8.7 KiB
Training Vision Models using Backbone API
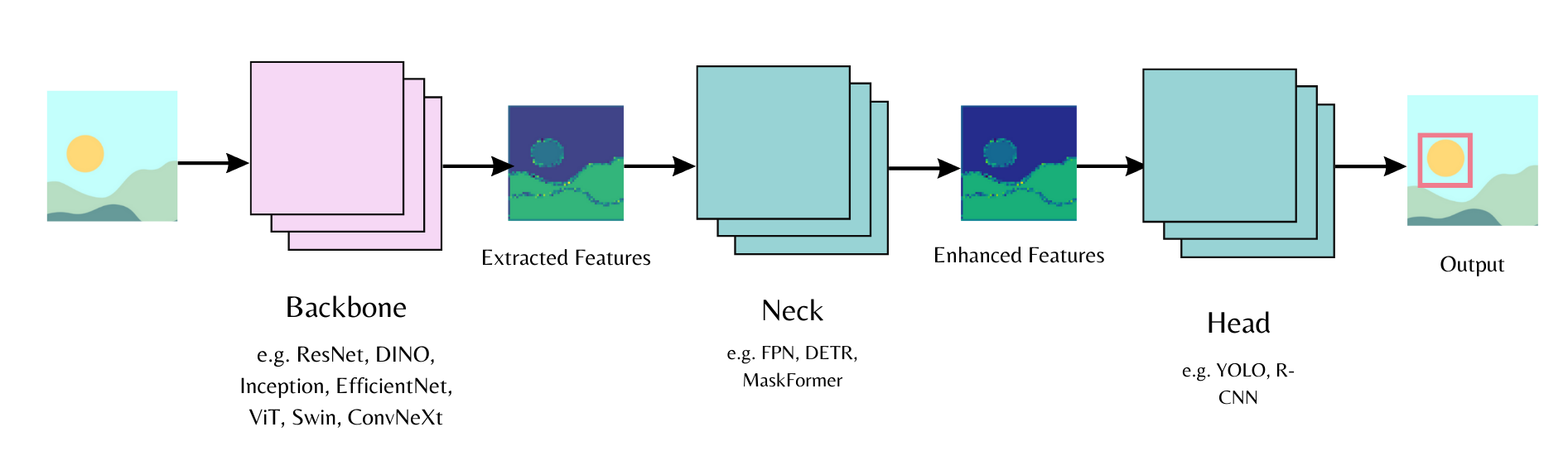
Computer vision workflows follow a common pattern. Use a pre-trained backbone for feature extraction (ViT, DINOv3). Add a "neck" for feature enhancement. Attach a task-specific head (DETR for object detection, MaskFormer for segmentation).
The Transformers library implements these models and the backbone API lets you swap different backbones and heads with minimal code.
This guide combines DINOv3 with ConvNext architecture and a DETR head. You'll train on the license plate detection dataset. DINOv3 delivers the best performance as of this writing.
Note
This model requires access approval. Visit the model repository to request access.
Install trackio for experiment tracking and albumentations for data augmentation. Use the latest transformers version.
pip install -Uq albumentations trackio transformers datasets
Initialize [DetrConfig] with the pre-trained DINOv3 ConvNext backbone. Use num_labels=1 to detect the license plate bounding boxes. Create [DetrForObjectDetection] with this configuration. Freeze the backbone to preserve DINOv3 features without updating weights. Load the [DetrImageProcessor].
from transformers import DetrConfig, DetrForObjectDetection, AutoImageProcessor
config = DetrConfig(backbone="facebook/dinov3-convnext-large-pretrain-lvd1689m",
use_pretrained_backbone=True, use_timm_backbone=False,
num_labels=1, id2label={0: "license_plate"}, label2id={"license_plate": 0})
model = DetrForObjectDetection(config)
for param in model.model.backbone.parameters():
param.requires_grad = False
image_processor = AutoImageProcessor.from_pretrained("facebook/detr-resnet-50")
Load the dataset and split it for training.
from datasets import load_dataset
ds = load_dataset("merve/license-plates")
ds = ds["train"]
ds = ds.train_test_split(test_size=0.05)
train_dataset = ds["train"]
val_dataset = ds["test"]
len(train_dataset)
# 5867
Augment the dataset. Rescale images to a maximum size, flip them, and apply affine transforms. Eliminate invalid bounding boxes and ensure annotations stay clean with rebuild_objects.
import albumentations as A
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
train_aug = A.Compose(
[
A.LongestMaxSize(max_size=1024, p=1.0),
A.HorizontalFlip(p=0.5),
A.Affine(rotate=(-5, 5), shear=(-5, 5), translate_percent=(0.05, 0.05), p=0.5),
],
bbox_params=A.BboxParams(format="coco", label_fields=["category_id"], min_visibility=0.0),
)
def train_transform(batch):
imgs_out, objs_out = [], []
original_imgs, original_objs = batch["image"], batch["objects"]
for i, (img_pil, objs) in enumerate(zip(original_imgs, original_objs)):
img = np.array(img_pil)
labels = [0] * len(objs["bbox"])
out = train_aug(image=img, bboxes=list(objs["bbox"]), category_id=labels)
if len(out["bboxes"]) == 0:
imgs_out.append(img_pil) # if no boxes left after augmentation, use original
objs_out.append(objs)
continue
H, W = out["image"].shape[:2]
clamped = []
for (x, y, w, h) in out["bboxes"]:
x = max(0.0, min(x, W - 1.0))
y = max(0.0, min(y, H - 1.0))
w = max(1.0, min(w, W - x))
h = max(1.0, min(h, H - y))
clamped.append([x, y, w, h])
imgs_out.append(Image.fromarray(out["image"]))
objs_out.append(rebuild_objects(clamped, out["category_id"]))
batch["image"] = imgs_out
batch["objects"] = objs_out
return batch
def rebuild_objects(bboxes, labels):
bboxes = [list(map(float, b)) for b in bboxes]
areas = [float(w*h) for (_, _, w, h) in bboxes]
ids = list(range(len(bboxes)))
return {
"id": ids,
"bbox": bboxes,
"category_id": list(map(int, labels)),
"area": areas,
"iscrowd": [0]*len(bboxes),
}
train_dataset = train_dataset.with_transform(train_transform)
Build COCO-style annotations for the image processor.
import torch
def format_annotations(image, objects, image_id):
n = len(objects["id"])
anns = []
iscrowd_list = objects.get("iscrowd", [0] * n)
area_list = objects.get("area", None)
for i in range(n):
x, y, w, h = objects["bbox"][i]
area = area_list[i] if area_list is not None else float(w * h)
anns.append({
"id": int(objects["id"][i]),
"iscrowd": int(iscrowd_list[i]),
"bbox": [float(x), float(y), float(w), float(h)],
"category_id": int(objects.get("category_id", objects.get("category"))[i]),
"area": float(area),
})
return {"image_id": int(image_id), "annotations": anns}
Create batches in the data collator. Format annotations and pass them with transformed images to the image processor.
def collate_fn(examples):
images = [example["image"] for example in examples]
ann_batch = [format_annotations(example["image"], example["objects"], example["image_id"]) for example in examples]
inputs = image_processor(images=images, annotations=ann_batch, return_tensors="pt")
return inputs
Initialize the [Trainer] and set up [TrainingArguments] for model convergence. Pass datasets, data collator, arguments, and model to Trainer to start training.
from transformers import Trainer, TrainingArguments
training_args = TrainingArguments(
output_dir="./license-plate-detr-dinov3",
per_device_train_batch_size=4,
per_device_eval_batch_size=4,
num_train_epochs=8,
learning_rate=1e-5,
weight_decay=1e-4,
warmup_steps=500,
eval_strategy="steps",
eval_steps=500,
save_total_limit=2,
dataloader_pin_memory=False,
fp16=True,
report_to="trackio",
load_best_model_at_end=True,
remove_unused_columns=False,
push_to_hub=True,
)
trainer = Trainer(
model=model,
args=training_args,
train_dataset=train_dataset,
eval_dataset=val_dataset,
data_collator=collate_fn,
)
trainer.train()
Push the trainer and image processor to the Hub.
trainer.push_to_hub()
image_processor.push_to_hub("merve/license-plate-detr-dinov3")
Test the model with an object detection pipeline.
from transformers import pipeline
obj_detector = pipeline(
"object-detection", model="merve/license-plate-detr-dinov3"
)
results = obj_detector("https://huggingface.co/datasets/merve/vlm_test_images/resolve/main/license-plates.jpg", threshold=0.05)
print(results)
Visualize the results.
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw
import numpy as np
import requests
def plot_results(image, results, threshold):
image = Image.fromarray(np.uint8(image))
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(image)
width, height = image.size
for result in results:
score = result["score"]
label = result["label"]
box = list(result["box"].values())
if score > threshold:
x1, y1, x2, y2 = tuple(box)
draw.rectangle((x1, y1, x2, y2), outline="red")
draw.text((x1 + 5, y1 + 10), f"{score:.2f}", fill="green" if score > 0.7 else "red")
return image
image = Image.open(requests.get("https://huggingface.co/datasets/merve/vlm_test_images/resolve/main/license-plates.jpg", stream=True).raw)
plot_results(image, results, threshold=0.05)