mirror of
https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git
synced 2025-10-21 01:23:56 +08:00
Compare commits
489 Commits
v4.19.4
...
custom_blo
| Author | SHA1 | Date | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 22ddccc40e | |||
| 8881e58b22 | |||
| 0d971be84f | |||
| ba552dd027 | |||
| 43a5375cc1 | |||
| 9f787ce874 | |||
| 5e2f2d7dd2 | |||
| d23cf5b1f1 | |||
| dbfeffd7c9 | |||
| ff56b8fbff | |||
| 9edff45362 | |||
| bc6fe6fbcf | |||
| dcec4c4387 | |||
| 0ed4d0dfb6 | |||
| 4b1ed7979f | |||
| 8a61fe0234 | |||
| ec6cd7633f | |||
| 05ed569c79 | |||
| 9f12ec7d87 | |||
| dc9147ff36 | |||
| 3bb6356d4d | |||
| ce0152819d | |||
| 798384467b | |||
| e630dad555 | |||
| 4bea6584e3 | |||
| 29fd471556 | |||
| bc8e30bab9 | |||
| 8e445ca51d | |||
| 6a1b1bf7a6 | |||
| c4cc894086 | |||
| 0a5b61d004 | |||
| ced1f1f5db | |||
| edadfc58af | |||
| aeeab1ffd0 | |||
| 45255814a2 | |||
| 6561fbcc6e | |||
| cb19c2afdc | |||
| 7417f3acb7 | |||
| 8c14b342aa | |||
| c1c79b0655 | |||
| a4f97e6ce0 | |||
| c46d39f390 | |||
| ccc0897804 | |||
| fca66ec4ef | |||
| 8581a798c0 | |||
| 7ea6ccc2b3 | |||
| 37aeb5787a | |||
| 0a21a48564 | |||
| 3564c65786 | |||
| 56e6487c40 | |||
| fde22c75a1 | |||
| 195133363e | |||
| 20509ab0e0 | |||
| fcefa200b2 | |||
| bc34c21191 | |||
| 981714efe1 | |||
| f5221c06e4 | |||
| d4ebd4e112 | |||
| b7d8bd378c | |||
| a462fc9232 | |||
| 5ff6f853d7 | |||
| b1b8222d80 | |||
| 6c8017a5c8 | |||
| b0520f594c | |||
| 1e8140caad | |||
| ac98a88fbc | |||
| 95113d1365 | |||
| ad28ca291b | |||
| 8b332a6a16 | |||
| 7c046c5c22 | |||
| 94ca7d2faa | |||
| 9bd3968509 | |||
| de46cde14b | |||
| 2544c1434f | |||
| 91c4a3ab1a | |||
| 1b749a7f8d | |||
| 1b5ea74783 | |||
| 870ff9e1da | |||
| 2e90c3df8f | |||
| be79cd7d8e | |||
| 360719a6a4 | |||
| bf37e5c7f6 | |||
| 22edb68d49 | |||
| f681437203 | |||
| 5ae087cf8e | |||
| ec07eccc7d | |||
| 97db5b4223 | |||
| f0982682bd | |||
| e3139ad301 | |||
| 96d833b211 | |||
| 6cb19540c9 | |||
| 7498db06a1 | |||
| 3cfdefaa4d | |||
| cf2578ae00 | |||
| 77ea5130a1 | |||
| 7b18702ca7 | |||
| a045cbd6c9 | |||
| 49c8c67fb8 | |||
| 6890d1960f | |||
| 6f0723a9be | |||
| 009171d1ba | |||
| d6cec45801 | |||
| 485bbe79d5 | |||
| 664688b94f | |||
| 8bb2c387f4 | |||
| b68d408f1b | |||
| 462b7f3a94 | |||
| 3a064bd4dd | |||
| 569b679adb | |||
| cb42502410 | |||
| 14fb8a63b9 | |||
| 49cd736a28 | |||
| 9cb7cef285 | |||
| fe14046421 | |||
| 91e1f24ef3 | |||
| f25457b273 | |||
| e4d2588573 | |||
| 4f8361afe7 | |||
| 205bc4152c | |||
| 692e61e91a | |||
| eb1493b15d | |||
| fbc7598bab | |||
| 5feac3d080 | |||
| bc019b0e5f | |||
| b089cca347 | |||
| d444edb3f6 | |||
| 9fe2403bc5 | |||
| 4c722e9e22 | |||
| 7c4c6f6084 | |||
| 77b76672e2 | |||
| 3cff4cc587 | |||
| 8f400775fc | |||
| 47b9165109 | |||
| 5cdfff5df3 | |||
| a7eba83161 | |||
| e6d27ca5c8 | |||
| b8142753f9 | |||
| e113c5cb64 | |||
| 90415475bb | |||
| babd7b1a92 | |||
| 6aae59d0b5 | |||
| 776855c752 | |||
| 5f1e67a566 | |||
| 5a3d0cbdda | |||
| 6c8f4c9a93 | |||
| b424f0b4a3 | |||
| 76d13de5ae | |||
| bfcd5743ee | |||
| f71895a633 | |||
| 0094565fc5 | |||
| 1dfa03f12b | |||
| 9eec4e937e | |||
| db2644b9eb | |||
| f717d47fe0 | |||
| 0b0dd97737 | |||
| e02037b352 | |||
| 6dd00f6bd4 | |||
| 71b2839fd3 | |||
| 98742829d3 | |||
| afb71b6726 | |||
| 9a3453846b | |||
| 3ec7d4cfe4 | |||
| ee0d001de7 | |||
| 401fcca6c5 | |||
| cc5c061e34 | |||
| e8eb699ee8 | |||
| b03be78a4b | |||
| 494aac65a7 | |||
| 0e0f1f4692 | |||
| 2ef94ee039 | |||
| ef28a402a9 | |||
| 061a73d16f | |||
| d6b6fb9963 | |||
| 447490015a | |||
| 73a0496c2f | |||
| bc7a6fdc02 | |||
| c2c0d9db5f | |||
| 0917870510 | |||
| 893ab12452 | |||
| 75259b44bf | |||
| 7c1b91281f | |||
| 7cf52a49de | |||
| acb709d551 | |||
| e70abdad1b | |||
| 1a7ef3349f | |||
| 18c263c4b6 | |||
| 6f29029b05 | |||
| 5bc779ae28 | |||
| 3eed5530ec | |||
| b2fdbaccdd | |||
| d37a68e685 | |||
| 4297f44b63 | |||
| 5cce3076c4 | |||
| ab223fc148 | |||
| 8d634b70e0 | |||
| df8e6804c0 | |||
| 0d0c392c45 | |||
| c366ce1011 | |||
| af0d21e741 | |||
| 56b83cf049 | |||
| 1357038164 | |||
| 16c6eb7ca1 | |||
| 3b00b623b7 | |||
| 3ccff0d400 | |||
| 26a6a42608 | |||
| abc400b06a | |||
| 52404cbad4 | |||
| ef23fae596 | |||
| 7cced021fa | |||
| f47afefb21 | |||
| 6a5272b205 | |||
| 7bc88c0511 | |||
| 27e907386a | |||
| b681e12d59 | |||
| 3fab17fce8 | |||
| da2bd2ae96 | |||
| eb16be415a | |||
| 8fcbe275c3 | |||
| da27c4b398 | |||
| d3cb28886a | |||
| fdb120805c | |||
| a2d34b7c04 | |||
| 132402d752 | |||
| 6589e510fa | |||
| 0d92798b45 | |||
| 522a9ece4b | |||
| 21a772426d | |||
| e44a569fef | |||
| 5089a2d412 | |||
| 2d7c1bb192 | |||
| ca169dbdf1 | |||
| 3c7e56fbb1 | |||
| 7c6ec195ad | |||
| 36d4647993 | |||
| f44e2c2b6f | |||
| 2eadb7e54a | |||
| 3981ee8650 | |||
| 66f893320c | |||
| c3c62b5d2c | |||
| 6ebeeeef81 | |||
| 50415b84d6 | |||
| 7f14839f55 | |||
| 242cc6e265 | |||
| b76290f44c | |||
| d453ea6120 | |||
| 120649bf3a | |||
| 7ec9128e5a | |||
| edb672ac5e | |||
| bd43151af4 | |||
| 3960ce917f | |||
| 9068fa6c57 | |||
| 53496ac510 | |||
| 3b29c9fdb7 | |||
| df15703b42 | |||
| a72f1c9f5b | |||
| 1690094bdb | |||
| 4aabf9b52c | |||
| 457d4a3245 | |||
| 5483388631 | |||
| a1344dbfb9 | |||
| 73083581a4 | |||
| c1daf724ea | |||
| 66336dc183 | |||
| a5282ab4bc | |||
| 224bde91ca | |||
| 39e146146b | |||
| 13e875cc07 | |||
| b4eef63a1d | |||
| 5e428b71b4 | |||
| 3114df41f4 | |||
| c99ddcc441 | |||
| 35b16032cb | |||
| b88090914d | |||
| fd1e67033e | |||
| cdaed367b0 | |||
| 2bc305107a | |||
| 1d463303fe | |||
| 49becbaa55 | |||
| 6e93d94792 | |||
| af4a1ecad0 | |||
| e0b58fb5ba | |||
| df1ec6b122 | |||
| fba0b6a820 | |||
| da0bed5f4a | |||
| 75343de938 | |||
| c38f4e1f1c | |||
| 90ed9ae2d1 | |||
| c70dacde94 | |||
| 2351729f7d | |||
| 29080643eb | |||
| 9fc34235fa | |||
| e0be053e43 | |||
| 5323094a22 | |||
| ca2a55e9df | |||
| dfc76b2542 | |||
| 66e8656778 | |||
| e9d5138768 | |||
| e160a5dd62 | |||
| 7d0b6fc340 | |||
| ee82c86bdc | |||
| 34097b3304 | |||
| ae7bae8fe7 | |||
| 264128cb9d | |||
| 9d99489f2f | |||
| 78c695eb62 | |||
| c6cea5a78c | |||
| 119e3c0fc8 | |||
| 706bb8364d | |||
| 5c8f601007 | |||
| 3cab90279f | |||
| 9e72eb4416 | |||
| b118730745 | |||
| b6a65ae52a | |||
| 9aa230aa2f | |||
| ad71965246 | |||
| 19a8a3036d | |||
| d28b7aa8cb | |||
| 34a886fce3 | |||
| 2e37ef35d1 | |||
| f6ad0e0556 | |||
| 4aed1dc81b | |||
| da71df1afc | |||
| 26e5e129b4 | |||
| 72f5b94984 | |||
| c4e58cd8ba | |||
| 254d9c068e | |||
| 8343901263 | |||
| 1c57242d7b | |||
| babeff5524 | |||
| 5c17918fe4 | |||
| 607acd4fbd | |||
| 1c220ced8e | |||
| 013462c57b | |||
| 2f59ad1609 | |||
| 046c5ea906 | |||
| 085321c9a1 | |||
| 048dd73bba | |||
| 588d8f1f26 | |||
| f128ccb997 | |||
| 216499bfcc | |||
| 659b27fd26 | |||
| 0932adb3e8 | |||
| 58fb3c9f98 | |||
| ca1f1c8685 | |||
| 3766df4fe1 | |||
| 028d4b7c8b | |||
| 84aaadd8c5 | |||
| 1d2b57b8a2 | |||
| 693720e567 | |||
| 4d1ce39683 | |||
| 4390151ba2 | |||
| 6813439fdc | |||
| 3042ea4f6f | |||
| bdc01711d6 | |||
| b1160c0b56 | |||
| d91da4c6df | |||
| 24092b1464 | |||
| 811da2b8c2 | |||
| 4f38808e9e | |||
| ba286fe7d5 | |||
| 7822a9b7a7 | |||
| f394a2a50d | |||
| 6ee1474b67 | |||
| 52e7c92920 | |||
| dfc38463b8 | |||
| 8f8b3cbce4 | |||
| 400b30936a | |||
| 5af38953bb | |||
| 567d9c061d | |||
| 975dd2bbbc | |||
| c1a138613d | |||
| b0e0ac8a67 | |||
| 2ef09ecfb8 | |||
| 28d0048218 | |||
| 04681c1d81 | |||
| 13fd67346a | |||
| d156898f3b | |||
| 7999ec125f | |||
| 98f6e1ee87 | |||
| 7535d92e71 | |||
| 2295bcaea8 | |||
| 8f46ac9849 | |||
| 5e7f085fcc | |||
| 70484a8d74 | |||
| a9eca74372 | |||
| 740a1574f1 | |||
| 284fc6c0bb | |||
| 35e2d13f3c | |||
| 897a8dd89f | |||
| 31484afbed | |||
| 56b35ce3eb | |||
| bd908e9bb1 | |||
| 4d727bd2df | |||
| 1ef9a1ed4a | |||
| 71e602725b | |||
| 374a2f693f | |||
| d980929803 | |||
| 31ee80d556 | |||
| 13541b4aa2 | |||
| 71cced8ae3 | |||
| 56f50590d5 | |||
| 2e7e4280aa | |||
| 1cd01b0af3 | |||
| c86aad6110 | |||
| 7b8cb26953 | |||
| b48ac1a094 | |||
| b9bb417324 | |||
| 3fd7de49f4 | |||
| 54192058f3 | |||
| 48c22691e3 | |||
| 5d6feecf16 | |||
| 518bd02c9b | |||
| e8714c0307 | |||
| 2b282296f1 | |||
| a4386d7e40 | |||
| 3601aa8fc9 | |||
| 1b20c970a2 | |||
| 6aad3872ce | |||
| 1762ded30a | |||
| 6e195eb9de | |||
| 060fe61dff | |||
| b3b9f99ed2 | |||
| 6da76b9c2a | |||
| adc0ff2502 | |||
| 4710702837 | |||
| 5fdb54ece7 | |||
| 91ede485a7 | |||
| fe28eb9452 | |||
| 2cb2ea3fa1 | |||
| 1c9d1f4ca8 | |||
| 60ad73448c | |||
| 7ba1d4e51f | |||
| d6b8e9cec7 | |||
| c35264007b | |||
| d9050dc768 | |||
| bad358398a | |||
| 0511305549 | |||
| 032d63b976 | |||
| 986dd5c5bf | |||
| 38ddab10da | |||
| 10704e1209 | |||
| 28a0811652 | |||
| 1f13ba818e | |||
| 349f1c85d3 | |||
| 651e48e1e5 | |||
| 6d211429ec | |||
| ec7f8af106 | |||
| a26ab95e30 | |||
| 1ac2b8fa7f | |||
| 5a9957358c | |||
| f0395cf58e | |||
| e705e1267c | |||
| f6a6388972 | |||
| 6cb7187324 | |||
| 053a80c606 | |||
| 8600d770d4 | |||
| 3fb82f74fd | |||
| 9b0d2860eb | |||
| 66b3e106a1 | |||
| ddb1a47ec8 | |||
| 2f611f85e2 | |||
| 95b6bef624 | |||
| a5d1839679 | |||
| 05a90579a8 | |||
| e730e12567 | |||
| 518dd1277e | |||
| 71d18d0831 | |||
| 71abd3ade1 | |||
| d3d87b451e | |||
| e86faecfd4 | |||
| ee393c009a | |||
| 16be422912 | |||
| f9024814e1 | |||
| 50d1867cf8 | |||
| 506899d147 | |||
| 7198b63362 | |||
| b96cb1693f | |||
| 9c8fde8e19 | |||
| 993553b2f1 | |||
| 38043d8453 | |||
| 18d6b356c5 | |||
| dfc76018c1 | |||
| 85fc455972 | |||
| 3f936df662 | |||
| afe5d42d8d | |||
| 9bd67ac7bb | |||
| 30be0da5da | |||
| f04257fdbc | |||
| 5294fa12ee |
@ -65,7 +65,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
run_tests_torch_and_tf:
|
||||
working_directory: ~/transformers
|
||||
docker:
|
||||
- image: circleci/python:3.7
|
||||
- image: cimg/python:3.7.12
|
||||
environment:
|
||||
OMP_NUM_THREADS: 1
|
||||
RUN_PT_TF_CROSS_TESTS: yes
|
||||
@ -76,9 +76,10 @@ jobs:
|
||||
- checkout
|
||||
- restore_cache:
|
||||
keys:
|
||||
- v0.4-torch_and_tf-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.4-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- run: sudo apt-get -y update && sudo apt-get install -y libsndfile1-dev espeak-ng
|
||||
- v0.5-torch_and_tf-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.5-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- run: sudo apt-get -y update && sudo apt-get install -y libsndfile1-dev espeak-ng git-lfs
|
||||
- run: git lfs install
|
||||
- run: pip install --upgrade pip
|
||||
- run: pip install .[sklearn,tf-cpu,torch,testing,sentencepiece,torch-speech,vision]
|
||||
- run: pip install torch-scatter -f https://pytorch-geometric.com/whl/torch-1.11.0+cpu.html
|
||||
@ -86,7 +87,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
- run: pip install https://github.com/kpu/kenlm/archive/master.zip
|
||||
- run: pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate
|
||||
- save_cache:
|
||||
key: v0.4-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
key: v0.5-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
paths:
|
||||
- '~/.cache/pip'
|
||||
- run: python utils/tests_fetcher.py | tee test_preparation.txt
|
||||
@ -94,7 +95,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
path: ~/transformers/test_preparation.txt
|
||||
- run: |
|
||||
if [ -f test_list.txt ]; then
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 8 --dist=loadfile -rA -s --make-reports=tests_torch_and_tf $(cat test_list.txt) -m is_pt_tf_cross_test --durations=0 | tee tests_output.txt
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 8 --max-worker-restart=0 --dist=loadfile -rA -s --make-reports=tests_torch_and_tf $(cat test_list.txt) -m is_pt_tf_cross_test --durations=0 | tee tests_output.txt
|
||||
fi
|
||||
- store_artifacts:
|
||||
path: ~/transformers/tests_output.txt
|
||||
@ -104,7 +105,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
run_tests_torch_and_tf_all:
|
||||
working_directory: ~/transformers
|
||||
docker:
|
||||
- image: circleci/python:3.7
|
||||
- image: cimg/python:3.7.12
|
||||
environment:
|
||||
OMP_NUM_THREADS: 1
|
||||
RUN_PT_TF_CROSS_TESTS: yes
|
||||
@ -115,9 +116,10 @@ jobs:
|
||||
- checkout
|
||||
- restore_cache:
|
||||
keys:
|
||||
- v0.4-torch_and_tf-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.4-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- run: sudo apt-get -y update && sudo apt-get install -y libsndfile1-dev espeak-ng
|
||||
- v0.5-torch_and_tf-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.5-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- run: sudo apt-get -y update && sudo apt-get install -y libsndfile1-dev espeak-ng git-lfs
|
||||
- run: git lfs install
|
||||
- run: pip install --upgrade pip
|
||||
- run: pip install .[sklearn,tf-cpu,torch,testing,sentencepiece,torch-speech,vision]
|
||||
- run: pip install torch-scatter -f https://pytorch-geometric.com/whl/torch-1.11.0+cpu.html
|
||||
@ -125,11 +127,11 @@ jobs:
|
||||
- run: pip install https://github.com/kpu/kenlm/archive/master.zip
|
||||
- run: pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate
|
||||
- save_cache:
|
||||
key: v0.4-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
key: v0.5-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
paths:
|
||||
- '~/.cache/pip'
|
||||
- run: |
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 8 --dist=loadfile -rA -s --make-reports=tests_torch_and_tf tests -m is_pt_tf_cross_test --durations=0 | tee tests_output.txt
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 8 --max-worker-restart=0 --dist=loadfile -rA -s --make-reports=tests_torch_and_tf tests -m is_pt_tf_cross_test --durations=0 | tee tests_output.txt
|
||||
- store_artifacts:
|
||||
path: ~/transformers/tests_output.txt
|
||||
- store_artifacts:
|
||||
@ -138,7 +140,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
run_tests_torch_and_flax:
|
||||
working_directory: ~/transformers
|
||||
docker:
|
||||
- image: circleci/python:3.7
|
||||
- image: cimg/python:3.7.12
|
||||
environment:
|
||||
OMP_NUM_THREADS: 1
|
||||
RUN_PT_FLAX_CROSS_TESTS: yes
|
||||
@ -149,8 +151,8 @@ jobs:
|
||||
- checkout
|
||||
- restore_cache:
|
||||
keys:
|
||||
- v0.4-torch_and_flax-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.4-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.5-torch_and_flax-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.5-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- run: sudo apt-get -y update && sudo apt-get install -y libsndfile1-dev espeak-ng
|
||||
- run: pip install --upgrade pip
|
||||
- run: pip install .[sklearn,flax,torch,testing,sentencepiece,torch-speech,vision]
|
||||
@ -158,7 +160,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
- run: pip install https://github.com/kpu/kenlm/archive/master.zip
|
||||
- run: pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate
|
||||
- save_cache:
|
||||
key: v0.4-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
key: v0.5-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
paths:
|
||||
- '~/.cache/pip'
|
||||
- run: python utils/tests_fetcher.py | tee test_preparation.txt
|
||||
@ -166,7 +168,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
path: ~/transformers/test_preparation.txt
|
||||
- run: |
|
||||
if [ -f test_list.txt ]; then
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 8 --dist=loadfile -rA -s --make-reports=tests_torch_and_flax $(cat test_list.txt) -m is_pt_flax_cross_test --durations=0 | tee tests_output.txt
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 8 --max-worker-restart=0 --dist=loadfile -rA -s --make-reports=tests_torch_and_flax $(cat test_list.txt) -m is_pt_flax_cross_test --durations=0 | tee tests_output.txt
|
||||
fi
|
||||
- store_artifacts:
|
||||
path: ~/transformers/tests_output.txt
|
||||
@ -176,7 +178,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
run_tests_torch_and_flax_all:
|
||||
working_directory: ~/transformers
|
||||
docker:
|
||||
- image: circleci/python:3.7
|
||||
- image: cimg/python:3.7.12
|
||||
environment:
|
||||
OMP_NUM_THREADS: 1
|
||||
RUN_PT_FLAX_CROSS_TESTS: yes
|
||||
@ -187,8 +189,8 @@ jobs:
|
||||
- checkout
|
||||
- restore_cache:
|
||||
keys:
|
||||
- v0.4-torch_and_flax-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.4-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.5-torch_and_flax-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.5-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- run: sudo apt-get -y update && sudo apt-get install -y libsndfile1-dev espeak-ng
|
||||
- run: pip install --upgrade pip
|
||||
- run: pip install .[sklearn,flax,torch,testing,sentencepiece,torch-speech,vision]
|
||||
@ -196,11 +198,11 @@ jobs:
|
||||
- run: pip install https://github.com/kpu/kenlm/archive/master.zip
|
||||
- run: pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate
|
||||
- save_cache:
|
||||
key: v0.4-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
key: v0.5-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
paths:
|
||||
- '~/.cache/pip'
|
||||
- run: |
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 8 --dist=loadfile -rA -s --make-reports=tests_torch_and_flax tests -m is_pt_flax_cross_test --durations=0 | tee tests_output.txt
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 8 --max-worker-restart=0 --dist=loadfile -rA -s --make-reports=tests_torch_and_flax tests -m is_pt_flax_cross_test --durations=0 | tee tests_output.txt
|
||||
- store_artifacts:
|
||||
path: ~/transformers/tests_output.txt
|
||||
- store_artifacts:
|
||||
@ -209,7 +211,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
run_tests_torch:
|
||||
working_directory: ~/transformers
|
||||
docker:
|
||||
- image: circleci/python:3.7
|
||||
- image: cimg/python:3.7.12
|
||||
environment:
|
||||
OMP_NUM_THREADS: 1
|
||||
TRANSFORMERS_IS_CI: yes
|
||||
@ -219,8 +221,8 @@ jobs:
|
||||
- checkout
|
||||
- restore_cache:
|
||||
keys:
|
||||
- v0.4-torch-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.4-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.5-torch-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.5-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- run: sudo apt-get -y update && sudo apt-get install -y libsndfile1-dev espeak-ng time
|
||||
- run: pip install --upgrade pip
|
||||
- run: pip install .[sklearn,torch,testing,sentencepiece,torch-speech,vision,timm]
|
||||
@ -228,7 +230,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
- run: pip install https://github.com/kpu/kenlm/archive/master.zip
|
||||
- run: pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate
|
||||
- save_cache:
|
||||
key: v0.4-torch-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
key: v0.5-torch-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
paths:
|
||||
- '~/.cache/pip'
|
||||
- run: python utils/tests_fetcher.py | tee test_preparation.txt
|
||||
@ -236,7 +238,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
path: ~/transformers/test_preparation.txt
|
||||
- run: |
|
||||
if [ -f test_list.txt ]; then
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 3 --dist=loadfile -s --make-reports=tests_torch $(cat test_list.txt) | tee tests_output.txt
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 3 --max-worker-restart=0 --dist=loadfile -s --make-reports=tests_torch $(cat test_list.txt) | tee tests_output.txt
|
||||
fi
|
||||
- store_artifacts:
|
||||
path: ~/transformers/tests_output.txt
|
||||
@ -246,7 +248,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
run_tests_torch_all:
|
||||
working_directory: ~/transformers
|
||||
docker:
|
||||
- image: circleci/python:3.7
|
||||
- image: cimg/python:3.7.12
|
||||
environment:
|
||||
OMP_NUM_THREADS: 1
|
||||
TRANSFORMERS_IS_CI: yes
|
||||
@ -256,8 +258,8 @@ jobs:
|
||||
- checkout
|
||||
- restore_cache:
|
||||
keys:
|
||||
- v0.4-torch-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.4-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.5-torch-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.5-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- run: sudo apt-get -y update && sudo apt-get install -y libsndfile1-dev espeak-ng
|
||||
- run: pip install --upgrade pip
|
||||
- run: pip install .[sklearn,torch,testing,sentencepiece,torch-speech,vision,timm]
|
||||
@ -265,11 +267,11 @@ jobs:
|
||||
- run: pip install https://github.com/kpu/kenlm/archive/master.zip
|
||||
- run: pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate
|
||||
- save_cache:
|
||||
key: v0.4-torch-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
key: v0.5-torch-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
paths:
|
||||
- '~/.cache/pip'
|
||||
- run: |
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 3 --dist=loadfile -s --make-reports=tests_torch tests | tee tests_output.txt
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 3 --max-worker-restart=0 --dist=loadfile -s --make-reports=tests_torch tests | tee tests_output.txt
|
||||
- store_artifacts:
|
||||
path: ~/transformers/tests_output.txt
|
||||
- store_artifacts:
|
||||
@ -278,7 +280,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
run_tests_tf:
|
||||
working_directory: ~/transformers
|
||||
docker:
|
||||
- image: circleci/python:3.7
|
||||
- image: cimg/python:3.7.12
|
||||
environment:
|
||||
OMP_NUM_THREADS: 1
|
||||
TRANSFORMERS_IS_CI: yes
|
||||
@ -288,15 +290,15 @@ jobs:
|
||||
- checkout
|
||||
- restore_cache:
|
||||
keys:
|
||||
- v0.4-tf-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.4-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.5-tf-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.5-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- run: sudo apt-get -y update && sudo apt-get install -y libsndfile1-dev espeak-ng
|
||||
- run: pip install --upgrade pip
|
||||
- run: pip install .[sklearn,tf-cpu,testing,sentencepiece,tf-speech,vision]
|
||||
- run: pip install tensorflow_probability
|
||||
- run: pip install https://github.com/kpu/kenlm/archive/master.zip
|
||||
- save_cache:
|
||||
key: v0.4-tf-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
key: v0.5-tf-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
paths:
|
||||
- '~/.cache/pip'
|
||||
- run: python utils/tests_fetcher.py | tee test_preparation.txt
|
||||
@ -304,7 +306,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
path: ~/transformers/test_preparation.txt
|
||||
- run: |
|
||||
if [ -f test_list.txt ]; then
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 8 --dist=loadfile -rA -s --make-reports=tests_tf $(cat test_list.txt) | tee tests_output.txt
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 8 --max-worker-restart=0 --dist=loadfile -rA -s --make-reports=tests_tf $(cat test_list.txt) | tee tests_output.txt
|
||||
fi
|
||||
- store_artifacts:
|
||||
path: ~/transformers/tests_output.txt
|
||||
@ -314,7 +316,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
run_tests_tf_all:
|
||||
working_directory: ~/transformers
|
||||
docker:
|
||||
- image: circleci/python:3.7
|
||||
- image: cimg/python:3.7.12
|
||||
environment:
|
||||
OMP_NUM_THREADS: 1
|
||||
TRANSFORMERS_IS_CI: yes
|
||||
@ -324,19 +326,19 @@ jobs:
|
||||
- checkout
|
||||
- restore_cache:
|
||||
keys:
|
||||
- v0.4-tf-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.4-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.5-tf-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.5-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- run: sudo apt-get -y update && sudo apt-get install -y libsndfile1-dev espeak-ng
|
||||
- run: pip install --upgrade pip
|
||||
- run: pip install .[sklearn,tf-cpu,testing,sentencepiece,tf-speech,vision]
|
||||
- run: pip install tensorflow_probability
|
||||
- run: pip install https://github.com/kpu/kenlm/archive/master.zip
|
||||
- save_cache:
|
||||
key: v0.4-tf-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
key: v0.5-tf-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
paths:
|
||||
- '~/.cache/pip'
|
||||
- run: |
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 8 --dist=loadfile -rA -s --make-reports=tests_tf tests | tee tests_output.txt
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 8 --max-worker-restart=0 --dist=loadfile -rA -s --make-reports=tests_tf tests | tee tests_output.txt
|
||||
- store_artifacts:
|
||||
path: ~/transformers/tests_output.txt
|
||||
- store_artifacts:
|
||||
@ -345,7 +347,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
run_tests_flax:
|
||||
working_directory: ~/transformers
|
||||
docker:
|
||||
- image: circleci/python:3.7
|
||||
- image: cimg/python:3.7.12
|
||||
environment:
|
||||
OMP_NUM_THREADS: 1
|
||||
TRANSFORMERS_IS_CI: yes
|
||||
@ -355,14 +357,14 @@ jobs:
|
||||
- checkout
|
||||
- restore_cache:
|
||||
keys:
|
||||
- v0.4-flax-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.4-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.5-flax-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.5-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- run: sudo apt-get -y update && sudo apt-get install -y libsndfile1-dev espeak-ng
|
||||
- run: pip install --upgrade pip
|
||||
- run: pip install .[flax,testing,sentencepiece,flax-speech,vision]
|
||||
- run: pip install https://github.com/kpu/kenlm/archive/master.zip
|
||||
- save_cache:
|
||||
key: v0.4-flax-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
key: v0.5-flax-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
paths:
|
||||
- '~/.cache/pip'
|
||||
- run: python utils/tests_fetcher.py | tee test_preparation.txt
|
||||
@ -370,7 +372,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
path: ~/transformers/test_preparation.txt
|
||||
- run: |
|
||||
if [ -f test_list.txt ]; then
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 8 --dist=loadfile -rA -s --make-reports=tests_flax $(cat test_list.txt) | tee tests_output.txt
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 8 --max-worker-restart=0 --dist=loadfile -rA -s --make-reports=tests_flax $(cat test_list.txt) | tee tests_output.txt
|
||||
fi
|
||||
- store_artifacts:
|
||||
path: ~/transformers/tests_output.txt
|
||||
@ -380,7 +382,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
run_tests_flax_all:
|
||||
working_directory: ~/transformers
|
||||
docker:
|
||||
- image: circleci/python:3.7
|
||||
- image: cimg/python:3.7.12
|
||||
environment:
|
||||
OMP_NUM_THREADS: 1
|
||||
TRANSFORMERS_IS_CI: yes
|
||||
@ -390,18 +392,18 @@ jobs:
|
||||
- checkout
|
||||
- restore_cache:
|
||||
keys:
|
||||
- v0.4-flax-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.4-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.5-flax-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.5-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- run: sudo apt-get -y update && sudo apt-get install -y libsndfile1-dev espeak-ng
|
||||
- run: pip install --upgrade pip
|
||||
- run: pip install .[flax,testing,sentencepiece,vision,flax-speech]
|
||||
- run: pip install https://github.com/kpu/kenlm/archive/master.zip
|
||||
- save_cache:
|
||||
key: v0.4-flax-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
key: v0.5-flax-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
paths:
|
||||
- '~/.cache/pip'
|
||||
- run: |
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 8 --dist=loadfile -rA -s --make-reports=tests_flax tests | tee tests_output.txt
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 8 --max-worker-restart=0 --dist=loadfile -rA -s --make-reports=tests_flax tests | tee tests_output.txt
|
||||
- store_artifacts:
|
||||
path: ~/transformers/tests_output.txt
|
||||
- store_artifacts:
|
||||
@ -410,7 +412,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
run_tests_pipelines_torch:
|
||||
working_directory: ~/transformers
|
||||
docker:
|
||||
- image: circleci/python:3.7
|
||||
- image: cimg/python:3.7.12
|
||||
environment:
|
||||
OMP_NUM_THREADS: 1
|
||||
RUN_PIPELINE_TESTS: yes
|
||||
@ -421,15 +423,15 @@ jobs:
|
||||
- checkout
|
||||
- restore_cache:
|
||||
keys:
|
||||
- v0.4-torch-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.4-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.5-torch-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.5-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- run: sudo apt-get -y update && sudo apt-get install -y libsndfile1-dev espeak-ng
|
||||
- run: pip install --upgrade pip
|
||||
- run: pip install .[sklearn,torch,testing,sentencepiece,torch-speech,vision,timm]
|
||||
- run: pip install torch-scatter -f https://pytorch-geometric.com/whl/torch-1.11.0+cpu.html
|
||||
- run: pip install https://github.com/kpu/kenlm/archive/master.zip
|
||||
- save_cache:
|
||||
key: v0.4-torch-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
key: v0.5-torch-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
paths:
|
||||
- '~/.cache/pip'
|
||||
- run: python utils/tests_fetcher.py | tee test_preparation.txt
|
||||
@ -437,7 +439,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
path: ~/transformers/test_preparation.txt
|
||||
- run: |
|
||||
if [ -f test_list.txt ]; then
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 8 --dist=loadfile -rA -s --make-reports=tests_pipelines_torch -m is_pipeline_test $(cat test_list.txt) | tee tests_output.txt
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 8 --max-worker-restart=0 --dist=loadfile -rA -s --make-reports=tests_pipelines_torch -m is_pipeline_test $(cat test_list.txt) | tee tests_output.txt
|
||||
fi
|
||||
- store_artifacts:
|
||||
path: ~/transformers/tests_output.txt
|
||||
@ -447,7 +449,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
run_tests_pipelines_torch_all:
|
||||
working_directory: ~/transformers
|
||||
docker:
|
||||
- image: circleci/python:3.7
|
||||
- image: cimg/python:3.7.12
|
||||
environment:
|
||||
OMP_NUM_THREADS: 1
|
||||
RUN_PIPELINE_TESTS: yes
|
||||
@ -458,19 +460,19 @@ jobs:
|
||||
- checkout
|
||||
- restore_cache:
|
||||
keys:
|
||||
- v0.4-torch-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.4-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.5-torch-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.5-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- run: sudo apt-get -y update && sudo apt-get install -y libsndfile1-dev espeak-ng
|
||||
- run: pip install --upgrade pip
|
||||
- run: pip install .[sklearn,torch,testing,sentencepiece,torch-speech,vision,timm]
|
||||
- run: pip install torch-scatter -f https://pytorch-geometric.com/whl/torch-1.11.0+cpu.html
|
||||
- run: pip install https://github.com/kpu/kenlm/archive/master.zip
|
||||
- save_cache:
|
||||
key: v0.4-torch-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
key: v0.5-torch-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
paths:
|
||||
- '~/.cache/pip'
|
||||
- run: |
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 8 --dist=loadfile -rA -s --make-reports=tests_pipelines_torch -m is_pipeline_test tests | tee tests_output.txt
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 8 --max-worker-restart=0 --dist=loadfile -rA -s --make-reports=tests_pipelines_torch -m is_pipeline_test tests | tee tests_output.txt
|
||||
- store_artifacts:
|
||||
path: ~/transformers/tests_output.txt
|
||||
- store_artifacts:
|
||||
@ -479,7 +481,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
run_tests_pipelines_tf:
|
||||
working_directory: ~/transformers
|
||||
docker:
|
||||
- image: circleci/python:3.7
|
||||
- image: cimg/python:3.7.12
|
||||
environment:
|
||||
OMP_NUM_THREADS: 1
|
||||
RUN_PIPELINE_TESTS: yes
|
||||
@ -490,13 +492,13 @@ jobs:
|
||||
- checkout
|
||||
- restore_cache:
|
||||
keys:
|
||||
- v0.4-tf-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.4-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.5-tf-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.5-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- run: pip install --upgrade pip
|
||||
- run: pip install .[sklearn,tf-cpu,testing,sentencepiece]
|
||||
- run: pip install tensorflow_probability
|
||||
- save_cache:
|
||||
key: v0.4-tf-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
key: v0.5-tf-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
paths:
|
||||
- '~/.cache/pip'
|
||||
- run: python utils/tests_fetcher.py | tee test_preparation.txt
|
||||
@ -504,7 +506,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
path: ~/transformers/test_preparation.txt
|
||||
- run: |
|
||||
if [ -f test_list.txt ]; then
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 8 --dist=loadfile -rA -s --make-reports=tests_pipelines_tf $(cat test_list.txt) -m is_pipeline_test | tee tests_output.txt
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 8 --max-worker-restart=0 --dist=loadfile -rA -s --make-reports=tests_pipelines_tf $(cat test_list.txt) -m is_pipeline_test | tee tests_output.txt
|
||||
fi
|
||||
- store_artifacts:
|
||||
path: ~/transformers/tests_output.txt
|
||||
@ -514,7 +516,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
run_tests_pipelines_tf_all:
|
||||
working_directory: ~/transformers
|
||||
docker:
|
||||
- image: circleci/python:3.7
|
||||
- image: cimg/python:3.7.12
|
||||
environment:
|
||||
OMP_NUM_THREADS: 1
|
||||
RUN_PIPELINE_TESTS: yes
|
||||
@ -525,17 +527,17 @@ jobs:
|
||||
- checkout
|
||||
- restore_cache:
|
||||
keys:
|
||||
- v0.4-tf-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.4-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.5-tf-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.5-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- run: pip install --upgrade pip
|
||||
- run: pip install .[sklearn,tf-cpu,testing,sentencepiece]
|
||||
- run: pip install tensorflow_probability
|
||||
- save_cache:
|
||||
key: v0.4-tf-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
key: v0.5-tf-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
paths:
|
||||
- '~/.cache/pip'
|
||||
- run: |
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 8 --dist=loadfile -rA -s --make-reports=tests_pipelines_tf tests -m is_pipeline_test | tee tests_output.txt
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 8 --max-worker-restart=0 --dist=loadfile -rA -s --make-reports=tests_pipelines_tf tests -m is_pipeline_test | tee tests_output.txt
|
||||
- store_artifacts:
|
||||
path: ~/transformers/tests_output.txt
|
||||
- store_artifacts:
|
||||
@ -544,7 +546,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
run_tests_custom_tokenizers:
|
||||
working_directory: ~/transformers
|
||||
docker:
|
||||
- image: circleci/python:3.7
|
||||
- image: cimg/python:3.7.12
|
||||
environment:
|
||||
RUN_CUSTOM_TOKENIZERS: yes
|
||||
TRANSFORMERS_IS_CI: yes
|
||||
@ -552,22 +554,22 @@ jobs:
|
||||
- checkout
|
||||
- restore_cache:
|
||||
keys:
|
||||
- v0.4-custom_tokenizers-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.4-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.5-custom_tokenizers-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.5-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- run: pip install --upgrade pip
|
||||
- run: pip install .[ja,testing,sentencepiece,jieba,spacy,ftfy,rjieba]
|
||||
- run: python -m unidic download
|
||||
- save_cache:
|
||||
key: v0.4-custom_tokenizers-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
key: v0.5-custom_tokenizers-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
paths:
|
||||
- '~/.cache/pip'
|
||||
- run: |
|
||||
if [ -f test_list.txt ]; then
|
||||
python -m pytest -s --make-reports=tests_custom_tokenizers ./tests/test_tokenization_bert_japanese.py ./tests/test_tokenization_openai.py | tee tests_output.txt
|
||||
python -m pytest --max-worker-restart=0 -s --make-reports=tests_custom_tokenizers ./tests/test_tokenization_bert_japanese.py ./tests/test_tokenization_openai.py | tee tests_output.txt
|
||||
fi
|
||||
- run: |
|
||||
if [ -f test_list.txt ]; then
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 1 tests/test_tokenization_clip.py --dist=loadfile -s --make-reports=tests_tokenization_clip --durations=100 | tee tests_output.txt
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 1 --max-worker-restart=0 tests/test_tokenization_clip.py --dist=loadfile -s --make-reports=tests_tokenization_clip --durations=100 | tee tests_output.txt
|
||||
fi
|
||||
- store_artifacts:
|
||||
path: ~/transformers/tests_output.txt
|
||||
@ -577,7 +579,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
run_examples_torch:
|
||||
working_directory: ~/transformers
|
||||
docker:
|
||||
- image: circleci/python:3.7
|
||||
- image: cimg/python:3.7.12
|
||||
environment:
|
||||
OMP_NUM_THREADS: 1
|
||||
TRANSFORMERS_IS_CI: yes
|
||||
@ -587,14 +589,14 @@ jobs:
|
||||
- checkout
|
||||
- restore_cache:
|
||||
keys:
|
||||
- v0.4-torch_examples-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.4-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.5-torch_examples-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.5-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- run: sudo apt-get -y update && sudo apt-get install -y libsndfile1-dev espeak-ng
|
||||
- run: pip install --upgrade pip
|
||||
- run: pip install .[sklearn,torch,sentencepiece,testing,torch-speech]
|
||||
- run: pip install -r examples/pytorch/_tests_requirements.txt
|
||||
- save_cache:
|
||||
key: v0.4-torch_examples-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
key: v0.5-torch_examples-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
paths:
|
||||
- '~/.cache/pip'
|
||||
- run: python utils/tests_fetcher.py --filters examples tests | tee test_preparation.txt
|
||||
@ -602,7 +604,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
path: ~/transformers/test_preparation.txt
|
||||
- run: |
|
||||
if [ -f test_list.txt ]; then
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 8 --dist=loadfile -s --make-reports=examples_torch ./examples/pytorch/ | tee tests_output.txt
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 8 --max-worker-restart=0 --dist=loadfile -s --make-reports=examples_torch ./examples/pytorch/ | tee tests_output.txt
|
||||
fi
|
||||
- store_artifacts:
|
||||
path: ~/transformers/examples_output.txt
|
||||
@ -612,7 +614,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
run_examples_torch_all:
|
||||
working_directory: ~/transformers
|
||||
docker:
|
||||
- image: circleci/python:3.7
|
||||
- image: cimg/python:3.7.12
|
||||
environment:
|
||||
OMP_NUM_THREADS: 1
|
||||
TRANSFORMERS_IS_CI: yes
|
||||
@ -622,18 +624,18 @@ jobs:
|
||||
- checkout
|
||||
- restore_cache:
|
||||
keys:
|
||||
- v0.4-torch_examples-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.4-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.5-torch_examples-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.5-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- run: sudo apt-get -y update && sudo apt-get install -y libsndfile1-dev espeak-ng
|
||||
- run: pip install --upgrade pip
|
||||
- run: pip install .[sklearn,torch,sentencepiece,testing,torch-speech]
|
||||
- run: pip install -r examples/pytorch/_tests_requirements.txt
|
||||
- save_cache:
|
||||
key: v0.4-torch_examples-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
key: v0.5-torch_examples-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
paths:
|
||||
- '~/.cache/pip'
|
||||
- run: |
|
||||
TRANSFORMERS_IS_CI=1 python -m pytest -n 8 --dist=loadfile -s --make-reports=examples_torch ./examples/pytorch/ | tee examples_output.txt
|
||||
TRANSFORMERS_IS_CI=1 python -m pytest -n 8 --max-worker-restart=0 --dist=loadfile -s --make-reports=examples_torch ./examples/pytorch/ | tee examples_output.txt
|
||||
- store_artifacts:
|
||||
path: ~/transformers/examples_output.txt
|
||||
- store_artifacts:
|
||||
@ -642,7 +644,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
run_examples_flax:
|
||||
working_directory: ~/transformers
|
||||
docker:
|
||||
- image: circleci/python:3.7
|
||||
- image: cimg/python:3.7.12
|
||||
environment:
|
||||
OMP_NUM_THREADS: 1
|
||||
TRANSFORMERS_IS_CI: yes
|
||||
@ -652,13 +654,13 @@ jobs:
|
||||
- checkout
|
||||
- restore_cache:
|
||||
keys:
|
||||
- v0.4-flax_examples-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.4-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.5-flax_examples-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.5-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- run: pip install --upgrade pip
|
||||
- run: sudo pip install .[flax,testing,sentencepiece]
|
||||
- run: pip install .[flax,testing,sentencepiece]
|
||||
- run: pip install -r examples/flax/_tests_requirements.txt
|
||||
- save_cache:
|
||||
key: v0.4-flax_examples-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
key: v0.5-flax_examples-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
paths:
|
||||
- '~/.cache/pip'
|
||||
- run: python utils/tests_fetcher.py --filters examples tests | tee test_preparation.txt
|
||||
@ -666,7 +668,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
path: ~/transformers/test_preparation.txt
|
||||
- run: |
|
||||
if [ -f test_list.txt ]; then
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 8 --dist=loadfile -s --make-reports=examples_flax ./examples/flax/ | tee tests_output.txt
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 8 --max-worker-restart=0 --dist=loadfile -s --make-reports=examples_flax ./examples/flax/ | tee tests_output.txt
|
||||
fi
|
||||
- store_artifacts:
|
||||
path: ~/transformers/flax_examples_output.txt
|
||||
@ -676,7 +678,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
run_examples_flax_all:
|
||||
working_directory: ~/transformers
|
||||
docker:
|
||||
- image: circleci/python:3.7
|
||||
- image: cimg/python:3.7.12
|
||||
environment:
|
||||
OMP_NUM_THREADS: 1
|
||||
TRANSFORMERS_IS_CI: yes
|
||||
@ -686,17 +688,17 @@ jobs:
|
||||
- checkout
|
||||
- restore_cache:
|
||||
keys:
|
||||
- v0.4-flax_examples-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.4-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.5-flax_examples-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.5-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- run: pip install --upgrade pip
|
||||
- run: sudo pip install .[flax,testing,sentencepiece]
|
||||
- run: pip install .[flax,testing,sentencepiece]
|
||||
- run: pip install -r examples/flax/_tests_requirements.txt
|
||||
- save_cache:
|
||||
key: v0.4-flax_examples-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
key: v0.5-flax_examples-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
paths:
|
||||
- '~/.cache/pip'
|
||||
- run: |
|
||||
TRANSFORMERS_IS_CI=1 python -m pytest -n 8 --dist=loadfile -s --make-reports=examples_flax ./examples/flax/ | tee examples_output.txt
|
||||
TRANSFORMERS_IS_CI=1 python -m pytest -n 8 --max-worker-restart=0 --dist=loadfile -s --make-reports=examples_flax ./examples/flax/ | tee examples_output.txt
|
||||
- store_artifacts:
|
||||
path: ~/transformers/flax_examples_output.txt
|
||||
- store_artifacts:
|
||||
@ -705,7 +707,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
run_tests_hub:
|
||||
working_directory: ~/transformers
|
||||
docker:
|
||||
- image: circleci/python:3.7
|
||||
- image: cimg/python:3.7.12
|
||||
environment:
|
||||
HUGGINGFACE_CO_STAGING: yes
|
||||
RUN_GIT_LFS_TESTS: yes
|
||||
@ -716,16 +718,16 @@ jobs:
|
||||
- checkout
|
||||
- restore_cache:
|
||||
keys:
|
||||
- v0.4-hub-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.4-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- run: sudo apt-get install git-lfs
|
||||
- v0.5-hub-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.5-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- run: sudo apt-get -y update && sudo apt-get install git-lfs
|
||||
- run: |
|
||||
git config --global user.email "ci@dummy.com"
|
||||
git config --global user.name "ci"
|
||||
- run: pip install --upgrade pip
|
||||
- run: pip install .[torch,sentencepiece,testing]
|
||||
- save_cache:
|
||||
key: v0.4-hub-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
key: v0.5-hub-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
paths:
|
||||
- '~/.cache/pip'
|
||||
- run: python utils/tests_fetcher.py | tee test_preparation.txt
|
||||
@ -733,7 +735,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
path: ~/transformers/test_preparation.txt
|
||||
- run: |
|
||||
if [ -f test_list.txt ]; then
|
||||
python -m pytest -sv --make-reports=tests_hub $(cat test_list.txt) -m is_staging_test | tee tests_output.txt
|
||||
python -m pytest --max-worker-restart=0 -sv --make-reports=tests_hub $(cat test_list.txt) -m is_staging_test | tee tests_output.txt
|
||||
fi
|
||||
- store_artifacts:
|
||||
path: ~/transformers/tests_output.txt
|
||||
@ -743,7 +745,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
run_tests_hub_all:
|
||||
working_directory: ~/transformers
|
||||
docker:
|
||||
- image: circleci/python:3.7
|
||||
- image: cimg/python:3.7.12
|
||||
environment:
|
||||
HUGGINGFACE_CO_STAGING: yes
|
||||
RUN_GIT_LFS_TESTS: yes
|
||||
@ -754,20 +756,20 @@ jobs:
|
||||
- checkout
|
||||
- restore_cache:
|
||||
keys:
|
||||
- v0.4-hub-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.4-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- run: sudo apt-get install git-lfs
|
||||
- v0.5-hub-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.5-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- run: sudo apt-get -y update && sudo apt-get install git-lfs
|
||||
- run: |
|
||||
git config --global user.email "ci@dummy.com"
|
||||
git config --global user.name "ci"
|
||||
- run: pip install --upgrade pip
|
||||
- run: pip install .[torch,sentencepiece,testing]
|
||||
- save_cache:
|
||||
key: v0.4-hub-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
key: v0.5-hub-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
paths:
|
||||
- '~/.cache/pip'
|
||||
- run: |
|
||||
python -m pytest -sv --make-reports=tests_hub tests -m is_staging_test | tee tests_output.txt
|
||||
python -m pytest --max-worker-restart=0 -sv --make-reports=tests_hub tests -m is_staging_test | tee tests_output.txt
|
||||
- store_artifacts:
|
||||
path: ~/transformers/tests_output.txt
|
||||
- store_artifacts:
|
||||
@ -776,7 +778,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
run_tests_onnxruntime:
|
||||
working_directory: ~/transformers
|
||||
docker:
|
||||
- image: circleci/python:3.7
|
||||
- image: cimg/python:3.7.12
|
||||
environment:
|
||||
OMP_NUM_THREADS: 1
|
||||
TRANSFORMERS_IS_CI: yes
|
||||
@ -786,12 +788,12 @@ jobs:
|
||||
- checkout
|
||||
- restore_cache:
|
||||
keys:
|
||||
- v0.4-torch-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.4-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.5-torch-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.5-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- run: pip install --upgrade pip
|
||||
- run: pip install .[torch,testing,sentencepiece,onnxruntime,vision,rjieba]
|
||||
- save_cache:
|
||||
key: v0.4-onnx-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
key: v0.5-onnx-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
paths:
|
||||
- '~/.cache/pip'
|
||||
- run: python utils/tests_fetcher.py | tee test_preparation.txt
|
||||
@ -799,7 +801,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
path: ~/transformers/test_preparation.txt
|
||||
- run: |
|
||||
if [ -f test_list.txt ]; then
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 1 --dist=loadfile -s --make-reports=tests_onnx $(cat test_list.txt) -k onnx | tee tests_output.txt
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 1 --max-worker-restart=0 --dist=loadfile -s --make-reports=tests_onnx $(cat test_list.txt) -k onnx | tee tests_output.txt
|
||||
fi
|
||||
- store_artifacts:
|
||||
path: ~/transformers/tests_output.txt
|
||||
@ -809,7 +811,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
run_tests_onnxruntime_all:
|
||||
working_directory: ~/transformers
|
||||
docker:
|
||||
- image: circleci/python:3.7
|
||||
- image: cimg/python:3.7.12
|
||||
environment:
|
||||
OMP_NUM_THREADS: 1
|
||||
TRANSFORMERS_IS_CI: yes
|
||||
@ -819,16 +821,16 @@ jobs:
|
||||
- checkout
|
||||
- restore_cache:
|
||||
keys:
|
||||
- v0.4-torch-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.4-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.5-torch-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.5-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- run: pip install --upgrade pip
|
||||
- run: pip install .[torch,testing,sentencepiece,onnxruntime,vision]
|
||||
- save_cache:
|
||||
key: v0.4-onnx-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
key: v0.5-onnx-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
paths:
|
||||
- '~/.cache/pip'
|
||||
- run: |
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 1 --dist=loadfile -s --make-reports=tests_onnx tests -k onnx | tee tests_output.txt
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 1 --max-worker-restart=0 --dist=loadfile -s --make-reports=tests_onnx tests -k onnx | tee tests_output.txt
|
||||
- store_artifacts:
|
||||
path: ~/transformers/tests_output.txt
|
||||
- store_artifacts:
|
||||
@ -837,7 +839,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
check_code_quality:
|
||||
working_directory: ~/transformers
|
||||
docker:
|
||||
- image: circleci/python:3.7
|
||||
- image: cimg/python:3.7.12
|
||||
resource_class: large
|
||||
environment:
|
||||
TRANSFORMERS_IS_CI: yes
|
||||
@ -846,24 +848,26 @@ jobs:
|
||||
- checkout
|
||||
- restore_cache:
|
||||
keys:
|
||||
- v0.4-code_quality-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.4-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.5-code_quality-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.5-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- run: pip install --upgrade pip
|
||||
- run: pip install .[all,quality]
|
||||
- save_cache:
|
||||
key: v0.4-code_quality-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
key: v0.5-code_quality-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
paths:
|
||||
- '~/.cache/pip'
|
||||
- run: black --check examples tests src utils
|
||||
- run: black --check --preview examples tests src utils
|
||||
- run: isort --check-only examples tests src utils
|
||||
- run: python utils/custom_init_isort.py --check_only
|
||||
- run: python utils/sort_auto_mappings.py --check_only
|
||||
- run: flake8 examples tests src utils
|
||||
- run: doc-builder style src/transformers docs/source --max_len 119 --check_only --path_to_docs docs/source
|
||||
- run: python utils/check_doc_toc.py
|
||||
|
||||
check_repository_consistency:
|
||||
working_directory: ~/transformers
|
||||
docker:
|
||||
- image: circleci/python:3.7
|
||||
- image: cimg/python:3.7.12
|
||||
resource_class: large
|
||||
environment:
|
||||
TRANSFORMERS_IS_CI: yes
|
||||
@ -872,12 +876,12 @@ jobs:
|
||||
- checkout
|
||||
- restore_cache:
|
||||
keys:
|
||||
- v0.4-repository_consistency-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.4-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.5-repository_consistency-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.5-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- run: pip install --upgrade pip
|
||||
- run: pip install .[all,quality]
|
||||
- save_cache:
|
||||
key: v0.4-repository_consistency-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
key: v0.5-repository_consistency-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
paths:
|
||||
- '~/.cache/pip'
|
||||
- run: python utils/check_copies.py
|
||||
@ -889,10 +893,10 @@ jobs:
|
||||
- run: make deps_table_check_updated
|
||||
- run: python utils/tests_fetcher.py --sanity_check
|
||||
|
||||
run_tests_layoutlmv2:
|
||||
run_tests_layoutlmv2_and_v3:
|
||||
working_directory: ~/transformers
|
||||
docker:
|
||||
- image: circleci/python:3.7
|
||||
- image: cimg/python:3.7.12
|
||||
environment:
|
||||
OMP_NUM_THREADS: 1
|
||||
TRANSFORMERS_IS_CI: yes
|
||||
@ -902,8 +906,8 @@ jobs:
|
||||
- checkout
|
||||
- restore_cache:
|
||||
keys:
|
||||
- v0.4-torch-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.4-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.5-torch-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.5-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- run: sudo apt-get -y update && sudo apt-get install -y libsndfile1-dev
|
||||
- run: pip install --upgrade pip
|
||||
- run: pip install .[torch,testing,vision]
|
||||
@ -912,7 +916,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
- run: sudo apt install tesseract-ocr
|
||||
- run: pip install pytesseract
|
||||
- save_cache:
|
||||
key: v0.4-torch-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
key: v0.5-torch-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
paths:
|
||||
- '~/.cache/pip'
|
||||
- run: python utils/tests_fetcher.py | tee test_preparation.txt
|
||||
@ -920,7 +924,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
path: ~/transformers/test_preparation.txt
|
||||
- run: |
|
||||
if [ -f test_list.txt ]; then
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 1 tests/models/*layoutlmv2* --dist=loadfile -s --make-reports=tests_layoutlmv2 --durations=100
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 1 --max-worker-restart=0 tests/models/*layoutlmv* --dist=loadfile -s --make-reports=tests_layoutlmv2_and_v3 --durations=100
|
||||
fi
|
||||
- store_artifacts:
|
||||
path: ~/transformers/tests_output.txt
|
||||
@ -930,7 +934,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
# TPU JOBS
|
||||
run_examples_tpu:
|
||||
docker:
|
||||
- image: circleci/python:3.7
|
||||
- image: cimg/python:3.7.12
|
||||
environment:
|
||||
OMP_NUM_THREADS: 1
|
||||
TRANSFORMERS_IS_CI: yes
|
||||
@ -950,7 +954,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
|
||||
cleanup-gke-jobs:
|
||||
docker:
|
||||
- image: circleci/python:3.7
|
||||
- image: cimg/python:3.7.12
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- gcp-gke/install
|
||||
- gcp-gke/update-kubeconfig-with-credentials:
|
||||
@ -981,7 +985,7 @@ workflows:
|
||||
- run_tests_pipelines_tf
|
||||
- run_tests_onnxruntime
|
||||
- run_tests_hub
|
||||
- run_tests_layoutlmv2
|
||||
- run_tests_layoutlmv2_and_v3
|
||||
nightly:
|
||||
triggers:
|
||||
- schedule:
|
||||
|
||||
3
.gitattributes
vendored
3
.gitattributes
vendored
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
||||
*.py eol=lf
|
||||
*.rst eol=lf
|
||||
*.md eol=lf
|
||||
*.md eol=lf
|
||||
*.mdx eol=lf
|
||||
4
.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/bug-report.yml
vendored
4
.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/bug-report.yml
vendored
@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
|
||||
name: "\U0001F41B Bug Report"
|
||||
description: Submit a bug report to help us import transformers
|
||||
description: Submit a bug report to help us improve transformers
|
||||
labels: [ "bug" ]
|
||||
body:
|
||||
- type: textarea
|
||||
@ -7,7 +7,6 @@ body:
|
||||
attributes:
|
||||
label: System Info
|
||||
description: Please share your system info with us. You can run the command `transformers-cli env` and copy-paste its output below.
|
||||
render: shell
|
||||
placeholder: transformers version, platform, python version, ...
|
||||
validations:
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
@ -118,4 +117,3 @@ body:
|
||||
attributes:
|
||||
label: Expected behavior
|
||||
description: "A clear and concise description of what you would expect to happen."
|
||||
render: shell
|
||||
5
.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/config.yml
vendored
5
.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/config.yml
vendored
@ -1,9 +1,12 @@
|
||||
blank_issues_enabled: true
|
||||
version: 2.1
|
||||
contact_links:
|
||||
- name: Model checkpoints on the Hugging Face Hub
|
||||
url: https://huggingface.co/models
|
||||
about: Open a Pull request / Discussion related to a specific model checkpoint directly on the Hugging Face Hub
|
||||
- name: Website Related
|
||||
url: https://github.com/huggingface/hub-docs/issues
|
||||
about: Feature requests and bug reports related to the website
|
||||
- name: Forum
|
||||
url: https://discuss.huggingface.co/
|
||||
about: General usage questions and community discussions
|
||||
about: General usage questions and community discussions
|
||||
|
||||
4
.github/conda/meta.yaml
vendored
4
.github/conda/meta.yaml
vendored
@ -25,7 +25,7 @@ requirements:
|
||||
- sacremoses
|
||||
- regex !=2019.12.17
|
||||
- protobuf
|
||||
- tokenizers >=0.10.1,<0.11.0
|
||||
- tokenizers >=0.11.1,!=0.11.3,<0.13
|
||||
- pyyaml >=5.1
|
||||
run:
|
||||
- python
|
||||
@ -40,7 +40,7 @@ requirements:
|
||||
- sacremoses
|
||||
- regex !=2019.12.17
|
||||
- protobuf
|
||||
- tokenizers >=0.10.1,<0.11.0
|
||||
- tokenizers >=0.11.1,!=0.11.3,<0.13
|
||||
- pyyaml >=5.1
|
||||
|
||||
test:
|
||||
|
||||
2
.github/workflows/add-model-like.yml
vendored
2
.github/workflows/add-model-like.yml
vendored
@ -27,7 +27,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
id: cache
|
||||
with:
|
||||
path: ~/venv/
|
||||
key: v3-tests_model_like-${{ hashFiles('setup.py') }}
|
||||
key: v4-tests_model_like-${{ hashFiles('setup.py') }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Create virtual environment on cache miss
|
||||
if: steps.cache.outputs.cache-hit != 'true'
|
||||
|
||||
57
.github/workflows/build-docker-images.yml
vendored
57
.github/workflows/build-docker-images.yml
vendored
@ -5,6 +5,7 @@ on:
|
||||
branches:
|
||||
- docker-image*
|
||||
repository_dispatch:
|
||||
workflow_call:
|
||||
schedule:
|
||||
- cron: "0 1 * * *"
|
||||
|
||||
@ -39,9 +40,35 @@ jobs:
|
||||
push: true
|
||||
tags: huggingface/transformers-all-latest-gpu
|
||||
|
||||
latest-with-torch-nightly-docker:
|
||||
name: "Nightly PyTorch + Stable TensorFlow"
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Set up Docker Buildx
|
||||
uses: docker/setup-buildx-action@v1
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Check out code
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v2
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Login to DockerHub
|
||||
uses: docker/login-action@v1
|
||||
with:
|
||||
username: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME }}
|
||||
password: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_PASSWORD }}
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Build and push
|
||||
uses: docker/build-push-action@v2
|
||||
with:
|
||||
context: ./docker/transformers-all-latest-gpu
|
||||
build-args: |
|
||||
REF=main
|
||||
PYTORCH=pre
|
||||
push: true
|
||||
tags: huggingface/transformers-all-latest-torch-nightly-gpu
|
||||
|
||||
latest-torch-deepspeed-docker:
|
||||
name: "Latest PyTorch + DeepSpeed"
|
||||
needs: latest-docker
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
-
|
||||
@ -66,6 +93,32 @@ jobs:
|
||||
push: true
|
||||
tags: huggingface/transformers-pytorch-deepspeed-latest-gpu
|
||||
|
||||
nightly-torch-deepspeed-docker:
|
||||
name: "Nightly PyTorch + DeepSpeed"
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Set up Docker Buildx
|
||||
uses: docker/setup-buildx-action@v1
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Check out code
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v2
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Login to DockerHub
|
||||
uses: docker/login-action@v1
|
||||
with:
|
||||
username: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME }}
|
||||
password: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_PASSWORD }}
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Build and push
|
||||
uses: docker/build-push-action@v2
|
||||
with:
|
||||
context: ./docker/transformers-pytorch-deepspeed-nightly-gpu
|
||||
build-args: |
|
||||
REF=main
|
||||
push: true
|
||||
tags: huggingface/transformers-pytorch-deepspeed-nightly-gpu
|
||||
|
||||
doc-builder:
|
||||
name: "Doc builder"
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
@ -93,7 +146,6 @@ jobs:
|
||||
latest-pytorch:
|
||||
name: "Latest PyTorch [dev]"
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
needs: latest-torch-deepspeed-docker
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Set up Docker Buildx
|
||||
@ -118,7 +170,6 @@ jobs:
|
||||
tags: huggingface/transformers-pytorch-gpu
|
||||
|
||||
latest-tensorflow:
|
||||
needs: latest-pytorch
|
||||
name: "Latest TensorFlow [dev]"
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
|
||||
108
.github/workflows/build-past-ci-docker-images.yml
vendored
Normal file
108
.github/workflows/build-past-ci-docker-images.yml
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,108 @@
|
||||
name: Build docker images (Past CI)
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
push:
|
||||
branches:
|
||||
- past-ci-docker-image*
|
||||
|
||||
concurrency:
|
||||
group: docker-images-builds
|
||||
cancel-in-progress: false
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
past-pytorch-docker:
|
||||
name: "Past PyTorch Docker"
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
fail-fast: false
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
version: ["1.10", "1.9", "1.8", "1.7", "1.6", "1.5", "1.4"]
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Set up Docker Buildx
|
||||
uses: docker/setup-buildx-action@v1
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Check out code
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v2
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Login to DockerHub
|
||||
uses: docker/login-action@v1
|
||||
with:
|
||||
username: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME }}
|
||||
password: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_PASSWORD }}
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Build and push
|
||||
uses: docker/build-push-action@v2
|
||||
with:
|
||||
context: ./docker/transformers-past-gpu
|
||||
build-args: |
|
||||
REF=main
|
||||
FRAMEWORK=pytorch
|
||||
VERSION=${{ matrix.version }}
|
||||
push: true
|
||||
tags: huggingface/transformers-pytorch-past-${{ matrix.version }}-gpu
|
||||
|
||||
past-tensorflow-docker:
|
||||
name: "Past TensorFlow Docker"
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
fail-fast: false
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
version: ["2.8", "2.7", "2.6", "2.5"]
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Set up Docker Buildx
|
||||
uses: docker/setup-buildx-action@v1
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Check out code
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v2
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Login to DockerHub
|
||||
uses: docker/login-action@v1
|
||||
with:
|
||||
username: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME }}
|
||||
password: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_PASSWORD }}
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Build and push
|
||||
uses: docker/build-push-action@v2
|
||||
with:
|
||||
context: ./docker/transformers-past-gpu
|
||||
build-args: |
|
||||
REF=main
|
||||
FRAMEWORK=tensorflow
|
||||
VERSION=${{ matrix.version }}
|
||||
push: true
|
||||
tags: huggingface/transformers-tensorflow-past-${{ matrix.version }}-gpu
|
||||
|
||||
past-tensorflow-docker-2-4:
|
||||
name: "Past TensorFlow Docker"
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
fail-fast: false
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
version: ["2.4"]
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Set up Docker Buildx
|
||||
uses: docker/setup-buildx-action@v1
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Check out code
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v2
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Login to DockerHub
|
||||
uses: docker/login-action@v1
|
||||
with:
|
||||
username: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME }}
|
||||
password: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_PASSWORD }}
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Build and push
|
||||
uses: docker/build-push-action@v2
|
||||
with:
|
||||
context: ./docker/transformers-past-gpu
|
||||
build-args: |
|
||||
REF=main
|
||||
BASE_DOCKER_IMAGE=nvidia/cuda:11.0.3-cudnn8-devel-ubuntu20.04
|
||||
FRAMEWORK=tensorflow
|
||||
VERSION=${{ matrix.version }}
|
||||
push: true
|
||||
tags: huggingface/transformers-tensorflow-past-${{ matrix.version }}-gpu
|
||||
2
.github/workflows/build_documentation.yml
vendored
2
.github/workflows/build_documentation.yml
vendored
@ -15,6 +15,6 @@ jobs:
|
||||
commit_sha: ${{ github.sha }}
|
||||
package: transformers
|
||||
notebook_folder: transformers_doc
|
||||
languages: en es
|
||||
languages: en es it pt
|
||||
secrets:
|
||||
token: ${{ secrets.HUGGINGFACE_PUSH }}
|
||||
|
||||
2
.github/workflows/build_pr_documentation.yml
vendored
2
.github/workflows/build_pr_documentation.yml
vendored
@ -14,4 +14,4 @@ jobs:
|
||||
commit_sha: ${{ github.event.pull_request.head.sha }}
|
||||
pr_number: ${{ github.event.number }}
|
||||
package: transformers
|
||||
languages: en es
|
||||
languages: en es it pt
|
||||
|
||||
4
.github/workflows/doctests.yml
vendored
4
.github/workflows/doctests.yml
vendored
@ -32,9 +32,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
|
||||
- name: GPU visibility
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
utils/print_env_pt.py
|
||||
TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL=3 python3 -c "import tensorflow as tf; print('TF GPUs available:', bool(tf.config.list_physical_devices('GPU')))"
|
||||
TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL=3 python3 -c "import tensorflow as tf; print('Number of TF GPUs available:', len(tf.config.list_physical_devices('GPU')))"
|
||||
python3 utils/print_env.py
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Prepare files for doctests
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
|
||||
2
.github/workflows/model-templates.yml
vendored
2
.github/workflows/model-templates.yml
vendored
@ -21,7 +21,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
id: cache
|
||||
with:
|
||||
path: ~/venv/
|
||||
key: v3-tests_templates-${{ hashFiles('setup.py') }}
|
||||
key: v4-tests_templates-${{ hashFiles('setup.py') }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Create virtual environment on cache miss
|
||||
if: steps.cache.outputs.cache-hit != 'true'
|
||||
|
||||
424
.github/workflows/self-nightly-scheduled.yml
vendored
424
.github/workflows/self-nightly-scheduled.yml
vendored
@ -1,250 +1,236 @@
|
||||
name: Self-hosted runner; Nightly (scheduled)
|
||||
name: Self-hosted runner (nightly)
|
||||
|
||||
# Note that each job's dependencies go into a corresponding docker file.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# For example for `run_all_tests_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu` the docker image is
|
||||
# `huggingface/transformers-pytorch-deepspeed-latest-gpu`, which can be found at
|
||||
# `docker/transformers-pytorch-deepspeed-latest-gpu/Dockerfile`
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
push:
|
||||
branches:
|
||||
- nightly_ci*
|
||||
repository_dispatch:
|
||||
schedule:
|
||||
- cron: "0 0 */3 * *"
|
||||
repository_dispatch:
|
||||
schedule:
|
||||
- cron: "0 16 * * *"
|
||||
|
||||
env:
|
||||
HF_HOME: /mnt/cache
|
||||
TRANSFORMERS_IS_CI: yes
|
||||
RUN_SLOW: yes
|
||||
OMP_NUM_THREADS: 16
|
||||
MKL_NUM_THREADS: 16
|
||||
PYTEST_TIMEOUT: 600
|
||||
SIGOPT_API_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.SIGOPT_API_TOKEN }}
|
||||
HF_HOME: /mnt/cache
|
||||
TRANSFORMERS_IS_CI: yes
|
||||
OMP_NUM_THREADS: 8
|
||||
MKL_NUM_THREADS: 8
|
||||
RUN_SLOW: yes
|
||||
SIGOPT_API_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.SIGOPT_API_TOKEN }}
|
||||
TF_FORCE_GPU_ALLOW_GROWTH: true
|
||||
RUN_PT_TF_CROSS_TESTS: 1
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
run_all_tests_torch_gpu:
|
||||
runs-on: [self-hosted, docker-gpu, single-gpu]
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: pytorch/pytorch:1.10.0-cuda11.3-cudnn8-runtime
|
||||
options: --gpus 0 --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Launcher docker
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v2
|
||||
setup:
|
||||
name: Setup
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
machine_type: [single-gpu, multi-gpu]
|
||||
runs-on: ${{ format('{0}-{1}', matrix.machine_type, 'docker') }}
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: huggingface/transformers-all-latest-torch-nightly-gpu
|
||||
options: --gpus 0 --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
outputs:
|
||||
matrix: ${{ steps.set-matrix.outputs.matrix }}
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Update clone
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
git fetch && git checkout ${{ github.sha }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NVIDIA-SMI
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
nvidia-smi
|
||||
- name: Cleanup
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
rm -rf tests/__pycache__
|
||||
rm -rf tests/models/__pycache__
|
||||
rm -rf reports
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Install dependencies
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
apt -y update && apt install -y libsndfile1-dev git espeak-ng
|
||||
pip install --upgrade pip
|
||||
pip install .[integrations,sklearn,testing,onnxruntime,sentencepiece,torch-speech,vision,timm]
|
||||
pip install https://github.com/kpu/kenlm/archive/master.zip
|
||||
pip install --pre torch torchvision torchaudio -f https://download.pytorch.org/whl/nightly/cu113/torch_nightly.html -U
|
||||
- id: set-matrix
|
||||
name: Identify models to test
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers/tests
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "::set-output name=matrix::$(python3 -c 'import os; tests = os.getcwd(); model_tests = os.listdir(os.path.join(tests, "models")); d1 = sorted(list(filter(os.path.isdir, os.listdir(tests)))); d2 = sorted(list(filter(os.path.isdir, [f"models/{x}" for x in model_tests]))); d1.remove("models"); d = d2 + d1; print(d)')"
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Are GPUs recognized by our DL frameworks
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
utils/print_env_pt.py
|
||||
- name: NVIDIA-SMI
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
nvidia-smi
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run all tests on GPU
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 1 -v --dist=loadfile --make-reports=tests_torch_gpu tests
|
||||
run_tests_single_gpu:
|
||||
name: Model tests
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
fail-fast: false
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
folders: ${{ fromJson(needs.setup.outputs.matrix) }}
|
||||
machine_type: [single-gpu]
|
||||
runs-on: ${{ format('{0}-{1}', matrix.machine_type, 'docker') }}
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: huggingface/transformers-all-latest-torch-nightly-gpu
|
||||
options: --gpus 0 --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
needs: setup
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Echo folder ${{ matrix.folders }}
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
# For folders like `models/bert`, set an env. var. (`matrix_folders`) to `models_bert`, which will be used to
|
||||
# set the artifact folder names (because the character `/` is not allowed).
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "${{ matrix.folders }}"
|
||||
matrix_folders=${{ matrix.folders }}
|
||||
matrix_folders=${matrix_folders/'models/'/'models_'}
|
||||
echo "$matrix_folders"
|
||||
echo "matrix_folders=$matrix_folders" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
run: cat reports/tests_torch_gpu/failures_short.txt
|
||||
- name: Update clone
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: git fetch && git checkout ${{ github.sha }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run examples tests on GPU
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
env:
|
||||
OMP_NUM_THREADS: 16
|
||||
MKL_NUM_THREADS: 16
|
||||
RUN_SLOW: yes
|
||||
HF_HOME: /mnt/cache
|
||||
TRANSFORMERS_IS_CI: yes
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
pip install -r examples/pytorch/_tests_requirements.txt
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 1 -v --dist=loadfile --make-reports=examples_torch_gpu examples
|
||||
- name: NVIDIA-SMI
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
nvidia-smi
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
run: cat reports/examples_torch_gpu/failures_short.txt
|
||||
- name: Environment
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python3 utils/print_env.py
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run all pipeline tests on GPU
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
env:
|
||||
RUN_PIPELINE_TESTS: yes
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 1 -v --dist=loadfile -m is_pipeline_test --make-reports=tests_torch_pipeline_gpu tests
|
||||
- name: Run all tests on GPU
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: python3 -m pytest -v --make-reports=${{ matrix.machine_type }}_tests_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }} tests/${{ matrix.folders }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
run: cat reports/tests_torch_pipeline_gpu/failures_short.txt
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
if: ${{ failure() }}
|
||||
continue-on-error: true
|
||||
run: cat /transformers/reports/${{ matrix.machine_type }}_tests_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}/failures_short.txt
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Test suite reports artifacts
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v2
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: run_all_tests_torch_gpu_test_reports
|
||||
path: reports
|
||||
- name: Test suite reports artifacts
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v2
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: ${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_all_tests_gpu_${{ env.matrix_folders }}_test_reports
|
||||
path: /transformers/reports/${{ matrix.machine_type }}_tests_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}
|
||||
|
||||
run_all_tests_torch_multi_gpu:
|
||||
runs-on: [self-hosted, docker-gpu, multi-gpu]
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: pytorch/pytorch:1.10.0-cuda11.3-cudnn8-runtime
|
||||
options: --gpus all --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Launcher docker
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v2
|
||||
run_tests_multi_gpu:
|
||||
name: Model tests
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
fail-fast: false
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
folders: ${{ fromJson(needs.setup.outputs.matrix) }}
|
||||
machine_type: [multi-gpu]
|
||||
runs-on: ${{ format('{0}-{1}', matrix.machine_type, 'docker') }}
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: huggingface/transformers-all-latest-torch-nightly-gpu
|
||||
options: --gpus all --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
needs: setup
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Echo folder ${{ matrix.folders }}
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
# For folders like `models/bert`, set an env. var. (`matrix_folders`) to `models_bert`, which will be used to
|
||||
# set the artifact folder names (because the character `/` is not allowed).
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "${{ matrix.folders }}"
|
||||
matrix_folders=${{ matrix.folders }}
|
||||
matrix_folders=${matrix_folders/'models/'/'models_'}
|
||||
echo "$matrix_folders"
|
||||
echo "matrix_folders=$matrix_folders" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NVIDIA-SMI
|
||||
continue-on-error: true
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
nvidia-smi
|
||||
- name: Update clone
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: git fetch && git checkout ${{ github.sha }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Install dependencies
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
apt -y update && apt install -y libsndfile1-dev git espeak-ng
|
||||
pip install --upgrade pip
|
||||
pip install .[integrations,sklearn,testing,onnxruntime,sentencepiece,torch-speech,vision,timm]
|
||||
pip install https://github.com/kpu/kenlm/archive/master.zip
|
||||
pip install --pre torch torchvision torchaudio -f https://download.pytorch.org/whl/nightly/cu113/torch_nightly.html -U
|
||||
- name: NVIDIA-SMI
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
nvidia-smi
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Are GPUs recognized by our DL frameworks
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
utils/print_env_pt.py
|
||||
- name: Environment
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python3 utils/print_env.py
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run all tests on GPU
|
||||
env:
|
||||
MKL_SERVICE_FORCE_INTEL: 1
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 1 -v --dist=loadfile --make-reports=tests_torch_multi_gpu tests
|
||||
- name: Run all tests on GPU
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: python3 -m pytest -v --make-reports=${{ matrix.machine_type }}_tests_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }} tests/${{ matrix.folders }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
run: cat reports/tests_torch_multi_gpu/failures_short.txt
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
if: ${{ failure() }}
|
||||
continue-on-error: true
|
||||
run: cat /transformers/reports/${{ matrix.machine_type }}_tests_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}/failures_short.txt
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run all pipeline tests on GPU
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
env:
|
||||
RUN_PIPELINE_TESTS: yes
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 1 -v --dist=loadfile -m is_pipeline_test --make-reports=tests_torch_pipeline_multi_gpu tests
|
||||
- name: Test suite reports artifacts
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v2
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: ${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_all_tests_gpu_${{ env.matrix_folders }}_test_reports
|
||||
path: /transformers/reports/${{ matrix.machine_type }}_tests_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
run: cat reports/tests_torch_pipeline_multi_gpu/failures_short.txt
|
||||
run_all_tests_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu:
|
||||
name: Torch CUDA extension tests
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
fail-fast: false
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
machine_type: [single-gpu, multi-gpu]
|
||||
runs-on: ${{ format('{0}-{1}', matrix.machine_type, 'docker') }}
|
||||
needs: setup
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: huggingface/transformers-pytorch-deepspeed-nightly-gpu
|
||||
options: --gpus all --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Update clone
|
||||
working-directory: /workspace/transformers
|
||||
run: git fetch && git checkout ${{ github.sha }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Test suite reports artifacts
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v2
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: run_all_tests_torch_multi_gpu_test_reports
|
||||
path: reports
|
||||
# To avoid unknown test failures
|
||||
- name: Pre build DeepSpeed *again*
|
||||
working-directory: /workspace
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python3 -m pip uninstall -y deepspeed
|
||||
rm -rf DeepSpeed
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/microsoft/DeepSpeed && cd DeepSpeed && rm -rf build
|
||||
DS_BUILD_CPU_ADAM=1 DS_BUILD_AIO=1 DS_BUILD_UTILS=1 python3 -m pip install . --global-option="build_ext" --global-option="-j8" --no-cache -v --disable-pip-version-check
|
||||
|
||||
run_all_tests_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu:
|
||||
runs-on: [self-hosted, docker-gpu, single-gpu]
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: nvcr.io/nvidia/pytorch:21.03-py3
|
||||
options: --gpus 0 --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Launcher docker
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v2
|
||||
- name: NVIDIA-SMI
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
nvidia-smi
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NVIDIA-SMI
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
nvidia-smi
|
||||
- name: Environment
|
||||
working-directory: /workspace/transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python utils/print_env.py
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Install dependencies
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
apt -y update && apt install -y libaio-dev libsndfile1-dev git espeak-ng
|
||||
pip install --upgrade pip
|
||||
pip install --pre torch torchvision torchaudio -f https://download.pytorch.org/whl/nightly/cu113/torch_nightly.html -U
|
||||
pip install .[deepspeed-testing]
|
||||
pip install https://github.com/kpu/kenlm/archive/master.zip
|
||||
pip install git+https://github.com/microsoft/DeepSpeed
|
||||
- name: Run all tests on GPU
|
||||
working-directory: /workspace/transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m pytest -v --make-reports=${{ matrix.machine_type }}_tests_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu tests/deepspeed tests/extended
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Are GPUs recognized by our DL frameworks
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
utils/print_env_pt.py
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
if: ${{ failure() }}
|
||||
continue-on-error: true
|
||||
run: cat /workspace/transformers/reports/${{ matrix.machine_type }}_tests_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu/failures_short.txt
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run all tests on GPU
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 1 -v --dist=loadfile --make-reports=tests_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu tests/deepspeed tests/extended
|
||||
- name: Test suite reports artifacts
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v2
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: ${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_tests_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu_test_reports
|
||||
path: /workspace/transformers/reports/${{ matrix.machine_type }}_tests_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
run: cat reports/tests_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu/failures_short.txt
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Test suite reports artifacts
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v2
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: run_tests_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu_test_reports
|
||||
path: reports
|
||||
|
||||
run_all_tests_torch_cuda_extensions_multi_gpu:
|
||||
runs-on: [self-hosted, docker-gpu, multi-gpu]
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: nvcr.io/nvidia/pytorch:21.03-py3
|
||||
options: --gpus 0 --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Launcher docker
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v2
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NVIDIA-SMI
|
||||
continue-on-error: true
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
nvidia-smi
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Install dependencies
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
apt -y update && apt install -y libaio-dev libsndfile1-dev git espeak-ng
|
||||
pip install --upgrade pip
|
||||
pip install --pre torch torchvision torchaudio -f https://download.pytorch.org/whl/nightly/cu113/torch_nightly.html -U
|
||||
rm -rf ~/.cache/torch_extensions/ # shared between conflicting builds
|
||||
pip install .[testing,fairscale]
|
||||
pip install https://github.com/kpu/kenlm/archive/master.zip
|
||||
pip install git+https://github.com/microsoft/DeepSpeed # testing bleeding edge
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Are GPUs recognized by our DL frameworks
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
utils/print_env_pt.py
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run all tests on GPU
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 1 -v --dist=loadfile --make-reports=tests_torch_cuda_extensions_multi_gpu tests/deepspeed tests/extended
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
run: cat reports/tests_torch_cuda_extensions_multi_gpu/failures_short.txt
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Test suite reports artifacts
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v2
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: run_tests_torch_cuda_extensions_multi_gpu_test_reports
|
||||
path: reports
|
||||
|
||||
send_results:
|
||||
name: Send results to webhook
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
needs: [
|
||||
run_all_tests_torch_gpu,
|
||||
run_all_tests_torch_multi_gpu,
|
||||
run_all_tests_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu,
|
||||
run_all_tests_torch_cuda_extensions_multi_gpu
|
||||
]
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@v2
|
||||
|
||||
- uses: actions/download-artifact@v2
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Send message to Slack
|
||||
env:
|
||||
CI_SLACK_BOT_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_ID: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_ID }}
|
||||
CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_ID_DAILY: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_ID_DAILY }}
|
||||
CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_ID_PAST_FUTURE: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_ID_PAST_FUTURE }}
|
||||
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
pip install slack_sdk
|
||||
python utils/notification_service.py scheduled nightly-torch
|
||||
send_results:
|
||||
name: Send results to webhook
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
needs: [setup, run_tests_single_gpu, run_tests_multi_gpu, run_all_tests_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu]
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@v2
|
||||
- uses: actions/download-artifact@v2
|
||||
- name: Send message to Slack
|
||||
env:
|
||||
CI_SLACK_BOT_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_ID: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_ID }}
|
||||
CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_ID_DAILY: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_ID_DAILY }}
|
||||
CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_DUMMY_TESTS: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_DUMMY_TESTS }}
|
||||
CI_SLACK_REPORT_CHANNEL_ID: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_ID_PAST_FUTURE }}
|
||||
CI_EVENT: nightly-build
|
||||
# We pass `needs.setup.outputs.matrix` as the argument. A processing in `notification_service.py` to change
|
||||
# `models/bert` to `models_bert` is required, as the artifact names use `_` instead of `/`.
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
pip install slack_sdk
|
||||
python utils/notification_service.py "${{ needs.setup.outputs.matrix }}"
|
||||
|
||||
126
.github/workflows/self-past-caller.yml
vendored
Normal file
126
.github/workflows/self-past-caller.yml
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,126 @@
|
||||
name: Self-hosted runner (past-ci-caller)
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
push:
|
||||
branches:
|
||||
- run-past-ci*
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
run_past_ci_pytorch_1-10:
|
||||
name: PyTorch 1.10
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
uses: ./.github/workflows/self-past.yml
|
||||
with:
|
||||
framework: pytorch
|
||||
version: "1.10"
|
||||
secrets: inherit
|
||||
|
||||
run_past_ci_pytorch_1-9:
|
||||
name: PyTorch 1.9
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
needs: [run_past_ci_pytorch_1-10]
|
||||
uses: ./.github/workflows/self-past.yml
|
||||
with:
|
||||
framework: pytorch
|
||||
version: "1.9"
|
||||
secrets: inherit
|
||||
|
||||
run_past_ci_pytorch_1-8:
|
||||
name: PyTorch 1.8
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
needs: [run_past_ci_pytorch_1-9]
|
||||
uses: ./.github/workflows/self-past.yml
|
||||
with:
|
||||
framework: pytorch
|
||||
version: "1.8"
|
||||
secrets: inherit
|
||||
|
||||
run_past_ci_pytorch_1-7:
|
||||
name: PyTorch 1.7
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
needs: [run_past_ci_pytorch_1-8]
|
||||
uses: ./.github/workflows/self-past.yml
|
||||
with:
|
||||
framework: pytorch
|
||||
version: "1.7"
|
||||
secrets: inherit
|
||||
|
||||
run_past_ci_pytorch_1-6:
|
||||
name: PyTorch 1.6
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
needs: [run_past_ci_pytorch_1-7]
|
||||
uses: ./.github/workflows/self-past.yml
|
||||
with:
|
||||
framework: pytorch
|
||||
version: "1.6"
|
||||
secrets: inherit
|
||||
|
||||
run_past_ci_pytorch_1-5:
|
||||
name: PyTorch 1.5
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
needs: [run_past_ci_pytorch_1-6]
|
||||
uses: ./.github/workflows/self-past.yml
|
||||
with:
|
||||
framework: pytorch
|
||||
version: "1.5"
|
||||
secrets: inherit
|
||||
|
||||
run_past_ci_pytorch_1-4:
|
||||
name: PyTorch 1.4
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
needs: [run_past_ci_pytorch_1-5]
|
||||
uses: ./.github/workflows/self-past.yml
|
||||
with:
|
||||
framework: pytorch
|
||||
version: "1.4"
|
||||
secrets: inherit
|
||||
|
||||
run_past_ci_tensorflow_2-8:
|
||||
name: TensorFlow 2.8
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
needs: [run_past_ci_pytorch_1-4]
|
||||
uses: ./.github/workflows/self-past.yml
|
||||
with:
|
||||
framework: tensorflow
|
||||
version: "2.8"
|
||||
secrets: inherit
|
||||
|
||||
run_past_ci_tensorflow_2-7:
|
||||
name: TensorFlow 2.7
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
needs: [run_past_ci_tensorflow_2-8]
|
||||
uses: ./.github/workflows/self-past.yml
|
||||
with:
|
||||
framework: tensorflow
|
||||
version: "2.7"
|
||||
secrets: inherit
|
||||
|
||||
run_past_ci_tensorflow_2-6:
|
||||
name: TensorFlow 2.6
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
needs: [run_past_ci_tensorflow_2-7]
|
||||
uses: ./.github/workflows/self-past.yml
|
||||
with:
|
||||
framework: tensorflow
|
||||
version: "2.6"
|
||||
secrets: inherit
|
||||
|
||||
run_past_ci_tensorflow_2-5:
|
||||
name: TensorFlow 2.5
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
needs: [run_past_ci_tensorflow_2-6]
|
||||
uses: ./.github/workflows/self-past.yml
|
||||
with:
|
||||
framework: tensorflow
|
||||
version: "2.5"
|
||||
secrets: inherit
|
||||
|
||||
run_past_ci_tensorflow_2-4:
|
||||
name: TensorFlow 2.4
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
needs: [run_past_ci_tensorflow_2-5]
|
||||
uses: ./.github/workflows/self-past.yml
|
||||
with:
|
||||
framework: tensorflow
|
||||
version: "2.4"
|
||||
secrets: inherit
|
||||
179
.github/workflows/self-past.yml
vendored
Normal file
179
.github/workflows/self-past.yml
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,179 @@
|
||||
name: Self-hosted runner (past)
|
||||
|
||||
# Note that each job's dependencies go into a corresponding docker file.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# For example for `run_all_tests_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu` the docker image is
|
||||
# `huggingface/transformers-pytorch-deepspeed-latest-gpu`, which can be found at
|
||||
# `docker/transformers-pytorch-deepspeed-latest-gpu/Dockerfile`
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
workflow_call:
|
||||
inputs:
|
||||
framework:
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
type: string
|
||||
version:
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
type: string
|
||||
|
||||
env:
|
||||
HF_HOME: /mnt/cache
|
||||
TRANSFORMERS_IS_CI: yes
|
||||
OMP_NUM_THREADS: 8
|
||||
MKL_NUM_THREADS: 8
|
||||
RUN_SLOW: yes
|
||||
SIGOPT_API_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.SIGOPT_API_TOKEN }}
|
||||
TF_FORCE_GPU_ALLOW_GROWTH: true
|
||||
RUN_PT_TF_CROSS_TESTS: 1
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
setup:
|
||||
name: Setup
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
outputs:
|
||||
matrix: ${{ steps.set-matrix.outputs.matrix }}
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Checkout transformers
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v2
|
||||
with:
|
||||
fetch-depth: 2
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Cleanup
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
rm -rf tests/__pycache__
|
||||
rm -rf tests/models/__pycache__
|
||||
rm -rf reports
|
||||
|
||||
- id: set-matrix
|
||||
name: Identify models to test
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
cd tests
|
||||
echo "::set-output name=matrix::$(python3 -c 'import os; tests = os.getcwd(); model_tests = os.listdir(os.path.join(tests, "models")); d1 = sorted(list(filter(os.path.isdir, os.listdir(tests)))); d2 = sorted(list(filter(os.path.isdir, [f"models/{x}" for x in model_tests]))); d1.remove("models"); d = d2 + d1; print(d)')"
|
||||
|
||||
run_tests_single_gpu:
|
||||
name: Model tests
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
fail-fast: false
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
folders: ${{ fromJson(needs.setup.outputs.matrix) }}
|
||||
machine_type: [single-gpu]
|
||||
runs-on: ${{ format('{0}-{1}', matrix.machine_type, 'docker-past-ci') }}
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: huggingface/transformers-${{ inputs.framework }}-past-${{ inputs.version }}-gpu
|
||||
options: --gpus 0 --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
needs: setup
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Update clone
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: git fetch && git checkout ${{ github.sha }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Echo folder ${{ matrix.folders }}
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
# For folders like `models/bert`, set an env. var. (`matrix_folders`) to `models_bert`, which will be used to
|
||||
# set the artifact folder names (because the character `/` is not allowed).
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "${{ matrix.folders }}"
|
||||
matrix_folders=${{ matrix.folders }}
|
||||
matrix_folders=${matrix_folders/'models/'/'models_'}
|
||||
echo "$matrix_folders"
|
||||
echo "matrix_folders=$matrix_folders" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NVIDIA-SMI
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
nvidia-smi
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Environment
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python3 utils/print_env.py
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run all tests on GPU
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: python3 -m pytest -v --make-reports=${{ matrix.machine_type }}_tests_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }} tests/${{ matrix.folders }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
if: ${{ failure() }}
|
||||
continue-on-error: true
|
||||
run: cat /transformers/reports/${{ matrix.machine_type }}_tests_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}/failures_short.txt
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Test suite reports artifacts
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v2
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: ${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_all_tests_gpu_${{ env.matrix_folders }}_test_reports
|
||||
path: /transformers/reports/${{ matrix.machine_type }}_tests_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}
|
||||
|
||||
run_tests_multi_gpu:
|
||||
name: Model tests
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
fail-fast: false
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
folders: ${{ fromJson(needs.setup.outputs.matrix) }}
|
||||
machine_type: [multi-gpu]
|
||||
runs-on: ${{ format('{0}-{1}', matrix.machine_type, 'docker-past-ci') }}
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: huggingface/transformers-${{ inputs.framework }}-past-${{ inputs.version }}-gpu
|
||||
options: --gpus all --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
needs: setup
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Update clone
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: git fetch && git checkout ${{ github.sha }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Echo folder ${{ matrix.folders }}
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
# For folders like `models/bert`, set an env. var. (`matrix_folders`) to `models_bert`, which will be used to
|
||||
# set the artifact folder names (because the character `/` is not allowed).
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "${{ matrix.folders }}"
|
||||
matrix_folders=${{ matrix.folders }}
|
||||
matrix_folders=${matrix_folders/'models/'/'models_'}
|
||||
echo "$matrix_folders"
|
||||
echo "matrix_folders=$matrix_folders" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NVIDIA-SMI
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
nvidia-smi
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Environment
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python3 utils/print_env.py
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run all tests on GPU
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: python3 -m pytest -v --make-reports=${{ matrix.machine_type }}_tests_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }} tests/${{ matrix.folders }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
if: ${{ failure() }}
|
||||
continue-on-error: true
|
||||
run: cat /transformers/reports/${{ matrix.machine_type }}_tests_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}/failures_short.txt
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Test suite reports artifacts
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v2
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: ${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_all_tests_gpu_${{ env.matrix_folders }}_test_reports
|
||||
path: /transformers/reports/${{ matrix.machine_type }}_tests_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}
|
||||
|
||||
send_results:
|
||||
name: Send results to webhook
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
needs: [setup, run_tests_single_gpu, run_tests_multi_gpu]
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@v2
|
||||
- uses: actions/download-artifact@v2
|
||||
- name: Send message to Slack
|
||||
env:
|
||||
CI_SLACK_BOT_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_ID: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_ID }}
|
||||
CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_ID_DAILY: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_ID_DAILY }}
|
||||
CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_DUMMY_TESTS: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_DUMMY_TESTS }}
|
||||
CI_SLACK_REPORT_CHANNEL_ID: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_ID_PAST_FUTURE }}
|
||||
CI_EVENT: Past CI - ${{ inputs.framework }}-${{ inputs.version }}
|
||||
# We pass `needs.setup.outputs.matrix` as the argument. A processing in `notification_service.py` to change
|
||||
# `models/bert` to `models_bert` is required, as the artifact names use `_` instead of `/`.
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
pip install slack_sdk
|
||||
python utils/notification_service.py "${{ needs.setup.outputs.matrix }}"
|
||||
52
.github/workflows/self-push-caller.yml
vendored
Normal file
52
.github/workflows/self-push-caller.yml
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,52 @@
|
||||
# Used to trigger self-push CI
|
||||
name: Self-hosted runner (push-caller)
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
push:
|
||||
branches:
|
||||
- main
|
||||
paths:
|
||||
- "src/**"
|
||||
- "tests/**"
|
||||
- ".github/**"
|
||||
- "templates/**"
|
||||
- "utils/**"
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
check-for-setup:
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
name: Check if setup was changed
|
||||
outputs:
|
||||
changed: ${{ steps.was_changed.outputs.changed }}
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@v3
|
||||
with:
|
||||
fetch-depth: "2"
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Get changed files
|
||||
id: changed-files
|
||||
uses: tj-actions/changed-files@v22.2
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Was setup changed
|
||||
id: was_changed
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
for file in ${{ steps.changed-files.outputs.all_changed_files }}; do
|
||||
if [ `basename "${file}"` = "setup.py" ]; then
|
||||
echo ::set-output name=changed::"1"
|
||||
fi
|
||||
done
|
||||
|
||||
build-docker-containers:
|
||||
needs: check-for-setup
|
||||
if: (github.event_name == 'push') && (needs.check-for-setup.outputs.changed == '1')
|
||||
uses: ./.github/workflows/build-docker-images.yml
|
||||
secrets: inherit
|
||||
|
||||
run_push_ci:
|
||||
name: Trigger Push CI
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
needs: build-docker-containers
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Trigger push CI via workflow_run
|
||||
run: echo "Trigger push CI via workflow_run"
|
||||
734
.github/workflows/self-push.yml
vendored
734
.github/workflows/self-push.yml
vendored
@ -1,9 +1,12 @@
|
||||
name: Self-hosted runner (push)
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
workflow_run:
|
||||
workflows: ["Self-hosted runner (push-caller)"]
|
||||
branches: ["main"]
|
||||
types: [completed]
|
||||
push:
|
||||
branches:
|
||||
- main
|
||||
- ci_*
|
||||
- ci-*
|
||||
paths:
|
||||
@ -20,37 +23,68 @@ env:
|
||||
OMP_NUM_THREADS: 8
|
||||
MKL_NUM_THREADS: 8
|
||||
PYTEST_TIMEOUT: 60
|
||||
TF_FORCE_GPU_ALLOW_GROWTH: true
|
||||
RUN_PT_TF_CROSS_TESTS: 1
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
run_tests_torch_gpu:
|
||||
runs-on: [self-hosted, docker-gpu, single-gpu]
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: pytorch/pytorch:1.9.0-cuda11.1-cudnn8-runtime
|
||||
options: --gpus 0 --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
setup:
|
||||
name: Setup
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
outputs:
|
||||
matrix: ${{ steps.set-matrix.outputs.matrix }}
|
||||
test_map: ${{ steps.set-matrix.outputs.test_map }}
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Install dependencies
|
||||
# Necessary to get the correct branch name and commit SHA for `workflow_run` event
|
||||
# We also take into account the `push` event (we might want to test some changes in a branch)
|
||||
- name: Prepare custom environment variables
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
# `CI_BRANCH_PUSH`: The branch name from the push event
|
||||
# `CI_BRANCH_WORKFLOW_RUN`: The name of the branch on which this workflow is triggered by `workflow_run` event
|
||||
# `CI_BRANCH`: The non-empty branch name from the above two (one and only one of them is empty)
|
||||
# `CI_SHA_PUSH`: The commit SHA from the push event
|
||||
# `CI_SHA_WORKFLOW_RUN`: The commit SHA that triggers this workflow by `workflow_run` event
|
||||
# `CI_SHA`: The non-empty commit SHA from the above two (one and only one of them is empty)
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
apt -y update && apt install -y software-properties-common && apt -y update && add-apt-repository -y ppa:git-core/ppa && apt -y update && apt install -y git
|
||||
apt install -y libsndfile1-dev espeak-ng
|
||||
pip install --upgrade pip
|
||||
pip install .[sklearn,testing,onnxruntime,sentencepiece,torch-speech,vision,timm]
|
||||
pip install https://github.com/kpu/kenlm/archive/master.zip
|
||||
CI_BRANCH_PUSH=${{ github.event.ref }}
|
||||
CI_BRANCH_PUSH=${CI_BRANCH_PUSH/'refs/heads/'/''}
|
||||
CI_BRANCH_WORKFLOW_RUN=${{ github.event.workflow_run.head_branch }}
|
||||
CI_SHA_PUSH=${{ github.event.head_commit.id }}
|
||||
CI_SHA_WORKFLOW_RUN=${{ github.event.workflow_run.head_sha }}
|
||||
echo $CI_BRANCH_PUSH
|
||||
echo $CI_BRANCH_WORKFLOW_RUN
|
||||
echo $CI_SHA_PUSH
|
||||
echo $CI_SHA_WORKFLOW_RUN
|
||||
[[ ! -z "$CI_BRANCH_PUSH" ]] && echo "CI_BRANCH=$CI_BRANCH_PUSH" >> $GITHUB_ENV || echo "CI_BRANCH=$CI_BRANCH_WORKFLOW_RUN" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
[[ ! -z "$CI_SHA_PUSH" ]] && echo "CI_SHA=$CI_SHA_PUSH" >> $GITHUB_ENV || echo "CI_SHA=$CI_SHA_WORKFLOW_RUN" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Launcher docker
|
||||
- name: print environment variables
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "env.CI_BRANCH = ${{ env.CI_BRANCH }}"
|
||||
echo "env.CI_SHA = ${{ env.CI_SHA }}"
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Checkout transformers
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v2
|
||||
with:
|
||||
fetch-depth: 2
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NVIDIA-SMI
|
||||
- name: Update clone using environment variables
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
nvidia-smi
|
||||
echo "original branch = $(git branch --show-current)"
|
||||
git fetch && git checkout ${{ env.CI_BRANCH }}
|
||||
echo "updated branch = $(git branch --show-current)"
|
||||
git checkout ${{ env.CI_SHA }}
|
||||
echo "log = $(git log -n 1)"
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Are GPUs recognized by our DL frameworks
|
||||
- name: Cleanup
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
utils/print_env_pt.py
|
||||
rm -rf tests/__pycache__
|
||||
rm -rf tests/models/__pycache__
|
||||
rm -rf reports
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Fetch the tests to run
|
||||
# TODO: add `git-python` in the docker images
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
pip install --upgrade git-python
|
||||
python utils/tests_fetcher.py --diff_with_last_commit | tee test_preparation.txt
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Report fetched tests
|
||||
@ -59,441 +93,413 @@ jobs:
|
||||
name: test_fetched
|
||||
path: test_preparation.txt
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run all non-slow tests on GPU
|
||||
- id: set-matrix
|
||||
name: Organize tests into models
|
||||
# The `keys` is used as GitHub actions matrix for jobs, i.e. `models/bert`, `tokenization`, `pipeline`, etc.
|
||||
# The `test_map` is used to get the actual identified test files under each key.
|
||||
# If no test to run (so no `test_map.json` file), create a dummy map (empty matrix will fail)
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
if [ -f test_list.txt ]; then
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 2 --dist=loadfile -v --make-reports=tests_torch_gpu $(cat test_list.txt)
|
||||
if [ -f test_map.json ]; then
|
||||
keys=$(python3 -c 'import json; fp = open("test_map.json"); test_map = json.load(fp); fp.close(); d = list(test_map.keys()); print(d)')
|
||||
test_map=$(python3 -c 'import json; fp = open("test_map.json"); test_map = json.load(fp); fp.close(); print(test_map)')
|
||||
else
|
||||
keys=$(python3 -c 'keys = ["dummy"]; print(keys)')
|
||||
test_map=$(python3 -c 'test_map = {"dummy": []}; print(test_map)')
|
||||
fi
|
||||
echo $keys
|
||||
echo $test_map
|
||||
echo "::set-output name=matrix::$keys"
|
||||
echo "::set-output name=test_map::$test_map"
|
||||
|
||||
run_tests_single_gpu:
|
||||
name: Model tests
|
||||
needs: setup
|
||||
# `dummy` means there is no test to run
|
||||
if: contains(fromJson(needs.setup.outputs.matrix), 'dummy') != true
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
fail-fast: false
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
folders: ${{ fromJson(needs.setup.outputs.matrix) }}
|
||||
machine_type: [single-gpu]
|
||||
runs-on: [self-hosted, docker-gpu, '${{ matrix.machine_type }}']
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: huggingface/transformers-all-latest-gpu
|
||||
options: --gpus 0 --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
# Necessary to get the correct branch name and commit SHA for `workflow_run` event
|
||||
# We also take into account the `push` event (we might want to test some changes in a branch)
|
||||
- name: Prepare custom environment variables
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
# For the meaning of these environment variables, see the job `Setup`
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
CI_BRANCH_PUSH=${{ github.event.ref }}
|
||||
CI_BRANCH_PUSH=${CI_BRANCH_PUSH/'refs/heads/'/''}
|
||||
CI_BRANCH_WORKFLOW_RUN=${{ github.event.workflow_run.head_branch }}
|
||||
CI_SHA_PUSH=${{ github.event.head_commit.id }}
|
||||
CI_SHA_WORKFLOW_RUN=${{ github.event.workflow_run.head_sha }}
|
||||
echo $CI_BRANCH_PUSH
|
||||
echo $CI_BRANCH_WORKFLOW_RUN
|
||||
echo $CI_SHA_PUSH
|
||||
echo $CI_SHA_WORKFLOW_RUN
|
||||
[[ ! -z "$CI_BRANCH_PUSH" ]] && echo "CI_BRANCH=$CI_BRANCH_PUSH" >> $GITHUB_ENV || echo "CI_BRANCH=$CI_BRANCH_WORKFLOW_RUN" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
[[ ! -z "$CI_SHA_PUSH" ]] && echo "CI_SHA=$CI_SHA_PUSH" >> $GITHUB_ENV || echo "CI_SHA=$CI_SHA_WORKFLOW_RUN" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
|
||||
- name: print environment variables
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "env.CI_BRANCH = ${{ env.CI_BRANCH }}"
|
||||
echo "env.CI_SHA = ${{ env.CI_SHA }}"
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Update clone using environment variables
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "original branch = $(git branch --show-current)"
|
||||
git fetch && git checkout ${{ env.CI_BRANCH }}
|
||||
echo "updated branch = $(git branch --show-current)"
|
||||
git checkout ${{ env.CI_SHA }}
|
||||
echo "log = $(git log -n 1)"
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Echo folder ${{ matrix.folders }}
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
# For folders like `models/bert`, set an env. var. (`matrix_folders`) to `models_bert`, which will be used to
|
||||
# set the artifact folder names (because the character `/` is not allowed).
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "${{ matrix.folders }}"
|
||||
echo "${{ fromJson(needs.setup.outputs.test_map)[matrix.folders] }}"
|
||||
matrix_folders=${{ matrix.folders }}
|
||||
matrix_folders=${matrix_folders/'models/'/'models_'}
|
||||
echo "$matrix_folders"
|
||||
echo "matrix_folders=$matrix_folders" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NVIDIA-SMI
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
nvidia-smi
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Environment
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python3 utils/print_env.py
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run all non-slow selected tests on GPU
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python3 -m pytest -n 2 --dist=loadfile -v --make-reports=${{ matrix.machine_type }}_tests_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }} ${{ fromJson(needs.setup.outputs.test_map)[matrix.folders] }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
if: ${{ failure() }}
|
||||
run: cat reports/tests_torch_gpu/failures_short.txt
|
||||
continue-on-error: true
|
||||
run: cat /transformers/reports/${{ matrix.machine_type }}_tests_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}/failures_short.txt
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Test suite reports artifacts
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v2
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: run_all_tests_torch_gpu_test_reports
|
||||
path: reports
|
||||
name: ${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_all_tests_gpu_${{ env.matrix_folders }}_test_reports
|
||||
path: /transformers/reports/${{ matrix.machine_type }}_tests_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}
|
||||
|
||||
# run_tests_flax_gpu:
|
||||
# runs-on: [self-hosted, docker-gpu-test, single-gpu]
|
||||
# container:
|
||||
# image: tensorflow/tensorflow:2.4.1-gpu
|
||||
# options: --gpus 0 --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
# steps:
|
||||
# - name: Set up Python 3.7
|
||||
# uses: actions/setup-python@v2
|
||||
# with:
|
||||
# python-version: 3.7
|
||||
#
|
||||
# - name: Install dependencies
|
||||
# run: |
|
||||
# apt -y update && apt install -y software-properties-common && apt -y update && add-apt-repository -y ppa:git-core/ppa && apt -y update && apt install -y git espeak-ng
|
||||
# pip install --upgrade "jax[cuda111]" -f https://storage.googleapis.com/jax-releases/jax_releases.html
|
||||
# pip install --upgrade pip
|
||||
# pip install .[sklearn,testing,sentencepiece,flax,flax-speech,vision]
|
||||
#
|
||||
# - name: Launcher docker
|
||||
# uses: actions/checkout@v2
|
||||
# with:
|
||||
# fetch-depth: 2
|
||||
#
|
||||
# - name: NVIDIA-SMI
|
||||
# continue-on-error: true
|
||||
# run: |
|
||||
# nvidia-smi
|
||||
#
|
||||
# - name: Are GPUs recognized by our DL frameworks
|
||||
# run: |
|
||||
# python -c "from jax.lib import xla_bridge; print('GPU available:', xla_bridge.get_backend().platform)"
|
||||
# python -c "import jax; print('Number of GPUs available:', len(jax.local_devices()))"
|
||||
#
|
||||
# - name: Fetch the tests to run
|
||||
# run: |
|
||||
# python utils/tests_fetcher.py --diff_with_last_commit | tee test_preparation.txt
|
||||
#
|
||||
# - name: Report fetched tests
|
||||
# uses: actions/upload-artifact@v2
|
||||
# with:
|
||||
# name: test_fetched
|
||||
# path: test_preparation.txt
|
||||
#
|
||||
# - name: Run all non-slow tests on GPU
|
||||
# run: |
|
||||
# if [ -f test_list.txt ]; then
|
||||
# python -m pytest -n 2 --dist=loadfile -v --make-reports=tests_flax_gpu $(cat test_list.txt)
|
||||
# fi
|
||||
#
|
||||
# - name: Failure short reports
|
||||
# if: ${{ failure() }}
|
||||
# run: cat reports/tests_flax_gpu/failures_short.txt
|
||||
#
|
||||
# - name: Test suite reports artifacts
|
||||
# if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
# uses: actions/upload-artifact@v2
|
||||
# with:
|
||||
# name: run_all_tests_flax_gpu_test_reports
|
||||
# path: reports
|
||||
#
|
||||
# run_tests_tf_gpu:
|
||||
# runs-on: [self-hosted, docker-gpu, single-gpu]
|
||||
# timeout-minutes: 120
|
||||
# container:
|
||||
# image: tensorflow/tensorflow:2.4.1-gpu
|
||||
# options: --gpus 0 --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
# steps:
|
||||
# - name: Install dependencies
|
||||
# run: |
|
||||
# apt -y update && apt install -y software-properties-common && apt -y update && add-apt-repository -y ppa:git-core/ppa && apt -y update && apt install -y git espeak-ng
|
||||
# pip install --upgrade pip
|
||||
# pip install .[sklearn,testing,onnxruntime,sentencepiece,tf-speech]
|
||||
# pip install https://github.com/kpu/kenlm/archive/master.zip
|
||||
#
|
||||
# - name: Launcher docker
|
||||
# uses: actions/checkout@v2
|
||||
# with:
|
||||
# fetch-depth: 2
|
||||
#
|
||||
# - name: NVIDIA-SMI
|
||||
# run: |
|
||||
# nvidia-smi
|
||||
#
|
||||
# - name: Are GPUs recognized by our DL frameworks
|
||||
# run: |
|
||||
# TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL=3 python -c "import tensorflow as tf; print('TF GPUs available:', bool(tf.config.list_physical_devices('GPU')))"
|
||||
# TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL=3 python -c "import tensorflow as tf; print('Number of TF GPUs available:', len(tf.config.list_physical_devices('GPU')))"
|
||||
#
|
||||
# - name: Fetch the tests to run
|
||||
# run: |
|
||||
# python utils/tests_fetcher.py --diff_with_last_commit | tee test_preparation.txt
|
||||
#
|
||||
# - name: Report fetched tests
|
||||
# uses: actions/upload-artifact@v2
|
||||
# with:
|
||||
# name: test_fetched
|
||||
# path: test_preparation.txt
|
||||
#
|
||||
# - name: Run all non-slow tests on GPU
|
||||
# env:
|
||||
# TF_NUM_INTRAOP_THREADS: 8
|
||||
# TF_NUM_INTEROP_THREADS: 1
|
||||
# run: |
|
||||
# if [ -f test_list.txt ]; then
|
||||
# python -m pytest -n 1 --dist=loadfile --make-reports=tests_tf_gpu $(cat test_list.txt)
|
||||
# fi
|
||||
#
|
||||
# - name: Failure short reports
|
||||
# if: ${{ failure() }}
|
||||
# run: cat reports/tests_tf_gpu/failures_short.txt
|
||||
#
|
||||
# - name: Test suite reports artifacts
|
||||
# if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
# uses: actions/upload-artifact@v2
|
||||
# with:
|
||||
# name: run_all_tests_tf_gpu_test_reports
|
||||
# path: reports
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
run_tests_torch_multi_gpu:
|
||||
runs-on: [self-hosted, docker-gpu, multi-gpu]
|
||||
run_tests_multi_gpu:
|
||||
name: Model tests
|
||||
needs: setup
|
||||
# `dummy` means there is no test to run
|
||||
if: contains(fromJson(needs.setup.outputs.matrix), 'dummy') != true
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
fail-fast: false
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
folders: ${{ fromJson(needs.setup.outputs.matrix) }}
|
||||
machine_type: [multi-gpu]
|
||||
runs-on: [self-hosted, docker-gpu, '${{ matrix.machine_type }}']
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: pytorch/pytorch:1.9.0-cuda11.1-cudnn8-runtime
|
||||
image: huggingface/transformers-all-latest-gpu
|
||||
options: --gpus all --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Install dependencies
|
||||
# Necessary to get the correct branch name and commit SHA for `workflow_run` event
|
||||
# We also take into account the `push` event (we might want to test some changes in a branch)
|
||||
- name: Prepare custom environment variables
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
# For the meaning of these environment variables, see the job `Setup`
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
apt -y update && apt install -y software-properties-common && apt -y update && add-apt-repository -y ppa:git-core/ppa && apt -y update && apt install -y git espeak-ng
|
||||
apt install -y libsndfile1-dev espeak-ng
|
||||
pip install --upgrade pip
|
||||
pip install .[sklearn,testing,onnxruntime,sentencepiece,torch-speech,vision,timm]
|
||||
pip install https://github.com/kpu/kenlm/archive/master.zip
|
||||
- name: Launcher docker
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v2
|
||||
with:
|
||||
fetch-depth: 2
|
||||
CI_BRANCH_PUSH=${{ github.event.ref }}
|
||||
CI_BRANCH_PUSH=${CI_BRANCH_PUSH/'refs/heads/'/''}
|
||||
CI_BRANCH_WORKFLOW_RUN=${{ github.event.workflow_run.head_branch }}
|
||||
CI_SHA_PUSH=${{ github.event.head_commit.id }}
|
||||
CI_SHA_WORKFLOW_RUN=${{ github.event.workflow_run.head_sha }}
|
||||
echo $CI_BRANCH_PUSH
|
||||
echo $CI_BRANCH_WORKFLOW_RUN
|
||||
echo $CI_SHA_PUSH
|
||||
echo $CI_SHA_WORKFLOW_RUN
|
||||
[[ ! -z "$CI_BRANCH_PUSH" ]] && echo "CI_BRANCH=$CI_BRANCH_PUSH" >> $GITHUB_ENV || echo "CI_BRANCH=$CI_BRANCH_WORKFLOW_RUN" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
[[ ! -z "$CI_SHA_PUSH" ]] && echo "CI_SHA=$CI_SHA_PUSH" >> $GITHUB_ENV || echo "CI_SHA=$CI_SHA_WORKFLOW_RUN" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
|
||||
- name: print environment variables
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "env.CI_BRANCH = ${{ env.CI_BRANCH }}"
|
||||
echo "env.CI_SHA = ${{ env.CI_SHA }}"
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Update clone using environment variables
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "original branch = $(git branch --show-current)"
|
||||
git fetch && git checkout ${{ env.CI_BRANCH }}
|
||||
echo "updated branch = $(git branch --show-current)"
|
||||
git checkout ${{ env.CI_SHA }}
|
||||
echo "log = $(git log -n 1)"
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Echo folder ${{ matrix.folders }}
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
# For folders like `models/bert`, set an env. var. (`matrix_folders`) to `models_bert`, which will be used to
|
||||
# set the artifact folder names (because the character `/` is not allowed).
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "${{ matrix.folders }}"
|
||||
echo "${{ fromJson(needs.setup.outputs.test_map)[matrix.folders] }}"
|
||||
matrix_folders=${{ matrix.folders }}
|
||||
matrix_folders=${matrix_folders/'models/'/'models_'}
|
||||
echo "$matrix_folders"
|
||||
echo "matrix_folders=$matrix_folders" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NVIDIA-SMI
|
||||
continue-on-error: true
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
nvidia-smi
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Are GPUs recognized by our DL frameworks
|
||||
- name: Environment
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
utils/print_env_pt.py
|
||||
python3 utils/print_env.py
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Fetch the tests to run
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python utils/tests_fetcher.py --diff_with_last_commit | tee test_preparation.txt
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Report fetched tests
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v2
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: test_fetched
|
||||
path: test_preparation.txt
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run all non-slow tests on GPU
|
||||
- name: Run all non-slow selected tests on GPU
|
||||
env:
|
||||
MKL_SERVICE_FORCE_INTEL: 1
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
if [ -f test_list.txt ]; then
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 2 --dist=loadfile -v --make-reports=tests_torch_multi_gpu $(cat test_list.txt)
|
||||
fi
|
||||
python3 -m pytest -n 2 --dist=loadfile -v --make-reports=${{ matrix.machine_type }}_tests_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }} ${{ fromJson(needs.setup.outputs.test_map)[matrix.folders] }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
if: ${{ failure() }}
|
||||
run: cat reports/tests_torch_multi_gpu/failures_short.txt
|
||||
continue-on-error: true
|
||||
run: cat /transformers/reports/${{ matrix.machine_type }}_tests_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}/failures_short.txt
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Test suite reports artifacts
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v2
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: run_all_tests_torch_multi_gpu_test_reports
|
||||
path: reports
|
||||
name: ${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_all_tests_gpu_${{ env.matrix_folders }}_test_reports
|
||||
path: /transformers/reports/${{ matrix.machine_type }}_tests_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}
|
||||
|
||||
# run_tests_flax_multi_gpu:
|
||||
# runs-on: [self-hosted, docker-gpu, multi-gpu]
|
||||
# container:
|
||||
# image: tensorflow/tensorflow:2.4.1-gpu
|
||||
# options: --gpus 0 --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
# steps:
|
||||
# - name: Install dependencies
|
||||
# run: |
|
||||
# apt -y update && apt install -y software-properties-common && apt -y update && add-apt-repository -y ppa:git-core/ppa && apt -y update && apt install -y git espeak-ng
|
||||
# pip install --upgrade "jax[cuda111]" -f https://storage.googleapis.com/jax-releases/jax_releases.html
|
||||
# pip install --upgrade pip
|
||||
# pip install .[sklearn,testing,sentencepiece,flax,flax-speech,vision]
|
||||
# pip install https://github.com/kpu/kenlm/archive/master.zip
|
||||
#
|
||||
# - name: Launcher docker
|
||||
# uses: actions/checkout@v2
|
||||
# with:
|
||||
# fetch-depth: 2
|
||||
#
|
||||
# - name: NVIDIA-SMI
|
||||
# continue-on-error: true
|
||||
# run: |
|
||||
# nvidia-smi
|
||||
#
|
||||
# - name: Are GPUs recognized by our DL frameworks
|
||||
# run: |
|
||||
# python -c "from jax.lib import xla_bridge; print('GPU available:', xla_bridge.get_backend().platform)"
|
||||
# python -c "import jax; print('Number of GPUs available:', len(jax.local_devices()))"
|
||||
#
|
||||
# - name: Fetch the tests to run
|
||||
# run: |
|
||||
# python utils/tests_fetcher.py --diff_with_last_commit | tee test_preparation.txt
|
||||
#
|
||||
# - name: Report fetched tests
|
||||
# uses: actions/upload-artifact@v2
|
||||
# with:
|
||||
# name: test_fetched
|
||||
# path: test_preparation.txt
|
||||
#
|
||||
# - name: Run all non-slow tests on GPU
|
||||
# run: |
|
||||
# if [ -f test_list.txt ]; then
|
||||
# python -m pytest -n 2 --dist=loadfile -v --make-reports=tests_flax_multi_gpu $(cat test_list.txt)
|
||||
# fi
|
||||
#
|
||||
# - name: Failure short reports
|
||||
# if: ${{ failure() }}
|
||||
# run: cat reports/tests_flax_multi_gpu/failures_short.txt
|
||||
#
|
||||
# - name: Test suite reports artifacts
|
||||
# if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
# uses: actions/upload-artifact@v2
|
||||
# with:
|
||||
# name: run_all_tests_flax_multi_gpu_test_reports
|
||||
# path: reports
|
||||
|
||||
# run_tests_tf_multi_gpu:
|
||||
# runs-on: [self-hosted, docker-gpu, multi-gpu]
|
||||
# timeout-minutes: 120
|
||||
# container:
|
||||
# image: tensorflow/tensorflow:2.4.1-gpu
|
||||
# options: --gpus all --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
# steps:
|
||||
# - name: Install dependencies
|
||||
# run: |
|
||||
# apt -y update && apt install -y software-properties-common && apt -y update && add-apt-repository -y ppa:git-core/ppa && apt -y update && apt install -y git espeak-ng
|
||||
# pip install --upgrade pip
|
||||
# pip install .[sklearn,testing,onnxruntime,sentencepiece,tf-speech]
|
||||
# pip install https://github.com/kpu/kenlm/archive/master.zip
|
||||
#
|
||||
# - name: Launcher docker
|
||||
# uses: actions/checkout@v2
|
||||
# with:
|
||||
# fetch-depth: 2
|
||||
#
|
||||
# - name: NVIDIA-SMI
|
||||
# run: |
|
||||
# nvidia-smi
|
||||
#
|
||||
# - name: Are GPUs recognized by our DL frameworks
|
||||
# run: |
|
||||
# TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL=3 python -c "import tensorflow as tf; print('TF GPUs available:', bool(tf.config.list_physical_devices('GPU')))"
|
||||
# TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL=3 python -c "import tensorflow as tf; print('Number of TF GPUs available:', len(tf.config.list_physical_devices('GPU')))"
|
||||
#
|
||||
# - name: Fetch the tests to run
|
||||
# run: |
|
||||
# python utils/tests_fetcher.py --diff_with_last_commit | tee test_preparation.txt
|
||||
#
|
||||
# - name: Report fetched tests
|
||||
# uses: actions/upload-artifact@v2
|
||||
# with:
|
||||
# name: test_fetched
|
||||
# path: test_preparation.txt
|
||||
#
|
||||
# - name: Run all non-slow tests on GPU
|
||||
# env:
|
||||
# TF_NUM_INTRAOP_THREADS: 8
|
||||
# TF_NUM_INTEROP_THREADS: 1
|
||||
# run: |
|
||||
# if [ -f test_list.txt ]; then
|
||||
# python -m pytest -n 1 --dist=loadfile --make-reports=tests_tf_multi_gpu $(cat test_list.txt)
|
||||
# fi
|
||||
#
|
||||
# - name: Failure short reports
|
||||
# if: ${{ failure() }}
|
||||
# run: cat reports/tests_tf_multi_gpu/failures_short.txt
|
||||
#
|
||||
# - name: Test suite reports artifacts
|
||||
# if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
# uses: actions/upload-artifact@v2
|
||||
# with:
|
||||
# name: run_all_tests_tf_multi_gpu_test_reports
|
||||
# path: reports
|
||||
|
||||
run_tests_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu:
|
||||
runs-on: [self-hosted, docker-gpu, single-gpu]
|
||||
run_tests_torch_cuda_extensions_single_gpu:
|
||||
name: Torch CUDA extension tests
|
||||
needs: setup
|
||||
if: contains(fromJson(needs.setup.outputs.matrix), 'deepspeed') || contains(fromJson(needs.setup.outputs.matrix), 'extended')
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
fail-fast: false
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
machine_type: [single-gpu]
|
||||
runs-on: [self-hosted, docker-gpu, '${{ matrix.machine_type }}']
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: nvcr.io/nvidia/pytorch:21.03-py3
|
||||
image: huggingface/transformers-pytorch-deepspeed-latest-gpu
|
||||
options: --gpus 0 --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Launcher docker
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v2
|
||||
with:
|
||||
fetch-depth: 2
|
||||
# Necessary to get the correct branch name and commit SHA for `workflow_run` event
|
||||
# We also take into account the `push` event (we might want to test some changes in a branch)
|
||||
- name: Prepare custom environment variables
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
# For the meaning of these environment variables, see the job `Setup`
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
CI_BRANCH_PUSH=${{ github.event.ref }}
|
||||
CI_BRANCH_PUSH=${CI_BRANCH_PUSH/'refs/heads/'/''}
|
||||
CI_BRANCH_WORKFLOW_RUN=${{ github.event.workflow_run.head_branch }}
|
||||
CI_SHA_PUSH=${{ github.event.head_commit.id }}
|
||||
CI_SHA_WORKFLOW_RUN=${{ github.event.workflow_run.head_sha }}
|
||||
echo $CI_BRANCH_PUSH
|
||||
echo $CI_BRANCH_WORKFLOW_RUN
|
||||
echo $CI_SHA_PUSH
|
||||
echo $CI_SHA_WORKFLOW_RUN
|
||||
[[ ! -z "$CI_BRANCH_PUSH" ]] && echo "CI_BRANCH=$CI_BRANCH_PUSH" >> $GITHUB_ENV || echo "CI_BRANCH=$CI_BRANCH_WORKFLOW_RUN" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
[[ ! -z "$CI_SHA_PUSH" ]] && echo "CI_SHA=$CI_SHA_PUSH" >> $GITHUB_ENV || echo "CI_SHA=$CI_SHA_WORKFLOW_RUN" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
|
||||
- name: print environment variables
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "env.CI_BRANCH = ${{ env.CI_BRANCH }}"
|
||||
echo "env.CI_SHA = ${{ env.CI_SHA }}"
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Update clone using environment variables
|
||||
working-directory: /workspace/transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "original branch = $(git branch --show-current)"
|
||||
git fetch && git checkout ${{ env.CI_BRANCH }}
|
||||
echo "updated branch = $(git branch --show-current)"
|
||||
git checkout ${{ env.CI_SHA }}
|
||||
echo "log = $(git log -n 1)"
|
||||
|
||||
# To avoid unknown test failures
|
||||
- name: Pre build DeepSpeed *again*
|
||||
working-directory: /workspace
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python3 -m pip uninstall -y deepspeed
|
||||
DS_BUILD_CPU_ADAM=1 DS_BUILD_AIO=1 DS_BUILD_UTILS=1 python3 -m pip install deepspeed --global-option="build_ext" --global-option="-j8" --no-cache -v --disable-pip-version-check
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NVIDIA-SMI
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
nvidia-smi
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Install dependencies
|
||||
- name: Environment
|
||||
working-directory: /workspace/transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
apt -y update && apt install -y libaio-dev
|
||||
pip install --upgrade pip
|
||||
pip install .[deepspeed-testing]
|
||||
python utils/print_env.py
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Are GPUs recognized by our DL frameworks
|
||||
- name: Run all non-slow selected tests on GPU
|
||||
working-directory: /workspace/transformers
|
||||
# TODO: Here we pass all tests in the 2 folders for simplicity. It's better to pass only the identified tests.
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
utils/print_env_pt.py
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Fetch the tests to run
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python utils/tests_fetcher.py --diff_with_last_commit --filters tests/deepspeed tests/extended | tee test_preparation.txt
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Report fetched tests
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v2
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: test_fetched
|
||||
path: test_preparation.txt
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run all tests on GPU
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
if [ -f test_list.txt ]; then
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 1 --dist=loadfile -v --make-reports=tests_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu $(cat test_list.txt)
|
||||
fi
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 1 --dist=loadfile -v --make-reports=${{ matrix.machine_type }}_tests_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu tests/deepspeed tests/extended
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
if: ${{ failure() }}
|
||||
run: cat reports/tests_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu/failures_short.txt
|
||||
continue-on-error: true
|
||||
run: cat /workspace/transformers/reports/${{ matrix.machine_type }}_tests_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu/failures_short.txt
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Test suite reports artifacts
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v2
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: run_tests_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu_test_reports
|
||||
path: reports
|
||||
name: ${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_tests_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu_test_reports
|
||||
path: /workspace/transformers/reports/${{ matrix.machine_type }}_tests_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu
|
||||
|
||||
run_tests_torch_cuda_extensions_multi_gpu:
|
||||
runs-on: [self-hosted, docker-gpu, multi-gpu]
|
||||
name: Torch CUDA extension tests
|
||||
needs: setup
|
||||
if: contains(fromJson(needs.setup.outputs.matrix), 'deepspeed') || contains(fromJson(needs.setup.outputs.matrix), 'extended')
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
fail-fast: false
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
machine_type: [multi-gpu]
|
||||
runs-on: [self-hosted, docker-gpu, '${{ matrix.machine_type }}']
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: nvcr.io/nvidia/pytorch:21.03-py3
|
||||
options: --gpus 0 --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
image: huggingface/transformers-pytorch-deepspeed-latest-gpu
|
||||
options: --gpus all --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Launcher docker
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v2
|
||||
with:
|
||||
fetch-depth: 2
|
||||
# Necessary to get the correct branch name and commit SHA for `workflow_run` event
|
||||
# We also take into account the `push` event (we might want to test some changes in a branch)
|
||||
- name: Prepare custom environment variables
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
# For the meaning of these environment variables, see the job `Setup`
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
CI_BRANCH_PUSH=${{ github.event.ref }}
|
||||
CI_BRANCH_PUSH=${CI_BRANCH_PUSH/'refs/heads/'/''}
|
||||
CI_BRANCH_WORKFLOW_RUN=${{ github.event.workflow_run.head_branch }}
|
||||
CI_SHA_PUSH=${{ github.event.head_commit.id }}
|
||||
CI_SHA_WORKFLOW_RUN=${{ github.event.workflow_run.head_sha }}
|
||||
echo $CI_BRANCH_PUSH
|
||||
echo $CI_BRANCH_WORKFLOW_RUN
|
||||
echo $CI_SHA_PUSH
|
||||
echo $CI_SHA_WORKFLOW_RUN
|
||||
[[ ! -z "$CI_BRANCH_PUSH" ]] && echo "CI_BRANCH=$CI_BRANCH_PUSH" >> $GITHUB_ENV || echo "CI_BRANCH=$CI_BRANCH_WORKFLOW_RUN" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
[[ ! -z "$CI_SHA_PUSH" ]] && echo "CI_SHA=$CI_SHA_PUSH" >> $GITHUB_ENV || echo "CI_SHA=$CI_SHA_WORKFLOW_RUN" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
|
||||
- name: print environment variables
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "env.CI_BRANCH = ${{ env.CI_BRANCH }}"
|
||||
echo "env.CI_SHA = ${{ env.CI_SHA }}"
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Update clone using environment variables
|
||||
working-directory: /workspace/transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "original branch = $(git branch --show-current)"
|
||||
git fetch && git checkout ${{ env.CI_BRANCH }}
|
||||
echo "updated branch = $(git branch --show-current)"
|
||||
git checkout ${{ env.CI_SHA }}
|
||||
echo "log = $(git log -n 1)"
|
||||
|
||||
# To avoid unknown test failures
|
||||
- name: Pre build DeepSpeed *again*
|
||||
working-directory: /workspace
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python3 -m pip uninstall -y deepspeed
|
||||
DS_BUILD_CPU_ADAM=1 DS_BUILD_AIO=1 DS_BUILD_UTILS=1 python3 -m pip install deepspeed --global-option="build_ext" --global-option="-j8" --no-cache -v --disable-pip-version-check
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NVIDIA-SMI
|
||||
continue-on-error: true
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
nvidia-smi
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Install dependencies
|
||||
- name: Environment
|
||||
working-directory: /workspace/transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
apt -y update && apt install -y libaio-dev
|
||||
pip install --upgrade pip
|
||||
rm -rf ~/.cache/torch_extensions/ # shared between conflicting builds
|
||||
pip install .[testing,deepspeed,fairscale]
|
||||
python utils/print_env.py
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Are GPUs recognized by our DL frameworks
|
||||
- name: Run all non-slow selected tests on GPU
|
||||
working-directory: /workspace/transformers
|
||||
# TODO: Here we pass all tests in the 2 folders for simplicity. It's better to pass only the identified tests.
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
utils/print_env_pt.py
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Fetch the tests to run
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python utils/tests_fetcher.py --diff_with_last_commit --filters tests/deepspeed tests/extended | tee test_preparation.txt
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Report fetched tests
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v2
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: test_fetched
|
||||
path: test_preparation.txt
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run all tests on GPU
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
if [ -f test_list.txt ]; then
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 1 --dist=loadfile -v --make-reports=tests_torch_cuda_extensions_multi_gpu $(cat test_list.txt)
|
||||
fi
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 1 --dist=loadfile -v --make-reports=${{ matrix.machine_type }}_tests_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu tests/deepspeed tests/extended
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
if: ${{ failure() }}
|
||||
run: cat reports/tests_torch_cuda_extensions_multi_gpu/failures_short.txt
|
||||
continue-on-error: true
|
||||
run: cat /workspace/transformers/reports/${{ matrix.machine_type }}_tests_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu/failures_short.txt
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Test suite reports artifacts
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v2
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: run_tests_torch_cuda_extensions_multi_gpu_test_reports
|
||||
path: reports
|
||||
|
||||
name: ${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_tests_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu_test_reports
|
||||
path: /workspace/transformers/reports/${{ matrix.machine_type }}_tests_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu
|
||||
|
||||
send_results:
|
||||
name: Send results to webhook
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
needs: [
|
||||
run_tests_torch_gpu,
|
||||
# run_tests_tf_gpu,
|
||||
run_tests_torch_multi_gpu,
|
||||
# run_tests_tf_multi_gpu,
|
||||
run_tests_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu,
|
||||
setup,
|
||||
run_tests_single_gpu,
|
||||
run_tests_multi_gpu,
|
||||
run_tests_torch_cuda_extensions_single_gpu,
|
||||
run_tests_torch_cuda_extensions_multi_gpu
|
||||
]
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
# Necessary to get the correct branch name and commit SHA for `workflow_run` event
|
||||
# We also take into account the `push` event (we might want to test some changes in a branch)
|
||||
- name: Prepare custom environment variables
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
# For the meaning of these environment variables, see the job `Setup`
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
CI_BRANCH_PUSH=${{ github.event.ref }}
|
||||
CI_BRANCH_PUSH=${CI_BRANCH_PUSH/'refs/heads/'/''}
|
||||
CI_BRANCH_WORKFLOW_RUN=${{ github.event.workflow_run.head_branch }}
|
||||
CI_SHA_PUSH=${{ github.event.head_commit.id }}
|
||||
CI_SHA_WORKFLOW_RUN=${{ github.event.workflow_run.head_sha }}
|
||||
echo $CI_BRANCH_PUSH
|
||||
echo $CI_BRANCH_WORKFLOW_RUN
|
||||
echo $CI_SHA_PUSH
|
||||
echo $CI_SHA_WORKFLOW_RUN
|
||||
[[ ! -z "$CI_BRANCH_PUSH" ]] && echo "CI_BRANCH=$CI_BRANCH_PUSH" >> $GITHUB_ENV || echo "CI_BRANCH=$CI_BRANCH_WORKFLOW_RUN" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
[[ ! -z "$CI_SHA_PUSH" ]] && echo "CI_SHA=$CI_SHA_PUSH" >> $GITHUB_ENV || echo "CI_SHA=$CI_SHA_WORKFLOW_RUN" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
|
||||
- name: print environment variables
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "env.CI_BRANCH = ${{ env.CI_BRANCH }}"
|
||||
echo "env.CI_SHA = ${{ env.CI_SHA }}"
|
||||
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@v2
|
||||
|
||||
- uses: actions/download-artifact@v2
|
||||
- name: Update clone using environment variables
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "original branch = $(git branch --show-current)"
|
||||
git fetch && git checkout ${{ env.CI_BRANCH }}
|
||||
echo "updated branch = $(git branch --show-current)"
|
||||
git checkout ${{ env.CI_SHA }}
|
||||
echo "log = $(git log -n 1)"
|
||||
|
||||
- uses: actions/download-artifact@v2
|
||||
- name: Send message to Slack
|
||||
env:
|
||||
CI_SLACK_BOT_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_ID: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_ID }}
|
||||
|
||||
CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_ID_DAILY: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_ID_DAILY }}
|
||||
CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_DUMMY_TESTS: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_DUMMY_TESTS }}
|
||||
CI_SLACK_REPORT_CHANNEL_ID: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_ID }}
|
||||
CI_EVENT: push
|
||||
CI_TITLE_PUSH: ${{ github.event.head_commit.message }}
|
||||
CI_TITLE_WORKFLOW_RUN: ${{ github.event.workflow_run.head_commit.message }}
|
||||
CI_SHA: ${{ env.CI_SHA }}
|
||||
# We pass `needs.setup.outputs.matrix` as the argument. A processing in `notification_service.py` to change
|
||||
# `models/bert` to `models_bert` is required, as the artifact names use `_` instead of `/`.
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
pip install slack_sdk
|
||||
python utils/notification_service_deprecated.py push
|
||||
python utils/notification_service.py "${{ needs.setup.outputs.matrix }}"
|
||||
|
||||
145
.github/workflows/self-scheduled.yml
vendored
145
.github/workflows/self-scheduled.yml
vendored
@ -26,8 +26,8 @@ jobs:
|
||||
name: Setup
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
machines: [multi-gpu-docker, single-gpu-docker]
|
||||
runs-on: ${{ matrix.machines }}
|
||||
machine_type: [single-gpu, multi-gpu]
|
||||
runs-on: ${{ format('{0}-{1}', matrix.machine_type, 'docker') }}
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: huggingface/transformers-all-latest-gpu
|
||||
options: --gpus 0 --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
@ -56,21 +56,14 @@ jobs:
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
nvidia-smi
|
||||
|
||||
- name: GPU visibility
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
utils/print_env_pt.py
|
||||
TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL=3 python3 -c "import tensorflow as tf; print('TF GPUs available:', bool(tf.config.list_physical_devices('GPU')))"
|
||||
TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL=3 python3 -c "import tensorflow as tf; print('Number of TF GPUs available:', len(tf.config.list_physical_devices('GPU')))"
|
||||
|
||||
run_tests_single_gpu:
|
||||
name: Model tests
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
fail-fast: false
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
folders: ${{ fromJson(needs.setup.outputs.matrix) }}
|
||||
machines: [single-gpu-docker]
|
||||
runs-on: ${{ matrix.machines }}
|
||||
machine_type: [single-gpu]
|
||||
runs-on: ${{ format('{0}-{1}', matrix.machine_type, 'docker') }}
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: huggingface/transformers-all-latest-gpu
|
||||
options: --gpus 0 --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
@ -83,7 +76,6 @@ jobs:
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "${{ matrix.folders }}"
|
||||
matrix_folders=${{ matrix.folders }}
|
||||
echo "$matrix_folders"
|
||||
matrix_folders=${matrix_folders/'models/'/'models_'}
|
||||
echo "$matrix_folders"
|
||||
echo "matrix_folders=$matrix_folders" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
@ -92,21 +84,30 @@ jobs:
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: git fetch && git checkout ${{ github.sha }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NVIDIA-SMI
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
nvidia-smi
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Environment
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python3 utils/print_env.py
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run all tests on GPU
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: python3 -m pytest -v --make-reports=${{ matrix.machines }}_tests_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }} tests/${{ matrix.folders }}
|
||||
run: python3 -m pytest -v --make-reports=${{ matrix.machine_type }}_tests_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }} tests/${{ matrix.folders }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
if: ${{ failure() }}
|
||||
continue-on-error: true
|
||||
run: cat /transformers/reports/${{ matrix.machines }}_tests_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}/failures_short.txt
|
||||
run: cat /transformers/reports/${{ matrix.machine_type }}_tests_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}/failures_short.txt
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Test suite reports artifacts
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v2
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: ${{ matrix.machines }}_run_all_tests_gpu_${{ env.matrix_folders }}_test_reports
|
||||
path: /transformers/reports/${{ matrix.machines }}_tests_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}
|
||||
name: ${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_all_tests_gpu_${{ env.matrix_folders }}_test_reports
|
||||
path: /transformers/reports/${{ matrix.machine_type }}_tests_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}
|
||||
|
||||
run_tests_multi_gpu:
|
||||
name: Model tests
|
||||
@ -114,11 +115,11 @@ jobs:
|
||||
fail-fast: false
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
folders: ${{ fromJson(needs.setup.outputs.matrix) }}
|
||||
machines: [multi-gpu-docker]
|
||||
runs-on: ${{ matrix.machines }}
|
||||
machine_type: [multi-gpu]
|
||||
runs-on: ${{ format('{0}-{1}', matrix.machine_type, 'docker') }}
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: huggingface/transformers-all-latest-gpu
|
||||
options: --gpus 0 --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
options: --gpus all --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
needs: setup
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Echo folder ${{ matrix.folders }}
|
||||
@ -128,7 +129,6 @@ jobs:
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "${{ matrix.folders }}"
|
||||
matrix_folders=${{ matrix.folders }}
|
||||
echo "$matrix_folders"
|
||||
matrix_folders=${matrix_folders/'models/'/'models_'}
|
||||
echo "$matrix_folders"
|
||||
echo "matrix_folders=$matrix_folders" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
@ -137,21 +137,30 @@ jobs:
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: git fetch && git checkout ${{ github.sha }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NVIDIA-SMI
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
nvidia-smi
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Environment
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python3 utils/print_env.py
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run all tests on GPU
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: python3 -m pytest -v --make-reports=${{ matrix.machines }}_tests_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }} tests/${{ matrix.folders }}
|
||||
run: python3 -m pytest -v --make-reports=${{ matrix.machine_type }}_tests_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }} tests/${{ matrix.folders }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
if: ${{ failure() }}
|
||||
continue-on-error: true
|
||||
run: cat /transformers/reports/${{ matrix.machines }}_tests_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}/failures_short.txt
|
||||
run: cat /transformers/reports/${{ matrix.machine_type }}_tests_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}/failures_short.txt
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Test suite reports artifacts
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v2
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: ${{ matrix.machines }}_run_all_tests_gpu_${{ env.matrix_folders }}_test_reports
|
||||
path: /transformers/reports/${{ matrix.machines }}_tests_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}
|
||||
name: ${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_all_tests_gpu_${{ env.matrix_folders }}_test_reports
|
||||
path: /transformers/reports/${{ matrix.machine_type }}_tests_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}
|
||||
|
||||
run_examples_gpu:
|
||||
name: Examples directory
|
||||
@ -165,6 +174,15 @@ jobs:
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: git fetch && git checkout ${{ github.sha }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NVIDIA-SMI
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
nvidia-smi
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Environment
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python3 utils/print_env.py
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run examples tests on GPU
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
@ -188,46 +206,55 @@ jobs:
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
fail-fast: false
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
machines: [multi-gpu-docker, single-gpu-docker]
|
||||
runs-on: ${{ matrix.machines }}
|
||||
machine_type: [single-gpu, multi-gpu]
|
||||
runs-on: ${{ format('{0}-{1}', matrix.machine_type, 'docker') }}
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: huggingface/transformers-pytorch-gpu
|
||||
options: --gpus 0 --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
options: --gpus all --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
needs: setup
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Update clone
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: git fetch && git checkout ${{ github.sha }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NVIDIA-SMI
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
nvidia-smi
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Environment
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python3 utils/print_env.py
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run all pipeline tests on GPU
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
env:
|
||||
RUN_PIPELINE_TESTS: yes
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python3 -m pytest -n 1 -v --dist=loadfile -m is_pipeline_test --make-reports=${{ matrix.machines }}_tests_torch_pipeline_gpu tests
|
||||
python3 -m pytest -n 1 -v --dist=loadfile -m is_pipeline_test --make-reports=${{ matrix.machine_type }}_tests_torch_pipeline_gpu tests
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
if: ${{ failure() }}
|
||||
continue-on-error: true
|
||||
run: cat /transformers/reports/${{ matrix.machines }}_tests_torch_pipeline_gpu/failures_short.txt
|
||||
run: cat /transformers/reports/${{ matrix.machine_type }}_tests_torch_pipeline_gpu/failures_short.txt
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Test suite reports artifacts
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v2
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: ${{ matrix.machines }}_run_tests_torch_pipeline_gpu
|
||||
path: /transformers/reports/${{ matrix.machines }}_tests_torch_pipeline_gpu
|
||||
name: ${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_tests_torch_pipeline_gpu
|
||||
path: /transformers/reports/${{ matrix.machine_type }}_tests_torch_pipeline_gpu
|
||||
|
||||
run_pipelines_tf_gpu:
|
||||
name: TensorFlow pipelines
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
fail-fast: false
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
machines: [multi-gpu-docker, single-gpu-docker]
|
||||
runs-on: ${{ matrix.machines }}
|
||||
machine_type: [single-gpu, multi-gpu]
|
||||
runs-on: ${{ format('{0}-{1}', matrix.machine_type, 'docker') }}
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: huggingface/transformers-tensorflow-gpu
|
||||
options: --gpus 0 --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
options: --gpus all --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
needs: setup
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Update clone
|
||||
@ -235,32 +262,41 @@ jobs:
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
git fetch && git checkout ${{ github.sha }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NVIDIA-SMI
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
nvidia-smi
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Environment
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python3 utils/print_env.py
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run all pipeline tests on GPU
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
env:
|
||||
RUN_PIPELINE_TESTS: yes
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python3 -m pytest -n 1 -v --dist=loadfile -m is_pipeline_test --make-reports=${{ matrix.machines }}_tests_tf_pipeline_gpu tests
|
||||
python3 -m pytest -n 1 -v --dist=loadfile -m is_pipeline_test --make-reports=${{ matrix.machine_type }}_tests_tf_pipeline_gpu tests
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
cat /transformers/reports/${{ matrix.machines }}_tests_tf_pipeline_gpu/failures_short.txt
|
||||
cat /transformers/reports/${{ matrix.machine_type }}_tests_tf_pipeline_gpu/failures_short.txt
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Test suite reports artifacts
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v2
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: ${{ matrix.machines }}_run_tests_tf_pipeline_gpu
|
||||
path: /transformers/reports/${{ matrix.machines }}_tests_tf_pipeline_gpu
|
||||
name: ${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_tests_tf_pipeline_gpu
|
||||
path: /transformers/reports/${{ matrix.machine_type }}_tests_tf_pipeline_gpu
|
||||
|
||||
run_all_tests_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu:
|
||||
name: Torch CUDA extension tests
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
fail-fast: false
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
machines: [multi-gpu-docker, single-gpu-docker]
|
||||
runs-on: ${{ matrix.machines }}
|
||||
machine_type: [single-gpu, multi-gpu]
|
||||
runs-on: ${{ format('{0}-{1}', matrix.machine_type, 'docker') }}
|
||||
needs: setup
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: huggingface/transformers-pytorch-deepspeed-latest-gpu
|
||||
@ -270,31 +306,38 @@ jobs:
|
||||
working-directory: /workspace/transformers
|
||||
run: git fetch && git checkout ${{ github.sha }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Re-compile DeepSpeed
|
||||
# To avoid unknown test failures
|
||||
- name: Pre build DeepSpeed *again*
|
||||
working-directory: /workspace
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
pip install deepspeed # installs the deps correctly
|
||||
rm -rf DeepSpeed
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/microsoft/DeepSpeed && cd DeepSpeed && rm -rf build
|
||||
DS_BUILD_CPU_ADAM=1 DS_BUILD_AIO=1 DS_BUILD_UTILS=1 python3 -m pip install -e . --global-option="build_ext" --global-option="-j8" --no-cache -v --disable-pip-version-check
|
||||
python3 -m pip uninstall -y deepspeed
|
||||
DS_BUILD_CPU_ADAM=1 DS_BUILD_AIO=1 DS_BUILD_UTILS=1 python3 -m pip install deepspeed --global-option="build_ext" --global-option="-j8" --no-cache -v --disable-pip-version-check
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NVIDIA-SMI
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
nvidia-smi
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Environment
|
||||
working-directory: /workspace/transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python utils/print_env.py
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run all tests on GPU
|
||||
working-directory: /workspace/transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m pytest -v --make-reports=${{ matrix.machines }}_tests_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu tests/deepspeed tests/extended
|
||||
python -m pytest -v --make-reports=${{ matrix.machine_type }}_tests_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu tests/deepspeed tests/extended
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
if: ${{ failure() }}
|
||||
continue-on-error: true
|
||||
run: cat /workspace/transformers/reports/${{ matrix.machines }}_tests_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu/failures_short.txt
|
||||
run: cat /workspace/transformers/reports/${{ matrix.machine_type }}_tests_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu/failures_short.txt
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Test suite reports artifacts
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v2
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: ${{ matrix.machines }}_run_tests_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu_test_reports
|
||||
path: /workspace/transformers/reports/${{ matrix.machines }}_tests_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu
|
||||
|
||||
name: ${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_tests_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu_test_reports
|
||||
path: /workspace/transformers/reports/${{ matrix.machine_type }}_tests_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu
|
||||
|
||||
send_results:
|
||||
name: Send results to webhook
|
||||
@ -310,6 +353,8 @@ jobs:
|
||||
CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_ID: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_ID }}
|
||||
CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_ID_DAILY: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_ID_DAILY }}
|
||||
CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_DUMMY_TESTS: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_DUMMY_TESTS }}
|
||||
CI_SLACK_REPORT_CHANNEL_ID: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_ID_DAILY }}
|
||||
CI_EVENT: scheduled
|
||||
# We pass `needs.setup.outputs.matrix` as the argument. A processing in `notification_service.py` to change
|
||||
# `models/bert` to `models_bert` is required, as the artifact names use `_` instead of `/`.
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
|
||||
2
.github/workflows/update_metdata.yml
vendored
2
.github/workflows/update_metdata.yml
vendored
@ -21,7 +21,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
id: cache
|
||||
with:
|
||||
path: ~/venv/
|
||||
key: v2-metadata-${{ hashFiles('setup.py') }}
|
||||
key: v3-metadata-${{ hashFiles('setup.py') }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Create virtual environment on cache miss
|
||||
if: steps.cache.outputs.cache-hit != 'true'
|
||||
|
||||
@ -128,7 +128,7 @@ You will need basic `git` proficiency to be able to contribute to
|
||||
manual. Type `git --help` in a shell and enjoy. If you prefer books, [Pro
|
||||
Git](https://git-scm.com/book/en/v2) is a very good reference.
|
||||
|
||||
Follow these steps to start contributing:
|
||||
Follow these steps to start contributing ([supported Python versions](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/setup.py#L426)):
|
||||
|
||||
1. Fork the [repository](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers) by
|
||||
clicking on the 'Fork' button on the repository's page. This creates a copy of the code
|
||||
|
||||
10
Makefile
10
Makefile
@ -9,7 +9,7 @@ modified_only_fixup:
|
||||
$(eval modified_py_files := $(shell python utils/get_modified_files.py $(check_dirs)))
|
||||
@if test -n "$(modified_py_files)"; then \
|
||||
echo "Checking/fixing $(modified_py_files)"; \
|
||||
black $(modified_py_files); \
|
||||
black --preview $(modified_py_files); \
|
||||
isort $(modified_py_files); \
|
||||
flake8 $(modified_py_files); \
|
||||
else \
|
||||
@ -45,22 +45,26 @@ repo-consistency:
|
||||
# this target runs checks on all files
|
||||
|
||||
quality:
|
||||
black --check $(check_dirs)
|
||||
black --check --preview $(check_dirs)
|
||||
isort --check-only $(check_dirs)
|
||||
python utils/custom_init_isort.py --check_only
|
||||
python utils/sort_auto_mappings.py --check_only
|
||||
flake8 $(check_dirs)
|
||||
doc-builder style src/transformers docs/source --max_len 119 --check_only --path_to_docs docs/source
|
||||
python utils/check_doc_toc.py
|
||||
|
||||
# Format source code automatically and check is there are any problems left that need manual fixing
|
||||
|
||||
extra_style_checks:
|
||||
python utils/custom_init_isort.py
|
||||
python utils/sort_auto_mappings.py
|
||||
doc-builder style src/transformers docs/source --max_len 119 --path_to_docs docs/source
|
||||
python utils/check_doc_toc.py --fix_and_overwrite
|
||||
|
||||
# this target runs checks on all files and potentially modifies some of them
|
||||
|
||||
style:
|
||||
black $(check_dirs)
|
||||
black --preview $(check_dirs)
|
||||
isort $(check_dirs)
|
||||
${MAKE} autogenerate_code
|
||||
${MAKE} extra_style_checks
|
||||
|
||||
110
README.md
110
README.md
@ -116,22 +116,46 @@ To immediately use a model on a given input (text, image, audio, ...), we provid
|
||||
|
||||
The second line of code downloads and caches the pretrained model used by the pipeline, while the third evaluates it on the given text. Here the answer is "positive" with a confidence of 99.97%.
|
||||
|
||||
Many NLP tasks have a pre-trained `pipeline` ready to go. For example, we can easily extract question answers given context:
|
||||
Many tasks have a pre-trained `pipeline` ready to go, in NLP but also in computer vision and speech. For example, we can easily extract detected objects in an image:
|
||||
|
||||
``` python
|
||||
>>> import requests
|
||||
>>> from PIL import Image
|
||||
>>> from transformers import pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
# Allocate a pipeline for question-answering
|
||||
>>> question_answerer = pipeline('question-answering')
|
||||
>>> question_answerer({
|
||||
... 'question': 'What is the name of the repository ?',
|
||||
... 'context': 'Pipeline has been included in the huggingface/transformers repository'
|
||||
... })
|
||||
{'score': 0.30970096588134766, 'start': 34, 'end': 58, 'answer': 'huggingface/transformers'}
|
||||
# Download an image with cute cats
|
||||
>>> url = "https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/coco_sample.png"
|
||||
>>> image_data = requests.get(url, stream=True).raw
|
||||
>>> image = Image.open(image_data)
|
||||
|
||||
# Allocate a pipeline for object detection
|
||||
>>> object_detector = pipeline('object_detection')
|
||||
>>> object_detector(image)
|
||||
[{'score': 0.9982201457023621,
|
||||
'label': 'remote',
|
||||
'box': {'xmin': 40, 'ymin': 70, 'xmax': 175, 'ymax': 117}},
|
||||
{'score': 0.9960021376609802,
|
||||
'label': 'remote',
|
||||
'box': {'xmin': 333, 'ymin': 72, 'xmax': 368, 'ymax': 187}},
|
||||
{'score': 0.9954745173454285,
|
||||
'label': 'couch',
|
||||
'box': {'xmin': 0, 'ymin': 1, 'xmax': 639, 'ymax': 473}},
|
||||
{'score': 0.9988006353378296,
|
||||
'label': 'cat',
|
||||
'box': {'xmin': 13, 'ymin': 52, 'xmax': 314, 'ymax': 470}},
|
||||
{'score': 0.9986783862113953,
|
||||
'label': 'cat',
|
||||
'box': {'xmin': 345, 'ymin': 23, 'xmax': 640, 'ymax': 368}}]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In addition to the answer, the pretrained model used here returned its confidence score, along with the start position and end position of the answer in the tokenized sentence. You can learn more about the tasks supported by the `pipeline` API in [this tutorial](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/task_summary).
|
||||
Here we get a list of objects detected in the image, with a box surrounding the object and a confidence score. Here is the original image on the right, with the predictions displayed on the left:
|
||||
|
||||
<h3 align="center">
|
||||
<a><img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/coco_sample.png" width="400"></a>
|
||||
<a><img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/coco_sample_post_processed.png" width="400"></a>
|
||||
</h3>
|
||||
|
||||
You can learn more about the tasks supported by the `pipeline` API in [this tutorial](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/task_summary).
|
||||
|
||||
To download and use any of the pretrained models on your given task, all it takes is three lines of code. Here is the PyTorch version:
|
||||
```python
|
||||
@ -143,6 +167,7 @@ To download and use any of the pretrained models on your given task, all it take
|
||||
>>> inputs = tokenizer("Hello world!", return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
>>> outputs = model(**inputs)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
And here is the equivalent code for TensorFlow:
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer, TFAutoModel
|
||||
@ -234,65 +259,77 @@ Current number of checkpoints: ** (from VinAI Research) released with the paper [BARTpho: Pre-trained Sequence-to-Sequence Models for Vietnamese](https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.09701) by Nguyen Luong Tran, Duong Minh Le and Dat Quoc Nguyen.
|
||||
1. **[BEiT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/beit)** (from Microsoft) released with the paper [BEiT: BERT Pre-Training of Image Transformers](https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.08254) by Hangbo Bao, Li Dong, Furu Wei.
|
||||
1. **[BERT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/bert)** (from Google) released with the paper [BERT: Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/1810.04805) by Jacob Devlin, Ming-Wei Chang, Kenton Lee and Kristina Toutanova.
|
||||
1. **[BERTweet](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/bertweet)** (from VinAI Research) released with the paper [BERTweet: A pre-trained language model for English Tweets](https://aclanthology.org/2020.emnlp-demos.2/) by Dat Quoc Nguyen, Thanh Vu and Anh Tuan Nguyen.
|
||||
1. **[BERT For Sequence Generation](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/bert-generation)** (from Google) released with the paper [Leveraging Pre-trained Checkpoints for Sequence Generation Tasks](https://arxiv.org/abs/1907.12461) by Sascha Rothe, Shashi Narayan, Aliaksei Severyn.
|
||||
1. **[BigBird-RoBERTa](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/big_bird)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [Big Bird: Transformers for Longer Sequences](https://arxiv.org/abs/2007.14062) by Manzil Zaheer, Guru Guruganesh, Avinava Dubey, Joshua Ainslie, Chris Alberti, Santiago Ontanon, Philip Pham, Anirudh Ravula, Qifan Wang, Li Yang, Amr Ahmed.
|
||||
1. **[BERTweet](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/bertweet)** (from VinAI Research) released with the paper [BERTweet: A pre-trained language model for English Tweets](https://aclanthology.org/2020.emnlp-demos.2/) by Dat Quoc Nguyen, Thanh Vu and Anh Tuan Nguyen.
|
||||
1. **[BigBird-Pegasus](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/bigbird_pegasus)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [Big Bird: Transformers for Longer Sequences](https://arxiv.org/abs/2007.14062) by Manzil Zaheer, Guru Guruganesh, Avinava Dubey, Joshua Ainslie, Chris Alberti, Santiago Ontanon, Philip Pham, Anirudh Ravula, Qifan Wang, Li Yang, Amr Ahmed.
|
||||
1. **[BigBird-RoBERTa](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/big_bird)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [Big Bird: Transformers for Longer Sequences](https://arxiv.org/abs/2007.14062) by Manzil Zaheer, Guru Guruganesh, Avinava Dubey, Joshua Ainslie, Chris Alberti, Santiago Ontanon, Philip Pham, Anirudh Ravula, Qifan Wang, Li Yang, Amr Ahmed.
|
||||
1. **[Blenderbot](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/blenderbot)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Recipes for building an open-domain chatbot](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.13637) by Stephen Roller, Emily Dinan, Naman Goyal, Da Ju, Mary Williamson, Yinhan Liu, Jing Xu, Myle Ott, Kurt Shuster, Eric M. Smith, Y-Lan Boureau, Jason Weston.
|
||||
1. **[BlenderbotSmall](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/blenderbot-small)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Recipes for building an open-domain chatbot](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.13637) by Stephen Roller, Emily Dinan, Naman Goyal, Da Ju, Mary Williamson, Yinhan Liu, Jing Xu, Myle Ott, Kurt Shuster, Eric M. Smith, Y-Lan Boureau, Jason Weston.
|
||||
1. **[BLOOM](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/bloom)** (from BigScience workshop) released by the [BigSicence Workshop](https://bigscience.huggingface.co/).
|
||||
1. **[BORT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/bort)** (from Alexa) released with the paper [Optimal Subarchitecture Extraction For BERT](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.10499) by Adrian de Wynter and Daniel J. Perry.
|
||||
1. **[ByT5](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/byt5)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [ByT5: Towards a token-free future with pre-trained byte-to-byte models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2105.13626) by Linting Xue, Aditya Barua, Noah Constant, Rami Al-Rfou, Sharan Narang, Mihir Kale, Adam Roberts, Colin Raffel.
|
||||
1. **[CamemBERT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/camembert)** (from Inria/Facebook/Sorbonne) released with the paper [CamemBERT: a Tasty French Language Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.03894) by Louis Martin*, Benjamin Muller*, Pedro Javier Ortiz Suárez*, Yoann Dupont, Laurent Romary, Éric Villemonte de la Clergerie, Djamé Seddah and Benoît Sagot.
|
||||
1. **[CANINE](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/canine)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [CANINE: Pre-training an Efficient Tokenization-Free Encoder for Language Representation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.06874) by Jonathan H. Clark, Dan Garrette, Iulia Turc, John Wieting.
|
||||
1. **[ConvNeXT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/model_doc/convnext)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [A ConvNet for the 2020s](https://arxiv.org/abs/2201.03545) by Zhuang Liu, Hanzi Mao, Chao-Yuan Wu, Christoph Feichtenhofer, Trevor Darrell, Saining Xie.
|
||||
1. **[CLIP](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/clip)** (from OpenAI) released with the paper [Learning Transferable Visual Models From Natural Language Supervision](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.00020) by Alec Radford, Jong Wook Kim, Chris Hallacy, Aditya Ramesh, Gabriel Goh, Sandhini Agarwal, Girish Sastry, Amanda Askell, Pamela Mishkin, Jack Clark, Gretchen Krueger, Ilya Sutskever.
|
||||
1. **[CodeGen](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/codegen)** (from Salesforce) released with the paper [A Conversational Paradigm for Program Synthesis](https://arxiv.org/abs/2203.13474) by Erik Nijkamp, Bo Pang, Hiroaki Hayashi, Lifu Tu, Huan Wang, Yingbo Zhou, Silvio Savarese, Caiming Xiong.
|
||||
1. **[ConvBERT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/convbert)** (from YituTech) released with the paper [ConvBERT: Improving BERT with Span-based Dynamic Convolution](https://arxiv.org/abs/2008.02496) by Zihang Jiang, Weihao Yu, Daquan Zhou, Yunpeng Chen, Jiashi Feng, Shuicheng Yan.
|
||||
1. **[ConvNeXT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/convnext)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [A ConvNet for the 2020s](https://arxiv.org/abs/2201.03545) by Zhuang Liu, Hanzi Mao, Chao-Yuan Wu, Christoph Feichtenhofer, Trevor Darrell, Saining Xie.
|
||||
1. **[CPM](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/cpm)** (from Tsinghua University) released with the paper [CPM: A Large-scale Generative Chinese Pre-trained Language Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/2012.00413) by Zhengyan Zhang, Xu Han, Hao Zhou, Pei Ke, Yuxian Gu, Deming Ye, Yujia Qin, Yusheng Su, Haozhe Ji, Jian Guan, Fanchao Qi, Xiaozhi Wang, Yanan Zheng, Guoyang Zeng, Huanqi Cao, Shengqi Chen, Daixuan Li, Zhenbo Sun, Zhiyuan Liu, Minlie Huang, Wentao Han, Jie Tang, Juanzi Li, Xiaoyan Zhu, Maosong Sun.
|
||||
1. **[CTRL](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/ctrl)** (from Salesforce) released with the paper [CTRL: A Conditional Transformer Language Model for Controllable Generation](https://arxiv.org/abs/1909.05858) by Nitish Shirish Keskar*, Bryan McCann*, Lav R. Varshney, Caiming Xiong and Richard Socher.
|
||||
1. **[Data2Vec](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/model_doc/data2vec)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Data2Vec: A General Framework for Self-supervised Learning in Speech, Vision and Language](https://arxiv.org/abs/2202.03555) by Alexei Baevski, Wei-Ning Hsu, Qiantong Xu, Arun Babu, Jiatao Gu, Michael Auli.
|
||||
1. **[CvT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/cvt)** (from Microsoft) released with the paper [CvT: Introducing Convolutions to Vision Transformers](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.15808) by Haiping Wu, Bin Xiao, Noel Codella, Mengchen Liu, Xiyang Dai, Lu Yuan, Lei Zhang.
|
||||
1. **[Data2Vec](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/data2vec)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Data2Vec: A General Framework for Self-supervised Learning in Speech, Vision and Language](https://arxiv.org/abs/2202.03555) by Alexei Baevski, Wei-Ning Hsu, Qiantong Xu, Arun Babu, Jiatao Gu, Michael Auli.
|
||||
1. **[DeBERTa](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/deberta)** (from Microsoft) released with the paper [DeBERTa: Decoding-enhanced BERT with Disentangled Attention](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.03654) by Pengcheng He, Xiaodong Liu, Jianfeng Gao, Weizhu Chen.
|
||||
1. **[DeBERTa-v2](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/deberta-v2)** (from Microsoft) released with the paper [DeBERTa: Decoding-enhanced BERT with Disentangled Attention](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.03654) by Pengcheng He, Xiaodong Liu, Jianfeng Gao, Weizhu Chen.
|
||||
1. **[Decision Transformer](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/decision_transformer)** (from Berkeley/Facebook/Google) released with the paper [Decision Transformer: Reinforcement Learning via Sequence Modeling](https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.01345) by Lili Chen, Kevin Lu, Aravind Rajeswaran, Kimin Lee, Aditya Grover, Michael Laskin, Pieter Abbeel, Aravind Srinivas, Igor Mordatch.
|
||||
1. **[DiT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/dit)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [DiT: Self-supervised Pre-training for Document Image Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2203.02378) by Junlong Li, Yiheng Xu, Tengchao Lv, Lei Cui, Cha Zhang, Furu Wei.
|
||||
1. **[DeiT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/deit)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Training data-efficient image transformers & distillation through attention](https://arxiv.org/abs/2012.12877) by Hugo Touvron, Matthieu Cord, Matthijs Douze, Francisco Massa, Alexandre Sablayrolles, Hervé Jégou.
|
||||
1. **[DETR](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/detr)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [End-to-End Object Detection with Transformers](https://arxiv.org/abs/2005.12872) by Nicolas Carion, Francisco Massa, Gabriel Synnaeve, Nicolas Usunier, Alexander Kirillov, Sergey Zagoruyko.
|
||||
1. **[DialoGPT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/dialogpt)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [DialoGPT: Large-Scale Generative Pre-training for Conversational Response Generation](https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.00536) by Yizhe Zhang, Siqi Sun, Michel Galley, Yen-Chun Chen, Chris Brockett, Xiang Gao, Jianfeng Gao, Jingjing Liu, Bill Dolan.
|
||||
1. **[DistilBERT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/distilbert)** (from HuggingFace), released together with the paper [DistilBERT, a distilled version of BERT: smaller, faster, cheaper and lighter](https://arxiv.org/abs/1910.01108) by Victor Sanh, Lysandre Debut and Thomas Wolf. The same method has been applied to compress GPT2 into [DistilGPT2](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples/research_projects/distillation), RoBERTa into [DistilRoBERTa](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples/research_projects/distillation), Multilingual BERT into [DistilmBERT](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples/research_projects/distillation) and a German version of DistilBERT.
|
||||
1. **[DPR](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/dpr)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Dense Passage Retrieval
|
||||
for Open-Domain Question Answering](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.04906) by Vladimir Karpukhin, Barlas Oğuz, Sewon
|
||||
Min, Patrick Lewis, Ledell Wu, Sergey Edunov, Danqi Chen, and Wen-tau Yih.
|
||||
1. **[DiT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/dit)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [DiT: Self-supervised Pre-training for Document Image Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2203.02378) by Junlong Li, Yiheng Xu, Tengchao Lv, Lei Cui, Cha Zhang, Furu Wei.
|
||||
1. **[DPR](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/dpr)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Dense Passage Retrieval for Open-Domain Question Answering](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.04906) by Vladimir Karpukhin, Barlas Oğuz, Sewon Min, Patrick Lewis, Ledell Wu, Sergey Edunov, Danqi Chen, and Wen-tau Yih.
|
||||
1. **[DPT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/master/model_doc/dpt)** (from Intel Labs) released with the paper [Vision Transformers for Dense Prediction](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.13413) by René Ranftl, Alexey Bochkovskiy, Vladlen Koltun.
|
||||
1. **[EncoderDecoder](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/encoder-decoder)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [Leveraging Pre-trained Checkpoints for Sequence Generation Tasks](https://arxiv.org/abs/1907.12461) by Sascha Rothe, Shashi Narayan, Aliaksei Severyn.
|
||||
1. **[ELECTRA](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/electra)** (from Google Research/Stanford University) released with the paper [ELECTRA: Pre-training text encoders as discriminators rather than generators](https://arxiv.org/abs/2003.10555) by Kevin Clark, Minh-Thang Luong, Quoc V. Le, Christopher D. Manning.
|
||||
1. **[EncoderDecoder](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/encoder-decoder)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [Leveraging Pre-trained Checkpoints for Sequence Generation Tasks](https://arxiv.org/abs/1907.12461) by Sascha Rothe, Shashi Narayan, Aliaksei Severyn.
|
||||
1. **[FlauBERT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/flaubert)** (from CNRS) released with the paper [FlauBERT: Unsupervised Language Model Pre-training for French](https://arxiv.org/abs/1912.05372) by Hang Le, Loïc Vial, Jibril Frej, Vincent Segonne, Maximin Coavoux, Benjamin Lecouteux, Alexandre Allauzen, Benoît Crabbé, Laurent Besacier, Didier Schwab.
|
||||
1. **[FLAVA](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/model_doc/flava)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [FLAVA: A Foundational Language And Vision Alignment Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.04482) by Amanpreet Singh, Ronghang Hu, Vedanuj Goswami, Guillaume Couairon, Wojciech Galuba, Marcus Rohrbach, and Douwe Kiela.
|
||||
1. **[FLAVA](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/flava)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [FLAVA: A Foundational Language And Vision Alignment Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.04482) by Amanpreet Singh, Ronghang Hu, Vedanuj Goswami, Guillaume Couairon, Wojciech Galuba, Marcus Rohrbach, and Douwe Kiela.
|
||||
1. **[FNet](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/fnet)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [FNet: Mixing Tokens with Fourier Transforms](https://arxiv.org/abs/2105.03824) by James Lee-Thorp, Joshua Ainslie, Ilya Eckstein, Santiago Ontanon.
|
||||
1. **[Funnel Transformer](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/funnel)** (from CMU/Google Brain) released with the paper [Funnel-Transformer: Filtering out Sequential Redundancy for Efficient Language Processing](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.03236) by Zihang Dai, Guokun Lai, Yiming Yang, Quoc V. Le.
|
||||
1. **[GLPN](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/model_doc/glpn)** (from KAIST) released with the paper [Global-Local Path Networks for Monocular Depth Estimation with Vertical CutDepth](https://arxiv.org/abs/2201.07436) by Doyeon Kim, Woonghyun Ga, Pyungwhan Ahn, Donggyu Joo, Sehwan Chun, Junmo Kim.
|
||||
1. **[GLPN](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/glpn)** (from KAIST) released with the paper [Global-Local Path Networks for Monocular Depth Estimation with Vertical CutDepth](https://arxiv.org/abs/2201.07436) by Doyeon Kim, Woonghyun Ga, Pyungwhan Ahn, Donggyu Joo, Sehwan Chun, Junmo Kim.
|
||||
1. **[GPT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/openai-gpt)** (from OpenAI) released with the paper [Improving Language Understanding by Generative Pre-Training](https://blog.openai.com/language-unsupervised/) by Alec Radford, Karthik Narasimhan, Tim Salimans and Ilya Sutskever.
|
||||
1. **[GPT Neo](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/gpt_neo)** (from EleutherAI) released in the repository [EleutherAI/gpt-neo](https://github.com/EleutherAI/gpt-neo) by Sid Black, Stella Biderman, Leo Gao, Phil Wang and Connor Leahy.
|
||||
1. **[GPT NeoX](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/gpt_neox)** (from EleutherAI) released with the paper [GPT-NeoX-20B: An Open-Source Autoregressive Language Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/2204.06745) by Sid Black, Stella Biderman, Eric Hallahan, Quentin Anthony, Leo Gao, Laurence Golding, Horace He, Connor Leahy, Kyle McDonell, Jason Phang, Michael Pieler, USVSN Sai Prashanth, Shivanshu Purohit, Laria Reynolds, Jonathan Tow, Ben Wang, Samuel Weinbach
|
||||
1. **[GPT-2](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/gpt2)** (from OpenAI) released with the paper [Language Models are Unsupervised Multitask Learners](https://blog.openai.com/better-language-models/) by Alec Radford*, Jeffrey Wu*, Rewon Child, David Luan, Dario Amodei** and Ilya Sutskever**.
|
||||
1. **[GPT-J](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/gptj)** (from EleutherAI) released in the repository [kingoflolz/mesh-transformer-jax](https://github.com/kingoflolz/mesh-transformer-jax/) by Ben Wang and Aran Komatsuzaki.
|
||||
1. **[GPT Neo](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/gpt_neo)** (from EleutherAI) released in the repository [EleutherAI/gpt-neo](https://github.com/EleutherAI/gpt-neo) by Sid Black, Stella Biderman, Leo Gao, Phil Wang and Connor Leahy.
|
||||
1. **[GroupViT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/model_doc/groupvit)** (from UCSD, NVIDIA) released with the paper [GroupViT: Semantic Segmentation Emerges from Text Supervision](https://arxiv.org/abs/2202.11094) by Jiarui Xu, Shalini De Mello, Sifei Liu, Wonmin Byeon, Thomas Breuel, Jan Kautz, Xiaolong Wang.
|
||||
1. **[Hubert](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/hubert)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [HuBERT: Self-Supervised Speech Representation Learning by Masked Prediction of Hidden Units](https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.07447) by Wei-Ning Hsu, Benjamin Bolte, Yao-Hung Hubert Tsai, Kushal Lakhotia, Ruslan Salakhutdinov, Abdelrahman Mohamed.
|
||||
1. **[I-BERT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/ibert)** (from Berkeley) released with the paper [I-BERT: Integer-only BERT Quantization](https://arxiv.org/abs/2101.01321) by Sehoon Kim, Amir Gholami, Zhewei Yao, Michael W. Mahoney, Kurt Keutzer.
|
||||
1. **[ImageGPT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/model_doc/imagegpt)** (from OpenAI) released with the paper [Generative Pretraining from Pixels](https://openai.com/blog/image-gpt/) by Mark Chen, Alec Radford, Rewon Child, Jeffrey Wu, Heewoo Jun, David Luan, Ilya Sutskever.
|
||||
1. **[ImageGPT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/imagegpt)** (from OpenAI) released with the paper [Generative Pretraining from Pixels](https://openai.com/blog/image-gpt/) by Mark Chen, Alec Radford, Rewon Child, Jeffrey Wu, Heewoo Jun, David Luan, Ilya Sutskever.
|
||||
1. **[LayoutLM](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/layoutlm)** (from Microsoft Research Asia) released with the paper [LayoutLM: Pre-training of Text and Layout for Document Image Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/1912.13318) by Yiheng Xu, Minghao Li, Lei Cui, Shaohan Huang, Furu Wei, Ming Zhou.
|
||||
1. **[LayoutLMv2](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/layoutlmv2)** (from Microsoft Research Asia) released with the paper [LayoutLMv2: Multi-modal Pre-training for Visually-Rich Document Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/2012.14740) by Yang Xu, Yiheng Xu, Tengchao Lv, Lei Cui, Furu Wei, Guoxin Wang, Yijuan Lu, Dinei Florencio, Cha Zhang, Wanxiang Che, Min Zhang, Lidong Zhou.
|
||||
1. **[LayoutLMv3](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/layoutlmv3)** (from Microsoft Research Asia) released with the paper [LayoutLMv3: Pre-training for Document AI with Unified Text and Image Masking](https://arxiv.org/abs/2204.08387) by Yupan Huang, Tengchao Lv, Lei Cui, Yutong Lu, Furu Wei.
|
||||
1. **[LayoutXLM](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/layoutlmv2)** (from Microsoft Research Asia) released with the paper [LayoutXLM: Multimodal Pre-training for Multilingual Visually-rich Document Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.08836) by Yiheng Xu, Tengchao Lv, Lei Cui, Guoxin Wang, Yijuan Lu, Dinei Florencio, Cha Zhang, Furu Wei.
|
||||
1. **[LED](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/led)** (from AllenAI) released with the paper [Longformer: The Long-Document Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.05150) by Iz Beltagy, Matthew E. Peters, Arman Cohan.
|
||||
1. **[LeViT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/levit)** (from Meta AI) released with the paper [LeViT: A Vision Transformer in ConvNet's Clothing for Faster Inference](https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.01136) by Ben Graham, Alaaeldin El-Nouby, Hugo Touvron, Pierre Stock, Armand Joulin, Hervé Jégou, Matthijs Douze.
|
||||
1. **[Longformer](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/longformer)** (from AllenAI) released with the paper [Longformer: The Long-Document Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.05150) by Iz Beltagy, Matthew E. Peters, Arman Cohan.
|
||||
1. **[LongT5](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/longt5)** (from Google AI) released with the paper [LongT5: Efficient Text-To-Text Transformer for Long Sequences](https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.07916) by Mandy Guo, Joshua Ainslie, David Uthus, Santiago Ontanon, Jianmo Ni, Yun-Hsuan Sung, Yinfei Yang.
|
||||
1. **[LUKE](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/luke)** (from Studio Ousia) released with the paper [LUKE: Deep Contextualized Entity Representations with Entity-aware Self-attention](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.01057) by Ikuya Yamada, Akari Asai, Hiroyuki Shindo, Hideaki Takeda, Yuji Matsumoto.
|
||||
1. **[mLUKE](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/mluke)** (from Studio Ousia) released with the paper [mLUKE: The Power of Entity Representations in Multilingual Pretrained Language Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.08151) by Ryokan Ri, Ikuya Yamada, and Yoshimasa Tsuruoka.
|
||||
1. **[LXMERT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/lxmert)** (from UNC Chapel Hill) released with the paper [LXMERT: Learning Cross-Modality Encoder Representations from Transformers for Open-Domain Question Answering](https://arxiv.org/abs/1908.07490) by Hao Tan and Mohit Bansal.
|
||||
1. **[M-CTC-T](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/mctct)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Pseudo-Labeling For Massively Multilingual Speech Recognition](https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.00161) by Loren Lugosch, Tatiana Likhomanenko, Gabriel Synnaeve, and Ronan Collobert.
|
||||
1. **[M2M100](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/m2m_100)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Beyond English-Centric Multilingual Machine Translation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11125) by Angela Fan, Shruti Bhosale, Holger Schwenk, Zhiyi Ma, Ahmed El-Kishky, Siddharth Goyal, Mandeep Baines, Onur Celebi, Guillaume Wenzek, Vishrav Chaudhary, Naman Goyal, Tom Birch, Vitaliy Liptchinsky, Sergey Edunov, Edouard Grave, Michael Auli, Armand Joulin.
|
||||
1. **[MarianMT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/marian)** Machine translation models trained using [OPUS](http://opus.nlpl.eu/) data by Jörg Tiedemann. The [Marian Framework](https://marian-nmt.github.io/) is being developed by the Microsoft Translator Team.
|
||||
1. **[MaskFormer](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/model_doc/maskformer)** (from Meta and UIUC) released with the paper [Per-Pixel Classification is Not All You Need for Semantic Segmentation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.06278) by Bowen Cheng, Alexander G. Schwing, Alexander Kirillov.
|
||||
1. **[MBart](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/mbart)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Multilingual Denoising Pre-training for Neural Machine Translation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2001.08210) by Yinhan Liu, Jiatao Gu, Naman Goyal, Xian Li, Sergey Edunov, Marjan Ghazvininejad, Mike Lewis, Luke Zettlemoyer.
|
||||
1. **[MBart-50](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/mbart)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Multilingual Translation with Extensible Multilingual Pretraining and Finetuning](https://arxiv.org/abs/2008.00401) by Yuqing Tang, Chau Tran, Xian Li, Peng-Jen Chen, Naman Goyal, Vishrav Chaudhary, Jiatao Gu, Angela Fan.
|
||||
1. **[MaskFormer](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/maskformer)** (from Meta and UIUC) released with the paper [Per-Pixel Classification is Not All You Need for Semantic Segmentation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.06278) by Bowen Cheng, Alexander G. Schwing, Alexander Kirillov.
|
||||
1. **[mBART](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/mbart)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Multilingual Denoising Pre-training for Neural Machine Translation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2001.08210) by Yinhan Liu, Jiatao Gu, Naman Goyal, Xian Li, Sergey Edunov, Marjan Ghazvininejad, Mike Lewis, Luke Zettlemoyer.
|
||||
1. **[mBART-50](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/mbart)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Multilingual Translation with Extensible Multilingual Pretraining and Finetuning](https://arxiv.org/abs/2008.00401) by Yuqing Tang, Chau Tran, Xian Li, Peng-Jen Chen, Naman Goyal, Vishrav Chaudhary, Jiatao Gu, Angela Fan.
|
||||
1. **[Megatron-BERT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/megatron-bert)** (from NVIDIA) released with the paper [Megatron-LM: Training Multi-Billion Parameter Language Models Using Model Parallelism](https://arxiv.org/abs/1909.08053) by Mohammad Shoeybi, Mostofa Patwary, Raul Puri, Patrick LeGresley, Jared Casper and Bryan Catanzaro.
|
||||
1. **[Megatron-GPT2](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/megatron_gpt2)** (from NVIDIA) released with the paper [Megatron-LM: Training Multi-Billion Parameter Language Models Using Model Parallelism](https://arxiv.org/abs/1909.08053) by Mohammad Shoeybi, Mostofa Patwary, Raul Puri, Patrick LeGresley, Jared Casper and Bryan Catanzaro.
|
||||
1. **[mLUKE](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/mluke)** (from Studio Ousia) released with the paper [mLUKE: The Power of Entity Representations in Multilingual Pretrained Language Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.08151) by Ryokan Ri, Ikuya Yamada, and Yoshimasa Tsuruoka.
|
||||
1. **[MobileBERT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/mobilebert)** (from CMU/Google Brain) released with the paper [MobileBERT: a Compact Task-Agnostic BERT for Resource-Limited Devices](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.02984) by Zhiqing Sun, Hongkun Yu, Xiaodan Song, Renjie Liu, Yiming Yang, and Denny Zhou.
|
||||
1. **[MobileViT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/model_doc/mobilevit)** (from Apple) released with the paper [MobileViT: Light-weight, General-purpose, and Mobile-friendly Vision Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.02178) by Sachin Mehta and Mohammad Rastegari.
|
||||
1. **[MPNet](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/mpnet)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [MPNet: Masked and Permuted Pre-training for Language Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.09297) by Kaitao Song, Xu Tan, Tao Qin, Jianfeng Lu, Tie-Yan Liu.
|
||||
1. **[MT5](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/mt5)** (from Google AI) released with the paper [mT5: A massively multilingual pre-trained text-to-text transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11934) by Linting Xue, Noah Constant, Adam Roberts, Mihir Kale, Rami Al-Rfou, Aditya Siddhant, Aditya Barua, Colin Raffel.
|
||||
1. **[MVP](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/model_doc/mvp)** (from RUC AI Box) released with the paper [MVP: Multi-task Supervised Pre-training for Natural Language Generation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.12131) by Tianyi Tang, Junyi Li, Wayne Xin Zhao and Ji-Rong Wen.
|
||||
1. **[Nezha](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/model_doc/nezha)** (from Huawei Noah’s Ark Lab) released with the paper [NEZHA: Neural Contextualized Representation for Chinese Language Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/1909.00204) by Junqiu Wei, Xiaozhe Ren, Xiaoguang Li, Wenyong Huang, Yi Liao, Yasheng Wang, Jiashu Lin, Xin Jiang, Xiao Chen and Qun Liu.
|
||||
1. **[NLLB](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/model_doc/nllb)** (from Meta) released with the paper [No Language Left Behind: Scaling Human-Centered Machine Translation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2207.04672) by the NLLB team.
|
||||
1. **[Nyströmformer](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/nystromformer)** (from the University of Wisconsin - Madison) released with the paper [Nyströmformer: A Nyström-Based Algorithm for Approximating Self-Attention](https://arxiv.org/abs/2102.03902) by Yunyang Xiong, Zhanpeng Zeng, Rudrasis Chakraborty, Mingxing Tan, Glenn Fung, Yin Li, Vikas Singh.
|
||||
1. **[OPT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/master/model_doc/opt)** (from Meta AI) released with the paper [OPT: Open Pre-trained Transformer Language Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.01068) by Susan Zhang, Stephen Roller, Naman Goyal, Mikel Artetxe, Moya Chen, Shuohui Chen et al.
|
||||
1. **[Pegasus](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/pegasus)** (from Google) released with the paper [PEGASUS: Pre-training with Extracted Gap-sentences for Abstractive Summarization](https://arxiv.org/abs/1912.08777) by Jingqing Zhang, Yao Zhao, Mohammad Saleh and Peter J. Liu.
|
||||
@ -302,10 +339,11 @@ Min, Patrick Lewis, Ledell Wu, Sergey Edunov, Danqi Chen, and Wen-tau Yih.
|
||||
1. **[PoolFormer](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/poolformer)** (from Sea AI Labs) released with the paper [MetaFormer is Actually What You Need for Vision](https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.11418) by Yu, Weihao and Luo, Mi and Zhou, Pan and Si, Chenyang and Zhou, Yichen and Wang, Xinchao and Feng, Jiashi and Yan, Shuicheng.
|
||||
1. **[ProphetNet](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/prophetnet)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [ProphetNet: Predicting Future N-gram for Sequence-to-Sequence Pre-training](https://arxiv.org/abs/2001.04063) by Yu Yan, Weizhen Qi, Yeyun Gong, Dayiheng Liu, Nan Duan, Jiusheng Chen, Ruofei Zhang and Ming Zhou.
|
||||
1. **[QDQBert](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/qdqbert)** (from NVIDIA) released with the paper [Integer Quantization for Deep Learning Inference: Principles and Empirical Evaluation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.09602) by Hao Wu, Patrick Judd, Xiaojie Zhang, Mikhail Isaev and Paulius Micikevicius.
|
||||
1. **[RAG](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/rag)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Knowledge-Intensive NLP Tasks](https://arxiv.org/abs/2005.11401) by Patrick Lewis, Ethan Perez, Aleksandara Piktus, Fabio Petroni, Vladimir Karpukhin, Naman Goyal, Heinrich Küttler, Mike Lewis, Wen-tau Yih, Tim Rocktäschel, Sebastian Riedel, Douwe Kiela.
|
||||
1. **[REALM](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/realm.html)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [REALM: Retrieval-Augmented Language Model Pre-Training](https://arxiv.org/abs/2002.08909) by Kelvin Guu, Kenton Lee, Zora Tung, Panupong Pasupat and Ming-Wei Chang.
|
||||
1. **[Reformer](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/reformer)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [Reformer: The Efficient Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2001.04451) by Nikita Kitaev, Łukasz Kaiser, Anselm Levskaya.
|
||||
1. **[RegNet](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/regnet)** (from META Platforms) released with the paper [Designing Network Design Space](https://arxiv.org/abs/2003.13678) by Ilija Radosavovic, Raj Prateek Kosaraju, Ross Girshick, Kaiming He, Piotr Dollár.
|
||||
1. **[RemBERT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/rembert)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [Rethinking embedding coupling in pre-trained language models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.12821) by Hyung Won Chung, Thibault Févry, Henry Tsai, M. Johnson, Sebastian Ruder.
|
||||
1. **[RegNet](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/model_doc/regnet)** (from META Platforms) released with the paper [Designing Network Design Space](https://arxiv.org/abs/2003.13678) by Ilija Radosavovic, Raj Prateek Kosaraju, Ross Girshick, Kaiming He, Piotr Dollár.
|
||||
1. **[ResNet](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/resnet)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition](https://arxiv.org/abs/1512.03385) by Kaiming He, Xiangyu Zhang, Shaoqing Ren, Jian Sun.
|
||||
1. **[RoBERTa](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/roberta)** (from Facebook), released together with the paper [RoBERTa: A Robustly Optimized BERT Pretraining Approach](https://arxiv.org/abs/1907.11692) by Yinhan Liu, Myle Ott, Naman Goyal, Jingfei Du, Mandar Joshi, Danqi Chen, Omer Levy, Mike Lewis, Luke Zettlemoyer, Veselin Stoyanov.
|
||||
1. **[RoFormer](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/roformer)** (from ZhuiyiTechnology), released together with the paper [RoFormer: Enhanced Transformer with Rotary Position Embedding](https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.09864) by Jianlin Su and Yu Lu and Shengfeng Pan and Bo Wen and Yunfeng Liu.
|
||||
@ -315,34 +353,36 @@ Min, Patrick Lewis, Ledell Wu, Sergey Edunov, Danqi Chen, and Wen-tau Yih.
|
||||
1. **[SpeechToTextTransformer](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/speech_to_text)** (from Facebook), released together with the paper [fairseq S2T: Fast Speech-to-Text Modeling with fairseq](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.05171) by Changhan Wang, Yun Tang, Xutai Ma, Anne Wu, Dmytro Okhonko, Juan Pino.
|
||||
1. **[SpeechToTextTransformer2](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/speech_to_text_2)** (from Facebook), released together with the paper [Large-Scale Self- and Semi-Supervised Learning for Speech Translation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.06678) by Changhan Wang, Anne Wu, Juan Pino, Alexei Baevski, Michael Auli, Alexis Conneau.
|
||||
1. **[Splinter](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/splinter)** (from Tel Aviv University), released together with the paper [Few-Shot Question Answering by Pretraining Span Selection](https://arxiv.org/abs/2101.00438) by Ori Ram, Yuval Kirstain, Jonathan Berant, Amir Globerson, Omer Levy.
|
||||
1. **[SqueezeBert](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/squeezebert)** (from Berkeley) released with the paper [SqueezeBERT: What can computer vision teach NLP about efficient neural networks?](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.11316) by Forrest N. Iandola, Albert E. Shaw, Ravi Krishna, and Kurt W. Keutzer.
|
||||
1. **[SqueezeBERT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/squeezebert)** (from Berkeley) released with the paper [SqueezeBERT: What can computer vision teach NLP about efficient neural networks?](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.11316) by Forrest N. Iandola, Albert E. Shaw, Ravi Krishna, and Kurt W. Keutzer.
|
||||
1. **[Swin Transformer](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/swin)** (from Microsoft) released with the paper [Swin Transformer: Hierarchical Vision Transformer using Shifted Windows](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.14030) by Ze Liu, Yutong Lin, Yue Cao, Han Hu, Yixuan Wei, Zheng Zhang, Stephen Lin, Baining Guo.
|
||||
1. **[T5](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/t5)** (from Google AI) released with the paper [Exploring the Limits of Transfer Learning with a Unified Text-to-Text Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/1910.10683) by Colin Raffel and Noam Shazeer and Adam Roberts and Katherine Lee and Sharan Narang and Michael Matena and Yanqi Zhou and Wei Li and Peter J. Liu.
|
||||
1. **[T5v1.1](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/t5v1.1)** (from Google AI) released in the repository [google-research/text-to-text-transfer-transformer](https://github.com/google-research/text-to-text-transfer-transformer/blob/main/released_checkpoints.md#t511) by Colin Raffel and Noam Shazeer and Adam Roberts and Katherine Lee and Sharan Narang and Michael Matena and Yanqi Zhou and Wei Li and Peter J. Liu.
|
||||
1. **[TAPAS](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/tapas)** (from Google AI) released with the paper [TAPAS: Weakly Supervised Table Parsing via Pre-training](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.02349) by Jonathan Herzig, Paweł Krzysztof Nowak, Thomas Müller, Francesco Piccinno and Julian Martin Eisenschlos.
|
||||
1. **[TAPEX](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/model_doc/tapex)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [TAPEX: Table Pre-training via Learning a Neural SQL Executor](https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.07653) by Qian Liu, Bei Chen, Jiaqi Guo, Morteza Ziyadi, Zeqi Lin, Weizhu Chen, Jian-Guang Lou.
|
||||
1. **[TAPEX](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/tapex)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [TAPEX: Table Pre-training via Learning a Neural SQL Executor](https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.07653) by Qian Liu, Bei Chen, Jiaqi Guo, Morteza Ziyadi, Zeqi Lin, Weizhu Chen, Jian-Guang Lou.
|
||||
1. **[Trajectory Transformer](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/trajectory_transformers)** (from the University of California at Berkeley) released with the paper [Offline Reinforcement Learning as One Big Sequence Modeling Problem](https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.02039) by Michael Janner, Qiyang Li, Sergey Levine
|
||||
1. **[Transformer-XL](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/transfo-xl)** (from Google/CMU) released with the paper [Transformer-XL: Attentive Language Models Beyond a Fixed-Length Context](https://arxiv.org/abs/1901.02860) by Zihang Dai*, Zhilin Yang*, Yiming Yang, Jaime Carbonell, Quoc V. Le, Ruslan Salakhutdinov.
|
||||
1. **[TrOCR](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/trocr)** (from Microsoft), released together with the paper [TrOCR: Transformer-based Optical Character Recognition with Pre-trained Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.10282) by Minghao Li, Tengchao Lv, Lei Cui, Yijuan Lu, Dinei Florencio, Cha Zhang, Zhoujun Li, Furu Wei.
|
||||
1. **[UL2](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/model_doc/ul2)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [Unifying Language Learning Paradigms](https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.05131v1) by Yi Tay, Mostafa Dehghani, Vinh Q. Tran, Xavier Garcia, Dara Bahri, Tal Schuster, Huaixiu Steven Zheng, Neil Houlsby, Donald Metzler
|
||||
1. **[UniSpeech](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/unispeech)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [UniSpeech: Unified Speech Representation Learning with Labeled and Unlabeled Data](https://arxiv.org/abs/2101.07597) by Chengyi Wang, Yu Wu, Yao Qian, Kenichi Kumatani, Shujie Liu, Furu Wei, Michael Zeng, Xuedong Huang.
|
||||
1. **[UniSpeechSat](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/unispeech-sat)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [UNISPEECH-SAT: UNIVERSAL SPEECH REPRESENTATION LEARNING WITH SPEAKER
|
||||
AWARE PRE-TRAINING](https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.05752) by Sanyuan Chen, Yu Wu, Chengyi Wang, Zhengyang Chen, Zhuo Chen, Shujie Liu, Jian Wu, Yao Qian, Furu Wei, Jinyu Li, Xiangzhan Yu.
|
||||
1. **[UniSpeechSat](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/unispeech-sat)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [UNISPEECH-SAT: UNIVERSAL SPEECH REPRESENTATION LEARNING WITH SPEAKER AWARE PRE-TRAINING](https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.05752) by Sanyuan Chen, Yu Wu, Chengyi Wang, Zhengyang Chen, Zhuo Chen, Shujie Liu, Jian Wu, Yao Qian, Furu Wei, Jinyu Li, Xiangzhan Yu.
|
||||
1. **[VAN](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/van)** (from Tsinghua University and Nankai University) released with the paper [Visual Attention Network](https://arxiv.org/abs/2202.09741) by Meng-Hao Guo, Cheng-Ze Lu, Zheng-Ning Liu, Ming-Ming Cheng, Shi-Min Hu.
|
||||
1. **[ViLT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/vilt)** (from NAVER AI Lab/Kakao Enterprise/Kakao Brain) released with the paper [ViLT: Vision-and-Language Transformer Without Convolution or Region Supervision](https://arxiv.org/abs/2102.03334) by Wonjae Kim, Bokyung Son, Ildoo Kim.
|
||||
1. **[Vision Transformer (ViT)](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/vit)** (from Google AI) released with the paper [An Image is Worth 16x16 Words: Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11929) by Alexey Dosovitskiy, Lucas Beyer, Alexander Kolesnikov, Dirk Weissenborn, Xiaohua Zhai, Thomas Unterthiner, Mostafa Dehghani, Matthias Minderer, Georg Heigold, Sylvain Gelly, Jakob Uszkoreit, Neil Houlsby.
|
||||
1. **[ViTMAE](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/vit_mae)** (from Meta AI) released with the paper [Masked Autoencoders Are Scalable Vision Learners](https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.06377) by Kaiming He, Xinlei Chen, Saining Xie, Yanghao Li, Piotr Dollár, Ross Girshick.
|
||||
1. **[VisualBERT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/visual_bert)** (from UCLA NLP) released with the paper [VisualBERT: A Simple and Performant Baseline for Vision and Language](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1908.03557) by Liunian Harold Li, Mark Yatskar, Da Yin, Cho-Jui Hsieh, Kai-Wei Chang.
|
||||
1. **[WavLM](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/wavlm)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [WavLM: Large-Scale Self-Supervised Pre-Training for Full Stack Speech Processing](https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.13900) by Sanyuan Chen, Chengyi Wang, Zhengyang Chen, Yu Wu, Shujie Liu, Zhuo Chen, Jinyu Li, Naoyuki Kanda, Takuya Yoshioka, Xiong Xiao, Jian Wu, Long Zhou, Shuo Ren, Yanmin Qian, Yao Qian, Jian Wu, Michael Zeng, Furu Wei.
|
||||
1. **[ViTMAE](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/vit_mae)** (from Meta AI) released with the paper [Masked Autoencoders Are Scalable Vision Learners](https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.06377) by Kaiming He, Xinlei Chen, Saining Xie, Yanghao Li, Piotr Dollár, Ross Girshick.
|
||||
1. **[Wav2Vec2](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/wav2vec2)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [wav2vec 2.0: A Framework for Self-Supervised Learning of Speech Representations](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.11477) by Alexei Baevski, Henry Zhou, Abdelrahman Mohamed, Michael Auli.
|
||||
1. **[Wav2Vec2-Conformer](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/wav2vec2-conformer)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [FAIRSEQ S2T: Fast Speech-to-Text Modeling with FAIRSEQ](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.05171) by Changhan Wang, Yun Tang, Xutai Ma, Anne Wu, Sravya Popuri, Dmytro Okhonko, Juan Pino.
|
||||
1. **[Wav2Vec2Phoneme](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/wav2vec2_phoneme)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [Simple and Effective Zero-shot Cross-lingual Phoneme Recognition](https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.11680) by Qiantong Xu, Alexei Baevski, Michael Auli.
|
||||
1. **[WavLM](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/wavlm)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [WavLM: Large-Scale Self-Supervised Pre-Training for Full Stack Speech Processing](https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.13900) by Sanyuan Chen, Chengyi Wang, Zhengyang Chen, Yu Wu, Shujie Liu, Zhuo Chen, Jinyu Li, Naoyuki Kanda, Takuya Yoshioka, Xiong Xiao, Jian Wu, Long Zhou, Shuo Ren, Yanmin Qian, Yao Qian, Jian Wu, Michael Zeng, Furu Wei.
|
||||
1. **[XGLM](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/xglm)** (From Facebook AI) released with the paper [Few-shot Learning with Multilingual Language Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.10668) by Xi Victoria Lin, Todor Mihaylov, Mikel Artetxe, Tianlu Wang, Shuohui Chen, Daniel Simig, Myle Ott, Naman Goyal, Shruti Bhosale, Jingfei Du, Ramakanth Pasunuru, Sam Shleifer, Punit Singh Koura, Vishrav Chaudhary, Brian O'Horo, Jeff Wang, Luke Zettlemoyer, Zornitsa Kozareva, Mona Diab, Veselin Stoyanov, Xian Li.
|
||||
1. **[XLM](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/xlm)** (from Facebook) released together with the paper [Cross-lingual Language Model Pretraining](https://arxiv.org/abs/1901.07291) by Guillaume Lample and Alexis Conneau.
|
||||
1. **[XLM-ProphetNet](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/xlm-prophetnet)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [ProphetNet: Predicting Future N-gram for Sequence-to-Sequence Pre-training](https://arxiv.org/abs/2001.04063) by Yu Yan, Weizhen Qi, Yeyun Gong, Dayiheng Liu, Nan Duan, Jiusheng Chen, Ruofei Zhang and Ming Zhou.
|
||||
1. **[XLM-RoBERTa](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/xlm-roberta)** (from Facebook AI), released together with the paper [Unsupervised Cross-lingual Representation Learning at Scale](https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.02116) by Alexis Conneau*, Kartikay Khandelwal*, Naman Goyal, Vishrav Chaudhary, Guillaume Wenzek, Francisco Guzmán, Edouard Grave, Myle Ott, Luke Zettlemoyer and Veselin Stoyanov.
|
||||
1. **[XLM-RoBERTa-XL](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/xlm-roberta-xl)** (from Facebook AI), released together with the paper [Larger-Scale Transformers for Multilingual Masked Language Modeling](https://arxiv.org/abs/2105.00572) by Naman Goyal, Jingfei Du, Myle Ott, Giri Anantharaman, Alexis Conneau.
|
||||
1. **[XLNet](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/xlnet)** (from Google/CMU) released with the paper [XLNet: Generalized Autoregressive Pretraining for Language Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/1906.08237) by Zhilin Yang*, Zihang Dai*, Yiming Yang, Jaime Carbonell, Ruslan Salakhutdinov, Quoc V. Le.
|
||||
1. **[XLSR-Wav2Vec2](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/xlsr_wav2vec2)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [Unsupervised Cross-Lingual Representation Learning For Speech Recognition](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.13979) by Alexis Conneau, Alexei Baevski, Ronan Collobert, Abdelrahman Mohamed, Michael Auli.
|
||||
1. **[XLS-R](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/xls_r)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [XLS-R: Self-supervised Cross-lingual Speech Representation Learning at Scale](https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.09296) by Arun Babu, Changhan Wang, Andros Tjandra, Kushal Lakhotia, Qiantong Xu, Naman Goyal, Kritika Singh, Patrick von Platen, Yatharth Saraf, Juan Pino, Alexei Baevski, Alexis Conneau, Michael Auli.
|
||||
1. **[YOLOS](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/model_doc/yolos)** (from Huazhong University of Science & Technology) released with the paper [You Only Look at One Sequence: Rethinking Transformer in Vision through Object Detection](https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.00666) by Yuxin Fang, Bencheng Liao, Xinggang Wang, Jiemin Fang, Jiyang Qi, Rui Wu, Jianwei Niu, Wenyu Liu.
|
||||
1. **[XLSR-Wav2Vec2](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/xlsr_wav2vec2)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [Unsupervised Cross-Lingual Representation Learning For Speech Recognition](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.13979) by Alexis Conneau, Alexei Baevski, Ronan Collobert, Abdelrahman Mohamed, Michael Auli.
|
||||
1. **[YOLOS](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/yolos)** (from Huazhong University of Science & Technology) released with the paper [You Only Look at One Sequence: Rethinking Transformer in Vision through Object Detection](https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.00666) by Yuxin Fang, Bencheng Liao, Xinggang Wang, Jiemin Fang, Jiyang Qi, Rui Wu, Jianwei Niu, Wenyu Liu.
|
||||
1. **[YOSO](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/yoso)** (from the University of Wisconsin - Madison) released with the paper [You Only Sample (Almost) Once: Linear Cost Self-Attention Via Bernoulli Sampling](https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.09714) by Zhanpeng Zeng, Yunyang Xiong, Sathya N. Ravi, Shailesh Acharya, Glenn Fung, Vikas Singh.
|
||||
1. Want to contribute a new model? We have added a **detailed guide and templates** to guide you in the process of adding a new model. You can find them in the [`templates`](./templates) folder of the repository. Be sure to check the [contributing guidelines](./CONTRIBUTING.md) and contact the maintainers or open an issue to collect feedbacks before starting your PR.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
42
README_ko.md
42
README_ko.md
@ -221,16 +221,19 @@ Flax, PyTorch, TensorFlow 설치 페이지에서 이들을 conda로 설치하는
|
||||
1. **[BigBird-RoBERTa](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/big_bird)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [Big Bird: Transformers for Longer Sequences](https://arxiv.org/abs/2007.14062) by Manzil Zaheer, Guru Guruganesh, Avinava Dubey, Joshua Ainslie, Chris Alberti, Santiago Ontanon, Philip Pham, Anirudh Ravula, Qifan Wang, Li Yang, Amr Ahmed.
|
||||
1. **[Blenderbot](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/blenderbot)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Recipes for building an open-domain chatbot](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.13637) by Stephen Roller, Emily Dinan, Naman Goyal, Da Ju, Mary Williamson, Yinhan Liu, Jing Xu, Myle Ott, Kurt Shuster, Eric M. Smith, Y-Lan Boureau, Jason Weston.
|
||||
1. **[BlenderbotSmall](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/blenderbot-small)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Recipes for building an open-domain chatbot](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.13637) by Stephen Roller, Emily Dinan, Naman Goyal, Da Ju, Mary Williamson, Yinhan Liu, Jing Xu, Myle Ott, Kurt Shuster, Eric M. Smith, Y-Lan Boureau, Jason Weston.
|
||||
1. **[BLOOM](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/bloom)** (from BigScience workshop) released by the [BigSicence Workshop](https://bigscience.huggingface.co/).
|
||||
1. **[BORT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/bort)** (from Alexa) released with the paper [Optimal Subarchitecture Extraction For BERT](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.10499) by Adrian de Wynter and Daniel J. Perry.
|
||||
1. **[ByT5](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/byt5)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [ByT5: Towards a token-free future with pre-trained byte-to-byte models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2105.13626) by Linting Xue, Aditya Barua, Noah Constant, Rami Al-Rfou, Sharan Narang, Mihir Kale, Adam Roberts, Colin Raffel.
|
||||
1. **[CamemBERT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/camembert)** (from Inria/Facebook/Sorbonne) released with the paper [CamemBERT: a Tasty French Language Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.03894) by Louis Martin*, Benjamin Muller*, Pedro Javier Ortiz Suárez*, Yoann Dupont, Laurent Romary, Éric Villemonte de la Clergerie, Djamé Seddah and Benoît Sagot.
|
||||
1. **[CANINE](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/canine)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [CANINE: Pre-training an Efficient Tokenization-Free Encoder for Language Representation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.06874) by Jonathan H. Clark, Dan Garrette, Iulia Turc, John Wieting.
|
||||
1. **[CLIP](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/clip)** (from OpenAI) released with the paper [Learning Transferable Visual Models From Natural Language Supervision](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.00020) by Alec Radford, Jong Wook Kim, Chris Hallacy, Aditya Ramesh, Gabriel Goh, Sandhini Agarwal, Girish Sastry, Amanda Askell, Pamela Mishkin, Jack Clark, Gretchen Krueger, Ilya Sutskever.
|
||||
1. **[CodeGen](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/codegen)** (from Salesforce) released with the paper [A Conversational Paradigm for Program Synthesis](https://arxiv.org/abs/2203.13474) by Erik Nijkamp, Bo Pang, Hiroaki Hayashi, Lifu Tu, Huan Wang, Yingbo Zhou, Silvio Savarese, Caiming Xiong.
|
||||
1. **[ConvBERT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/convbert)** (from YituTech) released with the paper [ConvBERT: Improving BERT with Span-based Dynamic Convolution](https://arxiv.org/abs/2008.02496) by Zihang Jiang, Weihao Yu, Daquan Zhou, Yunpeng Chen, Jiashi Feng, Shuicheng Yan.
|
||||
1. **[ConvNeXT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/model_doc/convnext)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [A ConvNet for the 2020s](https://arxiv.org/abs/2201.03545) by Zhuang Liu, Hanzi Mao, Chao-Yuan Wu, Christoph Feichtenhofer, Trevor Darrell, Saining Xie.
|
||||
1. **[ConvNeXT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/convnext)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [A ConvNet for the 2020s](https://arxiv.org/abs/2201.03545) by Zhuang Liu, Hanzi Mao, Chao-Yuan Wu, Christoph Feichtenhofer, Trevor Darrell, Saining Xie.
|
||||
1. **[CPM](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/cpm)** (from Tsinghua University) released with the paper [CPM: A Large-scale Generative Chinese Pre-trained Language Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/2012.00413) by Zhengyan Zhang, Xu Han, Hao Zhou, Pei Ke, Yuxian Gu, Deming Ye, Yujia Qin, Yusheng Su, Haozhe Ji, Jian Guan, Fanchao Qi, Xiaozhi Wang, Yanan Zheng, Guoyang Zeng, Huanqi Cao, Shengqi Chen, Daixuan Li, Zhenbo Sun, Zhiyuan Liu, Minlie Huang, Wentao Han, Jie Tang, Juanzi Li, Xiaoyan Zhu, Maosong Sun.
|
||||
1. **[CTRL](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/ctrl)** (from Salesforce) released with the paper [CTRL: A Conditional Transformer Language Model for Controllable Generation](https://arxiv.org/abs/1909.05858) by Nitish Shirish Keskar*, Bryan McCann*, Lav R. Varshney, Caiming Xiong and Richard Socher.
|
||||
1. **[Data2Vec](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/model_doc/data2vec)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Data2Vec: A General Framework for Self-supervised Learning in Speech, Vision and Language](https://arxiv.org/abs/2202.03555) by Alexei Baevski, Wei-Ning Hsu, Qiantong Xu, Arun Babu, Jiatao Gu, Michael Auli.
|
||||
1. **[CvT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/cvt)** (from Microsoft) released with the paper [CvT: Introducing Convolutions to Vision Transformers](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.15808) by Haiping Wu, Bin Xiao, Noel Codella, Mengchen Liu, Xiyang Dai, Lu Yuan, Lei Zhang.
|
||||
1. **[Data2Vec](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/data2vec)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Data2Vec: A General Framework for Self-supervised Learning in Speech, Vision and Language](https://arxiv.org/abs/2202.03555) by Alexei Baevski, Wei-Ning Hsu, Qiantong Xu, Arun Babu, Jiatao Gu, Michael Auli.
|
||||
1. **[DeBERTa](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/deberta)** (from Microsoft) released with the paper [DeBERTa: Decoding-enhanced BERT with Disentangled Attention](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.03654) by Pengcheng He, Xiaodong Liu, Jianfeng Gao, Weizhu Chen.
|
||||
1. **[DeBERTa-v2](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/deberta-v2)** (from Microsoft) released with the paper [DeBERTa: Decoding-enhanced BERT with Disentangled Attention](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.03654) by Pengcheng He, Xiaodong Liu, Jianfeng Gao, Weizhu Chen.
|
||||
1. **[Decision Transformer](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/decision_transformer)** (from Berkeley/Facebook/Google) released with the paper [Decision Transformer: Reinforcement Learning via Sequence Modeling](https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.01345) by Lili Chen, Kevin Lu, Aravind Rajeswaran, Kimin Lee, Aditya Grover, Michael Laskin, Pieter Abbeel, Aravind Srinivas, Igor Mordatch.
|
||||
@ -244,34 +247,45 @@ Flax, PyTorch, TensorFlow 설치 페이지에서 이들을 conda로 설치하는
|
||||
1. **[ELECTRA](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/electra)** (from Google Research/Stanford University) released with the paper [ELECTRA: Pre-training text encoders as discriminators rather than generators](https://arxiv.org/abs/2003.10555) by Kevin Clark, Minh-Thang Luong, Quoc V. Le, Christopher D. Manning.
|
||||
1. **[EncoderDecoder](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/encoder-decoder)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [Leveraging Pre-trained Checkpoints for Sequence Generation Tasks](https://arxiv.org/abs/1907.12461) by Sascha Rothe, Shashi Narayan, Aliaksei Severyn.
|
||||
1. **[FlauBERT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/flaubert)** (from CNRS) released with the paper [FlauBERT: Unsupervised Language Model Pre-training for French](https://arxiv.org/abs/1912.05372) by Hang Le, Loïc Vial, Jibril Frej, Vincent Segonne, Maximin Coavoux, Benjamin Lecouteux, Alexandre Allauzen, Benoît Crabbé, Laurent Besacier, Didier Schwab.
|
||||
1. **[FLAVA](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/model_doc/flava)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [FLAVA: A Foundational Language And Vision Alignment Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.04482) by Amanpreet Singh, Ronghang Hu, Vedanuj Goswami, Guillaume Couairon, Wojciech Galuba, Marcus Rohrbach, and Douwe Kiela.
|
||||
1. **[FLAVA](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/flava)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [FLAVA: A Foundational Language And Vision Alignment Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.04482) by Amanpreet Singh, Ronghang Hu, Vedanuj Goswami, Guillaume Couairon, Wojciech Galuba, Marcus Rohrbach, and Douwe Kiela.
|
||||
1. **[FNet](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/fnet)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [FNet: Mixing Tokens with Fourier Transforms](https://arxiv.org/abs/2105.03824) by James Lee-Thorp, Joshua Ainslie, Ilya Eckstein, Santiago Ontanon.
|
||||
1. **[Funnel Transformer](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/funnel)** (from CMU/Google Brain) released with the paper [Funnel-Transformer: Filtering out Sequential Redundancy for Efficient Language Processing](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.03236) by Zihang Dai, Guokun Lai, Yiming Yang, Quoc V. Le.
|
||||
1. **[GLPN](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/model_doc/glpn)** (from KAIST) released with the paper [Global-Local Path Networks for Monocular Depth Estimation with Vertical CutDepth](https://arxiv.org/abs/2201.07436) by Doyeon Kim, Woonghyun Ga, Pyungwhan Ahn, Donggyu Joo, Sehwan Chun, Junmo Kim.
|
||||
1. **[GLPN](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/glpn)** (from KAIST) released with the paper [Global-Local Path Networks for Monocular Depth Estimation with Vertical CutDepth](https://arxiv.org/abs/2201.07436) by Doyeon Kim, Woonghyun Ga, Pyungwhan Ahn, Donggyu Joo, Sehwan Chun, Junmo Kim.
|
||||
1. **[GPT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/openai-gpt)** (from OpenAI) released with the paper [Improving Language Understanding by Generative Pre-Training](https://blog.openai.com/language-unsupervised/) by Alec Radford, Karthik Narasimhan, Tim Salimans and Ilya Sutskever.
|
||||
1. **[GPT Neo](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/gpt_neo)** (from EleutherAI) released in the repository [EleutherAI/gpt-neo](https://github.com/EleutherAI/gpt-neo) by Sid Black, Stella Biderman, Leo Gao, Phil Wang and Connor Leahy.
|
||||
1. **[GPT NeoX](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/gpt_neox)** (from EleutherAI) released with the paper [GPT-NeoX-20B: An Open-Source Autoregressive Language Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/2204.06745) by Sid Black, Stella Biderman, Eric Hallahan, Quentin Anthony, Leo Gao, Laurence Golding, Horace He, Connor Leahy, Kyle McDonell, Jason Phang, Michael Pieler, USVSN Sai Prashanth, Shivanshu Purohit, Laria Reynolds, Jonathan Tow, Ben Wang, Samuel Weinbach
|
||||
1. **[GPT-2](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/gpt2)** (from OpenAI) released with the paper [Language Models are Unsupervised Multitask Learners](https://blog.openai.com/better-language-models/) by Alec Radford*, Jeffrey Wu*, Rewon Child, David Luan, Dario Amodei** and Ilya Sutskever**.
|
||||
1. **[GPT-J](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/gptj)** (from EleutherAI) released in the repository [kingoflolz/mesh-transformer-jax](https://github.com/kingoflolz/mesh-transformer-jax/) by Ben Wang and Aran Komatsuzaki.
|
||||
1. **[GroupViT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/model_doc/groupvit)** (from UCSD, NVIDIA) released with the paper [GroupViT: Semantic Segmentation Emerges from Text Supervision](https://arxiv.org/abs/2202.11094) by Jiarui Xu, Shalini De Mello, Sifei Liu, Wonmin Byeon, Thomas Breuel, Jan Kautz, Xiaolong Wang.
|
||||
1. **[Hubert](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/hubert)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [HuBERT: Self-Supervised Speech Representation Learning by Masked Prediction of Hidden Units](https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.07447) by Wei-Ning Hsu, Benjamin Bolte, Yao-Hung Hubert Tsai, Kushal Lakhotia, Ruslan Salakhutdinov, Abdelrahman Mohamed.
|
||||
1. **[I-BERT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/ibert)** (from Berkeley) released with the paper [I-BERT: Integer-only BERT Quantization](https://arxiv.org/abs/2101.01321) by Sehoon Kim, Amir Gholami, Zhewei Yao, Michael W. Mahoney, Kurt Keutzer.
|
||||
1. **[ImageGPT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/model_doc/imagegpt)** (from OpenAI) released with the paper [Generative Pretraining from Pixels](https://openai.com/blog/image-gpt/) by Mark Chen, Alec Radford, Rewon Child, Jeffrey Wu, Heewoo Jun, David Luan, Ilya Sutskever.
|
||||
1. **[ImageGPT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/imagegpt)** (from OpenAI) released with the paper [Generative Pretraining from Pixels](https://openai.com/blog/image-gpt/) by Mark Chen, Alec Radford, Rewon Child, Jeffrey Wu, Heewoo Jun, David Luan, Ilya Sutskever.
|
||||
1. **[LayoutLM](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/layoutlm)** (from Microsoft Research Asia) released with the paper [LayoutLM: Pre-training of Text and Layout for Document Image Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/1912.13318) by Yiheng Xu, Minghao Li, Lei Cui, Shaohan Huang, Furu Wei, Ming Zhou.
|
||||
1. **[LayoutLMv2](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/layoutlmv2)** (from Microsoft Research Asia) released with the paper [LayoutLMv2: Multi-modal Pre-training for Visually-Rich Document Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/2012.14740) by Yang Xu, Yiheng Xu, Tengchao Lv, Lei Cui, Furu Wei, Guoxin Wang, Yijuan Lu, Dinei Florencio, Cha Zhang, Wanxiang Che, Min Zhang, Lidong Zhou.
|
||||
1. **[LayoutLMv3](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/layoutlmv3)** (from Microsoft Research Asia) released with the paper [LayoutLMv3: Pre-training for Document AI with Unified Text and Image Masking](https://arxiv.org/abs/2204.08387) by Yupan Huang, Tengchao Lv, Lei Cui, Yutong Lu, Furu Wei.
|
||||
1. **[LayoutXLM](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/layoutlmv2)** (from Microsoft Research Asia) released with the paper [LayoutXLM: Multimodal Pre-training for Multilingual Visually-rich Document Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.08836) by Yiheng Xu, Tengchao Lv, Lei Cui, Guoxin Wang, Yijuan Lu, Dinei Florencio, Cha Zhang, Furu Wei.
|
||||
1. **[LED](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/led)** (from AllenAI) released with the paper [Longformer: The Long-Document Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.05150) by Iz Beltagy, Matthew E. Peters, Arman Cohan.
|
||||
1. **[LeViT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/levit)** (from Meta AI) released with the paper [LeViT: A Vision Transformer in ConvNet's Clothing for Faster Inference](https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.01136) by Ben Graham, Alaaeldin El-Nouby, Hugo Touvron, Pierre Stock, Armand Joulin, Hervé Jégou, Matthijs Douze.
|
||||
1. **[Longformer](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/longformer)** (from AllenAI) released with the paper [Longformer: The Long-Document Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.05150) by Iz Beltagy, Matthew E. Peters, Arman Cohan.
|
||||
1. **[LongT5](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/longt5)** (from Google AI) released with the paper [LongT5: Efficient Text-To-Text Transformer for Long Sequences](https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.07916) by Mandy Guo, Joshua Ainslie, David Uthus, Santiago Ontanon, Jianmo Ni, Yun-Hsuan Sung, Yinfei Yang.
|
||||
1. **[LUKE](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/luke)** (from Studio Ousia) released with the paper [LUKE: Deep Contextualized Entity Representations with Entity-aware Self-attention](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.01057) by Ikuya Yamada, Akari Asai, Hiroyuki Shindo, Hideaki Takeda, Yuji Matsumoto.
|
||||
1. **[LXMERT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/lxmert)** (from UNC Chapel Hill) released with the paper [LXMERT: Learning Cross-Modality Encoder Representations from Transformers for Open-Domain Question Answering](https://arxiv.org/abs/1908.07490) by Hao Tan and Mohit Bansal.
|
||||
1. **[M-CTC-T](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/mctct)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Pseudo-Labeling For Massively Multilingual Speech Recognition](https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.00161) by Loren Lugosch, Tatiana Likhomanenko, Gabriel Synnaeve, and Ronan Collobert.
|
||||
1. **[M2M100](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/m2m_100)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Beyond English-Centric Multilingual Machine Translation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11125) by Angela Fan, Shruti Bhosale, Holger Schwenk, Zhiyi Ma, Ahmed El-Kishky, Siddharth Goyal, Mandeep Baines, Onur Celebi, Guillaume Wenzek, Vishrav Chaudhary, Naman Goyal, Tom Birch, Vitaliy Liptchinsky, Sergey Edunov, Edouard Grave, Michael Auli, Armand Joulin.
|
||||
1. **[MarianMT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/marian)** Machine translation models trained using [OPUS](http://opus.nlpl.eu/) data by Jörg Tiedemann. The [Marian Framework](https://marian-nmt.github.io/) is being developed by the Microsoft Translator Team.
|
||||
1. **[MaskFormer](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/model_doc/maskformer)** (from Meta and UIUC) released with the paper [Per-Pixel Classification is Not All You Need for Semantic Segmentation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.06278) by Bowen Cheng, Alexander G. Schwing, Alexander Kirillov.
|
||||
1. **[MBart](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/mbart)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Multilingual Denoising Pre-training for Neural Machine Translation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2001.08210) by Yinhan Liu, Jiatao Gu, Naman Goyal, Xian Li, Sergey Edunov, Marjan Ghazvininejad, Mike Lewis, Luke Zettlemoyer.
|
||||
1. **[MBart-50](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/mbart)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Multilingual Translation with Extensible Multilingual Pretraining and Finetuning](https://arxiv.org/abs/2008.00401) by Yuqing Tang, Chau Tran, Xian Li, Peng-Jen Chen, Naman Goyal, Vishrav Chaudhary, Jiatao Gu, Angela Fan.
|
||||
1. **[MaskFormer](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/maskformer)** (from Meta and UIUC) released with the paper [Per-Pixel Classification is Not All You Need for Semantic Segmentation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.06278) by Bowen Cheng, Alexander G. Schwing, Alexander Kirillov.
|
||||
1. **[mBART](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/mbart)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Multilingual Denoising Pre-training for Neural Machine Translation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2001.08210) by Yinhan Liu, Jiatao Gu, Naman Goyal, Xian Li, Sergey Edunov, Marjan Ghazvininejad, Mike Lewis, Luke Zettlemoyer.
|
||||
1. **[mBART-50](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/mbart)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Multilingual Translation with Extensible Multilingual Pretraining and Finetuning](https://arxiv.org/abs/2008.00401) by Yuqing Tang, Chau Tran, Xian Li, Peng-Jen Chen, Naman Goyal, Vishrav Chaudhary, Jiatao Gu, Angela Fan.
|
||||
1. **[Megatron-BERT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/megatron-bert)** (from NVIDIA) released with the paper [Megatron-LM: Training Multi-Billion Parameter Language Models Using Model Parallelism](https://arxiv.org/abs/1909.08053) by Mohammad Shoeybi, Mostofa Patwary, Raul Puri, Patrick LeGresley, Jared Casper and Bryan Catanzaro.
|
||||
1. **[Megatron-GPT2](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/megatron_gpt2)** (from NVIDIA) released with the paper [Megatron-LM: Training Multi-Billion Parameter Language Models Using Model Parallelism](https://arxiv.org/abs/1909.08053) by Mohammad Shoeybi, Mostofa Patwary, Raul Puri, Patrick LeGresley, Jared Casper and Bryan Catanzaro.
|
||||
1. **[mLUKE](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/mluke)** (from Studio Ousia) released with the paper [mLUKE: The Power of Entity Representations in Multilingual Pretrained Language Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.08151) by Ryokan Ri, Ikuya Yamada, and Yoshimasa Tsuruoka.
|
||||
1. **[MobileBERT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/mobilebert)** (from CMU/Google Brain) released with the paper [MobileBERT: a Compact Task-Agnostic BERT for Resource-Limited Devices](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.02984) by Zhiqing Sun, Hongkun Yu, Xiaodan Song, Renjie Liu, Yiming Yang, and Denny Zhou.
|
||||
1. **[MobileViT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/model_doc/mobilevit)** (from Apple) released with the paper [MobileViT: Light-weight, General-purpose, and Mobile-friendly Vision Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.02178) by Sachin Mehta and Mohammad Rastegari.
|
||||
1. **[MPNet](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/mpnet)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [MPNet: Masked and Permuted Pre-training for Language Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.09297) by Kaitao Song, Xu Tan, Tao Qin, Jianfeng Lu, Tie-Yan Liu.
|
||||
1. **[MT5](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/mt5)** (from Google AI) released with the paper [mT5: A massively multilingual pre-trained text-to-text transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11934) by Linting Xue, Noah Constant, Adam Roberts, Mihir Kale, Rami Al-Rfou, Aditya Siddhant, Aditya Barua, Colin Raffel.
|
||||
1. **[MVP](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/model_doc/mvp)** (from RUC AI Box) released with the paper [MVP: Multi-task Supervised Pre-training for Natural Language Generation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.12131) by Tianyi Tang, Junyi Li, Wayne Xin Zhao and Ji-Rong Wen.
|
||||
1. **[Nezha](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/model_doc/nezha)** (from Huawei Noah’s Ark Lab) released with the paper [NEZHA: Neural Contextualized Representation for Chinese Language Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/1909.00204) by Junqiu Wei, Xiaozhe Ren, Xiaoguang Li, Wenyong Huang, Yi Liao, Yasheng Wang, Jiashu Lin, Xin Jiang, Xiao Chen and Qun Liu.
|
||||
1. **[NLLB](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/model_doc/nllb)** (from Meta) released with the paper [No Language Left Behind: Scaling Human-Centered Machine Translation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2207.04672) by the NLLB team.
|
||||
1. **[Nyströmformer](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/nystromformer)** (from the University of Wisconsin - Madison) released with the paper [Nyströmformer: A Nyström-Based Algorithm for Approximating Self-Attention](https://arxiv.org/abs/2102.03902) by Yunyang Xiong, Zhanpeng Zeng, Rudrasis Chakraborty, Mingxing Tan, Glenn Fung, Yin Li, Vikas Singh.
|
||||
1. **[OPT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/master/model_doc/opt)** (from Meta AI) released with the paper [OPT: Open Pre-trained Transformer Language Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.01068) by Susan Zhang, Stephen Roller, Naman Goyal, Mikel Artetxe, Moya Chen, Shuohui Chen et al.
|
||||
1. **[Pegasus](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/pegasus)** (from Google) released with the paper [PEGASUS: Pre-training with Extracted Gap-sentences for Abstractive Summarization](https://arxiv.org/abs/1912.08777) by Jingqing Zhang, Yao Zhao, Mohammad Saleh and Peter J. Liu.
|
||||
@ -281,9 +295,10 @@ Flax, PyTorch, TensorFlow 설치 페이지에서 이들을 conda로 설치하는
|
||||
1. **[PoolFormer](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/poolformer)** (from Sea AI Labs) released with the paper [MetaFormer is Actually What You Need for Vision](https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.11418) by Yu, Weihao and Luo, Mi and Zhou, Pan and Si, Chenyang and Zhou, Yichen and Wang, Xinchao and Feng, Jiashi and Yan, Shuicheng.
|
||||
1. **[ProphetNet](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/prophetnet)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [ProphetNet: Predicting Future N-gram for Sequence-to-Sequence Pre-training](https://arxiv.org/abs/2001.04063) by Yu Yan, Weizhen Qi, Yeyun Gong, Dayiheng Liu, Nan Duan, Jiusheng Chen, Ruofei Zhang and Ming Zhou.
|
||||
1. **[QDQBert](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/qdqbert)** (from NVIDIA) released with the paper [Integer Quantization for Deep Learning Inference: Principles and Empirical Evaluation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.09602) by Hao Wu, Patrick Judd, Xiaojie Zhang, Mikhail Isaev and Paulius Micikevicius.
|
||||
1. **[RAG](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/rag)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Knowledge-Intensive NLP Tasks](https://arxiv.org/abs/2005.11401) by Patrick Lewis, Ethan Perez, Aleksandara Piktus, Fabio Petroni, Vladimir Karpukhin, Naman Goyal, Heinrich Küttler, Mike Lewis, Wen-tau Yih, Tim Rocktäschel, Sebastian Riedel, Douwe Kiela.
|
||||
1. **[REALM](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/realm.html)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [REALM: Retrieval-Augmented Language Model Pre-Training](https://arxiv.org/abs/2002.08909) by Kelvin Guu, Kenton Lee, Zora Tung, Panupong Pasupat and Ming-Wei Chang.
|
||||
1. **[Reformer](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/reformer)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [Reformer: The Efficient Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2001.04451) by Nikita Kitaev, Łukasz Kaiser, Anselm Levskaya.
|
||||
1. **[RegNet](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/model_doc/regnet)** (from META Research) released with the paper [Designing Network Design Space](https://arxiv.org/abs/2003.13678) by Ilija Radosavovic, Raj Prateek Kosaraju, Ross Girshick, Kaiming He, Piotr Dollár.
|
||||
1. **[RegNet](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/regnet)** (from META Research) released with the paper [Designing Network Design Space](https://arxiv.org/abs/2003.13678) by Ilija Radosavovic, Raj Prateek Kosaraju, Ross Girshick, Kaiming He, Piotr Dollár.
|
||||
1. **[RemBERT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/rembert)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [Rethinking embedding coupling in pre-trained language models](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2010.12821.pdf) by Hyung Won Chung, Thibault Févry, Henry Tsai, M. Johnson, Sebastian Ruder.
|
||||
1. **[ResNet](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/resnet)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition](https://arxiv.org/abs/1512.03385) by Kaiming He, Xiangyu Zhang, Shaoqing Ren, Jian Sun.
|
||||
1. **[RoBERTa](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/roberta)** (from Facebook), released together with the paper a [Robustly Optimized BERT Pretraining Approach](https://arxiv.org/abs/1907.11692) by Yinhan Liu, Myle Ott, Naman Goyal, Jingfei Du, Mandar Joshi, Danqi Chen, Omer Levy, Mike Lewis, Luke Zettlemoyer, Veselin Stoyanov.
|
||||
@ -294,14 +309,16 @@ Flax, PyTorch, TensorFlow 설치 페이지에서 이들을 conda로 설치하는
|
||||
1. **[SpeechToTextTransformer](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/speech_to_text)** (from Facebook), released together with the paper [fairseq S2T: Fast Speech-to-Text Modeling with fairseq](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.05171) by Changhan Wang, Yun Tang, Xutai Ma, Anne Wu, Dmytro Okhonko, Juan Pino.
|
||||
1. **[SpeechToTextTransformer2](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/speech_to_text_2)** (from Facebook), released together with the paper [Large-Scale Self- and Semi-Supervised Learning for Speech Translation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.06678) by Changhan Wang, Anne Wu, Juan Pino, Alexei Baevski, Michael Auli, Alexis Conneau.
|
||||
1. **[Splinter](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/splinter)** (from Tel Aviv University), released together with the paper [Few-Shot Question Answering by Pretraining Span Selection](https://arxiv.org/abs/2101.00438) by Ori Ram, Yuval Kirstain, Jonathan Berant, Amir Globerson, Omer Levy.
|
||||
1. **[SqueezeBert](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/squeezebert)** (from Berkeley) released with the paper [SqueezeBERT: What can computer vision teach NLP about efficient neural networks?](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.11316) by Forrest N. Iandola, Albert E. Shaw, Ravi Krishna, and Kurt W. Keutzer.
|
||||
1. **[SqueezeBERT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/squeezebert)** (from Berkeley) released with the paper [SqueezeBERT: What can computer vision teach NLP about efficient neural networks?](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.11316) by Forrest N. Iandola, Albert E. Shaw, Ravi Krishna, and Kurt W. Keutzer.
|
||||
1. **[Swin Transformer](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/swin)** (from Microsoft) released with the paper [Swin Transformer: Hierarchical Vision Transformer using Shifted Windows](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.14030) by Ze Liu, Yutong Lin, Yue Cao, Han Hu, Yixuan Wei, Zheng Zhang, Stephen Lin, Baining Guo.
|
||||
1. **[T5](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/t5)** (from Google AI) released with the paper [Exploring the Limits of Transfer Learning with a Unified Text-to-Text Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/1910.10683) by Colin Raffel and Noam Shazeer and Adam Roberts and Katherine Lee and Sharan Narang and Michael Matena and Yanqi Zhou and Wei Li and Peter J. Liu.
|
||||
1. **[T5v1.1](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/t5v1.1)** (from Google AI) released in the repository [google-research/text-to-text-transfer-transformer](https://github.com/google-research/text-to-text-transfer-transformer/blob/main/released_checkpoints.md#t511) by Colin Raffel and Noam Shazeer and Adam Roberts and Katherine Lee and Sharan Narang and Michael Matena and Yanqi Zhou and Wei Li and Peter J. Liu.
|
||||
1. **[TAPAS](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/tapas)** (from Google AI) released with the paper [TAPAS: Weakly Supervised Table Parsing via Pre-training](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.02349) by Jonathan Herzig, Paweł Krzysztof Nowak, Thomas Müller, Francesco Piccinno and Julian Martin Eisenschlos.
|
||||
1. **[TAPEX](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/model_doc/tapex)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [TAPEX: Table Pre-training via Learning a Neural SQL Executor](https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.07653) by Qian Liu, Bei Chen, Jiaqi Guo, Morteza Ziyadi, Zeqi Lin, Weizhu Chen, Jian-Guang Lou.
|
||||
1. **[TAPEX](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/tapex)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [TAPEX: Table Pre-training via Learning a Neural SQL Executor](https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.07653) by Qian Liu, Bei Chen, Jiaqi Guo, Morteza Ziyadi, Zeqi Lin, Weizhu Chen, Jian-Guang Lou.
|
||||
1. **[Trajectory Transformer](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/trajectory_transformers)** (from the University of California at Berkeley) released with the paper [Offline Reinforcement Learning as One Big Sequence Modeling Problem](https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.02039) by Michael Janner, Qiyang Li, Sergey Levine
|
||||
1. **[Transformer-XL](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/transfo-xl)** (from Google/CMU) released with the paper [Transformer-XL: Attentive Language Models Beyond a Fixed-Length Context](https://arxiv.org/abs/1901.02860) by Zihang Dai*, Zhilin Yang*, Yiming Yang, Jaime Carbonell, Quoc V. Le, Ruslan Salakhutdinov.
|
||||
1. **[TrOCR](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/trocr)** (from Microsoft), released together with the paper [TrOCR: Transformer-based Optical Character Recognition with Pre-trained Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.10282) by Minghao Li, Tengchao Lv, Lei Cui, Yijuan Lu, Dinei Florencio, Cha Zhang, Zhoujun Li, Furu Wei.
|
||||
1. **[UL2](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/model_doc/ul2)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [Unifying Language Learning Paradigms](https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.05131v1) by Yi Tay, Mostafa Dehghani, Vinh Q. Tran, Xavier Garcia, Dara Bahri, Tal Schuster, Huaixiu Steven Zheng, Neil Houlsby, Donald Metzler
|
||||
1. **[UniSpeech](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/unispeech)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [UniSpeech: Unified Speech Representation Learning with Labeled and Unlabeled Data](https://arxiv.org/abs/2101.07597) by Chengyi Wang, Yu Wu, Yao Qian, Kenichi Kumatani, Shujie Liu, Furu Wei, Michael Zeng, Xuedong Huang.
|
||||
1. **[UniSpeechSat](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/unispeech-sat)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [UNISPEECH-SAT: UNIVERSAL SPEECH REPRESENTATION LEARNING WITH SPEAKER AWARE PRE-TRAINING](https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.05752) by Sanyuan Chen, Yu Wu, Chengyi Wang, Zhengyang Chen, Zhuo Chen, Shujie Liu, Jian Wu, Yao Qian, Furu Wei, Jinyu Li, Xiangzhan Yu.
|
||||
1. **[VAN](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/van)** (from Tsinghua University and Nankai University) released with the paper [Visual Attention Network](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2202.09741.pdf) by Meng-Hao Guo, Cheng-Ze Lu, Zheng-Ning Liu, Ming-Ming Cheng, Shi-Min Hu.
|
||||
@ -310,6 +327,7 @@ Flax, PyTorch, TensorFlow 설치 페이지에서 이들을 conda로 설치하는
|
||||
1. **[VisualBERT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/visual_bert)** (from UCLA NLP) released with the paper [VisualBERT: A Simple and Performant Baseline for Vision and Language](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1908.03557) by Liunian Harold Li, Mark Yatskar, Da Yin, Cho-Jui Hsieh, Kai-Wei Chang.
|
||||
1. **[ViTMAE](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/vit_mae)** (from Meta AI) released with the paper [Masked Autoencoders Are Scalable Vision Learners](https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.06377) by Kaiming He, Xinlei Chen, Saining Xie, Yanghao Li, Piotr Dollár, Ross Girshick.
|
||||
1. **[Wav2Vec2](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/wav2vec2)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [wav2vec 2.0: A Framework for Self-Supervised Learning of Speech Representations](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.11477) by Alexei Baevski, Henry Zhou, Abdelrahman Mohamed, Michael Auli.
|
||||
1. **[Wav2Vec2-Conformer](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/wav2vec2-conformer)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [FAIRSEQ S2T: Fast Speech-to-Text Modeling with FAIRSEQ](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.05171) by Changhan Wang, Yun Tang, Xutai Ma, Anne Wu, Sravya Popuri, Dmytro Okhonko, Juan Pino.
|
||||
1. **[Wav2Vec2Phoneme](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/wav2vec2_phoneme)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [Simple and Effective Zero-shot Cross-lingual Phoneme Recognition](https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.11680) by Qiantong Xu, Alexei Baevski, Michael Auli.
|
||||
1. **[WavLM](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/wavlm)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [WavLM: Large-Scale Self-Supervised Pre-Training for Full Stack Speech Processing](https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.13900) by Sanyuan Chen, Chengyi Wang, Zhengyang Chen, Yu Wu, Shujie Liu, Zhuo Chen, Jinyu Li, Naoyuki Kanda, Takuya Yoshioka, Xiong Xiao, Jian Wu, Long Zhou, Shuo Ren, Yanmin Qian, Yao Qian, Jian Wu, Michael Zeng, Furu Wei.
|
||||
1. **[XGLM](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/xglm)** (From Facebook AI) released with the paper [Few-shot Learning with Multilingual Language Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.10668) by Xi Victoria Lin, Todor Mihaylov, Mikel Artetxe, Tianlu Wang, Shuohui Chen, Daniel Simig, Myle Ott, Naman Goyal, Shruti Bhosale, Jingfei Du, Ramakanth Pasunuru, Sam Shleifer, Punit Singh Koura, Vishrav Chaudhary, Brian O'Horo, Jeff Wang, Luke Zettlemoyer, Zornitsa Kozareva, Mona Diab, Veselin Stoyanov, Xian Li.
|
||||
@ -320,7 +338,7 @@ Flax, PyTorch, TensorFlow 설치 페이지에서 이들을 conda로 설치하는
|
||||
1. **[XLNet](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/xlnet)** (from Google/CMU) released with the paper [XLNet: Generalized Autoregressive Pretraining for Language Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/1906.08237) by Zhilin Yang*, Zihang Dai*, Yiming Yang, Jaime Carbonell, Ruslan Salakhutdinov, Quoc V. Le.
|
||||
1. **[XLS-R](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/xls_r)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [XLS-R: Self-supervised Cross-lingual Speech Representation Learning at Scale](https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.09296) by Arun Babu, Changhan Wang, Andros Tjandra, Kushal Lakhotia, Qiantong Xu, Naman Goyal, Kritika Singh, Patrick von Platen, Yatharth Saraf, Juan Pino, Alexei Baevski, Alexis Conneau, Michael Auli.
|
||||
1. **[XLSR-Wav2Vec2](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/xlsr_wav2vec2)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [Unsupervised Cross-Lingual Representation Learning For Speech Recognition](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.13979) by Alexis Conneau, Alexei Baevski, Ronan Collobert, Abdelrahman Mohamed, Michael Auli.
|
||||
1. **[YOLOS](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/model_doc/yolos)** (from Huazhong University of Science & Technology) released with the paper [You Only Look at One Sequence: Rethinking Transformer in Vision through Object Detection](https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.00666) by Yuxin Fang, Bencheng Liao, Xinggang Wang, Jiemin Fang, Jiyang Qi, Rui Wu, Jianwei Niu, Wenyu Liu.
|
||||
1. **[YOLOS](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/yolos)** (from Huazhong University of Science & Technology) released with the paper [You Only Look at One Sequence: Rethinking Transformer in Vision through Object Detection](https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.00666) by Yuxin Fang, Bencheng Liao, Xinggang Wang, Jiemin Fang, Jiyang Qi, Rui Wu, Jianwei Niu, Wenyu Liu.
|
||||
1. **[YOSO](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/yoso)** (from the University of Wisconsin - Madison) released with the paper [You Only Sample (Almost) by Zhanpeng Zeng, Yunyang Xiong, Sathya N. Ravi, Shailesh Acharya, Glenn Fung, Vikas Singh.
|
||||
1. 새로운 모델을 올리고 싶나요? 우리가 **상세한 가이드와 템플릿** 으로 새로운 모델을 올리도록 도와드릴게요. 가이드와 템플릿은 이 저장소의 [`templates`](./templates) 폴더에서 확인하실 수 있습니다. [컨트리뷰션 가이드라인](./CONTRIBUTING.md)을 꼭 확인해주시고, PR을 올리기 전에 메인테이너에게 연락하거나 이슈를 오픈해 피드백을 받으시길 바랍니다.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -245,16 +245,19 @@ conda install -c huggingface transformers
|
||||
1. **[BigBird-RoBERTa](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/big_bird)** (来自 Google Research) 伴随论文 [Big Bird: Transformers for Longer Sequences](https://arxiv.org/abs/2007.14062) 由 Manzil Zaheer, Guru Guruganesh, Avinava Dubey, Joshua Ainslie, Chris Alberti, Santiago Ontanon, Philip Pham, Anirudh Ravula, Qifan Wang, Li Yang, Amr Ahmed 发布。
|
||||
1. **[Blenderbot](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/blenderbot)** (来自 Facebook) 伴随论文 [Recipes for building an open-domain chatbot](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.13637) 由 Stephen Roller, Emily Dinan, Naman Goyal, Da Ju, Mary Williamson, Yinhan Liu, Jing Xu, Myle Ott, Kurt Shuster, Eric M. Smith, Y-Lan Boureau, Jason Weston 发布。
|
||||
1. **[BlenderbotSmall](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/blenderbot-small)** (来自 Facebook) 伴随论文 [Recipes for building an open-domain chatbot](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.13637) 由 Stephen Roller, Emily Dinan, Naman Goyal, Da Ju, Mary Williamson, Yinhan Liu, Jing Xu, Myle Ott, Kurt Shuster, Eric M. Smith, Y-Lan Boureau, Jason Weston 发布。
|
||||
1. **[BLOOM](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/bloom)** (from BigScience workshop) released by the [BigSicence Workshop](https://bigscience.huggingface.co/).
|
||||
1. **[BORT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/bort)** (来自 Alexa) 伴随论文 [Optimal Subarchitecture Extraction For BERT](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.10499) 由 Adrian de Wynter and Daniel J. Perry 发布。
|
||||
1. **[ByT5](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/byt5)** (来自 Google Research) 伴随论文 [ByT5: Towards a token-free future with pre-trained byte-to-byte models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2105.13626) 由 Linting Xue, Aditya Barua, Noah Constant, Rami Al-Rfou, Sharan Narang, Mihir Kale, Adam Roberts, Colin Raffel 发布。
|
||||
1. **[CamemBERT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/camembert)** (来自 Inria/Facebook/Sorbonne) 伴随论文 [CamemBERT: a Tasty French Language Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.03894) 由 Louis Martin*, Benjamin Muller*, Pedro Javier Ortiz Suárez*, Yoann Dupont, Laurent Romary, Éric Villemonte de la Clergerie, Djamé Seddah and Benoît Sagot 发布。
|
||||
1. **[CANINE](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/canine)** (来自 Google Research) 伴随论文 [CANINE: Pre-training an Efficient Tokenization-Free Encoder for Language Representation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.06874) 由 Jonathan H. Clark, Dan Garrette, Iulia Turc, John Wieting 发布。
|
||||
1. **[CLIP](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/clip)** (来自 OpenAI) 伴随论文 [Learning Transferable Visual Models From Natural Language Supervision](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.00020) 由 Alec Radford, Jong Wook Kim, Chris Hallacy, Aditya Ramesh, Gabriel Goh, Sandhini Agarwal, Girish Sastry, Amanda Askell, Pamela Mishkin, Jack Clark, Gretchen Krueger, Ilya Sutskever 发布。
|
||||
1. **[CodeGen](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/codegen)** (来自 Salesforce) 伴随论文 [A Conversational Paradigm for Program Synthesis](https://arxiv.org/abs/2203.13474) 由 Erik Nijkamp, Bo Pang, Hiroaki Hayashi, Lifu Tu, Huan Wang, Yingbo Zhou, Silvio Savarese, Caiming Xiong 发布。
|
||||
1. **[ConvBERT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/convbert)** (来自 YituTech) 伴随论文 [ConvBERT: Improving BERT with Span-based Dynamic Convolution](https://arxiv.org/abs/2008.02496) 由 Zihang Jiang, Weihao Yu, Daquan Zhou, Yunpeng Chen, Jiashi Feng, Shuicheng Yan 发布。
|
||||
1. **[ConvNeXT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/model_doc/convnext)** (来自 Facebook AI) 伴随论文 [A ConvNet for the 2020s](https://arxiv.org/abs/2201.03545) 由 Zhuang Liu, Hanzi Mao, Chao-Yuan Wu, Christoph Feichtenhofer, Trevor Darrell, Saining Xie 发布。
|
||||
1. **[ConvNeXT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/convnext)** (来自 Facebook AI) 伴随论文 [A ConvNet for the 2020s](https://arxiv.org/abs/2201.03545) 由 Zhuang Liu, Hanzi Mao, Chao-Yuan Wu, Christoph Feichtenhofer, Trevor Darrell, Saining Xie 发布。
|
||||
1. **[CPM](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/cpm)** (来自 Tsinghua University) 伴随论文 [CPM: A Large-scale Generative Chinese Pre-trained Language Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/2012.00413) 由 Zhengyan Zhang, Xu Han, Hao Zhou, Pei Ke, Yuxian Gu, Deming Ye, Yujia Qin, Yusheng Su, Haozhe Ji, Jian Guan, Fanchao Qi, Xiaozhi Wang, Yanan Zheng, Guoyang Zeng, Huanqi Cao, Shengqi Chen, Daixuan Li, Zhenbo Sun, Zhiyuan Liu, Minlie Huang, Wentao Han, Jie Tang, Juanzi Li, Xiaoyan Zhu, Maosong Sun 发布。
|
||||
1. **[CTRL](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/ctrl)** (来自 Salesforce) 伴随论文 [CTRL: A Conditional Transformer Language Model for Controllable Generation](https://arxiv.org/abs/1909.05858) 由 Nitish Shirish Keskar*, Bryan McCann*, Lav R. Varshney, Caiming Xiong and Richard Socher 发布。
|
||||
1. **[Data2Vec](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/model_doc/data2vec)** (来自 Facebook) 伴随论文 [Data2Vec: A General Framework for Self-supervised Learning in Speech, Vision and Language](https://arxiv.org/abs/2202.03555) 由 Alexei Baevski, Wei-Ning Hsu, Qiantong Xu, Arun Babu, Jiatao Gu, Michael Auli 发布。
|
||||
1. **[CvT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/cvt)** (来自 Microsoft) 伴随论文 [CvT: Introducing Convolutions to Vision Transformers](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.15808) 由 Haiping Wu, Bin Xiao, Noel Codella, Mengchen Liu, Xiyang Dai, Lu Yuan, Lei Zhang 发布。
|
||||
1. **[Data2Vec](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/data2vec)** (来自 Facebook) 伴随论文 [Data2Vec: A General Framework for Self-supervised Learning in Speech, Vision and Language](https://arxiv.org/abs/2202.03555) 由 Alexei Baevski, Wei-Ning Hsu, Qiantong Xu, Arun Babu, Jiatao Gu, Michael Auli 发布。
|
||||
1. **[DeBERTa](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/deberta)** (来自 Microsoft) 伴随论文 [DeBERTa: Decoding-enhanced BERT with Disentangled Attention](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.03654) 由 Pengcheng He, Xiaodong Liu, Jianfeng Gao, Weizhu Chen 发布。
|
||||
1. **[DeBERTa-v2](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/deberta-v2)** (来自 Microsoft) 伴随论文 [DeBERTa: Decoding-enhanced BERT with Disentangled Attention](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.03654) 由 Pengcheng He, Xiaodong Liu, Jianfeng Gao, Weizhu Chen 发布。
|
||||
1. **[Decision Transformer](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/decision_transformer)** (来自 Berkeley/Facebook/Google) 伴随论文 [Decision Transformer: Reinforcement Learning via Sequence Modeling](https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.01345) 由 Lili Chen, Kevin Lu, Aravind Rajeswaran, Kimin Lee, Aditya Grover, Michael Laskin, Pieter Abbeel, Aravind Srinivas, Igor Mordatch 发布。
|
||||
@ -268,34 +271,45 @@ conda install -c huggingface transformers
|
||||
1. **[ELECTRA](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/electra)** (来自 Google Research/Stanford University) 伴随论文 [ELECTRA: Pre-training text encoders as discriminators rather than generators](https://arxiv.org/abs/2003.10555) 由 Kevin Clark, Minh-Thang Luong, Quoc V. Le, Christopher D. Manning 发布。
|
||||
1. **[EncoderDecoder](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/encoder-decoder)** (来自 Google Research) 伴随论文 [Leveraging Pre-trained Checkpoints for Sequence Generation Tasks](https://arxiv.org/abs/1907.12461) 由 Sascha Rothe, Shashi Narayan, Aliaksei Severyn 发布。
|
||||
1. **[FlauBERT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/flaubert)** (来自 CNRS) 伴随论文 [FlauBERT: Unsupervised Language Model Pre-training for French](https://arxiv.org/abs/1912.05372) 由 Hang Le, Loïc Vial, Jibril Frej, Vincent Segonne, Maximin Coavoux, Benjamin Lecouteux, Alexandre Allauzen, Benoît Crabbé, Laurent Besacier, Didier Schwab 发布。
|
||||
1. **[FLAVA](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/model_doc/flava)** (来自 Facebook AI) 伴随论文 [FLAVA: A Foundational Language And Vision Alignment Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.04482) 由 Amanpreet Singh, Ronghang Hu, Vedanuj Goswami, Guillaume Couairon, Wojciech Galuba, Marcus Rohrbach, and Douwe Kiela 发布。
|
||||
1. **[FLAVA](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/flava)** (来自 Facebook AI) 伴随论文 [FLAVA: A Foundational Language And Vision Alignment Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.04482) 由 Amanpreet Singh, Ronghang Hu, Vedanuj Goswami, Guillaume Couairon, Wojciech Galuba, Marcus Rohrbach, and Douwe Kiela 发布。
|
||||
1. **[FNet](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/fnet)** (来自 Google Research) 伴随论文 [FNet: Mixing Tokens with Fourier Transforms](https://arxiv.org/abs/2105.03824) 由 James Lee-Thorp, Joshua Ainslie, Ilya Eckstein, Santiago Ontanon 发布。
|
||||
1. **[Funnel Transformer](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/funnel)** (来自 CMU/Google Brain) 伴随论文 [Funnel-Transformer: Filtering out Sequential Redundancy for Efficient Language Processing](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.03236) 由 Zihang Dai, Guokun Lai, Yiming Yang, Quoc V. Le 发布。
|
||||
1. **[GLPN](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/model_doc/glpn)** (来自 KAIST) 伴随论文 [Global-Local Path Networks for Monocular Depth Estimation with Vertical CutDepth](https://arxiv.org/abs/2201.07436) 由 Doyeon Kim, Woonghyun Ga, Pyungwhan Ahn, Donggyu Joo, Sehwan Chun, Junmo Kim 发布。
|
||||
1. **[GLPN](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/glpn)** (来自 KAIST) 伴随论文 [Global-Local Path Networks for Monocular Depth Estimation with Vertical CutDepth](https://arxiv.org/abs/2201.07436) 由 Doyeon Kim, Woonghyun Ga, Pyungwhan Ahn, Donggyu Joo, Sehwan Chun, Junmo Kim 发布。
|
||||
1. **[GPT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/openai-gpt)** (来自 OpenAI) 伴随论文 [Improving Language Understanding by Generative Pre-Training](https://blog.openai.com/language-unsupervised/) 由 Alec Radford, Karthik Narasimhan, Tim Salimans and Ilya Sutskever 发布。
|
||||
1. **[GPT Neo](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/gpt_neo)** (来自 EleutherAI) 随仓库 [EleutherAI/gpt-neo](https://github.com/EleutherAI/gpt-neo) 发布。作者为 Sid Black, Stella Biderman, Leo Gao, Phil Wang and Connor Leahy 发布。
|
||||
1. **[GPT NeoX](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/gpt_neox)** (from EleutherAI) released with the paper [GPT-NeoX-20B: An Open-Source Autoregressive Language Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/2204.06745) by Sid Black, Stella Biderman, Eric Hallahan, Quentin Anthony, Leo Gao, Laurence Golding, Horace He, Connor Leahy, Kyle McDonell, Jason Phang, Michael Pieler, USVSN Sai Prashanth, Shivanshu Purohit, Laria Reynolds, Jonathan Tow, Ben Wang, Samuel Weinbach
|
||||
1. **[GPT-2](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/gpt2)** (来自 OpenAI) 伴随论文 [Language Models are Unsupervised Multitask Learners](https://blog.openai.com/better-language-models/) 由 Alec Radford*, Jeffrey Wu*, Rewon Child, David Luan, Dario Amodei** and Ilya Sutskever** 发布。
|
||||
1. **[GPT-J](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/gptj)** (来自 EleutherAI) 伴随论文 [kingoflolz/mesh-transformer-jax](https://github.com/kingoflolz/mesh-transformer-jax/) 由 Ben Wang and Aran Komatsuzaki 发布。
|
||||
1. **[GroupViT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/model_doc/groupvit)** (来自 UCSD, NVIDIA) 伴随论文 [GroupViT: Semantic Segmentation Emerges from Text Supervision](https://arxiv.org/abs/2202.11094) 由 Jiarui Xu, Shalini De Mello, Sifei Liu, Wonmin Byeon, Thomas Breuel, Jan Kautz, Xiaolong Wang 发布。
|
||||
1. **[Hubert](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/hubert)** (来自 Facebook) 伴随论文 [HuBERT: Self-Supervised Speech Representation Learning by Masked Prediction of Hidden Units](https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.07447) 由 Wei-Ning Hsu, Benjamin Bolte, Yao-Hung Hubert Tsai, Kushal Lakhotia, Ruslan Salakhutdinov, Abdelrahman Mohamed 发布。
|
||||
1. **[I-BERT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/ibert)** (来自 Berkeley) 伴随论文 [I-BERT: Integer-only BERT Quantization](https://arxiv.org/abs/2101.01321) 由 Sehoon Kim, Amir Gholami, Zhewei Yao, Michael W. Mahoney, Kurt Keutzer 发布。
|
||||
1. **[ImageGPT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/model_doc/imagegpt)** (来自 OpenAI) 伴随论文 [Generative Pretraining from Pixels](https://openai.com/blog/image-gpt/) 由 Mark Chen, Alec Radford, Rewon Child, Jeffrey Wu, Heewoo Jun, David Luan, Ilya Sutskever 发布。
|
||||
1. **[ImageGPT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/imagegpt)** (来自 OpenAI) 伴随论文 [Generative Pretraining from Pixels](https://openai.com/blog/image-gpt/) 由 Mark Chen, Alec Radford, Rewon Child, Jeffrey Wu, Heewoo Jun, David Luan, Ilya Sutskever 发布。
|
||||
1. **[LayoutLM](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/layoutlm)** (来自 Microsoft Research Asia) 伴随论文 [LayoutLM: Pre-training of Text and Layout for Document Image Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/1912.13318) 由 Yiheng Xu, Minghao Li, Lei Cui, Shaohan Huang, Furu Wei, Ming Zhou 发布。
|
||||
1. **[LayoutLMv2](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/layoutlmv2)** (来自 Microsoft Research Asia) 伴随论文 [LayoutLMv2: Multi-modal Pre-training for Visually-Rich Document Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/2012.14740) 由 Yang Xu, Yiheng Xu, Tengchao Lv, Lei Cui, Furu Wei, Guoxin Wang, Yijuan Lu, Dinei Florencio, Cha Zhang, Wanxiang Che, Min Zhang, Lidong Zhou 发布。
|
||||
1. **[LayoutLMv3](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/layoutlmv3)** (来自 Microsoft Research Asia) 伴随论文 [LayoutLMv3: Pre-training for Document AI with Unified Text and Image Masking](https://arxiv.org/abs/2204.08387) 由 Yupan Huang, Tengchao Lv, Lei Cui, Yutong Lu, Furu Wei 发布。
|
||||
1. **[LayoutXLM](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/layoutlmv2)** (来自 Microsoft Research Asia) 伴随论文 [LayoutXLM: Multimodal Pre-training for Multilingual Visually-rich Document Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.08836) 由 Yiheng Xu, Tengchao Lv, Lei Cui, Guoxin Wang, Yijuan Lu, Dinei Florencio, Cha Zhang, Furu Wei 发布。
|
||||
1. **[LED](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/led)** (来自 AllenAI) 伴随论文 [Longformer: The Long-Document Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.05150) 由 Iz Beltagy, Matthew E. Peters, Arman Cohan 发布。
|
||||
1. **[LeViT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/levit)** (来自 Meta AI) 伴随论文 [LeViT: A Vision Transformer in ConvNet's Clothing for Faster Inference](https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.01136) 由 Ben Graham, Alaaeldin El-Nouby, Hugo Touvron, Pierre Stock, Armand Joulin, Hervé Jégou, Matthijs Douze 发布。
|
||||
1. **[Longformer](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/longformer)** (来自 AllenAI) 伴随论文 [Longformer: The Long-Document Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.05150) 由 Iz Beltagy, Matthew E. Peters, Arman Cohan 发布。
|
||||
1. **[LongT5](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/longt5)** (来自 Google AI) released 伴随论文 [LongT5: Efficient Text-To-Text Transformer for Long Sequences](https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.07916) 由 Mandy Guo, Joshua Ainslie, David Uthus, Santiago Ontanon, Jianmo Ni, Yun-Hsuan Sung, Yinfei Yang 发布。
|
||||
1. **[LUKE](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/luke)** (来自 Studio Ousia) 伴随论文 [LUKE: Deep Contextualized Entity Representations with Entity-aware Self-attention](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.01057) 由 Ikuya Yamada, Akari Asai, Hiroyuki Shindo, Hideaki Takeda, Yuji Matsumoto 发布。
|
||||
1. **[LXMERT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/lxmert)** (来自 UNC Chapel Hill) 伴随论文 [LXMERT: Learning Cross-Modality Encoder Representations from Transformers for Open-Domain Question Answering](https://arxiv.org/abs/1908.07490) 由 Hao Tan and Mohit Bansal 发布。
|
||||
1. **[M-CTC-T](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/mctct)** (来自 Facebook) 伴随论文 [Pseudo-Labeling For Massively Multilingual Speech Recognition](https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.00161) 由 Loren Lugosch, Tatiana Likhomanenko, Gabriel Synnaeve, and Ronan Collobert 发布。
|
||||
1. **[M2M100](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/m2m_100)** (来自 Facebook) 伴随论文 [Beyond English-Centric Multilingual Machine Translation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11125) 由 Angela Fan, Shruti Bhosale, Holger Schwenk, Zhiyi Ma, Ahmed El-Kishky, Siddharth Goyal, Mandeep Baines, Onur Celebi, Guillaume Wenzek, Vishrav Chaudhary, Naman Goyal, Tom Birch, Vitaliy Liptchinsky, Sergey Edunov, Edouard Grave, Michael Auli, Armand Joulin 发布。
|
||||
1. **[MarianMT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/marian)** 用 [OPUS](http://opus.nlpl.eu/) 数据训练的机器翻译模型由 Jörg Tiedemann 发布。[Marian Framework](https://marian-nmt.github.io/) 由微软翻译团队开发。
|
||||
1. **[MaskFormer](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/model_doc/maskformer)** (from Meta and UIUC) released with the paper [Per-Pixel Classification is Not All You Need for Semantic Segmentation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.06278) by Bowen Cheng, Alexander G. Schwing, Alexander Kirillov
|
||||
1. **[MBart](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/mbart)** (来自 Facebook) 伴随论文 [Multilingual Denoising Pre-training for Neural Machine Translation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2001.08210) 由 Yinhan Liu, Jiatao Gu, Naman Goyal, Xian Li, Sergey Edunov, Marjan Ghazvininejad, Mike Lewis, Luke Zettlemoyer 发布。
|
||||
1. **[MBart-50](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/mbart)** (来自 Facebook) 伴随论文 [Multilingual Translation with Extensible Multilingual Pretraining and Finetuning](https://arxiv.org/abs/2008.00401) 由 Yuqing Tang, Chau Tran, Xian Li, Peng-Jen Chen, Naman Goyal, Vishrav Chaudhary, Jiatao Gu, Angela Fan 发布。
|
||||
1. **[MaskFormer](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/maskformer)** (from Meta and UIUC) released with the paper [Per-Pixel Classification is Not All You Need for Semantic Segmentation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.06278) by Bowen Cheng, Alexander G. Schwing, Alexander Kirillov
|
||||
1. **[mBART](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/mbart)** (来自 Facebook) 伴随论文 [Multilingual Denoising Pre-training for Neural Machine Translation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2001.08210) 由 Yinhan Liu, Jiatao Gu, Naman Goyal, Xian Li, Sergey Edunov, Marjan Ghazvininejad, Mike Lewis, Luke Zettlemoyer 发布。
|
||||
1. **[mBART-50](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/mbart)** (来自 Facebook) 伴随论文 [Multilingual Translation with Extensible Multilingual Pretraining and Finetuning](https://arxiv.org/abs/2008.00401) 由 Yuqing Tang, Chau Tran, Xian Li, Peng-Jen Chen, Naman Goyal, Vishrav Chaudhary, Jiatao Gu, Angela Fan 发布。
|
||||
1. **[Megatron-BERT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/megatron-bert)** (来自 NVIDIA) 伴随论文 [Megatron-LM: Training Multi-Billion Parameter Language Models Using Model Parallelism](https://arxiv.org/abs/1909.08053) 由 Mohammad Shoeybi, Mostofa Patwary, Raul Puri, Patrick LeGresley, Jared Casper and Bryan Catanzaro 发布。
|
||||
1. **[Megatron-GPT2](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/megatron_gpt2)** (来自 NVIDIA) 伴随论文 [Megatron-LM: Training Multi-Billion Parameter Language Models Using Model Parallelism](https://arxiv.org/abs/1909.08053) 由 Mohammad Shoeybi, Mostofa Patwary, Raul Puri, Patrick LeGresley, Jared Casper and Bryan Catanzaro 发布。
|
||||
1. **[mLUKE](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/mluke)** (来自 Studio Ousia) 伴随论文 [mLUKE: The Power of Entity Representations in Multilingual Pretrained Language Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.08151) 由 Ryokan Ri, Ikuya Yamada, and Yoshimasa Tsuruoka 发布。
|
||||
1. **[MobileBERT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/mobilebert)** (来自 CMU/Google Brain) 伴随论文 [MobileBERT: a Compact Task-Agnostic BERT for Resource-Limited Devices](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.02984) 由 Zhiqing Sun, Hongkun Yu, Xiaodan Song, Renjie Liu, Yiming Yang, and Denny Zhou 发布。
|
||||
1. **[MobileViT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/model_doc/mobilevit)** (来自 Apple) 伴随论文 [MobileViT: Light-weight, General-purpose, and Mobile-friendly Vision Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.02178) 由 Sachin Mehta and Mohammad Rastegari 发布。
|
||||
1. **[MPNet](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/mpnet)** (来自 Microsoft Research) 伴随论文 [MPNet: Masked and Permuted Pre-training for Language Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.09297) 由 Kaitao Song, Xu Tan, Tao Qin, Jianfeng Lu, Tie-Yan Liu 发布。
|
||||
1. **[MT5](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/mt5)** (来自 Google AI) 伴随论文 [mT5: A massively multilingual pre-trained text-to-text transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11934) 由 Linting Xue, Noah Constant, Adam Roberts, Mihir Kale, Rami Al-Rfou, Aditya Siddhant, Aditya Barua, Colin Raffel 发布。
|
||||
1. **[MVP](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/model_doc/mvp)** (来自 中国人民大学 AI Box) 伴随论文 [MVP: Multi-task Supervised Pre-training for Natural Language Generation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.12131) 由 Tianyi Tang, Junyi Li, Wayne Xin Zhao and Ji-Rong Wen 发布。
|
||||
1. **[Nezha](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/model_doc/nezha)** (来自华为诺亚方舟实验室) 伴随论文 [NEZHA: Neural Contextualized Representation for Chinese Language Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/1909.00204) 由 Junqiu Wei, Xiaozhe Ren, Xiaoguang Li, Wenyong Huang, Yi Liao, Yasheng Wang, Jiashu Lin, Xin Jiang, Xiao Chen and Qun Liu 发布。
|
||||
1. **[NLLB](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/model_doc/nllb)** (来自 Meta) 伴随论文 [No Language Left Behind: Scaling Human-Centered Machine Translation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2207.04672) 由 the NLLB team 发布。
|
||||
1. **[Nyströmformer](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/nystromformer)** (来自 the University of Wisconsin - Madison) 伴随论文 [Nyströmformer: A Nyström-Based Algorithm for Approximating Self-Attention](https://arxiv.org/abs/2102.03902) 由 Yunyang Xiong, Zhanpeng Zeng, Rudrasis Chakraborty, Mingxing Tan, Glenn Fung, Yin Li, Vikas Singh 发布。
|
||||
1. **[OPT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/master/model_doc/opt)** (来自 Meta AI) 伴随论文 [OPT: Open Pre-trained Transformer Language Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.01068) 由 Susan Zhang, Stephen Roller, Naman Goyal, Mikel Artetxe, Moya Chen, Shuohui Chen et al 发布。
|
||||
1. **[Pegasus](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/pegasus)** (来自 Google) 伴随论文 [PEGASUS: Pre-training with Extracted Gap-sentences for Abstractive Summarization](https://arxiv.org/abs/1912.08777) 由 Jingqing Zhang, Yao Zhao, Mohammad Saleh and Peter J. Liu 发布。
|
||||
@ -305,9 +319,10 @@ conda install -c huggingface transformers
|
||||
1. **[PoolFormer](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/poolformer)** (来自 Sea AI Labs) 伴随论文 [MetaFormer is Actually What You Need for Vision](https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.11418) 由 Yu, Weihao and Luo, Mi and Zhou, Pan and Si, Chenyang and Zhou, Yichen and Wang, Xinchao and Feng, Jiashi and Yan, Shuicheng 发布。
|
||||
1. **[ProphetNet](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/prophetnet)** (来自 Microsoft Research) 伴随论文 [ProphetNet: Predicting Future N-gram for Sequence-to-Sequence Pre-training](https://arxiv.org/abs/2001.04063) 由 Yu Yan, Weizhen Qi, Yeyun Gong, Dayiheng Liu, Nan Duan, Jiusheng Chen, Ruofei Zhang and Ming Zhou 发布。
|
||||
1. **[QDQBert](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/qdqbert)** (来自 NVIDIA) 伴随论文 [Integer Quantization for Deep Learning Inference: Principles and Empirical Evaluation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.09602) 由 Hao Wu, Patrick Judd, Xiaojie Zhang, Mikhail Isaev and Paulius Micikevicius 发布。
|
||||
1. **[RAG](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/rag)** (来自 Facebook) 伴随论文 [Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Knowledge-Intensive NLP Tasks](https://arxiv.org/abs/2005.11401) 由 Patrick Lewis, Ethan Perez, Aleksandara Piktus, Fabio Petroni, Vladimir Karpukhin, Naman Goyal, Heinrich Küttler, Mike Lewis, Wen-tau Yih, Tim Rocktäschel, Sebastian Riedel, Douwe Kiela 发布。
|
||||
1. **[REALM](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/realm.html)** (来自 Google Research) 伴随论文 [REALM: Retrieval-Augmented Language Model Pre-Training](https://arxiv.org/abs/2002.08909) 由 Kelvin Guu, Kenton Lee, Zora Tung, Panupong Pasupat and Ming-Wei Chang 发布。
|
||||
1. **[Reformer](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/reformer)** (来自 Google Research) 伴随论文 [Reformer: The Efficient Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2001.04451) 由 Nikita Kitaev, Łukasz Kaiser, Anselm Levskaya 发布。
|
||||
1. **[RegNet](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/model_doc/regnet)** (from META Research) released with the paper [Designing Network Design Space](https://arxiv.org/abs/2003.13678) by Ilija Radosavovic, Raj Prateek Kosaraju, Ross Girshick, Kaiming He, Piotr Dollár.
|
||||
1. **[RegNet](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/regnet)** (from META Research) released with the paper [Designing Network Design Space](https://arxiv.org/abs/2003.13678) by Ilija Radosavovic, Raj Prateek Kosaraju, Ross Girshick, Kaiming He, Piotr Dollár.
|
||||
1. **[RemBERT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/rembert)** (来自 Google Research) 伴随论文 [Rethinking embedding coupling in pre-trained language models](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2010.12821.pdf) 由 Hyung Won Chung, Thibault Févry, Henry Tsai, M. Johnson, Sebastian Ruder 发布。
|
||||
1. **[ResNet](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/resnet)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition](https://arxiv.org/abs/1512.03385) by Kaiming He, Xiangyu Zhang, Shaoqing Ren, Jian Sun.
|
||||
1. **[RoBERTa](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/roberta)** (来自 Facebook), 伴随论文 [Robustly Optimized BERT Pretraining Approach](https://arxiv.org/abs/1907.11692) 由 Yinhan Liu, Myle Ott, Naman Goyal, Jingfei Du, Mandar Joshi, Danqi Chen, Omer Levy, Mike Lewis, Luke Zettlemoyer, Veselin Stoyanov 发布。
|
||||
@ -318,14 +333,16 @@ conda install -c huggingface transformers
|
||||
1. **[SpeechToTextTransformer](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/speech_to_text)** (来自 Facebook), 伴随论文 [fairseq S2T: Fast Speech-to-Text Modeling with fairseq](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.05171) 由 Changhan Wang, Yun Tang, Xutai Ma, Anne Wu, Dmytro Okhonko, Juan Pino 发布。
|
||||
1. **[SpeechToTextTransformer2](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/speech_to_text_2)** (来自 Facebook) 伴随论文 [Large-Scale Self- and Semi-Supervised Learning for Speech Translation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.06678) 由 Changhan Wang, Anne Wu, Juan Pino, Alexei Baevski, Michael Auli, Alexis Conneau 发布。
|
||||
1. **[Splinter](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/splinter)** (来自 Tel Aviv University) 伴随论文 [Few-Shot Question Answering by Pretraining Span Selection](https://arxiv.org/abs/2101.00438) 由 Ori Ram, Yuval Kirstain, Jonathan Berant, Amir Globerson, Omer Levy 发布。
|
||||
1. **[SqueezeBert](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/squeezebert)** (来自 Berkeley) 伴随论文 [SqueezeBERT: What can computer vision teach NLP about efficient neural networks?](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.11316) 由 Forrest N. Iandola, Albert E. Shaw, Ravi Krishna, and Kurt W. Keutzer 发布。
|
||||
1. **[SqueezeBERT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/squeezebert)** (来自 Berkeley) 伴随论文 [SqueezeBERT: What can computer vision teach NLP about efficient neural networks?](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.11316) 由 Forrest N. Iandola, Albert E. Shaw, Ravi Krishna, and Kurt W. Keutzer 发布。
|
||||
1. **[Swin Transformer](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/swin)** (来自 Microsoft) 伴随论文 [Swin Transformer: Hierarchical Vision Transformer using Shifted Windows](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.14030) 由 Ze Liu, Yutong Lin, Yue Cao, Han Hu, Yixuan Wei, Zheng Zhang, Stephen Lin, Baining Guo 发布。
|
||||
1. **[T5](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/t5)** (来自 Google AI) 伴随论文 [Exploring the Limits of Transfer Learning with a Unified Text-to-Text Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/1910.10683) 由 Colin Raffel and Noam Shazeer and Adam Roberts and Katherine Lee and Sharan Narang and Michael Matena and Yanqi Zhou and Wei Li and Peter J. Liu 发布。
|
||||
1. **[T5v1.1](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/t5v1.1)** (来自 Google AI) 伴随论文 [google-research/text-to-text-transfer-transformer](https://github.com/google-research/text-to-text-transfer-transformer/blob/main/released_checkpoints.md#t511) 由 Colin Raffel and Noam Shazeer and Adam Roberts and Katherine Lee and Sharan Narang and Michael Matena and Yanqi Zhou and Wei Li and Peter J. Liu 发布。
|
||||
1. **[TAPAS](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/tapas)** (来自 Google AI) 伴随论文 [TAPAS: Weakly Supervised Table Parsing via Pre-training](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.02349) 由 Jonathan Herzig, Paweł Krzysztof Nowak, Thomas Müller, Francesco Piccinno and Julian Martin Eisenschlos 发布。
|
||||
1. **[TAPEX](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/model_doc/tapex)** (来自 Microsoft Research) 伴随论文 [TAPEX: Table Pre-training via Learning a Neural SQL Executor](https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.07653) 由 Qian Liu, Bei Chen, Jiaqi Guo, Morteza Ziyadi, Zeqi Lin, Weizhu Chen, Jian-Guang Lou 发布。
|
||||
1. **[TAPEX](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/tapex)** (来自 Microsoft Research) 伴随论文 [TAPEX: Table Pre-training via Learning a Neural SQL Executor](https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.07653) 由 Qian Liu, Bei Chen, Jiaqi Guo, Morteza Ziyadi, Zeqi Lin, Weizhu Chen, Jian-Guang Lou 发布。
|
||||
1. **[Trajectory Transformer](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/trajectory_transformers)** (from the University of California at Berkeley) released with the paper [Offline Reinforcement Learning as One Big Sequence Modeling Problem](https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.02039) by Michael Janner, Qiyang Li, Sergey Levine
|
||||
1. **[Transformer-XL](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/transfo-xl)** (来自 Google/CMU) 伴随论文 [Transformer-XL: Attentive Language Models Beyond a Fixed-Length Context](https://arxiv.org/abs/1901.02860) 由 Zihang Dai*, Zhilin Yang*, Yiming Yang, Jaime Carbonell, Quoc V. Le, Ruslan Salakhutdinov 发布。
|
||||
1. **[TrOCR](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/trocr)** (来自 Microsoft) 伴随论文 [TrOCR: Transformer-based Optical Character Recognition with Pre-trained Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.10282) 由 Minghao Li, Tengchao Lv, Lei Cui, Yijuan Lu, Dinei Florencio, Cha Zhang, Zhoujun Li, Furu Wei 发布。
|
||||
1. **[UL2](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/model_doc/ul2)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [Unifying Language Learning Paradigms](https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.05131v1) by Yi Tay, Mostafa Dehghani, Vinh Q. Tran, Xavier Garcia, Dara Bahri, Tal Schuster, Huaixiu Steven Zheng, Neil Houlsby, Donald Metzler
|
||||
1. **[UniSpeech](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/unispeech)** (来自 Microsoft Research) 伴随论文 [UniSpeech: Unified Speech Representation Learning with Labeled and Unlabeled Data](https://arxiv.org/abs/2101.07597) 由 Chengyi Wang, Yu Wu, Yao Qian, Kenichi Kumatani, Shujie Liu, Furu Wei, Michael Zeng, Xuedong Huang 发布。
|
||||
1. **[UniSpeechSat](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/unispeech-sat)** (来自 Microsoft Research) 伴随论文 [UNISPEECH-SAT: UNIVERSAL SPEECH REPRESENTATION LEARNING WITH SPEAKER AWARE PRE-TRAINING](https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.05752) 由 Sanyuan Chen, Yu Wu, Chengyi Wang, Zhengyang Chen, Zhuo Chen, Shujie Liu, Jian Wu, Yao Qian, Furu Wei, Jinyu Li, Xiangzhan Yu 发布。
|
||||
1. **[VAN](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/van)** (来自 Tsinghua University and Nankai University) 伴随论文 [Visual Attention Network](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2202.09741.pdf) 由 Meng-Hao Guo, Cheng-Ze Lu, Zheng-Ning Liu, Ming-Ming Cheng, Shi-Min Hu 发布。
|
||||
@ -334,6 +351,7 @@ conda install -c huggingface transformers
|
||||
1. **[VisualBERT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/visual_bert)** (来自 UCLA NLP) 伴随论文 [VisualBERT: A Simple and Performant Baseline for Vision and Language](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1908.03557) 由 Liunian Harold Li, Mark Yatskar, Da Yin, Cho-Jui Hsieh, Kai-Wei Chang 发布。
|
||||
1. **[ViTMAE](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/vit_mae)** (来自 Meta AI) 伴随论文 [Masked Autoencoders Are Scalable Vision Learners](https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.06377) 由 Kaiming He, Xinlei Chen, Saining Xie, Yanghao Li, Piotr Dollár, Ross Girshick 发布。
|
||||
1. **[Wav2Vec2](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/wav2vec2)** (来自 Facebook AI) 伴随论文 [wav2vec 2.0: A Framework for Self-Supervised Learning of Speech Representations](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.11477) 由 Alexei Baevski, Henry Zhou, Abdelrahman Mohamed, Michael Auli 发布。
|
||||
1. **[Wav2Vec2-Conformer](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/wav2vec2-conformer)** (来自 Facebook AI) 伴随论文 [FAIRSEQ S2T: Fast Speech-to-Text Modeling with FAIRSEQ](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.05171) 由 Changhan Wang, Yun Tang, Xutai Ma, Anne Wu, Sravya Popuri, Dmytro Okhonko, Juan Pino 发布。
|
||||
1. **[Wav2Vec2Phoneme](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/wav2vec2_phoneme)** (来自 Facebook AI) 伴随论文 [Simple and Effective Zero-shot Cross-lingual Phoneme Recognition](https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.11680) 由 Qiantong Xu, Alexei Baevski, Michael Auli 发布。
|
||||
1. **[WavLM](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/wavlm)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [WavLM: Large-Scale Self-Supervised Pre-Training for Full Stack Speech Processing](https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.13900) by Sanyuan Chen, Chengyi Wang, Zhengyang Chen, Yu Wu, Shujie Liu, Zhuo Chen, Jinyu Li, Naoyuki Kanda, Takuya Yoshioka, Xiong Xiao, Jian Wu, Long Zhou, Shuo Ren, Yanmin Qian, Yao Qian, Jian Wu, Michael Zeng, Furu Wei.
|
||||
1. **[XGLM](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/xglm)** (From Facebook AI) released with the paper [Few-shot Learning with Multilingual Language Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.10668) by Xi Victoria Lin, Todor Mihaylov, Mikel Artetxe, Tianlu Wang, Shuohui Chen, Daniel Simig, Myle Ott, Naman Goyal, Shruti Bhosale, Jingfei Du, Ramakanth Pasunuru, Sam Shleifer, Punit Singh Koura, Vishrav Chaudhary, Brian O'Horo, Jeff Wang, Luke Zettlemoyer, Zornitsa Kozareva, Mona Diab, Veselin Stoyanov, Xian Li.
|
||||
@ -344,7 +362,7 @@ conda install -c huggingface transformers
|
||||
1. **[XLNet](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/xlnet)** (来自 Google/CMU) 伴随论文 [XLNet: Generalized Autoregressive Pretraining for Language Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/1906.08237) 由 Zhilin Yang*, Zihang Dai*, Yiming Yang, Jaime Carbonell, Ruslan Salakhutdinov, Quoc V. Le 发布。
|
||||
1. **[XLS-R](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/xls_r)** (来自 Facebook AI) 伴随论文 [XLS-R: Self-supervised Cross-lingual Speech Representation Learning at Scale](https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.09296) 由 Arun Babu, Changhan Wang, Andros Tjandra, Kushal Lakhotia, Qiantong Xu, Naman Goyal, Kritika Singh, Patrick von Platen, Yatharth Saraf, Juan Pino, Alexei Baevski, Alexis Conneau, Michael Auli 发布。
|
||||
1. **[XLSR-Wav2Vec2](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/xlsr_wav2vec2)** (来自 Facebook AI) 伴随论文 [Unsupervised Cross-Lingual Representation Learning For Speech Recognition](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.13979) 由 Alexis Conneau, Alexei Baevski, Ronan Collobert, Abdelrahman Mohamed, Michael Auli 发布。
|
||||
1. **[YOLOS](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/model_doc/yolos)** (来自 Huazhong University of Science & Technology) 伴随论文 [You Only Look at One Sequence: Rethinking Transformer in Vision through Object Detection](https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.00666) 由 Yuxin Fang, Bencheng Liao, Xinggang Wang, Jiemin Fang, Jiyang Qi, Rui Wu, Jianwei Niu, Wenyu Liu 发布。
|
||||
1. **[YOLOS](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/yolos)** (来自 Huazhong University of Science & Technology) 伴随论文 [You Only Look at One Sequence: Rethinking Transformer in Vision through Object Detection](https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.00666) 由 Yuxin Fang, Bencheng Liao, Xinggang Wang, Jiemin Fang, Jiyang Qi, Rui Wu, Jianwei Niu, Wenyu Liu 发布。
|
||||
1. **[YOSO](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/yoso)** (来自 the University of Wisconsin - Madison) 伴随论文 [You Only Sample (Almost) 由 Zhanpeng Zeng, Yunyang Xiong, Sathya N. Ravi, Shailesh Acharya, Glenn Fung, Vikas Singh 发布。
|
||||
1. 想要贡献新的模型?我们这里有一份**详细指引和模板**来引导你添加新的模型。你可以在 [`templates`](./templates) 目录中找到他们。记得查看 [贡献指南](./CONTRIBUTING.md) 并在开始写 PR 前联系维护人员或开一个新的 issue 来获得反馈。
|
||||
|
||||
@ -360,7 +378,7 @@ conda install -c huggingface transformers
|
||||
| [文档](https://huggingface.co/transformers/) | 完整的 API 文档和教程 |
|
||||
| [任务总结](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/task_summary) | 🤗 Transformers 支持的任务 |
|
||||
| [预处理教程](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/preprocessing) | 使用 `Tokenizer` 来为模型准备数据 |
|
||||
| [训练和微调](https://huggingface.co/docstransformers/training) | 在 PyTorch/TensorFlow 的训练循环或 `Trainer` API 中使用 🤗 Transformers 提供的模型 |
|
||||
| [训练和微调](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/training) | 在 PyTorch/TensorFlow 的训练循环或 `Trainer` API 中使用 🤗 Transformers 提供的模型 |
|
||||
| [快速上手:微调和用例脚本](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples) | 为各种任务提供的用例脚本 |
|
||||
| [模型分享和上传](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_sharing) | 和社区上传和分享你微调的模型 |
|
||||
| [迁移](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/migration) | 从 `pytorch-transformers` 或 `pytorch-pretrained-bert` 迁移到 🤗 Transformers |
|
||||
|
||||
@ -257,16 +257,19 @@ conda install -c huggingface transformers
|
||||
1. **[BigBird-RoBERTa](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/big_bird)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [Big Bird: Transformers for Longer Sequences](https://arxiv.org/abs/2007.14062) by Manzil Zaheer, Guru Guruganesh, Avinava Dubey, Joshua Ainslie, Chris Alberti, Santiago Ontanon, Philip Pham, Anirudh Ravula, Qifan Wang, Li Yang, Amr Ahmed.
|
||||
1. **[Blenderbot](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/blenderbot)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Recipes for building an open-domain chatbot](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.13637) by Stephen Roller, Emily Dinan, Naman Goyal, Da Ju, Mary Williamson, Yinhan Liu, Jing Xu, Myle Ott, Kurt Shuster, Eric M. Smith, Y-Lan Boureau, Jason Weston.
|
||||
1. **[BlenderbotSmall](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/blenderbot-small)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Recipes for building an open-domain chatbot](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.13637) by Stephen Roller, Emily Dinan, Naman Goyal, Da Ju, Mary Williamson, Yinhan Liu, Jing Xu, Myle Ott, Kurt Shuster, Eric M. Smith, Y-Lan Boureau, Jason Weston.
|
||||
1. **[BLOOM](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/bloom)** (from BigScience workshop) released by the [BigSicence Workshop](https://bigscience.huggingface.co/).
|
||||
1. **[BORT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/bort)** (from Alexa) released with the paper [Optimal Subarchitecture Extraction For BERT](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.10499) by Adrian de Wynter and Daniel J. Perry.
|
||||
1. **[ByT5](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/byt5)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [ByT5: Towards a token-free future with pre-trained byte-to-byte models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2105.13626) by Linting Xue, Aditya Barua, Noah Constant, Rami Al-Rfou, Sharan Narang, Mihir Kale, Adam Roberts, Colin Raffel.
|
||||
1. **[CamemBERT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/camembert)** (from Inria/Facebook/Sorbonne) released with the paper [CamemBERT: a Tasty French Language Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.03894) by Louis Martin*, Benjamin Muller*, Pedro Javier Ortiz Suárez*, Yoann Dupont, Laurent Romary, Éric Villemonte de la Clergerie, Djamé Seddah and Benoît Sagot.
|
||||
1. **[CANINE](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/canine)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [CANINE: Pre-training an Efficient Tokenization-Free Encoder for Language Representation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.06874) by Jonathan H. Clark, Dan Garrette, Iulia Turc, John Wieting.
|
||||
1. **[CLIP](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/clip)** (from OpenAI) released with the paper [Learning Transferable Visual Models From Natural Language Supervision](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.00020) by Alec Radford, Jong Wook Kim, Chris Hallacy, Aditya Ramesh, Gabriel Goh, Sandhini Agarwal, Girish Sastry, Amanda Askell, Pamela Mishkin, Jack Clark, Gretchen Krueger, Ilya Sutskever.
|
||||
1. **[CodeGen](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/codegen)** (from Salesforce) released with the paper [A Conversational Paradigm for Program Synthesis](https://arxiv.org/abs/2203.13474) by Erik Nijkamp, Bo Pang, Hiroaki Hayashi, Lifu Tu, Huan Wang, Yingbo Zhou, Silvio Savarese, Caiming Xiong.
|
||||
1. **[ConvBERT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/convbert)** (from YituTech) released with the paper [ConvBERT: Improving BERT with Span-based Dynamic Convolution](https://arxiv.org/abs/2008.02496) by Zihang Jiang, Weihao Yu, Daquan Zhou, Yunpeng Chen, Jiashi Feng, Shuicheng Yan.
|
||||
1. **[ConvNeXT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/model_doc/convnext)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [A ConvNet for the 2020s](https://arxiv.org/abs/2201.03545) by Zhuang Liu, Hanzi Mao, Chao-Yuan Wu, Christoph Feichtenhofer, Trevor Darrell, Saining Xie.
|
||||
1. **[ConvNeXT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/convnext)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [A ConvNet for the 2020s](https://arxiv.org/abs/2201.03545) by Zhuang Liu, Hanzi Mao, Chao-Yuan Wu, Christoph Feichtenhofer, Trevor Darrell, Saining Xie.
|
||||
1. **[CPM](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/cpm)** (from Tsinghua University) released with the paper [CPM: A Large-scale Generative Chinese Pre-trained Language Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/2012.00413) by Zhengyan Zhang, Xu Han, Hao Zhou, Pei Ke, Yuxian Gu, Deming Ye, Yujia Qin, Yusheng Su, Haozhe Ji, Jian Guan, Fanchao Qi, Xiaozhi Wang, Yanan Zheng, Guoyang Zeng, Huanqi Cao, Shengqi Chen, Daixuan Li, Zhenbo Sun, Zhiyuan Liu, Minlie Huang, Wentao Han, Jie Tang, Juanzi Li, Xiaoyan Zhu, Maosong Sun.
|
||||
1. **[CTRL](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/ctrl)** (from Salesforce) released with the paper [CTRL: A Conditional Transformer Language Model for Controllable Generation](https://arxiv.org/abs/1909.05858) by Nitish Shirish Keskar*, Bryan McCann*, Lav R. Varshney, Caiming Xiong and Richard Socher.
|
||||
1. **[Data2Vec](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/model_doc/data2vec)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Data2Vec: A General Framework for Self-supervised Learning in Speech, Vision and Language](https://arxiv.org/abs/2202.03555) by Alexei Baevski, Wei-Ning Hsu, Qiantong Xu, Arun Babu, Jiatao Gu, Michael Auli.
|
||||
1. **[CvT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/cvt)** (from Microsoft) released with the paper [CvT: Introducing Convolutions to Vision Transformers](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.15808) by Haiping Wu, Bin Xiao, Noel Codella, Mengchen Liu, Xiyang Dai, Lu Yuan, Lei Zhang.
|
||||
1. **[Data2Vec](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/data2vec)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Data2Vec: A General Framework for Self-supervised Learning in Speech, Vision and Language](https://arxiv.org/abs/2202.03555) by Alexei Baevski, Wei-Ning Hsu, Qiantong Xu, Arun Babu, Jiatao Gu, Michael Auli.
|
||||
1. **[DeBERTa](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/deberta)** (from Microsoft) released with the paper [DeBERTa: Decoding-enhanced BERT with Disentangled Attention](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.03654) by Pengcheng He, Xiaodong Liu, Jianfeng Gao, Weizhu Chen.
|
||||
1. **[DeBERTa-v2](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/deberta-v2)** (from Microsoft) released with the paper [DeBERTa: Decoding-enhanced BERT with Disentangled Attention](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.03654) by Pengcheng He, Xiaodong Liu, Jianfeng Gao, Weizhu Chen.
|
||||
1. **[Decision Transformer](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/decision_transformer)** (from Berkeley/Facebook/Google) released with the paper [Decision Transformer: Reinforcement Learning via Sequence Modeling](https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.01345) by Lili Chen, Kevin Lu, Aravind Rajeswaran, Kimin Lee, Aditya Grover, Michael Laskin, Pieter Abbeel, Aravind Srinivas, Igor Mordatch.
|
||||
@ -280,34 +283,45 @@ conda install -c huggingface transformers
|
||||
1. **[ELECTRA](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/electra)** (from Google Research/Stanford University) released with the paper [ELECTRA: Pre-training text encoders as discriminators rather than generators](https://arxiv.org/abs/2003.10555) by Kevin Clark, Minh-Thang Luong, Quoc V. Le, Christopher D. Manning.
|
||||
1. **[EncoderDecoder](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/encoder-decoder)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [Leveraging Pre-trained Checkpoints for Sequence Generation Tasks](https://arxiv.org/abs/1907.12461) by Sascha Rothe, Shashi Narayan, Aliaksei Severyn.
|
||||
1. **[FlauBERT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/flaubert)** (from CNRS) released with the paper [FlauBERT: Unsupervised Language Model Pre-training for French](https://arxiv.org/abs/1912.05372) by Hang Le, Loïc Vial, Jibril Frej, Vincent Segonne, Maximin Coavoux, Benjamin Lecouteux, Alexandre Allauzen, Benoît Crabbé, Laurent Besacier, Didier Schwab.
|
||||
1. **[FLAVA](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/model_doc/flava)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [FLAVA: A Foundational Language And Vision Alignment Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.04482) by Amanpreet Singh, Ronghang Hu, Vedanuj Goswami, Guillaume Couairon, Wojciech Galuba, Marcus Rohrbach, and Douwe Kiela.
|
||||
1. **[FLAVA](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/flava)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [FLAVA: A Foundational Language And Vision Alignment Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.04482) by Amanpreet Singh, Ronghang Hu, Vedanuj Goswami, Guillaume Couairon, Wojciech Galuba, Marcus Rohrbach, and Douwe Kiela.
|
||||
1. **[FNet](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/fnet)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [FNet: Mixing Tokens with Fourier Transforms](https://arxiv.org/abs/2105.03824) by James Lee-Thorp, Joshua Ainslie, Ilya Eckstein, Santiago Ontanon.
|
||||
1. **[Funnel Transformer](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/funnel)** (from CMU/Google Brain) released with the paper [Funnel-Transformer: Filtering out Sequential Redundancy for Efficient Language Processing](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.03236) by Zihang Dai, Guokun Lai, Yiming Yang, Quoc V. Le.
|
||||
1. **[GLPN](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/model_doc/glpn)** (from KAIST) released with the paper [Global-Local Path Networks for Monocular Depth Estimation with Vertical CutDepth](https://arxiv.org/abs/2201.07436) by Doyeon Kim, Woonghyun Ga, Pyungwhan Ahn, Donggyu Joo, Sehwan Chun, Junmo Kim.
|
||||
1. **[GLPN](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/glpn)** (from KAIST) released with the paper [Global-Local Path Networks for Monocular Depth Estimation with Vertical CutDepth](https://arxiv.org/abs/2201.07436) by Doyeon Kim, Woonghyun Ga, Pyungwhan Ahn, Donggyu Joo, Sehwan Chun, Junmo Kim.
|
||||
1. **[GPT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/openai-gpt)** (from OpenAI) released with the paper [Improving Language Understanding by Generative Pre-Training](https://blog.openai.com/language-unsupervised/) by Alec Radford, Karthik Narasimhan, Tim Salimans and Ilya Sutskever.
|
||||
1. **[GPT Neo](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/gpt_neo)** (from EleutherAI) released in the repository [EleutherAI/gpt-neo](https://github.com/EleutherAI/gpt-neo) by Sid Black, Stella Biderman, Leo Gao, Phil Wang and Connor Leahy.
|
||||
1. **[GPT NeoX](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/gpt_neox)** (from EleutherAI) released with the paper [GPT-NeoX-20B: An Open-Source Autoregressive Language Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/2204.06745) by Sid Black, Stella Biderman, Eric Hallahan, Quentin Anthony, Leo Gao, Laurence Golding, Horace He, Connor Leahy, Kyle McDonell, Jason Phang, Michael Pieler, USVSN Sai Prashanth, Shivanshu Purohit, Laria Reynolds, Jonathan Tow, Ben Wang, Samuel Weinbach
|
||||
1. **[GPT-2](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/gpt2)** (from OpenAI) released with the paper [Language Models are Unsupervised Multitask Learners](https://blog.openai.com/better-language-models/) by Alec Radford*, Jeffrey Wu*, Rewon Child, David Luan, Dario Amodei** and Ilya Sutskever**.
|
||||
1. **[GPT-J](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/gptj)** (from EleutherAI) released with the paper [kingoflolz/mesh-transformer-jax](https://github.com/kingoflolz/mesh-transformer-jax/) by Ben Wang and Aran Komatsuzaki.
|
||||
1. **[GroupViT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/model_doc/groupvit)** (from UCSD, NVIDIA) released with the paper [GroupViT: Semantic Segmentation Emerges from Text Supervision](https://arxiv.org/abs/2202.11094) by Jiarui Xu, Shalini De Mello, Sifei Liu, Wonmin Byeon, Thomas Breuel, Jan Kautz, Xiaolong Wang.
|
||||
1. **[Hubert](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/hubert)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [HuBERT: Self-Supervised Speech Representation Learning by Masked Prediction of Hidden Units](https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.07447) by Wei-Ning Hsu, Benjamin Bolte, Yao-Hung Hubert Tsai, Kushal Lakhotia, Ruslan Salakhutdinov, Abdelrahman Mohamed.
|
||||
1. **[I-BERT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/ibert)** (from Berkeley) released with the paper [I-BERT: Integer-only BERT Quantization](https://arxiv.org/abs/2101.01321) by Sehoon Kim, Amir Gholami, Zhewei Yao, Michael W. Mahoney, Kurt Keutzer.
|
||||
1. **[ImageGPT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/model_doc/imagegpt)** (from OpenAI) released with the paper [Generative Pretraining from Pixels](https://openai.com/blog/image-gpt/) by Mark Chen, Alec Radford, Rewon Child, Jeffrey Wu, Heewoo Jun, David Luan, Ilya Sutskever.
|
||||
1. **[ImageGPT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/imagegpt)** (from OpenAI) released with the paper [Generative Pretraining from Pixels](https://openai.com/blog/image-gpt/) by Mark Chen, Alec Radford, Rewon Child, Jeffrey Wu, Heewoo Jun, David Luan, Ilya Sutskever.
|
||||
1. **[LayoutLM](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/layoutlm)** (from Microsoft Research Asia) released with the paper [LayoutLM: Pre-training of Text and Layout for Document Image Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/1912.13318) by Yiheng Xu, Minghao Li, Lei Cui, Shaohan Huang, Furu Wei, Ming Zhou.
|
||||
1. **[LayoutLMv2](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/layoutlmv2)** (from Microsoft Research Asia) released with the paper [LayoutLMv2: Multi-modal Pre-training for Visually-Rich Document Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/2012.14740) by Yang Xu, Yiheng Xu, Tengchao Lv, Lei Cui, Furu Wei, Guoxin Wang, Yijuan Lu, Dinei Florencio, Cha Zhang, Wanxiang Che, Min Zhang, Lidong Zhou.
|
||||
1. **[LayoutLMv3](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/layoutlmv3)** (from Microsoft Research Asia) released with the paper [LayoutLMv3: Pre-training for Document AI with Unified Text and Image Masking](https://arxiv.org/abs/2204.08387) by Yupan Huang, Tengchao Lv, Lei Cui, Yutong Lu, Furu Wei.
|
||||
1. **[LayoutXLM](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/layoutlmv2)** (from Microsoft Research Asia) released with the paper [LayoutXLM: Multimodal Pre-training for Multilingual Visually-rich Document Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.08836) by Yiheng Xu, Tengchao Lv, Lei Cui, Guoxin Wang, Yijuan Lu, Dinei Florencio, Cha Zhang, Furu Wei.
|
||||
1. **[LED](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/led)** (from AllenAI) released with the paper [Longformer: The Long-Document Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.05150) by Iz Beltagy, Matthew E. Peters, Arman Cohan.
|
||||
1. **[LeViT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/levit)** (from Meta AI) released with the paper [LeViT: A Vision Transformer in ConvNet's Clothing for Faster Inference](https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.01136) by Ben Graham, Alaaeldin El-Nouby, Hugo Touvron, Pierre Stock, Armand Joulin, Hervé Jégou, Matthijs Douze.
|
||||
1. **[Longformer](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/longformer)** (from AllenAI) released with the paper [Longformer: The Long-Document Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.05150) by Iz Beltagy, Matthew E. Peters, Arman Cohan.
|
||||
1. **[LongT5](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/longt5)** (from Google AI) released with the paper [LongT5: Efficient Text-To-Text Transformer for Long Sequences](https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.07916) by Mandy Guo, Joshua Ainslie, David Uthus, Santiago Ontanon, Jianmo Ni, Yun-Hsuan Sung, Yinfei Yang.
|
||||
1. **[LUKE](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/luke)** (from Studio Ousia) released with the paper [LUKE: Deep Contextualized Entity Representations with Entity-aware Self-attention](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.01057) by Ikuya Yamada, Akari Asai, Hiroyuki Shindo, Hideaki Takeda, Yuji Matsumoto.
|
||||
1. **[LXMERT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/lxmert)** (from UNC Chapel Hill) released with the paper [LXMERT: Learning Cross-Modality Encoder Representations from Transformers for Open-Domain Question Answering](https://arxiv.org/abs/1908.07490) by Hao Tan and Mohit Bansal.
|
||||
1. **[M-CTC-T](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/mctct)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Pseudo-Labeling For Massively Multilingual Speech Recognition](https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.00161) by Loren Lugosch, Tatiana Likhomanenko, Gabriel Synnaeve, and Ronan Collobert.
|
||||
1. **[M2M100](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/m2m_100)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Beyond English-Centric Multilingual Machine Translation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11125) by Angela Fan, Shruti Bhosale, Holger Schwenk, Zhiyi Ma, Ahmed El-Kishky, Siddharth Goyal, Mandeep Baines, Onur Celebi, Guillaume Wenzek, Vishrav Chaudhary, Naman Goyal, Tom Birch, Vitaliy Liptchinsky, Sergey Edunov, Edouard Grave, Michael Auli, Armand Joulin.
|
||||
1. **[MarianMT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/marian)** Machine translation models trained using [OPUS](http://opus.nlpl.eu/) data by Jörg Tiedemann. The [Marian Framework](https://marian-nmt.github.io/) is being developed by the Microsoft Translator Team.
|
||||
1. **[MaskFormer](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/model_doc/maskformer)** (from Meta and UIUC) released with the paper [Per-Pixel Classification is Not All You Need for Semantic Segmentation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.06278) by Bowen Cheng, Alexander G. Schwing, Alexander Kirillov
|
||||
1. **[MBart](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/mbart)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Multilingual Denoising Pre-training for Neural Machine Translation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2001.08210) by Yinhan Liu, Jiatao Gu, Naman Goyal, Xian Li, Sergey Edunov, Marjan Ghazvininejad, Mike Lewis, Luke Zettlemoyer.
|
||||
1. **[MBart-50](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/mbart)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Multilingual Translation with Extensible Multilingual Pretraining and Finetuning](https://arxiv.org/abs/2008.00401) by Yuqing Tang, Chau Tran, Xian Li, Peng-Jen Chen, Naman Goyal, Vishrav Chaudhary, Jiatao Gu, Angela Fan.
|
||||
1. **[MaskFormer](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/maskformer)** (from Meta and UIUC) released with the paper [Per-Pixel Classification is Not All You Need for Semantic Segmentation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.06278) by Bowen Cheng, Alexander G. Schwing, Alexander Kirillov
|
||||
1. **[mBART](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/mbart)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Multilingual Denoising Pre-training for Neural Machine Translation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2001.08210) by Yinhan Liu, Jiatao Gu, Naman Goyal, Xian Li, Sergey Edunov, Marjan Ghazvininejad, Mike Lewis, Luke Zettlemoyer.
|
||||
1. **[mBART-50](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/mbart)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Multilingual Translation with Extensible Multilingual Pretraining and Finetuning](https://arxiv.org/abs/2008.00401) by Yuqing Tang, Chau Tran, Xian Li, Peng-Jen Chen, Naman Goyal, Vishrav Chaudhary, Jiatao Gu, Angela Fan.
|
||||
1. **[Megatron-BERT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/megatron-bert)** (from NVIDIA) released with the paper [Megatron-LM: Training Multi-Billion Parameter Language Models Using Model Parallelism](https://arxiv.org/abs/1909.08053) by Mohammad Shoeybi, Mostofa Patwary, Raul Puri, Patrick LeGresley, Jared Casper and Bryan Catanzaro.
|
||||
1. **[Megatron-GPT2](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/megatron_gpt2)** (from NVIDIA) released with the paper [Megatron-LM: Training Multi-Billion Parameter Language Models Using Model Parallelism](https://arxiv.org/abs/1909.08053) by Mohammad Shoeybi, Mostofa Patwary, Raul Puri, Patrick LeGresley, Jared Casper and Bryan Catanzaro.
|
||||
1. **[mLUKE](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/mluke)** (from Studio Ousia) released with the paper [mLUKE: The Power of Entity Representations in Multilingual Pretrained Language Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.08151) by Ryokan Ri, Ikuya Yamada, and Yoshimasa Tsuruoka.
|
||||
1. **[MobileBERT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/mobilebert)** (from CMU/Google Brain) released with the paper [MobileBERT: a Compact Task-Agnostic BERT for Resource-Limited Devices](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.02984) by Zhiqing Sun, Hongkun Yu, Xiaodan Song, Renjie Liu, Yiming Yang, and Denny Zhou.
|
||||
1. **[MobileViT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/model_doc/mobilevit)** (from Apple) released with the paper [MobileViT: Light-weight, General-purpose, and Mobile-friendly Vision Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.02178) by Sachin Mehta and Mohammad Rastegari.
|
||||
1. **[MPNet](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/mpnet)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [MPNet: Masked and Permuted Pre-training for Language Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.09297) by Kaitao Song, Xu Tan, Tao Qin, Jianfeng Lu, Tie-Yan Liu.
|
||||
1. **[MT5](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/mt5)** (from Google AI) released with the paper [mT5: A massively multilingual pre-trained text-to-text transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11934) by Linting Xue, Noah Constant, Adam Roberts, Mihir Kale, Rami Al-Rfou, Aditya Siddhant, Aditya Barua, Colin Raffel.
|
||||
1. **[MVP](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/model_doc/mvp)** (from RUC AI Box) released with the paper [MVP: Multi-task Supervised Pre-training for Natural Language Generation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.12131) by Tianyi Tang, Junyi Li, Wayne Xin Zhao and Ji-Rong Wen.
|
||||
1. **[Nezha](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/model_doc/nezha)** (from Huawei Noah’s Ark Lab) released with the paper [NEZHA: Neural Contextualized Representation for Chinese Language Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/1909.00204) by Junqiu Wei, Xiaozhe Ren, Xiaoguang Li, Wenyong Huang, Yi Liao, Yasheng Wang, Jiashu Lin, Xin Jiang, Xiao Chen and Qun Liu.
|
||||
1. **[NLLB](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/model_doc/nllb)** (from Meta) released with the paper [No Language Left Behind: Scaling Human-Centered Machine Translation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2207.04672) by the NLLB team.
|
||||
1. **[Nyströmformer](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/nystromformer)** (from the University of Wisconsin - Madison) released with the paper [Nyströmformer: A Nyström-Based Algorithm for Approximating Self-Attention](https://arxiv.org/abs/2102.03902) by Yunyang Xiong, Zhanpeng Zeng, Rudrasis Chakraborty, Mingxing Tan, Glenn Fung, Yin Li, Vikas Singh.
|
||||
1. **[OPT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/master/model_doc/opt)** (from Meta AI) released with the paper [OPT: Open Pre-trained Transformer Language Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.01068) by Susan Zhang, Stephen Roller, Naman Goyal, Mikel Artetxe, Moya Chen, Shuohui Chen et al.
|
||||
1. **[Pegasus](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/pegasus)** (from Google) released with the paper [PEGASUS: Pre-training with Extracted Gap-sentences for Abstractive Summarization](https://arxiv.org/abs/1912.08777) by Jingqing Zhang, Yao Zhao, Mohammad Saleh and Peter J. Liu.
|
||||
@ -317,9 +331,10 @@ conda install -c huggingface transformers
|
||||
1. **[PoolFormer](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/poolformer)** (from Sea AI Labs) released with the paper [MetaFormer is Actually What You Need for Vision](https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.11418) by Yu, Weihao and Luo, Mi and Zhou, Pan and Si, Chenyang and Zhou, Yichen and Wang, Xinchao and Feng, Jiashi and Yan, Shuicheng.
|
||||
1. **[ProphetNet](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/prophetnet)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [ProphetNet: Predicting Future N-gram for Sequence-to-Sequence Pre-training](https://arxiv.org/abs/2001.04063) by Yu Yan, Weizhen Qi, Yeyun Gong, Dayiheng Liu, Nan Duan, Jiusheng Chen, Ruofei Zhang and Ming Zhou.
|
||||
1. **[QDQBert](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/qdqbert)** (from NVIDIA) released with the paper [Integer Quantization for Deep Learning Inference: Principles and Empirical Evaluation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.09602) by Hao Wu, Patrick Judd, Xiaojie Zhang, Mikhail Isaev and Paulius Micikevicius.
|
||||
1. **[RAG](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/rag)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Knowledge-Intensive NLP Tasks](https://arxiv.org/abs/2005.11401) by Patrick Lewis, Ethan Perez, Aleksandara Piktus, Fabio Petroni, Vladimir Karpukhin, Naman Goyal, Heinrich Küttler, Mike Lewis, Wen-tau Yih, Tim Rocktäschel, Sebastian Riedel, Douwe Kiela.
|
||||
1. **[REALM](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/realm.html)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [REALM: Retrieval-Augmented Language Model Pre-Training](https://arxiv.org/abs/2002.08909) by Kelvin Guu, Kenton Lee, Zora Tung, Panupong Pasupat and Ming-Wei Chang.
|
||||
1. **[Reformer](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/reformer)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [Reformer: The Efficient Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2001.04451) by Nikita Kitaev, Łukasz Kaiser, Anselm Levskaya.
|
||||
1. **[RegNet](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/model_doc/regnet)** (from META Research) released with the paper [Designing Network Design Space](https://arxiv.org/abs/2003.13678) by Ilija Radosavovic, Raj Prateek Kosaraju, Ross Girshick, Kaiming He, Piotr Dollár.
|
||||
1. **[RegNet](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/regnet)** (from META Research) released with the paper [Designing Network Design Space](https://arxiv.org/abs/2003.13678) by Ilija Radosavovic, Raj Prateek Kosaraju, Ross Girshick, Kaiming He, Piotr Dollár.
|
||||
1. **[RemBERT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/rembert)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [Rethinking embedding coupling in pre-trained language models](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2010.12821.pdf) by Hyung Won Chung, Thibault Févry, Henry Tsai, M. Johnson, Sebastian Ruder.
|
||||
1. **[ResNet](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/resnet)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition](https://arxiv.org/abs/1512.03385) by Kaiming He, Xiangyu Zhang, Shaoqing Ren, Jian Sun.
|
||||
1. **[RoBERTa](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/roberta)** (from Facebook), released together with the paper a [Robustly Optimized BERT Pretraining Approach](https://arxiv.org/abs/1907.11692) by Yinhan Liu, Myle Ott, Naman Goyal, Jingfei Du, Mandar Joshi, Danqi Chen, Omer Levy, Mike Lewis, Luke Zettlemoyer, Veselin Stoyanov.
|
||||
@ -330,14 +345,16 @@ conda install -c huggingface transformers
|
||||
1. **[SpeechToTextTransformer](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/speech_to_text)** (from Facebook), released together with the paper [fairseq S2T: Fast Speech-to-Text Modeling with fairseq](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.05171) by Changhan Wang, Yun Tang, Xutai Ma, Anne Wu, Dmytro Okhonko, Juan Pino.
|
||||
1. **[SpeechToTextTransformer2](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/speech_to_text_2)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Large-Scale Self- and Semi-Supervised Learning for Speech Translation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.06678) by Changhan Wang, Anne Wu, Juan Pino, Alexei Baevski, Michael Auli, Alexis Conneau.
|
||||
1. **[Splinter](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/splinter)** (from Tel Aviv University) released with the paper [Few-Shot Question Answering by Pretraining Span Selection](https://arxiv.org/abs/2101.00438) by Ori Ram, Yuval Kirstain, Jonathan Berant, Amir Globerson, Omer Levy.
|
||||
1. **[SqueezeBert](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/squeezebert)** (from Berkeley) released with the paper [SqueezeBERT: What can computer vision teach NLP about efficient neural networks?](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.11316) by Forrest N. Iandola, Albert E. Shaw, Ravi Krishna, and Kurt W. Keutzer.
|
||||
1. **[SqueezeBERT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/squeezebert)** (from Berkeley) released with the paper [SqueezeBERT: What can computer vision teach NLP about efficient neural networks?](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.11316) by Forrest N. Iandola, Albert E. Shaw, Ravi Krishna, and Kurt W. Keutzer.
|
||||
1. **[Swin Transformer](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/swin)** (from Microsoft) released with the paper [Swin Transformer: Hierarchical Vision Transformer using Shifted Windows](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.14030) by Ze Liu, Yutong Lin, Yue Cao, Han Hu, Yixuan Wei, Zheng Zhang, Stephen Lin, Baining Guo.
|
||||
1. **[T5](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/t5)** (from Google AI) released with the paper [Exploring the Limits of Transfer Learning with a Unified Text-to-Text Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/1910.10683) by Colin Raffel and Noam Shazeer and Adam Roberts and Katherine Lee and Sharan Narang and Michael Matena and Yanqi Zhou and Wei Li and Peter J. Liu.
|
||||
1. **[T5v1.1](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/t5v1.1)** (from Google AI) released with the paper [google-research/text-to-text-transfer-transformer](https://github.com/google-research/text-to-text-transfer-transformer/blob/main/released_checkpoints.md#t511) by Colin Raffel and Noam Shazeer and Adam Roberts and Katherine Lee and Sharan Narang and Michael Matena and Yanqi Zhou and Wei Li and Peter J. Liu.
|
||||
1. **[TAPAS](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/tapas)** (from Google AI) released with the paper [TAPAS: Weakly Supervised Table Parsing via Pre-training](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.02349) by Jonathan Herzig, Paweł Krzysztof Nowak, Thomas Müller, Francesco Piccinno and Julian Martin Eisenschlos.
|
||||
1. **[TAPEX](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/model_doc/tapex)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [TAPEX: Table Pre-training via Learning a Neural SQL Executor](https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.07653) by Qian Liu, Bei Chen, Jiaqi Guo, Morteza Ziyadi, Zeqi Lin, Weizhu Chen, Jian-Guang Lou.
|
||||
1. **[TAPEX](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/tapex)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [TAPEX: Table Pre-training via Learning a Neural SQL Executor](https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.07653) by Qian Liu, Bei Chen, Jiaqi Guo, Morteza Ziyadi, Zeqi Lin, Weizhu Chen, Jian-Guang Lou.
|
||||
1. **[Trajectory Transformer](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/trajectory_transformers)** (from the University of California at Berkeley) released with the paper [Offline Reinforcement Learning as One Big Sequence Modeling Problem](https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.02039) by Michael Janner, Qiyang Li, Sergey Levine
|
||||
1. **[Transformer-XL](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/transfo-xl)** (from Google/CMU) released with the paper [Transformer-XL: Attentive Language Models Beyond a Fixed-Length Context](https://arxiv.org/abs/1901.02860) by Zihang Dai*, Zhilin Yang*, Yiming Yang, Jaime Carbonell, Quoc V. Le, Ruslan Salakhutdinov.
|
||||
1. **[TrOCR](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/trocr)** (from Microsoft) released with the paper [TrOCR: Transformer-based Optical Character Recognition with Pre-trained Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.10282) by Minghao Li, Tengchao Lv, Lei Cui, Yijuan Lu, Dinei Florencio, Cha Zhang, Zhoujun Li, Furu Wei.
|
||||
1. **[UL2](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/model_doc/ul2)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [Unifying Language Learning Paradigms](https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.05131v1) by Yi Tay, Mostafa Dehghani, Vinh Q. Tran, Xavier Garcia, Dara Bahri, Tal Schuster, Huaixiu Steven Zheng, Neil Houlsby, Donald Metzler
|
||||
1. **[UniSpeech](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/unispeech)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [UniSpeech: Unified Speech Representation Learning with Labeled and Unlabeled Data](https://arxiv.org/abs/2101.07597) by Chengyi Wang, Yu Wu, Yao Qian, Kenichi Kumatani, Shujie Liu, Furu Wei, Michael Zeng, Xuedong Huang.
|
||||
1. **[UniSpeechSat](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/unispeech-sat)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [UNISPEECH-SAT: UNIVERSAL SPEECH REPRESENTATION LEARNING WITH SPEAKER AWARE PRE-TRAINING](https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.05752) by Sanyuan Chen, Yu Wu, Chengyi Wang, Zhengyang Chen, Zhuo Chen, Shujie Liu, Jian Wu, Yao Qian, Furu Wei, Jinyu Li, Xiangzhan Yu.
|
||||
1. **[VAN](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/van)** (from Tsinghua University and Nankai University) released with the paper [Visual Attention Network](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2202.09741.pdf) by Meng-Hao Guo, Cheng-Ze Lu, Zheng-Ning Liu, Ming-Ming Cheng, Shi-Min Hu.
|
||||
@ -346,6 +363,7 @@ conda install -c huggingface transformers
|
||||
1. **[VisualBERT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/visual_bert)** (from UCLA NLP) released with the paper [VisualBERT: A Simple and Performant Baseline for Vision and Language](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1908.03557) by Liunian Harold Li, Mark Yatskar, Da Yin, Cho-Jui Hsieh, Kai-Wei Chang.
|
||||
1. **[ViTMAE](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/vit_mae)** (from Meta AI) released with the paper [Masked Autoencoders Are Scalable Vision Learners](https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.06377) by Kaiming He, Xinlei Chen, Saining Xie, Yanghao Li, Piotr Dollár, Ross Girshick.
|
||||
1. **[Wav2Vec2](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/wav2vec2)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [wav2vec 2.0: A Framework for Self-Supervised Learning of Speech Representations](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.11477) by Alexei Baevski, Henry Zhou, Abdelrahman Mohamed, Michael Auli.
|
||||
1. **[Wav2Vec2-Conformer](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/wav2vec2-conformer)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [FAIRSEQ S2T: Fast Speech-to-Text Modeling with FAIRSEQ](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.05171) by Changhan Wang, Yun Tang, Xutai Ma, Anne Wu, Sravya Popuri, Dmytro Okhonko, Juan Pino.
|
||||
1. **[Wav2Vec2Phoneme](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/wav2vec2_phoneme)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [Simple and Effective Zero-shot Cross-lingual Phoneme Recognition](https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.11680) by Qiantong Xu, Alexei Baevski, Michael Auli.
|
||||
1. **[WavLM](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/wavlm)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [WavLM: Large-Scale Self-Supervised Pre-Training for Full Stack Speech Processing](https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.13900) by Sanyuan Chen, Chengyi Wang, Zhengyang Chen, Yu Wu, Shujie Liu, Zhuo Chen, Jinyu Li, Naoyuki Kanda, Takuya Yoshioka, Xiong Xiao, Jian Wu, Long Zhou, Shuo Ren, Yanmin Qian, Yao Qian, Jian Wu, Michael Zeng, Furu Wei.
|
||||
1. **[XGLM](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/xglm)** (From Facebook AI) released with the paper [Few-shot Learning with Multilingual Language Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.10668) by Xi Victoria Lin, Todor Mihaylov, Mikel Artetxe, Tianlu Wang, Shuohui Chen, Daniel Simig, Myle Ott, Naman Goyal, Shruti Bhosale, Jingfei Du, Ramakanth Pasunuru, Sam Shleifer, Punit Singh Koura, Vishrav Chaudhary, Brian O'Horo, Jeff Wang, Luke Zettlemoyer, Zornitsa Kozareva, Mona Diab, Veselin Stoyanov, Xian Li.
|
||||
@ -356,7 +374,7 @@ conda install -c huggingface transformers
|
||||
1. **[XLNet](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/xlnet)** (from Google/CMU) released with the paper [XLNet: Generalized Autoregressive Pretraining for Language Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/1906.08237) by Zhilin Yang*, Zihang Dai*, Yiming Yang, Jaime Carbonell, Ruslan Salakhutdinov, Quoc V. Le.
|
||||
1. **[XLS-R](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/xls_r)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [XLS-R: Self-supervised Cross-lingual Speech Representation Learning at Scale](https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.09296) by Arun Babu, Changhan Wang, Andros Tjandra, Kushal Lakhotia, Qiantong Xu, Naman Goyal, Kritika Singh, Patrick von Platen, Yatharth Saraf, Juan Pino, Alexei Baevski, Alexis Conneau, Michael Auli.
|
||||
1. **[XLSR-Wav2Vec2](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/xlsr_wav2vec2)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [Unsupervised Cross-Lingual Representation Learning For Speech Recognition](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.13979) by Alexis Conneau, Alexei Baevski, Ronan Collobert, Abdelrahman Mohamed, Michael Auli.
|
||||
1. **[YOLOS](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/model_doc/yolos)** (from Huazhong University of Science & Technology) released with the paper [You Only Look at One Sequence: Rethinking Transformer in Vision through Object Detection](https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.00666) by Yuxin Fang, Bencheng Liao, Xinggang Wang, Jiemin Fang, Jiyang Qi, Rui Wu, Jianwei Niu, Wenyu Liu.
|
||||
1. **[YOLOS](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/yolos)** (from Huazhong University of Science & Technology) released with the paper [You Only Look at One Sequence: Rethinking Transformer in Vision through Object Detection](https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.00666) by Yuxin Fang, Bencheng Liao, Xinggang Wang, Jiemin Fang, Jiyang Qi, Rui Wu, Jianwei Niu, Wenyu Liu.
|
||||
1. **[YOSO](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/yoso)** (from the University of Wisconsin - Madison) released with the paper [You Only Sample (Almost) by Zhanpeng Zeng, Yunyang Xiong, Sathya N. Ravi, Shailesh Acharya, Glenn Fung, Vikas Singh.
|
||||
1. 想要貢獻新的模型?我們這裡有一份**詳細指引和模板**來引導你加入新的模型。你可以在 [`templates`](./templates) 目錄中找到它們。記得查看[貢獻指引](./CONTRIBUTING.md)並在開始寫 PR 前聯繫維護人員或開一個新的 issue 來獲得 feedbacks。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -3,20 +3,48 @@ LABEL maintainer="Hugging Face"
|
||||
|
||||
ARG DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive
|
||||
|
||||
# Use login shell to read variables from `~/.profile` (to pass dynamic created variables between RUN commands)
|
||||
SHELL ["sh", "-lc"]
|
||||
|
||||
# The following `ARG` are mainly used to specify the versions explicitly & directly in this docker file, and not meant
|
||||
# to be used as arguments for docker build (so far).
|
||||
|
||||
ARG PYTORCH='1.12.0'
|
||||
# (not always a valid torch version)
|
||||
ARG INTEL_TORCH_EXT='1.11.0'
|
||||
# Example: `cu102`, `cu113`, etc.
|
||||
ARG CUDA='cu113'
|
||||
|
||||
RUN apt update
|
||||
RUN apt install -y git libsndfile1-dev tesseract-ocr espeak-ng python3 python3-pip ffmpeg
|
||||
RUN apt install -y git libsndfile1-dev tesseract-ocr espeak-ng python3 python3-pip ffmpeg git-lfs
|
||||
RUN git lfs install
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir --upgrade pip
|
||||
|
||||
ARG REF=main
|
||||
RUN git clone https://github.com/huggingface/transformers && cd transformers && git checkout $REF
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir -e ./transformers[dev,onnxruntime]
|
||||
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir -U torch tensorflow
|
||||
# TODO: Handle these in a python utility script
|
||||
RUN [ ${#PYTORCH} -gt 0 -a "$PYTORCH" != "pre" ] && VERSION='torch=='$PYTORCH'.*' || VERSION='torch'; echo "export VERSION='$VERSION'" >> ~/.profile
|
||||
RUN echo torch=$VERSION
|
||||
# `torchvision` and `torchaudio` should be installed along with `torch`, especially for nightly build.
|
||||
# Currently, let's just use their latest releases (when `torch` is installed with a release version)
|
||||
# TODO: We might need to specify proper versions that work with a specific torch version (especially for past CI).
|
||||
RUN [ "$PYTORCH" != "pre" ] && python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir -U $VERSION torchvision torchaudio --extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/$CUDA || python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir -U --pre torch torchvision torchaudio --extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/nightly/$CUDA
|
||||
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir -U tensorflow
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip uninstall -y flax jax
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir torch-scatter -f https://data.pyg.org/whl/torch-$(python3 -c "from torch import version; print(version.__version__.split('+')[0])")+cu102.html
|
||||
|
||||
# Use installed torch version for `torch-scatter` to avid to deal with PYTORCH='pre'.
|
||||
# If torch is nightly version, the link is likely to be invalid, but the installation falls back to the latest torch-scatter
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir torch-scatter -f https://data.pyg.org/whl/torch-$(python3 -c "from torch import version; print(version.__version__.split('+')[0])")+$CUDA.html
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir intel_extension_for_pytorch==$INTEL_TORCH_EXT+cpu -f https://software.intel.com/ipex-whl-stable
|
||||
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir git+https://github.com/facebookresearch/detectron2.git pytesseract https://github.com/kpu/kenlm/archive/master.zip
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install -U "itsdangerous<2.1.0"
|
||||
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir git+https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate@main#egg=accelerate
|
||||
|
||||
# When installing in editable mode, `transformers` is not recognized as a package.
|
||||
# this line must be added in order for python to be aware of transformers.
|
||||
RUN cd transformers && python3 setup.py develop
|
||||
|
||||
@ -15,5 +15,6 @@ RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir torchvision git+https://github.com/fac
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir pytorch-quantization --extra-index-url https://pypi.ngc.nvidia.com
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install -U "itsdangerous<2.1.0"
|
||||
|
||||
RUN doc-builder build transformers transformers/docs/source --build_dir doc-build-dev --notebook_dir notebooks/transformers_doc --clean --version pr_$PR_NUMBER
|
||||
# Test if the image could successfully build the doc. before publishing the image
|
||||
RUN doc-builder build transformers transformers/docs/source/en --build_dir doc-build-dev --notebook_dir notebooks/transformers_doc --clean
|
||||
RUN rm -rf doc-build-dev
|
||||
43
docker/transformers-past-gpu/Dockerfile
Normal file
43
docker/transformers-past-gpu/Dockerfile
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
|
||||
ARG BASE_DOCKER_IMAGE="nvidia/cuda:11.2.2-cudnn8-devel-ubuntu20.04"
|
||||
FROM $BASE_DOCKER_IMAGE
|
||||
LABEL maintainer="Hugging Face"
|
||||
|
||||
ARG DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive
|
||||
|
||||
# Use login shell to read variables from `~/.profile` (to pass dynamic created variables between RUN commands)
|
||||
SHELL ["sh", "-lc"]
|
||||
|
||||
RUN apt update
|
||||
RUN apt install -y git libsndfile1-dev tesseract-ocr espeak-ng python3 python3-pip ffmpeg git-lfs
|
||||
RUN git lfs install
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir --upgrade pip
|
||||
|
||||
ARG REF=main
|
||||
RUN git clone https://github.com/huggingface/transformers && cd transformers && git checkout $REF
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir -e ./transformers[dev,onnxruntime]
|
||||
|
||||
# When installing in editable mode, `transformers` is not recognized as a package.
|
||||
# this line must be added in order for python to be aware of transformers.
|
||||
RUN cd transformers && python3 setup.py develop
|
||||
|
||||
ARG FRAMEWORK
|
||||
ARG VERSION
|
||||
|
||||
# Remove all frameworks
|
||||
# (`accelerate` requires `torch`, and this causes import issues for TF-only testing)
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip uninstall -y torch torchvision torchaudio accelerate tensorflow jax flax
|
||||
|
||||
# Get the libraries and their versions to install, and write installation command to `~/.profile`.
|
||||
RUN python3 ./transformers/utils/past_ci_versions.py --framework $FRAMEWORK --version $VERSION
|
||||
|
||||
# Install the target framework
|
||||
RUN echo "INSTALL_CMD = $INSTALL_CMD"
|
||||
RUN $INSTALL_CMD
|
||||
|
||||
# Having installation problems for torch-scatter with torch <= 1.6. Disable so we have the same set of tests.
|
||||
# (This part will be removed once the logic of using `past_ci_versions.py` is used in other Dockerfile files.)
|
||||
# # Use installed torch version for `torch-scatter`.
|
||||
# # (The env. variable $CUDA is defined in `past_ci_versions.py`)
|
||||
# RUN [ "$FRAMEWORK" = "pytorch" ] && python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir torch-scatter -f https://data.pyg.org/whl/torch-$(python3 -c "from torch import version; print(version.__version__.split('+')[0])")+$CUDA.html || echo "torch-scatter not to be installed"
|
||||
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install -U "itsdangerous<2.1.0"
|
||||
@ -3,16 +3,30 @@ LABEL maintainer="Hugging Face"
|
||||
|
||||
ARG DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive
|
||||
|
||||
ARG PYTORCH='1.12.0'
|
||||
# Example: `cu102`, `cu113`, etc.
|
||||
ARG CUDA='cu113'
|
||||
|
||||
RUN apt -y update
|
||||
RUN apt install -y libaio-dev
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir --upgrade pip
|
||||
|
||||
ARG REF=main
|
||||
RUN git clone https://github.com/huggingface/transformers && cd transformers && git checkout $REF
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir -e ./transformers[deepspeed-testing]
|
||||
|
||||
RUN git clone https://github.com/microsoft/DeepSpeed && cd DeepSpeed && rm -rf build && \
|
||||
DS_BUILD_CPU_ADAM=1 DS_BUILD_AIO=1 DS_BUILD_UTILS=1 python3 -m pip install -e . --global-option="build_ext" --global-option="-j8" --no-cache -v --disable-pip-version-check 2>&1
|
||||
# Install latest release PyTorch
|
||||
# (PyTorch must be installed before pre-compiling any DeepSpeed c++/cuda ops.)
|
||||
# (https://www.deepspeed.ai/tutorials/advanced-install/#pre-install-deepspeed-ops)
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir -U torch==$PYTORCH torchvision torchaudio --extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/$CUDA
|
||||
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir ./transformers[deepspeed-testing]
|
||||
|
||||
# Pre-build **latest** DeepSpeed, so it would be ready for testing (otherwise, the 1st deepspeed test will timeout)
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip uninstall -y deepspeed
|
||||
# This has to be run (again) inside the GPU VMs running the tests.
|
||||
# The installation works here, but some tests fail, if we don't pre-build deepspeed again in the VMs running the tests.
|
||||
# TODO: Find out why test fail.
|
||||
RUN DS_BUILD_CPU_ADAM=1 DS_BUILD_AIO=1 DS_BUILD_UTILS=1 python3 -m pip install deepspeed --global-option="build_ext" --global-option="-j8" --no-cache -v --disable-pip-version-check 2>&1
|
||||
|
||||
# When installing in editable mode, `transformers` is not recognized as a package.
|
||||
# this line must be added in order for python to be aware of transformers.
|
||||
|
||||
35
docker/transformers-pytorch-deepspeed-nightly-gpu/Dockerfile
Normal file
35
docker/transformers-pytorch-deepspeed-nightly-gpu/Dockerfile
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
|
||||
FROM nvcr.io/nvidia/pytorch:21.03-py3
|
||||
LABEL maintainer="Hugging Face"
|
||||
|
||||
ARG DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive
|
||||
|
||||
# Example: `cu102`, `cu113`, etc.
|
||||
ARG CUDA='cu113'
|
||||
|
||||
RUN apt -y update
|
||||
RUN apt install -y libaio-dev
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir --upgrade pip
|
||||
|
||||
ARG REF=main
|
||||
RUN git clone https://github.com/huggingface/transformers && cd transformers && git checkout $REF
|
||||
|
||||
# Install **nightly** release PyTorch (flag `--pre`)
|
||||
# (PyTorch must be installed before pre-compiling any DeepSpeed c++/cuda ops.)
|
||||
# (https://www.deepspeed.ai/tutorials/advanced-install/#pre-install-deepspeed-ops)
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir -U --pre torch torchvision torchaudio --extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/nightly/$CUDA
|
||||
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir ./transformers[deepspeed-testing]
|
||||
|
||||
# Pre-build **nightly** release of DeepSpeed, so it would be ready for testing (otherwise, the 1st deepspeed test will timeout)
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip uninstall -y deepspeed
|
||||
# This has to be run inside the GPU VMs running the tests. (So far, it fails here due to GPU checks during compilation.)
|
||||
# Issue: https://github.com/microsoft/DeepSpeed/issues/2010
|
||||
# RUN git clone https://github.com/microsoft/DeepSpeed && cd DeepSpeed && rm -rf build && \
|
||||
# DS_BUILD_CPU_ADAM=1 DS_BUILD_AIO=1 DS_BUILD_UTILS=1 python3 -m pip install . --global-option="build_ext" --global-option="-j8" --no-cache -v --disable-pip-version-check 2>&1
|
||||
|
||||
# When installing in editable mode, `transformers` is not recognized as a package.
|
||||
# this line must be added in order for python to be aware of transformers.
|
||||
RUN cd transformers && python3 setup.py develop
|
||||
|
||||
# Disable for now as deepspeed is not installed above. To be enabled once the issue is fixed.
|
||||
# RUN python3 -c "from deepspeed.launcher.runner import main"
|
||||
@ -12,12 +12,17 @@ RUN git clone https://github.com/huggingface/transformers && cd transformers &&
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir -e ./transformers[dev-torch,testing]
|
||||
|
||||
# If set to nothing, will install the latest version
|
||||
ARG PYTORCH=''
|
||||
ARG PYTORCH='1.12.0'
|
||||
ARG TORCH_VISION=''
|
||||
ARG TORCH_AUDIO=''
|
||||
|
||||
RUN [ ${#PYTORCH} -gt 0 ] && VERSION='torch=='$PYTORCH'.*' || VERSION='torch'; python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir -U $VERSION --extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu113
|
||||
RUN [ ${#TORCH_VISION} -gt 0 ] && VERSION='torchvision=='TORCH_VISION'.*' || VERSION='torchvision'; python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir -U $VERSION --extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu113
|
||||
RUN [ ${#TORCH_AUDIO} -gt 0 ] && VERSION='torchaudio=='TORCH_AUDIO'.*' || VERSION='torchaudio'; python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir -U $VERSION --extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu113
|
||||
|
||||
RUN [ ${#PYTORCH} -gt 0 ] && VERSION='torch=='$PYTORCH'.*' || VERSION='torch'; python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir -U $VERSION
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip uninstall -y tensorflow flax
|
||||
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir torch-scatter -f https://data.pyg.org/whl/torch-$(python3 -c "from torch import version; print(version.__version__.split('+')[0])")+cu102.html
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir torch-scatter -f https://data.pyg.org/whl/torch-$(python3 -c "from torch import version; print(version.__version__.split('+')[0])")+cu113.html
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir git+https://github.com/facebookresearch/detectron2.git pytesseract https://github.com/kpu/kenlm/archive/master.zip
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install -U "itsdangerous<2.1.0"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -50,11 +50,32 @@ You can adapt the `--build_dir` to set any temporary folder that you prefer. Thi
|
||||
the MDX files that will be rendered as the documentation on the main website. You can inspect them in your favorite
|
||||
Markdown editor.
|
||||
|
||||
## Previewing the documentation
|
||||
|
||||
To preview the docs, first install the `watchdog` module with:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install watchdog
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then run the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
doc-builder preview {package_name} {path_to_docs}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For example:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
doc-builder preview transformers docs/source/en/
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The docs will be viewable at [http://localhost:3000](http://localhost:3000). You can also preview the docs once you have opened a PR. You will see a bot add a comment to a link where the documentation with your changes lives.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
**NOTE**
|
||||
|
||||
It's not possible to see locally how the final documentation will look like for now. Once you have opened a PR, you
|
||||
will see a bot add a comment to a link where the documentation with your changes lives.
|
||||
The `preview` command only works with existing doc files. When you add a completely new file, you need to update `_toctree.yml` & restart `preview` command (`ctrl-c` to stop it & call `doc-builder preview ...` again).
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
@ -407,4 +428,4 @@ Here are a few tips to help you debug the doctests and make them pass:
|
||||
* whitespace: one give whitespace (space, tabulation, new line) is equivalent to any number of whitespace, so you can add new lines where there are spaces to make your output more readable.
|
||||
* numerical values: you should never put more than 4 or 5 digits to expected results as different setups or library versions might get you slightly different results. `doctest` is configure to ignore any difference lower than the precision to which you wrote (so 1e-4 if you write 4 digits).
|
||||
- Don't leave a block of code that is very long to execute. If you can't make it fast, you can either not use the doctest syntax on it (so that it's ignored), or if you want to use the doctest syntax to show the results, you can add a comment `# doctest: +SKIP` at the end of the lines of code too long to execute
|
||||
- Each line of code that produces a result needs to have that result written below. You can ignore an output if you don't want to show it in your code example by adding a comment ` # doctest: +IGNORE_RESULT` at the end of the line of code produing it.
|
||||
- Each line of code that produces a result needs to have that result written below. You can ignore an output if you don't want to show it in your code example by adding a comment ` # doctest: +IGNORE_RESULT` at the end of the line of code producing it.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: index
|
||||
title: 🤗 Transformers
|
||||
- local: quicktour
|
||||
@ -22,7 +22,7 @@
|
||||
title: Tutorials
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: fast_tokenizers
|
||||
title: "Use tokenizers from 🤗 Tokenizers"
|
||||
title: Use tokenizers from 🤗 Tokenizers
|
||||
- local: create_a_model
|
||||
title: Create a custom architecture
|
||||
- local: custom_models
|
||||
@ -59,12 +59,32 @@
|
||||
title: Converting TensorFlow Checkpoints
|
||||
- local: serialization
|
||||
title: Export 🤗 Transformers models
|
||||
- local: performance
|
||||
title: 'Performance and Scalability: How To Fit a Bigger Model and Train It Faster'
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: performance
|
||||
title: Overview
|
||||
- local: perf_train_gpu_one
|
||||
title: Training on one GPU
|
||||
- local: perf_train_gpu_many
|
||||
title: Training on many GPUs
|
||||
- local: perf_train_cpu
|
||||
title: Training on CPU
|
||||
- local: perf_train_tpu
|
||||
title: Training on TPUs
|
||||
- local: perf_train_special
|
||||
title: Training on Specialized Hardware
|
||||
- local: perf_infer_cpu
|
||||
title: Inference on CPU
|
||||
- local: perf_infer_gpu_one
|
||||
title: Inference on one GPU
|
||||
- local: perf_infer_gpu_many
|
||||
title: Inference on many GPUs
|
||||
- local: perf_infer_special
|
||||
title: Inference on Specialized Hardware
|
||||
- local: perf_hardware
|
||||
title: Custom hardware for training
|
||||
title: Performance and scalability
|
||||
- local: big_models
|
||||
title: Instantiating a big model
|
||||
- local: parallelism
|
||||
title: Model Parallelism
|
||||
- local: benchmarks
|
||||
title: Benchmarks
|
||||
- local: migration
|
||||
@ -74,15 +94,15 @@
|
||||
- local: debugging
|
||||
title: Debugging
|
||||
- local: notebooks
|
||||
title: "🤗 Transformers Notebooks"
|
||||
title: 🤗 Transformers Notebooks
|
||||
- local: community
|
||||
title: Community
|
||||
- local: contributing
|
||||
title: How to contribute to transformers?
|
||||
- local: add_new_model
|
||||
title: "How to add a model to 🤗 Transformers?"
|
||||
title: How to add a model to 🤗 Transformers?
|
||||
- local: add_new_pipeline
|
||||
title: "How to add a pipeline to 🤗 Transformers?"
|
||||
title: How to create a custom pipeline?
|
||||
- local: testing
|
||||
title: Testing
|
||||
- local: pr_checks
|
||||
@ -156,12 +176,12 @@
|
||||
title: BEiT
|
||||
- local: model_doc/bert
|
||||
title: BERT
|
||||
- local: model_doc/bertweet
|
||||
title: Bertweet
|
||||
- local: model_doc/bert-generation
|
||||
title: BertGeneration
|
||||
- local: model_doc/bert-japanese
|
||||
title: BertJapanese
|
||||
- local: model_doc/bertweet
|
||||
title: Bertweet
|
||||
- local: model_doc/big_bird
|
||||
title: BigBird
|
||||
- local: model_doc/bigbird_pegasus
|
||||
@ -170,6 +190,8 @@
|
||||
title: Blenderbot
|
||||
- local: model_doc/blenderbot-small
|
||||
title: Blenderbot Small
|
||||
- local: model_doc/bloom
|
||||
title: BLOOM
|
||||
- local: model_doc/bort
|
||||
title: BORT
|
||||
- local: model_doc/byt5
|
||||
@ -178,16 +200,20 @@
|
||||
title: CamemBERT
|
||||
- local: model_doc/canine
|
||||
title: CANINE
|
||||
- local: model_doc/convnext
|
||||
title: ConvNeXT
|
||||
- local: model_doc/clip
|
||||
title: CLIP
|
||||
- local: model_doc/codegen
|
||||
title: CodeGen
|
||||
- local: model_doc/convbert
|
||||
title: ConvBERT
|
||||
- local: model_doc/convnext
|
||||
title: ConvNeXT
|
||||
- local: model_doc/cpm
|
||||
title: CPM
|
||||
- local: model_doc/ctrl
|
||||
title: CTRL
|
||||
- local: model_doc/cvt
|
||||
title: CvT
|
||||
- local: model_doc/data2vec
|
||||
title: Data2Vec
|
||||
- local: model_doc/deberta
|
||||
@ -226,8 +252,22 @@
|
||||
title: Funnel Transformer
|
||||
- local: model_doc/glpn
|
||||
title: GLPN
|
||||
- local: model_doc/openai-gpt
|
||||
title: GPT
|
||||
- local: model_doc/gpt_neo
|
||||
title: GPT Neo
|
||||
- local: model_doc/gpt_neox
|
||||
title: GPT NeoX
|
||||
- local: model_doc/gptj
|
||||
title: GPT-J
|
||||
- local: model_doc/gpt2
|
||||
title: GPT2
|
||||
- local: model_doc/groupvit
|
||||
title: GroupViT
|
||||
- local: model_doc/herbert
|
||||
title: HerBERT
|
||||
- local: model_doc/hubert
|
||||
title: Hubert
|
||||
- local: model_doc/ibert
|
||||
title: I-BERT
|
||||
- local: model_doc/imagegpt
|
||||
@ -236,24 +276,32 @@
|
||||
title: LayoutLM
|
||||
- local: model_doc/layoutlmv2
|
||||
title: LayoutLMV2
|
||||
- local: model_doc/layoutlmv3
|
||||
title: LayoutLMV3
|
||||
- local: model_doc/layoutxlm
|
||||
title: LayoutXLM
|
||||
- local: model_doc/led
|
||||
title: LED
|
||||
- local: model_doc/levit
|
||||
title: LeViT
|
||||
- local: model_doc/longformer
|
||||
title: Longformer
|
||||
- local: model_doc/longt5
|
||||
title: LongT5
|
||||
- local: model_doc/luke
|
||||
title: LUKE
|
||||
- local: model_doc/lxmert
|
||||
title: LXMERT
|
||||
- local: model_doc/m2m_100
|
||||
title: M2M100
|
||||
- local: model_doc/marian
|
||||
title: MarianMT
|
||||
- local: model_doc/maskformer
|
||||
title: MaskFormer
|
||||
- local: model_doc/m2m_100
|
||||
title: M2M100
|
||||
- local: model_doc/mbart
|
||||
title: MBart and MBart-50
|
||||
- local: model_doc/mctct
|
||||
title: MCTCT
|
||||
- local: model_doc/megatron-bert
|
||||
title: MegatronBERT
|
||||
- local: model_doc/megatron_gpt2
|
||||
@ -262,28 +310,26 @@
|
||||
title: mLUKE
|
||||
- local: model_doc/mobilebert
|
||||
title: MobileBERT
|
||||
- local: model_doc/mobilevit
|
||||
title: MobileViT
|
||||
- local: model_doc/mpnet
|
||||
title: MPNet
|
||||
- local: model_doc/mt5
|
||||
title: MT5
|
||||
- local: model_doc/mvp
|
||||
title: MVP
|
||||
- local: model_doc/nezha
|
||||
title: NEZHA
|
||||
- local: model_doc/nllb
|
||||
title: NLLB
|
||||
- local: model_doc/nystromformer
|
||||
title: Nyströmformer
|
||||
- local: model_doc/openai-gpt
|
||||
title: OpenAI GPT
|
||||
- local: model_doc/opt
|
||||
title: OPT
|
||||
- local: model_doc/gpt2
|
||||
title: OpenAI GPT2
|
||||
- local: model_doc/gptj
|
||||
title: GPT-J
|
||||
- local: model_doc/gpt_neo
|
||||
title: GPT Neo
|
||||
- local: model_doc/hubert
|
||||
title: Hubert
|
||||
- local: model_doc/perceiver
|
||||
title: Perceiver
|
||||
- local: model_doc/pegasus
|
||||
title: Pegasus
|
||||
- local: model_doc/perceiver
|
||||
title: Perceiver
|
||||
- local: model_doc/phobert
|
||||
title: PhoBERT
|
||||
- local: model_doc/plbart
|
||||
@ -300,10 +346,10 @@
|
||||
title: REALM
|
||||
- local: model_doc/reformer
|
||||
title: Reformer
|
||||
- local: model_doc/rembert
|
||||
title: RemBERT
|
||||
- local: model_doc/regnet
|
||||
title: RegNet
|
||||
- local: model_doc/rembert
|
||||
title: RemBERT
|
||||
- local: model_doc/resnet
|
||||
title: ResNet
|
||||
- local: model_doc/retribert
|
||||
@ -338,10 +384,14 @@
|
||||
title: TAPAS
|
||||
- local: model_doc/tapex
|
||||
title: TAPEX
|
||||
- local: model_doc/trajectory_transformer
|
||||
title: Trajectory Transformer
|
||||
- local: model_doc/transfo-xl
|
||||
title: Transformer XL
|
||||
- local: model_doc/trocr
|
||||
title: TrOCR
|
||||
- local: model_doc/ul2
|
||||
title: UL2
|
||||
- local: model_doc/unispeech
|
||||
title: UniSpeech
|
||||
- local: model_doc/unispeech-sat
|
||||
@ -356,12 +406,14 @@
|
||||
title: Vision Text Dual Encoder
|
||||
- local: model_doc/vit
|
||||
title: Vision Transformer (ViT)
|
||||
- local: model_doc/vit_mae
|
||||
title: ViTMAE
|
||||
- local: model_doc/visual_bert
|
||||
title: VisualBERT
|
||||
- local: model_doc/vit_mae
|
||||
title: ViTMAE
|
||||
- local: model_doc/wav2vec2
|
||||
title: Wav2Vec2
|
||||
- local: model_doc/wav2vec2-conformer
|
||||
title: Wav2Vec2-Conformer
|
||||
- local: model_doc/wav2vec2_phoneme
|
||||
title: Wav2Vec2Phoneme
|
||||
- local: model_doc/wavlm
|
||||
@ -378,10 +430,10 @@
|
||||
title: XLM-RoBERTa-XL
|
||||
- local: model_doc/xlnet
|
||||
title: XLNet
|
||||
- local: model_doc/xlsr_wav2vec2
|
||||
title: XLSR-Wav2Vec2
|
||||
- local: model_doc/xls_r
|
||||
title: XLS-R
|
||||
- local: model_doc/xlsr_wav2vec2
|
||||
title: XLSR-Wav2Vec2
|
||||
- local: model_doc/yolos
|
||||
title: YOLOS
|
||||
- local: model_doc/yoso
|
||||
|
||||
@ -9,7 +9,10 @@ Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# How to add a pipeline to 🤗 Transformers?
|
||||
# How to create a custom pipeline?
|
||||
|
||||
In this guide, we will see how to create a custom pipeline and share it on the [Hub](hf.co/models) or add it to the
|
||||
Transformers library.
|
||||
|
||||
First and foremost, you need to decide the raw entries the pipeline will be able to take. It can be strings, raw bytes,
|
||||
dictionaries or whatever seems to be the most likely desired input. Try to keep these inputs as pure Python as possible
|
||||
@ -99,7 +102,7 @@ def _sanitize_parameters(self, **kwargs):
|
||||
|
||||
postprocess_kwargs = {}
|
||||
if "top_k" in kwargs:
|
||||
preprocess_kwargs["top_k"] = kwargs["top_k"]
|
||||
postprocess_kwargs["top_k"] = kwargs["top_k"]
|
||||
return preprocess_kwargs, {}, postprocess_kwargs
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@ -111,12 +114,123 @@ of arguments for ease of use (audio files, can be filenames, URLs or pure bytes)
|
||||
|
||||
## Adding it to the list of supported tasks
|
||||
|
||||
Go to `src/transformers/pipelines/__init__.py` and fill in `SUPPORTED_TASKS` with your newly created pipeline.
|
||||
If possible it should provide a default model.
|
||||
To register your `new-task` to the list of supported tasks, you have to add it to the `PIPELINE_REGISTRY`:
|
||||
|
||||
## Adding tests
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers.pipelines import PIPELINE_REGISTRY
|
||||
|
||||
Create a new file `tests/test_pipelines_MY_PIPELINE.py` with example with the other tests.
|
||||
PIPELINE_REGISTRY.register_pipeline(
|
||||
"new-task",
|
||||
pipeline_class=MyPipeline,
|
||||
pt_model=AutoModelForSequenceClassification,
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can specify a default model if you want, in which case it should come with a specific revision (which can be the name of a branch or a commit hash, here we took `"abcdef"`) as well was the type:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
PIPELINE_REGISTRY.register_pipeline(
|
||||
"new-task",
|
||||
pipeline_class=MyPipeline,
|
||||
pt_model=AutoModelForSequenceClassification,
|
||||
default={"pt": ("user/awesome_model", "abcdef")},
|
||||
type="text", # current support type: text, audio, image, multimodal
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Share your pipeline on the Hub
|
||||
|
||||
To share your custom pipeline on the Hub, you just have to save the custom code of your `Pipeline` subclass in a
|
||||
python file. For instance, let's say we want to use a custom pipeline for sentence pair classification like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
|
||||
from transformers import Pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def softmax(outputs):
|
||||
maxes = np.max(outputs, axis=-1, keepdims=True)
|
||||
shifted_exp = np.exp(outputs - maxes)
|
||||
return shifted_exp / shifted_exp.sum(axis=-1, keepdims=True)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class PairClassificationPipeline(Pipeline):
|
||||
def _sanitize_parameters(self, **kwargs):
|
||||
preprocess_kwargs = {}
|
||||
if "second_text" in kwargs:
|
||||
preprocess_kwargs["second_text"] = kwargs["second_text"]
|
||||
return preprocess_kwargs, {}, {}
|
||||
|
||||
def preprocess(self, text, second_text=None):
|
||||
return self.tokenizer(text, text_pair=second_text, return_tensors=self.framework)
|
||||
|
||||
def _forward(self, model_inputs):
|
||||
return self.model(**model_inputs)
|
||||
|
||||
def postprocess(self, model_outputs):
|
||||
logits = model_outputs.logits[0].numpy()
|
||||
probabilities = softmax(logits)
|
||||
|
||||
best_class = np.argmax(probabilities)
|
||||
label = self.model.config.id2label[best_class]
|
||||
score = probabilities[best_class].item()
|
||||
logits = logits.tolist()
|
||||
return {"label": label, "score": score, "logits": logits}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The implementation is framework agnostic, and will work for PyTorch and TensorFlow models. If we have saved this in
|
||||
a file named `pair_classification.py`, we can then import it and register it like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from pair_classification import PairClassificationPipeline
|
||||
from transformers.pipelines import PIPELINE_REGISTRY
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForSequenceClassification, TFAutoModelForSequenceClassification
|
||||
|
||||
PIPELINE_REGISTRY.register_pipeline(
|
||||
"pair-classification",
|
||||
pipeline_class=PairClassificationPipeline,
|
||||
pt_model=AutoModelForSequenceClassification,
|
||||
tf_model=TFAutoModelForSequenceClassification,
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Once this is done, we can use it with a pretrained model. For instance `sgugger/finetuned-bert-mrpc` has been
|
||||
fine-tuned on the MRPC dataset, which classifies pairs of sentences as paraphrases or not.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
classifier = pipeline("pair-classification", model="sgugger/finetuned-bert-mrpc")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then we can share it on the Hub by using the `save_pretrained` method in a `Repository`:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from huggingface_hub import Repository
|
||||
|
||||
repo = Repository("test-dynamic-pipeline", clone_from="{your_username}/test-dynamic-pipeline")
|
||||
classifier.save_pretrained("test-dynamic-pipeline")
|
||||
repo.push_to_hub()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This will copy the file where you defined `PairClassificationPipeline` inside the folder `"test-dynamic-pipeline"`,
|
||||
along with saving the model and tokenizer of the pipeline, before pushing everything in the repository
|
||||
`{your_username}/test-dynamic-pipeline`. After that anyone can use it as long as they provide the option
|
||||
`trust_remote_code=True`:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
classifier = pipeline(model="{your_username}/test-dynamic-pipeline", trust_remote_code=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Add the pipeline to Transformers
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to contribute your pipeline to Transformers, you will need to add a new module in the `pipelines` submodule
|
||||
with the code of your pipeline, then add it in the list of tasks defined in `pipelines/__init__.py`.
|
||||
|
||||
Then you will need to add tests. Create a new file `tests/test_pipelines_MY_PIPELINE.py` with example with the other tests.
|
||||
|
||||
The `run_pipeline_test` function will be very generic and run on small random models on every possible
|
||||
architecture as defined by `model_mapping` and `tf_model_mapping`.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -114,15 +114,6 @@ If you want to directly load such a sharded checkpoint inside a model without us
|
||||
|
||||
## Low memory loading
|
||||
|
||||
Sharded checkpoints reduce the memory usage during step 2 of the worflow mentioned above, but when loadin a pretrained model, why keep the random weights in memory? The option `low_cpu_mem_usage` will destroy the weights of the randomly initialized model, then progressively load the weights inside, then perform a random initialization for potential missing weights (if you are loadding a model with a newly initialized head for a fine-tuning task for instance).
|
||||
|
||||
It's very easy to use, just add `low_cpu_mem_usage=True` to your call to [`~PreTrainedModel.from_pretrained`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForSequenceClas
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModel.from_pretrained("bert-base-cased", low_cpu_mem_usage=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This can be used in conjunction with a sharded checkpoint.
|
||||
Sharded checkpoints reduce the memory usage during step 2 of the workflow mentioned above, but in order to use that model in a low memory setting, we recommend leveraging our tools based on the Accelerate library.
|
||||
|
||||
Please read the following guide for more information: [Large model loading using Accelerate](./main_classes/model#large-model-loading)
|
||||
@ -289,7 +289,7 @@ from huggingface_hub import notebook_login
|
||||
notebook_login()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can then push to to your own namespace (or an organization you are a member of) like this:
|
||||
You can then push to your own namespace (or an organization you are a member of) like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
resnet50d.push_to_hub("custom-resnet50d")
|
||||
|
||||
@ -28,7 +28,7 @@ Each 🤗 Transformers architecture is defined in a standalone Python module so
|
||||
## If you are looking for custom support from the Hugging Face team
|
||||
|
||||
<a target="_blank" href="https://huggingface.co/support">
|
||||
<img alt="HuggingFace Expert Acceleration Program" src="https://huggingface.co/front/thumbnails/support.png" style="max-width: 600px; border: 1px solid #eee; border-radius: 4px; box-shadow: 0 1px 2px 0 rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.05);">
|
||||
<img alt="HuggingFace Expert Acceleration Program" src="https://cdn-media.huggingface.co/marketing/transformers/new-support-improved.png" style="max-width: 600px; border: 1px solid #eee; border-radius: 4px; box-shadow: 0 1px 2px 0 rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.05);">
|
||||
</a><br>
|
||||
|
||||
## Contents
|
||||
@ -57,63 +57,77 @@ The library currently contains JAX, PyTorch and TensorFlow implementations, pret
|
||||
1. **[BARTpho](model_doc/bartpho)** (from VinAI Research) released with the paper [BARTpho: Pre-trained Sequence-to-Sequence Models for Vietnamese](https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.09701) by Nguyen Luong Tran, Duong Minh Le and Dat Quoc Nguyen.
|
||||
1. **[BEiT](model_doc/beit)** (from Microsoft) released with the paper [BEiT: BERT Pre-Training of Image Transformers](https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.08254) by Hangbo Bao, Li Dong, Furu Wei.
|
||||
1. **[BERT](model_doc/bert)** (from Google) released with the paper [BERT: Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/1810.04805) by Jacob Devlin, Ming-Wei Chang, Kenton Lee and Kristina Toutanova.
|
||||
1. **[BERTweet](model_doc/bertweet)** (from VinAI Research) released with the paper [BERTweet: A pre-trained language model for English Tweets](https://aclanthology.org/2020.emnlp-demos.2/) by Dat Quoc Nguyen, Thanh Vu and Anh Tuan Nguyen.
|
||||
1. **[BERT For Sequence Generation](model_doc/bert-generation)** (from Google) released with the paper [Leveraging Pre-trained Checkpoints for Sequence Generation Tasks](https://arxiv.org/abs/1907.12461) by Sascha Rothe, Shashi Narayan, Aliaksei Severyn.
|
||||
1. **[BigBird-RoBERTa](model_doc/big_bird)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [Big Bird: Transformers for Longer Sequences](https://arxiv.org/abs/2007.14062) by Manzil Zaheer, Guru Guruganesh, Avinava Dubey, Joshua Ainslie, Chris Alberti, Santiago Ontanon, Philip Pham, Anirudh Ravula, Qifan Wang, Li Yang, Amr Ahmed.
|
||||
1. **[BERTweet](model_doc/bertweet)** (from VinAI Research) released with the paper [BERTweet: A pre-trained language model for English Tweets](https://aclanthology.org/2020.emnlp-demos.2/) by Dat Quoc Nguyen, Thanh Vu and Anh Tuan Nguyen.
|
||||
1. **[BigBird-Pegasus](model_doc/bigbird_pegasus)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [Big Bird: Transformers for Longer Sequences](https://arxiv.org/abs/2007.14062) by Manzil Zaheer, Guru Guruganesh, Avinava Dubey, Joshua Ainslie, Chris Alberti, Santiago Ontanon, Philip Pham, Anirudh Ravula, Qifan Wang, Li Yang, Amr Ahmed.
|
||||
1. **[BigBird-RoBERTa](model_doc/big_bird)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [Big Bird: Transformers for Longer Sequences](https://arxiv.org/abs/2007.14062) by Manzil Zaheer, Guru Guruganesh, Avinava Dubey, Joshua Ainslie, Chris Alberti, Santiago Ontanon, Philip Pham, Anirudh Ravula, Qifan Wang, Li Yang, Amr Ahmed.
|
||||
1. **[Blenderbot](model_doc/blenderbot)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Recipes for building an open-domain chatbot](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.13637) by Stephen Roller, Emily Dinan, Naman Goyal, Da Ju, Mary Williamson, Yinhan Liu, Jing Xu, Myle Ott, Kurt Shuster, Eric M. Smith, Y-Lan Boureau, Jason Weston.
|
||||
1. **[BlenderbotSmall](model_doc/blenderbot-small)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Recipes for building an open-domain chatbot](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.13637) by Stephen Roller, Emily Dinan, Naman Goyal, Da Ju, Mary Williamson, Yinhan Liu, Jing Xu, Myle Ott, Kurt Shuster, Eric M. Smith, Y-Lan Boureau, Jason Weston.
|
||||
1. **[BLOOM](model_doc/bloom)** (from BigScience workshop) released by the [BigSicence Workshop](https://bigscience.huggingface.co/).
|
||||
1. **[BORT](model_doc/bort)** (from Alexa) released with the paper [Optimal Subarchitecture Extraction For BERT](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.10499) by Adrian de Wynter and Daniel J. Perry.
|
||||
1. **[ByT5](model_doc/byt5)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [ByT5: Towards a token-free future with pre-trained byte-to-byte models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2105.13626) by Linting Xue, Aditya Barua, Noah Constant, Rami Al-Rfou, Sharan Narang, Mihir Kale, Adam Roberts, Colin Raffel.
|
||||
1. **[CamemBERT](model_doc/camembert)** (from Inria/Facebook/Sorbonne) released with the paper [CamemBERT: a Tasty French Language Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.03894) by Louis Martin*, Benjamin Muller*, Pedro Javier Ortiz Suárez*, Yoann Dupont, Laurent Romary, Éric Villemonte de la Clergerie, Djamé Seddah and Benoît Sagot.
|
||||
1. **[CANINE](model_doc/canine)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [CANINE: Pre-training an Efficient Tokenization-Free Encoder for Language Representation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.06874) by Jonathan H. Clark, Dan Garrette, Iulia Turc, John Wieting.
|
||||
1. **[ConvNeXT](model_doc/convnext)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [A ConvNet for the 2020s](https://arxiv.org/abs/2201.03545) by Zhuang Liu, Hanzi Mao, Chao-Yuan Wu, Christoph Feichtenhofer, Trevor Darrell, Saining Xie.
|
||||
1. **[CLIP](model_doc/clip)** (from OpenAI) released with the paper [Learning Transferable Visual Models From Natural Language Supervision](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.00020) by Alec Radford, Jong Wook Kim, Chris Hallacy, Aditya Ramesh, Gabriel Goh, Sandhini Agarwal, Girish Sastry, Amanda Askell, Pamela Mishkin, Jack Clark, Gretchen Krueger, Ilya Sutskever.
|
||||
1. **[CodeGen](model_doc/codegen)** (from Salesforce) released with the paper [A Conversational Paradigm for Program Synthesis](https://arxiv.org/abs/2203.13474) by Erik Nijkamp, Bo Pang, Hiroaki Hayashi, Lifu Tu, Huan Wang, Yingbo Zhou, Silvio Savarese, Caiming Xiong.
|
||||
1. **[ConvBERT](model_doc/convbert)** (from YituTech) released with the paper [ConvBERT: Improving BERT with Span-based Dynamic Convolution](https://arxiv.org/abs/2008.02496) by Zihang Jiang, Weihao Yu, Daquan Zhou, Yunpeng Chen, Jiashi Feng, Shuicheng Yan.
|
||||
1. **[ConvNeXT](model_doc/convnext)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [A ConvNet for the 2020s](https://arxiv.org/abs/2201.03545) by Zhuang Liu, Hanzi Mao, Chao-Yuan Wu, Christoph Feichtenhofer, Trevor Darrell, Saining Xie.
|
||||
1. **[CPM](model_doc/cpm)** (from Tsinghua University) released with the paper [CPM: A Large-scale Generative Chinese Pre-trained Language Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/2012.00413) by Zhengyan Zhang, Xu Han, Hao Zhou, Pei Ke, Yuxian Gu, Deming Ye, Yujia Qin, Yusheng Su, Haozhe Ji, Jian Guan, Fanchao Qi, Xiaozhi Wang, Yanan Zheng, Guoyang Zeng, Huanqi Cao, Shengqi Chen, Daixuan Li, Zhenbo Sun, Zhiyuan Liu, Minlie Huang, Wentao Han, Jie Tang, Juanzi Li, Xiaoyan Zhu, Maosong Sun.
|
||||
1. **[CTRL](model_doc/ctrl)** (from Salesforce) released with the paper [CTRL: A Conditional Transformer Language Model for Controllable Generation](https://arxiv.org/abs/1909.05858) by Nitish Shirish Keskar*, Bryan McCann*, Lav R. Varshney, Caiming Xiong and Richard Socher.
|
||||
1. **[CvT](model_doc/cvt)** (from Microsoft) released with the paper [CvT: Introducing Convolutions to Vision Transformers](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.15808) by Haiping Wu, Bin Xiao, Noel Codella, Mengchen Liu, Xiyang Dai, Lu Yuan, Lei Zhang.
|
||||
1. **[Data2Vec](model_doc/data2vec)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Data2Vec: A General Framework for Self-supervised Learning in Speech, Vision and Language](https://arxiv.org/abs/2202.03555) by Alexei Baevski, Wei-Ning Hsu, Qiantong Xu, Arun Babu, Jiatao Gu, Michael Auli.
|
||||
1. **[DeBERTa](model_doc/deberta)** (from Microsoft) released with the paper [DeBERTa: Decoding-enhanced BERT with Disentangled Attention](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.03654) by Pengcheng He, Xiaodong Liu, Jianfeng Gao, Weizhu Chen.
|
||||
1. **[DeBERTa-v2](model_doc/deberta-v2)** (from Microsoft) released with the paper [DeBERTa: Decoding-enhanced BERT with Disentangled Attention](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.03654) by Pengcheng He, Xiaodong Liu, Jianfeng Gao, Weizhu Chen.
|
||||
1. **[Decision Transformer](model_doc/decision_transformer)** (from Berkeley/Facebook/Google) released with the paper [Decision Transformer: Reinforcement Learning via Sequence Modeling](https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.01345) by Lili Chen, Kevin Lu, Aravind Rajeswaran, Kimin Lee, Aditya Grover, Michael Laskin, Pieter Abbeel, Aravind Srinivas, Igor Mordatch.
|
||||
1. **[DiT](model_doc/dit)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [DiT: Self-supervised Pre-training for Document Image Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2203.02378) by Junlong Li, Yiheng Xu, Tengchao Lv, Lei Cui, Cha Zhang, Furu Wei.
|
||||
1. **[DeiT](model_doc/deit)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Training data-efficient image transformers & distillation through attention](https://arxiv.org/abs/2012.12877) by Hugo Touvron, Matthieu Cord, Matthijs Douze, Francisco Massa, Alexandre Sablayrolles, Hervé Jégou.
|
||||
1. **[DETR](model_doc/detr)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [End-to-End Object Detection with Transformers](https://arxiv.org/abs/2005.12872) by Nicolas Carion, Francisco Massa, Gabriel Synnaeve, Nicolas Usunier, Alexander Kirillov, Sergey Zagoruyko.
|
||||
1. **[DialoGPT](model_doc/dialogpt)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [DialoGPT: Large-Scale Generative Pre-training for Conversational Response Generation](https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.00536) by Yizhe Zhang, Siqi Sun, Michel Galley, Yen-Chun Chen, Chris Brockett, Xiang Gao, Jianfeng Gao, Jingjing Liu, Bill Dolan.
|
||||
1. **[DistilBERT](model_doc/distilbert)** (from HuggingFace), released together with the paper [DistilBERT, a distilled version of BERT: smaller, faster, cheaper and lighter](https://arxiv.org/abs/1910.01108) by Victor Sanh, Lysandre Debut and Thomas Wolf. The same method has been applied to compress GPT2 into [DistilGPT2](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples/research_projects/distillation), RoBERTa into [DistilRoBERTa](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples/research_projects/distillation), Multilingual BERT into [DistilmBERT](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples/research_projects/distillation) and a German version of DistilBERT.
|
||||
1. **[DiT](model_doc/dit)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [DiT: Self-supervised Pre-training for Document Image Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2203.02378) by Junlong Li, Yiheng Xu, Tengchao Lv, Lei Cui, Cha Zhang, Furu Wei.
|
||||
1. **[DPR](model_doc/dpr)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Dense Passage Retrieval for Open-Domain Question Answering](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.04906) by Vladimir Karpukhin, Barlas Oğuz, Sewon Min, Patrick Lewis, Ledell Wu, Sergey Edunov, Danqi Chen, and Wen-tau Yih.
|
||||
1. **[DPT](master/model_doc/dpt)** (from Intel Labs) released with the paper [Vision Transformers for Dense Prediction](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.13413) by René Ranftl, Alexey Bochkovskiy, Vladlen Koltun.
|
||||
1. **[EncoderDecoder](model_doc/encoder-decoder)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [Leveraging Pre-trained Checkpoints for Sequence Generation Tasks](https://arxiv.org/abs/1907.12461) by Sascha Rothe, Shashi Narayan, Aliaksei Severyn.
|
||||
1. **[ELECTRA](model_doc/electra)** (from Google Research/Stanford University) released with the paper [ELECTRA: Pre-training text encoders as discriminators rather than generators](https://arxiv.org/abs/2003.10555) by Kevin Clark, Minh-Thang Luong, Quoc V. Le, Christopher D. Manning.
|
||||
1. **[EncoderDecoder](model_doc/encoder-decoder)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [Leveraging Pre-trained Checkpoints for Sequence Generation Tasks](https://arxiv.org/abs/1907.12461) by Sascha Rothe, Shashi Narayan, Aliaksei Severyn.
|
||||
1. **[FlauBERT](model_doc/flaubert)** (from CNRS) released with the paper [FlauBERT: Unsupervised Language Model Pre-training for French](https://arxiv.org/abs/1912.05372) by Hang Le, Loïc Vial, Jibril Frej, Vincent Segonne, Maximin Coavoux, Benjamin Lecouteux, Alexandre Allauzen, Benoît Crabbé, Laurent Besacier, Didier Schwab.
|
||||
1. **[FLAVA](model_doc/flava)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [FLAVA: A Foundational Language And Vision Alignment Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.04482) by Amanpreet Singh, Ronghang Hu, Vedanuj Goswami, Guillaume Couairon, Wojciech Galuba, Marcus Rohrbach, and Douwe Kiela.
|
||||
1. **[FNet](model_doc/fnet)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [FNet: Mixing Tokens with Fourier Transforms](https://arxiv.org/abs/2105.03824) by James Lee-Thorp, Joshua Ainslie, Ilya Eckstein, Santiago Ontanon.
|
||||
1. **[Funnel Transformer](model_doc/funnel)** (from CMU/Google Brain) released with the paper [Funnel-Transformer: Filtering out Sequential Redundancy for Efficient Language Processing](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.03236) by Zihang Dai, Guokun Lai, Yiming Yang, Quoc V. Le.
|
||||
1. **[GLPN](model_doc/glpn)** (from KAIST) released with the paper [Global-Local Path Networks for Monocular Depth Estimation with Vertical CutDepth](https://arxiv.org/abs/2201.07436) by Doyeon Kim, Woonghyun Ga, Pyungwhan Ahn, Donggyu Joo, Sehwan Chun, Junmo Kim.
|
||||
1. **[GPT](model_doc/openai-gpt)** (from OpenAI) released with the paper [Improving Language Understanding by Generative Pre-Training](https://blog.openai.com/language-unsupervised/) by Alec Radford, Karthik Narasimhan, Tim Salimans and Ilya Sutskever.
|
||||
1. **[GPT Neo](model_doc/gpt_neo)** (from EleutherAI) released in the repository [EleutherAI/gpt-neo](https://github.com/EleutherAI/gpt-neo) by Sid Black, Stella Biderman, Leo Gao, Phil Wang and Connor Leahy.
|
||||
1. **[GPT NeoX](model_doc/gpt_neox)** (from EleutherAI) released with the paper [GPT-NeoX-20B: An Open-Source Autoregressive Language Model](https://arxiv.org/abs/2204.06745) by Sid Black, Stella Biderman, Eric Hallahan, Quentin Anthony, Leo Gao, Laurence Golding, Horace He, Connor Leahy, Kyle McDonell, Jason Phang, Michael Pieler, USVSN Sai Prashanth, Shivanshu Purohit, Laria Reynolds, Jonathan Tow, Ben Wang, Samuel Weinbach
|
||||
1. **[GPT-2](model_doc/gpt2)** (from OpenAI) released with the paper [Language Models are Unsupervised Multitask Learners](https://blog.openai.com/better-language-models/) by Alec Radford*, Jeffrey Wu*, Rewon Child, David Luan, Dario Amodei** and Ilya Sutskever**.
|
||||
1. **[GPT-J](model_doc/gptj)** (from EleutherAI) released in the repository [kingoflolz/mesh-transformer-jax](https://github.com/kingoflolz/mesh-transformer-jax/) by Ben Wang and Aran Komatsuzaki.
|
||||
1. **[GPT Neo](model_doc/gpt_neo)** (from EleutherAI) released in the repository [EleutherAI/gpt-neo](https://github.com/EleutherAI/gpt-neo) by Sid Black, Stella Biderman, Leo Gao, Phil Wang and Connor Leahy.
|
||||
1. **[GroupViT](model_doc/groupvit)** (from UCSD, NVIDIA) released with the paper [GroupViT: Semantic Segmentation Emerges from Text Supervision](https://arxiv.org/abs/2202.11094) by Jiarui Xu, Shalini De Mello, Sifei Liu, Wonmin Byeon, Thomas Breuel, Jan Kautz, Xiaolong Wang.
|
||||
1. **[Hubert](model_doc/hubert)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [HuBERT: Self-Supervised Speech Representation Learning by Masked Prediction of Hidden Units](https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.07447) by Wei-Ning Hsu, Benjamin Bolte, Yao-Hung Hubert Tsai, Kushal Lakhotia, Ruslan Salakhutdinov, Abdelrahman Mohamed.
|
||||
1. **[I-BERT](model_doc/ibert)** (from Berkeley) released with the paper [I-BERT: Integer-only BERT Quantization](https://arxiv.org/abs/2101.01321) by Sehoon Kim, Amir Gholami, Zhewei Yao, Michael W. Mahoney, Kurt Keutzer.
|
||||
1. **[ImageGPT](model_doc/imagegpt)** (from OpenAI) released with the paper [Generative Pretraining from Pixels](https://openai.com/blog/image-gpt/) by Mark Chen, Alec Radford, Rewon Child, Jeffrey Wu, Heewoo Jun, David Luan, Ilya Sutskever.
|
||||
1. **[LayoutLM](model_doc/layoutlm)** (from Microsoft Research Asia) released with the paper [LayoutLM: Pre-training of Text and Layout for Document Image Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/1912.13318) by Yiheng Xu, Minghao Li, Lei Cui, Shaohan Huang, Furu Wei, Ming Zhou.
|
||||
1. **[LayoutLMv2](model_doc/layoutlmv2)** (from Microsoft Research Asia) released with the paper [LayoutLMv2: Multi-modal Pre-training for Visually-Rich Document Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/2012.14740) by Yang Xu, Yiheng Xu, Tengchao Lv, Lei Cui, Furu Wei, Guoxin Wang, Yijuan Lu, Dinei Florencio, Cha Zhang, Wanxiang Che, Min Zhang, Lidong Zhou.
|
||||
1. **[LayoutLMv3](model_doc/layoutlmv3)** (from Microsoft Research Asia) released with the paper [LayoutLMv3: Pre-training for Document AI with Unified Text and Image Masking](https://arxiv.org/abs/2204.08387) by Yupan Huang, Tengchao Lv, Lei Cui, Yutong Lu, Furu Wei.
|
||||
1. **[LayoutXLM](model_doc/layoutlmv2)** (from Microsoft Research Asia) released with the paper [LayoutXLM: Multimodal Pre-training for Multilingual Visually-rich Document Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.08836) by Yiheng Xu, Tengchao Lv, Lei Cui, Guoxin Wang, Yijuan Lu, Dinei Florencio, Cha Zhang, Furu Wei.
|
||||
1. **[LED](model_doc/led)** (from AllenAI) released with the paper [Longformer: The Long-Document Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.05150) by Iz Beltagy, Matthew E. Peters, Arman Cohan.
|
||||
1. **[LeViT](model_doc/levit)** (from Meta AI) released with the paper [LeViT: A Vision Transformer in ConvNet's Clothing for Faster Inference](https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.01136) by Ben Graham, Alaaeldin El-Nouby, Hugo Touvron, Pierre Stock, Armand Joulin, Hervé Jégou, Matthijs Douze.
|
||||
1. **[Longformer](model_doc/longformer)** (from AllenAI) released with the paper [Longformer: The Long-Document Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.05150) by Iz Beltagy, Matthew E. Peters, Arman Cohan.
|
||||
1. **[LongT5](model_doc/longt5)** (from Google AI) released with the paper [LongT5: Efficient Text-To-Text Transformer for Long Sequences](https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.07916) by Mandy Guo, Joshua Ainslie, David Uthus, Santiago Ontanon, Jianmo Ni, Yun-Hsuan Sung, Yinfei Yang.
|
||||
1. **[LUKE](model_doc/luke)** (from Studio Ousia) released with the paper [LUKE: Deep Contextualized Entity Representations with Entity-aware Self-attention](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.01057) by Ikuya Yamada, Akari Asai, Hiroyuki Shindo, Hideaki Takeda, Yuji Matsumoto.
|
||||
1. **[mLUKE](model_doc/mluke)** (from Studio Ousia) released with the paper [mLUKE: The Power of Entity Representations in Multilingual Pretrained Language Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.08151) by Ryokan Ri, Ikuya Yamada, and Yoshimasa Tsuruoka.
|
||||
1. **[LXMERT](model_doc/lxmert)** (from UNC Chapel Hill) released with the paper [LXMERT: Learning Cross-Modality Encoder Representations from Transformers for Open-Domain Question Answering](https://arxiv.org/abs/1908.07490) by Hao Tan and Mohit Bansal.
|
||||
1. **[M-CTC-T](model_doc/mctct)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Pseudo-Labeling For Massively Multilingual Speech Recognition](https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.00161) by Loren Lugosch, Tatiana Likhomanenko, Gabriel Synnaeve, and Ronan Collobert.
|
||||
1. **[M2M100](model_doc/m2m_100)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Beyond English-Centric Multilingual Machine Translation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11125) by Angela Fan, Shruti Bhosale, Holger Schwenk, Zhiyi Ma, Ahmed El-Kishky, Siddharth Goyal, Mandeep Baines, Onur Celebi, Guillaume Wenzek, Vishrav Chaudhary, Naman Goyal, Tom Birch, Vitaliy Liptchinsky, Sergey Edunov, Edouard Grave, Michael Auli, Armand Joulin.
|
||||
1. **[MarianMT](model_doc/marian)** Machine translation models trained using [OPUS](http://opus.nlpl.eu/) data by Jörg Tiedemann. The [Marian Framework](https://marian-nmt.github.io/) is being developed by the Microsoft Translator Team.
|
||||
1. **[MaskFormer](model_doc/maskformer)** (from Meta and UIUC) released with the paper [Per-Pixel Classification is Not All You Need for Semantic Segmentation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.06278) by Bowen Cheng, Alexander G. Schwing, Alexander Kirillov.
|
||||
1. **[MBart](model_doc/mbart)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Multilingual Denoising Pre-training for Neural Machine Translation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2001.08210) by Yinhan Liu, Jiatao Gu, Naman Goyal, Xian Li, Sergey Edunov, Marjan Ghazvininejad, Mike Lewis, Luke Zettlemoyer.
|
||||
1. **[MBart-50](model_doc/mbart)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Multilingual Translation with Extensible Multilingual Pretraining and Finetuning](https://arxiv.org/abs/2008.00401) by Yuqing Tang, Chau Tran, Xian Li, Peng-Jen Chen, Naman Goyal, Vishrav Chaudhary, Jiatao Gu, Angela Fan.
|
||||
1. **[mBART](model_doc/mbart)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Multilingual Denoising Pre-training for Neural Machine Translation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2001.08210) by Yinhan Liu, Jiatao Gu, Naman Goyal, Xian Li, Sergey Edunov, Marjan Ghazvininejad, Mike Lewis, Luke Zettlemoyer.
|
||||
1. **[mBART-50](model_doc/mbart)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Multilingual Translation with Extensible Multilingual Pretraining and Finetuning](https://arxiv.org/abs/2008.00401) by Yuqing Tang, Chau Tran, Xian Li, Peng-Jen Chen, Naman Goyal, Vishrav Chaudhary, Jiatao Gu, Angela Fan.
|
||||
1. **[Megatron-BERT](model_doc/megatron-bert)** (from NVIDIA) released with the paper [Megatron-LM: Training Multi-Billion Parameter Language Models Using Model Parallelism](https://arxiv.org/abs/1909.08053) by Mohammad Shoeybi, Mostofa Patwary, Raul Puri, Patrick LeGresley, Jared Casper and Bryan Catanzaro.
|
||||
1. **[Megatron-GPT2](model_doc/megatron_gpt2)** (from NVIDIA) released with the paper [Megatron-LM: Training Multi-Billion Parameter Language Models Using Model Parallelism](https://arxiv.org/abs/1909.08053) by Mohammad Shoeybi, Mostofa Patwary, Raul Puri, Patrick LeGresley, Jared Casper and Bryan Catanzaro.
|
||||
1. **[mLUKE](model_doc/mluke)** (from Studio Ousia) released with the paper [mLUKE: The Power of Entity Representations in Multilingual Pretrained Language Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.08151) by Ryokan Ri, Ikuya Yamada, and Yoshimasa Tsuruoka.
|
||||
1. **[MobileBERT](model_doc/mobilebert)** (from CMU/Google Brain) released with the paper [MobileBERT: a Compact Task-Agnostic BERT for Resource-Limited Devices](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.02984) by Zhiqing Sun, Hongkun Yu, Xiaodan Song, Renjie Liu, Yiming Yang, and Denny Zhou.
|
||||
1. **[MobileViT](model_doc/mobilevit)** (from Apple) released with the paper [MobileViT: Light-weight, General-purpose, and Mobile-friendly Vision Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.02178) by Sachin Mehta and Mohammad Rastegari.
|
||||
1. **[MPNet](model_doc/mpnet)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [MPNet: Masked and Permuted Pre-training for Language Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.09297) by Kaitao Song, Xu Tan, Tao Qin, Jianfeng Lu, Tie-Yan Liu.
|
||||
1. **[MT5](model_doc/mt5)** (from Google AI) released with the paper [mT5: A massively multilingual pre-trained text-to-text transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11934) by Linting Xue, Noah Constant, Adam Roberts, Mihir Kale, Rami Al-Rfou, Aditya Siddhant, Aditya Barua, Colin Raffel.
|
||||
1. **[MVP](model_doc/mvp)** (from RUC AI Box) released with the paper [MVP: Multi-task Supervised Pre-training for Natural Language Generation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.12131) by Tianyi Tang, Junyi Li, Wayne Xin Zhao and Ji-Rong Wen.
|
||||
1. **[Nezha](model_doc/nezha)** (from Huawei Noah’s Ark Lab) released with the paper [NEZHA: Neural Contextualized Representation for Chinese Language Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/1909.00204) by Junqiu Wei, Xiaozhe Ren, Xiaoguang Li, Wenyong Huang, Yi Liao, Yasheng Wang, Jiashu Lin, Xin Jiang, Xiao Chen and Qun Liu.
|
||||
1. **[NLLB](model_doc/nllb)** (from Meta) released with the paper [No Language Left Behind: Scaling Human-Centered Machine Translation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2207.04672) by the NLLB team.
|
||||
1. **[Nyströmformer](model_doc/nystromformer)** (from the University of Wisconsin - Madison) released with the paper [Nyströmformer: A Nyström-Based Algorithm for Approximating Self-Attention](https://arxiv.org/abs/2102.03902) by Yunyang Xiong, Zhanpeng Zeng, Rudrasis Chakraborty, Mingxing Tan, Glenn Fung, Yin Li, Vikas Singh.
|
||||
1. **[OPT](master/model_doc/opt)** (from Meta AI) released with the paper [OPT: Open Pre-trained Transformer Language Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.01068) by Susan Zhang, Stephen Roller, Naman Goyal, Mikel Artetxe, Moya Chen, Shuohui Chen et al.
|
||||
1. **[Pegasus](model_doc/pegasus)** (from Google) released with the paper [PEGASUS: Pre-training with Extracted Gap-sentences for Abstractive Summarization](https://arxiv.org/abs/1912.08777) by Jingqing Zhang, Yao Zhao, Mohammad Saleh and Peter J. Liu.
|
||||
@ -123,10 +137,11 @@ The library currently contains JAX, PyTorch and TensorFlow implementations, pret
|
||||
1. **[PoolFormer](model_doc/poolformer)** (from Sea AI Labs) released with the paper [MetaFormer is Actually What You Need for Vision](https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.11418) by Yu, Weihao and Luo, Mi and Zhou, Pan and Si, Chenyang and Zhou, Yichen and Wang, Xinchao and Feng, Jiashi and Yan, Shuicheng.
|
||||
1. **[ProphetNet](model_doc/prophetnet)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [ProphetNet: Predicting Future N-gram for Sequence-to-Sequence Pre-training](https://arxiv.org/abs/2001.04063) by Yu Yan, Weizhen Qi, Yeyun Gong, Dayiheng Liu, Nan Duan, Jiusheng Chen, Ruofei Zhang and Ming Zhou.
|
||||
1. **[QDQBert](model_doc/qdqbert)** (from NVIDIA) released with the paper [Integer Quantization for Deep Learning Inference: Principles and Empirical Evaluation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.09602) by Hao Wu, Patrick Judd, Xiaojie Zhang, Mikhail Isaev and Paulius Micikevicius.
|
||||
1. **[RAG](model_doc/rag)** (from Facebook) released with the paper [Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Knowledge-Intensive NLP Tasks](https://arxiv.org/abs/2005.11401) by Patrick Lewis, Ethan Perez, Aleksandara Piktus, Fabio Petroni, Vladimir Karpukhin, Naman Goyal, Heinrich Küttler, Mike Lewis, Wen-tau Yih, Tim Rocktäschel, Sebastian Riedel, Douwe Kiela.
|
||||
1. **[REALM](model_doc/realm.html)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [REALM: Retrieval-Augmented Language Model Pre-Training](https://arxiv.org/abs/2002.08909) by Kelvin Guu, Kenton Lee, Zora Tung, Panupong Pasupat and Ming-Wei Chang.
|
||||
1. **[Reformer](model_doc/reformer)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [Reformer: The Efficient Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2001.04451) by Nikita Kitaev, Łukasz Kaiser, Anselm Levskaya.
|
||||
1. **[RemBERT](model_doc/rembert)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [Rethinking embedding coupling in pre-trained language models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.12821) by Hyung Won Chung, Thibault Févry, Henry Tsai, M. Johnson, Sebastian Ruder.
|
||||
1. **[RegNet](model_doc/regnet)** (from META Platforms) released with the paper [Designing Network Design Space](https://arxiv.org/abs/2003.13678) by Ilija Radosavovic, Raj Prateek Kosaraju, Ross Girshick, Kaiming He, Piotr Dollár.
|
||||
1. **[RemBERT](model_doc/rembert)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [Rethinking embedding coupling in pre-trained language models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.12821) by Hyung Won Chung, Thibault Févry, Henry Tsai, M. Johnson, Sebastian Ruder.
|
||||
1. **[ResNet](model_doc/resnet)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition](https://arxiv.org/abs/1512.03385) by Kaiming He, Xiangyu Zhang, Shaoqing Ren, Jian Sun.
|
||||
1. **[RoBERTa](model_doc/roberta)** (from Facebook), released together with the paper [RoBERTa: A Robustly Optimized BERT Pretraining Approach](https://arxiv.org/abs/1907.11692) by Yinhan Liu, Myle Ott, Naman Goyal, Jingfei Du, Mandar Joshi, Danqi Chen, Omer Levy, Mike Lewis, Luke Zettlemoyer, Veselin Stoyanov.
|
||||
1. **[RoFormer](model_doc/roformer)** (from ZhuiyiTechnology), released together with the paper [RoFormer: Enhanced Transformer with Rotary Position Embedding](https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.09864) by Jianlin Su and Yu Lu and Shengfeng Pan and Bo Wen and Yunfeng Liu.
|
||||
@ -136,32 +151,35 @@ The library currently contains JAX, PyTorch and TensorFlow implementations, pret
|
||||
1. **[SpeechToTextTransformer](model_doc/speech_to_text)** (from Facebook), released together with the paper [fairseq S2T: Fast Speech-to-Text Modeling with fairseq](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.05171) by Changhan Wang, Yun Tang, Xutai Ma, Anne Wu, Dmytro Okhonko, Juan Pino.
|
||||
1. **[SpeechToTextTransformer2](model_doc/speech_to_text_2)** (from Facebook), released together with the paper [Large-Scale Self- and Semi-Supervised Learning for Speech Translation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.06678) by Changhan Wang, Anne Wu, Juan Pino, Alexei Baevski, Michael Auli, Alexis Conneau.
|
||||
1. **[Splinter](model_doc/splinter)** (from Tel Aviv University), released together with the paper [Few-Shot Question Answering by Pretraining Span Selection](https://arxiv.org/abs/2101.00438) by Ori Ram, Yuval Kirstain, Jonathan Berant, Amir Globerson, Omer Levy.
|
||||
1. **[SqueezeBert](model_doc/squeezebert)** (from Berkeley) released with the paper [SqueezeBERT: What can computer vision teach NLP about efficient neural networks?](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.11316) by Forrest N. Iandola, Albert E. Shaw, Ravi Krishna, and Kurt W. Keutzer.
|
||||
1. **[SqueezeBERT](model_doc/squeezebert)** (from Berkeley) released with the paper [SqueezeBERT: What can computer vision teach NLP about efficient neural networks?](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.11316) by Forrest N. Iandola, Albert E. Shaw, Ravi Krishna, and Kurt W. Keutzer.
|
||||
1. **[Swin Transformer](model_doc/swin)** (from Microsoft) released with the paper [Swin Transformer: Hierarchical Vision Transformer using Shifted Windows](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.14030) by Ze Liu, Yutong Lin, Yue Cao, Han Hu, Yixuan Wei, Zheng Zhang, Stephen Lin, Baining Guo.
|
||||
1. **[T5](model_doc/t5)** (from Google AI) released with the paper [Exploring the Limits of Transfer Learning with a Unified Text-to-Text Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/1910.10683) by Colin Raffel and Noam Shazeer and Adam Roberts and Katherine Lee and Sharan Narang and Michael Matena and Yanqi Zhou and Wei Li and Peter J. Liu.
|
||||
1. **[T5v1.1](model_doc/t5v1.1)** (from Google AI) released in the repository [google-research/text-to-text-transfer-transformer](https://github.com/google-research/text-to-text-transfer-transformer/blob/main/released_checkpoints.md#t511) by Colin Raffel and Noam Shazeer and Adam Roberts and Katherine Lee and Sharan Narang and Michael Matena and Yanqi Zhou and Wei Li and Peter J. Liu.
|
||||
1. **[TAPAS](model_doc/tapas)** (from Google AI) released with the paper [TAPAS: Weakly Supervised Table Parsing via Pre-training](https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.02349) by Jonathan Herzig, Paweł Krzysztof Nowak, Thomas Müller, Francesco Piccinno and Julian Martin Eisenschlos.
|
||||
1. **[TAPEX](model_doc/tapex)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [TAPEX: Table Pre-training via Learning a Neural SQL Executor](https://arxiv.org/abs/2107.07653) by Qian Liu, Bei Chen, Jiaqi Guo, Morteza Ziyadi, Zeqi Lin, Weizhu Chen, Jian-Guang Lou.
|
||||
1. **[Trajectory Transformer](model_doc/trajectory_transformers)** (from the University of California at Berkeley) released with the paper [Offline Reinforcement Learning as One Big Sequence Modeling Problem](https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.02039) by Michael Janner, Qiyang Li, Sergey Levine
|
||||
1. **[Transformer-XL](model_doc/transfo-xl)** (from Google/CMU) released with the paper [Transformer-XL: Attentive Language Models Beyond a Fixed-Length Context](https://arxiv.org/abs/1901.02860) by Zihang Dai*, Zhilin Yang*, Yiming Yang, Jaime Carbonell, Quoc V. Le, Ruslan Salakhutdinov.
|
||||
1. **[TrOCR](model_doc/trocr)** (from Microsoft), released together with the paper [TrOCR: Transformer-based Optical Character Recognition with Pre-trained Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.10282) by Minghao Li, Tengchao Lv, Lei Cui, Yijuan Lu, Dinei Florencio, Cha Zhang, Zhoujun Li, Furu Wei.
|
||||
1. **[UL2](model_doc/ul2)** (from Google Research) released with the paper [Unifying Language Learning Paradigms](https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.05131v1) by Yi Tay, Mostafa Dehghani, Vinh Q. Tran, Xavier Garcia, Dara Bahri, Tal Schuster, Huaixiu Steven Zheng, Neil Houlsby, Donald Metzler
|
||||
1. **[UniSpeech](model_doc/unispeech)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [UniSpeech: Unified Speech Representation Learning with Labeled and Unlabeled Data](https://arxiv.org/abs/2101.07597) by Chengyi Wang, Yu Wu, Yao Qian, Kenichi Kumatani, Shujie Liu, Furu Wei, Michael Zeng, Xuedong Huang.
|
||||
1. **[UniSpeechSat](model_doc/unispeech-sat)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [UNISPEECH-SAT: UNIVERSAL SPEECH REPRESENTATION LEARNING WITH SPEAKER AWARE PRE-TRAINING](https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.05752) by Sanyuan Chen, Yu Wu, Chengyi Wang, Zhengyang Chen, Zhuo Chen, Shujie Liu, Jian Wu, Yao Qian, Furu Wei, Jinyu Li, Xiangzhan Yu.
|
||||
1. **[VAN](model_doc/van)** (from Tsinghua University and Nankai University) released with the paper [Visual Attention Network](https://arxiv.org/abs/2202.09741) by Meng-Hao Guo, Cheng-Ze Lu, Zheng-Ning Liu, Ming-Ming Cheng, Shi-Min Hu.
|
||||
1. **[ViLT](model_doc/vilt)** (from NAVER AI Lab/Kakao Enterprise/Kakao Brain) released with the paper [ViLT: Vision-and-Language Transformer Without Convolution or Region Supervision](https://arxiv.org/abs/2102.03334) by Wonjae Kim, Bokyung Son, Ildoo Kim.
|
||||
1. **[Vision Transformer (ViT)](model_doc/vit)** (from Google AI) released with the paper [An Image is Worth 16x16 Words: Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11929) by Alexey Dosovitskiy, Lucas Beyer, Alexander Kolesnikov, Dirk Weissenborn, Xiaohua Zhai, Thomas Unterthiner, Mostafa Dehghani, Matthias Minderer, Georg Heigold, Sylvain Gelly, Jakob Uszkoreit, Neil Houlsby.
|
||||
1. **[ViTMAE](model_doc/vit_mae)** (from Meta AI) released with the paper [Masked Autoencoders Are Scalable Vision Learners](https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.06377) by Kaiming He, Xinlei Chen, Saining Xie, Yanghao Li, Piotr Dollár, Ross Girshick.
|
||||
1. **[VisualBERT](model_doc/visual_bert)** (from UCLA NLP) released with the paper [VisualBERT: A Simple and Performant Baseline for Vision and Language](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1908.03557) by Liunian Harold Li, Mark Yatskar, Da Yin, Cho-Jui Hsieh, Kai-Wei Chang.
|
||||
1. **[WavLM](model_doc/wavlm)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [WavLM: Large-Scale Self-Supervised Pre-Training for Full Stack Speech Processing](https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.13900) by Sanyuan Chen, Chengyi Wang, Zhengyang Chen, Yu Wu, Shujie Liu, Zhuo Chen, Jinyu Li, Naoyuki Kanda, Takuya Yoshioka, Xiong Xiao, Jian Wu, Long Zhou, Shuo Ren, Yanmin Qian, Yao Qian, Jian Wu, Michael Zeng, Furu Wei.
|
||||
1. **[ViTMAE](model_doc/vit_mae)** (from Meta AI) released with the paper [Masked Autoencoders Are Scalable Vision Learners](https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.06377) by Kaiming He, Xinlei Chen, Saining Xie, Yanghao Li, Piotr Dollár, Ross Girshick.
|
||||
1. **[Wav2Vec2](model_doc/wav2vec2)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [wav2vec 2.0: A Framework for Self-Supervised Learning of Speech Representations](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.11477) by Alexei Baevski, Henry Zhou, Abdelrahman Mohamed, Michael Auli.
|
||||
1. **[Wav2Vec2-Conformer](model_doc/wav2vec2-conformer)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [FAIRSEQ S2T: Fast Speech-to-Text Modeling with FAIRSEQ](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.05171) by Changhan Wang, Yun Tang, Xutai Ma, Anne Wu, Sravya Popuri, Dmytro Okhonko, Juan Pino.
|
||||
1. **[Wav2Vec2Phoneme](model_doc/wav2vec2_phoneme)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [Simple and Effective Zero-shot Cross-lingual Phoneme Recognition](https://arxiv.org/abs/2109.11680) by Qiantong Xu, Alexei Baevski, Michael Auli.
|
||||
1. **[WavLM](model_doc/wavlm)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [WavLM: Large-Scale Self-Supervised Pre-Training for Full Stack Speech Processing](https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.13900) by Sanyuan Chen, Chengyi Wang, Zhengyang Chen, Yu Wu, Shujie Liu, Zhuo Chen, Jinyu Li, Naoyuki Kanda, Takuya Yoshioka, Xiong Xiao, Jian Wu, Long Zhou, Shuo Ren, Yanmin Qian, Yao Qian, Jian Wu, Michael Zeng, Furu Wei.
|
||||
1. **[XGLM](model_doc/xglm)** (From Facebook AI) released with the paper [Few-shot Learning with Multilingual Language Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.10668) by Xi Victoria Lin, Todor Mihaylov, Mikel Artetxe, Tianlu Wang, Shuohui Chen, Daniel Simig, Myle Ott, Naman Goyal, Shruti Bhosale, Jingfei Du, Ramakanth Pasunuru, Sam Shleifer, Punit Singh Koura, Vishrav Chaudhary, Brian O'Horo, Jeff Wang, Luke Zettlemoyer, Zornitsa Kozareva, Mona Diab, Veselin Stoyanov, Xian Li.
|
||||
1. **[XLM](model_doc/xlm)** (from Facebook) released together with the paper [Cross-lingual Language Model Pretraining](https://arxiv.org/abs/1901.07291) by Guillaume Lample and Alexis Conneau.
|
||||
1. **[XLM-ProphetNet](model_doc/xlm-prophetnet)** (from Microsoft Research) released with the paper [ProphetNet: Predicting Future N-gram for Sequence-to-Sequence Pre-training](https://arxiv.org/abs/2001.04063) by Yu Yan, Weizhen Qi, Yeyun Gong, Dayiheng Liu, Nan Duan, Jiusheng Chen, Ruofei Zhang and Ming Zhou.
|
||||
1. **[XLM-RoBERTa](model_doc/xlm-roberta)** (from Facebook AI), released together with the paper [Unsupervised Cross-lingual Representation Learning at Scale](https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.02116) by Alexis Conneau*, Kartikay Khandelwal*, Naman Goyal, Vishrav Chaudhary, Guillaume Wenzek, Francisco Guzmán, Edouard Grave, Myle Ott, Luke Zettlemoyer and Veselin Stoyanov.
|
||||
1. **[XLM-RoBERTa-XL](model_doc/xlm-roberta-xl)** (from Facebook AI), released together with the paper [Larger-Scale Transformers for Multilingual Masked Language Modeling](https://arxiv.org/abs/2105.00572) by Naman Goyal, Jingfei Du, Myle Ott, Giri Anantharaman, Alexis Conneau.
|
||||
1. **[XLNet](model_doc/xlnet)** (from Google/CMU) released with the paper [XLNet: Generalized Autoregressive Pretraining for Language Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/1906.08237) by Zhilin Yang*, Zihang Dai*, Yiming Yang, Jaime Carbonell, Ruslan Salakhutdinov, Quoc V. Le.
|
||||
1. **[XLSR-Wav2Vec2](model_doc/xlsr_wav2vec2)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [Unsupervised Cross-Lingual Representation Learning For Speech Recognition](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.13979) by Alexis Conneau, Alexei Baevski, Ronan Collobert, Abdelrahman Mohamed, Michael Auli.
|
||||
1. **[XLS-R](model_doc/xls_r)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [XLS-R: Self-supervised Cross-lingual Speech Representation Learning at Scale](https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.09296) by Arun Babu, Changhan Wang, Andros Tjandra, Kushal Lakhotia, Qiantong Xu, Naman Goyal, Kritika Singh, Patrick von Platen, Yatharth Saraf, Juan Pino, Alexei Baevski, Alexis Conneau, Michael Auli.
|
||||
1. **[XLSR-Wav2Vec2](model_doc/xlsr_wav2vec2)** (from Facebook AI) released with the paper [Unsupervised Cross-Lingual Representation Learning For Speech Recognition](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.13979) by Alexis Conneau, Alexei Baevski, Ronan Collobert, Abdelrahman Mohamed, Michael Auli.
|
||||
1. **[YOLOS](model_doc/yolos)** (from Huazhong University of Science & Technology) released with the paper [You Only Look at One Sequence: Rethinking Transformer in Vision through Object Detection](https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.00666) by Yuxin Fang, Bencheng Liao, Xinggang Wang, Jiemin Fang, Jiyang Qi, Rui Wu, Jianwei Niu, Wenyu Liu.
|
||||
1. **[YOSO](model_doc/yoso)** (from the University of Wisconsin - Madison) released with the paper [You Only Sample (Almost) Once: Linear Cost Self-Attention Via Bernoulli Sampling](https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.09714) by Zhanpeng Zeng, Yunyang Xiong, Sathya N. Ravi, Shailesh Acharya, Glenn Fung, Vikas Singh.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -182,22 +200,25 @@ Flax), PyTorch, and/or TensorFlow.
|
||||
| BERT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| Bert Generation | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| BigBird | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
|
||||
| BigBirdPegasus | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| BigBird-Pegasus | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Blenderbot | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| BlenderbotSmall | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| BLOOM | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| CamemBERT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Canine | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| CANINE | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| CLIP | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| CodeGen | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| ConvBERT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| ConvNext | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| ConvNeXT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| CTRL | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| CvT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Data2VecAudio | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Data2VecText | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Data2VecVision | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| DeBERTa | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| DeBERTa-v2 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Decision Transformer | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| DeiT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| DeiT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| DETR | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| DistilBERT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| DPR | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
@ -206,33 +227,42 @@ Flax), PyTorch, and/or TensorFlow.
|
||||
| Encoder decoder | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| FairSeq Machine-Translation | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| FlauBERT | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Flava | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| FLAVA | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| FNet | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Funnel Transformer | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| GLPN | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| GPT Neo | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
|
||||
| GPT NeoX | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| GPT-J | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| GroupViT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Hubert | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| I-BERT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| ImageGPT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| LayoutLM | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| LayoutLMv2 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| LayoutLMv3 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| LED | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| LeViT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Longformer | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| LongT5 | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
|
||||
| LUKE | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| LXMERT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| M-CTC-T | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| M2M100 | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Marian | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| MaskFormer | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| mBART | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| MegatronBert | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Megatron-BERT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| MobileBERT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| MobileViT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| MPNet | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| mT5 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| Nystromformer | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| MT5 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| MVP | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Nezha | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Nyströmformer | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| OpenAI GPT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| OpenAI GPT-2 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| OPT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| OPT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| Pegasus | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| Perceiver | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| PLBart | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
@ -240,11 +270,11 @@ Flax), PyTorch, and/or TensorFlow.
|
||||
| ProphetNet | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| QDQBert | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| RAG | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Realm | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| REALM | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Reformer | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| RegNet | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| RegNet | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| RemBERT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| ResNet | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| ResNet | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| RetriBERT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| RoBERTa | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| RoFormer | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
@ -256,10 +286,10 @@ Flax), PyTorch, and/or TensorFlow.
|
||||
| Speech2Text2 | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Splinter | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| SqueezeBERT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Swin | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Swin Transformer | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| T5 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| TAPAS | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| TAPEX | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| Trajectory Transformer | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Transformer-XL | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| TrOCR | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| UniSpeech | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
@ -268,16 +298,17 @@ Flax), PyTorch, and/or TensorFlow.
|
||||
| ViLT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Vision Encoder decoder | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| VisionTextDualEncoder | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
|
||||
| VisualBert | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| VisualBERT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| ViT | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| ViTMAE | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| Wav2Vec2 | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| Wav2Vec2-Conformer | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| WavLM | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| XGLM | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
|
||||
| XLM | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| XLM-ProphetNet | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| XLM-RoBERTa | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| XLM-RoBERTa-XL | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| XLMProphetNet | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| XLNet | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| YOLOS | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| YOSO | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
|
||||
@ -34,11 +34,16 @@ Start by creating a virtual environment in your project directory:
|
||||
python -m venv .env
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Activate the virtual environment:
|
||||
Activate the virtual environment. On Linux and MacOs:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
source .env/bin/activate
|
||||
```
|
||||
Activate Virtual environment on Windows
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
.env/Scripts/activate
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now you're ready to install 🤗 Transformers with the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -127,6 +127,9 @@ generation.
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TopKLogitsWarper
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TypicalLogitsWarper
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] NoRepeatNGramLogitsProcessor
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -40,29 +40,17 @@ Additionally, some `warnings` can be disabled by setting the environment variabl
|
||||
TRANSFORMERS_NO_ADVISORY_WARNINGS=1 ./myprogram.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Here is an example of how to use `logging` in a module:
|
||||
Here is an example of how to use the same logger as the library in your own module or script:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers.utils import logging
|
||||
|
||||
logging.set_verbosity_info()
|
||||
logger = logging.get_logger(__name__)
|
||||
logger = logging.get_logger("transformers")
|
||||
logger.info("INFO")
|
||||
logger.warning("WARN")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Above, a `logger` instance is created from `logging.get_logger(__name__)`. If you want to use `logging` in a script, you shouldn't pass `__name__` to `logging.get_logger`. For example:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers.utils import logging
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
logging.set_verbosity_info()
|
||||
# leave it empy or use a string
|
||||
logger = logging.get_logger()
|
||||
logger.info("INFO")
|
||||
logger.warning("WARN")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
All the methods of this logging module are documented below, the main ones are
|
||||
[`logging.get_verbosity`] to get the current level of verbosity in the logger and
|
||||
|
||||
@ -38,6 +38,75 @@ for text generation, [`~generation_utils.GenerationMixin`] (for the PyTorch mode
|
||||
|
||||
<a id='from_pretrained-torch-dtype'></a>
|
||||
|
||||
### Large model loading
|
||||
|
||||
In Transformers 4.20.0, the [`~PreTrainedModel.from_pretrained`] method has been reworked to accommodate large models using [Accelerate](https://huggingface.co/docs/accelerate/big_modeling). This requires Accelerate >= 0.9.0 and PyTorch >= 1.9.0. Instead of creating the full model, then loading the pretrained weights inside it (which takes twice the size of the model in RAM, one for the randomly initialized model, one for the weights), there is an option to create the model as an empty shell, then only materialize its parameters when the pretrained weights are loaded.
|
||||
|
||||
This option can be activated with `low_cpu_mem_usage=True`. The model is first created on the Meta device (with empty weights) and the state dict is then loaded inside it (shard by shard in the case of a sharded checkpoint). This way the maximum RAM used is the full size of the model only.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM
|
||||
|
||||
t0pp = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained("bigscience/T0pp", low_cpu_mem_usage=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Moreover, you can directly place the model on different devices if it doesn't fully fit in RAM (only works for inference for now). With `device_map="auto"`, Accelerate will determine where to put each layer to maximize the use of your fastest devices (GPUs) and offload the rest on the CPU, or even the hard drive if you don't have enough GPU RAM (or CPU RAM). Even if the model is split across several devices, it will run as you would normally expect.
|
||||
|
||||
When passing a `device_map`, `low_cpu_mem_usage` is automatically set to `True`, so you don't need to specify it:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM
|
||||
|
||||
t0pp = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained("bigscience/T0pp", device_map="auto")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can inspect how the model was split across devices by looking at its `hf_device_map` attribute:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
t0pp.hf_device_map
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python out
|
||||
{'shared': 0,
|
||||
'decoder.embed_tokens': 0,
|
||||
'encoder': 0,
|
||||
'decoder.block.0': 0,
|
||||
'decoder.block.1': 1,
|
||||
'decoder.block.2': 1,
|
||||
'decoder.block.3': 1,
|
||||
'decoder.block.4': 1,
|
||||
'decoder.block.5': 1,
|
||||
'decoder.block.6': 1,
|
||||
'decoder.block.7': 1,
|
||||
'decoder.block.8': 1,
|
||||
'decoder.block.9': 1,
|
||||
'decoder.block.10': 1,
|
||||
'decoder.block.11': 1,
|
||||
'decoder.block.12': 1,
|
||||
'decoder.block.13': 1,
|
||||
'decoder.block.14': 1,
|
||||
'decoder.block.15': 1,
|
||||
'decoder.block.16': 1,
|
||||
'decoder.block.17': 1,
|
||||
'decoder.block.18': 1,
|
||||
'decoder.block.19': 1,
|
||||
'decoder.block.20': 1,
|
||||
'decoder.block.21': 1,
|
||||
'decoder.block.22': 'cpu',
|
||||
'decoder.block.23': 'cpu',
|
||||
'decoder.final_layer_norm': 'cpu',
|
||||
'decoder.dropout': 'cpu',
|
||||
'lm_head': 'cpu'}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can also write your own device map following the same format (a dictionary layer name to device). It should map all parameters of the model to a given device, but you don't have to detail where all the submosules of one layer go if that layer is entirely on the same device. For instance, the following device map would work properly for T0pp (as long as you have the GPU memory):
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
device_map = {"shared": 0, "encoder": 0, "decoder": 1, "lm_head": 1}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Another way to minimize the memory impact of your model is to instantiate it at a lower precision dtype (like `torch.float16`).
|
||||
|
||||
### Model Instantiation dtype
|
||||
|
||||
Under Pytorch a model normally gets instantiated with `torch.float32` format. This can be an issue if one tries to
|
||||
|
||||
@ -136,6 +136,30 @@ documented on their corresponding model page.
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] modeling_outputs.Seq2SeqQuestionAnsweringModelOutput
|
||||
|
||||
## SemanticSegmenterOutput
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] modeling_outputs.SemanticSegmenterOutput
|
||||
|
||||
## ImageClassifierOutput
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] modeling_outputs.ImageClassifierOutput
|
||||
|
||||
## ImageClassifierOutputWithNoAttention
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] modeling_outputs.ImageClassifierOutputWithNoAttention
|
||||
|
||||
## DepthEstimatorOutput
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] modeling_outputs.DepthEstimatorOutput
|
||||
|
||||
## Wav2Vec2BaseModelOutput
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] modeling_outputs.Wav2Vec2BaseModelOutput
|
||||
|
||||
## XVectorOutput
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] modeling_outputs.XVectorOutput
|
||||
|
||||
## TFBaseModelOutput
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] modeling_tf_outputs.TFBaseModelOutput
|
||||
|
||||
@ -38,6 +38,7 @@ There are two categories of pipeline abstractions to be aware about:
|
||||
- [`Text2TextGenerationPipeline`]
|
||||
- [`TokenClassificationPipeline`]
|
||||
- [`TranslationPipeline`]
|
||||
- [`VisualQuestionAnsweringPipeline`]
|
||||
- [`ZeroShotClassificationPipeline`]
|
||||
- [`ZeroShotImageClassificationPipeline`]
|
||||
|
||||
@ -423,6 +424,12 @@ See [`TokenClassificationPipeline`] for all details.
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
- all
|
||||
|
||||
### VisualQuestionAnsweringPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] VisualQuestionAnsweringPipeline
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
- all
|
||||
|
||||
### ZeroShotClassificationPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] ZeroShotClassificationPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
@ -291,10 +291,10 @@ Also if you do set this environment variable it's the best to set it in your `~/
|
||||
The [`Trainer`] has been extended to support libraries that may dramatically improve your training
|
||||
time and fit much bigger models.
|
||||
|
||||
Currently it supports third party solutions, [DeepSpeed](https://github.com/microsoft/DeepSpeed) and [FairScale](https://github.com/facebookresearch/fairscale/), which implement parts of the paper [ZeRO: Memory Optimizations
|
||||
Currently it supports third party solutions, [DeepSpeed](https://github.com/microsoft/DeepSpeed), [PyTorch FSDP](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/fsdp.html) and [FairScale](https://github.com/facebookresearch/fairscale/), which implement parts of the paper [ZeRO: Memory Optimizations
|
||||
Toward Training Trillion Parameter Models, by Samyam Rajbhandari, Jeff Rasley, Olatunji Ruwase, Yuxiong He](https://arxiv.org/abs/1910.02054).
|
||||
|
||||
This provided support is new and experimental as of this writing.
|
||||
This provided support is new and experimental as of this writing. While the support for DeepSpeed and PyTorch FSDP is active and we welcome issues around it, we don't support the FairScale integration anymore since it has been integrated in PyTorch main (see the [PyTorch FSDP integration](#pytorch-fully-sharded-data-parallel))
|
||||
|
||||
<a id='zero-install-notes'></a>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -408,6 +408,12 @@ As always make sure to edit the paths in the example to match your situation.
|
||||
|
||||
### FairScale
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
This integration is not supported anymore, we recommend you either use DeepSpeed or PyTorch FSDP.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
By integrating [FairScale](https://github.com/facebookresearch/fairscale/) the [`Trainer`]
|
||||
provides support for the following features from [the ZeRO paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/1910.02054):
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -122,6 +122,10 @@ Likewise, if your `NewModel` is a subclass of [`PreTrainedModel`], make sure its
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] AutoModelForVision2Seq
|
||||
|
||||
## AutoModelForVisualQuestionAnswering
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] AutoModelForVisualQuestionAnswering
|
||||
|
||||
## AutoModelForAudioClassification
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] AutoModelForAudioClassification
|
||||
|
||||
@ -58,6 +58,10 @@ This model was contributed by [thomwolf](https://huggingface.co/thomwolf). The o
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] BertTokenizerFast
|
||||
|
||||
## TFBertTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TFBertTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
## Bert specific outputs
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] models.bert.modeling_bert.BertForPreTrainingOutput
|
||||
|
||||
57
docs/source/en/model_doc/bloom.mdx
Normal file
57
docs/source/en/model_doc/bloom.mdx
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,57 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# BLOOM
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
The BLOOM model has been proposed with its various versions through the [BigScience Workshop](https://bigscience.huggingface.co/). BigScience is inspired by other open science initiatives where researchers have pooled their time and resources to collectively achieve a higher impact.
|
||||
The architecture of BLOOM is essentially similar to GPT3 (auto-regressive model for next token prediction), but has been trained on different 46 languages including code.
|
||||
Several smaller versions of the models have been trained on the same dataset. BLOOM is available in the following versions:
|
||||
|
||||
- [bloom-350m](https://huggingface.co/bigscience/bloom-350m)
|
||||
- [bloom-760m](https://huggingface.co/bigscience/bloom-760m)
|
||||
- [bloom-1b3](https://huggingface.co/bigscience/bloom-1b3)
|
||||
- [bloom-2b5](https://huggingface.co/bigscience/bloom-2b5)
|
||||
- [bloom-6b3](https://huggingface.co/bigscience/bloom-6b3)
|
||||
- [bloom](https://huggingface.co/bigscience/bloom) (175B parameters)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## BloomConfig
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] BloomConfig
|
||||
- all
|
||||
|
||||
## BloomModel
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] BloomModel
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
## BloomTokenizerFast
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] BloomTokenizerFast
|
||||
- all
|
||||
|
||||
## BloomForCausalLM
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] BloomForCausalLM
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
## BloomForSequenceClassification
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] BloomForSequenceClassification
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
## BloomForTokenClassification
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] BloomForTokenClassification
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
81
docs/source/en/model_doc/codegen.mdx
Normal file
81
docs/source/en/model_doc/codegen.mdx
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,81 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# CodeGen
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
The CodeGen model was proposed in [A Conversational Paradigm for Program Synthesis](https://arxiv.org/abs/2203.13474) by Erik Nijkamp, Bo Pang, Hiroaki Hayashi, Lifu Tu, Huan Wang, Yingbo Zhou, Silvio Savarese, and Caiming Xiong.
|
||||
|
||||
CodeGen is an autoregressive language model for program synthesis trained sequentially on [The Pile](https://pile.eleuther.ai/), BigQuery, and BigPython.
|
||||
|
||||
The abstract from the paper is the following:
|
||||
|
||||
*Program synthesis strives to generate a computer program as a solution to a given problem specification. We propose a conversational program synthesis approach via large language models, which addresses the challenges of searching over a vast program space and user intent specification faced in prior approaches. Our new approach casts the process of writing a specification and program as a multi-turn conversation between a user and a system. It treats program synthesis as a sequence prediction problem, in which the specification is expressed in natural language and the desired program is conditionally sampled. We train a family of large language models, called CodeGen, on natural language and programming language data. With weak supervision in the data and the scaling up of data size and model size, conversational capacities emerge from the simple autoregressive language modeling. To study the model behavior on conversational program synthesis, we develop a multi-turn programming benchmark (MTPB), where solving each problem requires multi-step synthesis via multi-turn conversation between the user and the model. Our findings show the emergence of conversational capabilities and the effectiveness of the proposed conversational program synthesis paradigm. In addition, our model CodeGen (with up to 16B parameters trained on TPU-v4) outperforms OpenAI's Codex on the HumanEval benchmark. We make the training library JaxFormer including checkpoints available as open source contribution: [this https URL](https://github.com/salesforce/codegen).*
|
||||
|
||||
This model was contributed by [Hiroaki Hayashi](https://huggingface.co/rooa).
|
||||
The original code can be found [here](https://github.com/salesforce/codegen).
|
||||
|
||||
## Checkpoint Naming
|
||||
|
||||
* CodeGen model [checkpoints](https://huggingface.co/models?other=codegen) are available on different pre-training data with variable sizes.
|
||||
* The format is: `Salesforce/codegen-{size}-{data}`, where
|
||||
* `size`: `350M`, `2B`, `6B`, `16B`
|
||||
* `data`:
|
||||
* `nl`: Pre-trained on the Pile
|
||||
* `multi`: Initialized with `nl`, then further pre-trained on multiple programming languages data
|
||||
* `mono`: Initialized with `multi`, then further pre-trained on Python data
|
||||
* For example, `Salesforce/codegen-350M-mono` offers a 350 million-parameter checkpoint pre-trained sequentially on the Pile, multiple programming languages, and Python.
|
||||
|
||||
## How to use
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
>>> checkpoint = "Salesforce/codegen-350M-mono"
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(checkpoint)
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(checkpoint)
|
||||
|
||||
>>> text = "def hello_world():"
|
||||
|
||||
>>> completion = model.generate(**tokenizer(text, return_tensors="pt"))
|
||||
|
||||
>>> print(tokenizer.decode(completion[0]))
|
||||
def hello_world():
|
||||
print("Hello World")
|
||||
|
||||
hello_world()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## CodeGenConfig
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] CodeGenConfig
|
||||
- all
|
||||
|
||||
## CodeGenTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] CodeGenTokenizer
|
||||
- save_vocabulary
|
||||
|
||||
## CodeGenTokenizerFast
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] CodeGenTokenizerFast
|
||||
|
||||
## CodeGenModel
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] CodeGenModel
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
## CodeGenForCausalLM
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] CodeGenForCausalLM
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
53
docs/source/en/model_doc/cvt.mdx
Normal file
53
docs/source/en/model_doc/cvt.mdx
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,53 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Convolutional Vision Transformer (CvT)
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
The CvT model was proposed in [CvT: Introducing Convolutions to Vision Transformers](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.15808) by Haiping Wu, Bin Xiao, Noel Codella, Mengchen Liu, Xiyang Dai, Lu Yuan and Lei Zhang. The Convolutional vision Transformer (CvT) improves the [Vision Transformer (ViT)](vit) in performance and efficiency by introducing convolutions into ViT to yield the best of both designs.
|
||||
|
||||
The abstract from the paper is the following:
|
||||
|
||||
*We present in this paper a new architecture, named Convolutional vision Transformer (CvT), that improves Vision Transformer (ViT)
|
||||
in performance and efficiency by introducing convolutions into ViT to yield the best of both designs. This is accomplished through
|
||||
two primary modifications: a hierarchy of Transformers containing a new convolutional token embedding, and a convolutional Transformer
|
||||
block leveraging a convolutional projection. These changes introduce desirable properties of convolutional neural networks (CNNs)
|
||||
to the ViT architecture (\ie shift, scale, and distortion invariance) while maintaining the merits of Transformers (\ie dynamic attention,
|
||||
global context, and better generalization). We validate CvT by conducting extensive experiments, showing that this approach achieves
|
||||
state-of-the-art performance over other Vision Transformers and ResNets on ImageNet-1k, with fewer parameters and lower FLOPs. In addition,
|
||||
performance gains are maintained when pretrained on larger datasets (\eg ImageNet-22k) and fine-tuned to downstream tasks. Pre-trained on
|
||||
ImageNet-22k, our CvT-W24 obtains a top-1 accuracy of 87.7\% on the ImageNet-1k val set. Finally, our results show that the positional encoding,
|
||||
a crucial component in existing Vision Transformers, can be safely removed in our model, simplifying the design for higher resolution vision tasks.*
|
||||
|
||||
Tips:
|
||||
|
||||
- CvT models are regular Vision Transformers, but trained with convolutions. They outperform the [original model (ViT)](vit) when fine-tuned on ImageNet-1K and CIFAR-100.
|
||||
- You can check out demo notebooks regarding inference as well as fine-tuning on custom data [here](https://github.com/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/tree/master/VisionTransformer) (you can just replace [`ViTFeatureExtractor`] by [`AutoFeatureExtractor`] and [`ViTForImageClassification`] by [`CvtForImageClassification`]).
|
||||
- The available checkpoints are either (1) pre-trained on [ImageNet-22k](http://www.image-net.org/) (a collection of 14 million images and 22k classes) only, (2) also fine-tuned on ImageNet-22k or (3) also fine-tuned on [ImageNet-1k](http://www.image-net.org/challenges/LSVRC/2012/) (also referred to as ILSVRC 2012, a collection of 1.3 million
|
||||
images and 1,000 classes).
|
||||
|
||||
This model was contributed by [anugunj](https://huggingface.co/anugunj). The original code can be found [here](https://github.com/microsoft/CvT).
|
||||
|
||||
## CvtConfig
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] CvtConfig
|
||||
|
||||
## CvtModel
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] CvtModel
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
## CvtForImageClassification
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] CvtForImageClassification
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
@ -42,7 +42,7 @@ Tips:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
This model was contributed by [edugp](https://huggingface.co/edugp) and [patrickvonplaten](https://huggingface.co/patrickvonplaten).
|
||||
[sayakpaul](https://github.com/sayakpaul) contributed Data2Vec for vision in TensorFlow.
|
||||
[sayakpaul](https://github.com/sayakpaul) and [Rocketknight1](https://github.com/Rocketknight1) contributed Data2Vec for vision in TensorFlow.
|
||||
|
||||
The original code (for NLP and Speech) can be found [here](https://github.com/pytorch/fairseq/tree/main/examples/data2vec).
|
||||
The original code for vision can be found [here](https://github.com/facebookresearch/data2vec_vision/tree/main/beit).
|
||||
@ -145,3 +145,8 @@ The original code for vision can be found [here](https://github.com/facebookrese
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TFData2VecVisionForImageClassification
|
||||
- call
|
||||
|
||||
## TFData2VecVisionForSemanticSegmentation
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TFData2VecVisionForSemanticSegmentation
|
||||
- call
|
||||
|
||||
@ -69,7 +69,7 @@ Tips:
|
||||
*facebook/deit-base-patch16-384*. Note that one should use [`DeiTFeatureExtractor`] in order to
|
||||
prepare images for the model.
|
||||
|
||||
This model was contributed by [nielsr](https://huggingface.co/nielsr).
|
||||
This model was contributed by [nielsr](https://huggingface.co/nielsr). The TensorFlow version of this model was added by [amyeroberts](https://huggingface.co/amyeroberts).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## DeiTConfig
|
||||
@ -100,3 +100,23 @@ This model was contributed by [nielsr](https://huggingface.co/nielsr).
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] DeiTForImageClassificationWithTeacher
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
## TFDeiTModel
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TFDeiTModel
|
||||
- call
|
||||
|
||||
## TFDeiTForMaskedImageModeling
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TFDeiTForMaskedImageModeling
|
||||
- call
|
||||
|
||||
## TFDeiTForImageClassification
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TFDeiTForImageClassification
|
||||
- call
|
||||
|
||||
## TFDeiTForImageClassificationWithTeacher
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TFDeiTForImageClassificationWithTeacher
|
||||
- call
|
||||
|
||||
@ -113,6 +113,28 @@ Tips:
|
||||
- The size of the images will determine the amount of memory being used, and will thus determine the `batch_size`.
|
||||
It is advised to use a batch size of 2 per GPU. See [this Github thread](https://github.com/facebookresearch/detr/issues/150) for more info.
|
||||
|
||||
There are three ways to instantiate a DETR model (depending on what you prefer):
|
||||
|
||||
Option 1: Instantiate DETR with pre-trained weights for entire model
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import DetrForObjectDetection
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = DetrForObjectDetection.from_pretrained("facebook/resnet-50")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Option 2: Instantiate DETR with randomly initialized weights for Transformer, but pre-trained weights for backbone
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import DetrConfig, DetrForObjectDetection
|
||||
|
||||
>>> config = DetrConfig()
|
||||
>>> model = DetrForObjectDetection(config)
|
||||
```
|
||||
Option 3: Instantiate DETR with randomly initialized weights for backbone + Transformer
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> config = DetrConfig(use_pretrained_backbone=False)
|
||||
>>> model = DetrForObjectDetection(config)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
As a summary, consider the following table:
|
||||
|
||||
| Task | Object detection | Instance segmentation | Panoptic segmentation |
|
||||
@ -166,4 +188,4 @@ mean Average Precision (mAP) and Panoptic Quality (PQ). The latter objects are i
|
||||
## DetrForSegmentation
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] DetrForSegmentation
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
@ -12,6 +12,8 @@ specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
# Encoder Decoder Models
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
The [`EncoderDecoderModel`] can be used to initialize a sequence-to-sequence model with any
|
||||
pretrained autoencoding model as the encoder and any pretrained autoregressive model as the decoder.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -25,15 +27,59 @@ any other models (see the examples for more information).
|
||||
An application of this architecture could be to leverage two pretrained [`BertModel`] as the encoder
|
||||
and decoder for a summarization model as was shown in: [Text Summarization with Pretrained Encoders](https://arxiv.org/abs/1908.08345) by Yang Liu and Mirella Lapata.
|
||||
|
||||
The [`~TFEncoderDecoderModel.from_pretrained`] currently doesn't support initializing the model from a
|
||||
## Randomly initializing [`EncoderDecoderModel`] from model configurations.
|
||||
|
||||
[`EncoderDecoderModel`] can be randomly initialized from an encoder and a decoder config. In the following example, we show how to do this using the default [`BertModel`] configuration for both the encoder and the decoder.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import BertConfig, EncoderDecoderConfig, EncoderDecoderModel
|
||||
|
||||
>>> config_encoder = BertConfig()
|
||||
>>> config_decoder = BertConfig()
|
||||
|
||||
>>> config = EncoderDecoderConfig.from_encoder_decoder_configs(config_encoder, config_decoder)
|
||||
>>> model = EncoderDecoderModel(config=config)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Initialising [`EncoderDecoderModel`] from a pretrained encoder and a pretrained decoder.
|
||||
|
||||
[`EncoderDecoderModel`] can be initialized from a pretrained encoder checkpoint and a pretrained decoder checkpoint. Note that any pretrained auto-encoding model, *e.g.* BERT, can serve as the encoder and both pretrained auto-encoding models, *e.g.* BERT, pretrained causal language models, *e.g.* GPT2, as well as the pretrained decoder part of sequence-to-sequence models, *e.g.* decoder of BART, can be used as the decoder.
|
||||
Depending on which architecture you choose as the decoder, the cross-attention layers might be randomly initialized.
|
||||
Initializing [`EncoderDecoderModel`] from a pretrained encoder and decoder checkpoint requires the model to be fine-tuned on a downstream task, as has been shown in [the *Warm-starting-encoder-decoder blog post*](https://huggingface.co/blog/warm-starting-encoder-decoder).
|
||||
To do so, the `EncoderDecoderModel` class provides a [`EncoderDecoderModel.from_encoder_decoder_pretrained`] method.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import EncoderDecoderModel, BertTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained("bert-base-uncased")
|
||||
>>> model = EncoderDecoderModel.from_encoder_decoder_pretrained("bert-base-uncased", "bert-base-uncased")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Loading an existing [`EncoderDecoderModel`] checkpoint.
|
||||
|
||||
To load fine-tuned checkpoints of the `EncoderDecoderModel` class, ['EncoderDecoderModel`] provides the `from_pretrained(...)` method just like any other model architecture in Transformers.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import EncoderDecoderModel
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = EncoderDecoderModel.from_pretrained("patrickvonplaten/bert2bert_cnn_daily_mail")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Loading a PyTorch checkpoint into `TFEncoderDecoderModel`.
|
||||
|
||||
[`TFEncoderDecoderModel.from_pretrained`] currently doesn't support initializing the model from a
|
||||
pytorch checkpoint. Passing `from_pt=True` to this method will throw an exception. If there are only pytorch
|
||||
checkpoints for a particular encoder-decoder model, a workaround is:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> # a workaround to load from pytorch checkpoint
|
||||
>>> from transformers import EncoderDecoderModel, TFEncoderDecoderModel
|
||||
|
||||
>>> _model = EncoderDecoderModel.from_pretrained("patrickvonplaten/bert2bert-cnn_dailymail-fp16")
|
||||
|
||||
>>> _model.encoder.save_pretrained("./encoder")
|
||||
>>> _model.decoder.save_pretrained("./decoder")
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = TFEncoderDecoderModel.from_encoder_decoder_pretrained(
|
||||
... "./encoder", "./decoder", encoder_from_pt=True, decoder_from_pt=True
|
||||
... )
|
||||
@ -41,6 +87,37 @@ checkpoints for a particular encoder-decoder model, a workaround is:
|
||||
>>> model.config = _model.config
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Training
|
||||
|
||||
Once the model is created, it can be fine-tuned similar to BART, T5 or any other encoder-decoder model.
|
||||
As you can see, only 2 inputs are required for the model in order to compute a loss: `input_ids` (which are the
|
||||
`input_ids` of the encoded input sequence) and `labels` (which are the `input_ids` of the encoded
|
||||
target sequence).
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import BertTokenizer, EncoderDecoderModel
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained("bert-base-uncased")
|
||||
>>> model = EncoderDecoderModel.from_encoder_decoder_pretrained("bert-base-uncased", "bert-base-uncased")
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model.config.decoder_start_token_id = tokenizer.cls_token_id
|
||||
>>> model.config.pad_token_id = tokenizer.pad_token_id
|
||||
|
||||
>>> input_ids = tokenizer(
|
||||
... "The tower is 324 metres (1,063 ft) tall, about the same height as an 81-storey building, and the tallest structure in Paris. Its base is square, measuring 125 metres (410 ft) on each side.During its construction, the Eiffel Tower surpassed the Washington Monument to become the tallest man-made structure in the world, a title it held for 41 years until the Chrysler Building in New York City was finished in 1930. It was the first structure to reach a height of 300 metres. Due to the addition of a broadcasting aerial at the top of the tower in 1957, it is now taller than the Chrysler Building by 5.2 metres (17 ft).Excluding transmitters, the Eiffel Tower is the second tallest free-standing structure in France after the Millau Viaduct.",
|
||||
... return_tensors="pt",
|
||||
... ).input_ids
|
||||
|
||||
>>> labels = tokenizer(
|
||||
... "the eiffel tower surpassed the washington monument to become the tallest structure in the world. it was the first structure to reach a height of 300 metres in paris in 1930. it is now taller than the chrysler building by 5. 2 metres ( 17 ft ) and is the second tallest free - standing structure in paris.",
|
||||
... return_tensors="pt",
|
||||
... ).input_ids
|
||||
|
||||
>>> # the forward function automatically creates the correct decoder_input_ids
|
||||
>>> loss = model(input_ids=input_ids, labels=labels).loss
|
||||
```
|
||||
Detailed [colab](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1WIk2bxglElfZewOHboPFNj8H44_VAyKE?usp=sharing#scrollTo=ZwQIEhKOrJpl) for training.
|
||||
|
||||
This model was contributed by [thomwolf](https://github.com/thomwolf). This model's TensorFlow and Flax versions
|
||||
were contributed by [ydshieh](https://github.com/ydshieh).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
76
docs/source/en/model_doc/gpt_neox.mdx
Normal file
76
docs/source/en/model_doc/gpt_neox.mdx
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,76 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# GPT-NeoX
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
We introduce GPT-NeoX-20B, a 20 billion parameter autoregressive language model trained on the Pile, whose weights will
|
||||
be made freely and openly available to the public through a permissive license. It is, to the best of our knowledge,
|
||||
the largest dense autoregressive model that has publicly available weights at the time of submission. In this work,
|
||||
we describe GPT-NeoX-20B's architecture and training and evaluate its performance on a range of language-understanding,
|
||||
mathematics, and knowledge-based tasks. We find that GPT-NeoX-20B is a particularly powerful few-shot reasoner and
|
||||
gains far more in performance when evaluated five-shot than similarly sized GPT-3 and FairSeq models. We open-source
|
||||
the training and evaluation code, as well as the model weights, at [https://github.com/EleutherAI/gpt-neox](https://github.com/EleutherAI/gpt-neox).
|
||||
|
||||
Development of the model was led by Sid Black, Stella Biderman and Eric Hallahan, and the model was trained with
|
||||
generous the support of [CoreWeave](https://www.coreweave.com/).
|
||||
|
||||
GPT-NeoX-20B was trained with fp16, thus it is recommended to initialize the model as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
model = GPTNeoXForCausalLM.from_pretrained("EleutherAI/gpt-neox-20b").half().cuda()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
GPT-NeoX-20B also has a different tokenizer from the one used in GPT-J-6B and GPT-Neo. The new tokenizer allocates
|
||||
additional tokens to whitespace characters, making the model more suitable for certain tasks like code generation.
|
||||
|
||||
### Generation
|
||||
|
||||
The `generate()` method can be used to generate text using GPT Neo model.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import GPTNeoXForCausalLM, GPTNeoXTokenizerFast
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = GPTNeoXForCausalLM.from_pretrained("EleutherAI/gpt-neox-20b")
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = GPTNeoXTokenizerFast.from_pretrained("EleutherAI/gpt-neox-20b")
|
||||
|
||||
>>> prompt = "GPTNeoX20B is a 20B-parameter autoregressive Transformer model developed by EleutherAI."
|
||||
|
||||
>>> input_ids = tokenizer(prompt, return_tensors="pt").input_ids
|
||||
|
||||
>>> gen_tokens = model.generate(
|
||||
... input_ids,
|
||||
... do_sample=True,
|
||||
... temperature=0.9,
|
||||
... max_length=100,
|
||||
... )
|
||||
>>> gen_text = tokenizer.batch_decode(gen_tokens)[0]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## GPTNeoXConfig
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] GPTNeoXConfig
|
||||
|
||||
## GPTNeoXTokenizerFast
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] GPTNeoXTokenizerFast
|
||||
|
||||
## GPTNeoXModel
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] GPTNeoXModel
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
## GPTNeoXForCausalLM
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] GPTNeoXForCausalLM
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
61
docs/source/en/model_doc/groupvit.mdx
Normal file
61
docs/source/en/model_doc/groupvit.mdx
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,61 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2022 NVIDIA and The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# GroupViT
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
The GroupViT model was proposed in [GroupViT: Semantic Segmentation Emerges from Text Supervision](https://arxiv.org/abs/2202.11094) by Jiarui Xu, Shalini De Mello, Sifei Liu, Wonmin Byeon, Thomas Breuel, Jan Kautz, Xiaolong Wang.
|
||||
Inspired by [CLIP](clip), GroupViT is a vision-language model that can perform zero-shot semantic segmentation on any given vocabulary categories.
|
||||
|
||||
The abstract from the paper is the following:
|
||||
|
||||
*Grouping and recognition are important components of visual scene understanding, e.g., for object detection and semantic segmentation. With end-to-end deep learning systems, grouping of image regions usually happens implicitly via top-down supervision from pixel-level recognition labels. Instead, in this paper, we propose to bring back the grouping mechanism into deep networks, which allows semantic segments to emerge automatically with only text supervision. We propose a hierarchical Grouping Vision Transformer (GroupViT), which goes beyond the regular grid structure representation and learns to group image regions into progressively larger arbitrary-shaped segments. We train GroupViT jointly with a text encoder on a large-scale image-text dataset via contrastive losses. With only text supervision and without any pixel-level annotations, GroupViT learns to group together semantic regions and successfully transfers to the task of semantic segmentation in a zero-shot manner, i.e., without any further fine-tuning. It achieves a zero-shot accuracy of 52.3% mIoU on the PASCAL VOC 2012 and 22.4% mIoU on PASCAL Context datasets, and performs competitively to state-of-the-art transfer-learning methods requiring greater levels of supervision.*
|
||||
|
||||
Tips:
|
||||
|
||||
- You may specify `output_segmentation=True` in the forward of `GroupViTModel` to get the segmentation logits of input texts.
|
||||
- The quickest way to get started with GroupViT is by checking the [example notebooks](https://github.com/xvjiarui/GroupViT/blob/main/demo/GroupViT_hf_inference_notebook.ipynb) (which showcase zero-shot segmentation inference). One can also check out the [HuggingFace Spaces demo](https://huggingface.co/spaces/xvjiarui/GroupViT) to play with GroupViT.
|
||||
|
||||
This model was contributed by [xvjiarui](https://huggingface.co/xvjiarui).
|
||||
The original code can be found [here](https://github.com/NVlabs/GroupViT).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## GroupViTConfig
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] GroupViTConfig
|
||||
- from_text_vision_configs
|
||||
|
||||
## GroupViTTextConfig
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] GroupViTTextConfig
|
||||
|
||||
## GroupViTVisionConfig
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] GroupViTVisionConfig
|
||||
|
||||
## GroupViTModel
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] GroupViTModel
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
- get_text_features
|
||||
- get_image_features
|
||||
|
||||
## GroupViTTextModel
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] GroupViTTextModel
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
## GroupViTVisionModel
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] GroupViTVisionModel
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
@ -44,6 +44,14 @@ including FUNSD (0.7895 -> 0.8420), CORD (0.9493 -> 0.9601), SROIE (0.9524 -> 0.
|
||||
RVL-CDIP (0.9443 -> 0.9564), and DocVQA (0.7295 -> 0.8672). The pre-trained LayoutLMv2 model is publicly available at
|
||||
this https URL.*
|
||||
|
||||
LayoutLMv2 depends on `detectron2`, `torchvision` and `tesseract`. Run the
|
||||
following to install them:
|
||||
```
|
||||
python -m pip install 'git+https://github.com/facebookresearch/detectron2.git'
|
||||
python -m pip install torchvision tesseract
|
||||
```
|
||||
(If you are developing for LayoutLMv2, note that passing the doctests also requires the installation of these packages.)
|
||||
|
||||
Tips:
|
||||
|
||||
- The main difference between LayoutLMv1 and LayoutLMv2 is that the latter incorporates visual embeddings during
|
||||
|
||||
85
docs/source/en/model_doc/layoutlmv3.mdx
Normal file
85
docs/source/en/model_doc/layoutlmv3.mdx
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,85 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# LayoutLMv3
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
The LayoutLMv3 model was proposed in [LayoutLMv3: Pre-training for Document AI with Unified Text and Image Masking](https://arxiv.org/abs/2204.08387) by Yupan Huang, Tengchao Lv, Lei Cui, Yutong Lu, Furu Wei.
|
||||
LayoutLMv3 simplifies [LayoutLMv2](layoutlmv2) by using patch embeddings (as in [ViT](vit)) instead of leveraging a CNN backbone, and pre-trains the model on 3 objectives: masked language modeling (MLM), masked image modeling (MIM)
|
||||
and word-patch alignment (WPA).
|
||||
|
||||
The abstract from the paper is the following:
|
||||
|
||||
*Self-supervised pre-training techniques have achieved remarkable progress in Document AI. Most multimodal pre-trained models use a masked language modeling objective to learn bidirectional representations on the text modality, but they differ in pre-training objectives for the image modality. This discrepancy adds difficulty to multimodal representation learning. In this paper, we propose LayoutLMv3 to pre-train multimodal Transformers for Document AI with unified text and image masking. Additionally, LayoutLMv3 is pre-trained with a word-patch alignment objective to learn cross-modal alignment by predicting whether the corresponding image patch of a text word is masked. The simple unified architecture and training objectives make LayoutLMv3 a general-purpose pre-trained model for both text-centric and image-centric Document AI tasks. Experimental results show that LayoutLMv3 achieves state-of-the-art performance not only in text-centric tasks, including form understanding, receipt understanding, and document visual question answering, but also in image-centric tasks such as document image classification and document layout analysis.*
|
||||
|
||||
Tips:
|
||||
|
||||
- In terms of data processing, LayoutLMv3 is identical to its predecessor [LayoutLMv2](layoutlmv2), except that:
|
||||
- images need to be resized and normalized with channels in regular RGB format. LayoutLMv2 on the other hand normalizes the images internally and expects the channels in BGR format.
|
||||
- text is tokenized using byte-pair encoding (BPE), as opposed to WordPiece.
|
||||
Due to these differences in data preprocessing, one can use [`LayoutLMv3Processor`] which internally combines a [`LayoutLMv3FeatureExtractor`] (for the image modality) and a [`LayoutLMv3Tokenizer`]/[`LayoutLMv3TokenizerFast`] (for the text modality) to prepare all data for the model.
|
||||
- Regarding usage of [`LayoutLMv3Processor`], we refer to the [usage guide](layoutlmv2#usage-LayoutLMv2Processor) of its predecessor.
|
||||
- Demo notebooks for LayoutLMv3 can be found [here](https://github.com/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/tree/master/LayoutLMv3).
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/layoutlmv3_architecture.png"
|
||||
alt="drawing" width="600"/>
|
||||
|
||||
<small> LayoutLMv3 architecture. Taken from the <a href="https://arxiv.org/abs/2204.08387">original paper</a>. </small>
|
||||
|
||||
This model was contributed by [nielsr](https://huggingface.co/nielsr). The original code can be found [here](https://github.com/microsoft/unilm/tree/master/layoutlmv3).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## LayoutLMv3Config
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] LayoutLMv3Config
|
||||
|
||||
## LayoutLMv3FeatureExtractor
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] LayoutLMv3FeatureExtractor
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
## LayoutLMv3Tokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] LayoutLMv3Tokenizer
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
- save_vocabulary
|
||||
|
||||
## LayoutLMv3TokenizerFast
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] LayoutLMv3TokenizerFast
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
## LayoutLMv3Processor
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] LayoutLMv3Processor
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
## LayoutLMv3Model
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] LayoutLMv3Model
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
## LayoutLMv3ForSequenceClassification
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] LayoutLMv3ForSequenceClassification
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
## LayoutLMv3ForTokenClassification
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] LayoutLMv3ForTokenClassification
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
## LayoutLMv3ForQuestionAnswering
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] LayoutLMv3ForQuestionAnswering
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
@ -44,8 +44,10 @@ Tips:
|
||||
- LED makes use of *global attention* by means of the `global_attention_mask` (see
|
||||
[`LongformerModel`]). For summarization, it is advised to put *global attention* only on the first
|
||||
`<s>` token. For question answering, it is advised to put *global attention* on all tokens of the question.
|
||||
- To fine-tune LED on all 16384, it is necessary to enable *gradient checkpointing* by executing
|
||||
`model.gradient_checkpointing_enable()`.
|
||||
- To fine-tune LED on all 16384, *gradient checkpointing* can be enabled in case training leads to out-of-memory (OOM)
|
||||
errors. This can be done by executing `model.gradient_checkpointing_enable()`.
|
||||
Moreover, the `use_cache=False`
|
||||
flag can be used to disable the caching mechanism to save memory.
|
||||
- A notebook showing how to evaluate LED, can be accessed [here](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/12INTTR6n64TzS4RrXZxMSXfrOd9Xzamo?usp=sharing).
|
||||
- A notebook showing how to fine-tune LED, can be accessed [here](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/12LjJazBl7Gam0XBPy_y0CTOJZeZ34c2v?usp=sharing).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
87
docs/source/en/model_doc/levit.mdx
Normal file
87
docs/source/en/model_doc/levit.mdx
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,87 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# LeViT
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
The LeViT model was proposed in [LeViT: Introducing Convolutions to Vision Transformers](https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.01136) by Ben Graham, Alaaeldin El-Nouby, Hugo Touvron, Pierre Stock, Armand Joulin, Hervé Jégou, Matthijs Douze. LeViT improves the [Vision Transformer (ViT)](vit) in performance and efficiency by a few architectural differences such as activation maps with decreasing resolutions in Transformers and the introduction of an attention bias to integrate positional information.
|
||||
|
||||
The abstract from the paper is the following:
|
||||
|
||||
*We design a family of image classification architectures that optimize the trade-off between accuracy
|
||||
and efficiency in a high-speed regime. Our work exploits recent findings in attention-based architectures,
|
||||
which are competitive on highly parallel processing hardware. We revisit principles from the extensive
|
||||
literature on convolutional neural networks to apply them to transformers, in particular activation maps
|
||||
with decreasing resolutions. We also introduce the attention bias, a new way to integrate positional information
|
||||
in vision transformers. As a result, we propose LeVIT: a hybrid neural network for fast inference image classification.
|
||||
We consider different measures of efficiency on different hardware platforms, so as to best reflect a wide range of
|
||||
application scenarios. Our extensive experiments empirically validate our technical choices and show they are suitable
|
||||
to most architectures. Overall, LeViT significantly outperforms existing convnets and vision transformers with respect
|
||||
to the speed/accuracy tradeoff. For example, at 80% ImageNet top-1 accuracy, LeViT is 5 times faster than EfficientNet on CPU. *
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/levit_architecture.png"
|
||||
alt="drawing" width="600"/>
|
||||
|
||||
<small> LeViT Architecture. Taken from the <a href="https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.01136">original paper</a>.</small>
|
||||
|
||||
Tips:
|
||||
|
||||
- Compared to ViT, LeViT models use an additional distillation head to effectively learn from a teacher (which, in the LeViT paper, is a ResNet like-model). The distillation head is learned through backpropagation under supervision of a ResNet like-model. They also draw inspiration from convolution neural networks to use activation maps with decreasing resolutions to increase the efficiency.
|
||||
- There are 2 ways to fine-tune distilled models, either (1) in a classic way, by only placing a prediction head on top
|
||||
of the final hidden state and not using the distillation head, or (2) by placing both a prediction head and distillation
|
||||
head on top of the final hidden state. In that case, the prediction head is trained using regular cross-entropy between
|
||||
the prediction of the head and the ground-truth label, while the distillation prediction head is trained using hard distillation
|
||||
(cross-entropy between the prediction of the distillation head and the label predicted by the teacher). At inference time,
|
||||
one takes the average prediction between both heads as final prediction. (2) is also called "fine-tuning with distillation",
|
||||
because one relies on a teacher that has already been fine-tuned on the downstream dataset. In terms of models, (1) corresponds
|
||||
to [`LevitForImageClassification`] and (2) corresponds to [`LevitForImageClassificationWithTeacher`].
|
||||
- All released checkpoints were pre-trained and fine-tuned on [ImageNet-1k](https://huggingface.co/datasets/imagenet-1k)
|
||||
(also referred to as ILSVRC 2012, a collection of 1.3 million images and 1,000 classes). only. No external data was used. This is in
|
||||
contrast with the original ViT model, which used external data like the JFT-300M dataset/Imagenet-21k for
|
||||
pre-training.
|
||||
- The authors of LeViT released 5 trained LeViT models, which you can directly plug into [`LevitModel`] or [`LevitForImageClassification`].
|
||||
Techniques like data augmentation, optimization, and regularization were used in order to simulate training on a much larger dataset
|
||||
(while only using ImageNet-1k for pre-training). The 5 variants available are (all trained on images of size 224x224):
|
||||
*facebook/levit-128S*, *facebook/levit-128*, *facebook/levit-192*, *facebook/levit-256* and
|
||||
*facebook/levit-384*. Note that one should use [`LevitFeatureExtractor`] in order to
|
||||
prepare images for the model.
|
||||
- [`LevitForImageClassificationWithTeacher`] currently supports only inference and not training or fine-tuning.
|
||||
- You can check out demo notebooks regarding inference as well as fine-tuning on custom data [here](https://github.com/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/tree/master/VisionTransformer)
|
||||
(you can just replace [`ViTFeatureExtractor`] by [`LevitFeatureExtractor`] and [`ViTForImageClassification`] by [`LevitForImageClassification`] or [`LevitForImageClassificationWithTeacher`]).
|
||||
|
||||
This model was contributed by [anugunj](https://huggingface.co/anugunj). The original code can be found [here](https://github.com/facebookresearch/LeViT).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## LevitConfig
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] LevitConfig
|
||||
|
||||
## LevitFeatureExtractor
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] LevitFeatureExtractor
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
## LevitModel
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] LevitModel
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
## LevitForImageClassification
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] LevitForImageClassification
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
## LevitForImageClassificationWithTeacher
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] LevitForImageClassificationWithTeacher
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
121
docs/source/en/model_doc/longt5.mdx
Normal file
121
docs/source/en/model_doc/longt5.mdx
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,121 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# LongT5
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
The LongT5 model was proposed in [LongT5: Efficient Text-To-Text Transformer for Long Sequences](https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.07916)
|
||||
by Mandy Guo, Joshua Ainslie, David Uthus, Santiago Ontanon, Jianmo Ni, Yun-Hsuan Sung and Yinfei Yang. It's an
|
||||
encoder-decoder transformer pre-trained in a text-to-text denoising generative setting. LongT5 model is an extension of
|
||||
T5 model, and it enables using one of the two different efficient attention mechanisms - (1) Local attention, or (2)
|
||||
Transient-Global attention.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
The abstract from the paper is the following:
|
||||
|
||||
*Recent work has shown that either (1) increasing the input length or (2) increasing model size can improve the
|
||||
performance of Transformer-based neural models. In this paper, we present a new model, called LongT5, with which we
|
||||
explore the effects of scaling both the input length and model size at the same time. Specifically, we integrated
|
||||
attention ideas from long-input transformers (ETC), and adopted pre-training strategies from summarization pre-training
|
||||
(PEGASUS) into the scalable T5 architecture. The result is a new attention mechanism we call {\em Transient Global}
|
||||
(TGlobal), which mimics ETC's local/global attention mechanism, but without requiring additional side-inputs. We are
|
||||
able to achieve state-of-the-art results on several summarization tasks and outperform the original T5 models on
|
||||
question answering tasks.*
|
||||
|
||||
Tips:
|
||||
|
||||
- [`LongT5ForConditionalGeneration`] is an extension of [`T5ForConditionalGeneration`] exchanging the traditional
|
||||
encoder *self-attention* layer with efficient either *local* attention or *transient-global* (*tglobal*) attention.
|
||||
- Unlike the T5 model, LongT5 does not use a task prefix. Furthermore, it uses a different pre-training objective
|
||||
inspired by the pre-training of `[PegasusForConditionalGeneration]`.
|
||||
- LongT5 model is designed to work efficiently and very well on long-range *sequence-to-sequence* tasks where the
|
||||
input sequence exceeds commonly used 512 tokens. It is capable of handling input sequences of a length up to 16,384 tokens.
|
||||
- For *Local Attention*, the sparse sliding-window local attention operation allows a given token to attend only `r`
|
||||
tokens to the left and right of it (with `r=127` by default). *Local Attention* does not introduce any new parameters
|
||||
to the model. The complexity of the mechanism is linear in input sequence length `l`: `O(l*r)`.
|
||||
- *Transient Global Attention* is an extension of the *Local Attention*. It, furthermore, allows each input token to
|
||||
interact with all other tokens in the layer. This is achieved via splitting an input sequence into blocks of a fixed
|
||||
length `k` (with a default `k=16`). Then, a global token for such a block is obtained via summing and normalizing the embeddings of every token
|
||||
in the block. Thanks to this, the attention allows each token to attend to both nearby tokens like in Local attention, and
|
||||
also every global token like in the case of standard global attention (*transient* represents the fact the global tokens
|
||||
are constructed dynamically within each attention operation). As a consequence, *TGlobal* attention introduces
|
||||
a few new parameters -- global relative position biases and a layer normalization for global token's embedding.
|
||||
The complexity of this mechanism is `O(l(r + l/k))`.
|
||||
- An example showing how to evaluate a fine-tuned LongT5 model on the [pubmed dataset](https://huggingface.co/datasets/scientific_papers) is below.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> import evaluate
|
||||
>>> from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer, LongT5ForConditionalGeneration
|
||||
|
||||
>>> dataset = load_dataset("scientific_papers", "pubmed", split="validation")
|
||||
>>> model = (
|
||||
... LongT5ForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained("Stancld/longt5-tglobal-large-16384-pubmed-3k_steps")
|
||||
... .to("cuda")
|
||||
... .half()
|
||||
... )
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("Stancld/longt5-tglobal-large-16384-pubmed-3k_steps")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
>>> def generate_answers(batch):
|
||||
... inputs_dict = tokenizer(
|
||||
... batch["article"], max_length=16384, padding="max_length", truncation=True, return_tensors="pt"
|
||||
... )
|
||||
... input_ids = inputs_dict.input_ids.to("cuda")
|
||||
... attention_mask = inputs_dict.attention_mask.to("cuda")
|
||||
... output_ids = model.generate(input_ids, attention_mask=attention_mask, max_length=512, num_beams=2)
|
||||
... batch["predicted_abstract"] = tokenizer.batch_decode(output_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)
|
||||
... return batch
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
>>> result = dataset.map(generate_answer, batched=True, batch_size=2)
|
||||
>>> rouge = evaluate.load("rouge")
|
||||
>>> rouge.compute(predictions=result["predicted_abstract"], references=result["abstract"])
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This model was contributed by [stancld](https://huggingface.co/stancld).
|
||||
The original code can be found [here](https://github.com/google-research/longt5).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## LongT5Config
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] LongT5Config
|
||||
|
||||
## LongT5Model
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] LongT5Model
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
## LongT5ForConditionalGeneration
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] LongT5ForConditionalGeneration
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
## LongT5EncoderModel
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] LongT5EncoderModel
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
## FlaxLongT5Model
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] FlaxLongT5Model
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
- encode
|
||||
- decode
|
||||
|
||||
## FlaxLongT5ForConditionalGeneration
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] FlaxLongT5ForConditionalGeneration
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
- encode
|
||||
- decode
|
||||
62
docs/source/en/model_doc/mctct.mdx
Normal file
62
docs/source/en/model_doc/mctct.mdx
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,62 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# M-CTC-T
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
The M-CTC-T model was proposed in [Pseudo-Labeling For Massively Multilingual Speech Recognition](https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.00161) by Loren Lugosch, Tatiana Likhomanenko, Gabriel Synnaeve, and Ronan Collobert. The model is a 1B-param transformer encoder, with a CTC head over 8065 character labels and a language identification head over 60 language ID labels. It is trained on Common Voice (version 6.1, December 2020 release) and VoxPopuli. After training on Common Voice and VoxPopuli, the model is trained on Common Voice only. The labels are unnormalized character-level transcripts (punctuation and capitalization are not removed). The model takes as input Mel filterbank features from a 16Khz audio signal.
|
||||
|
||||
The abstract from the paper is the following:
|
||||
|
||||
*Semi-supervised learning through pseudo-labeling has become a staple of state-of-the-art monolingual
|
||||
speech recognition systems. In this work, we extend pseudo-labeling to massively multilingual speech
|
||||
recognition with 60 languages. We propose a simple pseudo-labeling recipe that works well even
|
||||
with low-resource languages: train a supervised multilingual model, fine-tune it with semi-supervised
|
||||
learning on a target language, generate pseudo-labels for that language, and train a final model using
|
||||
pseudo-labels for all languages, either from scratch or by fine-tuning. Experiments on the labeled
|
||||
Common Voice and unlabeled VoxPopuli datasets show that our recipe can yield a model with better
|
||||
performance for many languages that also transfers well to LibriSpeech.*
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
This model was contributed by [cwkeam](https://huggingface.co/cwkeam). The original code can be found [here](https://github.com/flashlight/wav2letter/tree/main/recipes/mling_pl).
|
||||
|
||||
## MCTCTConfig
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] MCTCTConfig
|
||||
|
||||
## MCTCTFeatureExtractor
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] MCTCTFeatureExtractor
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
## MCTCTProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] MCTCTProcessor
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
- from_pretrained
|
||||
- save_pretrained
|
||||
- batch_decode
|
||||
- decode
|
||||
- as_target_processor
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## MCTCTModel
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] MCTCTModel
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
## MCTCTForCTC
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] MCTCTForCTC
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
55
docs/source/en/model_doc/mobilevit.mdx
Normal file
55
docs/source/en/model_doc/mobilevit.mdx
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,55 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# MobileViT
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
The MobileViT model was proposed in [MobileViT: Light-weight, General-purpose, and Mobile-friendly Vision Transformer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.02178) by Sachin Mehta and Mohammad Rastegari. MobileViT introduces a new layer that replaces local processing in convolutions with global processing using transformers.
|
||||
|
||||
The abstract from the paper is the following:
|
||||
|
||||
*Light-weight convolutional neural networks (CNNs) are the de-facto for mobile vision tasks. Their spatial inductive biases allow them to learn representations with fewer parameters across different vision tasks. However, these networks are spatially local. To learn global representations, self-attention-based vision trans-formers (ViTs) have been adopted. Unlike CNNs, ViTs are heavy-weight. In this paper, we ask the following question: is it possible to combine the strengths of CNNs and ViTs to build a light-weight and low latency network for mobile vision tasks? Towards this end, we introduce MobileViT, a light-weight and general-purpose vision transformer for mobile devices. MobileViT presents a different perspective for the global processing of information with transformers, i.e., transformers as convolutions. Our results show that MobileViT significantly outperforms CNN- and ViT-based networks across different tasks and datasets. On the ImageNet-1k dataset, MobileViT achieves top-1 accuracy of 78.4% with about 6 million parameters, which is 3.2% and 6.2% more accurate than MobileNetv3 (CNN-based) and DeIT (ViT-based) for a similar number of parameters. On the MS-COCO object detection task, MobileViT is 5.7% more accurate than MobileNetv3 for a similar number of parameters.*
|
||||
|
||||
Tips:
|
||||
|
||||
- MobileViT is more like a CNN than a Transformer model. It does not work on sequence data but on batches of images. Unlike ViT, there are no embeddings. The backbone model outputs a feature map.
|
||||
- One can use [`MobileViTFeatureExtractor`] to prepare images for the model. Note that if you do your own preprocessing, the pretrained checkpoints expect images to be in BGR pixel order (not RGB).
|
||||
- The available image classification checkpoints are pre-trained on [ImageNet-1k](https://huggingface.co/datasets/imagenet-1k) (also referred to as ILSVRC 2012, a collection of 1.3 million images and 1,000 classes).
|
||||
- The segmentation model uses a [DeepLabV3](https://arxiv.org/abs/1706.05587) head. The available semantic segmentation checkpoints are pre-trained on [PASCAL VOC](http://host.robots.ox.ac.uk/pascal/VOC/).
|
||||
|
||||
This model was contributed by [matthijs](https://huggingface.co/Matthijs). The original code and weights can be found [here](https://github.com/apple/ml-cvnets).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## MobileViTConfig
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] MobileViTConfig
|
||||
|
||||
## MobileViTFeatureExtractor
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] MobileViTFeatureExtractor
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
## MobileViTModel
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] MobileViTModel
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
## MobileViTForImageClassification
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] MobileViTForImageClassification
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
## MobileViTForSemanticSegmentation
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] MobileViTForSemanticSegmentation
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
@ -96,3 +96,7 @@ See [`T5TokenizerFast`] for all details.
|
||||
## FlaxMT5ForConditionalGeneration
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] FlaxMT5ForConditionalGeneration
|
||||
|
||||
## FlaxMT5EncoderModel
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] FlaxMT5EncoderModel
|
||||
|
||||
138
docs/source/en/model_doc/mvp.mdx
Normal file
138
docs/source/en/model_doc/mvp.mdx
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,138 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# MVP
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
The MVP model was proposed in [MVP: Multi-task Supervised Pre-training for Natural Language Generation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.12131) by Tianyi Tang, Junyi Li, Wayne Xin Zhao and Ji-Rong Wen.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
According to the abstract,
|
||||
|
||||
- MVP follows a standard Transformer encoder-decoder architecture.
|
||||
- MVP is supervised pre-trained using labeled datasets.
|
||||
- MVP also has task-specific soft prompts to stimulate the model's capacity in performing a certain task.
|
||||
- MVP is specially designed for natural language generation and can be adapted to a wide range of generation tasks, including but not limited to summarization, data-to-text generation, open-ended dialogue system, story generation, question answering, question generation, task-oriented dialogue system, commonsense generation, paraphrase generation, text style transfer, and text simplification. Our model can also be adapted to natural language understanding tasks such as sequence classification and (extractive) question answering.
|
||||
|
||||
Tips:
|
||||
- We have released a series of models [here](https://huggingface.co/models?filter=mvp), including MVP, MVP with task-specific prompts, and multi-task pre-trained variants.
|
||||
- If you want to use a model without prompts (standard Transformer), you can load it through `MvpForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained('RUCAIBox/mvp')`.
|
||||
- If you want to use a model with task-specific prompts, such as summarization, you can load it through `MvpForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained('RUCAIBox/mvp-summarization')`.
|
||||
- Our model supports lightweight prompt tuning following [Prefix-tuning](https://arxiv.org/abs/2101.00190) with method `set_lightweight_tuning()`.
|
||||
|
||||
This model was contributed by [Tianyi Tang](https://huggingface.co/StevenTang). The detailed information and instructions can be found [here](https://github.com/RUCAIBox/MVP).
|
||||
|
||||
## Examples
|
||||
For summarization, it is an example to use MVP and MVP with summarization-specific prompts.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import MvpTokenizer, MvpForConditionalGeneration
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = MvpTokenizer.from_pretrained("RUCAIBox/mvp")
|
||||
>>> model = MvpForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained("RUCAIBox/mvp")
|
||||
>>> model_with_prompt = MvpForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained("RUCAIBox/mvp-summarization")
|
||||
|
||||
>>> inputs = tokenizer(
|
||||
... "Summarize: You may want to stick it to your boss and leave your job, but don't do it if these are your reasons.",
|
||||
... return_tensors="pt",
|
||||
... )
|
||||
>>> generated_ids = model.generate(**inputs)
|
||||
>>> tokenizer.batch_decode(generated_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)
|
||||
["Why You Shouldn't Quit Your Job"]
|
||||
|
||||
>>> generated_ids = model_with_prompt.generate(**inputs)
|
||||
>>> tokenizer.batch_decode(generated_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)
|
||||
["Don't do it if these are your reasons"]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For data-to-text generation, it is an example to use MVP and multi-task pre-trained variants.
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import MvpTokenizerFast, MvpForConditionalGeneration
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = MvpTokenizerFast.from_pretrained("RUCAIBox/mvp")
|
||||
>>> model = MvpForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained("RUCAIBox/mvp")
|
||||
>>> model_with_mtl = MvpForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained("RUCAIBox/mtl-data-to-text")
|
||||
|
||||
>>> inputs = tokenizer(
|
||||
... "Describe the following data: Iron Man | instance of | Superhero [SEP] Stan Lee | creator | Iron Man",
|
||||
... return_tensors="pt",
|
||||
... )
|
||||
>>> generated_ids = model.generate(**inputs)
|
||||
>>> tokenizer.batch_decode(generated_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)
|
||||
['Stan Lee created the character of Iron Man, a fictional superhero appearing in American comic']
|
||||
|
||||
>>> generated_ids = model_with_mtl.generate(**inputs)
|
||||
>>> tokenizer.batch_decode(generated_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)
|
||||
['Iron Man is a fictional superhero appearing in American comic books published by Marvel Comics.']
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For lightweight tuning, *i.e.*, fixing the model and only tuning prompts, you can load MVP with randomly initialized prompts or with task-specific prompts. Our code also supports Prefix-tuning with BART following the [original paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2101.00190).
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import MvpForConditionalGeneration
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = MvpForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained("RUCAIBox/mvp", use_prompt=True)
|
||||
>>> # the number of trainable parameters (full tuning)
|
||||
>>> sum(p.numel() for p in model.parameters() if p.requires_grad)
|
||||
468116832
|
||||
|
||||
>>> # lightweight tuning with randomly initialized prompts
|
||||
>>> model.set_lightweight_tuning()
|
||||
>>> # the number of trainable parameters (lightweight tuning)
|
||||
>>> sum(p.numel() for p in model.parameters() if p.requires_grad)
|
||||
61823328
|
||||
|
||||
>>> # lightweight tuning with task-specific prompts
|
||||
>>> model = MvpForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained("RUCAIBox/mtl-data-to-text")
|
||||
>>> model.set_lightweight_tuning()
|
||||
>>> # original lightweight Prefix-tuning
|
||||
>>> model = MvpForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained("facebook/bart-large", use_prompt=True)
|
||||
>>> model.set_lightweight_tuning()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## MvpConfig
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] MvpConfig
|
||||
|
||||
## MvpTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] MvpTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
## MvpTokenizerFast
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] MvpTokenizerFast
|
||||
|
||||
## MvpModel
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] MvpModel
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
## MvpForConditionalGeneration
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] MvpForConditionalGeneration
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
## MvpForSequenceClassification
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] MvpForSequenceClassification
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
## MvpForQuestionAnswering
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] MvpForQuestionAnswering
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
## MvpForCausalLM
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] MvpForCausalLM
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
76
docs/source/en/model_doc/nezha.mdx
Normal file
76
docs/source/en/model_doc/nezha.mdx
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,76 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Nezha
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
The Nezha model was proposed in [NEZHA: Neural Contextualized Representation for Chinese Language Understanding](https://arxiv.org/abs/1909.00204) by Junqiu Wei et al.
|
||||
|
||||
The abstract from the paper is the following:
|
||||
|
||||
*The pre-trained language models have achieved great successes in various natural language understanding (NLU) tasks
|
||||
due to its capacity to capture the deep contextualized information in text by pre-training on large-scale corpora.
|
||||
In this technical report, we present our practice of pre-training language models named NEZHA (NEural contextualiZed
|
||||
representation for CHinese lAnguage understanding) on Chinese corpora and finetuning for the Chinese NLU tasks.
|
||||
The current version of NEZHA is based on BERT with a collection of proven improvements, which include Functional
|
||||
Relative Positional Encoding as an effective positional encoding scheme, Whole Word Masking strategy,
|
||||
Mixed Precision Training and the LAMB Optimizer in training the models. The experimental results show that NEZHA
|
||||
achieves the state-of-the-art performances when finetuned on several representative Chinese tasks, including
|
||||
named entity recognition (People's Daily NER), sentence matching (LCQMC), Chinese sentiment classification (ChnSenti)
|
||||
and natural language inference (XNLI).*
|
||||
|
||||
This model was contributed by [sijunhe](https://huggingface.co/sijunhe). The original code can be found [here](https://github.com/huawei-noah/Pretrained-Language-Model/tree/master/NEZHA-PyTorch).
|
||||
|
||||
## NezhaConfig
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] NezhaConfig
|
||||
|
||||
## NezhaModel
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] NezhaModel
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
## NezhaForPreTraining
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] NezhaForPreTraining
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
## NezhaForMaskedLM
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] NezhaForMaskedLM
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
## NezhaForNextSentencePrediction
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] NezhaForNextSentencePrediction
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
## NezhaForSequenceClassification
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] NezhaForSequenceClassification
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
## NezhaForMultipleChoice
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] NezhaForMultipleChoice
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
## NezhaForTokenClassification
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] NezhaForTokenClassification
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
## NezhaForQuestionAnswering
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] NezhaForQuestionAnswering
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
99
docs/source/en/model_doc/nllb.mdx
Normal file
99
docs/source/en/model_doc/nllb.mdx
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,99 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2020 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# NLLB
|
||||
|
||||
**DISCLAIMER:** If you see something strange, file a [Github Issue](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/issues/new?assignees=&labels=bug&template=bug-report.yml) and assign
|
||||
@LysandreJik
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview of NLLB
|
||||
|
||||
The NLLB model was presented in [No Language Left Behind: Scaling Human-Centered Machine Translation](https://arxiv.org/abs/2207.04672) by Marta R. Costa-jussà, James Cross, Onur Çelebi,
|
||||
Maha Elbayad, Kenneth Heafield, Kevin Heffernan, Elahe Kalbassi, Janice Lam, Daniel Licht, Jean Maillard, Anna Sun, Skyler Wang, Guillaume Wenzek, Al Youngblood, Bapi Akula,
|
||||
Loic Barrault, Gabriel Mejia Gonzalez, Prangthip Hansanti, John Hoffman, Semarley Jarrett, Kaushik Ram Sadagopan, Dirk Rowe, Shannon Spruit, Chau Tran, Pierre Andrews,
|
||||
Necip Fazil Ayan, Shruti Bhosale, Sergey Edunov, Angela Fan, Cynthia Gao, Vedanuj Goswami, Francisco Guzmán, Philipp Koehn, Alexandre Mourachko, Christophe Ropers,
|
||||
Safiyyah Saleem, Holger Schwenk, and Jeff Wang.
|
||||
|
||||
The abstract of the paper is the following:
|
||||
|
||||
*Driven by the goal of eradicating language barriers on a global scale, machine translation has solidified itself as a key focus of artificial intelligence research today.
|
||||
However, such efforts have coalesced around a small subset of languages, leaving behind the vast majority of mostly low-resource languages. What does it take to break the
|
||||
200 language barrier while ensuring safe, high quality results, all while keeping ethical considerations in mind? In No Language Left Behind, we took on this challenge by
|
||||
first contextualizing the need for low-resource language translation support through exploratory interviews with native speakers. Then, we created datasets and models aimed
|
||||
at narrowing the performance gap between low and high-resource languages. More specifically, we developed a conditional compute model based on Sparsely Gated Mixture of
|
||||
Experts that is trained on data obtained with novel and effective data mining techniques tailored for low-resource languages. We propose multiple architectural and training
|
||||
improvements to counteract overfitting while training on thousands of tasks. Critically, we evaluated the performance of over 40,000 different translation directions using
|
||||
a human-translated benchmark, Flores-200, and combined human evaluation with a novel toxicity benchmark covering all languages in Flores-200 to assess translation safety.
|
||||
Our model achieves an improvement of 44% BLEU relative to the previous state-of-the-art, laying important groundwork towards realizing a universal translation system.*
|
||||
|
||||
This implementation contains the dense models available on release. Let us know via a GitHub issue if you would like to see the MoE models as well.
|
||||
|
||||
This model was contributed by [Lysandre](https://huggingface.co/lysandre). The authors' code can be found [here](https://github.com/facebookresearch/fairseq/tree/nllb).
|
||||
|
||||
## Generating with NLLB
|
||||
|
||||
While generating the target text set the `forced_bos_token_id` to the target language id. The following
|
||||
example shows how to translate English to French using the *facebook/nllb-200-distilled-600M* model.
|
||||
|
||||
Note that we're using the BCP-47 code for French `fra_Latn`. See [here](https://github.com/facebookresearch/flores/blob/main/flores200/README.md#languages-in-flores-200)
|
||||
for the list of all BCP-47 in the Flores 200 dataset.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM, AutoTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("facebook/nllb-200-distilled-600M")
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained("facebook/nllb-200-distilled-600M")
|
||||
|
||||
>>> article = "UN Chief says there is no military solution in Syria"
|
||||
>>> inputs = tokenizer(article, return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
|
||||
>>> translated_tokens = model.generate(
|
||||
... **inputs, forced_bos_token_id=tokenizer.lang_code_to_id["fra_Latn"], max_length=30
|
||||
... )
|
||||
>>> tokenizer.batch_decode(translated_tokens, skip_special_tokens=True)[0]
|
||||
Le chef de l'ONU dit qu'il n'y a pas de solution militaire en Syrie
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Generating from any other language than English
|
||||
|
||||
English (`eng_Latn`) is set as the default language from which to translate. In order to specify that you'd like to translate from a different language,
|
||||
you should specify the BCP-47 code in the `src_lang` keyword argument of the tokenizer initialization.
|
||||
|
||||
See example below for a translation from romanian to german:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM, AutoTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(
|
||||
... "facebook/nllb-200-distilled-600M", use_auth_token=True, src_lang="ron_Latn"
|
||||
... )
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained("facebook/nllb-200-distilled-600M", use_auth_token=True)
|
||||
|
||||
>>> article = "Şeful ONU spune că nu există o soluţie militară în Siria"
|
||||
>>> inputs = tokenizer(article, return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
|
||||
>>> translated_tokens = model.generate(
|
||||
... **inputs, forced_bos_token_id=tokenizer.lang_code_to_id["deu_Latn"], max_length=30
|
||||
... )
|
||||
>>> tokenizer.batch_decode(translated_tokens, skip_special_tokens=True)[0]
|
||||
UN-Chef sagt, es gibt keine militärische Lösung in Syrien
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## NllbTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] NllbTokenizer
|
||||
- as_target_tokenizer
|
||||
- build_inputs_with_special_tokens
|
||||
|
||||
## NllbTokenizerFast
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] NllbTokenizerFast
|
||||
@ -39,9 +39,33 @@ The original code can be found [here](https://github.com/facebookresearch/metase
|
||||
[[autodoc]] OPTModel
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## OPTForCausalLM
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] OPTForCausalLM
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
## TFOPTModel
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TFOPTModel
|
||||
- call
|
||||
|
||||
## TFOPTForCausalLM
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TFOPTForCausalLM
|
||||
- call
|
||||
|
||||
## OPTForSequenceClassification
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] OPTForSequenceClassification
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
## FlaxOPTModel
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] FlaxOPTModel
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## FlaxOPTForCausalLM
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] FlaxOPTForCausalLM
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
@ -27,7 +27,8 @@ Tips:
|
||||
- One can use [`AutoFeatureExtractor`] to prepare images for the model.
|
||||
- The huge 10B model from [Self-supervised Pretraining of Visual Features in the Wild](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.01988), trained on one billion Instagram images, is available on the [hub](https://huggingface.co/facebook/regnet-y-10b-seer)
|
||||
|
||||
This model was contributed by [Francesco](https://huggingface.co/Francesco).
|
||||
This model was contributed by [Francesco](https://huggingface.co/Francesco). The TensorFlow version of the model
|
||||
was contributed by [sayakpaul](https://huggingface.com/sayakpaul) and [ariG23498](https://huggingface.com/ariG23498).
|
||||
The original code can be found [here](https://github.com/facebookresearch/pycls).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -45,4 +46,15 @@ The original code can be found [here](https://github.com/facebookresearch/pycls)
|
||||
## RegNetForImageClassification
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] RegNetForImageClassification
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
## TFRegNetModel
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TFRegNetModel
|
||||
- call
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## TFRegNetForImageClassification
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TFRegNetForImageClassification
|
||||
- call
|
||||
@ -31,7 +31,7 @@ The figure below illustrates the architecture of ResNet. Taken from the [origina
|
||||
|
||||
<img width="600" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/resnet_architecture.png"/>
|
||||
|
||||
This model was contributed by [Francesco](https://huggingface.co/Francesco). The original code can be found [here](https://github.com/KaimingHe/deep-residual-networks).
|
||||
This model was contributed by [Francesco](https://huggingface.co/Francesco). The TensorFlow version of this model was added by [amyeroberts](https://huggingface.co/amyeroberts). The original code can be found [here](https://github.com/KaimingHe/deep-residual-networks).
|
||||
|
||||
## ResNetConfig
|
||||
|
||||
@ -47,4 +47,16 @@ This model was contributed by [Francesco](https://huggingface.co/Francesco). The
|
||||
## ResNetForImageClassification
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] ResNetForImageClassification
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## TFResNetModel
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TFResNetModel
|
||||
- call
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## TFResNetForImageClassification
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TFResNetForImageClassification
|
||||
- call
|
||||
|
||||
@ -37,7 +37,7 @@ predicted token ids.
|
||||
|
||||
The feature extractor depends on `torchaudio` and the tokenizer depends on `sentencepiece` so be sure to
|
||||
install those packages before running the examples. You could either install those as extra speech dependencies with
|
||||
`pip install transformers"[speech, sentencepiece]"` or install the packages seperately with `pip install torchaudio sentencepiece`. Also `torchaudio` requires the development version of the [libsndfile](http://www.mega-nerd.com/libsndfile/) package which can be installed via a system package manager. On Ubuntu it can
|
||||
`pip install transformers"[speech, sentencepiece]"` or install the packages separately with `pip install torchaudio sentencepiece`. Also `torchaudio` requires the development version of the [libsndfile](http://www.mega-nerd.com/libsndfile/) package which can be installed via a system package manager. On Ubuntu it can
|
||||
be installed as follows: `apt install libsndfile1-dev`
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -72,3 +72,8 @@ This model was contributed by [yuvalkirstain](https://huggingface.co/yuvalkirsta
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] SplinterForQuestionAnswering
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
## SplinterForPreTraining
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] SplinterForPreTraining
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
@ -14,22 +14,22 @@ specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
The Swin Transformer was proposed in [Swin Transformer: Hierarchical Vision Transformer using Shifted Windows](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.14030)
|
||||
by Ze Liu, Yutong Lin, Yue Cao, Han Hu, Yixuan Wei, Zheng Zhang, Stephen Lin, Baining Guo.
|
||||
The Swin Transformer was proposed in [Swin Transformer: Hierarchical Vision Transformer using Shifted Windows](https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.14030)
|
||||
by Ze Liu, Yutong Lin, Yue Cao, Han Hu, Yixuan Wei, Zheng Zhang, Stephen Lin, Baining Guo.
|
||||
|
||||
The abstract from the paper is the following:
|
||||
|
||||
*This paper presents a new vision Transformer, called Swin Transformer, that capably serves as a general-purpose backbone
|
||||
for computer vision. Challenges in adapting Transformer from language to vision arise from differences between the two domains,
|
||||
such as large variations in the scale of visual entities and the high resolution of pixels in images compared to words in text.
|
||||
To address these differences, we propose a hierarchical Transformer whose representation is computed with \bold{S}hifted
|
||||
\bold{win}dows. The shifted windowing scheme brings greater efficiency by limiting self-attention computation to non-overlapping
|
||||
local windows while also allowing for cross-window connection. This hierarchical architecture has the flexibility to model at
|
||||
various scales and has linear computational complexity with respect to image size. These qualities of Swin Transformer make it
|
||||
compatible with a broad range of vision tasks, including image classification (87.3 top-1 accuracy on ImageNet-1K) and dense
|
||||
prediction tasks such as object detection (58.7 box AP and 51.1 mask AP on COCO test-dev) and semantic segmentation
|
||||
(53.5 mIoU on ADE20K val). Its performance surpasses the previous state-of-the-art by a large margin of +2.7 box AP and
|
||||
+2.6 mask AP on COCO, and +3.2 mIoU on ADE20K, demonstrating the potential of Transformer-based models as vision backbones.
|
||||
*This paper presents a new vision Transformer, called Swin Transformer, that capably serves as a general-purpose backbone
|
||||
for computer vision. Challenges in adapting Transformer from language to vision arise from differences between the two domains,
|
||||
such as large variations in the scale of visual entities and the high resolution of pixels in images compared to words in text.
|
||||
To address these differences, we propose a hierarchical Transformer whose representation is computed with \bold{S}hifted
|
||||
\bold{win}dows. The shifted windowing scheme brings greater efficiency by limiting self-attention computation to non-overlapping
|
||||
local windows while also allowing for cross-window connection. This hierarchical architecture has the flexibility to model at
|
||||
various scales and has linear computational complexity with respect to image size. These qualities of Swin Transformer make it
|
||||
compatible with a broad range of vision tasks, including image classification (87.3 top-1 accuracy on ImageNet-1K) and dense
|
||||
prediction tasks such as object detection (58.7 box AP and 51.1 mask AP on COCO test-dev) and semantic segmentation
|
||||
(53.5 mIoU on ADE20K val). Its performance surpasses the previous state-of-the-art by a large margin of +2.7 box AP and
|
||||
+2.6 mask AP on COCO, and +3.2 mIoU on ADE20K, demonstrating the potential of Transformer-based models as vision backbones.
|
||||
The hierarchical design and the shifted window approach also prove beneficial for all-MLP architectures.*
|
||||
|
||||
Tips:
|
||||
@ -38,11 +38,11 @@ Tips:
|
||||
- Swin can be used as a *backbone*. When `output_hidden_states = True`, it will output both `hidden_states` and `reshaped_hidden_states`. The `reshaped_hidden_states` have a shape of `(batch, num_channels, height, width)` rather than `(batch_size, sequence_length, num_channels)`.
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/swin_transformer_architecture.png"
|
||||
alt="drawing" width="600"/>
|
||||
alt="drawing" width="600"/>
|
||||
|
||||
<small> Swin Transformer architecture. Taken from the <a href="https://arxiv.org/abs/2102.03334">original paper</a>.</small>
|
||||
|
||||
This model was contributed by [novice03](https://huggingface.co/novice03>). The original code can be found [here](https://github.com/microsoft/Swin-Transformer).
|
||||
This model was contributed by [novice03](https://huggingface.co/novice03>). The Tensorflow version of this model was contributed by [amyeroberts](https://huggingface.co/amyeroberts). The original code can be found [here](https://github.com/microsoft/Swin-Transformer).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## SwinConfig
|
||||
@ -63,4 +63,19 @@ This model was contributed by [novice03](https://huggingface.co/novice03>). The
|
||||
## SwinForImageClassification
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] transformers.SwinForImageClassification
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
## TFSwinModel
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TFSwinModel
|
||||
- call
|
||||
|
||||
## TFSwinForMaskedImageModeling
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TFSwinForMaskedImageModeling
|
||||
- call
|
||||
|
||||
## TFSwinForImageClassification
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] transformers.TFSwinForImageClassification
|
||||
- call
|
||||
|
||||
@ -371,3 +371,8 @@ T5 is supported by several example scripts, both for pre-training and fine-tunin
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
- encode
|
||||
- decode
|
||||
|
||||
## FlaxT5EncoderModel
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] FlaxT5EncoderModel
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
49
docs/source/en/model_doc/trajectory_transformer.mdx
Normal file
49
docs/source/en/model_doc/trajectory_transformer.mdx
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,49 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Trajectory Transformer
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
The Trajectory Transformer model was proposed in [Offline Reinforcement Learning as One Big Sequence Modeling Problem](https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.02039) by Michael Janner, Qiyang Li, Sergey Levine.
|
||||
|
||||
The abstract from the paper is the following:
|
||||
|
||||
*Reinforcement learning (RL) is typically concerned with estimating stationary policies or single-step models,
|
||||
leveraging the Markov property to factorize problems in time. However, we can also view RL as a generic sequence
|
||||
modeling problem, with the goal being to produce a sequence of actions that leads to a sequence of high rewards.
|
||||
Viewed in this way, it is tempting to consider whether high-capacity sequence prediction models that work well
|
||||
in other domains, such as natural-language processing, can also provide effective solutions to the RL problem.
|
||||
To this end, we explore how RL can be tackled with the tools of sequence modeling, using a Transformer architecture
|
||||
to model distributions over trajectories and repurposing beam search as a planning algorithm. Framing RL as sequence
|
||||
modeling problem simplifies a range of design decisions, allowing us to dispense with many of the components common
|
||||
in offline RL algorithms. We demonstrate the flexibility of this approach across long-horizon dynamics prediction,
|
||||
imitation learning, goal-conditioned RL, and offline RL. Further, we show that this approach can be combined with
|
||||
existing model-free algorithms to yield a state-of-the-art planner in sparse-reward, long-horizon tasks.*
|
||||
|
||||
Tips:
|
||||
|
||||
This Transformer is used for deep reinforcement learning. To use it, you need to create sequences from
|
||||
actions, states and rewards from all previous timesteps. This model will treat all these elements together
|
||||
as one big sequence (a trajectory).
|
||||
|
||||
This model was contributed by [CarlCochet](https://huggingface.co/CarlCochet). The original code can be found [here](https://github.com/jannerm/trajectory-transformer).
|
||||
|
||||
## TrajectoryTransformerConfig
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TrajectoryTransformerConfig
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## TrajectoryTransformerModel
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TrajectoryTransformerModel
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
31
docs/source/en/model_doc/ul2.mdx
Normal file
31
docs/source/en/model_doc/ul2.mdx
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# UL2
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
The T5 model was presented in [Unifying Language Learning Paradigms](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2205.05131v1.pdf) by Yi Tay, Mostafa Dehghani, Vinh Q. Tran, Xavier Garcia, Dara Bahri, Tal Schuster, Huaixiu Steven Zheng, Neil Houlsby, Donald Metzler.
|
||||
|
||||
The abstract from the paper is the following:
|
||||
|
||||
*Existing pre-trained models are generally geared towards a particular class of problems. To date, there seems to be still no consensus on what the right architecture and pre-training setup should be. This paper presents a unified framework for pre-training models that are universally effective across datasets and setups. We begin by disentangling architectural archetypes with pre-training objectives -- two concepts that are commonly conflated. Next, we present a generalized and unified perspective for self-supervision in NLP and show how different pre-training objectives can be cast as one another and how interpolating between different objectives can be effective. We then propose Mixture-of-Denoisers (MoD), a pre-training objective that combines diverse pre-training paradigms together. We furthermore introduce a notion of mode switching, wherein downstream fine-tuning is associated with specific pre-training schemes. We conduct extensive ablative experiments to compare multiple pre-training objectives and find that our method pushes the Pareto-frontier by outperforming T5 and/or GPT-like models across multiple diverse setups. Finally, by scaling our model up to 20B parameters, we achieve SOTA performance on 50 well-established supervised NLP tasks ranging from language generation (with automated and human evaluation), language understanding, text classification, question answering, commonsense reasoning, long text reasoning, structured knowledge grounding and information retrieval. Our model also achieve strong results at in-context learning, outperforming 175B GPT-3 on zero-shot SuperGLUE and tripling the performance of T5-XXL on one-shot summarization.*
|
||||
|
||||
Tips:
|
||||
|
||||
- UL2 is an encoder-decoder model pre-trained on a mixture of denoising functions as well as fine-tuned on an array of downstream tasks.
|
||||
- UL2 has the same architecture as [T5v1.1](t5v1.1) but uses the Gated-SiLU activation function instead of Gated-GELU.
|
||||
- The authors release checkpoints of one architecture which can be seen [here](https://huggingface.co/google/ul2)
|
||||
|
||||
The original code can be found [here](https://github.com/google-research/google-research/tree/master/ul2).
|
||||
|
||||
This model was contributed by [DanielHesslow](https://huggingface.co/Seledorn).
|
||||
@ -51,8 +51,6 @@ found [here](https://github.com/microsoft/UniSpeech/tree/main/UniSpeech-SAT).
|
||||
|
||||
## UniSpeechSat specific outputs
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] models.unispeech_sat.modeling_unispeech_sat.UniSpeechSatBaseModelOutput
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] models.unispeech_sat.modeling_unispeech_sat.UniSpeechSatForPreTrainingOutput
|
||||
|
||||
## UniSpeechSatModel
|
||||
|
||||
@ -46,8 +46,6 @@ found [here](https://github.com/microsoft/UniSpeech/tree/main/UniSpeech).
|
||||
|
||||
## UniSpeech specific outputs
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] models.unispeech.modeling_unispeech.UniSpeechBaseModelOutput
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] models.unispeech.modeling_unispeech.UniSpeechForPreTrainingOutput
|
||||
|
||||
## UniSpeechModel
|
||||
|
||||
73
docs/source/en/model_doc/wav2vec2-conformer.mdx
Normal file
73
docs/source/en/model_doc/wav2vec2-conformer.mdx
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,73 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Wav2Vec2-Conformer
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
The Wav2Vec2-Conformer was added to an updated version of [fairseq S2T: Fast Speech-to-Text Modeling with fairseq](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.05171) by Changhan Wang, Yun Tang, Xutai Ma, Anne Wu, Sravya Popuri, Dmytro Okhonko, Juan Pino.
|
||||
|
||||
The official results of the model can be found in Table 3 and Table 4 of the paper.
|
||||
|
||||
The Wav2Vec2-Conformer weights were released by the Meta AI team within the [Fairseq library](https://github.com/pytorch/fairseq/blob/main/examples/wav2vec/README.md#pre-trained-models).
|
||||
|
||||
Tips:
|
||||
|
||||
- Wav2Vec2-Conformer follows the same architecture as Wav2Vec2, but replaces the *Attention*-block with a *Conformer*-block
|
||||
as introduced in [Conformer: Convolution-augmented Transformer for Speech Recognition](https://arxiv.org/abs/2005.08100).
|
||||
- For the same number of layers, Wav2Vec2-Conformer requires more parameters than Wav2Vec2, but also yields
|
||||
an improved word error rate.
|
||||
- Wav2Vec2-Conformer uses the same tokenizer and feature extractor as Wav2Vec2.
|
||||
- Wav2Vec2-Conformer can use either no relative position embeddings, Transformer-XL-like position embeddings, or
|
||||
rotary position embeddings by setting the correct `config.position_embeddings_type`.
|
||||
|
||||
This model was contributed by [patrickvonplaten](https://huggingface.co/patrickvonplaten).
|
||||
The original code can be found [here](https://github.com/pytorch/fairseq/tree/main/examples/wav2vec).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Wav2Vec2ConformerConfig
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] Wav2Vec2ConformerConfig
|
||||
|
||||
## Wav2Vec2Conformer specific outputs
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] models.wav2vec2_conformer.modeling_wav2vec2_conformer.Wav2Vec2ConformerForPreTrainingOutput
|
||||
|
||||
## Wav2Vec2ConformerModel
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] Wav2Vec2ConformerModel
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
## Wav2Vec2ConformerForCTC
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] Wav2Vec2ConformerForCTC
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
## Wav2Vec2ConformerForSequenceClassification
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] Wav2Vec2ConformerForSequenceClassification
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
## Wav2Vec2ConformerForAudioFrameClassification
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] Wav2Vec2ConformerForAudioFrameClassification
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
## Wav2Vec2ConformerForXVector
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] Wav2Vec2ConformerForXVector
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
## Wav2Vec2ConformerForPreTraining
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] Wav2Vec2ConformerForPreTraining
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
@ -49,10 +49,6 @@ found [here](https://github.com/microsoft/unilm/tree/master/wavlm).
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] WavLMConfig
|
||||
|
||||
## WavLM specific outputs
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] models.wavlm.modeling_wavlm.WavLMBaseModelOutput
|
||||
|
||||
## WavLMModel
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] WavLMModel
|
||||
|
||||
150
docs/source/en/perf_hardware.mdx
Normal file
150
docs/source/en/perf_hardware.mdx
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,150 @@
|
||||
<!---
|
||||
Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Custom hardware for training
|
||||
|
||||
The hardware you use to run model training and inference can have a big effect on performance. For a deep dive into GPUs make sure to check out Tim Dettmer's excellent [blog post](https://timdettmers.com/2020/09/07/which-gpu-for-deep-learning/).
|
||||
|
||||
Let's have a look at some practical advice for GPU setups.
|
||||
|
||||
## GPU
|
||||
When you train bigger models you have essentially three options:
|
||||
- bigger GPUs
|
||||
- more GPUs
|
||||
- more CPU and NVMe (offloaded to by [DeepSpeed-Infinity](main_classes/deepspeed#nvme-support))
|
||||
|
||||
Let's start at the case where you have a single GPU.
|
||||
|
||||
### Power and Cooling
|
||||
|
||||
If you bought an expensive high end GPU make sure you give it the correct power and sufficient cooling.
|
||||
|
||||
**Power**:
|
||||
|
||||
Some high end consumer GPU cards have 2 and sometimes 3 PCI-E 8-Pin power sockets. Make sure you have as many independent 12V PCI-E 8-Pin cables plugged into the card as there are sockets. Do not use the 2 splits at one end of the same cable (also known as pigtail cable). That is if you have 2 sockets on the GPU, you want 2 PCI-E 8-Pin cables going from your PSU to the card and not one that has 2 PCI-E 8-Pin connectors at the end! You won't get the full performance out of your card otherwise.
|
||||
|
||||
Each PCI-E 8-Pin power cable needs to be plugged into a 12V rail on the PSU side and can supply up to 150W of power.
|
||||
|
||||
Some other cards may use a PCI-E 12-Pin connectors, and these can deliver up to 500-600W of power.
|
||||
|
||||
Low end cards may use 6-Pin connectors, which supply up to 75W of power.
|
||||
|
||||
Additionally you want the high-end PSU that has stable voltage. Some lower quality ones may not give the card the stable voltage it needs to function at its peak.
|
||||
|
||||
And of course the PSU needs to have enough unused Watts to power the card.
|
||||
|
||||
**Cooling**:
|
||||
|
||||
When a GPU gets overheated it will start throttling down and will not deliver full performance and it can even shutdown if it gets too hot.
|
||||
|
||||
It's hard to tell the exact best temperature to strive for when a GPU is heavily loaded, but probably anything under +80C is good, but lower is better - perhaps 70-75C is an excellent range to be in. The throttling down is likely to start at around 84-90C. But other than throttling performance a prolonged very high temperature is likely to reduce the lifespan of a GPU.
|
||||
|
||||
Next let's have a look at one of the most important aspects when having multiple GPUs: connectivity.
|
||||
|
||||
### Multi-GPU Connectivity
|
||||
|
||||
If you use multiple GPUs the way cards are inter-connected can have a huge impact on the total training time. If the GPUs are on the same physical node, you can run:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
nvidia-smi topo -m
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
and it will tell you how the GPUs are inter-connected. On a machine with dual-GPU and which are connected with NVLink, you will most likely see something like:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
GPU0 GPU1 CPU Affinity NUMA Affinity
|
||||
GPU0 X NV2 0-23 N/A
|
||||
GPU1 NV2 X 0-23 N/A
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
on a different machine w/o NVLink we may see:
|
||||
```
|
||||
GPU0 GPU1 CPU Affinity NUMA Affinity
|
||||
GPU0 X PHB 0-11 N/A
|
||||
GPU1 PHB X 0-11 N/A
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The report includes this legend:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
X = Self
|
||||
SYS = Connection traversing PCIe as well as the SMP interconnect between NUMA nodes (e.g., QPI/UPI)
|
||||
NODE = Connection traversing PCIe as well as the interconnect between PCIe Host Bridges within a NUMA node
|
||||
PHB = Connection traversing PCIe as well as a PCIe Host Bridge (typically the CPU)
|
||||
PXB = Connection traversing multiple PCIe bridges (without traversing the PCIe Host Bridge)
|
||||
PIX = Connection traversing at most a single PCIe bridge
|
||||
NV# = Connection traversing a bonded set of # NVLinks
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
So the first report `NV2` tells us the GPUs are interconnected with 2 NVLinks, and the second report `PHB` we have a typical consumer-level PCIe+Bridge setup.
|
||||
|
||||
Check what type of connectivity you have on your setup. Some of these will make the communication between cards faster (e.g. NVLink), others slower (e.g. PHB).
|
||||
|
||||
Depending on the type of scalability solution used, the connectivity speed could have a major or a minor impact. If the GPUs need to sync rarely, as in DDP, the impact of a slower connection will be less significant. If the GPUs need to send messages to each other often, as in ZeRO-DP, then faster connectivity becomes super important to achieve faster training.
|
||||
|
||||
#### NVlink
|
||||
|
||||
[NVLink](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/NVLink) is a wire-based serial multi-lane near-range communications link developed by Nvidia.
|
||||
|
||||
Each new generation provides a faster bandwidth, e.g. here is a quote from [Nvidia Ampere GA102 GPU Architecture](https://www.nvidia.com/content/dam/en-zz/Solutions/geforce/ampere/pdf/NVIDIA-ampere-GA102-GPU-Architecture-Whitepaper-V1.pdf):
|
||||
|
||||
> Third-Generation NVLink®
|
||||
> GA102 GPUs utilize NVIDIA’s third-generation NVLink interface, which includes four x4 links,
|
||||
> with each link providing 14.0625 GB/sec bandwidth in each direction between two GPUs. Four
|
||||
> links provide 56.25 GB/sec bandwidth in each direction, and 112.5 GB/sec total bandwidth
|
||||
> between two GPUs. Two RTX 3090 GPUs can be connected together for SLI using NVLink.
|
||||
> (Note that 3-Way and 4-Way SLI configurations are not supported.)
|
||||
|
||||
So the higher `X` you get in the report of `NVX` in the output of `nvidia-smi topo -m` the better. The generation will depend on your GPU architecture.
|
||||
|
||||
Let's compare the execution of a gpt2 language model training over a small sample of wikitext.
|
||||
|
||||
The results are:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
| NVlink | Time |
|
||||
| ----- | ---: |
|
||||
| Y | 101s |
|
||||
| N | 131s |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
You can see that NVLink completes the training ~23% faster. In the second benchmark we use `NCCL_P2P_DISABLE=1` to tell the GPUs not to use NVLink.
|
||||
|
||||
Here is the full benchmark code and outputs:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# DDP w/ NVLink
|
||||
|
||||
rm -r /tmp/test-clm; CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1 python -m torch.distributed.launch \
|
||||
--nproc_per_node 2 examples/pytorch/language-modeling/run_clm.py --model_name_or_path gpt2 \
|
||||
--dataset_name wikitext --dataset_config_name wikitext-2-raw-v1 --do_train \
|
||||
--output_dir /tmp/test-clm --per_device_train_batch_size 4 --max_steps 200
|
||||
|
||||
{'train_runtime': 101.9003, 'train_samples_per_second': 1.963, 'epoch': 0.69}
|
||||
|
||||
# DDP w/o NVLink
|
||||
|
||||
rm -r /tmp/test-clm; CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1 NCCL_P2P_DISABLE=1 python -m torch.distributed.launch \
|
||||
--nproc_per_node 2 examples/pytorch/language-modeling/run_clm.py --model_name_or_path gpt2 \
|
||||
--dataset_name wikitext --dataset_config_name wikitext-2-raw-v1 --do_train
|
||||
--output_dir /tmp/test-clm --per_device_train_batch_size 4 --max_steps 200
|
||||
|
||||
{'train_runtime': 131.4367, 'train_samples_per_second': 1.522, 'epoch': 0.69}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Hardware: 2x TITAN RTX 24GB each + NVlink with 2 NVLinks (`NV2` in `nvidia-smi topo -m`)
|
||||
Software: `pytorch-1.8-to-be` + `cuda-11.0` / `transformers==4.3.0.dev0`
|
||||
57
docs/source/en/perf_infer_cpu.mdx
Normal file
57
docs/source/en/perf_infer_cpu.mdx
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,57 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Efficient Inference on CPU
|
||||
|
||||
This guide focuses on inferencing large models efficiently on CPU.
|
||||
|
||||
## PyTorch JIT-mode (TorchScript)
|
||||
TorchScript is a way to create serializable and optimizable models from PyTorch code. Any TorchScript program can be saved from a Python process and loaded in a process where there is no Python dependency.
|
||||
Comparing to default eager mode, jit mode in PyTorch normally yields better performance for model inference from optimization methodologies like operator fusion.
|
||||
|
||||
For a gentle introduction to TorchScript, see the Introduction to [PyTorch TorchScript tutorial](https://pytorch.org/tutorials/beginner/Intro_to_TorchScript_tutorial.html#tracing-modules).
|
||||
|
||||
### IPEX Graph Optimization with JIT-mode
|
||||
Intel® Extension for PyTorch provides further optimizations in jit mode for Transformers series models. It is highly recommended for users to take advantage of Intel® Extension for PyTorch with jit mode. Some frequently used operator patterns from Transformers models are already supported in Intel® Extension for PyTorch with jit mode fusions. Those fusion patterns like Multi-head-attention fusion, Concat Linear, Linear+Add, Linear+Gelu, Add+LayerNorm fusion and etc. are enabled and perform well. The benefit of the fusion is delivered to users in a transparent fashion. According to the analysis, ~70% of most popular NLP tasks in question-answering, text-classification, and token-classification can get performance benefits with these fusion patterns for both Float32 precision and BFloat16 Mixed precision.
|
||||
|
||||
Check more detailed information for [IPEX Graph Optimization](https://intel.github.io/intel-extension-for-pytorch/1.11.200/tutorials/features/graph_optimization.html).
|
||||
|
||||
#### IPEX installation:
|
||||
|
||||
IPEX release is following PyTorch, check the approaches for [IPEX installation](https://intel.github.io/intel-extension-for-pytorch/).
|
||||
|
||||
### Usage of JIT-mode
|
||||
To enable jit mode in Trainer, users should add `jit_mode_eval` in Trainer command arguments.
|
||||
|
||||
Take an example of the use cases on [Transformers question-answering](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples/pytorch/question-answering)
|
||||
|
||||
- Inference using jit mode on CPU:
|
||||
<pre>python run_qa.py \
|
||||
--model_name_or_path csarron/bert-base-uncased-squad-v1 \
|
||||
--dataset_name squad \
|
||||
--do_eval \
|
||||
--max_seq_length 384 \
|
||||
--doc_stride 128 \
|
||||
--output_dir /tmp/ \
|
||||
--no_cuda \
|
||||
<b>--jit_mode_eval </b></pre>
|
||||
|
||||
- Inference with IPEX using jit mode on CPU:
|
||||
<pre>python run_qa.py \
|
||||
--model_name_or_path csarron/bert-base-uncased-squad-v1 \
|
||||
--dataset_name squad \
|
||||
--do_eval \
|
||||
--max_seq_length 384 \
|
||||
--doc_stride 128 \
|
||||
--output_dir /tmp/ \
|
||||
--no_cuda \
|
||||
<b>--use_ipex \</b>
|
||||
<b>--jit_mode_eval</b></pre>
|
||||
14
docs/source/en/perf_infer_gpu_many.mdx
Normal file
14
docs/source/en/perf_infer_gpu_many.mdx
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,14 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Efficient Inference on a Multiple GPUs
|
||||
|
||||
This document will be completed soon with information on how to infer on a multiple GPUs. In the meantime you can check out [the guide for training on a single GPU](perf_train_gpu_one) and [the guide for inference on CPUs](perf_infer_cpu).
|
||||
14
docs/source/en/perf_infer_gpu_one.mdx
Normal file
14
docs/source/en/perf_infer_gpu_one.mdx
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,14 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Efficient Inference on a Single GPU
|
||||
|
||||
This document will be completed soon with information on how to infer on a single GPU. In the meantime you can check out [the guide for training on a single GPU](perf_train_gpu_one) and [the guide for inference on CPUs](perf_infer_cpu).
|
||||
14
docs/source/en/perf_infer_special.mdx
Normal file
14
docs/source/en/perf_infer_special.mdx
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,14 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Inference on Specialized Hardware
|
||||
|
||||
This document will be completed soon with information on how to infer on specialized hardware. In the meantime you can check out [the guide for inference on CPUs](perf_infer_cpu).
|
||||
61
docs/source/en/perf_train_cpu.mdx
Normal file
61
docs/source/en/perf_train_cpu.mdx
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,61 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Efficient Training on CPU
|
||||
|
||||
This guide focuses on training large models efficiently on CPU.
|
||||
|
||||
## Mixed precision with IPEX
|
||||
|
||||
IPEX is optimized for CPUs with AVX-512 or above, and functionally works for CPUs with only AVX2. So, it is expected to bring performance benefit for Intel CPU generations with AVX-512 or above while CPUs with only AVX2 (e.g., AMD CPUs or older Intel CPUs) might result in a better performance under IPEX, but not guaranteed. IPEX provides performance optimizations for CPU training with both Float32 and BFloat16. The usage of BFloat16 is the main focus of the following sections.
|
||||
|
||||
Low precision data type BFloat16 has been natively supported on the 3rd Generation Xeon® Scalable Processors (aka Cooper Lake) with AVX512 instruction set and will be supported on the next generation of Intel® Xeon® Scalable Processors with Intel® Advanced Matrix Extensions (Intel® AMX) instruction set with further boosted performance. The Auto Mixed Precision for CPU backend has been enabled since PyTorch-1.10. At the same time, the support of Auto Mixed Precision with BFloat16 for CPU and BFloat16 optimization of operators has been massively enabled in Intel® Extension for PyTorch, and partially upstreamed to PyTorch master branch. Users can get better performance and user experience with IPEX Auto Mixed Precision.
|
||||
|
||||
Check more detailed information for [Auto Mixed Precision](https://intel.github.io/intel-extension-for-pytorch/1.11.200/tutorials/features/amp.html).
|
||||
|
||||
### IPEX installation:
|
||||
|
||||
IPEX release is following PyTorch, to install via pip:
|
||||
|
||||
For PyTorch-1.10:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
pip install intel_extension_for_pytorch==1.10.100+cpu -f https://software.intel.com/ipex-whl-stable
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For PyTorch-1.11:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
pip install intel_extension_for_pytorch==1.11.200+cpu -f https://software.intel.com/ipex-whl-stable
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Check more approaches for [IPEX installation](https://intel.github.io/intel-extension-for-pytorch/1.11.200/tutorials/installation.html).
|
||||
|
||||
### Usage in Trainer
|
||||
To enable auto mixed precision with IPEX in Trainer, users should add `use_ipex`, `bf16` and `no_cuda` in training command arguments.
|
||||
|
||||
Take an example of the use cases on [Transformers question-answering](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples/pytorch/question-answering)
|
||||
|
||||
- Training with IPEX using BF16 auto mixed precision on CPU:
|
||||
<pre> python run_qa.py \
|
||||
--model_name_or_path bert-base-uncased \
|
||||
--dataset_name squad \
|
||||
--do_train \
|
||||
--do_eval \
|
||||
--per_device_train_batch_size 12 \
|
||||
--learning_rate 3e-5 \
|
||||
--num_train_epochs 2 \
|
||||
--max_seq_length 384 \
|
||||
--doc_stride 128 \
|
||||
--output_dir /tmp/debug_squad/ \
|
||||
<b>--use_ipex \</b>
|
||||
<b>--bf16 --no_cuda</b></pre>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,47 +1,163 @@
|
||||
<!---
|
||||
Copyright 2021 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
limitations under the License.
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Model Parallelism
|
||||
# Efficient Training on Multiple GPUs
|
||||
|
||||
When training on a single GPU is too slow or the model weights don't fit in a single GPUs memory we use a mutli-GPU setup. Switching from a single GPU to multiple requires some form of parallelism as the work needs to be distributed. There are several techniques to achieve parallism such as data, tensor, or pipeline parallism. However, there is no one solution to fit them all and which settings works best depends on the hardware you are running on. While the main concepts most likely will apply to any other framework, this article is focused on PyTorch-based implementations.
|
||||
|
||||
## Parallelism overview
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
In the modern machine learning the various approaches to parallelism are used to:
|
||||
1. fit very large models onto limited hardware - e.g. t5-11b is 45GB in just model params
|
||||
2. significantly speed up training - finish training that would take a year in hours
|
||||
Note: Most of the strategies introduced in the [single GPU section](perf_train_gpu_one) (such as mixed precision training or gradient accumulation) are generic and apply to training models in general so make sure to have a look at it before diving into the following sections such as multi-GPU or CPU training.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
We will first discuss in depth various 1D parallelism techniques and their pros and cons and then look at how they can be combined into 2D and 3D parallelism to enable an even faster training and to support even bigger models. Various other powerful alternative approaches will be presented.
|
||||
|
||||
While the main concepts most likely will apply to any other framework, this article is focused on PyTorch-based implementations.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Concepts
|
||||
|
||||
The following is the brief description of the main concepts that will be described later in depth in this document.
|
||||
|
||||
1. DataParallel (DP) - the same setup is replicated multiple times, and each being fed a slice of the data. The processing is done in parallel and all setups are synchronized at the end of each training step.
|
||||
2. TensorParallel (TP) - each tensor is split up into multiple chunks, so instead of having the whole tensor reside on a single gpu, each shard of the tensor resides on its designated gpu. During processing each shard gets processed separately and in parallel on different GPUs and the results are synced at the end of the step. This is what one may call horizontal parallelism, as the splitting happens on horizontal level.
|
||||
3. PipelineParallel (PP) - the model is split up vertically (layer-level) across multiple GPUs, so that only one or several layers of the model are places on a single gpu. Each gpu processes in parallel different stages of the pipeline and working on a small chunk of the batch.
|
||||
4. Zero Redundancy Optimizer (ZeRO) - Also performs sharding of the tensors somewhat similar to TP, except the whole tensor gets reconstructed in time for a forward or backward computation, therefore the model doesn't need to be modified. It also supports various offloading techniques to compensate for limited GPU memory.
|
||||
5. Sharded DDP - is another name for the foundational ZeRO concept as used by various other implementations of ZeRO.
|
||||
1. **DataParallel (DP)** - the same setup is replicated multiple times, and each being fed a slice of the data. The processing is done in parallel and all setups are synchronized at the end of each training step.
|
||||
2. **TensorParallel (TP)** - each tensor is split up into multiple chunks, so instead of having the whole tensor reside on a single gpu, each shard of the tensor resides on its designated gpu. During processing each shard gets processed separately and in parallel on different GPUs and the results are synced at the end of the step. This is what one may call horizontal parallelism, as the splitting happens on horizontal level.
|
||||
3. **PipelineParallel (PP)** - the model is split up vertically (layer-level) across multiple GPUs, so that only one or several layers of the model are places on a single gpu. Each gpu processes in parallel different stages of the pipeline and working on a small chunk of the batch.
|
||||
4. **Zero Redundancy Optimizer (ZeRO)** - Also performs sharding of the tensors somewhat similar to TP, except the whole tensor gets reconstructed in time for a forward or backward computation, therefore the model doesn't need to be modified. It also supports various offloading techniques to compensate for limited GPU memory.
|
||||
5. **Sharded DDP** - is another name for the foundational ZeRO concept as used by various other implementations of ZeRO.
|
||||
|
||||
Before diving deeper into the specifics of each concept we first have a look at the rough decision process when training large models on a large infrastructure.
|
||||
|
||||
## Scalability Strategy
|
||||
|
||||
**⇨ Single Node / Multi-GPU**
|
||||
* Model fits onto a single GPU:
|
||||
|
||||
1. DDP - Distributed DP
|
||||
2. ZeRO - may or may not be faster depending on the situation and configuration used
|
||||
|
||||
* Model doesn't fit onto a single GPU:
|
||||
|
||||
1. PP
|
||||
2. ZeRO
|
||||
3. TP
|
||||
|
||||
With very fast intra-node connectivity of NVLINK or NVSwitch all three should be mostly on par, without these PP will be faster than TP or ZeRO. The degree of TP may also make a difference. Best to experiment to find the winner on your particular setup.
|
||||
|
||||
TP is almost always used within a single node. That is TP size <= gpus per node.
|
||||
|
||||
* Largest Layer not fitting into a single GPU:
|
||||
|
||||
1. If not using ZeRO - must use TP, as PP alone won't be able to fit.
|
||||
2. With ZeRO see the same entry for "Single GPU" above
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**⇨ Multi-Node / Multi-GPU**
|
||||
|
||||
* When you have fast inter-node connectivity:
|
||||
|
||||
1. ZeRO - as it requires close to no modifications to the model
|
||||
2. PP+TP+DP - less communications, but requires massive changes to the model
|
||||
|
||||
* when you have slow inter-node connectivity and still low on GPU memory:
|
||||
|
||||
1. DP+PP+TP+ZeRO-1
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Data Parallelism
|
||||
|
||||
Most users with just 2 GPUs already enjoy the increased training speed up thanks to `DataParallel` (DP) and `DistributedDataParallel` (DDP) that are almost trivial to use. This is a built-in feature of Pytorch.
|
||||
Most users with just 2 GPUs already enjoy the increased training speed up thanks to `DataParallel` (DP) and `DistributedDataParallel` (DDP) that are almost trivial to use. This is a built-in feature of Pytorch. Note that in general it is advised to use DDP as it is better maintained and works for all models while DP might fail for some models. [PyTorch documentation](https://pytorch.org/docs/master/generated/torch.nn.DataParallel.html) itself recommends the use of DDP.
|
||||
|
||||
### DP vs DDP
|
||||
|
||||
`DistributedDataParallel` (DDP) is typically faster than `DataParallel` (DP), but it is not always the case:
|
||||
* while DP is python threads-based, DDP is multiprocess-based - and as such it has no python threads limitations, such as GIL
|
||||
* on the other hand a slow inter-connectivity between the GPU cards could lead to an actual slower outcome with DDP
|
||||
|
||||
Here are the main differences in the inter-GPU communication overhead between the two modes:
|
||||
|
||||
[DDP](https://pytorch.org/docs/master/notes/ddp.html):
|
||||
|
||||
- At the start time the main process replicates the model once from gpu 0 to the rest of gpus
|
||||
- Then for each batch:
|
||||
1. each gpu consumes each own mini-batch of data directly
|
||||
2. during `backward`, once the local gradients are ready, they are then averaged across all processes
|
||||
|
||||
[DP](https://pytorch.org/docs/master/generated/torch.nn.DataParallel.html):
|
||||
|
||||
For each batch:
|
||||
1. gpu 0 reads the batch of data and then sends a mini-batch to each gpu
|
||||
2. replicates the up-to-date model from gpu 0 to each gpu
|
||||
3. runs `forward` and sends output from each gpu to gpu 0, computes loss
|
||||
4. scatters loss from gpu 0 to all gpus, runs `backward`
|
||||
5. sends gradients from each gpu to gpu 0 and averages those
|
||||
|
||||
The only communication DDP performs per batch is sending gradients, whereas DP does 5 different data exchanges per batch.
|
||||
|
||||
DP copies data within the process via python threads, whereas DDP copies data via [torch.distributed](https://pytorch.org/docs/master/distributed.html).
|
||||
|
||||
Under DP gpu 0 performs a lot more work than the rest of the gpus, thus resulting in under-utilization of gpus.
|
||||
|
||||
You can use DDP across multiple machines, but this is not the case with DP.
|
||||
|
||||
There are other differences between DP and DDP but they aren't relevant to this discussion.
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to go really deep into understanding these 2 modes, this [article](https://www.telesens.co/2019/04/04/distributed-data-parallel-training-using-pytorch-on-aws/) is highly recommended, as it has great diagrams, includes multiple benchmarks and profiler outputs on various hardware, explains all the nuances that you may need to know.
|
||||
|
||||
Let's look at an actual benchmark:
|
||||
|
||||
| Type | NVlink | Time |
|
||||
| :----- | ----- | ---: |
|
||||
| 2:DP | Y | 110s |
|
||||
| 2:DDP | Y | 101s |
|
||||
| 2:DDP | N | 131s |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Analysis:
|
||||
|
||||
Here DP is ~10% slower than DDP w/ NVlink, but ~15% faster than DDP w/o NVlink
|
||||
|
||||
The real difference will depend on how much data each GPU needs to sync with the others - the more there is to sync, the more a slow link will slow down the total runtime.
|
||||
|
||||
Here is the full benchmark code and outputs:
|
||||
|
||||
`NCCL_P2P_DISABLE=1` was used to disable the NVLink feature on the corresponding benchmark.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
# DP
|
||||
rm -r /tmp/test-clm; CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1 \
|
||||
python examples/pytorch/language-modeling/run_clm.py \
|
||||
--model_name_or_path gpt2 --dataset_name wikitext --dataset_config_name wikitext-2-raw-v1 \
|
||||
--do_train --output_dir /tmp/test-clm --per_device_train_batch_size 4 --max_steps 200
|
||||
|
||||
{'train_runtime': 110.5948, 'train_samples_per_second': 1.808, 'epoch': 0.69}
|
||||
|
||||
# DDP w/ NVlink
|
||||
rm -r /tmp/test-clm; CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1 \
|
||||
python -m torch.distributed.launch --nproc_per_node 2 examples/pytorch/language-modeling/run_clm.py \
|
||||
--model_name_or_path gpt2 --dataset_name wikitext --dataset_config_name wikitext-2-raw-v1 \
|
||||
--do_train --output_dir /tmp/test-clm --per_device_train_batch_size 4 --max_steps 200
|
||||
|
||||
{'train_runtime': 101.9003, 'train_samples_per_second': 1.963, 'epoch': 0.69}
|
||||
|
||||
# DDP w/o NVlink
|
||||
rm -r /tmp/test-clm; NCCL_P2P_DISABLE=1 CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1 \
|
||||
python -m torch.distributed.launch --nproc_per_node 2 examples/pytorch/language-modeling/run_clm.py \
|
||||
--model_name_or_path gpt2 --dataset_name wikitext --dataset_config_name wikitext-2-raw-v1 \
|
||||
--do_train --output_dir /tmp/test-clm --per_device_train_batch_size 4 --max_steps 200
|
||||
|
||||
{'train_runtime': 131.4367, 'train_samples_per_second': 1.522, 'epoch': 0.69}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Hardware: 2x TITAN RTX 24GB each + NVlink with 2 NVLinks (`NV2` in `nvidia-smi topo -m`)
|
||||
Software: `pytorch-1.8-to-be` + `cuda-11.0` / `transformers==4.3.0.dev0`
|
||||
|
||||
## ZeRO Data Parallelism
|
||||
|
||||
@ -356,7 +472,7 @@ One very important aspect is that FlexFlow is designed for optimizing DNN parall
|
||||
|
||||
So the promise is very attractive - it runs a 30min simulation on the cluster of choice and it comes up with the best strategy to utilise this specific environment. If you add/remove/replace any parts it'll run and re-optimize the plan for that. And then you can train. A different setup will have its own custom optimization.
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 Transformers status: not yet integrated. We already have our models FX-trace-able via [transformers.utils.fx](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/src/transformers/utils/fx.py), which is a prerequisite for FlexFlow, so someone needs to figure out what needs to be done to make FlexFlow work with our models.
|
||||
🤗 Transformers status: not yet integrated. We already have our models FX-trace-able via [transformers.utils.fx](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/master/src/transformers/utils/fx.py), which is a prerequisite for FlexFlow, so someone needs to figure out what needs to be done to make FlexFlow work with our models.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Which Strategy To Use When
|
||||
732
docs/source/en/perf_train_gpu_one.mdx
Normal file
732
docs/source/en/perf_train_gpu_one.mdx
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,732 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Efficient Training on a Single GPU
|
||||
|
||||
This guide focuses on training large models efficiently on a single GPU. These approaches are still valid if you have access to a machine with multiple GPUs but you will also have access to additional methods outlined in the [multi-GPU section](perf_train_gpu_many).
|
||||
|
||||
In this section we have a look at a few tricks to reduce the memory footprint and speed up training for large models and how they are integrated in the [`Trainer`] and [🤗 Accelerate](https://huggingface.co/docs/accelerate/). Each method can improve speed or memory usage which is summarized in the table below:
|
||||
|
||||
|Method|Speed|Memory|
|
||||
|:-----|:----|:-----|
|
||||
| Gradient accumulation | No | Yes |
|
||||
| Gradient checkpointing | No| Yes |
|
||||
| Mixed precision training | Yes | (No) |
|
||||
| Batch size | Yes | Yes |
|
||||
| Optimizer choice | Yes | Yes |
|
||||
| DataLoader | Yes | No |
|
||||
| DeepSpeed Zero | No | Yes |
|
||||
|
||||
A bracket means that it might not be strictly the case but is usually either not a main concern or negligable. Before we start make sure you have installed the following libraries:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install transformers datasets accelerate nvidia-ml-py3
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The `nvidia-ml-py3` library allows us to monitor the memory usage of the models from within Python. You might be familiar with the `nvidia-smi` command in the terminal - this library allows to access the same information in Python directly.
|
||||
|
||||
Then we create some dummy data. We create random token IDs between 100 and 30000 and binary labels for a classifier. In total we get 512 sequences each with length 512 and store them in a [`~datasets.Dataset`] with PyTorch format.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
from datasets import Dataset
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
seq_len, dataset_size = 512, 512
|
||||
dummy_data = {
|
||||
"input_ids": np.random.randint(100, 30000, (dataset_size, seq_len)),
|
||||
"labels": np.random.randint(0, 1, (dataset_size)),
|
||||
}
|
||||
ds = Dataset.from_dict(dummy_data)
|
||||
ds.set_format("pt")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We want to print some summary statistics for the GPU utilization and the training run with the [`Trainer`]. We setup a two helper functions to do just that:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from pynvml import *
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def print_gpu_utilization():
|
||||
nvmlInit()
|
||||
handle = nvmlDeviceGetHandleByIndex(0)
|
||||
info = nvmlDeviceGetMemoryInfo(handle)
|
||||
print(f"GPU memory occupied: {info.used//1024**2} MB.")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def print_summary(result):
|
||||
print(f"Time: {result.metrics['train_runtime']:.2f}")
|
||||
print(f"Samples/second: {result.metrics['train_samples_per_second']:.2f}")
|
||||
print_gpu_utilization()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Let's verify that we start with a free GPU memory:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> print_gpu_utilization()
|
||||
GPU memory occupied: 0 MB.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
That looks good: the GPU memory is not occupied as we would expect before we load any models. If that's not the case on your machine make sure to stop all processes that are using GPU memory. However, not all free GPU memory can be used by the user. When a model is loaded to the GPU also the kernels are loaded which can take up 1-2GB of memory. To see how much it is we load a tiny tensor into the GPU which triggers the kernels to be loaded as well.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> import torch
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
>>> torch.ones((1, 1)).to("cuda")
|
||||
>>> print_gpu_utilization()
|
||||
GPU memory occupied: 1343 MB.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We see that the kernels alone take up 1.3GB of GPU memory. Now let's see how much space the model uses.
|
||||
|
||||
## Load Model
|
||||
|
||||
First, we load the `bert-large-uncased` model. We load the model weights directly to the GPU so that we can check how much space just weights use.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForSequenceClassification
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained("bert-large-uncased").to("cuda")
|
||||
>>> print_gpu_utilization()
|
||||
GPU memory occupied: 2631 MB.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We can see that the model weights alone take up 1.3 GB of the GPU memory. The exact number depends on the specific GPU you are using. Note that on newer GPUs a model can sometimes take up more space since the weights are loaded in an optimized fashion that speeds up the usage of the model. Now we can also quickly check if we get the same result as with `nvidia-smi` CLI:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
nvidia-smi
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
Tue Jan 11 08:58:05 2022
|
||||
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+
|
||||
| NVIDIA-SMI 460.91.03 Driver Version: 460.91.03 CUDA Version: 11.2 |
|
||||
|-------------------------------+----------------------+----------------------+
|
||||
| GPU Name Persistence-M| Bus-Id Disp.A | Volatile Uncorr. ECC |
|
||||
| Fan Temp Perf Pwr:Usage/Cap| Memory-Usage | GPU-Util Compute M. |
|
||||
| | | MIG M. |
|
||||
|===============================+======================+======================|
|
||||
| 0 Tesla V100-SXM2... On | 00000000:00:04.0 Off | 0 |
|
||||
| N/A 37C P0 39W / 300W | 2631MiB / 16160MiB | 0% Default |
|
||||
| | | N/A |
|
||||
+-------------------------------+----------------------+----------------------+
|
||||
|
||||
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+
|
||||
| Processes: |
|
||||
| GPU GI CI PID Type Process name GPU Memory |
|
||||
| ID ID Usage |
|
||||
|=============================================================================|
|
||||
| 0 N/A N/A 3721 C ...nvs/codeparrot/bin/python 2629MiB |
|
||||
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We get the same number as before and you can also see that we are using a V100 GPU with 16GB of memory. So now we can start training the model and see how the GPU memory consumption changes. First, we set up a few standard training arguments that we will use across all our experiments:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
default_args = {
|
||||
"output_dir": "tmp",
|
||||
"evaluation_strategy": "steps",
|
||||
"num_train_epochs": 1,
|
||||
"log_level": "error",
|
||||
"report_to": "none",
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Note: In order to properly clear the memory after experiments we need restart the Python kernel between experiments. Run all steps above and then just one of the experiments below.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## Vanilla Training
|
||||
|
||||
As a first experiment we will use the [`Trainer`] and train the model without any further modifications and a batch size of 4:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import TrainingArguments, Trainer, logging
|
||||
|
||||
logging.set_verbosity_error()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
training_args = TrainingArguments(per_device_train_batch_size=4, **default_args)
|
||||
trainer = Trainer(model=model, args=training_args, train_dataset=ds)
|
||||
result = trainer.train()
|
||||
print_summary(result)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Time: 57.82
|
||||
Samples/second: 8.86
|
||||
GPU memory occupied: 14949 MB.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We see that already a relatively small batch size almost fills up our GPU's entire memory. However, a larger batch size can often result in faster model convergence or better end performance. So ideally we want to tune the batch size to our model's needs and not to the GPU limitations. What's interesting is that we use much more memory than the size of the model. To understand a bit better why this is the case let's have look at a model's operations and memory needs.
|
||||
|
||||
## Anatomy of Model's Operations
|
||||
|
||||
Transformers architecture includes 3 main groups of operations grouped below by compute-intensity.
|
||||
|
||||
1. **Tensor Contractions**
|
||||
|
||||
Linear layers and components of Multi-Head Attention all do batched **matrix-matrix multiplications**. These operations are the most compute-intensive part of training a transformer.
|
||||
|
||||
2. **Statistical Normalizations**
|
||||
|
||||
Softmax and layer normalization are less compute-intensive than tensor contractions, and involve one or more **reduction operations**, the result of which is then applied via a map.
|
||||
|
||||
3. **Element-wise Operators**
|
||||
|
||||
These are the remaining operators: **biases, dropout, activations, and residual connections**. These are the least compute-intensive operations.
|
||||
|
||||
This knowledge can be helpful to know when analyzing performance bottlenecks.
|
||||
|
||||
This summary is derived from [Data Movement Is All You Need: A Case Study on Optimizing Transformers 2020](https://arxiv.org/abs/2007.00072)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Anatomy of Model's Memory
|
||||
We've seen that training the model uses much more memory than just putting the model on the GPU. This is because there are many components during training that use GPU memory. The components on GPU memory are the following:
|
||||
1. model weights
|
||||
2. optimizer states
|
||||
3. gradients
|
||||
4. forward activations saved for gradient computation
|
||||
5. temporary buffers
|
||||
6. functionality-specific memory
|
||||
|
||||
A typical model trained in mixed precision with AdamW requires 18 bytes per model parameter plus activation memory. For inference there are no optimizer states and gradients, so we can subtract those. And thus we end up with 6 bytes per model parameter for mixed precision inference, plus activation memory.
|
||||
|
||||
Let's look at the details.
|
||||
|
||||
**Model Weights:**
|
||||
|
||||
- 4 bytes * number of parameters for fp32 training
|
||||
- 6 bytes * number of parameters for mixed precision training (maintains a model in fp32 and one in fp16 in memory)
|
||||
|
||||
**Optimizer States:**
|
||||
|
||||
- 8 bytes * number of parameters for normal AdamW (maintains 2 states)
|
||||
- 2 bytes * number of parameters for 8-bit AdamW optimizers like [bitsandbytes](https://github.com/facebookresearch/bitsandbytes)
|
||||
- 4 bytes * number of parameters for optimizers like SGD with momentum (maintains only 1 state)
|
||||
|
||||
**Gradients**
|
||||
|
||||
- 4 bytes * number of parameters for either fp32 or mixed precision training (gradients are always kept in fp32)
|
||||
|
||||
**Forward Activations**
|
||||
|
||||
- size depends on many factors, the key ones being sequence length, hidden size and batch size.
|
||||
|
||||
There are the input and output that are being passed and returned by the forward and the backward functions and the forward activations saved for gradient computation.
|
||||
|
||||
**Temporary Memory**
|
||||
|
||||
Additionally there are all kinds of temporary variables which get released once the calculation is done, but in the moment these could require additional memory and could push to OOM. Therefore when coding it's crucial to think strategically about such temporary variables and sometimes to explicitly free those as soon as they are no longer needed.
|
||||
|
||||
**Functionality-specific memory**
|
||||
|
||||
Then your software could have special memory needs. For example, when generating text using beam search, the software needs to maintain multiple copies of inputs and outputs.
|
||||
|
||||
**`forward` vs `backward` Execution Speed**
|
||||
|
||||
For convolutions and linear layers there are 2x flops in the backward compared to the forward, which generally translates into ~2x slower (sometimes more, because sizes in the backward tend to be more awkward). Activations are usually bandwidth-limited, and it’s typical for an activation to have to read more data in the backward than in the forward (e.g. activation forward reads once, writes once, activation backward reads twice, gradOutput and output of the forward, and writes once, gradInput).
|
||||
|
||||
So there are potentially a few places where we could save GPU memory or speed up operations. Let's start with a simple optimization: choosing the right batch size.
|
||||
|
||||
## Batch sizes
|
||||
|
||||
One gets the most efficient performance when batch sizes and input/output neuron counts are divisible by a certain number, which typically starts at 8, but can be much higher as well. That number varies a lot depending on the specific hardware being used and the dtype of the model.
|
||||
|
||||
For example for fully connected layers (which correspond to GEMMs), NVIDIA provides recommendations for [input/output neuron counts](
|
||||
https://docs.nvidia.com/deeplearning/performance/dl-performance-fully-connected/index.html#input-features) and [batch size](https://docs.nvidia.com/deeplearning/performance/dl-performance-fully-connected/index.html#batch-size).
|
||||
|
||||
[Tensor Core Requirements](https://docs.nvidia.com/deeplearning/performance/dl-performance-matrix-multiplication/index.html#requirements-tc) define the multiplier based on the dtype and the hardware. For example, for fp16 a multiple of 8 is recommended, but on A100 it's 64!
|
||||
|
||||
For parameters that are small, there is also [Dimension Quantization Effects](https://docs.nvidia.com/deeplearning/performance/dl-performance-matrix-multiplication/index.html#dim-quantization) to consider, this is where tiling happens and the right multiplier can have a significant speedup.
|
||||
|
||||
## Gradient Accumulation
|
||||
|
||||
The idea behind gradient accumulation is to instead of calculating the gradients for the whole batch at once to do it in smaller steps. The way we do that is to calculate the gradients iteratively in smaller batches by doing a forward and backward pass through the model and accumulating the gradients in the process. When enough gradients are accumulated we run the model's optimization step. This way we can easily increase the overall batch size to numbers that would never fit into the GPU's memory. In turn, however, the added forward and backward passes can slow down the training a bit.
|
||||
|
||||
We can use gradient accumulation in the [`Trainer`] by simply adding the `gradient_accumulation_steps` argument to [`TrainingArguments`]. Let's see how it impacts the models memory footprint:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
training_args = TrainingArguments(per_device_train_batch_size=1, gradient_accumulation_steps=4, **default_args)
|
||||
|
||||
trainer = Trainer(model=model, args=training_args, train_dataset=ds)
|
||||
result = trainer.train()
|
||||
print_summary(result)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Time: 66.03
|
||||
Samples/second: 7.75
|
||||
GPU memory occupied: 8681 MB.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We can see that the memory footprint was dramatically reduced at the cost of being only slightly slower than the vanilla run. Of course, this would change as you increase the number of accumulation steps. In general you would want to max out the GPU usage as much as possible. So in our case, the batch_size of 4 was already pretty close to the GPU's limit. If we wanted to train with a batch size of 64 we should not use `per_device_train_batch_size=1` and `gradient_accumulation_steps=64` but instead `per_device_train_batch_size=4` and `gradient_accumulation_steps=16` which has the same effective batch size while making better use of the available GPU resources.
|
||||
|
||||
For more details see the benchmarks for [RTX-3090](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/issues/14608#issuecomment-1004392537)
|
||||
and [A100](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/issues/15026#issuecomment-1005033957).
|
||||
|
||||
Next we have a look at another trick to save a little bit more GPU memory called gradient checkpointing.
|
||||
|
||||
## Gradient Checkpointing
|
||||
|
||||
Even when we set the batch size to 1 and use gradient accumulation we can still run out of memory when working with large models. In order to compute the gradients during the backward pass all activations from the forward pass are normally saved. This can create a big memory overhead. Alternatively, one could forget all activations during the forward pass and recompute them on demand during the backward pass. This would however add a significant computational overhead and slow down training.
|
||||
|
||||
Gradient checkpointing strikes a compromise between the two approaches and saves strategically selected activations throughout the computational graph so only a fraction of the activations need to be re-computed for the gradients. See [this great article](https://medium.com/tensorflow/fitting-larger-networks-into-memory-583e3c758ff9) explaining the ideas behind gradient checkpointing.
|
||||
|
||||
To enable gradient checkpointing in the [`Trainer`] we only need ot pass it as a flag to the [`TrainingArguments`]. Everything else is handled under the hood:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
training_args = TrainingArguments(
|
||||
per_device_train_batch_size=1, gradient_accumulation_steps=4, gradient_checkpointing=True, **default_args
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
trainer = Trainer(model=model, args=training_args, train_dataset=ds)
|
||||
result = trainer.train()
|
||||
print_summary(result)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Time: 85.47
|
||||
Samples/second: 5.99
|
||||
GPU memory occupied: 6775 MB.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We can see that this saved some more memory but at the same time training became a bit slower. A general rule of thumb is that gradient checkpointing slows down training by about 20%. Let's have a look at another method with which we can regain some speed: mixed precision training.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Floating Data Types
|
||||
|
||||
The idea of mixed precision training is that no all variables need to be stored in full (32-bit) floating point precision. If we can reduce the precision the variales and their computations are faster. Here are the commonly used floating point data types choice of which impacts both memory usage and throughput:
|
||||
|
||||
- fp32 (`float32`)
|
||||
- fp16 (`float16`)
|
||||
- bf16 (`bfloat16`)
|
||||
- tf32 (CUDA internal data type)
|
||||
|
||||
Here is a diagram that shows how these data types correlate to each other.
|
||||
|
||||
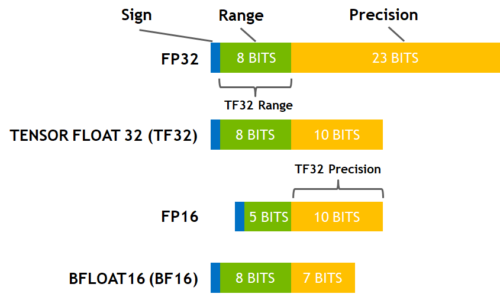
|
||||
(source: [NVIDIA Blog](https://developer.nvidia.com/blog/accelerating-ai-training-with-tf32-tensor-cores/))
|
||||
|
||||
While fp16 and fp32 have been around for quite some time, bf16 and tf32 are only available on the Ampere architecture GPUS and TPUs support bf16 as well. Let's start with the most commonly used method which is FP16 training/
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### FP16 Training
|
||||
|
||||
The idea of mixed precision training is that no all variables need to be stored in full (32-bit) floating point precision. If we can reduce the precision the variales and their computations are faster. The main advantage comes from saving the activations in half (16-bit) precision. Although the gradients are also computed in half precision they are converted back to full precision for the optimization step so no memory is saved here. Since the model is present on the GPU in both 16-bit and 32-bit precision this can use more GPU memory (1.5x the original model is on the GPU), especially for small batch sizes. Since some computations are performed in full and some in half precision this approach is also called mixed precision training. Enabling mixed precision training is also just a matter of setting the `fp16` flag to `True`:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
training_args = TrainingArguments(per_device_train_batch_size=4, fp16=True, **default_args)
|
||||
|
||||
trainer = Trainer(model=model, args=training_args, train_dataset=ds)
|
||||
result = trainer.train()
|
||||
print_summary(result)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Time: 27.46
|
||||
Samples/second: 18.64
|
||||
GPU memory occupied: 13939 MB.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We can see that this is almost twice as fast as the vanilla training. Let's add it to the mix of the previous methods:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
training_args = TrainingArguments(
|
||||
per_device_train_batch_size=1,
|
||||
gradient_accumulation_steps=4,
|
||||
gradient_checkpointing=True,
|
||||
fp16=True,
|
||||
**default_args,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
trainer = Trainer(model=model, args=training_args, train_dataset=ds)
|
||||
result = trainer.train()
|
||||
print_summary(result)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Time: 50.76
|
||||
Samples/second: 10.09
|
||||
GPU memory occupied: 7275 MB.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We can see that with these tweaks we use about half the GPU memory as at the beginning while also being slightly faster.
|
||||
|
||||
### BF16
|
||||
If you have access to a Ampere or newer hardware you can use bf16 for your training and evaluation. While bf16 has a worse precision than fp16, it has a much much bigger dynamic range. Therefore, if in the past you were experiencing overflow issues while training the model, bf16 will prevent this from happening most of the time. Remember that in fp16 the biggest number you can have is `65535` and any number above that will overflow. A bf16 number can be as large as `3.39e+38` (!) which is about the same as fp32 - because both have 8-bits used for the numerical range.
|
||||
|
||||
You can enable BF16 in the 🤗 Trainer with:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
TrainingArguments(bf16=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### TF32
|
||||
The Ampere hardware uses a magical data type called tf32. It has the same numerical range as fp32 (8-bits), but instead of 23 bits precision it has only 10 bits (same as fp16) and uses only 19 bits in total.
|
||||
|
||||
It's magical in the sense that you can use the normal fp32 training and/or inference code and by enabling tf32 support you can get up to 3x throughput improvement. All you need to do is to add this to your code:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
torch.backends.cuda.matmul.allow_tf32 = True
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
When this is done CUDA will automatically switch to using tf32 instead of fp32 where it's possible. This, of course, assumes that the used GPU is from the Ampere series.
|
||||
|
||||
Like all cases with reduced precision this may or may not be satisfactory for your needs, so you have to experiment and see. According to [NVIDIA research](https://developer.nvidia.com/blog/accelerating-ai-training-with-tf32-tensor-cores/) the majority of machine learning training shouldn't be impacted and showed the same perplexity and convergence as the fp32 training.
|
||||
|
||||
If you're already using fp16 or bf16 mixed precision it may help with the throughput as well.
|
||||
|
||||
You can enable this mode in the 🤗 Trainer with:
|
||||
```python
|
||||
TrainingArguments(tf32=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
By default the PyTorch default is used.
|
||||
|
||||
Note: tf32 mode is internal to CUDA and can't be accessed directly via `tensor.to(dtype=torch.tf32)` as `torch.tf32` doesn't exist.
|
||||
|
||||
Note: you need `torch>=1.7` to enjoy this feature.
|
||||
|
||||
You can also see a variety of benchmarks on tf32 vs other precisions:
|
||||
[RTX-3090](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/issues/14608#issuecomment-1004390803) and
|
||||
[A100](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/issues/15026#issuecomment-1004543189).
|
||||
|
||||
We've now seen how we can change the floating types to increase throughput, but we are not done, yet! There is another area where we can save GPU memory: the optimizer.
|
||||
|
||||
## Optimizer
|
||||
|
||||
The most common optimizer used to train transformer model is Adam or AdamW (Adam with weight decay). Adam achieves good convergence by storing the rolling average of the previous gradients which, however, adds an additional memory footprint of the order of the number of model parameters. One remedy to this is to use an alternative optimizer such as Adafactor, which works well for some models but often it has instability issues.
|
||||
|
||||
HF Trainer integrates a variety of optimisers that can be used out of box. To activate the desired optimizer simply pass the `--optim` flag to the command line.
|
||||
|
||||
To see which optimizers are currently supported:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ python examples/pytorch/translation/run_translation.py -h | grep "\-optim"
|
||||
[--optim {adamw_hf,adamw_torch,adamw_torch_xla,adamw_apex_fused,adafactor}]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For example, if you have [NVIDIA/apex](https://github.com/NVIDIA/apex) installed `--optim adamw_apex_fused` will give you the fastest training experience among all supported AdamW optimizers.
|
||||
|
||||
On the other hand [8bit BNB optimizer](https://github.com/facebookresearch/bitsandbytes) can save 3/4 of memory normally used by a typical AdamW optimizer if it is configured to quantize all optimizer states, but in some situations only some optimizer states are quintized and then more memory is used. XXX: update once https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/pull/15622 is merged.
|
||||
|
||||
Let's get a feel for the numbers and use for example use a 3B-parameter model, like `t5-3b`. Note that since a Gigabyte correpsonds to a billion bytes we can simply multiply the parameters (in billions) with the number of necessary bytes per parameter to get Gigabytes of GPU memory usage:
|
||||
|
||||
- A standard AdamW uses 8 bytes for each parameter, here the optimizer will need (`8*3`) 24GB of GPU memory.
|
||||
- Adafactor uses slightly more than 4 bytes, so (`4*3`) 12GB and then some extra.
|
||||
- 8bit BNB quantized optimizer will use only (`2*3`) 6GB if all optimizer states are quantized.
|
||||
|
||||
Let's have a look at Adafactor first.
|
||||
|
||||
### Adafactor
|
||||
|
||||
Instead of keeping the rolling average for each element in the weight matrices Adafactor only stores aggregated information (row- and column-wise sums of the rolling averages) which reduces the footprint considerably. One downside of Adafactor is that in some instances convergence can be slower than Adam's so some experimentation is advised here. We can use Adafactor simply by setting `optim="adafactor"`:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
training_args = TrainingArguments(per_device_train_batch_size=4, optim="adafactor", **default_args)
|
||||
|
||||
trainer = Trainer(model=model, args=training_args, train_dataset=ds)
|
||||
result = trainer.train()
|
||||
print_summary(result)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Time: 64.31
|
||||
Samples/second: 7.96
|
||||
GPU memory occupied: 12295 MB.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We can see that this saves a few more GB on the GPU. Let's see how it looks when we add it to the other methods we introduced earlier:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
training_args = TrainingArguments(
|
||||
per_device_train_batch_size=1,
|
||||
gradient_accumulation_steps=4,
|
||||
gradient_checkpointing=True,
|
||||
fp16=True,
|
||||
optim="adafactor",
|
||||
**default_args,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
trainer = Trainer(model=model, args=training_args, train_dataset=ds)
|
||||
result = trainer.train()
|
||||
print_summary(result)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Time: 56.54
|
||||
Samples/second: 9.06
|
||||
GPU memory occupied: 4847 MB.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We went from 15 GB memory usage to 5 GB - a 3x improvement while maintaining the throughput! However, as mentioned before, the convergence of Adafactor can be worse than Adam. There is an alternative to Adafactor called 8-bit Adam that takes a slightly different approach.
|
||||
|
||||
### 8-bit Adam
|
||||
|
||||
Instead of aggregating optimizer states like Adafactor, 8-bit Adam keeps the full state and quantizes it. Quantization means that it stores the state with lower precision and dequantizes it only for the optimization. This is similar to the idea behind FP16 training where using variables with lower precision saves memory.
|
||||
|
||||
In contrast to the previous approaches is this one not integrated into the [`Trainer`] as a simple flag. We need to install the 8-bit optimizer and then pass it as a custom optimizer to the [`Trainer`]. Follow the installation guide in the Github [repo](https://github.com/facebookresearch/bitsandbytes) to install the `bitsandbytes` library that implements the 8-bit Adam optimizer.
|
||||
|
||||
Once installed, we just need to initialize the the optimizer. Although this looks like a considerable amount of work it actually just involves two steps: first we need to group the model's parameters into two groups where to one group we apply weight decay and to the other we don't. Usually, biases and layer norm parameters are not weight decayed. Then in a second step we just do some argument housekeeping to use the same parameters as the previously used AdamW optimizer.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
Note that in order to use the 8-bit optimizer with an existing pretrained model a change to the embedding layer is needed.
|
||||
Read [this issue](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/issues/14819) for more information.
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
import bitsandbytes as bnb
|
||||
from torch import nn
|
||||
from transformers.trainer_pt_utils import get_parameter_names
|
||||
|
||||
training_args = TrainingArguments(per_device_train_batch_size=4, **default_args)
|
||||
|
||||
decay_parameters = get_parameter_names(model, [nn.LayerNorm])
|
||||
decay_parameters = [name for name in decay_parameters if "bias" not in name]
|
||||
optimizer_grouped_parameters = [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"params": [p for n, p in model.named_parameters() if n in decay_parameters],
|
||||
"weight_decay": training_args.weight_decay,
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"params": [p for n, p in model.named_parameters() if n not in decay_parameters],
|
||||
"weight_decay": 0.0,
|
||||
},
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
optimizer_kwargs = {
|
||||
"betas": (training_args.adam_beta1, training_args.adam_beta2),
|
||||
"eps": training_args.adam_epsilon,
|
||||
}
|
||||
optimizer_kwargs["lr"] = training_args.learning_rate
|
||||
adam_bnb_optim = bnb.optim.Adam8bit(
|
||||
optimizer_grouped_parameters,
|
||||
betas=(training_args.adam_beta1, training_args.adam_beta2),
|
||||
eps=training_args.adam_epsilon,
|
||||
lr=training_args.learning_rate,
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We can now pass the custom optimizer as an argument to the `Trainer`:
|
||||
```py
|
||||
trainer = Trainer(model=model, args=training_args, train_dataset=ds, optimizers=(adam_bnb_optim, None))
|
||||
result = trainer.train()
|
||||
print_summary(result)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Time: 55.95
|
||||
Samples/second: 9.15
|
||||
GPU memory occupied: 13085 MB.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We can see that we get a similar memory improvement as with Adafactor while keeping the full rolling average of the gradients. Let's repeat the experiment with the full settings:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
training_args = TrainingArguments(
|
||||
per_device_train_batch_size=1,
|
||||
gradient_accumulation_steps=4,
|
||||
gradient_checkpointing=True,
|
||||
fp16=True,
|
||||
**default_args,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
trainer = Trainer(model=model, args=training_args, train_dataset=ds, optimizers=(adam_bnb_optim, None))
|
||||
result = trainer.train()
|
||||
print_summary(result)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Time: 49.46
|
||||
Samples/second: 10.35
|
||||
GPU memory occupied: 5363 MB.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Again, we get about a 3x memory improvement and even slightly higher throughput as using Adafactor. So we have seen how we can optimize the memory footprint of large models. The following plot summarizes all our experiments:
|
||||
|
||||
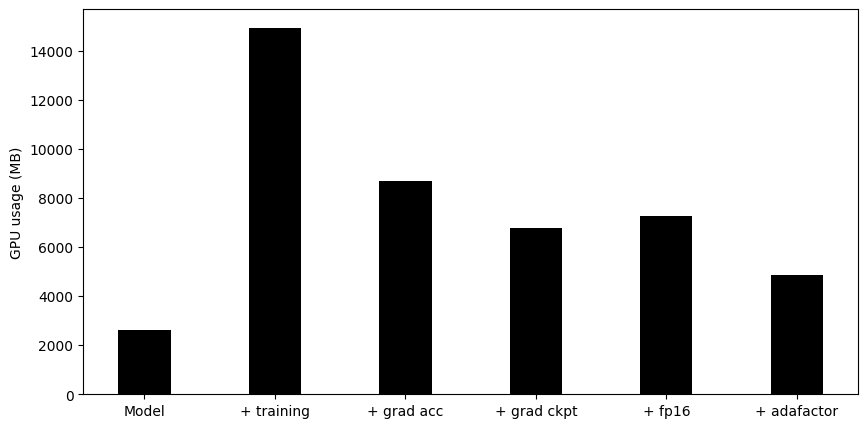
|
||||
|
||||
### `_multi_tensor`
|
||||
pytorch-nightly introduced `torch.optim._multi_tensor` which should significantly speed up the optimizers for situations with lots of small feature tensors. It should eventually become the default, but if you want to experiment with it sooner and don't mind using the bleed-edge, see: https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/issues/9965
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Using 🤗 Accelerate
|
||||
|
||||
So far we have used the [`Trainer`] to run the experiments but a more flexible alternative to that approach is to use 🤗 Accelerate. With 🤗 Accelerate you have full control over the training loop and can essentially write the loop in pure PyTorch with some minor modifications. In turn it allows you to easily scale across different infrastructures such as CPUs, GPUs, TPUs, or distributed multi-GPU setups without changing any code. Let's see what it takes to implement all of the above tweaks in 🤗 Accelerate. We can still use the [`TrainingArguments`] to wrap the training settings:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
training_args = TrainingArguments(
|
||||
per_device_train_batch_size=1,
|
||||
gradient_accumulation_steps=4,
|
||||
gradient_checkpointing=True,
|
||||
fp16=True,
|
||||
**default_args,
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The full example training loop with 🤗 Accelerate is only a handful of lines of code long:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from accelerate import Accelerator
|
||||
from torch.utils.data.dataloader import DataLoader
|
||||
|
||||
dataloader = DataLoader(ds, batch_size=training_args.per_device_train_batch_size)
|
||||
|
||||
if training_args.gradient_checkpointing:
|
||||
model.gradient_checkpointing_enable()
|
||||
|
||||
accelerator = Accelerator(fp16=training_args.fp16)
|
||||
model, optimizer, dataloader = accelerator.prepare(model, adam_bnb_optim, dataloader)
|
||||
|
||||
model.train()
|
||||
for step, batch in enumerate(dataloader, start=1):
|
||||
loss = model(**batch).loss
|
||||
loss = loss / training_args.gradient_accumulation_steps
|
||||
accelerator.backward(loss)
|
||||
if step % training_args.gradient_accumulation_steps == 0:
|
||||
optimizer.step()
|
||||
optimizer.zero_grad()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
First we wrap the dataset in a [`DataLoader`](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/data.html#torch.utils.data.DataLoader). Then we can enable gradient checkpointing by calling the model's [`~PreTrainedModel.gradient_checkpointing_enable`] method. When we initialize the [`Accelerator`](https://huggingface.co/docs/accelerate/accelerator.html#accelerate.Accelerator) we can specifiy if we want to use mixed precision training and it will take care of it for us in the [`prepare`] call. During the [`prepare`](https://huggingface.co/docs/accelerate/accelerator.html#accelerate.Accelerator.prepare) call the dataloader will also be distributed across workers should we use multiple GPUs. We use the same 8-bit optimizer from the earlier experiments.
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, we can write the main training loop. Note that the `backward` call is handled by 🤗 Accelerate. We can also see how gradient accumulation works: we normalize the loss so we get the average at the end of accumulation and once we have enough steps we run the optimization. Now the question is: does this use the same amount of memory as the previous steps? Let's check:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> print_gpu_utilization()
|
||||
GPU memory occupied: 5363 MB.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Indeed it does. Implementing these optimization techniques with 🤗 Accelerate only takes a handful of lines of code and comes with the benefit of more flexiblity in the training loop. For a full documentation of all features have a look at the [Accelerate documentation](https://huggingface.co/docs/accelerate/index).
|
||||
|
||||
## DataLoader
|
||||
|
||||
One of the important requirements to reach great training speed is the ability to feed the GPU at the maximum speed it can handle. By default everything happens in the main process and it might not be able to read the data from disk fast enough, and thus create a bottleneck, leading to GPU under-utilization.
|
||||
|
||||
- `DataLoader(pin_memory=True, ...)` which ensures that the data gets preloaded into the pinned memory on CPU and typically leads to much faster transfers from CPU to GPU memory.
|
||||
- `DataLoader(num_workers=4, ...)` - spawn several workers to pre-load data faster - during training watch the GPU utilization stats and if it's far from 100% experiment with raising the number of workers. Of course, the problem could be elsewhere so a very big number of workers won't necessarily lead to a better performance.
|
||||
|
||||
## DeepSpeed ZeRO
|
||||
|
||||
The in-depth details on how to use Deepspeed can be found [here](main_classes/deepspeed).
|
||||
|
||||
First, a quick decision tree:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Model fits onto a single GPU and you have enough space to fit a small batch size - you don't need to use Deepspeed as it'll only slow things down in this use case.
|
||||
2. Model doesn't fit onto a single GPU or you can't fit a small batch - use DeepSpeed ZeRO + CPU Offload and for much larger models NVMe Offload.
|
||||
|
||||
Now if the decision tree suggested you use DeepSpeed first you need to [install it](main_classes/deepspeed#installation), then follow one of the following guides to create a configuration file and launch DeepSpeed.
|
||||
|
||||
Activation:
|
||||
|
||||
- HF Trainer-based examples: see this [guide](main_classes/deepspeed#deployment-with-one-gpu).
|
||||
- Custom HF Trainer-based program: Same as above, but pass:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
TrainingArguments(deepspeed="/path/to/ds_config.json")
|
||||
```
|
||||
- Deployment in Notebooks: see this [guide](main_classes/deepspeed#deployment-in-notebooks).
|
||||
|
||||
- Custom training loop: This is somewhat complex but you can study how this is implemented in [HF Trainer](
|
||||
https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/master/src/transformers/trainer.py) - simply search for `deepspeed` in the code.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Choice of GPU
|
||||
Sometimes, even when applying all the above tweaks the throughput on a given GPU might still not be good enough. One easy solution is to change the type of GPU. For example switching from let's say a K80 (which you typically get on Google Colab) to a fancier GPU such as the V100 or A100. Although they are more expensive they are usually more cost effective than cheaper GPUs due to their larger memory and faster architecture.
|
||||
|
||||
Now, let's take a step back and discuss what we should optimize for when scaling the training of large models.
|
||||
|
||||
## How to scale
|
||||
|
||||
When we train models there are a two aspects we want to optimize at the same time:
|
||||
|
||||
- Data throughput/training time
|
||||
- Model performance
|
||||
|
||||
We have seen that each method changes the memory usage and throughput. In general we want to maximize the throughput (samples/second) to minimize the training cost. This is generally achieved by utilizing the GPU as much as possible and thus filling GPU memory to its limit. For example, as mentioned earlier, we only employ gradient accumulation when we want to use a batch size beyond the size of the GPU memory. If the desired batch size fits into memory then there is no reason to apply gradient accumulation which will only slow down training.
|
||||
|
||||
The second objective is model performance. Just because we can does not mean we should use a large batch size. As part of hyperparameter tuning you should determine which batch size yields the best result and then optimize the throughput accordingly.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Efficient Software Prebuilds
|
||||
|
||||
PyTorch's [pip and conda builds](https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/#start-locally) come prebuit with the cuda toolkit which is enough to run PyTorch, but it is insufficient if you need to build cuda extensions.
|
||||
|
||||
At times it may take an additional effort to pre-build some components, e.g., if you're using libraries like `apex` that don't come pre-compiled. In other situations figuring out how to install the right cuda toolkit system-wide can be complicated. To address these users' needs PyTorch and NVIDIA release a new version of NGC docker container which already comes with everything prebuilt and you just need to install your programs on it and it will run out of the box.
|
||||
|
||||
This approach is also useful if you want to tweak the pytorch source and/or make a new customized build.
|
||||
|
||||
To find the docker image version you want start [here](https://docs.nvidia.com/deeplearning/frameworks/pytorch-release-notes/), choose one of the latest monthly releases. Go into the release's notes for the desired release, check that the environment's components are matching your needs (including NVIDIA Driver requirements!) and then at the very top of that document go to the corresponding NGC page. If for some reason you get lost, here is [the index of all PyTorch NGC images](https://ngc.nvidia.com/catalog/containers/nvidia:pytorch).
|
||||
|
||||
Next follow the instructions to download and deploy the docker image.
|
||||
|
||||
## Sparsity
|
||||
|
||||
### Mixture of Experts
|
||||
|
||||
Quite a few of the recent papers reported a 4-5x training speedup and a faster inference by integrating
|
||||
Mixture of Experts (MoE) into the Transformer models.
|
||||
|
||||
Since it has been discovered that more parameters lead to better performance, this technique allows to increase the number of parameters by an order of magnitude without increasing training costs.
|
||||
|
||||
In this approach every other FFN layer is replaced with a MoE Layer which consists of many experts, with a gated function that trains each expert in a balanced way depending on the input token's position in a sequence.
|
||||
|
||||
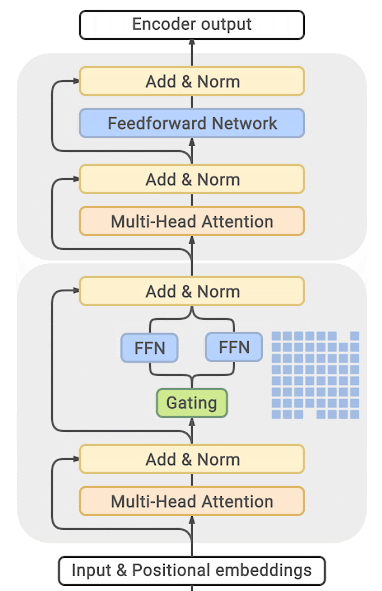
|
||||
|
||||
(source: [GLAM](https://ai.googleblog.com/2021/12/more-efficient-in-context-learning-with.html))
|
||||
|
||||
You can find exhaustive details and comparison tables in the papers listed at the end of this section.
|
||||
|
||||
The main drawback of this approach is that it requires staggering amounts of GPU memory - almost an order of magnitude larger than its dense equivalent. Various distillation and approaches are proposed to how to overcome the much higher memory requirements.
|
||||
|
||||
There is direct trade-off though, you can use just a few experts with a 2-3x smaller base model instead of dozens or hundreds experts leading to a 5x smaller model and thus increase the training speed moderately while increasing the memory requirements moderately as well.
|
||||
|
||||
Most related papers and implementations are built around Tensorflow/TPUs:
|
||||
|
||||
- [GShard: Scaling Giant Models with Conditional Computation and Automatic Sharding](https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.16668)
|
||||
- [Switch Transformers: Scaling to Trillion Parameter Models with Simple and Efficient Sparsity](https://arxiv.org/abs/2101.03961)
|
||||
- [GLaM: Generalist Language Model (GLaM)](https://ai.googleblog.com/2021/12/more-efficient-in-context-learning-with.html)
|
||||
|
||||
And for Pytorch DeepSpeed has built one as well: [DeepSpeed-MoE: Advancing Mixture-of-Experts Inference and Training to Power Next-Generation AI Scale](https://arxiv.org/abs/2201.05596), [Mixture of Experts](https://www.deepspeed.ai/tutorials/mixture-of-experts/) - blog posts: [1](https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/blog/deepspeed-powers-8x-larger-moe-model-training-with-high-performance/), [2](https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/publication/scalable-and-efficient-moe-training-for-multitask-multilingual-models/) and specific deployment with large transformer-based natural language generation models: [blog post](https://www.deepspeed.ai/news/2021/12/09/deepspeed-moe-nlg.html), [Megatron-Deepspeed branch](Thttps://github.com/microsoft/Megatron-DeepSpeed/tree/moe-training).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Scaling beyond a single GPU
|
||||
|
||||
For some applications, such as pretraining large language models, applying all the approaches above might still not be fast enough. In this case you want to scale your experiment to several GPUs.
|
||||
|
||||
Another use case for training on many GPUs is if the model does not fit on a single GPU with all the mentioned tricks. There are still more methods we can apply although life starts to get a bit more complicated. This usually involves some form of pipeline or tensor parallelism where the model itself is distributed across several GPUs. One can also make use of DeepSpeed which implements some of these parallelism strategies along with some more optimization to reduce the memory footprint such as partitioning the optimizer states. You can read more about this in the ["Multi-GPU training" section](perf_train_gpu_many).
|
||||
|
||||
## Inference with torchdynamo
|
||||
TorchDynamo is a new tracer that uses Python’s frame evaluation API to automatically create FX traces from existing PyTorch programs. After capturing the FX graph, different backends can be deployed to lower the graph to an optimized engine. One solution is using the [TensorRT](https://developer.nvidia.com/tensorrt) or NVFuser as backend. You can choose one option below for performance boost.
|
||||
```
|
||||
TrainingArguments(torchdynamo="eager") #enable eager model GPU. No performance boost
|
||||
TrainingArguments(torchdynamo="nvfuser") #enable nvfuser
|
||||
TrainingArguments(torchdynamo="fx2trt") #enable tensorRT fp32
|
||||
TrainingArguments(torchdynamo="fx2trt-f16") #enable tensorRT fp16
|
||||
```
|
||||
This feature involves 3 different libraries. To install them, please follow the instructions below:
|
||||
- [Torchdynamo installation](https://github.com/pytorch/torchdynamo#requirements-and-setup)
|
||||
- [Functorch installation](https://github.com/pytorch/functorch#install)
|
||||
- [Torch-TensorRT(FX) installation](https://github.com/pytorch/TensorRT/blob/master/docsrc/tutorials/getting_started_with_fx_path.rst#installation)
|
||||
20
docs/source/en/perf_train_special.mdx
Normal file
20
docs/source/en/perf_train_special.mdx
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,20 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Training on Specialized Hardware
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Note: Most of the strategies introduced in the [single GPU section](perf_train_gpu_one) (such as mixed precision training or gradient accumulation) and [mutli-GPU section](perf_train_gpu_many) are generic and apply to training models in general so make sure to have a look at it before diving into this section.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
This document will be completed soon with information on how to train on specialized hardware.
|
||||
20
docs/source/en/perf_train_tpu.mdx
Normal file
20
docs/source/en/perf_train_tpu.mdx
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,20 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Training on TPUs
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Note: Most of the strategies introduced in the [single GPU section](perf_train_gpu_one) (such as mixed precision training or gradient accumulation) and [mutli-GPU section](perf_train_gpu_many) are generic and apply to training models in general so make sure to have a look at it before diving into this section.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
This document will be completed soon with information on how to train on TPUs.
|
||||
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
@ -20,7 +20,7 @@ The [`pipeline`] makes it simple to use any model from the [Model Hub](https://h
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Take a look at the [`pipeline`] documentation for a complete list of supported taska.
|
||||
Take a look at the [`pipeline`] documentation for a complete list of supported tasks.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -244,7 +244,7 @@ For example, the [MInDS-14](https://huggingface.co/datasets/PolyAI/minds14) data
|
||||
'sampling_rate': 8000}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
1. Use 🤗 Datasets' [`cast_column`](https://huggingface.co/docs/datasets/package_reference/main_classes.html#datasets.Dataset.cast_column) method to upsample the sampling rate to 16kHz:
|
||||
1. Use 🤗 Datasets' [`~datasets.Dataset.cast_column`] method to upsample the sampling rate to 16kHz:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> dataset = dataset.cast_column("audio", Audio(sampling_rate=16_000))
|
||||
|
||||
@ -389,3 +389,42 @@ One particularly cool 🤗 Transformers feature is the ability to save a model a
|
||||
```
|
||||
</tf>
|
||||
</frameworkcontent>
|
||||
|
||||
## Custom model builds
|
||||
|
||||
You can modify the model's configuration class to change how a model is built. The configuration specifies a model's attributes, such as the number of hidden layers or attention heads. You start from scratch when you initialize a model from a custom configuration class. The model attributes are randomly initialized, and you'll need to train the model before you can use it to get meaningful results.
|
||||
|
||||
Start by importing [`AutoConfig`], and then load the pretrained model you want to modify. Within [`AutoConfig.from_pretrained`], you can specify the attribute you want to change, such as the number of attention heads:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoConfig
|
||||
|
||||
>>> my_config = AutoConfig.from_pretrained("distilbert-base-uncased", n_heads=12)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<frameworkcontent>
|
||||
<pt>
|
||||
Create a model from your custom configuration with [`AutoModel.from_config`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoModel
|
||||
|
||||
>>> my_model = AutoModel.from_config(my_config)
|
||||
```
|
||||
</pt>
|
||||
<tf>
|
||||
Create a model from your custom configuration with [`TFAutoModel.from_config`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import TFAutoModel
|
||||
|
||||
>>> my_model = TFAutoModel.from_config(my_config)
|
||||
```
|
||||
</tf>
|
||||
</frameworkcontent>
|
||||
|
||||
Take a look at the [Create a custom architecture](./create_a_model) guide for more information about building custom configurations.
|
||||
|
||||
## What's next?
|
||||
|
||||
Now that you've completed the 🤗 Transformers quick tour, check out our guides and learn how to do more specific things like writing a custom model, fine-tuning a model for a task, and how to train a model with a script. If you're interested in learning more about 🤗 Transformers core concepts, grab a cup of coffee and take a look at our Conceptual Guides!
|
||||
@ -50,14 +50,20 @@ Ready-made configurations include the following architectures:
|
||||
- BEiT
|
||||
- BERT
|
||||
- BigBird
|
||||
- BigBirdPegasus
|
||||
- BigBird-Pegasus
|
||||
- Blenderbot
|
||||
- BlenderbotSmall
|
||||
- BLOOM
|
||||
- CamemBERT
|
||||
- CodeGen
|
||||
- ConvBERT
|
||||
- ConvNeXT
|
||||
- Data2VecText
|
||||
- Data2VecVision
|
||||
- DeBERTa
|
||||
- DeBERTa-v2
|
||||
- DeiT
|
||||
- DETR
|
||||
- DistilBERT
|
||||
- ELECTRA
|
||||
- FlauBERT
|
||||
@ -65,19 +71,27 @@ Ready-made configurations include the following architectures:
|
||||
- GPT-J
|
||||
- I-BERT
|
||||
- LayoutLM
|
||||
- LayoutLMv3
|
||||
- LeViT
|
||||
- LongT5
|
||||
- M2M100
|
||||
- Marian
|
||||
- mBART
|
||||
- MobileBERT
|
||||
- MobileViT
|
||||
- OpenAI GPT-2
|
||||
- Perceiver
|
||||
- PLBart
|
||||
- ResNet
|
||||
- RoBERTa
|
||||
- RoFormer
|
||||
- SqueezeBERT
|
||||
- T5
|
||||
- TAPEX
|
||||
- ViT
|
||||
- XLM
|
||||
- XLM-RoBERTa
|
||||
- XLM-RoBERTa-XL
|
||||
- YOLOS
|
||||
|
||||
In the next two sections, we'll show you how to:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -117,7 +117,7 @@ The preprocessing function needs to:
|
||||
... return batch
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Use 🤗 Datasets [`map`](https://huggingface.co/docs/datasets/package_reference/main_classes.html#datasets.Dataset.map) function to apply the preprocessing function over the entire dataset. You can speed up the map function by increasing the number of processes with `num_proc`. Remove the columns you don't need:
|
||||
Use 🤗 Datasets [`~datasets.Dataset.map`] function to apply the preprocessing function over the entire dataset. You can speed up the map function by increasing the number of processes with `num_proc`. Remove the columns you don't need:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> encoded_minds = minds.map(prepare_dataset, remove_columns=minds.column_names["train"], num_proc=4)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -129,7 +129,7 @@ The preprocessing function needs to:
|
||||
... return inputs
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Use 🤗 Datasets [`map`](https://huggingface.co/docs/datasets/package_reference/main_classes.html#datasets.Dataset.map) function to apply the preprocessing function over the entire dataset. You can speed up the `map` function by setting `batched=True` to process multiple elements of the dataset at once. Remove the columns you don't need, and rename `intent_class` to `label` because that is what the model expects:
|
||||
Use 🤗 Datasets [`~datasets.Dataset.map`] function to apply the preprocessing function over the entire dataset. You can speed up the `map` function by setting `batched=True` to process multiple elements of the dataset at once. Remove the columns you don't need, and rename `intent_class` to `label` because that is what the model expects:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> encoded_minds = minds.map(preprocess_function, remove_columns="audio", batched=True)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -95,7 +95,7 @@ Create a preprocessing function that will apply the transforms and return the `p
|
||||
... return examples
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Use 🤗 Dataset's [`with_transform`](https://huggingface.co/docs/datasets/package_reference/main_classes.html?#datasets.Dataset.with_transform) method to apply the transforms over the entire dataset. The transforms are applied on-the-fly when you load an element of the dataset:
|
||||
Use 🤗 Dataset's [`~datasets.Dataset.with_transform`] method to apply the transforms over the entire dataset. The transforms are applied on-the-fly when you load an element of the dataset:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> food = food.with_transform(transforms)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -118,7 +118,7 @@ Here is how you can create a preprocessing function to convert the list to a str
|
||||
... return tokenizer([" ".join(x) for x in examples["answers.text"]], truncation=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Use 🤗 Datasets [`map`](https://huggingface.co/docs/datasets/package_reference/main_classes.html#datasets.Dataset.map) function to apply the preprocessing function over the entire dataset. You can speed up the `map` function by setting `batched=True` to process multiple elements of the dataset at once and increasing the number of processes with `num_proc`. Remove the columns you don't need:
|
||||
Use 🤗 Datasets [`~datasets.Dataset.map`] function to apply the preprocessing function over the entire dataset. You can speed up the `map` function by setting `batched=True` to process multiple elements of the dataset at once and increasing the number of processes with `num_proc`. Remove the columns you don't need:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> tokenized_eli5 = eli5.map(
|
||||
@ -141,6 +141,7 @@ Now you need a second preprocessing function to capture text truncated from any
|
||||
>>> def group_texts(examples):
|
||||
... concatenated_examples = {k: sum(examples[k], []) for k in examples.keys()}
|
||||
... total_length = len(concatenated_examples[list(examples.keys())[0]])
|
||||
... total_length = (total_length // block_size) * block_size
|
||||
... result = {
|
||||
... k: [t[i : i + block_size] for i in range(0, total_length, block_size)]
|
||||
... for k, t in concatenated_examples.items()
|
||||
@ -244,7 +245,7 @@ At this point, only three steps remain:
|
||||
```
|
||||
</pt>
|
||||
<tf>
|
||||
To fine-tune a model in TensorFlow, start by converting your datasets to the `tf.data.Dataset` format with [`to_tf_dataset`](https://huggingface.co/docs/datasets/package_reference/main_classes.html#datasets.Dataset.to_tf_dataset). Specify inputs and labels in `columns`, whether to shuffle the dataset order, batch size, and the data collator:
|
||||
To fine-tune a model in TensorFlow, start by converting your datasets to the `tf.data.Dataset` format with [`~datasets.Dataset.to_tf_dataset`]. Specify inputs and labels in `columns`, whether to shuffle the dataset order, batch size, and the data collator:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> tf_train_set = lm_dataset["train"].to_tf_dataset(
|
||||
@ -351,7 +352,7 @@ At this point, only three steps remain:
|
||||
```
|
||||
</pt>
|
||||
<tf>
|
||||
To fine-tune a model in TensorFlow, start by converting your datasets to the `tf.data.Dataset` format with [`to_tf_dataset`](https://huggingface.co/docs/datasets/package_reference/main_classes.html#datasets.Dataset.to_tf_dataset). Specify inputs and labels in `columns`, whether to shuffle the dataset order, batch size, and the data collator:
|
||||
To fine-tune a model in TensorFlow, start by converting your datasets to the `tf.data.Dataset` format with [`~datasets.Dataset.to_tf_dataset`]. Specify inputs and labels in `columns`, whether to shuffle the dataset order, batch size, and the data collator:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> tf_train_set = lm_dataset["train"].to_tf_dataset(
|
||||
|
||||
@ -79,7 +79,7 @@ The preprocessing function needs to do:
|
||||
... return {k: [v[i : i + 4] for i in range(0, len(v), 4)] for k, v in tokenized_examples.items()}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Use 🤗 Datasets [`map`](https://huggingface.co/docs/datasets/package_reference/main_classes.html#datasets.Dataset.map) function to apply the preprocessing function over the entire dataset. You can speed up the `map` function by setting `batched=True` to process multiple elements of the dataset at once:
|
||||
Use 🤗 Datasets [`~datasets.Dataset.map`] function to apply the preprocessing function over the entire dataset. You can speed up the `map` function by setting `batched=True` to process multiple elements of the dataset at once:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
tokenized_swag = swag.map(preprocess_function, batched=True)
|
||||
@ -224,7 +224,7 @@ At this point, only three steps remain:
|
||||
```
|
||||
</pt>
|
||||
<tf>
|
||||
To fine-tune a model in TensorFlow, start by converting your datasets to the `tf.data.Dataset` format with [`to_tf_dataset`](https://huggingface.co/docs/datasets/package_reference/main_classes.html#datasets.Dataset.to_tf_dataset). Specify inputs in `columns`, targets in `label_cols`, whether to shuffle the dataset order, batch size, and the data collator:
|
||||
To fine-tune a model in TensorFlow, start by converting your datasets to the `tf.data.Dataset` format with [`~datasets.Dataset.to_tf_dataset`]. Specify inputs in `columns`, targets in `label_cols`, whether to shuffle the dataset order, batch size, and the data collator:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> data_collator = DataCollatorForMultipleChoice(tokenizer=tokenizer)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -126,7 +126,7 @@ Here is how you can create a function to truncate and map the start and end toke
|
||||
... return inputs
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Use 🤗 Datasets [`map`](https://huggingface.co/docs/datasets/package_reference/main_classes.html#datasets.Dataset.map) function to apply the preprocessing function over the entire dataset. You can speed up the `map` function by setting `batched=True` to process multiple elements of the dataset at once. Remove the columns you don't need:
|
||||
Use 🤗 Datasets [`~datasets.Dataset.map`] function to apply the preprocessing function over the entire dataset. You can speed up the `map` function by setting `batched=True` to process multiple elements of the dataset at once. Remove the columns you don't need:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> tokenized_squad = squad.map(preprocess_function, batched=True, remove_columns=squad["train"].column_names)
|
||||
@ -199,7 +199,7 @@ At this point, only three steps remain:
|
||||
```
|
||||
</pt>
|
||||
<tf>
|
||||
To fine-tune a model in TensorFlow, start by converting your datasets to the `tf.data.Dataset` format with [`to_tf_dataset`](https://huggingface.co/docs/datasets/package_reference/main_classes.html#datasets.Dataset.to_tf_dataset). Specify inputs and the start and end positions of an answer in `columns`, whether to shuffle the dataset order, batch size, and the data collator:
|
||||
To fine-tune a model in TensorFlow, start by converting your datasets to the `tf.data.Dataset` format with [`~datasets.Dataset.to_tf_dataset`]. Specify inputs and the start and end positions of an answer in `columns`, whether to shuffle the dataset order, batch size, and the data collator:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> tf_train_set = tokenized_squad["train"].to_tf_dataset(
|
||||
|
||||
Some files were not shown because too many files have changed in this diff Show More
Reference in New Issue
Block a user