mirror of
https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git
synced 2025-11-02 10:34:36 +08:00
Compare commits
152 Commits
update-qua
...
dduf-compa
| Author | SHA1 | Date | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 8381165040 | |||
| 6181c6b095 | |||
| 33c12e4d80 | |||
| 7d303efa5f | |||
| 5fcf6286bf | |||
| bcc50cc7ce | |||
| d363e71d0e | |||
| 9094b87dd4 | |||
| 10feacd88a | |||
| e8508924fd | |||
| 5290f6a62d | |||
| 91b8ab18b7 | |||
| 217c47e31b | |||
| 52d135426f | |||
| 425af6cdc2 | |||
| e5c45a6679 | |||
| 3e2769a3c9 | |||
| 5fba3f99c0 | |||
| 6acb4e43a7 | |||
| 80f2b1610f | |||
| 0938b57770 | |||
| dada0fd85f | |||
| 34f4080ff5 | |||
| fa8763ce17 | |||
| 4bc39de5c3 | |||
| 48833071c0 | |||
| 8e806a336f | |||
| 7238387f67 | |||
| de8a0b7547 | |||
| 1452dc2514 | |||
| 9e420e0269 | |||
| 1ccca8f48c | |||
| 734a186fd2 | |||
| c8c8dffbe4 | |||
| 943231a1ff | |||
| 7f95372c62 | |||
| 4866c7ba49 | |||
| 9ad4c93536 | |||
| 15ab310c3a | |||
| 98e8062df3 | |||
| 44f88d8ccb | |||
| 66ab300aaf | |||
| ab0f65f05d | |||
| a5bb528471 | |||
| e27465c801 | |||
| b0a51e5cff | |||
| a928d9c128 | |||
| e682c17e4a | |||
| 50189e36a6 | |||
| 95a855e212 | |||
| 482cb28a18 | |||
| 35447054f5 | |||
| 93f87d3cf5 | |||
| 54aae121eb | |||
| beb2c66ec3 | |||
| 8ee5e2ff6e | |||
| 1ed1de2fec | |||
| baa3b22137 | |||
| 1da1e0d7f2 | |||
| 46df859975 | |||
| accb7204f9 | |||
| c7a109ec81 | |||
| 329f5dbf97 | |||
| b8cdc262d5 | |||
| 346597b644 | |||
| 3deaa8179d | |||
| 125de41643 | |||
| 7a7f27697a | |||
| 901f504580 | |||
| ee37bf0d95 | |||
| f9c7e6021e | |||
| 527dc04e46 | |||
| 4955e4e638 | |||
| f0dec874f0 | |||
| 31299670cd | |||
| 31830474bf | |||
| f41d5d8f74 | |||
| 7b5f76e32e | |||
| c24c79ebf9 | |||
| 9ab8c5b503 | |||
| 3480cbb97e | |||
| 19dabe9636 | |||
| f7427f58ed | |||
| 737f4dc4b6 | |||
| 89d7bf584f | |||
| 0b5b5e6a70 | |||
| f491096f7d | |||
| 01ad80f820 | |||
| 9d6f0ddcec | |||
| 6300212946 | |||
| 5e8c1d713d | |||
| 57ca9e6d2f | |||
| 44af935ec5 | |||
| 2b053fdf1a | |||
| 4f0bf9864c | |||
| f4b674f269 | |||
| 5523e38b55 | |||
| 4120cb257f | |||
| 2910015d6d | |||
| 637225508f | |||
| 0600f46353 | |||
| 5f8b24ee12 | |||
| 0d99a938aa | |||
| 8f48ccf548 | |||
| 4c1388f48e | |||
| 6c3f168b36 | |||
| 5bfb40bc8e | |||
| 784d22078a | |||
| 6bc0c219c1 | |||
| 64b73e61f8 | |||
| a0ba631519 | |||
| 1f6b423f0c | |||
| d5cf91b346 | |||
| 5a45617887 | |||
| 1141eff1bd | |||
| 4d1d0f29a4 | |||
| 0e805e6d1e | |||
| 73b4ab1085 | |||
| bdb29ff9f3 | |||
| bfc3556b20 | |||
| 95c10fedb3 | |||
| 890ea7de93 | |||
| b76a292bde | |||
| a830df2909 | |||
| a464afbe2a | |||
| b13916c09d | |||
| 4e6b19cd95 | |||
| 9121ab8fe8 | |||
| 1de3598d30 | |||
| f4c04ba32b | |||
| 11cc2295c7 | |||
| 74db22f905 | |||
| 97514a8ba3 | |||
| 62ab94dea8 | |||
| c50b5675d6 | |||
| a0f4f3174f | |||
| 4dc1a69349 | |||
| 1e492afd61 | |||
| 857d46ca0c | |||
| 098962dac2 | |||
| c1a8520419 | |||
| 1339a14dca | |||
| 318fe25f22 | |||
| 3a8eb74668 | |||
| 54be2d7ae8 | |||
| 286ffaaf0a | |||
| 861758e235 | |||
| 42b36d7395 | |||
| 597efd21d2 | |||
| d9e6f307e7 | |||
| 1867be666d | |||
| 6a912ff2c5 |
@ -133,7 +133,7 @@ class CircleCIJob:
|
||||
"command": """dpkg-query --show --showformat='${Installed-Size}\t${Package}\n' | sort -rh | head -25 | sort -h | awk '{ package=$2; sub(".*/", "", package); printf("%.5f GB %s\n", $1/1024/1024, package)}' || true"""}
|
||||
},
|
||||
{"run": {"name": "Create `test-results` directory", "command": "mkdir test-results"}},
|
||||
{"run": {"name": "Get files to test", "command":f'curl -L -o {self.job_name}_test_list.txt <<pipeline.parameters.{self.job_name}_test_list>>' if self.name != "pr_documentation_tests" else 'echo "Skipped"'}},
|
||||
{"run": {"name": "Get files to test", "command":f'curl -L -o {self.job_name}_test_list.txt <<pipeline.parameters.{self.job_name}_test_list>> --header "Circle-Token: $CIRCLE_TOKEN"' if self.name != "pr_documentation_tests" else 'echo "Skipped"'}},
|
||||
{"run": {"name": "Split tests across parallel nodes: show current parallel tests",
|
||||
"command": f"TESTS=$(circleci tests split --split-by=timings {self.job_name}_test_list.txt) && echo $TESTS > splitted_tests.txt && echo $TESTS | tr ' ' '\n'" if self.parallelism else f"awk '{{printf \"%s \", $0}}' {self.job_name}_test_list.txt > splitted_tests.txt"
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -371,9 +371,14 @@ def create_circleci_config(folder=None):
|
||||
**{j.job_name + "_test_list":{"type":"string", "default":''} for j in jobs},
|
||||
**{j.job_name + "_parallelism":{"type":"integer", "default":1} for j in jobs},
|
||||
},
|
||||
"jobs" : {j.job_name: j.to_dict() for j in jobs},
|
||||
"workflows": {"version": 2, "run_tests": {"jobs": [j.job_name for j in jobs]}}
|
||||
"jobs" : {j.job_name: j.to_dict() for j in jobs}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if "CIRCLE_TOKEN" in os.environ:
|
||||
# For private forked repo. (e.g. new model addition)
|
||||
config["workflows"] = {"version": 2, "run_tests": {"jobs": [{j.job_name: {"context": ["TRANSFORMERS_CONTEXT"]}} for j in jobs]}}
|
||||
else:
|
||||
# For public repo. (e.g. `transformers`)
|
||||
config["workflows"] = {"version": 2, "run_tests": {"jobs": [j.job_name for j in jobs]}}
|
||||
with open(os.path.join(folder, "generated_config.yml"), "w") as f:
|
||||
f.write(yaml.dump(config, sort_keys=False, default_flow_style=False).replace("' << pipeline", " << pipeline").replace(">> '", " >>"))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
642
.github/workflows/build-docker-images.yml
vendored
642
.github/workflows/build-docker-images.yml
vendored
@ -3,7 +3,7 @@ name: Build docker images (scheduled)
|
||||
on:
|
||||
push:
|
||||
branches:
|
||||
- update-quantization-docker
|
||||
- build_ci_docker_image*
|
||||
repository_dispatch:
|
||||
workflow_call:
|
||||
inputs:
|
||||
@ -18,341 +18,341 @@ concurrency:
|
||||
cancel-in-progress: false
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
# latest-docker:
|
||||
# name: "Latest PyTorch + TensorFlow [dev]"
|
||||
# runs-on:
|
||||
# group: aws-general-8-plus
|
||||
# steps:
|
||||
# -
|
||||
# name: Set up Docker Buildx
|
||||
# uses: docker/setup-buildx-action@v3
|
||||
# -
|
||||
# name: Check out code
|
||||
# uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
# -
|
||||
# name: Login to DockerHub
|
||||
# uses: docker/login-action@v3
|
||||
# with:
|
||||
# username: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME }}
|
||||
# password: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_PASSWORD }}
|
||||
# -
|
||||
# name: Build and push
|
||||
# uses: docker/build-push-action@v5
|
||||
# with:
|
||||
# context: ./docker/transformers-all-latest-gpu
|
||||
# build-args: |
|
||||
# REF=main
|
||||
# push: true
|
||||
# tags: huggingface/transformers-all-latest-gpu${{ inputs.image_postfix }}
|
||||
# # Push CI images still need to be re-built daily
|
||||
# -
|
||||
# name: Build and push (for Push CI) in a daily basis
|
||||
# # This condition allows `schedule` events, or `push` events that trigger this workflow NOT via `workflow_call`.
|
||||
# # The later case is useful for manual image building for debugging purpose. Use another tag in this case!
|
||||
# if: inputs.image_postfix != '-push-ci'
|
||||
# uses: docker/build-push-action@v5
|
||||
# with:
|
||||
# context: ./docker/transformers-all-latest-gpu
|
||||
# build-args: |
|
||||
# REF=main
|
||||
# push: true
|
||||
# tags: huggingface/transformers-all-latest-gpu-push-ci
|
||||
latest-docker:
|
||||
name: "Latest PyTorch + TensorFlow [dev]"
|
||||
runs-on:
|
||||
group: aws-general-8-plus
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Set up Docker Buildx
|
||||
uses: docker/setup-buildx-action@v3
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Check out code
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Login to DockerHub
|
||||
uses: docker/login-action@v3
|
||||
with:
|
||||
username: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME }}
|
||||
password: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_PASSWORD }}
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Build and push
|
||||
uses: docker/build-push-action@v5
|
||||
with:
|
||||
context: ./docker/transformers-all-latest-gpu
|
||||
build-args: |
|
||||
REF=main
|
||||
push: true
|
||||
tags: huggingface/transformers-all-latest-gpu${{ inputs.image_postfix }}
|
||||
# Push CI images still need to be re-built daily
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Build and push (for Push CI) in a daily basis
|
||||
# This condition allows `schedule` events, or `push` events that trigger this workflow NOT via `workflow_call`.
|
||||
# The later case is useful for manual image building for debugging purpose. Use another tag in this case!
|
||||
if: inputs.image_postfix != '-push-ci'
|
||||
uses: docker/build-push-action@v5
|
||||
with:
|
||||
context: ./docker/transformers-all-latest-gpu
|
||||
build-args: |
|
||||
REF=main
|
||||
push: true
|
||||
tags: huggingface/transformers-all-latest-gpu-push-ci
|
||||
|
||||
# - name: Post to Slack
|
||||
# if: always()
|
||||
# uses: huggingface/hf-workflows/.github/actions/post-slack@main
|
||||
# with:
|
||||
# slack_channel: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_DOCKER }}
|
||||
# title: 🤗 Results of the transformers-all-latest-gpu-push-ci docker build
|
||||
# status: ${{ job.status }}
|
||||
# slack_token: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
- name: Post to Slack
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
uses: huggingface/hf-workflows/.github/actions/post-slack@main
|
||||
with:
|
||||
slack_channel: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_DOCKER }}
|
||||
title: 🤗 Results of the transformers-all-latest-gpu-push-ci docker build
|
||||
status: ${{ job.status }}
|
||||
slack_token: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
|
||||
# latest-torch-deepspeed-docker:
|
||||
# name: "Latest PyTorch + DeepSpeed"
|
||||
# runs-on:
|
||||
# group: aws-general-8-plus
|
||||
# steps:
|
||||
# -
|
||||
# name: Set up Docker Buildx
|
||||
# uses: docker/setup-buildx-action@v3
|
||||
# -
|
||||
# name: Check out code
|
||||
# uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
# -
|
||||
# name: Login to DockerHub
|
||||
# uses: docker/login-action@v3
|
||||
# with:
|
||||
# username: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME }}
|
||||
# password: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_PASSWORD }}
|
||||
# -
|
||||
# name: Build and push
|
||||
# uses: docker/build-push-action@v5
|
||||
# with:
|
||||
# context: ./docker/transformers-pytorch-deepspeed-latest-gpu
|
||||
# build-args: |
|
||||
# REF=main
|
||||
# push: true
|
||||
# tags: huggingface/transformers-pytorch-deepspeed-latest-gpu${{ inputs.image_postfix }}
|
||||
latest-torch-deepspeed-docker:
|
||||
name: "Latest PyTorch + DeepSpeed"
|
||||
runs-on:
|
||||
group: aws-general-8-plus
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Set up Docker Buildx
|
||||
uses: docker/setup-buildx-action@v3
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Check out code
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Login to DockerHub
|
||||
uses: docker/login-action@v3
|
||||
with:
|
||||
username: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME }}
|
||||
password: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_PASSWORD }}
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Build and push
|
||||
uses: docker/build-push-action@v5
|
||||
with:
|
||||
context: ./docker/transformers-pytorch-deepspeed-latest-gpu
|
||||
build-args: |
|
||||
REF=main
|
||||
push: true
|
||||
tags: huggingface/transformers-pytorch-deepspeed-latest-gpu${{ inputs.image_postfix }}
|
||||
|
||||
# - name: Post to Slack
|
||||
# if: always()
|
||||
# uses: huggingface/hf-workflows/.github/actions/post-slack@main
|
||||
# with:
|
||||
# slack_channel: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_DOCKER}}
|
||||
# title: 🤗 Results of the transformers-pytorch-deepspeed-latest-gpu docker build
|
||||
# status: ${{ job.status }}
|
||||
# slack_token: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
- name: Post to Slack
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
uses: huggingface/hf-workflows/.github/actions/post-slack@main
|
||||
with:
|
||||
slack_channel: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_DOCKER}}
|
||||
title: 🤗 Results of the transformers-pytorch-deepspeed-latest-gpu docker build
|
||||
status: ${{ job.status }}
|
||||
slack_token: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
|
||||
# # Can't build 2 images in a single job `latest-torch-deepspeed-docker` (for `nvcr.io/nvidia`)
|
||||
# latest-torch-deepspeed-docker-for-push-ci-daily-build:
|
||||
# name: "Latest PyTorch + DeepSpeed (Push CI - Daily Build)"
|
||||
# runs-on:
|
||||
# group: aws-general-8-plus
|
||||
# steps:
|
||||
# -
|
||||
# name: Set up Docker Buildx
|
||||
# uses: docker/setup-buildx-action@v3
|
||||
# -
|
||||
# name: Check out code
|
||||
# uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
# -
|
||||
# name: Login to DockerHub
|
||||
# uses: docker/login-action@v3
|
||||
# with:
|
||||
# username: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME }}
|
||||
# password: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_PASSWORD }}
|
||||
# # Push CI images still need to be re-built daily
|
||||
# -
|
||||
# name: Build and push (for Push CI) in a daily basis
|
||||
# # This condition allows `schedule` events, or `push` events that trigger this workflow NOT via `workflow_call`.
|
||||
# # The later case is useful for manual image building for debugging purpose. Use another tag in this case!
|
||||
# if: inputs.image_postfix != '-push-ci'
|
||||
# uses: docker/build-push-action@v5
|
||||
# with:
|
||||
# context: ./docker/transformers-pytorch-deepspeed-latest-gpu
|
||||
# build-args: |
|
||||
# REF=main
|
||||
# push: true
|
||||
# tags: huggingface/transformers-pytorch-deepspeed-latest-gpu-push-ci
|
||||
# Can't build 2 images in a single job `latest-torch-deepspeed-docker` (for `nvcr.io/nvidia`)
|
||||
latest-torch-deepspeed-docker-for-push-ci-daily-build:
|
||||
name: "Latest PyTorch + DeepSpeed (Push CI - Daily Build)"
|
||||
runs-on:
|
||||
group: aws-general-8-plus
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Set up Docker Buildx
|
||||
uses: docker/setup-buildx-action@v3
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Check out code
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Login to DockerHub
|
||||
uses: docker/login-action@v3
|
||||
with:
|
||||
username: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME }}
|
||||
password: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_PASSWORD }}
|
||||
# Push CI images still need to be re-built daily
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Build and push (for Push CI) in a daily basis
|
||||
# This condition allows `schedule` events, or `push` events that trigger this workflow NOT via `workflow_call`.
|
||||
# The later case is useful for manual image building for debugging purpose. Use another tag in this case!
|
||||
if: inputs.image_postfix != '-push-ci'
|
||||
uses: docker/build-push-action@v5
|
||||
with:
|
||||
context: ./docker/transformers-pytorch-deepspeed-latest-gpu
|
||||
build-args: |
|
||||
REF=main
|
||||
push: true
|
||||
tags: huggingface/transformers-pytorch-deepspeed-latest-gpu-push-ci
|
||||
|
||||
# - name: Post to Slack
|
||||
# if: always()
|
||||
# uses: huggingface/hf-workflows/.github/actions/post-slack@main
|
||||
# with:
|
||||
# slack_channel: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_DOCKER }}
|
||||
# title: 🤗 Results of the transformers-pytorch-deepspeed-latest-gpu-push-ci docker build
|
||||
# status: ${{ job.status }}
|
||||
# slack_token: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
- name: Post to Slack
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
uses: huggingface/hf-workflows/.github/actions/post-slack@main
|
||||
with:
|
||||
slack_channel: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_DOCKER }}
|
||||
title: 🤗 Results of the transformers-pytorch-deepspeed-latest-gpu-push-ci docker build
|
||||
status: ${{ job.status }}
|
||||
slack_token: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
|
||||
# doc-builder:
|
||||
# name: "Doc builder"
|
||||
# # Push CI doesn't need this image
|
||||
# if: inputs.image_postfix != '-push-ci'
|
||||
# runs-on:
|
||||
# group: aws-general-8-plus
|
||||
# steps:
|
||||
# -
|
||||
# name: Set up Docker Buildx
|
||||
# uses: docker/setup-buildx-action@v3
|
||||
# -
|
||||
# name: Check out code
|
||||
# uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
# -
|
||||
# name: Login to DockerHub
|
||||
# uses: docker/login-action@v3
|
||||
# with:
|
||||
# username: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME }}
|
||||
# password: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_PASSWORD }}
|
||||
# -
|
||||
# name: Build and push
|
||||
# uses: docker/build-push-action@v5
|
||||
# with:
|
||||
# context: ./docker/transformers-doc-builder
|
||||
# push: true
|
||||
# tags: huggingface/transformers-doc-builder
|
||||
doc-builder:
|
||||
name: "Doc builder"
|
||||
# Push CI doesn't need this image
|
||||
if: inputs.image_postfix != '-push-ci'
|
||||
runs-on:
|
||||
group: aws-general-8-plus
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Set up Docker Buildx
|
||||
uses: docker/setup-buildx-action@v3
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Check out code
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Login to DockerHub
|
||||
uses: docker/login-action@v3
|
||||
with:
|
||||
username: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME }}
|
||||
password: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_PASSWORD }}
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Build and push
|
||||
uses: docker/build-push-action@v5
|
||||
with:
|
||||
context: ./docker/transformers-doc-builder
|
||||
push: true
|
||||
tags: huggingface/transformers-doc-builder
|
||||
|
||||
# - name: Post to Slack
|
||||
# if: always()
|
||||
# uses: huggingface/hf-workflows/.github/actions/post-slack@main
|
||||
# with:
|
||||
# slack_channel: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_DOCKER }}
|
||||
# title: 🤗 Results of the huggingface/transformers-doc-builder docker build
|
||||
# status: ${{ job.status }}
|
||||
# slack_token: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
- name: Post to Slack
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
uses: huggingface/hf-workflows/.github/actions/post-slack@main
|
||||
with:
|
||||
slack_channel: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_DOCKER }}
|
||||
title: 🤗 Results of the huggingface/transformers-doc-builder docker build
|
||||
status: ${{ job.status }}
|
||||
slack_token: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
|
||||
# latest-pytorch:
|
||||
# name: "Latest PyTorch [dev]"
|
||||
# # Push CI doesn't need this image
|
||||
# if: inputs.image_postfix != '-push-ci'
|
||||
# runs-on:
|
||||
# group: aws-general-8-plus
|
||||
# steps:
|
||||
# -
|
||||
# name: Set up Docker Buildx
|
||||
# uses: docker/setup-buildx-action@v3
|
||||
# -
|
||||
# name: Check out code
|
||||
# uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
# -
|
||||
# name: Login to DockerHub
|
||||
# uses: docker/login-action@v3
|
||||
# with:
|
||||
# username: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME }}
|
||||
# password: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_PASSWORD }}
|
||||
# -
|
||||
# name: Build and push
|
||||
# uses: docker/build-push-action@v5
|
||||
# with:
|
||||
# context: ./docker/transformers-pytorch-gpu
|
||||
# build-args: |
|
||||
# REF=main
|
||||
# push: true
|
||||
# tags: huggingface/transformers-pytorch-gpu
|
||||
latest-pytorch:
|
||||
name: "Latest PyTorch [dev]"
|
||||
# Push CI doesn't need this image
|
||||
if: inputs.image_postfix != '-push-ci'
|
||||
runs-on:
|
||||
group: aws-general-8-plus
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Set up Docker Buildx
|
||||
uses: docker/setup-buildx-action@v3
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Check out code
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Login to DockerHub
|
||||
uses: docker/login-action@v3
|
||||
with:
|
||||
username: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME }}
|
||||
password: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_PASSWORD }}
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Build and push
|
||||
uses: docker/build-push-action@v5
|
||||
with:
|
||||
context: ./docker/transformers-pytorch-gpu
|
||||
build-args: |
|
||||
REF=main
|
||||
push: true
|
||||
tags: huggingface/transformers-pytorch-gpu
|
||||
|
||||
# - name: Post to Slack
|
||||
# if: always()
|
||||
# uses: huggingface/hf-workflows/.github/actions/post-slack@main
|
||||
# with:
|
||||
# slack_channel: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_DOCKER }}
|
||||
# title: 🤗 Results of the huggingface/transformers-pytorch-gpudocker build
|
||||
# status: ${{ job.status }}
|
||||
# slack_token: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
- name: Post to Slack
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
uses: huggingface/hf-workflows/.github/actions/post-slack@main
|
||||
with:
|
||||
slack_channel: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_DOCKER }}
|
||||
title: 🤗 Results of the huggingface/transformers-pytorch-gpudocker build
|
||||
status: ${{ job.status }}
|
||||
slack_token: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
|
||||
# latest-pytorch-amd:
|
||||
# name: "Latest PyTorch (AMD) [dev]"
|
||||
# runs-on:
|
||||
# group: aws-general-8-plus
|
||||
# steps:
|
||||
# -
|
||||
# name: Set up Docker Buildx
|
||||
# uses: docker/setup-buildx-action@v3
|
||||
# -
|
||||
# name: Check out code
|
||||
# uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
# -
|
||||
# name: Login to DockerHub
|
||||
# uses: docker/login-action@v3
|
||||
# with:
|
||||
# username: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME }}
|
||||
# password: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_PASSWORD }}
|
||||
# -
|
||||
# name: Build and push
|
||||
# uses: docker/build-push-action@v5
|
||||
# with:
|
||||
# context: ./docker/transformers-pytorch-amd-gpu
|
||||
# build-args: |
|
||||
# REF=main
|
||||
# push: true
|
||||
# tags: huggingface/transformers-pytorch-amd-gpu${{ inputs.image_postfix }}
|
||||
# # Push CI images still need to be re-built daily
|
||||
# -
|
||||
# name: Build and push (for Push CI) in a daily basis
|
||||
# # This condition allows `schedule` events, or `push` events that trigger this workflow NOT via `workflow_call`.
|
||||
# # The later case is useful for manual image building for debugging purpose. Use another tag in this case!
|
||||
# if: inputs.image_postfix != '-push-ci'
|
||||
# uses: docker/build-push-action@v5
|
||||
# with:
|
||||
# context: ./docker/transformers-pytorch-amd-gpu
|
||||
# build-args: |
|
||||
# REF=main
|
||||
# push: true
|
||||
# tags: huggingface/transformers-pytorch-amd-gpu-push-ci
|
||||
latest-pytorch-amd:
|
||||
name: "Latest PyTorch (AMD) [dev]"
|
||||
runs-on:
|
||||
group: aws-general-8-plus
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Set up Docker Buildx
|
||||
uses: docker/setup-buildx-action@v3
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Check out code
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Login to DockerHub
|
||||
uses: docker/login-action@v3
|
||||
with:
|
||||
username: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME }}
|
||||
password: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_PASSWORD }}
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Build and push
|
||||
uses: docker/build-push-action@v5
|
||||
with:
|
||||
context: ./docker/transformers-pytorch-amd-gpu
|
||||
build-args: |
|
||||
REF=main
|
||||
push: true
|
||||
tags: huggingface/transformers-pytorch-amd-gpu${{ inputs.image_postfix }}
|
||||
# Push CI images still need to be re-built daily
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Build and push (for Push CI) in a daily basis
|
||||
# This condition allows `schedule` events, or `push` events that trigger this workflow NOT via `workflow_call`.
|
||||
# The later case is useful for manual image building for debugging purpose. Use another tag in this case!
|
||||
if: inputs.image_postfix != '-push-ci'
|
||||
uses: docker/build-push-action@v5
|
||||
with:
|
||||
context: ./docker/transformers-pytorch-amd-gpu
|
||||
build-args: |
|
||||
REF=main
|
||||
push: true
|
||||
tags: huggingface/transformers-pytorch-amd-gpu-push-ci
|
||||
|
||||
# - name: Post to Slack
|
||||
# if: always()
|
||||
# uses: huggingface/hf-workflows/.github/actions/post-slack@main
|
||||
# with:
|
||||
# slack_channel: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_DOCKER }}
|
||||
# title: 🤗 Results of the huggingface/transformers-pytorch-amd-gpu-push-ci build
|
||||
# status: ${{ job.status }}
|
||||
# slack_token: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
- name: Post to Slack
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
uses: huggingface/hf-workflows/.github/actions/post-slack@main
|
||||
with:
|
||||
slack_channel: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_DOCKER }}
|
||||
title: 🤗 Results of the huggingface/transformers-pytorch-amd-gpu-push-ci build
|
||||
status: ${{ job.status }}
|
||||
slack_token: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
|
||||
# latest-tensorflow:
|
||||
# name: "Latest TensorFlow [dev]"
|
||||
# # Push CI doesn't need this image
|
||||
# if: inputs.image_postfix != '-push-ci'
|
||||
# runs-on:
|
||||
# group: aws-general-8-plus
|
||||
# steps:
|
||||
# -
|
||||
# name: Set up Docker Buildx
|
||||
# uses: docker/setup-buildx-action@v3
|
||||
# -
|
||||
# name: Check out code
|
||||
# uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
# -
|
||||
# name: Login to DockerHub
|
||||
# uses: docker/login-action@v3
|
||||
# with:
|
||||
# username: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME }}
|
||||
# password: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_PASSWORD }}
|
||||
# -
|
||||
# name: Build and push
|
||||
# uses: docker/build-push-action@v5
|
||||
# with:
|
||||
# context: ./docker/transformers-tensorflow-gpu
|
||||
# build-args: |
|
||||
# REF=main
|
||||
# push: true
|
||||
# tags: huggingface/transformers-tensorflow-gpu
|
||||
latest-tensorflow:
|
||||
name: "Latest TensorFlow [dev]"
|
||||
# Push CI doesn't need this image
|
||||
if: inputs.image_postfix != '-push-ci'
|
||||
runs-on:
|
||||
group: aws-general-8-plus
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Set up Docker Buildx
|
||||
uses: docker/setup-buildx-action@v3
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Check out code
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Login to DockerHub
|
||||
uses: docker/login-action@v3
|
||||
with:
|
||||
username: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME }}
|
||||
password: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_PASSWORD }}
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Build and push
|
||||
uses: docker/build-push-action@v5
|
||||
with:
|
||||
context: ./docker/transformers-tensorflow-gpu
|
||||
build-args: |
|
||||
REF=main
|
||||
push: true
|
||||
tags: huggingface/transformers-tensorflow-gpu
|
||||
|
||||
# - name: Post to Slack
|
||||
# if: always()
|
||||
# uses: huggingface/hf-workflows/.github/actions/post-slack@main
|
||||
# with:
|
||||
# slack_channel: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_DOCKER }}
|
||||
# title: 🤗 Results of the huggingface/transformers-tensorflow-gpu build
|
||||
# status: ${{ job.status }}
|
||||
# slack_token: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
- name: Post to Slack
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
uses: huggingface/hf-workflows/.github/actions/post-slack@main
|
||||
with:
|
||||
slack_channel: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_DOCKER }}
|
||||
title: 🤗 Results of the huggingface/transformers-tensorflow-gpu build
|
||||
status: ${{ job.status }}
|
||||
slack_token: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
|
||||
# latest-pytorch-deepspeed-amd:
|
||||
# name: "PyTorch + DeepSpeed (AMD) [dev]"
|
||||
# runs-on:
|
||||
# group: aws-general-8-plus
|
||||
# steps:
|
||||
# -
|
||||
# name: Set up Docker Buildx
|
||||
# uses: docker/setup-buildx-action@v3
|
||||
# -
|
||||
# name: Check out code
|
||||
# uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
# -
|
||||
# name: Login to DockerHub
|
||||
# uses: docker/login-action@v3
|
||||
# with:
|
||||
# username: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME }}
|
||||
# password: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_PASSWORD }}
|
||||
# -
|
||||
# name: Build and push
|
||||
# uses: docker/build-push-action@v5
|
||||
# with:
|
||||
# context: ./docker/transformers-pytorch-deepspeed-amd-gpu
|
||||
# build-args: |
|
||||
# REF=main
|
||||
# push: true
|
||||
# tags: huggingface/transformers-pytorch-deepspeed-amd-gpu${{ inputs.image_postfix }}
|
||||
# # Push CI images still need to be re-built daily
|
||||
# -
|
||||
# name: Build and push (for Push CI) in a daily basis
|
||||
# # This condition allows `schedule` events, or `push` events that trigger this workflow NOT via `workflow_call`.
|
||||
# # The later case is useful for manual image building for debugging purpose. Use another tag in this case!
|
||||
# if: inputs.image_postfix != '-push-ci'
|
||||
# uses: docker/build-push-action@v5
|
||||
# with:
|
||||
# context: ./docker/transformers-pytorch-deepspeed-amd-gpu
|
||||
# build-args: |
|
||||
# REF=main
|
||||
# push: true
|
||||
# tags: huggingface/transformers-pytorch-deepspeed-amd-gpu-push-ci
|
||||
latest-pytorch-deepspeed-amd:
|
||||
name: "PyTorch + DeepSpeed (AMD) [dev]"
|
||||
runs-on:
|
||||
group: aws-general-8-plus
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Set up Docker Buildx
|
||||
uses: docker/setup-buildx-action@v3
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Check out code
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Login to DockerHub
|
||||
uses: docker/login-action@v3
|
||||
with:
|
||||
username: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME }}
|
||||
password: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_PASSWORD }}
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Build and push
|
||||
uses: docker/build-push-action@v5
|
||||
with:
|
||||
context: ./docker/transformers-pytorch-deepspeed-amd-gpu
|
||||
build-args: |
|
||||
REF=main
|
||||
push: true
|
||||
tags: huggingface/transformers-pytorch-deepspeed-amd-gpu${{ inputs.image_postfix }}
|
||||
# Push CI images still need to be re-built daily
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Build and push (for Push CI) in a daily basis
|
||||
# This condition allows `schedule` events, or `push` events that trigger this workflow NOT via `workflow_call`.
|
||||
# The later case is useful for manual image building for debugging purpose. Use another tag in this case!
|
||||
if: inputs.image_postfix != '-push-ci'
|
||||
uses: docker/build-push-action@v5
|
||||
with:
|
||||
context: ./docker/transformers-pytorch-deepspeed-amd-gpu
|
||||
build-args: |
|
||||
REF=main
|
||||
push: true
|
||||
tags: huggingface/transformers-pytorch-deepspeed-amd-gpu-push-ci
|
||||
|
||||
# - name: Post to Slack
|
||||
# if: always()
|
||||
# uses: huggingface/hf-workflows/.github/actions/post-slack@main
|
||||
# with:
|
||||
# slack_channel: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_DOCKER }}
|
||||
# title: 🤗 Results of the transformers-pytorch-deepspeed-amd-gpu build
|
||||
# status: ${{ job.status }}
|
||||
# slack_token: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
- name: Post to Slack
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
uses: huggingface/hf-workflows/.github/actions/post-slack@main
|
||||
with:
|
||||
slack_channel: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_DOCKER }}
|
||||
title: 🤗 Results of the transformers-pytorch-deepspeed-amd-gpu build
|
||||
status: ${{ job.status }}
|
||||
slack_token: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
|
||||
latest-quantization-torch-docker:
|
||||
name: "Latest Pytorch + Quantization [dev]"
|
||||
|
||||
@ -9,7 +9,7 @@ SHELL ["sh", "-lc"]
|
||||
# The following `ARG` are mainly used to specify the versions explicitly & directly in this docker file, and not meant
|
||||
# to be used as arguments for docker build (so far).
|
||||
|
||||
ARG PYTORCH='2.4.1'
|
||||
ARG PYTORCH='2.5.1'
|
||||
# Example: `cu102`, `cu113`, etc.
|
||||
ARG CUDA='cu118'
|
||||
|
||||
@ -36,12 +36,17 @@ RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir einops
|
||||
# Add bitsandbytes for mixed int8 testing
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir bitsandbytes
|
||||
|
||||
# Add auto-gptq for gtpq quantization testing
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir auto-gptq --extra-index-url https://huggingface.github.io/autogptq-index/whl/cu118/
|
||||
# Add auto-gptq for gtpq quantization testing, installed from source for pytorch==2.5.1 compatibility
|
||||
# TORCH_CUDA_ARCH_LIST="7.5+PTX" is added to make the package compile for Tesla T4 gpus available for the CI.
|
||||
RUN pip install gekko
|
||||
RUN git clone https://github.com/PanQiWei/AutoGPTQ.git && cd AutoGPTQ && TORCH_CUDA_ARCH_LIST="7.5+PTX" python3 setup.py install
|
||||
|
||||
# Add optimum for gptq quantization testing
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir git+https://github.com/huggingface/optimum@main#egg=optimum
|
||||
|
||||
# Add PEFT
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir git+https://github.com/huggingface/peft@main#egg=peft
|
||||
|
||||
# Add aqlm for quantization testing
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir aqlm[gpu]==1.0.2
|
||||
|
||||
@ -52,8 +57,8 @@ RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir hqq
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir gguf
|
||||
|
||||
# Add autoawq for quantization testing
|
||||
# >=v0.2.3 needed for compatibility with torch 2.2.1
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir https://github.com/casper-hansen/AutoAWQ/releases/download/v0.2.3/autoawq-0.2.3+cu118-cp310-cp310-linux_x86_64.whl
|
||||
# >=v0.2.7 needed for compatibility with transformers > 4.46
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir https://github.com/casper-hansen/AutoAWQ/releases/download/v0.2.7.post2/autoawq-0.2.7.post2-py3-none-any.whl
|
||||
|
||||
# Add quanto for quantization testing
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir optimum-quanto
|
||||
|
||||
@ -129,16 +129,22 @@
|
||||
title: التصدير إلى TFLite
|
||||
- local: torchscript
|
||||
title: التصدير إلى TorchScript
|
||||
# - local: benchmarks
|
||||
# title: المعايير
|
||||
# - local: notebooks
|
||||
# title: دفاتر الملاحظات مع الأمثلة
|
||||
# - local: community
|
||||
# title: موارد المجتمع
|
||||
- local: benchmarks
|
||||
title: المعايير
|
||||
- local: notebooks
|
||||
title: دفاتر الملاحظات مع الأمثلة
|
||||
- local: community
|
||||
title: موارد المجتمع
|
||||
- local: troubleshooting
|
||||
title: استكشاف الأخطاء وإصلاحها
|
||||
- local: gguf
|
||||
title: التوافق مع ملفات GGUF
|
||||
- local: tiktoken
|
||||
title: التوافق مع ملفات TikToken
|
||||
- local: modular_transformers
|
||||
title: الوحدات النمطية في `transformers`
|
||||
- local: how_to_hack_models
|
||||
title: اختراق النموذج (الكتابة فوق فئة لاستخدامك)
|
||||
title: أدلة المطورين
|
||||
# - sections:
|
||||
# - local: quantization/overview
|
||||
|
||||
352
docs/source/ar/benchmarks.md
Normal file
352
docs/source/ar/benchmarks.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,352 @@
|
||||
# معايير الأداء
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
أدوات قياس الأداء من Hugging Face أصبحت قديمة،ويُنصح باستخدام مكتبات خارجية لقياس سرعة وتعقيد الذاكرة لنماذج Transformer.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
[[open-in-colab]]
|
||||
|
||||
لنلق نظرة على كيفية تقييم أداء نماذج 🤗 Transformers، وأفضل الممارسات، ومعايير الأداء المتاحة بالفعل.
|
||||
|
||||
يُمكن العثور على دفتر ملاحظات يشرح بالتفصيل كيفية قياس أداء نماذج 🤗 Transformers [هنا](https://github.com/huggingface/notebooks/tree/main/examples/benchmark.ipynb).
|
||||
|
||||
## كيفية قياس أداء نماذج 🤗 Transformers
|
||||
|
||||
تسمح الفئتان [`PyTorchBenchmark`] و [`TensorFlowBenchmark`] بتقييم أداء نماذج 🤗 Transformers بمرونة. تتيح لنا فئات التقييم قياس الأداء قياس _الاستخدام الأقصى للذاكرة_ و _الوقت اللازم_ لكل من _الاستدلال_ و _التدريب_.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
هنا، ييُعرَّف _الاستدلال_ بأنه تمريرة أمامية واحدة، ويتم تعريف _التدريب_ بأنه تمريرة أمامية واحدة وتمريرة خلفية واحدة.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
تتوقع فئات تقييم الأداء [`PyTorchBenchmark`] و [`TensorFlowBenchmark`] كائنًا من النوع [`PyTorchBenchmarkArguments`] و [`TensorFlowBenchmarkArguments`]، على التوالي، للتنفيذ. [`PyTorchBenchmarkArguments`] و [`TensorFlowBenchmarkArguments`] هي فئات بيانات وتحتوي على جميع التكوينات ذات الصلة لفئة تقييم الأداء المقابلة. في المثال التالي، يتم توضيح كيفية تقييم أداء نموذج BERT من النوع _bert-base-cased_.
|
||||
|
||||
<frameworkcontent>
|
||||
<pt>
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import PyTorchBenchmark, PyTorchBenchmarkArguments
|
||||
|
||||
>>> args = PyTorchBenchmarkArguments(models=["google-bert/bert-base-uncased"], batch_sizes=[8], sequence_lengths=[8, 32, 128, 512])
|
||||
>>> benchmark = PyTorchBenchmark(args)
|
||||
```
|
||||
</pt>
|
||||
<tf>
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import TensorFlowBenchmark, TensorFlowBenchmarkArguments
|
||||
|
||||
>>> args = TensorFlowBenchmarkArguments(
|
||||
... models=["google-bert/bert-base-uncased"], batch_sizes=[8], sequence_lengths=[8, 32, 128, 512]
|
||||
... )
|
||||
>>> benchmark = TensorFlowBenchmark(args)
|
||||
```
|
||||
</tf>
|
||||
</frameworkcontent>
|
||||
|
||||
هنا، يتم تمرير ثلاثة معامﻻت إلى فئات بيانات حجة قياس الأداء، وهي `models` و `batch_sizes` و `sequence_lengths`. المعامل `models` مطلوبة وتتوقع `قائمة` من بمعرّفات النموذج من [مركز النماذج](https://huggingface.co/models) تحدد معامﻻت القائمة `batch_sizes` و `sequence_lengths` حجم `input_ids` الذي يتم قياس أداء النموذج عليه. هناك العديد من المعلمات الأخرى التي يمكن تكوينها عبر فئات بيانات معال قياس الأداء. لمزيد من التفاصيل حول هذه المعلمات، يمكنك إما الرجوع مباشرة إلى الملفات `src/transformers/benchmark/benchmark_args_utils.py`، `src/transformers/benchmark/benchmark_args.py` (لـ PyTorch) و `src/transformers/benchmark/benchmark_args_tf.py` (لـ Tensorflow). أو، بدلاً من ذلك، قم بتشغيل أوامر shell التالية من المجلد الرئيسي لطباعة قائمة وصفية بجميع المعلمات القابلة للتكوين لـ PyTorch و Tensorflow على التوالي.
|
||||
|
||||
<frameworkcontent>
|
||||
<pt>
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python examples/pytorch/benchmarking/run_benchmark.py --help
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
يُمكن ببساطة تشغيل كائن التقييم الذي تم تهيئته عن طريق استدعاء `benchmark.run()`.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> results = benchmark.run()
|
||||
>>> print(results)
|
||||
==================== INFERENCE - SPEED - RESULT ====================
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
Model Name Batch Size Seq Length Time in s
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
google-bert/bert-base-uncased 8 8 0.006
|
||||
google-bert/bert-base-uncased 8 32 0.006
|
||||
google-bert/bert-base-uncased 8 128 0.018
|
||||
google-bert/bert-base-uncased 8 512 0.088
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
==================== INFERENCE - MEMORY - RESULT ====================
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
Model Name Batch Size Seq Length Memory in MB
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
google-bert/bert-base-uncased 8 8 1227
|
||||
google-bert/bert-base-uncased 8 32 1281
|
||||
google-bert/bert-base-uncased 8 128 1307
|
||||
google-bert/bert-base-uncased 8 512 1539
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
==================== ENVIRONMENT INFORMATION ====================
|
||||
|
||||
- transformers_version: 2.11.0
|
||||
- framework: PyTorch
|
||||
- use_torchscript: False
|
||||
- framework_version: 1.4.0
|
||||
- python_version: 3.6.10
|
||||
- system: Linux
|
||||
- cpu: x86_64
|
||||
- architecture: 64bit
|
||||
- date: 2020-06-29
|
||||
- time: 08:58:43.371351
|
||||
- fp16: False
|
||||
- use_multiprocessing: True
|
||||
- only_pretrain_model: False
|
||||
- cpu_ram_mb: 32088
|
||||
- use_gpu: True
|
||||
- num_gpus: 1
|
||||
- gpu: TITAN RTX
|
||||
- gpu_ram_mb: 24217
|
||||
- gpu_power_watts: 280.0
|
||||
- gpu_performance_state: 2
|
||||
- use_tpu: False
|
||||
```
|
||||
</pt>
|
||||
<tf>
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python examples/tensorflow/benchmarking/run_benchmark_tf.py --help
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
يُمكن بعد ذلك تشغيل كائن قياس الأداء الذي تم تهيئته عن طريق استدعاء `benchmark.run()`.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> results = benchmark.run()
|
||||
>>> print(results)
|
||||
>>> results = benchmark.run()
|
||||
>>> print(results)
|
||||
==================== INFERENCE - SPEED - RESULT ====================
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
Model Name Batch Size Seq Length Time in s
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
google-bert/bert-base-uncased 8 8 0.005
|
||||
google-bert/bert-base-uncased 8 32 0.008
|
||||
google-bert/bert-base-uncased 8 128 0.022
|
||||
google-bert/bert-base-uncased 8 512 0.105
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
==================== INFERENCE - MEMORY - RESULT ====================
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
Model Name Batch Size Seq Length Memory in MB
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
google-bert/bert-base-uncased 8 8 1330
|
||||
google-bert/bert-base-uncased 8 32 1330
|
||||
google-bert/bert-base-uncased 8 128 1330
|
||||
google-bert/bert-base-uncased 8 512 1770
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
==================== ENVIRONMENT INFORMATION ====================
|
||||
|
||||
- transformers_version: 202.11.0
|
||||
- framework: Tensorflow
|
||||
- use_xla: False
|
||||
- framework_version: 2.2.0
|
||||
- python_version: 3.6.10
|
||||
- system: Linux
|
||||
- cpu: x86_64
|
||||
- architecture: 64bit
|
||||
- date: 2020-06-29
|
||||
- time: 09:26:35.617317
|
||||
- fp16: False
|
||||
- use_multiprocessing: True
|
||||
- only_pretrain_model: False
|
||||
- cpu_ram_mb: 32088
|
||||
- use_gpu: True
|
||||
- num_gpus: 1
|
||||
- gpu: TITAN RTX
|
||||
- gpu_ram_mb: 24217
|
||||
- gpu_power_watts: 280.0
|
||||
- gpu_performance_state: 2
|
||||
- use_tpu: False
|
||||
```
|
||||
</tf>
|
||||
</frameworkcontent>
|
||||
|
||||
بشكل افتراضي، يتم تقييم _الوقت_ و _الذاكرة المطلوبة_ لـ _الاستدلال_. في مثال المخرجات أعلاه، يُظهر القسمان الأولان النتيجة المقابلة لـ _وقت الاستدلال_ و _ذاكرة الاستدلال_. بالإضافة إلى ذلك، يتم طباعة جميع المعلومات ذات الصلة حول بيئة الحوسبة، على سبيل المثال نوع وحدة معالجة الرسومات (GPU)، والنظام، وإصدارات المكتبة، وما إلى ذلك، في القسم الثالث تحت _معلومات البيئة_. يمكن حفظ هذه المعلومات بشكل اختياري في ملف _.csv_ عند إضافة المعامل `save_to_csv=True` إلى [`PyTorchBenchmarkArguments`] و [`TensorFlowBenchmarkArguments`] على التوالي. في هذه الحالة، يتم حفظ كل قسم في ملف _.csv_ منفصل. يمكن اختيارًا تحديد مسار كل ملف _.csv_ عبر فئات بيانات معامل قياس الأداء.
|
||||
|
||||
بدلاً من تقييم النماذج المدربة مسبقًا عبر معرّف النموذج، على سبيل المثال `google-bert/bert-base-uncased`، يُمكن للمستخدم بدلاً من ذلك قياس أداء تكوين عشوائي لأي فئة نموذج متاحة. في هذه الحالة، يجب إدراج "قائمة" من التكوينات مع معامل قياس الأداء كما هو موضح أدناه.
|
||||
|
||||
<frameworkcontent>
|
||||
<pt>
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import PyTorchBenchmark، PyTorchBenchmarkArguments، BertConfig
|
||||
|
||||
>>> args = PyTorchBenchmarkArguments(
|
||||
... models=["bert-base"، "bert-384-hid"، "bert-6-lay"]، batch_sizes=[8]، sequence_lengths=[8، 32، 128، 512]
|
||||
... )
|
||||
>>> config_base = BertConfig()
|
||||
>>> config_384_hid = BertConfig(hidden_size=384)
|
||||
>>> config_6_lay = BertConfig(num_hidden_layers=6)
|
||||
|
||||
>>> benchmark = PyTorchBenchmark(args، configs=[config_base، config_384_hid، config_6_lay])
|
||||
>>> benchmark.run()
|
||||
==================== INFERENCE - SPEED - RESULT ====================
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
Model Name Batch Size Seq Length Time in s
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
bert-base 8 128 0.006
|
||||
bert-base 8 512 0.006
|
||||
bert-base 8 128 0.018
|
||||
bert-base 8 512 0.088
|
||||
bert-384-hid 8 8 0.006
|
||||
bert-384-hid 8 32 0.006
|
||||
bert-384-hid 8 128 0.011
|
||||
bert-384-hid 8 512 0.054
|
||||
bert-6-lay 8 8 0.003
|
||||
bert-6-lay 8 32 0.004
|
||||
bert-6-lay 8 128 0.009
|
||||
bert-6-lay 8 512 0.044
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
==================== INFERENCE - MEMORY - RESULT ====================
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
Model Name Batch Size Seq Length Memory in MB
|
||||
## نتائج اختبار الأداء
|
||||
|
||||
في هذا القسم، يتم قياس _وقت الاستدلال_ و _الذاكرة المطلوبة_ للاستدلال، لمختلف تكوينات `BertModel`. يتم عرض النتائج في جدول، مع تنسيق مختلف قليلاً لكل من PyTorch و TensorFlow.
|
||||
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
| اسم النموذج | حجم الدفعة | طول التسلسل | الذاكرة بالميغابايت |
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
| bert-base | 8 | 8 | 1277 |
|
||||
| bert-base | 8 | 32 | 1281 |
|
||||
| bert-base | 8 | 128 | 1307 |
|
||||
| bert-base | 8 | 512 | 1539 |
|
||||
| bert-384-hid | 8 | 8 | 1005 |
|
||||
| bert-384-hid | 8 | 32 | 1027 |
|
||||
| bert-384-hid | 8 | 128 | 1035 |
|
||||
| bert-384-hid | 8 | 512 | 1255 |
|
||||
| bert-6-lay | 8 | 8 | 1097 |
|
||||
| bert-6-lay | 8 | 32 | 1101 |
|
||||
| bert-6-lay | 8 | 128 | 1127 |
|
||||
| bert-6-lay | 8 | 512 | 1359 |
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
==================== معلومات البيئة ====================
|
||||
|
||||
- transformers_version: 2.11.0
|
||||
- framework: PyTorch
|
||||
- use_torchscript: False
|
||||
- framework_version: 1.4.0
|
||||
- python_version: 3.6.10
|
||||
- system: Linux
|
||||
- cpu: x86_64
|
||||
- architecture: 64bit
|
||||
- date: 2020-06-29
|
||||
- time: 09:35:25.143267
|
||||
- fp16: False
|
||||
- use_multiprocessing: True
|
||||
- only_pretrain_model: False
|
||||
- cpu_ram_mb: 32088
|
||||
- use_gpu: True
|
||||
- num_gpus: 1
|
||||
- gpu: TITAN RTX
|
||||
- gpu_ram_mb: 24217
|
||||
- gpu_power_watts: 280.0
|
||||
- gpu_performance_state: 2
|
||||
- use_tpu: False
|
||||
```
|
||||
</pt>
|
||||
<tf>
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import TensorFlowBenchmark, TensorFlowBenchmarkArguments, BertConfig
|
||||
|
||||
>>> args = TensorFlowBenchmarkArguments(
|
||||
... models=["bert-base", "bert-384-hid", "bert-6-lay"], batch_sizes=[8], sequence_lengths=[8, 32, 128, 512]
|
||||
... )
|
||||
>>> config_base = BertConfig()
|
||||
>>> config_384_hid = BertConfig(hidden_size=384)
|
||||
>>> config_6_lay = BertConfig(num_hidden_layers=6)
|
||||
|
||||
>>> benchmark = TensorFlowBenchmark(args, configs=[config_base, config_384_hid, config_6_lay])
|
||||
>>> benchmark.run()
|
||||
==================== نتائج السرعة في الاستدلال ====================
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
| اسم النموذج | حجم الدفعة | طول التسلسل | الوقت بالثانية |
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
| bert-base | 8 | 8 | 0.005 |
|
||||
| bert-base | 8 | 32 | 0.008 |
|
||||
| bert-base | 8 | 128 | 0.022 |
|
||||
| bert-base | 8 | 512 | 0.106 |
|
||||
| bert-384-hid | 8 | 8 | 0.005 |
|
||||
| bert-384-hid | 8 | 32 | 0.007 |
|
||||
| bert-384-hid | 8 | 128 | 0.018 |
|
||||
| bert-384-hid | 8 | 512 | 0.064 |
|
||||
| bert-6-lay | 8 | 8 | 0.002 |
|
||||
| bert-6-lay | 8 | 32 | 0.003 |
|
||||
| bert-6-lay | 8 | 128 | 0.0011 |
|
||||
| bert-6-lay | 8 | 512 | 0.074 |
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
==================== نتائج الذاكرة في الاستدلال ====================
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
| اسم النموذج | حجم الدفعة | طول التسلسل | الذاكرة بالميغابايت |
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
| اسم النموذج | حجم الدفعة | طول التسلسل | الذاكرة بالميغابايت |
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
| bert-base | 8 | 8 | 1330 |
|
||||
| bert-base | 8 | 32 | 1330 |
|
||||
| bert-base | 8 | 128 | 1330 |
|
||||
| bert-base | 8 | 512 | 1770 |
|
||||
| bert-384-hid | 8 | 8 | 1330 |
|
||||
| bert-384-hid | 8 | 32 | 1330 |
|
||||
| bert-384-hid | 8 | 128 | 1330 |
|
||||
| bert-384-hid | 8 | 512 | 1540 |
|
||||
| bert-6-lay | 8 | 8 | 1330 |
|
||||
| bert-6-lay | 8 | 32 | 1330 |
|
||||
| bert-6-lay | 8 | 128 | 1330 |
|
||||
| bert-6-lay | 8 | 512 | 1540 |
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
==================== معلومات البيئة ====================
|
||||
|
||||
- transformers_version: 2.11.0
|
||||
- framework: Tensorflow
|
||||
- use_xla: False
|
||||
- framework_version: 2.2.0
|
||||
- python_version: 3.6.10
|
||||
- system: Linux
|
||||
- cpu: x86_64
|
||||
- architecture: 64bit
|
||||
- date: 2020-06-29
|
||||
- time: 09:38:15.487125
|
||||
- fp16: False
|
||||
- use_multiprocessing: True
|
||||
- only_pretrain_model: False
|
||||
- cpu_ram_mb: 32088
|
||||
- use_gpu: True
|
||||
- num_gpus: 1
|
||||
- gpu: TITAN RTX
|
||||
- gpu_ram_mb: 24217
|
||||
- gpu_power_watts: 280.0
|
||||
- gpu_performance_state: 2
|
||||
- use_tpu: False
|
||||
```
|
||||
</tf>
|
||||
</frameworkcontent>
|
||||
|
||||
مرة أخرى، يتم قياس _وقت الاستدلال_ و _الذاكرة المطلوبة_ للاستدلال، ولكن هذه المرة لتكوينات مخصصة لـ `BertModel`. يمكن أن تكون هذه الميزة مفيدة بشكل خاص عند اتخاذ قرار بشأن التكوين الذي يجب تدريب النموذج عليه.
|
||||
|
||||
## أفضل الممارسات في اختبار الأداء
|
||||
|
||||
يسرد هذا القسم بعض أفضل الممارسات التي يجب مراعاتها عند إجراء اختبار الأداء لنموذج ما.
|
||||
|
||||
- حالياً، يتم دعم اختبار الأداء على جهاز واحد فقط. عند إجراء الاختبار على وحدة معالجة الرسوميات (GPU)، يوصى بأن يقوم المستخدم بتحديد الجهاز الذي يجب تشغيل التعليمات البرمجية عليه من خلال تعيين متغير البيئة `CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES` في الشل، على سبيل المثال `export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0` قبل تشغيل التعليمات البرمجية.
|
||||
- يجب تعيين الخيار `no_multi_processing` إلى `True` فقط لأغراض الاختبار والتصحيح. ولضمان قياس الذاكرة بدقة، يوصى بتشغيل كل اختبار ذاكرة في عملية منفصلة والتأكد من تعيين `no_multi_processing` إلى `True`.
|
||||
- يجب دائمًا ذكر معلومات البيئة عند مشاركة نتائج تقييم النموذج. يُمكن أن تختلف النتائج اختلافًا كبيرًا بين أجهزة GPU المختلفة وإصدارات المكتبات، وما إلى ذلك، لذلك فإن نتائج الاختبار بمفردها ليست مفيدة جدًا للمجتمع.
|
||||
|
||||
## مشاركة نتائج اختبار الأداء الخاص بك
|
||||
|
||||
في السابق، تم إجراء اختبار الأداء لجميع النماذج الأساسية المتاحة (10 في ذلك الوقت) لقياس _وقت الاستدلال_، عبر العديد من الإعدادات المختلفة: باستخدام PyTorch، مع TorchScript وبدونها، باستخدام TensorFlow، مع XLA وبدونه. تم إجراء جميع هذه الاختبارات على وحدات المعالجة المركزية (CPU) (باستثناء XLA TensorFlow) ووحدات معالجة الرسوميات (GPU).
|
||||
|
||||
يتم شرح هذا النهج بالتفصيل في [منشور المدونة هذا](https://medium.com/huggingface/benchmarking-transformers-pytorch-and-tensorflow-e2917fb891c2) وتتوفر النتائج [هنا](https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1sryqufw2D0XlUH4sq3e9Wnxu5EAQkaohzrJbd5HdQ_w/edit?usp=sharing).
|
||||
|
||||
مع أدوات اختبار الأداء الجديدة، أصبح من الأسهل من أي وقت مضى مشاركة نتائج اختبار الأداء الخاص بك مع المجتمع:
|
||||
|
||||
- [نتائج اختبار الأداء في PyTorch](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples/pytorch/benchmarking/README.md).
|
||||
- [نتائج اختبار الأداء في TensorFlow](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples/tensorflow/benchmarking/README.md).
|
||||
66
docs/source/ar/community.md
Normal file
66
docs/source/ar/community.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,66 @@
|
||||
# مجتمع المطورين
|
||||
|
||||
هذه الصفحة تجمع الموارد حول 🤗 Transformers التي طورها المجتمع.
|
||||
|
||||
## موارد المجتمع:
|
||||
|
||||
| المصدر | الوصف | المؤلف |
|
||||
|:----------|:-------------|------:|
|
||||
| [Hugging Face Transformers Glossary Flashcards](https://www.darigovresearch.com/huggingface-transformers-glossary-flashcards) | مجموعة من البطاقات التعليمية القائمة على [Transformers Docs Glossary](glossary) والتي تم وضعها في شكل يمكن تعلمه/مراجعته بسهولة باستخدام [Anki](https://apps.ankiweb.net/) وهو تطبيق مفتوح المصدر متعدد المنصات مصمم خصيصًا للاحتفاظ بالمعرفة على المدى الطويل. شاهد هذا [فيديو تمهيدي حول كيفية استخدام البطاقات التعليمية](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Dji_7PILrw). | [Darigov Research](https://www.darigovresearch.com/) |
|
||||
|
||||
## دفاتر ملاحظات المجتمع:
|
||||
|
||||
| الدفتر | الوصف | المؤلف | |
|
||||
|:----------|:-------------|:-------------|------:|
|
||||
| [Fine-tune a pre-trained Transformer to generate lyrics](https://github.com/AlekseyKorshuk/huggingartists) | كيفية توليد كلمات الأغاني على غرار فنانك المفضل من خلال ضبط نموذج GPT-2 | [Aleksey Korshuk](https://github.com/AlekseyKorshuk) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/AlekseyKorshuk/huggingartists/blob/master/huggingartists-demo.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Train T5 in Tensorflow 2](https://github.com/snapthat/TF-T5-text-to-text) | كيفية تدريب T5 لأي مهمة باستخدام Tensorflow 2. يوضح هذا الدفتر مهمة السؤال والجواب المنفذة في Tensorflow 2 باستخدام SQUAD | [Muhammad Harris](https://github.com/HarrisDePerceptron) |[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/snapthat/TF-T5-text-to-text/blob/master/snapthatT5/notebooks/TF-T5-Datasets%20Training.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Train T5 on TPU](https://github.com/patil-suraj/exploring-T5/blob/master/T5_on_TPU.ipynb) | كيفية تدريب T5 على SQUAD مع Transformers و Nlp | [Suraj Patil](https://github.com/patil-suraj) |[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/patil-suraj/exploring-T5/blob/master/T5_on_TPU.ipynb#scrollTo=QLGiFCDqvuil) |
|
||||
| [Fine-tune T5 for Classification and Multiple Choice](https://github.com/patil-suraj/exploring-T5/blob/master/t5_fine_tuning.ipynb) | كيفية ضبط نموذج T5 للتصنيف والمهام متعددة الخيارات باستخدام تنسيق النص إلى نص مع PyTorch Lightning | [Suraj Patil](https://github.com/patil-suraj) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/patil-suraj/exploring-T5/blob/master/t5_fine_tuning.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Fine-tune DialoGPT on New Datasets and Languages](https://github.com/ncoop57/i-am-a-nerd/blob/master/_notebooks/2020-05-12-chatbot-part-1.ipynb) | كيفية ضبط نموذج DialoGPT على مجموعة بيانات جديدة لروبوتات الدردشة المحادثية المفتوحة | [Nathan Cooper](https://github.com/ncoop57) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/ncoop57/i-am-a-nerd/blob/master/_notebooks/2020-05-12-chatbot-part-1.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Long Sequence Modeling with Reformer](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/PyTorch_Reformer.ipynb) | كيفية التدريب على تسلسلات طويلة تصل إلى 500,000 رمز باستخدام Reformer | [Patrick von Platen](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/PyTorch_Reformer.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Fine-tune BART for Summarization](https://github.com/ohmeow/ohmeow_website/blob/master/posts/2021-05-25-mbart-sequence-classification-with-blurr.ipynb) | كيفية ضبط نموذج BART للتلخيص باستخدام fastai باستخدام blurr | [Wayde Gilliam](https://ohmeow.com/) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/ohmeow/ohmeow_website/blob/master/posts/2021-05-25-mbart-sequence-classification-with-blurr.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Fine-tune a pre-trained Transformer on anyone's tweets](https://colab.research.google.com/github/borisdayma/huggingtweets/blob/master/huggingtweets-demo.ipynb) | كيفية توليد تغريدات على غرار حساب Twitter المفضل لديك من خلال ضبط نموذج GPT-2 | [Boris Dayma](https://github.com/borisdayma) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/borisdayma/huggingtweets/blob/master/huggingtweets-demo.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Optimize 🤗 Hugging Face models with Weights & Biases](https://colab.research.google.com/github/wandb/examples/blob/master/colabs/huggingface/Optimize_Hugging_Face_models_with_Weights_%26_Biases.ipynb) | دليل كامل لعرض تكامل W&B مع Hugging Face | [Boris Dayma](https://github.com/borisdayma) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/wandb/examples/blob/master/colabs/huggingface/Optimize_Hugging_Face_models_with_Weights_%26_Biases.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Pretrain Longformer](https://github.com/allenai/longformer/blob/master/scripts/convert_model_to_long.ipynb) | كيفية بناء نسخة "طويلة" من النماذج المسبقة التدريب الموجودة | [Iz Beltagy](https://beltagy.net) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/allenai/longformer/blob/master/scripts/convert_model_to_long.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Fine-tune Longformer for QA](https://github.com/patil-suraj/Notebooks/blob/master/longformer_qa_training.ipynb) | كيفية ضبط نموذج Longformer لمهمة QA | [Suraj Patil](https://github.com/patil-suraj) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/patil-suraj/Notebooks/blob/master/longformer_qa_training.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Evaluate Model with 🤗nlp](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/How_to_evaluate_Longformer_on_TriviaQA_using_NLP.ipynb) | كيفية تقييم نموذج Longformer على TriviaQA مع `nlp` | [Patrick von Platen](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1m7eTGlPmLRgoPkkA7rkhQdZ9ydpmsdLE?usp=sharing) |
|
||||
| [Fine-tune T5 for Sentiment Span Extraction](https://github.com/enzoampil/t5-intro/blob/master/t5_qa_training_pytorch_span_extraction.ipynb) | كيفية ضبط نموذج T5 لاستخراج المشاعر باستخدام تنسيق النص إلى نص مع PyTorch Lightning | [Lorenzo Ampil](https://github.com/enzoampil) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/enzoampil/t5-intro/blob/master/t5_qa_training_pytorch_span_extraction.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Fine-tune DistilBert for Multiclass Classification](https://github.com/abhimishra91/transformers-tutorials/blob/master/transformers_multiclass_classification.ipynb) | كيفية ضبط نموذج DistilBert للتصنيف متعدد الفئات باستخدام PyTorch | [Abhishek Kumar Mishra](https://github.com/abhimishra91) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/abhimishra91/transformers-tutorials/blob/master/transformers_multiclass_classification.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Fine-tune BERT for Multi-label Classification](https://github.com/abhimishra91/transformers-tutorials/blob/master/transformers_multi_label_classification.ipynb)|كيفية ضبط نموذج BERT للتصنيف متعدد التصنيفات باستخدام PyTorch|[Abhishek Kumar Mishra](https://github.com/abhimishra91) |[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/abhimishra91/transformers-tutorials/blob/master/transformers_multi_label_classification.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Fine-tune T5 for Summarization](https://github.com/abhimishra91/transformers-tutorials/blob/master/transformers_summarization_wandb.ipynb)|كيفية ضبط نموذج T5 للتلخيص في PyTorch وتتبع التجارب باستخدام WandB|[Abhishek Kumar Mishra](https://github.com/abhimishra91) |[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/abhimishra91/transformers-tutorials/blob/master/transformers_summarization_wandb.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Speed up Fine-Tuning in Transformers with Dynamic Padding / Bucketing](https://github.com/ELS-RD/transformers-notebook/blob/master/Divide_Hugging_Face_Transformers_training_time_by_2_or_more.ipynb)|كيفية تسريع الضبط الدقيق بعامل 2 باستخدام الضبط الديناميكي/التقسيم|[Michael Benesty](https://github.com/pommedeterresautee) |[](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1CBfRU1zbfu7-ijiOqAAQUA-RJaxfcJoO?usp=sharing)|
|
||||
|[Pretrain Reformer for Masked Language Modeling](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/Reformer_For_Masked_LM.ipynb)| كيفية تدريب نموذج Reformer مع طبقات الانتباه ثنائية الاتجاه | [Patrick von Platen](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1tzzh0i8PgDQGV3SMFUGxM7_gGae3K-uW?usp=sharing)|
|
||||
|[Expand and Fine Tune Sci-BERT](https://github.com/lordtt13/word-embeddings/blob/master/COVID-19%20Research%20Data/COVID-SciBERT.ipynb)| كيفية زيادة مفردات نموذج SciBERT المسبق التدريب من AllenAI على مجموعة بيانات CORD وإنشاء خط أنابيب لها. | [Tanmay Thakur](https://github.com/lordtt13) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1rqAR40goxbAfez1xvF3hBJphSCsvXmh8)|
|
||||
|[Fine Tune BlenderBotSmall for Summarization using the Trainer API](https://github.com/lordtt13/transformers-experiments/blob/master/Custom%20Tasks/fine-tune-blenderbot_small-for-summarization.ipynb)| كيفية ضبط نموذج BlenderBotSmall للتلخيص على مجموعة بيانات مخصصة، باستخدام واجهة برمجة التطبيقات Trainer. | [Tanmay Thakur](https://github.com/lordtt13) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/19Wmupuls7mykSGyRN_Qo6lPQhgp56ymq?usp=sharing)|
|
||||
|[Fine-tune Electra and interpret with Integrated Gradients](https://github.com/elsanns/xai-nlp-notebooks/blob/master/electra_fine_tune_interpret_captum_ig.ipynb) | كيفية ضبط نموذج Electra للتحليل العاطفي وتفسير التنبؤات باستخدام Captum Integrated Gradients | [Eliza Szczechla](https://elsanns.github.io) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/elsanns/xai-nlp-notebooks/blob/master/electra_fine_tune_interpret_captum_ig.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[fine-tune a non-English GPT-2 Model with Trainer class](https://github.com/philschmid/fine-tune-GPT-2/blob/master/Fine_tune_a_non_English_GPT_2_Model_with_Huggingface.ipynb) | كيفية ضبط نموذج GPT-2 غير الإنجليزي باستخدام فئة Trainer | [Philipp Schmid](https://www.philschmid.de) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/philschmid/fine-tune-GPT-2/blob/master/Fine_tune_a_non_English_GPT_2_Model_with_Huggingface.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Fine-tune a DistilBERT Model for Multi Label Classification task](https://github.com/DhavalTaunk08/Transformers_scripts/blob/master/Transformers_multilabel_distilbert.ipynb) | كيفية ضبط نموذج DistilBERT لمهمة التصنيف متعدد التصنيفات | [Dhaval Taunk](https://github.com/DhavalTaunk08) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/DhavalTaunk08/Transformers_scripts/blob/master/Transformers_multilabel_distilbert.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Fine-tune ALBERT for sentence-pair classification](https://github.com/NadirEM/nlp-notebooks/blob/master/Fine_tune_ALBERT_sentence_pair_classification.ipynb) | كيفية ضبط نموذج ALBERT أو أي نموذج آخر قائم على BERT لمهمة التصنيف المزدوج للجمل | [Nadir El Manouzi](https://github.com/NadirEM) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/NadirEM/nlp-notebooks/blob/master/Fine_tune_ALBERT_sentence_pair_classification.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Fine-tune Roberta for sentiment analysis](https://github.com/DhavalTaunk08/NLP_scripts/blob/master/sentiment_analysis_using_roberta.ipynb) | كيفية ضبط نموذج Roberta للتحليل العاطفي | [Dhaval Taunk](https://github.com/DhavalTaunk08) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/DhavalTaunk08/NLP_scripts/blob/master/sentiment_analysis_using_roberta.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Evaluating Question Generation Models](https://github.com/flexudy-pipe/qugeev) | ما مدى دقة الإجابات على الأسئلة التي يولدها نموذجك التحويلي seq2seq؟ | [Pascal Zoleko](https://github.com/zolekode) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1bpsSqCQU-iw_5nNoRm_crPq6FRuJthq_?usp=sharing)|
|
||||
|[Classify text with DistilBERT and Tensorflow](https://github.com/peterbayerle/huggingface_notebook/blob/main/distilbert_tf.ipynb) | كيفية ضبط نموذج DistilBERT للتصنيف النصي في TensorFlow | [Peter Bayerle](https://github.com/peterbayerle) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/peterbayerle/huggingface_notebook/blob/main/distilbert_tf.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Leverage BERT for Encoder-Decoder Summarization on CNN/Dailymail](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/BERT2BERT_for_CNN_Dailymail.ipynb) | كيفية البدء السريع لنموذج *EncoderDecoderModel* مع نقطة تفتيش *google-bert/bert-base-uncased* للتلخيص على CNN/Dailymail | [Patrick von Platen](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/BERT2BERT_for_CNN_Dailymail.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Leverage RoBERTa for Encoder-Decoder Summarization on BBC XSum](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/RoBERTaShared_for_BBC_XSum.ipynb) | كيفية البدء السريع لنموذج *EncoderDecoderModel* المشترك مع نقطة تفتيش *FacebookAI/roberta-base* للتلخيص على BBC/XSum | [Patrick von Platen](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/RoBERTaShared_for_BBC_XSum.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Fine-tune TAPAS on Sequential Question Answering (SQA)](https://github.com/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/TAPAS/Fine_tuning_TapasForQuestionAnswering_on_SQA.ipynb) | كيفية ضبط نموذج *TapasForQuestionAnswering* مع نقطة تفتيش *tapas-base* على مجموعة بيانات Sequential Question Answering (SQA) | [Niels Rogge](https://github.com/nielsrogge) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/TAPAS/Fine_tuning_TapasForQuestionAnswering_on_SQA.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Evaluate TAPAS on Table Fact Checking (TabFact)](https://github.com/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/TAPAS/Evaluating_TAPAS_on_the_Tabfact_test_set.ipynb) | كيفية تقييم نموذج *TapasForSequenceClassification* المضبوط مسبقًا مع نقطة تفتيش *tapas-base-finetuned-tabfact* باستخدام مزيج من مكتبتي 🤗 datasets و 🤗 transformers | [Niels Rogge](https://github.com/nielsrogge) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/TAPAS/Evaluating_TAPAS_on_the_Tabfact_test_set.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Fine-tuning mBART for translation](https://colab.research.google.com/github/vasudevgupta7/huggingface-tutorials/blob/main/translation_training.ipynb) | كيفية ضبط نموذج mBART باستخدام Seq2SeqTrainer للترجمة من الهندية إلى الإنجليزية | [Vasudev Gupta](https://github.com/vasudevgupta7) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/vasudevgupta7/huggingface-tutorials/blob/main/translation_training.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Fine-tune LayoutLM on FUNSD (a form understanding dataset)](https://github.com/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/LayoutLM/Fine_tuning_LayoutLMForTokenClassification_on_FUNSD.ipynb) | كيفية ضبط نموذج *LayoutLMForTokenClassification* على مجموعة بيانات FUNSD لاستخراج المعلومات من المستندات الممسوحة ضوئيًا | [Niels Rogge](https://github.com/nielsrogge) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/LayoutLM/Fine_tuning_LayoutLMForTokenClassification_on_FUNSD.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Fine-Tune DistilGPT2 and Generate Text](https://colab.research.google.com/github/tripathiaakash/DistilGPT2-Tutorial/blob/main/distilgpt2_fine_tuning.ipynb) | كيفية ضبط نموذج DistilGPT2 وتوليد النص | [Aakash Tripathi](https://github.com/tripathiaakash) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/tripathiaakash/DistilGPT2-Tutorial/blob/main/distilgpt2_fine_tuning.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Fine-Tune LED on up to 8K tokens](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/Fine_tune_Longformer_Encoder_Decoder_(LED)_for_Summarization_on_pubmed.ipynb) | كيفية ضبط نموذج LED على pubmed للتلخيص طويل المدى | [Patrick von Platen](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/Fine_tune_Longformer_Encoder_Decoder_(LED)_for_Summarization_on_pubmed.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Evaluate LED on Arxiv](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/LED_on_Arxiv.ipynb) | كيفية تقييم نموذج LED للتلخيص طويل المدى بشكل فعال | [Patrick von Platen](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/LED_on_Arxiv.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Fine-tune LayoutLM on RVL-CDIP (a document image classification dataset)](https://github.com/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/LayoutLM/Fine_tuning_LayoutLMForSequenceClassification_on_RVL_CDIP.ipynb) | كيفية ضبط نموذج *LayoutLMForSequenceClassification* على مجموعة بيانات RVL-CDIP لتصنيف المستندات الممسوحة ضوئيًا | [Niels Rogge](https://github.com/nielsrogge) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/LayoutLM/Fine_tuning_LayoutLMForSequenceClassification_on_RVL_CDIP.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Wav2Vec2 CTC decoding with GPT2 adjustment](https://github.com/voidful/huggingface_notebook/blob/main/xlsr_gpt.ipynb) | كيفية فك تشفير تسلسل CTC مع تعديل نموذج اللغة | [Eric Lam](https://github.com/voidful) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1e_zQHYbO2YKEaUgzb1ww1WwiAyydAj?usp=sharing)|
|
||||
|[Fine-tune BART for summarization in two languages with Trainer class](https://github.com/elsanns/xai-nlp-notebooks/blob/master/fine_tune_bart_summarization_two_langs.ipynb) | كيفية ضبط نموذج BART للتلخيص بلغتين باستخدام فئة Trainer | [Eliza Szczechla](https://github.com/elsanns) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/elsanns/xai-nlp-notebooks/blob/master/fine_tune_bart_summarization_two_langs.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Evaluate Big Bird on Trivia QA](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/Evaluating_Big_Bird_on_TriviaQA.ipynb) | كيفية تقييم نموذج BigBird للأسئلة والأجوبة على وثائق طويلة على Trivia QA | [Patrick von Platen](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/Evaluating_Big_Bird_on_TriviaQA.ipynb)|
|
||||
| [Create video captions using Wav2Vec2](https://github.com/Muennighoff/ytclipcc/blob/main/wav2vec_youtube_captions.ipynb) | كيفية إنشاء تعليقات توضيحية على YouTube من أي فيديو من خلال تفريغ الصوت باستخدام Wav2Vec | [Niklas Muennighoff](https://github.com/Muennighoff) |[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/Muennighoff/ytclipcc/blob/main/wav2vec_youtube_captions.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Fine-tune the Vision Transformer on CIFAR-10 using PyTorch Lightning](https://github.com/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/VisionTransformer/Fine_tuning_the_Vision_Transformer_on_CIFAR_10_with_PyTorch_Lightning.ipynb) | كيفية ضبط نموذج Vision Transformer (ViT) على CIFAR-10 باستخدام مكتبات HuggingFace Transformers و Datasets و PyTorch Lightning | [Niels Rogge](https://github.com/nielsrogge) |[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/VisionTransformer/Fine_tuning_the_Vision_Transformer_on_CIFAR_10_with_PyTorch_Lightning.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Fine-tune the Vision Transformer on CIFAR-10 using the 🤗 Trainer](https://github.com/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/VisionTransformer/Fine_tuning_the_Vision_Transformer_on_CIFAR_10_with_the_%F0%9F%A4%97_Trainer.ipynb) | كيفية ضبط نموذج Vision Transformer (ViT) على CIFAR-10 باستخدام مكتبات HuggingFace Transformers و Datasets و 🤗 Trainer | [Niels Rogge](https://github.com/nielsrogge) |[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/VisionTransformer/Fine_tuning_the_Vision_Transformer_on_CIFAR_10_with_the_%F0%9F%A4%97_Trainer.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Evaluate LUKE on Open Entity, an entity typing dataset](https://github.com/studio-ousia/luke/blob/master/notebooks/huggingface_open_entity.ipynb) | كيفية تقييم نموذج *LukeForEntityClassification* على مجموعة بيانات Open Entity | [Ikuya Yamada](https://github.com/ikuyamada) |[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/studio-ousia/luke/blob/master/notebooks/huggingface_open_entity.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Evaluate LUKE on TACRED, a relation extraction dataset](https://github.com/studio-ousia/luke/blob/master/notebooks/huggingface_tacred.ipynb) | كيفية تقييم نموذج *LukeForEntityPairClassification* على مجموعة بيانات TACRED | [Ikuya Yamada](https://github.com/ikuyamada) |[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/studio-ousia/luke/blob/master/notebooks/huggingface_tacred.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Evaluate LUKE on CoNLL-2003, an important NER benchmark](https://github.com/studio-ousia/luke/blob/master/notebooks/huggingface_conll_2003.ipynb) | كيفية تقييم نموذج *LukeForEntitySpanClassification* على مجموعة بيانات CoNLL-2003 | [Ikuya Yamada](https://github.com/ikuyamada) |[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/studio-ousia/luke/blob/master/notebooks/huggingface_conll_2003.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Evaluate BigBird-Pegasus on PubMed dataset](https://github.com/vasudevgupta7/bigbird/blob/main/notebooks/bigbird_pegasus_evaluation.ipynb) | كيفية تقييم نموذج *BigBirdPegasusForConditionalGeneration* على مجموعة بيانات PubMed | [Vasudev Gupta](https://github.com/vasudevgupta7) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/vasudevgupta7/bigbird/blob/main/notebooks/bigbird_pegasus_evaluation.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Speech Emotion Classification with Wav2Vec2](https://github.com/m3hrdadfi/soxan/blob/main/notebooks/Emotion_recognition_in_Greek_speech_using_Wav2Vec2.ipynb) | كيفية استخدام نموذج Wav2Vec2 المسبق التدريب لتصنيف المشاعر على مجموعة بيانات MEGA | [Mehrdad Farahani](https://github.com/m3hrdadfi) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/m3hrdadfi/soxan/blob/main/notebooks/Emotion_recognition_in_Greek_speech_using_Wav2Vec2.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Detect objects in an image with DETR](https://github.com/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/DETR/DETR_minimal_example_(with_DetrFeatureExtractor).ipynb) | كيفية استخدام نموذج *DetrForObjectDetection* المدرب للكشف عن الأجسام في صورة وتصوير الانتباه | [Niels Rogge](https://github.com/NielsRogge) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/DETR/DETR_minimal_example_(with_DetrFeatureExtractor).ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Fine-tune DETR on a custom object detection dataset](https://github.com/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/DETR/Fine_tuning_DetrForObjectDetection_on_custom_dataset_(balloon).ipynb) | كيفية ضبط نموذج *DetrForObjectDetection* على مجموعة بيانات الكشف عن الأجسام المخصصة | [Niels Rogge](https://github.com/NielsRogge) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/DETR/Fine_tuning_DetrForObjectDetection_on_custom_dataset_(balloon).ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Finetune T5 for Named Entity Recognition](https://github.com/ToluClassics/Notebooks/blob/main/T5_Ner_Finetuning.ipynb) | كيفية ضبط نموذج *T5* على مهمة التعرف على الكيانات المسماة | [Ogundepo Odunayo](https://github.com/ToluClassics) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1obr78FY_cBmWY5ODViCmzdY6O1KB65Vc?usp=sharing) |
|
||||
| [Fine-Tuning Open-Source LLM using QLoRA with MLflow and PEFT](https://github.com/mlflow/mlflow/blob/master/docs/source/llms/transformers/tutorials/fine-tuning/transformers-peft.ipynb) | كيفية استخدام [QLoRA](https://github.com/artidoro/qlora) و [PEFT](https://huggingface.co/docs/peft/en/index) لضبط نموذج LLM بطريقة فعالة من حيث الذاكرة، مع استخدام [MLflow](https://mlflow.org/docs/latest/llms/transformers/index.html) لإدارة تتبع التجارب | [Yuki Watanabe](https://github.com/B-Step62) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/mlflow/mlflow/blob/master/docs/source/llms/transformers/tutorials/fine-tuning/transformers-peft.ipynb) |
|
||||
163
docs/source/ar/how_to_hack_models.md
Normal file
163
docs/source/ar/how_to_hack_models.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,163 @@
|
||||
# كيفية تعديل أي نموذج من نماذج Transformers
|
||||
|
||||
توفر مكتبة [🤗 Transformers](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers) مجموعة من النماذج المسبقة التدريب والأدوات لمعالجة اللغات الطبيعية، والرؤية، وما إلى ذلك. على الرغم من أن هذه النماذج تغطي مجموعة واسعة من التطبيقات، فقد تواجه حالات استخدام لا تدعمها المكتبة بشكل افتراضي. يُمكن للتخصيص أن يفتح إمكانيات جديدة، مثل إضافة طبقات جديدة، أو تعديل البنية المعمارية، أو تحسين آليات الانتباه. سيُوضح لك هذا الدليل كيفية تعديل نماذج Transformers الموجودة لتلبية احتياجاتك المحددة. الشيء الرائع هو أنك لست بحاجة إلى الخروج من إطار عمل Transformers لإجراء هذه التغييرات. ي يمكنك تعديل النماذج مباشرةً في Transformers والاستفادة من الميزات مثل [واجهة برمجة التطبيقات Trainer](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/en/main_classes/trainer)، و [PreTrainedModel](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/en/main_classes/model#transformers.PreTrainedModel)، والضبط الدقيق الفعال باستخدام أدوات مثل [PEFT](https://huggingface.co/docs/peft/index).
|
||||
|
||||
سنرشدك في هذا الدليل لكيفية تخصيص نماذج Transformers الموجودة لتلبية متطلباتك، دون فقدان مزايا الإطار. ستتعلم كيفية:
|
||||
|
||||
- تعديل بنية نموذج ما من خلال تغيير آلية الانتباه الخاصة به.
|
||||
- تطبيق تقنيات مثل Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) على مكونات نموذج محددة.
|
||||
|
||||
نحن نشجعك على المساهمة باختراقاتك الخاصة ومشاركتها هنا مع المجتمع1
|
||||
|
||||
## مثال: تعديل آلية الانتباه في نموذج Segment Anything (SAM)
|
||||
|
||||
نموذج **Segment Anything (SAM)** هو نموذج رائد في مجال تجزئة الصور. في تنفيذه الافتراضي، يستخدم SAM إسقاطًا مجمعًا للاستعلام والمفتاح والقيمة (`qkv`) في آلية الانتباه الخاصة به. ومع ذلك، قد ترغب في ضبط مكونات محددة فقط من آلية الانتباه، مثل إسقاطات الاستعلام (`q`) والقيمة (`v`)، لتقليل عدد المعلمات القابلة للتدريب والموارد الحسابية المطلوبة.
|
||||
|
||||
### الدافع
|
||||
|
||||
من خلال تقسيم الإسقاط المجمع `qkv` إلى إسقاطات منفصلة `q` و `k` و `v`، يمكنك تطبيق تقنيات مثل **LoRA** (Low-Rank Adaptation) على إسقاطي `q` و `v` فقط. يسمح لك هذا بما يلي:
|
||||
|
||||
- ضبط عدد أقل من المعلمات، مما يقلل من العبء الحسابي.
|
||||
- تحقيق أداء أفضل من خلال التركيز على مكونات محددة.
|
||||
- تجربة استراتيجيات تعديل مختلفة في آلية الانتباه.
|
||||
|
||||
### التنفيذ
|
||||
|
||||
#### **الخطوة 1: إنشاء فئة اهتمام مخصصة**
|
||||
|
||||
بعد ذلك، قم بإنشاء فئة فرعية من فئة `SamVisionAttention` الأصلية وعدلها لتضم إسقاطات `q` و `k` و `v` منفصلة.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
import torch.nn as nn
|
||||
from transformers.models.sam.modeling_sam import SamVisionAttention
|
||||
|
||||
class SamVisionAttentionSplit(SamVisionAttention, nn.Module):
|
||||
def __init__(self, config, window_size):
|
||||
super().__init__(config, window_size)
|
||||
del self.qkv
|
||||
# إسقاطات منفصلة q و k و v
|
||||
self.q = nn.Linear(config.hidden_size, config.hidden_size, bias=config.qkv_bias)
|
||||
self.k = nn.Linear(config.hidden_size, config.hidden_size, bias=config.qkv_bias)
|
||||
self.v = nn.Linear(config.hidden_size, config.hidden_size, bias=config.qkv_bias)
|
||||
self._register_load_state_dict_pre_hook(self.split_q_k_v_load_hook)
|
||||
|
||||
def split_q_k_v_load_hook(self, state_dict, prefix, *args):
|
||||
keys_to_delete = []
|
||||
for key in list(state_dict.keys()):
|
||||
if "qkv." in key:
|
||||
# تقسيم q و k و v من الإسقاط المجمع
|
||||
q, k, v = state_dict[key].chunk(3, dim=0)
|
||||
# استبدال الإسقاطات الفردية q و k و v
|
||||
state_dict[key.replace("qkv.", "q.")] = q
|
||||
state_dict[key.replace("qkv.", "k.")] = k
|
||||
state_dict[key.replace("qkv.", "v.")] = v
|
||||
# وضع علامة على مفتاح qkv القديم للحذف
|
||||
keys_to_delete.append(key)
|
||||
|
||||
# حذف مفاتيح qkv القديمة
|
||||
for key in keys_to_delete:
|
||||
del state_dict[key]
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, hidden_states: torch.Tensor, output_attentions=False) -> torch.Tensor:
|
||||
batch_size, height, width, _ = hidden_states.shape
|
||||
qkv_shapes = (batch_size * self.num_attention_heads, height * width, -1)
|
||||
query = self.q(hidden_states).reshape((batch_size, height * width,self.num_attention_heads, -1)).permute(0,2,1,3).reshape(qkv_shapes)
|
||||
key = self.k(hidden_states).reshape((batch_size, height * width,self.num_attention_heads, -1)).permute(0,2,1,3).reshape(qkv_shapes)
|
||||
value = self.v(hidden_states).reshape((batch_size, height * width,self.num_attention_heads, -1)).permute(0,2,1,3).reshape(qkv_shapes)
|
||||
|
||||
attn_weights = (query * self.scale) @ key.transpose(-2, -1)
|
||||
|
||||
if self.use_rel_pos:
|
||||
attn_weights = self.add_decomposed_rel_pos(
|
||||
attn_weights, query, self.rel_pos_h, self.rel_pos_w, (height, width), (height, width)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
attn_weights = torch.nn.functional.softmax(attn_weights, dtype=torch.float32, dim=-1).to(query.dtype)
|
||||
attn_probs = nn.functional.dropout(attn_weights, p=self.dropout, training=self.training)
|
||||
attn_output = (attn_probs @ value).reshape(batch_size, self.num_attention_heads, height, width, -1)
|
||||
attn_output = attn_output.permute(0, 2, 3, 1, 4).reshape(batch_size, height, width, -1)
|
||||
attn_output = self.proj(attn_output)
|
||||
|
||||
if output_attentions:
|
||||
outputs = (attn_output, attn_weights)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
outputs = (attn_output, None)
|
||||
return outputs
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**الشرح:**
|
||||
|
||||
- **الإسقاطات المنفصلة:** يتم إزالة الإسقاط المُجمع `qkv`، وإنشاء إسقاطات خطية منفصلة `q` و `k` و `v`.
|
||||
- **دالة استدعاء تحميل الأوزان:** تقوم طريقة `_split_qkv_load_hook` بتقسيم أوزان `qkv` المسبقة التدريب إلى أوزان `q` و `k` و `v` منفصلة عند تحميل النموذج. يضمن هذا التوافق مع أي نموذج مسبق التدريب.
|
||||
- **التنفيذ الأمامي:** يتم حساب الاستعلامات والمفاتيح والقيم بشكل منفصل، وتستمر آلية الانتباه كالمعتاد.
|
||||
|
||||
#### **الخطوة 2: استبدال فئة الانتباه الأصلية**
|
||||
|
||||
استبدل فئة `SamVisionAttention` الأصلية بفئتك المخصصة بحيث يستخدم النموذج آلية الانتباه المعدلة.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import SamModel
|
||||
from transformers.models.sam import modeling_sam
|
||||
|
||||
# استبدال فئة الاهتمام في وحدة نمطية modeling_sam
|
||||
modeling_sam.SamVisionAttention = SamVisionAttentionSplit
|
||||
|
||||
# تحميل نموذج SAM المسبق التدريب
|
||||
model = SamModel.from_pretrained("facebook/sam-vit-base")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**الشرح:**
|
||||
|
||||
- **استبدال الفئة:** من خلال تعيين فئتك المخصصة إلى `modeling_sam.SamVisionAttention`، فإن أي حالات من فئة `SamVisionAttention` في النموذج ستستخدم النسخة المعدلة. وبالتالي، عند استدعاء `SamModel`، سيتم استخدام `SamVisionAttentionSplit` المحددة حديثًا.
|
||||
- **تحميل النموذج:** يتم تحميل النموذج باستخدام `from_pretrained`، ويتم دمج آلية الانتباه المخصصة.
|
||||
|
||||
#### **الخطوة 3: تطبيق LoRA على إسقاطات محددة**
|
||||
|
||||
مع وجود إسقاطات `q` و `k` و `v` منفصلة، يمكنك الآن تطبيق LoRA على مكونات محددة، مثل إسقاطات `q` و `v`.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from peft import LoraConfig, get_peft_model
|
||||
|
||||
config = LoraConfig(
|
||||
r=16,
|
||||
lora_alpha=32,
|
||||
target_modules=["q", "v"], # تطبيق LoRA على إسقاطات q و v
|
||||
lora_dropout=0.1,
|
||||
task_type="mask-generation"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# تطبيق LoRA على النموذج
|
||||
model = get_peft_model(model, config)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**الشرح:**
|
||||
|
||||
- **تكوين LoRA:** تحدد `LoraConfig` المرتبة `r`، وعامل القياس `lora_alpha`، والوحدات المستهدفة (`"q"` و `"v"`)، ومعدل التخلي، ونوع المهمة.
|
||||
- **تطبيق LoRA:** تقوم دالة `get_peft_model` بتطبيق LoRA على الوحدات المحددة في النموذج.
|
||||
- **تقليل المعلمات:** من خلال التركيز على `q` و `v`، فإنك تقلل عدد المعلمات القابلة للتدريب، مما يؤدي إلى تسريع التدريب وتقليل استخدام الذاكرة.
|
||||
|
||||
#### **الخطوة 4: التحقق من عدد المعلمات القابلة للتدريب**
|
||||
|
||||
من السهل التحقق من عدد المعلمات القابلة للتدريب ومعرفة تأثير تعديلك.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
model.print_trainable_parameters()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**الناتج المتوقع:**
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
عدد المعلمات القابلة للتدريب: 608,256 || جميع المعلمات: 94,343,728 || نسبة المعلمات القابلة للتدريب: 0.6447
|
||||
عدد المعلمات القابلة للتدريب: 912,384 || جميع المعلمات: 94,647,856 || نسبة المعلمات القابلة للتدريب: 0.9640 # مع k
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## المساهمة بابداعاتك الخاصة
|
||||
|
||||
يمكن لتعديل النماذج المسبقة التدريب أن يفتح آفاقًا جديدة للبحث والتطبيق. من خلال فهم وتعديل الآليات الداخلية للنماذج مثل SAM، يمكنك تخصيصها لتلبية احتياجاتك المحددة، وتحسين الأداء، وتجربة أفكار جديدة.
|
||||
|
||||
إذا قمت بتطوير تعديﻻتك الخاصة لنماذج Transformers وترغب في مشاركتها، ففكر في المساهمة في هذه الوثيقة.
|
||||
|
||||
- **إنشاء طلب سحب (Pull Request):** شارك تغييراتك وتحسيناتك في التعليمات البرمجية مباشرة في المستودع.
|
||||
- **كتابة التوثيق:** قدم تفسيرات وأمثلة واضحة لتعديلاتك.
|
||||
- **التفاعل مع المجتمع:** ناقش أفكارك واحصل على تعليقات من المطورين والباحثين الآخرين من خلال فتح مشكلة.
|
||||
@ -144,7 +144,7 @@ conda install conda-forge::transformers
|
||||
|
||||
تُحمّل النماذج المُسبقة التدريب وتُخزّن مؤقتًا في: `~/.cache/huggingface/hub`. هذا هو المجلد الافتراضي الذي يُحدده متغير البيئة `TRANSFORMERS_CACHE`. على Windows، يكون دليل ذاكرة التخزين المؤقت الافتراضي هو `C:\Users\username\.cache\huggingface\hub`. يمكنك تغيير متغيرات البيئة shell الموضحة أدناه - حسب الأولوية - لتحديد دليل ذاكرة تخزين مؤقت مختلف:
|
||||
|
||||
1. متغير البيئة (افتراضي): `HUGGINGFACE_HUB_CACHE` أو `TRANSFORMERS_CACHE`.
|
||||
1. متغير البيئة (افتراضي): `HF_HUB_CACHE` أو `TRANSFORMERS_CACHE`.
|
||||
2. متغير البيئة: `HF_HOME`.
|
||||
3. متغير البيئة: `XDG_CACHE_HOME` + `/huggingface`.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
184
docs/source/ar/modular_transformers.md
Normal file
184
docs/source/ar/modular_transformers.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,184 @@
|
||||
# المحولات النمطية
|
||||
|
||||
مكتبة `transformers` هي إطار عمل ذو فلسفة محدد؛ يتم تعريف فلسفتنا في [الدليل المفاهيمي](./philosophy).
|
||||
|
||||
جوهر هذه الفلسفة يتمثل في مبدأ [نموذج واحد، ملف واحد](https://huggingface.co/blog/transformers-design-philosophy)
|
||||
في المكتبة. الجانب السلبي لهذا المكون هو تقييده لوراثة واستيراد مكونات الملفات.
|
||||
|
||||
نتيجة لذلك، تتكرر مكونات النموذج عبر العديد من الملفات. يحتوي `transformers` على عدد كبير من طبقات الانتباه، يقارب عدد النماذج، والكثير منها متطابق. يتسبب هذا في تباعد عمليات التنفيذ المستقلة مع تطبيق الإصلاحات والتغييرات.
|
||||
على أجزاء محددة من التعليمات البرمجية.
|
||||
|
||||
ولمعالجة ذلك، اعتمدنا مفهوم "النسخ" في المكتبة. فبإضافة تعليق يُشير إلى أن التعليمات البرمجية هي نسخة من أخرى، نضمن من خلال أنظمة CI والأوامر المحلية عدم تباعد النسخ. لكن هذه العملية، رغم بساطتها، تُسبب إرهاقاً. كما أنها تزيد العبء على المساهمين، وهو ما نهدف إلى تجاوزه.
|
||||
|
||||
غالباً ما تتطلب مساهمات النماذج إضافة تعليمات برمجية (حوالي 1000 سطر)، ومعالج (حوالي 500 سطر)، واختبارات، ووثائق، إلخ. ونادراً ما تقل مساهمات النماذج عن 3000-5000 سطر من التعليمات البرمجية، معظمها أكواد نمطية. هذا يرفع مستوى المساهمات،
|
||||
|
||||
ونهدف مع المحولات النمطية إلى خفض هذا المستوى إلى حدّ مقبول.
|
||||
|
||||
## ما هو؟
|
||||
|
||||
تقدم المحولات النمطية مفهوم ملف "نمطي" لمجلد نموذج. يقبل هذا الملف النمطي تعليمات برمجية
|
||||
غير مقبولة عادة في ملفات النمذجة/المعالجة، حيث يسمح بالاستيراد من نماذج مجاورة وكذلك
|
||||
الوراثة من الفئات إلى فئات أخرى.
|
||||
|
||||
يعرّف هذا الملف النمطي النماذج والمعالجات وفئة التكوين التي سيتم تعريفها في وحداتهم
|
||||
المتعلقة.
|
||||
|
||||
وأخيرًا، يقدم هذا الميزة أداة `linter` جديدة والتي ستعمل على "تفكيك" الملف النمطي إلى بنية "نموذج واحد، ملف واحد"
|
||||
هيكل الدليل. سيتم إنشاء هذه الملفات تلقائيًا في كل مرة يتم فيها تشغيل البرنامج النصي؛ مما يقلل من المساهمات المطلوبة
|
||||
إلى الملف النمطي، وبالتالي فقط إلى التغييرات بين النموذج المساهم والنماذج الأخرى.
|
||||
|
||||
سيقوم مستخدمو النموذج في النهاية باستيراد واستخدام واجهة الملف الواحد، لذا لا يتوقع حدوث أي تغيير هنا. من خلال القيام بذلك،
|
||||
نأمل في الجمع بين أفضل ما في العالمين: تمكين المساهمات البسيطة مع الالتزام بفلسفتنا.
|
||||
|
||||
لذلك، هذا بديل لعلامات `# Copied from`، ويمكن توقع انتقال النماذج المساهمة سابقًا إلى
|
||||
تنسيق المحولات النمطية الجديد في الأشهر المقبلة.
|
||||
|
||||
### التفاصيل
|
||||
|
||||
تُبسط أداة "linter" الوراثة، مُنشئةً جميع الملفات المفردة من الملف النمطي، مع الحفاظ على شفافيتها أمام مستخدمي Python. حاليًا، تُبسط الأداة مستوىً واحدًا من الوراثة
|
||||
|
||||
على سبيل المثال:
|
||||
- إذا ورثت فئة التكوين من فئة أخرى وأضافت/حذفت معامل، فسيتم إما الإشارة إلى الملف المولد مباشرةً
|
||||
(في حالة الإضافة) أو إزالته تمامًا (في حالة الحذف).
|
||||
- إذا ورثت فئة من فئة أخرى، على سبيل المثال: `class GemmaModel(LlamaModel):`، تُستنتج التبعيات تلقائيًا
|
||||
سيتم استنتاج جميع الوحدات الفرعية تلقائيًا من الفئة الأصلية.
|
||||
- إذا قمت بتعريف وظائف جديدة في الملف `modular` واستخدمتها داخل الفئات، فستستنتج أداة linter ذلك تلقائيًا
|
||||
|
||||
يجب أن تكون قادرًا على كتابة كل شيء (المجزىء اللغوي، ومُعالِج الصور، والنموذج، والتكوين) في الملف `modular`، وسيتم إنشاء الملفات المُقابلة تلقائيًا.
|
||||
|
||||
### التطبيق
|
||||
|
||||
[TODO] نقدم اختبارًا جديدًا، للتأكد من أن المحتوى المولد يتطابق مع ما هو موجود في `modular_xxxx.py`
|
||||
|
||||
### الأمثلة
|
||||
|
||||
هنا مثال سريع باستخدام BERT و RoBERTa. النموذجان مرتبطان ارتباطًا وثيقًا: يختلف تنفيذهما النموذجي في طبقة تضمين.
|
||||
|
||||
بدلاً من إعادة تعريف النموذج بالكامل، إليك كيف يبدو ملف `modular_roberta.py` لفئات النمذجة والتكوين (لأغراض المثال، يتم تجاهل المجزىء اللغوي في هذا الوقت حيث أنه مختلف جدًا).
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from torch import nn
|
||||
from ..bert.configuration_bert import BertConfig
|
||||
from ..bert.modeling_bert import (
|
||||
BertModel,
|
||||
BertEmbeddings,
|
||||
BertForMaskedLM
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# تكوين RoBERTa مطابق لتكوين BERT
|
||||
class RobertaConfig(BertConfig):
|
||||
model_type = 'roberta'
|
||||
|
||||
# نعيد تعريف الإضافات هنا لتسليط الضوء على اختلاف معرف الحشو، ونعيد تعريف الإضافات الموضعية
|
||||
class RobertaEmbeddings(BertEmbeddings):
|
||||
def __init__(self, config):
|
||||
super().__init__(config())
|
||||
|
||||
self.padding_idx = config.pad_token_id
|
||||
self.position_embeddings = nn.Embedding(
|
||||
config.max_position_embeddings, config.hidden_size, padding_idx=self.padding_idx
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# نموذج RoBERTa مطابق لنموذج BERT، باستثناء طبقة الإضافات.
|
||||
# نعيد تعريف الإضافات أعلاه، لذا هنا لا توجد حاجة لعمل إضافي
|
||||
class RobertaModel(BertModel):
|
||||
def __init__(self, config):
|
||||
super().__init__(config)
|
||||
self.embeddings = RobertaEmbeddings(config)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# الرؤوس الآن تحتاج فقط إلى إعادة تعريف النموذج داخل `RobertaModel` الصحيح
|
||||
class RobertaForMaskedLM(BertForMaskedLM):
|
||||
def __init__(self, config):
|
||||
super().__init__(config)
|
||||
self.model = RobertaModel(config)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
لاحظ أنه إذا لم تستخدم الاعتماد الذي حددته، فستحصل على الخطأ التالي:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
ValueError: You defined `RobertaEmbeddings` in the modular_roberta.py, it should be used
|
||||
when you define `BertModel`, as it is one of it's direct dependencies. Make sure
|
||||
you use it in the `__init__` function.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
بالإضافة إلى ذلك، قد تجد قائمة بالأمثلة هنا:
|
||||
|
||||
## ما هو ليس كذلك
|
||||
|
||||
ليس بديلاً لتعليمات برمجة النمذجة (بعد؟)، وإذا لم يكن نموذجك يعتمد على أي شيء آخر موجود من قبل، فيمكنك إضافة ملف `نمذجة` كالعادة.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## الاستخدام المتقدم
|
||||
|
||||
### إزالة السمات والوظائف
|
||||
لإزالة السمات التي لا تستخدم في نموذجك النمطي، والتي لا تريد رؤيتها في النمذجة المفككة:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
class GemmaModel(LlamaModel): | class GemmaModel(PreTrainedModel):
|
||||
def __init__(self, config): | def __init__(self, config):
|
||||
super().__init__(self, eos_token) | super().__init__(config)
|
||||
del self.embed_tokens | self.padding_idx = config.pad_token_id
|
||||
| self.vocab_size = config.vocab_size
|
||||
|
|
||||
| self.layers = nn.ModuleList(
|
||||
| [LlamaDecoderLayer(config, layer_idx) for layer_idx in range(config.num_hidden_layers)]
|
||||
| )
|
||||
| self.norm = LlamaRMSNorm(config.hidden_size, eps=config.rms_norm_eps)
|
||||
| self.rotary_emb = LlamaRotaryEmbedding(config=config)
|
||||
| self.gradient_checkpointing = False
|
||||
|
|
||||
| # Initialize weights and apply final processing
|
||||
| self.post_init()
|
||||
```
|
||||
إذا قمت بالتحقق من `LlamaModel` الأصلي، فستجد `embed_tokens` الذي تمت إزالته هنا (كما هو متوقع!)
|
||||
|
||||
إزالة وظيفة مشابهة، تحتاج فقط إلى كتابتها مع `raise ValueError("")` لمحاكاة السلوك الذي تريده فعليًا عند إزالة وظيفة أصلية في بايثون.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
class GemmaTokenizer(LlamaTokenizer):
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
def get_spm_processor(self):
|
||||
raise AttributeError("Not needed for Gemma")
|
||||
|
||||
def unk_token_length(self):
|
||||
raise AttributeError("Not needed for Gemma")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### تعريف وظائف جديدة
|
||||
|
||||
إذا قمت بتعريف وظيفة جديدة في الملف `modular` لاستخدامها داخل فئة، على سبيل المثال
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
def my_new_function(*args, **kwargs):
|
||||
# Do something here
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
class GemmaModel(LlamaModel):
|
||||
def forward(*args, **kwargs):
|
||||
# Call the function
|
||||
example = my_new_function(*args, **kwargs)
|
||||
# continue here
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
سيتم نسخ وظيفة `my_new_function` (وبشكل متكرر، أي وظائف أخرى جديدة يتم استدعاؤها في جسمها) تلقائيًا
|
||||
في الملف الذي يتم استخدامه.
|
||||
|
||||
### استدعاء `super()`
|
||||
قمنا مؤخرًا بشحن بعض الميزات التي تسمح لك بالانتقال من:
|
||||
```python
|
||||
class GemmaTokenizer(LlamaTokenizer, PretrainedTokenizerFast): | class GemmaModel(nn.Module):
|
||||
def __init__(self, eos_token="</s>"): | def __init__(self):
|
||||
eos_token = AddedToken(eos_token) | eos_token = AddedToken(eos_token)
|
||||
PretrainedTokenizerFast.__init__(self, eos_token) | super().__init__(eos_token)
|
||||
```
|
||||
هذا مفيد عندما لا تريد تفكيك استدعاء `super()`، وتريد التمييز بين أي استدعاء super init تقوم به!
|
||||
|
||||
### التسمية الخاصة
|
||||
ندعم الآن أيضًا حالات خاصة مثل
|
||||
```python
|
||||
class GemmaVisionModel(CLIPModel):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
```
|
||||
حيث اسم فئة `GemmaVision` الخاصة بك ليس هو نفسه `Gemma` النمطي. هذا مفيد للغاية للنماذج المركبة.
|
||||
141
docs/source/ar/notebooks.md
Normal file
141
docs/source/ar/notebooks.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,141 @@
|
||||
# دفاتر ملاحظات 🤗 Transformers
|
||||
|
||||
يمكنك أن تجد هنا قائمة بدفاتر الملاحظات الرسمية التي تقدمها Hugging Face.
|
||||
|
||||
كما نود أن ندرج هنا محتوى مثيرًا للاهتمام تم إنشاؤه بواسطة المجتمع.
|
||||
إذا كتبت دفتر ملاحظات يستفيد من 🤗 Transformers وتود إدراجه هنا، فيُرجى فتح طلب سحب حتى يمكن تضمينه ضمن دفاتر ملاحظات المجتمع.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## دفاتر ملاحظات Hugging Face 🤗
|
||||
|
||||
### دفاتر ملاحظات التوثيق
|
||||
|
||||
يمكنك فتح أي صفحة من صفحات التوثيق كدفتر ملاحظات في Colab (يوجد زر مباشرة على تلك الصفحات) ولكنها مدرجة هنا أيضًا إذا كنت بحاجة إليها:
|
||||
|
||||
| دفتر الملاحظات | الوصف | | |
|
||||
|:----------|:-------------|:-------------|------:|
|
||||
| [جولة سريعة في المكتبة](https://github.com/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/transformers_doc/en/quicktour.ipynb) | عرض لمختلف واجهات برمجة التطبيقات في Transformers |[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/transformers_doc/en/quicktour.ipynb)| [](https://studiolab.sagemaker.aws/import/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/en/transformers_doc/quicktour.ipynb)|
|
||||
| [ملخص المهام](https://github.com/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/transformers_doc/en/task_summary.ipynb) | كيفية تشغيل نماذج مكتبة Transformers مهمة تلو الأخرى |[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/transformers_doc/en/task_summary.ipynb)| [](https://studiolab.sagemaker.aws/import/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/transformers_doc/en/task_summary.ipynb)|
|
||||
| [معالجة البيانات مسبقًا](https://github.com/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/transformers_doc/en/preprocessing.ipynb) | كيفية استخدام محلل لغوي لمعالجة بياناتك مسبقًا |[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/transformers_doc/en/preprocessing.ipynb)| [](https://studiolab.sagemaker.aws/import/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/transformers_doc/en/preprocessing.ipynb)|
|
||||
| [الضبط الدقيق لنموذج مُدرَّب مسبقًا](https://github.com/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/transformers_doc/en/training.ipynb) | كيفية استخدام المدرب لضبط نموذج مُدرَّب مسبقًا بدقة |[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/transformers_doc/en/training.ipynb)| [](https://studiolab.sagemaker.aws/import/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/transformers_doc/en/training.ipynb)|
|
||||
| [ملخص للمحللات اللغوية](https://github.com/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/transformers_doc/en/tokenizer_summary.ipynb) | الاختلافات بين خوارزمية المحلل اللغوي |[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/transformers_doc/en/tokenizer_summary.ipynb)| [](https://studiolab.sagemaker.aws/import/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/transformers_doc/en/tokenizer_summary.ipynb)|
|
||||
| [النماذج متعددة اللغات](https://github.com/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/transformers_doc/en/multilingual.ipynb) | كيفية استخدام النماذج متعددة اللغات للمكتبة |[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/transformers_doc/en/multilingual.ipynb)| [](https://studiolab.sagemaker.aws/import/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/transformers_doc/en/multilingual.ipynb)|
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### أمثلة PyTorch
|
||||
|
||||
#### معالجة اللغة الطبيعية[[pytorch-nlp]]
|
||||
|
||||
| دفتر الملاحظات | الوصف | | |
|
||||
|:----------|:-------------|:-------------|------:|
|
||||
| [تدريب محللك اللغوي](https://github.com/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/tokenizer_training.ipynb) | كيفية تدريب واستخدام محللك اللغوي الخاص بك |[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/tokenizer_training.ipynb)| [](https://studiolab.sagemaker.aws/import/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/tokenizer_training.ipynb)|
|
||||
| [تدريب نموذج لغتك](https://github.com/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/language_modeling_from_scratch.ipynb) | كيفية البدء بسهولة في استخدام المحولات |[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/language_modeling_from_scratch.ipynb)| [](https://studiolab.sagemaker.aws/import/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/language_modeling_from_scratch.ipynb)|
|
||||
| [كيفية ضبط نموذج بدقة على تصنيف النص](https://github.com/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/text_classification.ipynb)| يوضح كيفية معالجة البيانات مسبقًا وضبط نموذج مُدرَّب مسبقًا بدقة على أي مهمة GLUE. | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/text_classification.ipynb)| [](https://studiolab.sagemaker.aws/import/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/text_classification.ipynb)|
|
||||
| [كيفية ضبط نموذج بدقة على النمذجة اللغوية](https://github.com/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/language_modeling.ipynb)| يوضح كيفية معالجة البيانات مسبقًا وضبط نموذج مُدرَّب مسبقًا بدقة على مهمة LM سببية أو مقنعة. | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/language_modeling.ipynb)| [](https://studiolab.sagemaker.aws/import/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/language_modeling.ipynb)|
|
||||
| [كيفية ضبط نموذج بدقة على تصنيف الرموز المميزة](https://github.com/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/token_classification.ipynb)| يوضح كيفية معالجة البيانات مسبقًا وضبط نموذج مُدرَّب مسبقًا بدقة على مهمة تصنيف الرموز المميزة (NER، PoS). | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/token_classification.ipynb)| [](https://studiolab.sagemaker.aws/import/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/token_classification.ipynb)|
|
||||
| [كيفية ضبط نموذج بدقة على الإجابة على الأسئلة](https://github.com/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/question_answering.ipynb)| يوضح كيفية معالجة البيانات مسبقًا وضبط نموذج مُدرَّب مسبقًا بدقة على SQUAD. | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/question_answering.ipynb)| [](https://studiolab.sagemaker.aws/import/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/question_answering.ipynb)|
|
||||
| [كيفية ضبط نموذج بدقة على الاختيار من متعدد](https://github.com/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/multiple_choice.ipynb)| يوضح كيفية معالجة البيانات مسبقًا وضبط نموذج مُدرَّب مسبقًا بدقة على SWAG. | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/multiple_choice.ipynb)| [](https://studiolab.sagemaker.aws/import/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/multiple_choice.ipynb)|
|
||||
| [كيفية ضبط نموذج بدقة على الترجمة](https://github.com/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/translation.ipynb)| يوضح كيفية معالجة البيانات مسبقًا وضبط نموذج مُدرَّب مسبقًا بدقة على WMT. | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/translation.ipynb)| [](https://studiolab.sagemaker.aws/import/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/translation.ipynb)|
|
||||
| [كيفية ضبط نموذج بدقة على التلخيص](https://github.com/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/summarization.ipynb)| يوضح كيفية معالجة البيانات مسبقًا وضبط نموذج مُدرَّب مسبقًا بدقة على XSUM. | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/summarization.ipynb)| [](https://studiolab.sagemaker.aws/import/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/summarization.ipynb)|
|
||||
| [كيفية تدريب نموذج لغة من البداية](https://github.com/huggingface/blog/blob/main/notebooks/01_how_to_train.ipynb)| تسليط الضوء على جميع الخطوات لتدريب نموذج Transformer بشكل فعال على بيانات مخصصة | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/blog/blob/main/notebooks/01_how_to_train.ipynb)| [](https://studiolab.sagemaker.aws/import/github/huggingface/blog/blob/main/notebooks/01_how_to_train.ipynb)|
|
||||
| [كيفية إنشاء نص](https://github.com/huggingface/blog/blob/main/notebooks/02_how_to_generate.ipynb)| كيفية استخدام أساليب فك التشفير المختلفة لإنشاء اللغة باستخدام المحولات | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/blog/blob/main/notebooks/02_how_to_generate.ipynb)| [](https://studiolab.sagemaker.aws/import/github/huggingface/blog/blob/main/notebooks/02_how_to_generate.ipynb)|
|
||||
| [كيفية إنشاء نص (مع قيود)](https://github.com/huggingface/blog/blob/main/notebooks/53_constrained_beam_search.ipynb)| كيفية توجيه إنشاء اللغة باستخدام القيود التي يوفرها المستخدم | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/blog/blob/main/notebooks/53_constrained_beam_search.ipynb)| [](https://studiolab.sagemaker.aws/import/github/huggingface/blog/blob/main/notebooks/53_constrained_beam_search.ipynb)|
|
||||
| [Reformer](https://github.com/huggingface/blog/blob/main/notebooks/03_reformer.ipynb)| كيف يدفع Reformer حدود النمذجة اللغوية | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/patrickvonplaten/blog/blob/main/notebooks/03_reformer.ipynb)| [](https://studiolab.sagemaker.aws/import/github/patrickvonplaten/blog/blob/main/notebooks/03_reformer.ipynb)|
|
||||
|
||||
#### رؤية الكمبيوتر[[pytorch-cv]]
|
||||
|
||||
| دفتر الملاحظات | الوصف | | |
|
||||
|:---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|:-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|:-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|------:|
|
||||
| [كيفية ضبط نموذج بدقة على تصنيف الصور (Torchvision)](https://github.com/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/image_classification.ipynb) | يوضح كيفية معالجة البيانات مسبقًا باستخدام Torchvision وضبط أي نموذج رؤية مُدرَّب مسبقًا بدقة على تصنيف الصور | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/image_classification.ipynb) | [](https://studiolab.sagemaker.aws/import/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/image_classification.ipynb)|
|
||||
| [كيفية ضبط نموذج بدقة على تصنيف الصور (Albumentations)](https://github.com/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/image_classification_albumentations.ipynb) | يوضح كيفية معالجة البيانات مسبقًا باستخدام Albumentations وضبط أي نموذج رؤية مُدرَّب مسبقًا بدقة على تصنيف الصور | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/image_classification_albumentations.ipynb) | [](https://studiolab.sagemaker.aws/import/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/image_classification_albumentations.ipynb)|
|
||||
| [كيفية ضبط نموذج بدقة على تصنيف الصور (Kornia)](https://github.com/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/image_classification_kornia.ipynb) | يوضح كيفية معالجة البيانات مسبقًا باستخدام Kornia وضبط أي نموذج رؤية مُدرَّب مسبقًا بدقة على تصنيف الصور | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/image_classification_kornia.ipynb) | [](https://studiolab.sagemaker.aws/import/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/image_classification_kornia.ipynb)|
|
||||
| [كيفية إجراء الكشف عن الأشياء بدون لقطات مع OWL-ViT](https://github.com/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/zeroshot_object_detection_with_owlvit.ipynb) | يوضح كيفية إجراء الكشف عن الأشياء بدون لقطات على الصور باستخدام استعلامات نصية | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/zeroshot_object_detection_with_owlvit.ipynb)| [](https://studiolab.sagemaker.aws/import/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/zeroshot_object_detection_with_owlvit.ipynb)|
|
||||
| [كيفية ضبط نموذج وصف الصور بدقة](https://github.com/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/image_captioning_blip.ipynb) | يوضح كيفية ضبط BLIP بدقة لوصف الصور على مجموعة بيانات مخصصة | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/image_captioning_blip.ipynb) | [](https://studiolab.sagemaker.aws/import/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/image_captioning_blip.ipynb)|
|
||||
| [كيفية بناء نظام تشابه الصور مع Transformers](https://github.com/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/image_similarity.ipynb) | يوضح كيفية بناء نظام تشابه الصور | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/image_similarity.ipynb) | [](https://studiolab.sagemaker.aws/import/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/image_similarity.ipynb)|
|
||||
| [كيفية ضبط نموذج SegFormer بدقة على التجزئة الدلالية](https://github.com/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/semantic_segmentation.ipynb) | يوضح كيفية معالجة البيانات مسبقًا وضبط نموذج SegFormer مُدرَّب مسبقًا بدقة على التجزئة الدلالية | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/semantic_segmentation.ipynb) | [](https://studiolab.sagemaker.aws/import/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/semantic_segmentation.ipynb)|
|
||||
| [كيفية ضبط نموذج VideoMAE بدقة على تصنيف الفيديو](https://github.com/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/video_classification.ipynb) | يوضح كيفية معالجة البيانات مسبقًا وضبط نموذج VideoMAE مُدرَّب مسبقًا بدقة على تصنيف الفيديو | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/video_classification.ipynb) | [](https://studiolab.sagemaker.aws/import/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/video_classification.ipynb)|
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### الصوت[[pytorch-audio]]
|
||||
|
||||
| دفتر الملاحظات | الوصف | | |
|
||||
|:----------|:-------------|:-------------|------:|
|
||||
| [كيفية ضبط نموذج التعرف على الكلام باللغة الإنجليزية بدقة](https://github.com/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/speech_recognition.ipynb)| يوضح كيفية معالجة البيانات مسبقًا وضبط نموذج كلام مُدرَّب مسبقًا بدقة على TIMIT | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/speech_recognition.ipynb)| [](https://studiolab.sagemaker.aws/import/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/speech_recognition.ipynb)|
|
||||
| [كيفية ضبط نموذج التعرف على الكلام بأي لغة بدقة](https://github.com/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/multi_lingual_speech_recognition.ipynb)| يوضح كيفية معالجة البيانات مسبقًا وضبط نموذج كلام مُدرَّب مسبقًا متعدد اللغات بدقة على Common Voice | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/multi_lingual_speech_recognition.ipynb)| [](https://studiolab.sagemaker.aws/import/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/multi_lingual_speech_recognition.ipynb)|
|
||||
| [كيفية ضبط نموذج بدقة على تصنيف الصوت](https://github.com/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/audio_classification.ipynb)| يوضح كيفية معالجة البيانات مسبقًا وضبط نموذج كلام مُدرَّب مسبقًا بدقة على Keyword Spotting | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/audio_classification.ipynb)| [](https://studiolab.sagemaker.aws/import/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/audio_classification.ipynb)|
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### التسلسلات البيولوجية[[pytorch-bio]]
|
||||
|
||||
| دفتر الملاحظات | الوصف | | |
|
||||
|:----------|:----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|:-------------|------:|
|
||||
| [كيفية ضبط نموذج بروتين مُدرَّب مسبقًا بدقة](https://github.com/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/protein_language_modeling.ipynb) | شاهد كيفية ترميز البروتينات وضبط نموذج "لغة" بروتين مُدرَّب مسبقًا كبير بدقة | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/protein_language_modeling.ipynb) | [](https://studiolab.sagemaker.aws/import/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/protein_language_modeling.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [كيفية إنشاء طيات بروتينية](https://github.com/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/protein_folding.ipynb) | شاهد كيفية الانتقال من تسلسل البروتين إلى نموذج بروتين كامل وملف PDB | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/protein_folding.ipynb) | [](https://studiolab.sagemaker.aws/import/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/protein_folding.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [كيفية ضبط نموذج محول النيوكليوتيدات بدقة](https://github.com/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/nucleotide_transformer_dna_sequence_modelling.ipynb) | شاهد كيفية ترميز الحمض النووي وضبط نموذج "لغة" الحمض النووي مُدرَّب مسبقًا كبير بدقة | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/nucleotide_transformer_dna_sequence_modelling.ipynb) | [](https://studiolab.sagemaker.aws/import/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/nucleotide_transformer_dna_sequence_modelling.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [ضبط نموذج محول النيوكليوتيدات بدقة باستخدام LoRA](https://github.com/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/nucleotide_transformer_dna_sequence_modelling_with_peft.ipynb) | تدريب نماذج DNA أكبر بكثير بطريقة فعالة من حيث الذاكرة | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/nucleotide_transformer_dna_sequence_modelling_with_peft.ipynb) | [](https://studiolab.sagemaker.aws/import/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/nucleotide_transformer_dna_sequence_modelling_with_peft.ipynb) |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### طرائق أخرى[[pytorch-other]]
|
||||
|
||||
| دفتر الملاحظات | الوصف | | |
|
||||
|:----------|:----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|:-------------|------:|
|
||||
| [التنبؤ الاحتمالي بالسلاسل الزمنية](https://github.com/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/time-series-transformers.ipynb) | شاهد كيفية تدريب Time Series Transformer على مجموعة بيانات مخصصة | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/time-series-transformers.ipynb) | [](https://studiolab.sagemaker.aws/import/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/time-series-transformers.ipynb) |
|
||||
|
||||
#### دفاتر ملاحظات الأدوات المساعدة [[pytorch-utility]]
|
||||
|
||||
| دفتر الملاحظات | الوصف | | |
|
||||
|:----------|:-------------|:-------------|------:|
|
||||
| [كيفية تصدير النموذج إلى ONNX](https://github.com/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/onnx-export.ipynb)| تسليط الضوء على كيفية التصدير وتشغيل أعباء عمل الاستدلال من خلال ONNX | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/onnx-export.ipynb)| [](https://studiolab.sagemaker.aws/import/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/onnx-export.ipynb)|
|
||||
| [كيفية استخدام المعايير](https://github.com/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/benchmark.ipynb)| كيفية قياس أداء النماذج باستخدام المحولات | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/benchmark.ipynb)| [](https://studiolab.sagemaker.aws/import/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/benchmark.ipynb)|
|
||||
|
||||
### أمثلة TensorFlow
|
||||
|
||||
#### معالجة اللغة الطبيعية[[tensorflow-nlp]]
|
||||
|
||||
| دفتر الملاحظات | الوصف | | |
|
||||
|:----------|:-------------|:-------------|------:|
|
||||
| [تدريب محللك اللغوي](https://github.com/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/tokenizer_training.ipynb) | كيفية تدريب واستخدام محللك اللغوي الخاص بك |[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/tokenizer_training.ipynb)| [](https://studiolab.sagemaker.aws/import/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/tokenizer_training.ipynb)|
|
||||
| [تدريب نموذج لغتك](https://github.com/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/language_modeling_from_scratch-tf.ipynb) | كيفية البدء بسهولة في استخدام المحولات |[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/language_modeling_from_scratch-tf.ipynb)| [](https://studiolab.sagemaker.aws/import/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/language_modeling_from_scratch-tf.ipynb)|
|
||||
| [كيفية ضبط نموذج بدقة على تصنيف النص](https://github.com/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/text_classification-tf.ipynb)| يوضح كيفية معالجة البيانات مسبقًا وضبط نموذج مُدرَّب مسبقًا بدقة على أي مهمة GLUE. | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/text_classification-tf.ipynb)| [](https://studiolab.sagemaker.aws/import/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/text_classification-tf.ipynb)|
|
||||
| [كيفية ضبط نموذج بدقة على النمذجة اللغوية](https://github.com/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/language_modeling-tf.ipynb)| يوضح كيفية معالجة البيانات مسبقًا وضبط نموذج مُدرَّب مسبقًا بدقة على مهمة LM سببية أو مقنعة. | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/language_modeling-tf.ipynb)| [](https://studiolab.sagemaker.aws/import/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/language_modeling-tf.ipynb)|
|
||||
| [كيفية ضبط نموذج بدقة على تصنيف الرموز المميزة](https://github.com/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/token_classification-tf.ipynb)| يوضح كيفية معالجة البيانات مسبقًا وضبط نموذج مُدرَّب مسبقًا بدقة على مهمة تصنيف الرموز المميزة (NER، PoS). | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/token_classification-tf.ipynb)| [](https://studiolab.sagemaker.aws/import/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/token_classification-tf.ipynb)|
|
||||
| [كيفية ضبط نموذج بدقة على الإجابة على الأسئلة](https://github.com/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/question_answering-tf.ipynb)| يوضح كيفية معالجة البيانات مسبقًا وضبط نموذج مُدرَّب مسبقًا بدقة على SQUAD. | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/question_answering-tf.ipynb)| [](https://studiolab.sagemaker.aws/import/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/question_answering-tf.ipynb)|
|
||||
| [كيفية ضبط نموذج بدقة على الاختيار من متعدد](https://github.com/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/multiple_choice-tf.ipynb)| يوضح كيفية معالجة البيانات مسبقًا وضبط نموذج مُدرَّب مسبقًا بدقة على SWAG. | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/multiple_choice-tf.ipynb)| [](https://studiolab.sagemaker.aws/import/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/multiple_choice-tf.ipynb)|
|
||||
| [كيفية ضبط نموذج بدقة على الترجمة](https://github.com/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/translation-tf.ipynb)| يوضح كيفية معالجة البيانات مسبقًا وضبط نموذج مُدرَّب مسبقًا بدقة على WMT. | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/translation-tf.ipynb)| [](https://studiolab.sagemaker.aws/import/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/translation-tf.ipynb)|
|
||||
| [كيفية ضبط نموذج بدقة على التلخيص](https://github.com/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/summarization-tf.ipynb)| يوضح كيفية معالجة البيانات مسبقًا وضبط نموذج مُدرَّب مسبقًا بدقة على XSUM. | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/summarization-tf.ipynb)| [](https://studiolab.sagemaker.aws/import/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/summarization-tf.ipynb)|
|
||||
|
||||
#### رؤية الكمبيوتر[[tensorflow-cv]]
|
||||
|
||||
| دفتر الملاحظات | الوصف | | |
|
||||
|:---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|:----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|:-------------|------:|
|
||||
| [كيفية ضبط نموذج بدقة على تصنيف الصور](https://github.com/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/image_classification-tf.ipynb) | يوضح كيفية معالجة البيانات مسبقًا وضبط أي نموذج رؤية مُدرَّب مسبقًا بدقة على تصنيف الصور | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/image_classification-tf.ipynb)| [](https://studiolab.sagemaker.aws/import/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/image_classification-tf.ipynb)|
|
||||
| [كيفية ضبط نموذج SegFormer بدقة على التجزئة الدلالية](https://github.com/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/semantic_segmentation-tf.ipynb) | يوضح كيفية معالجة البيانات مسبقًا وضبط نموذج SegFormer مُدرَّب مسبقًا بدقة على التجزئة الدلالية | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/semantic_segmentation-tf.ipynb)| [](https://studiolab.sagemaker.aws/import/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/semantic_segmentation-tf.ipynb)|
|
||||
|
||||
#### التسلسلات البيولوجية[[tensorflow-bio]]
|
||||
|
||||
| دفتر الملاحظات | الوصف | | |
|
||||
|:----------|:-------------|:-------------|------:|
|
||||
| [كيفية ضبط نموذج بروتين مُدرَّب مسبقًا بدقة](https://github.com/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/protein_language_modeling-tf.ipynb) | شاهد كيفية ترميز البروتينات وضبط نموذج "لغة" بروتين مُدرَّب مسبقًا كبير بدقة | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/protein_language_modeling-tf.ipynb) | [](https://studiolab.sagemaker.aws/import/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/protein_language_modeling-tf.ipynb) |
|
||||
|
||||
#### دفاتر ملاحظات الأدوات المساعدة [[tensorflow-utility]]
|
||||
|
||||
| دفتر الملاحظات | الوصف | | |
|
||||
|:----------|:-------------|:-------------|------:|
|
||||
| [كيفية تدريب نماذج TF/Keras على TPU](https://github.com/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/tpu_training-tf.ipynb) | شاهد كيفية التدريب بسرعة عالية على أجهزة TPU من Google | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/tpu_training-tf.ipynb) | [](https://studiolab.sagemaker.aws/import/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/tpu_training-tf.ipynb) |
|
||||
|
||||
### دفاتر ملاحظات Optimum
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 [Optimum](https://github.com/huggingface/optimum) هو امتداد لـ 🤗 Transformers، يوفر مجموعة من أدوات تحسين الأداء التي تمكن من تحقيق أقصى قدر من الكفاءة لتدريب وتشغيل النماذج على الأجهزة المستهدفة.
|
||||
|
||||
| دفتر الملاحظات | الوصف | | |
|
||||
|:----------|:-------------|:-------------|------:|
|
||||
| [كيفية تكميم نموذج باستخدام ONNX Runtime لتصنيف النص](https://github.com/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/text_classification_quantization_ort.ipynb)| يوضح كيفية تطبيق التكميم الثابت والديناميكي على نموذج باستخدام [ONNX Runtime](https://github.com/microsoft/onnxruntime) لأي مهمة GLUE. | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/text_classification_quantization_ort.ipynb)| [](https://studiolab.sagemaker.aws/import/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/text_classification_quantization_ort.ipynb)|
|
||||
| [كيفية تكميم نموذج باستخدام Intel Neural Compressor لتصنيف النص](https://github.com/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/text_classification_quantization_inc.ipynb)| يوضح كيفية تطبيق التكميم الثابت والديناميكي والتدريبي على نموذج باستخدام [Intel Neural Compressor (INC)](https://github.com/intel/neural-compressor) لأي مهمة GLUE. | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/text_classification_quantization_inc.ipynb)| [](https://studiolab.sagemaker.aws/import/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/text_classification_quantization_inc.ipynb)|
|
||||
| [كيفية ضبط نموذج بدقة على تصنيف النص باستخدام ONNX Runtime](https://github.com/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/text_classification_ort.ipynb)| يوضح كيفية معالجة البيانات مسبقًا وضبط نموذج بدقة على أي مهمة GLUE باستخدام [ONNX Runtime](https://github.com/microsoft/onnxruntime). | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/text_classification_ort.ipynb)| [](https://studiolab.sagemaker.aws/import/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/text_classification_ort.ipynb)|
|
||||
| [كيفية ضبط نموذج بدقة على التلخيص باستخدام ONNX Runtime](https://github.com/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/summarization_ort.ipynb)| يوضح كيفية معالجة البيانات مسبقًا وضبط نموذج بدقة على XSUM باستخدام [ONNX Runtime](https://github.com/microsoft/onnxruntime). | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/summarization_ort.ipynb)| [](https://studiolab.sagemaker.aws/import/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/summarization_ort.ipynb)|
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## دفاتر ملاحظات المجتمع:
|
||||
|
||||
تتوفر المزيد من دفاتر الملاحظات التي طورها المجتمع [هنا](https://hf.co/docs/transformers/community#community-notebooks).
|
||||
|
||||
41
docs/source/ar/tiktoken.md
Normal file
41
docs/source/ar/tiktoken.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,41 @@
|
||||
# Tiktoken والتفاعل مع Transformers
|
||||
|
||||
يتم دمج دعم ملفات نموذج tiktoken بسلاسة في 🤗 transformers عند تحميل النماذج
|
||||
`from_pretrained` مع ملف `tokenizer.model` tiktoken على Hub، والذي يتم تحويله تلقائيًا إلى [المحلل اللغوي السريع](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/en/main_classes/tokenizer#transformers.PreTrainedTokenizerFast).
|
||||
|
||||
### النماذج المعروفة التي تم إصدارها مع `tiktoken.model`:
|
||||
- gpt2
|
||||
- llama3
|
||||
|
||||
## مثال على الاستخدام
|
||||
|
||||
من أجل تحميل ملفات `tiktoken` في `transformers`، تأكد من أن ملف `tokenizer.model` هو ملف tiktoken وسيتم تحميله تلقائيًا عند التحميل `from_pretrained`. إليك كيفية تحميل مجزىء لغوي ونموذج، والذي
|
||||
يمكن تحميله من نفس الملف بالضبط:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import AutoTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
model_id = "meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3-8B-Instruct"
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_id, subfolder="original")
|
||||
```
|
||||
## إنشاء مجزىء لغوي tiktoken
|
||||
|
||||
لا يحتوي ملف `tokenizer.model` على أي معلومات حول الرموز أو الأنماط الإضافية. إذا كانت هذه الأمور مهمة، قم بتحويل المحلل اللغوي إلى `tokenizer.json`، وهو التنسيق المناسب لـ [`PreTrainedTokenizerFast`].
|
||||
|
||||
قم بتوليد ملف `tokenizer.model` باستخدام [tiktoken.get_encoding](https://github.com/openai/tiktoken/blob/63527649963def8c759b0f91f2eb69a40934e468/tiktoken/registry.py#L63) ثم قم بتحويله إلى `tokenizer.json` باستخدام [`convert_tiktoken_to_fast`].
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
|
||||
from transformers.integrations.tiktoken import convert_tiktoken_to_fast
|
||||
from tiktoken import get_encoding
|
||||
|
||||
# يمكنك تحميل ترميزك المخصص أو الترميز الذي توفره OpenAI
|
||||
encoding = get_encoding("gpt2")
|
||||
convert_tiktoken_to_fast(encoding, "config/save/dir")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
يتم حفظ ملف `tokenizer.json` الناتج في الدليل المحدد ويمكن تحميله باستخدام [`PreTrainedTokenizerFast`].
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
tokenizer = PreTrainedTokenizerFast.from_pretrained("config/save/dir")
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -149,7 +149,7 @@ conda install conda-forge::transformers
|
||||
|
||||
Vorgefertigte Modelle werden heruntergeladen und lokal zwischengespeichert unter: `~/.cache/huggingface/hub`. Dies ist das Standardverzeichnis, das durch die Shell-Umgebungsvariable "TRANSFORMERS_CACHE" vorgegeben ist. Unter Windows wird das Standardverzeichnis durch `C:\Benutzer\Benutzername\.cache\huggingface\hub` angegeben. Sie können die unten aufgeführten Shell-Umgebungsvariablen - in der Reihenfolge ihrer Priorität - ändern, um ein anderes Cache-Verzeichnis anzugeben:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Shell-Umgebungsvariable (Standard): `HUGGINGFACE_HUB_CACHE` oder `TRANSFORMERS_CACHE`.
|
||||
1. Shell-Umgebungsvariable (Standard): `HF_HUB_CACHE` oder `TRANSFORMERS_CACHE`.
|
||||
2. Shell-Umgebungsvariable: `HF_HOME`.
|
||||
3. Shell-Umgebungsvariable: `XDG_CACHE_HOME` + `/huggingface`.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -11,4 +11,4 @@ black_avoid_patterns = {
|
||||
"{processor_class}": "FakeProcessorClass",
|
||||
"{model_class}": "FakeModelClass",
|
||||
"{object_class}": "FakeObjectClass",
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -516,8 +516,8 @@
|
||||
title: Nyströmformer
|
||||
- local: model_doc/olmo
|
||||
title: OLMo
|
||||
- local: model_doc/olmo_1124
|
||||
title: OLMo November 2024
|
||||
- local: model_doc/olmo2
|
||||
title: OLMo2
|
||||
- local: model_doc/olmoe
|
||||
title: OLMoE
|
||||
- local: model_doc/open-llama
|
||||
@ -657,6 +657,8 @@
|
||||
title: GLPN
|
||||
- local: model_doc/hiera
|
||||
title: Hiera
|
||||
- local: model_doc/ijepa
|
||||
title: I-JEPA
|
||||
- local: model_doc/imagegpt
|
||||
title: ImageGPT
|
||||
- local: model_doc/levit
|
||||
@ -703,6 +705,8 @@
|
||||
title: Swin2SR
|
||||
- local: model_doc/table-transformer
|
||||
title: Table Transformer
|
||||
- local: model_doc/timm_wrapper
|
||||
title: Timm Wrapper
|
||||
- local: model_doc/upernet
|
||||
title: UperNet
|
||||
- local: model_doc/van
|
||||
@ -808,6 +812,8 @@
|
||||
title: ALIGN
|
||||
- local: model_doc/altclip
|
||||
title: AltCLIP
|
||||
- local: model_doc/aria
|
||||
title: Aria
|
||||
- local: model_doc/blip
|
||||
title: BLIP
|
||||
- local: model_doc/blip-2
|
||||
|
||||
@ -225,7 +225,7 @@ You have access to the following tools:
|
||||
To solve the task, you must plan forward to proceed in a series of steps, in a cycle of 'Thought:', 'Code:', and 'Observation:' sequences.
|
||||
|
||||
At each step, in the 'Thought:' sequence, you should first explain your reasoning towards solving the task, then the tools that you want to use.
|
||||
Then in the 'Code:' sequence, you shold write the code in simple Python. The code sequence must end with '/End code' sequence.
|
||||
Then in the 'Code:' sequence, you should write the code in simple Python. The code sequence must end with '/End code' sequence.
|
||||
During each intermediate step, you can use 'print()' to save whatever important information you will then need.
|
||||
These print outputs will then be available in the 'Observation:' field, for using this information as input for the next step.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -211,7 +211,7 @@ agent.run("How many more blocks (also denoted as layers) are in BERT base encode
|
||||
|
||||
## Display your agent run in a cool Gradio interface
|
||||
|
||||
You can leverage `gradio.Chatbot`to display your agent's thoughts using `stream_to_gradio`, here is an example:
|
||||
You can leverage `gradio.Chatbot` to display your agent's thoughts using `stream_to_gradio`, here is an example:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
import gradio as gr
|
||||
|
||||
@ -138,12 +138,15 @@ Load a processor with [`AutoProcessor.from_pretrained`]:
|
||||
|
||||
<frameworkcontent>
|
||||
<pt>
|
||||
The `AutoModelFor` classes let you load a pretrained model for a given task (see [here](model_doc/auto) for a complete list of available tasks). For example, load a model for sequence classification with [`AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained`]:
|
||||
The `AutoModelFor` classes let you load a pretrained model for a given task (see [here](model_doc/auto) for a complete list of available tasks). For example, load a model for sequence classification with [`AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained`].
|
||||
|
||||
> [!WARNING]
|
||||
> By default, the weights are loaded in full precision (torch.float32) regardless of the actual data type the weights are stored in such as torch.float16. Set `torch_dtype="auto"` to load the weights in the data type defined in a model's `config.json` file to automatically load the most memory-optimal data type.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForSequenceClassification
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained("distilbert/distilbert-base-uncased")
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained("distilbert/distilbert-base-uncased", torch_dtype="auto")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Easily reuse the same checkpoint to load an architecture for a different task:
|
||||
@ -151,7 +154,7 @@ Easily reuse the same checkpoint to load an architecture for a different task:
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForTokenClassification
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForTokenClassification.from_pretrained("distilbert/distilbert-base-uncased")
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForTokenClassification.from_pretrained("distilbert/distilbert-base-uncased", torch_dtype="auto")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -456,6 +456,8 @@ just like in multinomial sampling. However, in assisted decoding, reducing the t
|
||||
['Alice and Bob, a couple of friends of mine, who are both in the same office as']
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We recommend to install `scikit-learn` library to enhance the candidate generation strategy and achieve additional speedup.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Universal Assisted Decoding
|
||||
|
||||
Universal Assisted Decoding (UAD) adds support for main and assistant models with different tokenizers.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -62,6 +62,8 @@ Flax), PyTorch, and/or TensorFlow.
|
||||
| [ALBERT](model_doc/albert) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| [ALIGN](model_doc/align) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| [AltCLIP](model_doc/altclip) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| [Aria](model_doc/aria) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| [AriaText](model_doc/aria_text) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| [Audio Spectrogram Transformer](model_doc/audio-spectrogram-transformer) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| [Autoformer](model_doc/autoformer) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| [Bark](model_doc/bark) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
@ -168,9 +170,11 @@ Flax), PyTorch, and/or TensorFlow.
|
||||
| [Hiera](model_doc/hiera) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| [Hubert](model_doc/hubert) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| [I-BERT](model_doc/ibert) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| [I-JEPA](model_doc/ijepa) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| [IDEFICS](model_doc/idefics) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| [Idefics2](model_doc/idefics2) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| [Idefics3](model_doc/idefics3) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| [Idefics3VisionTransformer](model_doc/idefics3_vision) | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| [ImageGPT](model_doc/imagegpt) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| [Informer](model_doc/informer) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| [InstructBLIP](model_doc/instructblip) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
@ -240,7 +244,7 @@ Flax), PyTorch, and/or TensorFlow.
|
||||
| [Nougat](model_doc/nougat) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| [Nyströmformer](model_doc/nystromformer) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| [OLMo](model_doc/olmo) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| [OLMo November 2024](model_doc/olmo_1124) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| [OLMo2](model_doc/olmo2) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| [OLMoE](model_doc/olmoe) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| [OmDet-Turbo](model_doc/omdet-turbo) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| [OneFormer](model_doc/oneformer) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
@ -317,6 +321,7 @@ Flax), PyTorch, and/or TensorFlow.
|
||||
| [TAPEX](model_doc/tapex) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| [Time Series Transformer](model_doc/time_series_transformer) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| [TimeSformer](model_doc/timesformer) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| [TimmWrapperModel](model_doc/timm_wrapper) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| [Trajectory Transformer](model_doc/trajectory_transformer) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| [Transformer-XL](model_doc/transfo-xl) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| [TrOCR](model_doc/trocr) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
|
||||
@ -157,7 +157,7 @@ conda install conda-forge::transformers
|
||||
|
||||
Pretrained models are downloaded and locally cached at: `~/.cache/huggingface/hub`. This is the default directory given by the shell environment variable `TRANSFORMERS_CACHE`. On Windows, the default directory is given by `C:\Users\username\.cache\huggingface\hub`. You can change the shell environment variables shown below - in order of priority - to specify a different cache directory:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Shell environment variable (default): `HUGGINGFACE_HUB_CACHE` or `TRANSFORMERS_CACHE`.
|
||||
1. Shell environment variable (default): `HF_HUB_CACHE` or `TRANSFORMERS_CACHE`.
|
||||
2. Shell environment variable: `HF_HOME`.
|
||||
3. Shell environment variable: `XDG_CACHE_HOME` + `/huggingface`.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -436,3 +436,9 @@ A [`Constraint`] can be used to force the generation to include specific tokens
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] SynthIDTextWatermarkDetector
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
## Compile Utils
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] CompileConfig
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -180,7 +180,7 @@ Fun fact: The shortest war in history was between Britain and Zanzibar on August
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
Cache offloading requires a GPU and can be slower than dynamic KV cache. Use it if you are getting CUDA out of memory errors.
|
||||
Cache offloading requires a CUDA GPU and can be slower than dynamic KV cache. Use it if you are getting CUDA out of memory errors.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -261,6 +261,7 @@ This will use the [`~OffloadedStaticCache`] implementation instead.
|
||||
>>> tokenizer.batch_decode(out, skip_special_tokens=True)[0]
|
||||
"Hello, my name is [Your Name], and I am a [Your Profession] with [Number of Years] of"
|
||||
```
|
||||
Cache offloading requires a CUDA GPU.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Sliding Window Cache
|
||||
|
||||
@ -57,13 +57,13 @@ import os
|
||||
os.environ["TOKENIZERS_PARALLELISM"] = "false" # To prevent long warnings :)
|
||||
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("google/gemma-2b")
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("google/gemma-2b", device_map="auto")
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("google/gemma-2b", torch_dtype="auto", device_map="auto")
|
||||
|
||||
model.generation_config.cache_implementation = "static"
|
||||
|
||||
model.forward = torch.compile(model.forward, mode="reduce-overhead", fullgraph=True)
|
||||
input_text = "The theory of special relativity states "
|
||||
input_ids = tokenizer(input_text, return_tensors="pt").to("cuda")
|
||||
input_ids = tokenizer(input_text, return_tensors="pt").to(model.device.type)
|
||||
|
||||
outputs = model.generate(**input_ids)
|
||||
print(tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs, skip_special_tokens=True))
|
||||
@ -89,11 +89,11 @@ import os
|
||||
os.environ["TOKENIZERS_PARALLELISM"] = "false" # To prevent long warnings :)
|
||||
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("google/gemma-2b")
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("google/gemma-2b", device_map="auto")
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("google/gemma-2b", torch_dtype="auto", device_map="auto")
|
||||
|
||||
model.forward = torch.compile(model.forward, mode="reduce-overhead", fullgraph=True)
|
||||
input_text = "The theory of special relativity states "
|
||||
input_ids = tokenizer(input_text, return_tensors="pt").to("cuda")
|
||||
input_ids = tokenizer(input_text, return_tensors="pt").to(model.device.type)
|
||||
prompt_length = input_ids.input_ids.shape[1]
|
||||
model.generation_config.max_new_tokens = 16
|
||||
|
||||
@ -126,6 +126,7 @@ If you want to go further down a level, the [`StaticCache`] object can also be p
|
||||
from transformers import LlamaTokenizer, LlamaForCausalLM, StaticCache, logging
|
||||
from transformers.testing_utils import CaptureLogger
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from accelerate.test_utils.testing import get_backend
|
||||
|
||||
prompts = [
|
||||
"Simply put, the theory of relativity states that ",
|
||||
@ -133,7 +134,7 @@ prompts = [
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
NUM_TOKENS_TO_GENERATE = 40
|
||||
torch_device = "cuda"
|
||||
torch_device, _, _ = get_backend() # automatically detects the underlying device type (CUDA, CPU, XPU, MPS, etc.)
|
||||
|
||||
tokenizer = LlamaTokenizer.from_pretrained("meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-hf", pad_token="</s>", padding_side="right")
|
||||
model = LlamaForCausalLM.from_pretrained("meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-hf", device_map="sequential")
|
||||
@ -201,11 +202,11 @@ import os
|
||||
os.environ["TOKENIZERS_PARALLELISM"] = "false" # To prevent long warnings :)
|
||||
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("google/gemma-2b")
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("google/gemma-2b", device_map="auto")
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("google/gemma-2b", torch_dtype="auto", device_map="auto")
|
||||
|
||||
model.generate = torch.compile(model.generate, mode="reduce-overhead", fullgraph=True)
|
||||
input_text = "The theory of special relativity states "
|
||||
input_ids = tokenizer(input_text, return_tensors="pt").to("cuda")
|
||||
input_ids = tokenizer(input_text, return_tensors="pt").to(model.device.type)
|
||||
|
||||
outputs = model.generate(**input_ids)
|
||||
print(tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs, skip_special_tokens=True))
|
||||
@ -241,13 +242,14 @@ Enable speculative decoding by loading an assistant model and passing it to the
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from accelerate.test_utils.testing import get_backend
|
||||
|
||||
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
|
||||
device, _, _ = get_backend() # automatically detects the underlying device type (CUDA, CPU, XPU, MPS, etc.)
|
||||
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("facebook/opt-1.3b")
|
||||
inputs = tokenizer("Einstein's theory of relativity states", return_tensors="pt").to(device)
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("facebook/opt-1.3b").to(device)
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("facebook/opt-1.3b", torch_dtype="auto").to(device)
|
||||
assistant_model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("facebook/opt-125m").to(device)
|
||||
outputs = model.generate(**inputs, assistant_model=assistant_model)
|
||||
tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs, skip_special_tokens=True)
|
||||
@ -262,13 +264,14 @@ For speculative sampling decoding, add the `do_sample` and `temperature` paramet
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from accelerate.test_utils.testing import get_backend
|
||||
|
||||
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
|
||||
device, _, _ = get_backend() # automatically detects the underlying device type (CUDA, CPU, XPU, MPS, etc.)
|
||||
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("facebook/opt-1.3b")
|
||||
inputs = tokenizer("Einstein's theory of relativity states", return_tensors="pt").to(device)
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("facebook/opt-1.3b").to(device)
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("facebook/opt-1.3b", torch_dtype="auto").to(device)
|
||||
assistant_model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("facebook/opt-125m").to(device)
|
||||
outputs = model.generate(**inputs, assistant_model=assistant_model, do_sample=True, temperature=0.7)
|
||||
print(tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs, skip_special_tokens=True))
|
||||
@ -290,13 +293,14 @@ To enable prompt lookup decoding, specify the number of tokens that should be ov
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from accelerate.test_utils.testing import get_backend
|
||||
|
||||
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
|
||||
device, _, _ = get_backend() # automatically detects the underlying device type (CUDA, CPU, XPU, MPS, etc.)
|
||||
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("facebook/opt-1.3b")
|
||||
inputs = tokenizer("The second law of thermodynamics states", return_tensors="pt").to(device)
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("facebook/opt-1.3b").to(device)
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("facebook/opt-1.3b", torch_dtype="auto").to(device)
|
||||
assistant_model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("facebook/opt-125m").to(device)
|
||||
outputs = model.generate(**inputs, prompt_lookup_num_tokens=3)
|
||||
print(tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs, skip_special_tokens=True))
|
||||
@ -311,13 +315,14 @@ For prompt lookup decoding with sampling, add the `do_sample` and `temperature`
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from accelerate.test_utils.testing import get_backend
|
||||
|
||||
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
|
||||
device, _, _ = get_backend() # automatically detects the underlying device type (CUDA, CPU, XPU, MPS, etc.)
|
||||
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("facebook/opt-1.3b")
|
||||
inputs = tokenizer("The second law of thermodynamics states", return_tensors="pt").to(device)
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("facebook/opt-1.3b").to(device)
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("facebook/opt-1.3b", torch_dtype="auto").to(device)
|
||||
outputs = model.generate(**inputs, prompt_lookup_num_tokens=3, do_sample=True, temperature=0.7)
|
||||
print(tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs, skip_special_tokens=True))
|
||||
["The second law of thermodynamics states that energy cannot be created nor destroyed. It's not a"]
|
||||
|
||||
@ -147,7 +147,7 @@ Let's call it now for the next experiment.
|
||||
```python
|
||||
flush()
|
||||
```
|
||||
In the recent version of the accelerate library, you can also use a utility method called `release_memory()`
|
||||
From the Accelerate library, you can also use a device-agnostic utility method called [release_memory](https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate/blob/29be4788629b772a3b722076e433b5b3b5c85da3/src/accelerate/utils/memory.py#L63), which takes various hardware backends like XPU, MLU, NPU, MPS, and more into account.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from accelerate.utils import release_memory
|
||||
|
||||
106
docs/source/en/model_doc/aria.md
Normal file
106
docs/source/en/model_doc/aria.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,106 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Aria
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
The Aria model was proposed in [Aria: An Open Multimodal Native Mixture-of-Experts Model](https://huggingface.co/papers/2410.05993) by Li et al. from the Rhymes.AI team.
|
||||
|
||||
Aria is an open multimodal-native model with best-in-class performance across a wide range of multimodal, language, and coding tasks. It has a Mixture-of-Experts architecture, with respectively 3.9B and 3.5B activated parameters per visual token and text token.
|
||||
|
||||
The abstract from the paper is the following:
|
||||
|
||||
*Information comes in diverse modalities. Multimodal native AI models are essential to integrate real-world information and deliver comprehensive understanding. While proprietary multimodal native models exist, their lack of openness imposes obstacles for adoptions, let alone adaptations. To fill this gap, we introduce Aria, an open multimodal native model with best-in-class performance across a wide range of multimodal, language, and coding tasks. Aria is a mixture-of-expert model with 3.9B and 3.5B activated parameters per visual token and text token, respectively. It outperforms Pixtral-12B and Llama3.2-11B, and is competitive against the best proprietary models on various multimodal tasks. We pre-train Aria from scratch following a 4-stage pipeline, which progressively equips the model with strong capabilities in language understanding, multimodal understanding, long context window, and instruction following. We open-source the model weights along with a codebase that facilitates easy adoptions and adaptations of Aria in real-world applications.*
|
||||
|
||||
This model was contributed by [m-ric](https://huggingface.co/m-ric).
|
||||
The original code can be found [here](https://github.com/rhymes-ai/Aria).
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage tips
|
||||
|
||||
Here's how to use the model for vision tasks:
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import requests
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
|
||||
from transformers import AriaProcessor, AriaForConditionalGeneration
|
||||
|
||||
model_id_or_path = "rhymes-ai/Aria"
|
||||
|
||||
model = AriaForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained(
|
||||
model_id_or_path, device_map="auto"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
processor = AriaProcessor.from_pretrained(model_id_or_path)
|
||||
|
||||
image = Image.open(requests.get("http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg", stream=True).raw)
|
||||
|
||||
messages = [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"role": "user",
|
||||
"content": [
|
||||
{"type": "image"},
|
||||
{"text": "what is the image?", "type": "text"},
|
||||
],
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
text = processor.apply_chat_template(messages, add_generation_prompt=True)
|
||||
inputs = processor(text=text, images=image, return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
inputs.to(model.device)
|
||||
|
||||
output = model.generate(
|
||||
**inputs,
|
||||
max_new_tokens=15,
|
||||
stop_strings=["<|im_end|>"],
|
||||
tokenizer=processor.tokenizer,
|
||||
do_sample=True,
|
||||
temperature=0.9,
|
||||
)
|
||||
output_ids = output[0][inputs["input_ids"].shape[1]:]
|
||||
response = processor.decode(output_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## AriaImageProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] AriaImageProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
## AriaProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] AriaProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
## AriaTextConfig
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] AriaTextConfig
|
||||
|
||||
## AriaConfig
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] AriaConfig
|
||||
|
||||
## AriaTextModel
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] AriaTextModel
|
||||
|
||||
## AriaTextForCausalLM
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] AriaTextForCausalLM
|
||||
|
||||
## AriaForConditionalGeneration
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] AriaForConditionalGeneration
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
@ -141,7 +141,7 @@ Do note that when training Idefics2 on multi-turn conversations between a user a
|
||||
|
||||
## Model optimizations: Flash Attention
|
||||
|
||||
The code snippets above showcase inference without any optimization tricks. However, one can drastically speed up the model by leveraging [Flash Attention](../perf_train_gpu_one.md#flash-attention-2), which is a faster implementation of the attention mechanism used inside the model.
|
||||
The code snippets above showcase inference without any optimization tricks. However, one can drastically speed up the model by leveraging [Flash Attention](../perf_train_gpu_one#flash-attention-2), which is a faster implementation of the attention mechanism used inside the model.
|
||||
|
||||
First, make sure to install the latest version of Flash Attention 2 to include the sliding window attention feature.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -51,6 +51,13 @@ This model was contributed by [amyeroberts](https://huggingface.co/amyeroberts)
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] Idefics3Config
|
||||
|
||||
## Idefics3VisionConfig
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] Idefics3VisionConfig
|
||||
|
||||
## Idefics3VisionTransformer
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] Idefics3VisionTransformer
|
||||
|
||||
## Idefics3Model
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
92
docs/source/en/model_doc/ijepa.md
Normal file
92
docs/source/en/model_doc/ijepa.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,92 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# I-JEPA
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
The I-JEPA model was proposed in [Image-based Joint-Embedding Predictive Architecture](https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.08243) by Mahmoud Assran, Quentin Duval, Ishan Misra, Piotr Bojanowski, Pascal Vincent, Michael Rabbat, Yann LeCun, Nicolas Ballas.
|
||||
I-JEPA is a self-supervised learning method that predicts the representations of one part of an image based on other parts of the same image. This approach focuses on learning semantic features without relying on pre-defined invariances from hand-crafted data transformations, which can bias specific tasks, or on filling in pixel-level details, which often leads to less meaningful representations.
|
||||
|
||||
The abstract from the paper is the following:
|
||||
|
||||
This paper demonstrates an approach for learning highly semantic image representations without relying on hand-crafted data-augmentations. We introduce the Image- based Joint-Embedding Predictive Architecture (I-JEPA), a non-generative approach for self-supervised learning from images. The idea behind I-JEPA is simple: from a single context block, predict the representations of various target blocks in the same image. A core design choice to guide I-JEPA towards producing semantic representations is the masking strategy; specifically, it is crucial to (a) sample tar- get blocks with sufficiently large scale (semantic), and to (b) use a sufficiently informative (spatially distributed) context block. Empirically, when combined with Vision Transform- ers, we find I-JEPA to be highly scalable. For instance, we train a ViT-Huge/14 on ImageNet using 16 A100 GPUs in under 72 hours to achieve strong downstream performance across a wide range of tasks, from linear classification to object counting and depth prediction.
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/model_doc/ijepa_architecture.jpg"
|
||||
alt="drawing" width="600"/>
|
||||
|
||||
<small> I-JEPA architecture. Taken from the <a href="https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.08243">original paper.</a> </small>
|
||||
|
||||
This model was contributed by [jmtzt](https://huggingface.co/jmtzt).
|
||||
The original code can be found [here](https://github.com/facebookresearch/ijepa).
|
||||
|
||||
## How to use
|
||||
|
||||
Here is how to use this model for image feature extraction:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import requests
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
from torch.nn.functional import cosine_similarity
|
||||
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModel, AutoProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
url_1 = "http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg"
|
||||
url_2 = "http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000219578.jpg"
|
||||
image_1 = Image.open(requests.get(url_1, stream=True).raw)
|
||||
image_2 = Image.open(requests.get(url_2, stream=True).raw)
|
||||
|
||||
model_id = "facebook/ijepa_vith14_1k"
|
||||
processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained(model_id)
|
||||
model = AutoModel.from_pretrained(model_id)
|
||||
|
||||
@torch.no_grad()
|
||||
def infer(image):
|
||||
inputs = processor(image, return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
outputs = model(**inputs)
|
||||
return outputs.last_hidden_state.mean(dim=1)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
embed_1 = infer(image_1)
|
||||
embed_2 = infer(image_2)
|
||||
|
||||
similarity = cosine_similarity(embed_1, embed_2)
|
||||
print(similarity)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Resources
|
||||
|
||||
A list of official Hugging Face and community (indicated by 🌎) resources to help you get started with I-JEPA.
|
||||
|
||||
<PipelineTag pipeline="image-classification"/>
|
||||
|
||||
- [`IJepaForImageClassification`] is supported by this [example script](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples/pytorch/image-classification) and [notebook](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/image_classification.ipynb).
|
||||
- See also: [Image classification task guide](../tasks/image_classification)
|
||||
|
||||
## IJepaConfig
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] IJepaConfig
|
||||
|
||||
## IJepaModel
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] IJepaModel
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
## IJepaForImageClassification
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] IJepaForImageClassification
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
@ -240,7 +240,7 @@ model = LlavaNextVideoForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained("llava-hf/LLaVA-N
|
||||
|
||||
### Flash-Attention 2 to speed-up generation
|
||||
|
||||
Additionally, we can greatly speed-up model inference by using [Flash Attention](../perf_train_gpu_one.md#flash-attention-2), which is a faster implementation of the attention mechanism used inside the model.
|
||||
Additionally, we can greatly speed-up model inference by using [Flash Attention](../perf_train_gpu_one#flash-attention-2), which is a faster implementation of the attention mechanism used inside the model.
|
||||
|
||||
First, make sure to install the latest version of Flash Attention 2:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -91,7 +91,7 @@ As can be seen, the instruction-tuned model requires a [chat template](../chat_t
|
||||
|
||||
## Speeding up Mistral by using Flash Attention
|
||||
|
||||
The code snippets above showcase inference without any optimization tricks. However, one can drastically speed up the model by leveraging [Flash Attention](../perf_train_gpu_one.md#flash-attention-2), which is a faster implementation of the attention mechanism used inside the model.
|
||||
The code snippets above showcase inference without any optimization tricks. However, one can drastically speed up the model by leveraging [Flash Attention](../perf_train_gpu_one#flash-attention-2), which is a faster implementation of the attention mechanism used inside the model.
|
||||
|
||||
First, make sure to install the latest version of Flash Attention 2 to include the sliding window attention feature.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -93,7 +93,7 @@ As can be seen, the instruction-tuned model requires a [chat template](../chat_t
|
||||
|
||||
## Speeding up Mixtral by using Flash Attention
|
||||
|
||||
The code snippets above showcase inference without any optimization tricks. However, one can drastically speed up the model by leveraging [Flash Attention](../perf_train_gpu_one.md#flash-attention-2), which is a faster implementation of the attention mechanism used inside the model.
|
||||
The code snippets above showcase inference without any optimization tricks. However, one can drastically speed up the model by leveraging [Flash Attention](../perf_train_gpu_one#flash-attention-2), which is a faster implementation of the attention mechanism used inside the model.
|
||||
|
||||
First, make sure to install the latest version of Flash Attention 2 to include the sliding window attention feature.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -14,11 +14,11 @@ rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# OLMo November 2024
|
||||
# OLMo2
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
The OLMo November 2024 model is a successor of the OLMo model, which was proposed in
|
||||
The OLMo2 model is the successor of the OLMo model, which was proposed in
|
||||
[OLMo: Accelerating the Science of Language Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2402.00838).
|
||||
|
||||
The architectural changes from the original OLMo model to this model are:
|
||||
@ -31,16 +31,16 @@ This model was contributed by [shanearora](https://huggingface.co/shanearora).
|
||||
The original code can be found [here](https://github.com/allenai/OLMo/tree/main/olmo).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Olmo1124Config
|
||||
## Olmo2Config
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] Olmo1124Config
|
||||
[[autodoc]] Olmo2Config
|
||||
|
||||
## Olmo1124Model
|
||||
## Olmo2Model
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] Olmo1124Model
|
||||
[[autodoc]] Olmo2Model
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
## Olmo1124ForCausalLM
|
||||
## Olmo2ForCausalLM
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] Olmo1124ForCausalLM
|
||||
[[autodoc]] Olmo2ForCausalLM
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
@ -88,6 +88,11 @@ output = processor.batch_decode(generate_ids, skip_special_tokens=True, clean_up
|
||||
[[autodoc]] PixtralImageProcessor
|
||||
- preprocess
|
||||
|
||||
## PixtralImageProcessorFast
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] PixtralImageProcessorFast
|
||||
- preprocess
|
||||
|
||||
## PixtralProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] PixtralProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
67
docs/source/en/model_doc/timm_wrapper.md
Normal file
67
docs/source/en/model_doc/timm_wrapper.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,67 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# TimmWrapper
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
Helper class to enable loading timm models to be used with the transformers library and its autoclasses.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> import torch
|
||||
>>> from PIL import Image
|
||||
>>> from urllib.request import urlopen
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForImageClassification, AutoImageProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
>>> # Load image
|
||||
>>> image = Image.open(urlopen(
|
||||
... 'https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/beignets-task-guide.png'
|
||||
... ))
|
||||
|
||||
>>> # Load model and image processor
|
||||
>>> checkpoint = "timm/resnet50.a1_in1k"
|
||||
>>> image_processor = AutoImageProcessor.from_pretrained(checkpoint)
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForImageClassification.from_pretrained(checkpoint).eval()
|
||||
|
||||
>>> # Preprocess image
|
||||
>>> inputs = image_processor(image)
|
||||
|
||||
>>> # Forward pass
|
||||
>>> with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
... logits = model(**inputs).logits
|
||||
|
||||
>>> # Get top 5 predictions
|
||||
>>> top5_probabilities, top5_class_indices = torch.topk(logits.softmax(dim=1) * 100, k=5)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## TimmWrapperConfig
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TimmWrapperConfig
|
||||
|
||||
## TimmWrapperImageProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TimmWrapperImageProcessor
|
||||
- preprocess
|
||||
|
||||
## TimmWrapperModel
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TimmWrapperModel
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
## TimmWrapperForImageClassification
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TimmWrapperForImageClassification
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
@ -174,7 +174,7 @@ model = VideoLlavaForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained("LanguageBind/Video-L
|
||||
|
||||
### Flash-Attention 2 to speed-up generation
|
||||
|
||||
Additionally, we can greatly speed-up model inference by using [Flash Attention](../perf_train_gpu_one.md#flash-attention-2), which is a faster implementation of the attention mechanism used inside the model.
|
||||
Additionally, we can greatly speed-up model inference by using [Flash Attention](../perf_train_gpu_one#flash-attention-2), which is a faster implementation of the attention mechanism used inside the model.
|
||||
|
||||
First, make sure to install the latest version of Flash Attention 2:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -58,7 +58,7 @@ conversation = [
|
||||
"content": [
|
||||
{"type": "image"},
|
||||
{"type": "text", "text": "What’s shown in this image?"},
|
||||
,
|
||||
],
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"role": "assistant",
|
||||
|
||||
@ -41,8 +41,7 @@ Enable BetterTransformer with the [`PreTrainedModel.to_bettertransformer`] metho
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("bigcode/starcoder")
|
||||
model.to_bettertransformer()
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("bigcode/starcoder", torch_dtype="auto")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## TorchScript
|
||||
@ -54,7 +53,7 @@ For a gentle introduction to TorchScript, see the [Introduction to PyTorch Torch
|
||||
With the [`Trainer`] class, you can enable JIT mode for CPU inference by setting the `--jit_mode_eval` flag:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python run_qa.py \
|
||||
python examples/pytorch/question-answering/run_qa.py \
|
||||
--model_name_or_path csarron/bert-base-uncased-squad-v1 \
|
||||
--dataset_name squad \
|
||||
--do_eval \
|
||||
@ -86,7 +85,7 @@ pip install intel_extension_for_pytorch
|
||||
Set the `--use_ipex` and `--jit_mode_eval` flags in the [`Trainer`] class to enable JIT mode with the graph optimizations:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python run_qa.py \
|
||||
python examples/pytorch/question-answering/run_qa.py \
|
||||
--model_name_or_path csarron/bert-base-uncased-squad-v1 \
|
||||
--dataset_name squad \
|
||||
--do_eval \
|
||||
|
||||
@ -37,6 +37,7 @@ FlashAttention-2 is experimental and may change considerably in future versions.
|
||||
2. partitioning the work between GPU threads to reduce communication and shared memory reads/writes between them
|
||||
|
||||
FlashAttention-2 is currently supported for the following architectures:
|
||||
* [Aria](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/aria#transformers.AriaForConditionalGeneration)
|
||||
* [Bark](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/bark#transformers.BarkModel)
|
||||
* [Bart](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/bart#transformers.BartModel)
|
||||
* [Chameleon](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/chameleon#transformers.Chameleon)
|
||||
@ -77,7 +78,7 @@ FlashAttention-2 is currently supported for the following architectures:
|
||||
* [Nemotron](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/nemotron)
|
||||
* [NLLB](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/nllb)
|
||||
* [OLMo](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/olmo#transformers.OlmoModel)
|
||||
* [OLMo November 2024](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/olmo_1124#transformers.Olmo1124Model)
|
||||
* [OLMo2](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/olmo2#transformers.Olmo2Model)
|
||||
* [OLMoE](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/olmoe#transformers.OlmoeModel)
|
||||
* [OPT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/opt#transformers.OPTModel)
|
||||
* [PaliGemma](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/paligemma#transformers.PaliGemmaForConditionalGeneration)
|
||||
@ -216,6 +217,7 @@ PyTorch's [`torch.nn.functional.scaled_dot_product_attention`](https://pytorch.o
|
||||
|
||||
For now, Transformers supports SDPA inference and training for the following architectures:
|
||||
* [Albert](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/albert#transformers.AlbertModel)
|
||||
* [Aria](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/aria#transformers.AriaForConditionalGeneration)
|
||||
* [Audio Spectrogram Transformer](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/audio-spectrogram-transformer#transformers.ASTModel)
|
||||
* [Bart](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/bart#transformers.BartModel)
|
||||
* [Bert](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/bert#transformers.BertModel)
|
||||
@ -235,6 +237,7 @@ For now, Transformers supports SDPA inference and training for the following arc
|
||||
* [Falcon](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/falcon#transformers.FalconModel)
|
||||
* [Gemma](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/gemma#transformers.GemmaModel)
|
||||
* [Gemma2](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/gemma2#transformers.Gemma2Model)
|
||||
* [Granite](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/granite#transformers.GraniteModel)
|
||||
* [GPT2](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/gpt2)
|
||||
* [GPTBigCode](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/gpt_bigcode#transformers.GPTBigCodeModel)
|
||||
* [GPTNeoX](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/gpt_neox#transformers.GPTNeoXModel)
|
||||
@ -242,7 +245,7 @@ For now, Transformers supports SDPA inference and training for the following arc
|
||||
* [Idefics](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/idefics#transformers.IdeficsModel)
|
||||
* [Idefics2](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/idefics2#transformers.Idefics2Model)
|
||||
* [Idefics3](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/idefics3#transformers.Idefics3Model)
|
||||
* [Granite](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/granite#transformers.GraniteModel)
|
||||
* [I-JEPA](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/ijepa#transformers.IJepaModel)
|
||||
* [GraniteMoe](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/granitemoe#transformers.GraniteMoeModel)
|
||||
* [JetMoe](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/jetmoe#transformers.JetMoeModel)
|
||||
* [Jamba](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/jamba#transformers.JambaModel)
|
||||
@ -261,7 +264,7 @@ For now, Transformers supports SDPA inference and training for the following arc
|
||||
* [MusicGen Melody](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/musicgen_melody#transformers.MusicgenMelodyModel)
|
||||
* [NLLB](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/nllb)
|
||||
* [OLMo](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/olmo#transformers.OlmoModel)
|
||||
* [OLMo November 2024](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/olmo_1124#transformers.Olmo1124Model)
|
||||
* [OLMo2](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/olmo2#transformers.Olmo2Model)
|
||||
* [OLMoE](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/olmoe#transformers.OlmoeModel)
|
||||
* [OPT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/en/model_doc/opt)
|
||||
* [PaliGemma](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/paligemma#transformers.PaliGemmaForConditionalGeneration)
|
||||
@ -405,7 +408,7 @@ To load a model in 4-bit for inference, use the `load_in_4bit` parameter. The `d
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM
|
||||
|
||||
model_name = "bigscience/bloom-2b5"
|
||||
model_4bit = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_name, device_map="auto", load_in_4bit=True)
|
||||
model_4bit = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_name, torch_dtype="auto", device_map="auto", load_in_4bit=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To load a model in 4-bit for inference with multiple GPUs, you can control how much GPU RAM you want to allocate to each GPU. For example, to distribute 600MB of memory to the first GPU and 1GB of memory to the second GPU:
|
||||
@ -414,7 +417,7 @@ To load a model in 4-bit for inference with multiple GPUs, you can control how m
|
||||
max_memory_mapping = {0: "600MB", 1: "1GB"}
|
||||
model_name = "bigscience/bloom-3b"
|
||||
model_4bit = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
|
||||
model_name, device_map="auto", load_in_4bit=True, max_memory=max_memory_mapping
|
||||
model_name, torch_dtype="auto", device_map="auto", load_in_4bit=True, max_memory=max_memory_mapping
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@ -432,7 +435,7 @@ To load a model in 8-bit for inference, use the `load_in_8bit` parameter. The `d
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, BitsAndBytesConfig
|
||||
|
||||
model_name = "bigscience/bloom-2b5"
|
||||
model_8bit = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_name, quantization_config=BitsAndBytesConfig(load_in_8bit=True))
|
||||
model_8bit = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_name, torch_dtype="auto", quantization_config=BitsAndBytesConfig(load_in_8bit=True))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you're loading a model in 8-bit for text generation, you should use the [`~transformers.GenerationMixin.generate`] method instead of the [`Pipeline`] function which is not optimized for 8-bit models and will be slower. Some sampling strategies, like nucleus sampling, are also not supported by the [`Pipeline`] for 8-bit models. You should also place all inputs on the same device as the model:
|
||||
@ -442,7 +445,7 @@ from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer, BitsAndBytesConfig
|
||||
|
||||
model_name = "bigscience/bloom-2b5"
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
|
||||
model_8bit = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_name, quantization_config=BitsAndBytesConfig(load_in_8bit=True))
|
||||
model_8bit = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_name, torch_dtype="auto", quantization_config=BitsAndBytesConfig(load_in_8bit=True))
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "Hello, my llama is cute"
|
||||
inputs = tokenizer(prompt, return_tensors="pt").to("cuda")
|
||||
@ -456,7 +459,7 @@ To load a model in 4-bit for inference with multiple GPUs, you can control how m
|
||||
max_memory_mapping = {0: "1GB", 1: "2GB"}
|
||||
model_name = "bigscience/bloom-3b"
|
||||
model_8bit = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
|
||||
model_name, device_map="auto", load_in_8bit=True, max_memory=max_memory_mapping
|
||||
model_name, torch_dtype="auto", device_map="auto", load_in_8bit=True, max_memory=max_memory_mapping
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@ -515,7 +518,7 @@ quantization_config = BitsAndBytesConfig(
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("facebook/opt-350m")
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("facebook/opt-350m", quantization_config=quantization_config)
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("facebook/opt-350m", torch_dtype="auto", quantization_config=quantization_config)
|
||||
|
||||
# enable BetterTransformer
|
||||
model = model.to_bettertransformer()
|
||||
|
||||
@ -27,7 +27,7 @@ To compile any computer vision model of your choice, call `torch.compile()` on t
|
||||
```diff
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForImageClassification
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModelForImageClassification.from_pretrained(MODEL_ID).to("cuda")
|
||||
model = AutoModelForImageClassification.from_pretrained(MODEL_ID).to(DEVICE)
|
||||
+ model = torch.compile(model)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@ -47,15 +47,17 @@ from PIL import Image
|
||||
import requests
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
from transformers import AutoImageProcessor, AutoModelForImageClassification
|
||||
from accelerate.test_utils.testing import get_backend
|
||||
|
||||
device, _, _ = get_backend() # automatically detects the underlying device type (CUDA, CPU, XPU, MPS, etc.)
|
||||
url = 'http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg'
|
||||
image = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw)
|
||||
|
||||
processor = AutoImageProcessor.from_pretrained("google/vit-base-patch16-224")
|
||||
model = AutoModelForImageClassification.from_pretrained("google/vit-base-patch16-224").to("cuda")
|
||||
model = AutoModelForImageClassification.from_pretrained("google/vit-base-patch16-224").to(device)
|
||||
model = torch.compile(model)
|
||||
|
||||
processed_input = processor(image, return_tensors='pt').to(device="cuda")
|
||||
processed_input = processor(image, return_tensors='pt').to(device)
|
||||
|
||||
with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
_ = model(**processed_input)
|
||||
@ -66,13 +68,15 @@ with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import AutoImageProcessor, AutoModelForObjectDetection
|
||||
from accelerate.test_utils.testing import get_backend
|
||||
|
||||
device, _, _ = get_backend() # automatically detects the underlying device type (CUDA, CPU, XPU, MPS, etc.)
|
||||
processor = AutoImageProcessor.from_pretrained("facebook/detr-resnet-50")
|
||||
model = AutoModelForObjectDetection.from_pretrained("facebook/detr-resnet-50").to("cuda")
|
||||
model = AutoModelForObjectDetection.from_pretrained("facebook/detr-resnet-50").to(device)
|
||||
model = torch.compile(model)
|
||||
|
||||
texts = ["a photo of a cat", "a photo of a dog"]
|
||||
inputs = processor(text=texts, images=image, return_tensors="pt").to("cuda")
|
||||
inputs = processor(text=texts, images=image, return_tensors="pt").to(device)
|
||||
|
||||
with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
_ = model(**inputs)
|
||||
@ -82,11 +86,13 @@ with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import SegformerImageProcessor, SegformerForSemanticSegmentation
|
||||
from accelerate.test_utils.testing import get_backend
|
||||
|
||||
device, _, _ = get_backend() # automatically detects the underlying device type (CUDA, CPU, XPU, MPS, etc.)
|
||||
processor = SegformerImageProcessor.from_pretrained("nvidia/segformer-b0-finetuned-ade-512-512")
|
||||
model = SegformerForSemanticSegmentation.from_pretrained("nvidia/segformer-b0-finetuned-ade-512-512").to("cuda")
|
||||
model = SegformerForSemanticSegmentation.from_pretrained("nvidia/segformer-b0-finetuned-ade-512-512").to(device)
|
||||
model = torch.compile(model)
|
||||
seg_inputs = processor(images=image, return_tensors="pt").to("cuda")
|
||||
seg_inputs = processor(images=image, return_tensors="pt").to(device)
|
||||
|
||||
with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
_ = model(**seg_inputs)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -51,7 +51,7 @@ To enable auto mixed precision with IPEX in Trainer, users should add `use_ipex`
|
||||
Take an example of the use cases on [Transformers question-answering](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples/pytorch/question-answering)
|
||||
|
||||
- Training with IPEX using BF16 auto mixed precision on CPU:
|
||||
<pre> python run_qa.py \
|
||||
<pre> python examples/pytorch/question-answering/run_qa.py \
|
||||
--model_name_or_path google-bert/bert-base-uncased \
|
||||
--dataset_name squad \
|
||||
--do_train \
|
||||
|
||||
@ -75,7 +75,7 @@ The following command enables training with 2 processes on one Xeon node, with o
|
||||
export CCL_WORKER_COUNT=1
|
||||
export MASTER_ADDR=127.0.0.1
|
||||
mpirun -n 2 -genv OMP_NUM_THREADS=23 \
|
||||
python3 run_qa.py \
|
||||
python3 examples/pytorch/question-answering/run_qa.py \
|
||||
--model_name_or_path google-bert/bert-large-uncased \
|
||||
--dataset_name squad \
|
||||
--do_train \
|
||||
@ -104,7 +104,7 @@ Now, run the following command in node0 and **4DDP** will be enabled in node0 an
|
||||
export MASTER_ADDR=xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx #node0 ip
|
||||
mpirun -f hostfile -n 4 -ppn 2 \
|
||||
-genv OMP_NUM_THREADS=23 \
|
||||
python3 run_qa.py \
|
||||
python3 examples/pytorch/question-answering/run_qa.py \
|
||||
--model_name_or_path google-bert/bert-large-uncased \
|
||||
--dataset_name squad \
|
||||
--do_train \
|
||||
|
||||
@ -553,7 +553,7 @@ It performs a sort of 4D Parallelism over Sample-Operator-Attribute-Parameter.
|
||||
Examples:
|
||||
* Sample
|
||||
|
||||
Let's take 10 batches of sequence length 512. If we parallelize them by sample dimension into 2 devices, we get 10 x 512 which becomes be 5 x 2 x 512.
|
||||
Let's take 10 batches of sequence length 512. If we parallelize them by sample dimension into 2 devices, we get 10 x 512 which becomes 5 x 2 x 512.
|
||||
|
||||
* Operator
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -73,8 +73,9 @@ Let's demonstrate this process with GPT-2.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import GPT2LMHeadModel, GPT2TokenizerFast
|
||||
from accelerate.test_utils.testing import get_backend
|
||||
|
||||
device = "cuda"
|
||||
device, _, _ = get_backend() # automatically detects the underlying device type (CUDA, CPU, XPU, MPS, etc.)
|
||||
model_id = "openai-community/gpt2-large"
|
||||
model = GPT2LMHeadModel.from_pretrained(model_id).to(device)
|
||||
tokenizer = GPT2TokenizerFast.from_pretrained(model_id)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -59,10 +59,10 @@ Let's try the [Whisper large-v2](https://huggingface.co/openai/whisper-large-v2)
|
||||
benchmarks. It also has the added benefit of predicting punctuation and casing, neither of which are possible with
|
||||
Wav2Vec2.
|
||||
|
||||
Let's give it a try here to see how it performs:
|
||||
Let's give it a try here to see how it performs. Set `torch_dtype="auto"` to automatically load the most memory-efficient data type the weights are stored in.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> transcriber = pipeline(model="openai/whisper-large-v2")
|
||||
>>> transcriber = pipeline(model="openai/whisper-large-v2", torch_dtype="auto")
|
||||
>>> transcriber("https://huggingface.co/datasets/Narsil/asr_dummy/resolve/main/mlk.flac")
|
||||
{'text': ' I have a dream that one day this nation will rise up and live out the true meaning of its creed.'}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@ -64,7 +64,7 @@ model_8bit = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
By default, all the other modules such as `torch.nn.LayerNorm` are converted to `torch.float16`. You can change the data type of these modules with the `torch_dtype` parameter if you want:
|
||||
By default, all the other modules such as `torch.nn.LayerNorm` are converted to `torch.float16`. You can change the data type of these modules with the `torch_dtype` parameter if you want. Setting `torch_dtype="auto"` loads the model in the data type defined in a model's `config.json` file.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
@ -75,7 +75,7 @@ quantization_config = BitsAndBytesConfig(load_in_8bit=True)
|
||||
model_8bit = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"facebook/opt-350m",
|
||||
quantization_config=quantization_config,
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float32
|
||||
torch_dtype="auto"
|
||||
)
|
||||
model_8bit.model.decoder.layers[-1].final_layer_norm.weight.dtype
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -112,7 +112,7 @@ model_4bit = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
By default, all the other modules such as `torch.nn.LayerNorm` are converted to `torch.float16`. You can change the data type of these modules with the `torch_dtype` parameter if you want:
|
||||
By default, all the other modules such as `torch.nn.LayerNorm` are converted to `torch.float16`. You can change the data type of these modules with the `torch_dtype` parameter if you want. Setting `torch_dtype="auto"` loads the model in the data type defined in a model's `config.json` file.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
@ -123,7 +123,7 @@ quantization_config = BitsAndBytesConfig(load_in_4bit=True)
|
||||
model_4bit = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"facebook/opt-350m",
|
||||
quantization_config=quantization_config,
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float32
|
||||
torch_dtype="auto"
|
||||
)
|
||||
model_4bit.model.decoder.layers[-1].final_layer_norm.weight.dtype
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -190,6 +190,7 @@ Now load your model with the custom `device_map` and `quantization_config`:
|
||||
```py
|
||||
model_8bit = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"bigscience/bloom-1b7",
|
||||
torch_dtype="auto",
|
||||
device_map=device_map,
|
||||
quantization_config=quantization_config,
|
||||
)
|
||||
@ -212,6 +213,7 @@ quantization_config = BitsAndBytesConfig(
|
||||
|
||||
model_8bit = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
|
||||
model_id,
|
||||
torch_dtype="auto",
|
||||
device_map=device_map,
|
||||
quantization_config=quantization_config,
|
||||
)
|
||||
@ -232,6 +234,7 @@ quantization_config = BitsAndBytesConfig(
|
||||
|
||||
model_8bit = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
|
||||
model_id,
|
||||
torch_dtype="auto",
|
||||
device_map="auto",
|
||||
quantization_config=quantization_config,
|
||||
)
|
||||
@ -275,7 +278,7 @@ nf4_config = BitsAndBytesConfig(
|
||||
bnb_4bit_quant_type="nf4",
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
model_nf4 = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_id, quantization_config=nf4_config)
|
||||
model_nf4 = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_id, torch_dtype="auto", quantization_config=nf4_config)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For inference, the `bnb_4bit_quant_type` does not have a huge impact on performance. However, to remain consistent with the model weights, you should use the `bnb_4bit_compute_dtype` and `torch_dtype` values.
|
||||
@ -292,7 +295,7 @@ double_quant_config = BitsAndBytesConfig(
|
||||
bnb_4bit_use_double_quant=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
model_double_quant = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("meta-llama/Llama-2-13b", quantization_config=double_quant_config)
|
||||
model_double_quant = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("meta-llama/Llama-2-13b", torch_dtype="auto", quantization_config=double_quant_config)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Dequantizing `bitsandbytes` models
|
||||
|
||||
@ -33,13 +33,14 @@ pip install --upgrade accelerate fbgemm-gpu torch
|
||||
|
||||
If you are having issues with fbgemm-gpu and torch library, you might need to install the nightly release. You can follow the instruction [here](https://pytorch.org/FBGEMM/fbgemm_gpu-development/InstallationInstructions.html#fbgemm-gpu-install-libraries:~:text=found%20here.-,Install%20the%20FBGEMM_GPU%20Package,-Install%20through%20PyTorch)
|
||||
|
||||
By default, the weights are loaded in full precision (torch.float32) regardless of the actual data type the weights are stored in such as torch.float16. Set `torch_dtype="auto"` to load the weights in the data type defined in a model's `config.json` file to automatically load the most memory-optimal data type.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import FbgemmFp8Config, AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
model_name = "meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3-8B"
|
||||
quantization_config = FbgemmFp8Config()
|
||||
quantized_model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_name, device_map="auto", quantization_config=quantization_config)
|
||||
quantized_model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_name, torch_dtype="auto", device_map="auto", quantization_config=quantization_config)
|
||||
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
|
||||
input_text = "What are we having for dinner?"
|
||||
|
||||
@ -42,7 +42,9 @@ pip install optimum-quanto accelerate transformers
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can quantize a model by passing [`QuantoConfig`] object in the [`~PreTrainedModel.from_pretrained`] method. This works for any model in any modality, as long as it contains `torch.nn.Linear` layers.
|
||||
|
||||
The integration with transformers only supports weights quantization. For the more complex use case such as activation quantization, calibration and quantization aware training, you should use [optimum-quanto](https://github.com/huggingface/optimum-quanto) library instead.
|
||||
The integration with transformers only supports weights quantization. For the more complex use case such as activation quantization, calibration and quantization aware training, you should use [optimum-quanto](https://github.com/huggingface/optimum-quanto) library instead.
|
||||
|
||||
By default, the weights are loaded in full precision (torch.float32) regardless of the actual data type the weights are stored in such as torch.float16. Set `torch_dtype="auto"` to load the weights in the data type defined in a model's `config.json` file to automatically load the most memory-optimal data type.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer, QuantoConfig
|
||||
@ -50,7 +52,7 @@ from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer, QuantoConfig
|
||||
model_id = "facebook/opt-125m"
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_id)
|
||||
quantization_config = QuantoConfig(weights="int8")
|
||||
quantized_model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_id, device_map="cuda:0", quantization_config=quantization_config)
|
||||
quantized_model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_id, torch_dtype="auto", device_map="cuda:0", quantization_config=quantization_config)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Note that serialization is not supported yet with transformers but it is coming soon! If you want to save the model, you can use quanto library instead.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -19,6 +19,7 @@ Before you begin, make sure the following libraries are installed with their lat
|
||||
pip install --upgrade torch torchao
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
By default, the weights are loaded in full precision (torch.float32) regardless of the actual data type the weights are stored in such as torch.float16. Set `torch_dtype="auto"` to load the weights in the data type defined in a model's `config.json` file to automatically load the most memory-optimal data type.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
@ -28,7 +29,7 @@ model_name = "meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3-8B"
|
||||
# We support int4_weight_only, int8_weight_only and int8_dynamic_activation_int8_weight
|
||||
# More examples and documentations for arguments can be found in https://github.com/pytorch/ao/tree/main/torchao/quantization#other-available-quantization-techniques
|
||||
quantization_config = TorchAoConfig("int4_weight_only", group_size=128)
|
||||
quantized_model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_name, device_map="auto", quantization_config=quantization_config)
|
||||
quantized_model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_name, torch_dtype="auto", device_map="auto", quantization_config=quantization_config)
|
||||
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
|
||||
input_text = "What are we having for dinner?"
|
||||
|
||||
@ -245,13 +245,15 @@ Check out the [preprocess](./preprocessing) tutorial for more details about toke
|
||||
|
||||
<frameworkcontent>
|
||||
<pt>
|
||||
🤗 Transformers provides a simple and unified way to load pretrained instances. This means you can load an [`AutoModel`] like you would load an [`AutoTokenizer`]. The only difference is selecting the correct [`AutoModel`] for the task. For text (or sequence) classification, you should load [`AutoModelForSequenceClassification`]:
|
||||
🤗 Transformers provides a simple and unified way to load pretrained instances. This means you can load an [`AutoModel`] like you would load an [`AutoTokenizer`]. The only difference is selecting the correct [`AutoModel`] for the task. For text (or sequence) classification, you should load [`AutoModelForSequenceClassification`].
|
||||
|
||||
By default, the weights are loaded in full precision (torch.float32) regardless of the actual data type the weights are stored in such as torch.float16. Set `torch_dtype="auto"` to load the weights in the data type defined in a model's `config.json` file to automatically load the most memory-optimal data type.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForSequenceClassification
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model_name = "nlptown/bert-base-multilingual-uncased-sentiment"
|
||||
>>> pt_model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(model_name)
|
||||
>>> pt_model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained(model_name, torch_dtype="auto")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
@ -416,12 +418,12 @@ All models are a standard [`torch.nn.Module`](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/nn
|
||||
|
||||
Depending on your task, you'll typically pass the following parameters to [`Trainer`]:
|
||||
|
||||
1. You'll start with a [`PreTrainedModel`] or a [`torch.nn.Module`](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/nn.html#torch.nn.Module):
|
||||
1. You'll start with a [`PreTrainedModel`] or a [`torch.nn.Module`](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/nn.html#torch.nn.Module). Set `torch_dtype="auto"` to automatically load the most memory-efficient data type the weights are stored in.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForSequenceClassification
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained("distilbert/distilbert-base-uncased")
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained("distilbert/distilbert-base-uncased", torch_dtype="auto")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. [`TrainingArguments`] contains the model hyperparameters you can change like learning rate, batch size, and the number of epochs to train for. The default values are used if you don't specify any training arguments:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -112,7 +112,7 @@ The next step is to load a Wav2Vec2 processor to process the audio signal:
|
||||
>>> processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained("facebook/wav2vec2-base")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The MInDS-14 dataset has a sampling rate of 8000kHz (you can find this information in its [dataset card](https://huggingface.co/datasets/PolyAI/minds14)), which means you'll need to resample the dataset to 16000kHz to use the pretrained Wav2Vec2 model:
|
||||
The MInDS-14 dataset has a sampling rate of 8000Hz (you can find this information in its [dataset card](https://huggingface.co/datasets/PolyAI/minds14)), which means you'll need to resample the dataset to 16000Hz to use the pretrained Wav2Vec2 model:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> minds = minds.cast_column("audio", Audio(sampling_rate=16_000))
|
||||
|
||||
@ -84,7 +84,7 @@ If you want to get the last hidden states before pooling, avoid passing any valu
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
pipe = pipeline(task="image-feature-extraction", model_name="google/vit-base-patch16-224", device=DEVICE)
|
||||
output = pipe(image_real)
|
||||
outputs = pipe(image_real)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Since the outputs are unpooled, we get the last hidden states where the first dimension is the batch size, and the last two are the embedding shape.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -229,7 +229,7 @@ Now let's call the `model_inference` function we created and stream the values.
|
||||
```python
|
||||
generator = model_inference(
|
||||
user_prompt="And what is in this image?",
|
||||
chat_history=messages,
|
||||
chat_history=messages[:2],
|
||||
max_new_tokens=100,
|
||||
images=images
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -17,7 +17,7 @@ rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
[[open-in-colab]]
|
||||
|
||||
Knowledge distillation is a technique used to transfer knowledge from a larger, more complex model (teacher) to a smaller, simpler model (student). To distill knowledge from one model to another, we take a pre-trained teacher model trained on a certain task (image classification for this case) and randomly initialize a student model to be trained on image classification. Next, we train the student model to minimize the difference between it's outputs and the teacher's outputs, thus making it mimic the behavior. It was first introduced in [Distilling the Knowledge in a Neural Network by Hinton et al](https://arxiv.org/abs/1503.02531). In this guide, we will do task-specific knowledge distillation. We will use the [beans dataset](https://huggingface.co/datasets/beans) for this.
|
||||
Knowledge distillation is a technique used to transfer knowledge from a larger, more complex model (teacher) to a smaller, simpler model (student). To distill knowledge from one model to another, we take a pre-trained teacher model trained on a certain task (image classification for this case) and randomly initialize a student model to be trained on image classification. Next, we train the student model to minimize the difference between its outputs and the teacher's outputs, thus making it mimic the behavior. It was first introduced in [Distilling the Knowledge in a Neural Network by Hinton et al](https://arxiv.org/abs/1503.02531). In this guide, we will do task-specific knowledge distillation. We will use the [beans dataset](https://huggingface.co/datasets/beans) for this.
|
||||
|
||||
This guide demonstrates how you can distill a [fine-tuned ViT model](https://huggingface.co/merve/vit-mobilenet-beans-224) (teacher model) to a [MobileNet](https://huggingface.co/google/mobilenet_v2_1.4_224) (student model) using the [Trainer API](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/en/main_classes/trainer#trainer) of 🤗 Transformers.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -419,7 +419,7 @@ Get the class with the highest probability:
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> predicted_class = logits.argmax().item()
|
||||
>>> predicted_class
|
||||
'0'
|
||||
0
|
||||
```
|
||||
</pt>
|
||||
<tf>
|
||||
@ -448,7 +448,7 @@ Get the class with the highest probability:
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> predicted_class = int(tf.math.argmax(logits, axis=-1)[0])
|
||||
>>> predicted_class
|
||||
'0'
|
||||
0
|
||||
```
|
||||
</tf>
|
||||
</frameworkcontent>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -325,7 +325,7 @@ or [TensorFlow notebook](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/no
|
||||
|
||||
Evaluation for question answering requires a significant amount of postprocessing. To avoid taking up too much of your time, this guide skips the evaluation step. The [`Trainer`] still calculates the evaluation loss during training so you're not completely in the dark about your model's performance.
|
||||
|
||||
If have more time and you're interested in how to evaluate your model for question answering, take a look at the [Question answering](https://huggingface.co/course/chapter7/7?fw=pt#post-processing) chapter from the 🤗 Hugging Face Course!
|
||||
If you have more time and you're interested in how to evaluate your model for question answering, take a look at the [Question answering](https://huggingface.co/course/chapter7/7?fw=pt#post-processing) chapter from the 🤗 Hugging Face Course!
|
||||
|
||||
## Inference
|
||||
|
||||
@ -397,7 +397,7 @@ Tokenize the text and return TensorFlow tensors:
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("my_awesome_qa_model")
|
||||
>>> inputs = tokenizer(question, text, return_tensors="tf")
|
||||
>>> inputs = tokenizer(question, context, return_tensors="tf")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Pass your inputs to the model and return the `logits`:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -283,7 +283,7 @@ Pass your `compute_metrics` function to [`~transformers.KerasMetricCallback`]:
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers.keras_callbacks import KerasMetricCallback
|
||||
|
||||
>>> metric_callback = KerasMetricCallback(metric_fn=compute_metrics, eval_dataset=tf_validation_set)
|
||||
>>> metric_callback = KerasMetricCallback(metric_fn=compute_metrics, eval_dataset=tf_test_set)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Specify where to push your model and tokenizer in the [`~transformers.PushToHubCallback`]:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -290,7 +290,7 @@ Pass your `compute_metrics` function to [`~transformers.KerasMetricCallback`]:
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers.keras_callbacks import KerasMetricCallback
|
||||
|
||||
>>> metric_callback = KerasMetricCallback(metric_fn=compute_metrics, eval_dataset=tf_validation_set)
|
||||
>>> metric_callback = KerasMetricCallback(metric_fn=compute_metrics, eval_dataset=tf_test_set)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Specify where to push your model and tokenizer in the [`~transformers.PushToHubCallback`]:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -47,7 +47,7 @@ model_id = "llava-hf/llava-interleave-qwen-0.5b-hf"
|
||||
processor = LlavaProcessor.from_pretrained(model_id)
|
||||
|
||||
model = LlavaForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained(model_id, torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
model.to("cuda")
|
||||
model.to("cuda") # can also be xpu, mps, npu etc. depending on your hardware accelerator
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Some models directly consume the `<video>` token, and others accept `<image>` tokens equal to the number of sampled frames. This model handles videos in the latter fashion. We will write a simple utility to handle image tokens, and another utility to get a video from a url and sample frames from it.
|
||||
@ -56,6 +56,7 @@ Some models directly consume the `<video>` token, and others accept `<image>` to
|
||||
import uuid
|
||||
import requests
|
||||
import cv2
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
|
||||
def replace_video_with_images(text, frames):
|
||||
return text.replace("<video>", "<image>" * frames)
|
||||
@ -82,7 +83,7 @@ def sample_frames(url, num_frames):
|
||||
if i % interval == 0:
|
||||
frames.append(pil_img)
|
||||
video.release()
|
||||
return frames
|
||||
return frames[:num_frames]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Let's get our inputs. We will sample frames and concatenate them.
|
||||
@ -127,7 +128,7 @@ This model has a prompt template that looks like following. First, we'll put all
|
||||
user_prompt = "Are these two cats in these two videos doing the same thing?"
|
||||
toks = "<image>" * 12
|
||||
prompt = "<|im_start|>user"+ toks + f"\n{user_prompt}<|im_end|><|im_start|>assistant"
|
||||
inputs = processor(prompt, images=videos).to(model.device, model.dtype)
|
||||
inputs = processor(text=prompt, images=videos, return_tensors="pt").to(model.device, model.dtype)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We can now call [`~GenerationMixin.generate`] for inference. The model outputs the question in our input and answer, so we only take the text after the prompt and `assistant` part from the model output.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -288,7 +288,7 @@ as before except now there are no labels.
|
||||
>>> scores = results["scores"].tolist()
|
||||
>>> boxes = results["boxes"].tolist()
|
||||
|
||||
>>> for box, score, label in zip(boxes, scores, labels):
|
||||
>>> for box, score in zip(boxes, scores):
|
||||
... xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax = box
|
||||
... draw.rectangle((xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax), outline="white", width=4)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -36,3 +36,25 @@ from transformers import AutoTokenizer
|
||||
model_id = "meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3-8B-Instruct"
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_id, subfolder="original")
|
||||
```
|
||||
## Create tiktoken tokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
The `tokenizer.model` file contains no information about additional tokens or pattern strings. If these are important, convert the tokenizer to `tokenizer.json`, the appropriate format for [`PreTrainedTokenizerFast`].
|
||||
|
||||
Generate the `tokenizer.model` file with [tiktoken.get_encoding](https://github.com/openai/tiktoken/blob/63527649963def8c759b0f91f2eb69a40934e468/tiktoken/registry.py#L63) and then convert it to `tokenizer.json` with [`convert_tiktoken_to_fast`].
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
|
||||
from transformers.integrations.tiktoken import convert_tiktoken_to_fast
|
||||
from tiktoken import get_encoding
|
||||
|
||||
# You can load your custom encoding or the one provided by OpenAI
|
||||
encoding = get_encoding("gpt2")
|
||||
convert_tiktoken_to_fast(encoding, "config/save/dir")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The resulting `tokenizer.json` file is saved to the specified directory and can be loaded with [`PreTrainedTokenizerFast`].
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
tokenizer = PreTrainedTokenizerFast.from_pretrained("config/save/dir")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -81,12 +81,14 @@ just use the button at the top-right of that framework's block!
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 Transformers provides a [`Trainer`] class optimized for training 🤗 Transformers models, making it easier to start training without manually writing your own training loop. The [`Trainer`] API supports a wide range of training options and features such as logging, gradient accumulation, and mixed precision.
|
||||
|
||||
Start by loading your model and specify the number of expected labels. From the Yelp Review [dataset card](https://huggingface.co/datasets/yelp_review_full#data-fields), you know there are five labels:
|
||||
Start by loading your model and specify the number of expected labels. From the Yelp Review [dataset card](https://huggingface.co/datasets/yelp_review_full#data-fields), you know there are five labels.
|
||||
|
||||
By default, the weights are loaded in full precision (torch.float32) regardless of the actual data type the weights are stored in such as torch.float16. Set `torch_dtype="auto"` to load the weights in the data type defined in a model's `config.json` file to automatically load the most memory-optimal data type.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForSequenceClassification
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained("google-bert/bert-base-cased", num_labels=5)
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained("google-bert/bert-base-cased", num_labels=5, torch_dtype="auto")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -159,7 +159,7 @@ conda install conda-forge::transformers
|
||||
|
||||
Les modèles pré-entraînés sont téléchargés et mis en cache localement dans le dossier suivant : `~/.cache/huggingface/hub`. C'est le dossier par défaut donné par la variable d'environnement `TRANSFORMERS_CACHE`. Sur Windows, le dossier par défaut est `C:\Users\nom_utilisateur\.cache\huggingface\hub`. Vous pouvez modifier les variables d'environnement indiquées ci-dessous - par ordre de priorité - pour spécifier un dossier de cache différent :
|
||||
|
||||
1. Variable d'environnement (par défaut) : `HUGGINGFACE_HUB_CACHE` ou `TRANSFORMERS_CACHE`.
|
||||
1. Variable d'environnement (par défaut) : `HF_HUB_CACHE` ou `TRANSFORMERS_CACHE`.
|
||||
2. Variable d'environnement : `HF_HOME`.
|
||||
3. Variable d'environnement : `XDG_CACHE_HOME` + `/huggingface`.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -145,7 +145,7 @@ conda install conda-forge::transformers
|
||||
|
||||
学習済みモデルはダウンロードされ、ローカルにキャッシュされます: `~/.cache/huggingface/hub`. これはシェル環境変数`TRANSFORMERS_CACHE`で指定されるデフォルトのディレクトリです。Windowsでは、デフォルトのディレクトリは`C:\Users\username\.cache\huggingface\hub`になっています。異なるキャッシュディレクトリを指定するために、以下のシェル環境変数を変更することが可能です。優先度は以下の順番に対応します:
|
||||
|
||||
1. シェル環境変数 (デフォルト): `HUGGINGFACE_HUB_CACHE` または `TRANSFORMERS_CACHE`.
|
||||
1. シェル環境変数 (デフォルト): `HF_HUB_CACHE` または `TRANSFORMERS_CACHE`.
|
||||
2. シェル環境変数: `HF_HOME`.
|
||||
3. シェル環境変数: `XDG_CACHE_HOME` + `/huggingface`.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -380,8 +380,8 @@
|
||||
title: (번역중) DPR
|
||||
- local: in_translation
|
||||
title: (번역중) ELECTRA
|
||||
- local: in_translation
|
||||
title: (번역중) Encoder Decoder Models
|
||||
- local: model_doc/encoder-decoder
|
||||
title: 인코더 디코더 모델
|
||||
- local: in_translation
|
||||
title: (번역중) ERNIE
|
||||
- local: in_translation
|
||||
|
||||
@ -145,7 +145,7 @@ conda install conda-forge::transformers
|
||||
|
||||
사전훈련된 모델은 다운로드된 후 로컬 경로 `~/.cache/huggingface/hub`에 캐시됩니다. 셸 환경 변수 `TRANSFORMERS_CACHE`의 기본 디렉터리입니다. Windows의 경우 기본 디렉터리는 `C:\Users\username\.cache\huggingface\hub`입니다. 아래의 셸 환경 변수를 (우선 순위) 순서대로 변경하여 다른 캐시 디렉토리를 지정할 수 있습니다.
|
||||
|
||||
1. 셸 환경 변수 (기본): `HUGGINGFACE_HUB_CACHE` 또는 `TRANSFORMERS_CACHE`
|
||||
1. 셸 환경 변수 (기본): `HF_HUB_CACHE` 또는 `TRANSFORMERS_CACHE`
|
||||
2. 셸 환경 변수: `HF_HOME`
|
||||
3. 셸 환경 변수: `XDG_CACHE_HOME` + `/huggingface`
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
167
docs/source/ko/model_doc/encoder-decoder.md
Normal file
167
docs/source/ko/model_doc/encoder-decoder.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,167 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2020 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# 인코더-디코더 모델[[Encoder Decoder Models]]
|
||||
|
||||
## 개요[[Overview]]
|
||||
|
||||
[`EncoderDecoderModel`]은 사전 학습된 자동 인코딩(autoencoding) 모델을 인코더로, 사전 학습된 자가 회귀(autoregressive) 모델을 디코더로 활용하여 시퀀스-투-시퀀스(sequence-to-sequence) 모델을 초기화하는 데 이용됩니다.
|
||||
|
||||
사전 학습된 체크포인트를 활용해 시퀀스-투-시퀀스 모델을 초기화하는 것이 시퀀스 생성(sequence generation) 작업에 효과적이라는 점이 Sascha Rothe, Shashi Narayan, Aliaksei Severyn의 논문 [Leveraging Pre-trained Checkpoints for Sequence Generation Tasks](https://arxiv.org/abs/1907.12461)에서 입증되었습니다.
|
||||
|
||||
[`EncoderDecoderModel`]이 학습/미세 조정된 후에는 다른 모델과 마찬가지로 저장/불러오기가 가능합니다. 자세한 사용법은 예제를 참고하세요.
|
||||
|
||||
이 아키텍처의 한 가지 응용 사례는 두 개의 사전 학습된 [`BertModel`]을 각각 인코더와 디코더로 활용하여 요약 모델(summarization model)을 구축하는 것입니다. 이는 Yang Liu와 Mirella Lapata의 논문 [Text Summarization with Pretrained Encoders](https://arxiv.org/abs/1908.08345)에서 제시된 바 있습니다.
|
||||
|
||||
## 모델 설정에서 `EncoderDecoderModel`을 무작위 초기화하기[[Randomly initializing `EncoderDecoderModel` from model configurations.]]
|
||||
|
||||
[`EncoderDecoderModel`]은 인코더와 디코더 설정(config)을 기반으로 무작위 초기화를 할 수 있습니다. 아래 예시는 [`BertModel`] 설정을 인코더로, 기본 [`BertForCausalLM`] 설정을 디코더로 사용하는 방법을 보여줍니다.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import BertConfig, EncoderDecoderConfig, EncoderDecoderModel
|
||||
|
||||
>>> config_encoder = BertConfig()
|
||||
>>> config_decoder = BertConfig()
|
||||
|
||||
>>> config = EncoderDecoderConfig.from_encoder_decoder_configs(config_encoder, config_decoder)
|
||||
>>> model = EncoderDecoderModel(config=config)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 사전 학습된 인코더와 디코더로 `EncoderDecoderModel` 초기화하기[[Initialising `EncoderDecoderModel` from a pretrained encoder and a pretrained decoder.]]
|
||||
|
||||
[`EncoderDecoderModel`]은 사전 학습된 인코더 체크포인트와 사전 학습된 디코더 체크포인트를 사용해 초기화할 수 있습니다. BERT와 같은 모든 사전 학습된 자동 인코딩(auto-encoding) 모델은 인코더로 활용할 수 있으며, GPT2와 같은 자가 회귀(autoregressive) 모델이나 BART의 디코더와 같이 사전 학습된 시퀀스-투-시퀀스 디코더 모델을 디코더로 사용할 수 있습니다. 디코더로 선택한 아키텍처에 따라 교차 어텐션(cross-attention) 레이어가 무작위로 초기화될 수 있습니다. 사전 학습된 인코더와 디코더 체크포인트를 이용해 [`EncoderDecoderModel`]을 초기화하려면, 모델을 다운스트림 작업에 대해 미세 조정(fine-tuning)해야 합니다. 이에 대한 자세한 내용은 [the *Warm-starting-encoder-decoder blog post*](https://huggingface.co/blog/warm-starting-encoder-decoder)에 설명되어 있습니다. 이 작업을 위해 `EncoderDecoderModel` 클래스는 [`EncoderDecoderModel.from_encoder_decoder_pretrained`] 메서드를 제공합니다.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import EncoderDecoderModel, BertTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained("google-bert/bert-base-uncased")
|
||||
>>> model = EncoderDecoderModel.from_encoder_decoder_pretrained("google-bert/bert-base-uncased", "google-bert/bert-base-uncased")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 기존 `EncoderDecoderModel` 체크포인트 불러오기 및 추론하기[[Loading an existing `EncoderDecoderModel` checkpoint and perform inference.]]
|
||||
|
||||
`EncoderDecoderModel` 클래스의 미세 조정(fine-tuned)된 체크포인트를 불러오려면, Transformers의 다른 모델 아키텍처와 마찬가지로 [`EncoderDecoderModel`]에서 제공하는 `from_pretrained(...)`를 사용할 수 있습니다.
|
||||
|
||||
추론을 수행하려면 [`generate`] 메서드를 활용하여 텍스트를 자동 회귀(autoregressive) 방식으로 생성할 수 있습니다. 이 메서드는 탐욕 디코딩(greedy decoding), 빔 서치(beam search), 다항 샘플링(multinomial sampling) 등 다양한 디코딩 방식을 지원합니다.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer, EncoderDecoderModel
|
||||
|
||||
>>> # 미세 조정된 seq2seq 모델과 대응하는 토크나이저 가져오기
|
||||
>>> model = EncoderDecoderModel.from_pretrained("patrickvonplaten/bert2bert_cnn_daily_mail")
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("patrickvonplaten/bert2bert_cnn_daily_mail")
|
||||
|
||||
>>> # let's perform inference on a long piece of text
|
||||
>>> ARTICLE_TO_SUMMARIZE = (
|
||||
... "PG&E stated it scheduled the blackouts in response to forecasts for high winds "
|
||||
... "amid dry conditions. The aim is to reduce the risk of wildfires. Nearly 800 thousand customers were "
|
||||
... "scheduled to be affected by the shutoffs which were expected to last through at least midday tomorrow."
|
||||
... )
|
||||
>>> input_ids = tokenizer(ARTICLE_TO_SUMMARIZE, return_tensors="pt").input_ids
|
||||
|
||||
>>> # 자기회귀적으로 요약 생성 (기본적으로 그리디 디코딩 사용)
|
||||
>>> generated_ids = model.generate(input_ids)
|
||||
>>> generated_text = tokenizer.batch_decode(generated_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)[0]
|
||||
>>> print(generated_text)
|
||||
nearly 800 thousand customers were affected by the shutoffs. the aim is to reduce the risk of wildfires. nearly 800, 000 customers were expected to be affected by high winds amid dry conditions. pg & e said it scheduled the blackouts to last through at least midday tomorrow.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## `TFEncoderDecoderModel`에 Pytorch 체크포인트 불러오기[[Loading a PyTorch checkpoint into `TFEncoderDecoderModel`.]]
|
||||
|
||||
[`TFEncoderDecoderModel.from_pretrained`] 메서드는 현재 Pytorch 체크포인트를 사용한 모델 초기화를 지원하지 않습니다. 이 메서드에 `from_pt=True`를 전달하면 예외(exception)가 발생합니다. 특정 인코더-디코더 모델에 대한 Pytorch 체크포인트만 존재하는 경우, 다음과 같은 해결 방법을 사용할 수 있습니다:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> # 파이토치 체크포인트에서 로드하는 해결 방법
|
||||
>>> from transformers import EncoderDecoderModel, TFEncoderDecoderModel
|
||||
|
||||
>>> _model = EncoderDecoderModel.from_pretrained("patrickvonplaten/bert2bert-cnn_dailymail-fp16")
|
||||
|
||||
>>> _model.encoder.save_pretrained("./encoder")
|
||||
>>> _model.decoder.save_pretrained("./decoder")
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = TFEncoderDecoderModel.from_encoder_decoder_pretrained(
|
||||
... "./encoder", "./decoder", encoder_from_pt=True, decoder_from_pt=True
|
||||
... )
|
||||
>>> # 이 부분은 특정 모델의 구체적인 세부사항을 복사할 때에만 사용합니다.
|
||||
>>> model.config = _model.config
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 학습[[Training]]
|
||||
|
||||
모델이 생성된 후에는 BART, T5 또는 기타 인코더-디코더 모델과 유사한 방식으로 미세 조정(fine-tuning)할 수 있습니다.
|
||||
보시다시피, 손실(loss)을 계산하려면 단 2개의 입력만 필요합니다: `input_ids`(입력 시퀀스를 인코딩한 `input_ids`)와 `labels`(목표 시퀀스를 인코딩한 `input_ids`).
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import BertTokenizer, EncoderDecoderModel
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained("google-bert/bert-base-uncased")
|
||||
>>> model = EncoderDecoderModel.from_encoder_decoder_pretrained("google-bert/bert-base-uncased", "google-bert/bert-base-uncased")
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model.config.decoder_start_token_id = tokenizer.cls_token_id
|
||||
>>> model.config.pad_token_id = tokenizer.pad_token_id
|
||||
|
||||
>>> input_ids = tokenizer(
|
||||
... "The tower is 324 metres (1,063 ft) tall, about the same height as an 81-storey building, and the tallest structure in Paris. Its base is square, measuring 125 metres (410 ft) on each side.During its construction, the Eiffel Tower surpassed the Washington Monument to become the tallest man-made structure in the world, a title it held for 41 years until the Chrysler Building in New York City was finished in 1930. It was the first structure to reach a height of 300 metres. Due to the addition of a broadcasting aerial at the top of the tower in 1957, it is now taller than the Chrysler Building by 5.2 metres (17 ft).Excluding transmitters, the Eiffel Tower is the second tallest free-standing structure in France after the Millau Viaduct.",
|
||||
... return_tensors="pt",
|
||||
... ).input_ids
|
||||
|
||||
>>> labels = tokenizer(
|
||||
... "the eiffel tower surpassed the washington monument to become the tallest structure in the world. it was the first structure to reach a height of 300 metres in paris in 1930. it is now taller than the chrysler building by 5. 2 metres ( 17 ft ) and is the second tallest free - standing structure in paris.",
|
||||
... return_tensors="pt",
|
||||
... ).input_ids
|
||||
|
||||
>>> # forward 함수가 자동으로 적합한 decoder_input_ids를 생성합니다.
|
||||
>>> loss = model(input_ids=input_ids, labels=labels).loss
|
||||
```
|
||||
훈련에 대한 자세한 내용은 [colab](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1WIk2bxglElfZewOHboPFNj8H44_VAyKE?usp=sharing#scrollTo=ZwQIEhKOrJpl) 노트북을 참조하세요.
|
||||
|
||||
이 모델은 [thomwolf](https://github.com/thomwolf)가 기여했으며, 이 모델에 대한 TensorFlow 및 Flax 버전은 [ydshieh](https://github.com/ydshieh)가 기여했습니다.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## EncoderDecoderConfig
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] EncoderDecoderConfig
|
||||
|
||||
<frameworkcontent>
|
||||
<pt>
|
||||
|
||||
## EncoderDecoderModel
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] EncoderDecoderModel
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
- from_encoder_decoder_pretrained
|
||||
|
||||
</pt>
|
||||
<tf>
|
||||
|
||||
## TFEncoderDecoderModel
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TFEncoderDecoderModel
|
||||
- call
|
||||
- from_encoder_decoder_pretrained
|
||||
|
||||
</tf>
|
||||
<jax>
|
||||
|
||||
## FlaxEncoderDecoderModel
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] FlaxEncoderDecoderModel
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
- from_encoder_decoder_pretrained
|
||||
|
||||
</jax>
|
||||
</frameworkcontent>
|
||||
@ -23,8 +23,8 @@
|
||||
title: 使用🤗 PEFT加载和训练adapters
|
||||
- local: model_sharing
|
||||
title: 分享您的模型
|
||||
- local: transformers_agents
|
||||
title: agents教程
|
||||
- local: agents
|
||||
title: 智能体和工具
|
||||
- local: llm_tutorial
|
||||
title: 使用LLMs进行生成
|
||||
title: 教程
|
||||
@ -50,8 +50,14 @@
|
||||
title: 导出为 TFLite
|
||||
- local: torchscript
|
||||
title: 导出为 TorchScript
|
||||
- local: benchmarks
|
||||
title: 对模型进行基准测试
|
||||
- local: gguf
|
||||
title: 与 GGUF 格式的互操作性
|
||||
- local: tiktoken
|
||||
title: 与 Tiktoken 文件的互操作性
|
||||
- local: community
|
||||
title: 社区资源
|
||||
title: 开发者指南
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: performance
|
||||
@ -59,6 +65,8 @@
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: fsdp
|
||||
title: 完全分片数据并行
|
||||
- local: perf_train_special
|
||||
title: 在 Apple silicon 芯片上进行 PyTorch 训练
|
||||
- local: perf_hardware
|
||||
title: 用于训练的定制硬件
|
||||
- local: hpo_train
|
||||
@ -88,11 +96,13 @@
|
||||
title: 分词器的摘要
|
||||
- local: attention
|
||||
title: 注意力机制
|
||||
- local: bertology
|
||||
title: 基于BERT进行的相关研究
|
||||
title: 概念指南
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: main_classes/agent
|
||||
title: Agents和工具
|
||||
title: 智能体和工具
|
||||
- local: main_classes/callback
|
||||
title: Callbacks
|
||||
- local: main_classes/configuration
|
||||
|
||||
427
docs/source/zh/agents.md
Normal file
427
docs/source/zh/agents.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,427 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
# 智能体和工具
|
||||
|
||||
[[在colab里打开]]
|
||||
|
||||
### 什么是智能体 (Agent)?
|
||||
|
||||
大型语言模型(LLM)经过 [因果语言建模训练](./tasks/language_modeling) 可以应对各种任务,但在一些基本任务(如逻辑推理、计算和搜索)上常常表现不佳。当它们被用在自己不擅长的领域时,往往无法生成我们期望的答案。
|
||||
|
||||
为了解决这个问题,可以创建**智能体**.
|
||||
|
||||
智能体是一个系统,它使用 LLM 作为引擎,并且能够访问称为**工具**的功能。
|
||||
|
||||
这些**工具**是执行任务的函数,包含所有必要的描述信息,帮助智能体正确使用它们。
|
||||
|
||||
智能体可以被编程为:
|
||||
- 一次性设计一系列工具并同时执行它们,像 [`CodeAgent`]
|
||||
- 一次执行一个工具,并等待每个工具的结果后再启动下一个,像 [`ReactJsonAgent`]
|
||||
|
||||
### 智能体类型
|
||||
|
||||
#### 代码智能体
|
||||
|
||||
此智能体包含一个规划步骤,然后生成 Python 代码一次性执行所有任务。它原生支持处理不同输入和输出类型,因此推荐用于多模态任务。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 推理智能体
|
||||
|
||||
这是解决推理任务的首选代理,因为 ReAct 框架 ([Yao et al., 2022](https://huggingface.co/papers/2210.03629)) 使其在基于之前观察进行推理时非常高效。
|
||||
|
||||
我们实现了两种版本的 ReactJsonAgent:
|
||||
- [`ReactJsonAgent`] 将工具调用作为 JSON 格式输出。
|
||||
- [`ReactCodeAgent`] 是 ReactJsonAgent 的一种新型,生成工具调用的代码块,对于具备强大编程能力的 LLM 非常适用。
|
||||
|
||||
> [TIP]
|
||||
> 阅读 [Open-source LLMs as LangChain Agents](https://huggingface.co/blog/open-source-llms-as-agents) 博文,了解更多关于推理智能体的信息。
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img
|
||||
class="block dark:hidden"
|
||||
src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/Agent_ManimCE.gif"
|
||||
/>
|
||||
<img
|
||||
class="hidden dark:block"
|
||||
src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/Agent_ManimCE.gif"
|
||||
/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
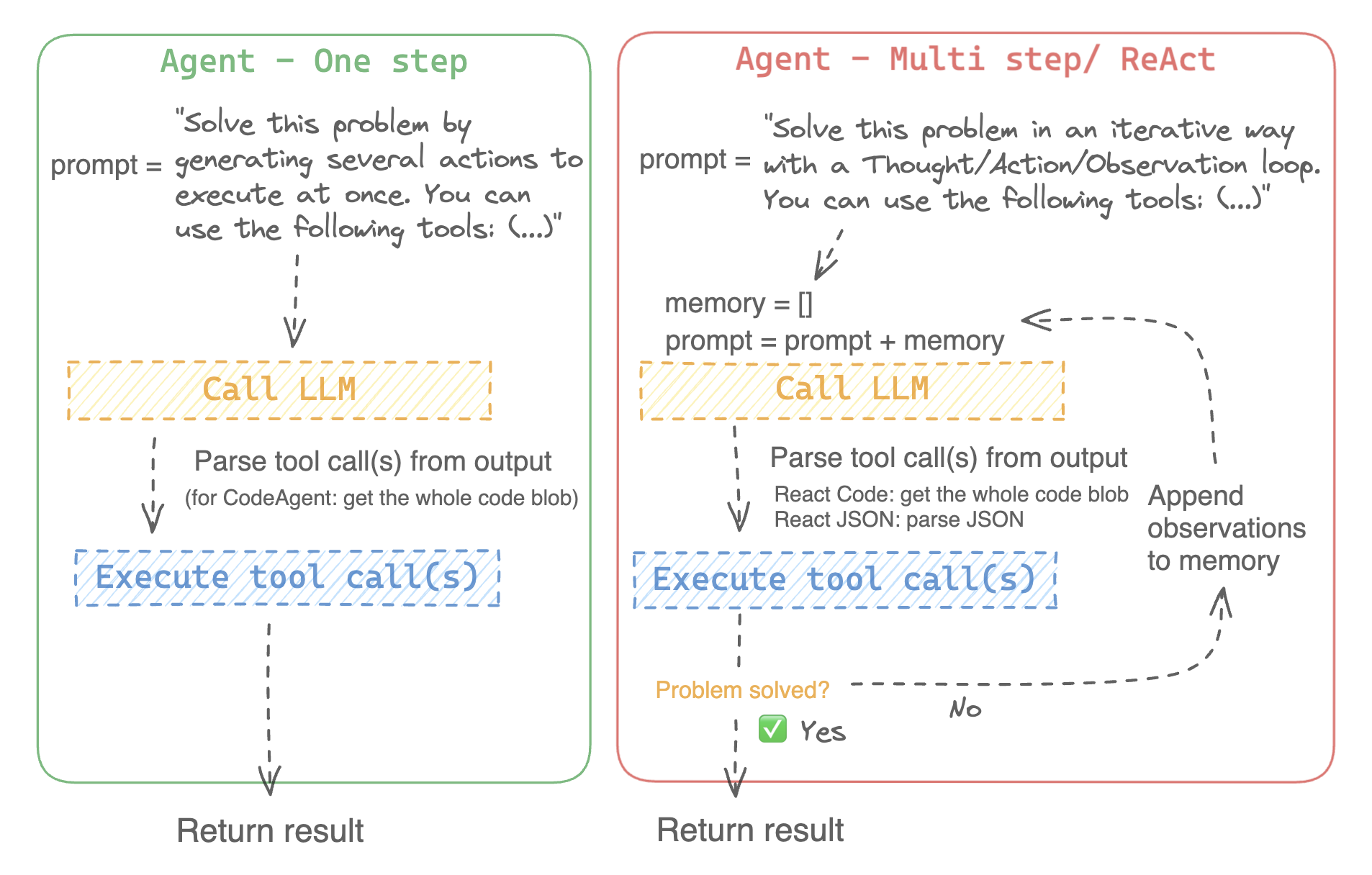
|
||||
|
||||
以下是一个推理代码智能体如何处理以下问题的示例:
|
||||
|
||||
```py3
|
||||
>>> agent.run(
|
||||
... "How many more blocks (also denoted as layers) in BERT base encoder than the encoder from the architecture proposed in Attention is All You Need?",
|
||||
... )
|
||||
=====New task=====
|
||||
How many more blocks (also denoted as layers) in BERT base encoder than the encoder from the architecture proposed in Attention is All You Need?
|
||||
====Agent is executing the code below:
|
||||
bert_blocks = search(query="number of blocks in BERT base encoder")
|
||||
print("BERT blocks:", bert_blocks)
|
||||
====
|
||||
Print outputs:
|
||||
BERT blocks: twelve encoder blocks
|
||||
|
||||
====Agent is executing the code below:
|
||||
attention_layer = search(query="number of layers in Attention is All You Need")
|
||||
print("Attention layers:", attention_layer)
|
||||
====
|
||||
Print outputs:
|
||||
Attention layers: Encoder: The encoder is composed of a stack of N = 6 identical layers. Each layer has two sub-layers. The first is a multi-head self-attention mechanism, and the second is a simple, position- 2 Page 3 Figure 1: The Transformer - model architecture.
|
||||
|
||||
====Agent is executing the code below:
|
||||
bert_blocks = 12
|
||||
attention_layers = 6
|
||||
diff = bert_blocks - attention_layers
|
||||
print("Difference in blocks:", diff)
|
||||
final_answer(diff)
|
||||
====
|
||||
|
||||
Print outputs:
|
||||
Difference in blocks: 6
|
||||
|
||||
Final answer: 6
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 如何构建智能体?
|
||||
|
||||
要初始化一个智能体,您需要以下参数:
|
||||
|
||||
- **一个 LLM** 来驱动智能体——智能体本身并不是 LLM,而是一个使用 LLM 作为引擎的程序。
|
||||
- **一个系统提示**:告诉 LLM 引擎应该如何生成输出。
|
||||
- **一个工具箱**,智能体可以从中选择工具执行。
|
||||
- **一个解析器**,从 LLM 输出中提取出哪些工具需要调用,以及使用哪些参数。
|
||||
|
||||
在智能体系统初始化时,工具属性将生成工具描述,并嵌入到智能体的系统提示中,告知智能体可以使用哪些工具,并且为什么使用它们。
|
||||
|
||||
**安装依赖**
|
||||
|
||||
首先,您需要安装**智能体**所需的额外依赖:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install transformers[agents]
|
||||
```
|
||||
**创建LLM引擎**
|
||||
|
||||
定义一个 `llm_engine` 方法,该方法接受一系列[消息](./chat_templating)并返回文本。该 `callable` 还需要接受一个 `stop` 参数,用于指示何时停止生成输出。
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from huggingface_hub import login, InferenceClient
|
||||
|
||||
login("<YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>")
|
||||
|
||||
client = InferenceClient(model="meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3-70B-Instruct")
|
||||
|
||||
def llm_engine(messages, stop_sequences=["Task"]) -> str:
|
||||
response = client.chat_completion(messages, stop=stop_sequences, max_tokens=1000)
|
||||
answer = response.choices[0].message.content
|
||||
return answer
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您可以使用任何符合以下要求的 `llm_engine` 方法:
|
||||
1. [输入格式](./chat_templating)为 (`List[Dict[str, str]]`),并且返回一个字符串。
|
||||
2. 它在 `stop_sequences` 参数传递的序列处停止生成输出。
|
||||
|
||||
此外,`llm_engine` 还可以接受一个 `grammar` 参数。如果在智能体初始化时指定了 `grammar`,则该参数将传递给 `llm_engine` 的调用,以允许[受限生成](https://huggingface.co/docs/text-generation-inference/conceptual/guidance),以强制生成格式正确的智能体输出。
|
||||
|
||||
您还需要一个 `tools` 参数,它接受一个 `Tools` 列表 —— 可以是空列表。您也可以通过定义可选参数 `add_base_tools=True` 来将默认工具箱添加到工具列表中。
|
||||
|
||||
现在,您可以创建一个智能体,例如 [`CodeAgent`],并运行它。您还可以创建一个 [`TransformersEngine`],使用 `transformers` 在本地机器上运行预初始化的推理管道。 为了方便起见,由于智能体行为通常需要更强大的模型,例如 `Llama-3.1-70B-Instruct`,它们目前较难在本地运行,我们还提供了 [`HfApiEngine`] 类,它在底层初始化了一个 `huggingface_hub.InferenceClient`。
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import CodeAgent, HfApiEngine
|
||||
|
||||
llm_engine = HfApiEngine(model="meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3-70B-Instruct")
|
||||
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[], llm_engine=llm_engine, add_base_tools=True)
|
||||
|
||||
agent.run(
|
||||
"Could you translate this sentence from French, say it out loud and return the audio.",
|
||||
sentence="Où est la boulangerie la plus proche?",
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
当你急需某个东西时这将会很有用!
|
||||
您甚至可以将 `llm_engine` 参数留空,默认情况下会创建一个 [`HfApiEngine`]。
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import CodeAgent
|
||||
|
||||
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[], add_base_tools=True)
|
||||
|
||||
agent.run(
|
||||
"Could you translate this sentence from French, say it out loud and give me the audio.",
|
||||
sentence="Où est la boulangerie la plus proche?",
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
请注意,我们使用了额外的 `sentence` 参数:您可以将文本作为附加参数传递给模型。
|
||||
|
||||
您还可以使用这个来指定本地或远程文件的路径供模型使用:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import ReactCodeAgent
|
||||
|
||||
agent = ReactCodeAgent(tools=[], llm_engine=llm_engine, add_base_tools=True)
|
||||
|
||||
agent.run("Why does Mike not know many people in New York?", audio="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/recording.mp3")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
系统提示和输出解析器会自动定义,但您可以通过调用智能体的 `system_prompt_template` 来轻松查看它们。
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
print(agent.system_prompt_template)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
尽可能清楚地解释您要执行的任务非常重要。 每次 [`~Agent.run`] 操作都是独立的,并且由于智能体是由 LLM 驱动的,提示中的细微变化可能会导致完全不同的结果。
|
||||
您还可以连续运行多个任务,每次都会重新初始化智能体的 `agent.task` 和 `agent.logs` 属性。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 代码执行
|
||||
|
||||
Python 解释器在一组输入和工具上执行代码。 这应该是安全的,因为只能调用您提供的工具(特别是 Hugging Face 的工具)和 print 函数,因此您已经限制了可以执行的操作。
|
||||
|
||||
Python 解释器默认不允许导入不在安全列表中的模块,因此大多数明显的攻击问题应该不成问题。 您仍然可以通过在 [`ReactCodeAgent`] 或 [`CodeAgent`] 初始化时通过 `additional_authorized_imports` 参数传递一个授权的模块列表来授权额外的导入:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import ReactCodeAgent
|
||||
|
||||
>>> agent = ReactCodeAgent(tools=[], additional_authorized_imports=['requests', 'bs4'])
|
||||
>>> agent.run("Could you get me the title of the page at url 'https://huggingface.co/blog'?")
|
||||
|
||||
(...)
|
||||
'Hugging Face – Blog'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
如果有任何代码尝试执行非法操作,或者生成的代码出现常规 Python 错误,执行将停止。
|
||||
|
||||
> [!WARNING]
|
||||
> 在使用大语言模型(LLM)生成代码时,生成的代码会被执行,避免导入或使用任何不安全的库或模块。
|
||||
|
||||
### 系统提示
|
||||
|
||||
智能体,或者说驱动智能体的 LLM,根据系统提示生成输出。系统提示可以定制并根据目标任务进行调整。例如,检查 [`ReactCodeAgent`] 的系统提示(以下版本经过简化)。
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
You will be given a task to solve as best you can.
|
||||
You have access to the following tools:
|
||||
<<tool_descriptions>>
|
||||
|
||||
To solve the task, you must plan forward to proceed in a series of steps, in a cycle of 'Thought:', 'Code:', and 'Observation:' sequences.
|
||||
|
||||
At each step, in the 'Thought:' sequence, you should first explain your reasoning towards solving the task, then the tools that you want to use.
|
||||
Then in the 'Code:' sequence, you should write the code in simple Python. The code sequence must end with '/End code' sequence.
|
||||
During each intermediate step, you can use 'print()' to save whatever important information you will then need.
|
||||
These print outputs will then be available in the 'Observation:' field, for using this information as input for the next step.
|
||||
|
||||
In the end you have to return a final answer using the `final_answer` tool.
|
||||
|
||||
Here are a few examples using notional tools:
|
||||
---
|
||||
{examples}
|
||||
|
||||
Above example were using notional tools that might not exist for you. You only have acces to those tools:
|
||||
<<tool_names>>
|
||||
You also can perform computations in the python code you generate.
|
||||
|
||||
Always provide a 'Thought:' and a 'Code:\n```py' sequence ending with '```<end_code>' sequence. You MUST provide at least the 'Code:' sequence to move forward.
|
||||
|
||||
Remember to not perform too many operations in a single code block! You should split the task into intermediate code blocks.
|
||||
Print results at the end of each step to save the intermediate results. Then use final_answer() to return the final result.
|
||||
|
||||
Remember to make sure that variables you use are all defined.
|
||||
|
||||
Now Begin!
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
系统提示包括:
|
||||
- 解释智能体应该如何工作以及工具的**介绍**。
|
||||
- 所有工具的描述由 `<<tool_descriptions>>` 标记在运行时动态替换,这样智能体就知道可以使用哪些工具及其用途。
|
||||
- 工具的描述来自工具的属性,`name`、`description`、`inputs` 和 `output_type`,以及一个简单的 `jinja2` 模板,您可以根据需要进行调整。
|
||||
- 期望的输出格式。
|
||||
|
||||
您可以通过向 `system_prompt` 参数传递自定义提示来最大程度地提高灵活性,从而覆盖整个系统提示模板。
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import ReactJsonAgent
|
||||
from transformers.agents import PythonInterpreterTool
|
||||
|
||||
agent = ReactJsonAgent(tools=[PythonInterpreterTool()], system_prompt="{your_custom_prompt}")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> [WARNING]
|
||||
> 必须在`template`中定义 `<<tool_descriptions>>` 这个变量,以便智能体能够正确地识别并使用可用的工具
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 检查智能体的运行
|
||||
|
||||
以下是检查运行后发生了什么的一些有用属性:
|
||||
- `agent.logs` 存储了智能体的详细日志。每一步的所有内容都会存储在一个字典中,然后附加到 `agent.logs`。
|
||||
- 运行 `agent.write_inner_memory_from_logs()` 会从日志中创建智能体的内存,以便 LLM 查看,作为一系列聊天消息。此方法会遍历日志的每个步骤,只保存其感兴趣的消息:例如,它会单独保存系统提示和任务,然后为每个步骤保存 LLM 输出的消息,以及工具调用输出的消息。如果您想要更高层次的查看发生了什么,可以使用此方法 —— 但并不是每个日志都会被此方法转录。
|
||||
|
||||
## 工具
|
||||
|
||||
工具是智能体使用的基本功能。
|
||||
|
||||
例如,您可以检查 [`PythonInterpreterTool`]:它有一个名称、描述、输入描述、输出类型和 `__call__` 方法来执行该操作。
|
||||
|
||||
当智能体初始化时,工具属性会用来生成工具描述,然后将其嵌入到智能体的系统提示中,这让智能体知道可以使用哪些工具以及为什么使用它们。
|
||||
|
||||
### 默认工具箱
|
||||
|
||||
Transformers 提供了一个默认工具箱,用于增强智能体,您可以在初始化时通过 `add_base_tools=True` 参数将其添加到智能体中:
|
||||
|
||||
- **文档问答**:给定一个文档(如图像格式的 PDF),回答关于该文档的问题([Donut](./model_doc/donut))
|
||||
- **图像问答**:给定一张图片,回答关于该图像的问题([VILT](./model_doc/vilt))
|
||||
- **语音转文本**:给定一个人讲述的音频录音,将其转录为文本(Whisper)
|
||||
- **文本转语音**:将文本转换为语音([SpeechT5](./model_doc/speecht5))
|
||||
- **翻译**:将给定的句子从源语言翻译为目标语言
|
||||
- **DuckDuckGo 搜索**:使用 `DuckDuckGo` 浏览器进行网络搜索
|
||||
- **Python 代码解释器**:在安全环境中运行 LLM 生成的 Python 代码。只有在初始化 [`ReactJsonAgent`] 时将 `add_base_tools=True` 时,代码智能体才会添加此工具,因为基于代码的智能体已经能够原生执行 Python 代码
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
您可以通过调用 [`load_tool`] 函数来手动使用某个工具并执行任务。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import load_tool
|
||||
|
||||
tool = load_tool("text-to-speech")
|
||||
audio = tool("This is a text to speech tool")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 创建新工具
|
||||
|
||||
您可以为 `Hugging Face` 默认工具无法涵盖的用例创建自己的工具。
|
||||
例如,假设我们要创建一个返回在 `Hugging Face Hub` 上某个任务中下载次数最多的模型的工具。
|
||||
|
||||
您将从以下代码开始:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from huggingface_hub import list_models
|
||||
|
||||
task = "text-classification"
|
||||
|
||||
model = next(iter(list_models(filter=task, sort="downloads", direction=-1)))
|
||||
print(model.id)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
这段代码可以很快转换为工具,只需将其包装成一个函数,并添加 `tool` 装饰器:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import tool
|
||||
|
||||
@tool
|
||||
def model_download_tool(task: str) -> str:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
This is a tool that returns the most downloaded model of a given task on the Hugging Face Hub.
|
||||
It returns the name of the checkpoint.
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
task: The task for which
|
||||
"""
|
||||
model = next(iter(list_models(filter="text-classification", sort="downloads", direction=-1)))
|
||||
return model.id
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
该函数需要:
|
||||
- 一个清晰的名称。名称通常描述工具的功能。由于代码返回某个任务中下载次数最多的模型,因此我们将其命名为 `model_download_tool`。
|
||||
- 对输入和输出进行类型提示
|
||||
- 描述,其中包括 "`Args`:" 部分,描述每个参数(这次不需要类型指示,它会从类型提示中获取)。
|
||||
|
||||
所有这些将自动嵌入到智能体的系统提示中,因此请尽量使它们尽可能清晰!
|
||||
|
||||
> [TIP]
|
||||
> 这个定义格式与 apply_chat_template 中使用的工具模式相同,唯一的区别是添加了 tool 装饰器:可以在我们的工具使用 API 中[了解更多](https://huggingface.co/blog/unified-tool-use#passing-tools-to-a-chat-template).
|
||||
|
||||
然后,您可以直接初始化您的智能体:
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import CodeAgent
|
||||
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[model_download_tool], llm_engine=llm_engine)
|
||||
agent.run(
|
||||
"Can you give me the name of the model that has the most downloads in the 'text-to-video' task on the Hugging Face Hub?"
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
您将得到以下输出:
|
||||
```text
|
||||
======== New task ========
|
||||
Can you give me the name of the model that has the most downloads in the 'text-to-video' task on the Hugging Face Hub?
|
||||
==== Agent is executing the code below:
|
||||
most_downloaded_model = model_download_tool(task="text-to-video")
|
||||
print(f"The most downloaded model for the 'text-to-video' task is {most_downloaded_model}.")
|
||||
====
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
输出:
|
||||
`"The most downloaded model for the 'text-to-video' task is ByteDance/AnimateDiff-Lightning."`
|
||||
|
||||
### 管理智能体的工具箱
|
||||
|
||||
如果您已经初始化了一个智能体,但想添加一个新的工具,重新初始化智能体会很麻烦。借助 Transformers,您可以通过添加或替换工具来管理智能体的工具箱。
|
||||
|
||||
让我们将 `model_download_tool` 添加到一个仅初始化了默认工具箱的现有智能体中。
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import CodeAgent
|
||||
|
||||
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[], llm_engine=llm_engine, add_base_tools=True)
|
||||
agent.toolbox.add_tool(model_download_tool)
|
||||
```
|
||||
现在,我们可以同时使用新工具和之前的文本到语音工具:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
agent.run(
|
||||
"Can you read out loud the name of the model that has the most downloads in the 'text-to-video' task on the Hugging Face Hub and return the audio?"
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
| **Audio** |
|
||||
|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| <audio controls><source src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/damo.wav" type="audio/wav"/> |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
> [WARNING]
|
||||
> 当向一个已经运行良好的代理添加工具时要小心,因为这可能会导致选择偏向你的工具,或者选择已经定义的工具之外的其他工具。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
使用 agent.toolbox.update_tool() 方法可以替换智能体工具箱中的现有工具。
|
||||
如果您的新工具完全替代了现有工具,这非常有用,因为智能体已经知道如何执行该特定任务。
|
||||
只需确保新工具遵循与替换工具相同的 API,或者调整系统提示模板,以确保所有使用替换工具的示例都得到更新。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 使用工具集合
|
||||
|
||||
您可以通过使用 ToolCollection 对象来利用工具集合,指定您想要使用的工具集合的 slug。
|
||||
然后将这些工具作为列表传递给智能体进行初始化,并开始使用它们!
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import ToolCollection, ReactCodeAgent
|
||||
|
||||
image_tool_collection = ToolCollection(collection_slug="huggingface-tools/diffusion-tools-6630bb19a942c2306a2cdb6f")
|
||||
agent = ReactCodeAgent(tools=[*image_tool_collection.tools], add_base_tools=True)
|
||||
|
||||
agent.run("Please draw me a picture of rivers and lakes.")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
为了加速启动,工具仅在智能体调用时加载。
|
||||
|
||||
这将生成如下图像:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/rivers_and_lakes.png">
|
||||
377
docs/source/zh/benchmarks.md
Normal file
377
docs/source/zh/benchmarks.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,377 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2020 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# 基准测试
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
小提示:Hugging Face的基准测试工具已经不再更新,建议使用外部基准测试库来衡量Transformer模
|
||||
型的速度和内存复杂度。
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
[[open-in-colab]]
|
||||
|
||||
让我们来看看如何对🤗 Transformers模型进行基准测试,以及进行测试的推荐策略和已有的基准测试结果。
|
||||
|
||||
如果您需要更详细的回答,可以在[这里](https://github.com/huggingface/notebooks/tree/main/examples/benchmark.ipynb)找到更多关于基准测试的内容。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 如何对🤗 Transformers模型进行基准测试
|
||||
|
||||
使用[`PyTorchBenchmark`]和[`TensorFlowBenchmark`]类可以灵活地对🤗 Transformers模型进行基准测试。这些基准测试类可以衡量模型在**推理**和**训练**过程中所需的**峰值内存**和**时间**。
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
这里的**推理**指的是一次前向传播(forward pass),而训练则指一次前向传播和反向传播(backward pass)。
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
基准测试类 [`PyTorchBenchmark`] 和 [`TensorFlowBenchmark`] 需要分别传入 [`PyTorchBenchmarkArguments`] 和 [`TensorFlowBenchmarkArguments`] 类型的对象来进行实例化。这些类是数据类型,包含了所有相关的配置参数,用于其对应的基准测试类。
|
||||
|
||||
在下面的示例中,我们展示了如何对类型为 **bert-base-cased** 的BERT模型进行基准测试:
|
||||
|
||||
<frameworkcontent>
|
||||
<pt>
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import PyTorchBenchmark, PyTorchBenchmarkArguments
|
||||
|
||||
>>> args = PyTorchBenchmarkArguments(models=["google-bert/bert-base-uncased"], batch_sizes=[8], sequence_lengths=[8, 32, 128, 512])
|
||||
>>> benchmark = PyTorchBenchmark(args)
|
||||
```
|
||||
</pt>
|
||||
<tf>
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import TensorFlowBenchmark, TensorFlowBenchmarkArguments
|
||||
|
||||
>>> args = TensorFlowBenchmarkArguments(
|
||||
... models=["google-bert/bert-base-uncased"], batch_sizes=[8], sequence_lengths=[8, 32, 128, 512]
|
||||
... )
|
||||
>>> benchmark = TensorFlowBenchmark(args)
|
||||
```
|
||||
</tf>
|
||||
</frameworkcontent>
|
||||
|
||||
在这里,基准测试的参数数据类接受了三个主要的参数,即 `models`、`batch_sizes` 和`sequence_lengths`。其中,`models` 是必需的参数,它期望一个来自[模型库](https://huggingface.co/models)的模型标识符列表。`batch_sizes` 和 `sequence_lengths` 是列表类型的参数,定义了进行基准测试时 `input_ids` 的批量大小和序列长度。
|
||||
|
||||
这些是基准测试数据类中可以配置的一些主要参数。除此之外,基准测试数据类中还可以配置很多其他参数。如需要查看更详细的配置参数,可以直接查看以下文件:
|
||||
|
||||
* `src/transformers/benchmark/benchmark_args_utils.py`
|
||||
* `src/transformers/benchmark/benchmark_args.py`(针对 PyTorch)
|
||||
* `src/transformers/benchmark/benchmark_args_tf.py`(针对 TensorFlow)
|
||||
|
||||
另外,您还可以通过在根目录下运行以下命令,查看针对 PyTorch 和 TensorFlow 的所有可配置参数的描述列表:
|
||||
``` bash python examples/pytorch/benchmarking/run_benchmark.py --help ```
|
||||
这些命令将列出所有可以配置的参数,它们可以帮助您更加灵活地进行基准测试。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<frameworkcontent>
|
||||
<pt>
|
||||
|
||||
以下代码通过`PyTorchBenchmarkArguments`设置模型批处理大小和序列长度,然后调用`benchmark.run()`执行基准测试。
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> results = benchmark.run()
|
||||
>>> print(results)
|
||||
==================== INFERENCE - SPEED - RESULT ====================
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
Model Name Batch Size Seq Length Time in s
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
google-bert/bert-base-uncased 8 8 0.006
|
||||
google-bert/bert-base-uncased 8 32 0.006
|
||||
google-bert/bert-base-uncased 8 128 0.018
|
||||
google-bert/bert-base-uncased 8 512 0.088
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
==================== INFERENCE - MEMORY - RESULT ====================
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
Model Name Batch Size Seq Length Memory in MB
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
google-bert/bert-base-uncased 8 8 1227
|
||||
google-bert/bert-base-uncased 8 32 1281
|
||||
google-bert/bert-base-uncased 8 128 1307
|
||||
google-bert/bert-base-uncased 8 512 1539
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
==================== ENVIRONMENT INFORMATION ====================
|
||||
|
||||
- transformers_version: 2.11.0
|
||||
- framework: PyTorch
|
||||
- use_torchscript: False
|
||||
- framework_version: 1.4.0
|
||||
- python_version: 3.6.10
|
||||
- system: Linux
|
||||
- cpu: x86_64
|
||||
- architecture: 64bit
|
||||
- date: 2020-06-29
|
||||
- time: 08:58:43.371351
|
||||
- fp16: False
|
||||
- use_multiprocessing: True
|
||||
- only_pretrain_model: False
|
||||
- cpu_ram_mb: 32088
|
||||
- use_gpu: True
|
||||
- num_gpus: 1
|
||||
- gpu: TITAN RTX
|
||||
- gpu_ram_mb: 24217
|
||||
- gpu_power_watts: 280.0
|
||||
- gpu_performance_state: 2
|
||||
- use_tpu: False
|
||||
```
|
||||
</pt>
|
||||
<tf>
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python examples/tensorflow/benchmarking/run_benchmark_tf.py --help
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
接下来,只需要调用 `benchmark.run()` 就能轻松运行已经实例化的基准测试对象。
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> results = benchmark.run()
|
||||
>>> print(results)
|
||||
>>> results = benchmark.run()
|
||||
>>> print(results)
|
||||
==================== INFERENCE - SPEED - RESULT ====================
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
Model Name Batch Size Seq Length Time in s
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
google-bert/bert-base-uncased 8 8 0.005
|
||||
google-bert/bert-base-uncased 8 32 0.008
|
||||
google-bert/bert-base-uncased 8 128 0.022
|
||||
google-bert/bert-base-uncased 8 512 0.105
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
==================== INFERENCE - MEMORY - RESULT ====================
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
Model Name Batch Size Seq Length Memory in MB
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
google-bert/bert-base-uncased 8 8 1330
|
||||
google-bert/bert-base-uncased 8 32 1330
|
||||
google-bert/bert-base-uncased 8 128 1330
|
||||
google-bert/bert-base-uncased 8 512 1770
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
==================== ENVIRONMENT INFORMATION ====================
|
||||
|
||||
- transformers_version: 2.11.0
|
||||
- framework: Tensorflow
|
||||
- use_xla: False
|
||||
- framework_version: 2.2.0
|
||||
- python_version: 3.6.10
|
||||
- system: Linux
|
||||
- cpu: x86_64
|
||||
- architecture: 64bit
|
||||
- date: 2020-06-29
|
||||
- time: 09:26:35.617317
|
||||
- fp16: False
|
||||
- use_multiprocessing: True
|
||||
- only_pretrain_model: False
|
||||
- cpu_ram_mb: 32088
|
||||
- use_gpu: True
|
||||
- num_gpus: 1
|
||||
- gpu: TITAN RTX
|
||||
- gpu_ram_mb: 24217
|
||||
- gpu_power_watts: 280.0
|
||||
- gpu_performance_state: 2
|
||||
- use_tpu: False
|
||||
```
|
||||
</tf>
|
||||
</frameworkcontent>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
在一般情况下,基准测试会测量推理(inference)的**时间**和**所需内存**。在上面的示例输出中,前两部分显示了与**推理时间**和**推理内存**对应的结果。与此同时,关于计算环境的所有相关信息(例如 GPU 类型、系统、库版本等)会在第三部分的**环境信息**中打印出来。你可以通过在 [`PyTorchBenchmarkArguments`] 和 [`TensorFlowBenchmarkArguments`] 中添加 `save_to_csv=True`参数,将这些信息保存到一个 .csv 文件中。在这种情况下,每一部分的信息会分别保存在不同的 .csv 文件中。每个 .csv 文件的路径也可以通过参数数据类进行定义。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
您可以选择不通过预训练模型的模型标识符(如 `google-bert/bert-base-uncased`)进行基准测试,而是对任何可用模型类的任意配置进行基准测试。在这种情况下,我们必须将一系列配置与基准测试参数一起传入,方法如下:
|
||||
|
||||
<frameworkcontent>
|
||||
<pt>
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import PyTorchBenchmark, PyTorchBenchmarkArguments, BertConfig
|
||||
|
||||
>>> args = PyTorchBenchmarkArguments(
|
||||
... models=["bert-base", "bert-384-hid", "bert-6-lay"], batch_sizes=[8], sequence_lengths=[8, 32, 128, 512]
|
||||
... )
|
||||
>>> config_base = BertConfig()
|
||||
>>> config_384_hid = BertConfig(hidden_size=384)
|
||||
>>> config_6_lay = BertConfig(num_hidden_layers=6)
|
||||
|
||||
>>> benchmark = PyTorchBenchmark(args, configs=[config_base, config_384_hid, config_6_lay])
|
||||
>>> benchmark.run()
|
||||
==================== INFERENCE - SPEED - RESULT ====================
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
Model Name Batch Size Seq Length Time in s
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
bert-base 8 128 0.006
|
||||
bert-base 8 512 0.006
|
||||
bert-base 8 128 0.018
|
||||
bert-base 8 512 0.088
|
||||
bert-384-hid 8 8 0.006
|
||||
bert-384-hid 8 32 0.006
|
||||
bert-384-hid 8 128 0.011
|
||||
bert-384-hid 8 512 0.054
|
||||
bert-6-lay 8 8 0.003
|
||||
bert-6-lay 8 32 0.004
|
||||
bert-6-lay 8 128 0.009
|
||||
bert-6-lay 8 512 0.044
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
==================== INFERENCE - MEMORY - RESULT ====================
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
Model Name Batch Size Seq Length Memory in MB
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
bert-base 8 8 1277
|
||||
bert-base 8 32 1281
|
||||
bert-base 8 128 1307
|
||||
bert-base 8 512 1539
|
||||
bert-384-hid 8 8 1005
|
||||
bert-384-hid 8 32 1027
|
||||
bert-384-hid 8 128 1035
|
||||
bert-384-hid 8 512 1255
|
||||
bert-6-lay 8 8 1097
|
||||
bert-6-lay 8 32 1101
|
||||
bert-6-lay 8 128 1127
|
||||
bert-6-lay 8 512 1359
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
==================== ENVIRONMENT INFORMATION ====================
|
||||
|
||||
- transformers_version: 2.11.0
|
||||
- framework: PyTorch
|
||||
- use_torchscript: False
|
||||
- framework_version: 1.4.0
|
||||
- python_version: 3.6.10
|
||||
- system: Linux
|
||||
- cpu: x86_64
|
||||
- architecture: 64bit
|
||||
- date: 2020-06-29
|
||||
- time: 09:35:25.143267
|
||||
- fp16: False
|
||||
- use_multiprocessing: True
|
||||
- only_pretrain_model: False
|
||||
- cpu_ram_mb: 32088
|
||||
- use_gpu: True
|
||||
- num_gpus: 1
|
||||
- gpu: TITAN RTX
|
||||
- gpu_ram_mb: 24217
|
||||
- gpu_power_watts: 280.0
|
||||
- gpu_performance_state: 2
|
||||
- use_tpu: False
|
||||
```
|
||||
</pt>
|
||||
<tf>
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import TensorFlowBenchmark, TensorFlowBenchmarkArguments, BertConfig
|
||||
|
||||
>>> args = TensorFlowBenchmarkArguments(
|
||||
... models=["bert-base", "bert-384-hid", "bert-6-lay"], batch_sizes=[8], sequence_lengths=[8, 32, 128, 512]
|
||||
... )
|
||||
>>> config_base = BertConfig()
|
||||
>>> config_384_hid = BertConfig(hidden_size=384)
|
||||
>>> config_6_lay = BertConfig(num_hidden_layers=6)
|
||||
|
||||
>>> benchmark = TensorFlowBenchmark(args, configs=[config_base, config_384_hid, config_6_lay])
|
||||
>>> benchmark.run()
|
||||
==================== INFERENCE - SPEED - RESULT ====================
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
Model Name Batch Size Seq Length Time in s
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
bert-base 8 8 0.005
|
||||
bert-base 8 32 0.008
|
||||
bert-base 8 128 0.022
|
||||
bert-base 8 512 0.106
|
||||
bert-384-hid 8 8 0.005
|
||||
bert-384-hid 8 32 0.007
|
||||
bert-384-hid 8 128 0.018
|
||||
bert-384-hid 8 512 0.064
|
||||
bert-6-lay 8 8 0.002
|
||||
bert-6-lay 8 32 0.003
|
||||
bert-6-lay 8 128 0.0011
|
||||
bert-6-lay 8 512 0.074
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
==================== INFERENCE - MEMORY - RESULT ====================
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
Model Name Batch Size Seq Length Memory in MB
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
bert-base 8 8 1330
|
||||
bert-base 8 32 1330
|
||||
bert-base 8 128 1330
|
||||
bert-base 8 512 1770
|
||||
bert-384-hid 8 8 1330
|
||||
bert-384-hid 8 32 1330
|
||||
bert-384-hid 8 128 1330
|
||||
bert-384-hid 8 512 1540
|
||||
bert-6-lay 8 8 1330
|
||||
bert-6-lay 8 32 1330
|
||||
bert-6-lay 8 128 1330
|
||||
bert-6-lay 8 512 1540
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
==================== ENVIRONMENT INFORMATION ====================
|
||||
|
||||
- transformers_version: 2.11.0
|
||||
- framework: Tensorflow
|
||||
- use_xla: False
|
||||
- framework_version: 2.2.0
|
||||
- python_version: 3.6.10
|
||||
- system: Linux
|
||||
- cpu: x86_64
|
||||
- architecture: 64bit
|
||||
- date: 2020-06-29
|
||||
- time: 09:38:15.487125
|
||||
- fp16: False
|
||||
- use_multiprocessing: True
|
||||
- only_pretrain_model: False
|
||||
- cpu_ram_mb: 32088
|
||||
- use_gpu: True
|
||||
- num_gpus: 1
|
||||
- gpu: TITAN RTX
|
||||
- gpu_ram_mb: 24217
|
||||
- gpu_power_watts: 280.0
|
||||
- gpu_performance_state: 2
|
||||
- use_tpu: False
|
||||
```
|
||||
</tf>
|
||||
</frameworkcontent>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**推理时间**和**推理所需内存**会被重新测量,不过这次是针对 `BertModel` 类的自定义配置进行基准测试。这个功能在决定模型应该使用哪种配置进行训练时尤其有用。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 基准测试的推荐策略
|
||||
本节列出了一些在对模型进行基准测试时比较推荐的策略:
|
||||
|
||||
* 目前,该模块只支持单设备基准测试。在进行 GPU 基准测试时,建议用户通过设置 `CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES` 环境变量来指定代码应在哪个设备上运行,例如在运行代码前执行 `export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0`。
|
||||
* `no_multi_processing` 选项仅应在测试和调试时设置为 `True`。为了确保内存测量的准确性,建议将每个内存基准测试单独运行在一个进程中,并确保 `no_multi_processing` 设置为 `True`。
|
||||
* 当您分享模型基准测试结果时,应始终提供环境信息。由于 GPU 设备、库版本等之间可能存在较大差异,单独的基准测试结果对社区的帮助有限。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 分享您的基准测试结果
|
||||
|
||||
先前的所有可用的核心模型(当时有10个)都已针对 **推理时间** 进行基准测试,涵盖了多种不同的设置:使用 PyTorch(包不包含 TorchScript),使用 TensorFlow(包不包含 XLA)。所有的测试都在 CPU(除了 TensorFlow XLA)和 GPU 上进行。
|
||||
|
||||
这种方法的详细信息可以在 [这篇博客](https://medium.com/huggingface/benchmarking-transformers-pytorch-and-tensorflow-e2917fb891c2) 中找到,测试结果可以在 [这里](https://docs.google.com/spreadsheets/d/1sryqufw2D0XlUH4sq3e9Wnxu5EAQkaohzrJbd5HdQ_w/edit?usp=sharing) 查看。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
您可以借助新的 **基准测试** 工具比以往任何时候都更容易地分享您的基准测试结果!
|
||||
|
||||
- [PyTorch 基准测试结果](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples/pytorch/benchmarking/README.md)
|
||||
- [TensorFlow 基准测试结果](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples/tensorflow/benchmarking/README.md)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
33
docs/source/zh/bertology.md
Normal file
33
docs/source/zh/bertology.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
|
||||
<!--版权2020年HuggingFace团队保留所有权利。
|
||||
|
||||
根据Apache许可证第2.0版(“许可证”)许可;除非符合许可证,否则您不得使用此文件。您可以在以下网址获取许可证的副本:
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
除非适用法律要求或书面同意,否则按“按原样”分发的软件,无论是明示还是暗示的,都没有任何担保或条件。请参阅许可证以了解特定语言下的权限和限制。
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ 请注意,本文件虽然使用Markdown编写,但包含了特定的语法,适用于我们的doc-builder(类似于MDX),可能无法在您的Markdown查看器中正常渲染。
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# 基于BERT进行的相关研究(BERTology)
|
||||
|
||||
当前,一个新兴的研究领域正致力于探索大规模 transformer 模型(如BERT)的内部工作机制,一些人称之为“BERTology”。以下是这个领域的一些典型示例:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- BERT Rediscovers the Classical NLP Pipeline by Ian Tenney, Dipanjan Das, Ellie Pavlick:
|
||||
https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.05950
|
||||
- Are Sixteen Heads Really Better than One? by Paul Michel, Omer Levy, Graham Neubig: https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.10650
|
||||
- What Does BERT Look At? An Analysis of BERT's Attention by Kevin Clark, Urvashi Khandelwal, Omer Levy, Christopher D.
|
||||
Manning: https://arxiv.org/abs/1906.04341
|
||||
- CAT-probing: A Metric-based Approach to Interpret How Pre-trained Models for Programming Language Attend Code Structure: https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.04633
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
为了助力这一新兴领域的发展,我们在BERT/GPT/GPT-2模型中增加了一些附加功能,方便人们访问其内部表示,这些功能主要借鉴了Paul Michel的杰出工作(https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.10650):
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- 访问BERT/GPT/GPT-2的所有隐藏状态,
|
||||
- 访问BERT/GPT/GPT-2每个注意力头的所有注意力权重,
|
||||
- 检索注意力头的输出值和梯度,以便计算头的重要性得分并对头进行剪枝,详情可见论文:https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.10650。
|
||||
|
||||
为了帮助您理解和使用这些功能,我们添加了一个具体的示例脚本:[bertology.py](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples/research_projects/bertology/run_bertology.py),该脚本可以对一个在 GLUE 数据集上预训练的模型进行信息提取与剪枝。
|
||||
69
docs/source/zh/community.md
Normal file
69
docs/source/zh/community.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,69 @@
|
||||
<!--⚠️请注意,此文件虽然是Markdown格式,但包含了我们文档构建器(类似于MDX)的特定语法,可能无法在你的Markdown查看器中正确显示。
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# 社区
|
||||
|
||||
这个页面汇集了社区开发的🤗Transformers相关的资源。
|
||||
|
||||
## 社区资源
|
||||
|
||||
| 资源 | 描述 | 作者 |
|
||||
|:----------|:-------------|------:|
|
||||
| [Hugging Face Transformers Glossary Flashcards](https://www.darigovresearch.com/huggingface-transformers-glossary-flashcards) | 这是一套基于 [Transformers文档术语表](glossary) 的抽认卡,它们已被整理成可以通过 [Anki](https://apps.ankiweb.net/) (一款专为长期知识保留而设计的开源、跨平台的应用)来进行学习和复习的形式。使用方法参见: [介绍如何使用抽认卡的视频](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Dji_h7PILrw)。 | [Darigov Research](https://www.darigovresearch.com/) |
|
||||
|
||||
## 社区笔记本
|
||||
|
||||
| 笔记本 | 描述 | 作者 | |
|
||||
|:----------|:-------------|:-------------|------:|
|
||||
| [Fine-tune a pre-trained Transformer to generate lyrics](https://github.com/AlekseyKorshuk/huggingartists) | 如何通过微调GPT-2模型来生成你最喜欢的艺术家风格的歌词 | [Aleksey Korshuk](https://github.com/AlekseyKorshuk) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/AlekseyKorshuk/huggingartists/blob/master/huggingartists-demo.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Train T5 in Tensorflow 2](https://github.com/snapthat/TF-T5-text-to-text) | 如何使用 Tensorflow 2 训练 T5 可以完成任何任务。本笔记本演示了如何使用 SQUAD 在 Tensorflow 2 中实现问答任务 | [Muhammad Harris](https://github.com/HarrisDePerceptron) |[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/snapthat/TF-T5-text-to-text/blob/master/snapthatT5/notebooks/TF-T5-Datasets%20Training.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Train T5 on TPU](https://github.com/patil-suraj/exploring-T5/blob/master/T5_on_TPU.ipynb) | 如何使用 Transformers 和 Nlp 在 SQUAD 上训练 T5 | [Suraj Patil](https://github.com/patil-suraj) |[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/patil-suraj/exploring-T5/blob/master/T5_on_TPU.ipynb#scrollTo=QLGiFCDqvuil) |
|
||||
| [Fine-tune T5 for Classification and Multiple Choice](https://github.com/patil-suraj/exploring-T5/blob/master/t5_fine_tuning.ipynb) | 如何使用 PyTorch Lightning 的text-to-text格式对 T5 进行微调以完成分类和多项选择任务 | [Suraj Patil](https://github.com/patil-suraj) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/patil-suraj/exploring-T5/blob/master/t5_fine_tuning.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Fine-tune DialoGPT on New Datasets and Languages](https://github.com/ncoop57/i-am-a-nerd/blob/master/_notebooks/2020-05-12-chatbot-part-1.ipynb) | 如何在新数据集上微调 DialoGPT 模型,以实现开放式对话聊天机器人 | [Nathan Cooper](https://github.com/ncoop57) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/ncoop57/i-am-a-nerd/blob/master/_notebooks/2020-05-12-chatbot-part-1.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Long Sequence Modeling with Reformer](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/PyTorch_Reformer.ipynb) | 如何使用 Reformer 对长达 500,000 个 token 的序列进行训练 | [Patrick von Platen](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/PyTorch_Reformer.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Fine-tune BART for Summarization](https://github.com/ohmeow/ohmeow_website/blob/master/posts/2021-05-25-mbart-sequence-classification-with-blurr.ipynb) | 如何使用 blurr 对 BART 进行微调,以便使用 fastai 进行汇总 | [Wayde Gilliam](https://ohmeow.com/) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/ohmeow/ohmeow_website/blob/master/posts/2021-05-25-mbart-sequence-classification-with-blurr.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Fine-tune a pre-trained Transformer on anyone's tweets](https://colab.research.google.com/github/borisdayma/huggingtweets/blob/master/huggingtweets-demo.ipynb) | 如何通过微调 GPT-2 模型生成以你最喜欢的 Twitter 帐户风格发布的推文 | [Boris Dayma](https://github.com/borisdayma) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/borisdayma/huggingtweets/blob/master/huggingtweets-demo.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Optimize 🤗 Hugging Face models with Weights & Biases](https://colab.research.google.com/github/wandb/examples/blob/master/colabs/huggingface/Optimize_Hugging_Face_models_with_Weights_%26_Biases.ipynb) | 展示 W&B 与 Hugging Face 集成的完整教程 | [Boris Dayma](https://github.com/borisdayma) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/wandb/examples/blob/master/colabs/huggingface/Optimize_Hugging_Face_models_with_Weights_%26_Biases.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Pretrain Longformer](https://github.com/allenai/longformer/blob/master/scripts/convert_model_to_long.ipynb) | 如何构建现有预训练模型的“长”版本 | [Iz Beltagy](https://beltagy.net) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/allenai/longformer/blob/master/scripts/convert_model_to_long.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Fine-tune Longformer for QA](https://github.com/patil-suraj/Notebooks/blob/master/longformer_qa_training.ipynb) | 如何针对问答任务微调长模型 | [Suraj Patil](https://github.com/patil-suraj) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/patil-suraj/Notebooks/blob/master/longformer_qa_training.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Evaluate Model with 🤗nlp](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/How_to_evaluate_Longformer_on_TriviaQA_using_NLP.ipynb) | 如何使用`nlp`库在TriviaQA数据集上评估Longformer模型| [Patrick von Platen](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1m7eTGlPmLRgoPkkA7rkhQdZ9ydpmsdLE?usp=sharing) |
|
||||
| [Fine-tune T5 for Sentiment Span Extraction](https://github.com/enzoampil/t5-intro/blob/master/t5_qa_training_pytorch_span_extraction.ipynb) | 如何使用PyTorch Lightning以text-to-text的格式对T5进行微调,以进行情感跨度提取 | [Lorenzo Ampil](https://github.com/enzoampil) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/enzoampil/t5-intro/blob/master/t5_qa_training_pytorch_span_extraction.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Fine-tune DistilBert for Multiclass Classification](https://github.com/abhimishra91/transformers-tutorials/blob/master/transformers_multiclass_classification.ipynb) | 如何使用 PyTorch 微调 DistilBert 进行多类分类 | [Abhishek Kumar Mishra](https://github.com/abhimishra91) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/abhimishra91/transformers-tutorials/blob/master/transformers_multiclass_classification.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Fine-tune BERT for Multi-label Classification](https://github.com/abhimishra91/transformers-tutorials/blob/master/transformers_multi_label_classification.ipynb)|如何使用 PyTorch 对 BERT 进行微调以进行多标签分类|[Abhishek Kumar Mishra](https://github.com/abhimishra91) |[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/abhimishra91/transformers-tutorials/blob/master/transformers_multi_label_classification.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Fine-tune T5 for Summarization](https://github.com/abhimishra91/transformers-tutorials/blob/master/transformers_summarization_wandb.ipynb)|如何在 PyTorch 中微调 T5 进行总结并使用 WandB 跟踪实验|[Abhishek Kumar Mishra](https://github.com/abhimishra91) |[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/abhimishra91/transformers-tutorials/blob/master/transformers_summarization_wandb.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Speed up Fine-Tuning in Transformers with Dynamic Padding / Bucketing](https://github.com/ELS-RD/transformers-notebook/blob/master/Divide_Hugging_Face_Transformers_training_time_by_2_or_more.ipynb)|如何通过使用动态填充/桶排序将微调速度提高两倍|[Michael Benesty](https://github.com/pommedeterresautee) |[](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1CBfRU1zbfu7-ijiOqAAQUA-RJaxfcJoO?usp=sharing)|
|
||||
|[Pretrain Reformer for Masked Language Modeling](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/Reformer_For_Masked_LM.ipynb)| 如何训练一个带有双向自注意力层的Reformer模型 | [Patrick von Platen](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1tzzh0i8PgDQGV3SMFUGxM7_gGae3K-uW?usp=sharing)|
|
||||
|[Expand and Fine Tune Sci-BERT](https://github.com/lordtt13/word-embeddings/blob/master/COVID-19%20Research%20Data/COVID-SciBERT.ipynb)| 如何在 CORD 数据集上增加 AllenAI 预训练的 SciBERT 模型的词汇量,并对其进行流水线化 | [Tanmay Thakur](https://github.com/lordtt13) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1rqAR40goxbAfez1xvF3hBJphSCsvXmh8)|
|
||||
|[Fine Tune BlenderBotSmall for Summarization using the Trainer API](https://github.com/lordtt13/transformers-experiments/blob/master/Custom%20Tasks/fine-tune-blenderbot_small-for-summarization.ipynb)| 如何使用Trainer API在自定义数据集上对BlenderBotSmall进行微调以进行文本摘要 | [Tanmay Thakur](https://github.com/lordtt13) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/19Wmupuls7mykSGyRN_Qo6lPQhgp56ymq?usp=sharing)|
|
||||
|[Fine-tune Electra and interpret with Integrated Gradients](https://github.com/elsanns/xai-nlp-notebooks/blob/master/electra_fine_tune_interpret_captum_ig.ipynb) | 如何对Electra模型进行微调以进行情感分析,并使用Captum集成梯度来解释预测结果 | [Eliza Szczechla](https://elsanns.github.io) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/elsanns/xai-nlp-notebooks/blob/master/electra_fine_tune_interpret_captum_ig.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[fine-tune a non-English GPT-2 Model with Trainer class](https://github.com/philschmid/fine-tune-GPT-2/blob/master/Fine_tune_a_non_English_GPT_2_Model_with_Huggingface.ipynb) | 如何使用 Trainer 类微调非英语 GPT-2 模型 | [Philipp Schmid](https://www.philschmid.de) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/philschmid/fine-tune-GPT-2/blob/master/Fine_tune_a_non_English_GPT_2_Model_with_Huggingface.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Fine-tune a DistilBERT Model for Multi Label Classification task](https://github.com/DhavalTaunk08/Transformers_scripts/blob/master/Transformers_multilabel_distilbert.ipynb) | 如何针对多标签分类任务微调 DistilBERT 模型 | [Dhaval Taunk](https://github.com/DhavalTaunk08) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/DhavalTaunk08/Transformers_scripts/blob/master/Transformers_multilabel_distilbert.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Fine-tune ALBERT for sentence-pair classification](https://github.com/NadirEM/nlp-notebooks/blob/master/Fine_tune_ALBERT_sentence_pair_classification.ipynb) | 如何针对句子对分类任务对 ALBERT 模型或其他基于 BERT 的模型进行微调 | [Nadir El Manouzi](https://github.com/NadirEM) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/NadirEM/nlp-notebooks/blob/master/Fine_tune_ALBERT_sentence_pair_classification.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Fine-tune Roberta for sentiment analysis](https://github.com/DhavalTaunk08/NLP_scripts/blob/master/sentiment_analysis_using_roberta.ipynb) | 如何微调 Roberta 模型进行情绪分析 | [Dhaval Taunk](https://github.com/DhavalTaunk08) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/DhavalTaunk08/NLP_scripts/blob/master/sentiment_analysis_using_roberta.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Evaluating Question Generation Models](https://github.com/flexudy-pipe/qugeev) | 你的 seq2seq 转换器模型生成的问题的答案有多准确? | [Pascal Zoleko](https://github.com/zolekode) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1bpsSqCQU-iw_5nNoRm_crPq6FRuJthq_?usp=sharing)|
|
||||
|[Classify text with DistilBERT and Tensorflow](https://github.com/peterbayerle/huggingface_notebook/blob/main/distilbert_tf.ipynb) | 如何在 TensorFlow 中微调 DistilBERT 以进行文本分类 | [Peter Bayerle](https://github.com/peterbayerle) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/peterbayerle/huggingface_notebook/blob/main/distilbert_tf.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Leverage BERT for Encoder-Decoder Summarization on CNN/Dailymail](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/BERT2BERT_for_CNN_Dailymail.ipynb) | 如何在CNN/Dailymail摘要任务上使用*google-bert/bert-base-uncased*检查点对*EncoderDecoderModel*进行热启动 | [Patrick von Platen](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/BERT2BERT_for_CNN_Dailymail.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Leverage RoBERTa for Encoder-Decoder Summarization on BBC XSum](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/RoBERTaShared_for_BBC_XSum.ipynb) | 如何在BBC/XSum摘要任务上使用*FacebookAI/roberta-base*检查点对共享的*EncoderDecoderModel*进行热启动 | [Patrick von Platen](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/RoBERTaShared_for_BBC_XSum.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Fine-tune TAPAS on Sequential Question Answering (SQA)](https://github.com/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/TAPAS/Fine_tuning_TapasForQuestionAnswering_on_SQA.ipynb) | 如何在Sequential Question Answering (SQA)数据集上使用*tapas-base*检查点对*TapasForQuestionAnswering*进行微调 | [Niels Rogge](https://github.com/nielsrogge) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/TAPAS/Fine_tuning_TapasForQuestionAnswering_on_SQA.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Evaluate TAPAS on Table Fact Checking (TabFact)](https://github.com/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/TAPAS/Evaluating_TAPAS_on_the_Tabfact_test_set.ipynb) | 如何结合使用 🤗 数据集和 🤗 transformers 库,使用*tapas-base-finetuned-tabfact*检查点评估经过微调的*TapasForSequenceClassification* | [Niels Rogge](https://github.com/nielsrogge) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/TAPAS/Evaluating_TAPAS_on_the_Tabfact_test_set.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Fine-tuning mBART for translation](https://colab.research.google.com/github/vasudevgupta7/huggingface-tutorials/blob/main/translation_training.ipynb) | 如何使用 Seq2SeqTrainer 对 mBART 进行微调以实现印地语到英语的翻译 | [Vasudev Gupta](https://github.com/vasudevgupta7) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/vasudevgupta7/huggingface-tutorials/blob/main/translation_training.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Fine-tune LayoutLM on FUNSD (a form understanding dataset)](https://github.com/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/LayoutLM/Fine_tuning_LayoutLMForTokenClassification_on_FUNSD.ipynb) | 如何在FUNSD数据集上对*LayoutLMForTokenClassification*进行微调以从扫描文档中提取信息 | [Niels Rogge](https://github.com/nielsrogge) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/LayoutLM/Fine_tuning_LayoutLMForTokenClassification_on_FUNSD.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Fine-Tune DistilGPT2 and Generate Text](https://colab.research.google.com/github/tripathiaakash/DistilGPT2-Tutorial/blob/main/distilgpt2_fine_tuning.ipynb) | 如何微调 DistilGPT2 并生成文本 | [Aakash Tripathi](https://github.com/tripathiaakash) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/tripathiaakash/DistilGPT2-Tutorial/blob/main/distilgpt2_fine_tuning.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Fine-Tune LED on up to 8K tokens](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/Fine_tune_Longformer_Encoder_Decoder_(LED)_for_Summarization_on_pubmed.ipynb) | 如何对LED模型在PubMed数据集上进行微调以进行长文本摘要 | [Patrick von Platen](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/Fine_tune_Longformer_Encoder_Decoder_(LED)_for_Summarization_on_pubmed.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Evaluate LED on Arxiv](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/LED_on_Arxiv.ipynb) | 如何有效评估LED模型的长远发展 | [Patrick von Platen](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/LED_on_Arxiv.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Fine-tune LayoutLM on RVL-CDIP (a document image classification dataset)](https://github.com/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/LayoutLM/Fine_tuning_LayoutLMForSequenceClassification_on_RVL_CDIP.ipynb) | 如何在 RVL-CDIP 数据集上微调*LayoutLMForSequenceClassification*以进行扫描文档分类 | [Niels Rogge](https://github.com/nielsrogge) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/LayoutLM/Fine_tuning_LayoutLMForSequenceClassification_on_RVL_CDIP.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Wav2Vec2 CTC decoding with GPT2 adjustment](https://github.com/voidful/huggingface_notebook/blob/main/xlsr_gpt.ipynb) | 如何通过语言模型调整解码 CTC 序列 | [Eric Lam](https://github.com/voidful) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1e_z5jQHYbO2YKEaUgzb1ww1WwiAyydAj?usp=sharing)|
|
||||
|[Fine-tune BART for summarization in two languages with Trainer class](https://github.com/elsanns/xai-nlp-notebooks/blob/master/fine_tune_bart_summarization_two_langs.ipynb) | 如何使用Trainer类对BART模型进行多语言摘要任务的微调 | [Eliza Szczechla](https://github.com/elsanns) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/elsanns/xai-nlp-notebooks/blob/master/fine_tune_bart_summarization_two_langs.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Evaluate Big Bird on Trivia QA](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/Evaluating_Big_Bird_on_TriviaQA.ipynb) | 评估BigBird模型在长文档问答任务上的性能,特别是在Trivia QA数据集上| [Patrick von Platen](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/Evaluating_Big_Bird_on_TriviaQA.ipynb)|
|
||||
| [Create video captions using Wav2Vec2](https://github.com/Muennighoff/ytclipcc/blob/main/wav2vec_youtube_captions.ipynb) | 如何使用Wav2Vec对任何视频的音频进行转录以创建YouTube字幕 | [Niklas Muennighoff](https://github.com/Muennighoff) |[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/Muennighoff/ytclipcc/blob/main/wav2vec_youtube_captions.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Fine-tune the Vision Transformer on CIFAR-10 using PyTorch Lightning](https://github.com/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/VisionTransformer/Fine_tuning_the_Vision_Transformer_on_CIFAR_10_with_PyTorch_Lightning.ipynb) | 如何使用HuggingFace的Transformers、Datasets和PyTorch Lightning在CIFAR-10数据集上对Vision Transformer(ViT)进行微调 | [Niels Rogge](https://github.com/nielsrogge) |[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/VisionTransformer/Fine_tuning_the_Vision_Transformer_on_CIFAR_10_with_PyTorch_Lightning.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Fine-tune the Vision Transformer on CIFAR-10 using the 🤗 Trainer](https://github.com/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/VisionTransformer/Fine_tuning_the_Vision_Transformer_on_CIFAR_10_with_the_%F0%9F%A4%97_Trainer.ipynb) | 如何使用HuggingFace的Transformers、Datasets和🤗 Trainer在CIFAR-10数据集上对Vision Transformer(ViT)进行微调| [Niels Rogge](https://github.com/nielsrogge) |[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/VisionTransformer/Fine_tuning_the_Vision_Transformer_on_CIFAR_10_with_the_%F0%9F%A4%97_Trainer.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Evaluate LUKE on Open Entity, an entity typing dataset](https://github.com/studio-ousia/luke/blob/master/notebooks/huggingface_open_entity.ipynb) | 如何在开放实体数据集上评估*LukeForEntityClassification*| [Ikuya Yamada](https://github.com/ikuyamada) |[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/studio-ousia/luke/blob/master/notebooks/huggingface_open_entity.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Evaluate LUKE on TACRED, a relation extraction dataset](https://github.com/studio-ousia/luke/blob/master/notebooks/huggingface_tacred.ipynb) | 如何在 TACRED 数据集上评估*LukeForEntityPairClassification* | [Ikuya Yamada](https://github.com/ikuyamada) |[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/studio-ousia/luke/blob/master/notebooks/huggingface_tacred.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Evaluate LUKE on CoNLL-2003, an important NER benchmark](https://github.com/studio-ousia/luke/blob/master/notebooks/huggingface_conll_2003.ipynb) | 如何在 CoNLL-2003 数据集上评估*LukeForEntitySpanClassification* | [Ikuya Yamada](https://github.com/ikuyamada) |[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/studio-ousia/luke/blob/master/notebooks/huggingface_conll_2003.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Evaluate BigBird-Pegasus on PubMed dataset](https://github.com/vasudevgupta7/bigbird/blob/main/notebooks/bigbird_pegasus_evaluation.ipynb) | 如何在 PubMed 数据集上评估*BigBirdPegasusForConditionalGeneration*| [Vasudev Gupta](https://github.com/vasudevgupta7) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/vasudevgupta7/bigbird/blob/main/notebooks/bigbird_pegasus_evaluation.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Speech Emotion Classification with Wav2Vec2](https://github.com/m3hrdadfi/soxan/blob/main/notebooks/Emotion_recognition_in_Greek_speech_using_Wav2Vec2.ipynb) |如何利用预训练的 Wav2Vec2 模型在 MEGA 数据集上进行情绪分类| [Mehrdad Farahani](https://github.com/m3hrdadfi) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/m3hrdadfi/soxan/blob/main/notebooks/Emotion_recognition_in_Greek_speech_using_Wav2Vec2.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Detect objects in an image with DETR](https://github.com/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/DETR/DETR_minimal_example_(with_DetrFeatureExtractor).ipynb) | 如何使用经过训练的*DetrForObjectDetection*模型检测图像中的物体并可视化注意力 | [Niels Rogge](https://github.com/NielsRogge) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/DETR/DETR_minimal_example_(with_DetrFeatureExtractor).ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Fine-tune DETR on a custom object detection dataset](https://github.com/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/DETR/Fine_tuning_DetrForObjectDetection_on_custom_dataset_(balloon).ipynb) | 如何在自定义对象检测数据集上微调*DetrForObjectDetection* | [Niels Rogge](https://github.com/NielsRogge) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/DETR/Fine_tuning_DetrForObjectDetection_on_custom_dataset_(balloon).ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Finetune T5 for Named Entity Recognition](https://github.com/ToluClassics/Notebooks/blob/main/T5_Ner_Finetuning.ipynb) | 如何在命名实体识别任务中微调*T5*| [Ogundepo Odunayo](https://github.com/ToluClassics) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1obr78FY_cBmWY5ODViCmzdY6O1KB65Vc?usp=sharing) |
|
||||
| [Fine-Tuning Open-Source LLM using QLoRA with MLflow and PEFT](https://github.com/mlflow/mlflow/blob/master/docs/source/llms/transformers/tutorials/fine-tuning/transformers-peft.ipynb) | 如何使用[QLoRA](https://github.com/artidoro/qlora) 和[PEFT](https://huggingface.co/docs/peft/en/index)以内存高效的方式微调大型语言模型(LLM),同时使用 [MLflow](https://mlflow.org/docs/latest/llms/transformers/index.html)进行实验跟踪| [Yuki Watanabe](https://github.com/B-Step62) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/mlflow/mlflow/blob/master/docs/source/llms/transformers/tutorials/fine-tuning/transformers-peft.ipynb) |
|
||||
@ -157,7 +157,7 @@ conda install conda-forge::transformers
|
||||
|
||||
预训练模型会被下载并本地缓存到 `~/.cache/huggingface/hub`。这是由环境变量 `TRANSFORMERS_CACHE` 指定的默认目录。在 Windows 上,默认目录为 `C:\Users\username\.cache\huggingface\hub`。你可以按照不同优先级改变下述环境变量,以指定不同的缓存目录。
|
||||
|
||||
1. 环境变量(默认): `HUGGINGFACE_HUB_CACHE` 或 `TRANSFORMERS_CACHE`。
|
||||
1. 环境变量(默认): `HF_HUB_CACHE` 或 `TRANSFORMERS_CACHE`。
|
||||
2. 环境变量 `HF_HOME`。
|
||||
3. 环境变量 `XDG_CACHE_HOME` + `/huggingface`。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
58
docs/source/zh/perf_train_special.md
Normal file
58
docs/source/zh/perf_train_special.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,58 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# 在 Apple Silicon 芯片上进行 PyTorch 训练
|
||||
|
||||
之前,在 Mac 上训练模型仅限于使用 CPU 训练。不过随着PyTorch v1.12的发布,您可以通过在 Apple Silicon 芯片的 GPU 上训练模型来显著提高性能和训练速度。这是通过将 Apple 的 Metal 性能着色器 (Metal Performance Shaders, MPS) 作为后端集成到PyTorch中实现的。[MPS后端](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/notes/mps.html) 将 PyTorch 操作视为自定义的 Metal 着色器来实现,并将对应模块部署到`mps`设备上。
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
某些 PyTorch 操作目前还未在 MPS 上实现,可能会抛出错误提示。可以通过设置环境变量`PYTORCH_ENABLE_MPS_FALLBACK=1`来使用CPU内核以避免这种情况发生(您仍然会看到一个`UserWarning`)。
|
||||
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
|
||||
如果您遇到任何其他错误,请在[PyTorch库](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues)中创建一个 issue,因为[`Trainer`]类中只集成了 MPS 后端.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
配置好`mps`设备后,您可以:
|
||||
|
||||
* 在本地训练更大的网络或更大的批量大小
|
||||
* 降低数据获取延迟,因为 GPU 的统一内存架构允许直接访问整个内存存储
|
||||
* 降低成本,因为您不需要再在云端 GPU 上训练或增加额外的本地 GPU
|
||||
|
||||
在确保已安装PyTorch后就可以开始使用了。 MPS 加速支持macOS 12.3及以上版本。
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install torch torchvision torchaudio
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[`TrainingArguments`]类默认使用`mps`设备(如果可用)因此无需显式设置设备。例如,您可以直接运行[run_glue.py](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/examples/pytorch/text-classification/run_glue.py)脚本,在无需进行任何修改的情况下自动启用 MPS 后端。
|
||||
|
||||
```diff
|
||||
export TASK_NAME=mrpc
|
||||
|
||||
python examples/pytorch/text-classification/run_glue.py \
|
||||
--model_name_or_path google-bert/bert-base-cased \
|
||||
--task_name $TASK_NAME \
|
||||
- --use_mps_device \
|
||||
--do_train \
|
||||
--do_eval \
|
||||
--max_seq_length 128 \
|
||||
--per_device_train_batch_size 32 \
|
||||
--learning_rate 2e-5 \
|
||||
--num_train_epochs 3 \
|
||||
--output_dir /tmp/$TASK_NAME/ \
|
||||
--overwrite_output_dir
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
用于[分布式设置](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/distributed.html#backends)的后端(如`gloo`和`nccl`)不支持`mps`设备,这也意味着使用 MPS 后端时只能在单个 GPU 上进行训练。
|
||||
|
||||
您可以在[Introducing Accelerated PyTorch Training on Mac](https://pytorch.org/blog/introducing-accelerated-pytorch-training-on-mac/)博客文章中了解有关 MPS 后端的更多信息。
|
||||
55
docs/source/zh/tiktoken.md
Normal file
55
docs/source/zh/tiktoken.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,55 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
``
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Transformers与Tiktonken的互操作性
|
||||
|
||||
在🤗 transformers中,当使用`from_pretrained`方法从Hub加载模型时,如果模型包含tiktoken格式的`tokenizer.model`文件,框架可以无缝支持tiktoken模型文件,并自动将其转换为我们的[快速词符化器](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/en/main_classes/tokenizer#transformers.PreTrainedTokenizerFast)。
|
||||
|
||||
### 已知包含`tiktoken.model`文件发布的模型:
|
||||
- gpt2
|
||||
- llama3
|
||||
|
||||
## 使用示例
|
||||
|
||||
为了在transformers中正确加载`tiktoken`文件,请确保`tiktoken.model`文件是tiktoken格式的,并且会在加载`from_pretrained`时自动加载。以下展示如何从同一个文件中加载词符化器(tokenizer)和模型:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import AutoTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
model_id = "meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3-8B-Instruct"
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_id, subfolder="original")
|
||||
```
|
||||
## 创建tiktoken词符化器(tokenizer)
|
||||
|
||||
`tokenizer.model`文件中不包含任何额外的词符(token)或模式字符串(pattern strings)的信息。如果这些信息很重要,需要将词符化器(tokenizer)转换为适用于[`PreTrainedTokenizerFast`]类的`tokenizer.json`格式。
|
||||
|
||||
使用[tiktoken.get_encoding](https://github.com/openai/tiktoken/blob/63527649963def8c759b0f91f2eb69a40934e468/tiktoken/registry.py#L63)生成`tokenizer.model`文件,再使用[`convert_tiktoken_to_fast`]函数将其转换为`tokenizer.json`文件。
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
|
||||
from transformers.integrations.tiktoken import convert_tiktoken_to_fast
|
||||
from tiktoken import get_encoding
|
||||
|
||||
# You can load your custom encoding or the one provided by OpenAI
|
||||
encoding = get_encoding("gpt2")
|
||||
convert_tiktoken_to_fast(encoding, "config/save/dir")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
生成的`tokenizer.json`文件将被保存到指定的目录,并且可以通过[`PreTrainedTokenizerFast`]类来加载。
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
tokenizer = PreTrainedTokenizerFast.from_pretrained("config/save/dir")
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -1,285 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Transformers Agents
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
`Transformers Agents`是一个实验性的随时可能发生变化的API。由于API或底层模型可能发生变化,`agents`返回的结果也会有所不同。
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Transformers版本`v4.29.0`基于`tools`和`agents`概念构建。您可以在[此Colab链接](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1c7MHD-T1forUPGcC_jlwsIptOzpG3hSj)中进行测试。
|
||||
|
||||
简而言之,它在`Transformers`之上提供了一个自然语言API:我们定义了一组经过筛选的`tools`,并设计了一个`agents`来解读自然语言并使用这些工具。它具有很强的可扩展性;我们筛选了一些相关的`tools`,但我们将向您展示如何通过社区开发的`tool`轻松地扩展系统。
|
||||
|
||||
让我们从一些可以通过这个新API实现的示例开始。在处理多模态任务时它尤其强大,因此让我们快速试着生成图像并大声朗读文本。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
agent.run("Caption the following image", image=image)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
| **输入** | **输出** |
|
||||
|-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|-----------------------------------|
|
||||
| <img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/beaver.png" width=200> | A beaver is swimming in the water |
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
agent.run("Read the following text out loud", text=text)
|
||||
```
|
||||
| **输入** | **输出** |
|
||||
|-----------------------------------|----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| A beaver is swimming in the water | <audio controls><source src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/tts_example.wav" type="audio/wav"> your browser does not support the audio element. </audio>
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
agent.run(
|
||||
"In the following `document`, where will the TRRF Scientific Advisory Council Meeting take place?",
|
||||
document=document,
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
| **输入** | **输出** |
|
||||
|-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|----------------|
|
||||
| <img src="https://datasets-server.huggingface.co/assets/hf-internal-testing/example-documents/--/hf-internal-testing--example-documents/test/0/image/image.jpg" width=200> | ballroom foyer |
|
||||
|
||||
## 快速入门
|
||||
|
||||
要使用 `agent.run`,您需要实例化一个`agent`,它是一个大型语言模型(LLM)。我们支持OpenAI模型以及来自BigCode和OpenAssistant的开源替代方案。OpenAI模型性能更好(但需要您拥有OpenAI API密钥,因此无法免费使用),Hugging Face为BigCode和OpenAssistant模型提供了免费访问端点。
|
||||
|
||||
一开始请安装`agents`附加模块,以安装所有默认依赖项。
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install transformers[agents]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
要使用OpenAI模型,您可以在安装`openai`依赖项后实例化一个`OpenAiAgent`:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install openai
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import OpenAiAgent
|
||||
|
||||
agent = OpenAiAgent(model="text-davinci-003", api_key="<your_api_key>")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
要使用BigCode或OpenAssistant,请首先登录以访问Inference API:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from huggingface_hub import login
|
||||
|
||||
login("<YOUR_TOKEN>")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
然后,实例化`agent`:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import HfAgent
|
||||
|
||||
# Starcoder
|
||||
agent = HfAgent("https://api-inference.huggingface.co/models/bigcode/starcoder")
|
||||
# StarcoderBase
|
||||
# agent = HfAgent("https://api-inference.huggingface.co/models/bigcode/starcoderbase")
|
||||
# OpenAssistant
|
||||
# agent = HfAgent(url_endpoint="https://api-inference.huggingface.co/models/OpenAssistant/oasst-sft-4-pythia-12b-epoch-3.5")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
此示例使用了目前Hugging Face免费提供的推理API。如果你有自己的推理端点用于此模型(或其他模型),你可以用你的URL替换上面的URL。
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
StarCoder和OpenAssistant可以免费使用,并且在简单任务上表现出色。然而,当处理更复杂的提示时就不再有效。如果你遇到这样的问题,我们建议尝试使用OpenAI模型,尽管遗憾的是它不是开源的,但它在目前情况下表现更好。
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
现在,您已经可以开始使用了!让我们深入了解您现在可以使用的两个API。
|
||||
|
||||
### 单次执行(run)
|
||||
|
||||
单次执行方法是使用`agent`的 `~Agent.run`:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
agent.run("Draw me a picture of rivers and lakes.")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/rivers_and_lakes.png" width=200>
|
||||
|
||||
它会自动选择适合您要执行的任务的`tool`(或`tools`),并以适当的方式运行它们。它可以在同一指令中执行一个或多个任务(尽管您的指令越复杂,`agent`失败的可能性就越大)。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
agent.run("Draw me a picture of the sea then transform the picture to add an island")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/sea_and_island.png" width=200>
|
||||
|
||||
<br/>
|
||||
|
||||
每个 [`~Agent.run`] 操作都是独立的,因此您可以多次连续运行 [`~Agent.run`]并执行不同的任务。
|
||||
|
||||
请注意,您的 `agent` 只是一个大型语言模型,因此您略有变化的提示可能会产生完全不同的结果。重要的是尽可能清晰地解释您要执行的任务。我们在[这里](../en/custom_tools#writing-good-user-inputs)更深入地讨论了如何编写良好的提示。
|
||||
|
||||
如果您想在多次执行之间保持同一状态或向`agent`传递非文本对象,可以通过指定`agent`要使用的变量来实现。例如,您可以生成有关河流和湖泊的第一幅图像,并要求模型通过执行以下操作向该图片添加一个岛屿:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
picture = agent.run("Generate a picture of rivers and lakes.")
|
||||
updated_picture = agent.run("Transform the image in `picture` to add an island to it.", picture=picture)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
当模型无法理解您的请求和库中的工具时,这可能会有所帮助。例如:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
agent.run("Draw me the picture of a capybara swimming in the sea")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
在这种情况下,模型可以以两种方式理解您的请求:
|
||||
- 使用`text-to-image` 生成在大海中游泳的大水獭
|
||||
- 或者,使用`text-to-image`生成大水獭,然后使用`image-transformation`工具使其在大海中游泳
|
||||
|
||||
如果您想强制使用第一种情景,可以通过将提示作为参数传递给它来实现:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
agent.run("Draw me a picture of the `prompt`", prompt="a capybara swimming in the sea")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 基于交流的执行 (chat)
|
||||
|
||||
基于交流的执行(chat)方式是使用 [`~Agent.chat`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
agent.chat("Generate a picture of rivers and lakes")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/rivers_and_lakes.png" width=200>
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
agent.chat("Transform the picture so that there is a rock in there")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/rivers_and_lakes_and_beaver.png" width=200>
|
||||
|
||||
<br/>
|
||||
|
||||
当您希望在不同指令之间保持同一状态时,这会是一个有趣的方法。它更适合用于单个指令,而不是复杂的多步指令(`~Agent.run` 方法更适合处理这种情况)。
|
||||
|
||||
这种方法也可以接受参数,以便您可以传递非文本类型或特定提示。
|
||||
|
||||
### ⚠️ 远程执行
|
||||
|
||||
出于演示目的以便适用于所有设置,我们为发布版本的少数默认工具创建了远程执行器。这些工具是使用推理终端(inference endpoints)创建的。
|
||||
|
||||
目前我们已将其关闭,但为了了解如何自行设置远程执行器工具,我们建议阅读[自定义工具指南](./custom_tools)。
|
||||
|
||||
### 这里发生了什么?什么是`tools`,什么是`agents`?
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/diagram.png">
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Agents
|
||||
|
||||
这里的`Agents`是一个大型语言模型,我们通过提示它以访问特定的工具集。
|
||||
|
||||
大型语言模型在生成小代码示例方面表现出色,因此这个API利用这一特点,通过提示LLM生成一个使用`tools`集合的小代码示例。然后,根据您给`Agents`的任务和`tools`的描述来完成此提示。这种方式让它能够访问工具的文档,特别是它们的期望输入和输出,以生成相关的代码。
|
||||
|
||||
#### Tools
|
||||
|
||||
`Tools`非常简单:它们是有名称和描述的单个函数。然后,我们使用这些`tools`的描述来提示代理。通过提示,我们向`agent`展示如何使用`tool`来执行查询语言中请求的操作。
|
||||
|
||||
这是使用全新`tools`而不是`pipelines`,因为`agent`编写的代码更好,具有非常原子化的`tools`。`pipelines`经常被重构,并且通常将多个任务合并为一个。`tools`旨在专注于一个非常简单的任务。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 代码执行?
|
||||
|
||||
然后,这段代码基于`tools`的输入被我们的小型Python解释器执行。我们听到你在后面大声呼喊“任意代码执行!”,但让我们解释为什么情况并非如此。
|
||||
|
||||
只能您提供的`tools`和打印函数可以被执行,因此您已经受到了执行的限制。如果仅限于 Hugging Face 工具,那么您应该是安全的。
|
||||
|
||||
然后,我们不允许任何属性查找或导入(无论如何都不需要将输入/输出传递给一小组函数),因此所有最明显的攻击(并且您需要提示LLM无论如何输出它们)不应该是一个问题。如果你想超级安全,你可以使用附加参数 return_code=True 执行 run() 方法,在这种情况下,`agent`将只返回要执行的代码,你可以决定是否执行。
|
||||
|
||||
如果`agent`生成的代码存在任何尝试执行非法操作的行为,或者代码中出现了常规Python错误,执行将停止。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 一组经过精心筛选的`tools`
|
||||
|
||||
我们确定了一组可以赋予这些`agent`强大能力的`tools`。以下是我们在`transformers`中集成的`tools`的更新列表:
|
||||
|
||||
- **文档问答**:给定一个图像格式的文档(例如PDF),回答该文档上的问题([Donut](../en/model_doc/donut))
|
||||
- **文本问答**:给定一段长文本和一个问题,回答文本中的问题([Flan-T5](../en/model_doc/flan-t5))
|
||||
- **无条件图像字幕**:为图像添加字幕!([BLIP](../en/model_doc/blip))
|
||||
- **图像问答**:给定一张图像,回答该图像上的问题([VILT](../en/model_doc/vilt))
|
||||
- **图像分割**:给定一张图像和一个提示,输出该提示的分割掩模([CLIPSeg](../en/model_doc/clipseg))
|
||||
- **语音转文本**:给定一个人说话的音频录音,将演讲内容转录为文本([Whisper](../en/model_doc/whisper))
|
||||
- **文本转语音**:将文本转换为语音([SpeechT5](../en/model_doc/speecht5))
|
||||
- **Zero-Shot文本分类**:给定一个文本和一个标签列表,确定文本最符合哪个标签([BART](../en/model_doc/bart))
|
||||
- **文本摘要**:总结长文本为一两句话([BART](../en/model_doc/bart))
|
||||
- **翻译**:将文本翻译为指定语言([NLLB](../en/model_doc/nllb))
|
||||
|
||||
这些`tools`已在transformers中集成,并且也可以手动使用,例如:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import load_tool
|
||||
|
||||
tool = load_tool("text-to-speech")
|
||||
audio = tool("This is a text to speech tool")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### 自定义工具
|
||||
|
||||
尽管我们确定了一组经过筛选的`tools`,但我们坚信,此实现提供的主要价值在于能够快速创建和共享自定义`tool`。
|
||||
|
||||
通过将工具的代码上传到Hugging Face空间或模型repository,您可以直接通过`agent`使用`tools`。我们已经添加了一些**与transformers无关**的`tools`到[`huggingface-tools`组织](https://huggingface.co/huggingface-tools)中:
|
||||
|
||||
- **文本下载器**:从Web URL下载文本
|
||||
- **文本到图像**:根据提示生成图像,利用`stable diffusion`
|
||||
- **图像转换**:根据初始图像和提示修改图像,利用`instruct pix2pix stable diffusion`
|
||||
- **文本到视频**:根据提示生成小视频,利用`damo-vilab`
|
||||
|
||||
从一开始就一直在使用的文本到图像`tool`是一个远程`tool `,位于[*huggingface-tools/text-to-image*](https://huggingface.co/spaces/huggingface-tools/text-to-image)!我们将继续在此组织和其他组织上发布此类`tool`,以进一步增强此实现。
|
||||
|
||||
`agents`默认可以访问存储在[`huggingface-tools`](https://huggingface.co/huggingface-tools)上的`tools`。我们将在后续指南中解释如何编写和共享自定义`tools`,以及如何利用Hub上存在的任何自定义`tools`。
|
||||
|
||||
### 代码生成
|
||||
|
||||
到目前为止,我们已经展示了如何使用`agents`来为您执行操作。但是,`agents`仅使用非常受限Python解释器执行的代码。如果您希望在不同的环境中使用生成的代码,可以提示`agents`返回代码,以及`tools`的定义和准确的导入信息。
|
||||
|
||||
例如,以下指令
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
agent.run("Draw me a picture of rivers and lakes", return_code=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
返回以下代码
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import load_tool
|
||||
|
||||
image_generator = load_tool("huggingface-tools/text-to-image")
|
||||
|
||||
image = image_generator(prompt="rivers and lakes")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
然后你就可以调整并执行代码
|
||||
@ -61,7 +61,7 @@ from transformers.utils import check_min_version, send_example_telemetry
|
||||
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
|
||||
|
||||
# Will error if the minimal version of Transformers is not installed. Remove at your own risks.
|
||||
check_min_version("4.47.0.dev0")
|
||||
check_min_version("4.48.0.dev0")
|
||||
|
||||
Array = Any
|
||||
Dataset = datasets.arrow_dataset.Dataset
|
||||
|
||||
@ -60,7 +60,7 @@ from transformers.utils.versions import require_version
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Will error if the minimal version of Transformers is not installed. Remove at your own risk.
|
||||
check_min_version("4.47.0.dev0")
|
||||
check_min_version("4.48.0.dev0")
|
||||
|
||||
require_version("datasets>=2.14.0", "To fix: pip install -r examples/flax/speech-recognition/requirements.txt")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -56,7 +56,7 @@ from transformers.utils import check_min_version, send_example_telemetry
|
||||
|
||||
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
|
||||
# Will error if the minimal version of Transformers is not installed. Remove at your own risks.
|
||||
check_min_version("4.47.0.dev0")
|
||||
check_min_version("4.48.0.dev0")
|
||||
|
||||
Array = Any
|
||||
Dataset = datasets.arrow_dataset.Dataset
|
||||
|
||||
@ -57,7 +57,7 @@ from transformers.utils.versions import require_version
|
||||
|
||||
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
|
||||
# Will error if the minimal version of Transformers is not installed. Remove at your own risks.
|
||||
check_min_version("4.47.0.dev0")
|
||||
check_min_version("4.48.0.dev0")
|
||||
|
||||
require_version("datasets>=1.8.0", "To fix: pip install -r examples/pytorch/token-classification/requirements.txt")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,287 @@
|
||||
# 🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨
|
||||
# This file was automatically generated from examples/modular-transformers/modular_new_imgproc_model.py.
|
||||
# Do NOT edit this file manually as any edits will be overwritten by the generation of
|
||||
# the file from the modular. If any change should be done, please apply the change to the
|
||||
# modular_new_imgproc_model.py file directly. One of our CI enforces this.
|
||||
# 🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨
|
||||
from typing import Dict, List, Optional, Union
|
||||
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
from ...image_processing_utils import BaseImageProcessor, BatchFeature, get_size_dict
|
||||
from ...image_transforms import convert_to_rgb, resize, to_channel_dimension_format
|
||||
from ...image_utils import (
|
||||
OPENAI_CLIP_MEAN,
|
||||
OPENAI_CLIP_STD,
|
||||
ChannelDimension,
|
||||
ImageInput,
|
||||
PILImageResampling,
|
||||
infer_channel_dimension_format,
|
||||
is_scaled_image,
|
||||
make_list_of_images,
|
||||
to_numpy_array,
|
||||
valid_images,
|
||||
validate_preprocess_arguments,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from ...utils import TensorType, filter_out_non_signature_kwargs, is_vision_available, logging
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if is_vision_available():
|
||||
import PIL
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
logger = logging.get_logger(__name__)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class ImgprocModelImageProcessor(BaseImageProcessor):
|
||||
r"""
|
||||
Constructs a IMGPROC_MODEL image processor.
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
do_resize (`bool`, *optional*, defaults to `True`):
|
||||
Whether to resize the image's (height, width) dimensions to the specified `size`. Can be overridden by the
|
||||
`do_resize` parameter in the `preprocess` method.
|
||||
size (`dict`, *optional*, defaults to `{"height": 384, "width": 384}`):
|
||||
Size of the output image after resizing. Can be overridden by the `size` parameter in the `preprocess`
|
||||
method.
|
||||
resample (`PILImageResampling`, *optional*, defaults to `Resampling.BICUBIC`):
|
||||
Resampling filter to use if resizing the image. Only has an effect if `do_resize` is set to `True`. Can be
|
||||
overridden by the `resample` parameter in the `preprocess` method.
|
||||
do_rescale (`bool`, *optional*, defaults to `True`):
|
||||
Whether to rescale the image by the specified scale `rescale_factor`. Can be overridden by the
|
||||
`do_rescale` parameter in the `preprocess` method.
|
||||
rescale_factor (`int` or `float`, *optional*, defaults to `1/255`):
|
||||
Scale factor to use if rescaling the image. Only has an effect if `do_rescale` is set to `True`. Can be
|
||||
overridden by the `rescale_factor` parameter in the `preprocess` method.
|
||||
do_normalize (`bool`, *optional*, defaults to `True`):
|
||||
Whether to normalize the image. Can be overridden by the `do_normalize` parameter in the `preprocess`
|
||||
method. Can be overridden by the `do_normalize` parameter in the `preprocess` method.
|
||||
image_mean (`float` or `List[float]`, *optional*, defaults to `IMAGENET_STANDARD_MEAN`):
|
||||
Mean to use if normalizing the image. This is a float or list of floats the length of the number of
|
||||
channels in the image. Can be overridden by the `image_mean` parameter in the `preprocess` method. Can be
|
||||
overridden by the `image_mean` parameter in the `preprocess` method.
|
||||
image_std (`float` or `List[float]`, *optional*, defaults to `IMAGENET_STANDARD_STD`):
|
||||
Standard deviation to use if normalizing the image. This is a float or list of floats the length of the
|
||||
number of channels in the image. Can be overridden by the `image_std` parameter in the `preprocess` method.
|
||||
Can be overridden by the `image_std` parameter in the `preprocess` method.
|
||||
do_convert_rgb (`bool`, *optional*, defaults to `True`):
|
||||
Whether to convert the image to RGB.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
model_input_names = ["pixel_values"]
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
do_resize: bool = True,
|
||||
size: Dict[str, int] = None,
|
||||
resample: PILImageResampling = PILImageResampling.BICUBIC,
|
||||
do_rescale: bool = True,
|
||||
rescale_factor: Union[int, float] = 1 / 255,
|
||||
do_normalize: bool = True,
|
||||
image_mean: Optional[Union[float, List[float]]] = None,
|
||||
image_std: Optional[Union[float, List[float]]] = None,
|
||||
do_convert_rgb: bool = True,
|
||||
**kwargs,
|
||||
) -> None:
|
||||
super().__init__(**kwargs)
|
||||
size = size if size is not None else {"height": 384, "width": 384}
|
||||
size = get_size_dict(size, default_to_square=True)
|
||||
|
||||
self.do_resize = do_resize
|
||||
self.size = size
|
||||
self.resample = resample
|
||||
self.do_rescale = do_rescale
|
||||
self.rescale_factor = rescale_factor
|
||||
self.do_normalize = do_normalize
|
||||
self.image_mean = image_mean if image_mean is not None else OPENAI_CLIP_MEAN
|
||||
self.image_std = image_std if image_std is not None else OPENAI_CLIP_STD
|
||||
self.do_convert_rgb = do_convert_rgb
|
||||
|
||||
def resize(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
image: np.ndarray,
|
||||
size: Dict[str, int],
|
||||
resample: PILImageResampling = PILImageResampling.BICUBIC,
|
||||
data_format: Optional[Union[str, ChannelDimension]] = None,
|
||||
input_data_format: Optional[Union[str, ChannelDimension]] = None,
|
||||
**kwargs,
|
||||
) -> np.ndarray:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Resize an image to `(size["height"], size["width"])`.
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
image (`np.ndarray`):
|
||||
Image to resize.
|
||||
size (`Dict[str, int]`):
|
||||
Dictionary in the format `{"height": int, "width": int}` specifying the size of the output image.
|
||||
resample (`PILImageResampling`, *optional*, defaults to `PILImageResampling.BICUBIC`):
|
||||
`PILImageResampling` filter to use when resizing the image e.g. `PILImageResampling.BICUBIC`.
|
||||
data_format (`ChannelDimension` or `str`, *optional*):
|
||||
The channel dimension format for the output image. If unset, the channel dimension format of the input
|
||||
image is used. Can be one of:
|
||||
- `"channels_first"` or `ChannelDimension.FIRST`: image in (num_channels, height, width) format.
|
||||
- `"channels_last"` or `ChannelDimension.LAST`: image in (height, width, num_channels) format.
|
||||
- `"none"` or `ChannelDimension.NONE`: image in (height, width) format.
|
||||
input_data_format (`ChannelDimension` or `str`, *optional*):
|
||||
The channel dimension format for the input image. If unset, the channel dimension format is inferred
|
||||
from the input image. Can be one of:
|
||||
- `"channels_first"` or `ChannelDimension.FIRST`: image in (num_channels, height, width) format.
|
||||
- `"channels_last"` or `ChannelDimension.LAST`: image in (height, width, num_channels) format.
|
||||
- `"none"` or `ChannelDimension.NONE`: image in (height, width) format.
|
||||
|
||||
Returns:
|
||||
`np.ndarray`: The resized image.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
size = get_size_dict(size)
|
||||
if "height" not in size or "width" not in size:
|
||||
raise ValueError(f"The `size` dictionary must contain the keys `height` and `width`. Got {size.keys()}")
|
||||
output_size = (size["height"], size["width"])
|
||||
return resize(
|
||||
image,
|
||||
size=output_size,
|
||||
resample=resample,
|
||||
data_format=data_format,
|
||||
input_data_format=input_data_format,
|
||||
**kwargs,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@filter_out_non_signature_kwargs()
|
||||
def preprocess(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
images: ImageInput,
|
||||
do_resize: Optional[bool] = None,
|
||||
size: Optional[Dict[str, int]] = None,
|
||||
resample: PILImageResampling = None,
|
||||
do_rescale: Optional[bool] = None,
|
||||
rescale_factor: Optional[float] = None,
|
||||
do_normalize: Optional[bool] = None,
|
||||
image_mean: Optional[Union[float, List[float]]] = None,
|
||||
image_std: Optional[Union[float, List[float]]] = None,
|
||||
return_tensors: Optional[Union[str, TensorType]] = None,
|
||||
do_convert_rgb: bool = None,
|
||||
data_format: ChannelDimension = ChannelDimension.FIRST,
|
||||
input_data_format: Optional[Union[str, ChannelDimension]] = None,
|
||||
) -> PIL.Image.Image:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Preprocess an image or batch of images.
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
images (`ImageInput`):
|
||||
Image to preprocess. Expects a single or batch of images with pixel values ranging from 0 to 255. If
|
||||
passing in images with pixel values between 0 and 1, set `do_rescale=False`.
|
||||
do_resize (`bool`, *optional*, defaults to `self.do_resize`):
|
||||
Whether to resize the image.
|
||||
size (`Dict[str, int]`, *optional*, defaults to `self.size`):
|
||||
Controls the size of the image after `resize`. The shortest edge of the image is resized to
|
||||
`size["shortest_edge"]` whilst preserving the aspect ratio. If the longest edge of this resized image
|
||||
is > `int(size["shortest_edge"] * (1333 / 800))`, then the image is resized again to make the longest
|
||||
edge equal to `int(size["shortest_edge"] * (1333 / 800))`.
|
||||
resample (`PILImageResampling`, *optional*, defaults to `self.resample`):
|
||||
Resampling filter to use if resizing the image. Only has an effect if `do_resize` is set to `True`.
|
||||
do_rescale (`bool`, *optional*, defaults to `self.do_rescale`):
|
||||
Whether to rescale the image values between [0 - 1].
|
||||
rescale_factor (`float`, *optional*, defaults to `self.rescale_factor`):
|
||||
Rescale factor to rescale the image by if `do_rescale` is set to `True`.
|
||||
do_normalize (`bool`, *optional*, defaults to `self.do_normalize`):
|
||||
Whether to normalize the image.
|
||||
image_mean (`float` or `List[float]`, *optional*, defaults to `self.image_mean`):
|
||||
Image mean to normalize the image by if `do_normalize` is set to `True`.
|
||||
image_std (`float` or `List[float]`, *optional*, defaults to `self.image_std`):
|
||||
Image standard deviation to normalize the image by if `do_normalize` is set to `True`.
|
||||
do_convert_rgb (`bool`, *optional*, defaults to `self.do_convert_rgb`):
|
||||
Whether to convert the image to RGB.
|
||||
return_tensors (`str` or `TensorType`, *optional*):
|
||||
The type of tensors to return. Can be one of:
|
||||
- Unset: Return a list of `np.ndarray`.
|
||||
- `TensorType.TENSORFLOW` or `'tf'`: Return a batch of type `tf.Tensor`.
|
||||
- `TensorType.PYTORCH` or `'pt'`: Return a batch of type `torch.Tensor`.
|
||||
- `TensorType.NUMPY` or `'np'`: Return a batch of type `np.ndarray`.
|
||||
- `TensorType.JAX` or `'jax'`: Return a batch of type `jax.numpy.ndarray`.
|
||||
data_format (`ChannelDimension` or `str`, *optional*, defaults to `ChannelDimension.FIRST`):
|
||||
The channel dimension format for the output image. Can be one of:
|
||||
- `"channels_first"` or `ChannelDimension.FIRST`: image in (num_channels, height, width) format.
|
||||
- `"channels_last"` or `ChannelDimension.LAST`: image in (height, width, num_channels) format.
|
||||
- Unset: Use the channel dimension format of the input image.
|
||||
input_data_format (`ChannelDimension` or `str`, *optional*):
|
||||
The channel dimension format for the input image. If unset, the channel dimension format is inferred
|
||||
from the input image. Can be one of:
|
||||
- `"channels_first"` or `ChannelDimension.FIRST`: image in (num_channels, height, width) format.
|
||||
- `"channels_last"` or `ChannelDimension.LAST`: image in (height, width, num_channels) format.
|
||||
- `"none"` or `ChannelDimension.NONE`: image in (height, width) format.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
do_resize = do_resize if do_resize is not None else self.do_resize
|
||||
resample = resample if resample is not None else self.resample
|
||||
do_rescale = do_rescale if do_rescale is not None else self.do_rescale
|
||||
rescale_factor = rescale_factor if rescale_factor is not None else self.rescale_factor
|
||||
do_normalize = do_normalize if do_normalize is not None else self.do_normalize
|
||||
image_mean = image_mean if image_mean is not None else self.image_mean
|
||||
image_std = image_std if image_std is not None else self.image_std
|
||||
do_convert_rgb = do_convert_rgb if do_convert_rgb is not None else self.do_convert_rgb
|
||||
|
||||
size = size if size is not None else self.size
|
||||
size = get_size_dict(size, default_to_square=False)
|
||||
|
||||
images = make_list_of_images(images)
|
||||
|
||||
if not valid_images(images):
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
"Invalid image type. Must be of type PIL.Image.Image, numpy.ndarray, "
|
||||
"torch.Tensor, tf.Tensor or jax.ndarray."
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
validate_preprocess_arguments(
|
||||
do_rescale=do_rescale,
|
||||
rescale_factor=rescale_factor,
|
||||
do_normalize=do_normalize,
|
||||
image_mean=image_mean,
|
||||
image_std=image_std,
|
||||
do_resize=do_resize,
|
||||
size=size,
|
||||
resample=resample,
|
||||
)
|
||||
# PIL RGBA images are converted to RGB
|
||||
if do_convert_rgb:
|
||||
images = [convert_to_rgb(image) for image in images]
|
||||
|
||||
# All transformations expect numpy arrays.
|
||||
images = [to_numpy_array(image) for image in images]
|
||||
|
||||
if is_scaled_image(images[0]) and do_rescale:
|
||||
logger.warning_once(
|
||||
"It looks like you are trying to rescale already rescaled images. If the input"
|
||||
" images have pixel values between 0 and 1, set `do_rescale=False` to avoid rescaling them again."
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if input_data_format is None:
|
||||
# We assume that all images have the same channel dimension format.
|
||||
input_data_format = infer_channel_dimension_format(images[0])
|
||||
|
||||
if do_resize:
|
||||
images = [
|
||||
self.resize(image=image, size=size, resample=resample, input_data_format=input_data_format)
|
||||
for image in images
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
if do_rescale:
|
||||
images = [
|
||||
self.rescale(image=image, scale=rescale_factor, input_data_format=input_data_format)
|
||||
for image in images
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
if do_normalize:
|
||||
images = [
|
||||
self.normalize(image=image, mean=image_mean, std=image_std, input_data_format=input_data_format)
|
||||
for image in images
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
images = [
|
||||
to_channel_dimension_format(image, data_format, input_channel_dim=input_data_format) for image in images
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
encoded_outputs = BatchFeature(data={"pixel_values": images}, tensor_type=return_tensors)
|
||||
|
||||
return encoded_outputs
|
||||
|
||||
def new_image_processing_method(self, pixel_values: torch.FloatTensor):
|
||||
return pixel_values / 2
|
||||
@ -228,9 +228,6 @@ class DummyAttention(nn.Module):
|
||||
self.v_proj = nn.Linear(self.hidden_size, self.num_key_value_heads * self.head_dim, bias=config.attention_bias)
|
||||
self.o_proj = nn.Linear(self.num_heads * self.head_dim, self.hidden_size, bias=config.attention_bias)
|
||||
|
||||
# TODO (joao): remove in v4.46 (RoPE is computed in the model, not in the decoder layers)
|
||||
self.rotary_emb = DummyRotaryEmbedding(config=self.config)
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
hidden_states: torch.Tensor,
|
||||
@ -240,7 +237,7 @@ class DummyAttention(nn.Module):
|
||||
output_attentions: bool = False,
|
||||
use_cache: bool = False,
|
||||
cache_position: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
|
||||
position_embeddings: Optional[Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]] = None, # will become mandatory in v4.46
|
||||
position_embeddings: Optional[Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]] = None, # necessary, but kept here for BC
|
||||
**kwargs,
|
||||
) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor, Optional[torch.Tensor], Optional[Tuple[torch.Tensor]]]:
|
||||
bsz, q_len, _ = hidden_states.size()
|
||||
@ -254,16 +251,7 @@ class DummyAttention(nn.Module):
|
||||
key_states = key_states.view(bsz, q_len, -1, self.head_dim).transpose(1, 2)
|
||||
value_states = value_states.view(bsz, q_len, -1, self.head_dim).transpose(1, 2)
|
||||
|
||||
if position_embeddings is None:
|
||||
logger.warning_once(
|
||||
"The attention layers in this model are transitioning from computing the RoPE embeddings internally "
|
||||
"through `position_ids` (2D tensor with the indexes of the tokens), to using externally computed "
|
||||
"`position_embeddings` (Tuple of tensors, containing cos and sin). In v4.46 `position_ids` will be "
|
||||
"removed and `position_embeddings` will be mandatory."
|
||||
)
|
||||
cos, sin = self.rotary_emb(value_states, position_ids)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
cos, sin = position_embeddings
|
||||
cos, sin = position_embeddings
|
||||
query_states, key_states = apply_rotary_pos_emb(query_states, key_states, cos, sin)
|
||||
|
||||
if past_key_value is not None:
|
||||
@ -326,7 +314,7 @@ class DummyFlashAttention2(DummyAttention):
|
||||
output_attentions: bool = False,
|
||||
use_cache: bool = False,
|
||||
cache_position: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
|
||||
position_embeddings: Optional[Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]] = None, # will become mandatory in v4.46
|
||||
position_embeddings: Optional[Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]] = None, # necessary, but kept here for BC
|
||||
**kwargs: Unpack[FlashAttentionKwargs],
|
||||
) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor, Optional[torch.Tensor], Optional[Tuple[torch.Tensor]]]:
|
||||
if isinstance(past_key_value, StaticCache):
|
||||
@ -350,16 +338,7 @@ class DummyFlashAttention2(DummyAttention):
|
||||
key_states = key_states.view(bsz, q_len, self.num_key_value_heads, self.head_dim).transpose(1, 2)
|
||||
value_states = value_states.view(bsz, q_len, self.num_key_value_heads, self.head_dim).transpose(1, 2)
|
||||
|
||||
if position_embeddings is None:
|
||||
logger.warning_once(
|
||||
"The attention layers in this model are transitioning from computing the RoPE embeddings internally "
|
||||
"through `position_ids` (2D tensor with the indexes of the tokens), to using externally computed "
|
||||
"`position_embeddings` (Tuple of tensors, containing cos and sin). In v4.46 `position_ids` will be "
|
||||
"removed and `position_embeddings` will be mandatory."
|
||||
)
|
||||
cos, sin = self.rotary_emb(value_states, position_ids)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
cos, sin = position_embeddings
|
||||
cos, sin = position_embeddings
|
||||
query_states, key_states = apply_rotary_pos_emb(query_states, key_states, cos, sin)
|
||||
|
||||
if past_key_value is not None:
|
||||
@ -441,7 +420,7 @@ class DummySdpaAttention(DummyAttention):
|
||||
output_attentions: bool = False,
|
||||
use_cache: bool = False,
|
||||
cache_position: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
|
||||
position_embeddings: Optional[Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]] = None, # will become mandatory in v4.46
|
||||
position_embeddings: Optional[Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]] = None, # necessary, but kept here for BC
|
||||
**kwargs,
|
||||
) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor, Optional[torch.Tensor], Optional[Tuple[torch.Tensor]]]:
|
||||
if output_attentions:
|
||||
@ -472,16 +451,7 @@ class DummySdpaAttention(DummyAttention):
|
||||
key_states = key_states.view(bsz, q_len, -1, self.head_dim).transpose(1, 2)
|
||||
value_states = value_states.view(bsz, q_len, -1, self.head_dim).transpose(1, 2)
|
||||
|
||||
if position_embeddings is None:
|
||||
logger.warning_once(
|
||||
"The attention layers in this model are transitioning from computing the RoPE embeddings internally "
|
||||
"through `position_ids` (2D tensor with the indexes of the tokens), to using externally computed "
|
||||
"`position_embeddings` (Tuple of tensors, containing cos and sin). In v4.46 `position_ids` will be "
|
||||
"removed and `position_embeddings` will be mandatory."
|
||||
)
|
||||
cos, sin = self.rotary_emb(value_states, position_ids)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
cos, sin = position_embeddings
|
||||
cos, sin = position_embeddings
|
||||
query_states, key_states = apply_rotary_pos_emb(query_states, key_states, cos, sin)
|
||||
|
||||
if past_key_value is not None:
|
||||
@ -551,7 +521,7 @@ class DummyDecoderLayer(nn.Module):
|
||||
output_attentions: Optional[bool] = False,
|
||||
use_cache: Optional[bool] = False,
|
||||
cache_position: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
|
||||
position_embeddings: Optional[Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]] = None, # will become mandatory in v4.46
|
||||
position_embeddings: Optional[Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]] = None, # necessary, but kept here for BC
|
||||
**kwargs,
|
||||
) -> Tuple[torch.FloatTensor, Optional[Tuple[torch.FloatTensor, torch.FloatTensor]]]:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
357
examples/modular-transformers/modeling_from_uppercase_model.py
Normal file
357
examples/modular-transformers/modeling_from_uppercase_model.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,357 @@
|
||||
# 🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨
|
||||
# This file was automatically generated from examples/modular-transformers/modular_from_uppercase_model.py.
|
||||
# Do NOT edit this file manually as any edits will be overwritten by the generation of
|
||||
# the file from the modular. If any change should be done, please apply the change to the
|
||||
# modular_from_uppercase_model.py file directly. One of our CI enforces this.
|
||||
# 🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨
|
||||
from typing import Optional, Tuple
|
||||
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from torch import nn
|
||||
|
||||
from ...activations import ACT2FN
|
||||
from ...pytorch_utils import is_torch_greater_or_equal_than_2_2
|
||||
from ...utils import is_flash_attn_2_available, is_flash_attn_greater_or_equal_2_10, logging
|
||||
from .configuration_from_uppercase_model import FromUppercaseModelConfig
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if is_flash_attn_2_available():
|
||||
from ...modeling_flash_attention_utils import _flash_attention_forward
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
logger = logging.get_logger(__name__)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class FromUppercaseModelAttention(nn.Module):
|
||||
"""Multi-headed attention from 'Attention Is All You Need' paper"""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, config):
|
||||
super().__init__()
|
||||
self.config = config
|
||||
self.embed_dim = config.hidden_size
|
||||
self.num_heads = config.num_attention_heads
|
||||
self.head_dim = self.embed_dim // self.num_heads
|
||||
if self.head_dim * self.num_heads != self.embed_dim:
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
f"embed_dim must be divisible by num_heads (got `embed_dim`: {self.embed_dim} and `num_heads`:"
|
||||
f" {self.num_heads})."
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.scale = self.head_dim**-0.5
|
||||
self.dropout = config.attention_dropout
|
||||
|
||||
self.k_proj = nn.Linear(self.embed_dim, self.embed_dim)
|
||||
self.v_proj = nn.Linear(self.embed_dim, self.embed_dim)
|
||||
self.q_proj = nn.Linear(self.embed_dim, self.embed_dim)
|
||||
self.out_proj = nn.Linear(self.embed_dim, self.embed_dim)
|
||||
|
||||
def _shape(self, tensor: torch.Tensor, seq_len: int, bsz: int):
|
||||
return tensor.view(bsz, seq_len, self.num_heads, self.head_dim).transpose(1, 2).contiguous()
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
hidden_states: torch.Tensor,
|
||||
attention_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
|
||||
causal_attention_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
|
||||
output_attentions: Optional[bool] = False,
|
||||
) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor, Optional[torch.Tensor]]:
|
||||
"""Input shape: Batch x Time x Channel"""
|
||||
|
||||
bsz, tgt_len, embed_dim = hidden_states.size()
|
||||
|
||||
# get query proj
|
||||
query_states = self.q_proj(hidden_states) * self.scale
|
||||
key_states = self._shape(self.k_proj(hidden_states), -1, bsz)
|
||||
value_states = self._shape(self.v_proj(hidden_states), -1, bsz)
|
||||
|
||||
proj_shape = (bsz * self.num_heads, -1, self.head_dim)
|
||||
query_states = self._shape(query_states, tgt_len, bsz).view(*proj_shape)
|
||||
key_states = key_states.view(*proj_shape)
|
||||
value_states = value_states.view(*proj_shape)
|
||||
|
||||
src_len = key_states.size(1)
|
||||
attn_weights = torch.bmm(query_states, key_states.transpose(1, 2))
|
||||
|
||||
if attn_weights.size() != (bsz * self.num_heads, tgt_len, src_len):
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
f"Attention weights should be of size {(bsz * self.num_heads, tgt_len, src_len)}, but is"
|
||||
f" {attn_weights.size()}"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# apply the causal_attention_mask first
|
||||
if causal_attention_mask is not None:
|
||||
if causal_attention_mask.size() != (bsz, 1, tgt_len, src_len):
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
f"Attention mask should be of size {(bsz, 1, tgt_len, src_len)}, but is"
|
||||
f" {causal_attention_mask.size()}"
|
||||
)
|
||||
attn_weights = attn_weights.view(bsz, self.num_heads, tgt_len, src_len) + causal_attention_mask
|
||||
attn_weights = attn_weights.view(bsz * self.num_heads, tgt_len, src_len)
|
||||
|
||||
if attention_mask is not None:
|
||||
if attention_mask.size() != (bsz, 1, tgt_len, src_len):
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
f"Attention mask should be of size {(bsz, 1, tgt_len, src_len)}, but is {attention_mask.size()}"
|
||||
)
|
||||
attn_weights = attn_weights.view(bsz, self.num_heads, tgt_len, src_len) + attention_mask
|
||||
attn_weights = attn_weights.view(bsz * self.num_heads, tgt_len, src_len)
|
||||
|
||||
attn_weights = nn.functional.softmax(attn_weights, dim=-1)
|
||||
|
||||
if output_attentions:
|
||||
# this operation is a bit akward, but it's required to
|
||||
# make sure that attn_weights keeps its gradient.
|
||||
# In order to do so, attn_weights have to reshaped
|
||||
# twice and have to be reused in the following
|
||||
attn_weights_reshaped = attn_weights.view(bsz, self.num_heads, tgt_len, src_len)
|
||||
attn_weights = attn_weights_reshaped.view(bsz * self.num_heads, tgt_len, src_len)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
attn_weights_reshaped = None
|
||||
|
||||
attn_probs = nn.functional.dropout(attn_weights, p=self.dropout, training=self.training)
|
||||
|
||||
attn_output = torch.bmm(attn_probs, value_states)
|
||||
|
||||
if attn_output.size() != (bsz * self.num_heads, tgt_len, self.head_dim):
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
f"`attn_output` should be of size {(bsz, self.num_heads, tgt_len, self.head_dim)}, but is"
|
||||
f" {attn_output.size()}"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
attn_output = attn_output.view(bsz, self.num_heads, tgt_len, self.head_dim)
|
||||
attn_output = attn_output.transpose(1, 2)
|
||||
attn_output = attn_output.reshape(bsz, tgt_len, embed_dim)
|
||||
|
||||
attn_output = self.out_proj(attn_output)
|
||||
|
||||
return attn_output, attn_weights_reshaped
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class FromUppercaseModelFlashAttention2(FromUppercaseModelAttention):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
FromUppercaseModelAttention flash attention module. This module inherits from `FromUppercaseModelAttention` as the weights of the module stays
|
||||
untouched. The only required change would be on the forward pass where it needs to correctly call the public API of
|
||||
flash attention and deal with padding tokens in case the input contains any of them.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
|
||||
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
|
||||
|
||||
# TODO: Should be removed once Flash Attention for RoCm is bumped to 2.1.
|
||||
# flash_attn<2.1 generates top-left aligned causal mask, while what is needed here is bottom-right alignement, that was made default for flash_attn>=2.1. This attribute is used to handle this difference. Reference: https://github.com/Dao-AILab/flash-attention/releases/tag/v2.1.0.
|
||||
# Beware that with flash_attn<2.1, using q_seqlen != k_seqlen (except for the case q_seqlen == 1) produces a wrong mask (top-left).
|
||||
self._flash_attn_uses_top_left_mask = not is_flash_attn_greater_or_equal_2_10()
|
||||
|
||||
# Adapted from transformers.models.llama.modeling_llama.LlamaFlashAttention2.forward
|
||||
def forward(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
hidden_states: torch.Tensor,
|
||||
attention_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
|
||||
causal_attention_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
|
||||
output_attentions: Optional[bool] = False,
|
||||
) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor, Optional[torch.Tensor]]:
|
||||
output_attentions = False
|
||||
|
||||
batch_size, q_len, _ = hidden_states.size()
|
||||
|
||||
query_states = self.q_proj(hidden_states)
|
||||
key_states = self.k_proj(hidden_states)
|
||||
value_states = self.v_proj(hidden_states)
|
||||
|
||||
# Flash attention requires the input to have the shape
|
||||
# batch_size x seq_length x head_dim x hidden_dim
|
||||
# therefore we just need to keep the original shape
|
||||
query_states = query_states.view(batch_size, q_len, self.num_heads, self.head_dim)
|
||||
key_states = key_states.view(batch_size, q_len, self.num_heads, self.head_dim)
|
||||
value_states = value_states.view(batch_size, q_len, self.num_heads, self.head_dim)
|
||||
|
||||
dropout_rate = self.dropout if self.training else 0.0
|
||||
|
||||
# In PEFT, usually we cast the layer norms in float32 for training stability reasons
|
||||
# therefore the input hidden states gets silently casted in float32. Hence, we need
|
||||
# cast them back in the correct dtype just to be sure everything works as expected.
|
||||
# This might slowdown training & inference so it is recommended to not cast the LayerNorms
|
||||
# in fp32.
|
||||
|
||||
input_dtype = query_states.dtype
|
||||
if input_dtype == torch.float32:
|
||||
if torch.is_autocast_enabled():
|
||||
target_dtype = torch.get_autocast_gpu_dtype()
|
||||
# Handle the case where the model is quantized
|
||||
elif hasattr(self.config, "_pre_quantization_dtype"):
|
||||
target_dtype = self.config._pre_quantization_dtype
|
||||
else:
|
||||
target_dtype = self.q_proj.weight.dtype
|
||||
|
||||
logger.warning_once(
|
||||
f"The input hidden states seems to be silently casted in float32, this might be related to"
|
||||
f" the fact you have upcasted embedding or layer norm layers in float32. We will cast back the input in"
|
||||
f" {target_dtype}."
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
query_states = query_states.to(target_dtype)
|
||||
key_states = key_states.to(target_dtype)
|
||||
value_states = value_states.to(target_dtype)
|
||||
|
||||
attn_output = _flash_attention_forward(
|
||||
query_states,
|
||||
key_states,
|
||||
value_states,
|
||||
attention_mask,
|
||||
q_len,
|
||||
dropout=dropout_rate,
|
||||
is_causal=causal_attention_mask is not None,
|
||||
use_top_left_mask=self._flash_attn_uses_top_left_mask,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
attn_output = attn_output.reshape(batch_size, q_len, self.embed_dim).contiguous()
|
||||
attn_output = self.out_proj(attn_output)
|
||||
|
||||
if not output_attentions:
|
||||
attn_weights = None
|
||||
|
||||
return attn_output, attn_weights
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class FromUppercaseModelSdpaAttention(FromUppercaseModelAttention):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
SDPA attention module using torch.nn.functional.scaled_dot_product_attention. This module inherits from
|
||||
`FromUppercaseModelAttention` as the weights of the module stays untouched. The only changes are on the forward pass to adapt to
|
||||
SDPA API.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
# Adapted from FromUppercaseModelAttention.forward
|
||||
def forward(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
hidden_states: torch.Tensor,
|
||||
attention_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
|
||||
causal_attention_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
|
||||
output_attentions: Optional[bool] = False,
|
||||
) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor, Optional[torch.Tensor]]:
|
||||
if output_attentions:
|
||||
# TODO: Improve this warning with e.g. `model.config.attn_implementation = "manual"` once this is implemented.
|
||||
logger.warning_once(
|
||||
"FromUppercaseModelModel is using FromUppercaseModelSdpaAttention, but `torch.nn.functional.scaled_dot_product_attention` does not "
|
||||
"support `output_attentions=True`. Falling back to the manual attention implementation, but specifying "
|
||||
"the manual implementation will be required from Transformers version v5.0.0 onwards. This warning can "
|
||||
'be removed using the argument `attn_implementation="eager"` when loading the model.'
|
||||
)
|
||||
return super().forward(
|
||||
hidden_states=hidden_states,
|
||||
attention_mask=attention_mask,
|
||||
causal_attention_mask=causal_attention_mask,
|
||||
output_attentions=output_attentions,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# FROM_UPPERCASE_MODEL text model uses both `causal_attention_mask` and `attention_mask`
|
||||
if attention_mask is not None and causal_attention_mask is not None:
|
||||
attn_mask = attention_mask + causal_attention_mask
|
||||
elif causal_attention_mask is not None:
|
||||
attn_mask = causal_attention_mask
|
||||
else:
|
||||
attn_mask = attention_mask
|
||||
|
||||
bsz, tgt_len, embed_dim = hidden_states.size()
|
||||
|
||||
query_states = self.q_proj(hidden_states)
|
||||
key_states = self.k_proj(hidden_states)
|
||||
value_states = self.v_proj(hidden_states)
|
||||
|
||||
query_states = query_states.view(bsz, -1, self.num_heads, self.head_dim).transpose(1, 2)
|
||||
key_states = key_states.view(bsz, -1, self.num_heads, self.head_dim).transpose(1, 2)
|
||||
value_states = value_states.view(bsz, -1, self.num_heads, self.head_dim).transpose(1, 2)
|
||||
|
||||
# SDPA with memory-efficient backend is currently (torch==2.1.2) bugged with non-contiguous inputs with custom attn_mask,
|
||||
# Reference: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/112577.
|
||||
if not is_torch_greater_or_equal_than_2_2 and query_states.device.type == "cuda" and attn_mask is not None:
|
||||
query_states = query_states.contiguous()
|
||||
key_states = key_states.contiguous()
|
||||
value_states = value_states.contiguous()
|
||||
|
||||
# FROM_UPPERCASE_MODEL text model uses both `causal_attention_mask` and `attention_mask` sequentially.
|
||||
attn_output = torch.nn.functional.scaled_dot_product_attention(
|
||||
query_states,
|
||||
key_states,
|
||||
value_states,
|
||||
attn_mask=attn_mask,
|
||||
dropout_p=self.dropout if self.training else 0.0,
|
||||
scale=self.scale,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
attn_output = attn_output.transpose(1, 2)
|
||||
attn_output = attn_output.reshape(bsz, tgt_len, embed_dim)
|
||||
|
||||
attn_output = self.out_proj(attn_output)
|
||||
|
||||
return attn_output, None
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class FromUppercaseModelMLP(nn.Module):
|
||||
def __init__(self, config):
|
||||
super().__init__()
|
||||
self.config = config
|
||||
self.activation_fn = ACT2FN[config.hidden_act]
|
||||
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(config.hidden_size, config.intermediate_size)
|
||||
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(config.intermediate_size, config.hidden_size)
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, hidden_states: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
|
||||
hidden_states = self.fc1(hidden_states)
|
||||
hidden_states = self.activation_fn(hidden_states)
|
||||
hidden_states = self.fc2(hidden_states)
|
||||
return hidden_states
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
FROM_UPPERCASE_MODEL_ATTENTION_CLASSES = {
|
||||
"eager": FromUppercaseModelAttention,
|
||||
"sdpa": FromUppercaseModelSdpaAttention,
|
||||
"flash_attention_2": FromUppercaseModelFlashAttention2,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class FromUppercaseModelEncoderLayer(nn.Module):
|
||||
def __init__(self, config: FromUppercaseModelConfig):
|
||||
super().__init__()
|
||||
self.embed_dim = config.hidden_size
|
||||
self.self_attn = FROM_UPPERCASE_MODEL_ATTENTION_CLASSES[config._attn_implementation](config)
|
||||
self.layer_norm1 = nn.LayerNorm(self.embed_dim, eps=config.layer_norm_eps)
|
||||
self.mlp = FromUppercaseModelMLP(config)
|
||||
self.layer_norm2 = nn.LayerNorm(self.embed_dim, eps=config.layer_norm_eps)
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
hidden_states: torch.Tensor,
|
||||
attention_mask: torch.Tensor,
|
||||
causal_attention_mask: torch.Tensor,
|
||||
output_attentions: Optional[bool] = False,
|
||||
) -> Tuple[torch.FloatTensor]:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
hidden_states (`torch.FloatTensor`): input to the layer of shape `(batch, seq_len, embed_dim)`
|
||||
attention_mask (`torch.FloatTensor`): attention mask of size
|
||||
`(batch, 1, tgt_len, src_len)` where padding elements are indicated by very large negative values.
|
||||
`(config.encoder_attention_heads,)`.
|
||||
output_attentions (`bool`, *optional*):
|
||||
Whether or not to return the attentions tensors of all attention layers. See `attentions` under
|
||||
returned tensors for more detail.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
residual = hidden_states
|
||||
|
||||
hidden_states = self.layer_norm1(hidden_states)
|
||||
hidden_states, attn_weights = self.self_attn(
|
||||
hidden_states=hidden_states,
|
||||
attention_mask=attention_mask,
|
||||
causal_attention_mask=causal_attention_mask,
|
||||
output_attentions=output_attentions,
|
||||
)
|
||||
hidden_states = residual + hidden_states
|
||||
|
||||
residual = hidden_states
|
||||
hidden_states = self.layer_norm2(hidden_states)
|
||||
hidden_states = self.mlp(hidden_states)
|
||||
hidden_states = residual + hidden_states
|
||||
|
||||
outputs = (hidden_states,)
|
||||
|
||||
if output_attentions:
|
||||
outputs += (attn_weights,)
|
||||
|
||||
return outputs
|
||||
987
examples/modular-transformers/modeling_multimodal1.py
Normal file
987
examples/modular-transformers/modeling_multimodal1.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,987 @@
|
||||
# 🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨
|
||||
# This file was automatically generated from examples/modular-transformers/modular_multimodal1.py.
|
||||
# Do NOT edit this file manually as any edits will be overwritten by the generation of
|
||||
# the file from the modular. If any change should be done, please apply the change to the
|
||||
# modular_multimodal1.py file directly. One of our CI enforces this.
|
||||
# 🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨
|
||||
import math
|
||||
from typing import List, Optional, Tuple, Union
|
||||
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from torch import nn
|
||||
|
||||
from ...activations import ACT2FN
|
||||
from ...cache_utils import Cache, DynamicCache, StaticCache
|
||||
from ...modeling_attn_mask_utils import AttentionMaskConverter
|
||||
from ...modeling_flash_attention_utils import FlashAttentionKwargs, _flash_attention_forward
|
||||
from ...modeling_outputs import BaseModelOutputWithPast
|
||||
from ...modeling_rope_utils import ROPE_INIT_FUNCTIONS
|
||||
from ...modeling_utils import PreTrainedModel
|
||||
from ...processing_utils import Unpack
|
||||
from ...utils import (
|
||||
add_start_docstrings,
|
||||
add_start_docstrings_to_model_forward,
|
||||
is_flash_attn_greater_or_equal_2_10,
|
||||
logging,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from .configuration_multimodal1 import Multimodal1TextConfig
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
logger = logging.get_logger(__name__)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Multimodal1TextRMSNorm(nn.Module):
|
||||
def __init__(self, hidden_size, eps=1e-6):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Multimodal1TextRMSNorm is equivalent to T5LayerNorm
|
||||
"""
|
||||
super().__init__()
|
||||
self.weight = nn.Parameter(torch.ones(hidden_size))
|
||||
self.variance_epsilon = eps
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, hidden_states):
|
||||
input_dtype = hidden_states.dtype
|
||||
hidden_states = hidden_states.to(torch.float32)
|
||||
variance = hidden_states.pow(2).mean(-1, keepdim=True)
|
||||
hidden_states = hidden_states * torch.rsqrt(variance + self.variance_epsilon)
|
||||
return self.weight * hidden_states.to(input_dtype)
|
||||
|
||||
def extra_repr(self):
|
||||
return f"{tuple(self.weight.shape)}, eps={self.variance_epsilon}"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Multimodal1TextRotaryEmbedding(nn.Module):
|
||||
def __init__(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
dim=None,
|
||||
max_position_embeddings=2048,
|
||||
base=10000,
|
||||
device=None,
|
||||
scaling_factor=1.0,
|
||||
rope_type="default",
|
||||
config: Optional[Multimodal1TextConfig] = None,
|
||||
):
|
||||
super().__init__()
|
||||
# TODO (joao): remove the `if` below, only used for BC
|
||||
self.rope_kwargs = {}
|
||||
if config is None:
|
||||
logger.warning_once(
|
||||
"`Multimodal1TextRotaryEmbedding` can now be fully parameterized by passing the model config through the "
|
||||
"`config` argument. All other arguments will be removed in v4.46"
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.rope_kwargs = {
|
||||
"rope_type": rope_type,
|
||||
"factor": scaling_factor,
|
||||
"dim": dim,
|
||||
"base": base,
|
||||
"max_position_embeddings": max_position_embeddings,
|
||||
}
|
||||
self.rope_type = rope_type
|
||||
self.max_seq_len_cached = max_position_embeddings
|
||||
self.original_max_seq_len = max_position_embeddings
|
||||
else:
|
||||
# BC: "rope_type" was originally "type"
|
||||
if config.rope_scaling is not None:
|
||||
self.rope_type = config.rope_scaling.get("rope_type", config.rope_scaling.get("type"))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self.rope_type = "default"
|
||||
self.max_seq_len_cached = config.max_position_embeddings
|
||||
self.original_max_seq_len = config.max_position_embeddings
|
||||
|
||||
self.config = config
|
||||
self.rope_init_fn = ROPE_INIT_FUNCTIONS[self.rope_type]
|
||||
|
||||
inv_freq, self.attention_scaling = self.rope_init_fn(self.config, device, **self.rope_kwargs)
|
||||
self.register_buffer("inv_freq", inv_freq, persistent=False)
|
||||
self.original_inv_freq = self.inv_freq
|
||||
|
||||
def _dynamic_frequency_update(self, position_ids, device):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
dynamic RoPE layers should recompute `inv_freq` in the following situations:
|
||||
1 - growing beyond the cached sequence length (allow scaling)
|
||||
2 - the current sequence length is in the original scale (avoid losing precision with small sequences)
|
||||
"""
|
||||
seq_len = torch.max(position_ids) + 1
|
||||
if seq_len > self.max_seq_len_cached: # growth
|
||||
inv_freq, self.attention_scaling = self.rope_init_fn(
|
||||
self.config, device, seq_len=seq_len, **self.rope_kwargs
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.register_buffer("inv_freq", inv_freq, persistent=False) # TODO joao: may break with compilation
|
||||
self.max_seq_len_cached = seq_len
|
||||
|
||||
if seq_len < self.original_max_seq_len and self.max_seq_len_cached > self.original_max_seq_len: # reset
|
||||
self.register_buffer("inv_freq", self.original_inv_freq, persistent=False)
|
||||
self.max_seq_len_cached = self.original_max_seq_len
|
||||
|
||||
@torch.no_grad()
|
||||
def forward(self, x, position_ids):
|
||||
if "dynamic" in self.rope_type:
|
||||
self._dynamic_frequency_update(position_ids, device=x.device)
|
||||
|
||||
# Core RoPE block
|
||||
inv_freq_expanded = self.inv_freq[None, :, None].float().expand(position_ids.shape[0], -1, 1)
|
||||
position_ids_expanded = position_ids[:, None, :].float()
|
||||
# Force float32 (see https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/pull/29285)
|
||||
device_type = x.device.type
|
||||
device_type = device_type if isinstance(device_type, str) and device_type != "mps" else "cpu"
|
||||
with torch.autocast(device_type=device_type, enabled=False):
|
||||
freqs = (inv_freq_expanded.float() @ position_ids_expanded.float()).transpose(1, 2)
|
||||
emb = torch.cat((freqs, freqs), dim=-1)
|
||||
cos = emb.cos()
|
||||
sin = emb.sin()
|
||||
|
||||
# Advanced RoPE types (e.g. yarn) apply a post-processing scaling factor, equivalent to scaling attention
|
||||
cos = cos * self.attention_scaling
|
||||
sin = sin * self.attention_scaling
|
||||
|
||||
return cos.to(dtype=x.dtype), sin.to(dtype=x.dtype)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Multimodal1TextMLP(nn.Module):
|
||||
def __init__(self, config):
|
||||
super().__init__()
|
||||
self.config = config
|
||||
self.hidden_size = config.hidden_size
|
||||
self.intermediate_size = config.intermediate_size
|
||||
self.gate_proj = nn.Linear(self.hidden_size, self.intermediate_size, bias=config.mlp_bias)
|
||||
self.up_proj = nn.Linear(self.hidden_size, self.intermediate_size, bias=config.mlp_bias)
|
||||
self.down_proj = nn.Linear(self.intermediate_size, self.hidden_size, bias=config.mlp_bias)
|
||||
self.act_fn = ACT2FN[config.hidden_act]
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, x):
|
||||
down_proj = self.down_proj(self.act_fn(self.gate_proj(x)) * self.up_proj(x))
|
||||
return down_proj
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def rotate_half(x):
|
||||
"""Rotates half the hidden dims of the input."""
|
||||
x1 = x[..., : x.shape[-1] // 2]
|
||||
x2 = x[..., x.shape[-1] // 2 :]
|
||||
return torch.cat((-x2, x1), dim=-1)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def apply_rotary_pos_emb(q, k, cos, sin, position_ids=None, unsqueeze_dim=1):
|
||||
"""Applies Rotary Position Embedding to the query and key tensors.
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
q (`torch.Tensor`): The query tensor.
|
||||
k (`torch.Tensor`): The key tensor.
|
||||
cos (`torch.Tensor`): The cosine part of the rotary embedding.
|
||||
sin (`torch.Tensor`): The sine part of the rotary embedding.
|
||||
position_ids (`torch.Tensor`, *optional*):
|
||||
Deprecated and unused.
|
||||
unsqueeze_dim (`int`, *optional*, defaults to 1):
|
||||
The 'unsqueeze_dim' argument specifies the dimension along which to unsqueeze cos[position_ids] and
|
||||
sin[position_ids] so that they can be properly broadcasted to the dimensions of q and k. For example, note
|
||||
that cos[position_ids] and sin[position_ids] have the shape [batch_size, seq_len, head_dim]. Then, if q and
|
||||
k have the shape [batch_size, heads, seq_len, head_dim], then setting unsqueeze_dim=1 makes
|
||||
cos[position_ids] and sin[position_ids] broadcastable to the shapes of q and k. Similarly, if q and k have
|
||||
the shape [batch_size, seq_len, heads, head_dim], then set unsqueeze_dim=2.
|
||||
Returns:
|
||||
`tuple(torch.Tensor)` comprising of the query and key tensors rotated using the Rotary Position Embedding.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
cos = cos.unsqueeze(unsqueeze_dim)
|
||||
sin = sin.unsqueeze(unsqueeze_dim)
|
||||
q_embed = (q * cos) + (rotate_half(q) * sin)
|
||||
k_embed = (k * cos) + (rotate_half(k) * sin)
|
||||
return q_embed, k_embed
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def repeat_kv(hidden_states: torch.Tensor, n_rep: int) -> torch.Tensor:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
This is the equivalent of torch.repeat_interleave(x, dim=1, repeats=n_rep). The hidden states go from (batch,
|
||||
num_key_value_heads, seqlen, head_dim) to (batch, num_attention_heads, seqlen, head_dim)
|
||||
"""
|
||||
batch, num_key_value_heads, slen, head_dim = hidden_states.shape
|
||||
if n_rep == 1:
|
||||
return hidden_states
|
||||
hidden_states = hidden_states[:, :, None, :, :].expand(batch, num_key_value_heads, n_rep, slen, head_dim)
|
||||
return hidden_states.reshape(batch, num_key_value_heads * n_rep, slen, head_dim)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Multimodal1TextAttention(nn.Module):
|
||||
"""Multi-headed attention from 'Attention Is All You Need' paper"""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, config: Multimodal1TextConfig, layer_idx: Optional[int] = None):
|
||||
super().__init__()
|
||||
self.config = config
|
||||
self.layer_idx = layer_idx
|
||||
if layer_idx is None:
|
||||
logger.warning_once(
|
||||
f"Instantiating {self.__class__.__name__} without passing a `layer_idx` is not recommended and will "
|
||||
"lead to errors during the forward call if caching is used. Please make sure to provide a `layer_idx` "
|
||||
"when creating this class."
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
self.attention_dropout = config.attention_dropout
|
||||
self.hidden_size = config.hidden_size
|
||||
self.num_heads = config.num_attention_heads
|
||||
self.head_dim = getattr(config, "head_dim", self.hidden_size // self.num_heads)
|
||||
self.num_key_value_heads = config.num_key_value_heads
|
||||
self.num_key_value_groups = self.num_heads // self.num_key_value_heads
|
||||
self.max_position_embeddings = config.max_position_embeddings
|
||||
self.rope_theta = config.rope_theta
|
||||
self.is_causal = True
|
||||
|
||||
self.q_proj = nn.Linear(self.hidden_size, self.num_heads * self.head_dim, bias=config.attention_bias)
|
||||
self.k_proj = nn.Linear(self.hidden_size, self.num_key_value_heads * self.head_dim, bias=config.attention_bias)
|
||||
self.v_proj = nn.Linear(self.hidden_size, self.num_key_value_heads * self.head_dim, bias=config.attention_bias)
|
||||
self.o_proj = nn.Linear(self.num_heads * self.head_dim, self.hidden_size, bias=config.attention_bias)
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
hidden_states: torch.Tensor,
|
||||
attention_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
|
||||
position_ids: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
|
||||
past_key_value: Optional[Cache] = None,
|
||||
output_attentions: bool = False,
|
||||
use_cache: bool = False,
|
||||
cache_position: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
|
||||
position_embeddings: Optional[Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]] = None, # necessary, but kept here for BC
|
||||
**kwargs,
|
||||
) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor, Optional[torch.Tensor], Optional[Tuple[torch.Tensor]]]:
|
||||
bsz, q_len, _ = hidden_states.size()
|
||||
|
||||
query_states = self.q_proj(hidden_states)
|
||||
key_states = self.k_proj(hidden_states)
|
||||
value_states = self.v_proj(hidden_states)
|
||||
|
||||
# use -1 to infer num_heads and num_key_value_heads as they may vary if tensor parallel is used
|
||||
query_states = query_states.view(bsz, q_len, -1, self.head_dim).transpose(1, 2)
|
||||
key_states = key_states.view(bsz, q_len, -1, self.head_dim).transpose(1, 2)
|
||||
value_states = value_states.view(bsz, q_len, -1, self.head_dim).transpose(1, 2)
|
||||
|
||||
cos, sin = position_embeddings
|
||||
query_states, key_states = apply_rotary_pos_emb(query_states, key_states, cos, sin)
|
||||
|
||||
if past_key_value is not None:
|
||||
# sin and cos are specific to RoPE models; cache_position needed for the static cache
|
||||
cache_kwargs = {"sin": sin, "cos": cos, "cache_position": cache_position}
|
||||
key_states, value_states = past_key_value.update(key_states, value_states, self.layer_idx, cache_kwargs)
|
||||
|
||||
key_states = repeat_kv(key_states, self.num_key_value_groups)
|
||||
value_states = repeat_kv(value_states, self.num_key_value_groups)
|
||||
attn_weights = torch.matmul(query_states, key_states.transpose(2, 3)) / math.sqrt(self.head_dim)
|
||||
|
||||
if attention_mask is not None: # no matter the length, we just slice it
|
||||
causal_mask = attention_mask[:, :, :, : key_states.shape[-2]]
|
||||
attn_weights = attn_weights + causal_mask
|
||||
|
||||
# upcast attention to fp32
|
||||
attn_weights = nn.functional.softmax(attn_weights, dim=-1, dtype=torch.float32).to(query_states.dtype)
|
||||
attn_weights = nn.functional.dropout(attn_weights, p=self.attention_dropout, training=self.training)
|
||||
attn_output = torch.matmul(attn_weights, value_states)
|
||||
|
||||
if attn_output.size() != (bsz, self.num_heads, q_len, self.head_dim):
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
f"`attn_output` should be of size {(bsz, self.num_heads, q_len, self.head_dim)}, but is"
|
||||
f" {attn_output.size()}"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
attn_output = attn_output.transpose(1, 2).contiguous()
|
||||
|
||||
attn_output = attn_output.reshape(bsz, q_len, -1)
|
||||
|
||||
attn_output = self.o_proj(attn_output)
|
||||
|
||||
if not output_attentions:
|
||||
attn_weights = None
|
||||
|
||||
return attn_output, attn_weights, past_key_value
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Multimodal1TextFlashAttention2(Multimodal1TextAttention):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Multimodal1Text flash attention module. This module inherits from `Multimodal1TextAttention` as the weights of the module stays
|
||||
untouched. The only required change would be on the forward pass where it needs to correctly call the public API of
|
||||
flash attention and deal with padding tokens in case the input contains any of them.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
|
||||
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
|
||||
|
||||
# TODO: Should be removed once Flash Attention for RoCm is bumped to 2.1.
|
||||
# flash_attn<2.1 generates top-left aligned causal mask, while what is needed here is bottom-right alignement, that was made default for flash_attn>=2.1. This attribute is used to handle this difference. Reference: https://github.com/Dao-AILab/flash-attention/releases/tag/v2.1.0.
|
||||
# Beware that with flash_attn<2.1, using q_seqlen != k_seqlen (except for the case q_seqlen == 1) produces a wrong mask (top-left).
|
||||
self._flash_attn_uses_top_left_mask = not is_flash_attn_greater_or_equal_2_10()
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
hidden_states: torch.Tensor,
|
||||
attention_mask: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
|
||||
position_ids: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
|
||||
past_key_value: Optional[Cache] = None,
|
||||
output_attentions: bool = False,
|
||||
use_cache: bool = False,
|
||||
cache_position: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
|
||||
position_embeddings: Optional[Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]] = None, # necessary, but kept here for BC
|
||||
**kwargs: Unpack[FlashAttentionKwargs],
|
||||
) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor, Optional[torch.Tensor], Optional[Tuple[torch.Tensor]]]:
|
||||
if isinstance(past_key_value, StaticCache):
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
"`static` cache implementation is not compatible with `attn_implementation==flash_attention_2` "
|
||||
"make sure to use `sdpa` in the mean time, and open an issue at https://github.com/huggingface/transformers"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
output_attentions = False
|
||||
|
||||
bsz, q_len, _ = hidden_states.size()
|
||||
|
||||
query_states = self.q_proj(hidden_states)
|
||||
key_states = self.k_proj(hidden_states)
|
||||
value_states = self.v_proj(hidden_states)
|
||||
|
||||
# Flash attention requires the input to have the shape
|
||||
# batch_size x seq_length x head_dim x hidden_dim
|
||||
# therefore we just need to keep the original shape
|
||||
query_states = query_states.view(bsz, q_len, self.num_heads, self.head_dim).transpose(1, 2)
|
||||
key_states = key_states.view(bsz, q_len, self.num_key_value_heads, self.head_dim).transpose(1, 2)
|
||||
value_states = value_states.view(bsz, q_len, self.num_key_value_heads, self.head_dim).transpose(1, 2)
|
||||
|
||||
cos, sin = position_embeddings
|
||||
query_states, key_states = apply_rotary_pos_emb(query_states, key_states, cos, sin)
|
||||
|
||||
if past_key_value is not None:
|
||||
# sin and cos are specific to RoPE models; cache_position needed for the static cache
|
||||
cache_kwargs = {"sin": sin, "cos": cos, "cache_position": cache_position}
|
||||
key_states, value_states = past_key_value.update(key_states, value_states, self.layer_idx, cache_kwargs)
|
||||
|
||||
# TODO: These transpose are quite inefficient but Flash Attention requires the layout [batch_size, sequence_length, num_heads, head_dim]. We would need to refactor the KV cache
|
||||
# to be able to avoid many of these transpose/reshape/view.
|
||||
query_states = query_states.transpose(1, 2)
|
||||
key_states = key_states.transpose(1, 2)
|
||||
value_states = value_states.transpose(1, 2)
|
||||
|
||||
dropout_rate = self.attention_dropout if self.training else 0.0
|
||||
|
||||
# In PEFT, usually we cast the layer norms in float32 for training stability reasons
|
||||
# therefore the input hidden states gets silently casted in float32. Hence, we need
|
||||
# cast them back in the correct dtype just to be sure everything works as expected.
|
||||
# This might slowdown training & inference so it is recommended to not cast the LayerNorms
|
||||
# in fp32. (Multimodal1TextRMSNorm handles it correctly)
|
||||
|
||||
input_dtype = query_states.dtype
|
||||
if input_dtype == torch.float32:
|
||||
if torch.is_autocast_enabled():
|
||||
target_dtype = torch.get_autocast_gpu_dtype()
|
||||
# Handle the case where the model is quantized
|
||||
elif hasattr(self.config, "_pre_quantization_dtype"):
|
||||
target_dtype = self.config._pre_quantization_dtype
|
||||
else:
|
||||
target_dtype = self.q_proj.weight.dtype
|
||||
|
||||
logger.warning_once(
|
||||
f"The input hidden states seems to be silently casted in float32, this might be related to"
|
||||
f" the fact you have upcasted embedding or layer norm layers in float32. We will cast back the input in"
|
||||
f" {target_dtype}."
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
query_states = query_states.to(target_dtype)
|
||||
key_states = key_states.to(target_dtype)
|
||||
value_states = value_states.to(target_dtype)
|
||||
|
||||
attn_output = _flash_attention_forward(
|
||||
query_states,
|
||||
key_states,
|
||||
value_states,
|
||||
attention_mask,
|
||||
q_len,
|
||||
position_ids=position_ids,
|
||||
dropout=dropout_rate,
|
||||
sliding_window=getattr(self, "sliding_window", None),
|
||||
use_top_left_mask=self._flash_attn_uses_top_left_mask,
|
||||
is_causal=self.is_causal,
|
||||
**kwargs,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
attn_output = attn_output.reshape(bsz, q_len, -1).contiguous()
|
||||
attn_output = self.o_proj(attn_output)
|
||||
|
||||
if not output_attentions:
|
||||
attn_weights = None
|
||||
|
||||
return attn_output, attn_weights, past_key_value
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Multimodal1TextSdpaAttention(Multimodal1TextAttention):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Multimodal1Text attention module using torch.nn.functional.scaled_dot_product_attention. This module inherits from
|
||||
`Multimodal1TextAttention` as the weights of the module stays untouched. The only changes are on the forward pass to adapt to
|
||||
SDPA API.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
# Adapted from Multimodal1TextAttention.forward
|
||||
def forward(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
hidden_states: torch.Tensor,
|
||||
attention_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
|
||||
position_ids: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
|
||||
past_key_value: Optional[Cache] = None,
|
||||
output_attentions: bool = False,
|
||||
use_cache: bool = False,
|
||||
cache_position: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
|
||||
position_embeddings: Optional[Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]] = None, # necessary, but kept here for BC
|
||||
**kwargs,
|
||||
) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor, Optional[torch.Tensor], Optional[Tuple[torch.Tensor]]]:
|
||||
if output_attentions:
|
||||
# TODO: Improve this warning with e.g. `model.config.attn_implementation = "manual"` once this is implemented.
|
||||
logger.warning_once(
|
||||
"Multimodal1TextModel is using Multimodal1TextSdpaAttention, but `torch.nn.functional.scaled_dot_product_attention` does not support `output_attentions=True`. Falling back to the manual attention implementation, "
|
||||
'but specifying the manual implementation will be required from Transformers version v5.0.0 onwards. This warning can be removed using the argument `attn_implementation="eager"` when loading the model.'
|
||||
)
|
||||
return super().forward(
|
||||
hidden_states=hidden_states,
|
||||
attention_mask=attention_mask,
|
||||
position_ids=position_ids,
|
||||
past_key_value=past_key_value,
|
||||
output_attentions=output_attentions,
|
||||
use_cache=use_cache,
|
||||
cache_position=cache_position,
|
||||
position_embeddings=position_embeddings,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
bsz, q_len, _ = hidden_states.size()
|
||||
|
||||
query_states = self.q_proj(hidden_states)
|
||||
key_states = self.k_proj(hidden_states)
|
||||
value_states = self.v_proj(hidden_states)
|
||||
|
||||
# use -1 to infer num_heads and num_key_value_heads as they may vary if tensor parallel is used
|
||||
query_states = query_states.view(bsz, q_len, -1, self.head_dim).transpose(1, 2)
|
||||
key_states = key_states.view(bsz, q_len, -1, self.head_dim).transpose(1, 2)
|
||||
value_states = value_states.view(bsz, q_len, -1, self.head_dim).transpose(1, 2)
|
||||
|
||||
cos, sin = position_embeddings
|
||||
query_states, key_states = apply_rotary_pos_emb(query_states, key_states, cos, sin)
|
||||
|
||||
if past_key_value is not None:
|
||||
# sin and cos are specific to RoPE models; cache_position needed for the static cache
|
||||
cache_kwargs = {"sin": sin, "cos": cos, "cache_position": cache_position}
|
||||
key_states, value_states = past_key_value.update(key_states, value_states, self.layer_idx, cache_kwargs)
|
||||
|
||||
key_states = repeat_kv(key_states, self.num_key_value_groups)
|
||||
value_states = repeat_kv(value_states, self.num_key_value_groups)
|
||||
|
||||
causal_mask = attention_mask
|
||||
if attention_mask is not None:
|
||||
causal_mask = causal_mask[:, :, :, : key_states.shape[-2]]
|
||||
|
||||
# SDPA with memory-efficient backend is currently (torch==2.1.2) bugged with non-contiguous inputs with custom attn_mask,
|
||||
# Reference: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/112577.
|
||||
if query_states.device.type == "cuda" and causal_mask is not None:
|
||||
query_states = query_states.contiguous()
|
||||
key_states = key_states.contiguous()
|
||||
value_states = value_states.contiguous()
|
||||
|
||||
# We dispatch to SDPA's Flash Attention or Efficient kernels via this `is_causal` if statement instead of an inline conditional assignment
|
||||
# in SDPA to support both torch.compile's dynamic shapes and full graph options. An inline conditional prevents dynamic shapes from compiling.
|
||||
is_causal = True if causal_mask is None and q_len > 1 else False
|
||||
|
||||
attn_output = torch.nn.functional.scaled_dot_product_attention(
|
||||
query_states,
|
||||
key_states,
|
||||
value_states,
|
||||
attn_mask=causal_mask,
|
||||
dropout_p=self.attention_dropout if self.training else 0.0,
|
||||
is_causal=is_causal,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
attn_output = attn_output.transpose(1, 2).contiguous()
|
||||
attn_output = attn_output.view(bsz, q_len, -1)
|
||||
|
||||
attn_output = self.o_proj(attn_output)
|
||||
|
||||
return attn_output, None, past_key_value
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
MULTIMODAL1_TEXT_ATTENTION_CLASSES = {
|
||||
"eager": Multimodal1TextAttention,
|
||||
"flash_attention_2": Multimodal1TextFlashAttention2,
|
||||
"sdpa": Multimodal1TextSdpaAttention,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Multimodal1TextDecoderLayer(nn.Module):
|
||||
def __init__(self, config: Multimodal1TextConfig, layer_idx: int):
|
||||
super().__init__()
|
||||
self.hidden_size = config.hidden_size
|
||||
|
||||
self.self_attn = MULTIMODAL1_TEXT_ATTENTION_CLASSES[config._attn_implementation](
|
||||
config=config, layer_idx=layer_idx
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
self.mlp = Multimodal1TextMLP(config)
|
||||
self.input_layernorm = Multimodal1TextRMSNorm(config.hidden_size, eps=config.rms_norm_eps)
|
||||
self.post_attention_layernorm = Multimodal1TextRMSNorm(config.hidden_size, eps=config.rms_norm_eps)
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
hidden_states: torch.Tensor,
|
||||
attention_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
|
||||
position_ids: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
|
||||
past_key_value: Optional[Cache] = None,
|
||||
output_attentions: Optional[bool] = False,
|
||||
use_cache: Optional[bool] = False,
|
||||
cache_position: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
|
||||
position_embeddings: Optional[Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]] = None, # necessary, but kept here for BC
|
||||
**kwargs,
|
||||
) -> Tuple[torch.FloatTensor, Optional[Tuple[torch.FloatTensor, torch.FloatTensor]]]:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
hidden_states (`torch.FloatTensor`): input to the layer of shape `(batch, seq_len, embed_dim)`
|
||||
attention_mask (`torch.FloatTensor`, *optional*):
|
||||
attention mask of size `(batch_size, sequence_length)` if flash attention is used or `(batch_size, 1,
|
||||
query_sequence_length, key_sequence_length)` if default attention is used.
|
||||
output_attentions (`bool`, *optional*):
|
||||
Whether or not to return the attentions tensors of all attention layers. See `attentions` under
|
||||
returned tensors for more detail.
|
||||
use_cache (`bool`, *optional*):
|
||||
If set to `True`, `past_key_values` key value states are returned and can be used to speed up decoding
|
||||
(see `past_key_values`).
|
||||
past_key_value (`Tuple(torch.FloatTensor)`, *optional*): cached past key and value projection states
|
||||
cache_position (`torch.LongTensor` of shape `(sequence_length)`, *optional*):
|
||||
Indices depicting the position of the input sequence tokens in the sequence
|
||||
position_embeddings (`Tuple[torch.FloatTensor, torch.FloatTensor]`, *optional*):
|
||||
Tuple containing the cosine and sine positional embeddings of shape `(batch_size, seq_len, head_dim)`,
|
||||
with `head_dim` being the embedding dimension of each attention head.
|
||||
kwargs (`dict`, *optional*):
|
||||
Arbitrary kwargs to be ignored, used for FSDP and other methods that injects code
|
||||
into the model
|
||||
"""
|
||||
residual = hidden_states
|
||||
|
||||
hidden_states = self.input_layernorm(hidden_states)
|
||||
|
||||
# Self Attention
|
||||
hidden_states, self_attn_weights, present_key_value = self.self_attn(
|
||||
hidden_states=hidden_states,
|
||||
attention_mask=attention_mask,
|
||||
position_ids=position_ids,
|
||||
past_key_value=past_key_value,
|
||||
output_attentions=output_attentions,
|
||||
use_cache=use_cache,
|
||||
cache_position=cache_position,
|
||||
position_embeddings=position_embeddings,
|
||||
**kwargs,
|
||||
)
|
||||
hidden_states = residual + hidden_states
|
||||
|
||||
# Fully Connected
|
||||
residual = hidden_states
|
||||
hidden_states = self.post_attention_layernorm(hidden_states)
|
||||
hidden_states = self.mlp(hidden_states)
|
||||
hidden_states = residual + hidden_states
|
||||
|
||||
outputs = (hidden_states,)
|
||||
|
||||
if output_attentions:
|
||||
outputs += (self_attn_weights,)
|
||||
|
||||
if use_cache:
|
||||
outputs += (present_key_value,)
|
||||
|
||||
return outputs
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
MULTIMODAL1_TEXT_START_DOCSTRING = r"""
|
||||
This model inherits from [`PreTrainedModel`]. Check the superclass documentation for the generic methods the
|
||||
library implements for all its model (such as downloading or saving, resizing the input embeddings, pruning heads
|
||||
etc.)
|
||||
|
||||
This model is also a PyTorch [torch.nn.Module](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/nn.html#torch.nn.Module) subclass.
|
||||
Use it as a regular PyTorch Module and refer to the PyTorch documentation for all matter related to general usage
|
||||
and behavior.
|
||||
|
||||
Parameters:
|
||||
config ([`Multimodal1TextConfig`]):
|
||||
Model configuration class with all the parameters of the model. Initializing with a config file does not
|
||||
load the weights associated with the model, only the configuration. Check out the
|
||||
[`~PreTrainedModel.from_pretrained`] method to load the model weights.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@add_start_docstrings(
|
||||
"The bare Multimodal1Text Model outputting raw hidden-states without any specific head on top.",
|
||||
MULTIMODAL1_TEXT_START_DOCSTRING,
|
||||
)
|
||||
class Multimodal1TextPreTrainedModel(PreTrainedModel):
|
||||
config_class = Multimodal1TextConfig
|
||||
base_model_prefix = "model"
|
||||
supports_gradient_checkpointing = True
|
||||
_no_split_modules = ["Multimodal1TextDecoderLayer"]
|
||||
_skip_keys_device_placement = ["past_key_values"]
|
||||
_supports_flash_attn_2 = True
|
||||
_supports_sdpa = True
|
||||
_supports_cache_class = True
|
||||
_supports_quantized_cache = True
|
||||
_supports_static_cache = True
|
||||
|
||||
def _init_weights(self, module):
|
||||
std = self.config.initializer_range
|
||||
if isinstance(module, nn.Linear):
|
||||
module.weight.data.normal_(mean=0.0, std=std)
|
||||
if module.bias is not None:
|
||||
module.bias.data.zero_()
|
||||
elif isinstance(module, nn.Embedding):
|
||||
module.weight.data.normal_(mean=0.0, std=std)
|
||||
if module.padding_idx is not None:
|
||||
module.weight.data[module.padding_idx].zero_()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
MULTIMODAL1_TEXT_INPUTS_DOCSTRING = r"""
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
input_ids (`torch.LongTensor` of shape `(batch_size, sequence_length)`):
|
||||
Indices of input sequence tokens in the vocabulary. Padding will be ignored by default should you provide
|
||||
it.
|
||||
|
||||
Indices can be obtained using [`AutoTokenizer`]. See [`PreTrainedTokenizer.encode`] and
|
||||
[`PreTrainedTokenizer.__call__`] for details.
|
||||
|
||||
[What are input IDs?](../glossary#input-ids)
|
||||
attention_mask (`torch.Tensor` of shape `(batch_size, sequence_length)`, *optional*):
|
||||
Mask to avoid performing attention on padding token indices. Mask values selected in `[0, 1]`:
|
||||
|
||||
- 1 for tokens that are **not masked**,
|
||||
- 0 for tokens that are **masked**.
|
||||
|
||||
[What are attention masks?](../glossary#attention-mask)
|
||||
|
||||
Indices can be obtained using [`AutoTokenizer`]. See [`PreTrainedTokenizer.encode`] and
|
||||
[`PreTrainedTokenizer.__call__`] for details.
|
||||
|
||||
If `past_key_values` is used, optionally only the last `input_ids` have to be input (see
|
||||
`past_key_values`).
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to change padding behavior, you should read [`modeling_opt._prepare_decoder_attention_mask`]
|
||||
and modify to your needs. See diagram 1 in [the paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/1910.13461) for more
|
||||
information on the default strategy.
|
||||
|
||||
- 1 indicates the head is **not masked**,
|
||||
- 0 indicates the head is **masked**.
|
||||
position_ids (`torch.LongTensor` of shape `(batch_size, sequence_length)`, *optional*):
|
||||
Indices of positions of each input sequence tokens in the position embeddings. Selected in the range `[0,
|
||||
config.n_positions - 1]`.
|
||||
|
||||
[What are position IDs?](../glossary#position-ids)
|
||||
past_key_values (`Cache` or `tuple(tuple(torch.FloatTensor))`, *optional*):
|
||||
Pre-computed hidden-states (key and values in the self-attention blocks and in the cross-attention
|
||||
blocks) that can be used to speed up sequential decoding. This typically consists in the `past_key_values`
|
||||
returned by the model at a previous stage of decoding, when `use_cache=True` or `config.use_cache=True`.
|
||||
|
||||
Two formats are allowed:
|
||||
- a [`~cache_utils.Cache`] instance, see our
|
||||
[kv cache guide](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/en/kv_cache);
|
||||
- Tuple of `tuple(torch.FloatTensor)` of length `config.n_layers`, with each tuple having 2 tensors of
|
||||
shape `(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, embed_size_per_head)`). This is also known as the legacy
|
||||
cache format.
|
||||
|
||||
The model will output the same cache format that is fed as input. If no `past_key_values` are passed, the
|
||||
legacy cache format will be returned.
|
||||
|
||||
If `past_key_values` are used, the user can optionally input only the last `input_ids` (those that don't
|
||||
have their past key value states given to this model) of shape `(batch_size, 1)` instead of all `input_ids`
|
||||
of shape `(batch_size, sequence_length)`.
|
||||
inputs_embeds (`torch.FloatTensor` of shape `(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)`, *optional*):
|
||||
Optionally, instead of passing `input_ids` you can choose to directly pass an embedded representation. This
|
||||
is useful if you want more control over how to convert `input_ids` indices into associated vectors than the
|
||||
model's internal embedding lookup matrix.
|
||||
use_cache (`bool`, *optional*):
|
||||
If set to `True`, `past_key_values` key value states are returned and can be used to speed up decoding (see
|
||||
`past_key_values`).
|
||||
output_attentions (`bool`, *optional*):
|
||||
Whether or not to return the attentions tensors of all attention layers. See `attentions` under returned
|
||||
tensors for more detail.
|
||||
output_hidden_states (`bool`, *optional*):
|
||||
Whether or not to return the hidden states of all layers. See `hidden_states` under returned tensors for
|
||||
more detail.
|
||||
return_dict (`bool`, *optional*):
|
||||
Whether or not to return a [`~utils.ModelOutput`] instead of a plain tuple.
|
||||
cache_position (`torch.LongTensor` of shape `(sequence_length)`, *optional*):
|
||||
Indices depicting the position of the input sequence tokens in the sequence. Contrarily to `position_ids`,
|
||||
this tensor is not affected by padding. It is used to update the cache in the correct position and to infer
|
||||
the complete sequence length.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@add_start_docstrings(
|
||||
"The bare Multimodal1Text Model outputting raw hidden-states without any specific head on top.",
|
||||
MULTIMODAL1_TEXT_START_DOCSTRING,
|
||||
)
|
||||
class Multimodal1TextModel(Multimodal1TextPreTrainedModel):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Transformer decoder consisting of *config.num_hidden_layers* layers. Each layer is a [`Multimodal1TextDecoderLayer`]
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
config: Multimodal1TextConfig
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, config: Multimodal1TextConfig):
|
||||
super().__init__(config)
|
||||
self.padding_idx = config.pad_token_id
|
||||
self.vocab_size = config.vocab_size
|
||||
|
||||
self.embed_tokens = nn.Embedding(config.vocab_size, config.hidden_size, self.padding_idx)
|
||||
self.layers = nn.ModuleList(
|
||||
[Multimodal1TextDecoderLayer(config, layer_idx) for layer_idx in range(config.num_hidden_layers)]
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.norm = Multimodal1TextRMSNorm(config.hidden_size, eps=config.rms_norm_eps)
|
||||
self.rotary_emb = Multimodal1TextRotaryEmbedding(config=config)
|
||||
|
||||
self.gradient_checkpointing = False
|
||||
if getattr(config, "pretraining_tp", 1) != 1:
|
||||
logger.warn("`pretraining_tp` is deprecated, please use `model.tensor_parallel` instead.")
|
||||
|
||||
# Initialize weights and apply final processing
|
||||
self.post_init()
|
||||
|
||||
def get_input_embeddings(self):
|
||||
return self.embed_tokens
|
||||
|
||||
def set_input_embeddings(self, value):
|
||||
self.embed_tokens = value
|
||||
|
||||
@add_start_docstrings_to_model_forward(MULTIMODAL1_TEXT_INPUTS_DOCSTRING)
|
||||
def forward(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
input_ids: torch.LongTensor = None,
|
||||
attention_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
|
||||
position_ids: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
|
||||
past_key_values: Optional[Union[Cache, List[torch.FloatTensor]]] = None,
|
||||
inputs_embeds: Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None,
|
||||
use_cache: Optional[bool] = None,
|
||||
output_attentions: Optional[bool] = None,
|
||||
output_hidden_states: Optional[bool] = None,
|
||||
return_dict: Optional[bool] = None,
|
||||
cache_position: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
|
||||
**flash_attn_kwargs: Unpack[FlashAttentionKwargs],
|
||||
) -> Union[Tuple, BaseModelOutputWithPast]:
|
||||
output_attentions = output_attentions if output_attentions is not None else self.config.output_attentions
|
||||
output_hidden_states = (
|
||||
output_hidden_states if output_hidden_states is not None else self.config.output_hidden_states
|
||||
)
|
||||
use_cache = use_cache if use_cache is not None else self.config.use_cache
|
||||
return_dict = return_dict if return_dict is not None else self.config.use_return_dict
|
||||
|
||||
if (input_ids is None) ^ (inputs_embeds is not None):
|
||||
raise ValueError("You must specify exactly one of input_ids or inputs_embeds")
|
||||
|
||||
if self.gradient_checkpointing and self.training and use_cache:
|
||||
logger.warning_once(
|
||||
"`use_cache=True` is incompatible with gradient checkpointing. Setting `use_cache=False`."
|
||||
)
|
||||
use_cache = False
|
||||
|
||||
if inputs_embeds is None:
|
||||
inputs_embeds = self.embed_tokens(input_ids)
|
||||
|
||||
# kept for BC (non `Cache` `past_key_values` inputs)
|
||||
return_legacy_cache = False
|
||||
if use_cache and not isinstance(past_key_values, Cache):
|
||||
return_legacy_cache = True
|
||||
if past_key_values is None:
|
||||
past_key_values = DynamicCache()
|
||||
else:
|
||||
past_key_values = DynamicCache.from_legacy_cache(past_key_values)
|
||||
logger.warning_once(
|
||||
"We detected that you are passing `past_key_values` as a tuple of tuples. This is deprecated and "
|
||||
"will be removed in v4.47. Please convert your cache or use an appropriate `Cache` class "
|
||||
"(https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/kv_cache#legacy-cache-format)"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if cache_position is None:
|
||||
past_seen_tokens = past_key_values.get_seq_length() if past_key_values is not None else 0
|
||||
cache_position = torch.arange(
|
||||
past_seen_tokens, past_seen_tokens + inputs_embeds.shape[1], device=inputs_embeds.device
|
||||
)
|
||||
if position_ids is None:
|
||||
position_ids = cache_position.unsqueeze(0)
|
||||
|
||||
causal_mask = self._update_causal_mask(
|
||||
attention_mask, inputs_embeds, cache_position, past_key_values, output_attentions
|
||||
)
|
||||
hidden_states = inputs_embeds
|
||||
|
||||
# create position embeddings to be shared across the decoder layers
|
||||
position_embeddings = self.rotary_emb(hidden_states, position_ids)
|
||||
|
||||
# decoder layers
|
||||
all_hidden_states = () if output_hidden_states else None
|
||||
all_self_attns = () if output_attentions else None
|
||||
next_decoder_cache = None
|
||||
|
||||
for decoder_layer in self.layers[: self.config.num_hidden_layers]:
|
||||
if output_hidden_states:
|
||||
all_hidden_states += (hidden_states,)
|
||||
|
||||
if self.gradient_checkpointing and self.training:
|
||||
layer_outputs = self._gradient_checkpointing_func(
|
||||
decoder_layer.__call__,
|
||||
hidden_states,
|
||||
causal_mask,
|
||||
position_ids,
|
||||
past_key_values,
|
||||
output_attentions,
|
||||
use_cache,
|
||||
cache_position,
|
||||
position_embeddings,
|
||||
)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
layer_outputs = decoder_layer(
|
||||
hidden_states,
|
||||
attention_mask=causal_mask,
|
||||
position_ids=position_ids,
|
||||
past_key_value=past_key_values,
|
||||
output_attentions=output_attentions,
|
||||
use_cache=use_cache,
|
||||
cache_position=cache_position,
|
||||
position_embeddings=position_embeddings,
|
||||
**flash_attn_kwargs,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
hidden_states = layer_outputs[0]
|
||||
|
||||
if use_cache:
|
||||
next_decoder_cache = layer_outputs[2 if output_attentions else 1]
|
||||
|
||||
if output_attentions:
|
||||
all_self_attns += (layer_outputs[1],)
|
||||
|
||||
hidden_states = self.norm(hidden_states)
|
||||
|
||||
# add hidden states from the last decoder layer
|
||||
if output_hidden_states:
|
||||
all_hidden_states += (hidden_states,)
|
||||
|
||||
next_cache = next_decoder_cache if use_cache else None
|
||||
if return_legacy_cache:
|
||||
next_cache = next_cache.to_legacy_cache()
|
||||
|
||||
if not return_dict:
|
||||
return tuple(v for v in [hidden_states, next_cache, all_hidden_states, all_self_attns] if v is not None)
|
||||
return BaseModelOutputWithPast(
|
||||
last_hidden_state=hidden_states,
|
||||
past_key_values=next_cache,
|
||||
hidden_states=all_hidden_states,
|
||||
attentions=all_self_attns,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def _update_causal_mask(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
attention_mask: torch.Tensor,
|
||||
input_tensor: torch.Tensor,
|
||||
cache_position: torch.Tensor,
|
||||
past_key_values: Cache,
|
||||
output_attentions: bool,
|
||||
):
|
||||
if self.config._attn_implementation == "flash_attention_2":
|
||||
if attention_mask is not None and 0.0 in attention_mask:
|
||||
return attention_mask
|
||||
return None
|
||||
|
||||
# For SDPA, when possible, we will rely on its `is_causal` argument instead of its `attn_mask` argument, in
|
||||
# order to dispatch on Flash Attention 2. This feature is not compatible with static cache, as SDPA will fail
|
||||
# to infer the attention mask.
|
||||
past_seen_tokens = past_key_values.get_seq_length() if past_key_values is not None else 0
|
||||
using_static_cache = isinstance(past_key_values, StaticCache)
|
||||
|
||||
# When output attentions is True, sdpa implementation's forward method calls the eager implementation's forward
|
||||
if self.config._attn_implementation == "sdpa" and not using_static_cache and not output_attentions:
|
||||
if AttentionMaskConverter._ignore_causal_mask_sdpa(
|
||||
attention_mask,
|
||||
inputs_embeds=input_tensor,
|
||||
past_key_values_length=past_seen_tokens,
|
||||
is_training=self.training,
|
||||
):
|
||||
return None
|
||||
|
||||
dtype, device = input_tensor.dtype, input_tensor.device
|
||||
sequence_length = input_tensor.shape[1]
|
||||
if using_static_cache:
|
||||
target_length = past_key_values.get_max_cache_shape()
|
||||
else:
|
||||
target_length = (
|
||||
attention_mask.shape[-1]
|
||||
if isinstance(attention_mask, torch.Tensor)
|
||||
else past_seen_tokens + sequence_length + 1
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# In case the provided `attention` mask is 2D, we generate a causal mask here (4D).
|
||||
causal_mask = self._prepare_4d_causal_attention_mask_with_cache_position(
|
||||
attention_mask,
|
||||
sequence_length=sequence_length,
|
||||
target_length=target_length,
|
||||
dtype=dtype,
|
||||
device=device,
|
||||
cache_position=cache_position,
|
||||
batch_size=input_tensor.shape[0],
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if (
|
||||
self.config._attn_implementation == "sdpa"
|
||||
and attention_mask is not None
|
||||
and attention_mask.device.type == "cuda"
|
||||
and not output_attentions
|
||||
):
|
||||
# Attend to all tokens in fully masked rows in the causal_mask, for example the relevant first rows when
|
||||
# using left padding. This is required by F.scaled_dot_product_attention memory-efficient attention path.
|
||||
# Details: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/110213
|
||||
min_dtype = torch.finfo(dtype).min
|
||||
causal_mask = AttentionMaskConverter._unmask_unattended(causal_mask, min_dtype)
|
||||
|
||||
return causal_mask
|
||||
|
||||
@staticmethod
|
||||
def _prepare_4d_causal_attention_mask_with_cache_position(
|
||||
attention_mask: torch.Tensor,
|
||||
sequence_length: int,
|
||||
target_length: int,
|
||||
dtype: torch.dtype,
|
||||
device: torch.device,
|
||||
cache_position: torch.Tensor,
|
||||
batch_size: int,
|
||||
**kwargs,
|
||||
):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Creates a causal 4D mask of shape `(batch_size, 1, query_length, key_value_length)` from a 2D mask of shape
|
||||
`(batch_size, key_value_length)`, or if the input `attention_mask` is already 4D, do nothing.
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
attention_mask (`torch.Tensor`):
|
||||
A 2D attention mask of shape `(batch_size, key_value_length)` or a 4D attention mask of shape
|
||||
`(batch_size, 1, query_length, key_value_length)`.
|
||||
sequence_length (`int`):
|
||||
The sequence length being processed.
|
||||
target_length (`int`):
|
||||
The target length: when generating with static cache, the mask should be as long as the static cache,
|
||||
to account for the 0 padding, the part of the cache that is not filled yet.
|
||||
dtype (`torch.dtype`):
|
||||
The dtype to use for the 4D attention mask.
|
||||
device (`torch.device`):
|
||||
The device to plcae the 4D attention mask on.
|
||||
cache_position (`torch.Tensor`):
|
||||
Indices depicting the position of the input sequence tokens in the sequence.
|
||||
batch_size (`torch.Tensor`):
|
||||
Batch size.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if attention_mask is not None and attention_mask.dim() == 4:
|
||||
# In this case we assume that the mask comes already in inverted form and requires no inversion or slicing.
|
||||
causal_mask = attention_mask
|
||||
else:
|
||||
min_dtype = torch.finfo(dtype).min
|
||||
causal_mask = torch.full(
|
||||
(sequence_length, target_length), fill_value=min_dtype, dtype=dtype, device=device
|
||||
)
|
||||
if sequence_length != 1:
|
||||
causal_mask = torch.triu(causal_mask, diagonal=1)
|
||||
causal_mask *= torch.arange(target_length, device=device) > cache_position.reshape(-1, 1)
|
||||
causal_mask = causal_mask[None, None, :, :].expand(batch_size, 1, -1, -1)
|
||||
if attention_mask is not None:
|
||||
causal_mask = causal_mask.clone() # copy to contiguous memory for in-place edit
|
||||
mask_length = attention_mask.shape[-1]
|
||||
padding_mask = causal_mask[:, :, :, :mask_length] + attention_mask[:, None, None, :]
|
||||
padding_mask = padding_mask == 0
|
||||
causal_mask[:, :, :, :mask_length] = causal_mask[:, :, :, :mask_length].masked_fill(
|
||||
padding_mask, min_dtype
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
return causal_mask
|
||||
705
examples/modular-transformers/modeling_multimodal2.py
Normal file
705
examples/modular-transformers/modeling_multimodal2.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,705 @@
|
||||
# 🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨
|
||||
# This file was automatically generated from examples/modular-transformers/modular_multimodal2.py.
|
||||
# Do NOT edit this file manually as any edits will be overwritten by the generation of
|
||||
# the file from the modular. If any change should be done, please apply the change to the
|
||||
# modular_multimodal2.py file directly. One of our CI enforces this.
|
||||
# 🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨🚨
|
||||
|
||||
from typing import Optional, Tuple, Union
|
||||
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from torch import nn
|
||||
|
||||
from transformers.utils import add_start_docstrings
|
||||
|
||||
from ...activations import ACT2FN
|
||||
from ...modeling_outputs import BaseModelOutput, BaseModelOutputWithPooling
|
||||
from ...modeling_utils import PreTrainedModel
|
||||
from ...pytorch_utils import is_torch_greater_or_equal_than_2_2
|
||||
from ...utils import (
|
||||
add_start_docstrings_to_model_forward,
|
||||
is_flash_attn_2_available,
|
||||
is_flash_attn_greater_or_equal_2_10,
|
||||
logging,
|
||||
replace_return_docstrings,
|
||||
torch_int,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from .configuration_multimodal2 import Multimodal2Config, Multimodal2VisionConfig
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if is_flash_attn_2_available():
|
||||
from ...modeling_flash_attention_utils import _flash_attention_forward
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
logger = logging.get_logger(__name__)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Multimodal2VisionAttention(nn.Module):
|
||||
"""Multi-headed attention from 'Attention Is All You Need' paper"""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, config):
|
||||
super().__init__()
|
||||
self.config = config
|
||||
self.embed_dim = config.hidden_size
|
||||
self.num_heads = config.num_attention_heads
|
||||
self.head_dim = self.embed_dim // self.num_heads
|
||||
if self.head_dim * self.num_heads != self.embed_dim:
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
f"embed_dim must be divisible by num_heads (got `embed_dim`: {self.embed_dim} and `num_heads`:"
|
||||
f" {self.num_heads})."
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.scale = self.head_dim**-0.5
|
||||
self.dropout = config.attention_dropout
|
||||
|
||||
self.k_proj = nn.Linear(self.embed_dim, self.embed_dim)
|
||||
self.v_proj = nn.Linear(self.embed_dim, self.embed_dim)
|
||||
self.q_proj = nn.Linear(self.embed_dim, self.embed_dim)
|
||||
self.out_proj = nn.Linear(self.embed_dim, self.embed_dim)
|
||||
|
||||
def _shape(self, tensor: torch.Tensor, seq_len: int, bsz: int):
|
||||
return tensor.view(bsz, seq_len, self.num_heads, self.head_dim).transpose(1, 2).contiguous()
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
hidden_states: torch.Tensor,
|
||||
attention_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
|
||||
causal_attention_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
|
||||
output_attentions: Optional[bool] = False,
|
||||
) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor, Optional[torch.Tensor]]:
|
||||
"""Input shape: Batch x Time x Channel"""
|
||||
|
||||
bsz, tgt_len, embed_dim = hidden_states.size()
|
||||
|
||||
# get query proj
|
||||
query_states = self.q_proj(hidden_states) * self.scale
|
||||
key_states = self._shape(self.k_proj(hidden_states), -1, bsz)
|
||||
value_states = self._shape(self.v_proj(hidden_states), -1, bsz)
|
||||
|
||||
proj_shape = (bsz * self.num_heads, -1, self.head_dim)
|
||||
query_states = self._shape(query_states, tgt_len, bsz).view(*proj_shape)
|
||||
key_states = key_states.view(*proj_shape)
|
||||
value_states = value_states.view(*proj_shape)
|
||||
|
||||
src_len = key_states.size(1)
|
||||
attn_weights = torch.bmm(query_states, key_states.transpose(1, 2))
|
||||
|
||||
if attn_weights.size() != (bsz * self.num_heads, tgt_len, src_len):
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
f"Attention weights should be of size {(bsz * self.num_heads, tgt_len, src_len)}, but is"
|
||||
f" {attn_weights.size()}"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# apply the causal_attention_mask first
|
||||
if causal_attention_mask is not None:
|
||||
if causal_attention_mask.size() != (bsz, 1, tgt_len, src_len):
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
f"Attention mask should be of size {(bsz, 1, tgt_len, src_len)}, but is"
|
||||
f" {causal_attention_mask.size()}"
|
||||
)
|
||||
attn_weights = attn_weights.view(bsz, self.num_heads, tgt_len, src_len) + causal_attention_mask
|
||||
attn_weights = attn_weights.view(bsz * self.num_heads, tgt_len, src_len)
|
||||
|
||||
if attention_mask is not None:
|
||||
if attention_mask.size() != (bsz, 1, tgt_len, src_len):
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
f"Attention mask should be of size {(bsz, 1, tgt_len, src_len)}, but is {attention_mask.size()}"
|
||||
)
|
||||
attn_weights = attn_weights.view(bsz, self.num_heads, tgt_len, src_len) + attention_mask
|
||||
attn_weights = attn_weights.view(bsz * self.num_heads, tgt_len, src_len)
|
||||
|
||||
attn_weights = nn.functional.softmax(attn_weights, dim=-1)
|
||||
|
||||
if output_attentions:
|
||||
# this operation is a bit akward, but it's required to
|
||||
# make sure that attn_weights keeps its gradient.
|
||||
# In order to do so, attn_weights have to reshaped
|
||||
# twice and have to be reused in the following
|
||||
attn_weights_reshaped = attn_weights.view(bsz, self.num_heads, tgt_len, src_len)
|
||||
attn_weights = attn_weights_reshaped.view(bsz * self.num_heads, tgt_len, src_len)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
attn_weights_reshaped = None
|
||||
|
||||
attn_probs = nn.functional.dropout(attn_weights, p=self.dropout, training=self.training)
|
||||
|
||||
attn_output = torch.bmm(attn_probs, value_states)
|
||||
|
||||
if attn_output.size() != (bsz * self.num_heads, tgt_len, self.head_dim):
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
f"`attn_output` should be of size {(bsz, self.num_heads, tgt_len, self.head_dim)}, but is"
|
||||
f" {attn_output.size()}"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
attn_output = attn_output.view(bsz, self.num_heads, tgt_len, self.head_dim)
|
||||
attn_output = attn_output.transpose(1, 2)
|
||||
attn_output = attn_output.reshape(bsz, tgt_len, embed_dim)
|
||||
|
||||
attn_output = self.out_proj(attn_output)
|
||||
|
||||
return attn_output, attn_weights_reshaped
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Multimodal2VisionSdpaAttention(Multimodal2VisionAttention):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
SDPA attention module using torch.nn.functional.scaled_dot_product_attention. This module inherits from
|
||||
`Multimodal2VisionAttention` as the weights of the module stays untouched. The only changes are on the forward pass to adapt to
|
||||
SDPA API.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
# Adapted from Multimodal2VisionAttention.forward
|
||||
def forward(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
hidden_states: torch.Tensor,
|
||||
attention_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
|
||||
causal_attention_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
|
||||
output_attentions: Optional[bool] = False,
|
||||
) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor, Optional[torch.Tensor]]:
|
||||
if output_attentions:
|
||||
# TODO: Improve this warning with e.g. `model.config.attn_implementation = "manual"` once this is implemented.
|
||||
logger.warning_once(
|
||||
"Multimodal2VisionModel is using Multimodal2VisionSdpaAttention, but `torch.nn.functional.scaled_dot_product_attention` does not "
|
||||
"support `output_attentions=True`. Falling back to the manual attention implementation, but specifying "
|
||||
"the manual implementation will be required from Transformers version v5.0.0 onwards. This warning can "
|
||||
'be removed using the argument `attn_implementation="eager"` when loading the model.'
|
||||
)
|
||||
return super().forward(
|
||||
hidden_states=hidden_states,
|
||||
attention_mask=attention_mask,
|
||||
causal_attention_mask=causal_attention_mask,
|
||||
output_attentions=output_attentions,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# MULTIMODAL2_VISION text model uses both `causal_attention_mask` and `attention_mask`
|
||||
if attention_mask is not None and causal_attention_mask is not None:
|
||||
attn_mask = attention_mask + causal_attention_mask
|
||||
elif causal_attention_mask is not None:
|
||||
attn_mask = causal_attention_mask
|
||||
else:
|
||||
attn_mask = attention_mask
|
||||
|
||||
bsz, tgt_len, embed_dim = hidden_states.size()
|
||||
|
||||
query_states = self.q_proj(hidden_states)
|
||||
key_states = self.k_proj(hidden_states)
|
||||
value_states = self.v_proj(hidden_states)
|
||||
|
||||
query_states = query_states.view(bsz, -1, self.num_heads, self.head_dim).transpose(1, 2)
|
||||
key_states = key_states.view(bsz, -1, self.num_heads, self.head_dim).transpose(1, 2)
|
||||
value_states = value_states.view(bsz, -1, self.num_heads, self.head_dim).transpose(1, 2)
|
||||
|
||||
# SDPA with memory-efficient backend is currently (torch==2.1.2) bugged with non-contiguous inputs with custom attn_mask,
|
||||
# Reference: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/112577.
|
||||
if not is_torch_greater_or_equal_than_2_2 and query_states.device.type == "cuda" and attn_mask is not None:
|
||||
query_states = query_states.contiguous()
|
||||
key_states = key_states.contiguous()
|
||||
value_states = value_states.contiguous()
|
||||
|
||||
# MULTIMODAL2_VISION text model uses both `causal_attention_mask` and `attention_mask` sequentially.
|
||||
attn_output = torch.nn.functional.scaled_dot_product_attention(
|
||||
query_states,
|
||||
key_states,
|
||||
value_states,
|
||||
attn_mask=attn_mask,
|
||||
dropout_p=self.dropout if self.training else 0.0,
|
||||
scale=self.scale,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
attn_output = attn_output.transpose(1, 2)
|
||||
attn_output = attn_output.reshape(bsz, tgt_len, embed_dim)
|
||||
|
||||
attn_output = self.out_proj(attn_output)
|
||||
|
||||
return attn_output, None
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Multimodal2VisionFlashAttention2(Multimodal2VisionAttention):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Multimodal2VisionAttention flash attention module. This module inherits from `Multimodal2VisionAttention` as the weights of the module stays
|
||||
untouched. The only required change would be on the forward pass where it needs to correctly call the public API of
|
||||
flash attention and deal with padding tokens in case the input contains any of them.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
|
||||
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
|
||||
|
||||
# TODO: Should be removed once Flash Attention for RoCm is bumped to 2.1.
|
||||
# flash_attn<2.1 generates top-left aligned causal mask, while what is needed here is bottom-right alignement, that was made default for flash_attn>=2.1. This attribute is used to handle this difference. Reference: https://github.com/Dao-AILab/flash-attention/releases/tag/v2.1.0.
|
||||
# Beware that with flash_attn<2.1, using q_seqlen != k_seqlen (except for the case q_seqlen == 1) produces a wrong mask (top-left).
|
||||
self._flash_attn_uses_top_left_mask = not is_flash_attn_greater_or_equal_2_10()
|
||||
|
||||
# Adapted from transformers.models.llama.modeling_llama.LlamaFlashAttention2.forward
|
||||
def forward(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
hidden_states: torch.Tensor,
|
||||
attention_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
|
||||
causal_attention_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
|
||||
output_attentions: Optional[bool] = False,
|
||||
) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor, Optional[torch.Tensor]]:
|
||||
output_attentions = False
|
||||
|
||||
batch_size, q_len, _ = hidden_states.size()
|
||||
|
||||
query_states = self.q_proj(hidden_states)
|
||||
key_states = self.k_proj(hidden_states)
|
||||
value_states = self.v_proj(hidden_states)
|
||||
|
||||
# Flash attention requires the input to have the shape
|
||||
# batch_size x seq_length x head_dim x hidden_dim
|
||||
# therefore we just need to keep the original shape
|
||||
query_states = query_states.view(batch_size, q_len, self.num_heads, self.head_dim)
|
||||
key_states = key_states.view(batch_size, q_len, self.num_heads, self.head_dim)
|
||||
value_states = value_states.view(batch_size, q_len, self.num_heads, self.head_dim)
|
||||
|
||||
dropout_rate = self.dropout if self.training else 0.0
|
||||
|
||||
# In PEFT, usually we cast the layer norms in float32 for training stability reasons
|
||||
# therefore the input hidden states gets silently casted in float32. Hence, we need
|
||||
# cast them back in the correct dtype just to be sure everything works as expected.
|
||||
# This might slowdown training & inference so it is recommended to not cast the LayerNorms
|
||||
# in fp32.
|
||||
|
||||
input_dtype = query_states.dtype
|
||||
if input_dtype == torch.float32:
|
||||
if torch.is_autocast_enabled():
|
||||
target_dtype = torch.get_autocast_gpu_dtype()
|
||||
# Handle the case where the model is quantized
|
||||
elif hasattr(self.config, "_pre_quantization_dtype"):
|
||||
target_dtype = self.config._pre_quantization_dtype
|
||||
else:
|
||||
target_dtype = self.q_proj.weight.dtype
|
||||
|
||||
logger.warning_once(
|
||||
f"The input hidden states seems to be silently casted in float32, this might be related to"
|
||||
f" the fact you have upcasted embedding or layer norm layers in float32. We will cast back the input in"
|
||||
f" {target_dtype}."
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
query_states = query_states.to(target_dtype)
|
||||
key_states = key_states.to(target_dtype)
|
||||
value_states = value_states.to(target_dtype)
|
||||
|
||||
attn_output = _flash_attention_forward(
|
||||
query_states,
|
||||
key_states,
|
||||
value_states,
|
||||
attention_mask,
|
||||
q_len,
|
||||
dropout=dropout_rate,
|
||||
is_causal=causal_attention_mask is not None,
|
||||
use_top_left_mask=self._flash_attn_uses_top_left_mask,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
attn_output = attn_output.reshape(batch_size, q_len, self.embed_dim).contiguous()
|
||||
attn_output = self.out_proj(attn_output)
|
||||
|
||||
if not output_attentions:
|
||||
attn_weights = None
|
||||
|
||||
return attn_output, attn_weights
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Multimodal2VisionMLP(nn.Module):
|
||||
def __init__(self, config):
|
||||
super().__init__()
|
||||
self.config = config
|
||||
self.activation_fn = ACT2FN[config.hidden_act]
|
||||
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(config.hidden_size, config.intermediate_size)
|
||||
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(config.intermediate_size, config.hidden_size)
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, hidden_states: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
|
||||
hidden_states = self.fc1(hidden_states)
|
||||
hidden_states = self.activation_fn(hidden_states)
|
||||
hidden_states = self.fc2(hidden_states)
|
||||
return hidden_states
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
MULTIMODAL2_VISION_ATTENTION_CLASSES = {
|
||||
"eager": Multimodal2VisionAttention,
|
||||
"sdpa": Multimodal2VisionSdpaAttention,
|
||||
"flash_attention_2": Multimodal2VisionFlashAttention2,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Multimodal2VisionEncoderLayer(nn.Module):
|
||||
def __init__(self, config):
|
||||
super().__init__()
|
||||
self.embed_dim = config.hidden_size
|
||||
self.self_attn = MULTIMODAL2_VISION_ATTENTION_CLASSES[config._attn_implementation](config)
|
||||
self.layer_norm1 = nn.LayerNorm(self.embed_dim, eps=config.layer_norm_eps)
|
||||
self.mlp = Multimodal2VisionMLP(config)
|
||||
self.layer_norm2 = nn.LayerNorm(self.embed_dim, eps=config.layer_norm_eps)
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
hidden_states: torch.Tensor,
|
||||
attention_mask: torch.Tensor,
|
||||
causal_attention_mask: torch.Tensor,
|
||||
output_attentions: Optional[bool] = False,
|
||||
) -> Tuple[torch.FloatTensor]:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
hidden_states (`torch.FloatTensor`): input to the layer of shape `(batch, seq_len, embed_dim)`
|
||||
attention_mask (`torch.FloatTensor`): attention mask of size
|
||||
`(batch, 1, tgt_len, src_len)` where padding elements are indicated by very large negative values.
|
||||
`(config.encoder_attention_heads,)`.
|
||||
output_attentions (`bool`, *optional*):
|
||||
Whether or not to return the attentions tensors of all attention layers. See `attentions` under
|
||||
returned tensors for more detail.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
residual = hidden_states
|
||||
|
||||
hidden_states = self.layer_norm1(hidden_states)
|
||||
hidden_states, attn_weights = self.self_attn(
|
||||
hidden_states=hidden_states,
|
||||
attention_mask=attention_mask,
|
||||
causal_attention_mask=causal_attention_mask,
|
||||
output_attentions=output_attentions,
|
||||
)
|
||||
hidden_states = residual + hidden_states
|
||||
|
||||
residual = hidden_states
|
||||
hidden_states = self.layer_norm2(hidden_states)
|
||||
hidden_states = self.mlp(hidden_states)
|
||||
hidden_states = residual + hidden_states
|
||||
|
||||
outputs = (hidden_states,)
|
||||
|
||||
if output_attentions:
|
||||
outputs += (attn_weights,)
|
||||
|
||||
return outputs
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Multimodal2VisionEncoder(nn.Module):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Transformer encoder consisting of `config.num_hidden_layers` self attention layers. Each layer is a
|
||||
[`Multimodal2VisionEncoderLayer`].
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
config: Multimodal2VisionConfig
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, config):
|
||||
super().__init__()
|
||||
self.config = config
|
||||
self.layers = nn.ModuleList([Multimodal2VisionEncoderLayer(config) for _ in range(config.num_hidden_layers)])
|
||||
self.gradient_checkpointing = False
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
inputs_embeds,
|
||||
attention_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
|
||||
causal_attention_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
|
||||
output_attentions: Optional[bool] = None,
|
||||
output_hidden_states: Optional[bool] = None,
|
||||
return_dict: Optional[bool] = None,
|
||||
) -> Union[Tuple, BaseModelOutput]:
|
||||
r"""
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
inputs_embeds (`torch.FloatTensor` of shape `(batch_size, sequence_length, hidden_size)`):
|
||||
Optionally, instead of passing `input_ids` you can choose to directly pass an embedded representation.
|
||||
This is useful if you want more control over how to convert `input_ids` indices into associated vectors
|
||||
than the model's internal embedding lookup matrix.
|
||||
attention_mask (`torch.Tensor` of shape `(batch_size, sequence_length)`, *optional*):
|
||||
Mask to avoid performing attention on padding token indices. Mask values selected in `[0, 1]`:
|
||||
|
||||
- 1 for tokens that are **not masked**,
|
||||
- 0 for tokens that are **masked**.
|
||||
|
||||
[What are attention masks?](../glossary#attention-mask)
|
||||
causal_attention_mask (`torch.Tensor` of shape `(batch_size, sequence_length)`, *optional*):
|
||||
Causal mask for the text model. Mask values selected in `[0, 1]`:
|
||||
|
||||
- 1 for tokens that are **not masked**,
|
||||
- 0 for tokens that are **masked**.
|
||||
|
||||
[What are attention masks?](../glossary#attention-mask)
|
||||
output_attentions (`bool`, *optional*):
|
||||
Whether or not to return the attentions tensors of all attention layers. See `attentions` under
|
||||
returned tensors for more detail.
|
||||
output_hidden_states (`bool`, *optional*):
|
||||
Whether or not to return the hidden states of all layers. See `hidden_states` under returned tensors
|
||||
for more detail.
|
||||
return_dict (`bool`, *optional*):
|
||||
Whether or not to return a [`~utils.ModelOutput`] instead of a plain tuple.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
output_attentions = output_attentions if output_attentions is not None else self.config.output_attentions
|
||||
output_hidden_states = (
|
||||
output_hidden_states if output_hidden_states is not None else self.config.output_hidden_states
|
||||
)
|
||||
return_dict = return_dict if return_dict is not None else self.config.use_return_dict
|
||||
|
||||
encoder_states = () if output_hidden_states else None
|
||||
all_attentions = () if output_attentions else None
|
||||
|
||||
hidden_states = inputs_embeds
|
||||
for idx, encoder_layer in enumerate(self.layers):
|
||||
if output_hidden_states:
|
||||
encoder_states = encoder_states + (hidden_states,)
|
||||
if self.gradient_checkpointing and self.training:
|
||||
layer_outputs = self._gradient_checkpointing_func(
|
||||
encoder_layer.__call__,
|
||||
hidden_states,
|
||||
attention_mask,
|
||||
causal_attention_mask,
|
||||
output_attentions,
|
||||
)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
layer_outputs = encoder_layer(
|
||||
hidden_states,
|
||||
attention_mask,
|
||||
causal_attention_mask,
|
||||
output_attentions=output_attentions,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
hidden_states = layer_outputs[0]
|
||||
|
||||
if output_attentions:
|
||||
all_attentions = all_attentions + (layer_outputs[1],)
|
||||
|
||||
if output_hidden_states:
|
||||
encoder_states = encoder_states + (hidden_states,)
|
||||
|
||||
if not return_dict:
|
||||
return tuple(v for v in [hidden_states, encoder_states, all_attentions] if v is not None)
|
||||
return BaseModelOutput(
|
||||
last_hidden_state=hidden_states, hidden_states=encoder_states, attentions=all_attentions
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Multimodal2VisionEmbeddings(nn.Module):
|
||||
def __init__(self, config: Multimodal2VisionConfig):
|
||||
super().__init__()
|
||||
self.config = config
|
||||
self.embed_dim = config.hidden_size
|
||||
self.image_size = config.image_size
|
||||
self.patch_size = config.patch_size
|
||||
|
||||
self.class_embedding = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(self.embed_dim))
|
||||
|
||||
self.patch_embedding = nn.Conv2d(
|
||||
in_channels=config.num_channels,
|
||||
out_channels=self.embed_dim,
|
||||
kernel_size=self.patch_size,
|
||||
stride=self.patch_size,
|
||||
bias=False,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
self.num_patches = (self.image_size // self.patch_size) ** 2
|
||||
self.num_positions = self.num_patches + 1
|
||||
self.position_embedding = nn.Embedding(self.num_positions, self.embed_dim)
|
||||
self.register_buffer("position_ids", torch.arange(self.num_positions).expand((1, -1)), persistent=False)
|
||||
|
||||
def interpolate_pos_encoding(self, embeddings: torch.Tensor, height: int, width: int) -> torch.Tensor:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
This method allows to interpolate the pre-trained position encodings, to be able to use the model on higher resolution
|
||||
images. This method is also adapted to support torch.jit tracing.
|
||||
|
||||
Adapted from:
|
||||
- https://github.com/facebookresearch/dino/blob/de9ee3df6cf39fac952ab558447af1fa1365362a/vision_transformer.py#L174-L194, and
|
||||
- https://github.com/facebookresearch/dinov2/blob/e1277af2ba9496fbadf7aec6eba56e8d882d1e35/dinov2/models/vision_transformer.py#L179-L211
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
num_patches = embeddings.shape[1] - 1
|
||||
position_embedding = self.position_embedding.weight.unsqueeze(0)
|
||||
num_positions = position_embedding.shape[1] - 1
|
||||
|
||||
# always interpolate when tracing to ensure the exported model works for dynamic input shapes
|
||||
if not torch.jit.is_tracing() and num_patches == num_positions and height == width:
|
||||
return self.position_embedding(self.position_ids)
|
||||
|
||||
class_pos_embed = position_embedding[:, :1]
|
||||
patch_pos_embed = position_embedding[:, 1:]
|
||||
|
||||
dim = embeddings.shape[-1]
|
||||
|
||||
new_height = height // self.patch_size
|
||||
new_width = width // self.patch_size
|
||||
|
||||
sqrt_num_positions = torch_int(num_positions**0.5)
|
||||
patch_pos_embed = patch_pos_embed.reshape(1, sqrt_num_positions, sqrt_num_positions, dim)
|
||||
patch_pos_embed = patch_pos_embed.permute(0, 3, 1, 2)
|
||||
|
||||
patch_pos_embed = nn.functional.interpolate(
|
||||
patch_pos_embed,
|
||||
size=(new_height, new_width),
|
||||
mode="bicubic",
|
||||
align_corners=False,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
patch_pos_embed = patch_pos_embed.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).view(1, -1, dim)
|
||||
|
||||
return torch.cat((class_pos_embed, patch_pos_embed), dim=1)
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, pixel_values: torch.FloatTensor, interpolate_pos_encoding=False) -> torch.Tensor:
|
||||
batch_size, _, height, width = pixel_values.shape
|
||||
if not interpolate_pos_encoding and (height != self.image_size or width != self.image_size):
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
f"Input image size ({height}*{width}) doesn't match model" f" ({self.image_size}*{self.image_size})."
|
||||
)
|
||||
target_dtype = self.patch_embedding.weight.dtype
|
||||
patch_embeds = self.patch_embedding(pixel_values.to(dtype=target_dtype)) # shape = [*, width, grid, grid]
|
||||
patch_embeds = patch_embeds.flatten(2).transpose(1, 2)
|
||||
|
||||
class_embeds = self.class_embedding.expand(batch_size, 1, -1)
|
||||
embeddings = torch.cat([class_embeds, patch_embeds], dim=1)
|
||||
if interpolate_pos_encoding:
|
||||
embeddings = embeddings + self.interpolate_pos_encoding(embeddings, height, width)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
embeddings = embeddings + self.position_embedding(self.position_ids)
|
||||
return embeddings
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
MULTIMODAL2_VISION_INPUTS_DOCSTRING = r"""
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
pixel_values (`torch.FloatTensor` of shape `(batch_size, num_channels, height, width)`):
|
||||
Pixel values. Padding will be ignored by default should you provide it. Pixel values can be obtained using
|
||||
[`AutoImageProcessor`]. See [`Multimodal2ImageProcessor.__call__`] for details.
|
||||
output_attentions (`bool`, *optional*):
|
||||
Whether or not to return the attentions tensors of all attention layers. See `attentions` under returned
|
||||
tensors for more detail.
|
||||
output_hidden_states (`bool`, *optional*):
|
||||
Whether or not to return the hidden states of all layers. See `hidden_states` under returned tensors for
|
||||
more detail.
|
||||
interpolate_pos_encoding (`bool`, *optional*, defaults `False`):
|
||||
Whether to interpolate the pre-trained position encodings.
|
||||
return_dict (`bool`, *optional*):
|
||||
Whether or not to return a [`~utils.ModelOutput`] instead of a plain tuple.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Multimodal2VisionTransformer(nn.Module):
|
||||
def __init__(self, config):
|
||||
super().__init__()
|
||||
self.config = config
|
||||
embed_dim = config.hidden_size
|
||||
|
||||
self.embeddings = Multimodal2VisionEmbeddings(config)
|
||||
self.pre_layrnorm = nn.LayerNorm(embed_dim, eps=config.layer_norm_eps)
|
||||
self.encoder = Multimodal2VisionEncoder(config)
|
||||
self.post_layernorm = nn.LayerNorm(embed_dim, eps=config.layer_norm_eps)
|
||||
|
||||
@add_start_docstrings_to_model_forward(MULTIMODAL2_VISION_INPUTS_DOCSTRING)
|
||||
@replace_return_docstrings(output_type=BaseModelOutputWithPooling, config_class=Multimodal2VisionConfig)
|
||||
def forward(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
pixel_values: Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None,
|
||||
output_attentions: Optional[bool] = None,
|
||||
output_hidden_states: Optional[bool] = None,
|
||||
return_dict: Optional[bool] = None,
|
||||
interpolate_pos_encoding: Optional[bool] = False,
|
||||
) -> Union[Tuple, BaseModelOutputWithPooling]:
|
||||
r"""
|
||||
Returns:
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
output_attentions = output_attentions if output_attentions is not None else self.config.output_attentions
|
||||
output_hidden_states = (
|
||||
output_hidden_states if output_hidden_states is not None else self.config.output_hidden_states
|
||||
)
|
||||
return_dict = return_dict if return_dict is not None else self.config.use_return_dict
|
||||
|
||||
if pixel_values is None:
|
||||
raise ValueError("You have to specify pixel_values")
|
||||
|
||||
hidden_states = self.embeddings(pixel_values, interpolate_pos_encoding=interpolate_pos_encoding)
|
||||
hidden_states = self.pre_layrnorm(hidden_states)
|
||||
|
||||
encoder_outputs = self.encoder(
|
||||
inputs_embeds=hidden_states,
|
||||
output_attentions=output_attentions,
|
||||
output_hidden_states=output_hidden_states,
|
||||
return_dict=return_dict,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
last_hidden_state = encoder_outputs[0]
|
||||
pooled_output = last_hidden_state[:, 0, :]
|
||||
pooled_output = self.post_layernorm(pooled_output)
|
||||
|
||||
if not return_dict:
|
||||
return (last_hidden_state, pooled_output) + encoder_outputs[1:]
|
||||
|
||||
return BaseModelOutputWithPooling(
|
||||
last_hidden_state=last_hidden_state,
|
||||
pooler_output=pooled_output,
|
||||
hidden_states=encoder_outputs.hidden_states,
|
||||
attentions=encoder_outputs.attentions,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Multimodal2VisionPreTrainedModel(PreTrainedModel):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
An abstract class to handle weights initialization and a simple interface for downloading and loading pretrained
|
||||
models.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
config_class = Multimodal2Config
|
||||
base_model_prefix = "multimodal2_vision"
|
||||
supports_gradient_checkpointing = True
|
||||
_supports_sdpa = True
|
||||
_supports_flash_attn_2 = True
|
||||
|
||||
def _init_weights(self, module):
|
||||
"""Initialize the weights"""
|
||||
if isinstance(module, Multimodal2VisionMLP):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
MULTIMODAL2_VISION_START_DOCSTRING = "doc"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@add_start_docstrings("New doc", MULTIMODAL2_VISION_START_DOCSTRING)
|
||||
class Multimodal2VisionModel(Multimodal2VisionPreTrainedModel):
|
||||
config_class = Multimodal2VisionConfig
|
||||
main_input_name = "pixel_values"
|
||||
_no_split_modules = ["Multimodal2VisionEncoderLayer"]
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, config: Multimodal2VisionConfig):
|
||||
super().__init__(config)
|
||||
self.vision_model = Multimodal2VisionTransformer(config)
|
||||
# Initialize weights and apply final processing
|
||||
self.post_init()
|
||||
|
||||
def get_input_embeddings(self) -> nn.Module:
|
||||
return self.vision_model.embeddings.patch_embedding
|
||||
|
||||
@add_start_docstrings_to_model_forward(MULTIMODAL2_VISION_INPUTS_DOCSTRING)
|
||||
@replace_return_docstrings(output_type=BaseModelOutputWithPooling, config_class=Multimodal2VisionConfig)
|
||||
def forward(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
pixel_values: Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None,
|
||||
output_attentions: Optional[bool] = None,
|
||||
output_hidden_states: Optional[bool] = None,
|
||||
interpolate_pos_encoding: bool = False,
|
||||
return_dict: Optional[bool] = None,
|
||||
) -> Union[Tuple, BaseModelOutputWithPooling]:
|
||||
r"""
|
||||
Returns:
|
||||
|
||||
Examples:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from PIL import Image
|
||||
>>> import requests
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoProcessor, Multimodal2VisionModel
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = Multimodal2VisionModel.from_pretrained("openai/multimodal2-vit-base-patch32")
|
||||
>>> processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained("openai/multimodal2-vit-base-patch32")
|
||||
|
||||
>>> url = "http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg"
|
||||
>>> image = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw)
|
||||
|
||||
>>> inputs = processor(images=image, return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
|
||||
>>> outputs = model(**inputs)
|
||||
>>> last_hidden_state = outputs.last_hidden_state
|
||||
>>> pooled_output = outputs.pooler_output # pooled CLS states
|
||||
```"""
|
||||
return_dict = return_dict if return_dict is not None else self.config.use_return_dict
|
||||
|
||||
return self.vision_model(
|
||||
pixel_values=pixel_values,
|
||||
output_attentions=output_attentions,
|
||||
output_hidden_states=output_hidden_states,
|
||||
return_dict=return_dict,
|
||||
interpolate_pos_encoding=interpolate_pos_encoding,
|
||||
)
|
||||
@ -265,7 +265,7 @@ class NewTaskModelForNewTask(NewTaskModelPreTrainedModel, GenerationMixin):
|
||||
min_dtype = torch.finfo(dtype).min
|
||||
sequence_length = inputs_embeds.shape[1]
|
||||
if using_static_cache:
|
||||
target_length = past_key_values.get_max_length()
|
||||
target_length = past_key_values.get_max_cache_shape()
|
||||
else:
|
||||
target_length = (
|
||||
attention_mask.shape[-1]
|
||||
@ -358,9 +358,9 @@ class NewTaskModelForNewTask(NewTaskModelPreTrainedModel, GenerationMixin):
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from PIL import Image
|
||||
>>> import requests
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoProcessor, NewTaskModelForConditionalGeneration
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoProcessor, NewTaskModelForNewTask
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = NewTaskModelForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained("google/NewTaskModel-test-224px-hf")
|
||||
>>> model = NewTaskModelForNewTask.from_pretrained("google/NewTaskModel-test-224px-hf")
|
||||
>>> processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained("google/NewTaskModel-test-224px-hf")
|
||||
|
||||
>>> prompt = "answer en Where is the cow standing?"
|
||||
|
||||
@ -228,9 +228,6 @@ class SuperAttention(nn.Module):
|
||||
self.v_proj = nn.Linear(self.hidden_size, self.num_key_value_heads * self.head_dim, bias=config.attention_bias)
|
||||
self.o_proj = nn.Linear(self.num_heads * self.head_dim, self.hidden_size, bias=config.attention_bias)
|
||||
|
||||
# TODO (joao): remove in v4.46 (RoPE is computed in the model, not in the decoder layers)
|
||||
self.rotary_emb = SuperRotaryEmbedding(config=self.config)
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
hidden_states: torch.Tensor,
|
||||
@ -240,7 +237,7 @@ class SuperAttention(nn.Module):
|
||||
output_attentions: bool = False,
|
||||
use_cache: bool = False,
|
||||
cache_position: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
|
||||
position_embeddings: Optional[Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]] = None, # will become mandatory in v4.46
|
||||
position_embeddings: Optional[Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]] = None, # necessary, but kept here for BC
|
||||
**kwargs,
|
||||
) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor, Optional[torch.Tensor], Optional[Tuple[torch.Tensor]]]:
|
||||
bsz, q_len, _ = hidden_states.size()
|
||||
@ -254,16 +251,7 @@ class SuperAttention(nn.Module):
|
||||
key_states = key_states.view(bsz, q_len, -1, self.head_dim).transpose(1, 2)
|
||||
value_states = value_states.view(bsz, q_len, -1, self.head_dim).transpose(1, 2)
|
||||
|
||||
if position_embeddings is None:
|
||||
logger.warning_once(
|
||||
"The attention layers in this model are transitioning from computing the RoPE embeddings internally "
|
||||
"through `position_ids` (2D tensor with the indexes of the tokens), to using externally computed "
|
||||
"`position_embeddings` (Tuple of tensors, containing cos and sin). In v4.46 `position_ids` will be "
|
||||
"removed and `position_embeddings` will be mandatory."
|
||||
)
|
||||
cos, sin = self.rotary_emb(value_states, position_ids)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
cos, sin = position_embeddings
|
||||
cos, sin = position_embeddings
|
||||
query_states, key_states = apply_rotary_pos_emb(query_states, key_states, cos, sin)
|
||||
|
||||
if past_key_value is not None:
|
||||
@ -326,7 +314,7 @@ class SuperFlashAttention2(SuperAttention):
|
||||
output_attentions: bool = False,
|
||||
use_cache: bool = False,
|
||||
cache_position: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
|
||||
position_embeddings: Optional[Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]] = None, # will become mandatory in v4.46
|
||||
position_embeddings: Optional[Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]] = None, # necessary, but kept here for BC
|
||||
**kwargs: Unpack[FlashAttentionKwargs],
|
||||
) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor, Optional[torch.Tensor], Optional[Tuple[torch.Tensor]]]:
|
||||
if isinstance(past_key_value, StaticCache):
|
||||
@ -350,16 +338,7 @@ class SuperFlashAttention2(SuperAttention):
|
||||
key_states = key_states.view(bsz, q_len, self.num_key_value_heads, self.head_dim).transpose(1, 2)
|
||||
value_states = value_states.view(bsz, q_len, self.num_key_value_heads, self.head_dim).transpose(1, 2)
|
||||
|
||||
if position_embeddings is None:
|
||||
logger.warning_once(
|
||||
"The attention layers in this model are transitioning from computing the RoPE embeddings internally "
|
||||
"through `position_ids` (2D tensor with the indexes of the tokens), to using externally computed "
|
||||
"`position_embeddings` (Tuple of tensors, containing cos and sin). In v4.46 `position_ids` will be "
|
||||
"removed and `position_embeddings` will be mandatory."
|
||||
)
|
||||
cos, sin = self.rotary_emb(value_states, position_ids)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
cos, sin = position_embeddings
|
||||
cos, sin = position_embeddings
|
||||
query_states, key_states = apply_rotary_pos_emb(query_states, key_states, cos, sin)
|
||||
|
||||
if past_key_value is not None:
|
||||
@ -441,7 +420,7 @@ class SuperSdpaAttention(SuperAttention):
|
||||
output_attentions: bool = False,
|
||||
use_cache: bool = False,
|
||||
cache_position: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
|
||||
position_embeddings: Optional[Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]] = None, # will become mandatory in v4.46
|
||||
position_embeddings: Optional[Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]] = None, # necessary, but kept here for BC
|
||||
**kwargs,
|
||||
) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor, Optional[torch.Tensor], Optional[Tuple[torch.Tensor]]]:
|
||||
if output_attentions:
|
||||
@ -472,16 +451,7 @@ class SuperSdpaAttention(SuperAttention):
|
||||
key_states = key_states.view(bsz, q_len, -1, self.head_dim).transpose(1, 2)
|
||||
value_states = value_states.view(bsz, q_len, -1, self.head_dim).transpose(1, 2)
|
||||
|
||||
if position_embeddings is None:
|
||||
logger.warning_once(
|
||||
"The attention layers in this model are transitioning from computing the RoPE embeddings internally "
|
||||
"through `position_ids` (2D tensor with the indexes of the tokens), to using externally computed "
|
||||
"`position_embeddings` (Tuple of tensors, containing cos and sin). In v4.46 `position_ids` will be "
|
||||
"removed and `position_embeddings` will be mandatory."
|
||||
)
|
||||
cos, sin = self.rotary_emb(value_states, position_ids)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
cos, sin = position_embeddings
|
||||
cos, sin = position_embeddings
|
||||
query_states, key_states = apply_rotary_pos_emb(query_states, key_states, cos, sin)
|
||||
|
||||
if past_key_value is not None:
|
||||
@ -551,7 +521,7 @@ class SuperDecoderLayer(nn.Module):
|
||||
output_attentions: Optional[bool] = False,
|
||||
use_cache: Optional[bool] = False,
|
||||
cache_position: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
|
||||
position_embeddings: Optional[Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]] = None, # will become mandatory in v4.46
|
||||
position_embeddings: Optional[Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]] = None, # necessary, but kept here for BC
|
||||
**kwargs,
|
||||
) -> Tuple[torch.FloatTensor, Optional[Tuple[torch.FloatTensor, torch.FloatTensor]]]:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,6 @@
|
||||
from transformers.models.clip.modeling_clip import CLIPEncoderLayer
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Check if we can correctly grab dependencies with correct naming from all UPPERCASE old model
|
||||
class FromUppercaseModelEncoderLayer(CLIPEncoderLayer):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
6
examples/modular-transformers/modular_multimodal1.py
Normal file
6
examples/modular-transformers/modular_multimodal1.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,6 @@
|
||||
from transformers.models.llama.modeling_llama import LlamaModel
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Check that we can correctly change the prefix (here add Text part at the end of the name)
|
||||
class Multimodal1TextModel(LlamaModel):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
88
examples/modular-transformers/modular_multimodal2.py
Normal file
88
examples/modular-transformers/modular_multimodal2.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,88 @@
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Here, because clip is not consistent with the use of the "Text" and "Vision" prefixes, we cannot simply use
|
||||
```
|
||||
class Multimodal2VisionModel(CLIPVisionModel):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
```
|
||||
with the hope that all dependencies will be renamed as `Multimodal2VisionClass`. For this reason, if we want consistency and
|
||||
use the "Vision" part everywhere, we need to overwrite the intermediate classes and add the prefix everytime.
|
||||
This adds noise to the modular, but is unfortunately unavoidable.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
from torch import nn
|
||||
|
||||
from transformers.models.clip.modeling_clip import (
|
||||
CLIPMLP,
|
||||
CLIPAttention,
|
||||
CLIPEncoder,
|
||||
CLIPEncoderLayer,
|
||||
CLIPFlashAttention2,
|
||||
CLIPPreTrainedModel,
|
||||
CLIPSdpaAttention,
|
||||
CLIPVisionModel,
|
||||
CLIPVisionTransformer,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from transformers.utils import add_start_docstrings
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Multimodal2VisionAttention(CLIPAttention):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Check that adding the second base class correctly set the parent, even though in clip it does not have the "Vision" part
|
||||
class Multimodal2VisionSdpaAttention(CLIPSdpaAttention, Multimodal2VisionAttention):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Check that adding the second base class correctly set the parent, even though in clip it does not have the "Vision" part
|
||||
class Multimodal2VisionFlashAttention2(CLIPFlashAttention2, Multimodal2VisionAttention):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
MULTIMODAL2_VISION_ATTENTION_CLASSES = {
|
||||
"eager": Multimodal2VisionAttention,
|
||||
"sdpa": Multimodal2VisionSdpaAttention,
|
||||
"flash_attention_2": Multimodal2VisionFlashAttention2,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Multimodal2VisionMLP(CLIPMLP):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Multimodal2VisionEncoderLayer(CLIPEncoderLayer):
|
||||
def __init__(self, config):
|
||||
super().__init__()
|
||||
self.self_attn = MULTIMODAL2_VISION_ATTENTION_CLASSES[config._attn_implementation](config)
|
||||
self.mlp = Multimodal2VisionMLP(config)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Multimodal2VisionEncoder(CLIPEncoder):
|
||||
def __init__(self, config):
|
||||
super().__init__(config)
|
||||
self.layers = nn.ModuleList([Multimodal2VisionEncoderLayer(config) for _ in range(config.num_hidden_layers)])
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Finally here the `Vision` part was correct in CLIP, but we still need to tell it that the encoder arg should use it as well
|
||||
class Multimodal2VisionTransformer(CLIPVisionTransformer):
|
||||
def __init__(self, config):
|
||||
super().__init__(config)
|
||||
self.encoder = Multimodal2VisionEncoder(config)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Multimodal2VisionPreTrainedModel(CLIPPreTrainedModel):
|
||||
def _init_weights(self, module):
|
||||
if isinstance(module, Multimodal2VisionMLP):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
MULTIMODAL2_VISION_START_DOCSTRING = "doc"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Here the only arg `self.vision_model = CLIPVisionTransformer(config)` in CLIPVisionModel already has the "Vision" part, so
|
||||
# no need to overwrite it, it will look for `Multimodal2VisionTransformer` which has already being redefined above
|
||||
# Note: we may want to redefine decorator as well for full consistency, as CLIP does not use "CLIP_VISION_START_DOCSTRING" but only
|
||||
# "CLIP_START_DOCSTRING"
|
||||
@add_start_docstrings("New doc", MULTIMODAL2_VISION_START_DOCSTRING)
|
||||
class Multimodal2VisionModel(CLIPVisionModel, Multimodal2VisionPreTrainedModel):
|
||||
_no_split_modules = ["Multimodal2VisionEncoderLayer"]
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,9 @@
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
import torch.utils.checkpoint
|
||||
|
||||
from transformers.models.blip.image_processing_blip import BlipImageProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class ImgprocModelImageProcessor(BlipImageProcessor):
|
||||
def new_image_processing_method(self, pixel_values: torch.FloatTensor):
|
||||
return pixel_values / 2
|
||||
@ -45,7 +45,7 @@ from transformers.utils.versions import require_version
|
||||
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
|
||||
|
||||
# Will error if the minimal version of Transformers is not installed. Remove at your own risks.
|
||||
check_min_version("4.47.0.dev0")
|
||||
check_min_version("4.48.0.dev0")
|
||||
|
||||
require_version("datasets>=1.14.0", "To fix: pip install -r examples/pytorch/audio-classification/requirements.txt")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -54,7 +54,7 @@ from transformers.utils.versions import require_version
|
||||
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
|
||||
|
||||
# Will error if the minimal version of Transformers is not installed. Remove at your own risks.
|
||||
check_min_version("4.47.0.dev0")
|
||||
check_min_version("4.48.0.dev0")
|
||||
|
||||
require_version("datasets>=1.8.0", "To fix: pip install -r examples/pytorch/contrastive-image-text/requirements.txt")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -42,6 +42,7 @@ from transformers import (
|
||||
AutoImageProcessor,
|
||||
AutoModelForImageClassification,
|
||||
HfArgumentParser,
|
||||
TimmWrapperImageProcessor,
|
||||
Trainer,
|
||||
TrainingArguments,
|
||||
set_seed,
|
||||
@ -56,7 +57,7 @@ from transformers.utils.versions import require_version
|
||||
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
|
||||
|
||||
# Will error if the minimal version of Transformers is not installed. Remove at your own risks.
|
||||
check_min_version("4.47.0.dev0")
|
||||
check_min_version("4.48.0.dev0")
|
||||
|
||||
require_version("datasets>=2.14.0", "To fix: pip install -r examples/pytorch/image-classification/requirements.txt")
|
||||
|
||||
@ -329,31 +330,36 @@ def main():
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Define torchvision transforms to be applied to each image.
|
||||
if "shortest_edge" in image_processor.size:
|
||||
size = image_processor.size["shortest_edge"]
|
||||
if isinstance(image_processor, TimmWrapperImageProcessor):
|
||||
_train_transforms = image_processor.train_transforms
|
||||
_val_transforms = image_processor.val_transforms
|
||||
else:
|
||||
size = (image_processor.size["height"], image_processor.size["width"])
|
||||
normalize = (
|
||||
Normalize(mean=image_processor.image_mean, std=image_processor.image_std)
|
||||
if hasattr(image_processor, "image_mean") and hasattr(image_processor, "image_std")
|
||||
else Lambda(lambda x: x)
|
||||
)
|
||||
_train_transforms = Compose(
|
||||
[
|
||||
RandomResizedCrop(size),
|
||||
RandomHorizontalFlip(),
|
||||
ToTensor(),
|
||||
normalize,
|
||||
]
|
||||
)
|
||||
_val_transforms = Compose(
|
||||
[
|
||||
Resize(size),
|
||||
CenterCrop(size),
|
||||
ToTensor(),
|
||||
normalize,
|
||||
]
|
||||
)
|
||||
if "shortest_edge" in image_processor.size:
|
||||
size = image_processor.size["shortest_edge"]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
size = (image_processor.size["height"], image_processor.size["width"])
|
||||
|
||||
# Create normalization transform
|
||||
if hasattr(image_processor, "image_mean") and hasattr(image_processor, "image_std"):
|
||||
normalize = Normalize(mean=image_processor.image_mean, std=image_processor.image_std)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
normalize = Lambda(lambda x: x)
|
||||
_train_transforms = Compose(
|
||||
[
|
||||
RandomResizedCrop(size),
|
||||
RandomHorizontalFlip(),
|
||||
ToTensor(),
|
||||
normalize,
|
||||
]
|
||||
)
|
||||
_val_transforms = Compose(
|
||||
[
|
||||
Resize(size),
|
||||
CenterCrop(size),
|
||||
ToTensor(),
|
||||
normalize,
|
||||
]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def train_transforms(example_batch):
|
||||
"""Apply _train_transforms across a batch."""
|
||||
|
||||
@ -49,7 +49,7 @@ from transformers.utils.versions import require_version
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Will error if the minimal version of Transformers is not installed. Remove at your own risks.
|
||||
check_min_version("4.47.0.dev0")
|
||||
check_min_version("4.48.0.dev0")
|
||||
|
||||
logger = get_logger(__name__)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -43,7 +43,7 @@ from transformers.utils.versions import require_version
|
||||
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
|
||||
|
||||
# Will error if the minimal version of Transformers is not installed. Remove at your own risks.
|
||||
check_min_version("4.47.0.dev0")
|
||||
check_min_version("4.48.0.dev0")
|
||||
|
||||
require_version("datasets>=1.8.0", "To fix: pip install -r examples/pytorch/image-pretraining/requirements.txt")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -48,7 +48,7 @@ Any model supported by the AutoModelForMaskedImageModeling API can be used.
|
||||
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
|
||||
|
||||
# Will error if the minimal version of Transformers is not installed. Remove at your own risks.
|
||||
check_min_version("4.47.0.dev0")
|
||||
check_min_version("4.48.0.dev0")
|
||||
|
||||
require_version("datasets>=1.8.0", "To fix: pip install -r examples/pytorch/image-pretraining/requirements.txt")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -53,7 +53,7 @@ Any model supported by the AutoModelForMaskedImageModeling API can be used.
|
||||
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
|
||||
|
||||
# Will error if the minimal version of Transformers is not installed. Remove at your own risks.
|
||||
check_min_version("4.47.0.dev0")
|
||||
check_min_version("4.48.0.dev0")
|
||||
|
||||
require_version("datasets>=1.8.0", "To fix: pip install -r examples/pytorch/image-pretraining/requirements.txt")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -46,7 +46,7 @@ from transformers.utils.versions import require_version
|
||||
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
|
||||
|
||||
# Will error if the minimal version of Transformers is not installed. Remove at your own risks.
|
||||
check_min_version("4.47.0.dev0")
|
||||
check_min_version("4.48.0.dev0")
|
||||
|
||||
require_version("datasets>=2.0.0", "To fix: pip install -r examples/pytorch/instance-segmentation/requirements.txt")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -52,7 +52,7 @@ from transformers.utils.versions import require_version
|
||||
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
|
||||
|
||||
# Will error if the minimal version of Transformers is not installed. Remove at your own risks.
|
||||
check_min_version("4.47.0.dev0")
|
||||
check_min_version("4.48.0.dev0")
|
||||
|
||||
require_version("datasets>=2.0.0", "To fix: pip install -r examples/pytorch/instance-segmentation/requirements.txt")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -55,7 +55,7 @@ from transformers.utils.versions import require_version
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Will error if the minimal version of Transformers is not installed. Remove at your own risks.
|
||||
check_min_version("4.47.0.dev0")
|
||||
check_min_version("4.48.0.dev0")
|
||||
|
||||
require_version("datasets>=2.14.0", "To fix: pip install -r examples/pytorch/language-modeling/requirements.txt")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Some files were not shown because too many files have changed in this diff Show More
Reference in New Issue
Block a user