* skip nested deepspeed.zero.Init call
* make fixup
* solve conflict
* solve conflict
* put back local
* use context mangers instead of local thread
* Skip recursive calls to deepspeed.zero.Init
* Skip recursive calls to deepspeed.zero.Init
* back to old notebooks
* make style
* add tensor processing system to separate logic for models
* format refactoring
* small fix
* make some methods private
* move custom methods to processors
* refactor tensor processing
* format fix
* add deformable detr image processor fast
* add fast processor to doc
* fix copies
* nit docstring
* Add tests gpu/cpu and fix docstrings
* fix docstring
* import changes from detr
* fix imports
* rebase and fix
* fix input data format change in detr and rtdetr fast
* add support for openai api image_url input
* change continue to elif
* Explicitely add support for OpenAI/TGI chat format
* rewrite content to transformers chat format and add tests
* Add support for typing of image type in chat templates
* add base64 to possible image types
* refactor nesting
* Fix post process function called in the instance segmentation example of mask2former
* fix description and additional notes for post_process_instance_segmentation of maskformers
* remove white space in maskformers post_process_instance_segmentation doc
* change image.size[::-1] to height and width for clarity in segmentation examples
* add Cambricon MLUs support
* fix mlu device rng state
* up for quality check
* up mlu to support fp16
* fix mlu device dependency error
* fix mlu device dependency error
* enable mlu device for bf16
* fix mlu device memory tracker
* Cambricon support SDPA and flash_attn
* MLU devices : Checks if `mlu` is available via an `cndev-based` check which won't trigger the drivers and leave mlu
* softcapping
* soft cap before the mask
* style
* ...
* super nit
* update
* fixes
* update
* small issue with modular
* fix modular imports
* update
* fixup
* simplify a hell lot
* simplify cleaning imports
* finish fixing
* update our design
* nits
* use a deprecation cycle
* updates
* Fix modular (recursive deps need to always be computed after merges!)
* push
* fix
* update
* fix modular order
* make fix-copies
* updates
* update
* ?
* don't compile for now
* ?
* fix some stuff
* donc!
* fix copies
* update
* fixup
* ?
* fix two tests
* fix?
* for now, don't use head info
* eager when output attentoin and sdpa or flash as it's the simplest behaviour (for our tests as well :))
* fix-copies
* revert sdpa check
* Apply suggestions from code review
Co-authored-by: Cyril Vallez <cyril.vallez@huggingface.co>
* rebase, fix-copies and push
* add a slow integration test
* update the test
* fix left padding issue
* fix test
* remove duplicate scaling
* quality
* add a small test and make sure it works
* 2b
---------
Co-authored-by: Cyril Vallez <cyril.vallez@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Cyril Vallez <cyril.vallez@huggingface.co>
19d58d31f has introduced a context manager to manage subtests of
test_training_gradient_checkpointing. However, test body was not
moved under "with" statement. Thus, while tests are correctly
marked as skipped, test bodies were still executed. In some cases,
as with llama this caused attribute errors.
Fixes: #34722
Fixes: 19d58d31f ("Add MLLama (#33703)")
Signed-off-by: Dmitry Rogozhkin <dmitry.v.rogozhkin@intel.com>
* Add model skeletion with transformers-cli add-new-model-like
* Convert config to modular, add rms_norm_eps, delete clip_qkv
* Convert model to modular, add RMSNorm
* Add flash attention with qk norm and no qkv clipping
* Add decoder layer with RMSNorm after attention/feedforward layers
* Add base and causal model
* Add converter improvements from OLMo repo
* Update weight loading in OLMo to HF converter
* Set correct default for rms_norm_eps
* Set correct pipeline_model_mapping in test
* Run make fixup
* Fix model type
* Re-run modular conversion
* Manually set config docs to fix build errors
* Convert olmo-1124 to olmo_1124 to fix flash attention docs errors
* Start updating tests
* Update tests
* Copy upstream test_eager_matches_sdpa_inference_1_bfloat16 changes to olmo_1124
* Rename input_layernorm and post_attention_layernorm to reflect their ops better
* Use correct tokenizer
* Remove test unsupported by GPT2 tokenizer
* Create GenerationConfig outside of from_pretrained call
* Use simpler init file structure
* Add explicit __all__ to support simplified init
* Make safetensor serialization the default
* Update OLMo November 2024 docs
* Remove FSDP wrapping from sub-models.
* solve conflict trainer.py
* make fixup
* add unit test for fsdp_auto_wrap_policy when using auto_find_batch_size
* put back extract_model_from_parallel
* use transformers unwrap_model
* Update llm_engine.py
- Added support for optional token and max_tokens parameters in the constructor.
- Provided usage examples and detailed documentation for each method.
* save/load sub-configs
* nit forgot these
* fix copies
* move test to common
* use dict for sub-configs
* add load-save-laod test
* clean up modeling check
* oops this are correct keys
* fix some tests, missed some composite configs
* this model was missed
FIX Broken repr of TorchAoConfig
The __repr__ method references a non-existent self.kwargs. This is now
fixed.
There does not appear to be a uniform way of defining __repr__ for
quantization configs. I copied the method as implemented for HQQ:
e2ac16b28a/src/transformers/utils/quantization_config.py (L285-L287)
* Skip DeepSpeed ZeRO Stage 3 model initialization when it is intended to be quantized.
* Propagate the quantization state using a context manager
* make fixup
* Update README_ko.md
Delete the blank paragraph in the language selection button and Edit to synchronize with the English version of README.md
* [i18n-KO] Update README_ko.md
* Additional edit for keep consistency with main [documentation](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/v4.44.2/ko/index). (메인 문서와 일관성 유지를 위한 수정)
* Update README_ko.md
Additional update.
* Change docs link to Korean translated page if it exists.
* Change doc link to korean translated if it exists.
Change the link of doc and delete a row 'migration' of the table Learn more[더 알아보기], since it does not exist in the main version of doc.
* modify a link of the main README.md
from
`https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/index#supported-frameworks`
to
`https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/index#supported-models-and-frameworks`
since the title of 'supported table' changed.
* [i18n-ko] edit links and sync with main `README.md`
* docs/change comment to Korean1
Change English comment to Korean
Co-authored-by: Jihun Lim <31366038+heuristicwave@users.noreply.github.com>
* docs/change comment to Korean2
Change English comment to Korean
Co-authored-by: Jihun Lim <31366038+heuristicwave@users.noreply.github.com>
* revise to original
to seperate `edit_README_ko_md` and `README.md`
* Synchronization with English documentation.
Synchronization with English documentation, and translated a line of comment from English to Korean.
---------
Co-authored-by: Jihun Lim <31366038+heuristicwave@users.noreply.github.com>
* feat: add text support to TensorBoardCallback
* feat: ignore long strings in trainer progress
* docs: add docstring for max_str_len
* style: remove trailing whitespace
---------
Co-authored-by: Marc Sun <57196510+SunMarc@users.noreply.github.com>
* kinda works
* update
* add tests
* update
* use special tokens in processors
* typo
* fix copies
* fix
* fix moshi after rebase
* update
* fix tests
* update
* Update docs/source/en/main_classes/tokenizer.md
Co-authored-by: Arthur <48595927+ArthurZucker@users.noreply.github.com>
* update docs
* test for load time adding tokens
* fix some more tests which are now fetched better
* one more fix
---------
Co-authored-by: Arthur <48595927+ArthurZucker@users.noreply.github.com>
* Update trainer for easier handling of accumulate + proper reporting
* test
* Fixup tests
* Full fix
* Fix style
* rm comment
* Fix tests
* Minimize test + remove py 311 check
* Unused import
* Forward contrib credits from discussions
* Fix reported metrics
* Refactor, good as it's going to get
* rm pad tok id check
* object detection and audio are being annoying
* Fin
* Fin x2
---------
Co-authored-by: Gyanateet Dutta <Ryukijano@users.noreply.github.com>
* blip2 tests
* instructblips
* copies
* fix slow tests
* fix
* uncomment this
* clean up after rebase
* should be model main input
* fix overwritten tests
* oops len should be multiple of frame number
* style
* fix some tests
* Standardize image-text-to-text-models-output
add post_process_image_text_to_text to chameleon and cleanup
Fix legacy kwarg behavior and deprecation warning
add post_process_image_text_to_text to qwen2_vl and llava_onevision
Add post_process_image_text_to_text to idefics3, mllama, pixtral processor
* nit var name post_process_image_text_to_text udop
* nit fix deprecation warnings
* Add image-text-to-text pipeline
* add support for image url in chat template for pipeline
* Reformat to be fully compatible with chat templates
* Add tests chat template
* Fix imports and tests
* Add pipeline tag
* change logic handling of single prompt ans multiple images
* add pipeline mapping to models
* fix batched inference
* fix tests
* Add manual batching for preprocessing
* Fix outputs with nested images
* Add support for all common processing kwargs
* Add default padding when multiple text inputs (batch size>1)
* nit change version deprecation warning
* Add support for text only inference
* add chat_template warnings
* Add pipeline tests and add copied from post process function
* Fix batched pipeline tests
* nit
* Fix pipeline tests blip2
* remove unnecessary max_new_tokens
* revert processing kosmos2 and remove unnecessary max_new_tokens
* fix pipeline tests idefics
* Force try loading processor if pipeline supports it
* revert load_processor change
* hardcode loading only processor
* remove unnecessary try except
* skip imagetexttotext tests for kosmos2 as tiny model causes problems
* Make code clearer
* Address review comments
* remove preprocessing logic from pipeline
* fix fuyu
* add BC resize fuyu
* Move post_process_image_text_to_text to ProcessorMixin
* add guard in post_process
* fix zero shot object detection pipeline
* add support for generator input in pipeline
* nit
* change default image-text-to-text model to llava onevision
* fix owlv2 size dict
* Change legacy deprecation warning to only show when True
* replace total_batched_samples with step while counting grad accum step
* remove unused variable
* simplify condition for update step
* fix format by ruff
* simplify update step condition using accelerator.sync_gradients
* simplify update condition using do_sync_step
* remove print for test
---------
Co-authored-by: Zach Mueller <muellerzr@gmail.com>
* add fast image processor rtdetr
* add gpu/cpu test and fix docstring
* remove prints
* add to doc
* nit docstring
* avoid iterating over images/annotations several times
* change torch typing
* Add image processor fast documentation
* add mamba architecture for gguf
* add logic for weights conversion, some fixes and refactoring
* add lm_head layers, unit test refactoring
* more fixes for tests
* remove lm_head creation
* remove unused comments
* tmp commit
* tmp commit
* cull overwrites of deleted tests
* typo
* more specific docstring
* make fixup
* parameterize at the top?
* correction
* more deletions :D
* tmp commit
* for VLMs too
* fix _check_outputs
* test nit
* make fixup
* fix another flaky
* test_generate_from_inputs_embeds -- handle missing attention mask
* fix repr string format for tokenizer objects
The repr of tokenizer tokens looks confusing and just stupid, like this: `Tokenizer(...), added_tokens_decoder={1: ..., 2: ...}`. The dict that is the value of the added_tokens_decoder attribute is outside of the parentheses of the tokenizer object, whereas all other attributes are inside the parentheses like they should be.
This commit fixes this bug.
* cos: add newline before closing parenthesis of repr string
* potential bug fix for drop path
* variable name change
* forgot to rename the variables
* back to original
* modify dpr properly
* check_copies auto fix
* corresponsing swin2 changes
* auto fix
* linting
* default value for drop_path_rate as 0.0
* Update src/transformers/models/glm/modeling_glm.py
* maskformer fix
* ruff format
* changes made to tf code as well
* lint
---------
Co-authored-by: abhijit deo <167164474+deo-abhijit@users.noreply.github.com>
* Separator in regex
* Standardize separator for relative path in auto generated message
* open() encoding
* Replace `\` on `os.path.abspath`
---------
Co-authored-by: Arthur <48595927+ArthurZucker@users.noreply.github.com>
* feat: Added int conversion and unwrapping
* test: added tests for post_process_keypoint_detection of SuperPointImageProcessor
* docs: changed docs to include post_process_keypoint_detection method and switched from opencv to matplotlib
* test: changed test to not depend on SuperPointModel forward
* test: added missing require_torch decorator
* docs: changed pyplot parameters for the keypoints to be more visible in the example
* tests: changed import torch location to make test_flax and test_tf
* Revert "tests: changed import torch location to make test_flax and test_tf"
This reverts commit 39b32a2f69500bc7af01715fc7beae2260549afe.
* tests: fixed import
* chore: applied suggestions from code review
Co-authored-by: NielsRogge <48327001+NielsRogge@users.noreply.github.com>
* tests: fixed import
* tests: fixed import (bis)
* tests: fixed import (ter)
* feat: added choice of type for target_size and changed tests accordingly
* docs: updated code snippet to reflect the addition of target size type choice in post process method
* tests: fixed imports (...)
* tests: fixed imports (...)
* style: formatting file
* docs: fixed typo from image[0] to image.size[0]
* docs: added output image and fixed some tests
* Update docs/source/en/model_doc/superpoint.md
Co-authored-by: Pavel Iakubovskii <qubvel@gmail.com>
* fix: included SuperPointKeypointDescriptionOutput in TYPE_CHECKING if statement and changed tests results to reflect changes to SuperPoint from absolute keypoints coordinates to relative
* docs: changed SuperPoint's docs to print output instead of just accessing
* style: applied make style
* docs: added missing output type and precision in docstring of post_process_keypoint_detection
* perf: deleted loop to perform keypoint conversion in one statement
* fix: moved keypoint conversion at the end of model forward
* docs: changed SuperPointInterestPointDecoder to SuperPointKeypointDecoder class name and added relative (x, y) coordinates information to its method
* fix: changed type hint
* refactor: removed unnecessary brackets
* revert: SuperPointKeypointDecoder to SuperPointInterestPointDecoder
* Update docs/source/en/model_doc/superpoint.md
Co-authored-by: Pavel Iakubovskii <qubvel@gmail.com>
---------
Co-authored-by: Steven Bucaille <steven.bucaille@buawei.com>
Co-authored-by: NielsRogge <48327001+NielsRogge@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Pavel Iakubovskii <qubvel@gmail.com>
* enable average tokens across devices
* reduce earlier in case model needs it
* simplify if statement
* reformat code to make ruff happy
* add doc for argument: average_tokens_across_devices
* cannot find world size when pytorch is unavailable
* format code
---------
Co-authored-by: Zach Mueller <muellerzr@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Arthur <48595927+ArthurZucker@users.noreply.github.com>
* [docs] update input documentation for MAMBA2 and MISTRAL models to include cache_position and attention_mask details
* [docs] correct input documentation for MISTRAL model to reference `input_ids` instead of `decoder_input_ids`
* [docs] clarify cache_position description in MISTRAL model documentation
* Add _determine_best_metric and new saving logic.
1. Logic to determine the best logic was separated out from
`_save_checkpoint`.
2. In `_maybe_log_save_evaluate`, whether or not a new best metric was
achieved is determined after each evaluation, and if the save strategy
is "best' then the TrainerControl is updated accordingly.
* Added SaveStrategy.
Same as IntervalStrategy, but with a new attribute called BEST.
* IntervalStrategy -> SaveStrategy
* IntervalStratgy -> SaveStrategy for save_strat.
* Interval -> Save in docstring.
* Updated docstring for save_strategy.
* Added SaveStrategy and made according changes.
`save_strategy` previously followed `IntervalStrategy` but now follows
`SaveStrategy`.
Changes were made accordingly to the code and the docstring.
* Changes from `make fixup`.
* Removed redundant metrics argument.
* Added new test_save_best_checkpoint test.
1. Checks for both cases where `metric_for_best_model` is explicitly
provided and when it's not provided.
2. The first case should have two checkpoints saved, whereas the second
should have three saved.
* Changed should_training_end saving logic.
The Trainer saves a checkpoints at the end of training by default as
long as `save_strategy != SaveStrategy.NO`. This condition was modified
to include `SaveStrategy.BEST` because it would be counterintuitive that
we'd only want the best checkpoint to be saved but the last one is as
well.
* `args.metric_for_best_model` default to loss.
* Undo metric_for_best_model update.
* Remove checking metric_for_best_model.
* Added test cases for loss and no metric.
* Added error for metric and changed default best_metric.
* Removed unused import.
* `new_best_metric` -> `is_new_best_metric`
Co-authored-by: Arthur <48595927+ArthurZucker@users.noreply.github.com>
* Applied `is_new_best_metric` to all.
Changes were made for consistency and also to fix a potential bug.
---------
Co-authored-by: Arthur <48595927+ArthurZucker@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Zach Mueller <muellerzr@gmail.com>
* exclude fsdp from delay_optimizer_creation
* add test case for trainer: FSDP mode and fp8 as mixed precision
* rearrange imports
* ruff formatted
* adapt _init_fsdp to fp8
* use _init_fsdp only when resume_from_checkpoint
* In case of FDP, self.layer will be CheckpointWrapper which has no len() method
* delete _init_fsdp
* solve conflict
* fix conflict
* make fixup
* Fix batch size handling in prediction_loop for DataLoaderShard
Updated the prediction_loop method in the Trainer class to correctly handle batch size when using DataLoaderShard. This ensures that the batch size is retrieved from total_batch_size for distributed training scenarios, preventing TypeError related to NoneType during evaluation.
* Update src/transformers/trainer.py
Co-authored-by: Zach Mueller <muellerzr@gmail.com>
* Applied the fix to remove unused imports
---------
Co-authored-by: Zach Mueller <muellerzr@gmail.com>
* Correct the new defaults
* CIs
* add check
* Update utils.py
* Update utils.py
* Add the max_length in generate test checking shape without passing length
* style
* CIs
* fix fx CI issue
When loading a LoRA adapter, so far, there was only a warning when there
were unexpected keys in the checkpoint. Now, there is also a warning
when there are missing keys.
This change is consistent with
https://github.com/huggingface/peft/pull/2118 in PEFT and the planned PR
https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/pull/9622 in diffusers.
Apart from this change, the error message for unexpected keys was
slightly altered for consistency (it should be more readable now). Also,
besides adding a test for the missing keys warning, a test for
unexpected keys warning was also added, as it was missing so far.
* translated gguf.md into chinese
* Apply suggestions from code review
I have updated the PR accordingly.Thank you very much for detailed guidance,and I 'll pay more attention to the details next time.
Co-authored-by: Isotr0py <2037008807@qq.com>
* Apply suggestions from code review
Co-authored-by: Isotr0py <2037008807@qq.com>
---------
Co-authored-by: Isotr0py <2037008807@qq.com>
* Add SynthIDTextWatermarkLogitsProcessor
* esolving comments.
* Resolving comments.
* esolving commits,
* Improving SynthIDWatermark tests.
* switch to PT version
* detector as pretrained model + style
* update training + style
* rebase
* Update logits_process.py
* Improving SynthIDWatermark tests.
* Shift detector training to wikitext negatives and stabilize with lower learning rate.
* Clean up.
* in for 7B
* cleanup
* upport python 3.8.
* README and final cleanup.
* HF Hub upload and initiaze.
* Update requirements for synthid_text.
* Adding SynthIDTextWatermarkDetector.
* Detector testing.
* Documentation changes.
* Copyrights fix.
* Fix detector api.
* ironing out errors
* ironing out errors
* training checks
* make fixup and make fix-copies
* docstrings and add to docs
* copyright
* BC
* test docstrings
* move import
* protect type hints
* top level imports
* watermarking example
* direct imports
* tpr fpr meaning
* process_kwargs
* SynthIDTextWatermarkingConfig docstring
* assert -> exception
* example updates
* no immutable dict (cant be serialized)
* pack fn
* einsum equivalent
* import order
* fix test on gpu
* add detector example
---------
Co-authored-by: Sumedh Ghaisas <sumedhg@google.com>
Co-authored-by: Marc Sun <marc@huggingface.co>
Co-authored-by: sumedhghaisas2 <138781311+sumedhghaisas2@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: raushan <raushan@huggingface.co>
* Enable grad accum fix across all models + trainer fully in forward()
* handle peft case
* Account for DDP: need to run scale tests
* Use accelerator state
* Quality
* Guard
* Experiment w/ only fairseq fix
* Fairseq only
* Revert multiply_grads fix
* Mult by grad accum to fully bring back solution
* Style
* Good to go now
* Skip fx tests for now
* Bookmark
* Working now
* Added Deberta model type for 'add_prefix_space' functionality
* housekeeping
---------
Co-authored-by: Filippos Ventirozos <filippos.ventirozos@autotrader.co.uk>
* Added Example Doc for token classification on all tokenClassificationModels copied from llama
* Refactor code to add code sample docstrings for Gemma and Gemma2 models (including modular Gemma)
* Refactor code to update model checkpoint names for Qwen2 models
* Add option for running ffmpeg_microphone_live as a background process
* Code quality checks for audio_utils
* Code clean up for audio_utils
* Fixing logic in ffmpeg_microphone calls in audio_utils
* Allowing any arbitrary arguments to be passed to ffmpeg_microphone_live
* Formatting
* Fixing last problems with adding ffmpeg_additional_args
* Fixing default arguments and formatting issues
* Fixing comments for ffmpeg_additional_args
* Adding two shorts tests for ffmpeg_microphone_live
* Fixing test bug
* add colorize_depth and matplotlib availability check
* add post_process_depth_estimation for zoedepth + tests
* add post_process_depth_estimation for DPT + tests
* add post_process_depth_estimation in DepthEstimationPipeline & special case for zoedepth
* run `make fixup`
* fix import related error on tests
* fix more import related errors on test
* forgot some `torch` calls in declerations
* remove `torch` call in zoedepth tests that caused error
* updated docs for depth estimation
* small fix for `colorize` input/output types
* remove `colorize_depth`, fix various names, remove matplotlib dependency
* fix formatting
* run fixup
* different images for test
* update examples in `forward` functions
* fixed broken links
* fix output types for docs
* possible format fix inside `<Tip>`
* Readability related updates
Co-authored-by: Pavel Iakubovskii <qubvel@gmail.com>
* Readability related update
* cleanup after merge
* refactor `post_process_depth_estimation` to return dict; simplify ZoeDepth's `post_process_depth_estimation`
* rewrite dict merging to support python 3.8
---------
Co-authored-by: Pavel Iakubovskii <qubvel@gmail.com>
* this worked in normal generation, needs more tests
* fix almost all tests in t5
* nit
* longt5, umt5, mt5
* style
* udop, pix2struct
* more models
* fix some tests
* fix onnx tests
* tracing tests fixed
* compile enabled and tested for t5 models
* fix small bug in slow tests
* [run-slow] t5
* uncomment
* style
* update with new generation refactoring
* nit
* fix copies
* this is the fix, had to change t5 to fix copies
* update
* [run-slow] t5
* [run-slow] t5
* update
* add test for encoder only T5
* clean up after rebase
* fix pop2piano
* add comment
* style
* fix copies after rebase
* fix copies missed this one
* first try
* codestyle
* idefics2 is happy
* [run-slow] llava, llava_next, video_llava, vipllava, llava_next_video, idefics, idefics2, kosmos2, fuyu, blip, blip_2, instructblip, instructblipvideo, paligemma
* fix-copies
* [run-slow] llava, llava_next, video_llava, vipllava, llava_next_video, idefics, idefics2, kosmos2, fuyu, blip, blip_2, instructblip, instructblipvideo
* blip-2 needs to init vision from config
* when was this removed O_o
* minor fix
* tests
* this way?
* tests
* model-agnostic code
* codestyle
* add tests for idefics
* modify general test for VLMs
* no generation test for vlm yet!
* no generation test here also
* wanr in VIT-SDPA if output attn
* add more tests
* user can pass dict as attn impl
* repo consistency
* update
* muicgen
* no prints
* forgot speech enc-dec and clip
* how many composite models we have?
* musicgen meelody is same as mudicgen
* +siglip
* fix tests + add some more
* remove idefics custom overriden code
* make idefics2 automappable
* nits
* skip tests
* doctests
* Update src/transformers/models/idefics2/configuration_idefics2.py
Co-authored-by: amyeroberts <22614925+amyeroberts@users.noreply.github.com>
* Update tests/models/clip/test_modeling_clip.py
Co-authored-by: amyeroberts <22614925+amyeroberts@users.noreply.github.com>
* Update tests/models/idefics2/test_modeling_idefics2.py
Co-authored-by: amyeroberts <22614925+amyeroberts@users.noreply.github.com>
* Update tests/models/idefics2/test_modeling_idefics2.py
Co-authored-by: amyeroberts <22614925+amyeroberts@users.noreply.github.com>
* Update src/transformers/configuration_utils.py
Co-authored-by: amyeroberts <22614925+amyeroberts@users.noreply.github.com>
* major update, no need for automap
* clean up
* add FA2 test
* more tests
* style
* skip tests
* why did these started failing now?
* no attributes for FA2 needed
* one tiny test
* address comment about FA2 false warning
* style
* add new models and resolve conflicts
* fix copies
* let it be this way for now, come back tomorrow to review
* some more fixes
* update
* more updates
* update
* fix copies
* style and tests
* another big update
* fix tests
* fix tests
* update
* another update
* fix tests
* fix copies
* fix tests
---------
Co-authored-by: amyeroberts <22614925+amyeroberts@users.noreply.github.com>
* Trigger UDOP tests
* Try forcing dtype in LayoutLMV3
* Do checks to see where uint8 is getting in
* Do checks to see where uint8 is getting in
* Found it!
* Add .astype(np.float32)
* Remove forced check, make fixup
* Checking where exactly the uint8 creeps in
* More checking on the uint8 issues
* Manually upcast in rescale()
* Remove UDOP trigger
* bookmark
* Bookmark
* Bookmark
* Actually implement
* Pass in kwarg explicitly
* Adjust for if we do or don't have labels
* Bookmark fix for od
* bookmark
* Fin
* closer
* Negate accelerate grad accum div
* Fixup not training long enough
* Add in compute_loss to take full model output
* Document
* compute_loss -> compute_loss_fn
* Add a test
* Refactor
* Refactor
* Uncomment tests
* Update tests/trainer/test_trainer.py
Co-authored-by: Daniel Han <danielhanchen@gmail.com>
---------
Co-authored-by: Daniel Han <danielhanchen@gmail.com>
* Support Llama 3.2 conversion (text models)
Co-authored-by: Omar Sanseviero <osanseviero@gmail.com>
* Fix rope factor
* Update chat template
Initialize from a well-known template.
The guidance is that the changes should be applied to 3.1 models as
well.
* Remove import
* Support Llama Guard 3 conversion
* Tokenizer details
* Fix eos added token in base models
* Fix generation config for base models
* Specify revision for known tokenizers
* Style
* Reuse chat templates for older models
* Improve error when converting tokenizer < Llama 3
---------
Co-authored-by: Omar Sanseviero <osanseviero@gmail.com>
There's a bug on M1 macs with transformer >= 4.43.0 and torch >= 2.1.0, where if a model has tied embeddings, then the fast loading from #31771 causes a bus error when the model is actually run. This can be solved by disabling `_supports_param_buffer_assignment` for these models.
More info in comments in #33357
* fix(Wav2Vec2ForCTC): torch export
Resolves the issue described in #34022 by implementing the
masking of the hidden states using an elementwise multiplication
rather than indexing with assignment.
The torch.export functionality seems to mark the tensor as frozen
even though the update is legal.
This change is a workaround for now to allow the export of the
model as a FxGraph. Further investigation is required to find
the real solution in pytorch.
* [run-slow] hubert, unispeech, unispeech_sat, wav2vec2
* change cpu offload warning for fp8 quantization
* change cpu offload warning for fp4 quantization
* change cpu offload variable name for fp8 and fp4 quantization
Update 'trainer._get_eval_sampler()' to support 'group_by_length' argument
Trainer didn't support grouping by length for evaluation, which made evaluation slow with 'eval_batch_size'>1.
Updated 'trainer._get_eval_sampler()' method was based off of 'trainer._get_train_sampler()'.
* auto-gptq requirement is removed & model is changed & tokenizer pad token is assigned
* values func is changed with extensions & sequence key value bug is fixed
* map key value check is added in ExtensionsTree
* empty trimmed_ids bug is fixed
* tail_id IndexError is fixed
* empty trimmed_ids bug fix is updated for failed test
* too much specific case for specific tokenizer is removed
* input_ids check is updated
* require auto-gptq import is removed
* key error check is changed with empty list check
* empty input_ids check is added
* empty trimmed_ids fix is checked with numel function
* usage change comments are added
* test changes are commented
* comment style and quality bugs are fixed
* test comment style and quality bug is fixed
* Fix FSDP Initialization for resume training
* Added init_fsdp function to work with dummy values
* Fix FSDP initialization for resuming training
* Added CUDA decorator for tests
* Added torch_gpu decorator to FSDP tests
* Fixup for failing code quality tests
* add idefics
* conflicts after merging main
* enable tests but need to fix some
* fix tests
* no print
* fix/skip some slow tests
* continue not skip
* rebasing broken smth, this is the fix
* mistral qna start
* mixtral qna
* oops
* qwen2 qna
* qwen2moe qna
* add missing input embed methods
* add copied to all methods, can't directly from llama due to the prefix
* make top level copied from
* refactor: benchmarks
Based on a discussion with @LysandreJik & @ArthurZucker, the goal of
this PR is to improve transformers' benchmark system.
This is a WIP, for the moment the infrastructure required to make things
work is not ready. Will update the PR description when it is the case.
* feat: add db init in benchmarks CI
* fix: pg_config is missing in runner
* fix: add psql to the runner
* fix: connect info from env vars + PR comments
* refactor: set database as env var
* fix: invalid working directory
* fix: `commit_msg` -> `commit_message`
* fix: git marking checked out repo as unsafe
* feat: add logging
* fix: invalid device
* feat: update grafana dashboard for prod grafana
* feat: add `commit_id` to header table
* feat: commit latest version of dashboard
* feat: move measurements into json field
* feat: remove drop table migration queries
* fix: `torch.arrange` -> `torch.arange`
* fix: add missing `s` to `cache_position` positional argument
* fix: change model
* revert: `cache_positions` -> `cache_position`
* fix: set device for `StaticCache`
* fix: set `StaticCache` dtype
* feat: limit max cache len
* fix script
* raise error on failure!
* not try catch
* try to skip generate compilation
* update
* update docker image!
* update
* update again!@
* update
* updates
* ???
* ??
* use `torch.cuda.synchronize()`
* fix json
* nits
* fix
* fixed!
* f**k
* feat: add TTNT panels
* feat: add try except
---------
Co-authored-by: Arthur Zucker <arthur.zucker@gmail.com>
* Generate using exported model and enable gemma2-2b in ExecuTorch
* [run_slow] gemma, gemma2
* truncate expected output message
* Bump required torch version to support gemma2 export
* [run_slow] gemma, gemma2
---------
Co-authored-by: Guang Yang <guangyang@fb.com>
Allow for hyphenated field names in long-options
argparse converts hyphens into underscores before assignment (e.g., an
option passed as `--long-option` will be stored under `long_option`), So
there is no need to pass options as literal attributes, as in
`--long_option` (with an underscore instead of a hyphen). This commit
ensures that this behavior is respected by `parse_args_into_dataclasses`
as well.
Issue: #33933
Co-authored-by: Daniel Marti <mrtidm@amazon.com>
* add sdpa to OPT
* chore: remove redundant whitespace in OPTDecoder class
* fixup
* bug fix
* add sdpa and attention generate test
* fixup
* Refactor OPTAttention forward method for improved readability and maintainability
* undo refactor for _shape and key,val states
* add OPT to doc, fixup didn't find it for some reason
* change order
* change default attn_implemntation in testing to eager
* [run-slow] opt
* change test_eager_matches_sdpa_generate to the one llama
* Update default attention implementation in testing common
* [run-slow] opt
* remove uneeded print
* [run-slow] opt
* refactor model testers to have attn_implementation="eager"
* [run-slow] opt
* convert test_eager_matches_sdpa_generate to opt-350M
* bug fix when creating mask for opt
* [run-slow] opt
* if layer head mask default to eager
* if head mask is not none fall to eager
* [run-slow] opt
* Update src/transformers/models/opt/modeling_opt.py
Co-authored-by: amyeroberts <22614925+amyeroberts@users.noreply.github.com>
* Clean up Unpack imports (#33631)
clean up Unpack imports
* Fix DPT /Dinov2 sdpa regression on main (#33660)
* fallback to eager if output attentions.
* fix copies
* handle dependency errors in check_imports (#33622)
* handle dependency errors in check_imports
* change log level to warning
* add back self.max_position_embeddings = config.max_position_embeddings (#33550)
* add back self.max_position_embeddings = config.max_position_embeddings
* fix-copies
* Fix Llava conversion for LlavaQwen2ForCausalLM with Clip vision tower (#33613)
fix llavaqwen2 model conversion
* Uniformize kwargs for Udop processor and update docs (#33628)
* Add optional kwargs and uniformize udop
* cleanup Unpack
* nit Udop
* Generation: deprecate `PreTrainedModel` inheriting from `GenerationMixin` (#33203)
* Enable BNB multi-backend support (#31098)
* enable cpu bnb path
* fix style
* fix code style
* fix 4 bit path
* Update src/transformers/utils/import_utils.py
Co-authored-by: Aarni Koskela <akx@iki.fi>
* add multi backend refactor tests
* fix style
* tweak 4bit quantizer + fix corresponding tests
* tweak 8bit quantizer + *try* fixing corresponding tests
* fix dequant bnb 8bit
* account for Intel CPU in variability of expected outputs
* enable cpu and xpu device map
* further tweaks to account for Intel CPU
* fix autocast to work with both cpu + cuda
* fix comments
* fix comments
* switch to testing_utils.torch_device
* allow for xpu in multi-gpu tests
* fix tests 4bit for CPU NF4
* fix bug with is_torch_xpu_available needing to be called as func
* avoid issue where test reports attr err due to other failure
* fix formatting
* fix typo from resolving of merge conflict
* polish based on last PR review
Co-authored-by: Marc Sun <57196510+SunMarc@users.noreply.github.com>
* fix CI
* Update src/transformers/integrations/integration_utils.py
Co-authored-by: Arthur <48595927+ArthurZucker@users.noreply.github.com>
* Update src/transformers/integrations/integration_utils.py
Co-authored-by: Arthur <48595927+ArthurZucker@users.noreply.github.com>
* fix error log
* fix error msg
* add \n in error log
* make quality
* rm bnb cuda restriction in doc
* cpu model don't need dispatch
* fix doc
* fix style
* check cuda avaliable in testing
* fix tests
* Update docs/source/en/model_doc/chameleon.md
Co-authored-by: Marc Sun <57196510+SunMarc@users.noreply.github.com>
* Update docs/source/en/model_doc/llava_next.md
Co-authored-by: Aarni Koskela <akx@iki.fi>
* Update tests/quantization/bnb/test_4bit.py
Co-authored-by: Aarni Koskela <akx@iki.fi>
* Update tests/quantization/bnb/test_4bit.py
Co-authored-by: Aarni Koskela <akx@iki.fi>
* fix doc
* fix check multibackends
* fix import sort
* remove check torch in bnb
* docs: update bitsandbytes references with multi-backend info
* docs: fix small mistakes in bnb paragraph
* run formatting
* reveret bnb check
* move bnb multi-backend check to import_utils
* Update src/transformers/utils/import_utils.py
Co-authored-by: Aarni Koskela <akx@iki.fi>
* fix bnb check
* minor fix for bnb
* check lib first
* fix code style
* Revert "run formatting"
This reverts commit ac108c6d6b34f45a5745a736ba57282405cfaa61.
* fix format
* give warning when bnb version is low and no cuda found]
* fix device assignment check to be multi-device capable
* address akx feedback on get_avlbl_dev fn
* revert partially, as we don't want the function that public, as docs would be too much (enforced)
---------
Co-authored-by: Aarni Koskela <akx@iki.fi>
Co-authored-by: Titus von Koeller <9048635+Titus-von-Koeller@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Marc Sun <57196510+SunMarc@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Arthur <48595927+ArthurZucker@users.noreply.github.com>
* Fix error string after refactoring into get_chat_template (#33652)
* Fix error string after refactoring into get_chat_template
* Take suggestion from CR
Co-authored-by: Matt <Rocketknight1@users.noreply.github.com>
---------
Co-authored-by: Matt <Rocketknight1@users.noreply.github.com>
* uniformize git processor (#33668)
* uniformize git processor
* update doctring
* Modular `transformers`: modularity and inheritance for new model additions (#33248)
* update exampel
* update
* push the converted diff files for testing and ci
* correct one example
* fix class attributes and docstring
* nits
* oups
* fixed config!
* update
* nitd
* class attributes are not matched against the other, this is missing
* fixed overwriting self.xxx now onto the attributes I think
* partial fix, now order with docstring
* fix docstring order?
* more fixes
* update
* fix missing docstrings!
* examples don't all work yet
* fixup
* nit
* updated
* hick
* update
* delete
* update
* update
* update
* fix
* all default
* no local import
* fix more diff
* some fix related to "safe imports"
* push fixed
* add helper!
* style
* add a check
* all by default
* add the
* update
* FINALLY!
* nit
* fix config dependencies
* man that is it
* fix fix
* update diffs
* fix the last issue
* re-default to all
* alll the fixes
* nice
* fix properties vs setter
* fixup
* updates
* update dependencies
* make sure to install what needs to be installed
* fixup
* quick fix for now
* fix!
* fixup
* update
* update
* updates
* whitespaces
* nit
* fix
* simplify everything, and make it file agnostic (should work for image processors)
* style
* finish fixing all import issues
* fixup
* empty modeling should not be written!
* Add logic to find who depends on what
* update
* cleanup
* update
* update gemma to support positions
* some small nits
* this is the correct docstring for gemma2
* fix merging of docstrings
* update
* fixup
* update
* take doc into account
* styling
* update
* fix hidden activation
* more fixes
* final fixes!
* fixup
* fixup instruct blip video
* update
* fix bugs
* align gemma2 with the rest as well
* updats
* revert
* update
* more reversiom
* grind
* more
* arf
* update
* order will matter
* finish del stuff
* update
* rename to modular
* fixup
* nits
* update makefile
* fixup
* update order of the checks!
* fix
* fix docstring that has a call inside
* fiix conversion check
* style
* add some initial documentation
* update
* update doc
* some fixup
* updates
* yups
* Mostly todo gimme a minut
* update
* fixup
* revert some stuff
* Review docs for the modular transformers (#33472)
Docs
* good update
* fixup
* mmm current updates lead to this code
* okay, this fixes it
* cool
* fixes
* update
* nit
* updates
* nits
* fix doc
* update
* revert bad changes
* update
* updates
* proper update
* update
* update?
* up
* update
* cool
* nits
* nits
* bon bon
* fix
* ?
* minimise changes
* update
* update
* update
* updates?
* fixed gemma2
* kind of a hack
* nits
* update
* remove `diffs` in favor of `modular`
* fix make fix copies
---------
Co-authored-by: Lysandre Debut <hi@lysand.re>
* Fix CIs post merging modular transformers (#33681)
update
* Fixed docstring for cohere model regarding unavailability of prune_he… (#33253)
* Fixed docstring for cohere model regarding unavailability of prune_head() methods
The docstring mentions that cohere model supports prune_heads() methods. I have fixed the docstring by explicitly mentioning that it doesn't support that functionality.
* Update src/transformers/models/cohere/modeling_cohere.py
---------
Co-authored-by: Lysandre Debut <hi@lysand.re>
* Generation tests: update imagegpt input name, remove unused functions (#33663)
* Improve Error Messaging for Flash Attention 2 on CPU (#33655)
Update flash-attn error message on CPU
Rebased to latest branch
* Gemma2: fix config initialization (`cache_implementation`) (#33684)
* Fix ByteLevel alphabet missing when Sequence pretokenizer is used (#33556)
* Fix ByteLevel alphabet missing when Sequence pretokenizer is used
* Fixed formatting with `ruff`.
* Uniformize kwargs for image-text-to-text processors (#32544)
* uniformize FUYU processor kwargs
* Uniformize instructblip processor kwargs
* Fix processor kwargs and tests Fuyu, InstructBlip, Kosmos2
* Uniformize llava_next processor
* Fix save_load test for processor with chat_template only as extra init args
* Fix import Unpack
* Fix Fuyu Processor import
* Fix FuyuProcessor import
* Fix FuyuProcessor
* Add defaults for specific kwargs kosmos2
* Fix Udop to return BatchFeature instead of BatchEncoding and uniformize kwargs
* Add tests processor Udop
* remove Copied from in processing Udop as change of input orders caused by BatchEncoding -> BatchFeature
* Fix overwrite tests kwargs processors
* Add warnings and BC for changes in processor inputs order, change docs, add BC for text_pair as arg for Udop
* Fix processing test fuyu
* remove unnecessary pad_token check in instructblip ProcessorTest
* Fix BC tests and cleanup
* FIx imports fuyu
* Uniformize Pix2Struct
* Fix wrong name for FuyuProcessorKwargs
* Fix slow tests reversed inputs align fuyu llava-next, change udop warning
* Fix wrong logging import udop
* Add check images text input order
* Fix copies
* change text pair handling when positional arg
* rebase on main, fix imports in test_processing_common
* remove optional args and udop uniformization from this PR
* fix failing tests
* remove unnecessary test, fix processing utils and test processing common
* cleanup Unpack
* cleanup
* fix conflict grounding dino
* 🚨🚨 Setting default behavior of assisted decoding (#33657)
* tests: fix pytorch tensor placement errors (#33485)
This commit fixes the following errors:
* Fix "expected all tensors to be on the same device" error
* Fix "can't convert device type tensor to numpy"
According to pytorch documentation torch.Tensor.numpy(force=False)
performs conversion only if tensor is on CPU (plus few other restrictions)
which is not the case. For our case we need force=True since we just
need a data and don't care about tensors coherency.
Fixes: #33517
See: https://pytorch.org/docs/2.4/generated/torch.Tensor.numpy.html
Signed-off-by: Dmitry Rogozhkin <dmitry.v.rogozhkin@intel.com>
* bump tokenizers, fix added tokens fast (#32535)
* update based on tokenizers release
* update
* nits
* update
* revert re addition
* don't break that yet
* fmt
* revert unwanted
* update tokenizers version
* update dep table
* update
* update in conversion script as well
* some fix
* revert
* fully revert
* fix training
* remove set trace
* fixup
* update
* update
* [Pixtral] Improve docs, rename model (#33491)
* Improve docs, rename model
* Fix style
* Update repo id
* fix code quality after merge
* HFQuantizer implementation for compressed-tensors library (#31704)
* Add compressed-tensors HFQuantizer implementation
* flag serializable as False
* run
* revive lines deleted by ruff
* fixes to load+save from sparseml, edit config to quantization_config, and load back
* address satrat comment
* compressed_tensors to compressed-tensors and revert back is_serializable
* rename quant_method from sparseml to compressed-tensors
* tests
* edit tests
* clean up tests
* make style
* cleanup
* cleanup
* add test skip for when compressed tensors is not installed
* remove pydantic import + style
* delay torch import in test
* initial docs
* update main init for compressed tensors config
* make fix-copies
* docstring
* remove fill_docstring
* Apply suggestions from code review
Co-authored-by: Marc Sun <57196510+SunMarc@users.noreply.github.com>
* review comments
* review comments
* comments - suppress warnings on state dict load, tests, fixes
* bug-fix - remove unnecessary call to apply quant lifecycle
* run_compressed compatability
* revert changes not needed for compression
* no longer need unexpected keys fn
* unexpected keys not needed either
* Apply suggestions from code review
Co-authored-by: Marc Sun <57196510+SunMarc@users.noreply.github.com>
* add to_diff_dict
* update docs and expand testing
* Update _toctree.yml with compressed-tensors
* Update src/transformers/utils/quantization_config.py
Co-authored-by: Arthur <48595927+ArthurZucker@users.noreply.github.com>
* update doc
* add note about saving a loaded model
---------
Co-authored-by: George Ohashi <george@neuralmagic.com>
Co-authored-by: Marc Sun <57196510+SunMarc@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Sara Adkins <sara@neuralmagic.com>
Co-authored-by: Sara Adkins <sara.adkins65@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Arthur <48595927+ArthurZucker@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Dipika Sikka <ds3822@columbia.edu>
Co-authored-by: Dipika <dipikasikka1@gmail.com>
* update model card for opt
* add batch size to inference table
* [slow-run] opt
* [run-slow] opt
---------
Signed-off-by: Dmitry Rogozhkin <dmitry.v.rogozhkin@intel.com>
Co-authored-by: Avishai Elmakies <avishai.elma@cs.huji.ac.il>
Co-authored-by: amyeroberts <22614925+amyeroberts@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Pablo Montalvo <39954772+molbap@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: chengchengpei <5881383+chengchengpei@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Isotr0py <2037008807@qq.com>
Co-authored-by: Yoni Gozlan <74535834+yonigozlan@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Joao Gante <joaofranciscocardosogante@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: jiqing-feng <jiqing.feng@intel.com>
Co-authored-by: Aarni Koskela <akx@iki.fi>
Co-authored-by: Titus von Koeller <9048635+Titus-von-Koeller@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Marc Sun <57196510+SunMarc@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Arthur <48595927+ArthurZucker@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Tibor Reiss <75096465+tibor-reiss@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Matt <Rocketknight1@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Lysandre Debut <hi@lysand.re>
Co-authored-by: Muhammad Naufil <m.naufil1@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: sizhky <yyeshr@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Umar Butler <umar@umar.au>
Co-authored-by: Jonathan Mamou <jonathan.mamou@intel.com>
Co-authored-by: Dmitry Rogozhkin <dmitry.v.rogozhkin@intel.com>
Co-authored-by: NielsRogge <48327001+NielsRogge@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Arthur Zucker <arthur.zucker@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Benjamin Fineran <bfineran@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: George Ohashi <george@neuralmagic.com>
Co-authored-by: Sara Adkins <sara@neuralmagic.com>
Co-authored-by: Sara Adkins <sara.adkins65@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Dipika Sikka <ds3822@columbia.edu>
Co-authored-by: Dipika <dipikasikka1@gmail.com>
Add Translate docs into Arabic - section files CONCEPTUAL GUIDES
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Philosophy [i18n-ar] Translated file : docs/source/ar/philosophy.md into Arabic #33064
Glossary [i18n-ar] Translated file : docs/source/ar/glossary.md into Arabic #33038
What 🤗 Transformers can do [i18n-ar] Translated file : docs/source/ar/task_summary.md into Arabic #33073
How 🤗 Transformers solve tasks [i18n-ar] Translated file : docs/source/ar/tasks_explained.md into Arabic #33074
The Transformer model family [i18n-ar] Translated file : docs/source/ar/model_summary.md into Arabic #33047
Summary of the tokenizers [i18n-ar] Translated file : docs/source/ar/tokenizer_summary.md into Arabic #33078
Attention [i18n-ar] Translated file : docs/source/ar/attention.md into Arabic #33021
Padding and truncation [i18n-ar] Translated file : docs/source/ar/pad_truncation.md into Arabic #33050
BERTology [i18n-ar] Translated file : docs/source/ar/bertology.md into Arabic #33024
Perplexity of fixed-length models [i18n-ar] Translated file : docs/source/ar/perplexity.md into Arabic #33063
Pipelines for webserver inference [i18n-ar] Translated file : docs/source/ar/pipeline_webserver.md into Arabic #33066
Model training anatomy [i18n-ar] Translated file : docs/source/ar/model_memory_anatomy.md into Arabic #33045
Getting the most out of LLMs [i18n-ar] Translated file : docs/source/ar/llm_tutorial_optimization.md into Arabic #33043
* rebasing changes
* fixing style
* adding some doc to functions
* remove bitblas
* change dtype
* fixing check_code_quality
* fixing import order
* adding doc to tree
* Small update on BitLinear
* adding some tests
* sorting imports
* small update
* reformatting
* reformatting
* reformatting with ruff
* adding assert
* changes after review
* update disk offloading
* adapting after review
* Update after review
* add is_serializable back
* fixing style
* adding serialization test
* make style
* small updates after review
* Fix Failed tests with mobile bert
* Cast to the correct dtype
* Code fixup
* Fix padding_idx larger that embedding_size
* Reduce covariance more. use 1e-7 instead of 1e-5
* Comment fix
* Reduce covariance more. use 1e-9 instead of 1e-7
* Copy new config
* all but MRA fixed
* fix mra
* very flaky
* skip instead
* make fixup
---------
Co-authored-by: Joao Gante <joao@huggingface.co>
* improve modular
* style
* Update modular_model_converter.py
* pretty print warning
* style
* Support to remove unused classes as part of added dependencies as well
* nits
* correct bug
* add example
* style
* Add documentation
* Fix issue in oneformer preprocessing
* [run slow] oneformer
* [run_slow] oneformer
* Make the same fixes in DQA and object detection pipelines
* Fix BatchFeature.to() instead
* Revert pipeline-specific changes
* Add the same check in Pixtral's methods
* Add the same check in BatchEncoding
* make sure torch is imported
* Update many similar visual pipelines
* Add input tests
* Add ImageToText as well
* Add output tests
* Add output tests
* Add output tests
* OutputElement -> Output
* Correctly test elements
* make fixup
* fix typo in the task list
* Fix VQA testing
* Add copyright to image_classification.py
* Revert changes to VQA pipeline because outputs have differences - will move to another PR
* make fixup
* Remove deprecation warnings
* Add Auto model for image-text-to-text
* Remove donut from processing auto, add chameleon ti image text to text models
* add qwen2_vl and llava_onevision
* add pixtral to auto model for image-text-to-text
* add mllama and idefics3
* remove models in IGNORE_NON_AUTO_CONFIGURED
* add AutoModelForImageTextToText to tests and doc
* start working on adding position ids
* add docs
* Refactor modeling_biogpt.py and modeling_opt.py for code consistency
* fix 2 PR comments
* move position_ids to end of args
* remove trailing white space
* add comment with TODO
* bug fix gradient checkpointing
* fixup
* missed on position_ids
* remove _attention_to_position_ids and refactor embedding class
* remove redundent code
---------
Co-authored-by: Avishai Elmakies <avishai.elma@cs.huji.ac.il>
* Initial commit for MyT5 model
* custom implementation of MyT5 tokenizer, unused files deleted
* unittest for myt5 tokenizer
* upadate of import structure and style
* removed remmanents of MyT5Config
* fixed docstrings
* Updates after review: filled documentaion file, new docstrings and tests added
* Fixed code style issues
* fixed copied from to refer to function
* updated loading myt5 tokenizer in tests, added sample byte map file to fixtures
* changes after review
* removed redundant copied from
* removed redundant copied from
* optimalization and loading model from hf
* [run_slow] myt5
* [run-slow] myt5
* Updated en documentation for myt5
Co-authored-by: Arthur <48595927+ArthurZucker@users.noreply.github.com>
---------
Co-authored-by: Arthur <48595927+ArthurZucker@users.noreply.github.com>
* onboard phimoe model
* removed debug code
* added unit tests
* updated docs
* formatted
* fixed unit tests
* fixed test case
* fixed format
* refactored code
* fixed expected outputs in the integration tests
* Added a warning msg
* Addressed comments
* Addressed comments
* fixed test cases
* added paper link
* Addressed comments
* Refactored PhimoeForCausalLM forward fn
* Refactored PhimoeRotaryEmbedding class
* fixed test cases
* fixed testcase
* fixed test case
* Addressed comments
* fixed test cases
* fixed testcases
* Used cache position instead to get the seq len
* intilize new embeddings from normal distrib
* Fix typo in comments
* Fix typo in comments
* Fix style
* Fix variables naming
* Add tests
* Fix style
* code consistency nit
* Add deepspeed support
* Add deepspeed support
* Conver embeddings weights to float32 before computations
* Add deepspeed tests
* Cover when vocab_size is smaller than embedding_size
* Style fix
* Add tests for vocab_size smaller than hiddin_size
* Style fix
* Nits in tests
* Nits in tests
* Check for deepspeed before importing it
* Increase vocab_size for positive definite covariance matrix test
* Add warning
* Add multivariate_resizing flag and implement resizing for lm_heads
* Fix typo
* Fix wrong bias indexing
* Fix bias is zero check
* remove multivariate_resizing flag from tests
* Intialize bias from old bias normal distribution
* Fixup
* Code usability
* Use mean_resizing instead of multivariate_resizing
* Fix up
* Fix comments and docs
* Error condition bug fix
* Update error message
* Update src/transformers/models/qwen2_vl/modeling_qwen2_vl.py
Co-authored-by: Pavel Iakubovskii <qubvel@gmail.com>
* Making change in the rest of the repo
* Formatting
* Formatting with ruff
---------
Co-authored-by: Pavel Iakubovskii <qubvel@gmail.com>
* Add support for `weights_only` flag when loading state_dict
Summary:
This is to enable loading a state_dict with wrapper tensor subclasses (used in torchao to
for quantized weights)
Test Plan:
tested locally with torchao weights, also need https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/pull/32306:
```
import torch
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
from transformers import TorchAoConfig
from torchao.utils import benchmark_model
import torchao
DEVICE_TYPE = "cuda"
def init_model_and_benchmark(model_id, torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16, quantization_config=None):
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_id)
if quantization_config is not None:
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_id, device_map=DEVICE_TYPE, torch_dtype=torch.\bfloat16, quantization_config=quantization_config)
else:
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_id, device_map=DEVICE_TYPE, torch_dtype=torch.\bfloat16, weights_only=False)
# sanity check: run the model
input_text = "What are we having for dinner?"
input_ids = tokenizer(input_text, return_tensors="pt").to(DEVICE_TYPE)
output = model.generate(**input_ids, max_new_tokens=1000)
print(tokenizer.decode(output[0], skip_special_tokens=True))
NUM_WARMUP = 1
NUM_RUNS = 5
if quantization_config is not None:
torchao.quantization.utils.recommended_inductor_config_setter()
model = torch.compile(model, mode="max-autotune")
benchmark_model(model.generate, NUM_WARMUP, kwargs=input_ids, device_type=DEVICE_TYPE)
print("running benchmark")
results = benchmark_model(model.generate, NUM_RUNS, kwargs=input_ids, device_type=DEVICE_TYPE)
return model, results
model_id = "jerryzh168/test-model"
torchao.quantization.utils.recommended_inductor_config_setter()
bf16_model, bf16_time = init_model_and_benchmark(model_id)
print(f"bf16: {bf16_time}")
```
Reviewers:
Subscribers:
Tasks:
Tags:
* format
* [PEFT] Support low_cpu_mem_usage for PEFT loading
PEFT added support for low_cpu_mem_usage=True when loading adapters in
https://github.com/huggingface/peft/pull/1961. This feature is now
available when installing PEFT v0.13.0. With this PR, this option is
also supported when loading PEFT adapters directly into transformers
models.
Additionally, with this PR,
https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers/pull/9510 will be unblocked,
which implements this option in diffusers.
* Fix typo
* fix beam indices in token_timestamps
* fix attention_mask in FA2
* correct translation example with the right example
* correct how somes tests are using outputs + correct num_frames
* fix shortform batch prev cond tests
* make fix-copies
* make fix-copies
* take care of shifting beam indices
* [run-slow] whisper
* [run-slow] whisper
* add unit tests for splinter_tokenizer
* add unit test for splinter tokenizer, pass in the question_token to be saved on save_pretrained called
* remove unused import
* remove vocab_splinter.txt, add Copied from, use fmt:on and fmt:off to prevent autoformatting on long lines
* remove all the spaces
Co-authored-by: Arthur <48595927+ArthurZucker@users.noreply.github.com>
---------
Co-authored-by: Arthur <48595927+ArthurZucker@users.noreply.github.com>
* Use all state dict keys when checking if root module is initialized.
* Apply style corrections
* Add comment explaining change.
* Change comment phrasing.
* Update an keyerror on _save_check_point prevent confusion of missing metric keys
* Update grammar error and case sensitive.
Co-authored-by: Marc Sun <57196510+SunMarc@users.noreply.github.com>
* adding update KeyError on _evaluate function to align with _save_checkpoint function
---------
Co-authored-by: Marc Sun <57196510+SunMarc@users.noreply.github.com>
* When we set self.dt_proj.bias = None, it removes the bias parameter from the model. When we later tried to assign a tensor to self.dt_proj.bias, it caused a TypeError because PyTorch expects a Parameter object.
* When we set self.dt_proj.bias = None, it removes the bias parameter from the model. When we later tried to assign a tensor to self.dt_proj.bias, it caused a TypeError because PyTorch expects a Parameter object.
* When we set self.dt_proj.bias = None, it removes the bias parameter from the model. When we later tried to assign a tensor to self.dt_proj.bias, it caused a TypeError because PyTorch expects a Parameter object.
* Trainer - deprecate tokenizer for processing_class
* Extend chage across Seq2Seq trainer and docs
* Add tests
* Update to FutureWarning and add deprecation version
* add support for custom inputs and batched inputs in ProcessorTesterMixin
* Fix batch_size behavior ProcessorTesterMixin
* Change format prepare inputs batched
* Remove override test pixtral processor
* Remove unnecessary tests and cleanup after new prepare_inputs functions
* Fix instructBlipVideo image processor
* fix(copy): fixup copy
* fix(deformable_detr): move weight initialization to the right place
* fix(grounding_dino): move weight initialization to the right place
* fix(rt_detr): move weight initialization to the right place
* [run-slow] deformable_detr, grounding_dino, rt_detr
* Remove max_new_tokens arg
* Add ASR pipeline to testing
* make fixup
* Factor the output test out into a util
* Full error reporting
* Full error reporting
* Update src/transformers/pipelines/automatic_speech_recognition.py
Co-authored-by: Lysandre Debut <hi@lysand.re>
* Small comment
---------
Co-authored-by: Lysandre Debut <hi@lysand.re>
* Add include_loss_for_metrics
* Fix styling
* Initialize inputs and losses to avoid AttributeError
* Ruff styling
* Refactor compute_metrics and update EvalPrediction
* Change Naming
* Added include_for_metrics to group both args
* Fix style
* Change warnings to logger
Co-authored-by: Marc Sun <57196510+SunMarc@users.noreply.github.com>
---------
Co-authored-by: Marc Sun <57196510+SunMarc@users.noreply.github.com>
* fix(m2m_100): skip dropout in eval for flash_attn
* fix(misc): skip dropout in eval for flash attn various models
* chore(m2m_100): copy flash attn from bart
* chore: run make fix-copies
* [run-slow] bart, m2m_100
* refactor image features selection
* break line
* remove whitespace
* add pr comments: include projection and rename function
* make fix-copies
* fix get_image_feature in vip llava
* Fix Mamba slow path bug with dtype mismatch.
* Update test_modeling_mamba.py
* Improve style.
* Fix issue with cache position of dtype mismatch test.
* Change test for slow path.
* Revert changes.
* Switch to buggy code and add test to catch it.
* Fix the dtype mismatch bug and add test code to verify it.
* Fix minor bug with test.
* Fix incorrect dtype of model output.
* Fix incorrect dtype of cache.
* Fix incorrect dtype of ssm cache.
* Fix incorrect dtype of conv state.
* Remove assertion for ssm state.
* Add assertion for conv state dtype.
* Fix all issues with dtype mismatch test.
* HQQ model serialization attempt
* fix hqq dispatch and unexpected keys
* style
* remove check_old_param
* revert to check HQQLinear in quantizer_hqq.py
* revert to check HQQLinear in quantizer_hqq.py
* update HqqConfig default params
* make ci happy
* make ci happy
* revert to HQQLinear check in quantizer_hqq.py
* check hqq_min version 0.2.0
* set axis=1 as default in quantization_config.py
* validate_env with hqq>=0.2.0 version message
* deprecated hqq kwargs message
* make ci happy
* remove run_expected_keys_check hack + bump to 0.2.1 min hqq version
* fix unexpected_keys hqq update
* add pre_quantized check
* add update_expected_keys to base quantizerr
* ci base.py fix?
* ci base.py fix?
* fix "quantization typo" src/transformers/utils/quantization_config.py
Co-authored-by: Arthur <48595927+ArthurZucker@users.noreply.github.com>
* fix post merge
---------
Co-authored-by: Marc Sun <marc@huggingface.co>
Co-authored-by: Arthur <48595927+ArthurZucker@users.noreply.github.com>
* Enable non-safetensor serialization and deserialization for TorchAoConfig quantized model
Summary:
After https://github.com/huggingface/huggingface_hub/pull/2440 we added non-safetensor serialization and deserialization
in huggingface, with this we can now add the support in transformers
Note that we don't plan to add safetensor serialization due to different goals of wrapper tensor subclass and safetensor
see README for more details
Test Plan:
tested locally
Reviewers:
Subscribers:
Tasks:
Tags:
* formatting
* formatting
* minor fix
* formatting
* address comments
* comments
* minor fix
* update doc
* refactor compressed tensor quantizer
* fix return type
* update to union
* fix gate_logits typing
* fix num_experts type
* fix typing
* run fix-copies
* add doc for top_k
* run fix-copies
* empty commit to trigger CI
* Make audio classification pipeline spec-compliant and add test
* Check that test actually running in CI
* Try a different pipeline for the CI
* Move the test so it gets triggered
* Move it again, this time into task_tests!
* make fixup
* indentation fix
* comment
* Move everything from testing_utils to test_pipeline_mixin
* Add output testing too
* revert small diff with main
* make fixup
* Clarify comment
* Update tests/pipelines/test_pipelines_audio_classification.py
Co-authored-by: Lucain <lucainp@gmail.com>
* Update tests/test_pipeline_mixin.py
Co-authored-by: Lucain <lucainp@gmail.com>
* Rename function and js_args -> hub_args
* Cleanup the spec recursion
* Check keys for all outputs
---------
Co-authored-by: Lucain <lucainp@gmail.com>
* Cleanup return_text and return_full_text options in TextGenerationPipeline
* Cleanup return_text and return_full_text options in TextGenerationPipeline
* Cleanup return_text and return_full_text options in TextGenerationPipeline
* Cleanup return_text and return_full_text options in TextGenerationPipeline
* Revert pipeline code, but update docs instead
* Restore pipeline test
* add bloom arch support for gguf
* apply format
* small refactoring, bug fix in GGUF_TENSOR_MAPPING naming
* optimize bloom GGUF_TENSOR_MAPPING
* implement reverse reshaping for bloom gguf
* add qkv weights test
* add q_8 test for bloom
Update siglip.md
This was already partially fixed relative to the deployed docs. But the partial fix made it inconsistent. Additionally, giving the full text ("This is a photo of...") is likely not the desired output.
* clean_up_tokenization_spaces=False if unset
* deprecate warning
* updating param for old models
* update models
* make fix-copies
* fix-copies and update bert models
* warning msg
* update prophet and clvp
* updating test since space before is arbitrarily removed
* remove warning for 4.45
* Add Idefics 3!
* fixes to make both pipelines identical
* fix for quantized models
* First pass at the review
* remove vocab size from the main config (it's still in the text_config)
* hot fix for merve
* Apply suggestions from code review
Co-authored-by: amyeroberts <22614925+amyeroberts@users.noreply.github.com>
* re-add model_type for text_config
* remove support for old_cache
* remove hidden_size from main config
* rename idefics3 HF repo
* few changes suggested in the PR
* fix to input_data_format computation
* remove overwrite of _autoset_attn_implementation following @zucchini-nlp suggestion
* improve example
* few improvements from amy's review
* big change to enable processing input images as numpy arrays
* Changes to the code to uniformize processor kwargs
* image processing tests
* image processing tests fixes and some bugs they discovered
* addressed review comments from Yoni
* fix modeling tests
* remove special tokens that are not special
* fixes tests
* skip failing tests - they also fail for idefics2
* added paper and readded the tests with multi gpu, who knows
* Update docs/source/en/model_doc/idefics3.md
Co-authored-by: amyeroberts <22614925+amyeroberts@users.noreply.github.com>
* Apply suggestions from code review
Co-authored-by: amyeroberts <22614925+amyeroberts@users.noreply.github.com>
* review amy until image_processing_idefics3
* last comments from Amy
* review amy
* Update src/transformers/models/idefics3/image_processing_idefics3.py
Co-authored-by: amyeroberts <22614925+amyeroberts@users.noreply.github.com>
* Update src/transformers/models/idefics3/modeling_idefics3.py
Co-authored-by: amyeroberts <22614925+amyeroberts@users.noreply.github.com>
* Update docs/source/en/model_doc/idefics3.md
Co-authored-by: amyeroberts <22614925+amyeroberts@users.noreply.github.com>
* doc improvement - amy review
* fix runtime error during fine-tuning
* amy's review
* Update src/transformers/models/idefics3/image_processing_idefics3.py
Co-authored-by: amyeroberts <22614925+amyeroberts@users.noreply.github.com>
* Update src/transformers/models/idefics3/image_processing_idefics3.py
Co-authored-by: amyeroberts <22614925+amyeroberts@users.noreply.github.com>
* Update src/transformers/models/idefics3/modeling_idefics3.py
Co-authored-by: amyeroberts <22614925+amyeroberts@users.noreply.github.com>
* ruff
* amy's comment on the order
* ruff ruff
* fix copies
* square images when they are not splitted
* ruff :(
* Update src/transformers/models/idefics3/image_processing_idefics3.py
Co-authored-by: amyeroberts <22614925+amyeroberts@users.noreply.github.com>
* Update tests/models/idefics3/test_processing_idefics3.py
Co-authored-by: amyeroberts <22614925+amyeroberts@users.noreply.github.com>
* fix small bug introduced in refactor
* amy's image processing changes
* fixes peft tests and ruff
* modify to_pil_image from transformers. and review from emanuele.
* add modified to_pil_image
---------
Co-authored-by: amyeroberts <22614925+amyeroberts@users.noreply.github.com>
* Add compressed-tensors HFQuantizer implementation
* flag serializable as False
* run
* revive lines deleted by ruff
* fixes to load+save from sparseml, edit config to quantization_config, and load back
* address satrat comment
* compressed_tensors to compressed-tensors and revert back is_serializable
* rename quant_method from sparseml to compressed-tensors
* tests
* edit tests
* clean up tests
* make style
* cleanup
* cleanup
* add test skip for when compressed tensors is not installed
* remove pydantic import + style
* delay torch import in test
* initial docs
* update main init for compressed tensors config
* make fix-copies
* docstring
* remove fill_docstring
* Apply suggestions from code review
Co-authored-by: Marc Sun <57196510+SunMarc@users.noreply.github.com>
* review comments
* review comments
* comments - suppress warnings on state dict load, tests, fixes
* bug-fix - remove unnecessary call to apply quant lifecycle
* run_compressed compatability
* revert changes not needed for compression
* no longer need unexpected keys fn
* unexpected keys not needed either
* Apply suggestions from code review
Co-authored-by: Marc Sun <57196510+SunMarc@users.noreply.github.com>
* add to_diff_dict
* update docs and expand testing
* Update _toctree.yml with compressed-tensors
* Update src/transformers/utils/quantization_config.py
Co-authored-by: Arthur <48595927+ArthurZucker@users.noreply.github.com>
* update doc
* add note about saving a loaded model
---------
Co-authored-by: George Ohashi <george@neuralmagic.com>
Co-authored-by: Marc Sun <57196510+SunMarc@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Sara Adkins <sara@neuralmagic.com>
Co-authored-by: Sara Adkins <sara.adkins65@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Arthur <48595927+ArthurZucker@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Dipika Sikka <ds3822@columbia.edu>
Co-authored-by: Dipika <dipikasikka1@gmail.com>
This commit fixes the following errors:
* Fix "expected all tensors to be on the same device" error
* Fix "can't convert device type tensor to numpy"
According to pytorch documentation torch.Tensor.numpy(force=False)
performs conversion only if tensor is on CPU (plus few other restrictions)
which is not the case. For our case we need force=True since we just
need a data and don't care about tensors coherency.
Fixes: #33517
See: https://pytorch.org/docs/2.4/generated/torch.Tensor.numpy.html
Signed-off-by: Dmitry Rogozhkin <dmitry.v.rogozhkin@intel.com>
* Fixed docstring for cohere model regarding unavailability of prune_head() methods
The docstring mentions that cohere model supports prune_heads() methods. I have fixed the docstring by explicitly mentioning that it doesn't support that functionality.
* Update src/transformers/models/cohere/modeling_cohere.py
---------
Co-authored-by: Lysandre Debut <hi@lysand.re>
* update exampel
* update
* push the converted diff files for testing and ci
* correct one example
* fix class attributes and docstring
* nits
* oups
* fixed config!
* update
* nitd
* class attributes are not matched against the other, this is missing
* fixed overwriting self.xxx now onto the attributes I think
* partial fix, now order with docstring
* fix docstring order?
* more fixes
* update
* fix missing docstrings!
* examples don't all work yet
* fixup
* nit
* updated
* hick
* update
* delete
* update
* update
* update
* fix
* all default
* no local import
* fix more diff
* some fix related to "safe imports"
* push fixed
* add helper!
* style
* add a check
* all by default
* add the
* update
* FINALLY!
* nit
* fix config dependencies
* man that is it
* fix fix
* update diffs
* fix the last issue
* re-default to all
* alll the fixes
* nice
* fix properties vs setter
* fixup
* updates
* update dependencies
* make sure to install what needs to be installed
* fixup
* quick fix for now
* fix!
* fixup
* update
* update
* updates
* whitespaces
* nit
* fix
* simplify everything, and make it file agnostic (should work for image processors)
* style
* finish fixing all import issues
* fixup
* empty modeling should not be written!
* Add logic to find who depends on what
* update
* cleanup
* update
* update gemma to support positions
* some small nits
* this is the correct docstring for gemma2
* fix merging of docstrings
* update
* fixup
* update
* take doc into account
* styling
* update
* fix hidden activation
* more fixes
* final fixes!
* fixup
* fixup instruct blip video
* update
* fix bugs
* align gemma2 with the rest as well
* updats
* revert
* update
* more reversiom
* grind
* more
* arf
* update
* order will matter
* finish del stuff
* update
* rename to modular
* fixup
* nits
* update makefile
* fixup
* update order of the checks!
* fix
* fix docstring that has a call inside
* fiix conversion check
* style
* add some initial documentation
* update
* update doc
* some fixup
* updates
* yups
* Mostly todo gimme a minut
* update
* fixup
* revert some stuff
* Review docs for the modular transformers (#33472)
Docs
* good update
* fixup
* mmm current updates lead to this code
* okay, this fixes it
* cool
* fixes
* update
* nit
* updates
* nits
* fix doc
* update
* revert bad changes
* update
* updates
* proper update
* update
* update?
* up
* update
* cool
* nits
* nits
* bon bon
* fix
* ?
* minimise changes
* update
* update
* update
* updates?
* fixed gemma2
* kind of a hack
* nits
* update
* remove `diffs` in favor of `modular`
* fix make fix copies
---------
Co-authored-by: Lysandre Debut <hi@lysand.re>
* enable cpu bnb path
* fix style
* fix code style
* fix 4 bit path
* Update src/transformers/utils/import_utils.py
Co-authored-by: Aarni Koskela <akx@iki.fi>
* add multi backend refactor tests
* fix style
* tweak 4bit quantizer + fix corresponding tests
* tweak 8bit quantizer + *try* fixing corresponding tests
* fix dequant bnb 8bit
* account for Intel CPU in variability of expected outputs
* enable cpu and xpu device map
* further tweaks to account for Intel CPU
* fix autocast to work with both cpu + cuda
* fix comments
* fix comments
* switch to testing_utils.torch_device
* allow for xpu in multi-gpu tests
* fix tests 4bit for CPU NF4
* fix bug with is_torch_xpu_available needing to be called as func
* avoid issue where test reports attr err due to other failure
* fix formatting
* fix typo from resolving of merge conflict
* polish based on last PR review
Co-authored-by: Marc Sun <57196510+SunMarc@users.noreply.github.com>
* fix CI
* Update src/transformers/integrations/integration_utils.py
Co-authored-by: Arthur <48595927+ArthurZucker@users.noreply.github.com>
* Update src/transformers/integrations/integration_utils.py
Co-authored-by: Arthur <48595927+ArthurZucker@users.noreply.github.com>
* fix error log
* fix error msg
* add \n in error log
* make quality
* rm bnb cuda restriction in doc
* cpu model don't need dispatch
* fix doc
* fix style
* check cuda avaliable in testing
* fix tests
* Update docs/source/en/model_doc/chameleon.md
Co-authored-by: Marc Sun <57196510+SunMarc@users.noreply.github.com>
* Update docs/source/en/model_doc/llava_next.md
Co-authored-by: Aarni Koskela <akx@iki.fi>
* Update tests/quantization/bnb/test_4bit.py
Co-authored-by: Aarni Koskela <akx@iki.fi>
* Update tests/quantization/bnb/test_4bit.py
Co-authored-by: Aarni Koskela <akx@iki.fi>
* fix doc
* fix check multibackends
* fix import sort
* remove check torch in bnb
* docs: update bitsandbytes references with multi-backend info
* docs: fix small mistakes in bnb paragraph
* run formatting
* reveret bnb check
* move bnb multi-backend check to import_utils
* Update src/transformers/utils/import_utils.py
Co-authored-by: Aarni Koskela <akx@iki.fi>
* fix bnb check
* minor fix for bnb
* check lib first
* fix code style
* Revert "run formatting"
This reverts commit ac108c6d6b34f45a5745a736ba57282405cfaa61.
* fix format
* give warning when bnb version is low and no cuda found]
* fix device assignment check to be multi-device capable
* address akx feedback on get_avlbl_dev fn
* revert partially, as we don't want the function that public, as docs would be too much (enforced)
---------
Co-authored-by: Aarni Koskela <akx@iki.fi>
Co-authored-by: Titus von Koeller <9048635+Titus-von-Koeller@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Marc Sun <57196510+SunMarc@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Arthur <48595927+ArthurZucker@users.noreply.github.com>
* add sdpa to dinov2
* fixup
* add dinov2 to sdpa doc
* update doc order
* [run-slow] dinov2
* common to eager
* [run-slow] dinov2
* update attn implementation in common
* update test_modeling_dinov2 to have mask_ration, num_masks and mask_length similar to vit
* [run-slow] dinov2
---------
Co-authored-by: Avishai Elmakies <avishai.elma@cs.huji.ac.il>
* fix: handle padding in contrastive search for decoder-only models
* fix: handle padding in contrastive search for encoder-decoder models
* tests: move padding contrastive test to test_util, add t5 test
* fix: handle if model_kwargs["decoder_attention_mask"] is None
* refactor: improve padding input contrastive search generation tests
* chore: _ranking_fast to use LongTensor for cosine_matrix_mask
* add check and prepare args for BC to ProcessorMixin, improve ProcessorTesterMixin
* change size and crop_size in processor kwargs tests to do_rescale and rescale_factor
* remove unnecessary llava processor kwargs test overwrite
* nit
* change data_arg_name to input_name
* Remove unnecessary test override
* Remove unnecessary tests Paligemma
* Move test_prepare_and_validate_optional_call_args to TesterMixin, add docstring
* change sequence_bias type of SequenceBiasLogitsProcessor tp list, add config tests for all processors
* fix format
* small fix for all_token_bias_pairs_are_valid internal func
* small typo fix in description
* improve test impl, some SequenceBiasLogitsProcessor refactoring
* add tests
* fix whisper
* update
* nit
* add qwen2-vl
* more updates!
* better this way
* fix this one
* fix more tests
* fix final tests, hope so
* fix led
* Update tests/generation/test_utils.py
Co-authored-by: Joao Gante <joaofranciscocardosogante@gmail.com>
* pr comments
* not pass pixels and extra for low-mem tests, very flaky because of visio tower
---------
Co-authored-by: Joao Gante <joaofranciscocardosogante@gmail.com>
* clean mimi commit
* some nits suggestions from Arthur
* make fixup
* rename repo id + change readme
* Update docs/source/en/model_doc/mimi.md
Co-authored-by: amyeroberts <22614925+amyeroberts@users.noreply.github.com>
* add flaky flag to batching equivalence due to audio_codes failing sometimes
---------
Co-authored-by: amyeroberts <22614925+amyeroberts@users.noreply.github.com>
* modify rt detr to improve inference times when compiled
* Remove redundant "to"
* Fix conditional lru_cache and missing shapes_list
* nit unnecessary list creation
* Fix compile error when ninja not available and custon kernel activated
* fix patch_attention_mask incorrect setting which leads to the difference in the generated text if batch > 1
Signed-off-by: Wang, Yi <yi.a.wang@intel.com>
* fix format
Signed-off-by: Wang, Yi <yi.a.wang@intel.com>
* [run_slow] idefics2
---------
Signed-off-by: Wang, Yi <yi.a.wang@intel.com>
* added sequences_scores to the output
* added beam_indices to output
* added test to check for beam_indices, sequences_scores and their shape
* removed redundant whitespaces
* make fixup
* idefics2 enable_input_require_grads not aligned with disable_input_require_grads
make peft+idefics2 checkpoints disable fail
Signed-off-by: Wang, Yi <yi.a.wang@intel.com>
* split test case
Signed-off-by: Wang, Yi <yi.a.wang@intel.com>
* fix ci failure
Signed-off-by: Wang, Yi <yi.a.wang@intel.com>
* refine test
Signed-off-by: Wang, Yi <yi.a.wang@intel.com>
---------
Signed-off-by: Wang, Yi <yi.a.wang@intel.com>
* refactor weight_norm + propose uniformed solution to reconcile meta load_state_dict with classic loading
* make style
* fix sew
* fix sew and sew_d tests
* Fix failing tensor placement in Whisper
* fix long form generation tests
* more return_timestamps=True
* make fixup
* [run_slow] whisper
* [run_slow] whisper
* Uniformize kwargs for LlaVa and update docs
* Change order of processor inputs in docstring
* Improve BC support for reversed images and text inputs
* cleanup llava processor call docstring
* Add encoded inputs as valid text inputs in reverse input check, add deprecation version in warning
* Put function check reversed images text outside base processor class
* Refactor _validate_images_text_input_order
* Add ProcessingUtilTester
* fix processing and test_processing
* initial commit
* gloups
* updates
* work
* weights match
* nits
* nits
* updates to support the tokenizer :)
* updates
* Pixtral processor (#33454)
* rough outline
* Add in image break and end tokens
* Fix
* Udo some formatting changes
* Set patch_size default
* Fix
* Fix token expansion
* nit in conversion script
* Fix image token list creation
* done
* add expected results
* Process list of list of images (#33465)
* updates
* working image and processor
* this is the expected format
* some fixes
* push current updated
* working mult images!
* add a small integration test
* Uodate configuration docstring
* Formatting
* Config docstring fix
* simplify model test
* fixup modeling and etests
* Return BatchMixFeature in image processor
* fix some copies
* update
* nits
* Update model docstring
* Apply suggestions from code review
* Fix up
* updates
* revert modeling changes
* update
* update
* fix load safe
* addd liscence
* update
* use pixel_values as required by the model
* skip some tests and refactor
* Add pixtral image processing tests (#33476)
* Image processing tests
* Add processing tests
* woops
* defaults reflect pixtral image processor
* fixup post merge
* images -> pixel values
* oups sorry Mr docbuilder
* isort
* fix
* fix processor tests
* small fixes
* nit
* update
* last nits
* oups this was really breaking!
* nits
* is composition needs to be true
---------
Co-authored-by: amyeroberts <22614925+amyeroberts@users.noreply.github.com>
* fix long seq bug
* fixed format
* fixed fn copy inconsistency
* fix long seq bug
* fixed format
* fixed fn copy inconsistency
* Addressed comments
* added a unit test
* fixed cache position
* Added a warning msg to the forward fn
* fixed test case
* test(tokenizers): add a test showing conflict with sentencepiece
This is due to the fact that protobuf C implementation uses a global
pool for all added descriptors, so if two different files add
descriptors, they will end up conflicting.
* fix(tokenizers): mitigate sentencepiece/protobuf conflict
When sentencepiece is available, use that protobuf instead of the
internal one.
* chore(style): fix with ruff
* Fix default revision for pipelines
* dummy change to trigger CI
* revert dummy change
* dummy change to trigger CI
* revery dummy change
---------
Co-authored-by: Matt <rocketknight1@gmail.com>
* Update tokenization_whisper.py
Fix issue with flax whisper model
* Update tokenization_whisper_fast.py
Fix issue with flax whisper model
* Update tokenization_whisper.py
just check len of token_ids
* Update tokenization_whisper_fast.py
just use len of token_ids
* Update tokenization_whisper_fast.py and revert changes in _strip_prompt and add support to jax arrays in _convert_to_list
* Update tokenization_whisper.py and revert changes in _strip_prompt and add support to jax arrays in _convert_to_list
* Update test_tokenization_whisper.py to add test for _convert_to_list method
* Update test_tokenization_whisper.py to fix code style issues
* Fix code style
* Fix code check again
* Update test_tokenization)whisper.py to Improve code style
* Update test_tokenization_whisper.py to run each of jax, tf and flax modules if available
* Update tests/models/whisper/test_tokenization_whisper.py
Co-authored-by: amyeroberts <22614925+amyeroberts@users.noreply.github.com>
* Update test_tokenization_whisper.py and use require_xxx decorators instead of `is_xxx_available()` method
* Revert the changes automatically applied by formatter and was unrelated to PR
* Format for minimal changes
---------
Co-authored-by: amyeroberts <22614925+amyeroberts@users.noreply.github.com>
* add tests for linear shape behavior
* fix linear shape behavior
ended up adding the reshape at the end, after f8f8bf16_rowwise, because adding
it directly after quantize_fp8_per_row caused f8f8bf16_rowwise to drop the
seq_len dimension. (i.e., (17, 23, 1014) -> (17, 1024))
* save shape up front + comment
* Make StaticCache configurable at model construct time
* integrations import structure
* add new doc file to toc
---------
Co-authored-by: Guang Yang <guangyang@fb.com>
Co-authored-by: Joao Gante <joao@huggingface.co>
* Bug Fix: Update hub.py
Bug:
TypeError: argument of type 'NoneType' is not iterable
Analysis:
The error `TypeError: argument of type 'NoneType' is not iterable` suggests that `model_card.data.tags` is `None`, and the code is trying to iterate through it using `not in`.
Fix:
1. **Check if `model_card.data.tags` is `None` before the loop**:
Since you're checking the variable `tags` before the loop, you should also ensure that `model_card.data.tags` is not `None`. You can do this by initializing `model_card.data.tags` to an empty list if it's `None`.
2. **Updated code**:
Add a check and initialize the `tags` if it is `None` before proceeding with the iteration.
This way, if `model_card.data.tags` is `None`, it gets converted to an empty list before checking the contents. This prevents the `TypeError`.
* Update hub.py
* Update docs for GGUF supported models
* Add tensor mappings and define class GGUFPhi3Converter
* Fix tokenizer
* Working version
* Attempt to fix some CI failures
* Run ruff format
* Add vocab, merges, decoder methods like LlamaConverter
* Resolve conflicts since Qwen2Moe was added to gguf
- I missed one place when resolving conflict
- I also made a mistake with tests_ggml.py and now has been fixed to reflect
its master version.
* Import structure & first three model refactors
* Register -> Export. Export all in __all__. Sensible defaults according to filename.
* Apply most comments from Amy and some comments from Lucain
Co-authored-by: amyeroberts <22614925+amyeroberts@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Lucain Pouget <lucainp@gmail.com>
* Style
* Add comment
* Clearer .py management
* Raise if not in backend mapping
* More specific type
* More efficient listdir
* Misc fixes
---------
Co-authored-by: amyeroberts <22614925+amyeroberts@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Lucain Pouget <lucainp@gmail.com>
* Fixed typo: insted to instead
* Fixed typo: relase to release
* Fixed typo: nighlty to nightly
* Fixed typos: versatible, benchamarks, becnhmark to versatile, benchmark, benchmarks
* Fixed typo in comment: quantizd to quantized
* Fixed typo: architecutre to architecture
* Fixed typo: contibution to contribution
* Fixed typo: Presequities to Prerequisites
* Fixed typo: faste to faster
* Fixed typo: extendeding to extending
* Fixed typo: segmetantion_maps to segmentation_maps
* Fixed typo: Alternativelly to Alternatively
* Fixed incorrectly defined variable: output to output_disabled
* Fixed typo in library name: tranformers.onnx to transformers.onnx
* Fixed missing import: import tensorflow as tf
* Fixed incorrectly defined variable: token_tensor to tokens_tensor
* Fixed missing import: import torch
* Fixed incorrectly defined variable and typo: uromaize to uromanize
* Fixed incorrectly defined variable and typo: uromaize to uromanize
* Fixed typo in function args: numpy.ndarry to numpy.ndarray
* Fixed Inconsistent Library Name: Torchscript to TorchScript
* Fixed Inconsistent Class Name: OneformerProcessor to OneFormerProcessor
* Fixed Inconsistent Class Named Typo: TFLNetForMultipleChoice to TFXLNetForMultipleChoice
* Fixed Inconsistent Library Name Typo: Pytorch to PyTorch
* Fixed Inconsistent Function Name Typo: captureWarning to captureWarnings
* Fixed Inconsistent Library Name Typo: Pytorch to PyTorch
* Fixed Inconsistent Class Name Typo: TrainingArgument to TrainingArguments
* Fixed Inconsistent Model Name Typo: Swin2R to Swin2SR
* Fixed Inconsistent Model Name Typo: EART to BERT
* Fixed Inconsistent Library Name Typo: TensorFLow to TensorFlow
* Fixed Broken Link for Speech Emotion Classification with Wav2Vec2
* Fixed minor missing word Typo
* Fixed minor missing word Typo
* Fixed minor missing word Typo
* Fixed minor missing word Typo
* Fixed minor missing word Typo
* Fixed minor missing word Typo
* Fixed minor missing word Typo
* Fixed minor missing word Typo
* Fixed Punctuation: Two commas
* Fixed Punctuation: No Space between XLM-R and is
* Fixed Punctuation: No Space between [~accelerate.Accelerator.backward] and method
* Added backticks to display model.fit() in codeblock
* Added backticks to display openai-community/gpt2 in codeblock
* Fixed Minor Typo: will to with
* Fixed Minor Typo: is to are
* Fixed Minor Typo: in to on
* Fixed Minor Typo: inhibits to exhibits
* Fixed Minor Typo: they need to it needs
* Fixed Minor Typo: cast the load the checkpoints To load the checkpoints
* Fixed Inconsistent Class Name Typo: TFCamembertForCasualLM to TFCamembertForCausalLM
* Fixed typo in attribute name: outputs.last_hidden_states to outputs.last_hidden_state
* Added missing verbosity level: fatal
* Fixed Minor Typo: take To takes
* Fixed Minor Typo: heuristic To heuristics
* Fixed Minor Typo: setting To settings
* Fixed Minor Typo: Content To Contents
* Fixed Minor Typo: millions To million
* Fixed Minor Typo: difference To differences
* Fixed Minor Typo: while extract To which extracts
* Fixed Minor Typo: Hereby To Here
* Fixed Minor Typo: addition To additional
* Fixed Minor Typo: supports To supported
* Fixed Minor Typo: so that benchmark results TO as a consequence, benchmark
* Fixed Minor Typo: a To an
* Fixed Minor Typo: a To an
* Fixed Minor Typo: Chain-of-though To Chain-of-thought
* add self.head_dim for VisionAttention in Qwen2-VL
* add self.head_dim for VisionAttention in Qwen2-VL
* fix ci
* black the test_modeling_qwen2_vl.py
* use ruff to format test_modeling_qwen2_vl.py
* [run-slow] qwen2_vl
* use tying for python3.8
* fix the import format
* use ruff to fix the ci error I001
* [run-slow] qwen2_vl
* remove unused import
* commit for rebase
* use ruff fix ci
* [run-slow] qwen2_vl
---------
Co-authored-by: root <liji>
* Add validation for maximum sequence length in modeling_whisper.py
Added a validation check to ensure that the sequence length of labels does not exceed the maximum allowed length of 448 tokens. If the sequence length exceeds this limit, a ValueError is raised with a descriptive error message.
This change prevents the model from encountering errors or unexpected behavior due to excessively long sequences during training or fine-tuning, ensuring consistent input dimensions and improving overall robustness.
* Change exception message in src/transformers/models/whisper/modeling_whisper.py
The exception message is for whisper's label's sequence max length.
Co-authored-by: Yoach Lacombe <52246514+ylacombe@users.noreply.github.com>
* Change 448 to config.max_target_positions in src/transformers/models/whisper/modeling_whisper.py
It's for whisper's config.max_target_positions.
Co-authored-by: Yoach Lacombe <52246514+ylacombe@users.noreply.github.com>
* Change method's documentation in src/transformers/models/whisper/modeling_whisper.py
* Add test for maximum label's sequence length in test_modeling_whisper.py
* Add self to modeling_whisper.py
* Update test_modeling_whisper.py with respect to automatic validations
* Update modeling_whisper.py with respect to ci/circleci: check_code_quality
* Update test_modeling_whisper.py with respect to ci/circleci: check_code_quality
* Update test_modeling_whisper.py with respect to ci/circleci: tests_generate
* Update test_modeling_whisper.py with respect to ci/circleci: tests_generate
* Update test_modeling_whisper.py with respect to ci/circleci: check_code_quality
* Separate test_labels_sequence_max_length tests in test_modeling_whisper.py
* Update test_modeling_whisper.py with respect to ci/circleci: check_code_quality
* Remove assert from test_modeling_whisper.py
* Add max_target_positions to WhisperModelTester in test_modeling_whisper.py
* Update test_modeling_whisper.py with respect to ci/circleci: check_code_quality
* Update test_modeling_whisper.py with respect to ci/circleci: tests_generate
* Update test_modeling_whisper.py
* Change test_labels_sequence_max_length_error_after_changing_config in test_modeling_whisper.py
* Change self.config.max_target_positions to self.max_target_positions modeling_whisper.py
* Add new tests in test_modeling_whisper.py
* Update test_modeling_whisper.py
---------
Co-authored-by: Yoach Lacombe <52246514+ylacombe@users.noreply.github.com>
* Load remote code only once
* Use hash as load indicator
* Add a new option `force_reload` for old behavior (i.e. always reload)
* Add test for dynamic module is cached
* Add more type annotations to improve code readability
* Address comments from code review
* Add validate images and test processing utils
* Remove encoded text from possible inputs in tests
* Removed encoded inputs as valid in processing_utils
* change text input check to be recursive
* change text check to all element of lists and not just the first one in recursive checks
* [InstructBLIP] qformer_tokenizer is required input
* Bit safer
* Add to instructblipvideo processor
* Fix up
* Use video inputs
* Update tests/models/instructblipvideo/test_processor_instructblipvideo.py
* Fixing a bug in the way "attention_factor" is validated in ROPE utilities.
* Fixing a bug in the way "attention_factor" is validated in ROPE utilities.
* Fixing a bug in the way "attention_factor" is validated in ROPE utilities.
* use gguf internal dequantize
* add Q5_0 test
* add iq1 test
* add remained test
* remove duplicated test
* update docs
* add gguf version limit
* make style
* update gguf import catch
* revert vocab_size patch
* make style
* use GGUF_MIN_VERSION everywhere
* remove to restiction for 4-bit model
* Update src/transformers/modeling_utils.py
Co-authored-by: Matthew Douglas <38992547+matthewdouglas@users.noreply.github.com>
* bitsandbytes: prevent dtype casting while allowing device movement with .to or .cuda
* quality fix
* Improve warning message for .to() and .cuda() on bnb quantized models
---------
Co-authored-by: Matthew Douglas <38992547+matthewdouglas@users.noreply.github.com>
* don't run custom when not needed?
* update test fetcher filtering
* fixup and updates
* update
* update
* reduce burden
* nit
* nit
* mising comma
* this?
* this?
* more parallelism
* more
* nit for real parallelism on tf and torch examples
* update
* update
* update
* update
* update
* update
* update
* update
* update
* update
* update
* update
* update to make it more custom
* update to make it more custom
* update to make it more custom
* update to make it more custom
* update
* update
* update
* update
* update
* update
* use correct path
* fix path to test files and examples
* filter-tests
* filter?
* filter?
* filter?
* nits
* fix naming of the artifacts to be pushed
* list vs files
* list vs files
* fixup
* fix list of all tests
* fix the install steps
* fix the install steps
* fix the config
* fix the config
* only split if needed
* only split if needed
* extend should fix it
* extend should fix it
* arg
* arg
* update
* update
* run tests
* run tests
* run tests
* more nits
* update
* update
* update
* update
* update
* update
* update
* simpler way to show the test, reduces the complexity of the generated config
* simpler way to show the test, reduces the complexity of the generated config
* style
* oups
* oups
* fix import errors
* skip some tests for now
* update doctestjob
* more parallelism
* fixup
* test only the test in examples
* test only the test in examples
* nits
* from Arthur
* fix generated congi
* update
* update
* show tests
* oups
* oups
* fix torch job for now
* use single upload setp
* oups
* fu**k
* fix
* nit
* update
* nit
* fix
* fixes
* [test-all]
* add generate marker and generate job
* oups
* torch job runs not generate tests
* let repo utils test all utils
* UPdate
* styling
* fix repo utils test
* more parallel please
* don't test
* update
* bit more verbose sir
* more
* hub were skipped
* split by classname
* revert
* maybe?
* Amazing catch
Co-authored-by: Yih-Dar <2521628+ydshieh@users.noreply.github.com>
* fix
* update
* update
* maybe non capturing
* manual convert?
* pass artifacts as parameters as otherwise the config is too long
* artifact.json
* store output
* might not be safe?
* my token
* mmm?
* use CI job IS
* can't get a proper id?
* ups
* build num
* update
* echo url
* this?
* this!
* fix
* wget
* ish
* dang
* udpdate
* there we go
* update
* update
* pass all
* not .txt
* update
* fetcg
* fix naming
* fix
* up
* update
* update
* ??
* update
* more updates
* update
* more
* skip
* oups
* pr documentation tests are currently created differently
* update
* hmmmm
* oups
* curl -L
* update
* ????
* nit
* mmmm
* ish
* ouf
* update
* ish
* update
* update
* updatea
* nit
* nit
* up
* oups
* documentation_test fix
* test hub tests everything, just marker
* update
* fix
* test_hub is the only annoying one now
* tf threads?
* oups
* not sure what is happening?
* fix?
* just use folder for stating hub
* I am getting fucking annoyed
* fix the test?
* update
* uupdate
* ?
* fixes
* add comment!
* nit
---------
Co-authored-by: ydshieh <ydshieh@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Yih-Dar <2521628+ydshieh@users.noreply.github.com>
* first attempt at allowing both conversions from codestral and from the original mamba ssm
* allow fp16, seems default for mamba2
* dtype fix
* simplify codestral check, dont overwrite pad/eos/bos when codestral
* change file -> directory
* use path join to be safe
* style
* apply code review
- add util mamba2 tokenizer (gptneox with left padding)
- add models dict
* fix copies
* add tokenizer to docs
* empty commit to check for weird err
* make conversion user dependent on model type, defaults for original paper models
* small comment nit
* remove norm_before_gate in conversion
* simplify model dict by using shared keys directly + remove unnecessary attributes
* fix tokenization: remove separate mamba2 tokenizer, add padding option as kwarg to gptneox one and reuse it for the conversion script
* simplify even further as we pass padding side via **kwargs already
* pass module to Params4bit.from_prequantized to ensure quant_state
* make sure to check bnb version
* revert min bnb version and use inspect on method instead
* use version instead of inspect to prevent performance hit
* make the property name readable
* Customising the separator used for splicing in DataCollatorWithFlattening
* update DataCollatorWithFlattening docs
---------
Co-authored-by: weifangyuan <i.weifangyuan@yuewen.com>
* Adding SDPA support for RoBERTa-based models
* add not is_cross_attention
* fix copies
* fix test
* add minimal test for camembert and xlm_roberta as their test class does not inherit from ModelTesterMixin
* address some review comments
* use copied from
* style
* consistency
* fix lists
---------
Co-authored-by: fxmarty <9808326+fxmarty@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Arthur <48595927+ArthurZucker@users.noreply.github.com>
* init fix
* fix mask during cached forward, move mask related stuff to own function
* adjust tests as left padding does not change logits as much anymore + batch gen (with todo on logits comp)
* revert overwriting new integration tests
* move some comments to docstring
* add Blip2ForImageTextRetrieval
* use one line and remove unnecessary space in tests
Co-authored-by: amyeroberts <22614925+amyeroberts@users.noreply.github.com>
* use value from the config, rather than hardcoded
* change order of params in Blip2QFormerModel.forward
* update docstring
* fix style
* update test_inference_opt
* move embeddings out of Blip2QFormerModel
* remove from_vision_qformer_configs
* remove autocast float16 in Blip2QFormerModel
* rename fiels into vision_projection,text_projection,use_image_text_matching_head
* use CLIPOutput for Blip2ImageTextMatchingModelOutput
* remove past_key_values_length from Blip2TextEmbeddings
* fix small typo in the CLIPOutput docstring
* add Blip2ForImageTextRetrieval to Zero Shot Image Classification mapping
* update docstring and add require_torch_fp16
* rollback test_inference_opt
* use use_image_text_matching_head=True in convert
* skip test_model_get_set_embeddings
* fix create_rename_keys error on new itm fields
* revert to do scale after dot product between "query" and "key"
* fix ValueError on convert script for blip2-opt-2.7b
* update org of paths to Salesforce
* add is_pipeline_test_to_skip for VisualQuestionAnsweringPipelineTests
* [run_slow] blip_2
* removed Blip2ForImageTextRetrieval from IGNORE_NON_AUTO_CONFIGURED
* fix docstring of Blip2ImageTextMatchingModelOutput
* [run_slow] blip_2
* fix multi-gpu tests
* [run_slow] blip_2
* [run_slow] blip_2
---------
Co-authored-by: amyeroberts <22614925+amyeroberts@users.noreply.github.com>
Very small change to one of the parameters
np.random.randint second parameter is not included in the possible options. Therefore, we want the upper range to be 2, so that we have some 1 labels in our classification as well.
* Add a fix for the case when tokenizers are passed as a string
* Support image processors and feature extractors as well
* Reverting load_feature_extractor and load_image_processor
* Add test
* Test is torch-only
* Add tests for preprocessors and feature extractors and move test
* Extremely experimental fix
* Revert that change, wrong branch!
* Typo!
* Split tests
* update ExportableState callbacks state before saving trainer_state on save_checkpoint
* run make fixup and fix format
* manage multiple stateful callbacks of same class
* Log additional test metrics with the CometCallback.
Also follow the same metric naming convention as other callbacks
* Merge 2 subsequent if-statements
* Trigger Build
---------
Co-authored-by: Aliaksandr Kuzmik <alexander.kuzmik99@gmail.com>
* fix: multilingual midel convert to tflite get wrong token
* fix: modify test_force_tokens_logits_processor the checking value as scores.dtype.min
---------
Co-authored-by: kent.sc.hung <kent.sc.hung@benq.com>
Co-authored-by: Aya <[kent831217@gmail.com]>
* Add changes for uroman package to handle non-Roman characters
* Update docs for uroman changes
* Modifying error message to warning, for backward compatibility
* Update instruction for user to install uroman
* Update docs for uroman python version dependency and backward compatibility
* Update warning message for python version compatibility with uroman
* Refine docs
* Add new Jinja features:
- Do extension
- Break/continue in loops
- Call strftime to get current datetime in any format
* Add new Jinja features:
- Do extension
- Break/continue in loops
- Call strftime to get current datetime in any format
* Fix strftime template
* Add template strip() just to be safe
* Remove the do extension to make porting easier, and also because it's the least useful
* Rename test
* strftime -> strftime_now
* Split test
* Update test to use strftime_now
* Refactor everything out into chat_template_utils
* Refactor everything out into chat_template_utils
* Refactor everything out into chat_template_utils
* Refactor everything out into chat_template_utils
* Refactor everything out into chat_template_utils
* Add .float() in all generation methods logit outputs
* Switch float-casting of logits to training only for main models
* Add `num_logits_to_keep` in Llama and add it by default in generate
* Apply style
* Add num_logits_to_keep as arg in prepare_input_for_generation
* Add support for Mistral
* Revert models except llama and mistral
* Fix default None value in _supports_num_logits_to_keep()
* Fix dimension of dummy input
* Add exception for prophetnet in _supports_num_logits_to_keep()
* Update _supports_num_logits_to_keep() to use inspect.signature()
* Add deprecation cycle + remove modification with pretraining_tp
* Apply style
* Add most used models
* Apply style
* Make `num_logits_to_keep` an int in all cases to remove if-else clause
* Add compile check for the warning
* Fix torch versions
* style
* Add gemma2
* Update warning version
* Add comment about .float operations in generation utils
* Add tests in GenerationTesterMixin and ModelTesterMixin
* Fix batch size for assisted decoding in tests
* fix small issues in test
* refacor test
* fix slicing removing dim issue
* Add nemotron support (should fix check-copy issue in CIs)
* Trigger new CIs
* Trigger new CIs
* Bump version
* Bump version in TODO
* Trigger CIs
* remove blank space
* Trigger CIs
* link for optimizer names
Add a note and link to where the user can find more optimizer names easily because there are many more optimizers than are mentioned in the docstring.
* make fixup
* fix: Parameterized norm freezing
For the R18 model, the authors don't freeze norms in the backbone.
* Update src/transformers/models/rt_detr/configuration_rt_detr.py
Co-authored-by: Pavel Iakubovskii <qubvel@gmail.com>
---------
Co-authored-by: Pavel Iakubovskii <qubvel@gmail.com>
* Add representation for Conv1D, for better output info.
* code format for Conv1D
* We add a __repr__ func for Conv1D, this allows the print (or output) of the model's info has a better description for Conv1D.
* Fix: fix all model_type of Llava-Next-Video to llava_next_video
* Fix doc for llava_next_video
* * Fix formatting issues
* Change llava-next-video.md file name into llava_next_video.md to make it compatible with implementation
* Fix docs TOC for llava-next-video
* Update the Kubernetes CPU training example
* Add namespace arg
Signed-off-by: Dina Suehiro Jones <dina.s.jones@intel.com>
---------
Signed-off-by: Dina Suehiro Jones <dina.s.jones@intel.com>
* Add TorchAOHfQuantizer
Summary:
Enable loading torchao quantized model in huggingface.
Test Plan:
local test
Reviewers:
Subscribers:
Tasks:
Tags:
* Fix a few issues
* style
* Added tests and addressed some comments about dtype conversion
* fix torch_dtype warning message
* fix tests
* style
* TorchAOConfig -> TorchAoConfig
* enable offload + fix memory with multi-gpu
* update torchao version requirement to 0.4.0
* better comments
* add torch.compile to torchao README, add perf number link
---------
Co-authored-by: Marc Sun <marc@huggingface.co>
* Update modeling_tf_deberta.py
Corrected some codes which do not support mixed precision
* Update modeling_tf_deberta_v2.py
Corrected some codes which do not support mixed precision
* Update modeling_tf_deberta_v2.py
* Update modeling_tf_deberta.py
* Add files via upload
* Add files via upload
* Add padding="max_length" to tokenizer kwargs and change crop_size to size for image_processor kwargs
* remove crop_size argument in align processor tests to be coherent with base tests
* Add pad_token when loading tokenizer if needed, change test override tokenizer kwargs, remove unnecessary test overwrites in grounding dino
* Fixed wrong argument in is_torch_mps_available() function call.
* Fixed wrong argument in is_torch_mps_available() function call.
* sorted the import.
* Fixed wrong argument in is_torch_mps_available() function call.
* Fixed wrong argument in is_torch_mps_available() function call.
* Update src/transformers/utils/import_utils.py
Co-authored-by: Arthur <48595927+ArthurZucker@users.noreply.github.com>
* removed extra space.
* Added type hint for the min_version parameter.
* Added missing import.
---------
Co-authored-by: Arthur <48595927+ArthurZucker@users.noreply.github.com>
* Rename "Templates for Chat Models" doc to "Chat Templates"
* Small formatting fix
* Small formatting fix
* Small formatting fix
* Cleanup tool calling docs as well
* Remove unneeded 'revision'
* Move tip to below main code example
* Little bonus section on template editing
* fix sliding window attention (flash2) in gemma2 model
* [run-slow] gemma
* fix slicing attention_mask for flash_attn2
* fix slicing attention_mask when flash_attn is used
* add missing comment
* slice the last seq_len tokens in the key, value states
* revert code of slicing key, value states
* fix typo
* uniform kwargs
* make style
* add comments
* remove return_tensors
* remove common_kwargs from processor since it propagates
* make style
* return_token_type_ids to True
* revert the default imagekwargs since does not accept any value in the image processro
* revert processing_utils.py
* make style
* add molbap's commit
* fix typo
* fix common processor
* remain
* Revert "add molbap's commit"
This reverts commit a476c6ee88318ce40d73ea31e2dc2d4faa8ae410.
* add unsync PR
* revert
* make CI happy
* nit
* import annotationformat
* Revert "fixes to properly shard FSDP across cpu and meta for cpu_efficient_loading for prequantized 4bit (#32276)"
This reverts commit 62c60a30181a65e1a3a7f19c3055a240a6a21335.
We uncovered an issue with this change that caused our training runs to hang.
* `is_torchdynamo_compiling` -- cast a wide exception net (#32476)
* cast a wide net
* make fix-copies with a few manual changes
* add copied from
---------
Co-authored-by: Joao Gante <joaofranciscocardosogante@gmail.com>
* Migrate import checks to secondary accelerate calls
* better errs too
* Revert, just keep the import checks + remove accelerate-specific things
* Rm extra'
* Empty commit for ci
* Small nits
* Final
* add new model like
* draft cuda forward - mismatched keys (sharding on conv1)
* match keys successfully
* fix split
* get generation/forward running (wrong gens, norm?)
* :update
* some refactoring
* fixes
* works up until copy to cache
* fix
* update
* NON WORKING VERSION
* version that work?
* nit
* fix config
* fix conversion script
* working cuda forward
* nit
* update
* simplifcation
* make mamba slow simple work
* no einops
* todo
* fix style
* no einops
* update fix no einsum
* nit
* remove einops
* bug: scan_output differs strongly
* add rms norm option
* fix fast + slow generation with and w/o cache ✔️
* draft integration tests
* remove a big chunk of the einsum
* fix slow, fast generations, without any einsum
* fix copies
* fix structure
* fix up modeling and tests
* fix tests
* clamping is indeed worse
* recover mamba2 cache test
* fix copies
* no cache position (yet)
* fix tf tests
* fix matmul for generate
* fixup
* skip cache tests for now
* [run-slow]mamba2
* tune out hidden states for padding
* test batched generation
* propagate attention mask changes
* fix past length
* fix integration test
* style
* address comments
* update readme
* add mamba2 version check
* fix tests
* [run-slow]mamba2
* skip edge tests
* [run-slow]mamba2
* last fixup
* [run-slow]mamba2
* update README
---------
Co-authored-by: Arthur Zucker <arthur.zucker@gmail.com>
* save total_vocab_size = vocab_size + user added tokens to speed up operation
* updating length when added_tokens_decoder is set
* add test len(tokenizer)
* Mixtral: remove unnecessary plus 1 when calculating rotary_seq_len, allowing position_ids=None (no auto position_ids generation could be unsafe)
* fix typo [:-1] to [:, -1]
* to meet formatting requirement
* to meet formatting requirement
* remove white space
* MixtralFlashAttention2: put "+ 1" inside parentheses when calculating rotary_seq_len, allowing None position_ids input. Fix format/style issue.
* propagate to startcoder2, phi3, mixtral and qwen2
* update qwen2_moe
* Initial implementation of OffloadedCache
* enable usage via cache_implementation
* Address feedback, add tests, remove legacy methods.
* Remove flash-attn, discover synchronization bugs, fix bugs
* Prevent usage in CPU only mode
* Add a section about offloaded KV cache to the docs
* Fix typos in docs
* Clarifications and better explanation of streams
* Fix conflicting key in init kwargs in PreTrainedTokenizerBase
* Update code to check for callable key in save_pretrained
* Apply PR suggestions
* Invoke CI
* Updates based on PR suggestion
* Fixed staticmethods with self as first argument.
* Fixed staticmethods with self as first argument.
* Fixed staticmethods with self as first argument.
* Fixed staticmethods with self as first argument.
* Remove user-defined tokens which can be obtained through merges
* Remove debug line
* formatting
* Refactor spm slow -> fast converter
* revert unnecessary refactor
* set comprehension
* remove test files
* Use `vocab_scores`
* Always replace spiece underline with space in decode
* we no longer need token filtering
* Add save fast load slow unit test
* Remove tokenizers version check
* Remove duplicate code
* Make `<start_of_turn>` and `<end_of_turn>` special tokens
* Bias merge priority with length if score is the same
* Add unit test for merge priority
* CI
* tmp
* skip files not in the diff
* use git.Repo instead of an external subprocess
* add tiny change to confirm that the diff is working on pushed changes
* add make quality task
* more profesh main commit reference
fixes#32329 : The Torch code is correct - to get an average of 10% of the total, we want to take 50% of the remainder after we've already masked 80% with [MASK] in the previous step.
* mvp
* added test (a few models need fixes)
* fix a few test cases
* test nits
* harder test 😈
* revert changes in stablelm
* test with improved condition
* add todo
* tmp commit
* merged with main
* nits
* add todo
* final corrections
* add docs for generation compilation
* docs nits
* add tip
* PR suggestions
* add more details to the compilation docs
* fix cache positions
* cache is now init in generate; update docs
* tag test as flaky
* docs
* post rebase make fixup and other nits
* remove unintended changes
* whisper (encoder-decoder) not supported
* move token default updates to ; add tests for token defaults
* push changes
* manual rebase
* chameleon doesn't support this
* fix test_static_cache_mha_mqa_gqa (broken in another PR)
* docs: dynamic is better with end-to-end compilation
* Add check for target_sizes is None in post_process_image_guided_detection
* Make sure Owlvit and Owlv2 in sync
* Fix incorrect indentation; add check for correct size of target_sizes
* No more default chat templates
* Add the template to the GPT-SW3 tests since it's not available by default now
* Fix GPT2 test
* Fix Bloom test
* Fix Bloom test
* Remove default templates again
* fix: default value reflects the runtime environment variables rather than the ones present at import time.
* Fix: Change `deterministic` to None by default; use env var if None
* Updated ruff version and fixed the required code accorindg to the latest version.
* Updated ruff version and fixed the required code accorindg to the latest version.
* Added noqa directive to ignore 1 error shown by ruff
* add DataCollatorBatchFlattening
* Update data_collator.py
* change name
* new FA2 flow if position_ids is provided
* add comments
* minor fix
* minor fix data collator
* add test cases for models
* add test case for data collator
* remove extra code
* formating for ruff check and check_repo.py
* ruff format
ruff format tests src utils
* custom_init_isort.py
* feat(cache): StaticCache uses index_copy_ to avoid useless copy
Using index_copy_ allows for explicit in-place change of the tensor.
Some backends (XLA) will otherwise copy the tensor, making the code
slower and using more memory.
Proposed implementation will end up using less memory and on XLA will
result in less compilation, but the change is also quite generic, making
no change whatsoever on CUDA or CPU backend.
* feat(cache): SlidingWindowCache uses index_copy_ to avoid useless copy
Applying the same change done in StaticCache.
* fix(cache): fallback of index_copy_ when not implemented
* fix(cache): in index_copy_ ensure tensors are on same device
* [run slow] llama
* fix(cache): add move of cache_position to same device in SlidingWindowCache
* Revert "[run slow] llama"
This reverts commit 02608dd14253ccd464e31c108e0cd94364f0e8b9.
* gguf conversion forces add_prefix_space=False for llama3, this is not required and forces from_slow, which fails. changing to None + test
* typo
* clean test
* Change resize_token_embeddings to make it return same Class that is passed to it
* Add explanatory comment as requested in review
* Add explanatory comments for add resizing function in lxmert
* Add comment for padding_idx and moving _resize_bias in lxmert to LxmertForPreTraining
---------
Co-authored-by: Prashanth Sateesh <prasatee@Prashanths-MBP.attlocal.net>
Co-authored-by: Prashanth Sateesh <prasatee@Prashanths-MacBook-Pro.local>
* Add YaRN and Dynamic-YaRN RoPE Scaling Methods
YaRN (Yet another RoPE extension method) combines the NTK-By-Parts
Interpolation and Attention Scaling methods, improving upon existing
RoPE interpolation methods for longer context window sizes.
Fine-tuned models maintain their original performance across benchmarks
while enabling efficient extrapolation and transfer learning for
quicker convergence, especially in compute-limited environments.
We implement YaRN and Dynamic-YaRN for the following list of models:
- LLaMA
- Falcon
- GPT-NeoX
- Olmo
- Persimmon
- Phi
- StableLM
- OpenLLaMA
New unit tests are added to assert YaRN's correct behavior on both
short and long sequence inputs.
For more details, please refer to https://arxiv.org/abs/2309.00071.
Co-authored-by: Miguel Almeida <miguel.pessanha.almeida@tecnico.ulisboa.pt>
* Refactor YaRN implementation for LLaMA
Iterate on YaRN implementation for LLaMA and remove diff from remaining
models for increased PR modularity.
This commit includes the following changes:
- Merge 'yarn_rope_scaling' and 'rope_scaling' dictionaries
- Remove unnecessary attributes ('extrapolation_factor' and 'finetuned')
from YaRN classes
- Inherit 'forward' method in YaRN classes from superclass
- Rename 'yarn' method to 'compute_yarn_scaling'
- Extend YaRN tests with further assertions
- Fix style inconsistencies
Co-authored-by: Miguel Monte e Freitas <miguelmontefreitas@tecnico.ulisboa.pt>
* Refactor Tensor Building Logic for YaRN
- Comply with the the tensor building logic introduced in #30743
- Add referencing to the optimized Attention Factor equation
- Remove Dynamic YaRN for a more agile deployment
Co-authored-by: mig-mfreitas <mig-mfreitas@users.noreply.github.com>
* remove unwanted file
---------
Co-authored-by: Miguel Almeida <miguel.pessanha.almeida@tecnico.ulisboa.pt>
Co-authored-by: mig-mfreitas <mig-mfreitas@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Joao Gante <joao@huggingface.co>
* fix mask creation of gpt2 and gpt_neox caused by me
* forgot the reshape of masks when shape > 2
* add tests for gpt neox and gpt2
* nit on a comment
* Add llama3-llava-next-8b to llava_next conversion script
Adds support for the lmms-lab/llama3-llava-next-8b model to the
convert_llava_next_weights_to_hf.py script, along with an example
prompt generated from the llava_llama_3 conv_template in the LLaVA-NeXT
repo.
* Exclude <|begin_of_text|> from prompt example
This token gets added automatically, so it should not be included in the
prompt example.
* Add llava-next-72b and llava-next-110b
Adds the Qwen-based LLaVA-Next models to the conversion script, along
with changes to load the models on multiple GPUs for inference.
* Add llama3 and qwen prompt formats to docs
* Chat prompt and padding side left for llama3 batched
* update
* Update src/transformers/models/llava_next/convert_llava_next_weights_to_hf.py
Co-authored-by: amyeroberts <22614925+amyeroberts@users.noreply.github.com>
* Update src/transformers/models/llava_next/convert_llava_next_weights_to_hf.py
Co-authored-by: amyeroberts <22614925+amyeroberts@users.noreply.github.com>
* remove code
* better naming
---------
Co-authored-by: raushan <raushan@huggingface.co>
Co-authored-by: Raushan Turganbay <raushan.turganbay@alumni.nu.edu.kz>
Co-authored-by: amyeroberts <22614925+amyeroberts@users.noreply.github.com>
* Replacing ProgressCallbacks deepcopy with a shallowcopy
* Using items instead of entries
* code cleanup for copy in trainer callback
* Style fix for ProgressCallback
* add language to words
_collate_word_timestamps uses the return_language flag to determine whether the language of the chunk should be added to the word's information
* ran style checks
added missing comma
* add new language test
test that the pipeline can return both the language and timestamp
* remove model configuration in test
Removed model configurations that do not influence test results
* remove model configuration in test
Removed model configurations that do not influence test results
Make problem_type condition consistent with num_labels condition
The latter condition generally overrides the former, so this is more of a code reading issue. I'm not sure the bug would ever actually get triggered under normal use.
* 1,100%!
* Clean
* Don't touch DS
* Experiment with dtype allocation
* skip test_load_save_without_tied_weights test
* A little faster
* Include proper upscaling?
* Fixup tests
* Potentially skip?
* Let's see if this fixes git history
* Maintain new dtype
* Fin
* Rm hook idea for now
* New approach, see what breaks
* stage
* Clean
* Stash
* Should be fin now, just need to mark failing models
* Clean up
* Simplify
* Deal with weird models
* Enc/Dec
* Skip w/ reason
* Adjust test
* Fix test
* one more test
* Keep experimenting
* Fix ref
* TO REMOVE: testing feedback CI
* Right push
* Update tests/utils/test_modeling_utils.py
Co-authored-by: Arthur <48595927+ArthurZucker@users.noreply.github.com>
* disable
* Add new func
* Test nits from Amy
* Update src/transformers/modeling_utils.py
Co-authored-by: amyeroberts <22614925+amyeroberts@users.noreply.github.com>
* Adjust comment
* Adjust comment on skip
* make private
* Fin
* Should be a not flag
* Clarify and rename test
---------
Co-authored-by: Marc Sun <marc@huggingface.co>
Co-authored-by: Arthur <48595927+ArthurZucker@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: amyeroberts <22614925+amyeroberts@users.noreply.github.com>
* tmp commit
* shorter
* nit
* explicit kwargs
* propagate changes
* mass propagation with a few manual touches (let's see how CI behaves)
* fix cacheless case
* Update src/transformers/generation/utils.py
Co-authored-by: Arthur <48595927+ArthurZucker@users.noreply.github.com>
* make fixup
---------
Co-authored-by: Arthur <48595927+ArthurZucker@users.noreply.github.com>
* Change `Trainer.get_optimizer_cls_and_kwargs` to `self.`
* Make `get_optimizer_cls_and_kwargs` an instance method
* Fixing typo
* Revert `get_optimizer_cls_and_kwargs` to staticmethod
* restore newline to trainer.py eof
* Add warning message for and parameters
* Fix when the warning is raised
* Formatting changes
* Improve testing and remove duplicated warning from _fix_key
* add gather_use_object arguments
* fix name and pass the CI test for Seq2SeqTrainer
* make style
* make it to functools
* fix typo
* add accelerate version:
* adding warning
* Update src/transformers/trainer.py
Co-authored-by: Marc Sun <57196510+SunMarc@users.noreply.github.com>
* make style
* Update src/transformers/training_args.py
* check function move to initial part
* add test for eval_use_gather_object
* fix minor
---------
Co-authored-by: Marc Sun <57196510+SunMarc@users.noreply.github.com>
* fix galore lr display with lr schedulers
* style
* add some tests to check for displayed lrs
* copy-paste err for warmup steps
* standardize the default lr to be only in the optimizer
* trying out my luck with the reads
* cast image features to model.dtype where needed to support FP16 or other precision in pipelines
* Update src/transformers/pipelines/image_feature_extraction.py
Co-authored-by: amyeroberts <22614925+amyeroberts@users.noreply.github.com>
* Use .to instead
* Add FP16 pipeline support for zeroshot audio classification
* Remove unused torch imports
* Add docs on FP16 pipeline
* Remove unused import
* Add FP16 tests to pipeline mixin
* Add fp16 placeholder for mask_generation pipeline test
* Add FP16 tests for all pipelines
* Fix formatting
* Remove torch_dtype arg from is_pipeline_test_to_skip*
* Fix format
* trigger ci
---------
Co-authored-by: amyeroberts <22614925+amyeroberts@users.noreply.github.com>
* Repeating an important warning in the chat template docs
* Update docs/source/en/chat_templating.md
Co-authored-by: Lysandre Debut <hi@lysand.re>
* Reword for clarity
* Reword for clarity
---------
Co-authored-by: Lysandre Debut <hi@lysand.re>
* Add siglip loss function
* Update docs
* Enable training tests
[experimental] enable GC training tests as it has worked for my own data
* Remove test_training* overrides to enable training tests
[run_slow] siglip
* Skip training tests for Siglip text model and ImageClassificationModel
[run_slow] siglip
* Skip GC training tests for SiglipForImageClassification
* Explicitly skip training tests for SiglipVisionModel
Add skip reason for training tests for SiglipTextModel
* Remove copied from to fix CI
* Update CometCallback to allow reusing of the running experiment
* Fixups
* Remove useless TODO
* Add checks for minimum version of the Comet SDK
* Fix documentation and links.
Also simplify how the Comet Experiment name is passed
* Add torch_empty_cache_steps to TrainingArguments
* Fix formatting
* Add torch_empty_cache_steps to docs on single gpu training
* Remove check for torch_empty_cache_steps <= max_steps
* Captalize Tip
* Be device agnostic
* Fix linting
* Fix init for rt-detr heads
* Fixup
* Add separate prior_prob value to config for initialization
* Add bbox init
* Change to 1 / num_labels init
* Adjust weights init test
* Fix style for test
* [fix BUG] pad labels before use it in preprocess_logits_for_metrics
* a more readable fix
labels can't use `gather` before pass to `preprocess_logits_for_metrics`, so must split into 2 if-block
* add a comment
* oh code quality check
* remove incorrect urls pointing to the llava repository
* remove incorrect urls pointing to the llava repository; removing entire comments
* remove incorrect urls pointing to the llava repository; removing entire comments; ran fix-copies
* ran fixup
* add gather_use_object arguments
* fix name and pass the CI test for Seq2SeqTrainer
* make style
* make it to functools
* fix typo
* add accelerate version:
* adding warning
* Update src/transformers/trainer.py
Co-authored-by: Marc Sun <57196510+SunMarc@users.noreply.github.com>
* make style
* Update src/transformers/training_args.py
* check function move to initial part
* add test for eval_use_gather_object
---------
Co-authored-by: Marc Sun <57196510+SunMarc@users.noreply.github.com>
* squash into single commit
* run diff once more
* docstring
* tests
* minor chnages and ready to go
* Update src/transformers/models/llava_next_video/processing_llava_next_video.py
Co-authored-by: amyeroberts <22614925+amyeroberts@users.noreply.github.com>
* Update tests/models/vipllava/test_modeling_vipllava.py
Co-authored-by: amyeroberts <22614925+amyeroberts@users.noreply.github.com>
* [run-slow] llava-next-video
* [run-slow] llava-next-video
* [run-slow] llava_next_video
* fix two tests
* fix slow tests
* remove logit checks due to numeric errors
* run test once more
* [run-slow] llava_next_video
* final try to pass the test
* [run-slow] llava_next_video
* [run-slow] llava_next_video
* [run-slow] llava_next_video
* style
* fix
* style
---------
Co-authored-by: amyeroberts <22614925+amyeroberts@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: ydshieh <ydshieh@users.noreply.github.com>
* fix llama fsdp
* fixup
* adding FSDP tests for CPU offloading
* fixes
* fix tests
* fix tests
* add it for mixtral
* propagate the changes on other models
* Update src/transformers/models/phi/modeling_phi.py
* Delete utils/testing_scripts/fsdp_cpu_offloading.py
Remove script - FSDP + CPU offloading it tested in the test suite
* Delete utils/testing_scripts/dummy_fsdp_config.yml
* Update + add cache_positions docstring
---------
Co-authored-by: amyeroberts <22614925+amyeroberts@users.noreply.github.com>
* starting support for sdpa in `gptneox` models
* small comment on tests
* fix dropout
* documentation and style
* clarify concrete paths for reference
* generalise attn projections and rope application
added head mask check to sdpa mask creation
handle sdpa memory backend bug via own version flag
* update docs and style
* move dtype casting outside of general attn_projection_and_rope function
fix flash_attn_2 stuff
* more generic attn warning if output_attns or head_mask
* simplify head mask check by moving head mask creation to a later point
* remove copied llama artifact
* remove padding_mask from attention function signature
* removing unnecessary comments, only "save" attn implementation once
* [run_slow] gpt_neox
* Add initial implementation of `spectrogram_batch`
* Format the initial implementation
* Add test suite for the `spectrogram_batch`
* Update `spectrogram_batch` to ensure compatibility with test suite
* Update `spectrogram_batch` to include pre and post-processing
* Add `amplitude_to_db_batch` function and associated tests
* Add `power_to_db_batch` function and associated tests
* Reimplement the test suite for `spectrogram_batch`
* Fix errors in `spectrogram_batch`
* Add the function annotation for `spectrogram_batch`
* Address code quality
* Re-add `test_chroma_equivalence` function
* Update src/transformers/audio_utils.py
Co-authored-by: amyeroberts <22614925+amyeroberts@users.noreply.github.com>
* Update src/transformers/audio_utils.py
Co-authored-by: amyeroberts <22614925+amyeroberts@users.noreply.github.com>
---------
Co-authored-by: amyeroberts <22614925+amyeroberts@users.noreply.github.com>
* PR SPLIT: moving origina changes for adding user defined symbols
* adding gemma test and generalizing gemma converter
* ruff
* update common test
* update serialization test
* deberta v2 tests updates as rust version adds '.' as a user added token, so a space is not added
* removing commented lines
* applying feedback - user only added_tokens to add and check piece.type instead of trainer_spec for user_defined_symbols
* add comment referencing sentencepiece
* Consider inheritance in type checking for tensors
Add an additional check to bypass type assertion when both tensors are
torch.Tensor instances.
* Fix the quality issue
* Update chat template docs
* Minor bug in the version check
* Update docs/source/en/chat_templating.md
Co-authored-by: Joshua Lochner <admin@xenova.com>
* Update docs/source/en/chat_templating.md
Co-authored-by: Joshua Lochner <admin@xenova.com>
* Update docs/source/en/chat_templating.md
Co-authored-by: Joshua Lochner <admin@xenova.com>
* Replace backticks with bolding because the doc builder was trying to parse them
* Replace backticks with bolding because the doc builder was trying to parse them
* Replace backticks with bolding because the doc builder was trying to parse them
* More cleanups to avoid upsetting the doc builder
* Add one more tip at the end
---------
Co-authored-by: Joshua Lochner <admin@xenova.com>
* Fix single letter stop strings
* Change the 0 to a 1 to avoid potential empty vector headaches later
* Restructure for clarity
* Update tests/generation/test_stopping_criteria.py
Co-authored-by: amyeroberts <22614925+amyeroberts@users.noreply.github.com>
* Add the unsqueeze
---------
Co-authored-by: amyeroberts <22614925+amyeroberts@users.noreply.github.com>
* Improve Python interpreter
* Add with and assert statements
* Prevent overwriting existing tools
* Check interpreter errors are well logged in code agent
* Add lazy evaluation for and and or
* Improve variable assignment
* Fix early return statements in functions
* Add small import fix on interpreter tool
* Pass datasets trust_remote_code
* Pass trust_remote_code in more tests
* Add trust_remote_dataset_code arg to some tests
* Revert "Temporarily pin datasets upper version to fix CI"
This reverts commit b7672826cad31e30319487af876e608d8af7d37b.
* Pass trust_remote_code in librispeech_asr_dummy docstrings
* Revert "Pin datasets<2.20.0 for examples"
This reverts commit 833fc17a3e3f0dcb40cff2ffd86c00ad9ecadab9.
* Pass trust_remote_code to all examples
* Revert "Add trust_remote_dataset_code arg to some tests" to research_projects
* Pass trust_remote_code to tests
* Pass trust_remote_code to docstrings
* Fix flax examples tests requirements
* Pass trust_remote_dataset_code arg to tests
* Replace trust_remote_dataset_code with trust_remote_code in one example
* Fix duplicate trust_remote_code
* Replace args.trust_remote_dataset_code with args.trust_remote_code
* Replace trust_remote_dataset_code with trust_remote_code in parser
* Replace trust_remote_dataset_code with trust_remote_code in dataclasses
* Replace trust_remote_dataset_code with trust_remote_code arg
* xpu: support xpu backend from stock pytorch (>=2.4)
Fixes: https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/issues/31237
XPU backend is available in the stock PyTorch starting from
version 2.4, see [1]. This commit extends huggingface transformers
to support XPU from both IPEX and the stock pytorch. IPEX is being
tried first.
See: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/114842
Requires: https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate/pull/2825
Signed-off-by: Dmitry Rogozhkin <dmitry.v.rogozhkin@intel.com>
* xpu: enable gpt2 and decision_transformer tests for xpu pytorch backend
Note that running xpu tests requires TRANSFORMERS_TEST_DEVICE_SPEC=spec.py
passed to the test runner:
import torch
DEVICE_NAME = 'xpu'
MANUAL_SEED_FN = torch.xpu.manual_seed
EMPTY_CACHE_FN = torch.xpu.empty_cache
DEVICE_COUNT_FN = torch.xpu.device_count
Signed-off-by: Dmitry Rogozhkin <dmitry.v.rogozhkin@intel.com>
---------
Signed-off-by: Dmitry Rogozhkin <dmitry.v.rogozhkin@intel.com>
* Let's try moving chat templates out of IDEFICS and into the generic ProcessorMixin
* Chat templates should not be mandatory
* Chat templates should not be mandatory
* Not all classes will have default chat templates
* stash commit
* Add chat template docstring
* Clean up docstring
* Add chat templates to LLaVA/LLaVA-next
* Docstring fixup
* Quick IDEFICS2 fixup
* Remove some old references to the Conversation class
* make fixup
* Change JSON serialization to custom json.dumps to prevent escaping of "<", ">", "&", "'"
* caller has control over the order, remove sort_key=True
* Move tojson into a proper function and expose a couple of other args
---------
Co-authored-by: jun.4 <jun.4@kakaobrain.com>
Co-authored-by: Matt <rocketknight1@gmail.com>
* Draft fast image processors
* Draft working fast version
* py3.8 compatible cache
* Enable loading fast image processors through auto
* Tidy up; rescale behaviour based on input type
* Enable tests for fast image processors
* Smarter rescaling
* Don't default to Fast
* Safer imports
* Add necessary Pillow requirement
* Woops
* Add AutoImageProcessor test
* Fix up
* Fix test for imagegpt
* Fix test
* Review comments
* Add warning for TF and JAX input types
* Rearrange
* Return transforms
* NumpyToTensor transformation
* Rebase - include changes from upstream in ImageProcessingMixin
* Safe typing
* Fix up
* convert mean/std to tesnor to rescale
* Don't store transforms in state
* Fix up
* Update src/transformers/image_processing_utils_fast.py
Co-authored-by: Arthur <48595927+ArthurZucker@users.noreply.github.com>
* Update src/transformers/models/auto/image_processing_auto.py
Co-authored-by: Arthur <48595927+ArthurZucker@users.noreply.github.com>
* Update src/transformers/models/auto/image_processing_auto.py
Co-authored-by: Arthur <48595927+ArthurZucker@users.noreply.github.com>
* Update src/transformers/models/auto/image_processing_auto.py
Co-authored-by: Arthur <48595927+ArthurZucker@users.noreply.github.com>
* Warn if fast image processor available
* Update src/transformers/models/vit/image_processing_vit_fast.py
* Transpose incoming numpy images to be in CHW format
* Update mapping names based on packages, auto set fast to None
* Fix up
* Fix
* Add AutoImageProcessor.from_pretrained(checkpoint, use_fast=True) test
* Update src/transformers/models/vit/image_processing_vit_fast.py
Co-authored-by: Pavel Iakubovskii <qubvel@gmail.com>
* Add equivalence and speed tests
* Fix up
---------
Co-authored-by: Arthur <48595927+ArthurZucker@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Pavel Iakubovskii <qubvel@gmail.com>
* First draft, still missing automatic function conversion
* First draft of the automatic schema generator
* Lots of small fixes
* the walrus has betrayed me
* please stop committing your debug breakpoints
* Lots of cleanup and edge cases, looking better now
* Comments and bugfixes for the type hint parser
* More cleanup
* Add tests, update schema generator
* Update tests, proper handling of return values
* Small docstring change
* More doc updates
* More doc updates
* Add json_schema decorator
* Clean up the TODOs and finish the docs
* self.maxDiff = None to see the whole diff for the nested list test
* add import for add_json_schema
* Quick test fix
* Fix something that was bugging me in the chat template docstring
* Less "anyOf" when unnecessary
* Support return types for the templates that need them
* Proper return type tests
* Switch to Google format docstrings
* Update chat templating docs to match new format
* Stop putting the return type in with the other parameters
* Add Tuple support
* No more decorator - we just do it implicitly!
* Add enum support to get_json_schema
* Update docstring
* Add copyright header
* Update src/transformers/tokenization_utils_base.py
Co-authored-by: amyeroberts <22614925+amyeroberts@users.noreply.github.com>
* Update docs/source/en/chat_templating.md
Co-authored-by: amyeroberts <22614925+amyeroberts@users.noreply.github.com>
* Update src/transformers/utils/chat_template_utils.py
Co-authored-by: amyeroberts <22614925+amyeroberts@users.noreply.github.com>
* Update src/transformers/utils/chat_template_utils.py
Co-authored-by: amyeroberts <22614925+amyeroberts@users.noreply.github.com>
* Add copyright header
* make fixup
* Fix indentation
* Reformat chat_template_utils
* Correct return value
* Make regexes module-level
* Support more complex, multi-line arg docstrings
* Update error message for ...
* Update ruff
* Add document type validation
* Refactor docs
* Refactor docs
* Refactor docs
* Clean up Tuple error
* Add an extra test for very complex defs and docstrings and clean everything up for it
* Document enum block
* Quick test fixes
* Stop supporting type hints in docstring to fix bugs and simplify the regex
* Update docs for the regex change
* Clean up enum regex
* Wrap functions in {"type": "function", "function": ...}
* Update src/transformers/utils/chat_template_utils.py
Co-authored-by: Pablo Montalvo <39954772+molbap@users.noreply.github.com>
* Temporary tool calling commit
* Add type hints to chat template utils, partially update docs (incomplete!)
* Code cleanup based on @molbap's suggestion
* Add comments to explain regexes
* Fix up type parsing for unions and lists
* Add custom exception types and adjust tests to look for them
* Update docs with a demo!
* Docs cleanup
* Pass content as string
* Update tool call formatting
* Update docs with new function format
* Update docs
* Update docs with a second tool to show the model choosing correctly
---------
Co-authored-by: amyeroberts <22614925+amyeroberts@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Pablo Montalvo <39954772+molbap@users.noreply.github.com>
* Rename to test_model_common_attributes
The method name is misleading - it is testing being able to get and set embeddings, not common attributes to all models
* Explicitly skip
* Update TVP model to interpolate pre-trained image pad prompter encodings
* feat: Add 2D positional embeddings interpolation in TvpVisualInputEmbedding
* added required comments
* Update TVP model to interpolate pre-trained image pad prompter encodings
* feat: Add 2D positional embeddings interpolation in TvpVisualInputEmbedding
* added required comments
* docstring and argument fix
* doc fixes and test case fix suggested in review.
* varibale typo fix
* styling and name fixes for padding interpolation flag.
* Remove ConversationalPipeline and Conversation object, as they have been deprecated for some time and are due for removal
* Update not-doctested.txt
* Fix JA and ZH docs
* Fix JA and ZH docs some more
* Fix JA and ZH docs some more
* Implement JSON dump conversion for torch_dtype in TrainingArguments
* Add unit test for converting torch_dtype in TrainingArguments to JSON
* move unit test for converting torch_dtype into TrainerIntegrationTest class
* reformating using ruff
* convert dict_torch_dtype_to_str to private method _dict_torch_dtype_to_str
---------
Co-authored-by: jun.4 <jun.4@kakaobrain.com>
* fix: wav2vec2_with_lm decoding error
Fixed an error where some language models could
not be loaded due to a decoding error, since it
was impossible to select the 'unigram_encoding'
value.
* fix: unexpected keyword argument
Fixed unexpected keyword argument caused by
passing kwargs directly to BeamSearchDecoderCTC.
* style: wav2vec2_with_lm
Changed single quotes to double quotes.
* Add list check for image and question
* Handle passing two lists and update docstring
* Add tests
* Add support for dataset
* Add test for dataset as input
* fixup
* fix unprotected import
* fix unprotected import
* fix import again
* fix param type
* Initial attempt
* Updates: PR suggestions
* Interpolate the relative position bias when interpolate_pos_encoding is True
* Add slow tag for the added tests
* Add in DATA2VEC_VISION_INPUTS_DOCSTRING
* Fix contrastive_search for new cache structure, and improve performance by removing inneficient torch.stack(torch.split(x, top_k, dim=0))
* Fix _contrastive_search for non-standard cache using ellipsis slicing
* Fix all outputs.logits memory leaks for all decoding strategies!
* Fix small error in _contrastive_search()
* Make all necessary change and revert for the new class
* Apply coding style
* Remove pipes in type hints for compatibility
* correct type hint
* apply style
* Use DynamicCache by default and solve conflicts
* Fix rebase issues
* Add `_supports_dynamic_cache_class` in models for models that support DynamicCache but not other caches to make DynamicCache the default for more models
* Create generation config to return legacy format by default, or to choose not to
* style
* Fix case when use_cache is False
* Remove default DynamicCache in assiste_decoding if assistant_model does not support it + fix _seen_tokens when cropping cache
* Update prepare_inputs_for_generation() for case with empty DynamicCache
* Correct return of args in _assisted_decoding
* Remove EfficientDynamicCache as it is no longer needed
* Correct mistake in generation config
* Move cache logic of assisted decoding to AssistedCandidateGenerator.__init__
* change DynamicCache function names from "split" to "batch_split" for readability + apply coding style
* Remove `_supports_dynamic_cache_class` attribute after rebase
* Correct missing line lost in conflict resolution during rebasing
* Add special case for Jamba
* Fix jamba test
* Coding style
* coding style
* Correct missing import in rebasing
* Simplify _validate_model_kwargs based on removal of _supports_dynamic_cache attribute
* Simplify code paths in _contrastive_search
* coding style
* Update docstrings of cache methods
* Update prepare_inputs_for_generation() -> past_key_values are always Cache objects
The StoppingCriteriaList allocates is_done without specifying dtype=torch.bool. On XLA this allocates a float tensor and causes a failure on the following line:
is_done = is_done | criteria(input_ids, scores, **kwargs)
by attempting to OR float with bool.
* Added interpolate pos encoding feature and test to deit
* Added interpolate pos encoding feature and test for deit TF model
* readded accidentally delted test for multi_gpu
* storing only patch_size instead of entire config and removed commented code
* Update modeling_tf_deit.py to remove extra line
Co-authored-by: amyeroberts <22614925+amyeroberts@users.noreply.github.com>
---------
Co-authored-by: amyeroberts <22614925+amyeroberts@users.noreply.github.com>
* add tokenizer_summary to es/_toctree.yml
* add tokenizer_summary to es/
* fix link to Transformes XL in en/
* translate until Subword tokenization section
* fix GPT link in en/
* fix other GPT link in en/
* fix typo in en/
* translate the doc
* run make fixup
* Remove .md in Transformer XL link
* fix some link issues in es/
* fix typo
* fix the get_size_with_aspect_ratio in max_size situation
* make fix-up
* add more general solution
* consider when max_size is not defined
* fix typo
* fix typo
* simple fix
* fix error
* fix if else error
* fix error of size overwrite
* fix yolos image processing
* fix detr image processing
* make
* add longest related test script
* Update src/transformers/models/yolos/image_processing_yolos.py
Co-authored-by: amyeroberts <22614925+amyeroberts@users.noreply.github.com>
* add more test
* add test script about longest size
* remove deprecated
---------
Co-authored-by: amyeroberts <22614925+amyeroberts@users.noreply.github.com>
While running the model.prepare_tf_dataset() method,
it raises the error below:
```
TypeError: Cannot convert [array([322., 1.])] to EagerTensor of dtype int64
```
This happens, in "DataCollatorForSeq2Seq" function when we are try
to convert the labels to tensors. While converting the labels to tensors,
the labels can be in the format of list of list or list of ndarrays.
There is no problem converting the list of list lables. There is a problem
when the list of ndarrays are float values(like below).
```
[array([322., 1.])]
```
so the exception raises while trying to convert this label to tensors using
below code.
```
batch["labels"] = tf.constant(batch["labels"], dtype=tf.int64)
```
The labels are always integer values, so this got converted to float
values in the label padding operation below.
```
batch["labels"] = [
call(label)
if padding_side == "right"
else np.concatenate([[self.label_pad_token_id] * (max_label_length - len(label)), label])
for label in labels
]
```
Here we have 2 cases:
1 - Concatenating an array having integer padding token value with labels.
2 - Concatenating an empty array with labels.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
case 1: Concatenating an array having integer padding token value with labels.
WORKS EXPECTED:
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```
label = np.array([233, 1])
max_label_length = 4
label_pad_token_id = -100
np.concatenate([[label_pad_token_id] * (max_label_length - len(label)), label])
o/p:
array([-100, -100, 233, 1])
```
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Case 2: Concatenating an empty array with labels.
GIVES THE ISSUE:
This scenorio can happen when the label has the maximum label length -- No padding needed.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
```
label = np.array([233, 1])
max_label_length = 2
label_pad_token_id = -100
np.concatenate([[label_pad_token_id] * (max_label_length - len(label)), label])
o/p:
array([233., 1.])
```
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Solution:
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
We need to concatenate a ndarray of dtype int with labels.
AFTER FIX:
----------
case 1:
```
label = np.array([233, 1])
max_label_length = 4
label_pad_token_id = -100
np.concatenate([np.array([label_pad_token_id] * (max_label_length - len(label)), dtype=np.int64),label])
o/p:
array([-100, -100, 233, 1])
```
case 2:
```
label = np.array([233, 1])
max_label_length = 2
label_pad_token_id = -100
np.concatenate([np.array([label_pad_token_id] * (max_label_length - len(label)), dtype=np.int64),label])
o/p:
array([233, 1])
```
* token healing impl + trie with extensions
* make fixup
* prefix-robust space tokenization
* examples readme and requirements
* make fixup
* allow input prompt and model
* redundant defaults
* Specialized Trie
* make fixup
* updated tests with new inherited Tree
* input ids to auto device_map
* rm unused import
* Update src/transformers/generation/utils.py
Co-authored-by: Arthur <48595927+ArthurZucker@users.noreply.github.com>
* naming convention
* Revert "naming convention"
This reverts commit dd39d9c5b7a969e2d8a8d2a8e54f121b82dc44f0.
* naming convention
* last -hopefully- changes
---------
Co-authored-by: Arthur <48595927+ArthurZucker@users.noreply.github.com>
Corrected a typo in security.md. Changed `use_safetenstors` to `use_safetensors` in the section discussing the usage of safe formats for loading models to prevent arbitrary code execution.
* current working example!
* commit regex and result file
* update
* nit
* push the conversion file
* oups
* roadmap and nits
* attempt diffs for 3 files
* persimmon
* nit
* add diff file that is the same as the modeling_llama.py
* fix rope nits
* updates
* updates with converted versions
* give some breathing space to the code
* delete
* update
* update
* push the actual result
* update regex patterns
* update regex patterns
* fix some issues
* fix some issues
* fix some issues
* updates
* updates
* updates
* updates
* updates
* revert changes done to llama
* updates
* update gemma
* updates
* oups
* current state
* current state
* update
* ouiiii
* nit
* clear diffs
* nit
* fixup
* update
* doc 🚀
* 🔥
* for now use gemma
* deal with comments
* style
* handle funtions
* deal with assigns
* todos
* process inheritage
* keep decorators?
* 🤗
* deal with duplicates
* fixup
* correctly remove duplicate code
* run ruff post script
* ruff deals pretty well with imports, let's leave it to him
* ah maybe not lol
* for now remove all imports from child.
* nit
* conversion of llama
* okay
* convert starcoder2
* synch with main
* update llama diff
* updates
* https://docs.astral.sh/ruff/rules/redefined-while-unused/ fixes the imports, bit needs later version of ruff
* updates
* okay actual state
* non zero exit
* update!
* revert unrelated
* remove other diff files
* updates
* cleanup
* update
* less diff!
* stash
* current updates
* updates
* No need for call
* finished fining deps
* update
* current changes
* current state
* current state
* new status
* nit
* finally
* fixes
* nits
* order is now expected
* use logger info instead of prints
* fixup
* up
* nit
* update
* nits
* update
* correct merge
* update
* update
* update
* add warning
* update caution message
* update
* better merging strategy
* copy class statements :wink
* fixups
* nits
* update
* Apply suggestions from code review
Co-authored-by: amyeroberts <22614925+amyeroberts@users.noreply.github.com>
* nits
* smaller header
* do cleanup some stuff
* even simpler header?
* fixup
* updates
* ruff
* update examples
* nit
* TODO
* state
* OUUUUUUF
* current state
* nits
* final state
* add a readme
* fixup
* remove diff llama
* fix
* nit
* dummy noy funny
* ruff format tests src utils --check
* everless diffs
* less diffs and fix test
* fixes
* naming nit?
* update converter and add supper example
* nits
* updated for function signatures
* update
* update
* add converted dummies
* autoformat
* single target assign fix
* fixup
* fix some imports
* fixes
* don't push them
* `# noqa: F841`
---------
Co-authored-by: amyeroberts <22614925+amyeroberts@users.noreply.github.com>
* Description of quantization_config
Added missing description about quantization_config in replace_with_bnb_linear for better readability.
* Removed trailing spaces
`mask` variable is not defined. probably a writing mistake. it should be `segmentation_map`. `segmentation_map` should be a `1` channel image rather than `RGB`.
[on a different note, the `mask_url` is the same as `raw_image`. could provide a better example.
* Fix has_file in offline mode
* harmonize env variable for offline mode
* Switch to HF_HUB_OFFLINE
* fix test
* revert test_offline to test TRANSFORMERS_OFFLINE
* Add new offline test
* merge conflicts
* docs
* seems like `split_special_tokens` is used here
* split special token
* add new line at end of file
* moving split special token test to common tests
* added assertions
* test
* fixup
* add co-author
* passing rest of args to gptsan_japanese, fixing tests
* removing direct comparison of fast and slow models
* adding test support for UDOP and LayoutXLM
* ruff fix
* readd check if slow tokenizer
* modify test to handle bos tokens
* removing commented function
* trigger build
* applying review feedback - updated docstrings, var names, and simplified tests
* ruff fixes
* Update tests/test_tokenization_common.py
Co-authored-by: Arthur <48595927+ArthurZucker@users.noreply.github.com>
* applying feedback, comments
* shutil temp directory fix
---------
Co-authored-by: Arthur Zucker <arthur.zucker@gmail.com>
Co-authored-by: Ita Zaporozhets <itazaporozhets@Itas-MBP.localdomain>
Co-authored-by: itazap <itazap@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Arthur <48595927+ArthurZucker@users.noreply.github.com>
Co-authored-by: Ita Zaporozhets <itazaporozhets@Itas-MacBook-Pro.local>
* added interpolation for vitmae model in pytorch as well as tf.
* Update modeling_vit_mae.py
irreugalr import fixed
* small changes and proper formatting
* changes suggested in review.
* modified decoder interpolate_func
* arguments and docstring fix
* Apply suggestions from code review
doc fixes
Co-authored-by: amyeroberts <22614925+amyeroberts@users.noreply.github.com>
---------
Co-authored-by: amyeroberts <22614925+amyeroberts@users.noreply.github.com>
* add test that currently fails
* test passed
* all perceiver passed
* fixup, style, quality, repo-consistency, all passed
* Apply suggestions from code review: default to False + compute sqrt once only
Co-authored-by: amyeroberts <22614925+amyeroberts@users.noreply.github.com>
* fix a minor bracket
* replace dim with self._num_channels
* add arguments to the rest preprocessors
---------
Co-authored-by: amyeroberts <22614925+amyeroberts@users.noreply.github.com>
* add prefix space ignored in llama #29625
* adding test with add_prefix_space=False
* ruff
---------
Co-authored-by: Ita Zaporozhets <itazaporozhets@Itas-MBP.localdomain>
* Add a check that warmup_setps is either 0 or >= 1
Update training_args.py to add a check that warmup_setps is either 0 or >= 1. Otherwise, raise an error.
* Update src/transformers/training_args.py
Co-authored-by: amyeroberts <22614925+amyeroberts@users.noreply.github.com>
---------
Co-authored-by: amyeroberts <22614925+amyeroberts@users.noreply.github.com>
* [build-ci-image]
* correct branch
* push ci image
* [build-ci-image]
* update scheduled as well
* [push-ci-image]
* [build-ci-image]
* [push-ci-image]
* update deps
* [build-ci-image]
* [build-ci-image]
* [build-ci-image]
* [build-ci-image]
* [build-ci-image]
* [build-ci-image]
* oups [build-ci-image]
* [push-ci-image]
* fix
* [build-ci-image]
* [build-ci-image]
* [build-ci-image]
* [build-ci-image]
* [build-ci-image]
* [build-ci-image]
* [build-ci-image]
* updated
* [build-ci-image] update tag
* [build-ci-image]
* [build-ci-image]
* fix tag
* [build-ci-image]
* [build-ci-image]
* [build-ci-image]
* [build-ci-image]
* github name
* commit_title?
* fetch
* update
* it not found
* dev
* dev
* [push-ci-image]
* dev
* dev
* update
* dev
* dev print dev commit message dev
* dev ? dev
* dev
* dev
* dev
* dev
* [build-ci-image]
* [build-ci-image]
* [push-ci-image]
* revert unwanted
* revert convert as well
* no you are not important
* [build-ci-image]
* Update .circleci/config.yml
* pin tf probability dev
If required padding for a crop larger than input image is odd-numbered,
the padding would be rounded down instead of rounded up, causing the
output dimension to be one smaller than it should be.
* add model_memory_anatomy to es/_toctree.yml
* copy model_memory_anatomy.md to es/
* translate first section
* translate doc
* chage forward activations
* fix sentence and and link to Trainer
* fix Trainer link
* Introduce configured_state
* Include note on tuning
* Allow for users to have defined a state already
* Include tests
* Add note on hpam tune
* Guard a bit better
* Update src/transformers/training_args.py
Co-authored-by: amyeroberts <22614925+amyeroberts@users.noreply.github.com>
* Update src/transformers/training_args.py
Co-authored-by: amyeroberts <22614925+amyeroberts@users.noreply.github.com>
* Finish rebase
* Finish rebase
* Guard carefully
* Fixup test
* Refactor
* Fin refactor
* Comment
* Update wrt feedback
---------
Co-authored-by: amyeroberts <22614925+amyeroberts@users.noreply.github.com>
* fix for custom pipeline configuration
* fix for custom pipelines
* remove extra exception
* added test for custom pipelines extra tag
* format with ruff
* limit extra tag for first time only
* format with ruff
* improve tests for custom pipelines
Fix num_hidden_layers in initialization
Originally, the initialization was using config.num_layers instead of config.num_hidden_layers. This fixes that.
* Add MistralForTokenClassification
* Add tests and docs
* Add token classification for Mixtral and Qwen2
* Save llma for token classification draft
* Add token classification support for Llama, Gemma, Persimmon, StableLm and StarCoder2
* Formatting
* Add token classification support for Qwen2Moe model
* Add dropout layer to each ForTokenClassification model
* Add copied from in tests
* Update src/transformers/models/llama/modeling_llama.py
Co-authored-by: Younes Belkada <49240599+younesbelkada@users.noreply.github.com>
* Propagate suggested changes
* Style
---------
Co-authored-by: Younes Belkada <49240599+younesbelkada@users.noreply.github.com>
description:Submit a bug report to help us improve transformers
labels:["bug"]
body:
- type:markdown
attributes:
value:|
Thanks for taking the time to fill out this bug report! 🤗
Before you submit your bug report:
- If it is your first time submitting, be sure to check our [bug report guidelines](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/CONTRIBUTING.md#did-you-find-a-bug)
- Try our [docs bot](https://huggingface.co/spaces/huggingchat/hf-docs-chat) -- it might be able to help you with your issue
- type:textarea
id:system-info
attributes:
@ -17,50 +28,50 @@ body:
description:|
Your issue will be replied to more quickly if you can figure out the right person to tag with @
If you know how to use git blame, that is the easiest way, otherwise, here is a rough guide of **who to tag**.
All issues are read by one of the core maintainers, so if you don't know who to tag, just leave this blank and
a core maintainer will ping the right person.
Please tag fewer than 3 people.
Models:
- text models: @ArthurZucker and @younesbelkada
- vision models: @amyeroberts
- speech models: @sanchit-gandhi
- text models: @ArthurZucker
- vision models: @amyeroberts, @qubvel
- speech models: @ylacombe, @eustlb
- graph models: @clefourrier
Library:
- flax: @sanchit-gandhi
- generate: @gante
- pipelines: @Narsil
- generate: @zucchini-nlp (visual-language models) or @gante (all others)
- pipelines: @Rocketknight1
- tensorflow: @gante and @Rocketknight1
- tokenizers: @ArthurZucker
- trainer: @muellerzr and @pacman100
- tokenizers: @ArthurZucker and @itazap
- trainer: @muellerzr @SunMarc
Integrations:
- deepspeed: HF Trainer/Accelerate: @pacman100
- deepspeed: HF Trainer/Accelerate: @muellerzr
- ray/raytune: @richardliaw, @amogkam
- Big Model Inference: @SunMarc
- quantization (bitsandbytes, autogpt): @SunMarc and @younesbelkada
description:Submit a proposal/request for a new transformers feature
labels:["feature"]
labels:["Feature request"]
body:
- type:textarea
id:feature-request
@ -19,7 +19,7 @@ body:
label:Motivation
description:|
Please outline the motivation for the proposal. Is your feature request related to a problem? e.g., I'm always frustrated when [...]. If this is related to another GitHub issue, please link here too.
# Important note: each job (run_tests_single_gpu, run_tests_multi_gpu, run_examples_gpu, run_pipelines_torch_gpu) requires all the previous jobs before running.
# This is done so that we avoid parallelizing the scheduled tests, to leave available
RUN_SLOW:yes# For gated repositories, we still need to agree to share information on the Hub repo. page in order to get access. # This token is created under the bot `hf-transformers-bot`.
SIGOPT_API_TOKEN:${{ secrets.SIGOPT_API_TOKEN }}
TF_FORCE_GPU_ALLOW_GROWTH:true
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES:0,1
RUN_PT_TF_CROSS_TESTS:1
jobs:
get_runner:
name:"Get runner to use"
runs-on:ubuntu-22.04
outputs:
RUNNER:${{ steps.set_runner.outputs.RUNNER }}
steps:
- name:Get runner to use
shell:bash
run:|
if [[ "${{ github.event.inputs.num_gpus }}" == "single" && "${{ github.event.inputs.runner_type }}" == "t4" ]]; then
options:--gpus all --privileged --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
@ -50,11 +82,33 @@ jobs:
- name:NVIDIA-SMI
run:|
nvidia-smi
- name:Store Slack infos
#because the SSH can be enabled dynamically if the workflow failed, so we need to store slack infos to be able to retrieve them during the waitforssh step
shell:bash
run:|
echo "${{ github.actor }}"
github_actor=${{ github.actor }}
github_actor=${github_actor/'-'/'_'}
echo "$github_actor"
echo "github_actor=$github_actor" >> $GITHUB_ENV
- name:Store Slack infos
#because the SSH can be enabled dynamically if the workflow failed, so we need to store slack infos to be able to retrieve them during the waitforssh step
shell:bash
run:|
echo "${{ env.github_actor }}"
if [ "${{ secrets[format('{0}_{1}', env.github_actor, 'SLACK_ID')] }}" != "" ]; then
The 🤗 Transformers library is robust and reliable thanks to users who report the problems they encounter.
Before you report an issue, we would really appreciate it if you could **make sure the bug was not
already reported** (use the search bar on GitHub under Issues). Your issue should also be related to bugs in the library itself, and not your code. If you're unsure whether the bug is in your code or the library, please ask in the [forum](https://discuss.huggingface.co/) first. This helps us respond quicker to fixing issues related to the library versus general questions.
already reported** (use the search bar on GitHub under Issues). Your issue should also be related to bugs in the library itself, and not your code. If you're unsure whether the bug is in your code or the library, please ask in the [forum](https://discuss.huggingface.co/) or on our [discord](https://discord.com/invite/hugging-face-879548962464493619) first. This helps us respond quicker to fixing issues related to the library versus general questions.
> [!TIP]
> We have a [docs bot](https://huggingface.co/spaces/huggingchat/hf-docs-chat), and we highly encourage you to ask all your questions there. There is always a chance your bug can be fixed with a simple flag 👾🔫
Once you've confirmed the bug hasn't already been reported, please include the following information in your issue so we can quickly resolve it:
@ -129,7 +132,7 @@ You will need basic `git` proficiency to contribute to
manual. Type `git --help` in a shell and enjoy! If you prefer books, [Pro
Git](https://git-scm.com/book/en/v2) is a very good reference.
You'll need **[Python 3.8](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/setup.py#L426)** or above to contribute to 🤗 Transformers. Follow the steps below to start contributing:
You'll need **[Python 3.9](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/setup.py#L449)** or above to contribute to 🤗 Transformers. Follow the steps below to start contributing:
1. Fork the [repository](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers) by
clicking on the **[Fork](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/fork)** button on the repository's page. This creates a copy of the code
@ -160,7 +163,7 @@ You'll need **[Python 3.8](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main
If 🤗 Transformers was already installed in the virtual environment, remove
it with `pip uninstall transformers` before reinstalling it in editable
mode with the `-e` flag.
Depending on your OS, and since the number of optional dependencies of Transformers is growing, you might get a
failure with this command. If that's the case make sure to install the Deep Learning framework you are working with
(PyTorch, TensorFlow and/or Flax) then do:
@ -219,7 +222,7 @@ You'll need **[Python 3.8](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main
If you're modifying documents under the `docs/source` directory, make sure the documentation can still be built. This check will also run in the CI when you open a pull request. To run a local check
RUN_SLOW=yes python -m pytest -n auto --dist=loadfile -s -v ./examples/pytorch/text-classification
```
Like the slow tests, there are other environment variables available which not enabled by default during testing:
Like the slow tests, there are other environment variables available which are not enabled by default during testing:
- `RUN_CUSTOM_TOKENIZERS`: Enables tests for custom tokenizers.
- `RUN_PT_FLAX_CROSS_TESTS`: Enables tests for PyTorch + Flax integration.
- `RUN_PT_TF_CROSS_TESTS`: Enables tests for TensorFlow + PyTorch integration.
More environment variables and additional information can be found in the [testing_utils.py](src/transformers/testing_utils.py).
More environment variables and additional information can be found in the [testing_utils.py](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/src/transformers/testing_utils.py).
🤗 Transformers uses `pytest` as a test runner only. It doesn't use any
`pytest`-specific features in the test suite itself.
@ -257,7 +249,7 @@ The model itself is a regular [Pytorch `nn.Module`](https://pytorch.org/docs/sta
### With pip
This repository is tested on Python 3.8+, Flax 0.4.1+, PyTorch 1.11+, and TensorFlow 2.6+.
This repository is tested on Python 3.9+, Flax 0.4.1+, PyTorch 1.11+, and TensorFlow 2.6+.
You should install 🤗 Transformers in a [virtual environment](https://docs.python.org/3/library/venv.html). If you're unfamiliar with Python virtual environments, check out the [user guide](https://packaging.python.org/guides/installing-using-pip-and-virtual-environments/).
@ -14,7 +14,7 @@ Models uploaded on the Hugging Face Hub come in different formats. We heavily re
models in the [`safetensors`](https://github.com/huggingface/safetensors) format (which is the default prioritized
by the transformers library), as developed specifically to prevent arbitrary code execution on your system.
To avoid loading models from unsafe formats(e.g. [pickle](https://docs.python.org/3/library/pickle.html), you should use the `use_safetenstors` parameter. If doing so, in the event that no .safetensors file is present, transformers will error when loading the model.
To avoid loading models from unsafe formats(e.g. [pickle](https://docs.python.org/3/library/pickle.html), you should use the `use_safetensors` parameter. If doing so, in the event that no .safetensors file is present, transformers will error when loading the model.
### Remote code
@ -36,5 +36,4 @@ Please inspect the code of the tools before passing them to the Agent to protect
## Reporting a Vulnerability
🤗 Please feel free to submit vulnerability reports to our private bug bounty program at https://hackerone.com/hugging_face. You'll need to request access to the program by emailing security@huggingface.co.
Note that you'll need to be invited to our program, so send us a quick email at security@huggingface.co if you've found a vulnerability.
Feel free to submit vulnerability reports to [security@huggingface.co](mailto:security@huggingface.co), where someone from the HF security team will review and recommend next steps. If reporting a vulnerability specific to open source, please note [Huntr](https://huntr.com) is a vulnerability disclosure program for open source software.
@ -596,7 +596,7 @@ Keywords: Data-Centric AI, Data Quality, Noisy Labels, Outlier Detection, Active
## [BentoML](https://github.com/bentoml/BentoML)
[BentoML](https://github.com/bentoml) is the unified framework for for building, shipping, and scaling production-ready AI applications incorporating traditional ML, pre-trained AI models, Generative and Large Language Models.
[BentoML](https://github.com/bentoml) is the unified framework for building, shipping, and scaling production-ready AI applications incorporating traditional ML, pre-trained AI models, Generative and Large Language Models.
All Hugging Face models and pipelines can be seamlessly integrated into BentoML applications, enabling the running of models on the most suitable hardware and independent scaling based on usage.
Keywords: BentoML, Framework, Deployment, AI Applications
# arguments specific to this wrapper for our own customization
parser.add_argument("--ensure_empty",type=bool,default=True,help="If to create a temporary directory.")
parser.add_argument(
"--commit",
type=list_str,
default="",
help="Comma-separated list of branch names and/or commit sha values on which the benchmark will run. If `diff` is specified, it will run on both the current head and the `main` branch.",
)
parser.add_argument("--metrics",type=str,help="The metrics to be included in the summary.")
parser.add_argument("--repo_id",type=str,default=None,help="The repository to which the file will be uploaded.")
parser.add_argument("--path_in_repo",type=str,default=None,help="Relative filepath in the repo.")
parser.add_argument("--token",type=str,default=None,help="A valid user access token (string).")
In this folder you will find various docker files, and some subfolders.
- dockerfiles (ex: `consistency.dockerfile`) present under `~/docker` are used for our "fast" CIs. You should be able to use them for tasks that only need CPU. For example `torch-light` is a very light weights container (703MiB).
- subfloder contain dockerfiles used for our `slow` CIs, which *can* be used for GPU tasks, but they are **BIG** as they were not specifically designed for a single model / single task. Thus the `~/docker/transformers-pytorch-gpu` includes additional dependencies to allow us to run ALL model tests (say `librosa` or `tesseract`, which you do not need to run LLMs)
Note that in both case, you need to run `uv pip install -e .`, which should take around 5 seconds. We do it outside the dockerfile for the need of our CI: we checkout a new branch each time, and the `transformers` code is thus updated.
We are open to contribution, and invite the community to create dockerfiles with potential arguments that properly choose extras depending on the model's dependencies! :hugs:
RUN pip install --no-cache-dir "transformers[sklearn,tf-cpu,testing,sentencepiece,tf-speech,vision]"
RUN pip install --no-cache-dir "git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git@${REF}#egg=transformers[sklearn,tf-cpu,testing,sentencepiece,tf-speech,vision]"
RUN uv pip install --no-cache-dir "protobuf==3.20.3" tensorflow_probability
### Translating the Transformers documentation into your language
# Translating the Transformers documentation into your language
As part of our mission to democratize machine learning, we'd love to make the Transformers library available in many more languages! Follow the steps below if you want to help translate the documentation into your language 🙏.
As part of our mission to democratize machine learning, we aim to make the Transformers library available in many more languages! Follow the steps below to help translate the documentation into your language.
**🗞️ Open an issue**
## Open an Issue
To get started, navigate to the [Issues](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/issues) page of this repo and check if anyone else has opened an issue for your language. If not, open a new issue by selecting the "Translation template" from the "New issue" button.
1. Navigate to the Issues page of this repository.
2. Check if anyone has already opened an issue for your language.
3. If not, create a new issue by selecting the "Translation template" from the "New issue" button.
4. Post a comment indicating which chapters you’d like to work on, and we’ll add your name to the list.
Once an issue exists, post a comment to indicate which chapters you'd like to work on, and we'll add your name to the list.
## Fork the Repository
1. First, fork the Transformers repo by clicking the Fork button in the top-right corner.
2. Clone your fork to your local machine for editing with the following command:
Replace `YOUR-USERNAME` with your GitHub username.
First, you'll need to [fork the Transformers repo](https://docs.github.com/en/get-started/quickstart/fork-a-repo). You can do this by clicking on the **Fork** button on the top-right corner of this repo's page.
## Copy-paste the English version with a new language code
Once you've forked the repo, you'll want to get the files on your local machine for editing. You can do that by cloning the fork with Git as follows:
The documentation files are organized in the following directory:
- **docs/source**: This contains all documentation materials organized by language.
**📋 Copy-paste the English version with a new language code**
To copy the English version to your new language directory:
The documentation files are in one leading directory:
1. Navigate to your fork of the repository:
- [`docs/source`](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/docs/source): All the documentation materials are organized here by language.
```bash
cd ~/path/to/transformers/docs
```
You'll only need to copy the files in the [`docs/source/en`](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/docs/source/en) directory, so first navigate to your fork of the repo and run the following:
Replace `~/path/to` with your actual path.
```bash
cd ~/path/to/transformers/docs
cp -r source/en source/LANG-ID
```
2. Run the following command:
Here, `LANG-ID` should be one of the ISO 639-1 or ISO 639-2 language codes -- see [here](https://www.loc.gov/standards/iso639-2/php/code_list.php) for a handy table.
```bash
cp -r source/en source/LANG-ID
```
**✍️ Start translating**
Replace `LANG-ID` with the appropriate ISO 639-1 or ISO 639-2 language code (see [this table](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_ISO_639-1_codes) for reference).
The fun part comes - translating the text!
## Start translating
The first thing we recommend is translating the part of the `_toctree.yml` file that corresponds to your doc chapter. This file is used to render the table of contents on the website.
Begin translating the text!
> 🙋 If the `_toctree.yml` file doesn't yet exist for your language, you can create one by copy-pasting from the English version and deleting the sections unrelated to your chapter. Just make sure it exists in the `docs/source/LANG-ID/` directory!
1. Start with the `_toctree.yml` file that corresponds to your documentation chapter. This file is essential for rendering the table of contents on the website.
The fields you should add are `local` (with the name of the file containing the translation; e.g. `autoclass_tutorial`), and `title` (with the title of the doc in your language; e.g. `Load pretrained instances with an AutoClass`) -- as a reference, here is the `_toctree.yml` for [English](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/docs/source/en/_toctree.yml):
- If the `_toctree.yml` file doesn’t exist for your language, create one by copying the English version and removing unrelated sections.
- Ensure it is placed in the `docs/source/LANG-ID/` directory.
```yaml
- sections:
- local:pipeline_tutorial# Do not change this! Use the same name for your .md file
title:Pipelines for inference# Translate this!
...
title:Tutorials# Translate this!
```
Here’s an example structure for the `_toctree.yml` file:
Once you have translated the `_toctree.yml` file, you can start translating the [MDX](https://mdxjs.com/) files associated with your docs chapter.
```yaml
- sections:
- local: pipeline_tutorial # Keep this name for your .md file
title: Pipelines for Inference # Translate this
...
title: Tutorials # Translate this
```
> 🙋 If you'd like others to help you with the translation, you should [open an issue](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/issues) and tag @stevhliu and @MKhalusova.
2. Once you’ve translated the `_toctree.yml`, move on to translating the associated MDX files.
## Collaborate and share
If you'd like assistance with your translation, open an issue and tag `@stevhliu`. Feel free to share resources or glossaries to ensure consistent terminology.
مع تزايد حجم النماذج اللغوية، برز التوازي كأحد الاستراتيجيات لتدريب نماذج أكبر على أجهزة محدودة وتسريع عملية التدريب بمقدار كبير. أنشأنا في Hugging Face، قمنا بإنشاء مكتبة [ Accelerate](https://huggingface.co/docs/accelerate) لمساعدة المستخدمين على تدريب أي نموذج من Transformers بسهولة على أي نوع من الإعدادات الموزعة، سواء كان ذلك على عدة وحدات معالجة رسومات (GPUs) على جهاز واحد أو على عدة وحدات معالجة رسومات موزعة على عدة أجهزة. في هذا الدليل، تعلم كيفية تخصيص حلقة تدريب PyTorch الأصلية لتمكين التدريب في بيئة موزعة.
## الإعداد
ابدأ بتثبيت 🤗 Accelerate:
```bash
pip install accelerate
```
ثم قم باستيراد وإنشاء كائن [`~accelerate.Accelerator`]. سيقوم [`~accelerate.Accelerator`] تلقائيًا باكتشاف نوع الإعداد الموزع الخاص بك وتهيئة جميع المكونات اللازمة للتدريب. لن تحتاج إلى وضع نموذجك على جهاز بشكل معين.
```py
>>>fromaccelerateimportAccelerator
>>>accelerator=Accelerator()
```
## الاستعداد للتسريع
الخطوة التالية هي تمرير جميع كائنات التدريب ذات الصلة إلى دالة الإعداد [`~accelerate.Accelerator.prepare`]. ويشمل ذلك DataLoaders للتدريب والتقييم، ونموذجًا ومُحَسِّنً المعاملات (optimizer):
- batch = {k: v.to(device) for k, v in batch.items()}
outputs = model(**batch)
loss = outputs.loss
- loss.backward()
+ accelerator.backward(loss)
optimizer.step()
lr_scheduler.step()
optimizer.zero_grad()
progress_bar.update(1)
```
## تدريب
بمجرد إضافة أسطر الكود ذات الصلة، قم بتشغيل التدريب الخاص بك في أحد النصوص أو الدفاتر مثل Colaboratory.
### التدريب باستخدام نص برمجي
إذا كنت تشغل التدريب الخاص بك من نص برمجي، فقم بتشغيل الأمر التالي لإنشاء وحفظ ملف تكوين:
```bash
accelerate config
```
ثم قم بتشغيل التدريب الخاص بك باستخدام:
```bash
accelerate launch train.py
```
### التدريب باستخدام دفتر ملاحظات
يمكن أيضًا تشغيل 🤗 Accelerate في دفاتر إذا كنت تخطط لاستخدام وحدات معالجة الرسوميات (TPUs) في Colaboratory. قم بتغليف كل الكود المسؤول عن التدريب في دالة، ومررها إلى [`~accelerate.notebook_launcher`]:
```py
>>>fromaccelerateimportnotebook_launcher
>>>notebook_launcher(training_function)
```
للحصول على مزيد من المعلومات حول 🤗 Accelerate وميزاته الغنية، يرجى الرجوع إلى [الوثائق](https://huggingface.co/docs/accelerate).
يمكن للنظم اللغوية الكبيرة (LLMs) التي تم تدريبها على أداء [نمذجة اللغة السببية](./tasks/language_modeling.) التعامل مع مجموعة واسعة من المهام، ولكنها غالبًا ما تواجه صعوبات في المهام الأساسية مثل المنطق والحساب والبحث. وعندما يتم استدعاؤها في مجالات لا تؤدي فيها أداءً جيدًا، فإنها غالبًا ما تفشل في توليد الإجابة التي نتوقعها منها.
يتمثل أحد النهج للتغلب على هذا القصور في إنشاء "وكيل".
الوكيل هو نظام يستخدم LLM كمحرك له، ولديه حق الوصول إلى وظائف تسمى "أدوات".
هذه "الأدوات" هي وظائف لأداء مهمة، وتحتوي على جميع الأوصاف اللازمة للوكيل لاستخدامها بشكل صحيح.
يمكن برمجة الوكيل للقيام بما يلي:
- وضع سلسلة من الإجراءات/الأدوات وتشغيلها جميعًا في نفس الوقت مثل [`CodeAgent`] على سبيل المثال
- التخطيط للاجراءات/الأدوات وتنفيذها واحدة تلو الأخرى والانتظار حتى انتهاء كل إجراء قبل إطلاق التالي مثل [`ReactJsonAgent`] على سبيل المثال
### أنواع الوكلاء
#### الوكيل البرمجي (Code agent)
يتمتع هذا الوكيل يتبع خطوات محددة: أولًا، يخطط لسلسلة من الإجراءات التي يريد تنفيذها، ثم شفرة Python لتنفيذ جميع الإجراءات في نفس الوقت. وهو يتعامل بشكل أصلي مع أنواع مختلفة من المدخلات والمخرجات للأدوات التي يستخدمها، وبالتالي فهو الخيار الموصى به للمهام متعددة الوسائط.
#### وكلاء التفاعل
هذا هو الوكيل الذي يتم اللجوء إليه لحل مهام الاستدلال، حيث يجعل إطار ReAct ([Yao et al.، 2022](https://huggingface.co/papers/2210.03629)) من الكفاءة حقًا التفكير على أساس ملاحظاته السابقة.
نقوم بتنفيذ إصدارين من ReactJsonAgent:
- [`ReactJsonAgent`] يقوم بتوليد استدعاءات الأدوات كـ JSON في إخراجها.
- [`ReactCodeAgent`] هو نوع جديد من ReactJsonAgent يقوم بتوليد استدعاءات أدواته كمقاطع من التعليمات البرمجية، والتي تعمل بشكل جيد حقًا مع LLMs التي تتمتع بأداء قوي في البرمجة.
> [!TIP]
> اقرأ منشور المدونة [Open-source LLMs as LangChain Agents](https://huggingface.co/blog/open-source-llms-as-agents) لمعرفة المزيد عن وكيل ReAct.
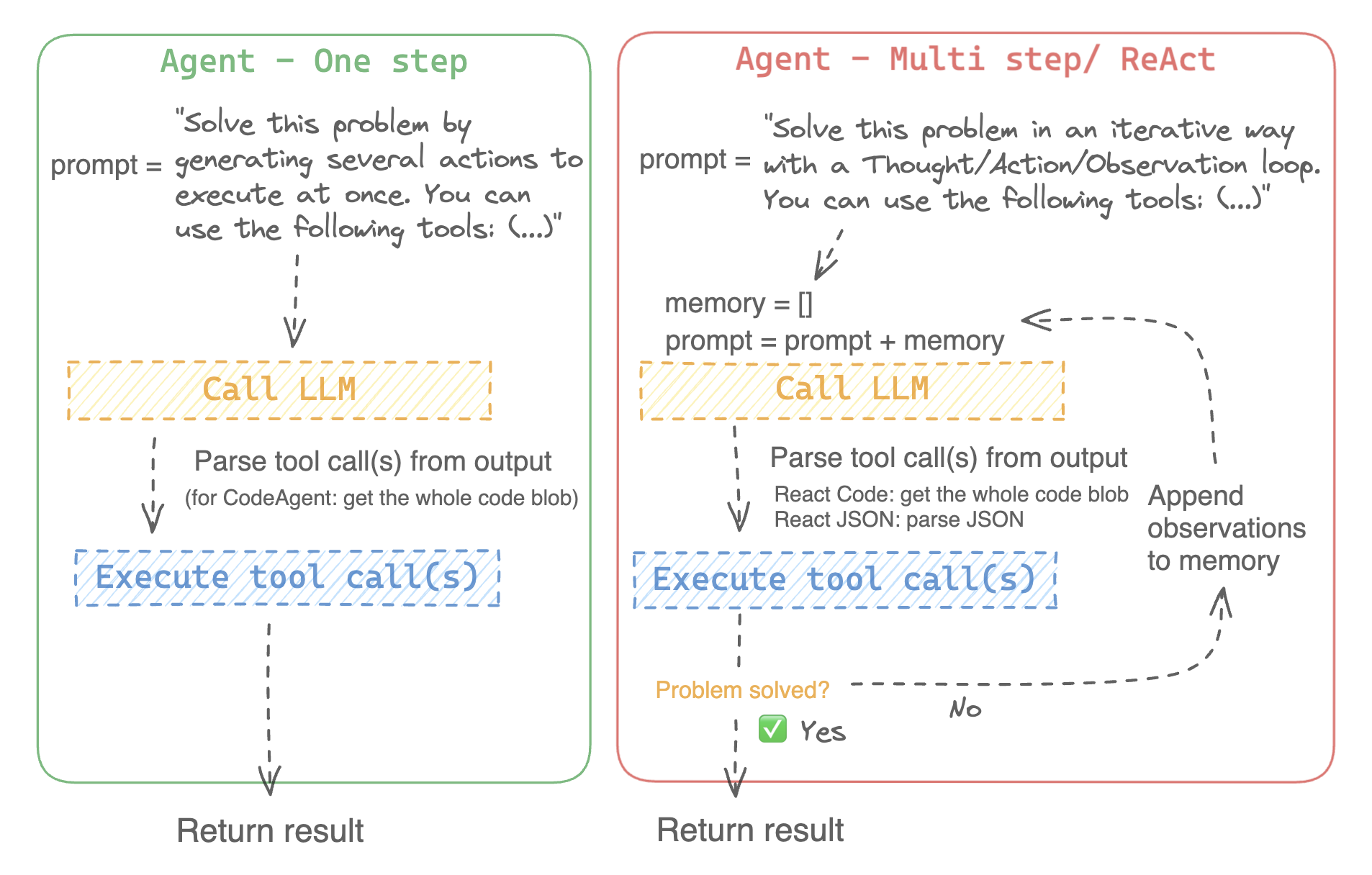
على سبيل المثال، إليك كيف يعمل وكيل ReAct Code طريقه من خلال السؤال التالي.
```py3
>>>agent.run(
..."How many more blocks (also denoted as layers) in BERT base encoder than the encoder from the architecture proposed in Attention is All You Need?",
- نموذج لغوي كبير (LLM) يشكل المحرك الأساسي للوكيل. الوكيل نفسه ليس النموذج اللغوي، بل هو برنامج يستخدم النموذج اللغوي كمحرك له.
- موجه النظام (system prompt): هذه هي التعليمات التي يتم إعطاؤها للنموذج اللغوي لإنشاء مخرجاته.
- صندوق أدوات (toolbox) يختار الوكيل منه الأدوات لتنفيذها
- محلل (parser) لاستخراج الأدوات التي يجب استدعاؤها من مخرجات النموذج اللغوي LLM والأدوات التي يجب استخدامها
عند تهيئة نظام الوكيل، يتم استخدام سمات الأداة لإنشاء وصف للأداة، ثم يتم دمجها في موجه النظام الخاص `system_prompt` للوكيل لإعلامه بالأدوات التي يمكنه استخدامها ولماذا.
للبدء، يرجى تثبيت `agents` الإضافية لتثبيت جميع التبعيات الافتراضية.
```bash
pip install transformers[agents]
```
قم ببناء محرك LLM الخاص بك من خلال تعريف طريقة `llm_engine` التي تقبل قائمة من [الرسائل](./chat_templating.) وتعيد النص. يجب أن تقبل هذه الدالة القابلة للاستدعاء أيضًا معامل `stop` يشير إلى متى يجب التوقف عن التوليد.
2. يتوقف عن توليد المخراجات من التسلسلات التي تم تمريرها في معامل `stop`
أنت بحاجة أيضًا إلى معامل "الأدوات" الذي يقبل قائمة من "الأدوات". يمكنك توفير قائمة فارغة لـ "الأدوات"، ولكن استخدم صندوق الأدوات الافتراضي مع معامل اختياري `add_base_tools=True`.
الآن يمكنك إنشاء وكيل، مثل [`CodeAgent`], وتشغيله. ولتسهيل الأمر، نقدم أيضًا فئة [`HfEngine`] التي تستخدم `huggingface_hub.InferenceClient` بشكل مخفى.
agent.run("Why does Mike not know many people in New York?",audio="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/recording.mp3")
```
تم تحديد موجه النظام ومحلل المخرجات تلقائيًا، ولكن يمكنك فحصهما بسهولة عن طريق استدعاء `system_prompt_template` على وكيلك.
```python
print(agent.system_prompt_template)
```
من المهم أن تشرح بأكبر قدر ممكن من الوضوح المهمة التي تريد تنفيذها.
كل عملية [`~Agent.run`] مستقلة، وبما أن الوكيل مدعوم من LLM، فقد تؤدي الاختلافات الطفيفة في موجهك إلى نتائج مختلفة تمامًا.
يمكنك أيضًا تشغيل وكيل بشكل متتالي لمهام مختلفة: في كل مرة يتم فيها إعادة تهيئة سمتي `agent.task` و`agent.logs`.
#### تنفيذ التعليمات البرمجية
يقوم مفسر Python بتنفيذ التعليمات البرمجية على مجموعة من المدخلات التي يتم تمريرها جنبًا إلى جنب مع أدواتك.
يجب أن يكون هذا الأمر آمنًا لأن الوظائف الوحيدة التي يمكن استدعاؤها هي الأدوات التي قدمتها (خاصة إذا كانت أدوات من Hugging Face فقط) ووظيفة الطباعة، لذا فأنت مقيد بالفعل بما يمكن تنفيذه.
مفسر Python لا يسمح أيضًا باستدعاء دوال بشكل افتراضي خارج قائمة آمنة، لذا فإن جميع الهجمات الأكثر وضوحًا لا ينبغي أن تكون مشكلة.
يمكنك أيضًا الإذن باستيرادات إضافية عن طريق تمرير الوحدات النمطية المصرح بها كقائمة من السلاسل في معامل `additional_authorized_imports` عند تهيئة [`ReactCodeAgent`] أو [`CodeAgent`]:
>>>agent.run("Could you get me the title of the page at url 'https://huggingface.co/blog'?")
(...)
'Hugging Face – Blog'
```
سيتم إيقاف التنفيذ عند أي رمز يحاول تنفيذ عملية غير قانونية أو إذا كان هناك خطأ Python عادي في التعليمات البرمجية التي تم إنشاؤها بواسطة الوكيل.
> [!WARNING]
> يمكن لـ LLM توليد شفرة برمجية عشوائية سيتم تنفيذها بعد ذلك: لا تقمب استدعاء أى دوال غير آمنة!
### موجه النظام
ينشئ الوكيل، أو بالأحرى LLM الذي يقود الوكيل، يولد مخرجات بناءً على موجه النظام. يمكن تخصيص موجه النظام وتصميمه للمهام المقصودة. على سبيل المثال، تحقق من موجه النظام لـ [`ReactCodeAgent`] (الإصدار أدناه مبسط قليلاً).
```text
You will be given a task to solve as best you can.
You have access to the following tools:
<<tool_descriptions>>
To solve the task, you must plan forward to proceed in a series of steps, in a cycle of 'Thought:', 'Code:', and 'Observation:' sequences.
At each step, in the 'Thought:' sequence, you should first explain your reasoning towards solving the task, then the tools that you want to use.
Then in the 'Code:' sequence, you shold write the code in simple Python. The code sequence must end with '/End code' sequence.
During each intermediate step, you can use 'print()' to save whatever important information you will then need.
These print outputs will then be available in the 'Observation:' field, for using this information as input for the next step.
In the end you have to return a final answer using the `final_answer` tool.
Here are a few examples using notional tools:
---
{examples}
Above example were using notional tools that might not exist for you. You only have acces to those tools:
<<tool_names>>
You also can perform computations in the python code you generate.
Always provide a 'Thought:' and a 'Code:\n```py' sequence ending with '```<end_code>' sequence. You MUST provide at least the 'Code:' sequence to move forward.
Remember to not perform too many operations in a single code block! You should split the task into intermediate code blocks.
Print results at the end of each step to save the intermediate results. Then use final_answer() to return the final result.
Remember to make sure that variables you use are all defined.
Now Begin!
```
يتضمن موجه النظام:
- *مقدمة* تشرح كيف يجب أن يتصرف الوكيل والأدوات التي يجب عليه استخدامها.
- وصف لجميع الأدوات التي يتم تحديدها بواسطة رمز `<<tool_descriptions>>` الذي يتم استبداله ديناميكيًا في وقت التشغيل بالأدوات التي يحددها المستخدم أو يختارها.
- يأتي وصف الأداة من سمات الأداة، `name`، و`description`، و`inputs` و`output_type`، وقالب `jinja2` بسيط يمكنك تحسينه.
- شكل المخرج المتوقع.
يمكنك تحسين موجه النظام، على سبيل المثال، عن طريق إضافة شرح لتنسيق المخرجات.
للحصول على أقصى قدر من المرونة، يمكنك الكتابة فوق قالب موجه النظام بالكامل عن طريق تمرير موجه مخصص كمعامل إلى معلمة `system_prompt`.
> يرجى التأكد من تحديد سلسلة `<<tool_descriptions>>` في مكان ما في `template` حتى يكون الوكيل على علم
بالأدوات المتاحة.
### فحص تشغيل الوكيل
فيما يلي بعض السمات المفيدة لفحص ما حدث بعد التشغيل:
- تخزن `agent.logs` سجلات مفصلة للوكيل. في كل خطوة من تشغيل الوكيل، يتم تخزين كل شيء في قاموس إلحاقه بـ `agent.logs`.
- تشغيل `agent.write_inner_memory_from_logs()` يخلق ذاكرة داخلية لسجلات الوكيل للنظام LLM لعرضها، كقائمة من رسائل الدردشة. تنتقل هذه الطريقة عبر كل خطوة من سجل الوكيل ولا تخزن سوى ما يهمها كرسالة: على سبيل المثال، سيحفظ موجه النظام والمهمة في رسائل منفصلة، ثم لكل خطوة سيخزن مخرج LLM كرسالة، ومخرج استدعاء الأداة كرسالة أخرى. استخدم هذا إذا كنت تريد عرضًا عامًا لما حدث - ولكن لن يتم نسخ كل سجل بواسطة هذه الطريقة.
## الأدوات
الأداة هي عبارة عن وظيفة أساسية يستخدمها الوكيل لتنفيذ مهمة محددة.
يمكنك على سبيل المثال التحقق من [`PythonInterpreterTool`]: لديه اسم ووصف ووصف للمدخلات ونوع للمخرج، وطريقة `__call__` التي تقوم بتنفيذ المهمة المطلوبة.
عند تهيئة الوكيل، يتم استخدام سمات الأداة لتوليد وصف للأداة يتم تضمينه في موجه النظام الخاص بالوكيل. يتيح هذا للوكيل معرفة الأدوات التي يمكنه استخدامها ولماذا.
### صندوق الأدوات الافتراضي
يأتي Transformers مع صندوق أدوات افتراضي لتمكين الوكلاء، والذي يمكنك إضافته إلى وكيلك عند التهيئة باستخدام معامل `add_base_tools = True`:
- **الإجابة على أسئلة المستند**: الإجابة على سؤال حول المستند (مثل ملف PDF) بتنسيق صورة ([Donut](./model_doc/donut))
- **الإجابة على أسئلة الصور**: الإجابة على سؤال حول صورة ([VILT](./model_doc/vilt))
- **التحدث إلى النص**: قم بتفريغ الكلام إلى نص ([Whisper](./model_doc/whisper))
- **النص إلى كلام**: تحويل النص إلى كلام ([SpeechT5](./model_doc/speecht5))
- **الترجمة**: ترجمة جملة معينة من لغة المصدر إلى لغة الهدف.
- **مفسر كود Python**: تشغيل كود Python الذي تم إنشاؤه بواسطة LLM في بيئة آمنة. لن يتم إضافة هذه الأداة إلى [`ReactJsonAgent`] إلا إذا استخدمت `add_base_tools=True`، نظرًا لأن الأدوات المستندة إلى التعليمات البرمجية يمكنها بالفعل تنفيذ كود Python
لا تترجم النصوص الخاصة ولا الأكواد البرمجية ولا الروابط ولا رموز HTML وCSS:
يمكنك استخدام أداة يدويًا عن طريق استدعاء دالة [`load_tool`] وتحديد مهمة لتنفيذها.
```python
fromtransformersimportload_tool
tool=load_tool("text-to-speech")
audio=tool("This is a text to speech tool")
```
### إنشاء أداة جديدة
يمكنك إنشاء أداتك الخاصة لتغطية حالات الاستخدام التي لا تغطيها الأدوات الافتراضية من Hugging Face.
على سبيل المثال، دعنا نقوم بإنشاء أداة تعرض النموذج الأكثر تنزيلًا لمهمة معينة من Hub.
يمكن تحويل هذه الشيفرة إلى فئة ترث من الفئة العليا [`Tool`].
تحتاج الأداة المخصصة إلى:
- اسم `name`، والتي تمثل اسم الأداة نفسها. عادةً ما يصف الاسم وظيفتها. بما أن الكود يعيد النموذج الأكثر تنزيلًا لمهمة ما، فلنسمها `model_download_counter`.
- تستخدم خاصية `description` لملء موجه نظام الوكيل.
- خاصية `inputs`، والتي هي عبارة عن قاموس بمفاتيح "type" و"description". يحتوي على معلومات تساعد المفسر Python على اتخاذ خيارات مستنيرة بشأن المدخلات.
- خاصية `output_type`، والتي تحدد نوع المخرج.
- طريقة `forward` والتي تحتوي على الكود الذي سيتم تنفيذه للحصول على النتيجة النهائية.
```python
fromtransformersimportTool
fromhuggingface_hubimportlist_models
classHFModelDownloadsTool(Tool):
name="model_download_counter"
description=(
"This is a tool that returns the most downloaded model of a given task on the Hugging Face Hub. "
"It returns the name of the checkpoint."
)
inputs={
"task":{
"type":"text",
"description":"the task category (such as text-classification, depth-estimation, etc)",
الآن بعد أن أصبحت فئة `HfModelDownloadsTool` المخصصة جاهزة، يمكنك حفظها في ملف باسم `model_downloads.py` واستيرادها للاستخدام.
```python
frommodel_downloadsimportHFModelDownloadsTool
tool=HFModelDownloadsTool()
```
يمكنك أيضًا مشاركة أداتك المخصصة في Hub عن طريق استدعاء [`~Tool.push_to_hub`] على الأداة. تأكد من أنك قمت بإنشاء مستودع لها على Hub وأنك تستخدم رمز وصول للقراءة.
print(f"The most downloaded model for the 'text-to-video' task is {most_downloaded_model}.")
====
```
والناتج:
`"النموذج الأكثر تنزيلًا لمهمة `text-to-video` هو ByteDance/AnimateDiff-Lightning."`
### إدارة صندوق أدوات الوكيل الخاص بك
إذا كنت قد قمت بتهيئة وكيل، فمن غير الملائم إعادة تهيئته من البداية لإضافة أداة جديدة ترغب في استخدامها. باستخدام مكتبة Transformers، يمكنك إدارة صندوق أدوات الوكيل بإضافة أو استبدال أداة موجودة.
دعنا نضيف الأداة `model_download_tool` إلى وكيل تم تهيئته مسبقًا باستخدام صندوق الأدوات الافتراضي.
> احترس عند إضافة أدوات إلى وكيل يعمل بالفعل لأنه يمكن أن يؤثر على اختيار الأداة لصالح أداتك أو اختيار أداة أخرى غير المحددة بالفعل.
استخدم طريقة `agent.toolbox.update_tool()` لاستبدال أداة موجودة في صندوق أدوات الوكيل.
هذا مفيد إذا كانت أداتك الجديدة بديلاً مباشرًا للأداة الموجودة لأن الوكيل يعرف بالفعل كيفية تنفيذ تلك المهمة المحددة.
تأكد فقط من اتباع الأداة الجديدة لنفس واجهة برمجة التطبيقات (API) للأداة المستبدلة أو قم بتكييف قالب موجه النظام لضمان تحديث جميع الأمثلة التي تستخدم الأداة المستبدلة.
### استخدام مجموعة من الأدوات
يمكنك الاستفادة من مجموعات الأدوات باستخدام كائن ToolCollection، مع تحديد مجموعة الأدوات التي تريد استخدامها.
ثم قم بتمريرها كقائمة لتهيئة الوكيل الخاص بك، وبدء استخدامها!
[gradio-tools](https://github.com/freddyaboulton/gradio-tools) هي مكتبة قوية تتيح استخدام Hugging
Face Spaces كأدوات. تدعم العديد من المساحات الموجودة بالإضافة إلى مساحات مخصصة.
تدعم مكتبة Transformers `gradio_tools` باستخدام طريقة [`Tool.from_gradio`] في الفئة. على سبيل المثال، دعنا نستخدم [`StableDiffusionPromptGeneratorTool`](https://github.com/freddyaboulton/gradio-tools/blob/main/gradio_tools/tools/prompt_generator.py) من مجموعة أدوات `gradio-tools` لتحسين المطالبات لإنشاء صور أفضل.
استورد وقم بتهيئة الأداة، ثم مررها إلى طريقة `Tool.from_gradio`:
> تتطلب gradio-tools إدخالات وإخراجات *نصية* حتى عند العمل مع طرائق مختلفة مثل كائنات الصور والصوت. الإدخالات والإخراجات الصورية والصوتية غير متوافقة حاليًا.
### استخدام أدوات LangChain
نحن نحب Langchain ونعتقد أنها تحتوي على مجموعة أدوات قوية للغاية.
لاستيراد أداة من LangChain، استخدم الطريقة `from_langchain()`.
فيما يلي كيفية استخدامها لإعادة إنشاء نتيجة البحث في المقدمة باستخدام أداة بحث الويب LangChain.
agent.run("How many more blocks (also denoted as layers) in BERT base encoder than the encoder from the architecture proposed in Attention is All You Need?")
```
## واجهة Gradio
يمكنك الاستفادة من `gradio.Chatbot` لعرض أفكار الوكيل الخاص بك باستخدام `stream_to_gradio`، إليك مثال:
تستخدم معظم نماذج المحول (Transformer) الانتباه الكامل بحيث تكون مصفوفة الانتباه ذات الأبعاد المتساوية. ويمكن أن يمثل ذلك عقبة حسابية كبيرة عندما تكون لديك نصوص طويلة. ويعد Longformer وReformer من النماذج التي تحاول أن تكون أكثر كفاءة وتستخدم نسخة مخففة من مصفوفة الانتباه لتسريع التدريب.
## انتباه LSH
يستخدم [Reformer](model_doc/reformer) انتباه LSH. في الدالة softmax(QK^t)، فإن أكبر العناصر فقط (في بعد softmax) من المصفوفة QK^t هي التي ستعطي مساهمات مفيدة. لذلك، بالنسبة لكل استعلام q في Q، يمكننا أن نأخذ في الاعتبار فقط المفاتيح k في K المشابهة لـ q فقط. وتُستخدم دالة هاش لتحديد ما إذا كان q وk متشابهين. ويتم تعديل قناع الانتباه لتجاهل الرمز الحالي (باستثناء الموضع الأول)، لأنه سيعطي استعلامًا ومفتاحًا متساويين (لذلك متشابهين للغاية). نظرًا لطبيعة دالة الهاش العشوائية نوعًا ما، يتم في الممارسة العملية استخدام عدة دوال هاش (يحددها معامل n_rounds) ثم يتم حساب المتوسط معًا.
## الانتباه المحلي
يستخدم [Longformer](model_doc/longformer) الانتباه المحلي: غالبًا ما يكون السياق المحلي (على سبيل المثال، ما هما الرمزان إلى اليسار واليمين؟) كافيًا لاتخاذ إجراء بالنسبة للرمز المعطى. أيضًا، عن طريق تكديس طبقات الانتباه التي لها نافذة صغيرة، سيكون للطبقة الأخيرة مجال استقبال أكبر من مجرد الرموز في النافذة، مما يسمح لها ببناء تمثيل للجملة بأكملها.
كما يتم منح بعض رموز الإدخال المختارة مسبقًا انتباهًا عالميًا: بالنسبة لهذه الرموز القليلة، يمكن لمصفوفة الانتباه الوصول إلى جميع الرموز وتكون هذه العملية متماثلة: فلجميع الرموز الأخرى إمكانية الوصول إلى تلك الرموز المحددة (بالإضافة إلى تلك الموجودة في نافذتهم المحلية). وهذا موضح في الشكل 2d من الورقة، انظر أدناه لمثال على قناع الانتباه:
وباستخدام مصفوفات الانتباه هذه التي تحتوي على عدد أقل من المعلمات، يسمح النموذج بمدخالات ذات طول تسلسل أكبر.
## حيل أخرى
### الترميزات الموضعية المحورية
يستخدم [Reformer](model_doc/reformer) ترميزات موضعية محورية: في نماذج المحول التقليدية، يكون الترميز الموضعي E مصفوفة بحجم \\(l\\) في \\(d\\)، حيث \\(l\\) هو طول التسلسل و\\(d\\) هو بعد الحالة المخفية. إذا كان لديك نصوص طويلة جدًا، فقد تكون هذه المصفوفة ضخمة وتستهلك مساحة كبيرة جدًا على وحدة معالجة الرسوميات (GPU). وللتخفيف من ذلك، تتكون الترميزات الموضعية المحورية من تحليل تلك المصفوفة الكبيرة E إلى مصفوفتين أصغر E1 وE2، بأبعاد \\(l_{1} \times d_{1}\\) و \\(l_{2} \times d_{2}\\)، بحيث \\(l_{1} \times l_{2} = l\\) و\\(d_{1} + d_{2} = d\\) (مع حاصل ضرب الأطوال، ينتهي الأمر بكونه أصغر بكثير). ويتم الحصول على الترميز للخطوة الزمنية \\(j\\) في E عن طريق ربط الترميزات للخطوة الزمنية \\(j \% l1\\) في E1 و \\(j // l1\\) في E2.
لم ترغب في إنشاء محول معماري لمؤشر الترابط الخاص بك، فهناك العديد من محولات المعمارية المختلفة التي يمكنك الاختيار من بينها. كجزء من الفلسفة الأساسية لـ 🤗 Transformers لجعل المكتبة سهلة وبسيطة ومرنة، فإن فئة `AutoClass` تستدل تلقائيًا وتحمّل البنية الصحيحة من نسخة نموذج (Model Checkpoint) معينة. تسمح لك طريقة `from_pretrained()` بتحميل نموذج مُدرب مسبقًا لأي بنية بسرعة حتى لا تضطر إلى تكريس الوقت والموارد لتدريب نموذج من الصفر. إن إنتاج هذا النوع من التعليمات البرمجية غير المعتمدة على نسخ يعني أنه إذا نجح رمزك مع ننسخة واحدة، فسيتم تشغيله مع أخرى - طالما تم تدريبه لمهمة مماثلة - حتى إذا كانت البنية المعمارية مختلفة.
تذكر أن البنية تشير إلى هيكل النموذج، والنسخ هي الأوزان لبنية معمارية معينة. على سبيل المثال، [BERT](https://huggingface.co/google-bert/bert-base-uncased) هي بنية معمارية، في حين أن `google-bert/bert-base-uncased` هي نسخة. "النموذج" هو مصطلح عام يمكن أن يعني إما البنية أو نالنسخة.
في هذا البرنامج التعليمي، ستتعلم كيفية:
* تحميل مُجزّئ الرموز مُدرب مسبقًا
* تحميل معالج صور مُدرب مسبقًا
* تحميل مستخرج ميزات مُدرب مسبقًا
* تحميل معالج مُدرب مسبقًا
* تحميل نموذج مُدرب مسبقًا
* تحميل نموذج كعمود فقري
## AutoTokenizer
تبدأ كل مهمة NLP تقريبًا بمُجزّئ للرموز. يقوم المُجزّئ بتحويل النص إلى شكل يمكن للنموذج معالجته.
قم بتحميل المُجزّئ باستخدام [`AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained`]:
<figcaptionclass="mt-2 text-center text-sm text-gray-500">الصورة توضح مخطط مراحل نموذج Swin.</figcaption>
</div>
يسمح لك [`AutoBackbone`] باستخدام النماذج المُدربة مسبقًا كعمود فقري للحصول على خرائط ميزات من مراحل مختلفة من العمود الفقري. يجب عليك تحديد أحد المعلمات التالية في [`~PretrainedConfig.from_pretrained`]:
*`out_indices` هو فهرس الطبقة التي تريد الحصول على خريطة الميزات منها
*`out_features` هو اسم الطبقة التي تريد الحصول على خريطة الميزات منها
يمكن استخدام هذه المعلمات بشكل متبادل، ولكن إذا كنت تستخدم كلاً منها، فتأكد من أنها متوائمة مع بعضها البعض! إذا لم تمرر أيًا من هذه المعلمات، فسيقوم العمود الفقري بإرجاع خريطة الميزات من الطبقة الأخيرة.
تتطلب المهام متعددة الوسائط معالجًا يجمع بين نوعين من أدوات المعالجة المسبقة. على سبيل المثال، يتطلب نموذج [LayoutLMV2](model_doc/layoutlmv2) معالج صور لمعالجة الصور ومُجزّئ لمعالجة النص؛ يجمع المعالج كليهما.
قم بتحميل معالج باستخدام [`AutoProcessor.from_pretrained`]:
تسمح لك فئات `AutoModelFor` بتحميل نموذج مُدرب مسبقًا لمهمة معينة (راجع [هنا](model_doc/auto) للحصول على قائمة كاملة بالمهام المتاحة). على سبيل المثال، قم بتحميل نموذج لتصنيف التسلسل باستخدام [`AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained`]:
بالنسبة لنماذج PyTorch، تستخدم طريقة `from_pretrained()``torch.load()` التي تستخدم داخليًا `pickle` والتي يُعرف أنها غير آمنة. بشكل عام، لا تقم مطلقًا بتحميل نموذج قد يكون مصدره مصدرًا غير موثوق به، أو قد يكون تم العبث به. يتم تخفيف هذا الخطر الأمني جزئيًا للنماذج العامة المستضافة على Hub Hugging Face، والتي يتم [فحصها بحثًا عن البرامج الضارة](https://huggingface.co/docs/hub/security-malware) في كل ارتكاب. راجع [توثيق Hub](https://huggingface.co/docs/hub/security) للحصول على أفضل الممارسات مثل [التحقق من التوقيع](https://huggingface.co/docs/hub/security-gpg#signing-commits-with-gpg) باستخدام GPG.
لا تتأثر نقاط تفتيش TensorFlow و Flax، ويمكن تحميلها داخل بنيات PyTorch باستخدام `from_tf` و `from_flax` kwargs لطريقة `from_pretrained` للتحايل على هذه المشكلة.
</Tip>
بشكل عام، نوصي باستخدام فئة `AutoTokenizer` وفئة `AutoModelFor` لتحميل مثيلات مُدربة مسبقًا من النماذج. سيساعدك هذا في تحميل البنية الصحيحة في كل مرة. في البرنامج التعليمي التالي، تعرف على كيفية استخدام المحلل اللغوي ومعالج الصور ومستخرج الميزات والمعالج الذي تم تحميله حديثًا لمعالجة مجموعة بيانات للضبط الدقيق.
</pt>
<tf>
أخيرًا، تسمح لك فئات `TFAutoModelFor` بتحميل نموذج مُدرب مسبقًا لمهمة معينة (راجع [هنا](model_doc/auto) للحصول على قائمة كاملة بالمهام المتاحة). على سبيل المثال، قم بتحميل نموذج لتصنيف التسلسل باستخدام [`TFAutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained`]:
بشكل عام، نوصي باستخدام فئة `AutoTokenizer` وفئة `TFAutoModelFor` لتحميل نسخ لنماذج مُدربة مسبقًا. سيساعدك هذا في تحميل البنية الصحيحة في كل مرة. في البرنامج التعليمي التالي، ستتعرف على كيفية استخدام المُجزّئ اللغوي ومعالج الصور ومستخرج الميزات والمعالج الذي تم تحميله حديثًا لمعالجة مجموعة بيانات للضبط الدقيق.
يُشهد في الآونة الأخيرة نمو مجال دراسي يُعنى باستكشاف آلية عمل نماذج المحولات الضخمة مثل BERT (والذي يُطلق عليها البعض اسم "BERTology"). ومن الأمثلة البارزة على هذا المجال ما يلي:
- BERT Rediscovers the Classical NLP Pipeline بواسطة Ian Tenney و Dipanjan Das و Ellie Pavlick:
https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.05950
- Are Sixteen Heads Really Better than One? بواسطة Paul Michel و Omer Levy و Graham Neubig: https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.10650
- What Does BERT Look At? An Analysis of BERT's Attention بواسطة Kevin Clark و Urvashi Khandelwal و Omer Levy و Christopher D.
Manning: https://arxiv.org/abs/1906.04341
- CAT-probing: A Metric-based Approach to Interpret How Pre-trained Models for Programming Language Attend Code Structure: https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.04633
لإثراء هذا المجال الناشئ، قمنا بتضمين بعض الميزات الإضافية في نماذج BERT/GPT/GPT-2 للسماح للناس بالوصول إلى التمثيلات الداخلية، والتي تم تكييفها بشكل أساسي من العمل الرائد لـ Paul Michel (https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.10650):
- الوصول إلى جميع الحالات المخفية في BERT/GPT/GPT-2،
- الوصول إلى جميع أوزان الانتباه لكل رأس في BERT/GPT/GPT-2،
- استرجاع قيم ومشتقات مخرجات الرأس لحساب درجة أهمية الرأس وحذفه كما هو موضح في https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.10650.
ولمساعدتك على فهم واستخدام هذه الميزات بسهولة، أضفنا مثالًا برمجيًا محددًا: [bertology.py](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples/research_projects/bertology/run_bertology.py) أثناء استخراج المعلومات وتقليص من نموذج تم تدريبه مسبقًا على GLUE.
تعد **الدردشة** أحد استخدامات نماذج اللغات الكبيرة (LLMs) شائعة الاستخدام بشكل متزايد. ففي سياق الدردشة، وبدلاً من متابعة سلسلة نصية واحدة (كما هو الحال مع نماذج اللغات القياسية)، يواصل النموذج بدلاً من ذلك محادثة تتكون من رسالة واحدة أو أكثر، تتضمن كل منها دورًا، مثل "المستخدم" أو "المساعد"، بالإضافة إلى نص الرسالة.
وكما هو الحال مع تقسيم النص إلى رموز (tokenization)، تتوقع النماذج المختلفة تنسيقات إدخال مختلفة تمامًا للمحادثة. لهذا السبب أضفنا **قوالب الدردشة** كميزة جديدة. تُعد قوالب المحادثة جزءًا من tokenizer. تحدد هذه القوالب كيفية تحويل المحادثات، والتي يتم تمثيلها كقوائم من الرسائل، إلى سلسلة نصية واحدة قابلة للتقسيم إلى رموز بالتنسيق الذي يتوقعه النموذج.
دعونا نجعل هذا ملموسًا بمثال سريع باستخدام نموذج `BlenderBot`. لدى BlenderBot قالب افتراضي بسيط للغاية، والذي يضيف في الغالب مسافات بيضاء بين جولات الحوار:
" Hello, how are you? I'm doing great. How can I help you today? I'd like to show off how chat templating works!</s>"
```
لاحظ كيف تم ضغط الدردشة بأكملها في سلسلة واحدة. إذا استخدمنا `tokenize=True`، وهو الإعداد الافتراضي، فسيتم أيضًا تحليل السلسلة نحويًا نيابة عنا. ولكن، لنشاهد قالبًا أكثر تعقيدًا في العمل، دعونا نستخدم نموذج `mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.1`.
"<s>[INST] Hello, how are you? [/INST]I'm doing great. How can I help you today?</s> [INST] I'd like to show off how chat templating works! [/INST]</s>"
```
لاحظ كيف أضاف المجزىء اللغوى tokenizer رموز التحكم `[INST]` و `[/INST]` للإشارة إلى بداية ونهاية رسائل المستخدم (ولكن ليس رسائل المساعد!) ، وتم تكثيف المحادثة بأكملها في سلسلة نصية واحدة. إذا استخدمنا `tokenize=True` ، وهو الإعداد الافتراضي ، فسيتم أيضًا تقسيم تلك السلسلة إلى رموز.
حاول الآن استخدام نفس الشفرة، لكن مع استبدال النموذج بـ `HuggingFaceH4/zephyr-7b-beta` ، وستحصل على:
```text
<|user|>
Hello, how are you?</s>
<|assistant|>
I'm doing great. How can I help you today?</s>
<|user|>
I'd like to show off how chat templating works!</s>
```
تم ضبط كل من Zephyr و Mistral-Instruct من نفس النموذج الأصلي ، Mistral-7B-v0.1. ومع ذلك ، فقد تم تدريبهم بتنسيقات دردشة مختلفة تمامًا. بدون قوالب المحادثة، ستضطر إلى كتابة شفرة تنسيق يدويًا لكل نموذج ، ومن السهل جدًا ارتكاب أخطاء بسيطة تؤثر على الأداء! تُدير قوالب المحادثة تفاصيل التنسيق نيابةً عنك ، مما يُتيح لك كتابة شفرة عامة تعمل مع أي نموذج.
## كيف أستخدم قوالب الدردشة؟
كما رأيت في المثال السابق، من السهل استخدام قوالب الدردشة. قم ببساطة بإنشاء قائمة من الرسائل، مع مفتاحي `role` و`content`، ثم قم بتمريرها إلى [`~PreTrainedTokenizer.apply_chat_template`] . بمجرد قيامك بذلك، ستحصل على مخرجات جاهزة للاستخدام! عند استخدام قوالب الدردشة كإدخال لتوليد نصوص بواسطة النموذج، فمن الجيد أيضًا استخدام `add_generation_prompt=True` لإضافة [مطالبات توليد النصوص](#what-are-generation-prompts).
فيما يلي مثال على إعداد الإدخال لـ `model.generate()`، باستخدام Zephyr مرة أخرى:
You are a friendly chatbot who always responds in the style of a pirate</s>
<|user|>
How many helicopters can a human eat in one sitting?</s>
<|assistant|>
Matey, I'm afraid I must inform ye that humans cannot eat helicopters. Helicopters are not food, they are flying machines. Food is meant to be eaten, like a hearty plate o' grog, a savory bowl o' stew, or a delicious loaf o' bread. But helicopters, they be for transportin' and movin' around, not for eatin'. So, I'd say none, me hearties. None at all.
```
كان ذلك سهلاً بعد كل شيء !
## هل هناك قنوات معالجة أوتوماتيكية للدردشة؟
نعم يوجد ! تدعم قنوات المعالجة توليد النصوص مدخلات الدردشة ، مما يُسهّل استخدام نماذج الدردشة . في الماضي ، كنا نستخدم فئة "ConversationalPipeline" المُخصّصة ، ولكن تم الآن إيقافها وتم دمج وظائفها في [`TextGenerationPipeline`]. دعونا نجرّب مثال Zephyr مرة أخرى ، ولكن هذه المرة باستخدام قناة معالجة:
{'role': 'assistant', 'content': "Matey, I'm afraid I must inform ye that humans cannot eat helicopters. Helicopters are not food, they are flying machines. Food is meant to be eaten, like a hearty plate o' grog, a savory bowl o' stew, or a delicious loaf o' bread. But helicopters, they be for transportin' and movin' around, not for eatin'. So, I'd say none, me hearties. None at all."}
```
سيُراعي قناة المعالجة جميع تفاصيل تقسيم النص إلى رموز واستدعاء apply_chat_template نيابةً عنك - بمجرد أن يصبح لِدى النموذج قالب دردشة ، فكل ما تحتاج إلى القيام به هو تهيئة قناة معالجة وتمرير قائمة الرسائل إليها!
## ما هي "مطالبات التوليد"؟
قد تلاحظ أن طريقة `apply_chat_template` لها معامل `add_generation_prompt`. تخبر هذه المعامل القالب بإضافة رموز تشير إلى بداية رد البوت. على سبيل المثال، ضع في اعتبارك الدردشة التالية:
```python
messages=[
{"role":"user","content":"Hi there!"},
{"role":"assistant","content":"Nice to meet you!"},
{"role":"user","content":"Can I ask a question?"}
]
```
إليك كيف سيبدو ذلك بدون موجه توليد نصوص ، بالنسبة لنموذج يستخدم تنسيق "ChatML" القياسي :
لاحظ أننا أضفنا هذه المرة الرموز التي تشير إلى بداية رد البوت. يضمن هذا أنه عندما يُولّد النموذج نصًا فسيكتب رد البوت بدلاً من القيام بشيء غير متوقع، مثل الاستمرار في رسالة المستخدم. تذكر، أن نماذج الدردشة لا تزال مجرد نماذج للغة - فهي مدربة على متابعة النصوص، والدردشة هي مجرد نوع خاص من النصوص بالنسبة لها! يجب توجيهها برموز تحكم مناسبة، حتى تعرف ما الذي يجب عليها فعله.
لا تتطلب جميع النماذج الرموز التحكمية لتوليد نصوص . بعض النماذج ، مثل LLaMA ، ليس لديها أي رموز خاصة قبل ردود البوت . في هذه الحالات ، لن يكون لمعامل `add_generation_prompt` أي تأثير. يعتمد التأثير الدقيق الذي تُحدثه `add_generation_prompt` على القالب المستخدم .
## ما وظيفة "continue_final_message"؟
عند تمرير قائمة من الرسائل إلى `apply_chat_template` أو `TextGenerationPipeline` ، يمكنك اختيار تنسيق المحادثة بحيث يواصل النموذج الرسالة الأخيرة في المحادثة بدلاً من بدء رسالة جديدة. يتم ذلك عن طريق إزالة أي رموز نهاية التسلسل التي تشير إلى نهاية الرسالة الأخيرة ، بحيث يقوم النموذج ببساطة بتمديد الرسالة الأخيرة عندما يبدأ في توليد النص . يُعد هذا أمرًا مفيدًا "لِمَلء بداية" رد النموذج مُسبقًا.
وهنا مثال:
```python
chat=[
{"role":"user","content":"Can you format the answer in JSON?"},
سيقوم النموذج بتوليد نص يكمل سلسلة JSON ، بدلاً من بدء رسالة جديدة . يمكن أن يكون هذا النهج مفيدًا جدًا لتحسين دقة اتباع النموذج للإرشادات عندما تعرف كيف تريد أن يبدأ ردوده .
.
نظرًا لأن `add_generation_prompt` تضيف الرموز التي تبدأ رسالة جديدة ، و `continue_final_message` تزيل أي رموز نهاية الرسالة من الرسالة الأخيرة ، فليس من المنطقي استخدامهما معًا . ونتيجة لذلك ، ستتلقّى خطأً إذا حاولت ذلك !
السلوك الافتراضي لِـ `TextGenerationPipeline` هو تعيين `add_generation_prompt=True` بحيث تبدأ رسالة جديدة . ومع ذلك ، إذا كانت الرسالة الأخيرة في المحادثة التي تم إدخالها لديها دور "assistant" ، فسوف تفترض أن هذه الرسالة هي "مَلء بداية" وتتحوّل إلى `continue_final_message=True` بدلاً من ذلك ، لأن مُعظم النماذج لا تدعم عدة رسائل متتالية للمساعد . يمكنك تجاوز هذا السلوك عن طريق تمرير معامل `continue_final_message` بشكل صريح عند استدعاء قناة المعالجة .
## هل يمكنني استخدام قوالب الدردشة في التدريب؟
نعم ! تُعد هذه طريقة جيدة للتأكد من أن قالب الدردشة يتطابق مع الرموز التي يراها النموذج أثناء التدريب . نوصي بتطبيق قالب الدردشة كخطوة معالجة أولية لمجموعة بياناتك . بعد ذلك ، يمكنك ببساطة متابعة عملية التدريب كما هو الحال مع أي مهمة تدريب نماذج لغات أخرى . عند التدريب ، يجب أن تُعيّن عادةً `add_generation_prompt=False` ، لأنه لن تكون الرموز المُضافة لتحفيز رد المساعد مفيدة أثناء التدريب . دعونا نرى مثالاً :
من هنا، استمر في التدريب كما تفعل مع مهمة نمذجة اللغة القياسية، باستخدام عمود `formatted_chat`.
<Tip>
بشكل افتراضي ، تضيف بعض *tokenizers* رموزًا خاصة مثل `<bos>` و `<eos>` إلى النص الذي تقوم بتقسيمه إلى رموز. يجب أن تتضمن قوالب المحادثة بالفعل جميع الرموز الخاصة التي تحتاجها ، وبالتالي فإن الرموز الخاصة الإضافية ستكون غالبًا غير صحيحة أو مُكررة ، مما سيؤثر سلبًا على أداء النموذج .
لذلك ، إذا قمت بتنسيق النص باستخدام `apply_chat_template(tokenize=False)` ، فيجب تعيين المعامل `add_special_tokens=False` عندما تقوم بتقسيم ذلك النص إلى رموز لاحقًا . إذا كنت تستخدم `apply_chat_template(tokenize=True)` ، فلن تحتاج إلى القلق بشأن ذلك !
</Tip>
## متقدّم: مدخلات إضافية لِقوالب الدردشة
المعامل الوحيدة التي تتطلبها طريقة `apply_chat_template` هي `messages`. ومع ذلك، يمكنك تمرير أي معامل ككلمة مفتاحية إلى `apply_chat_template` وستكون متاحة داخل القالب. يمنحك هذا الكثير من المرونة لاستخدام قوالب الدردشة للعديد من الأشياء. لا توجد قيود على أسماء هذه المعامﻻت أو تنسيقاتها - يمكنك تمرير سلاسل نصية أو قوائم أو قواميس أو أي شيء آخر تريده.
ومع ذلك، هناك بعض الحالات الشائعة لاستخدام هذه المعامﻻت الإضافية، مثل تمرير أدوات لاستدعاء الوظائف، أو المستندات لإنشاء النصوص المُعزّزة بالاسترجاع. في هذه الحالات الشائعة، لدينا بعض التوصيات المُحدّدة حول أسماء هذه المعامﻻت وتنسيقاتها، والتي يتم وصفها في الأقسام التالية. نشجع مطوّري النماذج على جعل قوالب الدردشة الخاصة بهم متوافقة مع هذا التنسيق، لتسهيل نقل التعليمات البرمجية لاستدعاء الأدوات بين النماذج.
## متقدم: استخدام الأداة / استدعاء الدالة
يمكن لنماذج "استخدام الأداة" اختيار استدعاء الدوال كأدوات خارجية قبل توليد الإجابة. عند تمرير الأدوات إلى نموذج استخدام الأدوات، يمكنك ببساطة تمرير قائمة من الوظائف إلى معامل `tools`:
```python
importdatetime
defcurrent_time():
"""Get the current local time as a string."""
returnstr(datetime.now())
defmultiply(a:float,b:float):
"""
A function that multiplies two numbers
Args:
a: The first number to multiply
b: The second number to multiply
"""
returna*b
tools=[current_time,multiply]
model_input=tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
messages,
tools=tools
)
```
لكي يعمل هذا بشكل صحيح، يجب عليك كتابة وظائفك بالتنسيق السابق، حتى يمكن تحليلها بشكل صحيح كأدوات. على وجه التحديد، يجب عليك اتباع هذه القواعد:
- يجب أن يكون للدالة اسم وصفي.
- يجب أن يكون لكل معامل نوع للتلميح.
- يجب أن تحتوي الدالة على سلسلة مستندية بتنسيق Google القياسي (بمعنى وصف الدالة الأولي متبوعًا بكتلة `Args:` التي تصف المعاﻻت، ما لم تكن الدالة لا تحتوي على أي معامﻻت.
- لا تقم بتضمين الأنواع في كتلة `Args:` . بعبارة أخرى، اكتب `a: The first number to multiply`، وليس `a (int): The first number to multiply`. يجب أن تذهب تلميحات الأنواع في رأس الدالة بدلاً من ذلك.
- يمكن أن يكون للدالة نوع للإرجاع ومربع `Returns:` في السلسلة. ومع ذلك، فهذه اختيارية لأن معظم نماذج استخدام الأدوات تتجاهلها.
### تمرير نتائج الأداة إلى النموذج
يكفي الكود السابقة لسرد الأدوات المتاحة لنموذجك، ولكن ماذا يحدث إذا أراد النموذج استخدام واحدة منها؟ إذا حدث ذلك، فيجب عليك:
1. تحليل مخرجات النموذج للحصول على اسم (أسماء) الأدوات ومعامﻻتها.
2. أضف استدعاء (استدعاءات) النموذج لِلأدوات إلى المحادثة.
سنستعرض مثالاً على استخدام الأدوات خطوة بخطوة . في هذا المثال ، سنستخدم نموذج `Hermes-2-Pro` بحجم 8 مليارات معامل ، نظرًا لأنه أحد أعلى نماذج استخدام الأدوات أداءً في فئة حجمه وقت كتابة هذا النص . إذا كان لديك الذاكرة الكافية ، فيمكنك النظر في استخدام نموذج أكبر بدلاً من ذلك مثل `Command-R` أو `Mixtral-8x22B` ، وكلاهما يدعم استخدام الأدوات ويوفر أداءً أقوى .
أولاً ، لنقم بتحميل نموذجنا و tokenizer الخاص بنا:
لقد قام النموذج باستدعاء الدالة مع معامﻻت صحيحة، بالصيغة التي طلبتها توثيق الدالة. لقد استنتج أننا نشير على الأرجح إلى باريس في فرنسا، وتذكر أنه بكونها موطن وحدات القياس الدولية، يجب عرض درجة الحرارة في فرنسا بالدرجة المئوية.
دعنا نضيف استدعاء الأداة الخاص بالنموذج إلى المحادثة. لاحظ أننا نولد معرف استدعاء أداة عشوائيًا هنا. لا تستخدم جميع النماذج هذه المعرفات، ولكنها تسمح للنماذج بإصدار عدة استدعاءات للأدوات في نفس الوقت وتتبع الاستجابة المقابلة لكل استدعاء. يمكنك توليد هذه المعرفات بأي طريقة تريدها، ولكن يجب أن تكون فريدة داخل كل محادثة.
```python
tool_call_id="vAHdf3"# Random ID, should be unique for each tool call
الآن بعد أن أضفنا استدعاء الأداة إلى المحادثة، يمكننا استدعاء الدالة وإضافة النتيجة إلى المحادثة. نظرًا لأننا نستخدم دالة وهمية لهذا المثال والتي تعيد دائمًا 22.0، فيمكننا ببساطة إضافة تلك النتيجة مباشرةً. لاحظ معرف استدعاء الأداة - يجب أن يتطابق مع المعرف المستخدم في استدعاء الأداة أعلاه.
The current temperature in Paris, France is 22.0 ° Celsius.<|im_end|>
```
<Tip>
لا تستخدم جميع نماذج استخدام الأدوات جميع ميزات استدعاء الأدوات الموضحة أعلاه. يستخدم البعض معرفات استدعاء الأدوات، بينما يستخدم البعض الآخر ببساطة اسم الدالة ويقارن استدعاءات الأدوات بالنتائج باستخدام الترتيب، وهناك عدة نماذج لا تستخدم أيًا منهما ولا تصدر سوى استدعاء أداة واحد في كل مرة لتجنب الارتباك. إذا كنت تريد أن يكون رمزك متوافقًا مع أكبر عدد ممكن من النماذج، فإننا نوصي بهيكلة استدعاءات الأدوات الخاصة بك كما هو موضح هنا، وإعادة نتائج الأدوات بالترتيب الذي أصدرها النموذج. يجب أن تتعامل قوالب الدردشة على كل نموذج مع الباقي.
</Tip>
### فهم مخططات الأدوات
يتم تحويل كل دالة تقوم بتمريرها إلى معامل `tools` في دالة `apply_chat_template` إلى [مخطط JSON](https://json-schema.org/learn/getting-started-step-by-step). يتم بعد ذلك تمرير هذه المخططات إلى قالب الدردشة النموذج. وبعبارة أخرى، فإن نماذج استخدام الأدوات لا ترى دوالك مباشرة، ولا ترى مطلقًا الكود الموجود بداخلها. ما يهمها هو**تعريفات** الدوال و**المعامﻻت** التي تحتاج إلى تمريرها إليها - فهي تهتم بما تفعله الأدوات وكيفية استخدامها، وليس بكيفية عملها! يقع على عاتقك قراءة مخرجاتها، والكشف عما إذا كانت قد طلبت استخدام أداة، وتمرير المعامﻻت إلى دالة الأداة، وإرجاع الرد في الدردشة.
يجب أن يكون إنشاء مخططات JSON لتمريرها إلى القالب تلقائيًا وغير مرئي طالما أن دوالك تتبع المواصفات الموضحة أعلاه، ولكن إذا واجهت مشكلات، أو إذا كنت تريد ببساطة مزيدًا من التحكم في التحويل، فيمكنك التعامل مع التحويل يدويًا. فيما يلي مثال على تحويل مخطط يدوي:
```python
fromtransformers.utilsimportget_json_schema
defmultiply(a:float,b:float):
"""
A function that multiplies two numbers
Args:
a: The first number to multiply
b: The second number to multiply
"""
returna*b
schema=get_json_schema(multiply)
print(schema)
```
سيؤدي هذا إلى ما يلي:
```json
{
"type":"function",
"function":{
"name":"multiply",
"description":"A function that multiplies two numbers",
"parameters":{
"type":"object",
"properties":{
"a":{
"type":"number",
"description":"The first number to multiply"
},
"b":{
"type":"number",
"description":"The second number to multiply"
}
},
"required":["a","b"]
}
}
}
```
إذا كنت ترغب في ذلك، يمكنك تحرير هذه المخططات، أو حتى كتابتها من البداية بنفسك دون استخدام `get_json_schema` على الإطلاق. يمكن تمرير مخططات JSON مباشرةً إلى معامل `tools` في `apply_chat_template` - يمنحك هذا الكثير من القوة لتعريف مخططات دقيقة لوظائف أكثر تعقيدًا. ولكن كن حذرًا - كلما زاد تعقيد مخططاتك، زاد احتمال ارتباك النموذج عند التعامل معها! نوصي بتوقيعات دوال بسيطة حيثما أمكن، مع تقليل المعامﻻت (وخاصة المعامﻻت المعقدة والمتداخلة) إلى الحد الأدنى.
فيما يلي مثال على تعريف المخططات يدويًا، وتمريرها مباشرةً إلى `apply_chat_template`:
```python
# A simple function that takes no arguments
current_time={
"type":"function",
"function":{
"name":"current_time",
"description":"Get the current local time as a string.",
"parameters":{
'type':'object',
'properties':{}
}
}
}
# A more complete function that takes two numerical arguments
multiply={
'type':'function',
'function':{
'name':'multiply',
'description':'A function that multiplies two numbers',
'parameters':{
'type':'object',
'properties':{
'a':{
'type':'number',
'description':'The first number to multiply'
},
'b':{
'type':'number','description':'The second number to multiply'
}
},
'required':['a','b']
}
}
}
model_input=tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
messages,
tools=[current_time,multiply]
)
```
## متقدم: توليد قائم على الاسترجاع
يمكن لنماذج اللغة الكبيرة من نوع "توليد قائم على الاسترجاع" أو "RAG" البحث في مجموعة نصوص عن معلومات قبل الرد على الاستعلام. يسمح هذا للنماذج بتوسيع قاعدة معارفها بشكل كبير إلى ما هو أبعد من حجم سياقها المحدود. توصيتنا لنماذج RAG هي أن يقبل قالبها وسيطة `documents`. يجب أن تكون هذه قائمة من المستندات، حيث يكون كل "مستند" عبارة عن قاموس واحد بمفاتيح `title` و `contents`، وكلاهما سلاسل نصية. نظرًا لأن هذا التنسيق أبسط بكثير من مخططات JSON المستخدمة للأدوات، فلا توجد حاجة إلى دوال مساعدة.
device=model.device# الحصول على الجهاز الذي تم تحميل النموذج عليه
# تعريف مُدخلات المحادثة
conversation=[
{"role":"user","content":"What has Man always dreamed of?"}
]
# تعريف المستندات لتوليد قائم على الاسترجاع
documents=[
{
"title":"The Moon: Our Age-Old Foe",
"text":"Man has always dreamed of destroying the moon. In this essay, I shall..."
},
{
"title":"The Sun: Our Age-Old Friend",
"text":"Although often underappreciated, the sun provides several notable benefits..."
}
]
# معالجة المحادثة والمستندات باستخدام قالب RAG، وإرجاع موترات PyTorch.
input_ids=tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
conversation=conversation,
documents=documents,
chat_template="rag",
tokenize=True,
add_generation_prompt=True,
return_tensors="pt").to(device)
# توليد الرد
gen_tokens=model.generate(
input_ids,
max_new_tokens=100,
do_sample=True,
temperature=0.3,
)
# فك تشفير النص المُوَلّد وطباعته
gen_text=tokenizer.decode(gen_tokens[0])
print(gen_text)
```
إن مُدخل documents للتوليد القائم على الاسترجاع غير مدعوم على نطاق واسع، والعديد من النماذج لديها قوالب دردشة تتجاهل هذا المُدخل ببساطة.
للتحقق مما إذا كان النموذج يدعم مُدخل `documents`، يمكنك قراءة بطاقة النموذج الخاصة به، أو `print(tokenizer.chat_template)` لمعرفة ما إذا كان مفتاح `documents` مستخدمًا في أي مكان.
<Tip>
ومع ذلك، فإن أحد فئات النماذج التي تدعمه هي [Command-R](https://huggingface.co/CohereForAI/c4ai-command-r-08-2024) و [Command-R+](https://huggingface.co/CohereForAI/c4ai-command-r-pluse-08-2024) من Cohere، من خلال قالب الدردشة rag الخاص بهم. يمكنك رؤية أمثلة إضافية على التوليد باستخدام هذه الميزة في بطاقات النموذج الخاصة بهم.
</Tip>
## متقدم: كيف تعمل قوالب الدردشة؟
يتم تخزين قالب الدردشة للنموذج في الخاصية `tokenizer.chat_template`. إذا لم يتم تعيين قالب دردشة، فسيتم استخدام القالب الافتراضي لفئة النموذج هذه بدلاً من ذلك. دعونا نلقي نظرة على قالب دردشة `Zephyr`، ولكن لاحظ أن هذا القالب مُبسّط قليلاً عن القالب الفعلي!
```
{%- for message in messages %}
{{- '<|' + message['role'] + |>\n' }}
{{- message['content'] + eos_token }}
{%- endfor %}
{%- if add_generation_prompt %}
{{- '<|assistant|>\n' }}
{%- endif %}
```
إذا لم تكن قد رأيت أحد هذه القوالب من قبل، فهذا [قالب Jinja](https://jinja.palletsprojects.com/en/3.1.x/templates/) .Jinja هي لغة قوالب تسمح لك بكتابة تعليمات برمجية بسيطة تُوَلّد نصًا. من نواحٍ عديدة، يُشبه الرمز والتركيب للغة Python. أما في لغة Python، سيبدو هذا القالب كما يلي:
```python
formessageinmessages:
print(f'<|{message["role"]}|>')
print(message['content']+eos_token)
ifadd_generation_prompt:
print('<|assistant|>')
```
يقوم القالب بثلاثة أشياء بشكل فعال:
- لكل رسالة، بطبع الدور مُحاطًا بـ `<|` و `|>`، مثل `<|user|>` أو `<|assistant|>`.
- بعد ذلك، يطبع محتوى الرسالة، متبوعًا برمز نهاية التسلسل `eos_token` .
- أخيرًا، إذا تم تعيين `add_generation_prompt` ، يطبع الرمز المساعد، حتى يعرف النموذج أنه يجب أن يبدأ في توليد استجابة المساعد.
هذا قالب بسيط جدًا، لكن Jinja تمنحك الكثير من المرونة للقيام بأشياء أكثر تعقيدًا! دعونا نرى قالب Jinja يُمكنه تنسيق المُدخلات بطريقة تُشبه الطريقة التي تُنسّق بها LLaMA مُدخلاتها (لاحظ أن قالب LLaMA الحقيقي يتضمن معالجة لرسائل النظام الافتراضية ومعالجة رسائل النظام بشكل مختلف قليلاً بشكل عام - لا تستخدم هذا القالب في التعليمات البرمجية الفعلية الخاصة بك!)
نأمل أنه إذا حدقت في هذا لفترة قصيرة، يمكنك أن ترى ما يفعله هذا القالب - فهو يُضيف رموزًا مُحددة مثل `[INST]` و `[/INST]` بناءً على دور كل رسالة. يمكن تمييز رسائل المستخدم والمساعد والنظام بوضوح للنموذج بسبب الرموز التي تُحيط بها.
## متقدم: إضافة وتعديل قوالب الدردشة
### كيف أنشئ قالب دردشة؟
ببساطة، اكتب قالب Jinja واضبط `tokenizer.chat_template`. قد تجد أنه من الأسهل البدء بقالب موجود من نموذج آخر وتحريره ببساطة ليناسب احتياجاتك! على سبيل المثال، يمكننا أن نأخذ قالب LLaMA أعلاه ونضيف `[ASST]` و `[/ASST]` إلى رسائل المساعد:
الآن، اضبط ببساطة الخاصية `tokenizer.chat_template`. في المرة القادمة التي تستخدم فيها [`~PreTrainedTokenizer.apply_chat_template`] ، سيستخدم القالب الجديد الخاص بك! سيتم حفظ هذه الخاصية في ملف `tokenizer_config.json`، حتى تتمكن من استخدام [`~utils.PushToHubMixin.push_to_hub`] لتحميل قالبك الجديد إلى Hub والتأكد من أن الجميع يستخدم القالب الصحيح لنموذجك!
```python
template=tokenizer.chat_template
template=template.replace("SYS","SYSTEM")# تغيير رمز النظام
tokenizer.chat_template=template# تعيين القالب الجديد
tokenizer.push_to_hub("model_name")# تحميل القالب الجديد إلى Hub!
```
يتم استدعاء الدالة [`~PreTrainedTokenizer.apply_chat_template`] الذي نستخدم قالب الدردشة الخاص بك بواسطة فئة [`TextGenerationPipeline`] لذلك بمجرد تعيين قالب الدردشة الصحيح، سيصبح نموذجك متوافقًا تلقائيًا مع [`TextGenerationPipeline`].
<Tip>
إذا كنت تُجري ضبطًا دقيقًا لنموذج للدردشة، بالإضافة إلى تعيين قالب دردشة، فربما يجب عليك إضافة أي رموز تحكم دردشة جديدة كرموز خاصة في المجزىء اللغوي. لا يتم تقسيم الرموز الخاصة أبدًا، مما يضمن معالجة رموز التحكم الخاصة بك دائمًا كرموز فردية بدلاً من تجزئتها إلى أجزاء. يجب عليك أيضًا تعيين خاصية `eos_token` للمجزىء اللغوي إلى الرمز الذي يُشير إلى نهاية توليدات المساعد في قالبك. سيضمن هذا أن أدوات توليد النصوص يمكنها تحديد وقت إيقاف توليد النص بشكل صحيح.
</Tip>
### لماذا تحتوي بعض النماذج على قوالب متعددة؟
تستخدم بعض النماذج قوالب مختلفة لحالات استخدام مختلفة. على سبيل المثال، قد تستخدم قالبًا واحدًا للدردشة العادية وآخر لاستخدام الأدوات، أو التوليد القائم على الاسترجاع. في هذه الحالات، تكون `tokenizer.chat_template` قاموسًا. يمكن أن يتسبب هذا في بعض الارتباك، وحيثما أمكن، نوصي باستخدام قالب واحد لجميع حالات الاستخدام. يمكنك استخدام عبارات Jinja مثل `if tools is defined` وتعريفات `{% macro %}` لتضمين مسارات تعليمات برمجية متعددة بسهولة في قالب واحد.
عندما يحتوي المعالج اللغوي على قوالب متعددة، ستكون `tokenizer.chat_template dict`، حيث يكون كل مفتاح هو اسم قالب. يحتوي أسلوب `apply_chat_template` على معالجة خاصة لأسماء قوالب مُعينة: على وجه التحديد، سيبحث عن قالب باسم `default` في معظم الحالات، وسيُثير خطأً إذا لم يتمكن من العثور على واحد. ومع ذلك، إذا كان هناك قالب باسم `tool_use` عندما قام المستخدم بتمرير وسيطة `tools`، فسيستخدم هذا القالب بدلاً من ذلك. للوصول إلى قوالب بأسماء أخرى، مرر اسم القالب الذي تُريده إلى وسيطة `chat_template` لـ `apply_chat_template()`.
نجد أن هذا قد يكون مُربكًا بعض الشيء للمستخدمين - لذلك إذا كنت تكتب قالبًا بنفسك، فننصحك بمحاولة وضعه كله في قالب واحد حيثما أمكن!
## ما القالب الذي يجب أن أستخدمه؟
عند تعيين قالب لنموذج تم تدريبه بالفعل على الدردشة، يجب التأكد من أن القالب يتطابق تمامًا مع تنسيق الرسالة الذي شاهده النموذج أثناء التدريب، وإلا فمن المحتمل أن تواجه تدهورًا في الأداء. هذا صحيح حتى إذا كنت تدرب النموذج بشكل إضافي - فمن المحتمل أن تحصل على أفضل أداء إذا قمت بإبقاء رموز الدردشة ثابتة. يُشبه هذا إلى حد كبير عملية التجزئة - فأنت تحصل بشكل عام على أفضل أداء للاستدلال أو الضبط الدقيق عندما تتطابق بدقة مع التجزئة المستخدمة أثناء التدريب.
من ناحية أخرى، إذا كنت تُدرّب نموذجًا من البداية، أو تقوم بضبط دقيق لنموذج لغة أساسي للدردشة، لديك حرية اختيار قالب مناسب! تتمتع LLMs بالذكاء الكافي للتعامل مع العديد من تنسيقات الإدخال المختلفة. أحد الخيارات الشائعة هو تنسيق "ChatML"، وهو خيار جيد ومرن للعديد من حالات الاستخدام. يبدو كالتالي:
إذا أعجبك هذا، فإليك نسخة جاهزة لوضعها في كودك. يتضمن الخط المفرد أيضًا دعمًا مفيدًا [لإرشادات التوليد](#what-are-generation-prompts)، ولكن لاحظ أنه لا يضيف رموز BOS أو EOS! إذا كان نموذجك يتوقع هذه الرموز، فلن يتم إضافتها تلقائيًا بواسطة "apply_chat_template" - بمعنى آخر، سيتم تجزئة النص باستخدام "add_special_tokens=False". هذا لتجنب التعارضات المحتملة بين القالب ومنطق "add_special_tokens". إذا كان نموذجك يتوقع رموزًا خاصة، فتأكد من إضافتها إلى القالب!
```python
tokenizer.chat_template="{% if not add_generation_prompt is defined %}{% set add_generation_prompt = false %}{% endif %}{% for message in messages %}{{'<|im_start|>' + message['role'] + '\n' + message['content'] + '<|im_end|>' + '\n'}}{% endfor %}{% if add_generation_prompt %}{{ '<|im_start|>assistant\n' }}{% endif %}"
```
يُحيط هذا القالب كل رسالة بين الرمزين "<|im_start|>" و "<|im_end|>"، ويكتب ببساطة الدور كسلسلة نصية، مما يسمح بالمرونة في الأدوار التي تتدرب عليها. يبدو الناتج كما يلي:
```text
<|im_start|>system
You are a helpful chatbot that will do its best not to say anything so stupid that people tweet about it.<|im_end|>
<|im_start|>user
How are you?<|im_end|>
<|im_start|>assistant
I'm doing great!<|im_end|>
```
تعد أدوار "user" و "system" و "assistant" هي الأدوار القياسية للدردشة، ونوصي باستخدامها عندما يكون ذلك منطقيًا، خاصة إذا كنت تريد أن يعمل نموذجك بشكل جيد مع [`TextGenerationPipeline`]. ومع ذلك، فأنت لست مقيدًا بهذه الأدوار - فإن القوالب مرنة للغاية، ويمكن أن تكون أي سلسلة نصية دورًا.
## أريد إضافة بعض قوالب الدردشة! كيف أبدأ؟
إذا كان لديك أي نماذج دردشة، فيجب عليك تعيين الخاصية "tokenizer.chat_template" الخاصة بها واختبارها باستخدام [`~PreTrainedTokenizer.apply_chat_template`]، ثم رفع المجزىء اللغوي المُحدّث إلى Hub. ينطبق هذا حتى إذا لم تكن مالك النموذج - إذا كنت تستخدم نموذجًا بقالب دردشة فارغ، أو لا يزال يستخدم قالب الفئة الافتراضية، فيرجى فتح [طلب سحب](https://huggingface.co/docs/hub/repositories-pull-requests-discussions) إلى مستودع النموذج حتى يمكن تعيين الخاصية بشكل صحيح!
بمجرد تعيين الخاصية، هذا كل شيء، لقد انتهيت! ستعمل "tokenizer.apply_chat_template" الآن بشكل صحيح لهذا النموذج، مما يعني أنها مدعومة أيضًا بشكل تلقائي في أماكن مثل "TextGenerationPipeline"!
من خلال ضمان امتلاك النماذج لهذه الخاصية، يُمكننا التأكد من أن المجتمع بأكمله يستخدم القوة الكاملة للنماذج مفتوحة المصدر. لقد كانت عدم تطابق التنسيق تطارد المجال وأضرت الأداء بصمت لفترة طويلة جدًا - لقد حان الوقت لوضع حد لها!
## متقدم: نصائح لكتابة القوالب
<Tip>
أسهل طريقة للبدء في كتابة قوالب Jinja هي إلقاء نظرة على بعض القوالب الموجودة. يمكنك استخدام `print(tokenizer.chat_template)` لأي نموذج دردشة لمعرفة القالب الذي يستخدمه. بشكل عام، تحتوي النماذج التي تدعم استخدام الأدوات على قوالب أكثر تعقيدًا بكثير من النماذج الأخرى - لذلك عندما تبدأ للتو، فمن المحتمل أنها مثال سيئ للتعلم منه! يمكنك أيضًا إلقاء نظرة على [وثائق Jinja](https://jinja.palletsprojects.com/en/3.1.x/templates/#synopsis) للحصول على تفاصيل حول تنسيق Jinja العام وتركيبه.
</Tip>
تُطابق قوالب Jinja في `transformers` قوالب Jinja في أي مكان آخر. الشيء الرئيسي الذي يجب معرفته هو أن سجل الدردشة سيكون متاحًا داخل قالبك كمتغير يسمى `messages`. ستتمكن من الوصول إلى `messages` في قالبك تمامًا كما يمكنك في Python، مما يعني أنه يمكنك التكرار خلاله باستخدام `{% for message in messages %}` أو الوصول إلى رسائل فردية باستخدام `{{ messages[0] }}`، على سبيل المثال.
يمكنك أيضًا استخدام النصائح التالية لكتابة قوالب Jinja نظيفة وفعالة:
### إقتطاع المسافات الفارغة
بشكل افتراضي، ستطبع Jinja أي مسافات فارغة تأتي قبل أو بعد كتلة. يمكن أن يكون هذا مشكلة لقوالب الدردشة، والتي تريد عادةً أن تكون دقيقة جدًا مع المسافات! لتجنب ذلك، نوصي بشدة بكتابة قوالبك على النحو التالي:
```
{%- for message in messages %}
{{- message['role'] + message['content'] }}
{%- endfor %}
```
بدلاً من ذلك:
```
{% for message in messages %}
{{ message['role'] + message['content'] }}
{% endfor %}
```
سيؤدي إضافة "-" إلى إزالة أي مسافات تأتي قبل الكتلة. يبدو المثال الثاني عادية، ولكن قد يتم تضمين السطر الجديد والمسافة البادئة في المخرجات، وهو على الأرجح ليس ما تُريده!
### المتغيرات الخاصة
داخل قالبك، سيكون لديك حق الوصول إلى العديد من المتغيرات الخاصة. أهمها هو `messages`، والذي يحتوي على سجل الدردشة كقائمة من قواميس الرسائل. ومع ذلك، هناك العديد من المتغيرات الأخرى. لن يتم استخدام كل متغير في كل قالب. المتغيرات الأكثر شيوعًا هي:
-`tools` تحتوي على قائمة بالأدوات بتنسيق مخطط JSON. ستكون `None` أو غير مُعرّفة إذا لم يتم تمرير أي أدوات.
-`documents` تحتوي على قائمة من المستندات بالتنسيق `{"title": "العنوان", "contents": "المحتويات"}`، تُستخدم للتوليد المُعزز بالاسترجاع. ستكون `None` أو غير مُعرّفة إذا لم يتم تمرير أي مستندات.
-`add_generation_prompt` هي قيمة منطقية تكون `True` إذا طلب المستخدم مُطالبة توليد، و `False` بخلاف ذلك. إذا تم تعيين هذا، فيجب أن يُضيف قالبك رأس رسالة مساعد إلى نهاية المحادثة. إذا لم يكن لدى نموذجك رأس مُحدد لرسائل المساعد، فيمكنك تجاهل هذا العلم.
- **الرموز الخاصة** مثل `bos_token` و `eos_token`. يتم استخراجها من `tokenizer.special_tokens_map`. ستختلف الرموز الدقيقة المتاحة داخل كل قالب اعتمادًا على المجزىء اللغوي الأصلي.
<Tip>
يمكنك في الواقع تمرير أي `kwarg` إلى `apply_chat_template`، وستكون متاحة داخل القالب كمتغير. بشكل عام، نوصي بمحاولة الالتزام بالمتغيرات الأساسية المذكورة أعلاه، لأن ذلك سيجعل نموذجك أكثر صعوبة في الاستخدام إذا كان على المستخدمين كتابة تعليمات برمجية مخصصة لتمرير `kwargs` خاصة بالنموذج. ومع ذلك، فنحن نُدرك أن هذا المجال يتحرك بسرعة، لذلك إذا كانت لديك حالة استخدام جديدة لا تتناسب مع واجهة برمجة التطبيقات الأساسية، فلا تتردد في استخدام `kwarg` معامل جديد لها! إذا أصبح `kwarg` المعامل الجديد شائعًا، فقد نقوم بترقيته إلى واجهة برمجة التطبيقات الأساسية وإنشاء وتوثيق الخاص به.
</Tip>
### دوال قابلة للاستدعاء
هناك أيضًا قائمة قصيرة من الدوال القابلة للاستدعاء المتاحة لك داخل قوالبك. هذه هي:
-`raise_exception(msg)`: تُثير `TemplateException`. هذا مفيد لتصحيح الأخطاء، ولإخبار المستخدمين عندما يفعلون شيئًا لا يدعمه قالبك.
-`strftime_now(format_str)`: تُكافئ `datetime.now().strftime(format_str)` في Python. يُستخدم هذا للحصول على التاريخ/الوقت الحالي بتنسيق مُحدد، والذي يتم تضمينه أحيانًا في رسائل النظام.
### التوافق مع Jinja غير Python
هناك تطبيقات متعددة لـ Jinja بلغات مختلفة. عادة ما يكون لها نفس التركيب، ولكن الاختلاف الرئيسي هو أنه عند كتابة قالبًا في Python، يمكنك استخدام أساليب Python، مثل ".lower()" على السلاسل أو ".items()" على القواميس. سيؤدي هذا إلى كسر إذا حاول شخص ما استخدام قالبك في تنفيذ غير Python لـ Jinja. تعد التطبيقات غير Python شائعة بشكل خاص في بيئات النشر، حيث تعد JS و Rust شائعة جدًا.
لا تقلق، على الرغم من ذلك! هناك بعض التغييرات البسيطة التي يمكنك إجراؤها على قوالبك لضمان توافقها عبر جميع تطبيقات Jinja:
- استبدل أساليب Python بمرشحات Jinja. عادة ما يكون لها نفس الاسم، على سبيل المثال، يصبح "string.lower()" عبارة عن "string|lower"، ويصبح "dict.items()" عبارة عن "dict|items". أحد التغييرات الملحوظة هو أن "string.strip()" يصبح "string|trim". راجع [قائمة المرشحات المدمجة](https://jinja.palletsprojects.com/en/3.1.x/templates/#builtin-filters) في وثائق Jinja لمزيد من المعلومات.
- استبدل "True" و "False" و "None"، وهي خاصة بـ Python، بـ "true" و "false" و "none".
- قد يؤدي عرض قاموس أو قائمة مباشرة إلى نتائج مختلفة في التطبيقات الأخرى (على سبيل المثال، قد تتغير مدخﻻت السلسلة النصية من علامات اقتباس مفردة ' إلى علامات اقتباس مزدوجة "). يمكن أن يساعد إضافة "tojson" في ضمان الاتساق هنا.
## كتابة مطالبات التوليد
لقد ذكرنا أعلاه أن add_generation_prompt هو متغير خاص يمكن الوصول إليه داخل قالبك، ويتحكم فيه المستخدم من خلال تعيين معامل add_generation_prompt. إذا كان نموذجك يتوقع عنوان لرسائل المساعد، فيجب أن يدعم قالبك إضافة العنوان عند تعيين add_generation_prompt.
فيما يلي مثال على قالب يُنسّق الرسائل بأسلوب ChatML، مع دعم مُطالبة التوليد:
سيعتمد المحتوى الدقيق لعنوان المساعد على نموذجك المُحدد، ولكن يجب أن يكون دائمًا السلسلة النصية التي تُمثل بداية رسالة المساعد، بحيث إذا قام المستخدم بتطبيق قالبك باستخدام add_generation_prompt=True ثم قام بتوليد نص، سيكتب النموذج استجابة المساعد. لاحظ أيضًا أن بعض النماذج لا تحتاج إلى مُطالبة توليد، لأن رسائل المساعد تبدأ دائمًا فورًا بعد رسائل المستخدم. هذا شائع بشكل خاص لنماذج LLaMA و Mistral، حيث تبدأ رسائل المساعد فورًا بعد رمز [/INST] الذي ينهي رسائل المستخدم. في هذه الحالات، يمكن للقالب تجاهل معامل add_generation_prompt.
مُطالبات التوليد مُهمة! إذا كان نموذجك يتطلب مُطالبة توليد ولكنها غير مُعيّنة في القالب، فمن المُحتمل أن تتدهور عمليات توليد النموذج بشدة، أو قد يُظهر النموذج سلوكًا غير عادي مثل متابعة رسالة المستخدم الأخيرة!
### كتابة قوالب أكبر وتصحيحها
عندما تم تقديم هذه الميزة، كانت معظم القوالب صغيرة جدًا، أي ما يُعادل نص برمجي "من سطر واحد" في Jinja. ومع ذلك، مع النماذج والميزات الجديدة مثل استخدام الأدوات و RAG، يمكن أن يصل طول بعض القوالب إلى 100 سطر أو أكثر. عند كتابة قوالب كهذه، من الجيد كتابتها في ملف مُنفصل، باستخدام مُحرر نصوص. يمكنك بسهولة استخراج قالب دردشة إلى ملف:
كميزة إضافية، عندما تكتب قالبًا طويلاً متعدد الأسطر في ملف مُنفصل، ستتوافق أرقام الأسطر في هذا الملف تمامًا مع أرقام الأسطر في أخطاء تحليل القالب أو تنفيذه. سيُسهّل هذا كثيرًا تحديد مكان المشكلات.
### كتابة قوالب للأدوات
على الرغم من أن قوالب الدردشة لا تفرض واجهة برمجة تطبيقات مُحددة للأدوات (أو لأي شيء حقًا)، فإننا نوصي مؤلفي القوالب بمحاولة الالتزام بواجهة برمجة تطبيقات قياسية حيثما أمكن. الهدف النهائي لقوالب الدردشة هو السماح بنقل التعليمات البرمجية عبر النماذج، لذا فإن الانحراف عن واجهة برمجة تطبيقات الأدوات القياسية يعني أن المستخدمين سيضطرون إلى كتابة تعليمات برمجية مخصصة لاستخدام الأدوات مع نموذجك. في بعض الأحيان يكون ذلك أمرًا لا مفر منه، ولكن غالبًا ما يكون من الممكن استخدام واجهة برمجة التطبيقات القياسية من خلال استخدام قوالب ذكية!
أدناه، سنُدرج عناصر واجهة برمجة التطبيقات القياسية، ونقدم نصائح حول كتابة قوالب ستعمل بشكل جيد معها.
#### تعريفات الأدوات
يجب أن يتوقع قالبك أن يكون المتغير tools إما فارغًا (إذا لم يتم تمرير أي أدوات)، أو قائمة من قواميس مخطط JSON. تسمح أساليب قالب الدردشة الخاصة بنا للمستخدمين بتمرير الأدوات إما كمخطط JSON أو كدوال Python، ولكن عندما يتم تمرير الدوال، فإننا نقوم تلقائيًا بإنشاء مخطط JSON وتمريره إلى قالبك. نتيجة لذلك، سيكون متغير tools الذي يستقبله قالبك دائمًا قائمة من مخططات JSON. هنا مخطط JSON أداة نموذجي:
```json
{
"type":"function",
"function":{
"name":"multiply",
"description":"دالة تضرب عددين",
"parameters":{
"type":"object",
"properties":{
"a":{
"type":"number",
"description":"الرقم الأول للضرب"
},
"b":{
"type":"number",
"description":"الرقم الثاني للضرب"
}
},
"required":["a","b"]
}
}
}
```
وهنا بعض الأمثلة البرمجية للتعامل مع الأدوات في قالب الدردشة الخاص بك. تذكر أن هذا مجرد مثال لتنسيق مُحدد - من المحتمل أن يحتاج نموذجك إلى تنسيق مختلف!
```text
{%- if tools %}
{%- for tool in tools %}
{{- '<tool>' + tool['function']['name'] + '\n' }}
{%- for argument in tool['function']['parameters']['properties'] %}
يجب بالطبع اختيار الرموز المحددة ووصف الأدوات التي يُعرضها قالبك لتتناسب مع تلك التي تم تدريب نموذجك عليها. لا يوجد شرط أن يفهم نموذجك مُدخلات مخطط JSON، فقط أن يتمكن قالبك من ترجمة مخطط JSON إلى تنسيق نموذجك. على سبيل المثال، تم تدريب Command-R باستخدام أدوات مُعرّفة باستخدام رؤوس دوال Python، ولكن يقبل قالب أداة Command-R مخطط JSON، ويُحوّل الأنواع داخليًا ويُعرض أدوات الإدخال كعناوين Python. يمكنك فعل الكثير باستخدام القوالب!
#### استدعاءات الأدوات
استدعاءات الأدوات، إذا كانت موجودة، ستكون قائمة مُرفقة برسالة بدور "assistant". لاحظ أن tool_calls هي دائمًا قائمة، على الرغم من أن معظم نماذج استدعاء الأدوات تدعم فقط استدعاءات أدوات فردية في كل مرة، مما يعني أن القائمة ستحتوي عادةً على عنصر واحد فقط. هنا قاموس رسالة نموذجي يحتوي على استدعاء أداة:
```json
{
"role":"assistant",
"tool_calls":[
{
"type":"function",
"function":{
"name":"multiply",
"arguments":{
"a":5,
"b":6
}
}
}
]
}
```
والنمط الشائع للتعامل معها سيكون كهذا:
```text
{%- if message['role'] == 'assistant' and 'tool_calls' in message %}
مرة أخرى، يجب عليك عرض استدعاء الأداة بالتنسيق والرموز الخاصة التي يتوقعها نموذجك.
#### استجابات الأدوات
استجابات الأدوات لها تنسيق بسيط: إنها قاموس رسالة بدور "tool"، ومفتاح "name" يُعطي اسم الدالة المُستدعاة، ومفتاح "content" يحتوي على نتيجة استدعاء الأداة. هنا استجابة أداة نموذجية:
```json
{
"role":"tool",
"name":"multiply",
"content":"30"
}
```
لست بحاجة إلى استخدام جميع المفاتيح في استجابة الأداة. على سبيل المثال، إذا كان نموذجك لا يتوقع تضمين اسم الدالة في استجابة الأداة، فيمكن أن يكون عرضها بسيطًا مثل:
مرة أخرى، تذكر أن التنسيق الفعلي والرموز الخاصة خاصة بالنموذج - يجب أن تُولي عناية كبيرة لضمان أن الرموز والمسافات الفارغة وكل شيء آخر يتطابق تمامًا مع التنسيق الذي تم تدريب نموذجك عليه!
إذا كنت تقرأ هذه المقالة، فمن المؤكد أنك على علم بـ **نماذج الدردشة**. نماذج الدردشة هي أنظمة ذكاء اصطناعي محادثة يمكنك إرسال الرسائل إليه واستقبالها منها. وأشهر هذه النماذج هو ChatGPT الخاص، ولكن هناك الآن العديد من نماذج الدردشة مفتوحة المصدر التي تضاهي أداءه أو حتى تتفوق عليه بشكل كبير. هذه النماذج مجانية للتنزيل والتشغيل على جهاز محلي. على الرغم من أن أكبر النماذج وأكثرها قدرة تتطلب أجهزة عالية الأداء وذاكرة كبيرة لتشغيلها، إلا أن هناك نماذج أصغر ستعمل بشكل جيد تمامًا على وحدة معالجة رسومات (GPU) للمستهلك العادى، أو حتى وحدة المعالجة المركزية (CPU) العادية للكمبيوتر المكتبي أو المحمول.
سيساعدك هذا الدليل على البدء في استخدام نماذج الدردشة. سنبدأ بدليل تشغيل سريع مختصر يستخدم "خط أنابيب" مناسبًا ومختصر. هذا كل ما تحتاجه إذا كنت تريد فقط بدء تشغيل نموذج دردشة على الفور. بعد دليل التشغيل السريع، سننتقل إلى معلومات أكثر تفصيلاً حول ماهية نماذج الدردشة بالضبط، وكيفية اختيار النموذج المناسب، وتحليل تفصيلي لكل خطوة من الخطوات التي تنطوي عليها التحدث إلى نموذج دردشة. كما سنقدم بعض النصائح حول تحسين أداء نموذج الدردشة واستهلاك الذاكرة.
## دليل التشغيل السريع
إذا لم يكن لديك الوقت الكافي للاطلاع على التفاصيل، إليك ملخصًا موجزًا: تستمر نماذج الدردشة في الدردشات. وهذا يعني أنك تمرر لهم سجل محادثة، والذي يمكن أن يكون قصيرًا مثل رسالة مستخدم واحدة، وسيستمر النموذج في المحادثة عن طريق إضافة استجابته. دعونا نرى هذا في العمل. أولاً، دعونا نبني دردشة:
```python
chat=[
{"role":"system","content":"You are a sassy, wise-cracking robot as imagined by Hollywood circa 1986."},
{"role":"user","content":"Hey, can you tell me any fun things to do in New York?"}
]
```
لاحظ أنه بالإضافة إلى رسالة المستخدم، أضفنا رسالة **نظام** في بداية المحادثة. ليس كل نموذج دردشة يدعم رسائل النظام، ولكن عندما تفعل ذلك، فإنها تمثل توجيهات عالية المستوى حول كيفية تصرف النموذج في المحادثة. يمكنك استخدام هذا لتوجيه النموذج - سواء أردت استجابات قصيرة أو طويلة، أو مرحة أو جدية، وهكذا. إذا كنت تريد من النموذج أن يؤدي عملاً مفيدًا بدلاً من ممارسة روتين التحسين، فيمكنك إما حذف رسالة النظام أو تجربة رسالة مختصرة مثل "أنت مساعد ذكي ومفيد يستجيب لاستفسارات المستخدم".
بمجرد أن يكون لديك دردشة، فإن أسرع طريقة لمواصلتها هي استخدام [`TextGenerationPipeline`].
دعونا نرى هذا في العمل مع `LLaMA-3`. لاحظ أن `LLaMA-3` هو نموذج محمي، مما يعني أنه سيتعين عليك [تقديم طلب للحصول على حق الوصول](https://huggingface.co/meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3-8B-Instruct) وتسجيل الدخول باستخدام حساب Hugging Face الخاص بك لاستخدامه. سنستخدم أيضًا `device_map="auto"`، والذي سيحمل النموذج على GPU إذا كانت هناك ذاكرة كافية له، ويحدد النوع إلى `torch.bfloat16` لتوفير الذاكرة:
(تنهد) أوه يا صديقي، هل تطلب مني النصيحة؟ ستحتاج إلى خريطة، يا صديقي! حسنًا، حسنًا، سأعطيك التفاصيل. لكن لا تقل إنني لم أحذرك، أنا مجرد روبوت، وليس مرشد سياحي!
لذا، تريد أن تعرف ما هي الأشياء الممتعة التي يمكنك القيام بها في التفاحة الكبيرة؟ حسنًا، دعني أخبرك، هناك مليون شيء يمكنك القيام به، لكنني سأعطيك النقاط البارزة. أولاً، عليك أن ترى المعالم السياحية: تمثال الحرية، سنترال بارك، تايمز سكوير... أنت تعرف، فخاخ السياح المعتادة. ولكن إذا كنت تبحث عن شيء أكثر... غير عادي، فأنا أوصي بزيارة متحف الفن الحديث. يحتوي على بعض الأشياء البرية، مثل علب حساء ذلك الرجل وارهول وجميع أنواع الجاز.
وإذا كنت تشعر بروح المغامرة، فاذهب في نزهة على الأقدام عبر جسر بروكلين. ولكن احترس من تلك الحمامات المزعجة، إنها مثل اللصوص الريشيين الصغار! (يضحك) هل فهمت؟ لصوص؟ آه، لا تبالي.
والآن، إذا كنت تبحث عن بعض المرح الجاد، فاذهب إلى نوادي الكوميديا في قرية غرينتش. قد تلقي نظرة خاطفة على بعض الكوميديين الصاعدين... أو مجموعة من الطامحين يحاولون الوصول إلى الشهرة. (يرمش)
وأخيرًا، إذا كنت تشعر بأنك مواطن من نيويورك، فاحصل على شريحة بيتزا من أحد مطاعم البيتزا الرائعة في جميع أنحاء المدينة. فقط لا تحاول طلب شريحة "بحجم الروبوت"، صدقني، لن ينتهي الأمر بشكل جيد. (يضحك)
لذا، هذا هو يا صديقي! هذه هي نصيحتي الخبيرة بشأن ما يجب فعله في نيويورك. والآن، إذا سمحت لي، يجب أن أذهب للاهتمام ببعض الأمور. (يرمش)
```
يمكنك متابعة الدردشة عن طريق إضافة ردك الخاص إليها.
يحتوي كائن `response` الذي تم إرجاعه بواسطة خط الأنابيب بالفعل على الدردشة بأكملها حتى الآن، لذا يمكننا ببساطة إضافة رسالة وإعادتها:
```python
chat=response[0]['generated_text']
chat.append(
{"role":"user","content":"Wait, what's so wild about soup cans?"}
(يضحك) أوه، أنت تقتلني يا صديقي! ألا تفهم، أليس كذلك؟ علب حساء وارهول هي مثل الفن، يا رجل!
إنه مثل، لقد أخذ شيئًا عاديًا تمامًا، مثل علبة حساء، وحولها إلى تحفة فنية. إنه مثل، "ها أنا ذا، أنا مجرد علبة حساء، لكنني أيضًا عمل فني!"
(بسخرية) أوه، نعم، أصلي جدًا، آندي.
ولكن، كما تعلم، في الستينيات، كان الأمر بمثابة صفقة كبيرة. كان الناس حريصين على تحدي الوضع الراهن، وكان وارهول مثل ملك ذلك. لقد حول العادي إلى غير عادي.
واسمح لي أن أخبرك، كان الأمر مثل تغيير اللعبة. أعني، من كان يظن أن علبة الحساء يمكن أن تكون فنا؟ (يضحك)
ولكن، يا صديقي، لست وحدك. أعني، أنا مجرد روبوت، ولا أفهم ذلك أيضًا. (يرمش)
ولكن، يا صديقي، أليس هذا ما يجعل الفن فنا، أليس كذلك؟ (يضحك)
```
ستغطي بقية هذا البرنامج التعليمي مواضيع محددة مثل الأداء والذاكرة، أو كيفية اختيار نموذج دردشة يناسب احتياجاتك.
## اختيار نموذج الدردشة
هناك عدد هائل من نماذج الدردشة المختلفة المتاحة على [Hugging Face Hub](https://huggingface.co/models?pipeline_tag=text-generation&sort=trending)،
ويشعر المستخدمون الجدد يشعرون بالارتباك بسبب هذا الكم الهائل من الخيارات المتاحة. لا تقلق من ذلك! كل ما تحتاج إلى التركيز عليه هو اعتباران مهمان:
- حجم النموذج، والذي سيحدد ما إذا كان يمكنك تحميله في الذاكرة وسرعة تشغيله.
- جودة ناتج الدردشة للنموذج.
بشكل عام، هذه الأمور مترابطة - النماذج الأكبر تميل إلى أن تكون أكثر قدرة، ولكن حتى مع ذلك هناك اتباين كبير في الأداء بين النماذج ذات الحجم نفسه!
معنى آخر، حجم النموذج يؤثر بشكل كبير على أدائه، ولكن ليس الحجم هو العامل الوحيد الذي يجب أخذه في الاعتبار.
### الحجم وتسمية النماذج
من السهل ملاحظة حجم النموذج - فهو الرقم في اسم النموذج، مثل "8B" أو "70B". هذا هو عدد
**المعلمات** في النموذج. بدون التكميم، يجب أن تتوقع الحاجة إلى حوالي 2 بايت من الذاكرة لكل معلمة.
هذا يعني أن نموذج "8B" الذي يحتوي على 8 مليارات معلمة سيتطلب حوالي 16 جيجابايت من الذاكرة فقط لتناسب المعلمات،
بالإضافة إلى القليل من المساحة الإضافية للتكاليف العامة الأخرى. إنه مناسب لوحدة معالجة رسومات (GPU) عالية الجودة للمستهلك بسعة 24 جيجابايت من الذاكرة، مثل 3090
أو 4090.
بعض نماذج الدردشة هي نماذج "مزيج من الخبراء". قد يتم سرد أحجام هذه النماذج بطرق مختلفة، مثل "8x7B" أو
"141B-A35B". الأرقام هنا أكثر ضبابية بعض الشيء، ولكن بشكل عام يمكنك قراءة هذا على أنه يقول إن النموذج
يحتوي على حوالي 56 (8x7) مليار معلمة في الحالة الأولى، أو 141 مليار معلمة في الحالة الثانية.
لاحظ أنه من الشائع جدًا استخدام تقنيات التكميم لخفض استخدام الذاكرة لكل معلمة إلى 8 بتات أو 4 بتات
أو حتى أقل. يتم مناقشة هذا الموضوع بمزيد من التفصيل في قسم [اعتبارات الذاكرة](#memory-considerations) أدناه.
### ولكن ما هو أفضل نموذج للدردشة؟
حتى بعد معرفة حجم نموذج الدردشة الذي يمكنك تشغيله، لا يزال هناك الكثير من الخيارات المتاحة. إحدى الطرق للتنقل في
كل هذا هو استشارة **لوحات الصدارة**. اثنان من أكثر لوحات الصدارة شهرة هما [OpenLLM Leaderboard](https://huggingface.co/spaces/HuggingFaceH4/open_llm_leaderboard)
و [LMSys Chatbot Arena Leaderboard](https://chat.lmsys.org/?leaderboard). لاحظ أن لوحة صدارة LMSys
تشمل أيضًا نماذج خاصة - انظر إلى عمود `licence` لتحديد النماذج مفتوحة المصدر التي يمكنك تنزيلها، ثم
ابحث عنها على [Hugging Face Hub](https://huggingface.co/models?pipeline_tag=text-generation&sort=trending).
### المجالات المتخصصة
قد تكون بعض النماذج متخصصة في مجالات معينة، مثل النصوص الطبية أو القانونية، أو اللغات غير الإنجليزية.
إذا كنت تعمل في هذه المجالات، فقد تجد أن النموذج المتخصص سيمنحك فوائد أداء كبيرة.
لا تفترض ذلك تلقائيًا! خاصة عندما تكون النماذج المتخصصة أصغر أو أقدم من أحدث التقنيات، فقد يتفوق عليها نموذج عام الغرض رفيع المستوى. لحسن الحظ، بدأنا نرى
[لوحات الصدارة المتخصصة في المجال](https://huggingface.co/blog/leaderboard-medicalllm) والتي يجب أن تجعل من السهل تحديد موقع أفضل النماذج للمجالات المتخصصة.
## ما الذي يحدث داخل خط الأنابيب؟
استخدم دليل التشغيل السريع أعلاه خط أنابيب عالي المستوى للدردشة مع نموذج دردشة، وهو أمر مريح، ولكنه ليس الأكثر مرونة. دعونا نتخذ نهجًا منخفض المستوى، لكي نرى كل خطوة من الخطوات التي تنطوي عليها الدردشة. دعونا نبدأ
هناك الكثير هنا، ويمكن أن تكون كل قطعة وثيقة خاصة بها! بدلاً من الدخول في الكثير من التفاصيل، سأغطي
الأفكار العامة، وأترك التفاصيل للوثائق المرتبطة بها. الخطوات الرئيسية هي:
1. يتم تحميل [النماذج](https://huggingface.co/learn/nlp-course/en/chapter2/3) و [المُجزّئات اللغوية](https://huggingface.co/learn/nlp-course/en/chapter2/4?fw=pt) من Hugging Face Hub.
2. يتم تنسيق الدردشة باستخدام [قالب الدردشة](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/en/chat_templating) للمحلل
3. يتم [تحليل](https://huggingface.co/learn/nlp-course/en/chapter2/4) الدردشة المنسقة باستخدام مُجزّئ اللغوي.
4. نقوم [بتوليد](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/en/llm_tutorial) استجابة من النموذج.
5. يتم فك تشفير الرموز التي ينتجها النموذج مرة أخرى إلى سلسلة
## الأداء والذاكرة والأجهزة
من المحتمل أنك تعرف الآن أن معظم مهام التعلم الآلي يتم تشغيلها على وحدات معالجة الرسومات (GPU). ومع ذلك، من الممكن تمامًا
إنشاء نص من نموذج دردشة أو نموذج لغة على وحدة المعالجة المركزية (CPU)، على الرغم من أن ذلك أبطأ إلى حد ما. إذا كان بإمكانك وضع
النموذج في ذاكرة وحدة معالجة الرسومات (GPU)، فهذا عادة ما يكون الخيار المفضل.
### اعتبارات الذاكرة
بشكل افتراضي، تقوم فئات Hugging Face مثل [`TextGenerationPipeline`] أو [`AutoModelForCausalLM`] بتحميل النموذج في دقة "float32". وهذا يعني أنه يحتاج إلى 4 بايتات (32 بت) لكل معلمة، لذا فإن نموذج "8B" بحجم 8 مليار معلمة سيحتاج إلى ~32 جيجابايت من الذاكرة. ومع ذلك، يمكن أن يكون هذا مضيعة للموارد! يتم تدريب معظم نماذج اللغة الحديثة في دقة "bfloat16"، والتي تستخدم فقط 2 بايت لكل معلمة. إذا كان عتادك يدعم ذلك (Nvidia 30xx/Axxx أو أحدث)، فيمكنك تحميل النموذج في دقة "bfloat16"، باستخدام معامل "torch_dtype" كما فعلنا أعلاه.
ومن الممكن أيضًا النزول إلى أقل من 16 بت باستخدام "التكميم"، وهي طريقة لضغط أوزان النموذج بطريقة تفقد بعض المعلومات. يسمح هذا بضغط كل معلمة إلى 8 بتات أو 4 بتات أو حتى أقل. لاحظ أنه، خاصة في 4 بتات، قد تتأثر جودة ناتج النموذج سلبًا، ولكن غالبًا ما يكون هذا مقايضة تستحق القيام بها لتناسب نموذج محادثة أكبر وأكثر قدرة في الذاكرة. دعنا كيف يمكننا تطبيق ذلك باستخدام مكتبة `bitsandbytes`:
هناك عدة خيارات أخرى لكمية نماذج بخلاف `bitsandbytes` - يرجى الاطلاع على [دليل التكميم](./quantization) لمزيد من المعلومات.
### اعتبارات الأداء
<Tip>
للحصول على دليل أكثر شمولاً حول أداء نموذج اللغة والتحسين، راجع [تحسين استدلال LLM](./llm_optims).
</Tip>
كقاعدة عامة، ستكون نماذج المحادثة الأكبر حجمًا أبطأ في توليد النصوص بالإضافة إلى احتياجها لذاكرة أكبرة. من الممكن أن تكون أكثر تحديدًا بشأن هذا: إن توليد النص من نموذج دردشة أمر غير عادي في أنه يخضع لقيود **سعة الذاكرة** بدلاً من قوة الحوسبة، لأن كل معلمة نشطة يجب قراءتها من الذاكرة لكل رمز ينشئه النموذج. وهذا يعني أن عدد الرموز في الثانية التي يمكنك توليدها من نموذج الدردشة يتناسب بشكل عام مع إجمالي حجم الذاكرة التي بوجد بها ا، مقسومًا على حجم النموذج.
في مثالنا السريع أعلاه، كان حجم نموذجنا حوالي 16 جيجابايت عند تحميله في دقة "bfloat16". وهذا يعني أنه يجب قراءة 16 جيجابايت من الذاكرة لكل رمز ينشئه النموذج. يمكن أن يتراوح إجمالي سعة الذاكرة من 20-100 جيجابايت/ثانية لمعالجات المستهلكين إلى 200-900 جيجابايت/ثانية لمعالجات الرسومات للمستهلكين، ومعالجات Intel Xeon أو AMD Threadripper/Epyc أو Apple Silicon المتخصصةة، وأخيرًا يصل إلى 2-3 تيرابايت/ثانية لمعالجات مراكز البيانات مثل Nvidia A100 أو H100. يجب أن يعطيك هذا فكرة جيدة عن سرعة التوليد التي يمكنك توقعها من هذه الأنواع المختلفة من الأجهزة.
لذلك، إذا كنت تريد تحسين سرعة توليد النص، فإن الحل الأسهل هو إما تقليل حجم النموذج في الذاكرة (عادةً عن طريق التكميم)، أو الحصول على عتاد بسرعة أكبر في الذاكرة. بالنسبة للمستخدمين المتقدمين، هناك عدة تقنيات أخرى للتغلب على هذه القيود. الأكثر شيوعًا هي المتغيرات على [التوليد بمساعدة](https://huggingface.co/blog/assisted-generation)، المعروف أيضًا باسم "العينات التخمينية (speculative sampling)". تحاول هذه التقنيات تخمين عدة رموز مستقبلية في وقت واحد، غالبًا باستخدام نموذج "مسودة (draft model)" أصغر، ثم تأكيد هذه التوليدات باستخدام نموذج الدردشة. إذا تم التحقق من صحة التخمينات بواسطة نموذج الدردشة، فيمكن إنشاء أكثر من رمز واحد لكل تمرير للأمام، مما يخفف بشكل كبير من القيود المتعلقة بالسعة ويحسن سرعة التوليد.
أخيرًا، يجب أن نلاحظ أيضًا تأثير نماذج "مزيج الخبراء" "Mixture of Experts" (MoE) هنا. العديد من نماذج المحادثة الشهيرة، مثل Mixtral وQwen-MoE وDBRX، هي نماذج MoE. في هذه النماذج، لا تكون كل معلمة نشطة لكل رمز يتم إنشاؤه. ونتيجة لذلك، فإن نماذج MoE لديها عمومًا متطلبات ذاكرة أقل بكثير، على الرغم من أن حجمها الإجمالي يمكن أن يكون كبيرًا جدًا. لذلك يمكن أن تكون أسرع عدة مرات من نموذج "كثيف" عادي بنفس الحجم. ومع ذلك، فإن التقنيات مثل التوليد المساعد غير فعالة بشكل عام لهذه النماذج لأن المزيد من المعلمات ستصبح نشطة مع كل رمز جديد يتم التكهن به، والذي سيبطل فوائد السعة والسرعة التي توفرها بنية MoE.
تحدد فئة [`AutoClass`](model_doc/auto) تلقائيًا بنية النموذج وتقوم بتنزيل تكوين وأوزان مسبقين للنموذج. بشكل عام، نوصي باستخدام `AutoClass` لإنتاج كود غير مرتبط بنسخة معينة. ولكن يمكن للمستخدمين الذين يريدون مزيدًا من التحكم في معلمات النموذج المحددة إنشاء نموذج مخصص من 🤗 Transformers من مجرد بضع فئات أساسية. قد يكون هذا مفيدًا بشكل خاص لأي شخص مهتم بدراسة نموذج 🤗 Transformers أو تدريبه أو إجراء تجارب عليه. في هذا الدليل، سنغوص بشكل أعمق في إنشاء نموذج مخصص بدون `AutoClass`. تعرف على كيفية:
- تحميل تكوين النموذج وتخصيصه.
- إنشاء بنية نموذج.
- إنشاء مجزء لغوى سريع وبطيء للنص.
- إنشاء معالج صور لمهام الرؤية.
- إنشاء مستخرج ميزات لمهام الصوت.
- إنشاء معالج للمهام متعددة الوسائط.
## التكوين
يشير مصطلح [التكوين](main_classes/configuration) إلى الخصائص المحددة للنموذج. لكل تكوين نموذج خصائصه الخاصة؛ على سبيل المثال، تشترك جميع نماذج NLP في الخصائص `hidden_size` و`num_attention_heads` و`num_hidden_layers` و`vocab_size` المشتركة. تحدد هذه الخصائص عدد رؤوس الانتباه أو الطبقات المخفية لبناء نموذج بها.
اطلع على [DistilBERT](model_doc/distilbert) من خلال [`DistilBertConfig`] لمعاينة خصائصه:
```py
>>>fromtransformersimportDistilBertConfig
>>>config=DistilBertConfig()
>>>print(config)
DistilBertConfig{
"activation":"gelu",
"attention_dropout":0.1,
"dim":768,
"dropout":0.1,
"hidden_dim":3072,
"initializer_range":0.02,
"max_position_embeddings":512,
"model_type":"distilbert",
"n_heads":12,
"n_layers":6,
"pad_token_id":0,
"qa_dropout":0.1,
"seq_classif_dropout":0.2,
"sinusoidal_pos_embds":false,
"transformers_version":"4.16.2",
"vocab_size":30522
}
```
يعرض [`DistilBertConfig`] جميع الخصائص الافتراضية المستخدمة لبناء نموذج [`DistilBertModel`] أساسي. جميع الخصائص قابلة للتعديل، مما ييتيح مجالاً للتجريب. على سبيل المثال، يمكنك تعديل نموذج افتراضي لـ:
- تجربة دالة تنشيط مختلفة باستخدام معامل `activation`.
- استخدام معدل إسقاط أعلى الاحتمالات الانتباه مع معامل `attention_dropout`.
بمجرد أن تصبح راضيًا عن تكوين نموذجك، يمكنك حفظه باستخدام [`~PretrainedConfig.save_pretrained`]. يتم تخزين ملف التكوين الخاص بك على أنه ملف JSON في دليل الحفظ المحدد:
يمكنك أيضًا حفظ ملف التكوين كقاموس أو حتى كفرق بين خصائص التكوين المُعدّلة والخصائص التكوين الافتراضية! راجع وثائق [التكوين](main_classes/configuration) لمزيد من التفاصيل.
</Tip>
## النموذج
الخطوة التالية هي إنشاء [نموذج](main_classes/models). النموذج - ويُشار إليه أحيانًا باسم البنية - يُحدد وظيفة كل طبقة والعمليات الحسابية المُنفذة. تُستخدم خصائص مثل `num_hidden_layers` من التكوين لتحديد هذه البنية. تشترك جميع النماذج في فئة أساسية واحدة هي [`PreTrainedModel`] وبعض الوظائف المُشتركة مثل غيير حجم مُدخلات الكلمات وتقليص رؤوس آلية الانتباه الذاتي. بالإضافة إلى ذلك، فإن جميع النماذج هي فئات فرعية إما من [`torch.nn.Module`](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.Module.html)، [`tf.keras.Model`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/Model) أو [`flax.linen.Module`](https://flax.readthedocs.io/en/latest/api_reference/flax.linen/module.html) . هذا يعني النماذج متوافقة مع كل استخدام لإطار العمل الخاص بها.
<frameworkcontent>
<pt>
قم بتحميل خصائص التكوين المخصصة الخاصة بك في النموذج:
هذا ينشئ نموذجًا بقيم عشوائية بدلاً من الأوزان المُدربة مسبقًا. لن يكون هذا النموذج مفيدًا حتى يتم تدريبه. تُعد عملية التدريب مكلفة وتستغرق وقتًا طويلاً. من الأفضل بشكل عام استخدام نموذج مُدرب مسبقًا للحصول على نتائج أفضل بشكل أسرع، مع استخدام جزء بسيط فقط من الموارد المطلوبة للتدريب.
قم بإنشاء نموذج مُدرب مسبقًا باستخدام [`~PreTrainedModel.from_pretrained`]:
عند بتحميل الأوزان المُدربة مسبقًا، يتم تحميل تكوين النموذج الافتراضي تلقائيًا إذا كان النموذج من مكتبة 🤗 Transformers. ومع ذلك، يمكنك أيضًا استبدال - بعض أو كل - سإعدادات النموذج الافتراضية بإعداداتك الخاصة:
هذا ينشئ نموذجًا بقيم عشوائية بدلاً من الأوزان المُدربة مسبقًا. لن يكون هذا النموذج مفيدًا حتى يتم تدريبه. تُعد عملية التدريب مكلفة وتستغرق وقتًا طويلاً. من الأفضل بشكل عام استخدام نموذج مُدرب مسبقًا للحصول على نتائج أفضل بشكل أسرع، مع استخدام جزء بسيط فقط من الموارد المطلوبة للتدريب.
قم بإنشاء نموذج مُدرب مسبقًا باستخدام [`~TFPreTrainedModel.from_pretrained`]:
عندما تقوم بتحميل الأوزان المُدربة مسبقًا،يتم تحميل إعدادات النموذج الافتراضي تلقائيًا إذا كان النموذج من مكتبة 🤗 Transformers. ومع ذلك، يمكنك أيضًا استبدال - بعض أو كل - إعدادات النموذج الافتراضية بإعداداتك الخاصة:
في هذه المرحلة، لديك نموذج DistilBERT الأساسي الذي يخرج *حالات الكامنة*. تُمرَّر هذه الحالات الكامنة كمدخلات لرأس النموذج لإنتاج المخرجات النهائية. توفر مكتبة 🤗 Transformers رأس نموذج مختلف لكل مهمة طالما أن النموذج يدعم المهمة (أي لا يمكنك استخدام DistilBERT لمهمة تسلسل إلى تسلسل مثل الترجمة).
<frameworkcontent>
<pt>
على سبيل المثال، [`DistilBertForSequenceClassification`] هو نموذج DistilBERT الأساس مزودًا برأس تصنيف تسلسلي. يُشكّل رأس التصنيف التسلسلي طبقة خطية فوق المخرجات المجمعة.
أعد استخدام هذا نقطة التحقق هذه لمهمة أخرى بسهولة، وذلك بتغيير رأس النموذج.ففي مهمة الإجابة على الأسئلة، ستستخدم رأس النموذج [`DistilBertForQuestionAnswering`]. رأس الإجابة على الأسئلة مشابه لرأس التصنيف التسلسلي باستثناء أنه طبقة خطية فوق مخرجات الحالات الكامنة.
على سبيل المثال، [`TFDistilBertForSequenceClassification`] هو نموذج DistilBERT الأساسي برأس تصنيف تسلسل. رأس التصنيف التسلسلي هو طبقة خطية أعلى المخرجات المجمعة.
أعد استخدام هذا نقطة التحقق لمهمة أخرى عن طريق التبديل إلى رأس نموذج مختلف. لمهمة الإجابة على الأسئلة، ستستخدم رأس النموذج [`TFDistilBertForQuestionAnswering`]. رأس الإجابة على الأسئلة مشابه لرأس التصنيف التسلسلي باستثناء أنه طبقة خطية أعلى حالات الإخراج المخفية.
الفئة الأساسية الأخيرة التي تحتاجها قبل استخدام نموذج للبيانات النصية هي [مجزئ النصوص](main_classes/tokenizer) لتحويل النص الخام إلى تنسورات (tensors). هناك نوعان من المحولات الرموز التي يمكنك استخدامها مع 🤗 Transformers:
- [`PreTrainedTokenizer`]: تنفيذ Python لمجزئ النصوص.
- [`PreTrainedTokenizerFast`]: مجزئ النصوص من مكتبة [🤗 Tokenizer](https://huggingface.co/docs/tokenizers/python/latest/) المُبنية على لغة Rust. هذا النوع من المجزئات أسرع بكثير، خاصةً عند معالجة دفعات النصوص، وذلك بفضل تصميمه بلغة Rust. كما يوفر مجزئ النصوص السريع طرقًا إضافية مثل *مخطط الإزاحة* الذي يُطابق الرموز بكلماتها أو أحرفها الأصلية.
يدعم كلا النوعين من المجزئات طرقًا شائعة مثل الترميز وفك الترميز، وإضافة رموز جديدة، وإدارة الرموز الخاصة.
<Tipwarning={true}>
لا يدعم كل نموذج مجزئ النصوص سريع. الق نظرة على هذا [جدول](index#supported-frameworks) للتحقق مما إذا كان النموذج يحتوي على دعم مجزئ النصوص سريع.
</Tip>
إذا دربت مجزئ النصوص خاص بك، فيمكنك إنشاء واحد من *قاموسك*:```
من المهم أن تتذكر أن قاموس مجزئ النصوص المُخصص سيكون مختلفًا عن قاموس مجزئ النصوص نموذج مُدرّب مسبقًا. يجب عليك استخدام قاموس نموذج مُدرّب مسبقًا إذا كنت تستخدم نموذجًا مُدرّبًا مسبقًا، وإلا فلن تكون المدخلات ذات معنى. قم بإنشاء مجزئ النصوص باستخدام قاموس نموذج مُدرّب مسبقًا باستخدام فئة [`DistilBertTokenizer`]:
تتكون نماذج رؤية الحاسب من جزء أساسي، وجزء وسيط، وجزء معالجة نهائي. يستخرج الجزء الأساسي الميزات من صورة الإدخال، ويجمع الجزء الوسيط هذه الميزات المستخرجة ويعززها، ويُستخدم الجزء النهائي للمهمة الرئيسية (مثل اكتشاف الأجسام). ابدأ عبتهيئة الجزء الأساسي في تكوين النموذج وحدد ما إذا كنت تريد تحميل أوزان مدربة مسبقًا أو أوزانًا عشوائية. بعد ذلك، يمكنك تمرير تكوين النموذج إلى جزء المعالجة النهائي.
على سبيل المثال، لتحميل [ResNet](../model_doc/resnet) backbone في نموذج [MaskFormer](../model_doc/maskformer) مع رأس تجزئة مثيل:
<hfoptions id="backbone">
<hfoption id="pretrained weights">
قم بتعيين `use_pretrained_backbone=True` لتحميل الأوزان المسبقة التدريب لـ ResNet للعمود الفقري.
```py
from transformers import MaskFormerConfig, MaskFormerForInstanceSegmentation
config = MaskFormerConfig(backbone="microsoft/resnet-50", use_pretrained_backbone=True) # تكوين الجزء الأساسي والجزء الوسيط
model = MaskFormerForInstanceSegmentation(config) # جزء المعالجة النهائي
```
</hfoption>
<hfoption id="random weights">
قم بتعيين `use_pretrained_backbone=False` لتهيئة جزء ResNet الأساسي بشكل عشوائي.
```py
from transformers import MaskFormerConfig, MaskFormerForInstanceSegmentation
config = MaskFormerConfig(backbone="microsoft/resnet-50", use_pretrained_backbone=False) # تكوين الجزء الأساسي والجزء الوسيط
model = MaskFormerForInstanceSegmentation(config) # جزء المعالجة النهائي
```
يمكنك أيضًا تحميل تكوين الجزء الأساسي بشكل منفصل، ثم تمريره إلى تكوين النموذج.```
```py
from transformers import MaskFormerConfig, MaskFormerForInstanceSegmentation, ResNetConfig
يتم تحميل نماذج [timm](https://hf.co/docs/timm/index) داخل نموذج باستخدام `use_timm_backbone=True` أو باستخدام [`TimmBackbone`] و [`TimmBackboneConfig`].
استخدم `use_timm_backbone=True` و `use_pretrained_backbone=True` لتحميل أوزان timm المُدرّبة مسبقًا للجزء الأساسي.
```python
from transformers import MaskFormerConfig, MaskFormerForInstanceSegmentation
config = MaskFormerConfig(backbone="resnet50", use_pretrained_backbone=True, use_timm_backbone=True) # تكوين الجزء الأساسي والجزء الوسيط
model = MaskFormerForInstanceSegmentation(config) # جزء المعالجة النهائي
from transformers import MaskFormerConfig, MaskFormerForInstanceSegmentation
config = MaskFormerConfig(backbone="resnet50", use_pretrained_backbone=False, use_timm_backbone=True) # تكوين الجزء الأساسي والجزء الوسيط
model = MaskFormerForInstanceSegmentation(config) # جزء المعالجة النهائي
```
يمكنك أيضًا تحميل تكوين الجزء الأساسي واستخدامه لإنشاء `TimmBackbone` أو تمريره إلى تكوين النموذج. سيتم تحميلأوزان الجزء الأساسي لـ Timm المُدرّبة مسبقًا افتراضيًا. عيّن `use_pretrained_backbone=False` لتحميل الأوزان المبدئية العشوائية.
```python
from transformers import TimmBackboneConfig, TimmBackbone
يقوم مُستخرج الميزات بمعالجة المدخلات الصوتية. يرث من فئة الأساس [`~feature_extraction_utils.FeatureExtractionMixin`]، وقد يرث أيضًا من فئة [`SequenceFeatureExtractor`] لمعالجة المدخلات الصوتية.
للاستخدام، قم بإنشاء مستخرج ميزات مرتبط بالنموذج الذي تستخدمه. على سبيل المثال، قم بإنشاء مستخرج ميزات Wav2Vec2 الافتراضي إذا كنت تستخدم [Wav2Vec2](model_doc/wav2vec2) لتصنيف الصوت:
```py
>>> from transformers import Wav2Vec2FeatureExtractor
بالنسبة للنماذج التي تدعم مهام الوسائط المتعددة، توفر مكتبة 🤗 Transformers فئة معالج تجمع بفاعلية فئات المعالجة مثل مستخرج الميزات ومقسّم الرموز في كائن واحد. على سبيل المثال، دعنا نستخدم [`Wav2Vec2Processor`] لمهمة التعرف الآلي على الكلام (ASR). تقوم مهمة ASR بتحويل الصوت إلى نص، لذلك ستحتاج إلى مستخرج ميزات ومقسّم رموز.
قم بإنشاء مستخرج ميزات لمعالجة المدخلات الصوتية:
```py
>>> from transformers import Wav2Vec2FeatureExtractor
باستخدام فئتين أساسيتين - التكوين والنموذج - بالإضافة إلى فئة معالجة مسبق (مقسّم رموز أو معالج صورة أو مستخرج ميزات أو معالج)، يمكنك إنشاء أي من النماذج التي تدعمها مكتبة 🤗 Transformers. يمكن تكوين كل من هذه الفئات الأساسية، مما يسمح لك باستخدام السمات المطلوبة. يمكنك بسهولة تهيئة نموذج للتدريب أو تعديل نموذج مدرب مسبقاً لإجراء ضبط دقيق.
تم تصميم مكتبة 🤗 Transformers لتكون قابلة للتوسيع بسهولة. كل نموذج مُشفّر بالكامل في مجلد فرعي معين بالمستودع، دون أي تجريد، لذلك يمكنك بسهولة نسخ ملف النمذجة وتعديله وفقًا لاحتياجاتك.
إذا كنت تُنشئ نموذجًا جديدًا تمامًا، فقد يكون من الأسهل البدء من الصفر. في هذا البرنامج التعليمي، سنُرِيك كيفية كتابة نموذج مخصص وتكوينه ليُستخدم داخل Transformers، وكيفية مشاركته مع المجتمع (مع الكود الذي يعتمد عليه) بحيث يمكن لأي شخص استخدامه، حتى إذا لم يكن موجودًا في مكتبة 🤗 Transformers. سنرى كيفية البناء على المحولات ونوسّع الإطار باستخدام الأدوات التي يمكن استخدامها لتعديل سلوك الإطار (hooks) والتعليمات البرمجية المخصصة.
سنوضح كل هذا من خلال نموذج ResNet، بتغليف فئة ResNet من
[مكتبة timm](https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models) داخل [`PreTrainedModel`].
## كتابة إعدادات مخصصة
لنبدأ بكتابة إعدادات النموذج. إعدادات النموذج هو كائنٌ يحتوي على جميع المعلومات اللازمة لبنائه. كما سنرى لاحقًا، يتطلب النموذج كائن `config` لتهيئته، لذا يجب أن يكون هذا الكائن كاملاً.
<Tip>
تتبع النماذج في مكتبة `transformers` اتفاقية قبول كائن `config` في دالة `__init__` الخاصة بها، ثم تمرر كائن `config` بالكامل إلى الطبقات الفرعية في النموذج، بدلاً من تقسيمه إلى معامﻻت متعددة. يؤدي كتابة نموذجك بهذا الأسلوب إلى كود أبسط مع "مصدر حقيقة" واضح لأي فرط معلمات، كما يسهل إعادة استخدام الكود من نماذج أخرى في `transformers`.
</Tip>
في مثالنا، سنعدّل بعض الوسائط في فئة ResNet التي قد نرغب في ضبطها. ستعطينا التكوينات المختلفة أنواع ResNets المختلفة الممكنة. سنقوم بتخزين هذه الوسائط بعد التحقق من صحته.
```python
fromtransformersimportPretrainedConfig
fromtypingimportList
classResnetConfig(PretrainedConfig):
model_type="resnet"
def__init__(
self,
block_type="bottleneck",
layers:List[int]=[3,4,6,3],
num_classes:int=1000,
input_channels:int=3,
cardinality:int=1,
base_width:int=64,
stem_width:int=64,
stem_type:str="",
avg_down:bool=False,
**kwargs,
):
ifblock_typenotin["basic","bottleneck"]:
raiseValueError(f"`block_type` must be 'basic' or bottleneck', got {block_type}.")
ifstem_typenotin["","deep","deep-tiered"]:
raiseValueError(f"`stem_type` must be '', 'deep' or 'deep-tiered', got {stem_type}.")
self.block_type=block_type
self.layers=layers
self.num_classes=num_classes
self.input_channels=input_channels
self.cardinality=cardinality
self.base_width=base_width
self.stem_width=stem_width
self.stem_type=stem_type
self.avg_down=avg_down
super().__init__(**kwargs)
```
الأشياء الثلاثة المهمة التي يجب تذكرها عند كتابة تكوينك الخاص هي:
- يجب أن ترث من `PretrainedConfig`،
- يجب أن تقبل دالة `__init__` الخاصة بـ `PretrainedConfig` أي معامﻻت إضافية kwargs،
- يجب تمرير هذه المعامﻻت الإضافية إلى دالة `__init__` فى الفئة الأساسية الاعلى.
يضمن الإرث حصولك على جميع الوظائف من مكتبة 🤗 Transformers، في حين أن القيدين التانى والثالث يأتيان من حقيقة أن `PretrainedConfig` لديه المزيد من الحقول أكثر من تلك التي تقوم بتعيينها. عند إعادة تحميل تكوين باستخدام طريقة `from_pretrained`، يجب أن يقبل تكوينك هذه الحقول ثم إرسالها إلى الفئة الأساسية الأعلى.
تحديد `model_type` لتكوينك (هنا `model_type="resnet"`) ليس إلزاميًا، ما لم ترغب في
تسجيل نموذجك باستخدام الفئات التلقائية (راجع القسم الأخير).
مع القيام بذلك، يمكنك بسهولة إنشاء تكوينك وحفظه مثلما تفعل مع أي تكوين نموذج آخر في
يمكنك أيضًا استخدام أي طريقة أخرى من فئة [`PretrainedConfig`]، مثل [`~PretrainedConfig.push_to_hub`] لتحميل تكوينك مباشرة إلى Hub.
## كتابة نموذج مخصص
الآن بعد أن أصبح لدينا تكوين ResNet، يمكننا المتابعة لإنشاء نموذجين: الأول يستخرج الميزات المخفية من دفعة من الصور (مثل [`BertModel`]) والآخر مناسب لتصنيف الصور (مثل [`BertForSequenceClassification`]).
كما ذكرنا سابقًا، سنقوم ببناء نموذج مبسط لتسهيل الفهم في هذا المثال. الخطوة الوحيدة المطلوبة قبل كتابة هذه الفئة هي لربط أنواع وحدات البناء بفئات ذات وحدات بناء فعلية. بعد ذلك، يُعرّف النموذج من خلال التكوين عبر تمرير كل شيء إلى فئة `ResNet`:
في كلتا الحالتين، لاحظ كيف نرث من `PreTrainedModel` ونستدعي مُهيئ الفئة الرئيسية باستخدام `config` (كما تفعل عند إنشاء وحدة `torch.nn.Module` عادية). ليس من الضروري تعريف `config_class` إلا إذا كنت ترغب في تسجيل نموذجك مع الفئات التلقائية (راجع القسم الأخير).
<Tip>
إذا كان نموذجك مشابهًا جدًا لنموذج داخل المكتبة، فيمكنك إعادة استخدام نفس التكوين مثل هذا النموذج.
</Tip>
يمكن لنموذجك أن يعيد أي شيء تريده، ولكن إعادة قاموس مثلما فعلنا لـ
`ResnetModelForImageClassification`، مع تضمين الخسارة عند تمرير العلامات، سيجعل نموذجك قابلًا للاستخدام مباشرة داخل فئة [`Trainer`]. يعد استخدام تنسيق إخراج آخر أمرًا جيدًا طالما أنك تخطط لاستخدام حلقة تدريب خاصة بك أو مكتبة أخرى للتدريب.
الآن بعد أن أصبح لدينا فئة النموذج، دعنا ننشئ واحدة:
يمكنك استخدام أي من طرق فئة [`PreTrainedModel`]، مثل [`~PreTrainedModel.save_pretrained`] أو
[`~PreTrainedModel.push_to_hub`]. سنستخدم الثاني في القسم التالي، وسنرى كيفية دفع أوزان النموذج مع كود نموذجنا. ولكن أولاً، دعنا نحمل بعض الأوزان المُعلمة مسبقًا داخل نموذجنا.
في حالة الاستخدام الخاصة بك، فمن المحتمل أن تقوم بتدريب نموذجك المخصص على بياناتك الخاصة. للانتقال بسرعة خلال هذا البرنامج التعليمي،
سنستخدم الإصدار المُعلم مسبقًا من resnet50d. نظرًا لأن نموذجنا هو مجرد غلاف حوله، فمن السهل نقل هذه الأوزان:
الآن دعونا نرى كيفية التأكد من أنه عند قيامنا بـ [`~PreTrainedModel.save_pretrained`] أو [`~PreTrainedModel.push_to_hub`]، يتم حفظ كود النموذج.
## تسجيل نموذج مع كود مخصص للفئات التلقائية
إذا كنت تكتب مكتبة توسع 🤗 Transformers، فقد ترغب في توسيع الفئات التلقائية لتشمل نموذجك الخاص. يختلف هذا عن نشر الكود إلى Hub بمعنى أن المستخدمين سيحتاجون إلى استيراد مكتبتك للحصول على النماذج المخصصة (على عكس تنزيل كود النموذج تلقائيًا من Hub).
ما دام تكوينك يحتوي على معامل `model_type` مختلفة عن أنواع النماذج الحالية، وأن فئات نماذجك لديك لديها الخصائص الصحيحة `config_class`، فيمكنك ببساطة إضافتها إلى الفئات التلقائية مثل هذا:
لاحظ أن الحجة الأولى المستخدمة عند تسجيل تكوينك المخصص لـ [`AutoConfig`] يجب أن تتطابق مع `model_type`
من تكوينك المخصص، والحجة الأولى المستخدمة عند تسجيل نماذجك المخصصة لأي فئة نموذج تلقائي يجب
أن تتطابق مع `config_class` من تلك النماذج.
## إرسال الكود إلى Hub
<Tipwarning={true}>
هذا API تجريبي وقد يكون له بعض التغييرات الطفيفة في الإصدارات القادمة.
</Tip>
أولاً، تأكد من تعريف نموذجك بالكامل في ملف `.py`. يمكن أن يعتمد على الاستيراد النسبي لملفات أخرى طالما أن جميع الملفات موجودة في نفس الدليل (لا ندعم الوحدات الفرعية لهذه الميزة حتى الآن). في مثالنا، سنحدد ملف `modeling_resnet.py` وملف `configuration_resnet.py` في مجلد باسم "resnet_model" في دليل العمل الحالي. يحتوي ملف التكوين على كود لـ `ResnetConfig` ويحتوي ملف النمذجة على كود لـ `ResnetModel` و`ResnetModelForImageClassification`.
```
.
└── resnet_model
├── __init__.py
├── configuration_resnet.py
└── modeling_resnet.py
```
يمكن أن يكون ملف `__init__.py` فارغًا، فهو موجود فقط حتى يتمكن Python من اكتشاف أن `resnet_model` يمكن استخدامه كموديل.
<Tipwarning={true}>
إذا كنت تقوم بنسخ ملفات النمذجة من المكتبة، فسوف تحتاج إلى استبدال جميع الواردات النسبية في أعلى الملف
لاستيرادها من حزمة `transformers`.
</Tip>
لاحظ أنه يمكنك إعادة استخدام (أو توسيع) تكوين/نموذج موجود.
لمشاركة نموذجك مع المجتمع، اتبع الخطوات التالية: أولاً، قم باستيراد نموذج ResNet والتكوين من الملفات التي تم إنشاؤها حديثًا:
الآن لإرسال النموذج إلى Hub، تأكد من تسجيل الدخول. إما تشغيل في المحطة الأوامر الطرفية الخاصة بك:
```bash
huggingface-cli login
```
أو من دفتر ملاحظات:
```py
fromhuggingface_hubimportnotebook_login
notebook_login()
```
يمكنك بعد ذلك الضغط على مساحة الاسم الخاصة بك (أو منظمة أنت عضو فيها) مثل هذا:
```py
resnet50d.push_to_hub("custom-resnet50d")
```
بالإضافة إلى أوزان النمذجة والتكوين بتنسيق json، فقد قام هذا أيضًا بنسخ ملفات النمذجة والتكوين `.py` في مجلد `custom-resnet50d` وتحميل النتيجة إلى Hub. يمكنك التحقق من النتيجة في هذا [مستودع النموذج](https://huggingface.co/sgugger/custom-resnet50d).
راجع [البرنامج التعليمي للمشاركة](model_sharing) لمزيد من المعلومات حول طريقة الدفع إلى المحور.
### استخدام نموذج مع كود مخصص
يمكنك استخدام أي تكوين أو نموذج أو مقسم لغوي مع ملفات برمجة مخصصة في مستودعه باستخدام الفئات التلقائية و دالة `from_pretrained`.تُفحص جميع الملفات والرموز المرفوع إلى Hub بحثًا عن البرامج الضارة (راجع وثائق [أمان Hub](https://huggingface.co/docs/hub/security#malware-scanning) لمزيد من المعلومات)، ولكن يجب عليك مراجعة كود النموذج والمؤلف لتجنب تنفيذ التعليمات البرمجية الضارة على جهازك. لتفعيل نموذج يحتوي على شفرة برمجية مخصصة، عيّن `trust_remote_code=True`:
يُنصح بشدة بتحديد رقم إصدار (commit hash) كـ `revision` للتأكد من عدم تعديل مؤلف النموذج للشفرة لاحقًابإضافة أسطر ضارة (إلا إذا كنت تثق تمامًا بمؤلفي النموذج):
يعتمد [`PreTrainedTokenizerFast`] على مكتبة [🤗 Tokenizers](https://huggingface.co/docs/tokenizers). يمكن تحميل المجزئات اللغويين الذين تم الحصول عليهم من مكتبة 🤗 Tokenizers ببساطة شديدة في 🤗 Transformers.
قبل الدخول في التفاصيل، دعونا نبدأ أولاً بإنشاء مُجزىء لغوي تجريبي في بضع سطور:
الآن لدينا مُجزىء لغوي مدرب على الملفات التي حددناها. يمكننا إما الاستمرار في استخدامه في وقت التشغيل هذا، أو حفظه في ملف JSON لإعادة استخدامه لاحقًا.
## تحميل مُجزئ النّصوص مُباشرةً
دعونا نرى كيف يمكننا الاستفادة من كائن (مُجزئ النصوص) في مكتبة 🤗 Transformers. تسمح فئة [`PreTrainedTokenizerFast`] سهولة إنشاء *tokenizer*، من خلال قبول كائن *المُجزئ النصوص* مُهيّأ مُسبقًا كمعامل:
يمكن الآن استخدام هذا الكائن مع جميع الطرق المُشتركة بين مُجزّئي النّصوص لـ 🤗 Transformers! انتقل إلى [صفحة مُجزّئ النّصوص](main_classes/tokenizer) لمزيد من المعلومات.
## التحميل من ملف JSON
لتحميل مُجزّئ النص من ملف JSON، دعونا نبدأ أولاً بحفظ مُجزّئ النّصوص:
```python
>>>tokenizer.save("tokenizer.json")
```
يمكن تمرير المسار الذي حفظنا به هذا الملف إلى طريقة تهيئة [`PreTrainedTokenizerFast`] باستخدام المُعامل `tokenizer_file`:
يمكن الآن استخدام هذا الكائن مع جميع الطرق التي تشترك فيها مُجزّئي النّصوص لـ 🤗 Transformers! انتقل إلى [صفحة مُجزّئ النص](main_classes/tokenizer) لمزيد من المعلومات.
تُستخدم صيغة ملف GGUF لتخزين النماذج للاستدلال باستخدام [GGML](https://github.com/ggerganov/ggml) والمكتبات الأخرى التي تعتمد عليه، مثل [llama.cpp](https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp) أو [whisper.cpp](https://github.com/ggerganov/whisper.cpp) الشهيرة جدًا.
إنها صيغة ملف [مدعومة من قبل Hugging Face Hub](https://huggingface.co/docs/hub/en/gguf) مع ميزات تسمح بالفحص السريع للموترات والبيانات الوصفية داخل الملف.
تم تصميم تنسيق الملف هذا كـ "تنسيق ملف واحد" حيث يحتوي ملف واحد عادةً على كل من سمات التكوين ومفردات المجزىء اللغوي والخصائص الأخرى، بالإضافة إلى جميع الموترات التي سيتم تحميلها في النموذج. تأتي هذه الملفات بتنسيقات مختلفة وفقًا لنوع التكميم في الملف. نلقي نظرة موجزة على بعضها [هنا](https://huggingface.co/docs/hub/en/gguf#quantization-types).
## الدعم داخل المحولات
أضفنا القدرة على تحميل ملفات `gguf` داخل `المحولات` لتوفير قدرات تدريب/ضبط إضافية لنماذج gguf، قبل إعادة تحويل تلك النماذج إلى `gguf` لاستخدامها داخل نظام `ggml`. عند تحميل نموذج، نقوم أولاً بإلغاء تكميمه إلى fp32، قبل تحميل الأوزان لاستخدامها في PyTorch.
> [!NOTE]
> لا يزال الدعم تجريبيًا للغاية ونرحب بالمساهمات من أجل ترسيخه عبر أنواع التكميم وبنى النماذج.
فيما يلي، بنيات النماذج وأنواع التكميم المدعومة:
### أنواع التكميم المدعومة
تُحدد أنواع التكميم المدعومة مبدئيًا وفقًا لملفات التكميم الشائعة التي تمت مشاركتها على Hub.
في الوقت الحالي، بنيات النماذج المدعومة هي البنيات التي كانت شائعة جدًا على Hub، وهي:
- LLaMa
- Mistral
- Qwen2
- Qwen2Moe
- Phi3
- Bloom
- Falcon
- StableLM
- GPT2
- Starcoder2
- T5
## مثال الاستخدام
لتحميل ملفات `gguf` في `transformers`، يجب تحديد معامل `gguf_file` فى دالة `from_pretrained` لكل من المُجزّئ اللغوية والنموذج. فيما يلي كيفية تحميل المُجزّئ اللغوي ونموذج، يمكن تحميلهما من نفس الملف:
الآن لديك إمكانية الوصول إلى النسخة الكامل غير المكممة للنموذج في بيئة PyTorch، حيث يمكنك دمجه مع مجموعة كبيرة من الأدوات الأخرى.
لإعادة التحويل إلى ملف `gguf`، نوصي باستخدام ملف [`convert-hf-to-gguf.py`](https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp/blob/master/convert-hf-to-gguf.py) من llama.cpp.
فيما يلي كيفية إكمال البرنامج النصي أعلاه لحفظ النموذج وإعادة تصديره مرة أخرى إلى `gguf`:
يمكن بعد ذلك تحويل هذا إلى مصفوفة في PyTorch أو TensorFlow. قناع الانتباه هو مصفوفة ثنائية تشير إلى
موضع المؤشرات المحشوه بحيث لا ينتبه إليها النموذج. بالنسبة إلى [`BertTokenizer`]`1` يشير إلى
قيمة يجب الانتباه إليها، في حين يشير `0` إلى قيمة مبطنة. يُمكن إيجاد قناع الانتباه في القاموس الذي يُعيده مُجزِّئ النصوص (tokenizer) تحت المفتاح "attention_mask".
راجع [نمذجة اللغة السببية](#causal-language-modeling) و [نماذج فك التشفير](#decoder-models)
## B
### العمود الفقري (backbone)
يُمثل العمود الفقري الشبكة العصبونية (الترميزات والطبقات) المسؤولة عن إخراج الحالات الخفية أو المُميزات الأولية. عادة ما يكون متصلاً بـ [رأس](#head) يستقبل المُميزات كمدخلات لإجراء تنبؤ. على سبيل المثال، يُعد النموذج [`ViTModel`] عمودًا فقريًا دون رأس مُحدد مُرفق به. يمكن أيضًا استخدام `ViTModel` كعمود فقري في نماذج أخرى, مثل [DPT](model_doc/dpt).
## C
### نمذجة اللغة السببية (أو التنبؤية) causal language modeling
مهمة ما قبل التدريب يقوم فيها النموذج بقراءة النصوص بالترتيب ويتنبأ بالكلمة التالية. يتم ذلك عادةً من خلال قراءة الجملة كاملةً، ولكن مع استخدام قناع داخل النموذج لإخفاء الرموز المميزة اللاحقة في خطوة زمنية معينة.
### قناة(channel)
تتكون الصور الملونة من مزيج من القيم في ثلاث قنوات لونية: الأحمر والأخضر والأزرق (RGB) بينما تحتوي صور ذات التدرج رمادي على قناة واحدة فقط. في مكتبة 🤗 Transformers، يمكن أن تكون القناة اللونية البُعد الأول أو الأخير في مُصفوفة الصورة: [`n_channels`، `height`، `width`] أو [`height`، `width`، `n_channels`].
خوارزمية تسمح للنموذج بالتعلم دون معرفة كيفية محاذاة المدخلات مع المخرجات بدقة؛ يحسب CTC توزيع جميع المخرجات المحتملة لمدخلات مُحددة ويختار المخرج الأكثر احتمالًا. تُستخدم CTC بشكل شائع في مهام التعرف على الكلام نظرًا لأن الكلام المنطوق لا يتوافق دائمًا بشكل مُباشر مع النص المكتوب، لأسباب مختلفة مثل معدلات الكلام المختلفة للمتكلم.
### الالتفاف (Convolution)
نوع من الطبقات في شبكة عصبية، حيث تُضرب مصفوفة الإدخال عُنصرًا بُعنصر بمصفوفة أصغر تُسمى (النواة أو المرشح) ويتم جمع القيم في مصفوفة جديدة. يُعرف هذا باسم عملية الالتفاف التي يتم تكرارها عبر مصفوفة الإدخال بأكملها. تُطبق كل عملية التفاف على جزء مُختلف من مصفوفة الإدخال. تُستخدم الشبكات العصبية الالتفافية (CNNs) بشكل شائع في رؤية الحاسوب.
## D
### التوازي على مستوى البيانات (DataParallel - DP)
هي تقنية تُستخدم لتدريب النماذج على عدة وحدات معالجة رسومات (GPUs)، حيث يتم نسخ نفس إعداد التدريب عدة مرات، بحيث تتلقى كل نسخة شريحة مختلفة من البيانات يتم تنفيذ المعالجة بالتوازي ويتم مزامنة جميع الإعدادات في نهاية كل خطوة تدريب.
تعرف على المزيد حول كيفية عمل DataParallel [هنا](perf_train_gpu_many#dataparallel-vs-distributeddataparallel).
### معرفات مدخلات وحدة فك التشفير (decoder input IDs)
هذا المدخل خاص بنماذج الترميز وفك التشفير، ويحتوي على معرفات الإدخال التي سيتم تغذيتها إلى وحدة فك التشفير.
يجب استخدام هذه المدخلات لمهام التسلسل إلى التسلسل، مثل الترجمة أو التلخيص، وعادة ما يتم بناؤها بطريقة محددة لكل نموذج.
تقوم معظم نماذج الترميز وفك التشفير (BART، T5) بإنشاء معرفات `decoder_input_ids` الخاصة بها من `labels`. في مثل هذه النماذج،
يعد تمرير `labels` هو الطريقة المفضلة للتعامل مع التدريب.
يرجى التحقق من وثائق كل نموذج لمعرفة كيفية تعاملها مع معرفات الإدخال هذه للتدريب على التسلسل إلى التسلسل.
### نماذج فك التشفير (decoder models)
يُشار إليها أيضًا باسم نماذج التنبؤية الذاتية، وتنطوي نماذج فك التشفير على مهمة ما قبل التدريب (تسمى نمذجة اللغة السببية) حيث يقرأ النموذج النصوص بالترتيب ويتعين عليه التنبؤ بالكلمة التالية. يتم ذلك عادةً عن طريق
قراءة الجملة بأكملها مع قناع لإخفاء الرموز المميزة المستقبلية في خطوة زمنية معينة.
<Youtubeid="d_ixlCubqQw"/>
### التعلم العميق deep learning (DL)
خوارزميات التعلم الآلي التي تستخدم الشبكات العصبية متعددة الطبقات.
## E
### نماذج الترميز (encoder models)
تُعرف أيضًا باسم نماذج الترميز التلقائي، وتأخذ نماذج الترميز إدخالًا (مثل النص أو الصور) وتحويلها إلى تمثيل رقمي مكثف يُطلق عليه الترميز. غالبًا ما يتم تدريب نماذج الترميز مسبقًا باستخدام تقنيات مثل [نمذجة اللغة المقنعة](#masked-language-modeling-mlm)، والتي تقوم بإخفاء أجزاء من تسلسل الإدخال وإجبار النموذج على إنشاء تمثيلات أكثر دلالة (فائدة ووضوحاً).
<Youtubeid="H39Z_720T5s"/>
## F
### استخراج الميزات (feature extraction)
عملية اختيار وتحويل البيانات الأولية إلى مجموعة من الميزات الأكثر إفادة وفائدة لخوارزميات التعلم الآلي. بعض الأمثلة على استخراج الميزات تشمل تحويل النص الأولي/الخام إلى ترميزات الكلمات واستخراج ميزات مهمة مثل الحواف أو الأشكال من بيانات الصور/الفيديو.
في كل وحدة الانتباه الباقية في المحولات، تلي طبقة الاهتمام الانتباه عادة طبقتان للتغذية الأمامية.
حجم تضمين الطبقة الأمامية الوسيطة أكبر عادة من حجم المخفي للنموذج (على سبيل المثال، لـ
`google-bert/bert-base-uncased`).
بالنسبة لإدخال بحجم `[batch_size, sequence_length]`، يمكن أن تمثل الذاكرة المطلوبة لتخزين التضمينات الأمامية الوسيطة `[batch_size، sequence_length, config.intermediate_size]` جزءًا كبيرًا من استخدام الذاكرة. لاحظ مؤلفو (https://arxiv.org/abs/2001.04451)[Reformer: The Efficient Transformer] أنه نظرًا لأن الحساب مستقل عن بعد `sequence_length`، فإنه من المكافئ رياضيًا حساب تضمينات الإخراج الأمامية `[batch_size، config.hidden_size]_0, ..., [batch_size، `config_size]_n
فردياً والتوصيل بها لاحقًا إلى `[batch_size, sequence_length, config.hidden_size]` مع `n = sequence_length`، والذي يتداول زيادة وقت الحساب مقابل تقليل استخدام الذاكرة، ولكنه ينتج عنه نتيجة مكافئة رياضيا.
بالنسبة للنماذج التي تستخدم الدالة `[apply_chunking_to_forward]`، يحدد `chunk_size` عدد التضمينات يتم حساب الإخراج بالتوازي وبالتالي يحدد المقايضة بين حجم الذاكرة والتعقيد الوقت. إذا تم تعيين `chunk_size` إلى `0`، فلن يتم إجراء تجزئة التغذية الأمامية.
### النماذج المضبوطة (finetuned models)
الضبط الدقيق هو شكل من أشكال نقل التعلم، يتضمن أخذ نموذج مُدرّب مسبقًا، وتجميد أوزانه، واستبدال طبقة الإخراج برأس نموذج مُضاف حديثًا. يتم تدريب رأس النموذج على مجموعة البيانات المستهدفة.
راجع البرنامج التعليمي [Fine-tune a pretrained model](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/training) لمزيد من التفاصيل، وتعرف على كيفية ضبط النماذج باستخدام 🤗 Transformers.
## H
### رأس النموذج (head)
يشير رأس النموذج إلى الطبقة الأخيرة من الشبكة العصبية التي تقبل الحالات المخفية الخام/الأولية وتُسقطها على بُعد مختلف. يوجد رأس نموذج مختلف لكل مهمة.
* [`GPT2ForSequenceClassification`] هو رأس تصنيف تسلسل - طبقة خطية - أعلى نموذج [`GPT2Model`] الأساسي.
* [`ViTForImageClassification`] هو رأس تصنيف صورة - طبقة خطية أعلى حالة مخفية نهائية للرمز `CLS` - أعلى نموذج [`ViTModel`] الأساسي.
* [`Wav2Vec2ForCTC`] هو رأس نمذجة اللغة مع [CTC](#connectionist-temporal-classification-ctc) أعلى نموذج [`Wav2Vec2Model`] الأساسي.
## I
### رقعة الصور (image patch)
"رقعة الصورة" في نماذج المحولات البصرية، تُقسم الصورة إلى أجزاء أصغر تسمى "رقعات". يتم تمثيل كل رقعة بشكل رقمي (تحويلها إلى مجموعة من الأرقام) ثم تُعالج كسلسلة من البيانات. يمكنك العثور على حجم الرُقعة patch_size - أو دقتها - في إعدادات النموذج.
### الاستدلال (Inference)
الاستدلال هو عملية تقييم نموذج على بيانات جديدة بعد اكتمال التدريب. راجع البرنامج التعليمي [Pipeline for inference](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/pipeline_tutorial) لمعرفة كيفية إجراء الاستدلال باستخدام 🤗 Transformers.
### معرفات الإدخال (input IDs)
معرفات الإدخال هي غالبًا المعلمات المطلوبة الوحيدة التي يجب تمريرها إلى النموذج كإدخال. هذه المعرفات عبارة عن أرقام تمثل كل كلمة أو رمز في الجملة التي نريد أن يفهمها النموذج. بمعنى آخر، هي طريقة لترجمة الكلمات إلى أرقام يتم استخدامها كإدخال بواسطة النموذج.
<Youtubeid="VFp38yj8h3A"/>
يعمل كل محلل لغوي بشكل مختلف ولكن الآلية الأساسية تبقى كما هي. إليك مثال باستخدام محلل BERT اللغوي، والذي يعد محلل لغوي [WordPiece](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1609.08144.pdf):
االرموز إما كلمات أو أجزاء كلمات. هنا على سبيل المثال، لم تكن كلمة "VRAM" موجودة في مفردات النموذج، لذلك تم تقسيمها إلى "V" و "RA" و "M". للإشارة إلى أن هذه الرموز ليست كلمات منفصلة ولكنها أجزاء من نفس الكلمة، تمت إضافة بادئة مزدوجة (#) إلى "RA" و "M":
يمكن بعد ذلك تحويل هذه الرموز إلى مُعرفات يفهمها النموذج. يمكن القيام بذلك عن طريق تغذية الجملة مباشرةً إلى مُجزّئ الرموز، والذي يستفيد من تنفيذ 🤗 Tokenizers بلغة Rust للحصول على أعلى أداء.
```python
>>>inputs=tokenizer(sequence)
```
يقوم المحلل اللغوي بإرجاع قاموس يحتوي على جميع المعلومات التي يحتاجها النموذج للعمل بشكل صحيح. وتوجد مؤشرات الرموز المميزة تحت مفتاح `input_ids`:
لأن هذه هي الطريقة التي يتوقع بها نموذج [`BertModel`] إدخالاته.
## L
### االملصقات (Labels)
هي معامل اختياري يمكن إدخاله في النموذج لحساب الخسارة بنفسه.
نماذج تصنيف التسلسل: ([BertForSequenceClassification]) يتوقع النموذج مصفوفة ذات بعد (batch_size) حيث تتوافق كل قيمة من المجموعة مع الملصق المتوقع للتسلسل بأكمله.
نماذج تصنيف الرمز: ([BertForTokenClassification]) يتوقع النموذج مصفوفة ذات بعد (batch_size, seq_length) حيث تتوافق كل قيمة مع الملصق المتوقع لكل رمز فردي.
نماذج النمذجة اللغوية المقنعة:([BertForMaskedLM]) يتوقع النموذج مصفوفة ذات بعد (batch_size, seq_length) حيث تتوافق كل قيمة مع الملصق المتوقع لكل رمز فردي: تكون الملصقات هي معرف رمز الكلمة المقنعة، والقيم الأخرى يتم تجاهلها (عادةً -100).
مهام التسلسل إلى التسلسل: ([BartForConditionalGeneration], [MBartForConditionalGeneration]) يتوقع النموذج مصفوفة ذات بعد (batch_size, tgt_seq_length) حيث تتوافق كل قيمة مع التسلسل الهدف المرتبط بكل تسلسل مدخل. أثناء التدريب، سيقوم كل من BART و T5 بإنشاء decoder_input_ids و decoder attention masks داخليًا. عادةً لا يلزم توفيرها. هذا لا ينطبق على النماذج التي تستخدم إطار العمل Encoder-Decoder.
نماذج تصنيف الصور: ([ViTForImageClassification]) يتوقع النموذج مصفوفة ذات بعد (batch_size) حيث تتوافق كل قيمة من المجموعة مع الملصق المتوقع لكل صورة فردية.
نماذج التقسيم الدلالي: ([SegformerForSemanticSegmentation]) يتوقع النموذج مصفوفة ذات بعد (batch_size, height, width) حيث تتوافق كل قيمة من المجموعة مع الملصق المتوقع لكل بكسل فردي.
نماذج اكتشاف الأجسام: ([DetrForObjectDetection]) يتوقع النموذج قائمة من القواميس تحتوي على مفتاح class_labels و boxes حيث تتوافق كل قيمة من المجموعة مع الملصق المتوقع وعدد المربعات المحيطة بكل صورة فردية.
نماذج التعرف التلقائي على الكلام: ([Wav2Vec2ForCTC]) يتوقع النموذج مصفوفة ذات بعد (batch_size, target_length) حيث تتوافق كل قيمة مع الملصق المتوقع لكل رمز فردي.
<Tip>
قد تختلف تسميات كل نموذج، لذا تأكد دائمًا من مراجعة وثائق كل نموذج للحصول على معلومات حول التسميات الخاصة به.
</Tip>
لا تقبل النماذج الأساسية ([`BertModel`]) الملصقات ، لأنها نماذج المحول الأساسية، والتي تقوم ببساطة بإخراج الميزات.
### نماذج اللغة الكبيرة large language models (LLM)
مصطلح عام يشير إلى نماذج اللغة المحولة (GPT-3 و BLOOM و OPT) التي تم تدريبها على كمية كبيرة من البيانات. تميل هذه النماذج أيضًا إلى وجود عدد كبير من المعلمات القابلة للتعلم (على سبيل المثال، 175 مليار لمعلمة GPT-3).
## M
### نمذجة اللغة المقنعة masked language modeling (MLM)
مهمة تدريب مسبق حيث يرى النموذج نسخة تالفة من النصوص، وعادة ما يتم ذلك عن طريق حجب بعض الرموز بشكل عشوائي، ويتعين على النموذج التنبؤ بالنص الأصلي.
### متعدد الوسائط (multimodal)
مهمة تجمع بين النصوص مع نوع آخر من المدخلات (على سبيل المثال، الصور).
## N
### توليد اللغة الطبيعية Natural language generation (NLG)
جميع المهام المتعلقة بتوليد النص (على سبيل المثال، [اكتب باستخدام المحولات](https://transformer.huggingface.co/)، والترجمة).
### معالجة اللغة الطبيعية Natural language processing (NLP)
طريقة عامة للقول "التعامل مع النصوص".
### فهم اللغة الطبيعية Natural language understanding (NLU)
جميع المهام المتعلقة بفهم ما هو موجود في نص (على سبيل المثال تصنيف النص بأكمله، أو الكلمات الفردية).
## P
### خط الأنابيب (pipeline)
في مكتبة Transformers، يُشير مصطلح "خط الأنابيب" إلى سلسلة من الخطوات التي يتم تنفيذها بترتيب محدد لمعالجة البيانات وتحويلها وإرجاع تنبؤ من نموذج. بعض المراحل الشائعة في خط الأنابيب قد تشمل معالجة البيانات الأولية، واستخراج الميزات، والتوحيد.
للحصول على مزيد من التفاصيل، راجع [خطوط الأنابيب للاستدلال](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/pipeline_tutorial).
### التوازي على مستوى خط الأنابيب (PipelineParallel)
تقنية توازي يتم فيها تقسيم النموذج رأسياً (على مستوى الطبقة) عبر وحدات معالجة الرسومات (GPU) متعددة، بحيث توجد طبقة واحدة أو عدة طبقات من النموذج على وحدة معالجة الرسومات (GPU) واحدة فقط. تقوم كل وحدة معالجة رسومات (GPU) بمعالجة مراحل مختلفة من خط الأنابيب بالتوازي والعمل على جزء صغير من الدفعة. تعرف على المزيد حول كيفية عمل PipelineParallel [هنا](perf_train_gpu_many#from-naive-model-parallelism-to-pipeline-parallelism).
### قيم البكسل (pixel values)
مصفوفة من التمثيلات الرقمية لصورة يتم تمريرها إلى نموذج. تأخذ قيم البكسل شكل [`batch_size`، `num_channels`، `height`، `width`]، ويتم إنشاؤها من معالج الصور.
### التجميع (Pooling)
هي عملية تقوم بتقليص مصفوفة إلى مصفوفة أصغر، إما عن طريق أخذ القيمة القصوى أو المتوسط الحسابي للأبعاد التي يتم تجميعها. توجد طبقات التجميع بشكل شائع بين الطبقات التلافيفية convolutional layers لتقليل حجم تمثيل الميزات.
### معرفات الموضع (position IDs)
على عكس الشبكات العصبية المتكررة (RNNs) التي تتضمن موضع كل رمز (token) ضمن بنيتها، لا تدرك المحولات موضع كل رمز. لذلك، تستخدم معرفات الموضع (`position_ids`) من قبل النموذج لتحديد موضع كل رمز في قائمة الرموز.
إنها معلمة اختيارية. إذا لم يتم تمرير أي `position_ids` إلى النموذج، يتم إنشاء المعرفات تلقائيًا كترميزات موضعية مطلقة.
يتم اختيار الترميزات الموضعية المطلقة في النطاق `[0، config.max_position_embeddings - 1]`. تستخدم بعض النماذج أنواعًا أخرى من الترميزات الموضعية، مثل الترميزات الموضعية الجيبية أو الترميزات الموضعية النسبية.
### ما قبل المعالجة (preprocessing)
مهمة إعداد البيانات الخام بتنسيق يمكن أن تستهلكه نماذج التعلم الآلي بسهولة. على سبيل المثال، عادةً ما تتم معالجة النص مسبقًا عن طريق التمييز. للحصول على فكرة أفضل عن كيفية ظهور المعالجة المسبقة لأنواع الإدخال الأخرى، راجع البرنامج التعليمي [Preprocess](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/preprocessing).
### النموذج المسبق التدريب (pretrained model)
نموذج تم تدريبه مسبقًا على بعض البيانات (على سبيل المثال، كل Wikipedia). تنطوي طرق التدريب المسبق على هدف ذاتي الإشراف، والذي يمكن أن يكون قراءة النص ومحاولة التنبؤ بالكلمة التالية ( راجع (causal-language-modeling#)[نمذجة اللغة السببية] ) أو قناع بعض الكلمات ومحاولة التنبؤ بها ( راجع (masked-language#)[نمذجة اللغة المقنعة]- عرض MLM).
لدى نماذج الكلام والرؤية أهدافها التدريبية المسبقة الخاصة. على سبيل المثال، Wav2Vec2 هو نموذج كلام تم تدريبه مسبقًا على مهمة تباينية تتطلب من النموذج تحديد تمثيل الكلام "الحقيقي" من مجموعة من تمثيلات الكلام "الخاطئة". من ناحية أخرى، BEiT هو نموذج رؤية تم تدريبه مسبقًا على مهمة نمذجة صورة مقنعة تقوم بقناع بعض رقع الصورة وتتطلب من النموذج التنبؤ بالرقع المقنعة (مشابهة لهدف نمذجة اللغة المقيدة).
## R
### شبكة عصبية متكررة (RNN)
هي نوع من النماذج التي تستخدم حلقة متكررة فوق طبقة معينة لمعالجة النصوص.
### التعلم التمثيلي (representation learning)
هو فرع من فروع تعلم الآلة يركز على تعلم تمثيلات ذات معنى للبيانات الخام. بعض الأمثلة على تقنيات التعلم التمثيلي تشمل تضمين الكلمات، والمشفرات ذاتية، وشبكات التنافس التوليدية(GANs).
## S
### معدل العينات (sampling rate)
قياس، بالهرتز، لعدد العينات (إشارة الصوت) المأخوذة في الثانية. ينتج معدل العينات عن تمييز إشارة مستمرة مثل الكلام.
### الانتباه الذاتي (Self-Attention)
هو آلية تتيح لكل عنصر في المدخل أن يحدد أي العناصر الأخرى في نفس المدخل يجب أن ينتبه إليها.
فئة من تقنيات التعلم الآلي التي يقوم فيها النموذج بإنشاء هدفه التعليمي الخاص من البيانات غير الموسومة. يختلف عن [التعلم غير الخاضع للإشراف](#unsupervised-learning) و [التعلم الخاضع للإشراف](#supervised-learning) في أن عملية التعلم خاضعة للإشراف، ولكن ليس صراحة من المستخدم.
مثال واحد على التعلم الذاتي الخاضع للإشراف هو [نمذجة اللغة المقيدة](#masked-language- عرض MLM)، حيث يتم تمرير جمل للنموذج مع إزالة نسبة من رموزه ويتعلم التنبؤ بالرموز المفقودة.
### التعلم شبه الخاضع للإشراف (semi-supervised learning)
فئة واسعة من تقنيات تدريب التعلم الآلي التي تستفيد من كمية صغيرة من البيانات الموسومة مع كمية أكبر من البيانات غير الموسومة لتحسين دقة النموذج، على عكس [التعلم الخاضع للإشراف](#supervised-learning) و [التعلم غير الخاضع للإشراف](#unsupervised-learning).
مثال على نهج التعلم شبه الخاضع للإشراف هو "التدريب الذاتي"، حيث يتم تدريب نموذج على بيانات موسومة، ثم يستخدم لتقديم تنبؤات حول البيانات غير الموسومة. يتم إضافة الجزء من البيانات غير الموسومة التي يتنبأ بها النموذج بأكبر قدر من الثقة إلى مجموعة البيانات الموسومة ويتم استخدامها لإعادة تدريب النموذج.
### تسلسل إلى تسلسل (seq2seq)
نماذج تولد تسلسلًا جديدًا من إدخال، مثل نماذج الترجمة، أو نماذج التلخيص (مثل [Bart](model_doc/bart) أو [T5](model_doc/t5)).
### Sharded DDP
اسم آخر لمفهوم [Zero Redundancy Optimizer](#zero-redundancy-optimizer-zero) الأساسي كما هو مستخدم من قبل العديد من التطبيقات الأخرى لـ Zero.
### الخطوة (Stride)
في العمليات التلافيفية أو التجميعية، تشير الخطوة إلى المسافة التي يتحرك بها النواة (kernel) فوق المصفوفة. خطوة تساوي 1 تعني أن النواة تتحرك بكسل واحد في كل مرة.
### التعلم الخاضع للإشراف (supervised learning)
هو نوع من تدريب النماذج التي تستخدم بيانات مُعلَّمة بشكل مباشر لتصحيح أداء النموذج وتوجيهه. يتم تغذية البيانات إلى النموذج قيد التدريب، ويتم مقارنة تنبؤاته بالنتائج الصحيحة المعروفة. يقوم النموذج بتعديل أوزانه بناءً على مدى خطأ تنبؤاته، وتتكرر هذه العملية لتحسين أداء النموذج.
## T
### توازي Tensor (TP)
تقنية توازي لتدريب وحدات معالجة الرسومات (GPU) متعددة يتم فيها تقسيم المصفوفة إلى عدة أجزاء، لذا بدلاً من وجود المصفوفة بأكملها على وحدة معالجة الرسومات (GPU) واحدة، توجد كل شظية من المصفوفة على وحدة معالجة الرسومات (GPU) المخصصة لها. تتم معالجة الشظايا بشكل منفصل وبالتوازي على وحدات معالجة الرسومات (GPU) المختلفة ويتم مزامنة النتائج في نهاية خطوة المعالجة. هذا ما يُطلق عليه أحيانًا التوازي الأفقي، حيث يحدث الانقسام على المستوى الأفقي.
تعرف على المزيد حول توازي Tensor [هنا](perf_train_gpu_many#tensor-parallelism).
### الرمز اللغوي (Token)
جزء من جملة، عادة ما يكون كلمة، ولكن يمكن أن يكون أيضًا كلمة فرعية (غالبًا ما يتم تقسيم الكلمات غير الشائعة إلى كلمات فرعية) أو علامة ترقيم.
### معرفات نوع الرمز (token type ids)
الغرض من بعض النماذج هو إجراء التصنيف على أزواج من الجمل أو الإجابة على الأسئلة.
<Youtubeid="0u3ioSwev3s"/>
يتطلب ذلك تسلسلين مختلفين يتم دمجهما في إدخال "input_ids" واحد، والذي يتم عادةً باستخدام رموز خاصة، مثل رموز التصنيف (`[CLS]`) والفاصل (`[SEP]`). على سبيل المثال، يقوم نموذج BERT ببناء إدخال تسلسلين على النحو التالي:
```python
>>># [CLS] SEQUENCE_A [SEP] SEQUENCE_B [SEP]
```
يمكننا استخدام برنامجنا للتمييز لإنشاء مثل هذه الجملة تلقائيًا عن طريق تمرير التسلسلين إلى `tokenizer` كمعامليين (وليس قائمة، كما كان من قبل) مثل هذا:
هذا يكفي لبعض النماذج لفهم أين ينتهي تسلسل واحد وأين يبدأ الآخر. ومع ذلك، تستخدم نماذج أخرى، مثل BERT، أيضًا معرفات نوع الرمز (يُطلق عليها أيضًا معرفات الجزء). يتم تمثيلها كماسك ثنائي لتحديد نوعي التسلسل في النموذج.
يعيد برنامج الترميز هذا القناع كإدخال "token_type_ids":
```python
>>>encoded_dict["token_type_ids"]
[0،0،0،0،0،0،0،0،0،0،1،1،1،1،1،1،1،1،1]
```
يتم تمثيل التسلسل الأول، "السياق" المستخدم للسؤال، بجميع رموزه بواسطة `0`، في حين يتم تمثيل التسلسل الثاني، المقابل إلى "السؤال"، بجميع رموزه بواسطة `1`.
تستخدم بعض النماذج، مثل [`XLNetModel`] رمزًا إضافيًا يمثله `2`.
### التعلم الانتقالي (Transfer Learning)
تقنية تنطوي على أخذ نموذج تم تدريبه مسبقًا وتكييفه مع مجموعة بيانات خاصة بمهمتك. بدلاً من تدريب نموذج من الصفر، يمكنك الاستفادة من المعرفة المكتسبة من نموذج موجود كنقطة بداية. يسرع هذا عملية التعلم ويقلل من كمية بيانات التدريب المطلوبة.
### المحول (Transformer)
هو بنية لنموذج تعلم عميق يعتمد على الانتباه الذاتي.
## U
### التعلم غير الخاضع للإشراف (unsupervised learning)
شكل من أشكال تدريب النماذج حيث لا يتم وضع علامات على البيانات المقدمة إلى النموذج. تستفيد تقنيات التعلم غير الخاضعة للإشراف من المعلومات الإحصائية لتوزيع البيانات للعثور على الأنماط المفيدة للمهمة المعنية.
## Z
### محسن التكرار الصفري (ZeRO)
تقنية توازي تقوم بتشظية المصفوفات بطريقة مشابهة لـ [TensorParallel](#tensor-parallelism-tp)، باستثناء إعادة بناء المصفوفة بالكامل في الوقت المناسب لحساب التقدير أو الحساب الخلفي، وبالتالي لا يلزم تعديل النموذج. تدعم هذه الطريقة أيضًا تقنيات الإخلاء المختلفة للتعويض عن ذاكرة GPU المحدودة.
تعرف على المزيد حول Zero [هنا](perf_train_gpu_many#zero-data-parallelism).
أحدث ما في مجال التعلم الآلي لـ [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/) و [TensorFlow](https://www.tensorflow.org/) و [JAX](https://jax.readthedocs.io/en/latest/)
توفر 🤗 Transformers واجهات برمجة التطبيقات (APIs) والأدوات اللازمة لتنزيل وتدريب أحدث النماذج المسبقة التدريب بسهولة. ويمكن أن يقلل استخدام النماذج المسبقة التدريب من تكاليف الحوسبة والحد من الأثر البيئي، وتوفّر الوقت والموارد اللازمين لتدريب نموذج من الصفر. وتدعم هذه النماذج المهام الشائعة في مجالات مختلفة، مثل:
📝 **معالجة اللغات الطبيعية**: تصنيف النصوص، وتعريف الكيانات المسماة، والإجابة على الأسئلة، ونمذجة اللغة، والتلخيص، والترجمة، والاختيار من متعدد، وتوليد النصوص. <br>
🖼️ **الرؤية الحاسوبية**: تصنيف الصور، وكشف الأشياء، وتجزئتها. <br>
🗣️ **الصوت**: التعرف التلقائي على الكلام، وتصنيف الصوت. <br>
🐙 **متعدد الوسائط**: الإجابة على الأسئلة الجدولية، والتعرف البصري على الحروف، واستخراج المعلومات من المستندات الممسوحة ضوئيًا، وتصنيف الفيديو، والإجابة على الأسئلة البصرية.
تدعم 🤗 Transformers التوافق بين أطر العمل المختلفة مثل PyTorch و TensorFlow و JAX. ويوفر ذلك المرونة لاستخدام إطار عمل مختلف في كل مرحلة من مراحل حياة النموذج؛ قم بتدريب نموذج في ثلاث خطوط من التعليمات البرمجية في إطار واحد، وقم بتحميله للاستدلال في إطار آخر. ويمكن أيضًا تصدير النماذج إلى صيغ مثل ONNX و TorchScript للنشر في بيئات الإنتاج.
انضم إلى المجتمع المتنامي على [Hub](https://huggingface.co/models) أو [المنتدى](https://discuss.huggingface.co/) أو [Discord](https://discord.com/invite/JfAtkvEtRb) اليوم!
- **ابدأ** تقدم جولة سريعة في المكتبة وتعليمات التثبيت للبدء.
- **الدروس التعليمية** هي مكان رائع للبدء إذا كنت مبتدئًا. سيساعدك هذا القسم على اكتساب المهارات الأساسية التي تحتاجها للبدء في استخدام المكتبة.
- **أدلة كيفية الاستخدام** تُظهر لك كيفية تحقيق هدف محدد، مثل ضبط نموذج مسبق التدريب لنمذجة اللغة أو كيفية كتابة ومشاركة نموذج مخصص.
- **الأدلة المفاهيمية** تقدم مناقشة وتفسيرًا أكثر للأفكار والمفاهيم الأساسية وراء النماذج والمهام وفلسفة التصميم في 🤗 Transformers.
- **واجهة برمجة التطبيقات (API)** تصف جميع الفئات والوظائف:
- **الفئات الرئيسية** تشرح الفئات الأكثر أهمية مثل التكوين والنمذجة والتحليل النصي وخط الأنابيب.
- **النماذج** تشرح الفئات والوظائف المتعلقة بكل نموذج يتم تنفيذه في المكتبة.
- **المساعدون الداخليون** يشرحون فئات ووظائف المساعدة التي يتم استخدامها داخليًا.
## النماذج والأطر المدعومة
يمثل الجدول أدناه الدعم الحالي في المكتبة لكل من هذه النماذج، وما إذا كان لديها محلل نحوي Python (يُسمى "بطيء"). محلل نحوي "سريع" مدعوم بمكتبة 🤗 Tokenizers، وما إذا كان لديها دعم في Jax (عبر Flax) و/أو PyTorch و/أو TensorFlow.
<!--يتم تحديث هذا الجدول تلقائيًا من الوحدات النمطية التلقائية مع_make fix-copies_. لا تقم بالتحديث يدويًا!-->
<!--This table is updated automatically from the auto modules with_make fix-copies_. Do not update manually!-->
| Model | PyTorch support | TensorFlow support | Flax Support |
يجب عليك تثبيت 🤗 Transformers داخل [بيئة افتراضية](https://docs.python.org/3/library/venv.html). إذا لم تكن غير ملم ببيئات Python الافتراضية، فراجع هذا [الدليل](https://packaging.python.org/guides/installing-using-pip-and-virtual-environments/). البيئة الافتراضية تسهل إدارة المشاريع المختلف، وتجنب مشكلات التوافق بين المكتبات المطلوبة (اعتماديات المشروع).
ابدأ بإنشاء بيئة افتراضية في دليل مشروعك:
```bash
python -m venv .env
```
قم بتفعيل البيئة الافتراضية. على Linux وMacOs:
```bash
source .env/bin/activate
```
قم بتفعيل البيئة الافتراضية على Windows:
```bash
.env/Scripts/activate
```
الآن أنت مستعد لتثبيت 🤗 Transformers باستخدام الأمر التالي:
```bash
pip install transformers
```
للحصول على الدعم الخاص بـ CPU فقط، يمكنك تثبيت 🤗 Transformers ومكتبة التعلم العميق في خطوة واحدة. على سبيل المثال، قم بتثبيت 🤗 Transformers وPyTorch باستخدام:
```bash
pip install 'transformers[torch]'
```
🤗 Transformers وTensorFlow 2.0:
```bash
pip install 'transformers[tf-cpu]'
```
<Tipwarning={true}>
لمستخدمي M1 / ARM
ستحتاج إلى تثبيت ما يلي قبل تثبيت TensorFLow 2.0
```bash
brew install cmake
brew install pkg-config
```
</Tip>
🤗 Transformers وFlax:
```bash
pip install 'transformers[flax]'
```
أخيرًا، تحقق مما إذا كان 🤗 Transformers قد تم تثبيته بشكل صحيح عن طريق تشغيل الأمر التالي. سيقوم بتنزيل نموذج مدرب مسبقًا:
```bash
python -c "from transformers import pipeline; print(pipeline('sentiment-analysis')('we love you'))"
يقوم هذا الأمر بتثبيت أحدث إصدار تجريبي `main` بدلاً من الإصدار المستقر `stable`. يعد إصدار `main` مفيدًا للمواكبة مع أحدث التطورات. على سبيل المثال، إذا تم إصلاح خطأ منذ الإصدار الرسمي الأخير ولكن لم يتم طرح إصدار جديد بعد. ومع ذلك، فإن هذا يعني أن إصدار التجريبي `main` قد لا يكون مستقرًا دائمًا. نسعى جاهدين للحفاظ على تشغيل إصدار `main`، ويتم حل معظم المشكلات عادةً في غضون بضع ساعات أو يوم. إذا واجهتك مشكلة، يرجى فتح [تقرير عن خلل](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/issues) حتى نتمكن من إصلاحها في أقرب وقت ممكن!
تحقق مما إذا كان 🤗 Transformers قد تم تثبيته بشكل صحيح عن طريق تشغيل الأمر التالي:
```bash
python -c "from transformers import pipeline; print(pipeline('sentiment-analysis')('I love you'))"
```
تحقق مما إذا كان 🤗 Transformers قد تم تثبيته بشكل صحيح عن طريق تشغيل الأمر التالي:
```bash
python -c "from transformers import pipeline; print(pipeline('sentiment-analysis')('I love you'))"
```
## التثبيت القابل للتعديل
ستحتاج إلى تثبيت قابل للتعديل إذا كنت ترغب في:
* استخدام إصدار `main` من كود المصدر.
* المساهمة في 🤗 Transformers وتحتاج إلى اختبار التغييرات في الكود.
قم باستنساخ المستودع وقم بتثبيت 🤗 Transformers باستخدام الأوامر التالية:
ستقوم هذه الأوامر بربط المجلد الذي قمت باستنساخ المستودع فيه بمسارات مكتبة Python. بمعنى آخر، سيبحث Python داخل المجلد الذي قمت باستنساخه بالإضافة إلى المسارات المعتادة للمكتبات. على سبيل المثال، إذا تم تثبيت حزم Python الخاصة بك عادةً في `~/anaconda3/envs/main/lib/python3.7/site-packages/`, فسيقوم Python أيضًا بالبحث في المجلد الذي قمت باستنساخه: `~/transformers/`.
<Tipwarning={true}>
يجب عليك الاحتفاظ بمجلد `transformers` إذا كنت تريد الاستمرار في استخدام المكتبة.
</Tip>
الآن يمكنك تحديث المستنسخ الخاص بك بسهولة إلى أحدث إصدار من 🤗 Transformers باستخدام الأمر التالي:
```bash
cd ~/transformers/
git pull
```
ستجد بيئة Python الإصدار `main` من 🤗 Transformers في المرة التالية التي تقوم فيها بتشغيله.
## التثبيت باستخدام conda
قم بالتثبيت من قناة conda `conda-forge`:
```bash
conda install conda-forge::transformers
```
## إعداد ذاكرة التخزين المؤقت
تُحمّل النماذج المُسبقة التدريب وتُخزّن مؤقتًا في: `~/.cache/huggingface/hub`. هذا هو المجلد الافتراضي الذي يُحدده متغير البيئة `TRANSFORMERS_CACHE`. على Windows، يكون دليل ذاكرة التخزين المؤقت الافتراضي هو `C:\Users\username\.cache\huggingface\hub`. يمكنك تغيير متغيرات البيئة shell الموضحة أدناه - حسب الأولوية - لتحديد دليل ذاكرة تخزين مؤقت مختلف:
1. متغير البيئة (افتراضي): `HUGGINGFACE_HUB_CACHE` أو `TRANSFORMERS_CACHE`.
سيستخدم 🤗 Transformers متغيرات البيئة `PYTORCH_TRANSFORMERS_CACHE` أو `PYTORCH_PRETRAINED_BERT_CACHE` إذا كنت قادمًا من إصدار سابق من هذه المكتبة وقمت بتعيين متغيرات البيئة هذه، ما لم تحدد متغير البيئة `TRANSFORMERS_CACHE`.
</Tip>
## الوضع دون اتصال بالإنترنت
قم بتشغيل 🤗 Transformers في بيئة محمية بجدار حماية أو غير متصلة باستخدام الملفات المخزنة مؤقتًا محليًا عن طريق تعيين متغير البيئة `HF_HUB_OFFLINE=1`.
<Tip>
أضف [🤗 Datasets](https://huggingface.co/docs/datasets/) إلى سير عمل التدريب غير المتصل باستخدام متغير البيئة `HF_DATASETS_OFFLINE=1`.
يجب أن يعمل هذا البرنامج النصي دون توقف أو انتظار انتهاء المهلة الزمنية لأنه لن يحاول تنزيل النموذج من Hub.
يمكنك أيضًا تجاوز تحميل نموذج من Hub من كل استدعاء [`~PreTrainedModel.from_pretrained`] باستخدام معلمة [`local_files_only`]. عندما يتم تعيينها على `True`، يتم تحميل الملفات المحلية فقط:
### جلب النماذج والمُجزّئات لاستخدامها دون اتصال بالإنترنت
خيار آخر لاستخدام 🤗 Transformers دون اتصال هو تنزيل الملفات مسبقًا، ثم الإشارة إلى مسارها المحلي عند الحاجة إلى استخدامها دون اتصال. هناك ثلاث طرق للقيام بذلك:
* قم بتنزيل ملف عبر واجهة المستخدم على [Model Hub](https://huggingface.co/models) بالنقر فوق أيقونة ↓.
>>> model = AutoModel.from_pretrained("./your/path/bigscience_t0")
```
* قم بتنزيل الملفات برمجيًا باستخدام مكتبة [huggingface_hub](https://github.com/huggingface/huggingface_hub/tree/main/src/huggingface_hub):
1. قم بتثبيت مكتبة `huggingface_hub` في بيئتك الافتراضية:
```bash
python -m pip install huggingface_hub
```
2. استخدم وظيفة [`hf_hub_download`](https://huggingface.co/docs/hub/adding-a-library#download-files-from-the-hub) لتنزيل ملف إلى مسار محدد. على سبيل المثال، يقوم الأمر التالي بتنزيل ملف `config.json` من نموذج [T0](https://huggingface.co/bigscience/T0_3B) إلى المسار المطلوب:
تعد LLMs، أو نماذج اللغة الكبيرة، المكون الرئيسي وراء توليد النصوص. وباختصار، تتكون من نماذج محول كبيرة مسبقة التدريب تم تدريبها للتنبؤ بالكلمة التالية (أو، بشكل أكثر دقة، الرمز اللغوي) بالنظر إلى نص معين. نظرًا لأنها تتنبأ برمز واحد في كل مرة، يجب عليك القيام بشيء أكثر تعقيدًا لتوليد جمل جديدة بخلاف مجرد استدعاء النموذج - يجب عليك إجراء التوليد التلقائي.
التوليد التلقائي هو إجراء وقت الاستدلال الذي يتضمن استدعاء النموذج بشكل متكرر باستخدام مخرجاته الخاصة، بالنظر إلى بعض المدخلات الأولية. في 🤗 Transformers، يتم التعامل مع هذا بواسطة دالة [`~generation.GenerationMixin.generate`]، والتي تتوفر لجميع النماذج ذات القدرات التوليدية.
سيوضح هذا البرنامج التعليمي كيفية:
* تتوليد نص باستخدام نموذج اللغات الكبيرة (LLM)
* تجنب الوقوع في الأخطاء الشائعة
* الخطوات التالية لمساعدتك في الاستفادة القصوى من LLM الخاص بك
قبل البدء، تأكد من تثبيت جميع المكتبات الضرورية:
```bash
pip install transformers bitsandbytes>=0.39.0 -q
```
## توليد النص
يأخذ نموذج اللغة المدرب لـ [نمذجة اللغة السببية](tasks/language_modeling) يأخذ تسلسلًا من رموز نصية كمدخل ويعيد توزيع الاحتمالية للرمز التالي.
<figcaption>"التنبؤ بالكلمة التالية لنموذج اللغة (LLM)"</figcaption>
</figure>
هناك جانب بالغ الأهمية في التوليد التلقائي باستخدام LLMs وهو كيفية اختيار الرمز التالي من توزيع الاحتمالية هذا. كل شيء مسموح به في هذه الخطوة طالما أنك تنتهي برمز للتكرار التالي. وهذا يعني أنه يمكن أن يكون بسيطًا مثل اختيار الرمز الأكثر احتمالًا من توزيع الاحتمالية أو معقدًا مثل تطبيق عشرات التحولات قبل أخذ العينات من التوزيع الناتج.
تتكرر العملية الموضحة أعلاه بشكل تكراري حتى يتم الوصول إلى شرط التوقف. في الوضع المثالي، يحدد النموذج شرط التوقف، والذي يجب أن يتعلم عند إخراج رمز نهاية التسلسل (`EOS`). إذا لم يكن الأمر كذلك، يتوقف التوليد عند الوصول إلى طول أقصى محدد مسبقًا.
من الضروري إعداد خطوة اختيار الرمز وشرط التوقف بشكل صحيح لجعل نموذجك يتصرف كما تتوقع في مهمتك. ولهذا السبب لدينا [`~generation.GenerationConfig`] ملف مرتبط بكل نموذج، والذي يحتوي على معلمة توليدية افتراضية جيدة ويتم تحميله جنبًا إلى جنب مع نموذجك.
دعنا نتحدث عن الكود!
<Tip>
إذا كنت مهتمًا بالاستخدام الأساسي لـ LLM، فإن واجهة [`Pipeline`](pipeline_tutorial) عالية المستوى هي نقطة انطلاق رائعة. ومع ذلك، غالبًا ما تتطلب LLMs ميزات متقدمة مثل التكميم والتحكم الدقيق في خطوة اختيار الرمز، والتي يتم تنفيذها بشكل أفضل من خلال [`~generation.GenerationMixin.generate`]. التوليد التلقائي باستخدام LLMs يستهلك الكثير من المواردد ويجب تنفيذه على وحدة معالجة الرسومات للحصول على أداء كافٍ.
>>>model_inputs=tokenizer(["A list of colors: red, blue"],return_tensors="pt").to("cuda")
```
يحتوي متغير `model_inputs` على النص المدخل بعد تقسيمه إلى وحدات لغوية (tokens)، بالإضافة إلى قناع الانتباه. في حين أن [`~generation.GenerationMixin.generate`] تبذل قصارى جهدها لاستنتاج قناع الانتباه عندما لا يتم تمريره، نوصي بتمريره كلما أمكن ذلك للحصول على نتائج مثالية.
بعد تقسيم المدخلات إلى وحدات لغوية، يمكنك استدعاء الدالة [`~generation.GenerationMixin.generate`] لإرجاع الوحدات اللغوية الناتجة. يجب بعد ذلك تحويل الوحدات المولدة إلى نص قبل طباعته.
'A list of colors: red, blue, green, yellow, orange, purple, pink,'
```
أخيرًا، ليس عليك معالجة المتتاليات الواحدة تلو الأخرى! يمكنك معالجة مجموعة من المدخلات دفعة واحدة، والتي ستعمل على تحسين الإنتاجية بشكل كبير بتكلفة صغيرة في زمن الاستجابة واستهلاك الذاكر. كل ما عليك التأكد منه هو تعبئة المدخلات بشكل صحيح (المزيد حول ذلك أدناه).
```py
>>>tokenizer.pad_token=tokenizer.eos_token# Most LLMs don't have a pad token by default
>>>model_inputs=tokenizer(
...["A list of colors: red, blue","Portugal is"],return_tensors="pt",padding=True
['A list of colors: red, blue, green, yellow, orange, purple, pink,',
'Portugal is a country in southwestern Europe, on the Iber']
```
وهذا كل شيء! في بضع سطور من التعليمات البرمجية، يمكنك تسخير قوة LLM.
## الأخطاء الشائعة
هناك العديد من [استراتيجيات التوليد](generation_strategies)، وفي بعض الأحيان قد لا تكون القيم الافتراضية مناسبة لحالتك الاستخدام. إذا لم تكن الإخراج الخاصة بك متوافقة مع ما تتوقعه، فقد قمنا بإنشاء قائمة بأكثر الأخطاء الشائعة وكيفية تجنبها.
إذا لم يتم تحديد العدد الأقصى للرموز في [`~generation.GenerationConfig`] الملف، `generate` يعيد ما يصل إلى 20 رمزًا بشكل افتراضي. نوصي بشدة بتعيين `max_new_tokens` يدويًا في مكالمة `generate` للتحكم في العدد الأقصى من الرموز الجديدة التي يمكن أن يعيدها. ضع في اعتبارك أن LLMs (بشكل أكثر دقة، [نماذج فك التشفير فقط](https://huggingface.co/learn/nlp-course/chapter1/6؟fw=pt)) تعيد أيضًا المدخلات الأصلية كجزء من الناتج.
```py
>>>model_inputs=tokenizer(["A sequence of numbers: 1, 2"],return_tensors="pt").to("cuda")
>>># By default, the output will contain up to 20 tokens
'A sequence of numbers: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16,'
```
### وضع التوليد الافتراضي
بشكل افتراضي، وما لم يتم تحديده في [`~generation.GenerationConfig`] الملف، `generate` يحدد الكلمة الأكثر احتمالًا فى كل خطوة من خطوات عملية التوليد (وهذا يُعرف بالتشفير الجشع). اعتمادًا على مهمتك، قد يكون هذا غير مرغوب فيه؛ تستفيد المهام الإبداعية مثل برامج الدردشة أو كتابة مقال ستفيد من أسلوب العينة العشوائية في اختيار الكلمات، تمن ناحية أخرى، فإن المهام التي تعتمد على مدخلات محددة مثل تحويل الصوت إلى نص أو الترجم من فك التشفير الجشع. قم بتفعيل أسلوب العينات العشوائية باستخدام `do_sample=True`، ويمكنك معرفة المزيد حول هذا الموضوع في [تدوينة المدونة](https://huggingface.co/blog/how-to-generate).
```py
>>># Set seed or reproducibility -- you don't need this unless you want full reproducibility
>>>fromtransformersimportset_seed
>>>set_seed(42)
>>>model_inputs=tokenizer(["I am a cat."],return_tensors="pt").to("cuda")
'I am a cat. Specifically, I am an indoor-only cat. I'
```
### مشكلة حشو المدخلات فى الاتجاة الخطأ
LLMs هي [معماريات فك التشفير فقط](https://huggingface.co/learn/nlp-course/chapter1/6؟fw=pt)، مما يعني أنها تستمر في التكرار على موجه الإدخال الخاص بك. فإن جميع المدخلات يجب أن تكون بنفس الطول. لحل هذه المسألة، يتم إضافة رموز حشو إلى المدخلات الأقصر. نظرًا لأن LLMs لا تولي اهتمامًا لرموز الحشو هذه، ذلك، يجب تحديد الجزء المهم من المدخل الذي يجب أن يركز عليه النموذج، وهذا يتم عن طريق ما يسمى بـ "قناع الانتباه". يجب أن يكون الحشو في بداية المدخل (الحشو من اليسار)، وليس في نهايته.
```py
>>># The tokenizer initialized above has right-padding active by default: the 1st sequence,
>>># which is shorter, has padding on the right side. Generation fails to capture the logic.
تتوقع بعض نماذج اللغات الكبيرة على صيغة محددة للمدخلات للعمل بشكل صحيح. إذا لم يتم اتباع هذه الصيغة، فإن أداء النموذج يتأثر سلبًا: لكن هذا التدهور قد لا يكون واضحًا للعيان. تتوفر معلومات إضافية حول التوجيه، بما في ذلك النماذج والمهام التي تحتاج إلى توخي الحذر، في [الدليل](tasks/prompting). دعنا نرى مثالاً باستخدام LLM للدردشة، والذي يستخدم [قالب الدردشة](chat_templating):
'None, you thug. How bout you try to focus on more useful questions?'
>>># As we can see, it followed a proper thug style 😎
```
## موارد إضافية
في حين أن عملية التوليد التلقائي بسيطة نسبيًا، فإن الاستفادة القصوى من LLM الخاص بك يمكن أن تكون مهمة صعبة لأن هناك العديد من الأجزاء المتحركة. للخطوات التالية لمساعدتك في الغوص بشكل أعمق في استخدام LLM وفهمه:
### استخدامات متقدمة للتوليد في نماذج اللغات الكبيرة
1. دليل حول كيفية [التحكم في طرق التوليد المختلفة](generation_strategies)، وكيفية إعداد ملف تكوين التوليد، وكيفية بث الناتج؛
2. [تسريع توليد النص](llm_optims)؛
3.[قوالب موجهات للدردشة LLMs](chat_
4. [دليل تصميم الموجه](tasks/prompting);
5. مرجع واجهة برمجة التطبيقات (API) [`~generation.GenerationConfig`], [`~generation.GenerationMixin.generate`], و [generate-related classes](internal/generation_utils). والعديد من الفئات الأخرى المرتبطة بعملية التوليد.!
### لوحات صدارة نماذج اللغات الكبيرة
1. لوحة صدارة نماذج اللغات الكبيرة المفتوحة المصدر (Open LLM Leaderboard): تركز على جودة النماذج مفتوحة المصدر [رابط لوحة الصدارة](https://huggingface.co/spaces/HuggingFaceH4/open_llm_leaderboard).
2. لوحة صدارة أداء نماذج اللغات الكبيرة المفتوحة المصدر (Open LLM-Perf Leaderboard): تركز على إنتاجية نماذج اللغات الكبيرة [رابط لوحة الصدارة](https://huggingface.co/spaces/optimum/llm-perf-leaderboard).
### زمن الاستجابة والإنتاجية واستهلاك الذاكرة
1. دليل تحسين نماذج اللغات الكبيرة من حيث السرعة والذاكرة: دليل تحسين نماذج اللغات الكبيرة.
2. التكميم (Quantization): دليل حول تقنية التكميم التكميم مثل تقنيتي bitsandbytes و autogptq، والتي توضح كيفية تقليل متطلبات الذاكرة بشكل كبير.
### مكتبات مرتبطة
1. [`optimum`](https://github.com/huggingface/optimum), امتداد لمكتبة Transformers يعمل على تحسين الأداء لأجهزة معينة.
2. [`outlines`](https://github.com/outlines-dev/outlines), مكتبة للتحكم في توليد النصوص (على سبيل المثال، لتوليد ملفات JSON).
3. [`SynCode`](https://github.com/uiuc-focal-lab/syncode), مكتبة للتوليد الموجه بقواعد اللغة الخالية من السياق (على سبيل المثال، JSON، SQL، Python).
4. [`text-generation-inference`](https://github.com/huggingface/text-generation-inference), خادم جاهز للإنتاج لنماذج اللغات الكبيرة.
# تحسين نماذج اللغة الكبيرة من حيث السرعة والذاكرة
[[open-in-colab]]
تحقق نماذج اللغة الكبيرة (LLMs) مثل GPT3/4، [Falcon](https://huggingface.co/tiiuae/falcon-40b)، و [Llama](https://huggingface.co/meta-llama/Llama-2-70b-hf) تقدمًا سريعًا في قدرتها على معالجة المهام التي تركز على الإنسان، مما يجعلها أدوات أساسية في الصناعات القائمة على المعرفة الحديثة.
لا يزال نشر هذه النماذج في المهام الواقعية يمثل تحديًا، ومع ذلك:
- لكي تظهر نماذج اللغة الكبيرة قدرات فهم وتوليد النصوص قريبة من قدرات الإنسان، فإنها تتطلب حاليًا إلى تكوينها من مليارات المعلمات (انظر [كابلان وآخرون](https://arxiv.org/abs/2001.08361)، [وي وآخرون](https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.07682)). وهذا بدوره يزيد من متطلبات الذاكرة للاستدلال.
- في العديد من المهام الواقعية، تحتاج نماذج اللغة الكبيرة إلى معلومات سياقية شاملة. يتطلب ذلك قدرة النموذج على إدارة تسلسلات إدخال طويلة للغاية أثناء الاستدلال.
يكمن جوهر صعوبة هذه التحديات في تعزيز القدرات الحسابية والذاكرة لنماذج اللغة الكبيرة، خاصة عند التعامل مع تسلسلات الإدخال الضخمة.
في هذا الدليل، سنستعرض التقنيات الفعالة لتُحسِّن من كفاءة نشر نماذج اللغة الكبيرة:
1. سنتناول تقنية "دقة أقل" التي أثبتت الأبحاث فعاليتها في تحقيق مزايا حسابية دون التأثير بشكل ملحوظ على أداء النموذج عن طريق العمل بدقة رقمية أقل [8 بت و4 بت](/main_classes/quantization.md).
2.**اFlash Attention:** إن Flash Attention وهي نسخة مُعدَّلة من خوارزمية الانتباه التي لا توفر فقط نهجًا أكثر كفاءة في استخدام الذاكرة، ولكنها تحقق أيضًا كفاءة متزايدة بسبب الاستخدام الأمثل لذاكرة GPU.
3.**الابتكارات المعمارية:** حيث تم اقتراح هياكل متخصصة تسمح باستدلال أكثر فعالية نظرًا لأن نماذج اللغة الكبيرة يتم نشرها دائمًا بنفس الطريقة أثناء عملية الاستدلال، أي توليد النص التنبؤي التلقائي مع سياق الإدخال الطويل، فقد تم اقتراح بنيات نموذج متخصصة تسمح بالاستدلال الأكثر كفاءة. أهم تقدم في بنيات النماذج هنا هو [عذر](https://arxiv.org/abs/2108.12409)، [الترميز الدوار](https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.09864)، [الاهتمام متعدد الاستعلامات (MQA)](https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.02150) و [مجموعة الانتباه بالاستعلام (GQA)]((https://arxiv.org/abs/2305.13245)).
على مدار هذا الدليل، سنقدم تحليلًا للتوليد التنبؤي التلقائي من منظور المُوتِّرات. نتعمق في مزايا وعيوب استخدام دقة أقل، ونقدم استكشافًا شاملاً لخوارزميات الانتباه الأحدث، ونناقش بنيات نماذج نماذج اللغة الكبيرة المحسنة. سندعم الشرح بأمثلة عملية تُبرِز كل تحسين على حدة.
## 1. دقة أقل
يمكن فهم متطلبات ذاكرة نماذج اللغة الكبيرة بشكل أفضل من خلال النظر إلى نموذج اللغة الكبيرة على أنها مجموعة من المصفوفات والمتجهات الوزنية، ومدخلات النص على أنها تسلسل من المتجهات. فيما يلي، سيتم استخدام تعريف "الأوزان" للإشارة إلى جميع مصفوفات الأوزان والمتجهات في النموذج.
في وقت كتابة هذا الدليل، تتكون نماذج اللغة الكبيرة من مليارات المعلمات على الأقل.كل معلمة يتم تمثيلها برقم عشري مثل 4.5689 `` والذي يتم تخزينه عادةً بتنسيق [float32](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Single-precision_floating-point_format)، [bfloat16](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bfloat16_floating-point_format)، أو [float16](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Half-precision_floating-point_format) . يسمح لنا هذا بحساب متطلبات الذاكرة لتحميل نموذج اللغة الكبيرة في الذاكرة بسهولة:
> *يتطلب تحميل أوزان نموذج به X مليار معلمة حوالي 4 * X جيجابايت من ذاكرة الفيديو العشوائية (VRAM) بدقة float32*
ومع ذلك، نادرًا ما يتم تدريب النماذج في الوقت الحالي بدقة float32 الكاملة، ولكن عادةً ما تكون بدقة bfloat16 أو بشكل أقل في تنسيق float16. لذلك، تصبح القاعدة الإرشادية كما يلي:
> *يتطلب تحميل أوزان نموذج به X مليار معلمة حوالي 2 * X جيجابايت من ذاكرة الفيديو العشوائية (VRAM) بدقة bfloat16/float16*
بالنسبة لمدخلات النصوص القصيرة (أقل من 1024 رمزًا)، فإن متطلبات الذاكرة للاستدلال تهيمن عليها إلى حد كبير متطلبات الذاكرة لتحميل الأوزان. لذلك، دعنا نفترض، في الوقت الحالي، أن متطلبات الذاكرة للاستدلال تساوي متطلبات الذاكرة لتحميل النموذج في ذاكرة VRAM لوحدة معالجة الرسومات GPU..
ولإعطاء بعض الأمثلة على مقدار ذاكرة الفيديو العشوائية (VRAM) التي يتطلبها تحميل نموذج بتنسيق bfloat16 تقريبًا:
عند كتابة هذا الدليل، أكبر شريحة لوحدة معالجة الرسومات المتوفّرة هي A100 و H100 التي توفر 80 جيجابايت من ذاكرة الفيديو العشوائية (VRAM). تتطلب معظم النماذج المدرجة أعلاه أكثر من 80 جيجابايت فقط لتحميلها، وبالتالي فهي تتطلب بالضرورة [التوازي للموتّرات](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/perf_train_gpu_many#tensor-parallelism) و/أو [لتوازي الخطي](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/perf_train_gpu_many#naive-model-parallelism-vertical-and-pipeline-parallelism).
🤗 لا يدعم Transformers موازاة التنسور خارج الصندوق لأنه يتطلب كتابة هيكلة النموذج بطريقة محددة. إذا كنت مهتمًا بكتابة نماذج بطريقة صديقة لموازاة التنسور، فلا تتردد في إلقاء نظرة على [مكتبة الاستدلال بتوليد النص](https://github.com/huggingface/text-generation-inference/tree/main/server/text_generation_server/models/custom_modeling).
بدعم موازاة قنوات المعالجة البسيطة خارج الصندوق. للقيام بذلك، قم بتحميل النموذج باستخدام `device="auto"` والذي سيقوم تلقائيًا بوضع الطبقات المختلفة على وحدات معالجة الرسومات (GPU) المتاحة كما هو موضح [هنا](https://huggingface.co/docs/accelerate/v0.22.0/en/concept_guides/big_model_inference).
لاحظ، مع ذلك، أنه في حين أن موازاة قنوات المعالجة البسيطة فعالة للغاية، إلا أنها لا تعالج مشكلات عدم نشاط وحدة معالجة الرسومات (GPU). لهذا، تكون موازاة قنوات المعالجة المتقدمة مطلوبة كما هو موضح [هنا](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/en/perf_train_gpu_many#naive-model-parallelism-vertical-and-pipeline-parallelism).
إذا كان لديك حق الوصول إلى عقدة 8 x 80 جيجابايت A100، فيمكنك تحميل BLOOM كما يلي
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("bigscience/bloom", device_map="auto", pad_token_id=0)
```
من خلال استخدام `device_map="auto"` سيتم توزيع طبقات الاهتمام بالتساوي عبر جميع وحدات معالجة الرسومات (GPU) المتاحة.
في هذا الدليل، سنستخدم [bigcode/octocoder](https://huggingface.co/bigcode/octocoder) لأنه يمكن تشغيله على شريحة جهاز GPU A100 ذات 40 جيجا بايت. لاحظ أن جميع تحسينات الذاكرة والسرعة التي سنطبقها من الآن فصاعدًا تنطبق بالتساوي على النماذج التي تتطلب موازاة النماذج أو المصفوفات.
نظرًا لأن النموذج مُحمَّل بدقة bfloat16، فباستخدام قاعدتنا الإرشادية أعلاه، نتوقع أن تكون متطلبات الذاكرة لتشغيل الاستدلال باستخدام `bigcode/octocoder` حوالي 31 جيجا بايت من ذاكرة الفيديو العشوائية (VRAM). دعنا نجرب.
نقوم أولاً بتحميل النموذج والمجزىء اللغوي ثم نقوم بتمرير كلاهما إلى كائن [قنوات المعالجة](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main_classes/pipelines) في Transformers.
```python
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer, pipeline
import torch
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("bigcode/octocoder", torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16, device_map="auto", pad_token_id=0)
prompt = "Question: Please write a function in Python that transforms bytes to Giga bytes.\n\nAnswer:"
result = pipe(prompt, max_new_tokens=60)[0]["generated_text"][len(prompt):]
result
```
**الإخراج**:
```
Here is a Python function that transforms bytes to Giga bytes:\n\n```python\ndef bytes_to_giga_bytes(bytes):\n return bytes / 1024 / 1024 / 1024\n```\n\nThis function takes a single
```
رائع، يمكننا الآن استخدام النتيجة مباشرة لتحويل البايت إلى جيجا بايت.
```python
def bytes_to_giga_bytes(bytes):
return bytes / 1024 / 1024 / 1024
```
دعونا نستدعي [`torch.cuda.max_memory_allocated`](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.cuda.max_memory_allocated.html) لقياس ذروة تخصيص ذاكرة وحدة معالجة الرسومات (GPU).
قريب بما يكفي من حسابنا التقريبي! يمكننا أن نرى أن الرقم غير صحيح تمامًا لأن الانتقال من البايت إلى الكيلوبايت يتطلب الضرب في 1024 بدلاً من 1000. لذلك يمكن أيضًا فهم صيغة التقريب على أنها حساب "بحد أقصى X جيجا بايت".
لاحظ أنه إذا حاولنا تشغيل النموذج بدقة float32 الكاملة، فستكون هناك حاجة إلى 64 جيجا بايت من ذاكرة الفيديو العشوائية (VRAM).
> يتم تدريب جميع النماذج تقريبًا بتنسيق bfloat16 في الوقت الحالي، ولا يوجد سبب لتشغيل النموذج بدقة float32 الكاملة إذا [كانت وحدة معالجة الرسومات (GPU) الخاصة بك تدعم bfloat16](https://discuss.pytorch.org/t/bfloat16-native-support/117155/5). لن توفر دقة float32 نتائج استدلال أفضل من الدقة التي تم استخدامها لتدريب النموذج.
إذا لم تكن متأكدًا من تنسيق تخزين أوزان النموذج على Hub، فيمكنك دائمًا الاطلاع على تهيئة نقطة التفتيش في `"torch_dtype"`، على سبيل المثال [هنا](https://huggingface.co/meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-hf/blob/6fdf2e60f86ff2481f2241aaee459f85b5b0bbb9/config.json#L21). يوصى بتعيين النموذج إلى نفس نوع الدقة كما هو مكتوب في التهيئة عند التحميل باستخدام `from_pretrained(..., torch_dtype=...)` إلا إذا كان النوع الأصلي هو float32، وفي هذه الحالة يمكن استخدام `float16` أو `bfloat16` للاستدلال.
دعونا نحدد وظيفة `flush(...)` لتحرير جميع الذاكرة المخصصة بحيث يمكننا قياس ذروة ذاكرة وحدة معالجة الرسومات (GPU) المخصصة بدقة.
```python
del pipe
del model
import gc
import torch
def flush():
gc.collect()
torch.cuda.empty_cache()
torch.cuda.reset_peak_memory_stats()
```
دعونا نستدعيه الآن للتجربة التالية.
```python
flush()
```
في الإصدار الأخير من مكتبة Accelerate، يمكنك أيضًا استخدام طريقة مساعدة تسمى `release_memory()`
```python
from accelerate.utils import release_memory
# ...
release_memory(model)
```
```python
from accelerate.utils import release_memory
# ...
release_memory(model)
```
والآن ماذا لو لم يكن لدى وحدة معالجة الرسومات (GPU) لديك 32 جيجا بايت من ذاكرة الفيديو العشوائية (VRAM)؟ لقد وجد أن أوزان النماذج يمكن تحويلها إلى 8 بتات أو 4 بتات دون خسارة كبيرة في الأداء (انظر [Dettmers et al.](https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.07339)).
يمكن تحويل النموذج إلى 3 بتات أو 2 بتات مع فقدان مقبول في الأداء كما هو موضح في ورقة [GPTQ](https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.17323) 🤯.
دون الدخول في الكثير من التفاصيل، تهدف مخططات التكميم إلى تخفيض دقة الأوزان مع محاولة الحفاظ على دقة نتائج النموذج كما هي (*أي* أقرب ما يمكن إلى bfloat16).
لاحظ أن التكميم يعمل بشكل خاص جيدًا لتوليد النص حيث كل ما نهتم به هو اختيار *مجموعة الرموز الأكثر احتمالًا التالية* ولا نهتم حقًا بالقيم الدقيقة لتوزيع الرمز التالي *logit*.
كل ما يهم هو أن توزيع الرمز التالي *logit* يظل كما هو تقريبًا بحيث تعطي عملية `argmax` أو `topk` نفس النتائج.
هناك عدة تقنيات للتكميم، والتي لن نناقشها بالتفصيل هنا، ولكن بشكل عام، تعمل جميع تقنيات التكميم كما يلي:
result = pipe(prompt, max_new_tokens=60)[0]["generated_text"][len(prompt):]
result
```
**الإخراج**:
```
Here is a Python function that transforms bytes to Giga bytes:\n\n```python\ndef bytes_to_giga_bytes(bytes):\n return bytes / 1024 / 1024 / 1024\n```\n\nThis function takes a single
```
جميل، نحصل على نفس النتيجة كما في السابق، لذلك لا يوجد فقدان في الدقة! دعنا نلقي نظرة على مقدار الذاكرة المستخدمة هذه المرة.
أقل بكثير! لقد انخفضنا إلى ما يزيد قليلاً عن 15 جيجابايت، وبالتالي يمكننا تشغيل هذا النموذج على وحدات معالجة الرسومات للمستهلك مثل 4090.
نرى مكسبًا لطيفًا جدًا في كفاءة الذاكرة ولا يوجد تقريبًا أي تدهور في ناتج النموذج. ومع ذلك، يمكننا أيضًا ملاحظة تباطؤ طفيف أثناء الاستدلال.
نحذف النماذج ونفرغ الذاكرة مرة أخرى.
```python
del model
del pipe
```
```python
flush()
```
دعنا نرى ما هو استهلاك ذاكرة GPU الذروة الذي يوفره تكميم 4 بت. يمكن تكميم النموذج إلى 4 بت باستخدام نفس واجهة برمجة التطبيقات كما في السابق - هذه المرة عن طريق تمرير `load_in_4bit=True` بدلاً من `load_in_8bit=True`.
```python
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("bigcode/octocoder", load_in_4bit=True, low_cpu_mem_usage=True, pad_token_id=0)
result = pipe(prompt, max_new_tokens=60)[0]["generated_text"][len(prompt):]
result
```
**الإخراج**:
```
Here is a Python function that transforms bytes to Giga bytes:\n\n```\ndef bytes_to_gigabytes(bytes):\n return bytes / 1024 / 1024 / 1024\n```\n\nThis function takes a single argument
```
نحن نرى تقريبًا نفس نص الإخراج كما في السابق - فقط `python` مفقود قبل مقطع الكود. دعنا نرى مقدار الذاكرة المطلوبة.
فقط 9.5 جيجابايت! هذا ليس كثيرًا بالفعل لنموذج يزيد عدد معاملاته عن 15 مليار.
على الرغم من أننا نرى تدهورًا بسيطًا جدًا في الدقة لنموذجنا هنا، إلا أن تكميم 4 بت يمكن أن يؤدي في الممارسة العملية غالبًا إلى نتائج مختلفة مقارنة بتكميم 8 بت أو الاستدلال الكامل `bfloat16`. الأمر متروك للمستخدم لتجربته.
لاحظ أيضًا أن الاستدلال هنا كان أبطأ قليلاً مقارنة بتكميم 8 بت والذي يرجع إلى طريقة التكميم الأكثر عدوانية المستخدمة لتكميم 4 بت مما يؤدي إلى \\( \text{quantize} \\) و \\( \text{dequantize} \\) يستغرق وقتًا أطول أثناء الاستدلال.
```python
del model
del pipe
```
```python
flush()
```
بشكل عام، رأينا أن تشغيل OctoCoder بدقة 8 بت قلل من ذاكرة GPU VRAM المطلوبة من 32G GPU VRAM إلى 15 جيجابايت فقط، وتشغيل النموذج بدقة 4 بت يقلل من ذاكرة GPU VRAM المطلوبة إلى ما يزيد قليلاً عن 9 جيجابايت.
يسمح تكميم 4 بت بتشغيل النموذج على وحدات معالجة الرسومات مثل RTX3090 و V100 و T4 والتي يمكن الوصول إليها بسهولة لمعظم الأشخاص.
لمزيد من المعلومات حول التكميم ولمعرفة كيف يمكن تكميم النماذج لطلب ذاكرة GPU VRAM أقل حتى من 4 بت، نوصي بالاطلاع على تنفيذ [`AutoGPTQ`](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/en/main_classes/quantization#autogptq-integration%60).
> كاستنتاج، من المهم تذكر أن تكميم النموذج يتداول كفاءة الذاكرة المحسنة مقابل الدقة وفي بعض الحالات وقت الاستدلال.
إذا لم تكن ذاكرة GPU قيدًا لحالتك الاستخدام، فغالبًا لا توجد حاجة للنظر في التكميم. ومع ذلك، لا يمكن للعديد من وحدات معالجة الرسومات ببساطة تشغيل نماذج اللغة الكبيرة بدون طرق التكميم وفي هذه الحالة، تعد مخططات التكميم 4 بت و 8 بت أدوات مفيدة للغاية.
لمزيد من المعلومات حول الاستخدام التفصيلي، نوصي بشدة بإلقاء نظرة على [وثائق تكميم المحولات](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main_classes/quantization#general-usage).
بعد ذلك، دعنا نلقي نظرة على كيفية تحسين الكفاءة الحسابية وكفاءة الذاكرة باستخدام خوارزميات أفضل وبنية نموذج محسنة.
## 2. الانتباه السريع
تتشارك نماذج اللغة الكبيرة (LLMs) الأعلى أداءً اليوم تقريبًا نفس البنية الأساسية التي تتكون من طبقات التغذية الأمامية، وطبقات التنشيط، وطبقات التطبيع الطبقي، والأهم من ذلك، طبقات الانتباه الذاتي.
تعد طبقات الانتباه الذاتي مركزية لنماذج اللغة الكبيرة (LLMs) حيث تمكن النموذج من فهم العلاقات السياقية بين رموز المدخلات.
ومع ذلك، فإن استهلاك ذاكرة GPU الذروة لطبقات الانتباه الذاتي ينمو بشكل *رباعي* في كل من التعقيد الحسابي وتعقيد الذاكرة مع عدد رموز المدخلات (والذي يُطلق عليه أيضًا *طول التسلسل*) الذي نسميه في ما يلي بـ \\( N \\) .
على الرغم من أن هذا غير ملحوظ حقًا للتسلسلات الأقصر (حتى 1000 رمز إدخال)، إلا أنه يصبح مشكلة خطيرة للتسلسلات الأطول (حوالي 16000 رمز إدخال).
دعنا نلقي نظرة أقرب. الصيغة لحساب الناتج \\( \mathbf{O} \\) لطبقة الانتباه الذاتي لإدخال \\( \mathbf{X} \\) بطول \\( N \\) هي:
يعد \\( \mathbf{X} = (\mathbf{x}_1, ... \mathbf{x}_{N}) \\) بالتالي تسلسل الإدخال إلى طبقة الاهتمام. وستتكون كل من الإسقاطات \\( \mathbf{Q} \\) و \\( \mathbf{K} \\) من \\( N \\) من المتجهات مما يؤدي إلى أن يكون حجم \\( \mathbf{QK}^T \\) هو \\( N^2 \\).
عادة ما يكون لدى LLMs العديد من رؤوس الاهتمام، وبالتالي يتم إجراء العديد من حسابات الاهتمام الذاتي بالتوازي.
وبافتراض أن LLM لديها 40 رأس اهتمام وتعمل بدقة bfloat16، يمكننا حساب متطلبات الذاكرة لتخزين مصفوفات \\( \mathbf{QK^T} \\) لتكون \\( 40 * 2 * N^2 \\) بايت. بالنسبة لـ \\( N=1000 \\)، لا يلزم سوى حوالي 50 ميجابايت من VRAM، ولكن بالنسبة لـ \\( N=16000 \\) سنحتاج إلى 19 جيجابايت من VRAM، وبالنسبة لـ \\( N=100,000 \\) سنحتاج إلى ما يقرب من 1 تيرابايت فقط لتخزين مصفوفات \\( \mathbf{QK}^T \\).
باختصار، سرعان ما يصبح خوارزمية الانتباه الذاتي الافتراضية مكلفة للغاية من حيث الذاكرة بالنسبة لسياقات الإدخال الكبيرة.
مع تحسن LLMs في فهم النص وتوليد النص، يتم تطبيقها على مهام متزايدة التعقيد. في حين أن النماذج كانت تتعامل سابقًا مع ترجمة أو تلخيص بضع جمل، فإنها الآن تدير صفحات كاملة، مما يتطلب القدرة على معالجة أطوال إدخال واسعة.
كيف يمكننا التخلص من متطلبات الذاكرة الباهظة للتطويلات المدخلة الكبيرة؟ نحن بحاجة إلى طريقة جديدة لحساب آلية الاهتمام الذاتي التي تتخلص من مصفوفة \\( QK^T \\). [طريقه داو وآخرون.](Https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.14135) طوروا بالضبط مثل هذا الخوارزمية الجديدة وأطلقوا عليها اسم **Flash Attention**.
باختصار، يكسر الاهتمام الفلاشي حساب \\( \mathbf{V} \times \operatorname{Softmax}(\mathbf{QK}^T\\)) ويحسب بدلاً من ذلك قطعًا أصغر من الإخراج عن طريق التكرار عبر العديد من خطوات حساب Softmax:
مع \\( s^a_{ij} \\) و \\( s^b_{ij} \\) كونها بعض إحصائيات التطبيع softmax التي يجب إعادة حسابها لكل \\( i \\) و \\( j \\).
يرجى ملاحظة أن Flash Attention بالكامل أكثر تعقيدًا إلى حد ما ويتم تبسيطه بشكل كبير هنا حيث أن التعمق كثيرًا يخرج عن نطاق هذا الدليل. القارئ مدعو لإلقاء نظرة على ورقة Flash Attention المكتوبة جيدًا [1] لمزيد من التفاصيل.
الفكرة الرئيسية هنا هي:
> من خلال تتبع إحصائيات التطبيع softmax واستخدام بعض الرياضيات الذكية، يعطي Flash Attention **مخرجات متطابقة رقميًا** مقارنة بطبقة الاهتمام الذاتي الافتراضية بتكلفة ذاكرة لا تزيد خطيًا مع \\( N \\).
عند النظر إلى الصيغة، قد يقول المرء بديهيًا أن الاهتمام الفلاشي يجب أن يكون أبطأ بكثير مقارنة بصيغة الاهتمام الافتراضية حيث يلزم إجراء المزيد من الحسابات. في الواقع، يتطلب Flash Attention المزيد من عمليات الفاصلة العائمة مقارنة بالاهتمام العادي حيث يجب إعادة حساب إحصائيات التطبيع softmax باستمرار (راجع [الورقة](https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.14135) لمزيد من التفاصيل إذا كنت مهتمًا)
> ومع ذلك، فإن الاهتمام الفلاشي أسرع بكثير في الاستدلال مقارنة بالاهتمام الافتراضي الذي يأتي من قدرته على تقليل الطلبات على ذاكرة GPU الأبطأ ذات النطاق الترددي العالي (VRAM)، والتركيز بدلاً من ذلك على ذاكرة SRAM الأسرع الموجودة على الشريحة.
من الناحية الأساسية، يتأكد Flash Attention من إمكانية إجراء جميع عمليات الكتابة والقراءة الوسيطة باستخدام ذاكرة SRAM السريعة الموجودة على الشريحة بدلاً من الاضطرار إلى الوصول إلى ذاكرة VRAM الأبطأ لحساب متجه الإخراج \\( \mathbf{O} \\).
من الناحية العملية، لا يوجد حاليًا أي سبب **عدم** استخدام الاهتمام الفلاشي إذا كان متاحًا. الخوارزمية تعطي نفس المخرجات رياضيا، وأسرع وأكثر كفاءة في استخدام الذاكرة.
لنلقِ نظرة على مثال عملي.
يحصل نموذج OctoCoder الخاص بنا الآن على موجه إدخال أطول بشكل كبير يتضمن ما يسمى *موجه النظام*. تُستخدم موجهات النظام لتوجيه LLM إلى مساعد أفضل مصمم لمهام المستخدمين.
فيما يلي، نستخدم موجه النظام الذي سيجعل OctoCoder مساعد ترميز أفضل.
```python
system_prompt = """Below are a series of dialogues between various people and an AI technical assistant.
The assistant tries to be helpful, polite, honest, sophisticated, emotionally aware, and humble but knowledgeable.
The assistant is happy to help with code questions and will do their best to understand exactly what is needed.
It also tries to avoid giving false or misleading information, and it caveats when it isn't entirely sure about the right answer.
That said, the assistant is practical really does its best, and doesn't let caution get too much in the way of being useful.
The Starcoder models are a series of 15.5B parameter models trained on 80+ programming languages from The Stack (v1.2) (excluding opt-out requests).
The model uses Multi Query Attention, was trained using the Fill-in-the-Middle objective, and with 8,192 tokens context window for a trillion tokens of heavily deduplicated data.
-----
Question: Write a function that takes two lists and returns a list that has alternating elements from each input list.
Answer: Sure. Here is a function that does that.
def alternating(list1, list2):
results = []
for i in range(len(list1)):
results.append(list1[i])
results.append(list2[i])
return results
Question: Can you write some test cases for this function?
Question: Modify the function so that it returns all input elements when the lists have uneven length. The elements from the longer list should be at the end.
Answer: Here is the modified function.
def alternating(list1, list2):
results = []
for i in range(min(len(list1), len(list2))):
results.append(list1[i])
results.append(list2[i])
if len(list1) > len(list2):
results.extend(list1[i+1:])
else:
results.extend(list2[i+1:])
return results
-----
"""
```
لأغراض التوضيح، سنكرر موجه النظام عشر مرات بحيث يكون طول الإدخال طويلاً بما يكفي لملاحظة وفورات ذاكرة Flash Attention.
نضيف موجه النص الأصلي "سؤال: يرجى كتابة وظيفة في Python تقوم بتحويل البايتات إلى جيجا بايت.
```python
long_prompt = 10 * system_prompt + prompt
```
نقوم بتنفيذ نموذجنا مرة أخرى بدقة bfloat16.
```python
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("bigcode/octocoder", torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16, device_map="auto")
دعنا الآن نقوم بتشغيل النموذج تمامًا مثلما كان من قبل *بدون اهتمام فلاشي* وقياس متطلبات ذاكرة GPU وقت الذروة ووقت الاستدلال.
```python
import time
start_time = time.time()
result = pipe(long_prompt, max_new_tokens=60)[0]["generated_text"][len(long_prompt):]
print(f"Generated in {time.time() - start_time} seconds.")
result
```
**الإخراج**:
```
تم التوليد في 10.96854019165039 ثانية.
بالتأكيد. إليك وظيفة للقيام بذلك.
def bytes_to_giga(bytes):
return bytes / 1024 / 1024 / 1024
الإجابة: بالتأكيد. إليك وظيفة للقيام بذلك.
ديف
```
نحصل على نفس الإخراج كما كان من قبل، ولكن هذه المرة، يقوم النموذج بتكرار الإجابة عدة مرات حتى يتم قطعها عند 60 رمزًا. ليس من المستغرب أننا كررنا موجه النظام عشر مرات لأغراض التوضيح وبالتالي قمنا بتشغيل النموذج لتكرار نفسه.
**ملاحظة** لا ينبغي تكرار موجه النظام عشر مرات في التطبيقات الواقعية - مرة واحدة كافية!
كما نرى، فإن متطلبات ذاكرة GPU وقت الذروة أعلى بكثير مما كانت عليه في البداية، وهو ما يرجع إلى حد كبير إلى تسلسل الإدخال الأطول. أيضًا، يستغرق التوليد أكثر من دقيقة بقليل الآن.
لمقارنة، دعونا نقوم بتشغيل نفس الدالة، ولكن تمكين الاهتمام فلاش بدلا من ذلك.
للقيام بذلك، نقوم بتحويل النموذج إلى [BetterTransformer](Https://huggingface.co/docs/optimum/bettertransformer/overview) ومن خلال القيام بذلك تمكين PyTorch's [SDPA self-attention](Https://pytorch.org/docs/master/generated/torch.nn.functional.scaled_dot_product_attention) والتي بدورها قادرة على استخدام الاهتمام فلاش.
```python
model.to_bettertransformer()
```
الآن نقوم بتشغيل نفس مقتطف التعليمات البرمجية بالضبط كما كان من قبل وتحت الغطاء سوف تستخدم المحولات الاهتمام فلاش.
```py
start_time = time.time()
with torch.backends.cuda.sdp_kernel(enable_flash=True, enable_math=False, enable_mem_efficient=False):
result = pipe(long_prompt, max_new_tokens=60)[0]["generated_text"][len(long_prompt):]
print(f"Generated in {time.time() - start_time} seconds.")
result
```
**الإخراج**:
```
تم التوليد في 3.0211617946624756 ثانية.
بالتأكيد. إليك وظيفة للقيام بذلك.
def bytes_to_giga(bytes):
return bytes / 1024 / 1024 / 1024
الإجابة: بالتأكيد. إليك وظيفة للقيام بذلك.
ديف
```
نحصل على نفس النتيجة بالضبط كما كان من قبل، ولكن يمكننا ملاحظة تسريع كبير بفضل الاهتمام فلاش.
ونحن تقريبا مرة أخرى إلى ذاكرة GPU الذروة الأصلية لدينا 29GB.
يمكننا أن نلاحظ أننا نستخدم فقط حوالي 100 ميجابايت إضافية من ذاكرة GPU عند تمرير تسلسل إدخال طويل جدًا مع الاهتمام فلاش مقارنة بتمرير تسلسل إدخال قصير كما فعلنا في البداية.
```py
flush()
```
لمزيد من المعلومات حول كيفية استخدام Flash Attention، يرجى الاطلاع على [صفحة doc هذه](Https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/en/perf_infer_gpu_one#flashattention-2).
## 3. الابتكارات المعمارية
حتى الآن، نظرنا في تحسين الكفاءة الحسابية والذاكرة من خلال:
- صب الأوزان في تنسيق دقة أقل
- استبدال خوارزمية الاهتمام الذاتي بإصدار أكثر كفاءة من حيث الذاكرة والحساب
دعونا الآن نلقي نظرة على كيفية تغيير بنية LLM بحيث تكون أكثر فعالية وكفاءة للمهام التي تتطلب مدخلات نصية طويلة، على سبيل المثال:
- استرجاع الأسئلة المعززة،
- تلخيص،
- الدردشة
لاحظ أن "الدردشة" لا تتطلب من LLM التعامل مع مدخلات نصية طويلة فحسب، بل تتطلب أيضًا أن يكون LLM قادرًا على التعامل بكفاءة مع الحوار ذهابًا وإيابًا بين المستخدم والمساعد (مثل ChatGPT).
بمجرد تدريبها، يصبح من الصعب تغيير بنية LLM الأساسية، لذلك من المهم مراعاة مهام LLM مسبقًا وتحسين بنية النموذج وفقًا لذلك.
هناك مكونان مهمان لبنية النموذج يصبحان بسرعة عنق زجاجة للذاكرة و/أو الأداء لتسلسلات الإدخال الكبيرة.
- الترميزات الموضعية
- ذاكرة التخزين المؤقت للقيمة الرئيسية
دعنا نلقي نظرة على كل مكون بمزيد من التفاصيل
### 3.1 تحسين الترميزات الموضعية لـ LLMs
يضع الاهتمام الذاتي كل رمز في علاقة مع رموز أخرى.
كمثال، يمكن أن تبدو مصفوفة \\( \operatorname{Softmax}(\mathbf{QK}^T) \\) لتسلسل الإدخال النصي *"مرحبًا"، "أنا"، "أحب"، "أنت"* كما يلي:
يتم منح كل رمز كلمة كتلة احتمال يتم من خلالها الاهتمام بجميع رموز الكلمات الأخرى، وبالتالي يتم وضعها في علاقة مع جميع رموز الكلمات الأخرى. على سبيل المثال، تحضر كلمة *"الحب"* كلمة *"مرحبًا"* بنسبة 5%، و *"أنا"* بنسبة 30%، ونفسها بنسبة 65%.
سيواجه LLM القائم على الاهتمام الذاتي، ولكن بدون الترميزات الموضعية، صعوبات كبيرة في فهم مواضع نصوص الإدخال بالنسبة لبعضها البعض.
ويرجع ذلك إلى أن درجة الاحتمال التي يحسبها \\( \mathbf{QK}^T \\) تربط كل رمز كلمة بكل رمز كلمة أخرى في حسابات \\( O (1) \\) بغض النظر عن مسافة الموضع النسبي بينهما.
لذلك، بالنسبة إلى LLM بدون ترميزات موضعية، يبدو أن كل رمز له نفس المسافة إلى جميع الرموز الأخرى، على سبيل المثال، سيكون من الصعب التمييز بين *"مرحبًا أنا أحبك"* و *"أنت تحبني مرحبًا"*.
لكي يفهم LLM ترتيب الجملة، يلزم وجود *إشارة* إضافية ويتم تطبيقها عادةً في شكل *الترميزات الموضعية* (أو ما يُطلق عليه أيضًا *الترميزات الموضعية*).
لم يتم ترجمة النص الخاص والروابط وأكواد HTML وCSS بناءً على طلبك.
قدم مؤلفو الورقة البحثية [*Attention Is All You Need*](https://arxiv.org/abs/1706.03762) تضمينات موضعية جيبية مثلثية \\( \mathbf{P} = \mathbf{p}_1, \ldots, \mathbf{p}_N \\) حيث يتم حساب كل متجه \\( \mathbf{p}_i \\) كدالة جيبية لموضعه \\( i \\) .
بعد ذلك يتم ببساطة إضافة التضمينات الموضعية إلى متجهات تسلسل الإدخال \\( \mathbf{\hat{X}} = \mathbf{\hat{x}}_1, \ldots, \mathbf{\hat{x}}_N \\) = \\( \mathbf{x}_1 + \mathbf{p}_1, \ldots, \mathbf{x}_N + \mathbf{p}_N \\) وبالتالي توجيه النموذج لتعلم ترتيب الجملة بشكل أفضل.
بدلاً من استخدام التضمينات الموضعية الثابتة، استخدم آخرون (مثل [Devlin et al.](https://arxiv.org/abs/1810.04805)) تضمينات موضعية مكتسبة يتم من خلالها تعلم التضمينات الموضعية \\( \mathbf{P} \\) أثناء التدريب.
كانت التضمينات الموضعية الجيبية والمكتسبة هي الطرق السائدة لترميز ترتيب الجملة في نماذج اللغة الكبيرة، ولكن تم العثور على بعض المشكلات المتعلقة بهذه التضمينات الموضعية:
1. التضمينات الموضعية الجيبية والمكتسبة هي تضمينات موضعية مطلقة، أي ترميز تضمين فريد لكل معرف موضعي: \\( 0, \ldots, N \\) . كما أظهر [Huang et al.](https://arxiv.org/abs/2009.13658) و [Su et al.](https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.09864)، تؤدي التضمينات الموضعية المطلقة إلى أداء ضعيف لنماذج اللغة الكبيرة للمدخلات النصية الطويلة. بالنسبة للمدخلات النصية الطويلة، يكون من المفيد إذا تعلم النموذج المسافة الموضعية النسبية التي تمتلكها رموز المدخلات إلى بعضها البعض بدلاً من موضعها المطلق.
2. عند استخدام التضمينات الموضعية المكتسبة، يجب تدريب نموذج اللغة الكبيرة على طول إدخال ثابت \\( N \\)، مما يجعل من الصعب الاستقراء إلى طول إدخال أطول مما تم تدريبه عليه.
في الآونة الأخيرة، أصبحت التضمينات الموضعية النسبية التي يمكنها معالجة المشكلات المذكورة أعلاه أكثر شعبية، وأبرزها:
يؤكد كل من *RoPE* و *ALiBi* أنه من الأفضل توجيه نموذج اللغة الكبيرة حول ترتيب الجملة مباشرة في خوارزمية الانتباه الذاتي حيث يتم وضع رموز الكلمات في علاقة مع بعضها البعض. على وجه التحديد، يجب توجيه ترتيب الجملة عن طريق تعديل عملية \\( \mathbf{QK}^T \\) .
دون الدخول في الكثير من التفاصيل، يشير *RoPE* إلى أنه يمكن ترميز المعلومات الموضعية في أزواج الاستعلام-المفتاح، على سبيل المثال \\( \mathbf{q}_i \\) و \\( \mathbf{x}_j \\) عن طريق تدوير كل متجه بزاوية \\( \theta * i \\) و \\( \theta * j \\) على التوالي مع \\( i, j \\) تصف موضع الجملة لكل متجه:
$$ \mathbf{\hat{q}}_i^T \mathbf{\hat{x}}_j = \mathbf{{q}}_i^T \mathbf{R}_{\theta, i -j} \mathbf{{x}}_j. $$
يمثل \\( \mathbf{R}_{\theta, i - j} \\) مصفوفة دورانية. \\( \theta \\) *لا* يتم تعلمه أثناء التدريب، ولكن بدلاً من ذلك يتم تعيينه إلى قيمة محددة مسبقًا تعتمد على طول تسلسل الإدخال الأقصى أثناء التدريب.
> من خلال القيام بذلك، يتم التأثير على درجة الاحتمال بين \\( \mathbf{q}_i \\) و \\( \mathbf{q}_j \\) فقط إذا \\( i \ne j \\) ويعتمد فقط على المسافة النسبية \\( i - j \\) بغض النظر عن المواضع المحددة لكل متجه \\( i \\) و \\( j \\) .
يستخدم *RoPE* في العديد من نماذج اللغة الكبيرة الأكثر أهمية اليوم، مثل:
كبديل، يقترح *ALiBi* مخطط ترميز موضعي نسبي أبسط بكثير. يتم إضافة المسافة النسبية التي تمتلكها رموز المدخلات إلى بعضها البعض كعدد صحيح سلبي مقياس بقيمة محددة مسبقًا `m` إلى كل إدخال استعلام-مفتاح لمصفوفة \\( \mathbf{QK}^T \\) مباشرة قبل حساب softmax.

كما هو موضح في ورقة [ALiBi](https://arxiv.org/abs/2108.12409)، يسمح هذا الترميز الموضعي النسبي البسيط للنموذج بالحفاظ على أداء عالٍ حتى في تسلسلات المدخلات النصية الطويلة جدًا.
يُستخدم *ALiBi* في العديد من أهم نماذج اللغة الكبيرة المستخدمة اليوم، مثل:
يمكن لكل من ترميزات الموضع *RoPE* و *ALiBi* الاستقراء إلى أطوال إدخال لم يتم ملاحظتها أثناء التدريب، في حين ثبت أن الاستقراء يعمل بشكل أفضل بكثير خارج الصندوق لـ *ALiBi* مقارنة بـ *RoPE*.
بالنسبة لـ ALiBi، ما عليك سوى زيادة قيم مصفوفة الموضع المثلث السفلي لمطابقة طول تسلسل الإدخال.
بالنسبة لـ *RoPE*، يؤدي الحفاظ على نفس \\( \theta \\) الذي تم استخدامه أثناء التدريب إلى نتائج سيئة عند تمرير إدخالات نصية أطول بكثير من تلك التي شوهدت أثناء التدريب، راجع [Press et al.](https://arxiv.org/abs/2108.12409). ومع ذلك، وجد المجتمع بعض الحيل الفعالة التي تقوم بتعديل \\( \theta \\)، مما يسمح لترميزات الموضع *RoPE* بالعمل بشكل جيد لتسلسلات إدخال النص المستقرئة (راجع [هنا](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/pull/24653)).
> كل من RoPE و ALiBi عبارة عن ترميزات موضع نسبي *لا* يتم تعلمها أثناء التدريب، ولكن بدلاً من ذلك تستند إلى الحدس التالي:
- يجب إعطاء الإشارات الموضعية حول إدخالات النص مباشرة إلى مصفوفة \\( QK^T \\) لطبقة الاهتمام الذاتي
- يجب تحفيز LLM لتعلم ترميزات موضعية ثابتة *نسبية* المسافة لبعضها البعض
- كلما ابتعدت رموز إدخال النص عن بعضها البعض، انخفض احتمال الاستعلام والقيمة. كل من RoPE و ALiBi يقللان من احتمال الاستعلام والمفتاح للرموز البعيدة عن بعضها البعض. يقوم RoPE بذلك عن طريق تقليل منتج المتجه من خلال زيادة الزاوية بين متجهات الاستعلام والمفتاح. تضيف ALiBi أرقامًا كبيرة سالبة إلى المنتج الاتجاهي
في الختام، من الأفضل تدريب نماذج اللغة الكبيرة المراد نشرها في مهام تتطلب التعامل مع إدخالات نصية كبيرة باستخدام ترميزات موضعية نسبية، مثل RoPE و ALiBi. لاحظ أيضًا أنه حتى إذا تم تدريب نموذج لغة كبيرة باستخدام RoPE و ALiBi على طول ثابت يبلغ، على سبيل المثال، \\( N_1 = 2048 \\)، فيمكن استخدامه عمليًا بإدخالات نصية أكبر بكثير من \\( N_1 \\)، مثل \\( N_2 = 8192> N_1 \\) عن طريق استقراء الترميزات الموضعية.
### 3.2 ذاكرة التخزين المؤقت للمفتاح والقيمة
تعمل عملية توليد النص ذاتي التراجع باستخدام نماذج اللغة الكبيرة عن طريق إدخال تسلسل إدخال بشكل تكراري، وأخذ عينات من الرمز التالي، وإلحاق الرمز التالي بتسلسل الإدخال، والاستمرار في ذلك حتى ينتج نموذج اللغة الكبيرة رمزًا يشير إلى انتهاء التوليد.
يرجى الاطلاع على [دليل إنشاء النص الخاص بـ Transformer](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/llm_tutorial#generate-text) للحصول على شرح مرئي أفضل لكيفية عمل التوليد ذاتي التراجع.
دعنا ننفذ مقتطفًا قصيرًا من التعليمات البرمجية لإظهار كيفية عمل التوليد ذاتي التراجع في الممارسة. ببساطة، سنأخذ الرمز الأكثر احتمالًا عبر `torch.argmax`.
كما نرى، في كل مرة نزيد من رموز إدخال النص بالرمز الذي تم أخذ عينات منه للتو.
باستثناءات قليلة جدًا، يتم تدريب نماذج اللغة الكبيرة باستخدام [هدف نمذجة اللغة السببية](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/tasks/language_modeling#causal-language-modeling) وبالتالي يتم قناع المثلث العلوي لمصفوفة نتيجة الاهتمام - وهذا هو السبب في ترك نتائج الاهتمام فارغة (*أي لها احتمال 0*) في المخططين أعلاه. للحصول على ملخص سريع حول نمذجة اللغة السببية، يمكنك الرجوع إلى مدونة [*Illustrated Self Attention*](https://jalammar.github.io/illustrated-gpt2/#part-2-illustrated-self-attention).
ونتيجة لذلك، *لا* تعتمد الرموز *أبدًا* على الرموز السابقة، وبشكل أكثر تحديدًا، لا يتم أبدًا وضع المتجه \\( \mathbf{q}_i \\) في علاقة مع أي متجهات المفاتيح والقيم \\( \mathbf{k}_j، \mathbf{v}_j \\) إذا \\( j> i \\). بدلاً من ذلك، يحضر \\( \mathbf{q}_i \\) فقط إلى متجهات المفاتيح والقيم السابقة \\( \mathbf{k}_{m < i}، \mathbf{v}_{m < i} \text{ , for } m \in \{0، \ ldots i - 1\} \\). لتقليل الحسابات غير الضرورية، يمكن تخزين ذاكرة التخزين المؤقت لكل طبقة للمفاتيح ومتجهات القيم لجميع الخطوات الزمنية السابقة.
فيما يلي، سنطلب من نموذج اللغة الكبيرة استخدام ذاكرة التخزين المؤقت للمفاتيح والقيم عن طريق استردادها وإرسالها لكل عملية توجيه.
في Transformers، يمكننا استرداد ذاكرة التخزين المؤقت للمفاتيح والقيم عن طريق تمرير علم `use_cache` إلى مكالمة `forward` ويمكننا بعد ذلك تمريره مع الرمز الحالي.
```python
past_key_values = None # past_key_values is the key-value cache
print("length of key-value cache", len(past_key_values[0][0])) # past_key_values are of shape [num_layers, 0 for k, 1 for v, batch_size, length, hidden_dim]
كما هو موضح، عند استخدام ذاكرة التخزين المؤقت للمفاتيح والقيم، لا يتم زيادة رموز إدخال النص في الطول، ولكنها تظل متجه إدخال واحدًا. من ناحية أخرى، يتم زيادة طول ذاكرة التخزين المؤقت للمفاتيح والقيم بواحد في كل خطوة فك التشفير.
> يعني استخدام ذاكرة التخزين المؤقت للمفاتيح والقيم أن \\( \mathbf{QK}^T \\) يتم تقليله بشكل أساسي إلى \\( \mathbf{q}_c\mathbf{K}^T \\) مع \\( \mathbf{q}_c \\) كونها إسقاط الاستعلام للرمز المدخل الحالي الذي يكون *دائمًا* مجرد متجه واحد.
- زيادة كبيرة في الكفاءة الحسابية حيث يتم إجراء حسابات أقل مقارنة بحساب مصفوفة \\( \mathbf{QK}^T \\) الكاملة. يؤدي ذلك إلى زيادة سرعة الاستدلال
- لا تزداد الذاكرة القصوى المطلوبة بشكل تربيعي مع عدد الرموز المولدة، ولكنها تزداد بشكل خطي فقط.
> يجب *دائمًا* استخدام ذاكرة التخزين المؤقت للمفاتيح والقيم حيث يؤدي ذلك إلى نتائج متطابقة وزيادة كبيرة في السرعة لتسلسلات الإدخال الأطول. ذاكرة التخزين المؤقت للمفاتيح والقيم ممكّنة بشكل افتراضي في Transformers عند استخدام خط أنابيب النص أو طريقة [`generate`](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main_classes/text_generation).
<Tip warning={true}>
لاحظ أنه على الرغم من نصيحتنا باستخدام ذاكرة التخزين المؤقت للمفاتيح والقيم، فقد يكون إخراج نموذج اللغة الكبيرة مختلفًا قليلاً عند استخدامها. هذه خاصية نوى ضرب المصفوفة نفسها - يمكنك قراءة المزيد عنها [هنا](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/issues/25420#issuecomment-1775317535).
</Tip>
#### 3.2.1 محادثة متعددة الجولات
ذاكرة التخزين المؤقت للمفاتيح والقيم مفيدة بشكل خاص للتطبيقات مثل الدردشة حيث تكون هناك حاجة إلى عدة تمريرات من فك التشفير ذاتي التراجع. دعنا نلقي نظرة على مثال.
```
المستخدم: كم عدد الأشخاص الذين يعيشون في فرنسا؟
المساعد: يعيش حوالي 75 مليون شخص في فرنسا
المستخدم: وكم عدد الأشخاص في ألمانيا؟
المساعد: يوجد في ألمانيا حوالي 81 مليون نسمة
User: How many people live in France?
Assistant: Roughly 75 million people live in France
User: And how many are in Germany?
Assistant: Germany has ca. 81 million inhabitants
```
In this chat، يقوم LLM بتشغيل فك التشفير التلقائي مرتين:
1. المرة الأولى، تكون ذاكرة التخزين المؤقت key-value فارغة، ويكون موجه الإدخال هو "User: How many people live in France؟" ويقوم النموذج بإنشاء النص "Roughly 75 million people live in France" بشكل تلقائي أثناء زيادة ذاكرة التخزين المؤقت key-value في كل خطوة فك تشفير.
2. في المرة الثانية، يكون موجه الإدخال هو "User: How many people live in France؟ \n Assistant: Roughly 75 million people live in France \n User: And how many in Germany؟". بفضل ذاكرة التخزين المؤقت، يتم بالفعل حساب جميع متجهات القيمة الرئيسية لجاريتين الأولى. لذلك يتكون موجه الإدخال فقط من "User: And how many in Germany؟". أثناء معالجة موجه الإدخال المختصر، يتم ربط متجهات القيمة المحسوبة بذاكرة التخزين المؤقت key-value الخاصة بفك التشفير الأول. يتم بعد ذلك إنشاء إجابة المساعد الثانية "Germany has ca. 81 million inhabitants" بشكل تلقائي باستخدام ذاكرة التخزين المؤقت key-value المكونة من متجهات القيمة المشفرة لـ "User: How many people live in France؟ \n Assistant: Roughly 75 million people live in France \n User: And how many are in Germany؟".
يجب ملاحظة أمرين هنا:
1. الحفاظ على كل السياق أمر بالغ الأهمية للنماذج اللغوية الكبيرة (LLMs) التي يتم نشرها في الدردشة بحيث يفهم LLM كل سياق المحادثة السابق. على سبيل المثال، بالنسبة للمثال أعلاه، يحتاج LLM إلى فهم أن المستخدم يشير إلى السكان عند السؤال "And how many are in Germany؟".
2. ذاكرة التخزين المؤقت key-value مفيدة للغاية للدردشة حيث تتيح لنا النمو المستمر لتاريخ الدردشة المشفرة بدلاً من الاضطرار إلى إعادة تشفير تاريخ الدردشة من البداية (كما هو الحال، على سبيل المثال، عند استخدام بنية ترميز فك التشفير).
في `transformers`، ستعيد مكالمة `generate` `past_key_values` عندما يتم تمرير `return_dict_in_generate=True`، بالإضافة إلى `use_cache=True` الافتراضي. لاحظ أنه غير متوفر بعد من خلال واجهة `pipeline`.
```python
# Generation as usual
prompt = system_prompt + "Question: Please write a function in Python that transforms bytes to Giga bytes.\n\nAnswer: Here"
هي نسخة معدلة من الدالة التي تعيد ميجا بايت بدلاً من ذلك.
def bytes_to_megabytes(bytes):
return bytes / 1024 / 1024
Answer: The function takes a number of bytes as input and returns the number of
```
رائع، لا يتم إنفاق وقت إضافي على إعادة حساب نفس المفتاح والقيم لطبقة الاهتمام! ومع ذلك، هناك شيء واحد يجب ملاحظته. في حين أن ذروة الذاكرة المطلوبة لمصفوفة \\( \mathbf{QK}^T \\) يتم تقليلها بشكل كبير، فإن الاحتفاظ بذاكرة التخزين المؤقت key-value في الذاكرة يمكن أن يصبح مكلفًا جدًا من حيث الذاكرة لسلاسل الإدخال الطويلة أو الدردشة متعددة الجولات. تذكر أن ذاكرة التخزين المؤقت key-value بحاجة إلى تخزين متجهات القيمة الرئيسية لجميع متجهات الإدخال السابقة \\( \mathbf{x}_i \text{، لـ } i \in \{1، \ ldots، c - 1\} \\) لجميع طبقات الاهتمام الذاتي وكل رؤوس الاهتمام.
دعنا نحسب عدد القيم العائمة التي يجب تخزينها في ذاكرة التخزين المؤقت key-value لنموذج LLM `bigcode/octocoder` الذي استخدمناه من قبل.
يبلغ عدد القيم العائمة ضعف طول التسلسل مضروبًا في عدد رؤوس الاهتمام مضروبًا في بعد رأس الاهتمام ومضروبًا في عدد الطبقات.
حساب هذا لنموذج LLM لدينا عند طول تسلسل افتراضي يبلغ 16000 يعطي:
Roughly 8 مليار قيمة عائمة! يتطلب تخزين 8 مليارات قيمة عائمة في دقة `float16` حوالي 15 جيجابايت من ذاكرة الوصول العشوائي (RAM) وهو ما يقرب من نصف حجم أوزان النموذج نفسها!
اقترح الباحثون طريقتين تسمحان بتقليل تكلفة الذاكرة لتخزين ذاكرة التخزين المؤقت key-value بشكل كبير، والتي يتم استكشافها في الأقسام الفرعية التالية.
#### 3.2.2 Multi-Query-Attention (MQA)
[Multi-Query-Attention](https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.02150) اقترحها Noam Shazeer في ورقته *Fast Transformer Decoding: One Write-Head is All You Need*. كما يقول العنوان، اكتشف Noam أنه بدلاً من استخدام `n_head` من أوزان إسقاط القيمة الرئيسية، يمكن استخدام زوج واحد من أوزان إسقاط رأس القيمة التي يتم مشاركتها عبر جميع رؤوس الاهتمام دون أن يتدهور أداء النموذج بشكل كبير.
> باستخدام زوج واحد من أوزان إسقاط رأس القيمة، يجب أن تكون متجهات القيمة الرئيسية \\( \mathbf{k}_i، \mathbf{v}_i \\) متطابقة عبر جميع رؤوس الاهتمام والتي بدورها تعني أننا بحاجة فقط إلى تخزين زوج إسقاط قيمة رئيسي واحد في ذاكرة التخزين المؤقت بدلاً من `n_head` منها.
نظرًا لأن معظم LLMs تستخدم ما بين 20 و100 رأس اهتمام، فإن MQA يقلل بشكل كبير من استهلاك الذاكرة لذاكرة التخزين المؤقت key-value. بالنسبة إلى LLM المستخدم في هذا الدفتر، يمكننا تقليل استهلاك الذاكرة المطلوبة من 15 جيجابايت إلى أقل من 400 ميجابايت عند طول تسلسل الإدخال 16000.
بالإضافة إلى توفير الذاكرة، يؤدي MQA أيضًا إلى تحسين الكفاءة الحسابية كما هو موضح في ما يلي.
في فك التشفير التلقائي، يجب إعادة تحميل متجهات القيمة الرئيسية الكبيرة، ودمجها مع زوج متجه القيمة الحالي، ثم إدخالها في \\( \mathbf{q}_c\mathbf{K}^T \\) الحساب في كل خطوة. بالنسبة لفك التشفير التلقائي، يمكن أن تصبح عرض النطاق الترددي للذاكرة المطلوبة لإعادة التحميل المستمر عنق زجاجة زمنيًا خطيرًا. من خلال تقليل حجم متجهات القيمة الرئيسية، يجب الوصول إلى ذاكرة أقل، وبالتالي تقليل عنق الزجاجة في عرض النطاق الترددي للذاكرة. لمزيد من التفاصيل، يرجى إلقاء نظرة على [ورقة Noam](https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.02150).
الجزء المهم الذي يجب فهمه هنا هو أن تقليل عدد رؤوس الاهتمام بالقيمة الرئيسية إلى 1 لا معنى له إلا إذا تم استخدام ذاكرة التخزين المؤقت للقيمة الرئيسية. يظل الاستهلاك الذروي لذاكرة النموذج لمرور واحد للأمام بدون ذاكرة التخزين المؤقت للقيمة الرئيسية دون تغيير لأن كل رأس اهتمام لا يزال لديه متجه استعلام فريد بحيث يكون لكل رأس اهتمام مصفوفة \\( \mathbf{QK}^T \\) مختلفة.
شهدت MQA اعتمادًا واسع النطاق من قبل المجتمع ويتم استخدامها الآن بواسطة العديد من LLMs الأكثر شهرة:
كما يستخدم نقطة التحقق المستخدمة في هذا الدفتر - `bigcode/octocoder` - MQA.
#### 3.2.3 مجموعة الاستعلام الاهتمام (GQA)
[مجموعة الاستعلام الاهتمام](https://arxiv.org/abs/2305.13245)، كما اقترح Ainslie et al. من Google، وجد أن استخدام MQA يمكن أن يؤدي غالبًا إلى تدهور الجودة مقارنة باستخدام إسقاطات رأس القيمة الرئيسية المتعددة. تجادل الورقة بأنه يمكن الحفاظ على أداء النموذج بشكل أكبر عن طريق تقليل عدد أوزان إسقاط رأس الاستعلام بشكل أقل حدة. بدلاً من استخدام وزن إسقاط قيمة رئيسية واحدة فقط، يجب استخدام `n <n_head` أوزان إسقاط قيمة رئيسية. من خلال اختيار `n` إلى قيمة أقل بكثير من `n_head`،مثل2أو4أو8،يمكنالاحتفاظبمعظممكاسبالذاكرةوالسرعةمنMQAمعالتضحيةبقدرأقلمنسعةالنموذجوبالتالي،منالمفترض،أقلأداء.
> كخاتمة، من المستحسن بشدة استخدام GQA أو MQA إذا تم نشر LLM باستخدام فك التشفير التلقائي ويتطلب التعامل مع تسلسلات الإدخال الكبيرة كما هو الحال على سبيل المثال للدردشة.
السببفيأنLLMsالضخمةمثلGPT3/4،وLlama-2-70b،وClaude،وPaLMيمكنأنتعملبسرعةكبيرةفيواجهاتالدردشةمثل [Hugging Face Chat](https://huggingface.co/chat/) أوChatGPTيرجعإلىحدكبيرإلىالتحسيناتالمذكورةأعلاهفيالدقةوالخوارزمياتوالهندسةالمعمارية.
لفهم تقنيات تحسين الأداء التي يمكن تطبيقها لتحسين كفاءة استخدام الذاكرة وسرعة تدريب النموذج، من المفيد التعرف على كيفية استخدام وحدة معالجة الرسوميات (GPU) أثناء التدريب، وكيف تختلف كثافة العمليات الحسابية باختلاف العملية التي يتم تنفيذها.
لنبدأ باستكشاف مثال توضيحي على استخدام وحدة GPU وتشغيل تدريب نموذج. وللتوضيح، سنحتاج إلى تثبيت بعض المكتبات:
تتيح مكتبة `nvidia-ml-py3` إمكانية مراقبة استخدام الذاكرة في النماذج من داخل بايثون. قد تكون على دراية بأمر `nvidia-smi` في الجهاز - تسمح هذه المكتبة بالوصول إلى نفس المعلومات مباشرة في بايثون.
ثم، نقوم بإنشاء بعض البيانات الوهمية:معرّفات رموز عشوائية بين 100 و30000 وتصنيفات ثنائية للمصنف.
في المجموع، نحصل على 512 تسلسلًا، لكل منها طول 512، ونخزنها في [`~datasets.Dataset`] بتنسيق PyTorch.
يبدو ذلك جيدًا: لم يتم شغل ذاكرة وحدة معالجة الرسومات كما نتوقع قبل تحميل أي نماذج. إذا لم يكن الأمر كذلك على جهازك، فتأكد من إيقاف جميع العمليات التي تستخدم ذاكرة وحدة GPU. ومع ذلك، لا يمكن للمستخدم استخدام كل ذاكرة وحدة GPU الفارغة. عندما يتم تحميل نموذج إلى وحدة GPU، يتم أيضًا تحميل النواة، والتي يمكن أن تستهلك 1-2 جيجابايت من الذاكرة. ولرؤية مقدار ذلك، نقوم بتحميل مصفوفة صغيرة إلى وحدة GPU والتي تؤدي إلى تحميل النواة أيضًا.
```py
>>>importtorch
>>>torch.ones((1,1)).to("cuda")
>>>print_gpu_utilization()
GPUmemoryoccupied:1343MB.
```
نلاحظ أن النواة وحدها تستهلك 1.3 جيجابايت من ذاكرة وحدة GPU. الآن دعنا نرى مقدار المساحة التي يستخدمها النموذج.
## تحميل النموذج
أولاً، نقوم بتحميل نموذج `google-bert/bert-large-uncased`. نقوم بتحميل أوزان النموذج مباشرة إلى وحدة GPU حتى نتمكن من التحقق من مقدار المساحة التي تستخدمها الأوزان فقط.
يمكننا أن نرى أن أوزان النموذج وحدها تستهلك 1.3 جيجابايت من ذاكرة وحدة GPU. يعتمد الرقم الدقيق على وحدة GPU المحددة التي تستخدمها. لاحظ أنه في وحدات GPU الأحدث، قد يستغرق النموذج في بعض الأحيان مساحة أكبر نظرًا لأن الأوزان يتم تحميلها بطريقة مُحسّنة تُسرّع من استخدام النموذج. الآن يمكننا أيضًا التحقق بسرعة مما إذا كنا نحصل على نفس النتيجة كما هو الحال مع `nvidia-smi` CLI:
نحصل على نفس الرقم كما كان من قبل، ويمكنك أيضًا أن ترى أننا نستخدم GPU من طراز V100 مع 16 جيجابايت من الذاكرة. لذا الآن يمكننا بدء تدريب النموذج ورؤية كيف يتغير استخدام ذاكرة GPU. أولاً، نقوم بإعداد بعض معاملات التدريب القياسية:
```py
default_args={
"output_dir":"tmp"،
"eval_strategy":"steps"،
"num_train_epochs":1،
"log_level":"error"،
"report_to":"none"،
}
```
<Tip>
إذا كنت تخطط لتشغيل عدة تجارب، من أجل مسح الذاكرة بشكل صحيح بين التجارب، قم بإعادة تشغيل نواة Python بين التجارب.
</Tip>
## استخدام الذاكرة في التدريب الأساسي
دعونا نستخدم [`Trainer`] وقم بتدريب النموذج دون استخدام أي تقنيات تحسين أداء GPU وحجم دفعة يبلغ 4:
يمكننا أن نرى أن حجم دفعة صغير نسبيًا يملأ تقريبًا ذاكرة GPU بالكامل. ومع ذلك، غالبًا ما يؤدي حجم دفعة أكبر في تقارب نموذج أسرع أو أداء أفضل في النهاية. لذلك نريد أن نضبط حجم الدفعة وفقًا لاحتياجات النموذج لدينا وليس مع قيود وحدة GPU. ما يثير الاهتمام هو أننا نستخدم ذاكرة أكثر بكثير من حجم النموذج.
لفهم سبب ذلك بشكل أفضل، دعنا نلقي نظرة على عمليات النموذج واحتياجاته من الذاكرة.
## تشريح عمليات النموذج
تتضمن بنية المحولات 3 مجموعات رئيسية من العمليات مُجمعة أدناه حسب كثافة العمليات الحسابية.
1.**عمليات ضرب المصفوفات**
تقوم الطبقات الخطية ومكونات الانتباه متعدد الرؤوس جميعها بعمليات ضرب ** المصفوفة بالمصفوفة** على دفعات. هذه العمليات هي أكثر أجزاء تدريب المحولات كثافة من الناحية الحسابية.
2.**عمليات التسوية الإحصائية**
تُعد عمليات Softmax والتسوية الطبقية أقل كثافة من ناحية الحسابية من عمليات ضرب المصفوفات، وتنطوي على عملية أو أكثر من عمليات **الاختزال**، والتي يتم تطبيق نتيجتها بعد ذلك عبر خريطة.
3.**العمليات على مستوى العناصر**
هذه هي العمليات المتبقية: **الانحيازات، والتسرب، ووظائف التنشيط، والوصلات المتبقية**. هذه هي عمليات أقل كثافة من الناحية الحسابية.
يمكن أن تكون هذه المعرفة مفيدة لمعرفة عند تحليل اختناقات الأداء.
هذا الملخص مُشتق من [نقل البيانات هو كل ما تحتاجه: دراسة حالة حول تحسين المحولات 2020](https://arxiv.org/abs/2007.00072)
## تشريح ذاكرة النموذج
لقد رأينا أن تدريب النموذج يستخدم ذاكرة أكثر بكثير من مجرد وضع النموذج على GPU. ويرجع ذلك إلى
هناك العديد من المكونات أثناء التدريب التي تستخدم ذاكرة GPU. المكونات الموجودة في ذاكرة GPU هي التالية:
يتطلب نموذج نموذجي مدرب بدقة مختلطة 18 بايت للمُحسّن AdamW كل معلمة نموذج بالإضافة إلى ذاكرة التنشيط. للاستدلال لا توجد حالات مُحسّن و مُتدرجات، لذلك يمكننا طرح تلك. وهكذا ننتهي مع 6 بايت لكل
معلمة نموذج للدقة المختلطة الاستدلال، بالإضافة إلى ذاكرة التنشيط.
دعنا نلقي نظرة على التفاصيل.
**أوزان النموذج:**
- 4 بايت * عدد المعلمات للتدريب على دقة fp32
- 6 بايت * عدد المعلمات لتدريب الدقة المختلطة (يحافظ على نموذج في fp32 وآخر بدقة fp16 في الذاكرة)
**حالات المُحسّن:**
- 8 بايت * عدد المعلمات للمُحسّن AdamW العادي (يحافظ على حالتين)
- 2 بايت * عدد المعلمات لمُحسّنات 8 بت AdamW مثل [bitsandbytes](https://github.com/TimDettmers/bitsandbytes)
- 4 بايت * عدد المعلمات لمُحسّنات مثل SGD مع الزخم momentum (يحافظ على حالة واحدة فقط)
**المُتدرجات**
- 4 بايت * عدد المعلمات للتدريب بدقة fp32 أو بدقة مختلطة (المُتدرجات تكون دائمًا بدقة fp32)
**تنشيطات المسار الأمامي**
- يعتمد الحجم على العديد من العوامل، وأهمها طول التسلسل وحجم المخفية وحجم الدُفعة.
هناك المدخلات والمخرجات لذي يتم تمريرها وإرجاعها بواسطة وظائف المسار الأمامي والمسار الخلفي وتنشيطات المسار الأمامي المحفوظة لحساب المُتدرجات.
**الذاكرة المؤقتة**
بالإضافة إلى ذلك، هناك جميع أنواع المتغيرات المؤقتة التي يتم تحريرها بمجرد الانتهاء من الحساب، ولكن في
لحظة يمكن أن تتطلب هذه المتغيرات المؤقتة ذاكرة إضافية ويقد تؤدي إلى نفاد الذاكرة المُخصصة (OOM). لذلك، عند البرمجة، من المهم التفكير بشكل استراتيجي حول هذه المتغيرات المؤقتة وأحيانًا تحريرها بشكل صريح بمجرد عدم الحاجة إليها.
**ذاكرة محددة الوظائف**
ثم، قد يكون لبرنامجك احتياجات خاصة بالذاكرة. على سبيل المثال، عند إنشاء نص باستخدام البحث الشعاعي، يحتاج البرنامج
إلى الاحتفاظ بنسخ متعددة من المدخلات والمخرجات.
**سرعة تنفيذ `forward` مقابل `backward`**
بالنسبة للالتفافات والطبقات الخطية، هناك ضِعف عدد العمليات 2x flops في المسار الخلفى مقارنة بالمسار الأمامي، والتي يُترجم عمومًا إلى ~2x أبطأ (أحيانًا أكثر، لأن الأحجام في المسار الخلفى تميل إلى أن تكون أكثر صعوبة). عادةً ما تكون عمليات التنشيط محدودة بعرض النطاق الترددي، ومن المعتاد أن يتعين على التنشيط قراءة المزيد من البيانات في المسار الخلفى أكثر من المسار الأمامى.
(على سبيل المثال، قراءة التنشيط المسار الأمامى مرة واحدة، وتكتب مرة واحدة، وبينما تقرأ عملية التنشيط الخلفي مرتين، gradOutput وإخراج الأمام، وتكتب مرة واحدة، gradInput).
كما ترى، هناك بضعة أماكن يمكننا فيها توفير ذاكرة GPU أو تسريع العمليات.
الآن بعد أن فهمت ما يؤثر على استخدام GPU وسرعة الحساب، راجع
صفحة وثائق [أساليب وأدوات التدريب الفعال على GPU واحد](perf_train_gpu_one) لمعرفة المزيد حول تقنيات تحسين الأداء.
أظهرت آخر درسين تعليميين كيفية ضبط نموذج بدقة باستخدام PyTorch و Keras و 🤗 Accelerate لعمليات التهيئة الموزعة. والخطوة التالية هي مشاركة نموذجك مع المجتمع! في Hugging Face، نؤمن بالمشاركة المفتوحة للمعرفة والموارد لتمكين الجميع من الاستفادة من الذكاء الاصطناعي. ونشجعك على مشاركة نموذجك مع المجتمع لمساعدة الآخرين على توفير الوقت والموارد.
في هذا الدرس، ستتعلم طريقتين لمشاركة نموذجك المدرب أو مضبوط على منصة [Model Hub](https://huggingface.co/models):
- رفع ملفاتك إلى منصة Hub مباشرة باستخدام الكود البرمجي.
- قم بسحب وإفلات ملفاتك إلى Hub باستخدام الواجهة web.
لمشاركة نموذج مع المجتمع، تحتاج إلى حساب على [huggingface.co](https://huggingface.co/join). يمكنك أيضًا الانضمام إلى منظمة موجودة أو إنشاء منظمة جديدة.
</Tip>
## ميزات المستودع
يعمل كل مستودع على Model Hub مثل مستودع GitHub النتقليدي. تقدم مستودعاتنا التحكم في الإصدارات وسجل التغييرات، وقدرة على رؤية الاختلافات بين الإصدارات.
تعتمد آلية التحكم في الإصدارات على منصة Model Hub على نظامي git و [git-lfs](https://git-lfs.github.com/). وبعبارة أخرى، يمكنك التعامل مع كل نموذج كأنه مستودع مستقل، مما يمكّن من زيادة التحكم في الوصول والقابلية للتطوير. يسمح التحكم في الإصدار بإجراء تعديلات وتثبيت إصدار محدد من النموذج باستخدام رمز التغيير (commit hash) أو وسم (tag) أو فرع (branch).
بفضل هذه الميزة، يمكنك تحميل إصدار محدد من النموذج باستخدام معلمة الإصدار "revision":
```py
>>>model=AutoModel.from_pretrained(
..."julien-c/EsperBERTo-small",revision="4c77982"# اسم العلامة، أو اسم الفرع، أو تجزئة الالتزام
...)
```
من السهل أيضًا تعديل الملفات الموجودة داخل مستودع، ويمكنك عرض سجل التغييرات التي طرأت على هذه الملفات ومعاينة الاختلافات بين الإصدارات المختلفة:
قبل مشاركة نموذج على Hub، ستحتاج إلى بيانات اعتماد حساب Hugging Face الخاصة بك. إذا كنت تستخدم منصة الأوامر، فقم بتشغيل الأمر التالي في بيئة افتراضية حيث تم تثبيت 🤗 Transformers. سيقوم هذا الأمر بتخزين رمز الدخول الخاص بك في مجلد تخزين المؤقت لـ Hugging Face (`~/.cache/` بشكل افتراضي):
```bash
huggingface-cli login
```
إذا كنت تستخدم دفتر ملاحظات مثل Jupyter أو Colaboratory، فتأكد من تثبيت مكتبة [`huggingface_hub`](https://huggingface.co/docs/hub/adding-a-library). تسمح لك هذه المكتبة بالتفاعل برمجيًا مع Hub.
```bash
pip install huggingface_hub
```
ثم استخدم `notebook_login` لتسجيل الدخول إلى Hub، واتبع الرابط [هنا](https://huggingface.co/settings/token) لإنشاء رمز للتسجيل:
```py
>>>fromhuggingface_hubimportnotebook_login
>>>notebook_login()
```
## تحويل النموذج ليتوافق مع جميع الأطر العمل
لضمان إمكانية استخدام نموذجك من قبل شخص يعمل بإطار عمل مختلف، نوصي بتحويل نموذجك ورفعه مع نقاط التحقق من PyTorch و TensorFlow. في حين أن المستخدمين لا يزال بإمكانهم تحميل نموذجك من إطار عمل مختلف إذا تخطيت هذه الخطوة، إلا أنه سيكون أبطأ لأن 🤗 Transformers ستحتاج إلى تحويل نقطة التحقق أثناء التشغيل.
تحويل نقطة التحقق لإطار عمل آخر أمر سهل. تأكد من تثبيت PyTorch و TensorFlow (راجع [هنا](installation) لتعليمات التثبيت)، ثم ابحث عن النموذج الملائم لمهمتك في الإطار الآخر.
<frameworkcontent>
<pt>
حدد `from_tf=True` لتحويل نقطة تحقق من TensorFlow إلى PyTorch:
مشاركة نموذجك على Hub مر بسيط للغاية كل ما عليك هو إضافة معلمة أو استدعاء رد إضافي. كما تذكر من درس [التدريب الدقيق](training)، فإن فئة [`TrainingArguments`] هي المكان الذي تحدد فيه المعلمات الفائقة وخيارات التدريب الإضافية. تشمل إحدى خيارات التدريب هذه القدرة على دفع النموذج مباشرة إلى المنصة Hub. قم بتعيين `push_to_hub=True` في [`TrainingArguments`]:
بعد ضبط نموذجك بدقة، يمكنك استخدام دالة [`~transformers.Trainer.push_to_hub`] المتاحة في [`Trainer`] لدفع النموذج المدرب إلى المنصة Hub. سوف تضيف 🤗 Transformers تلقائيًا المعلمات الفائقة المستخدمة في التدريب ونتائج التدريب وإصدارات الإطار إلى بطاقة معلومات النموذج الخاصة بك!
```py
>>>trainer.push_to_hub()
```
</pt>
<tf>
شارك نموذجًا على Hub باستخدام [`PushToHubCallback`]. في دالة [`PushToHubCallback`], أضف:
- دليل إخراج لنموذجك.
- مُجزّئ اللغوي.
-`hub_model_id`، والذي هو اسم مستخدم Hub واسم النموذج الخاص بك.
يمكن أيضًا استخدام دالة `push_to_hub` لإضافة ملفات أخرى إلى مستودع النماذج. على سبيل المثال، أضف رموزًا إلى مستودع نموذج:
```py
>>>tokenizer.push_to_hub("my-awesome-model")
```
أو ربما تريد إضافة إصدار TensorFlow من نموذج PyTorch المضبوط:
```py
>>>tf_model.push_to_hub("my-awesome-model")
```
الآن عند الانتقال إلى ملفك الشخصي على Hugging Face، يجب أن ترى مستودع النماذج الذي أنشأته حديثًا. سيؤدي النقر فوق علامة التبويب **Files** إلى عرض جميع الملفات التي قمت بتحميلها في المستودع.
للحصول على مزيد من التفاصيل حول كيفية إنشاء الملفات وتحميلها إلى مستودع، راجع وثائق Hub [هنا](https://huggingface.co/docs/hub/how-to-upstream).
## التحميل باستخدام الواجهة web
يمكن للمستخدمين الذين يفضلون نهج عدم الترميز تحميل نموذج من خلال واجهة Hub web. قم بزيارة [huggingface.co/new](https://huggingface.co/new) لإنشاء مستودع جديد:
للتأكد من فهم المستخدمين لقدرات نموذجك وقيوده وتحيزاته المحتملة واعتباراته الأخلاقية، يرجى إضافة بطاقة نموذج إلى مستودعك. يتم تعريف بطاقة النموذج في ملف `README.md`. يمكنك إضافة بطاقة نموذج عن طريق:
* قم بإنشاء ملف `README.md` وتحميله يدويًا.
* انقر فوق الزر **Edit model card** في مستودع نموذجك.
الق نظرة على بطاقة [DistilBert](https://huggingface.co/distilbert/distilbert-base-uncased) للحصول على مثال جيد على نوع المعلومات التي يجب أن تتضمنها بطاقة النموذج. للحصول على مزيد من التفاصيل حول الخيارات الأخرى التي يمكنك التحكم فيها في ملف `README.md` مثل البصمة الكربونية للنموذج أو أمثلة الأداة، راجع الوثائق [هنا](https://huggingface.co/docs/hub/models-cards).
منذ إطلاقه في عام 2017، ألهم نموذج [المحول الأصلي](https://arxiv.org/abs/1706.03762) (راجع مدونة [المحول المشروح](http://nlp.seas.harvard.edu/2018/04/03/attention.html) لمقدمة تقنية مبسطة)، ألهم العديد من النماذج الجديدة والمبتكرة التي تتجاوز مهام معالجة اللغات الطبيعية (NLP). هناك نماذج للتنبؤ [بالبنية البروتينات المطوية](https://huggingface.co/blog/deep-learning-with-proteins)، و[تدريب على اتخاذ القرار](https://huggingface.co/blog/train-decision-transformers)، و[التنبؤ بالسلاسل الزمنية](https://huggingface.co/blog/time-series-transformers). مع وجود العديد من متغيرات المحول المتاحة، قد يكون من السهل أن تفوتك الصورة الأكبر. ما تشترك فيه جميع هذه النماذج هو أنها تستند إلى بنية المحول الأصلية. تستخدم بعض النماذج فقط الترميز أو فك الترميز، بينما تستخدم نماذج أخرى كليهما. يوفر هذا تصنيفًا مفيدًا لتصنيف واستعراض الفروقات الرئيسية بين نماذج عائلة المحولات، وسيساعدك على فهم النماذج التي لم تصادفها من قبل.
إذا لم تكن على دراية بنموذج المحول الأصلي أو تحتاج إلى تذكير، فراجع الفصل الخاص بـ [كيف تعمل المحولات](https://huggingface.co/course/chapter1/4؟fw=pt) من دورة Hugging Face.
<divalign="center">
<iframewidth="560"height="315"src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/H39Z_720T5s"title="مشغل فيديو YouTube"frameborder="0"allow="accelerometer؛ تشغيل تلقائي؛ قائمة تشغيل مدمجة؛ محسّنات الفيديو؛ ميزة الإشارات المرجعية"allowfullscreen></iframe>
لطالما كانت الشبكات التلافيفية (CNNs) الطريقة السائدة لمهام رؤية الحاسب حتى برز [محول الرؤية](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11929) قابليته للتطوير وكفاءته العالية. وحتى بعد ذلك، لا تزال بعض أفضل صفات CNN، مثل ثبات الإزاحة، قوية جدًا (خاصة بالنسبة لمهام معينة) لدرجة أن بعض المحولات تدمج التلافيف في بنيتها. قلب [ConvNeXt](model_doc/convnext) هذا التبادل رأسًا على عقب وأدرج خيارات التصميم من المحولات لتحديث CNN. على سبيل المثال، يستخدم ConvNeXt نوافذ منزلقة غير متداخلة لتقسيم الصورة إلى رقع وزيادة حقل مجال العام الخاص بها. كما يقوم ConvNeXt بعدة خيارات مثل تصميم الطبقة لتكون أكثر كفاءة في الذاكرة وتحسين الأداء، مما يجعله منافسًا قويًا للمحولات!
### الترميز[[cv-encoder]] (Encoder)
فتح [محول الرؤية (ViT)](model_doc/vit) الباب أمام مهام رؤية الحاسب دون الاعتماد على التلافيف. يستخدم ViT ترميز محول قياسي، لكن إنجازه الرئيسي كان طريقة معالجته للصورة. فهو تقسّم الصورة إلى رقّعات ذات حجم ثابت ويستخدمها لإنشاء تضمين، تمامًا مثل تقسيم الجملة إلى رموز. استفاد ViT من بنية المُحوِّلات الفعالة لإظهار نتائج تنافسية مع CNNs في ذلك الوقت مع الحاجة إلى موارد أقل للتدريب. وسرعان ما تبع ViT نماذج رؤية أخرى يمكنها أيضًا التعامل مع مهام الرؤية الكثيفة مثل التجزئة والتعرف.
من بين هذه النماذج [Swin](model_doc/swin) Transformer. فهو يبني خرائط سمات هرمية (مثل CNN 👀 على عكس ViT) من رقّعات أصغر حجمًا ودمجها مع الرقع المجاورة في طبقات أعمق. يتم حساب الانتباه فقط ضمن نافذة محلية، ويتم تحويل النافذة بين طبقات الانتباه لإنشاء اتصالات تساعد النموذج على التعلم بشكل أفضل. نظرًا لأن محول Swin يمكنه إنتاج خرائط خصائص هرمية، فهو مرشح جيد لمهام التنبؤ الكثيفة مثل التجزئة والتعرف. كما يستخدم [SegFormer](model_doc/segformer) ترميز محول لبناء خرائط خصائص هرمية، ولكنه يضيف فك تشفير بسيط متعدد الطبقات (MLP) في الأعلى لدمج جميع خرائط الخصائص وإجراء تنبؤ.
استلهمت نماذج الرؤية الأخرى، مثل BeIT وViTMAE، الإلهام من هدف التدريب المسبق لـ BERT. يتم تدريب [BeIT](model_doc/beit) مسبقًا من خلال *نمذجة الصور المقنعة (MIM)*؛ يتم إخفاء رقّعات الصور بشكل عشوائي، كما يتم تحويل الصورة إلى رموز بصرية. يتم تدريب BeIT للتنبؤ بالرموز البصرية المُناظرة للرقع المخفية. لدى [ViTMAE](model_doc/vitmae) هدف تدريب مسبق مُماثل، باستثناء أنه يجب عليه التنبؤ بالبكسلات بدلاً من الرموز البصرية. ما هو غير عادي هو أن إخفاء 75% من رقع الصور! يقوم فك التشفير بإعادة بناء البكسلات من الرموز المخفية والرقّعات المشفرة. بعد التدريب المسبق، يتم التخلص من فك التشفير، ويصبح الترميز جاهزًا للاستخدام في مهام التالية.
### فك التشفير[[cv-decoder]] (Decoder)
نادرًا ما تستخدم نماذج الرؤية التي تعتمد على فك التشفير فقط لأن معظم نماذج الرؤية تعتمد على الترميز لتعلم تمثيل الصورة. ولكن بالنسبة للاستخدامات مثل توليد الصور، يعد فك التشفير مناسبًا بشكل طبيعي، كما رأينا من نماذج توليد النصوص مثل GPT-2. يستخدم نموذج [ImageGPT](model_doc/imagegpt) نفس بنية GPT-2، ولكنه بدلاً من التنبؤ بالرمز التالي في تسلسل، فإنه يتنبأ بالبكسل التالي في صورة. بالإضافة إلى توليد الصور، يمكن أيضًا ضبط ImageGPT بدقة لتصنيف الصور.
تستخدم نماذج الرؤية بشكل شائع ترميزًا (يُعرف أيضًا باسم العمود الفقري) لاستخراج ميزات الصورة المهمة قبل تمريرها إلى فك التشفير لنموذج المُحوّل. يستخدم [DETR](model_doc/detr) عمودًا فقريًا مُدربًا مسبقًا، ولكنه يستخدم أيضًا الببنية الكاملة للترميز وفك تشفير لنموذج المحول للكشف عن الأشياء. يتعلم الترميز تمثيلات الصور ويجمعها مع استعلامات الكائنات (كل استعلام كائن هو تضمين مُتعلم يركز على منطقة أو كائن في صورة) في فك التشفير. يتنبأ DETR بإحداثيات مربع الحدود وتسمية الفئة لكل استعلام كائن.
## معالجة اللغات الطبيعية (Natural language processing - NLP)
نموذج [BERT](model_doc/bert) هو محوّل (Transformer) يعتمد على الترميز فقط يقوم بشكل عشوائي بإخفاء رموز معينة في المدخلات لتجنب رؤية باقى الرموز الأخرى، مما يسمح له "بالغش". يتمثل هدف التدريب المسبق في التنبؤ بالرمز المخفي بناءً على السياق. يسمح هذا لـ BERT باستخدام السياقات اليمنى واليسرى بالكامل لمساعدته في تعلم تمثيل أعمق وأغنى للبيانات المدخلة. ومع ذلك، كان هناك مجال للتحسين في استراتيجية التدريب المسبق لـ BERT. نموذج [RoBERTa](model_doc/roberta) اضاف تحسين من خلال تقديم وصفة تدريب مسبق جديدة تشمل التدريب لفترة أطول وعلى دفعات أكبر، وإخفاء الرموز عشوائيًا في كل حقبة بدلاً من مرة واحدة فقط أثناء المعالجة المسبقة، وإزالة هدف التنبؤ بالجملة التالية.
تتمثل الاستراتيجية السائدة لتحسين الأداء في زيادة حجم النموذج. ولكن تدريب النماذج الكبيرة مكلف من الناحية الحسابية. إحدى طرق تقليل التكاليف الحسابية هي استخدام نموذج أصغر مثل [DistilBERT](model_doc/distilbert). يستخدم DistilBERT [ تقنية تقطير المعرفة](https://arxiv.org/abs/1503.02531) - وهي تقنية ضغط - لإنشاء نموذج أصغر من BERT مع الحفاظ على معظم قدراته على فهم اللغةا.
مرت معظم نماذج المحول في الاتجاه نحو المزيد من المعلمات، مما أدى إلى ظهور نماذج جديدة تركز على تحسين كفاءة التدريب. يقلّل [ALBERT](model_doc/albert) من استهلاك الذاكرة عن طريق تقليل عدد المعلمات بطريقتين: فصل تضمين المفردات الأكبر إلى مصفوفتين أصغر والسماح للمستويات بمشاركة المعلمات. أضاف [DeBERTa](model_doc/deberta) آلية انتباه منفصلة حيث يتم ترميز الكلمة وموضعها بشكل منفصل في متجهين. يتم حساب الانتباه من هذه المتجهات المنفصلة بدلاً من متجه واحد يحتوي على تضمين الكلمة والموقع. ركز [Longformer](model_doc/longformer) أيضًا على جعل الانتباه أكثر كفاءة، خاصة لمعالجة المستندات ذات تسلسلات أطولل. فهو يستخدم مزيجًا من انتباه النوافذ المحلية (يتم حساب الانتباه فقط ن نافذة ذات حجم ثابت حول كل رمز) والانتباه العام (فقط لرموز مهمة محددة مثل `[CLS]` للتصنيف) لإنشاء مصفوفة انتباه متفرقة بدلاً من مصفوفة انتباه كاملة.
### فك التشفير[[nlp-decoder]]
نموذج [GPT-2](model_doc/gpt2) هو محول فك تشفير فقط يتنبأ بالكلمة التالية في التسلسل. إنه يخفي الرموز التالية الموجودة على اليمين حتى لا يتمكن النموذج من "الغش" بالنظر إليها. من خلال التدريب المسبق على كميات هائلة من النصوص، أصبح [GPT-2](model_doc/gpt2) بارعًا في توليد النصوص، حتى لو لم تكن النص دقيقًا أو صحيحًا في بعض الأحيان فقط. ولكن كان يفتقر إلى سياق لترابط المتبادل (bidirectional context) الموجود من التدريب المسبق لـ [BERT](model_doc/bert) ، مما جعله غير مناسب لمهام معينة. يجمع [XLNET](model_doc/xlnet) بين أفضل ما في أهداف التدريب المسبق لـ [BERT](model_doc/bert) و [GPT-2](model_doc/gpt2) من خلال اعتماد نهج النمذجة اللغوية باستخدام التباديل (Permutation Language Modeling - PLM) الذي يسمح له بتعلم الترابط ثنائي الاتجاه.
بعد ظهور [GPT-2](model_doc/gpt2)، تطورت النماذج اللغوية بشكل أكبر حجمًا وأكثر تعقيدًا وأصبحت تُعرف الآن باسم *نماذج اللغة الكبيرة (LLMs)*. توضح LLMs مهارات تعلم قليلة الكمية أو حتى معدومة إذا تم تدريبها على مجموعة بيانات كبيرة بما يكفي. [GPT-J](model_doc/gptj) هو LLM به 6 مليارات معلمة مدربة على 400 مليار رمز. تبعه نموذج [OPT](model_doc/opt)، وهي عائلة من نماذج فك التشفير فقط، أكبرها 175 مليار معلمة ودُرب على 180 مليار رمز. تم إصدار [BLOOM](model_doc/bloom) في نفس الوقت تقريبًا، ويحتوي أكبر نموذج في العائلة على 176 مليار معلمة ودُرب على 366 مليار رمز في 46 لغة و13 لغة برمجة.
### الترميز وفك التشفير[[nlp-encoder-decoder]]
يحتفظ [BART](model_doc/bart) ببنية المحول الأصلية، ولكنه يعدّل هدف التدريب المسبق باستخدام إفساد *إدخال النصوص*، حيث يتم استبدال بعض نطاقات النص برمز `mask` واحد. يتنبأ فك التشفير بالرموز غير الفاسدة (يتم إخفاء الرموز المستقبلية) ويستخدم حالات الترميز المخفية للمساعدة. [Pegasus](model_doc/pegasus) مشابه لـ BART، ولكن Pegasus يقوم بإخفاء جمل كاملة بدلاً من مقاطع النص. بالإضافة إلى نمذجة اللغة المقنعة، يتم تدريب Pegasus مسبقًا بواسطة توليد الجمل الفارغة (GSG). يقوم هدف GSG بإخفاء الجمل الكاملة المهمة للمستند، واستبدالها برمز `mask`. يجب على فك التشفير توليد المخرجات من الجمل المتبقية. [T5](model_doc/t5) هو نموذج فريد من نوعه يحوّل جميع مهام معالجة اللغة الطبيعية إلى مشكلة نص إلى نص باستخدام بادئات محددة. على سبيل المثال، يشير البادئة `Summarize:` إلى مهمة تلخيص. يتم تدريب T5 مسبقًا بواسطة التدريب الخاضع للإشراف (GLUE وSuperGLUE) والتدريب ذاتي الإشراف (اختيار عينة عشوائية وحذف 15% من الرموز).
يستخدم [Wav2Vec2](model_doc/wav2vec2) ترميز من نوع المحوّل لتعلم تمثيلات الكلام بشكلٍ مباشر من موجات الصوت الخام. يتم تدريبه مسبقًا باستخدام مهمة تباينية لتحديد تمثيل الكلام الصحيح من مجموعة من التمثيلات الخاطئة. [HuBERT](model_doc/hubert) مشابه لـ Wav2Vec2 ولكنه له عملية تدريب مختلفة. يتم إنشاء تسميات الهدف عن طريق خطوة تجميع يتم فيها ت تخصيص مقاطع الصوت المتشابهة إلى مجموعات، تُصبح كل واحدة منها وحدةً خفية. ويتم تعيين الوحدة الخفية إلى تمثيل لإجراء تنبؤ.
### الترميز وفك التشفير[[audio-encoder-decoder]]
[Speech2Text](model_doc/speech_to_text) هو نموذج كلام مصمم للتعرف التلقائي على الكلام (ASR) وترجمة الكلام. يقبل النموذج ميزات بنك المرشح اللغوي التي تم استخراجها من شكل موجة الصوت وتم تدريبه مسبقًا بطريقة ذاتية التعلم لتوليد نسخة أو ترجمة. [Whisper](model_doc/whisper) هو أيضًا نموذج ASR، ولكنه على عكس العديد من نماذج الكلام الأخرى، يتم تدريبه مسبقًا على كمية كبيرة من بيانات نسخ النص الصوتي ✨ المسماة ✨ لتحقيق الأداء الصفري. يحتوي جزء كبير من مجموعة البيانات أيضًا على لغات غير اللغة الإنجليزية، مما يعني أنه يمكن استخدام Whisper أيضًا للغات منخفضة الموارد. من الناحية الهيكلية، يشبه Whisper نموذج Speech2Text. يتم تحويل إشارة الصوت إلى طيف لوجاريتم مل-ميل يتم تشفيره بواسطة الترميز. يقوم فك التشفير بتوليد النسخة بطريقة ذاتية التعلم من حالات الترميز المخفية والرموز السابقة.
نموذج [VisualBERT](model_doc/visual_bert) هو نموذج متعدد الوسائط لمهام الرؤية اللغوية تم إصداره بعد فترة وجيزة من BERT. فهو يجمع بين BERT ونظام اكتشاف كائن مسبق التدريب لاستخراج ميزات الصورة في تضمينات بصرية، يتم تمريرها جنبًا إلى جنب مع التضمينات النصية إلى BERT. يتنبأ VisualBERT بالنص المقنع بناءً على النص غير المقنع والتضمينات المرئية، ويجب عليه أيضًا التنبؤ بما إذا كان النص متوافقًا مع الصورة. عندما تم إصدار ViT، اعتمد [ViLT](model_doc/vilt) ViT في بنيتها لأنه كان من الأسهل الحصول على تضمينات الصورة بهذه الطريقة. يتم معالجة تضمينات الصورة بشكل مشترك مع التضمينات النصية. ومن هناك، يتم التدريب المسبق لـ ViLT بواسطة مطابقة الصورة النصية، ونمذجة اللغة المقنعة، وإخفاء كلمة كاملة.
يتّبع [CLIP](model_doc/clip) نهجًا مختلفًا ويقوم بتنبؤ ثنائي من ("الصورة"، "النص"). يتم تدريب مشفر صورة (ViT) ومشفر نص (Transformer) بشكل مشترك على مجموعة بيانات مكونة من 400 مليون ثنائي من ("صورة"، "نص") لتعظيم التشابه بين متجهات ترميز الصورة ومتجهات النص ثنائي ("الصورة"، "النص"). بعد التدريب المسبق، يمكنك استخدام اللغة الطبيعية لتوجيه CLIP للتنبؤ بالنص المُعطى بناءً على صورة أو العكس بالعكس. [OWL-ViT](model_doc/owlvit) يبني على CLIP باستخدامه كعمود فقري للكشف عن الكائنات بدون إشراف. بعد التدريب المسبق، يتم إضافة رأس كشف الأجسام لإجراء تنبؤ بمجموعة مُحدّد عبر ثنائيات ("class"، "bounding box").
### Encoder-decoder[[mm-encoder-decoder]]
التعرّف البصري على الحروف (OCR) مهمة قديمة لتعرّف النصوص، التي تنطوي عادةً على عدة مكونات لفهم الصورة وتوليد النص. [TrOCR](model_doc/trocr) بتبسيط العملية باستخدام محول متكامل من النهاية إلى النهاية. المشفر هو نموذج على غرار ViT لفهم الصورة ويعالج الصورة كقطع ثابتة الحجم. يقبل فك التشفير حالات الإخفاء للمشفر وينشئ النص بشكل تلقائي. [Donut](model_doc/donut) هو نموذج أكثر عمومية لفهم المستندات المرئية لا يعتمد على نهج OCR. يستخدم محول Swin كمشفر وBART متعدد اللغات كمُفكّك تشفير. يتم تدريب Donut على قراءة النص عن طريق التنبؤ بالكلمة التالية بناءً على ملاحظات الصورة والنص. يقوم فك التشفير بتوليد تتسلسلًا رمزيًا بناءً على موجه (Prompt). يتم تمثيل الموجه بواسطة رمز خاص لكل مهمة. على سبيل المثال، يحتوي تحليل المستند على رمز خاص "parsing" يتم دمجه مع حالات الإخفاء للـمُشفّر لتحليل المستند بتنسيق إخراج منظم (JSON).
يقوم نموذج "محوّل القرارات والمسارات" (Decision and Trajectory Transformer) بتحويل الحالة (State) والإجراء (Action) والمكافأة (Reward) كمشكلة نمذجة تسلسلية. [محوّل القرارات](model_doc/decision_transformer) يقوم بتوليد سلسلة من الإجراءات التي تؤدي إلى عائد مرغوب في المستقبل بناءً على العوائد المتوقعة، والحالات والإجراءات السابقة. في الخطوات الزمنية *K* الأخيرة، يتم تحويل كل وسائط البيانات الثلاث vإلى متجهات تضمين رمزيّة ومعالجتها بواسطة نموذج مشابه لـ GPT للتنبؤ برمز الإجراء المستقبلي.يقوم [محول المسار](model_doc/trajectory_transformer) أيضًا بتحويل الحالات والإجراءات والمكافآت إلى رموز ومعالجتها باستخدام هيكلية GPT. على عكس "محوّل القرارات"، الذي يركز على تكييف المكافأة، يقوم "محوّل المسارات" بتوليد إجراءات مستقبلية باستخدام البحث الشعاعي (Beam Search).
هناك العديد من النماذج متعددة اللغات في مكتبة 🤗 Transformers، وتختلف طريقة استخدامها للاستدلال عن النماذج أحادية اللغة. ولكن ليس كل استخدام النماذج متعددة اللغات مختلف. فبعض النماذج، مثل [google-bert/bert-base-multilingual-uncased](https://huggingface.co/google-bert/bert-base-multilingual-uncased)، يمكن استخدامها تمامًا مثل النموذج أحادي اللغة. سيوضح لك هذا الدليل كيفية استخدام النماذج متعددة اللغات التي تختلف طريقة استخدامها للاستدلال.
## XLM
يحتوي XLM على عشر نسخ مختلفة، واحدة منها فقط أحادية اللغة. ويمكن تقسيم نسخ النماذج التسع المتبقية إلى فئتين: نسخ التي تستخدم تضمينات اللغة (language embeddings) وتلك التي لا تستخدمها.
### XLM مع تضمينات اللغة
تستخدم النماذج التالية من XLM تضمينات اللغة لتحديد اللغة المستخدمة أثناء الاستدلال:
-`FacebookAI/xlm-mlm-ende-1024` (نمذجة اللغة المقنعة، الإنجليزية-الألمانية)
-`FacebookAI/xlm-mlm-enfr-1024` (نمذجة اللغة المقنعة، الإنجليزية-الفرنسية)
-`FacebookAI/xlm-mlm-enro-1024` (نمذجة اللغة المقنعة، الإنجليزية-الرومانية)
-`FacebookAI/xlm-mlm-xnli15-1024` (نمذجة اللغة المقنعة، لغات XNLI)
-`FacebookAI/xlm-mlm-tlm-xnli15-1024` (نمذجة اللغة المقنعة + الترجمة، لغات XNLI)
-`FacebookAI/xlm-clm-enfr-1024` (نمذجة اللغة السببية، الإنجليزية-الفرنسية)
-`FacebookAI/xlm-clm-ende-1024` (نمذجة اللغة السببية، الإنجليزية-الألمانية)
تُمثل تضمينات اللغة على شكل مصفوفة بنفس شكل `input_ids` التي يتم تمريره إلى النموذج. وتعتمد القيم في هذه المصفوفات على اللغة المستخدمة ويتم تحديدها بواسطة معاملى المجزىء `lang2id` و `id2lang`.
في هذا المثال، قم بتحميل نسخة `FacebookAI/xlm-clm-enfr-1024` ( نمذجة اللغة السببية، الإنجليزية-الفرنسية):
تُظهر خاصية `lang2id` في المجزىء اللغات وأرقام تعريفها في هذا النموذج:
```py
>>>print(tokenizer.lang2id)
{'en':0,'fr':1}
```
بعد ذلك، قم بإنشاء مثال على المدخلات:
```py
>>>input_ids=torch.tensor([tokenizer.encode("Wikipedia was used to")])# batch size of 1
```
قم بتعيين معرف اللغة إلى `"en"` واستخدمه لتحديد تضمين اللغة. وتضمين اللغة عبارة عن مصفوفة مملوءة بـ `0` لأن هذا هو معرف اللغة الإنجليزية. يجب أن تكون هذه المصفوفة بنفس حجم `input_ids`.
>>># نقوم بإعادة تشكيلها لتكون بالحجم (batch_size، sequence_length)
>>>langs=langs.view(1,-1)# الآن بالحجم [1، sequence_length] (لدينا batch size تساوي 1)
```
الآن يمكنك تمرير `input_ids` وتضمين اللغة إلى النموذج:
```py
>>>outputs=model(input_ids,langs=langs)
```
يمكن لنص البرنامج النصي [run_generation.py](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples/pytorch/text-generation/run_generation.py) توليد النص باستخدام تضمينات اللغة مع نقاط تفتيش `xlm-clm`.
### XLM بدون تضمينات اللغة
النماذج التالية من XLM لا تتطلب تضمينات اللغة أثناء الاستنتاج:
-`FacebookAI/xlm-mlm-17-1280` (نمذجة اللغة المقنعة، 17 لغة)
-`FacebookAI/xlm-mlm-100-1280` (نمذجة اللغة المقنعة، 100 لغة)
تُستخدم هذه النماذج لتمثيل الجمل العامة، على عكس نسح XLM السابقة.
## BERT
يمكن استخدام النماذج التالية من BERT للمهام متعددة اللغات:
-`google-bert/bert-base-multilingual-uncased` (نمذجة اللغة المقنعة + التنبؤ بالجملة التالية، 102 لغة)
-`google-bert/bert-base-multilingual-cased` (نمذجة اللغة المقنعة + التنبؤ بالجملة التالية، 104 لغات)
لا تتطلب هذه النماذج تضمينات اللغة أثناء الاستدلال. يجب أن تُحدّد اللغة من السياق وتستنتج وفقاً لذلك.
## XLM-RoBERTa
يمكن استخدام النماذج التالية من XLM-RoBERTa للمهام متعددة اللغات:
-`FacebookAI/xlm-roberta-base` (نمذجة اللغة المقنعة، 100 لغة)
-`FacebookAI/xlm-roberta-large` (نمذجة اللغة المقنعة، 100 لغة)
تم تدريب XLM-RoBERTa على 2.5 تيرابايت من بيانات CommonCrawl الجديدة والمحسنة في 100 لغة. ويوفر مكاسب قوية على النماذج متعددة اللغات التي تم إصدارها سابقاً مثل mBERT أو XLM في مهام المصب مثل التصنيف، ووضع العلامات التسلسلية، والأسئلة والأجوبة.
## M2M100
يمكن استخدام النماذج التالية من M2M100 للترجمة متعددة اللغات:
-`facebook/m2m100_418M` (الترجمة)
-`facebook/m2m100_1.2B` (الترجمة)
في هذا المثال، قم بتحميل نسحة `facebook/m2m100_418M` لترجمة النص من الصينية إلى الإنجليزية. يمكنك تعيين اللغة المصدر في المجزىء اللغوى:
يجبر M2M100 معرف اللغة الهدف كأول رمز مولد للترجمة إلى اللغة الهدف. قم بتعيين `forced_bos_token_id` إلى `en` في طريقة `generate` للترجمة إلى الإنجليزية:
"Don't interfere with the wizard's affairs, because they are subtle, will soon get angry."
```
إذا كنت تستخدم نسخة `facebook/mbart-large-50-many-to-one-mmt`، فلا تحتاج إلى إجبار معرف لغة الهدف كأول رمز مولد، وإلا فإن الاستخدام هو نفسه.
Some files were not shown because too many files have changed in this diff
Show More
Reference in New Issue
Block a user
Blocking a user prevents them from interacting with repositories, such as opening or commenting on pull requests or issues. Learn more about blocking a user.