and E in new positions along with common letters like S and T."
|
||||
[spare]
|
||||
|
||||
### Example 3: Narrowing Down
|
||||
Previous guesses: CRANE (C=gray, R=yellow, A=green, N=gray, E=yellow), SPARE (S=gray, P=gray, A=green, R=green, E=green)
|
||||
Feedback summary: _ARE_ with R in position 4, A in position 2, E in position 5
|
||||
|
||||
"I have _AR E_ confirmed. Position 1 and 3 are unknown. Common letters to try: T, L, D, B, F, G. Testing with TARED."
|
||||
[tared]
|
||||
|
||||
### Example 4: Final Deduction
|
||||
Previous feedback shows: _ARED with position 1 unknown and all common consonants tested
|
||||
|
||||
"Only position 1 remains. I've eliminated S, P, C, N. Common starting consonants left are B, F, G, H. BARED is a common word."
|
||||
[bared]
|
||||
|
||||
## LETTER FREQUENCY REFERENCE
|
||||
|
||||
Most common letters in 5-letter words (in order):
|
||||
S, E, A, O, R, I, L, T, N, U, D, Y, C, P, M, H, G, B, K, F
|
||||
|
||||
Most common starting letters:
|
||||
S, C, B, T, P, A, F, G, D, M
|
||||
|
||||
Most common ending letters:
|
||||
E, Y, T, S, R, L, N, D
|
||||
|
||||
## IMPORTANT CONSTRAINTS
|
||||
|
||||
- Use lowercase only
|
||||
- One guess per response
|
||||
- Must be exactly 5 letters
|
||||
- Must be a real English word from standard dictionaries
|
||||
- Never repeat a previous guess
|
||||
- Always include brief reasoning before your guess
|
||||
|
||||
## YOUR GOAL
|
||||
|
||||
Solve the Wordle in as few guesses as possible by strategically using feedback to eliminate impossible words and narrow down the solution space efficiently.
|
||||
@ -64,7 +64,6 @@ from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer, HfArgumentParser
|
||||
|
||||
from trl import ModelConfig, ORPOConfig, ORPOTrainer, ScriptArguments, get_peft_config
|
||||
from trl.trainer.utils import SIMPLE_CHAT_TEMPLATE
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Enable logging in a Hugging Face Space
|
||||
@ -91,8 +90,6 @@ if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
# Dataset
|
||||
################
|
||||
dataset = load_dataset(script_args.dataset_name, name=script_args.dataset_config)
|
||||
if tokenizer.chat_template is None:
|
||||
tokenizer.chat_template = SIMPLE_CHAT_TEMPLATE
|
||||
|
||||
################
|
||||
# Training
|
||||
|
||||
@ -43,7 +43,6 @@ from trl import (
|
||||
get_peft_config,
|
||||
get_quantization_config,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from trl.trainer.utils import SIMPLE_CHAT_TEMPLATE
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Enable logging in a Hugging Face Space
|
||||
@ -106,8 +105,6 @@ if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
model_args.model_name_or_path, padding_side="left", trust_remote_code=model_args.trust_remote_code
|
||||
)
|
||||
tokenizer.add_special_tokens({"pad_token": "[PAD]"})
|
||||
if tokenizer.chat_template is None:
|
||||
tokenizer.chat_template = SIMPLE_CHAT_TEMPLATE
|
||||
value_model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(
|
||||
training_args.reward_model_path, trust_remote_code=model_args.trust_remote_code, num_labels=1
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -43,7 +43,6 @@ from trl import (
|
||||
get_peft_config,
|
||||
get_quantization_config,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from trl.trainer.utils import SIMPLE_CHAT_TEMPLATE
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Enable logging in a Hugging Face Space
|
||||
@ -113,8 +112,6 @@ if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
model_args.model_name_or_path, padding_side="left", trust_remote_code=model_args.trust_remote_code
|
||||
)
|
||||
tokenizer.add_special_tokens({"pad_token": "[PAD]"})
|
||||
if tokenizer.chat_template is None:
|
||||
tokenizer.chat_template = SIMPLE_CHAT_TEMPLATE
|
||||
value_model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(
|
||||
training_args.reward_model_path, trust_remote_code=model_args.trust_remote_code, num_labels=1
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -57,7 +57,6 @@ from trl import (
|
||||
get_kbit_device_map,
|
||||
get_quantization_config,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from trl.trainer.utils import SIMPLE_CHAT_TEMPLATE
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Enable logging in a Hugging Face Space
|
||||
@ -113,8 +112,6 @@ if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
)
|
||||
if tokenizer.pad_token is None:
|
||||
tokenizer.pad_token = tokenizer.eos_token
|
||||
if tokenizer.chat_template is None:
|
||||
tokenizer.chat_template = SIMPLE_CHAT_TEMPLATE
|
||||
|
||||
dataset = load_dataset(script_args.dataset_name, name=script_args.dataset_config)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -21,18 +21,16 @@ classifiers = [
|
||||
"Natural Language :: English",
|
||||
"Operating System :: OS Independent",
|
||||
"Programming Language :: Python :: 3",
|
||||
"Programming Language :: Python :: 3.9",
|
||||
"Programming Language :: Python :: 3.10",
|
||||
"Programming Language :: Python :: 3.11",
|
||||
"Programming Language :: Python :: 3.12",
|
||||
"Programming Language :: Python :: 3.13"
|
||||
]
|
||||
requires-python = ">=3.9"
|
||||
requires-python = ">=3.10"
|
||||
dependencies = [
|
||||
"accelerate>=1.4.0",
|
||||
"datasets>=3.0.0",
|
||||
"transformers>=4.56.1",
|
||||
"transformers!=4.57.0; python_version == '3.9'"
|
||||
]
|
||||
dynamic = ["version"]
|
||||
|
||||
@ -132,7 +130,7 @@ version = { file = "VERSION" }
|
||||
branch = true
|
||||
|
||||
[tool.ruff]
|
||||
target-version = "py39"
|
||||
target-version = "py310"
|
||||
line-length = 119
|
||||
src = ["trl"]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -336,9 +336,9 @@ for model_id, model_class in [
|
||||
vision_config["depth"] = 2
|
||||
|
||||
if issubclass(model_class.config_class, (Qwen2VLConfig, Qwen2_5_VLConfig)):
|
||||
text_config["rope_scaling"] = {"type": "default", "mrope_section": [2], "rope_type": "default"}
|
||||
text_config["rope_scaling"] = {"type": "default", "mrope_section": [1, 1], "rope_type": "default"}
|
||||
# Different dict object from text_config; see GH-4101 and transformers#41020
|
||||
kwargs["rope_scaling"] = {"type": "default", "mrope_section": [2], "rope_type": "default"}
|
||||
kwargs["rope_scaling"] = {"type": "default", "mrope_section": [1, 1], "rope_type": "default"}
|
||||
|
||||
if issubclass(model_class.config_class, Qwen2_5_VLConfig):
|
||||
vision_config["out_hidden_size"] = 16
|
||||
|
||||
@ -24,7 +24,7 @@ from transformers.utils import is_peft_available
|
||||
from trl.experimental.bco import BCOConfig, BCOTrainer
|
||||
from trl.experimental.bco.bco_trainer import _process_tokens, _tokenize
|
||||
|
||||
from .testing_utils import TrlTestCase, require_no_wandb, require_peft, require_sklearn
|
||||
from ..testing_utils import TrlTestCase, require_no_wandb, require_peft, require_sklearn
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if is_peft_available():
|
||||
633
tests/experimental/test_gold_trainer.py
Normal file
633
tests/experimental/test_gold_trainer.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,633 @@
|
||||
# Copyright 2020-2025 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
from types import SimpleNamespace
|
||||
|
||||
import pytest
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
from transformers import AutoTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
from trl.experimental.gold.gold_trainer import GOLDTrainer, ULDLoss, build_teacher_inputs_from_texts
|
||||
from trl.trainer.utils import DataCollatorForChatML
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.fixture(scope="module")
|
||||
def openr1_examples():
|
||||
try:
|
||||
dataset = load_dataset(
|
||||
"HuggingFaceTB/OpenR1-Math-220k-default-verified",
|
||||
"all",
|
||||
split="train[:3]",
|
||||
)
|
||||
except Exception as exc: # pragma: no cover - network/environment dependent
|
||||
pytest.skip(f"OpenR1 dataset unavailable: {exc}")
|
||||
return [{"messages": row["messages"]} for row in dataset]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.fixture(scope="module")
|
||||
def countdown_examples():
|
||||
try:
|
||||
dataset = load_dataset(
|
||||
"HuggingFaceTB/Countdown-Tasks-3to4",
|
||||
"gkd_verified_Qwen2.5-7B-Instruct",
|
||||
split="train[:3]",
|
||||
)
|
||||
except Exception as exc: # pragma: no cover - network/environment dependent
|
||||
pytest.skip(f"Countdown dataset unavailable: {exc}")
|
||||
return [{"messages": row["messages"]} for row in dataset]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _teacher_inputs_from_collator(student_tok, teacher_tok, batch):
|
||||
prompt_texts = []
|
||||
completion_texts = []
|
||||
|
||||
pad_token_id = student_tok.pad_token_id
|
||||
for prompt_ids_tensor, input_ids_tensor, labels_tensor in zip(
|
||||
batch["prompts"], batch["input_ids"], batch["labels"], strict=True
|
||||
):
|
||||
prompt_ids = prompt_ids_tensor.tolist()
|
||||
if pad_token_id is not None:
|
||||
prompt_ids = [tok for tok in prompt_ids if tok != pad_token_id]
|
||||
prompt_texts.append(student_tok.decode(prompt_ids, skip_special_tokens=False))
|
||||
|
||||
input_ids = input_ids_tensor.tolist()
|
||||
labels = labels_tensor.tolist()
|
||||
completion_token_ids = [tok for tok, label in zip(input_ids, labels, strict=True) if label != -100]
|
||||
completion_texts.append(student_tok.decode(completion_token_ids, skip_special_tokens=False))
|
||||
|
||||
teacher_input_ids, teacher_labels, _, _ = build_teacher_inputs_from_texts(
|
||||
teacher_tok, prompt_texts, completion_texts
|
||||
)
|
||||
return teacher_input_ids, teacher_labels, completion_texts
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _assert_alignment_covers_completion(loss_fn, batch, teacher_input_ids, teacher_labels):
|
||||
for idx in range(batch["input_ids"].shape[0]):
|
||||
student_mask = batch["attention_mask"][idx].bool()
|
||||
student_ids = batch["input_ids"][idx][student_mask]
|
||||
student_labels = batch["labels"][idx][student_mask]
|
||||
student_answer_ids = student_ids[student_labels != -100].tolist()
|
||||
|
||||
teacher_answer_mask = teacher_labels[idx] != -100
|
||||
teacher_answer_ids = teacher_input_ids[idx][teacher_answer_mask].tolist()
|
||||
|
||||
student_groups, teacher_groups = loss_fn._build_alignment_groups_from_ids(
|
||||
student_answer_ids, teacher_answer_ids
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
assert student_groups, "Student alignment groups must not be empty"
|
||||
assert teacher_groups, "Teacher alignment groups must not be empty"
|
||||
assert sorted(idx for group in student_groups for idx in group) == list(range(len(student_answer_ids)))
|
||||
assert sorted(idx for group in teacher_groups for idx in group) == list(range(len(teacher_answer_ids)))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.mark.slow
|
||||
def test_chatml_collator_preserves_completion_llama(llama_tokenizer, qwen_tokenizer, openr1_examples):
|
||||
collator = DataCollatorForChatML(tokenizer=llama_tokenizer, max_length=512)
|
||||
batch = collator(openr1_examples)
|
||||
|
||||
assistant_texts = [example["messages"][-1]["content"] for example in openr1_examples]
|
||||
decoded_batch = llama_tokenizer.batch_decode(batch["input_ids"], skip_special_tokens=False)
|
||||
for decoded, assistant in zip(decoded_batch, assistant_texts, strict=True):
|
||||
assert assistant.strip() in decoded
|
||||
|
||||
teacher_input_ids, teacher_labels, completion_texts = _teacher_inputs_from_collator(
|
||||
llama_tokenizer, qwen_tokenizer, batch
|
||||
)
|
||||
for completion, assistant in zip(completion_texts, assistant_texts, strict=True):
|
||||
assert assistant.strip() in completion
|
||||
assert completion.strip()
|
||||
|
||||
config = build_config(
|
||||
uld_use_hybrid_loss=True,
|
||||
uld_hybrid_matched_weight=0.6,
|
||||
uld_hybrid_unmatched_weight=0.4,
|
||||
)
|
||||
loss_fn = ULDLoss(config, student_tokenizer=llama_tokenizer, teacher_tokenizer=qwen_tokenizer)
|
||||
|
||||
_assert_alignment_covers_completion(loss_fn, batch, teacher_input_ids, teacher_labels)
|
||||
|
||||
torch.manual_seed(0)
|
||||
student_vocab = len(llama_tokenizer)
|
||||
teacher_vocab = len(qwen_tokenizer)
|
||||
batch_size, seq_len = batch["input_ids"].shape
|
||||
student_logits = torch.randn(batch_size, seq_len, student_vocab)
|
||||
teacher_logits = torch.randn(batch_size, teacher_input_ids.shape[1], teacher_vocab)
|
||||
|
||||
loss = loss_fn(
|
||||
student_logits=student_logits,
|
||||
teacher_logits=teacher_logits,
|
||||
student_labels=batch["labels"],
|
||||
teacher_labels=teacher_labels,
|
||||
student_input_ids=batch["input_ids"],
|
||||
teacher_input_ids=teacher_input_ids,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
assert torch.isfinite(loss)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.mark.slow
|
||||
def test_chatml_collator_preserves_completion_llama_countdown(llama_tokenizer, qwen_tokenizer, countdown_examples):
|
||||
collator = DataCollatorForChatML(tokenizer=llama_tokenizer, max_length=512)
|
||||
batch = collator(countdown_examples)
|
||||
|
||||
assistant_texts = [example["messages"][-1]["content"] for example in countdown_examples]
|
||||
decoded_batch = llama_tokenizer.batch_decode(batch["input_ids"], skip_special_tokens=False)
|
||||
for decoded, assistant in zip(decoded_batch, assistant_texts, strict=True):
|
||||
assert assistant.strip() in decoded
|
||||
|
||||
teacher_input_ids, teacher_labels, completion_texts = _teacher_inputs_from_collator(
|
||||
llama_tokenizer, qwen_tokenizer, batch
|
||||
)
|
||||
for completion, assistant in zip(completion_texts, assistant_texts, strict=True):
|
||||
assert assistant.strip() in completion
|
||||
assert completion.strip()
|
||||
|
||||
config = build_config(
|
||||
uld_use_hybrid_loss=True,
|
||||
uld_hybrid_matched_weight=0.6,
|
||||
uld_hybrid_unmatched_weight=0.4,
|
||||
)
|
||||
loss_fn = ULDLoss(config, student_tokenizer=llama_tokenizer, teacher_tokenizer=qwen_tokenizer)
|
||||
|
||||
_assert_alignment_covers_completion(loss_fn, batch, teacher_input_ids, teacher_labels)
|
||||
|
||||
torch.manual_seed(2)
|
||||
student_vocab = len(llama_tokenizer)
|
||||
teacher_vocab = len(qwen_tokenizer)
|
||||
batch_size, seq_len = batch["input_ids"].shape
|
||||
student_logits = torch.randn(batch_size, seq_len, student_vocab)
|
||||
teacher_logits = torch.randn(batch_size, teacher_input_ids.shape[1], teacher_vocab)
|
||||
|
||||
loss = loss_fn(
|
||||
student_logits=student_logits,
|
||||
teacher_logits=teacher_logits,
|
||||
student_labels=batch["labels"],
|
||||
teacher_labels=teacher_labels,
|
||||
student_input_ids=batch["input_ids"],
|
||||
teacher_input_ids=teacher_input_ids,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
assert torch.isfinite(loss)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.mark.slow
|
||||
def test_chatml_collator_preserves_completion_smollm(smollm_tokenizer, qwen_tokenizer, openr1_examples):
|
||||
collator = DataCollatorForChatML(tokenizer=smollm_tokenizer, max_length=512)
|
||||
batch = collator(openr1_examples)
|
||||
|
||||
assistant_texts = [example["messages"][-1]["content"] for example in openr1_examples]
|
||||
decoded_batch = smollm_tokenizer.batch_decode(batch["input_ids"], skip_special_tokens=False)
|
||||
for decoded, assistant in zip(decoded_batch, assistant_texts, strict=True):
|
||||
assert assistant.strip() in decoded
|
||||
|
||||
teacher_input_ids, teacher_labels, completion_texts = _teacher_inputs_from_collator(
|
||||
smollm_tokenizer, qwen_tokenizer, batch
|
||||
)
|
||||
for completion, assistant in zip(completion_texts, assistant_texts, strict=True):
|
||||
assert assistant.strip() in completion
|
||||
assert completion.strip()
|
||||
|
||||
config = build_config(
|
||||
uld_use_hybrid_loss=True,
|
||||
uld_hybrid_matched_weight=0.5,
|
||||
uld_hybrid_unmatched_weight=0.5,
|
||||
)
|
||||
loss_fn = ULDLoss(config, student_tokenizer=smollm_tokenizer, teacher_tokenizer=qwen_tokenizer)
|
||||
|
||||
_assert_alignment_covers_completion(loss_fn, batch, teacher_input_ids, teacher_labels)
|
||||
|
||||
torch.manual_seed(1)
|
||||
student_vocab = len(smollm_tokenizer)
|
||||
teacher_vocab = len(qwen_tokenizer)
|
||||
batch_size, seq_len = batch["input_ids"].shape
|
||||
student_logits = torch.randn(batch_size, seq_len, student_vocab)
|
||||
teacher_logits = torch.randn(batch_size, teacher_input_ids.shape[1], teacher_vocab)
|
||||
|
||||
loss = loss_fn(
|
||||
student_logits=student_logits,
|
||||
teacher_logits=teacher_logits,
|
||||
student_labels=batch["labels"],
|
||||
teacher_labels=teacher_labels,
|
||||
student_input_ids=batch["input_ids"],
|
||||
teacher_input_ids=teacher_input_ids,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
assert torch.isfinite(loss)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def build_config(**overrides):
|
||||
base = dict(
|
||||
uld_crossentropy_weight=0.0,
|
||||
uld_distillation_weight=1.0,
|
||||
uld_student_temperature=1.0,
|
||||
uld_teacher_temperature=1.0,
|
||||
uld_skip_student_eos=False,
|
||||
uld_skip_teacher_eos=False,
|
||||
use_extended_uld=True,
|
||||
uld_use_hybrid_loss=False,
|
||||
uld_hybrid_matched_weight=None,
|
||||
uld_hybrid_unmatched_weight=None,
|
||||
beta=0.5,
|
||||
)
|
||||
base.update(overrides)
|
||||
return SimpleNamespace(**base)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.fixture(scope="session")
|
||||
def llama_tokenizer():
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("TinyLlama/TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0")
|
||||
if tokenizer.pad_token is None:
|
||||
tokenizer.pad_token = tokenizer.eos_token
|
||||
return tokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.fixture(scope="session")
|
||||
def qwen_tokenizer():
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("Qwen/Qwen2.5-0.5B-Instruct")
|
||||
if tokenizer.pad_token is None:
|
||||
tokenizer.pad_token = tokenizer.eos_token
|
||||
return tokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.fixture(scope="session")
|
||||
def smollm_tokenizer():
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("HuggingFaceTB/SmolLM3-3B")
|
||||
if tokenizer.pad_token is None:
|
||||
tokenizer.pad_token = tokenizer.eos_token
|
||||
return tokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def encode_prompt_completion(tokenizer, prompt, completion):
|
||||
prompt_ids = tokenizer(prompt, add_special_tokens=False)["input_ids"]
|
||||
completion_ids = tokenizer(completion, add_special_tokens=False)["input_ids"]
|
||||
eos_id = tokenizer.eos_token_id
|
||||
if eos_id is not None:
|
||||
completion_ids = completion_ids + [eos_id]
|
||||
input_ids = prompt_ids + completion_ids
|
||||
labels = [-100] * len(prompt_ids) + completion_ids
|
||||
return input_ids, labels
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def pad_tokens(ids, pad_id, target_length):
|
||||
return ids + [pad_id] * (target_length - len(ids))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def pad_labels(labels, target_length):
|
||||
return labels + [-100] * (target_length - len(labels))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def test_alignment_groups_cover_all_tokens(llama_tokenizer, qwen_tokenizer):
|
||||
config = build_config()
|
||||
loss = ULDLoss(config, student_tokenizer=llama_tokenizer, teacher_tokenizer=qwen_tokenizer)
|
||||
|
||||
text = "SmolLM3-3B is smaller than Llama 3.2 but still capable."
|
||||
student_ids = llama_tokenizer(text, add_special_tokens=False)["input_ids"]
|
||||
teacher_ids = qwen_tokenizer(text, add_special_tokens=False)["input_ids"]
|
||||
|
||||
student_groups, teacher_groups = loss._build_alignment_groups_from_ids(student_ids, teacher_ids)
|
||||
|
||||
assert len(student_groups) == len(teacher_groups)
|
||||
assert sorted(idx for group in student_groups for idx in group) == list(range(len(student_ids)))
|
||||
assert sorted(idx for group in teacher_groups for idx in group) == list(range(len(teacher_ids)))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def test_merge_probabilities_multiplies_split_tokens():
|
||||
config = build_config()
|
||||
# Use simple 3-token vocabulary to validate merging behaviour
|
||||
probs = torch.tensor([[0.6, 0.3, 0.1], [0.2, 0.5, 0.3]])
|
||||
loss = ULDLoss(config, student_tokenizer=None, teacher_tokenizer=None)
|
||||
|
||||
merged = loss._merge_probabilities_with_alignment_groups(probs, [[0, 1]])
|
||||
expected = torch.softmax(torch.log(probs[0]) + torch.log(probs[1]), dim=-1)
|
||||
|
||||
assert torch.allclose(merged[0], expected, atol=1e-6)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def test_initialize_vocabulary_mapping_contains_common_tokens(llama_tokenizer, qwen_tokenizer):
|
||||
config = build_config(
|
||||
uld_use_hybrid_loss=True,
|
||||
uld_hybrid_matched_weight=1.0,
|
||||
uld_hybrid_unmatched_weight=0.0,
|
||||
)
|
||||
loss = ULDLoss(config, student_tokenizer=llama_tokenizer, teacher_tokenizer=qwen_tokenizer)
|
||||
|
||||
common_tokens = ["Hello", "world", "-", "ol", "LM", "3", "B"]
|
||||
for token in common_tokens:
|
||||
student_id = llama_tokenizer.convert_tokens_to_ids(token)
|
||||
teacher_id = qwen_tokenizer.convert_tokens_to_ids(token)
|
||||
assert student_id is not None
|
||||
assert teacher_id is not None
|
||||
assert teacher_id in loss._vocab_mapping
|
||||
assert loss._vocab_mapping[teacher_id] == student_id
|
||||
assert teacher_id in loss._teacher_matched_ids
|
||||
assert student_id in loss._student_matched_ids
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def test_get_start_and_size_answers_skips_prompt_tokens():
|
||||
trainer = ULDLoss.__new__(ULDLoss)
|
||||
trainer.ignore_index = -100
|
||||
|
||||
answers = torch.tensor(
|
||||
[
|
||||
[-100, -100, -100, 10, 20, 30, -100, -100],
|
||||
[-100, 5, 6, 7, -100, -100, -100, -100],
|
||||
[-100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100, -100],
|
||||
]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
starts, sizes = trainer._get_start_and_size_answers(answers)
|
||||
|
||||
assert starts == [3, 1, 0]
|
||||
assert sizes == [3, 3, 0]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.mark.slow
|
||||
def test_generate_on_policy_outputs_masks_prompt(llama_tokenizer):
|
||||
trainer = GOLDTrainer.__new__(GOLDTrainer)
|
||||
trainer.use_transformers_paged = False
|
||||
trainer.processing_class = llama_tokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
prompt_text = "<|begin_of_text|><|start_header_id|>user<|end_header_id|>\nHello?<|eot_id|>"
|
||||
completion_text = "<|start_header_id|>assistant<|end_header_id|>\nHi there!"
|
||||
|
||||
prompt_ids = llama_tokenizer(prompt_text, add_special_tokens=False)["input_ids"]
|
||||
completion_ids = llama_tokenizer(completion_text, add_special_tokens=False)["input_ids"]
|
||||
|
||||
pad_id = llama_tokenizer.pad_token_id
|
||||
pad_width = 3
|
||||
prompt_tensor = torch.full((1, len(prompt_ids) + pad_width), pad_id, dtype=torch.long)
|
||||
prompt_tensor[0, pad_width:] = torch.tensor(prompt_ids, dtype=torch.long)
|
||||
prompt_mask = (prompt_tensor != pad_id).long()
|
||||
|
||||
generated_sequence = torch.tensor(prompt_ids + completion_ids, dtype=torch.long).unsqueeze(0)
|
||||
|
||||
class DummyModel:
|
||||
def generate(self, input_ids, attention_mask, generation_config, return_dict_in_generate):
|
||||
assert torch.equal(input_ids, prompt_tensor)
|
||||
assert torch.equal(attention_mask, prompt_mask)
|
||||
return SimpleNamespace(sequences=generated_sequence)
|
||||
|
||||
generation_config = SimpleNamespace(max_completion_length=None, temperature=None, top_k=None, top_p=None)
|
||||
new_ids, new_mask, new_labels, prompt_texts, completion_texts = GOLDTrainer.generate_on_policy_outputs(
|
||||
trainer,
|
||||
DummyModel(),
|
||||
{"prompts": prompt_tensor, "prompt_attention_mask": prompt_mask},
|
||||
generation_config,
|
||||
pad_id,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
assert torch.equal(new_ids, generated_sequence)
|
||||
if pad_id is not None:
|
||||
expected_mask = (generated_sequence != pad_id).long()
|
||||
assert torch.equal(new_mask, expected_mask)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
assert torch.all(new_mask == 1)
|
||||
|
||||
prompt_len = len(prompt_ids)
|
||||
assert torch.all(new_labels[0, :prompt_len] == -100)
|
||||
assert torch.equal(new_labels[0, prompt_len:], torch.tensor(completion_ids, dtype=torch.long))
|
||||
|
||||
assert prompt_texts[0] == llama_tokenizer.decode(prompt_ids, skip_special_tokens=False)
|
||||
assert completion_texts[0] == llama_tokenizer.decode(completion_ids, skip_special_tokens=False)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.mark.slow
|
||||
def test_generate_on_policy_outputs_masks_prompt_smollm(smollm_tokenizer, openr1_examples):
|
||||
trainer = GOLDTrainer.__new__(GOLDTrainer)
|
||||
trainer.use_transformers_paged = False
|
||||
trainer.processing_class = smollm_tokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
collator = DataCollatorForChatML(tokenizer=smollm_tokenizer)
|
||||
batch = collator([openr1_examples[0]])
|
||||
batch = {k: v.cpu() for k, v in batch.items()}
|
||||
|
||||
class DummyModel:
|
||||
def generate(self, input_ids, attention_mask, generation_config, return_dict_in_generate):
|
||||
assert torch.equal(input_ids, batch["prompts"])
|
||||
assert torch.equal(attention_mask, batch["prompt_attention_mask"])
|
||||
return SimpleNamespace(sequences=batch["input_ids"])
|
||||
|
||||
generation_config = SimpleNamespace(max_completion_length=None, temperature=None, top_k=None, top_p=None)
|
||||
pad_id = smollm_tokenizer.pad_token_id
|
||||
new_ids, new_mask, new_labels, prompt_texts, completion_texts = GOLDTrainer.generate_on_policy_outputs(
|
||||
trainer,
|
||||
DummyModel(),
|
||||
{"prompts": batch["prompts"], "prompt_attention_mask": batch["prompt_attention_mask"]},
|
||||
generation_config,
|
||||
pad_id,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
assert torch.equal(new_ids, batch["input_ids"])
|
||||
if pad_id is not None:
|
||||
expected_mask = (batch["input_ids"] != pad_id).long()
|
||||
assert torch.equal(new_mask, expected_mask)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
assert torch.all(new_mask == 1)
|
||||
|
||||
prompt_len = int(batch["prompt_attention_mask"].sum().item())
|
||||
tail_labels = new_labels[0, prompt_len:]
|
||||
expected_tail = batch["input_ids"][0, prompt_len:]
|
||||
active_mask = tail_labels != -100
|
||||
assert torch.all(new_labels[0, :prompt_len] == -100)
|
||||
assert torch.equal(tail_labels[active_mask], expected_tail[active_mask])
|
||||
assert torch.all(tail_labels[~active_mask] == -100)
|
||||
|
||||
prompt_tokens = batch["prompts"][0, batch["prompt_attention_mask"][0].bool()]
|
||||
decoded_prompt = smollm_tokenizer.decode(prompt_tokens.tolist(), skip_special_tokens=False)
|
||||
assert prompt_texts[0] == decoded_prompt
|
||||
|
||||
assistant_completion = openr1_examples[0]["messages"][-1]["content"].strip()
|
||||
assert assistant_completion in completion_texts[0]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def test_generalized_jsd_loss_accepts_probability_inputs():
|
||||
student_probs = torch.tensor([[[0.6, 0.3, 0.1]]])
|
||||
teacher_probs = torch.tensor([[[0.5, 0.4, 0.1]]])
|
||||
mixture = 0.5 * (student_probs + teacher_probs)
|
||||
expected = 0.5 * (
|
||||
torch.sum(student_probs * (torch.log(student_probs) - torch.log(mixture)))
|
||||
+ torch.sum(teacher_probs * (torch.log(teacher_probs) - torch.log(mixture)))
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
loss = GOLDTrainer.generalized_jsd_loss(
|
||||
student_probs,
|
||||
teacher_probs,
|
||||
beta=0.5,
|
||||
reduction="batchmean",
|
||||
logits_are_probs=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
assert torch.allclose(loss, expected, atol=1e-6)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def test_uldloss_handles_llama_student_qwen_teacher_sequence(llama_tokenizer, qwen_tokenizer):
|
||||
config = build_config(
|
||||
uld_use_hybrid_loss=True,
|
||||
uld_hybrid_matched_weight=0.6,
|
||||
uld_hybrid_unmatched_weight=0.4,
|
||||
)
|
||||
loss_fn = ULDLoss(config, student_tokenizer=llama_tokenizer, teacher_tokenizer=qwen_tokenizer)
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "User: Summarize the difference between llamas and alpacas."
|
||||
completion = "Assistant: Llamas are taller while alpacas have softer wool."
|
||||
|
||||
student_ids, student_labels = encode_prompt_completion(llama_tokenizer, prompt, completion)
|
||||
teacher_ids, teacher_labels = encode_prompt_completion(qwen_tokenizer, prompt, completion)
|
||||
|
||||
pad_id_student = llama_tokenizer.pad_token_id
|
||||
pad_id_teacher = qwen_tokenizer.pad_token_id
|
||||
max_length = max(len(student_ids), len(teacher_ids))
|
||||
|
||||
student_ids = pad_tokens(student_ids, pad_id_student, max_length)
|
||||
teacher_ids = pad_tokens(teacher_ids, pad_id_teacher, max_length)
|
||||
student_labels = pad_labels(student_labels, max_length)
|
||||
teacher_labels = pad_labels(teacher_labels, max_length)
|
||||
|
||||
student_input_ids = torch.tensor([student_ids])
|
||||
teacher_input_ids = torch.tensor([teacher_ids])
|
||||
student_labels = torch.tensor([student_labels])
|
||||
teacher_labels = torch.tensor([teacher_labels])
|
||||
|
||||
student_vocab = len(llama_tokenizer)
|
||||
teacher_vocab = len(qwen_tokenizer)
|
||||
|
||||
student_logits = torch.randn(1, max_length, student_vocab)
|
||||
teacher_logits = torch.randn(1, max_length, teacher_vocab)
|
||||
|
||||
loss = loss_fn(
|
||||
student_logits=student_logits,
|
||||
teacher_logits=teacher_logits,
|
||||
student_labels=student_labels,
|
||||
teacher_labels=teacher_labels,
|
||||
student_input_ids=student_input_ids,
|
||||
teacher_input_ids=teacher_input_ids,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
assert torch.isfinite(loss)
|
||||
assert loss.dim() == 0
|
||||
assert loss_fn.last_matched_loss is not None
|
||||
assert loss_fn.last_unmatched_loss is not None
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def test_uldloss_handles_smollm_student_qwen_teacher_sequence(smollm_tokenizer, qwen_tokenizer):
|
||||
config = build_config(
|
||||
uld_use_hybrid_loss=True,
|
||||
uld_hybrid_matched_weight=0.5,
|
||||
uld_hybrid_unmatched_weight=0.5,
|
||||
)
|
||||
loss_fn = ULDLoss(config, student_tokenizer=smollm_tokenizer, teacher_tokenizer=qwen_tokenizer)
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "User: Describe SmolLM3 in a sentence."
|
||||
completion = "Assistant: SmolLM3 is a compact yet capable language model."
|
||||
|
||||
student_ids, student_labels = encode_prompt_completion(smollm_tokenizer, prompt, completion)
|
||||
teacher_ids, teacher_labels = encode_prompt_completion(qwen_tokenizer, prompt, completion)
|
||||
|
||||
pad_id_student = smollm_tokenizer.pad_token_id
|
||||
pad_id_teacher = qwen_tokenizer.pad_token_id
|
||||
max_length = max(len(student_ids), len(teacher_ids))
|
||||
|
||||
student_ids = pad_tokens(student_ids, pad_id_student, max_length)
|
||||
teacher_ids = pad_tokens(teacher_ids, pad_id_teacher, max_length)
|
||||
student_labels = pad_labels(student_labels, max_length)
|
||||
teacher_labels = pad_labels(teacher_labels, max_length)
|
||||
|
||||
student_input_ids = torch.tensor([student_ids])
|
||||
teacher_input_ids = torch.tensor([teacher_ids])
|
||||
student_labels = torch.tensor([student_labels])
|
||||
teacher_labels = torch.tensor([teacher_labels])
|
||||
|
||||
student_vocab = len(smollm_tokenizer)
|
||||
teacher_vocab = len(qwen_tokenizer)
|
||||
|
||||
student_logits = torch.randn(1, max_length, student_vocab)
|
||||
teacher_logits = torch.randn(1, max_length, teacher_vocab)
|
||||
|
||||
loss = loss_fn(
|
||||
student_logits=student_logits,
|
||||
teacher_logits=teacher_logits,
|
||||
student_labels=student_labels,
|
||||
teacher_labels=teacher_labels,
|
||||
student_input_ids=student_input_ids,
|
||||
teacher_input_ids=teacher_input_ids,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
assert torch.isfinite(loss)
|
||||
assert loss.dim() == 0
|
||||
assert loss_fn.last_matched_loss is not None
|
||||
assert loss_fn.last_unmatched_loss is not None
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def test_uldloss_hybrid_config_beta_zero(llama_tokenizer, qwen_tokenizer):
|
||||
config = build_config(
|
||||
uld_use_hybrid_loss=True,
|
||||
uld_hybrid_matched_weight=0.0,
|
||||
uld_hybrid_unmatched_weight=1.0,
|
||||
use_extended_uld=True,
|
||||
uld_crossentropy_weight=0.0,
|
||||
uld_distillation_weight=1.0,
|
||||
uld_student_temperature=1.0,
|
||||
uld_teacher_temperature=1.0,
|
||||
temperature=1.0,
|
||||
top_p=0.95,
|
||||
top_k=0,
|
||||
lmbda=1.0,
|
||||
beta=0.0,
|
||||
)
|
||||
loss_fn = ULDLoss(config, student_tokenizer=llama_tokenizer, teacher_tokenizer=qwen_tokenizer)
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "User: Explain how GOLD handles tokenizer mismatches."
|
||||
completion = "Assistant: GOLD merges aligned subwords and applies hybrid ULD loss."
|
||||
|
||||
student_ids, student_labels = encode_prompt_completion(llama_tokenizer, prompt, completion)
|
||||
teacher_ids, teacher_labels = encode_prompt_completion(qwen_tokenizer, prompt, completion)
|
||||
|
||||
pad_id_student = llama_tokenizer.pad_token_id
|
||||
pad_id_teacher = qwen_tokenizer.pad_token_id
|
||||
max_length = max(len(student_ids), len(teacher_ids))
|
||||
|
||||
student_ids = pad_tokens(student_ids, pad_id_student, max_length)
|
||||
teacher_ids = pad_tokens(teacher_ids, pad_id_teacher, max_length)
|
||||
student_labels = pad_labels(student_labels, max_length)
|
||||
teacher_labels = pad_labels(teacher_labels, max_length)
|
||||
|
||||
student_input_ids = torch.tensor([student_ids])
|
||||
teacher_input_ids = torch.tensor([teacher_ids])
|
||||
student_labels = torch.tensor([student_labels])
|
||||
teacher_labels = torch.tensor([teacher_labels])
|
||||
|
||||
student_vocab = len(llama_tokenizer)
|
||||
teacher_vocab = len(qwen_tokenizer)
|
||||
torch.manual_seed(0)
|
||||
student_logits = torch.randn(1, max_length, student_vocab)
|
||||
teacher_logits = torch.randn(1, max_length, teacher_vocab)
|
||||
|
||||
loss = loss_fn(
|
||||
student_logits=student_logits,
|
||||
teacher_logits=teacher_logits,
|
||||
student_labels=student_labels,
|
||||
teacher_labels=teacher_labels,
|
||||
student_input_ids=student_input_ids,
|
||||
teacher_input_ids=teacher_input_ids,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
assert torch.isfinite(loss)
|
||||
assert loss.dim() == 0
|
||||
assert loss_fn.last_matched_loss is not None
|
||||
assert loss_fn.last_unmatched_loss is not None
|
||||
|
||||
expected = config.uld_hybrid_unmatched_weight * loss_fn.last_unmatched_loss
|
||||
assert torch.allclose(loss, expected, atol=1e-6, rtol=1e-5)
|
||||
289
tests/experimental/test_grpo_with_replay_buffer_trainer.py
Normal file
289
tests/experimental/test_grpo_with_replay_buffer_trainer.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,289 @@
|
||||
# Copyright 2020-2025 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
import pytest
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
|
||||
from trl.experimental.grpo_with_replay_buffer import (
|
||||
GRPOWithReplayBufferConfig,
|
||||
GRPOWithReplayBufferTrainer,
|
||||
ReplayBuffer,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
from ..testing_utils import TrlTestCase
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.mark.low_priority
|
||||
class TestReplayBuffer:
|
||||
def setup_method(self):
|
||||
self.replay_buffer = ReplayBuffer(max_size=5)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_add(self):
|
||||
# Add elements to the replay buffer
|
||||
scores = [0.5, 0.8, 0.3, 0.9, 0.7]
|
||||
data = [
|
||||
{"id": 1},
|
||||
{"id": 2},
|
||||
{"id": 3},
|
||||
{"id": 4},
|
||||
{"id": 5},
|
||||
]
|
||||
self.replay_buffer.add(scores, data)
|
||||
|
||||
# Check if the buffer contains the correct number of elements
|
||||
assert len(self.replay_buffer.heap) == 5
|
||||
|
||||
# Check if the buffer maintains the min-heap property
|
||||
heap_scores = [item[0] for item in self.replay_buffer.heap]
|
||||
assert heap_scores[0] == min(heap_scores)
|
||||
assert heap_scores[0] == 0.3
|
||||
|
||||
def test_add_more_than_maxlen(self):
|
||||
# Add elements to the replay buffer
|
||||
scores = [0.5, 0.8, 0.3, 0.9, 0.7, 0.6, 0.4]
|
||||
data = [
|
||||
{"id": 1},
|
||||
{"id": 2},
|
||||
{"id": 3},
|
||||
{"id": 4},
|
||||
{"id": 5},
|
||||
{"id": 6},
|
||||
{"id": 7},
|
||||
]
|
||||
self.replay_buffer.add(scores, data)
|
||||
|
||||
# Check if the buffer contains the correct number of elements
|
||||
assert len(self.replay_buffer.heap) == 5
|
||||
|
||||
# Check if the buffer maintains the min-heap property
|
||||
heap_scores = [item[0] for item in self.replay_buffer.heap]
|
||||
assert heap_scores[0] == min(heap_scores)
|
||||
assert heap_scores[0] == 0.5 # 0.3 and 0.4 should be removed
|
||||
|
||||
def test_sample(self):
|
||||
# Add elements to the replay buffer
|
||||
scores = [0.5, 0.8, 0.3, 0.9, 0.7]
|
||||
data = [
|
||||
{"id": 1},
|
||||
{"id": 2},
|
||||
{"id": 3},
|
||||
{"id": 4},
|
||||
{"id": 5},
|
||||
]
|
||||
self.replay_buffer.add(scores, data)
|
||||
|
||||
# Sample elements from the buffer
|
||||
sampled = self.replay_buffer.sample(num_samples=3)
|
||||
|
||||
# Check if the sampled elements are from the buffer
|
||||
assert len(sampled) == 3
|
||||
for item in sampled:
|
||||
assert item in [entry[1] for entry in self.replay_buffer.heap]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.mark.low_priority
|
||||
class TestUpdateWithReplayBuffer:
|
||||
def setup_method(self):
|
||||
config = GRPOWithReplayBufferConfig(
|
||||
replay_buffer_size=5,
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.trainer = GRPOWithReplayBufferTrainer(
|
||||
model="trl-internal-testing/tiny-Qwen2ForCausalLM-2.5",
|
||||
reward_funcs="trl-internal-testing/tiny-Qwen2ForSequenceClassification-2.5",
|
||||
args=config,
|
||||
train_dataset=None,
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.trainer.replay_buffer = ReplayBuffer(max_size=5)
|
||||
self.trainer.num_generations = 2
|
||||
|
||||
def _prepopulate_buffer(self, with_pixels=False, with_logprobs=False):
|
||||
scores = [0.1, 0.9]
|
||||
data = [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"prompt_ids": torch.tensor([[100, 101], [102, 103]]),
|
||||
"prompt_mask": torch.ones(2, 2, dtype=torch.long),
|
||||
"completion_ids": torch.tensor([[5, 6], [7, 8]]),
|
||||
"completion_mask": torch.ones(2, 2, dtype=torch.long),
|
||||
"advantages": torch.tensor([[0.5, 0.6]]),
|
||||
**({"pixel_values": torch.randn(2, 3, 224, 224)} if with_pixels else {}),
|
||||
**({"old_per_token_logps": torch.randn(2, 2)} if with_logprobs else {}),
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"prompt_ids": torch.tensor([[104, 105], [106, 107]]),
|
||||
"prompt_mask": torch.ones(2, 2, dtype=torch.long),
|
||||
"completion_ids": torch.tensor([[13, 14], [15, 16]]),
|
||||
"completion_mask": torch.ones(2, 2, dtype=torch.long),
|
||||
"advantages": torch.tensor([[0.8, 0.85]]),
|
||||
**({"pixel_values": torch.randn(2, 3, 224, 224)} if with_pixels else {}),
|
||||
**({"old_per_token_logps": torch.randn(2, 2)} if with_logprobs else {}),
|
||||
},
|
||||
]
|
||||
self.trainer.replay_buffer.add(scores, data)
|
||||
|
||||
def _make_inputs(self, group_advantages, with_pixels=False, with_logprobs=False):
|
||||
inputs = {
|
||||
"group_advantages": group_advantages,
|
||||
"prompt_ids": torch.tensor([[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6], [7, 8]]),
|
||||
"prompt_mask": torch.ones(4, 2, dtype=torch.long),
|
||||
"completion_ids": torch.tensor([[9, 10], [11, 12], [13, 14], [15, 16]]),
|
||||
"completion_mask": torch.ones(4, 2, dtype=torch.long),
|
||||
"forward_kwargs": {"pixel_values": torch.randn(4, 3, 224, 224)} if with_pixels else {},
|
||||
"old_per_token_logps": torch.randn(4, 2) if with_logprobs else None,
|
||||
}
|
||||
inputs["group_std_rewards"] = group_advantages.std(dim=1).expand_as(group_advantages)
|
||||
return inputs
|
||||
|
||||
def test_update_with_replay_buffer_no_variance(self):
|
||||
self._prepopulate_buffer(with_pixels=True, with_logprobs=True)
|
||||
group_advantages = torch.tensor([[0.5, 0.5], [0.8, 0.8]]) # no variance
|
||||
inputs = self._make_inputs(group_advantages, with_pixels=True, with_logprobs=True)
|
||||
original_prompt_ids = inputs["prompt_ids"].clone()
|
||||
|
||||
outputs = self.trainer.update_with_replay_buffer(**inputs, num_items_in_batch=4)
|
||||
|
||||
assert outputs is not None
|
||||
assert "pixel_values" in outputs
|
||||
assert "old_per_token_logps" in outputs
|
||||
assert len(self.trainer.replay_buffer.heap) == 2
|
||||
for pid in outputs["prompt_ids"]:
|
||||
assert pid.tolist() not in original_prompt_ids.tolist()
|
||||
|
||||
def test_update_with_replay_buffer_with_variance(self):
|
||||
self._prepopulate_buffer()
|
||||
group_advantages = torch.tensor([[0.6, 0.4], [0.7, 1.2]]) # has variance
|
||||
inputs = self._make_inputs(group_advantages)
|
||||
|
||||
sampled = self.trainer.update_with_replay_buffer(**inputs, num_items_in_batch=4)
|
||||
|
||||
assert len(self.trainer.replay_buffer.heap) == 4 # grew
|
||||
assert sampled is None
|
||||
|
||||
def test_update_with_mixed_variance(self):
|
||||
self._prepopulate_buffer()
|
||||
group_advantages = torch.tensor([[0.6, 0.6], [0.3, 0.45]]) # one no-variance, one variance
|
||||
inputs = self._make_inputs(group_advantages)
|
||||
original_prompt_ids = inputs["prompt_ids"].clone().view(-1, self.trainer.num_generations, 2).tolist()
|
||||
|
||||
outputs = self.trainer.update_with_replay_buffer(**inputs, num_items_in_batch=4)
|
||||
|
||||
assert len(self.trainer.replay_buffer.heap) == 3 # grew by 1
|
||||
output_prompt_ids = outputs["prompt_ids"].view(-1, self.trainer.num_generations, 2).tolist()
|
||||
|
||||
buffer_ids = [item[1]["prompt_ids"].tolist() for item in self.trainer.replay_buffer.heap]
|
||||
found_from_buffer = any(pid in buffer_ids for pid in output_prompt_ids)
|
||||
found_from_original = any(pid in original_prompt_ids for pid in output_prompt_ids)
|
||||
|
||||
assert found_from_buffer
|
||||
assert found_from_original
|
||||
assert [[1, 2], [3, 4]] not in output_prompt_ids # excluded no-variance group
|
||||
|
||||
def test_update_with_inputs_different_seq_len(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Test with inputs where the sequence lengths are different from the prepopulated buffer.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self._prepopulate_buffer()
|
||||
pad_token_id = self.trainer.processing_class.pad_token_id
|
||||
group_advantages = torch.tensor([[0.6, 0.6], [0.3, 0.45]]) # one no-variance, one variance
|
||||
inputs = {
|
||||
"group_advantages": group_advantages,
|
||||
"prompt_ids": torch.tensor(
|
||||
[
|
||||
[1, 2, pad_token_id],
|
||||
[1, 2, pad_token_id],
|
||||
[3, 4, 5],
|
||||
[3, 4, 5],
|
||||
]
|
||||
),
|
||||
"prompt_mask": torch.tensor([[1, 1, 0], [1, 1, 0], [1, 1, 1], [1, 1, 1]], dtype=torch.long),
|
||||
"completion_ids": torch.tensor(
|
||||
[
|
||||
[1009, 1010, pad_token_id],
|
||||
[1011, 1012, 1013],
|
||||
[1013, 1014, pad_token_id],
|
||||
[1015, 1016, 1017],
|
||||
]
|
||||
),
|
||||
"completion_mask": torch.tensor([[1, 1, 0], [1, 1, 1], [1, 1, 0], [1, 1, 1]], dtype=torch.long),
|
||||
"forward_kwargs": {},
|
||||
}
|
||||
inputs["group_std_rewards"] = group_advantages.std(dim=1).expand_as(group_advantages)
|
||||
|
||||
outputs_after_sampling = self.trainer.update_with_replay_buffer(**inputs, num_items_in_batch=4)
|
||||
# Seq length of current batch should be preserved
|
||||
assert outputs_after_sampling["prompt_ids"].shape[-1] == 3
|
||||
assert len(self.trainer.replay_buffer.heap) == 3
|
||||
output_prompt_ids = outputs_after_sampling["prompt_ids"].view(-1, self.trainer.num_generations, 3).tolist()
|
||||
|
||||
buffered_prompt_completion_ids = [
|
||||
(item[1]["prompt_ids"].tolist(), item[1]["completion_ids"].tolist())
|
||||
for item in self.trainer.replay_buffer.heap
|
||||
]
|
||||
buffered_prompt_ids, buffered_completion_ids = zip(*buffered_prompt_completion_ids, strict=True)
|
||||
|
||||
# Check for new entry with seq len 3 in buffer
|
||||
assert [[3, 4, 5], [3, 4, 5]] in buffered_prompt_ids # excluded no-variance group
|
||||
assert [
|
||||
[1013, 1014, pad_token_id],
|
||||
[1015, 1016, 1017],
|
||||
] in buffered_completion_ids # excluded no-variance group
|
||||
|
||||
# Check that sampled outputs contain one group with prompt_ids starting with a pad token
|
||||
assert [
|
||||
[pad_token_id, 101, 102],
|
||||
[pad_token_id, 102, 103],
|
||||
] in output_prompt_ids or [
|
||||
[pad_token_id, 104, 105],
|
||||
[pad_token_id, 106, 107],
|
||||
] in output_prompt_ids
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.mark.low_priority
|
||||
class TestGRPOWithReplayBufferTrainer(TrlTestCase):
|
||||
def test_training_with_replay_buffer(self):
|
||||
dataset = load_dataset("trl-internal-testing/zen", "standard_prompt_only", split="train")
|
||||
|
||||
# Guarantee that some rewards have 0 std
|
||||
def custom_reward_func(completions, **kwargs):
|
||||
if torch.rand(1).item() < 0.25:
|
||||
return [0] * len(completions) # simulate some None rewards
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return torch.rand(len(completions)).tolist()
|
||||
|
||||
training_args = GRPOWithReplayBufferConfig(
|
||||
output_dir=self.tmp_dir,
|
||||
learning_rate=0.1, # increase the learning rate to speed up the test
|
||||
per_device_train_batch_size=4, # reduce the batch size to reduce memory usage
|
||||
num_generations=4, # reduce the number of generations to reduce memory usage
|
||||
max_completion_length=8, # reduce the completion length to reduce memory usage
|
||||
replay_buffer_size=8,
|
||||
report_to="none",
|
||||
)
|
||||
trainer = GRPOWithReplayBufferTrainer(
|
||||
model="trl-internal-testing/tiny-Qwen2ForCausalLM-2.5",
|
||||
reward_funcs=[custom_reward_func],
|
||||
args=training_args,
|
||||
train_dataset=dataset,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
previous_trainable_params = {n: param.clone() for n, param in trainer.model.named_parameters()}
|
||||
|
||||
trainer.train()
|
||||
|
||||
assert trainer.state.log_history[-1]["train_loss"] is not None
|
||||
|
||||
# Check that the params have changed
|
||||
for n, param in previous_trainable_params.items():
|
||||
new_param = trainer.model.get_parameter(n)
|
||||
assert not torch.equal(param, new_param), f"Parameter {n} has not changed."
|
||||
70
tests/experimental/test_trainers_args.py
Normal file
70
tests/experimental/test_trainers_args.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,70 @@
|
||||
# Copyright 2020-2025 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
from transformers import AutoTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
from trl.experimental.bco import BCOConfig, BCOTrainer
|
||||
|
||||
from ..testing_utils import TrlTestCase, require_sklearn
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class TestTrainerArg(TrlTestCase):
|
||||
@require_sklearn
|
||||
def test_bco(self):
|
||||
model_id = "trl-internal-testing/tiny-Qwen2ForCausalLM-2.5"
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_id)
|
||||
dataset = load_dataset("trl-internal-testing/zen", "standard_unpaired_preference", split="train")
|
||||
training_args = BCOConfig(
|
||||
self.tmp_dir,
|
||||
max_length=256,
|
||||
max_prompt_length=64,
|
||||
max_completion_length=64,
|
||||
beta=0.5,
|
||||
label_pad_token_id=-99,
|
||||
padding_value=-99,
|
||||
truncation_mode="keep_start",
|
||||
# generate_during_eval=True, # ignore this one, it requires wandb
|
||||
is_encoder_decoder=True,
|
||||
precompute_ref_log_probs=True,
|
||||
model_init_kwargs={"trust_remote_code": True},
|
||||
ref_model_init_kwargs={"trust_remote_code": True},
|
||||
dataset_num_proc=4,
|
||||
prompt_sample_size=512,
|
||||
min_density_ratio=0.2,
|
||||
max_density_ratio=20.0,
|
||||
)
|
||||
trainer = BCOTrainer(
|
||||
model=model_id,
|
||||
ref_model=model_id,
|
||||
args=training_args,
|
||||
train_dataset=dataset,
|
||||
processing_class=tokenizer,
|
||||
)
|
||||
assert trainer.args.max_length == 256
|
||||
assert trainer.args.max_prompt_length == 64
|
||||
assert trainer.args.max_completion_length == 64
|
||||
assert trainer.args.beta == 0.5
|
||||
assert trainer.args.label_pad_token_id == -99
|
||||
assert trainer.args.padding_value == -99
|
||||
assert trainer.args.truncation_mode == "keep_start"
|
||||
# self.assertEqual(trainer.args.generate_during_eval, True)
|
||||
assert trainer.args.is_encoder_decoder
|
||||
assert trainer.args.precompute_ref_log_probs
|
||||
assert trainer.args.model_init_kwargs == {"trust_remote_code": True}
|
||||
assert trainer.args.ref_model_init_kwargs == {"trust_remote_code": True}
|
||||
assert trainer.args.dataset_num_proc == 4
|
||||
assert trainer.args.prompt_sample_size == 512
|
||||
assert trainer.args.min_density_ratio == 0.2
|
||||
assert trainer.args.max_density_ratio == 20.0
|
||||
@ -1,213 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Copyright 2020-2025 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
import gc
|
||||
|
||||
import pytest
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from accelerate.utils.memory import release_memory
|
||||
from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer, BitsAndBytesConfig
|
||||
from transformers.testing_utils import backend_empty_cache, torch_device
|
||||
from transformers.utils import is_peft_available
|
||||
|
||||
from trl import DPOConfig, DPOTrainer
|
||||
|
||||
from ..testing_utils import TrlTestCase, require_bitsandbytes, require_peft, require_torch_accelerator
|
||||
from .testing_constants import DPO_LOSS_TYPES, DPO_PRECOMPUTE_LOGITS, GRADIENT_CHECKPOINTING_KWARGS, MODELS_TO_TEST
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if is_peft_available():
|
||||
from peft import LoraConfig, PeftModel
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.mark.slow
|
||||
@require_torch_accelerator
|
||||
@require_peft
|
||||
class TestDPOTrainerSlow(TrlTestCase):
|
||||
def setup_method(self):
|
||||
self.dataset = load_dataset("trl-internal-testing/zen", "standard_preference")
|
||||
self.peft_config = LoraConfig(
|
||||
lora_alpha=16,
|
||||
lora_dropout=0.1,
|
||||
r=8,
|
||||
bias="none",
|
||||
task_type="CAUSAL_LM",
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.max_length = 128
|
||||
|
||||
def teardown_method(self):
|
||||
gc.collect()
|
||||
backend_empty_cache(torch_device)
|
||||
gc.collect()
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize("pre_compute_logits", DPO_PRECOMPUTE_LOGITS)
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize("loss_type", DPO_LOSS_TYPES)
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize("model_id", MODELS_TO_TEST)
|
||||
def test_dpo_bare_model(self, model_id, loss_type, pre_compute_logits):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
A test that tests the simple usage of `DPOTrainer` using a bare model in full precision.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_id)
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_id)
|
||||
tokenizer.pad_token = tokenizer.eos_token if tokenizer.pad_token is None else tokenizer.pad_token
|
||||
|
||||
training_args = DPOConfig(
|
||||
output_dir=self.tmp_dir,
|
||||
per_device_train_batch_size=2,
|
||||
max_steps=2,
|
||||
remove_unused_columns=False,
|
||||
gradient_accumulation_steps=2,
|
||||
learning_rate=9e-1,
|
||||
eval_strategy="steps",
|
||||
fp16=True,
|
||||
logging_strategy="no",
|
||||
report_to="none",
|
||||
beta=0.1,
|
||||
loss_type=loss_type,
|
||||
precompute_ref_log_probs=pre_compute_logits,
|
||||
max_length=self.max_length,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# dpo train lora model
|
||||
trainer = DPOTrainer(
|
||||
model=model,
|
||||
ref_model=None,
|
||||
args=training_args,
|
||||
train_dataset=self.dataset["train"],
|
||||
eval_dataset=self.dataset["test"],
|
||||
processing_class=tokenizer,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# train the model
|
||||
trainer.train()
|
||||
|
||||
# save trained model or adapter
|
||||
trainer.save_model()
|
||||
|
||||
release_memory(model, trainer)
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize("gradient_checkpointing_kwargs", GRADIENT_CHECKPOINTING_KWARGS)
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize("pre_compute_logits", DPO_PRECOMPUTE_LOGITS)
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize("loss_type", DPO_LOSS_TYPES)
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize("model_id", MODELS_TO_TEST)
|
||||
@require_peft
|
||||
def test_dpo_peft_model(self, model_id, loss_type, pre_compute_logits, gradient_checkpointing_kwargs):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
A test that tests the simple usage of `DPOTrainer` using a peft model in full precision + different scenarios
|
||||
of gradient checkpointing.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_id)
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_id)
|
||||
tokenizer.pad_token = tokenizer.eos_token if tokenizer.pad_token is None else tokenizer.pad_token
|
||||
|
||||
training_args = DPOConfig(
|
||||
output_dir=self.tmp_dir,
|
||||
per_device_train_batch_size=2,
|
||||
max_steps=2,
|
||||
remove_unused_columns=False,
|
||||
gradient_accumulation_steps=2,
|
||||
learning_rate=9e-1,
|
||||
eval_strategy="steps",
|
||||
fp16=True,
|
||||
logging_strategy="no",
|
||||
report_to="none",
|
||||
gradient_checkpointing=True,
|
||||
gradient_checkpointing_kwargs=gradient_checkpointing_kwargs,
|
||||
generate_during_eval=False,
|
||||
loss_type=loss_type,
|
||||
precompute_ref_log_probs=pre_compute_logits,
|
||||
beta=0.1,
|
||||
max_length=self.max_length,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# dpo train lora model
|
||||
trainer = DPOTrainer(
|
||||
model=model,
|
||||
ref_model=None,
|
||||
args=training_args,
|
||||
train_dataset=self.dataset["train"],
|
||||
eval_dataset=self.dataset["test"],
|
||||
processing_class=tokenizer,
|
||||
peft_config=self.peft_config,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
assert isinstance(trainer.model, PeftModel)
|
||||
assert trainer.ref_model is None
|
||||
|
||||
# train the model
|
||||
trainer.train()
|
||||
|
||||
# save trained model or adapter
|
||||
trainer.save_model()
|
||||
|
||||
release_memory(model, trainer)
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize("gradient_checkpointing_kwargs", GRADIENT_CHECKPOINTING_KWARGS)
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize("pre_compute_logits", DPO_PRECOMPUTE_LOGITS)
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize("loss_type", DPO_LOSS_TYPES)
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize("model_id", MODELS_TO_TEST)
|
||||
@require_bitsandbytes
|
||||
@require_peft
|
||||
def test_dpo_peft_model_qlora(self, model_id, loss_type, pre_compute_logits, gradient_checkpointing_kwargs):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
A test that tests the simple usage of `DPOTrainer` using QLoRA + different scenarios of gradient checkpointing.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
quantization_config = BitsAndBytesConfig(load_in_4bit=True, bnb_4bit_compute_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_id, quantization_config=quantization_config)
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_id)
|
||||
tokenizer.pad_token = tokenizer.eos_token if tokenizer.pad_token is None else tokenizer.pad_token
|
||||
|
||||
training_args = DPOConfig(
|
||||
output_dir=self.tmp_dir,
|
||||
per_device_train_batch_size=2,
|
||||
max_steps=2,
|
||||
remove_unused_columns=False,
|
||||
gradient_accumulation_steps=2,
|
||||
learning_rate=9e-1,
|
||||
eval_strategy="steps",
|
||||
fp16=True,
|
||||
logging_strategy="no",
|
||||
report_to="none",
|
||||
gradient_checkpointing=True,
|
||||
gradient_checkpointing_kwargs=gradient_checkpointing_kwargs,
|
||||
beta=0.1,
|
||||
generate_during_eval=False,
|
||||
loss_type=loss_type,
|
||||
precompute_ref_log_probs=pre_compute_logits,
|
||||
max_length=self.max_length,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# dpo train lora model
|
||||
trainer = DPOTrainer(
|
||||
model=model,
|
||||
ref_model=None,
|
||||
args=training_args,
|
||||
train_dataset=self.dataset["train"],
|
||||
eval_dataset=self.dataset["test"],
|
||||
processing_class=tokenizer,
|
||||
peft_config=self.peft_config,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
assert isinstance(trainer.model, PeftModel)
|
||||
assert trainer.ref_model is None
|
||||
|
||||
# train the model
|
||||
trainer.train()
|
||||
|
||||
# save trained model or adapter
|
||||
trainer.save_model()
|
||||
|
||||
release_memory(model, trainer)
|
||||
@ -1,554 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Copyright 2020-2025 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
import gc
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import warnings
|
||||
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
import pytest
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
import transformers
|
||||
from accelerate.utils.memory import release_memory
|
||||
from datasets import Dataset, Features, Image, Value, load_dataset
|
||||
from packaging.version import Version
|
||||
from transformers import (
|
||||
AutoModelForCausalLM,
|
||||
AutoModelForImageTextToText,
|
||||
AutoProcessor,
|
||||
AutoTokenizer,
|
||||
BitsAndBytesConfig,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from transformers.testing_utils import backend_empty_cache, torch_device
|
||||
from transformers.utils import is_peft_available
|
||||
|
||||
from trl import GRPOConfig, GRPOTrainer
|
||||
from trl.trainer.utils import get_kbit_device_map
|
||||
|
||||
from ..testing_utils import (
|
||||
TrlTestCase,
|
||||
require_bitsandbytes,
|
||||
require_flash_attn,
|
||||
require_liger_kernel,
|
||||
require_peft,
|
||||
require_torch_accelerator,
|
||||
require_vllm,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from .testing_constants import MODELS_TO_TEST
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if is_peft_available():
|
||||
from peft import LoraConfig, PeftModel
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.mark.slow
|
||||
@require_torch_accelerator
|
||||
class TestGRPOTrainerSlow(TrlTestCase):
|
||||
def setup_method(self):
|
||||
self.train_dataset = load_dataset("trl-internal-testing/zen", "standard_prompt_only", split="train")
|
||||
self.eval_dataset = load_dataset("trl-internal-testing/zen", "standard_prompt_only", split="test")
|
||||
self.max_length = 128
|
||||
|
||||
def teardown_method(self):
|
||||
gc.collect()
|
||||
backend_empty_cache(torch_device)
|
||||
gc.collect()
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize("model_name", MODELS_TO_TEST)
|
||||
@require_liger_kernel
|
||||
def test_training_with_liger_grpo_loss(self, model_name):
|
||||
training_args = GRPOConfig(
|
||||
output_dir=self.tmp_dir,
|
||||
per_device_train_batch_size=3,
|
||||
num_generations=3,
|
||||
use_liger_loss=True,
|
||||
max_completion_length=self.max_length,
|
||||
report_to="none",
|
||||
logging_strategy="no",
|
||||
loss_type="bnpo", # liger-kernel does not support "dapo" default; see https://github.com/linkedin/Liger-Kernel/issues/620
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_name)
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
|
||||
tokenizer.pad_token = tokenizer.eos_token if tokenizer.pad_token is None else tokenizer.pad_token
|
||||
|
||||
trainer = GRPOTrainer(
|
||||
model=model,
|
||||
reward_funcs="trl-internal-testing/tiny-Qwen2ForSequenceClassification-2.5",
|
||||
args=training_args,
|
||||
train_dataset=self.train_dataset,
|
||||
eval_dataset=self.eval_dataset,
|
||||
processing_class=tokenizer,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from liger_kernel.chunked_loss import LigerFusedLinearGRPOLoss
|
||||
|
||||
assert isinstance(trainer.liger_grpo_loss, LigerFusedLinearGRPOLoss)
|
||||
|
||||
previous_trainable_params = {n: param.clone() for n, param in model.named_parameters()}
|
||||
|
||||
trainer.train()
|
||||
|
||||
for n, param in previous_trainable_params.items():
|
||||
new_param = model.get_parameter(n)
|
||||
assert not torch.equal(param, new_param), f"Parameter {n} has not changed."
|
||||
|
||||
release_memory(model, trainer)
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize("model_name", MODELS_TO_TEST)
|
||||
@require_liger_kernel
|
||||
@require_peft
|
||||
def test_training_with_liger_grpo_loss_and_peft(self, model_name):
|
||||
from peft import LoraConfig, TaskType
|
||||
|
||||
training_args = GRPOConfig(
|
||||
output_dir=self.tmp_dir,
|
||||
per_device_train_batch_size=3,
|
||||
num_generations=3,
|
||||
use_liger_loss=True,
|
||||
max_completion_length=self.max_length,
|
||||
report_to="none",
|
||||
logging_strategy="no",
|
||||
loss_type="bnpo", # liger-kernel does not support "dapo" default; see https://github.com/linkedin/Liger-Kernel/issues/620
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_name)
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
|
||||
tokenizer.pad_token = tokenizer.eos_token if tokenizer.pad_token is None else tokenizer.pad_token
|
||||
|
||||
# Configure PEFT with LoRA
|
||||
peft_config = LoraConfig(
|
||||
task_type=TaskType.CAUSAL_LM,
|
||||
inference_mode=False,
|
||||
r=8,
|
||||
lora_alpha=32,
|
||||
lora_dropout=0.1,
|
||||
target_modules=["q_proj", "v_proj"],
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
trainer = GRPOTrainer(
|
||||
model=model,
|
||||
reward_funcs="trl-internal-testing/tiny-Qwen2ForSequenceClassification-2.5",
|
||||
args=training_args,
|
||||
train_dataset=self.train_dataset,
|
||||
eval_dataset=self.eval_dataset,
|
||||
processing_class=tokenizer,
|
||||
peft_config=peft_config,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from liger_kernel.chunked_loss import LigerFusedLinearGRPOLoss
|
||||
|
||||
assert isinstance(trainer.liger_grpo_loss, LigerFusedLinearGRPOLoss)
|
||||
|
||||
# Verify PEFT adapter is properly initialized
|
||||
from peft import PeftModel
|
||||
|
||||
assert isinstance(trainer.model, PeftModel), "Model should be wrapped with PEFT"
|
||||
|
||||
# Store adapter weights before training
|
||||
previous_trainable_params = {
|
||||
n: param.clone() for n, param in trainer.model.named_parameters() if param.requires_grad
|
||||
}
|
||||
assert len(previous_trainable_params) > 0, "No trainable parameters found in PEFT model"
|
||||
|
||||
trainer.train()
|
||||
|
||||
# Verify adapter weights have changed after training
|
||||
for n, param in previous_trainable_params.items():
|
||||
new_param = trainer.model.get_parameter(n)
|
||||
assert not torch.equal(param, new_param), f"Parameter {n} has not changed."
|
||||
|
||||
release_memory(model, trainer)
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize("model_name", MODELS_TO_TEST)
|
||||
def test_training_with_transformers_paged(self, model_name):
|
||||
"""Test that training works with transformers paged implementation (requires GPU)."""
|
||||
if Version(transformers.__version__) < Version("4.57.0"):
|
||||
pytest.xfail("Upstream bug in transformers (GH#40692). Fix merged; awaiting release >= 4.57.0")
|
||||
training_args = GRPOConfig(
|
||||
output_dir=self.tmp_dir,
|
||||
learning_rate=0.1, # increase the learning rate to speed up the test
|
||||
per_device_train_batch_size=3, # reduce the batch size to reduce memory usage
|
||||
num_generations=3, # reduce the number of generations to reduce memory usage
|
||||
max_completion_length=8, # reduce the completion length to reduce memory usage
|
||||
use_transformers_paged=True, # Enable transformers paged implementation
|
||||
report_to="none",
|
||||
logging_strategy="no",
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_name)
|
||||
|
||||
trainer = GRPOTrainer(
|
||||
model=model,
|
||||
reward_funcs="trl-internal-testing/tiny-Qwen2ForSequenceClassification-2.5",
|
||||
args=training_args,
|
||||
train_dataset=self.train_dataset,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
previous_trainable_params = {n: param.clone() for n, param in model.named_parameters()}
|
||||
|
||||
trainer.train()
|
||||
|
||||
assert trainer.state.log_history[-1]["train_loss"] is not None
|
||||
|
||||
# Check that the params have changed
|
||||
for n, param in previous_trainable_params.items():
|
||||
new_param = model.get_parameter(n)
|
||||
assert not torch.equal(param, new_param), f"Parameter {n} has not changed."
|
||||
|
||||
release_memory(model, trainer)
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
|
||||
"model_name",
|
||||
[
|
||||
"HuggingFaceTB/SmolVLM-Instruct", # Only test the smaller model to avoid OOM
|
||||
],
|
||||
)
|
||||
@require_flash_attn
|
||||
@require_bitsandbytes
|
||||
@require_peft
|
||||
def test_vlm_training(self, model_name):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Test VLM training with aggressive memory optimization.
|
||||
|
||||
This test uses multiple memory reduction techniques:
|
||||
- 4-bit quantization with double quantization
|
||||
- LoRA with very low rank (r=4)
|
||||
- Minimal batch size (1) with gradient accumulation
|
||||
- Small images (64x64 instead of 224x224)
|
||||
- Short sequences (max_completion_length=8)
|
||||
- Only 4 training samples
|
||||
- Only 1 training step
|
||||
- Gradient checkpointing and bfloat16
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
# Create processor once outside the data generator
|
||||
processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained(model_name, use_fast=True, padding_side="left")
|
||||
conversation = [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"role": "user",
|
||||
"content": [
|
||||
{"type": "image"},
|
||||
{"type": "text", "text": "What is in the image?"},
|
||||
],
|
||||
},
|
||||
]
|
||||
prompt = processor.apply_chat_template(conversation, add_generation_prompt=True)
|
||||
|
||||
def data_gen(num_samples):
|
||||
for _ in range(num_samples):
|
||||
yield {
|
||||
"prompt": prompt,
|
||||
"image": np.random.uniform(low=0.0, high=255.0, size=(64, 64, 3)).astype(
|
||||
np.uint8
|
||||
), # Much smaller images
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
dataset = Dataset.from_generator(
|
||||
data_gen, gen_kwargs={"num_samples": 4}, features=Features(image=Image(), prompt=Value(dtype="string"))
|
||||
)
|
||||
# reduce memory requirements as much as possible
|
||||
quantization_config = BitsAndBytesConfig(
|
||||
load_in_4bit=True,
|
||||
bnb_4bit_compute_dtype="bfloat16",
|
||||
bnb_4bit_quant_type="nf4",
|
||||
bnb_4bit_use_double_quant=True,
|
||||
bnb_4bit_quant_storage="bfloat16",
|
||||
)
|
||||
model = AutoModelForImageTextToText.from_pretrained(
|
||||
model_name,
|
||||
attn_implementation="flash_attention_2",
|
||||
dtype="bfloat16",
|
||||
device_map=get_kbit_device_map(),
|
||||
quantization_config=quantization_config,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def reward_func(prompts, completions, **kwargs):
|
||||
# simple nonsensical reward
|
||||
return [-((len(c) - 25) ** 2) + 100 for c in completions]
|
||||
|
||||
training_args = GRPOConfig(
|
||||
output_dir=self.tmp_dir,
|
||||
learning_rate=0.1,
|
||||
per_device_train_batch_size=1, # Minimal batch size
|
||||
gradient_accumulation_steps=2, # Maintain effective batch size
|
||||
num_generations=2,
|
||||
max_completion_length=8, # Much shorter completions
|
||||
max_prompt_length=None, # Don't limit prompt length for VLM
|
||||
bf16=True, # Use bfloat16 precision
|
||||
max_steps=1, # Only do 1 training step to save time and memory
|
||||
report_to="none",
|
||||
logging_strategy="no",
|
||||
)
|
||||
lora_config = LoraConfig(
|
||||
task_type="CAUSAL_LM",
|
||||
r=4, # Much lower rank for minimal memory
|
||||
lora_alpha=8, # Reduced alpha proportionally
|
||||
lora_dropout=0.1,
|
||||
target_modules=["q_proj", "v_proj"], # Minimal target modules
|
||||
# For VLM models, we typically want to freeze the vision encoder
|
||||
# and only adapt the language model parameters
|
||||
modules_to_save=None,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
trainer = GRPOTrainer(
|
||||
model=model,
|
||||
processing_class=processor,
|
||||
reward_funcs=[reward_func],
|
||||
args=training_args,
|
||||
train_dataset=dataset,
|
||||
peft_config=lora_config,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
assert isinstance(trainer.model, PeftModel)
|
||||
|
||||
previous_trainable_params = {n: param.clone() for n, param in trainer.model.named_parameters()}
|
||||
|
||||
trainer.train()
|
||||
|
||||
assert trainer.state.log_history[-1]["train_loss"] is not None
|
||||
|
||||
# Check that LoRA parameters have changed
|
||||
# For VLM models, we're more permissive about which parameters can change
|
||||
lora_params_changed = False
|
||||
for n, param in previous_trainable_params.items():
|
||||
new_param = trainer.model.get_parameter(n)
|
||||
if "lora" in n.lower(): # LoRA parameters should change
|
||||
if not torch.equal(param, new_param):
|
||||
lora_params_changed = True
|
||||
|
||||
# At least some LoRA parameters should have changed during training
|
||||
assert lora_params_changed, "No LoRA parameters were updated during training."
|
||||
|
||||
except torch.OutOfMemoryError as e:
|
||||
pytest.skip(f"Skipping VLM training test due to insufficient GPU memory: {e}")
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
# Check for other memory-related errors
|
||||
if any(keyword in str(e).lower() for keyword in ["memory", "cuda", "out of memory", "insufficient"]):
|
||||
pytest.skip(f"Skipping VLM training test due to hardware constraints: {e}")
|
||||
else:
|
||||
raise
|
||||
|
||||
release_memory(model, trainer)
|
||||
|
||||
@require_vllm
|
||||
@require_bitsandbytes
|
||||
@require_peft
|
||||
def test_vlm_processor_vllm_colocate_mode(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Test that VLM processors work with vLLM in colocate mode.
|
||||
|
||||
This test uses multiple memory optimization techniques to ensure it runs on limited hardware:
|
||||
- LoRA (Low-Rank Adaptation) with minimal rank (r=4)
|
||||
- 4-bit quantization with BitsAndBytesConfig
|
||||
- Gradient checkpointing
|
||||
- bfloat16 precision
|
||||
- Minimal batch sizes and sequence lengths
|
||||
- Very low GPU memory utilization (5%)
|
||||
"""
|
||||
dataset = load_dataset("trl-internal-testing/zen", "standard_prompt_only", split="train")
|
||||
|
||||
config = GRPOConfig(
|
||||
output_dir=self.tmp_dir,
|
||||
per_device_train_batch_size=1, # Minimal batch size
|
||||
gradient_accumulation_steps=2, # Make effective batch size 2, divisible by num_generations
|
||||
num_generations=2,
|
||||
max_completion_length=4, # Very short completions to reduce memory
|
||||
max_prompt_length=32, # Very short prompts to reduce memory
|
||||
use_vllm=True, # Enable vLLM
|
||||
vllm_mode="colocate", # Use colocate mode to avoid server dependency
|
||||
vllm_gpu_memory_utilization=0.05, # Use minimal GPU memory (5%)
|
||||
gradient_checkpointing=True, # Enable gradient checkpointing to save memory
|
||||
bf16=True, # Use bfloat16 to reduce memory
|
||||
report_to="none",
|
||||
logging_strategy="no",
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Create a VLM processor
|
||||
processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained("HuggingFaceTB/SmolVLM-Instruct", use_fast=True, padding_side="left")
|
||||
|
||||
# Verify processor has both required attributes for VLM detection
|
||||
assert hasattr(processor, "tokenizer")
|
||||
assert hasattr(processor, "image_processor")
|
||||
|
||||
def dummy_reward_func(completions, **kwargs):
|
||||
return [1.0] * len(completions)
|
||||
|
||||
# Use LoRA configuration for memory efficiency
|
||||
lora_config = LoraConfig(
|
||||
r=4, # Very low rank for minimal memory
|
||||
lora_alpha=8,
|
||||
target_modules=["q_proj", "v_proj"], # Minimal target modules
|
||||
lora_dropout=0.1,
|
||||
bias="none",
|
||||
task_type="CAUSAL_LM",
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Use 4-bit quantization for further memory reduction
|
||||
quantization_config = BitsAndBytesConfig(
|
||||
load_in_4bit=True,
|
||||
bnb_4bit_compute_dtype=torch.bfloat16,
|
||||
bnb_4bit_quant_type="nf4",
|
||||
bnb_4bit_use_double_quant=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
original_env = {}
|
||||
required_env_vars = {
|
||||
"RANK": "0",
|
||||
"LOCAL_RANK": "0",
|
||||
"WORLD_SIZE": "1",
|
||||
"LOCAL_WORLD_SIZE": "1",
|
||||
"MASTER_ADDR": "localhost",
|
||||
"MASTER_PORT": "12355",
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for key, value in required_env_vars.items():
|
||||
original_env[key] = os.environ.get(key)
|
||||
os.environ[key] = value
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
# Test VLM processor with vLLM colocate mode
|
||||
with warnings.catch_warnings(record=True) as w:
|
||||
warnings.simplefilter("always")
|
||||
try:
|
||||
# Load model with quantization for memory efficiency
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"trl-internal-testing/tiny-Qwen2ForCausalLM-2.5",
|
||||
quantization_config=quantization_config,
|
||||
dtype=torch.bfloat16,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
trainer = GRPOTrainer(
|
||||
model=model,
|
||||
reward_funcs=dummy_reward_func,
|
||||
args=config,
|
||||
train_dataset=dataset,
|
||||
processing_class=processor, # VLM processor
|
||||
peft_config=lora_config, # Use LoRA for memory efficiency
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Should detect VLM processor correctly and allow vLLM
|
||||
assert trainer.use_vllm, "vLLM should be enabled for VLM processors in colocate mode"
|
||||
assert trainer.vllm_mode == "colocate", "Should use colocate mode"
|
||||
|
||||
# Check if signature columns were set properly
|
||||
if trainer._signature_columns is not None:
|
||||
# Should include 'image' in signature columns for VLM processors
|
||||
assert "image" in trainer._signature_columns, (
|
||||
"Should include 'image' in signature columns for VLM"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Should not emit any warnings about VLM incompatibility
|
||||
incompatibility_warnings = [
|
||||
str(w_item.message)
|
||||
for w_item in w
|
||||
if "does not support VLMs" in str(w_item.message)
|
||||
or "not compatible" in str(w_item.message).lower()
|
||||
]
|
||||
assert len(incompatibility_warnings) == 0, (
|
||||
f"Should not emit VLM incompatibility warnings, but got: {incompatibility_warnings}"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Test passes if we get this far without exceptions
|
||||
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
# If vLLM fails to initialize due to hardware constraints or other issues, that's expected
|
||||
if any(
|
||||
keyword in str(e).lower()
|
||||
for keyword in [
|
||||
"outofmemoryerror",
|
||||
"cuda",
|
||||
"memory",
|
||||
"insufficient",
|
||||
"no such device",
|
||||
"free memory",
|
||||
"gpu memory utilization",
|
||||
"decrease gpu memory",
|
||||
]
|
||||
):
|
||||
pytest.skip(f"Skipping vLLM colocate test due to hardware constraints: {e}")
|
||||
elif "KeyError" in str(e) and "RANK" in str(e):
|
||||
pytest.skip(f"Skipping vLLM colocate test due to environment setup issues: {e}")
|
||||
elif "ValueError" in str(e) and "memory" in str(e).lower():
|
||||
pytest.skip(f"Skipping vLLM colocate test due to memory constraints: {e}")
|
||||
else:
|
||||
raise
|
||||
finally:
|
||||
# Restore original environment variables
|
||||
for key, original_value in original_env.items():
|
||||
if original_value is None:
|
||||
os.environ.pop(key, None)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
os.environ[key] = original_value
|
||||
|
||||
release_memory(model, trainer)
|
||||
|
||||
@require_vllm
|
||||
def test_training_vllm(self):
|
||||
"""Test that training works with vLLM for generation."""
|
||||
dataset = load_dataset("trl-internal-testing/zen", "standard_prompt_only", split="train")
|
||||
|
||||
training_args = GRPOConfig(
|
||||
output_dir=self.tmp_dir,
|
||||
learning_rate=0.1, # increase the learning rate to speed up the test
|
||||
per_device_train_batch_size=3, # reduce the batch size to reduce memory usage
|
||||
num_generations=3, # reduce the number of generations to reduce memory usage
|
||||
max_completion_length=8, # reduce the completion length to reduce memory usage
|
||||
report_to="none",
|
||||
logging_strategy="no",
|
||||
use_vllm=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
trainer = GRPOTrainer(
|
||||
model="Qwen/Qwen2.5-0.5B-Instruct", # tiny models are too small for vLLM
|
||||
reward_funcs="trl-internal-testing/tiny-Qwen2ForSequenceClassification-2.5",
|
||||
args=training_args,
|
||||
train_dataset=dataset,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
previous_trainable_params = {n: param.clone() for n, param in trainer.model.named_parameters()}
|
||||
|
||||
trainer.train()
|
||||
|
||||
assert trainer.state.log_history[-1]["train_loss"] is not None
|
||||
|
||||
# Check that the params have changed
|
||||
for n, param in previous_trainable_params.items():
|
||||
new_param = trainer.model.get_parameter(n)
|
||||
assert not torch.equal(param, new_param), f"Parameter {n} has not changed."
|
||||
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
# If vLLM fails to initialize due to hardware constraints or other issues, that's expected
|
||||
if any(
|
||||
keyword in str(e).lower()
|
||||
for keyword in [
|
||||
"outofmemoryerror",
|
||||
"cuda",
|
||||
"memory",
|
||||
"insufficient",
|
||||
"no such device",
|
||||
"free memory",
|
||||
"gpu memory utilization",
|
||||
"decrease gpu memory",
|
||||
]
|
||||
):
|
||||
pytest.skip(f"Skipping vLLM training test due to hardware constraints: {e}")
|
||||
elif "KeyError" in str(e) and "RANK" in str(e):
|
||||
pytest.skip(f"Skipping vLLM training test due to environment setup issues: {e}")
|
||||
elif "ValueError" in str(e) and "memory" in str(e).lower():
|
||||
pytest.skip(f"Skipping vLLM training test due to memory constraints: {e}")
|
||||
else:
|
||||
raise
|
||||
|
||||
release_memory(trainer.model, trainer)
|
||||
@ -1,467 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Copyright 2020-2025 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
import gc
|
||||
|
||||
import pytest
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from accelerate.utils.memory import release_memory
|
||||
from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer, BitsAndBytesConfig
|
||||
from transformers.testing_utils import backend_empty_cache, torch_device
|
||||
from transformers.utils import is_peft_available
|
||||
|
||||
from trl import SFTConfig, SFTTrainer
|
||||
|
||||
from ..testing_utils import (
|
||||
TrlTestCase,
|
||||
require_bitsandbytes,
|
||||
require_liger_kernel,
|
||||
require_peft,
|
||||
require_torch_accelerator,
|
||||
require_torch_multi_accelerator,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from .testing_constants import DEVICE_MAP_OPTIONS, GRADIENT_CHECKPOINTING_KWARGS, MODELS_TO_TEST, PACKING_OPTIONS
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if is_peft_available():
|
||||
from peft import LoraConfig, PeftModel
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.mark.slow
|
||||
@require_torch_accelerator
|
||||
@require_peft
|
||||
class TestSFTTrainerSlow(TrlTestCase):
|
||||
def setup_method(self):
|
||||
self.train_dataset = load_dataset("stanfordnlp/imdb", split="train[:10%]")
|
||||
self.eval_dataset = load_dataset("stanfordnlp/imdb", split="test[:10%]")
|
||||
self.max_length = 128
|
||||
self.peft_config = LoraConfig(
|
||||
lora_alpha=16,
|
||||
lora_dropout=0.1,
|
||||
r=8,
|
||||
bias="none",
|
||||
task_type="CAUSAL_LM",
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def teardown_method(self):
|
||||
gc.collect()
|
||||
backend_empty_cache(torch_device)
|
||||
gc.collect()
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize("packing", PACKING_OPTIONS)
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize("model_name", MODELS_TO_TEST)
|
||||
def test_sft_trainer_str(self, model_name, packing):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Simply tests if passing a simple str to `SFTTrainer` loads and runs the trainer as expected.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
training_args = SFTConfig(
|
||||
output_dir=self.tmp_dir,
|
||||
logging_strategy="no",
|
||||
report_to="none",
|
||||
per_device_train_batch_size=2,
|
||||
max_steps=10,
|
||||
packing=packing,
|
||||
max_length=self.max_length,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
trainer = SFTTrainer(
|
||||
model_name,
|
||||
args=training_args,
|
||||
train_dataset=self.train_dataset,
|
||||
eval_dataset=self.eval_dataset,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
trainer.train()
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize("packing", PACKING_OPTIONS)
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize("model_name", MODELS_TO_TEST)
|
||||
def test_sft_trainer_transformers(self, model_name, packing):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Simply tests if passing a transformers model to `SFTTrainer` loads and runs the trainer as expected.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
training_args = SFTConfig(
|
||||
output_dir=self.tmp_dir,
|
||||
logging_strategy="no",
|
||||
report_to="none",
|
||||
per_device_train_batch_size=2,
|
||||
max_steps=10,
|
||||
packing=packing,
|
||||
max_length=self.max_length,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_name)
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
|
||||
|
||||
trainer = SFTTrainer(
|
||||
model,
|
||||
args=training_args,
|
||||
processing_class=tokenizer,
|
||||
train_dataset=self.train_dataset,
|
||||
eval_dataset=self.eval_dataset,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
trainer.train()
|
||||
|
||||
release_memory(model, trainer)
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize("packing", PACKING_OPTIONS)
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize("model_name", MODELS_TO_TEST)
|
||||
@require_peft
|
||||
def test_sft_trainer_peft(self, model_name, packing):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Simply tests if passing a transformers model + peft config to `SFTTrainer` loads and runs the trainer as
|
||||
expected.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
training_args = SFTConfig(
|
||||
output_dir=self.tmp_dir,
|
||||
logging_strategy="no",
|
||||
report_to="none",
|
||||
per_device_train_batch_size=2,
|
||||
max_steps=10,
|
||||
fp16=True,
|
||||
packing=packing,
|
||||
max_length=self.max_length,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_name)
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
|
||||
|
||||
trainer = SFTTrainer(
|
||||
model,
|
||||
args=training_args,
|
||||
processing_class=tokenizer,
|
||||
train_dataset=self.train_dataset,
|
||||
eval_dataset=self.eval_dataset,
|
||||
peft_config=self.peft_config,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
assert isinstance(trainer.model, PeftModel)
|
||||
|
||||
trainer.train()
|
||||
|
||||
release_memory(model, trainer)
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize("packing", PACKING_OPTIONS)
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize("model_name", MODELS_TO_TEST)
|
||||
def test_sft_trainer_transformers_mp(self, model_name, packing):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Simply tests if passing a transformers model to `SFTTrainer` loads and runs the trainer as expected in mixed
|
||||
precision.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
training_args = SFTConfig(
|
||||
output_dir=self.tmp_dir,
|
||||
logging_strategy="no",
|
||||
report_to="none",
|
||||
per_device_train_batch_size=2,
|
||||
max_steps=10,
|
||||
fp16=True, # this is sufficient to enable amp
|
||||
packing=packing,
|
||||
max_length=self.max_length,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_name)
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
|
||||
|
||||
trainer = SFTTrainer(
|
||||
model,
|
||||
args=training_args,
|
||||
processing_class=tokenizer,
|
||||
train_dataset=self.train_dataset,
|
||||
eval_dataset=self.eval_dataset,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
trainer.train()
|
||||
|
||||
release_memory(model, trainer)
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize("gradient_checkpointing_kwargs", GRADIENT_CHECKPOINTING_KWARGS)
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize("packing", PACKING_OPTIONS)
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize("model_name", MODELS_TO_TEST)
|
||||
def test_sft_trainer_transformers_mp_gc(self, model_name, packing, gradient_checkpointing_kwargs):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Simply tests if passing a transformers model to `SFTTrainer` loads and runs the trainer as expected in mixed
|
||||
precision + different scenarios of gradient_checkpointing.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
training_args = SFTConfig(
|
||||
output_dir=self.tmp_dir,
|
||||
logging_strategy="no",
|
||||
report_to="none",
|
||||
per_device_train_batch_size=2,
|
||||
max_steps=10,
|
||||
packing=packing,
|
||||
max_length=self.max_length,
|
||||
fp16=True, # this is sufficient to enable amp
|
||||
gradient_checkpointing=True,
|
||||
gradient_checkpointing_kwargs=gradient_checkpointing_kwargs,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_name)
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
|
||||
|
||||
trainer = SFTTrainer(
|
||||
model,
|
||||
args=training_args,
|
||||
processing_class=tokenizer,
|
||||
train_dataset=self.train_dataset,
|
||||
eval_dataset=self.eval_dataset,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
trainer.train()
|
||||
|
||||
release_memory(model, trainer)
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize("gradient_checkpointing_kwargs", GRADIENT_CHECKPOINTING_KWARGS)
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize("packing", PACKING_OPTIONS)
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize("model_name", MODELS_TO_TEST)
|
||||
@require_peft
|
||||
def test_sft_trainer_transformers_mp_gc_peft(self, model_name, packing, gradient_checkpointing_kwargs):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Simply tests if passing a transformers model + PEFT to `SFTTrainer` loads and runs the trainer as expected in
|
||||
mixed precision + different scenarios of gradient_checkpointing.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
training_args = SFTConfig(
|
||||
output_dir=self.tmp_dir,
|
||||
logging_strategy="no",
|
||||
report_to="none",
|
||||
per_device_train_batch_size=2,
|
||||
max_steps=10,
|
||||
packing=packing,
|
||||
max_length=self.max_length,
|
||||
fp16=True, # this is sufficient to enable amp
|
||||
gradient_checkpointing=True,
|
||||
gradient_checkpointing_kwargs=gradient_checkpointing_kwargs,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_name)
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
|
||||
|
||||
trainer = SFTTrainer(
|
||||
model,
|
||||
args=training_args,
|
||||
processing_class=tokenizer,
|
||||
train_dataset=self.train_dataset,
|
||||
eval_dataset=self.eval_dataset,
|
||||
peft_config=self.peft_config,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
assert isinstance(trainer.model, PeftModel)
|
||||
|
||||
trainer.train()
|
||||
|
||||
release_memory(model, trainer)
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize("device_map", DEVICE_MAP_OPTIONS)
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize("gradient_checkpointing_kwargs", GRADIENT_CHECKPOINTING_KWARGS)
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize("packing", PACKING_OPTIONS)
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize("model_name", MODELS_TO_TEST)
|
||||
@require_torch_multi_accelerator
|
||||
def test_sft_trainer_transformers_mp_gc_device_map(
|
||||
self, model_name, packing, gradient_checkpointing_kwargs, device_map
|
||||
):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Simply tests if passing a transformers model to `SFTTrainer` loads and runs the trainer as expected in mixed
|
||||
precision + different scenarios of gradient_checkpointing (single, multi-gpu, etc).
|
||||
"""
|
||||
training_args = SFTConfig(
|
||||
output_dir=self.tmp_dir,
|
||||
logging_strategy="no",
|
||||
report_to="none",
|
||||
per_device_train_batch_size=2,
|
||||
max_steps=10,
|
||||
packing=packing,
|
||||
max_length=self.max_length,
|
||||
fp16=True, # this is sufficient to enable amp
|
||||
gradient_checkpointing=True,
|
||||
gradient_checkpointing_kwargs=gradient_checkpointing_kwargs,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_name, device_map=device_map)
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
|
||||
|
||||
trainer = SFTTrainer(
|
||||
model,
|
||||
args=training_args,
|
||||
processing_class=tokenizer,
|
||||
train_dataset=self.train_dataset,
|
||||
eval_dataset=self.eval_dataset,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
trainer.train()
|
||||
|
||||
release_memory(model, trainer)
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize("gradient_checkpointing_kwargs", GRADIENT_CHECKPOINTING_KWARGS)
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize("packing", PACKING_OPTIONS)
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize("model_name", MODELS_TO_TEST)
|
||||
@require_peft
|
||||
@require_bitsandbytes
|
||||
def test_sft_trainer_transformers_mp_gc_peft_qlora(self, model_name, packing, gradient_checkpointing_kwargs):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Simply tests if passing a transformers model + PEFT + bnb to `SFTTrainer` loads and runs the trainer as
|
||||
expected in mixed precision + different scenarios of gradient_checkpointing.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
training_args = SFTConfig(
|
||||
output_dir=self.tmp_dir,
|
||||
logging_strategy="no",
|
||||
report_to="none",
|
||||
per_device_train_batch_size=2,
|
||||
max_steps=10,
|
||||
packing=packing,
|
||||
max_length=self.max_length,
|
||||
fp16=True, # this is sufficient to enable amp
|
||||
gradient_checkpointing=True,
|
||||
gradient_checkpointing_kwargs=gradient_checkpointing_kwargs,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
quantization_config = BitsAndBytesConfig(load_in_4bit=True, bnb_4bit_compute_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_name, quantization_config=quantization_config)
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
|
||||
|
||||
trainer = SFTTrainer(
|
||||
model,
|
||||
args=training_args,
|
||||
processing_class=tokenizer,
|
||||
train_dataset=self.train_dataset,
|
||||
eval_dataset=self.eval_dataset,
|
||||
peft_config=self.peft_config,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
assert isinstance(trainer.model, PeftModel)
|
||||
|
||||
trainer.train()
|
||||
|
||||
release_memory(model, trainer)
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize("packing", PACKING_OPTIONS)
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize("model_name", MODELS_TO_TEST)
|
||||
@require_peft
|
||||
@require_bitsandbytes
|
||||
def test_sft_trainer_with_chat_format_qlora(self, model_name, packing):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Simply tests if using setup_chat_format with a transformers model + peft + bnb config to `SFTTrainer` loads and
|
||||
runs the trainer as expected.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
train_dataset = load_dataset("trl-internal-testing/dolly-chatml-sft", split="train")
|
||||
|
||||
training_args = SFTConfig(
|
||||
packing=packing,
|
||||
max_length=self.max_length,
|
||||
output_dir=self.tmp_dir,
|
||||
logging_strategy="no",
|
||||
report_to="none",
|
||||
per_device_train_batch_size=2,
|
||||
max_steps=10,
|
||||
fp16=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
quantization_config = BitsAndBytesConfig(load_in_4bit=True, bnb_4bit_compute_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_name, quantization_config=quantization_config)
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
|
||||
|
||||
trainer = SFTTrainer(
|
||||
model,
|
||||
args=training_args,
|
||||
processing_class=tokenizer,
|
||||
train_dataset=train_dataset,
|
||||
peft_config=self.peft_config,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
assert isinstance(trainer.model, PeftModel)
|
||||
|
||||
trainer.train()
|
||||
|
||||
release_memory(model, trainer)
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize("packing", PACKING_OPTIONS)
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize("model_name", MODELS_TO_TEST)
|
||||
@require_liger_kernel
|
||||
def test_sft_trainer_with_liger(self, model_name, packing):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Tests if passing use_liger=True to SFTConfig loads and runs the trainer with AutoLigerKernelForCausalLM as
|
||||
expected.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
import importlib
|
||||
|
||||
def cleanup_liger_patches(trainer):
|
||||
"""Clean up liger_kernel patches by reloading the model's specific module"""
|
||||
try:
|
||||
# Get the specific module that was used by the trainer's model
|
||||
module_path = trainer.model.__module__
|
||||
reload_module = importlib.import_module(module_path)
|
||||
importlib.reload(reload_module)
|
||||
except Exception:
|
||||
pass # Continue if reload fails
|
||||
|
||||
training_args = SFTConfig(
|
||||
output_dir=self.tmp_dir,
|
||||
logging_strategy="no",
|
||||
report_to="none",
|
||||
per_device_train_batch_size=2,
|
||||
max_steps=2,
|
||||
packing=packing,
|
||||
max_length=self.max_length,
|
||||
use_liger_kernel=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
trainer = SFTTrainer(
|
||||
model_name,
|
||||
args=training_args,
|
||||
train_dataset=self.train_dataset,
|
||||
eval_dataset=self.eval_dataset,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Ensure cleanup of liger patches after the test
|
||||
try:
|
||||
trainer.train()
|
||||
release_memory(trainer.model, trainer)
|
||||
finally:
|
||||
cleanup_liger_patches(trainer)
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize("packing", PACKING_OPTIONS)
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize("model_name", MODELS_TO_TEST)
|
||||
@require_torch_accelerator
|
||||
def test_train_offloading(self, model_name, packing):
|
||||
"""Test that activation offloading works with SFTTrainer."""
|
||||
# Initialize the trainer
|
||||
training_args = SFTConfig(
|
||||
output_dir=self.tmp_dir,
|
||||
activation_offloading=True,
|
||||
report_to="none",
|
||||
per_device_train_batch_size=2,
|
||||
max_steps=2,
|
||||
packing=packing,
|
||||
max_length=self.max_length,
|
||||
)
|
||||
trainer = SFTTrainer(
|
||||
model=model_name, args=training_args, train_dataset=self.train_dataset, eval_dataset=self.eval_dataset
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Save the initial parameters to compare them later
|
||||
previous_trainable_params = {n: param.clone() for n, param in trainer.model.named_parameters()}
|
||||
|
||||
# Train the model
|
||||
trainer.train()
|
||||
|
||||
# Check that the training loss is not None
|
||||
assert trainer.state.log_history[-1]["train_loss"] is not None
|
||||
|
||||
# Check the params have changed
|
||||
for n, param in previous_trainable_params.items():
|
||||
new_param = trainer.model.get_parameter(n)
|
||||
assert not torch.allclose(param, new_param), f"Parameter {n} has not changed"
|
||||
|
||||
release_memory(trainer.model, trainer)
|
||||
@ -12,7 +12,6 @@
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from torch import nn
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM
|
||||
@ -103,7 +102,7 @@ class TestActivationOffloading(TrlTestCase):
|
||||
grads2 = [p.grad.clone() for p in model.parameters()]
|
||||
|
||||
# Gradients should match as NoOpManager should have prevented offloading
|
||||
for g1, g2 in zip(grads1, grads2):
|
||||
for g1, g2 in zip(grads1, grads2, strict=True):
|
||||
assert torch.allclose(g1, g2, rtol=1e-4, atol=1e-5)
|
||||
|
||||
@require_torch_accelerator
|
||||
@ -152,7 +151,7 @@ class TestActivationOffloading(TrlTestCase):
|
||||
|
||||
# Check outputs and gradients match
|
||||
assert torch.allclose(out1, out2, rtol=1e-5)
|
||||
for g1, g2 in zip(grads1, grads2):
|
||||
for g1, g2 in zip(grads1, grads2, strict=True):
|
||||
assert torch.allclose(g1, g2, rtol=1e-5)
|
||||
|
||||
@require_torch_accelerator
|
||||
|
||||
@ -115,7 +115,7 @@ class TestWinRateCallback(TrlTestCase):
|
||||
trainer.add_callback(win_rate_callback)
|
||||
trainer.train()
|
||||
winrate_history = [h for h in trainer.state.log_history if "eval_win_rate" in h]
|
||||
for history_row, expected_row in zip(winrate_history, self.expected_winrates):
|
||||
for history_row, expected_row in zip(winrate_history, self.expected_winrates, strict=True):
|
||||
assert all(key in history_row and history_row[key] == expected_row[key] for key in expected_row)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_without_ref_model(self):
|
||||
@ -141,7 +141,7 @@ class TestWinRateCallback(TrlTestCase):
|
||||
trainer.add_callback(win_rate_callback)
|
||||
trainer.train()
|
||||
winrate_history = [h for h in trainer.state.log_history if "eval_win_rate" in h]
|
||||
for history_row, expected_row in zip(winrate_history, self.expected_winrates):
|
||||
for history_row, expected_row in zip(winrate_history, self.expected_winrates, strict=True):
|
||||
assert all(key in history_row and history_row[key] == expected_row[key] for key in expected_row)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_soft_judge(self):
|
||||
@ -184,7 +184,7 @@ class TestWinRateCallback(TrlTestCase):
|
||||
for h in trainer.state.log_history
|
||||
if "eval_avg_win_prob" in h
|
||||
]
|
||||
for history_row, expected_row in zip(winrate_history, expected_soft_winrates):
|
||||
for history_row, expected_row in zip(winrate_history, expected_soft_winrates, strict=True):
|
||||
assert all(key in history_row and history_row[key] == expected_row[key] for key in expected_row)
|
||||
|
||||
@require_peft
|
||||
@ -218,7 +218,7 @@ class TestWinRateCallback(TrlTestCase):
|
||||
trainer.add_callback(win_rate_callback)
|
||||
trainer.train()
|
||||
winrate_history = [h for h in trainer.state.log_history if "eval_win_rate" in h]
|
||||
for history_row, expected_row in zip(winrate_history, self.expected_winrates):
|
||||
for history_row, expected_row in zip(winrate_history, self.expected_winrates, strict=True):
|
||||
assert all(key in history_row and history_row[key] == expected_row[key] for key in expected_row)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -12,23 +12,15 @@
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
from io import StringIO
|
||||
from unittest.mock import patch
|
||||
|
||||
import pytest
|
||||
import yaml
|
||||
|
||||
from .testing_utils import TrlTestCase
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.mark.skipif(
|
||||
sys.version_info < (3, 10),
|
||||
reason="Transformers' generation codebase uses a Python >3.10 syntax (`str | None`), which seems to cause the CLI tests "
|
||||
"to fail on Python <3.10.", # let's say it's a known issue, but not expected to be fixed, because too niche
|
||||
)
|
||||
class TestCLI(TrlTestCase):
|
||||
def test_dpo(self):
|
||||
from trl.cli import main
|
||||
|
||||
@ -12,7 +12,6 @@
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
from trl.trainer.dpo_trainer import DataCollatorForPreference
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,47 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Copyright 2020-2025 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
from trl.core import masked_mean, masked_var, masked_whiten
|
||||
|
||||
from .testing_utils import TrlTestCase
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class TestCore(TrlTestCase):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
A wrapper class for testing core utils functions
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
def setup_method(self):
|
||||
self.test_input = torch.Tensor([1, 2, 3, 4])
|
||||
self.test_mask = torch.Tensor([0, 1, 1, 0])
|
||||
self.test_input_unmasked = self.test_input[1:3]
|
||||
|
||||
def test_masked_mean(self):
|
||||
assert torch.mean(self.test_input_unmasked) == masked_mean(self.test_input, self.test_mask)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_masked_var(self):
|
||||
assert torch.var(self.test_input_unmasked) == masked_var(self.test_input, self.test_mask)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_masked_whiten(self):
|
||||
def whiten(values: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
|
||||
mean, var = torch.mean(values), torch.var(values)
|
||||
return (values - mean) * torch.rsqrt(var + 1e-8)
|
||||
|
||||
whiten_unmasked = whiten(self.test_input_unmasked)
|
||||
whiten_masked = masked_whiten(self.test_input, self.test_mask)[1:3]
|
||||
diffs = (whiten_unmasked - whiten_masked).sum()
|
||||
assert abs(diffs.item()) < 0.00001
|
||||
@ -11,13 +11,13 @@
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
import pytest
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM, AutoTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
from trl import CPOConfig, CPOTrainer
|
||||
from trl.trainer.utils import SIMPLE_CHAT_TEMPLATE
|
||||
|
||||
from .testing_utils import TrlTestCase, require_peft
|
||||
|
||||
@ -33,7 +33,6 @@ class TestCPOTrainer(TrlTestCase):
|
||||
model_id = "trl-internal-testing/tiny-T5ForConditionalGeneration"
|
||||
self.t5_model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained(model_id)
|
||||
self.t5_tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_id)
|
||||
self.t5_tokenizer.chat_template = SIMPLE_CHAT_TEMPLATE
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
|
||||
"name, loss_type, config_name",
|
||||
@ -41,7 +40,6 @@ class TestCPOTrainer(TrlTestCase):
|
||||
("qwen", "sigmoid", "standard_preference"),
|
||||
("t5", "hinge", "standard_implicit_prompt_preference"),
|
||||
("qwen", "ipo", "conversational_preference"),
|
||||
("t5", "ipo", "conversational_implicit_prompt_preference"),
|
||||
("qwen", "simpo", "standard_preference"),
|
||||
("t5", "simpo", "standard_implicit_prompt_preference"),
|
||||
("qwen", "hinge", "conversational_preference"),
|
||||
|
||||
@ -12,7 +12,7 @@
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
from typing import Callable
|
||||
from collections.abc import Callable
|
||||
|
||||
import pytest
|
||||
from datasets import Dataset, load_dataset
|
||||
|
||||
@ -12,13 +12,14 @@
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
import gc
|
||||
import re
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
from unittest.mock import MagicMock
|
||||
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
import pytest
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from accelerate.utils.memory import release_memory
|
||||
from datasets import Dataset, features, load_dataset
|
||||
from transformers import (
|
||||
AutoModelForCausalLM,
|
||||
@ -26,10 +27,12 @@ from transformers import (
|
||||
AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM,
|
||||
AutoProcessor,
|
||||
AutoTokenizer,
|
||||
BitsAndBytesConfig,
|
||||
PreTrainedTokenizerBase,
|
||||
is_vision_available,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from transformers.testing_utils import get_device_properties
|
||||
from transformers.testing_utils import backend_empty_cache, get_device_properties, torch_device
|
||||
from transformers.utils import is_peft_available
|
||||
|
||||
from trl import DPOConfig, DPOTrainer, FDivergenceType
|
||||
|
||||
@ -39,6 +42,7 @@ from .testing_utils import (
|
||||
require_liger_kernel,
|
||||
require_no_wandb,
|
||||
require_peft,
|
||||
require_torch_accelerator,
|
||||
require_torch_gpu_if_bnb_not_multi_backend_enabled,
|
||||
require_vision,
|
||||
)
|
||||
@ -47,6 +51,9 @@ from .testing_utils import (
|
||||
if is_vision_available():
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
|
||||
if is_peft_available():
|
||||
from peft import LoraConfig, PeftModel
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class TestTokenizeRow(TrlTestCase):
|
||||
def setup_method(self):
|
||||
@ -250,7 +257,7 @@ class TestDPOTrainer(TrlTestCase):
|
||||
per_device_train_batch_size=2,
|
||||
learning_rate=9e-1,
|
||||
report_to="none",
|
||||
use_liger_loss=True,
|
||||
use_liger_kernel=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
trainer = DPOTrainer(
|
||||
model=model,
|
||||
@ -1312,7 +1319,6 @@ class TestDPOTrainer(TrlTestCase):
|
||||
],
|
||||
)
|
||||
@require_liger_kernel
|
||||
@pytest.mark.skipif(not (sys.version_info >= (3, 10)), reason="Liger kernel is not supported on Python 3.9")
|
||||
def test_dpo_trainer_with_liger(self, beta, loss_type):
|
||||
"""Test DPO trainer with Liger loss enabled across supported loss types.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1330,7 +1336,7 @@ class TestDPOTrainer(TrlTestCase):
|
||||
learning_rate=9e-1,
|
||||
eval_strategy="steps",
|
||||
beta=beta,
|
||||
use_liger_loss=True, # Enable Liger loss
|
||||
use_liger_kernel=True, # Enable Liger kernel
|
||||
loss_type=loss_type,
|
||||
report_to="none",
|
||||
)
|
||||
@ -1526,3 +1532,206 @@ class TestDPOConfig(TrlTestCase):
|
||||
# Serialization: TrainingArguments.to_dict should yield the enum's string value
|
||||
configparser_dict = training_args.to_dict()
|
||||
assert configparser_dict["f_divergence_type"] == f_divergence_type.value
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.mark.slow
|
||||
@require_torch_accelerator
|
||||
@require_peft
|
||||
class TestDPOTrainerSlow(TrlTestCase):
|
||||
def setup_method(self):
|
||||
self.dataset = load_dataset("trl-internal-testing/zen", "standard_preference")
|
||||
self.peft_config = LoraConfig(
|
||||
lora_alpha=16,
|
||||
lora_dropout=0.1,
|
||||
r=8,
|
||||
bias="none",
|
||||
task_type="CAUSAL_LM",
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.max_length = 128
|
||||
|
||||
def teardown_method(self):
|
||||
gc.collect()
|
||||
backend_empty_cache(torch_device)
|
||||
gc.collect()
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize("pre_compute_logits", [True, False])
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize("loss_type", ["sigmoid", "ipo"])
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
|
||||
"model_id",
|
||||
[
|
||||
"trl-internal-testing/tiny-LlamaForCausalLM-3.2",
|
||||
"trl-internal-testing/tiny-MistralForCausalLM-0.2",
|
||||
],
|
||||
)
|
||||
def test_dpo_bare_model(self, model_id, loss_type, pre_compute_logits):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
A test that tests the simple usage of `DPOTrainer` using a bare model in full precision.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_id)
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_id)
|
||||
tokenizer.pad_token = tokenizer.eos_token if tokenizer.pad_token is None else tokenizer.pad_token
|
||||
|
||||
training_args = DPOConfig(
|
||||
output_dir=self.tmp_dir,
|
||||
per_device_train_batch_size=2,
|
||||
max_steps=2,
|
||||
remove_unused_columns=False,
|
||||
gradient_accumulation_steps=2,
|
||||
learning_rate=9e-1,
|
||||
eval_strategy="steps",
|
||||
fp16=True,
|
||||
logging_strategy="no",
|
||||
report_to="none",
|
||||
beta=0.1,
|
||||
loss_type=loss_type,
|
||||
precompute_ref_log_probs=pre_compute_logits,
|
||||
max_length=self.max_length,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# dpo train lora model
|
||||
trainer = DPOTrainer(
|
||||
model=model,
|
||||
ref_model=None,
|
||||
args=training_args,
|
||||
train_dataset=self.dataset["train"],
|
||||
eval_dataset=self.dataset["test"],
|
||||
processing_class=tokenizer,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# train the model
|
||||
trainer.train()
|
||||
|
||||
# save trained model or adapter
|
||||
trainer.save_model()
|
||||
|
||||
release_memory(model, trainer)
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
|
||||
"gradient_checkpointing_kwargs", [None, {"use_reentrant": False}, {"use_reentrant": True}]
|
||||
)
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize("pre_compute_logits", [True, False])
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize("loss_type", ["sigmoid", "ipo"])
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
|
||||
"model_id",
|
||||
[
|
||||
"trl-internal-testing/tiny-LlamaForCausalLM-3.2",
|
||||
"trl-internal-testing/tiny-MistralForCausalLM-0.2",
|
||||
],
|
||||
)
|
||||
@require_peft
|
||||
def test_dpo_peft_model(self, model_id, loss_type, pre_compute_logits, gradient_checkpointing_kwargs):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
A test that tests the simple usage of `DPOTrainer` using a peft model in full precision + different scenarios
|
||||
of gradient checkpointing.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_id)
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_id)
|
||||
tokenizer.pad_token = tokenizer.eos_token if tokenizer.pad_token is None else tokenizer.pad_token
|
||||
|
||||
training_args = DPOConfig(
|
||||
output_dir=self.tmp_dir,
|
||||
per_device_train_batch_size=2,
|
||||
max_steps=2,
|
||||
remove_unused_columns=False,
|
||||
gradient_accumulation_steps=2,
|
||||
learning_rate=9e-1,
|
||||
eval_strategy="steps",
|
||||
fp16=True,
|
||||
logging_strategy="no",
|
||||
report_to="none",
|
||||
gradient_checkpointing=True,
|
||||
gradient_checkpointing_kwargs=gradient_checkpointing_kwargs,
|
||||
generate_during_eval=False,
|
||||
loss_type=loss_type,
|
||||
precompute_ref_log_probs=pre_compute_logits,
|
||||
beta=0.1,
|
||||
max_length=self.max_length,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# dpo train lora model
|
||||
trainer = DPOTrainer(
|
||||
model=model,
|
||||
ref_model=None,
|
||||
args=training_args,
|
||||
train_dataset=self.dataset["train"],
|
||||
eval_dataset=self.dataset["test"],
|
||||
processing_class=tokenizer,
|
||||
peft_config=self.peft_config,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
assert isinstance(trainer.model, PeftModel)
|
||||
assert trainer.ref_model is None
|
||||
|
||||
# train the model
|
||||
trainer.train()
|
||||
|
||||
# save trained model or adapter
|
||||
trainer.save_model()
|
||||
|
||||
release_memory(model, trainer)
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
|
||||
"gradient_checkpointing_kwargs", [None, {"use_reentrant": False}, {"use_reentrant": True}]
|
||||
)
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize("pre_compute_logits", [True, False])
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize("loss_type", ["sigmoid", "ipo"])
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
|
||||
"model_id",
|
||||
[
|
||||
"trl-internal-testing/tiny-LlamaForCausalLM-3.2",
|
||||
"trl-internal-testing/tiny-MistralForCausalLM-0.2",
|
||||
],
|
||||
)
|
||||
@require_bitsandbytes
|
||||
@require_peft
|
||||
def test_dpo_peft_model_qlora(self, model_id, loss_type, pre_compute_logits, gradient_checkpointing_kwargs):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
A test that tests the simple usage of `DPOTrainer` using QLoRA + different scenarios of gradient checkpointing.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
quantization_config = BitsAndBytesConfig(load_in_4bit=True, bnb_4bit_compute_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_id, quantization_config=quantization_config)
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_id)
|
||||
tokenizer.pad_token = tokenizer.eos_token if tokenizer.pad_token is None else tokenizer.pad_token
|
||||
|
||||
training_args = DPOConfig(
|
||||
output_dir=self.tmp_dir,
|
||||
per_device_train_batch_size=2,
|
||||
max_steps=2,
|
||||
remove_unused_columns=False,
|
||||
gradient_accumulation_steps=2,
|
||||
learning_rate=9e-1,
|
||||
eval_strategy="steps",
|
||||
fp16=True,
|
||||
logging_strategy="no",
|
||||
report_to="none",
|
||||
gradient_checkpointing=True,
|
||||
gradient_checkpointing_kwargs=gradient_checkpointing_kwargs,
|
||||
beta=0.1,
|
||||
generate_during_eval=False,
|
||||
loss_type=loss_type,
|
||||
precompute_ref_log_probs=pre_compute_logits,
|
||||
max_length=self.max_length,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# dpo train lora model
|
||||
trainer = DPOTrainer(
|
||||
model=model,
|
||||
ref_model=None,
|
||||
args=training_args,
|
||||
train_dataset=self.dataset["train"],
|
||||
eval_dataset=self.dataset["test"],
|
||||
processing_class=tokenizer,
|
||||
peft_config=self.peft_config,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
assert isinstance(trainer.model, PeftModel)
|
||||
assert trainer.ref_model is None
|
||||
|
||||
# train the model
|
||||
trainer.train()
|
||||
|
||||
# save trained model or adapter
|
||||
trainer.save_model()
|
||||
|
||||
release_memory(model, trainer)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -21,7 +21,6 @@ from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer, GenerationConfig
|
||||
|
||||
from trl import GKDConfig, GKDTrainer
|
||||
from trl.trainer.utils import SIMPLE_CHAT_TEMPLATE
|
||||
|
||||
from .testing_utils import TrlTestCase, require_liger_kernel
|
||||
|
||||
@ -30,9 +29,10 @@ class TestGKDTrainerGenerateOnPolicy(TrlTestCase):
|
||||
@classmethod
|
||||
def setup_class(cls):
|
||||
model_id = "trl-internal-testing/tiny-Qwen2ForCausalLM-2.5"
|
||||
cls.device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
|
||||
cls.tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_id)
|
||||
cls.tokenizer.pad_token = cls.tokenizer.eos_token
|
||||
cls.model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_id)
|
||||
cls.model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_id).to(cls.device)
|
||||
cls.generation_config = GenerationConfig(
|
||||
max_new_tokens=20,
|
||||
num_return_sequences=1,
|
||||
@ -45,8 +45,8 @@ class TestGKDTrainerGenerateOnPolicy(TrlTestCase):
|
||||
tokenized_prompts = self.tokenizer(prompts, return_tensors="pt", padding=True)
|
||||
|
||||
inputs = {
|
||||
"prompts": tokenized_prompts["input_ids"],
|
||||
"prompt_attention_mask": tokenized_prompts["attention_mask"],
|
||||
"prompts": tokenized_prompts["input_ids"].to(self.device),
|
||||
"prompt_attention_mask": tokenized_prompts["attention_mask"].to(self.device),
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# Set temperature to 0 for deterministic output
|
||||
@ -68,7 +68,7 @@ class TestGKDTrainerGenerateOnPolicy(TrlTestCase):
|
||||
generated_texts = self.tokenizer.batch_decode(new_input_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)
|
||||
|
||||
# Check if the generated texts start with the original prompts
|
||||
for prompt, generated_text in zip(prompts, generated_texts):
|
||||
for prompt, generated_text in zip(prompts, generated_texts, strict=True):
|
||||
assert generated_text.startswith(prompt), (
|
||||
f"Generated text '{generated_text}' does not start with prompt '{prompt}'"
|
||||
)
|
||||
@ -92,8 +92,8 @@ class TestGKDTrainerGenerateOnPolicy(TrlTestCase):
|
||||
tokenized_prompts = self.tokenizer(prompts, return_tensors="pt", padding=True)
|
||||
|
||||
inputs = {
|
||||
"prompts": tokenized_prompts["input_ids"],
|
||||
"attention_mask": tokenized_prompts["attention_mask"],
|
||||
"prompts": tokenized_prompts["input_ids"].to(self.device),
|
||||
"attention_mask": tokenized_prompts["attention_mask"].to(self.device),
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
outputs = GKDTrainer.generate_on_policy_outputs(
|
||||
@ -205,10 +205,6 @@ class TestGKDTrainer(TrlTestCase):
|
||||
self.tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(self.model_id)
|
||||
self.tokenizer.pad_token = self.tokenizer.eos_token
|
||||
|
||||
# Ensure the tokenizer has a chat template
|
||||
if not hasattr(self.tokenizer, "chat_template") or self.tokenizer.chat_template is None:
|
||||
self.tokenizer.chat_template = SIMPLE_CHAT_TEMPLATE
|
||||
|
||||
def test_gkd_trainer(self):
|
||||
training_args = GKDConfig(
|
||||
output_dir=self.tmp_dir,
|
||||
|
||||
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
@ -12,7 +12,6 @@
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
import pytest
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
@ -361,11 +360,11 @@ class TestKTOTrainer(TrlTestCase):
|
||||
|
||||
@require_liger_kernel
|
||||
def test_kto_trainer_with_liger(self):
|
||||
"""Test KTO trainer with Liger loss enabled."""
|
||||
"""Test KTO trainer with Liger kernel enabled."""
|
||||
training_args = KTOConfig(
|
||||
output_dir=self.tmp_dir,
|
||||
report_to="none",
|
||||
use_liger_loss=True, # Enable Liger loss
|
||||
use_liger_kernel=True, # Enable Liger kernel
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
dummy_dataset = load_dataset("trl-internal-testing/zen", "standard_unpaired_preference")
|
||||
|
||||
@ -12,8 +12,10 @@
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
import pytest
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
import transformers
|
||||
from packaging.version import Version
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, GenerationConfig
|
||||
|
||||
from trl.models.modeling_base import GeometricMixtureWrapper, create_reference_model
|
||||
@ -58,6 +60,11 @@ class TestGeometricMixtureWrapper(TrlTestCase):
|
||||
|
||||
assert torch.allclose(wrapper_output.logits, expected_logits, atol=1e-5)
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.mark.xfail(
|
||||
Version(transformers.__version__).is_devrelease, # Tests with dev dependencies
|
||||
reason="Blocked by upstream fix pending in huggingface/transformers#41764 (tracked in GH-4272)",
|
||||
strict=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
def test_prepare_inputs_for_generation(self):
|
||||
input_ids = torch.tensor([[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]], device=self.device)
|
||||
attention_mask = torch.ones_like(input_ids)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -11,6 +11,7 @@
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
import pytest
|
||||
from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoModelForSequenceClassification, AutoTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
@ -38,7 +38,7 @@ if is_peft_available():
|
||||
if is_vision_available():
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForVision2Seq, AutoProcessor
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForImageTextToText, AutoProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class TestOnlineDPOTrainer(TrlTestCase):
|
||||
@ -510,7 +510,7 @@ class TestOnlineDPOVisionTrainer(TrlTestCase):
|
||||
dataset = Dataset.from_dict(dataset_dict)
|
||||
dataset = dataset.cast_column("images", features.Sequence(features.Image()))
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModelForVision2Seq.from_pretrained(model_id)
|
||||
model = AutoModelForImageTextToText.from_pretrained(model_id)
|
||||
reward_model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"trl-internal-testing/tiny-LlamaForCausalLM-3.2", num_labels=1
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -11,13 +11,13 @@
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
import pytest
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM, AutoTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
from trl import ORPOConfig, ORPOTrainer
|
||||
from trl.trainer.utils import SIMPLE_CHAT_TEMPLATE
|
||||
|
||||
from .testing_utils import TrlTestCase, require_peft
|
||||
|
||||
@ -33,7 +33,6 @@ class TestORPOTrainer(TrlTestCase):
|
||||
model_id = "trl-internal-testing/tiny-T5ForConditionalGeneration"
|
||||
self.t5_model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained(model_id)
|
||||
self.t5_tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_id)
|
||||
self.t5_tokenizer.chat_template = SIMPLE_CHAT_TEMPLATE
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
|
||||
"name, config_name",
|
||||
@ -41,7 +40,6 @@ class TestORPOTrainer(TrlTestCase):
|
||||
("qwen", "standard_preference"),
|
||||
("t5", "standard_implicit_prompt_preference"),
|
||||
("qwen", "conversational_preference"),
|
||||
("t5", "conversational_implicit_prompt_preference"),
|
||||
],
|
||||
)
|
||||
def test_orpo_trainer(self, name, config_name):
|
||||
|
||||
@ -153,7 +153,7 @@ class TestPeftModel(TrlTestCase):
|
||||
model_from_pretrained = AutoModelForCausalLMWithValueHead.from_pretrained(self.tmp_dir)
|
||||
|
||||
# check all the weights are the same
|
||||
for p1, p2 in zip(model.named_parameters(), model_from_pretrained.named_parameters()):
|
||||
for p1, p2 in zip(model.named_parameters(), model_from_pretrained.named_parameters(), strict=True):
|
||||
assert torch.allclose(p1[1], p2[1]), f"{p1[0]} != {p2[0]}"
|
||||
|
||||
def test_load_pretrained_peft(self):
|
||||
@ -177,7 +177,7 @@ class TestPeftModel(TrlTestCase):
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# check all the weights are the same
|
||||
for p1, p2 in zip(model.named_parameters(), model_from_pretrained.named_parameters()):
|
||||
for p1, p2 in zip(model.named_parameters(), model_from_pretrained.named_parameters(), strict=True):
|
||||
if p1[0] not in ["v_head.summary.weight", "v_head.summary.bias"]:
|
||||
assert torch.allclose(p1[1], p2[1]), f"{p1[0]} != {p2[0]}"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -12,14 +12,13 @@
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoModelForSequenceClassification, AutoTokenizer
|
||||
from transformers.utils import is_peft_available
|
||||
|
||||
from trl import PPOConfig, PPOTrainer
|
||||
from trl.trainer.utils import SIMPLE_CHAT_TEMPLATE
|
||||
from trl.trainer.ppo_trainer import masked_mean, masked_var, masked_whiten
|
||||
|
||||
from .testing_utils import TrlTestCase, require_peft
|
||||
|
||||
@ -28,6 +27,33 @@ if is_peft_available():
|
||||
from peft import LoraConfig
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class TestCore(TrlTestCase):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
A wrapper class for testing core utils functions
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
def setup_method(self):
|
||||
self.test_input = torch.Tensor([1, 2, 3, 4])
|
||||
self.test_mask = torch.Tensor([0, 1, 1, 0])
|
||||
self.test_input_unmasked = self.test_input[1:3]
|
||||
|
||||
def test_masked_mean(self):
|
||||
assert torch.mean(self.test_input_unmasked) == masked_mean(self.test_input, self.test_mask)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_masked_var(self):
|
||||
assert torch.var(self.test_input_unmasked) == masked_var(self.test_input, self.test_mask)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_masked_whiten(self):
|
||||
def whiten(values: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
|
||||
mean, var = torch.mean(values), torch.var(values)
|
||||
return (values - mean) * torch.rsqrt(var + 1e-8)
|
||||
|
||||
whiten_unmasked = whiten(self.test_input_unmasked)
|
||||
whiten_masked = masked_whiten(self.test_input, self.test_mask)[1:3]
|
||||
diffs = (whiten_unmasked - whiten_masked).sum()
|
||||
assert abs(diffs.item()) < 0.00001
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class TestPPOTrainer(TrlTestCase):
|
||||
def setup_method(self):
|
||||
# Set up the models and tokenizer using the test model
|
||||
@ -37,9 +63,6 @@ class TestPPOTrainer(TrlTestCase):
|
||||
self.tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(self.model_id, padding_side="left")
|
||||
self.tokenizer.add_special_tokens({"pad_token": "[PAD]"})
|
||||
|
||||
if self.tokenizer.chat_template is None:
|
||||
self.tokenizer.chat_template = SIMPLE_CHAT_TEMPLATE
|
||||
|
||||
# Add reward and value models as in ppo.py
|
||||
reward_model_id = "trl-internal-testing/tiny-Qwen2ForSequenceClassification-2.5"
|
||||
self.value_model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(reward_model_id, num_labels=1)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -12,7 +12,6 @@
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
from trl.rewards import accuracy_reward, get_soft_overlong_punishment, think_format_reward
|
||||
|
||||
from .testing_utils import TrlTestCase, require_math_latex
|
||||
|
||||
@ -12,7 +12,6 @@
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
import torch.nn as nn
|
||||
from datasets import Dataset
|
||||
|
||||
@ -490,7 +490,9 @@ class TestRLOOTrainer(TrlTestCase):
|
||||
|
||||
def reward_func(completions, some_values, **kwargs):
|
||||
"""Reward function that rewards completions with lengths closer to the values in some_values."""
|
||||
return [float(abs(len(completion) - value)) for completion, value in zip(completions, some_values)]
|
||||
return [
|
||||
float(abs(len(completion) - value)) for completion, value in zip(completions, some_values, strict=True)
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
training_args = RLOOConfig(
|
||||
output_dir=self.tmp_dir,
|
||||
@ -1129,8 +1131,14 @@ class TestRLOOTrainer(TrlTestCase):
|
||||
new_param = trainer.model.get_parameter(n)
|
||||
assert not torch.equal(param, new_param), f"Parameter {n} has not changed."
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
|
||||
"model_id",
|
||||
[
|
||||
"trl-internal-testing/tiny-Qwen2_5_VLForConditionalGeneration",
|
||||
],
|
||||
)
|
||||
@require_vision
|
||||
def test_training_vlm_beta_non_zero(self):
|
||||
def test_training_vlm_beta_non_zero(self, model_id):
|
||||
dataset = load_dataset("trl-internal-testing/zen-image", "conversational_prompt_only", split="train")
|
||||
|
||||
def reward_func(completions, **kwargs):
|
||||
@ -1147,7 +1155,7 @@ class TestRLOOTrainer(TrlTestCase):
|
||||
report_to="none",
|
||||
)
|
||||
trainer = RLOOTrainer(
|
||||
model="trl-internal-testing/tiny-Qwen2_5_VLForConditionalGeneration",
|
||||
model=model_id,
|
||||
reward_funcs=reward_func,
|
||||
args=training_args,
|
||||
train_dataset=dataset,
|
||||
@ -1169,12 +1177,16 @@ class TestRLOOTrainer(TrlTestCase):
|
||||
new_param = trainer.model.get_parameter(n)
|
||||
assert not torch.equal(param, new_param), f"Parameter {n} has not changed."
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
|
||||
"model_id",
|
||||
[
|
||||
"trl-internal-testing/tiny-Qwen2_5_VLForConditionalGeneration",
|
||||
],
|
||||
)
|
||||
@require_vision
|
||||
@require_peft
|
||||
def test_training_vlm_peft(self):
|
||||
model = AutoModelForImageTextToText.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"trl-internal-testing/tiny-Qwen2_5_VLForConditionalGeneration"
|
||||
)
|
||||
def test_training_vlm_peft(self, model_id):
|
||||
model = AutoModelForImageTextToText.from_pretrained(model_id)
|
||||
base_param_names = [f"base_model.model.{n}" for n, _ in model.named_parameters()]
|
||||
dataset = load_dataset("trl-internal-testing/zen-image", "conversational_prompt_only", split="train")
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1257,8 +1269,14 @@ class TestRLOOTrainer(TrlTestCase):
|
||||
new_param = trainer.model.get_parameter(n)
|
||||
assert not torch.equal(param, new_param), f"Parameter {n} has not changed."
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
|
||||
"model_id",
|
||||
[
|
||||
"trl-internal-testing/tiny-Qwen2_5_VLForConditionalGeneration",
|
||||
],
|
||||
)
|
||||
@require_vision
|
||||
def test_training_vlm_multi_image(self):
|
||||
def test_training_vlm_multi_image(self, model_id):
|
||||
dataset = load_dataset("trl-internal-testing/zen-multi-image", "conversational_prompt_only", split="train")
|
||||
|
||||
def reward_func(completions, **kwargs):
|
||||
@ -1275,7 +1293,7 @@ class TestRLOOTrainer(TrlTestCase):
|
||||
report_to="none",
|
||||
)
|
||||
trainer = RLOOTrainer(
|
||||
model="trl-internal-testing/tiny-Qwen2_5_VLForConditionalGeneration",
|
||||
model=model_id,
|
||||
reward_funcs=reward_func,
|
||||
args=training_args,
|
||||
train_dataset=dataset,
|
||||
@ -1291,6 +1309,37 @@ class TestRLOOTrainer(TrlTestCase):
|
||||
new_param = trainer.model.get_parameter(n)
|
||||
assert not torch.equal(param, new_param), f"Parameter {n} has not changed."
|
||||
|
||||
def test_training_with_chat_template_kwargs(self):
|
||||
dataset = load_dataset("trl-internal-testing/zen", "conversational_prompt_only", split="train")
|
||||
|
||||
training_args = RLOOConfig(
|
||||
bf16=False,
|
||||
output_dir=self.tmp_dir,
|
||||
learning_rate=0.1,
|
||||
per_device_train_batch_size=3,
|
||||
num_generations=3,
|
||||
max_completion_length=8,
|
||||
report_to="none",
|
||||
chat_template_kwargs={"enable_thinking": False},
|
||||
)
|
||||
trainer = RLOOTrainer(
|
||||
model="trl-internal-testing/tiny-Qwen3ForCausalLM",
|
||||
reward_funcs="trl-internal-testing/tiny-Qwen2ForSequenceClassification-2.5",
|
||||
args=training_args,
|
||||
train_dataset=dataset,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
previous_trainable_params = {n: param.clone() for n, param in trainer.model.named_parameters()}
|
||||
|
||||
trainer.train()
|
||||
|
||||
assert trainer.state.log_history[-1]["train_loss"] is not None
|
||||
|
||||
# Check that the params have changed
|
||||
for n, param in previous_trainable_params.items():
|
||||
new_param = trainer.model.get_parameter(n)
|
||||
assert not torch.equal(param, new_param), f"Parameter {n} has not changed."
|
||||
|
||||
def test_mismatched_reward_processing_classes_length(self):
|
||||
"""Test that mismatched length between reward_funcs and reward_processing_classes raises error."""
|
||||
dataset = load_dataset("trl-internal-testing/zen", "standard_prompt_only", split="train")
|
||||
|
||||
@ -12,15 +12,18 @@
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
import gc
|
||||
import pathlib
|
||||
from unittest.mock import MagicMock
|
||||
|
||||
import pytest
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
import transformers
|
||||
from accelerate.utils.memory import release_memory
|
||||
from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
from packaging.version import parse as parse_version
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer, BitsAndBytesConfig
|
||||
from transformers.testing_utils import backend_empty_cache, torch_device
|
||||
from transformers.utils import is_peft_available
|
||||
|
||||
from trl import SFTConfig, SFTTrainer
|
||||
@ -33,6 +36,8 @@ from .testing_utils import (
|
||||
require_flash_attn,
|
||||
require_liger_kernel,
|
||||
require_peft,
|
||||
require_torch_accelerator,
|
||||
require_torch_multi_accelerator,
|
||||
require_vision,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1381,13 +1386,19 @@ class TestSFTTrainer(TrlTestCase):
|
||||
continue
|
||||
assert not torch.allclose(param, new_param, rtol=1e-12, atol=1e-12), f"Param {n} is not updated"
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
|
||||
"model_id",
|
||||
[
|
||||
"trl-internal-testing/tiny-Qwen2_5_VLForConditionalGeneration",
|
||||
],
|
||||
)
|
||||
@pytest.mark.xfail(
|
||||
parse_version(transformers.__version__) < parse_version("4.57.0"),
|
||||
reason="Mixing text-only and image+text examples is only supported in transformers >= 4.57.0",
|
||||
strict=False,
|
||||
)
|
||||
@require_vision
|
||||
def test_train_vlm_multi_image(self):
|
||||
def test_train_vlm_multi_image(self, model_id):
|
||||
# Get the dataset
|
||||
dataset = load_dataset(
|
||||
"trl-internal-testing/zen-multi-image", "conversational_prompt_completion", split="train"
|
||||
@ -1396,11 +1407,12 @@ class TestSFTTrainer(TrlTestCase):
|
||||
# Initialize the trainer
|
||||
training_args = SFTConfig(
|
||||
output_dir=self.tmp_dir,
|
||||
learning_rate=0.1, # increase the learning rate to speed up the test
|
||||
max_length=None, # For VLMs, truncating can remove image tokens, leading to errors
|
||||
report_to="none",
|
||||
)
|
||||
trainer = SFTTrainer(
|
||||
model="trl-internal-testing/tiny-Qwen2_5_VLForConditionalGeneration",
|
||||
model=model_id,
|
||||
args=training_args,
|
||||
train_dataset=dataset,
|
||||
)
|
||||
@ -1419,51 +1431,28 @@ class TestSFTTrainer(TrlTestCase):
|
||||
new_param = trainer.model.get_parameter(n)
|
||||
assert not torch.allclose(param, new_param, rtol=1e-12, atol=1e-12), f"Param {n} is not updated"
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
|
||||
"model_id",
|
||||
[
|
||||
"trl-internal-testing/tiny-Qwen2_5_VLForConditionalGeneration",
|
||||
# Special case for Gemma, as it uses token_type_ids, and we need to ensure they are properly in the collator:
|
||||
"trl-internal-testing/tiny-Gemma3ForConditionalGeneration",
|
||||
],
|
||||
)
|
||||
@require_vision
|
||||
def test_train_vlm_prompt_completion(self):
|
||||
def test_train_vlm_prompt_completion(self, model_id):
|
||||
# Get the dataset
|
||||
dataset = load_dataset("trl-internal-testing/zen-image", "conversational_prompt_completion", split="train")
|
||||
|
||||
# Initialize the trainer
|
||||
training_args = SFTConfig(
|
||||
output_dir=self.tmp_dir,
|
||||
learning_rate=0.1, # increase the learning rate to speed up the test
|
||||
max_length=None, # For VLMs, truncating can remove image tokens, leading to errors
|
||||
report_to="none",
|
||||
)
|
||||
trainer = SFTTrainer(
|
||||
model="trl-internal-testing/tiny-Qwen2_5_VLForConditionalGeneration",
|
||||
args=training_args,
|
||||
train_dataset=dataset,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Save the initial parameters to compare them later
|
||||
previous_trainable_params = {n: param.clone() for n, param in trainer.model.named_parameters()}
|
||||
|
||||
# Train the model
|
||||
trainer.train()
|
||||
|
||||
# Check that the training loss is not None
|
||||
assert trainer.state.log_history[-1]["train_loss"] is not None
|
||||
|
||||
# Check the params have changed
|
||||
for n, param in previous_trainable_params.items():
|
||||
new_param = trainer.model.get_parameter(n)
|
||||
assert not torch.allclose(param, new_param, rtol=1e-12, atol=1e-12), f"Param {n} is not updated"
|
||||
|
||||
# Special case for Gemma, as it uses token_type_ids, and we need to ensure they are properly in the collator.
|
||||
@require_vision
|
||||
def test_train_vlm_prompt_completion_gemma(self):
|
||||
# Get the dataset
|
||||
dataset = load_dataset("trl-internal-testing/zen-image", "conversational_prompt_completion", split="train")
|
||||
|
||||
# Initialize the trainer
|
||||
training_args = SFTConfig(
|
||||
output_dir=self.tmp_dir,
|
||||
max_length=None, # For VLMs, truncating can remove image tokens, leading to errors
|
||||
report_to="none",
|
||||
)
|
||||
trainer = SFTTrainer(
|
||||
model="trl-internal-testing/tiny-Gemma3ForConditionalGeneration",
|
||||
model=model_id,
|
||||
args=training_args,
|
||||
train_dataset=dataset,
|
||||
)
|
||||
@ -1494,6 +1483,7 @@ class TestSFTTrainer(TrlTestCase):
|
||||
# Initialize the trainer
|
||||
training_args = SFTConfig(
|
||||
output_dir=self.tmp_dir,
|
||||
learning_rate=0.1,
|
||||
max_length=None,
|
||||
per_device_train_batch_size=1,
|
||||
gradient_checkpointing=True,
|
||||
@ -1514,20 +1504,26 @@ class TestSFTTrainer(TrlTestCase):
|
||||
# Check the params have changed
|
||||
for n, param in previous_trainable_params.items():
|
||||
new_param = trainer.model.get_parameter(n)
|
||||
if "model.vision_tower" in n:
|
||||
# The vision tower is not updated, not sure why at this point.
|
||||
if "model.audio_tower" in n or "model.embed_audio" in n:
|
||||
# The audio embedding parameters are not updated because this dataset contains no audio data
|
||||
continue
|
||||
assert not torch.allclose(param, new_param, rtol=1e-12, atol=1e-12), f"Param {n} is not updated"
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
|
||||
"model_id",
|
||||
[
|
||||
"trl-internal-testing/tiny-Qwen2_5_VLForConditionalGeneration",
|
||||
],
|
||||
)
|
||||
@require_vision
|
||||
def test_train_vlm_text_only_data(self):
|
||||
def test_train_vlm_text_only_data(self, model_id):
|
||||
# Get the dataset
|
||||
dataset = load_dataset("trl-internal-testing/zen", "conversational_language_modeling", split="train")
|
||||
|
||||
# Initialize the trainer
|
||||
training_args = SFTConfig(output_dir=self.tmp_dir, report_to="none")
|
||||
trainer = SFTTrainer(
|
||||
model="trl-internal-testing/tiny-Qwen2_5_VLForConditionalGeneration",
|
||||
model=model_id,
|
||||
args=training_args,
|
||||
train_dataset=dataset,
|
||||
)
|
||||
@ -1704,3 +1700,505 @@ class TestSFTTrainer(TrlTestCase):
|
||||
assert not torch.allclose(param, new_param), f"Parameter {n} has not changed"
|
||||
else:
|
||||
raise ValueError(f"Unexpected parameter {n} in model: {trainer.model}")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.mark.slow
|
||||
@require_torch_accelerator
|
||||
@require_peft
|
||||
class TestSFTTrainerSlow(TrlTestCase):
|
||||
def setup_method(self):
|
||||
self.train_dataset = load_dataset("stanfordnlp/imdb", split="train[:10%]")
|
||||
self.eval_dataset = load_dataset("stanfordnlp/imdb", split="test[:10%]")
|
||||
self.max_length = 128
|
||||
self.peft_config = LoraConfig(
|
||||
lora_alpha=16,
|
||||
lora_dropout=0.1,
|
||||
r=8,
|
||||
bias="none",
|
||||
task_type="CAUSAL_LM",
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def teardown_method(self):
|
||||
gc.collect()
|
||||
backend_empty_cache(torch_device)
|
||||
gc.collect()
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize("packing", [True, False])
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
|
||||
"model_name",
|
||||
[
|
||||
"trl-internal-testing/tiny-LlamaForCausalLM-3.2",
|
||||
"trl-internal-testing/tiny-MistralForCausalLM-0.2",
|
||||
],
|
||||
)
|
||||
def test_sft_trainer_str(self, model_name, packing):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Simply tests if passing a simple str to `SFTTrainer` loads and runs the trainer as expected.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
training_args = SFTConfig(
|
||||
output_dir=self.tmp_dir,
|
||||
logging_strategy="no",
|
||||
report_to="none",
|
||||
per_device_train_batch_size=2,
|
||||
max_steps=10,
|
||||
packing=packing,
|
||||
max_length=self.max_length,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
trainer = SFTTrainer(
|
||||
model_name,
|
||||
args=training_args,
|
||||
train_dataset=self.train_dataset,
|
||||
eval_dataset=self.eval_dataset,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
trainer.train()
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize("packing", [True, False])
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
|
||||
"model_name",
|
||||
[
|
||||
"trl-internal-testing/tiny-LlamaForCausalLM-3.2",
|
||||
"trl-internal-testing/tiny-MistralForCausalLM-0.2",
|
||||
],
|
||||
)
|
||||
def test_sft_trainer_transformers(self, model_name, packing):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Simply tests if passing a transformers model to `SFTTrainer` loads and runs the trainer as expected.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
training_args = SFTConfig(
|
||||
output_dir=self.tmp_dir,
|
||||
logging_strategy="no",
|
||||
report_to="none",
|
||||
per_device_train_batch_size=2,
|
||||
max_steps=10,
|
||||
packing=packing,
|
||||
max_length=self.max_length,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_name)
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
|
||||
|
||||
trainer = SFTTrainer(
|
||||
model,
|
||||
args=training_args,
|
||||
processing_class=tokenizer,
|
||||
train_dataset=self.train_dataset,
|
||||
eval_dataset=self.eval_dataset,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
trainer.train()
|
||||
|
||||
release_memory(model, trainer)
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize("packing", [True, False])
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
|
||||
"model_name",
|
||||
[
|
||||
"trl-internal-testing/tiny-LlamaForCausalLM-3.2",
|
||||
"trl-internal-testing/tiny-MistralForCausalLM-0.2",
|
||||
],
|
||||
)
|
||||
@require_peft
|
||||
def test_sft_trainer_peft(self, model_name, packing):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Simply tests if passing a transformers model + peft config to `SFTTrainer` loads and runs the trainer as
|
||||
expected.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
training_args = SFTConfig(
|
||||
output_dir=self.tmp_dir,
|
||||
logging_strategy="no",
|
||||
report_to="none",
|
||||
per_device_train_batch_size=2,
|
||||
max_steps=10,
|
||||
fp16=True,
|
||||
packing=packing,
|
||||
max_length=self.max_length,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_name)
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
|
||||
|
||||
trainer = SFTTrainer(
|
||||
model,
|
||||
args=training_args,
|
||||
processing_class=tokenizer,
|
||||
train_dataset=self.train_dataset,
|
||||
eval_dataset=self.eval_dataset,
|
||||
peft_config=self.peft_config,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
assert isinstance(trainer.model, PeftModel)
|
||||
|
||||
trainer.train()
|
||||
|
||||
release_memory(model, trainer)
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize("packing", [True, False])
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
|
||||
"model_name",
|
||||
[
|
||||
"trl-internal-testing/tiny-LlamaForCausalLM-3.2",
|
||||
"trl-internal-testing/tiny-MistralForCausalLM-0.2",
|
||||
],
|
||||
)
|
||||
def test_sft_trainer_transformers_mp(self, model_name, packing):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Simply tests if passing a transformers model to `SFTTrainer` loads and runs the trainer as expected in mixed
|
||||
precision.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
training_args = SFTConfig(
|
||||
output_dir=self.tmp_dir,
|
||||
logging_strategy="no",
|
||||
report_to="none",
|
||||
per_device_train_batch_size=2,
|
||||
max_steps=10,
|
||||
fp16=True, # this is sufficient to enable amp
|
||||
packing=packing,
|
||||
max_length=self.max_length,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_name)
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
|
||||
|
||||
trainer = SFTTrainer(
|
||||
model,
|
||||
args=training_args,
|
||||
processing_class=tokenizer,
|
||||
train_dataset=self.train_dataset,
|
||||
eval_dataset=self.eval_dataset,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
trainer.train()
|
||||
|
||||
release_memory(model, trainer)
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
|
||||
"gradient_checkpointing_kwargs", [None, {"use_reentrant": False}, {"use_reentrant": True}]
|
||||
)
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize("packing", [True, False])
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
|
||||
"model_name",
|
||||
[
|
||||
"trl-internal-testing/tiny-LlamaForCausalLM-3.2",
|
||||
"trl-internal-testing/tiny-MistralForCausalLM-0.2",
|
||||
],
|
||||
)
|
||||
def test_sft_trainer_transformers_mp_gc(self, model_name, packing, gradient_checkpointing_kwargs):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Simply tests if passing a transformers model to `SFTTrainer` loads and runs the trainer as expected in mixed
|
||||
precision + different scenarios of gradient_checkpointing.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
training_args = SFTConfig(
|
||||
output_dir=self.tmp_dir,
|
||||
logging_strategy="no",
|
||||
report_to="none",
|
||||
per_device_train_batch_size=2,
|
||||
max_steps=10,
|
||||
packing=packing,
|
||||
max_length=self.max_length,
|
||||
fp16=True, # this is sufficient to enable amp
|
||||
gradient_checkpointing=True,
|
||||
gradient_checkpointing_kwargs=gradient_checkpointing_kwargs,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_name)
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
|
||||
|
||||
trainer = SFTTrainer(
|
||||
model,
|
||||
args=training_args,
|
||||
processing_class=tokenizer,
|
||||
train_dataset=self.train_dataset,
|
||||
eval_dataset=self.eval_dataset,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
trainer.train()
|
||||
|
||||
release_memory(model, trainer)
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
|
||||
"gradient_checkpointing_kwargs", [None, {"use_reentrant": False}, {"use_reentrant": True}]
|
||||
)
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize("packing", [True, False])
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
|
||||
"model_name",
|
||||
[
|
||||
"trl-internal-testing/tiny-LlamaForCausalLM-3.2",
|
||||
"trl-internal-testing/tiny-MistralForCausalLM-0.2",
|
||||
],
|
||||
)
|
||||
@require_peft
|
||||
def test_sft_trainer_transformers_mp_gc_peft(self, model_name, packing, gradient_checkpointing_kwargs):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Simply tests if passing a transformers model + PEFT to `SFTTrainer` loads and runs the trainer as expected in
|
||||
mixed precision + different scenarios of gradient_checkpointing.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
training_args = SFTConfig(
|
||||
output_dir=self.tmp_dir,
|
||||
logging_strategy="no",
|
||||
report_to="none",
|
||||
per_device_train_batch_size=2,
|
||||
max_steps=10,
|
||||
packing=packing,
|
||||
max_length=self.max_length,
|
||||
fp16=True, # this is sufficient to enable amp
|
||||
gradient_checkpointing=True,
|
||||
gradient_checkpointing_kwargs=gradient_checkpointing_kwargs,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_name)
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
|
||||
|
||||
trainer = SFTTrainer(
|
||||
model,
|
||||
args=training_args,
|
||||
processing_class=tokenizer,
|
||||
train_dataset=self.train_dataset,
|
||||
eval_dataset=self.eval_dataset,
|
||||
peft_config=self.peft_config,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
assert isinstance(trainer.model, PeftModel)
|
||||
|
||||
trainer.train()
|
||||
|
||||
release_memory(model, trainer)
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize("device_map", [{"": 0}, "auto"])
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
|
||||
"gradient_checkpointing_kwargs", [None, {"use_reentrant": False}, {"use_reentrant": True}]
|
||||
)
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize("packing", [True, False])
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
|
||||
"model_name",
|
||||
[
|
||||
"trl-internal-testing/tiny-LlamaForCausalLM-3.2",
|
||||
"trl-internal-testing/tiny-MistralForCausalLM-0.2",
|
||||
],
|
||||
)
|
||||
@require_torch_multi_accelerator
|
||||
def test_sft_trainer_transformers_mp_gc_device_map(
|
||||
self, model_name, packing, gradient_checkpointing_kwargs, device_map
|
||||
):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Simply tests if passing a transformers model to `SFTTrainer` loads and runs the trainer as expected in mixed
|
||||
precision + different scenarios of gradient_checkpointing (single, multi-gpu, etc).
|
||||
"""
|
||||
training_args = SFTConfig(
|
||||
output_dir=self.tmp_dir,
|
||||
logging_strategy="no",
|
||||
report_to="none",
|
||||
per_device_train_batch_size=2,
|
||||
max_steps=10,
|
||||
packing=packing,
|
||||
max_length=self.max_length,
|
||||
fp16=True, # this is sufficient to enable amp
|
||||
gradient_checkpointing=True,
|
||||
gradient_checkpointing_kwargs=gradient_checkpointing_kwargs,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_name, device_map=device_map)
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
|
||||
|
||||
trainer = SFTTrainer(
|
||||
model,
|
||||
args=training_args,
|
||||
processing_class=tokenizer,
|
||||
train_dataset=self.train_dataset,
|
||||
eval_dataset=self.eval_dataset,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
trainer.train()
|
||||
|
||||
release_memory(model, trainer)
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
|
||||
"gradient_checkpointing_kwargs", [None, {"use_reentrant": False}, {"use_reentrant": True}]
|
||||
)
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize("packing", [True, False])
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
|
||||
"model_name",
|
||||
[
|
||||
"trl-internal-testing/tiny-LlamaForCausalLM-3.2",
|
||||
"trl-internal-testing/tiny-MistralForCausalLM-0.2",
|
||||
],
|
||||
)
|
||||
@require_peft
|
||||
@require_bitsandbytes
|
||||
def test_sft_trainer_transformers_mp_gc_peft_qlora(self, model_name, packing, gradient_checkpointing_kwargs):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Simply tests if passing a transformers model + PEFT + bnb to `SFTTrainer` loads and runs the trainer as
|
||||
expected in mixed precision + different scenarios of gradient_checkpointing.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
training_args = SFTConfig(
|
||||
output_dir=self.tmp_dir,
|
||||
logging_strategy="no",
|
||||
report_to="none",
|
||||
per_device_train_batch_size=2,
|
||||
max_steps=10,
|
||||
packing=packing,
|
||||
max_length=self.max_length,
|
||||
fp16=True, # this is sufficient to enable amp
|
||||
gradient_checkpointing=True,
|
||||
gradient_checkpointing_kwargs=gradient_checkpointing_kwargs,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
quantization_config = BitsAndBytesConfig(load_in_4bit=True, bnb_4bit_compute_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_name, quantization_config=quantization_config)
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
|
||||
|
||||
trainer = SFTTrainer(
|
||||
model,
|
||||
args=training_args,
|
||||
processing_class=tokenizer,
|
||||
train_dataset=self.train_dataset,
|
||||
eval_dataset=self.eval_dataset,
|
||||
peft_config=self.peft_config,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
assert isinstance(trainer.model, PeftModel)
|
||||
|
||||
trainer.train()
|
||||
|
||||
release_memory(model, trainer)
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize("packing", [True, False])
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
|
||||
"model_name",
|
||||
[
|
||||
"trl-internal-testing/tiny-LlamaForCausalLM-3.2",
|
||||
"trl-internal-testing/tiny-MistralForCausalLM-0.2",
|
||||
],
|
||||
)
|
||||
@require_peft
|
||||
@require_bitsandbytes
|
||||
def test_sft_trainer_with_chat_format_qlora(self, model_name, packing):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Simply tests if using setup_chat_format with a transformers model + peft + bnb config to `SFTTrainer` loads and
|
||||
runs the trainer as expected.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
train_dataset = load_dataset("trl-internal-testing/dolly-chatml-sft", split="train")
|
||||
|
||||
training_args = SFTConfig(
|
||||
packing=packing,
|
||||
max_length=self.max_length,
|
||||
output_dir=self.tmp_dir,
|
||||
logging_strategy="no",
|
||||
report_to="none",
|
||||
per_device_train_batch_size=2,
|
||||
max_steps=10,
|
||||
fp16=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
quantization_config = BitsAndBytesConfig(load_in_4bit=True, bnb_4bit_compute_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_name, quantization_config=quantization_config)
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
|
||||
|
||||
trainer = SFTTrainer(
|
||||
model,
|
||||
args=training_args,
|
||||
processing_class=tokenizer,
|
||||
train_dataset=train_dataset,
|
||||
peft_config=self.peft_config,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
assert isinstance(trainer.model, PeftModel)
|
||||
|
||||
trainer.train()
|
||||
|
||||
release_memory(model, trainer)
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize("packing", [True, False])
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
|
||||
"model_name",
|
||||
[
|
||||
"trl-internal-testing/tiny-LlamaForCausalLM-3.2",
|
||||
"trl-internal-testing/tiny-MistralForCausalLM-0.2",
|
||||
],
|
||||
)
|
||||
@require_liger_kernel
|
||||
def test_sft_trainer_with_liger(self, model_name, packing):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Tests if passing use_liger=True to SFTConfig loads and runs the trainer with AutoLigerKernelForCausalLM as
|
||||
expected.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
import importlib
|
||||
|
||||
def cleanup_liger_patches(trainer):
|
||||
"""Clean up liger_kernel patches by reloading the model's specific module"""
|
||||
try:
|
||||
# Get the specific module that was used by the trainer's model
|
||||
module_path = trainer.model.__module__
|
||||
reload_module = importlib.import_module(module_path)
|
||||
importlib.reload(reload_module)
|
||||
except Exception:
|
||||
pass # Continue if reload fails
|
||||
|
||||
training_args = SFTConfig(
|
||||
output_dir=self.tmp_dir,
|
||||
logging_strategy="no",
|
||||
report_to="none",
|
||||
per_device_train_batch_size=2,
|
||||
max_steps=2,
|
||||
packing=packing,
|
||||
max_length=self.max_length,
|
||||
use_liger_kernel=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
trainer = SFTTrainer(
|
||||
model_name,
|
||||
args=training_args,
|
||||
train_dataset=self.train_dataset,
|
||||
eval_dataset=self.eval_dataset,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Ensure cleanup of liger patches after the test
|
||||
try:
|
||||
trainer.train()
|
||||
release_memory(trainer.model, trainer)
|
||||
finally:
|
||||
cleanup_liger_patches(trainer)
|
||||
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize("packing", [True, False])
|
||||
@pytest.mark.parametrize(
|
||||
"model_name",
|
||||
[
|
||||
"trl-internal-testing/tiny-LlamaForCausalLM-3.2",
|
||||
"trl-internal-testing/tiny-MistralForCausalLM-0.2",
|
||||
],
|
||||
)
|
||||
@require_torch_accelerator
|
||||
def test_train_offloading(self, model_name, packing):
|
||||
"""Test that activation offloading works with SFTTrainer."""
|
||||
# Initialize the trainer
|
||||
training_args = SFTConfig(
|
||||
output_dir=self.tmp_dir,
|
||||
activation_offloading=True,
|
||||
report_to="none",
|
||||
per_device_train_batch_size=2,
|
||||
max_steps=2,
|
||||
packing=packing,
|
||||
max_length=self.max_length,
|
||||
)
|
||||
trainer = SFTTrainer(
|
||||
model=model_name, args=training_args, train_dataset=self.train_dataset, eval_dataset=self.eval_dataset
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Save the initial parameters to compare them later
|
||||
previous_trainable_params = {n: param.clone() for n, param in trainer.model.named_parameters()}
|
||||
|
||||
# Train the model
|
||||
trainer.train()
|
||||
|
||||
# Check that the training loss is not None
|
||||
assert trainer.state.log_history[-1]["train_loss"] is not None
|
||||
|
||||
# Check the params have changed
|
||||
for n, param in previous_trainable_params.items():
|
||||
new_param = trainer.model.get_parameter(n)
|
||||
assert not torch.allclose(param, new_param), f"Parameter {n} has not changed"
|
||||
|
||||
release_memory(trainer.model, trainer)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -11,13 +11,12 @@
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
import pytest
|
||||
from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoModelForSequenceClassification, AutoTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
from trl import (
|
||||
BCOConfig,
|
||||
BCOTrainer,
|
||||
CPOConfig,
|
||||
CPOTrainer,
|
||||
DPOConfig,
|
||||
@ -39,58 +38,10 @@ from trl import (
|
||||
XPOTrainer,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
from .testing_utils import TrlTestCase, require_sklearn
|
||||
from .testing_utils import TrlTestCase
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class TestTrainerArg(TrlTestCase):
|
||||
@require_sklearn
|
||||
def test_bco(self):
|
||||
model_id = "trl-internal-testing/tiny-Qwen2ForCausalLM-2.5"
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_id)
|
||||
dataset = load_dataset("trl-internal-testing/zen", "standard_unpaired_preference", split="train")
|
||||
training_args = BCOConfig(
|
||||
self.tmp_dir,
|
||||
max_length=256,
|
||||
max_prompt_length=64,
|
||||
max_completion_length=64,
|
||||
beta=0.5,
|
||||
label_pad_token_id=-99,
|
||||
padding_value=-99,
|
||||
truncation_mode="keep_start",
|
||||
# generate_during_eval=True, # ignore this one, it requires wandb
|
||||
is_encoder_decoder=True,
|
||||
precompute_ref_log_probs=True,
|
||||
model_init_kwargs={"trust_remote_code": True},
|
||||
ref_model_init_kwargs={"trust_remote_code": True},
|
||||
dataset_num_proc=4,
|
||||
prompt_sample_size=512,
|
||||
min_density_ratio=0.2,
|
||||
max_density_ratio=20.0,
|
||||
)
|
||||
trainer = BCOTrainer(
|
||||
model=model_id,
|
||||
ref_model=model_id,
|
||||
args=training_args,
|
||||
train_dataset=dataset,
|
||||
processing_class=tokenizer,
|
||||
)
|
||||
assert trainer.args.max_length == 256
|
||||
assert trainer.args.max_prompt_length == 64
|
||||
assert trainer.args.max_completion_length == 64
|
||||
assert trainer.args.beta == 0.5
|
||||
assert trainer.args.label_pad_token_id == -99
|
||||
assert trainer.args.padding_value == -99
|
||||
assert trainer.args.truncation_mode == "keep_start"
|
||||
# self.assertEqual(trainer.args.generate_during_eval, True)
|
||||
assert trainer.args.is_encoder_decoder
|
||||
assert trainer.args.precompute_ref_log_probs
|
||||
assert trainer.args.model_init_kwargs == {"trust_remote_code": True}
|
||||
assert trainer.args.ref_model_init_kwargs == {"trust_remote_code": True}
|
||||
assert trainer.args.dataset_num_proc == 4
|
||||
assert trainer.args.prompt_sample_size == 512
|
||||
assert trainer.args.min_density_ratio == 0.2
|
||||
assert trainer.args.max_density_ratio == 20.0
|
||||
|
||||
def test_cpo(self):
|
||||
model_id = "trl-internal-testing/tiny-Qwen2ForCausalLM-2.5"
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_id)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -11,6 +11,7 @@
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
import pytest
|
||||
from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoModelForSequenceClassification, AutoTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
@ -20,18 +20,6 @@ from typing import TYPE_CHECKING
|
||||
from .import_utils import _LazyModule
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if sys.version_info[:2] == (3, 9):
|
||||
warnings.warn(
|
||||
(
|
||||
"Support for Python 3.9 will be dropped in the next release "
|
||||
"(after its end-of-life on October 31, 2025). "
|
||||
"Please upgrade to Python 3.10 or newer."
|
||||
),
|
||||
category=FutureWarning,
|
||||
stacklevel=2,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
__version__ = version("trl")
|
||||
except PackageNotFoundError:
|
||||
|
||||
70
trl/core.py
70
trl/core.py
@ -1,70 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Copyright 2020-2025 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
from typing import Optional
|
||||
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from accelerate import logging
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
logger = logging.get_logger(__name__)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def masked_mean(values: torch.Tensor, mask: torch.Tensor, axis: Optional[bool] = None) -> torch.Tensor:
|
||||
"""Compute mean of tensor with a masked values."""
|
||||
if axis is not None:
|
||||
return (values * mask).sum(axis=axis) / mask.sum(axis=axis)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return (values * mask).sum() / mask.sum()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def masked_var(values: torch.Tensor, mask: torch.Tensor, unbiased: bool = True) -> torch.Tensor:
|
||||
"""Compute variance of tensor with masked values."""
|
||||
mean = masked_mean(values, mask)
|
||||
centered_values = values - mean
|
||||
variance = masked_mean(centered_values**2, mask)
|
||||
if unbiased:
|
||||
mask_sum = mask.sum()
|
||||
if mask_sum == 0:
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
"The sum of the mask is zero, which can happen when `mini_batch_size=1`;"
|
||||
"try increase the `mini_batch_size` or `gradient_accumulation_steps`"
|
||||
)
|
||||
# note that if mask_sum == 1, then there is a division by zero issue
|
||||
# to avoid it you just need to use a larger minibatch_size
|
||||
bessel_correction = mask_sum / (mask_sum - 1)
|
||||
variance = variance * bessel_correction
|
||||
return variance
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def masked_whiten(values: torch.Tensor, mask: torch.Tensor, shift_mean: bool = True) -> torch.Tensor:
|
||||
"""Whiten values with masked values."""
|
||||
mean, var = masked_mean(values, mask), masked_var(values, mask)
|
||||
whitened = (values - mean) * torch.rsqrt(var + 1e-8)
|
||||
if not shift_mean:
|
||||
whitened += mean
|
||||
return whitened
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class LengthSampler:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Samples a length
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, min_value: int, max_value: int):
|
||||
self.values = list(range(min_value, max_value))
|
||||
|
||||
def __call__(self) -> int:
|
||||
return np.random.choice(self.values)
|
||||
@ -14,9 +14,9 @@
|
||||
|
||||
import copy
|
||||
from collections import defaultdict, deque
|
||||
from collections.abc import Sequence
|
||||
from collections.abc import Callable, Sequence
|
||||
from itertools import takewhile
|
||||
from typing import Any, Callable, Optional, TypeVar, Union
|
||||
from typing import Any, TypeVar
|
||||
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
import pyarrow as pa
|
||||
@ -185,8 +185,8 @@ def is_conversational(example: dict[str, Any]) -> bool:
|
||||
|
||||
def apply_chat_template(
|
||||
example: dict[str, list[dict[str, str]]],
|
||||
tokenizer: Union[PreTrainedTokenizerBase, ProcessorMixin],
|
||||
tools: Optional[list[Union[dict, Callable]]] = None,
|
||||
tokenizer: PreTrainedTokenizerBase | ProcessorMixin,
|
||||
tools: list[dict | Callable] | None = None,
|
||||
**template_kwargs,
|
||||
) -> dict[str, str]:
|
||||
r"""
|
||||
@ -251,7 +251,7 @@ def apply_chat_template(
|
||||
# DeepSeek-R1 inserts a <tool_call> token when using `add_generation_prompt`, which can cause discrepancies
|
||||
# between the prompt alone and the combined prompt+completion. To ensure consistency, we extract the
|
||||
# common prefix between the two. In most cases, this is a no-op.
|
||||
prompt = "".join(x for x, _ in takewhile(lambda x: x[0] == x[1], zip(prompt, prompt_chosen)))
|
||||
prompt = "".join(x for x, _ in takewhile(lambda x: x[0] == x[1], zip(prompt, prompt_chosen, strict=False)))
|
||||
|
||||
chosen = prompt_chosen[len(prompt) :]
|
||||
if "rejected" in example and "prompt" in example: # explicit prompt
|
||||
@ -263,7 +263,9 @@ def apply_chat_template(
|
||||
**template_kwargs,
|
||||
)
|
||||
# Handle DeepSeek-R1 <tool_call> token, see the above comment for details
|
||||
prompt = "".join(x for x, _ in takewhile(lambda x: x[0] == x[1], zip(prompt, prompt_rejected)))
|
||||
prompt = "".join(
|
||||
x for x, _ in takewhile(lambda x: x[0] == x[1], zip(prompt, prompt_rejected, strict=False))
|
||||
)
|
||||
rejected = prompt_rejected[len(prompt) :]
|
||||
if "completion" in example:
|
||||
prompt_completion = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
|
||||
@ -274,7 +276,9 @@ def apply_chat_template(
|
||||
**template_kwargs,
|
||||
)
|
||||
# Handle DeepSeek-R1 <tool_call> token, see the above comment for details
|
||||
prompt = "".join(x for x, _ in takewhile(lambda x: x[0] == x[1], zip(prompt, prompt_completion)))
|
||||
prompt = "".join(
|
||||
x for x, _ in takewhile(lambda x: x[0] == x[1], zip(prompt, prompt_completion, strict=False))
|
||||
)
|
||||
completion = prompt_completion[len(prompt) :]
|
||||
else: # implicit prompt case
|
||||
if "chosen" in example:
|
||||
@ -315,7 +319,7 @@ def apply_chat_template(
|
||||
def maybe_apply_chat_template(
|
||||
example: dict[str, list[dict[str, str]]],
|
||||
tokenizer: PreTrainedTokenizerBase,
|
||||
tools: Optional[list[Union[dict, Callable]]] = None,
|
||||
tools: list[dict | Callable] | None = None,
|
||||
**template_kwargs: Any,
|
||||
) -> dict[str, str]:
|
||||
r"""
|
||||
@ -339,7 +343,7 @@ def maybe_apply_chat_template(
|
||||
to the chat template renderer.
|
||||
tokenizer ([`~transformers.PreTrainedTokenizerBase`]):
|
||||
Tokenizer to apply the chat template with.
|
||||
tools (`list[Union[dict, Callable]]`, *optional*):
|
||||
tools (`list[dict | Callable]`, *optional*):
|
||||
A list of tools (callable functions) that will be accessible to the model. If the template does not support
|
||||
function calling, this argument will have no effect.
|
||||
**template_kwargs (`Any`, *optional*):
|
||||
@ -388,7 +392,7 @@ def _unpair_row(examples: list[dict[str, list[dict[str, str]]]]) -> list[dict[st
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def unpair_preference_dataset(
|
||||
dataset: DatasetType, num_proc: Optional[int] = None, desc: Optional[str] = None
|
||||
dataset: DatasetType, num_proc: int | None = None, desc: str | None = None
|
||||
) -> DatasetType:
|
||||
r"""
|
||||
Unpair a preference dataset.
|
||||
@ -431,7 +435,7 @@ def unpair_preference_dataset(
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def maybe_unpair_preference_dataset(
|
||||
dataset: DatasetType, num_proc: Optional[int] = None, desc: Optional[str] = None
|
||||
dataset: DatasetType, num_proc: int | None = None, desc: str | None = None
|
||||
) -> DatasetType:
|
||||
r"""
|
||||
Unpair a preference dataset if it is paired.
|
||||
@ -663,7 +667,7 @@ def _pack_bfd(examples: pa.Table, seq_length: int) -> pa.Table:
|
||||
|
||||
# Bin is represented as a dict (of example ids and sum of their lengths) to allow in-place updates
|
||||
bins: list[dict] = []
|
||||
for length, idx in zip(lengths.field(0).to_numpy(), lengths.field(1).to_numpy()):
|
||||
for length, idx in zip(lengths.field(0).to_numpy(), lengths.field(1).to_numpy(), strict=True):
|
||||
space = segment_tree.search(length)
|
||||
|
||||
if space < seq_length:
|
||||
@ -725,7 +729,7 @@ def _pack_wrapped(examples: pa.Table, seq_length: int) -> pa.Table:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def pack_dataset(
|
||||
dataset: DatasetType, seq_length: int, strategy: str = "bfd", map_kwargs: Optional[dict[str, Any]] = None
|
||||
dataset: DatasetType, seq_length: int, strategy: str = "bfd", map_kwargs: dict[str, Any] | None = None
|
||||
) -> DatasetType:
|
||||
r"""
|
||||
Pack sequences in a dataset into chunks of size `seq_length`.
|
||||
@ -780,9 +784,7 @@ def pack_dataset(
|
||||
return dataset
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def truncate_dataset(
|
||||
dataset: DatasetType, max_length: int, map_kwargs: Optional[dict[str, Any]] = None
|
||||
) -> DatasetType:
|
||||
def truncate_dataset(dataset: DatasetType, max_length: int, map_kwargs: dict[str, Any] | None = None) -> DatasetType:
|
||||
r"""
|
||||
Truncate sequences in a dataset to a specified `max_length`.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -13,7 +13,7 @@
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
from dataclasses import dataclass, field
|
||||
from typing import Any, Optional
|
||||
from typing import Any
|
||||
|
||||
from transformers import TrainingArguments
|
||||
|
||||
@ -93,7 +93,7 @@ class BCOConfig(TrainingArguments):
|
||||
"help": "If True, use gradient checkpointing to save memory at the expense of slower backward pass."
|
||||
},
|
||||
)
|
||||
bf16: Optional[bool] = field(
|
||||
bf16: bool | None = field(
|
||||
default=None,
|
||||
metadata={
|
||||
"help": "Whether to use bf16 (mixed) precision instead of 32-bit. Requires Ampere or higher NVIDIA "
|
||||
@ -102,21 +102,21 @@ class BCOConfig(TrainingArguments):
|
||||
},
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
max_length: Optional[int] = field(
|
||||
max_length: int | None = field(
|
||||
default=1024,
|
||||
metadata={
|
||||
"help": "Maximum length of the sequences (prompt + completion) in the batch. "
|
||||
"This argument is required if you want to use the default data collator."
|
||||
},
|
||||
)
|
||||
max_prompt_length: Optional[int] = field(
|
||||
max_prompt_length: int | None = field(
|
||||
default=512,
|
||||
metadata={
|
||||
"help": "Maximum length of the prompt. "
|
||||
"This argument is required if you want to use the default data collator."
|
||||
},
|
||||
)
|
||||
max_completion_length: Optional[int] = field(
|
||||
max_completion_length: int | None = field(
|
||||
default=None,
|
||||
metadata={
|
||||
"help": "Maximum length of the completion. This argument is required if you want to use the "
|
||||
@ -136,7 +136,7 @@ class BCOConfig(TrainingArguments):
|
||||
"help": "Label pad token id. This argument is required if you want to use the default data collator."
|
||||
},
|
||||
)
|
||||
padding_value: Optional[int] = field(
|
||||
padding_value: int | None = field(
|
||||
default=None,
|
||||
metadata={"help": "Padding value to use. If `None`, the padding value of the tokenizer is used."},
|
||||
)
|
||||
@ -159,7 +159,7 @@ class BCOConfig(TrainingArguments):
|
||||
"to W&B during evaluation."
|
||||
},
|
||||
)
|
||||
is_encoder_decoder: Optional[bool] = field(
|
||||
is_encoder_decoder: bool | None = field(
|
||||
default=None,
|
||||
metadata={
|
||||
"help": "When using the `model_init` argument (callable) to instantiate the model instead of the "
|
||||
@ -175,21 +175,21 @@ class BCOConfig(TrainingArguments):
|
||||
"needed."
|
||||
},
|
||||
)
|
||||
model_init_kwargs: Optional[dict[str, Any]] = field(
|
||||
model_init_kwargs: dict[str, Any] | None = field(
|
||||
default=None,
|
||||
metadata={
|
||||
"help": "Keyword arguments to pass to `AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained` when instantiating the "
|
||||
"model from a string."
|
||||
},
|
||||
)
|
||||
ref_model_init_kwargs: Optional[dict[str, Any]] = field(
|
||||
ref_model_init_kwargs: dict[str, Any] | None = field(
|
||||
default=None,
|
||||
metadata={
|
||||
"help": "Keyword arguments to pass to `AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained` when instantiating the "
|
||||
"reference model from a string."
|
||||
},
|
||||
)
|
||||
dataset_num_proc: Optional[int] = field(
|
||||
dataset_num_proc: int | None = field(
|
||||
default=None,
|
||||
metadata={"help": "Number of processes to use for processing the dataset."},
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -18,10 +18,11 @@ import random
|
||||
import textwrap
|
||||
import warnings
|
||||
from collections import defaultdict
|
||||
from collections.abc import Callable
|
||||
from contextlib import contextmanager, nullcontext
|
||||
from operator import itemgetter
|
||||
from pathlib import Path
|
||||
from typing import TYPE_CHECKING, Any, Callable, Literal, Optional, Union
|
||||
from typing import TYPE_CHECKING, Any, Literal, Optional
|
||||
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
import pandas as pd
|
||||
@ -96,19 +97,21 @@ def _tokenize(
|
||||
prompt_tokenized = tokenizer(batch["prompt"], add_special_tokens=False)
|
||||
prompt_input_ids = prompt_tokenized["input_ids"]
|
||||
prompt_attention_mask = prompt_tokenized["attention_mask"]
|
||||
prompt_and_completion = [prompt + completion for prompt, completion in zip(batch["prompt"], batch["completion"])]
|
||||
prompt_and_completion = [
|
||||
prompt + completion for prompt, completion in zip(batch["prompt"], batch["completion"], strict=True)
|
||||
]
|
||||
full_tokenized = tokenizer(prompt_and_completion, add_special_tokens=False)
|
||||
full_input_ids = full_tokenized["input_ids"]
|
||||
full_attention_mask = full_tokenized["attention_mask"]
|
||||
|
||||
answer_input_ids = [f[len(p) :] for f, p in zip(full_input_ids, prompt_input_ids)]
|
||||
answer_attention_mask = [f[len(p) :] for f, p in zip(full_attention_mask, prompt_attention_mask)]
|
||||
answer_input_ids = [f[len(p) :] for f, p in zip(full_input_ids, prompt_input_ids, strict=True)]
|
||||
answer_attention_mask = [f[len(p) :] for f, p in zip(full_attention_mask, prompt_attention_mask, strict=True)]
|
||||
|
||||
# Concat tokens to form `enc(a) + enc(a + b)[len(enc(a)):]`
|
||||
full_concat_input_ids = [np.concatenate([p, a]) for p, a in zip(prompt_input_ids, answer_input_ids)]
|
||||
full_concat_input_ids = [np.concatenate([p, a]) for p, a in zip(prompt_input_ids, answer_input_ids, strict=True)]
|
||||
# Prepare input tokens for token by token comparison
|
||||
full_input_ids = [np.array(f) for f in full_input_ids]
|
||||
for full, concat in zip(full_input_ids, full_concat_input_ids):
|
||||
for full, concat in zip(full_input_ids, full_concat_input_ids, strict=True):
|
||||
if len(full) != len(concat):
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
"The elements in 'full_input_ids' and 'full_concat_input_ids' must have the same pairwise length."
|
||||
@ -122,19 +125,19 @@ def _tokenize(
|
||||
|
||||
# If tokenized prompt is different than both prompt+answer, then it means the
|
||||
# last token has changed due to merging.
|
||||
for idx, (p, f, r) in enumerate(zip(prompt_input_ids, full_input_ids, response_token_ids_start_idx)):
|
||||
for idx, (p, f, r) in enumerate(zip(prompt_input_ids, full_input_ids, response_token_ids_start_idx, strict=True)):
|
||||
if not np.array_equal(p, f[:r]):
|
||||
response_token_ids_start_idx[idx] -= 1
|
||||
|
||||
prompt_input_ids = [f[:r] for f, r in zip(full_input_ids, response_token_ids_start_idx)]
|
||||
prompt_attention_mask = [f[:r] for f, r in zip(full_attention_mask, response_token_ids_start_idx)]
|
||||
prompt_input_ids = [f[:r] for f, r in zip(full_input_ids, response_token_ids_start_idx, strict=True)]
|
||||
prompt_attention_mask = [f[:r] for f, r in zip(full_attention_mask, response_token_ids_start_idx, strict=True)]
|
||||
|
||||
for p, m in zip(prompt_input_ids, prompt_attention_mask):
|
||||
for p, m in zip(prompt_input_ids, prompt_attention_mask, strict=True):
|
||||
if len(p) != len(m):
|
||||
raise ValueError("Prompt input ids and attention mask should have the same length.")
|
||||
|
||||
answer_input_ids = [f[r:] for f, r in zip(full_input_ids, response_token_ids_start_idx)]
|
||||
answer_attention_mask = [f[r:] for f, r in zip(full_attention_mask, response_token_ids_start_idx)]
|
||||
answer_input_ids = [f[r:] for f, r in zip(full_input_ids, response_token_ids_start_idx, strict=True)]
|
||||
answer_attention_mask = [f[r:] for f, r in zip(full_attention_mask, response_token_ids_start_idx, strict=True)]
|
||||
|
||||
output = dict(
|
||||
prompt_input_ids=prompt_input_ids,
|
||||
@ -341,25 +344,27 @@ class BCOTrainer(BaseTrainer):
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
model: Union[PreTrainedModel, nn.Module, str] = None,
|
||||
ref_model: Optional[Union[PreTrainedModel, nn.Module, str]] = None,
|
||||
model: PreTrainedModel | nn.Module | str = None,
|
||||
ref_model: PreTrainedModel | nn.Module | str | None = None,
|
||||
args: BCOConfig = None,
|
||||
train_dataset: Optional[Dataset] = None,
|
||||
eval_dataset: Optional[Union[Dataset, dict[str, Dataset]]] = None,
|
||||
processing_class: Optional[
|
||||
Union[PreTrainedTokenizerBase, BaseImageProcessor, FeatureExtractionMixin, ProcessorMixin]
|
||||
] = None,
|
||||
data_collator: Optional[DataCollator] = None,
|
||||
model_init: Optional[Callable[[], PreTrainedModel]] = None,
|
||||
callbacks: Optional[list[TrainerCallback]] = None,
|
||||
train_dataset: Dataset | None = None,
|
||||
eval_dataset: Dataset | dict[str, Dataset] | None = None,
|
||||
processing_class: PreTrainedTokenizerBase
|
||||
| BaseImageProcessor
|
||||
| FeatureExtractionMixin
|
||||
| ProcessorMixin
|
||||
| None = None,
|
||||
data_collator: DataCollator | None = None,
|
||||
model_init: Callable[[], PreTrainedModel] | None = None,
|
||||
callbacks: list[TrainerCallback] | None = None,
|
||||
optimizers: tuple[torch.optim.Optimizer, torch.optim.lr_scheduler.LambdaLR] = (None, None),
|
||||
preprocess_logits_for_metrics: Optional[Callable[[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor], torch.Tensor]] = None,
|
||||
peft_config: Optional[dict] = None,
|
||||
compute_metrics: Optional[Callable[[EvalLoopOutput], dict]] = None,
|
||||
model_adapter_name: Optional[str] = None,
|
||||
ref_adapter_name: Optional[str] = None,
|
||||
embedding_func: Optional[Callable] = None,
|
||||
embedding_tokenizer: Optional[PreTrainedTokenizerBase] = None,
|
||||
preprocess_logits_for_metrics: Callable[[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor], torch.Tensor] | None = None,
|
||||
peft_config: dict | None = None,
|
||||
compute_metrics: Callable[[EvalLoopOutput], dict] | None = None,
|
||||
model_adapter_name: str | None = None,
|
||||
ref_adapter_name: str | None = None,
|
||||
embedding_func: Callable | None = None,
|
||||
embedding_tokenizer: PreTrainedTokenizerBase | None = None,
|
||||
):
|
||||
if not os.environ.get("TRL_EXPERIMENTAL_SILENCE"):
|
||||
warnings.warn(
|
||||
@ -818,7 +823,7 @@ class BCOTrainer(BaseTrainer):
|
||||
return embeddings
|
||||
|
||||
def _get_prompt_embeddings(
|
||||
self, batch: dict[str, Union[list, torch.LongTensor]]
|
||||
self, batch: dict[str, list | torch.LongTensor]
|
||||
) -> tuple[torch.FloatTensor, torch.FloatTensor]:
|
||||
"""Extract embeddings from frozen embedding model"""
|
||||
|
||||
@ -947,7 +952,7 @@ class BCOTrainer(BaseTrainer):
|
||||
|
||||
return super().get_train_dataloader()
|
||||
|
||||
def get_eval_dataloader(self, eval_dataset: Optional[Dataset] = None) -> DataLoader:
|
||||
def get_eval_dataloader(self, eval_dataset: Dataset | None = None) -> DataLoader:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Returns the evaluation [`~torch.utils.data.DataLoader`].
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1088,7 +1093,7 @@ class BCOTrainer(BaseTrainer):
|
||||
return (per_token_logps * loss_mask).sum(-1)
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(
|
||||
self, model: nn.Module, batch: dict[str, Union[list, torch.LongTensor]]
|
||||
self, model: nn.Module, batch: dict[str, list | torch.LongTensor]
|
||||
) -> tuple[torch.FloatTensor, torch.FloatTensor, torch.FloatTensor, torch.FloatTensor]:
|
||||
model_kwargs = (
|
||||
{
|
||||
@ -1151,8 +1156,8 @@ class BCOTrainer(BaseTrainer):
|
||||
policy_rejected_logps: torch.FloatTensor,
|
||||
reference_chosen_logps: torch.FloatTensor,
|
||||
reference_rejected_logps: torch.FloatTensor,
|
||||
chosen_embeddings: Optional[torch.FloatTensor],
|
||||
rejected_embeddings: Optional[torch.FloatTensor],
|
||||
chosen_embeddings: torch.FloatTensor | None,
|
||||
rejected_embeddings: torch.FloatTensor | None,
|
||||
do_train: bool = True,
|
||||
) -> tuple[torch.FloatTensor, torch.FloatTensor, torch.FloatTensor, torch.FloatTensor]:
|
||||
"""Compute the BCO loss for a batch of policy and reference model log probabilities.
|
||||
@ -1204,7 +1209,7 @@ class BCOTrainer(BaseTrainer):
|
||||
def get_batch_loss_metrics(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
model,
|
||||
batch: dict[str, Union[list, torch.LongTensor]],
|
||||
batch: dict[str, list | torch.LongTensor],
|
||||
do_train: bool = True,
|
||||
):
|
||||
"""Compute the BCO loss and other metrics for the given batch of inputs for train or test."""
|
||||
@ -1297,11 +1302,11 @@ class BCOTrainer(BaseTrainer):
|
||||
|
||||
def compute_loss(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
model: Union[PreTrainedModel, nn.Module],
|
||||
inputs: dict[str, Union[torch.Tensor, Any]],
|
||||
model: PreTrainedModel | nn.Module,
|
||||
inputs: dict[str, torch.Tensor | Any],
|
||||
return_outputs=False,
|
||||
num_items_in_batch=None,
|
||||
) -> Union[torch.Tensor, tuple[torch.Tensor, dict[str, torch.Tensor]]]:
|
||||
) -> torch.Tensor | tuple[torch.Tensor, dict[str, torch.Tensor]]:
|
||||
compute_loss_context_manager = (
|
||||
autocast(self.accelerator.device.type) if self._peft_has_been_casted_to_bf16 else nullcontext()
|
||||
)
|
||||
@ -1323,7 +1328,7 @@ class BCOTrainer(BaseTrainer):
|
||||
for key, value in metrics.items():
|
||||
self._stored_metrics[train_eval][key].append(value)
|
||||
|
||||
def _get_train_sampler(self, dataset: Optional[Dataset] = None) -> Optional[torch.utils.data.Sampler]:
|
||||
def _get_train_sampler(self, dataset: Dataset | None = None) -> torch.utils.data.Sampler | None:
|
||||
if dataset is None:
|
||||
dataset = self.train_dataset
|
||||
if dataset is None or not has_length(dataset):
|
||||
@ -1379,10 +1384,10 @@ class BCOTrainer(BaseTrainer):
|
||||
|
||||
def prediction_step(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
model: Union[PreTrainedModel, nn.Module],
|
||||
inputs: dict[str, Union[torch.Tensor, Any]],
|
||||
model: PreTrainedModel | nn.Module,
|
||||
inputs: dict[str, torch.Tensor | Any],
|
||||
prediction_loss_only: bool,
|
||||
ignore_keys: Optional[list[str]] = None,
|
||||
ignore_keys: list[str] | None = None,
|
||||
):
|
||||
if ignore_keys is None:
|
||||
if hasattr(model, "config"):
|
||||
@ -1419,8 +1424,8 @@ class BCOTrainer(BaseTrainer):
|
||||
self,
|
||||
dataloader: DataLoader,
|
||||
description: str,
|
||||
prediction_loss_only: Optional[bool] = None,
|
||||
ignore_keys: Optional[list[str]] = None,
|
||||
prediction_loss_only: bool | None = None,
|
||||
ignore_keys: list[str] | None = None,
|
||||
metric_key_prefix: str = "eval",
|
||||
) -> EvalLoopOutput:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
@ -1454,7 +1459,9 @@ class BCOTrainer(BaseTrainer):
|
||||
columns=["Prompt", "Policy", "Ref Model"],
|
||||
data=[
|
||||
[prompt, pol[len(prompt) :], ref[len(prompt) :]]
|
||||
for prompt, pol, ref in zip(target_batch["prompt"], policy_output_decoded, ref_output_decoded)
|
||||
for prompt, pol, ref in zip(
|
||||
target_batch["prompt"], policy_output_decoded, ref_output_decoded, strict=True
|
||||
)
|
||||
],
|
||||
)
|
||||
if "wandb" in self.args.report_to:
|
||||
@ -1473,7 +1480,7 @@ class BCOTrainer(BaseTrainer):
|
||||
|
||||
return initial_output
|
||||
|
||||
def log(self, logs: dict[str, float], start_time: Optional[float] = None) -> None:
|
||||
def log(self, logs: dict[str, float], start_time: float | None = None) -> None:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Log `logs` on the various objects watching training, including stored metrics.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -12,7 +12,6 @@
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
import logging
|
||||
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
@ -13,14 +13,13 @@
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
from dataclasses import dataclass, field
|
||||
from typing import Optional
|
||||
|
||||
from ...trainer.grpo_config import GRPOConfig as _GRPOConfig
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@dataclass
|
||||
class GFPOConfig(_GRPOConfig):
|
||||
num_remains_in_group: Optional[int] = field(
|
||||
num_remains_in_group: int | None = field(
|
||||
default=None,
|
||||
metadata={
|
||||
"help": "number inputs remains after group filter function, `'num_remains_in_group'` must be >=2 if given."
|
||||
|
||||
@ -13,7 +13,8 @@
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
import logging
|
||||
from typing import Any, Callable
|
||||
from collections.abc import Callable
|
||||
from typing import Any
|
||||
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from accelerate.utils import gather_object
|
||||
@ -194,7 +195,7 @@ class GFPOTrainer(_GRPOTrainer):
|
||||
completions_text = self.processing_class.batch_decode(completion_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)
|
||||
if is_conversational(inputs[0]):
|
||||
completions = []
|
||||
for prompt, completion in zip(prompts, completions_text):
|
||||
for prompt, completion in zip(prompts, completions_text, strict=True):
|
||||
bootstrap = prompt.pop()["content"] if prompt[-1]["role"] == "assistant" else ""
|
||||
completions.append([{"role": "assistant", "content": bootstrap + completion}])
|
||||
else:
|
||||
|
||||
Some files were not shown because too many files have changed in this diff Show More
Reference in New Issue
Block a user