mirror of
https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git
synced 2025-10-26 05:34:35 +08:00
Compare commits
2 Commits
ssh_new_cl
...
disable_mu
| Author | SHA1 | Date | |
|---|---|---|---|
| aa60ef9910 | |||
| 21814b8355 |
@ -34,44 +34,64 @@ jobs:
|
||||
- run: echo 'export "GIT_COMMIT_MESSAGE=$(git show -s --format=%s)"' >> "$BASH_ENV" && source "$BASH_ENV"
|
||||
- run: mkdir -p test_preparation
|
||||
- run: python utils/tests_fetcher.py | tee tests_fetched_summary.txt
|
||||
- store_artifacts:
|
||||
path: ~/transformers/tests_fetched_summary.txt
|
||||
- run: |
|
||||
if [ -f test_list.txt ]; then
|
||||
cp test_list.txt test_preparation/test_list.txt
|
||||
else
|
||||
touch test_preparation/test_list.txt
|
||||
fi
|
||||
- run: |
|
||||
if [ -f examples_test_list.txt ]; then
|
||||
mv examples_test_list.txt test_preparation/examples_test_list.txt
|
||||
else
|
||||
touch test_preparation/examples_test_list.txt
|
||||
fi
|
||||
- run: |
|
||||
if [ -f filtered_test_list_cross_tests.txt ]; then
|
||||
mv filtered_test_list_cross_tests.txt test_preparation/filtered_test_list_cross_tests.txt
|
||||
else
|
||||
touch test_preparation/filtered_test_list_cross_tests.txt
|
||||
fi
|
||||
- run: |
|
||||
if [ -f doctest_list.txt ]; then
|
||||
cp doctest_list.txt test_preparation/doctest_list.txt
|
||||
else
|
||||
touch test_preparation/doctest_list.txt
|
||||
fi
|
||||
- run: |
|
||||
if [ -f test_repo_utils.txt ]; then
|
||||
mv test_repo_utils.txt test_preparation/test_repo_utils.txt
|
||||
else
|
||||
touch test_preparation/test_repo_utils.txt
|
||||
fi
|
||||
- run: python utils/tests_fetcher.py --filter_tests
|
||||
- run: |
|
||||
if [ -f test_list.txt ]; then
|
||||
mv test_list.txt test_preparation/filtered_test_list.txt
|
||||
else
|
||||
touch test_preparation/filtered_test_list.txt
|
||||
fi
|
||||
- store_artifacts:
|
||||
path: test_preparation/test_list.txt
|
||||
- store_artifacts:
|
||||
path: test_preparation/doctest_list.txt
|
||||
- store_artifacts:
|
||||
path: ~/transformers/test_preparation/filtered_test_list.txt
|
||||
- store_artifacts:
|
||||
path: test_preparation/examples_test_list.txt
|
||||
- run: export "GIT_COMMIT_MESSAGE=$(git show -s --format=%s)" && echo $GIT_COMMIT_MESSAGE && python .circleci/create_circleci_config.py --fetcher_folder test_preparation
|
||||
- run: |
|
||||
if [ ! -s test_preparation/generated_config.yml ]; then
|
||||
echo "No tests to run, exiting early!"
|
||||
circleci-agent step halt
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
if [ ! -s test_preparation/generated_config.yml ]; then
|
||||
echo "No tests to run, exiting early!"
|
||||
circleci-agent step halt
|
||||
fi
|
||||
- store_artifacts:
|
||||
path: test_preparation
|
||||
|
||||
- run:
|
||||
name: "Retrieve Artifact Paths"
|
||||
env:
|
||||
CIRCLE_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.CI_ARTIFACT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
command: |
|
||||
project_slug="gh/${CIRCLE_PROJECT_USERNAME}/${CIRCLE_PROJECT_REPONAME}"
|
||||
job_number=${CIRCLE_BUILD_NUM}
|
||||
url="https://circleci.com/api/v2/project/${project_slug}/${job_number}/artifacts"
|
||||
curl -o test_preparation/artifacts.json ${url}
|
||||
- run:
|
||||
name: "Prepare pipeline parameters"
|
||||
command: |
|
||||
python utils/process_test_artifacts.py
|
||||
|
||||
# To avoid too long generated_config.yaml on the continuation orb, we pass the links to the artifacts as parameters.
|
||||
# Otherwise the list of tests was just too big. Explicit is good but for that it was a limitation.
|
||||
# We used:
|
||||
|
||||
# https://circleci.com/docs/api/v2/index.html#operation/getJobArtifacts : to get the job artifacts
|
||||
# We could not pass a nested dict, which is why we create the test_file_... parameters for every single job
|
||||
|
||||
path: test_preparation/generated_config.yml
|
||||
- store_artifacts:
|
||||
path: test_preparation/transformed_artifacts.json
|
||||
- store_artifacts:
|
||||
path: test_preparation/artifacts.json
|
||||
path: test_preparation/filtered_test_list_cross_tests.txt
|
||||
- continuation/continue:
|
||||
parameters: test_preparation/transformed_artifacts.json
|
||||
configuration_path: test_preparation/generated_config.yml
|
||||
|
||||
# To run all tests for the nightly build
|
||||
|
||||
@ -32,7 +32,7 @@ COMMON_ENV_VARIABLES = {
|
||||
"RUN_PT_FLAX_CROSS_TESTS": False,
|
||||
}
|
||||
# Disable the use of {"s": None} as the output is way too long, causing the navigation on CircleCI impractical
|
||||
COMMON_PYTEST_OPTIONS = {"max-worker-restart": 0, "dist": "loadfile", "vvv": None, "rsf":None}
|
||||
COMMON_PYTEST_OPTIONS = {"max-worker-restart": 0, "dist": "loadfile", "v": None}
|
||||
DEFAULT_DOCKER_IMAGE = [{"image": "cimg/python:3.8.12"}]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -50,15 +50,16 @@ class EmptyJob:
|
||||
class CircleCIJob:
|
||||
name: str
|
||||
additional_env: Dict[str, Any] = None
|
||||
cache_name: str = None
|
||||
cache_version: str = "0.8.2"
|
||||
docker_image: List[Dict[str, str]] = None
|
||||
install_steps: List[str] = None
|
||||
marker: Optional[str] = None
|
||||
parallelism: Optional[int] = 0
|
||||
parallelism: Optional[int] = 1
|
||||
pytest_num_workers: int = 12
|
||||
pytest_options: Dict[str, Any] = None
|
||||
resource_class: Optional[str] = "2xlarge"
|
||||
tests_to_run: Optional[List[str]] = None
|
||||
num_test_files_per_worker: Optional[int] = 10
|
||||
# This should be only used for doctest job!
|
||||
command_timeout: Optional[int] = None
|
||||
|
||||
@ -66,6 +67,8 @@ class CircleCIJob:
|
||||
# Deal with defaults for mutable attributes.
|
||||
if self.additional_env is None:
|
||||
self.additional_env = {}
|
||||
if self.cache_name is None:
|
||||
self.cache_name = self.name
|
||||
if self.docker_image is None:
|
||||
# Let's avoid changing the default list and make a copy.
|
||||
self.docker_image = copy.deepcopy(DEFAULT_DOCKER_IMAGE)
|
||||
@ -76,96 +79,156 @@ class CircleCIJob:
|
||||
self.docker_image[0]["image"] = f"{self.docker_image[0]['image']}:dev"
|
||||
print(f"Using {self.docker_image} docker image")
|
||||
if self.install_steps is None:
|
||||
self.install_steps = ["uv venv && uv pip install ."]
|
||||
self.install_steps = []
|
||||
if self.pytest_options is None:
|
||||
self.pytest_options = {}
|
||||
if isinstance(self.tests_to_run, str):
|
||||
self.tests_to_run = [self.tests_to_run]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
test_file = os.path.join("test_preparation" , f"{self.job_name}_test_list.txt")
|
||||
print("Looking for ", test_file)
|
||||
if os.path.exists(test_file):
|
||||
with open(test_file) as f:
|
||||
expanded_tests = f.read().strip().split("\n")
|
||||
self.tests_to_run = expanded_tests
|
||||
print("Found:", expanded_tests)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self.tests_to_run = []
|
||||
print("not Found")
|
||||
if self.parallelism is None:
|
||||
self.parallelism = 1
|
||||
|
||||
def to_dict(self):
|
||||
env = COMMON_ENV_VARIABLES.copy()
|
||||
env.update(self.additional_env)
|
||||
|
||||
cache_branch_prefix = os.environ.get("CIRCLE_BRANCH", "pull")
|
||||
if cache_branch_prefix != "main":
|
||||
cache_branch_prefix = "pull"
|
||||
|
||||
job = {
|
||||
"docker": self.docker_image,
|
||||
"environment": env,
|
||||
}
|
||||
if self.resource_class is not None:
|
||||
job["resource_class"] = self.resource_class
|
||||
if self.parallelism is not None:
|
||||
job["parallelism"] = self.parallelism
|
||||
steps = [
|
||||
"checkout",
|
||||
{"attach_workspace": {"at": "test_preparation"}},
|
||||
]
|
||||
steps.extend([{"run": l} for l in self.install_steps])
|
||||
steps.append({"run": {"name": "Show installed libraries and their size", "command": """du -h -d 1 "$(pip -V | cut -d ' ' -f 4 | sed 's/pip//g')" | grep -vE "dist-info|_distutils_hack|__pycache__" | sort -h | tee installed.txt || true"""}})
|
||||
steps.append({"run": {"name": "Show installed libraries and their versions", "command": """pip list --format=freeze | tee installed.txt || true"""}})
|
||||
|
||||
steps.append({"run":{"name":"Show biggest libraries","command":"""dpkg-query --show --showformat='${Installed-Size}\t${Package}\n' | sort -rh | head -25 | sort -h | awk '{ package=$2; sub(".*/", "", package); printf("%.5f GB %s\n", $1/1024/1024, package)}' || true"""}})
|
||||
steps.append({"store_artifacts": {"path": "installed.txt"}})
|
||||
|
||||
all_options = {**COMMON_PYTEST_OPTIONS, **self.pytest_options}
|
||||
pytest_flags = [f"--{key}={value}" if (value is not None or key in ["doctest-modules"]) else f"-{key}" for key, value in all_options.items()]
|
||||
pytest_flags.append(
|
||||
f"--make-reports={self.name}" if "examples" in self.name else f"--make-reports=tests_{self.name}"
|
||||
)
|
||||
# Examples special case: we need to download NLTK files in advance to avoid cuncurrency issues
|
||||
timeout_cmd = f"timeout {self.command_timeout} " if self.command_timeout else ""
|
||||
marker_cmd = f"-m '{self.marker}'" if self.marker is not None else ""
|
||||
additional_flags = f" -p no:warning -o junit_family=xunit1 --junitxml=test-results/junit.xml"
|
||||
parallel = f' << pipeline.parameters.{self.job_name}_parallelism >> '
|
||||
steps = [
|
||||
"checkout",
|
||||
{"attach_workspace": {"at": "test_preparation"}},
|
||||
{"run": "apt-get update && apt-get install -y curl"},
|
||||
{"run": " && ".join(self.install_steps)},
|
||||
{"run": {"name": "Download NLTK files", "command": """python -c "import nltk; nltk.download('punkt', quiet=True)" """} if "example" in self.name else "echo Skipping"},
|
||||
{"run": {
|
||||
"name": "Show installed libraries and their size",
|
||||
"command": """du -h -d 1 "$(pip -V | cut -d ' ' -f 4 | sed 's/pip//g')" | grep -vE "dist-info|_distutils_hack|__pycache__" | sort -h | tee installed.txt || true"""}
|
||||
},
|
||||
{"run": {
|
||||
"name": "Show installed libraries and their versions",
|
||||
"command": """pip list --format=freeze | tee installed.txt || true"""}
|
||||
},
|
||||
{"run": {
|
||||
"name": "Show biggest libraries",
|
||||
"command": """dpkg-query --show --showformat='${Installed-Size}\t${Package}\n' | sort -rh | head -25 | sort -h | awk '{ package=$2; sub(".*/", "", package); printf("%.5f GB %s\n", $1/1024/1024, package)}' || true"""}
|
||||
},
|
||||
{"run": {"name": "Create `test-results` directory", "command": "mkdir test-results"}},
|
||||
{"run": {"name": "Get files to test", "command":f'curl -L -o {self.job_name}_test_list.txt <<pipeline.parameters.{self.job_name}_test_list>>' if self.name != "pr_documentation_tests" else 'echo "Skipped"'}},
|
||||
{"run": {"name": "Split tests across parallel nodes: show current parallel tests",
|
||||
"command": f"TESTS=$(circleci tests split --split-by=timings {self.job_name}_test_list.txt) && echo $TESTS > splitted_tests.txt && echo $TESTS | tr ' ' '\n'" if self.parallelism else f"awk '{{printf \"%s \", $0}}' {self.job_name}_test_list.txt > splitted_tests.txt"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
{"run": {
|
||||
"name": "Run tests",
|
||||
"command": f"({timeout_cmd} python3 -m pytest {marker_cmd} -n {self.pytest_num_workers} {additional_flags} {' '.join(pytest_flags)} $(cat splitted_tests.txt) | tee tests_output.txt)"}
|
||||
},
|
||||
{"run": {"name": "Expand to show skipped tests", "when": "always", "command": f"python3 .circleci/parse_test_outputs.py --file tests_output.txt --skip"}},
|
||||
{"run": {"name": "Failed tests: show reasons", "when": "always", "command": f"python3 .circleci/parse_test_outputs.py --file tests_output.txt --fail"}},
|
||||
{"run": {"name": "Errors", "when": "always", "command": f"python3 .circleci/parse_test_outputs.py --file tests_output.txt --errors"}},
|
||||
{"store_test_results": {"path": "test-results"}},
|
||||
{"store_artifacts": {"path": "test-results/junit.xml"}},
|
||||
{"store_artifacts": {"path": "reports"}},
|
||||
{"store_artifacts": {"path": "tests.txt"}},
|
||||
{"store_artifacts": {"path": "splitted_tests.txt"}},
|
||||
{"store_artifacts": {"path": "installed.txt"}},
|
||||
]
|
||||
if self.parallelism:
|
||||
job["parallelism"] = parallel
|
||||
|
||||
steps.append({"run": {"name": "Create `test-results` directory", "command": "mkdir test-results"}})
|
||||
|
||||
# Examples special case: we need to download NLTK files in advance to avoid cuncurrency issues
|
||||
if "examples" in self.name:
|
||||
steps.append({"run": {"name": "Download NLTK files", "command": """python -c "import nltk; nltk.download('punkt', quiet=True)" """}})
|
||||
|
||||
test_command = ""
|
||||
if self.command_timeout:
|
||||
test_command = f"timeout {self.command_timeout} "
|
||||
# junit familiy xunit1 is necessary to support splitting on test name or class name with circleci split
|
||||
test_command += f"python3 -m pytest -rsfE -p no:warnings --tb=short -o junit_family=xunit1 --junitxml=test-results/junit.xml -n {self.pytest_num_workers} " + " ".join(pytest_flags)
|
||||
|
||||
if self.parallelism == 1:
|
||||
if self.tests_to_run is None:
|
||||
test_command += " << pipeline.parameters.tests_to_run >>"
|
||||
else:
|
||||
test_command += " " + " ".join(self.tests_to_run)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
# We need explicit list instead of `pipeline.parameters.tests_to_run` (only available at job runtime)
|
||||
tests = self.tests_to_run
|
||||
if tests is None:
|
||||
folder = os.environ["test_preparation_dir"]
|
||||
test_file = os.path.join(folder, "filtered_test_list.txt")
|
||||
if os.path.exists(test_file): # We take this job's tests from the filtered test_list.txt
|
||||
with open(test_file) as f:
|
||||
tests = f.read().split(" ")
|
||||
|
||||
# expand the test list
|
||||
if tests == ["tests"]:
|
||||
tests = [os.path.join("tests", x) for x in os.listdir("tests")]
|
||||
expanded_tests = []
|
||||
for test in tests:
|
||||
if test.endswith(".py"):
|
||||
expanded_tests.append(test)
|
||||
elif test == "tests/models":
|
||||
if "tokenization" in self.name:
|
||||
expanded_tests.extend(glob.glob("tests/models/**/test_tokenization*.py", recursive=True))
|
||||
elif self.name in ["flax","torch","tf"]:
|
||||
name = self.name if self.name != "torch" else ""
|
||||
if self.name == "torch":
|
||||
all_tests = glob.glob(f"tests/models/**/test_modeling_{name}*.py", recursive=True)
|
||||
filtered = [k for k in all_tests if ("_tf_") not in k and "_flax_" not in k]
|
||||
expanded_tests.extend(filtered)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
expanded_tests.extend(glob.glob(f"tests/models/**/test_modeling_{name}*.py", recursive=True))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
expanded_tests.extend(glob.glob("tests/models/**/test_modeling*.py", recursive=True))
|
||||
elif test == "tests/pipelines":
|
||||
expanded_tests.extend(glob.glob("tests/models/**/test_modeling*.py", recursive=True))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
expanded_tests.append(test)
|
||||
tests = " ".join(expanded_tests)
|
||||
|
||||
# Each executor to run ~10 tests
|
||||
n_executors = max(len(expanded_tests) // 10, 1)
|
||||
# Avoid empty test list on some executor(s) or launching too many executors
|
||||
if n_executors > self.parallelism:
|
||||
n_executors = self.parallelism
|
||||
job["parallelism"] = n_executors
|
||||
|
||||
# Need to be newline separated for the command `circleci tests split` below
|
||||
command = f'echo {tests} | tr " " "\\n" >> tests.txt'
|
||||
steps.append({"run": {"name": "Get tests", "command": command}})
|
||||
|
||||
command = 'TESTS=$(circleci tests split tests.txt) && echo $TESTS > splitted_tests.txt'
|
||||
steps.append({"run": {"name": "Split tests", "command": command}})
|
||||
|
||||
steps.append({"store_artifacts": {"path": "tests.txt"}})
|
||||
steps.append({"store_artifacts": {"path": "splitted_tests.txt"}})
|
||||
|
||||
test_command += " $(cat splitted_tests.txt)"
|
||||
if self.marker is not None:
|
||||
test_command += f" -m {self.marker}"
|
||||
|
||||
if self.name == "pr_documentation_tests":
|
||||
# can't use ` | tee tee tests_output.txt` as usual
|
||||
test_command += " > tests_output.txt"
|
||||
# Save the return code, so we can check if it is timeout in the next step.
|
||||
test_command += '; touch "$?".txt'
|
||||
# Never fail the test step for the doctest job. We will check the results in the next step, and fail that
|
||||
# step instead if the actual test failures are found. This is to avoid the timeout being reported as test
|
||||
# failure.
|
||||
test_command = f"({test_command}) || true"
|
||||
else:
|
||||
test_command = f"({test_command} | tee tests_output.txt)"
|
||||
steps.append({"run": {"name": "Run tests", "command": test_command}})
|
||||
|
||||
steps.append({"run": {"name": "Skipped tests", "when": "always", "command": f"python3 .circleci/parse_test_outputs.py --file tests_output.txt --skip"}})
|
||||
steps.append({"run": {"name": "Failed tests", "when": "always", "command": f"python3 .circleci/parse_test_outputs.py --file tests_output.txt --fail"}})
|
||||
steps.append({"run": {"name": "Errors", "when": "always", "command": f"python3 .circleci/parse_test_outputs.py --file tests_output.txt --errors"}})
|
||||
|
||||
steps.append({"store_test_results": {"path": "test-results"}})
|
||||
steps.append({"store_artifacts": {"path": "tests_output.txt"}})
|
||||
steps.append({"store_artifacts": {"path": "test-results/junit.xml"}})
|
||||
steps.append({"store_artifacts": {"path": "reports"}})
|
||||
|
||||
job["steps"] = steps
|
||||
return job
|
||||
|
||||
@property
|
||||
def job_name(self):
|
||||
return self.name if ("examples" in self.name or "pipeline" in self.name or "pr_documentation" in self.name) else f"tests_{self.name}"
|
||||
return self.name if "examples" in self.name else f"tests_{self.name}"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# JOBS
|
||||
torch_and_tf_job = CircleCIJob(
|
||||
"torch_and_tf",
|
||||
docker_image=[{"image":"huggingface/transformers-torch-tf-light"}],
|
||||
install_steps=["uv venv && uv pip install ."],
|
||||
additional_env={"RUN_PT_TF_CROSS_TESTS": True},
|
||||
marker="is_pt_tf_cross_test",
|
||||
pytest_options={"rA": None, "durations": 0},
|
||||
@ -176,6 +239,7 @@ torch_and_flax_job = CircleCIJob(
|
||||
"torch_and_flax",
|
||||
additional_env={"RUN_PT_FLAX_CROSS_TESTS": True},
|
||||
docker_image=[{"image":"huggingface/transformers-torch-jax-light"}],
|
||||
install_steps=["uv venv && uv pip install ."],
|
||||
marker="is_pt_flax_cross_test",
|
||||
pytest_options={"rA": None, "durations": 0},
|
||||
)
|
||||
@ -183,46 +247,35 @@ torch_and_flax_job = CircleCIJob(
|
||||
torch_job = CircleCIJob(
|
||||
"torch",
|
||||
docker_image=[{"image": "huggingface/transformers-torch-light"}],
|
||||
marker="not generate",
|
||||
install_steps=["uv venv && uv pip install ."],
|
||||
parallelism=6,
|
||||
pytest_num_workers=8
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
generate_job = CircleCIJob(
|
||||
"generate",
|
||||
docker_image=[{"image": "huggingface/transformers-torch-light"}],
|
||||
marker="generate",
|
||||
parallelism=6,
|
||||
pytest_num_workers=8
|
||||
pytest_num_workers=4
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
tokenization_job = CircleCIJob(
|
||||
"tokenization",
|
||||
docker_image=[{"image": "huggingface/transformers-torch-light"}],
|
||||
parallelism=8,
|
||||
pytest_num_workers=16
|
||||
install_steps=["uv venv && uv pip install ."],
|
||||
parallelism=6,
|
||||
pytest_num_workers=4
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
processor_job = CircleCIJob(
|
||||
"processors",
|
||||
docker_image=[{"image": "huggingface/transformers-torch-light"}],
|
||||
parallelism=8,
|
||||
pytest_num_workers=6
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
tf_job = CircleCIJob(
|
||||
"tf",
|
||||
docker_image=[{"image":"huggingface/transformers-tf-light"}],
|
||||
install_steps=["uv venv", "uv pip install -e."],
|
||||
parallelism=6,
|
||||
pytest_num_workers=16,
|
||||
pytest_num_workers=4,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
flax_job = CircleCIJob(
|
||||
"flax",
|
||||
docker_image=[{"image":"huggingface/transformers-jax-light"}],
|
||||
install_steps=["uv venv && uv pip install ."],
|
||||
parallelism=6,
|
||||
pytest_num_workers=16
|
||||
pytest_num_workers=4
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -230,8 +283,8 @@ pipelines_torch_job = CircleCIJob(
|
||||
"pipelines_torch",
|
||||
additional_env={"RUN_PIPELINE_TESTS": True},
|
||||
docker_image=[{"image":"huggingface/transformers-torch-light"}],
|
||||
install_steps=["uv venv && uv pip install ."],
|
||||
marker="is_pipeline_test",
|
||||
parallelism=4
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -239,8 +292,8 @@ pipelines_tf_job = CircleCIJob(
|
||||
"pipelines_tf",
|
||||
additional_env={"RUN_PIPELINE_TESTS": True},
|
||||
docker_image=[{"image":"huggingface/transformers-tf-light"}],
|
||||
install_steps=["uv venv && uv pip install ."],
|
||||
marker="is_pipeline_test",
|
||||
parallelism=4
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -248,24 +301,34 @@ custom_tokenizers_job = CircleCIJob(
|
||||
"custom_tokenizers",
|
||||
additional_env={"RUN_CUSTOM_TOKENIZERS": True},
|
||||
docker_image=[{"image": "huggingface/transformers-custom-tokenizers"}],
|
||||
install_steps=["uv venv","uv pip install -e ."],
|
||||
parallelism=None,
|
||||
resource_class=None,
|
||||
tests_to_run=[
|
||||
"./tests/models/bert_japanese/test_tokenization_bert_japanese.py",
|
||||
"./tests/models/openai/test_tokenization_openai.py",
|
||||
"./tests/models/clip/test_tokenization_clip.py",
|
||||
],
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
examples_torch_job = CircleCIJob(
|
||||
"examples_torch",
|
||||
additional_env={"OMP_NUM_THREADS": 8},
|
||||
cache_name="torch_examples",
|
||||
docker_image=[{"image":"huggingface/transformers-examples-torch"}],
|
||||
# TODO @ArthurZucker remove this once docker is easier to build
|
||||
install_steps=["uv venv && uv pip install . && uv pip install -r examples/pytorch/_tests_requirements.txt"],
|
||||
pytest_num_workers=8,
|
||||
pytest_num_workers=1,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
examples_tensorflow_job = CircleCIJob(
|
||||
"examples_tensorflow",
|
||||
additional_env={"OMP_NUM_THREADS": 8},
|
||||
cache_name="tensorflow_examples",
|
||||
docker_image=[{"image":"huggingface/transformers-examples-tf"}],
|
||||
pytest_num_workers=16,
|
||||
install_steps=["uv venv && uv pip install . && uv pip install -r examples/tensorflow/_tests_requirements.txt"],
|
||||
parallelism=8
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -274,12 +337,12 @@ hub_job = CircleCIJob(
|
||||
additional_env={"HUGGINGFACE_CO_STAGING": True},
|
||||
docker_image=[{"image":"huggingface/transformers-torch-light"}],
|
||||
install_steps=[
|
||||
'uv venv && uv pip install .',
|
||||
"uv venv && uv pip install .",
|
||||
'git config --global user.email "ci@dummy.com"',
|
||||
'git config --global user.name "ci"',
|
||||
],
|
||||
marker="is_staging_test",
|
||||
pytest_num_workers=2,
|
||||
pytest_num_workers=1,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -287,7 +350,8 @@ onnx_job = CircleCIJob(
|
||||
"onnx",
|
||||
docker_image=[{"image":"huggingface/transformers-torch-tf-light"}],
|
||||
install_steps=[
|
||||
"uv venv",
|
||||
"uv venv && uv pip install .",
|
||||
"uv pip install --upgrade eager pip",
|
||||
"uv pip install .[torch,tf,testing,sentencepiece,onnxruntime,vision,rjieba]",
|
||||
],
|
||||
pytest_options={"k onnx": None},
|
||||
@ -297,7 +361,15 @@ onnx_job = CircleCIJob(
|
||||
|
||||
exotic_models_job = CircleCIJob(
|
||||
"exotic_models",
|
||||
install_steps=["uv venv && uv pip install ."],
|
||||
docker_image=[{"image":"huggingface/transformers-exotic-models"}],
|
||||
tests_to_run=[
|
||||
"tests/models/*layoutlmv*",
|
||||
"tests/models/*nat",
|
||||
"tests/models/deta",
|
||||
"tests/models/udop",
|
||||
"tests/models/nougat",
|
||||
],
|
||||
pytest_num_workers=12,
|
||||
parallelism=4,
|
||||
pytest_options={"durations": 100},
|
||||
@ -307,8 +379,11 @@ exotic_models_job = CircleCIJob(
|
||||
repo_utils_job = CircleCIJob(
|
||||
"repo_utils",
|
||||
docker_image=[{"image":"huggingface/transformers-consistency"}],
|
||||
pytest_num_workers=4,
|
||||
install_steps=["uv venv && uv pip install ."],
|
||||
parallelism=None,
|
||||
pytest_num_workers=1,
|
||||
resource_class="large",
|
||||
tests_to_run="tests/repo_utils",
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -317,18 +392,28 @@ repo_utils_job = CircleCIJob(
|
||||
# the bash output redirection.)
|
||||
py_command = 'from utils.tests_fetcher import get_doctest_files; to_test = get_doctest_files() + ["dummy.py"]; to_test = " ".join(to_test); print(to_test)'
|
||||
py_command = f"$(python3 -c '{py_command}')"
|
||||
command = f'echo """{py_command}""" > pr_documentation_tests_temp.txt'
|
||||
command = f'echo "{py_command}" > pr_documentation_tests_temp.txt'
|
||||
doc_test_job = CircleCIJob(
|
||||
"pr_documentation_tests",
|
||||
docker_image=[{"image":"huggingface/transformers-consistency"}],
|
||||
additional_env={"TRANSFORMERS_VERBOSITY": "error", "DATASETS_VERBOSITY": "error", "SKIP_CUDA_DOCTEST": "1"},
|
||||
install_steps=[
|
||||
# Add an empty file to keep the test step running correctly even no file is selected to be tested.
|
||||
"uv venv && pip install .",
|
||||
"touch dummy.py",
|
||||
command,
|
||||
"cat pr_documentation_tests_temp.txt",
|
||||
"tail -n1 pr_documentation_tests_temp.txt | tee pr_documentation_tests_test_list.txt"
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "Get files to test",
|
||||
"command": command,
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "Show information in `Get files to test`",
|
||||
"command":
|
||||
"cat pr_documentation_tests_temp.txt"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "Get the last line in `pr_documentation_tests.txt`",
|
||||
"command":
|
||||
"tail -n1 pr_documentation_tests_temp.txt | tee pr_documentation_tests.txt"
|
||||
},
|
||||
],
|
||||
tests_to_run="$(cat pr_documentation_tests.txt)", # noqa
|
||||
pytest_options={"-doctest-modules": None, "doctest-glob": "*.md", "dist": "loadfile", "rvsA": None},
|
||||
@ -336,37 +421,121 @@ doc_test_job = CircleCIJob(
|
||||
pytest_num_workers=1,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
REGULAR_TESTS = [torch_and_tf_job, torch_and_flax_job, torch_job, tf_job, flax_job, hub_job, onnx_job, tokenization_job, processor_job, generate_job] # fmt: skip
|
||||
EXAMPLES_TESTS = [examples_torch_job, examples_tensorflow_job]
|
||||
PIPELINE_TESTS = [pipelines_torch_job, pipelines_tf_job]
|
||||
REGULAR_TESTS = [
|
||||
torch_and_tf_job,
|
||||
torch_and_flax_job,
|
||||
torch_job,
|
||||
tf_job,
|
||||
flax_job,
|
||||
custom_tokenizers_job,
|
||||
hub_job,
|
||||
onnx_job,
|
||||
exotic_models_job,
|
||||
tokenization_job
|
||||
]
|
||||
EXAMPLES_TESTS = [
|
||||
examples_torch_job,
|
||||
examples_tensorflow_job,
|
||||
]
|
||||
PIPELINE_TESTS = [
|
||||
pipelines_torch_job,
|
||||
pipelines_tf_job,
|
||||
]
|
||||
REPO_UTIL_TESTS = [repo_utils_job]
|
||||
DOC_TESTS = [doc_test_job]
|
||||
ALL_TESTS = REGULAR_TESTS + EXAMPLES_TESTS + PIPELINE_TESTS + REPO_UTIL_TESTS + DOC_TESTS + [custom_tokenizers_job] + [exotic_models_job] # fmt: skip
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def create_circleci_config(folder=None):
|
||||
if folder is None:
|
||||
folder = os.getcwd()
|
||||
# Used in CircleCIJob.to_dict() to expand the test list (for using parallelism)
|
||||
os.environ["test_preparation_dir"] = folder
|
||||
jobs = [k for k in ALL_TESTS if os.path.isfile(os.path.join("test_preparation" , f"{k.job_name}_test_list.txt") )]
|
||||
print("The following jobs will be run ", jobs)
|
||||
jobs = []
|
||||
all_test_file = os.path.join(folder, "test_list.txt")
|
||||
if os.path.exists(all_test_file):
|
||||
with open(all_test_file) as f:
|
||||
all_test_list = f.read()
|
||||
else:
|
||||
all_test_list = []
|
||||
if len(all_test_list) > 0:
|
||||
jobs.extend(PIPELINE_TESTS)
|
||||
|
||||
test_file = os.path.join(folder, "filtered_test_list.txt")
|
||||
if os.path.exists(test_file):
|
||||
with open(test_file) as f:
|
||||
test_list = f.read()
|
||||
else:
|
||||
test_list = []
|
||||
if len(test_list) > 0:
|
||||
jobs.extend(REGULAR_TESTS)
|
||||
|
||||
extended_tests_to_run = set(test_list.split())
|
||||
# Extend the test files for cross test jobs
|
||||
for job in jobs:
|
||||
if job.job_name in ["tests_torch_and_tf", "tests_torch_and_flax"]:
|
||||
for test_path in copy.copy(extended_tests_to_run):
|
||||
dir_path, fn = os.path.split(test_path)
|
||||
if fn.startswith("test_modeling_tf_"):
|
||||
fn = fn.replace("test_modeling_tf_", "test_modeling_")
|
||||
elif fn.startswith("test_modeling_flax_"):
|
||||
fn = fn.replace("test_modeling_flax_", "test_modeling_")
|
||||
else:
|
||||
if job.job_name == "test_torch_and_tf":
|
||||
fn = fn.replace("test_modeling_", "test_modeling_tf_")
|
||||
elif job.job_name == "test_torch_and_flax":
|
||||
fn = fn.replace("test_modeling_", "test_modeling_flax_")
|
||||
new_test_file = str(os.path.join(dir_path, fn))
|
||||
if os.path.isfile(new_test_file):
|
||||
if new_test_file not in extended_tests_to_run:
|
||||
extended_tests_to_run.add(new_test_file)
|
||||
extended_tests_to_run = sorted(extended_tests_to_run)
|
||||
for job in jobs:
|
||||
if job.job_name in ["tests_torch_and_tf", "tests_torch_and_flax"]:
|
||||
job.tests_to_run = extended_tests_to_run
|
||||
fn = "filtered_test_list_cross_tests.txt"
|
||||
f_path = os.path.join(folder, fn)
|
||||
with open(f_path, "w") as fp:
|
||||
fp.write(" ".join(extended_tests_to_run))
|
||||
|
||||
example_file = os.path.join(folder, "examples_test_list.txt")
|
||||
if os.path.exists(example_file) and os.path.getsize(example_file) > 0:
|
||||
with open(example_file, "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
|
||||
example_tests = f.read()
|
||||
for job in EXAMPLES_TESTS:
|
||||
framework = job.name.replace("examples_", "").replace("torch", "pytorch")
|
||||
if example_tests == "all":
|
||||
job.tests_to_run = [f"examples/{framework}"]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
job.tests_to_run = [f for f in example_tests.split(" ") if f.startswith(f"examples/{framework}")]
|
||||
|
||||
if len(job.tests_to_run) > 0:
|
||||
jobs.append(job)
|
||||
|
||||
doctest_file = os.path.join(folder, "doctest_list.txt")
|
||||
if os.path.exists(doctest_file):
|
||||
with open(doctest_file) as f:
|
||||
doctest_list = f.read()
|
||||
else:
|
||||
doctest_list = []
|
||||
if len(doctest_list) > 0:
|
||||
jobs.extend(DOC_TESTS)
|
||||
|
||||
repo_util_file = os.path.join(folder, "test_repo_utils.txt")
|
||||
if os.path.exists(repo_util_file) and os.path.getsize(repo_util_file) > 0:
|
||||
jobs.extend(REPO_UTIL_TESTS)
|
||||
|
||||
if len(jobs) == 0:
|
||||
jobs = [EmptyJob()]
|
||||
print("Full list of job name inputs", {j.job_name + "_test_list":{"type":"string", "default":''} for j in jobs})
|
||||
config = {
|
||||
"version": "2.1",
|
||||
"parameters": {
|
||||
# Only used to accept the parameters from the trigger
|
||||
"nightly": {"type": "boolean", "default": False},
|
||||
"tests_to_run": {"type": "string", "default": ''},
|
||||
**{j.job_name + "_test_list":{"type":"string", "default":''} for j in jobs},
|
||||
**{j.job_name + "_parallelism":{"type":"integer", "default":1} for j in jobs},
|
||||
},
|
||||
"jobs" : {j.job_name: j.to_dict() for j in jobs},
|
||||
"workflows": {"version": 2, "run_tests": {"jobs": [j.job_name for j in jobs]}}
|
||||
config = {"version": "2.1"}
|
||||
config["parameters"] = {
|
||||
# Only used to accept the parameters from the trigger
|
||||
"nightly": {"type": "boolean", "default": False},
|
||||
"tests_to_run": {"type": "string", "default": test_list},
|
||||
}
|
||||
config["jobs"] = {j.job_name: j.to_dict() for j in jobs}
|
||||
config["workflows"] = {"version": 2, "run_tests": {"jobs": [j.job_name for j in jobs]}}
|
||||
with open(os.path.join(folder, "generated_config.yml"), "w") as f:
|
||||
f.write(yaml.dump(config, sort_keys=False, default_flow_style=False).replace("' << pipeline", " << pipeline").replace(">> '", " >>"))
|
||||
f.write(yaml.dump(config, indent=2, width=1000000, sort_keys=False))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
|
||||
@ -67,4 +67,4 @@ def main():
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
main()
|
||||
main()
|
||||
37
.github/workflows/self-push-amd.yml
vendored
37
.github/workflows/self-push-amd.yml
vendored
@ -64,24 +64,23 @@ jobs:
|
||||
outputs:
|
||||
matrix: ${{ steps.set-matrix.outputs.matrix }}
|
||||
test_map: ${{ steps.set-matrix.outputs.test_map }}
|
||||
env:
|
||||
# `CI_BRANCH_PUSH`: The branch name from the push event
|
||||
# `CI_BRANCH_WORKFLOW_RUN`: The name of the branch on which this workflow is triggered by `workflow_run` event
|
||||
# `CI_SHA_PUSH`: The commit SHA from the push event
|
||||
# `CI_SHA_WORKFLOW_RUN`: The commit SHA that triggers this workflow by `workflow_run` event
|
||||
CI_BRANCH_PUSH: ${{ github.event.ref }}
|
||||
CI_BRANCH_WORKFLOW_RUN: ${{ github.event.workflow_run.head_branch }}
|
||||
CI_SHA_PUSH: ${{ github.event.head_commit.id }}
|
||||
CI_SHA_WORKFLOW_RUN: ${{ github.event.workflow_run.head_sha }}
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
# Necessary to get the correct branch name and commit SHA for `workflow_run` event
|
||||
# We also take into account the `push` event (we might want to test some changes in a branch)
|
||||
- name: Prepare custom environment variables
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
# `CI_BRANCH_PUSH`: The branch name from the push event
|
||||
# `CI_BRANCH_WORKFLOW_RUN`: The name of the branch on which this workflow is triggered by `workflow_run` event
|
||||
# `CI_BRANCH`: The non-empty branch name from the above two (one and only one of them is empty)
|
||||
# `CI_SHA_PUSH`: The commit SHA from the push event
|
||||
# `CI_SHA_WORKFLOW_RUN`: The commit SHA that triggers this workflow by `workflow_run` event
|
||||
# `CI_SHA`: The non-empty commit SHA from the above two (one and only one of them is empty)
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
CI_BRANCH_PUSH=${{ github.event.ref }}
|
||||
CI_BRANCH_PUSH=${CI_BRANCH_PUSH/'refs/heads/'/''}
|
||||
CI_BRANCH_WORKFLOW_RUN=${{ github.event.workflow_run.head_branch }}
|
||||
CI_SHA_PUSH=${{ github.event.head_commit.id }}
|
||||
CI_SHA_WORKFLOW_RUN=${{ github.event.workflow_run.head_sha }}
|
||||
echo $CI_BRANCH_PUSH
|
||||
echo $CI_BRANCH_WORKFLOW_RUN
|
||||
echo $CI_SHA_PUSH
|
||||
@ -160,12 +159,6 @@ jobs:
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: huggingface/transformers-pytorch-amd-gpu-push-ci # <--- We test only for PyTorch for now
|
||||
options: --device /dev/kfd --device /dev/dri --env ROCR_VISIBLE_DEVICES --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
env:
|
||||
# For the meaning of these environment variables, see the job `Setup`
|
||||
CI_BRANCH_PUSH: ${{ github.event.ref }}
|
||||
CI_BRANCH_WORKFLOW_RUN: ${{ github.event.workflow_run.head_branch }}
|
||||
CI_SHA_PUSH: ${{ github.event.head_commit.id }}
|
||||
CI_SHA_WORKFLOW_RUN: ${{ github.event.workflow_run.head_sha }}
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
# Necessary to get the correct branch name and commit SHA for `workflow_run` event
|
||||
# We also take into account the `push` event (we might want to test some changes in a branch)
|
||||
@ -173,7 +166,11 @@ jobs:
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
# For the meaning of these environment variables, see the job `Setup`
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
CI_BRANCH_PUSH=${{ github.event.ref }}
|
||||
CI_BRANCH_PUSH=${CI_BRANCH_PUSH/'refs/heads/'/''}
|
||||
CI_BRANCH_WORKFLOW_RUN=${{ github.event.workflow_run.head_branch }}
|
||||
CI_SHA_PUSH=${{ github.event.head_commit.id }}
|
||||
CI_SHA_WORKFLOW_RUN=${{ github.event.workflow_run.head_sha }}
|
||||
echo $CI_BRANCH_PUSH
|
||||
echo $CI_BRANCH_WORKFLOW_RUN
|
||||
echo $CI_SHA_PUSH
|
||||
@ -259,12 +256,6 @@ jobs:
|
||||
# run_tests_torch_cuda_extensions_single_gpu,
|
||||
# run_tests_torch_cuda_extensions_multi_gpu
|
||||
]
|
||||
env:
|
||||
# For the meaning of these environment variables, see the job `Setup`
|
||||
CI_BRANCH_PUSH: ${{ github.event.ref }}
|
||||
CI_BRANCH_WORKFLOW_RUN: ${{ github.event.workflow_run.head_branch }}
|
||||
CI_SHA_PUSH: ${{ github.event.head_commit.id }}
|
||||
CI_SHA_WORKFLOW_RUN: ${{ github.event.workflow_run.head_sha }}
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Preliminary job status
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
@ -280,7 +271,11 @@ jobs:
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
# For the meaning of these environment variables, see the job `Setup`
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
CI_BRANCH_PUSH=${{ github.event.ref }}
|
||||
CI_BRANCH_PUSH=${CI_BRANCH_PUSH/'refs/heads/'/''}
|
||||
CI_BRANCH_WORKFLOW_RUN=${{ github.event.workflow_run.head_branch }}
|
||||
CI_SHA_PUSH=${{ github.event.head_commit.id }}
|
||||
CI_SHA_WORKFLOW_RUN=${{ github.event.workflow_run.head_sha }}
|
||||
echo $CI_BRANCH_PUSH
|
||||
echo $CI_BRANCH_WORKFLOW_RUN
|
||||
echo $CI_SHA_PUSH
|
||||
|
||||
67
.github/workflows/self-push.yml
vendored
67
.github/workflows/self-push.yml
vendored
@ -40,24 +40,23 @@ jobs:
|
||||
outputs:
|
||||
matrix: ${{ steps.set-matrix.outputs.matrix }}
|
||||
test_map: ${{ steps.set-matrix.outputs.test_map }}
|
||||
env:
|
||||
# `CI_BRANCH_PUSH`: The branch name from the push event
|
||||
# `CI_BRANCH_WORKFLOW_RUN`: The name of the branch on which this workflow is triggered by `workflow_run` event
|
||||
# `CI_SHA_PUSH`: The commit SHA from the push event
|
||||
# `CI_SHA_WORKFLOW_RUN`: The commit SHA that triggers this workflow by `workflow_run` event
|
||||
CI_BRANCH_PUSH: ${{ github.event.ref }}
|
||||
CI_BRANCH_WORKFLOW_RUN: ${{ github.event.workflow_run.head_branch }}
|
||||
CI_SHA_PUSH: ${{ github.event.head_commit.id }}
|
||||
CI_SHA_WORKFLOW_RUN: ${{ github.event.workflow_run.head_sha }}
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
# Necessary to get the correct branch name and commit SHA for `workflow_run` event
|
||||
# We also take into account the `push` event (we might want to test some changes in a branch)
|
||||
- name: Prepare custom environment variables
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
# `CI_BRANCH_PUSH`: The branch name from the push event
|
||||
# `CI_BRANCH_WORKFLOW_RUN`: The name of the branch on which this workflow is triggered by `workflow_run` event
|
||||
# `CI_BRANCH`: The non-empty branch name from the above two (one and only one of them is empty)
|
||||
# `CI_SHA_PUSH`: The commit SHA from the push event
|
||||
# `CI_SHA_WORKFLOW_RUN`: The commit SHA that triggers this workflow by `workflow_run` event
|
||||
# `CI_SHA`: The non-empty commit SHA from the above two (one and only one of them is empty)
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
CI_BRANCH_PUSH=${{ github.event.ref }}
|
||||
CI_BRANCH_PUSH=${CI_BRANCH_PUSH/'refs/heads/'/''}
|
||||
CI_BRANCH_WORKFLOW_RUN=${{ github.event.workflow_run.head_branch }}
|
||||
CI_SHA_PUSH=${{ github.event.head_commit.id }}
|
||||
CI_SHA_WORKFLOW_RUN=${{ github.event.workflow_run.head_sha }}
|
||||
echo $CI_BRANCH_PUSH
|
||||
echo $CI_BRANCH_WORKFLOW_RUN
|
||||
echo $CI_SHA_PUSH
|
||||
@ -136,12 +135,6 @@ jobs:
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: huggingface/transformers-all-latest-gpu-push-ci
|
||||
options: --gpus 0 --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
env:
|
||||
# For the meaning of these environment variables, see the job `Setup`
|
||||
CI_BRANCH_PUSH: ${{ github.event.ref }}
|
||||
CI_BRANCH_WORKFLOW_RUN: ${{ github.event.workflow_run.head_branch }}
|
||||
CI_SHA_PUSH: ${{ github.event.head_commit.id }}
|
||||
CI_SHA_WORKFLOW_RUN: ${{ github.event.workflow_run.head_sha }}
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
# Necessary to get the correct branch name and commit SHA for `workflow_run` event
|
||||
# We also take into account the `push` event (we might want to test some changes in a branch)
|
||||
@ -149,7 +142,11 @@ jobs:
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
# For the meaning of these environment variables, see the job `Setup`
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
CI_BRANCH_PUSH=${{ github.event.ref }}
|
||||
CI_BRANCH_PUSH=${CI_BRANCH_PUSH/'refs/heads/'/''}
|
||||
CI_BRANCH_WORKFLOW_RUN=${{ github.event.workflow_run.head_branch }}
|
||||
CI_SHA_PUSH=${{ github.event.head_commit.id }}
|
||||
CI_SHA_WORKFLOW_RUN=${{ github.event.workflow_run.head_sha }}
|
||||
echo $CI_BRANCH_PUSH
|
||||
echo $CI_BRANCH_WORKFLOW_RUN
|
||||
echo $CI_SHA_PUSH
|
||||
@ -231,12 +228,6 @@ jobs:
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: huggingface/transformers-all-latest-gpu-push-ci
|
||||
options: --gpus all --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
env:
|
||||
# For the meaning of these environment variables, see the job `Setup`
|
||||
CI_BRANCH_PUSH: ${{ github.event.ref }}
|
||||
CI_BRANCH_WORKFLOW_RUN: ${{ github.event.workflow_run.head_branch }}
|
||||
CI_SHA_PUSH: ${{ github.event.head_commit.id }}
|
||||
CI_SHA_WORKFLOW_RUN: ${{ github.event.workflow_run.head_sha }}
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
# Necessary to get the correct branch name and commit SHA for `workflow_run` event
|
||||
# We also take into account the `push` event (we might want to test some changes in a branch)
|
||||
@ -244,7 +235,11 @@ jobs:
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
# For the meaning of these environment variables, see the job `Setup`
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
CI_BRANCH_PUSH=${{ github.event.ref }}
|
||||
CI_BRANCH_PUSH=${CI_BRANCH_PUSH/'refs/heads/'/''}
|
||||
CI_BRANCH_WORKFLOW_RUN=${{ github.event.workflow_run.head_branch }}
|
||||
CI_SHA_PUSH=${{ github.event.head_commit.id }}
|
||||
CI_SHA_WORKFLOW_RUN=${{ github.event.workflow_run.head_sha }}
|
||||
echo $CI_BRANCH_PUSH
|
||||
echo $CI_BRANCH_WORKFLOW_RUN
|
||||
echo $CI_SHA_PUSH
|
||||
@ -326,12 +321,6 @@ jobs:
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: huggingface/transformers-pytorch-deepspeed-latest-gpu-push-ci
|
||||
options: --gpus 0 --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
env:
|
||||
# For the meaning of these environment variables, see the job `Setup`
|
||||
CI_BRANCH_PUSH: ${{ github.event.ref }}
|
||||
CI_BRANCH_WORKFLOW_RUN: ${{ github.event.workflow_run.head_branch }}
|
||||
CI_SHA_PUSH: ${{ github.event.head_commit.id }}
|
||||
CI_SHA_WORKFLOW_RUN: ${{ github.event.workflow_run.head_sha }}
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
# Necessary to get the correct branch name and commit SHA for `workflow_run` event
|
||||
# We also take into account the `push` event (we might want to test some changes in a branch)
|
||||
@ -339,7 +328,11 @@ jobs:
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
# For the meaning of these environment variables, see the job `Setup`
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
CI_BRANCH_PUSH=${{ github.event.ref }}
|
||||
CI_BRANCH_PUSH=${CI_BRANCH_PUSH/'refs/heads/'/''}
|
||||
CI_BRANCH_WORKFLOW_RUN=${{ github.event.workflow_run.head_branch }}
|
||||
CI_SHA_PUSH=${{ github.event.head_commit.id }}
|
||||
CI_SHA_WORKFLOW_RUN=${{ github.event.workflow_run.head_sha }}
|
||||
echo $CI_BRANCH_PUSH
|
||||
echo $CI_BRANCH_WORKFLOW_RUN
|
||||
echo $CI_SHA_PUSH
|
||||
@ -418,12 +411,6 @@ jobs:
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: huggingface/transformers-pytorch-deepspeed-latest-gpu-push-ci
|
||||
options: --gpus all --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
env:
|
||||
# For the meaning of these environment variables, see the job `Setup`
|
||||
CI_BRANCH_PUSH: ${{ github.event.ref }}
|
||||
CI_BRANCH_WORKFLOW_RUN: ${{ github.event.workflow_run.head_branch }}
|
||||
CI_SHA_PUSH: ${{ github.event.head_commit.id }}
|
||||
CI_SHA_WORKFLOW_RUN: ${{ github.event.workflow_run.head_sha }}
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
# Necessary to get the correct branch name and commit SHA for `workflow_run` event
|
||||
# We also take into account the `push` event (we might want to test some changes in a branch)
|
||||
@ -431,7 +418,11 @@ jobs:
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
# For the meaning of these environment variables, see the job `Setup`
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
CI_BRANCH_PUSH=${{ github.event.ref }}
|
||||
CI_BRANCH_PUSH=${CI_BRANCH_PUSH/'refs/heads/'/''}
|
||||
CI_BRANCH_WORKFLOW_RUN=${{ github.event.workflow_run.head_branch }}
|
||||
CI_SHA_PUSH=${{ github.event.head_commit.id }}
|
||||
CI_SHA_WORKFLOW_RUN=${{ github.event.workflow_run.head_sha }}
|
||||
echo $CI_BRANCH_PUSH
|
||||
echo $CI_BRANCH_WORKFLOW_RUN
|
||||
echo $CI_SHA_PUSH
|
||||
@ -509,12 +500,6 @@ jobs:
|
||||
run_tests_torch_cuda_extensions_single_gpu,
|
||||
run_tests_torch_cuda_extensions_multi_gpu
|
||||
]
|
||||
env:
|
||||
# For the meaning of these environment variables, see the job `Setup`
|
||||
CI_BRANCH_PUSH: ${{ github.event.ref }}
|
||||
CI_BRANCH_WORKFLOW_RUN: ${{ github.event.workflow_run.head_branch }}
|
||||
CI_SHA_PUSH: ${{ github.event.head_commit.id }}
|
||||
CI_SHA_WORKFLOW_RUN: ${{ github.event.workflow_run.head_sha }}
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Preliminary job status
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
@ -528,7 +513,11 @@ jobs:
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
# For the meaning of these environment variables, see the job `Setup`
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
CI_BRANCH_PUSH=${{ github.event.ref }}
|
||||
CI_BRANCH_PUSH=${CI_BRANCH_PUSH/'refs/heads/'/''}
|
||||
CI_BRANCH_WORKFLOW_RUN=${{ github.event.workflow_run.head_branch }}
|
||||
CI_SHA_PUSH=${{ github.event.head_commit.id }}
|
||||
CI_SHA_WORKFLOW_RUN=${{ github.event.workflow_run.head_sha }}
|
||||
echo $CI_BRANCH_PUSH
|
||||
echo $CI_BRANCH_WORKFLOW_RUN
|
||||
echo $CI_SHA_PUSH
|
||||
|
||||
2
.github/workflows/self-scheduled.yml
vendored
2
.github/workflows/self-scheduled.yml
vendored
@ -102,7 +102,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
fail-fast: false
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
machine_type: [single-gpu, multi-gpu]
|
||||
machine_type: [single-gpu]
|
||||
slice_id: ${{ fromJSON(needs.setup.outputs.slice_ids) }}
|
||||
uses: ./.github/workflows/model_jobs.yml
|
||||
with:
|
||||
|
||||
20
.github/workflows/ssh-runner.yml
vendored
20
.github/workflows/ssh-runner.yml
vendored
@ -1,9 +1,17 @@
|
||||
name: SSH into our runners
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
push:
|
||||
branches:
|
||||
- ssh_new_cluster
|
||||
workflow_dispatch:
|
||||
inputs:
|
||||
runner_type:
|
||||
description: 'Type of runner to test (a10 or t4)'
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
docker_image:
|
||||
description: 'Name of the Docker image'
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
num_gpus:
|
||||
description: 'Type of the number of gpus to use (`single` or `multi`)'
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
|
||||
env:
|
||||
HF_HUB_READ_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.HF_HUB_READ_TOKEN }}
|
||||
@ -20,10 +28,9 @@ env:
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
ssh_runner:
|
||||
name: "SSH"
|
||||
runs-on:
|
||||
group: aws-g4dn-2xlarge-cache-test
|
||||
runs-on: ["${{ github.event.inputs.num_gpus }}-gpu", nvidia-gpu, "${{ github.event.inputs.runner_type }}", ci]
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: huggingface/transformers-all-latest-gpu
|
||||
image: ${{ github.event.inputs.docker_image }}
|
||||
options: --gpus all --privileged --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
@ -54,4 +61,3 @@ jobs:
|
||||
slackChannel: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_CHANNEL }}
|
||||
slackToken: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
waitForSSH: true
|
||||
sshTimeout: 30m
|
||||
|
||||
@ -36,4 +36,5 @@ Please inspect the code of the tools before passing them to the Agent to protect
|
||||
|
||||
## Reporting a Vulnerability
|
||||
|
||||
Feel free to submit vulnerability reports to [security@huggingface.co](mailto:security@huggingface.co), where someone from the HF security team will review and recommend next steps. If reporting a vulnerability specific to open source, please note [Huntr](https://huntr.com) is a vulnerability disclosure program for open source software.
|
||||
🤗 Please feel free to submit vulnerability reports to our private bug bounty program at https://hackerone.com/hugging_face. You'll need to request access to the program by emailing security@huggingface.co.
|
||||
Note that you'll need to be invited to our program, so send us a quick email at security@huggingface.co if you've found a vulnerability.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -24,9 +24,7 @@
|
||||
- local: model_sharing
|
||||
title: Share your model
|
||||
- local: agents
|
||||
title: Agents 101
|
||||
- local: agents_advanced
|
||||
title: Agents, supercharged - Multi-agents, External tools, and more
|
||||
title: Agents
|
||||
- local: llm_tutorial
|
||||
title: Generation with LLMs
|
||||
- local: conversations
|
||||
@ -96,8 +94,6 @@
|
||||
title: Text to speech
|
||||
- local: tasks/image_text_to_text
|
||||
title: Image-text-to-text
|
||||
- local: tasks/video_text_to_text
|
||||
title: Video-text-to-text
|
||||
title: Multimodal
|
||||
- isExpanded: false
|
||||
sections:
|
||||
@ -492,8 +488,6 @@
|
||||
title: Nyströmformer
|
||||
- local: model_doc/olmo
|
||||
title: OLMo
|
||||
- local: model_doc/olmoe
|
||||
title: OLMoE
|
||||
- local: model_doc/open-llama
|
||||
title: Open-Llama
|
||||
- local: model_doc/opt
|
||||
@ -836,8 +830,6 @@
|
||||
title: LLaVA-NeXT
|
||||
- local: model_doc/llava_next_video
|
||||
title: LLaVa-NeXT-Video
|
||||
- local: model_doc/llava_onevision
|
||||
title: LLaVA-Onevision
|
||||
- local: model_doc/lxmert
|
||||
title: LXMERT
|
||||
- local: model_doc/matcha
|
||||
|
||||
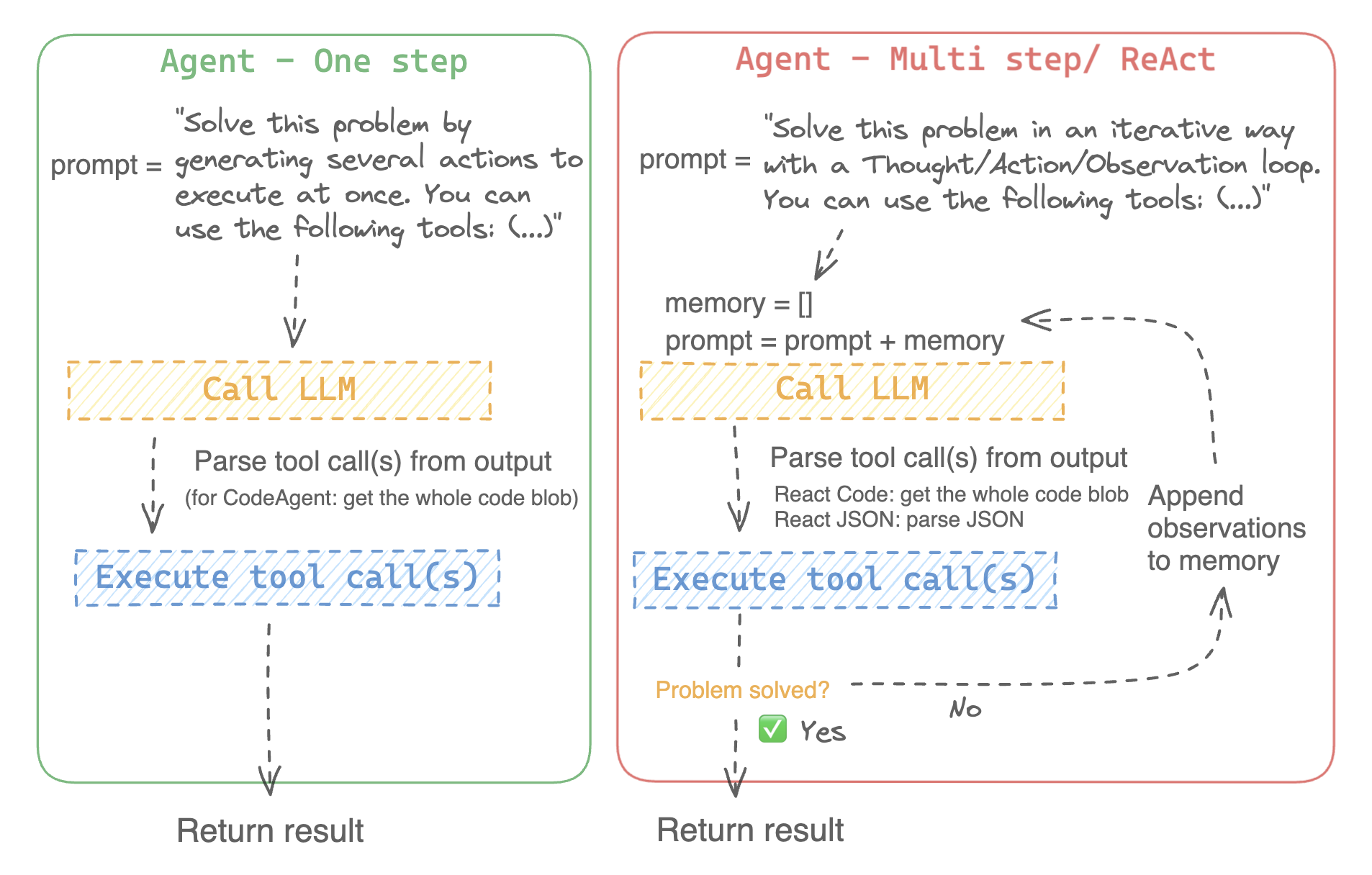
@ -28,8 +28,8 @@ An agent is a system that uses an LLM as its engine, and it has access to functi
|
||||
These *tools* are functions for performing a task, and they contain all necessary description for the agent to properly use them.
|
||||
|
||||
The agent can be programmed to:
|
||||
- devise a series of actions/tools and run them all at once, like the [`CodeAgent`]
|
||||
- plan and execute actions/tools one by one and wait for the outcome of each action before launching the next one, like the [`ReactJsonAgent`]
|
||||
- devise a series of actions/tools and run them all at once like the [`CodeAgent`] for example
|
||||
- plan and execute actions/tools one by one and wait for the outcome of each action before launching the next one like the [`ReactJsonAgent`] for example
|
||||
|
||||
### Types of agents
|
||||
|
||||
@ -46,18 +46,7 @@ We implement two versions of ReactJsonAgent:
|
||||
- [`ReactCodeAgent`] is a new type of ReactJsonAgent that generates its tool calls as blobs of code, which works really well for LLMs that have strong coding performance.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!TIP]
|
||||
> Read [Open-source LLMs as LangChain Agents](https://huggingface.co/blog/open-source-llms-as-agents) blog post to learn more about ReAct agents.
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img
|
||||
class="block dark:hidden"
|
||||
src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/Agent_ManimCE.gif"
|
||||
/>
|
||||
<img
|
||||
class="hidden dark:block"
|
||||
src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/Agent_ManimCE.gif"
|
||||
/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
> Read [Open-source LLMs as LangChain Agents](https://huggingface.co/blog/open-source-llms-as-agents) blog post to learn more the ReAct agent.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -137,13 +126,12 @@ Additionally, `llm_engine` can also take a `grammar` argument. In the case where
|
||||
|
||||
You will also need a `tools` argument which accepts a list of `Tools` - it can be an empty list. You can also add the default toolbox on top of your `tools` list by defining the optional argument `add_base_tools=True`.
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can create an agent, like [`CodeAgent`], and run it. You can also create a [`TransformersEngine`] with a pre-initialized pipeline to run inference on your local machine using `transformers`.
|
||||
For convenience, since agentic behaviours generally require stronger models such as `Llama-3.1-70B-Instruct` that are harder to run locally for now, we also provide the [`HfApiEngine`] class that initializes a `huggingface_hub.InferenceClient` under the hood.
|
||||
Now you can create an agent, like [`CodeAgent`], and run it. For convenience, we also provide the [`HfEngine`] class that uses `huggingface_hub.InferenceClient` under the hood.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import CodeAgent, HfApiEngine
|
||||
from transformers import CodeAgent, HfEngine
|
||||
|
||||
llm_engine = HfApiEngine(model="meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3-70B-Instruct")
|
||||
llm_engine = HfEngine(model="meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3-70B-Instruct")
|
||||
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[], llm_engine=llm_engine, add_base_tools=True)
|
||||
|
||||
agent.run(
|
||||
@ -153,7 +141,7 @@ agent.run(
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This will be handy in case of emergency baguette need!
|
||||
You can even leave the argument `llm_engine` undefined, and an [`HfApiEngine`] will be created by default.
|
||||
You can even leave the argument `llm_engine` undefined, and an [`HfEngine`] will be created by default.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import CodeAgent
|
||||
@ -294,8 +282,7 @@ Transformers comes with a default toolbox for empowering agents, that you can ad
|
||||
- **Speech to text**: given an audio recording of a person talking, transcribe the speech into text ([Whisper](./model_doc/whisper))
|
||||
- **Text to speech**: convert text to speech ([SpeechT5](./model_doc/speecht5))
|
||||
- **Translation**: translates a given sentence from source language to target language.
|
||||
- **DuckDuckGo search***: performs a web search using DuckDuckGo browser.
|
||||
- **Python code interpreter**: runs your the LLM generated Python code in a secure environment. This tool will only be added to [`ReactJsonAgent`] if you initialize it with `add_base_tools=True`, since code-based agent can already natively execute Python code
|
||||
- **Python code interpreter**: runs your the LLM generated Python code in a secure environment. This tool will only be added to [`ReactJsonAgent`] if you use `add_base_tools=True`, since code-based tools can already execute Python code
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
You can manually use a tool by calling the [`load_tool`] function and a task to perform.
|
||||
@ -455,3 +442,123 @@ To speed up the start, tools are loaded only if called by the agent.
|
||||
This gets you this image:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/rivers_and_lakes.png">
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Use gradio-tools
|
||||
|
||||
[gradio-tools](https://github.com/freddyaboulton/gradio-tools) is a powerful library that allows using Hugging
|
||||
Face Spaces as tools. It supports many existing Spaces as well as custom Spaces.
|
||||
|
||||
Transformers supports `gradio_tools` with the [`Tool.from_gradio`] method. For example, let's use the [`StableDiffusionPromptGeneratorTool`](https://github.com/freddyaboulton/gradio-tools/blob/main/gradio_tools/tools/prompt_generator.py) from `gradio-tools` toolkit for improving prompts to generate better images.
|
||||
|
||||
Import and instantiate the tool, then pass it to the `Tool.from_gradio` method:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from gradio_tools import StableDiffusionPromptGeneratorTool
|
||||
from transformers import Tool, load_tool, CodeAgent
|
||||
|
||||
gradio_prompt_generator_tool = StableDiffusionPromptGeneratorTool()
|
||||
prompt_generator_tool = Tool.from_gradio(gradio_prompt_generator_tool)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can use it just like any other tool. For example, let's improve the prompt `a rabbit wearing a space suit`.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
image_generation_tool = load_tool('huggingface-tools/text-to-image')
|
||||
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[prompt_generator_tool, image_generation_tool], llm_engine=llm_engine)
|
||||
|
||||
agent.run(
|
||||
"Improve this prompt, then generate an image of it.", prompt='A rabbit wearing a space suit'
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The model adequately leverages the tool:
|
||||
```text
|
||||
======== New task ========
|
||||
Improve this prompt, then generate an image of it.
|
||||
You have been provided with these initial arguments: {'prompt': 'A rabbit wearing a space suit'}.
|
||||
==== Agent is executing the code below:
|
||||
improved_prompt = StableDiffusionPromptGenerator(query=prompt)
|
||||
while improved_prompt == "QUEUE_FULL":
|
||||
improved_prompt = StableDiffusionPromptGenerator(query=prompt)
|
||||
print(f"The improved prompt is {improved_prompt}.")
|
||||
image = image_generator(prompt=improved_prompt)
|
||||
====
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Before finally generating the image:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/rabbit.png">
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
> [!WARNING]
|
||||
> gradio-tools require *textual* inputs and outputs even when working with different modalities like image and audio objects. Image and audio inputs and outputs are currently incompatible.
|
||||
|
||||
### Use LangChain tools
|
||||
|
||||
We love Langchain and think it has a very compelling suite of tools.
|
||||
To import a tool from LangChain, use the `from_langchain()` method.
|
||||
|
||||
Here is how you can use it to recreate the intro's search result using a LangChain web search tool.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from langchain.agents import load_tools
|
||||
from transformers import Tool, ReactCodeAgent
|
||||
|
||||
search_tool = Tool.from_langchain(load_tools(["serpapi"])[0])
|
||||
|
||||
agent = ReactCodeAgent(tools=[search_tool])
|
||||
|
||||
agent.run("How many more blocks (also denoted as layers) in BERT base encoder than the encoder from the architecture proposed in Attention is All You Need?")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Gradio interface
|
||||
|
||||
You can leverage `gradio.Chatbot`to display your agent's thoughts using `stream_to_gradio`, here is an example:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
import gradio as gr
|
||||
from transformers import (
|
||||
load_tool,
|
||||
ReactCodeAgent,
|
||||
HfEngine,
|
||||
stream_to_gradio,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Import tool from Hub
|
||||
image_generation_tool = load_tool("m-ric/text-to-image")
|
||||
|
||||
llm_engine = HfEngine("meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3-70B-Instruct")
|
||||
|
||||
# Initialize the agent with the image generation tool
|
||||
agent = ReactCodeAgent(tools=[image_generation_tool], llm_engine=llm_engine)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def interact_with_agent(task):
|
||||
messages = []
|
||||
messages.append(gr.ChatMessage(role="user", content=task))
|
||||
yield messages
|
||||
for msg in stream_to_gradio(agent, task):
|
||||
messages.append(msg)
|
||||
yield messages + [
|
||||
gr.ChatMessage(role="assistant", content="⏳ Task not finished yet!")
|
||||
]
|
||||
yield messages
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
with gr.Blocks() as demo:
|
||||
text_input = gr.Textbox(lines=1, label="Chat Message", value="Make me a picture of the Statue of Liberty.")
|
||||
submit = gr.Button("Run illustrator agent!")
|
||||
chatbot = gr.Chatbot(
|
||||
label="Agent",
|
||||
type="messages",
|
||||
avatar_images=(
|
||||
None,
|
||||
"https://em-content.zobj.net/source/twitter/53/robot-face_1f916.png",
|
||||
),
|
||||
)
|
||||
submit.click(interact_with_agent, [text_input], [chatbot])
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
demo.launch()
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -1,182 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
# Agents, supercharged - Multi-agents, External tools, and more
|
||||
|
||||
[[open-in-colab]]
|
||||
|
||||
### What is an agent?
|
||||
|
||||
> [!TIP]
|
||||
> If you're new to `transformers.agents`, make sure to first read the main [agents documentation](./agents).
|
||||
|
||||
In this page we're going to highlight several advanced uses of `transformers.agents`.
|
||||
|
||||
## Multi-agents
|
||||
|
||||
Multi-agent has been introduced in Microsoft's framework [Autogen](https://huggingface.co/papers/2308.08155).
|
||||
It simply means having several agents working together to solve your task instead of only one.
|
||||
It empirically yields better performance on most benchmarks. The reason for this better performance is conceptually simple: for many tasks, rather than using a do-it-all system, you would prefer to specialize units on sub-tasks. Here, having agents with separate tool sets and memories allows to achieve efficient specialization.
|
||||
|
||||
You can easily build hierarchical multi-agent systems with `transformers.agents`.
|
||||
|
||||
To do so, encapsulate the agent in a [`ManagedAgent`] object. This object needs arguments `agent`, `name`, and a `description`, which will then be embedded in the manager agent's system prompt to let it know how to call this managed agent, as we also do for tools.
|
||||
|
||||
Here's an example of making an agent that managed a specitif web search agent using our [`DuckDuckGoSearchTool`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers.agents import ReactCodeAgent, HfApiEngine, DuckDuckGoSearchTool, ManagedAgent
|
||||
|
||||
llm_engine = HfApiEngine()
|
||||
|
||||
web_agent = ReactCodeAgent(tools=[DuckDuckGoSearchTool()], llm_engine=llm_engine)
|
||||
|
||||
managed_web_agent = ManagedAgent(
|
||||
agent=web_agent,
|
||||
name="web_search",
|
||||
description="Runs web searches for you. Give it your query as an argument."
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
manager_agent = ReactCodeAgent(
|
||||
tools=[], llm_engine=llm_engine, managed_agents=[managed_web_agent]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
manager_agent.run("Who is the CEO of Hugging Face?")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> [!TIP]
|
||||
> For an in-depth example of an efficient multi-agent implementation, see [how we pushed our multi-agent system to the top of the GAIA leaderboard](https://huggingface.co/blog/beating-gaia).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Use tools from gradio or LangChain
|
||||
|
||||
### Use gradio-tools
|
||||
|
||||
[gradio-tools](https://github.com/freddyaboulton/gradio-tools) is a powerful library that allows using Hugging
|
||||
Face Spaces as tools. It supports many existing Spaces as well as custom Spaces.
|
||||
|
||||
Transformers supports `gradio_tools` with the [`Tool.from_gradio`] method. For example, let's use the [`StableDiffusionPromptGeneratorTool`](https://github.com/freddyaboulton/gradio-tools/blob/main/gradio_tools/tools/prompt_generator.py) from `gradio-tools` toolkit for improving prompts to generate better images.
|
||||
|
||||
Import and instantiate the tool, then pass it to the `Tool.from_gradio` method:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from gradio_tools import StableDiffusionPromptGeneratorTool
|
||||
from transformers import Tool, load_tool, CodeAgent
|
||||
|
||||
gradio_prompt_generator_tool = StableDiffusionPromptGeneratorTool()
|
||||
prompt_generator_tool = Tool.from_gradio(gradio_prompt_generator_tool)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can use it just like any other tool. For example, let's improve the prompt `a rabbit wearing a space suit`.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
image_generation_tool = load_tool('huggingface-tools/text-to-image')
|
||||
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[prompt_generator_tool, image_generation_tool], llm_engine=llm_engine)
|
||||
|
||||
agent.run(
|
||||
"Improve this prompt, then generate an image of it.", prompt='A rabbit wearing a space suit'
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The model adequately leverages the tool:
|
||||
```text
|
||||
======== New task ========
|
||||
Improve this prompt, then generate an image of it.
|
||||
You have been provided with these initial arguments: {'prompt': 'A rabbit wearing a space suit'}.
|
||||
==== Agent is executing the code below:
|
||||
improved_prompt = StableDiffusionPromptGenerator(query=prompt)
|
||||
while improved_prompt == "QUEUE_FULL":
|
||||
improved_prompt = StableDiffusionPromptGenerator(query=prompt)
|
||||
print(f"The improved prompt is {improved_prompt}.")
|
||||
image = image_generator(prompt=improved_prompt)
|
||||
====
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Before finally generating the image:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/rabbit.png">
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
> [!WARNING]
|
||||
> gradio-tools require *textual* inputs and outputs even when working with different modalities like image and audio objects. Image and audio inputs and outputs are currently incompatible.
|
||||
|
||||
### Use LangChain tools
|
||||
|
||||
We love Langchain and think it has a very compelling suite of tools.
|
||||
To import a tool from LangChain, use the `from_langchain()` method.
|
||||
|
||||
Here is how you can use it to recreate the intro's search result using a LangChain web search tool.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from langchain.agents import load_tools
|
||||
from transformers import Tool, ReactCodeAgent
|
||||
|
||||
search_tool = Tool.from_langchain(load_tools(["serpapi"])[0])
|
||||
|
||||
agent = ReactCodeAgent(tools=[search_tool])
|
||||
|
||||
agent.run("How many more blocks (also denoted as layers) in BERT base encoder than the encoder from the architecture proposed in Attention is All You Need?")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Display your agent run in a cool Gradio interface
|
||||
|
||||
You can leverage `gradio.Chatbot`to display your agent's thoughts using `stream_to_gradio`, here is an example:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
import gradio as gr
|
||||
from transformers import (
|
||||
load_tool,
|
||||
ReactCodeAgent,
|
||||
HfApiEngine,
|
||||
stream_to_gradio,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Import tool from Hub
|
||||
image_generation_tool = load_tool("m-ric/text-to-image")
|
||||
|
||||
llm_engine = HfApiEngine("meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3-70B-Instruct")
|
||||
|
||||
# Initialize the agent with the image generation tool
|
||||
agent = ReactCodeAgent(tools=[image_generation_tool], llm_engine=llm_engine)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def interact_with_agent(task):
|
||||
messages = []
|
||||
messages.append(gr.ChatMessage(role="user", content=task))
|
||||
yield messages
|
||||
for msg in stream_to_gradio(agent, task):
|
||||
messages.append(msg)
|
||||
yield messages + [
|
||||
gr.ChatMessage(role="assistant", content="⏳ Task not finished yet!")
|
||||
]
|
||||
yield messages
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
with gr.Blocks() as demo:
|
||||
text_input = gr.Textbox(lines=1, label="Chat Message", value="Make me a picture of the Statue of Liberty.")
|
||||
submit = gr.Button("Run illustrator agent!")
|
||||
chatbot = gr.Chatbot(
|
||||
label="Agent",
|
||||
type="messages",
|
||||
avatar_images=(
|
||||
None,
|
||||
"https://em-content.zobj.net/source/twitter/53/robot-face_1f916.png",
|
||||
),
|
||||
)
|
||||
submit.click(interact_with_agent, [text_input], [chatbot])
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
demo.launch()
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -26,7 +26,26 @@ Much like tokenization, different models expect very different input formats for
|
||||
**chat templates** as a feature. Chat templates are part of the tokenizer. They specify how to convert conversations,
|
||||
represented as lists of messages, into a single tokenizable string in the format that the model expects.
|
||||
|
||||
Let's make this concrete with a quick example using the `mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.1` model:
|
||||
Let's make this concrete with a quick example using the `BlenderBot` model. BlenderBot has an extremely simple default
|
||||
template, which mostly just adds whitespace between rounds of dialogue:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("facebook/blenderbot-400M-distill")
|
||||
|
||||
>>> chat = [
|
||||
... {"role": "user", "content": "Hello, how are you?"},
|
||||
... {"role": "assistant", "content": "I'm doing great. How can I help you today?"},
|
||||
... {"role": "user", "content": "I'd like to show off how chat templating works!"},
|
||||
... ]
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenizer.apply_chat_template(chat, tokenize=False)
|
||||
" Hello, how are you? I'm doing great. How can I help you today? I'd like to show off how chat templating works!</s>"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Notice how the entire chat is condensed into a single string. If we use `tokenize=True`, which is the default setting,
|
||||
that string will also be tokenized for us. To see a more complex template in action, though, let's use the
|
||||
`mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.1` model.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer
|
||||
@ -42,26 +61,8 @@ Let's make this concrete with a quick example using the `mistralai/Mistral-7B-In
|
||||
"<s>[INST] Hello, how are you? [/INST]I'm doing great. How can I help you today?</s> [INST] I'd like to show off how chat templating works! [/INST]"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Notice how the tokenizer has added the control tokens [INST] and [/INST] to indicate the start and end of
|
||||
user messages (but not assistant messages!), and the entire chat is condensed into a single string.
|
||||
If we use `tokenize=True`, which is the default setting, that string will also be tokenized for us.
|
||||
|
||||
Now, try the same code, but swap in the `HuggingFaceH4/zephyr-7b-beta` model instead, and you should get:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
<|user|>
|
||||
Hello, how are you?</s>
|
||||
<|assistant|>
|
||||
I'm doing great. How can I help you today?</s>
|
||||
<|user|>
|
||||
I'd like to show off how chat templating works!</s>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Both Zephyr and Mistral-Instruct were fine-tuned from the same base model, `Mistral-7B-v0.1`. However, they were trained
|
||||
with totally different chat formats. Without chat templates, you would have to write manual formatting code for each
|
||||
model, and it's very easy to make minor errors that hurt performance! Chat templates handle the details of formatting
|
||||
for you, allowing you to write universal code that works for any model.
|
||||
|
||||
Note that this time, the tokenizer has added the control tokens [INST] and [/INST] to indicate the start and end of
|
||||
user messages (but not assistant messages!). Mistral-instruct was trained with these tokens, but BlenderBot was not.
|
||||
|
||||
## How do I use chat templates?
|
||||
|
||||
@ -70,7 +71,7 @@ and `content` keys, and then pass it to the [`~PreTrainedTokenizer.apply_chat_te
|
||||
you'll get output that's ready to go! When using chat templates as input for model generation, it's also a good idea
|
||||
to use `add_generation_prompt=True` to add a [generation prompt](#what-are-generation-prompts).
|
||||
|
||||
Here's an example of preparing input for `model.generate()`, using `Zephyr` again:
|
||||
Here's an example of preparing input for `model.generate()`, using the `Zephyr` assistant model:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
|
||||
@ -159,7 +160,7 @@ messages = [
|
||||
]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Here's what this will look like without a generation prompt, for a model that uses standard "ChatML" formatting:
|
||||
Here's what this will look like without a generation prompt, using the ChatML template we saw in the Zephyr example:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
tokenizer.apply_chat_template(messages, tokenize=False, add_generation_prompt=False)
|
||||
@ -192,47 +193,10 @@ message. Remember, chat models are still just language models - they're trained
|
||||
special kind of text to them! You need to guide them with appropriate control tokens, so they know what they're
|
||||
supposed to be doing.
|
||||
|
||||
Not all models require generation prompts. Some models, like LLaMA, don't have any
|
||||
Not all models require generation prompts. Some models, like BlenderBot and LLaMA, don't have any
|
||||
special tokens before bot responses. In these cases, the `add_generation_prompt` argument will have no effect. The exact
|
||||
effect that `add_generation_prompt` has will depend on the template being used.
|
||||
|
||||
## What does "continue_last_message" do?
|
||||
|
||||
When passing a list of messages to `apply_chat_template` or `TextGenerationPipeline`, you can choose
|
||||
to format the chat so the model will continue the final message in the chat instead of starting a new one. This is done
|
||||
by removing any end-of-sequence tokens that indicate the end of the final message, so that the model will simply
|
||||
extend the final message when it begins to generate text. This is useful for "prefilling" the model's response.
|
||||
|
||||
Here's an example:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
chat = [
|
||||
{"role": "user", "content": "Can you format the answer in JSON?"},
|
||||
{"role": "assistant", "content": '{"name": "'},
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
formatted_chat = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(chat, tokenize=True, return_dict=True, continue_last_message=True)
|
||||
model.generate(**formatted_chat)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The model will generate text that continues the JSON string, rather than starting a new message. This approach
|
||||
can be very useful for improving the accuracy of the model's instruction-following when you know how you want
|
||||
it to start its replies.
|
||||
|
||||
Because `add_generation_prompt` adds the tokens that start a new message, and `continue_last_message` removes any
|
||||
end-of-message tokens from the final message, it does not make sense to use them together. As a result, you'll
|
||||
get an error if you try!
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
The default behaviour of `TextGenerationPipeline` is to set `add_generation_prompt=True` so that it starts a new
|
||||
message. However, if the final message in the input chat has the "assistant" role, it will assume that this message is
|
||||
a prefill and switch to `continue_final_message=True` instead, because most models do not support multiple
|
||||
consecutive assistant messages. You can override this behaviour by explicitly passing the `continue_last_message`
|
||||
argument when calling the pipeline.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## Can I use chat templates in training?
|
||||
|
||||
Yes! This is a good way to ensure that the chat template matches the tokens the model sees during training.
|
||||
@ -441,12 +405,6 @@ tool_call = {"name": "get_current_temperature", "arguments": {"location": "Paris
|
||||
messages.append({"role": "assistant", "tool_calls": [{"type": "function", "function": tool_call}]})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
If you're familiar with the OpenAI API, you should pay attention to an important difference here - the `tool_call` is
|
||||
a dict, but in the OpenAI API it's a JSON string. Passing a string may cause errors or strange model behaviour!
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Now that we've added the tool call to the conversation, we can call the function and append the result to the
|
||||
conversation. Since we're just using a dummy function for this example that always returns 22.0, we can just append
|
||||
@ -635,17 +593,32 @@ model_input = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
|
||||
## Advanced: How do chat templates work?
|
||||
|
||||
The chat template for a model is stored on the `tokenizer.chat_template` attribute. If no chat template is set, the
|
||||
default template for that model class is used instead. Let's take a look at a `Zephyr` chat template, though note this
|
||||
one is a little simplified from the actual one!
|
||||
default template for that model class is used instead. Let's take a look at the template for `BlenderBot`:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("facebook/blenderbot-400M-distill")
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenizer.chat_template
|
||||
"{% for message in messages %}{% if message['role'] == 'user' %}{{ ' ' }}{% endif %}{{ message['content'] }}{% if not loop.last %}{{ ' ' }}{% endif %}{% endfor %}{{ eos_token }}"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
That's kind of intimidating. Let's clean it up a little to make it more readable. In the process, though, we also make
|
||||
sure that the newlines and indentation we add don't end up being included in the template output - see the tip on
|
||||
[trimming whitespace](#trimming-whitespace) below!
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
{%- for message in messages %}
|
||||
{{- '<|' + message['role'] + |>\n' }}
|
||||
{{- message['content'] + eos_token }}
|
||||
{%- if message['role'] == 'user' %}
|
||||
{{- ' ' }}
|
||||
{%- endif %}
|
||||
{{- message['content'] }}
|
||||
{%- if not loop.last %}
|
||||
{{- ' ' }}
|
||||
{%- endif %}
|
||||
{%- endfor %}
|
||||
{%- if add_generation_prompt %}
|
||||
{{- '<|assistant|>\n' }}
|
||||
{%- endif %}
|
||||
{{- eos_token }}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you've never seen one of these before, this is a [Jinja template](https://jinja.palletsprojects.com/en/3.1.x/templates/).
|
||||
@ -653,23 +626,25 @@ Jinja is a templating language that allows you to write simple code that generat
|
||||
syntax resembles Python. In pure Python, this template would look something like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
for message in messages:
|
||||
print(f'<|{message["role"]}|>')
|
||||
print(message['content'] + eos_token)
|
||||
if add_generation_prompt:
|
||||
print('<|assistant|>')
|
||||
for idx, message in enumerate(messages):
|
||||
if message['role'] == 'user':
|
||||
print(' ')
|
||||
print(message['content'])
|
||||
if not idx == len(messages) - 1: # Check for the last message in the conversation
|
||||
print(' ')
|
||||
print(eos_token)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Effectively, the template does three things:
|
||||
1. For each message, print the role enclosed in `<|` and `|>`, like `<|user|>` or `<|assistant|>`.
|
||||
2. Next, print the content of the message, followed by the end-of-sequence token.
|
||||
3. Finally, if `add_generation_prompt` is set, print the assistant token, so that the model knows to start generating
|
||||
an assistant response.
|
||||
1. For each message, if the message is a user message, add a blank space before it, otherwise print nothing.
|
||||
2. Add the message content
|
||||
3. If the message is not the last message, add two spaces after it. After the final message, print the EOS token.
|
||||
|
||||
This is a pretty simple template but Jinja gives you a lot of flexibility to do more complex things! Let's see a Jinja
|
||||
template that can format inputs similarly to the way LLaMA formats them (note that the real LLaMA template includes
|
||||
handling for default system messages and slightly different system message handling in general - don't use this one
|
||||
in your actual code!)
|
||||
This is a pretty simple template - it doesn't add any control tokens, and it doesn't support "system" messages, which
|
||||
are a common way to give the model directives about how it should behave in the subsequent conversation.
|
||||
But Jinja gives you a lot of flexibility to do those things! Let's see a Jinja template that can format inputs
|
||||
similarly to the way LLaMA formats them (note that the real LLaMA template includes handling for default system
|
||||
messages and slightly different system message handling in general - don't use this one in your actual code!)
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
{%- for message in messages %}
|
||||
@ -683,8 +658,8 @@ in your actual code!)
|
||||
{%- endfor %}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Hopefully if you stare at this for a little bit you can see what this template is doing - it adds specific tokens like
|
||||
`[INST]` and `[/INST]` based on the role of each message. User, assistant and system messages are clearly
|
||||
Hopefully if you stare at this for a little bit you can see what this template is doing - it adds specific tokens based
|
||||
on the "role" of each message, which represents who sent it. User, assistant and system messages are clearly
|
||||
distinguishable to the model because of the tokens they're wrapped in.
|
||||
|
||||
## Advanced: Adding and editing chat templates
|
||||
|
||||
@ -67,4 +67,3 @@ This page regroups resources around 🤗 Transformers developed by the community
|
||||
| [Detect objects in an image with DETR](https://github.com/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/DETR/DETR_minimal_example_(with_DetrFeatureExtractor).ipynb) | How to use a trained *DetrForObjectDetection* model to detect objects in an image and visualize attention | [Niels Rogge](https://github.com/NielsRogge) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/DETR/DETR_minimal_example_(with_DetrFeatureExtractor).ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Fine-tune DETR on a custom object detection dataset](https://github.com/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/DETR/Fine_tuning_DetrForObjectDetection_on_custom_dataset_(balloon).ipynb) | How to fine-tune *DetrForObjectDetection* on a custom object detection dataset | [Niels Rogge](https://github.com/NielsRogge) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/DETR/Fine_tuning_DetrForObjectDetection_on_custom_dataset_(balloon).ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Finetune T5 for Named Entity Recognition](https://github.com/ToluClassics/Notebooks/blob/main/T5_Ner_Finetuning.ipynb) | How to fine-tune *T5* on a Named Entity Recognition Task | [Ogundepo Odunayo](https://github.com/ToluClassics) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1obr78FY_cBmWY5ODViCmzdY6O1KB65Vc?usp=sharing) |
|
||||
| [Fine-Tuning Open-Source LLM using QLoRA with MLflow and PEFT](https://github.com/mlflow/mlflow/blob/master/docs/source/llms/transformers/tutorials/fine-tuning/transformers-peft.ipynb) | How to use [QLoRA](https://github.com/artidoro/qlora) and [PEFT](https://huggingface.co/docs/peft/en/index) to fine-tune an LLM in a memory-efficient way, while using [MLflow](https://mlflow.org/docs/latest/llms/transformers/index.html) to manage experiment tracking | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/mlflow/mlflow/blob/master/docs/source/llms/transformers/tutorials/fine-tuning/transformers-peft.ipynb) |
|
||||
|
||||
@ -46,30 +46,16 @@ The initial supported quantization types are decided according to the popular qu
|
||||
on the Hub.
|
||||
|
||||
- F32
|
||||
- F16
|
||||
- BF16
|
||||
- Q4_0
|
||||
- Q4_1
|
||||
- Q5_0
|
||||
- Q5_1
|
||||
- Q8_0
|
||||
- Q2_K
|
||||
- Q3_K
|
||||
- Q4_0
|
||||
- Q4_K
|
||||
- Q5_K
|
||||
- Q6_K
|
||||
- IQ1_S
|
||||
- IQ1_M
|
||||
- IQ2_XXS
|
||||
- IQ2_XS
|
||||
- IQ2_S
|
||||
- IQ3_XXS
|
||||
- IQ3_S
|
||||
- IQ4_XS
|
||||
- IQ4_NL
|
||||
- Q8_0
|
||||
|
||||
> [!NOTE]
|
||||
> To support gguf dequantization, `gguf>=0.10.0` installation is required.
|
||||
We take example from the excellent [99991/pygguf](https://github.com/99991/pygguf) Python parser to dequantize the
|
||||
weights.
|
||||
|
||||
### Supported model architectures
|
||||
|
||||
@ -78,7 +64,6 @@ For now the supported model architectures are the architectures that have been v
|
||||
- LLaMa
|
||||
- Mistral
|
||||
- Qwen2
|
||||
- Qwen2Moe
|
||||
|
||||
## Example usage
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -189,7 +189,6 @@ Flax), PyTorch, and/or TensorFlow.
|
||||
| [LLaVa](model_doc/llava) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| [LLaVA-NeXT](model_doc/llava_next) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| [LLaVa-NeXT-Video](model_doc/llava_next_video) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| [LLaVA-Onevision](model_doc/llava_onevision) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| [Longformer](model_doc/longformer) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| [LongT5](model_doc/longt5) | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
|
||||
| [LUKE](model_doc/luke) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
@ -234,7 +233,6 @@ Flax), PyTorch, and/or TensorFlow.
|
||||
| [Nougat](model_doc/nougat) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| [Nyströmformer](model_doc/nystromformer) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| [OLMo](model_doc/olmo) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| [OLMoE](model_doc/olmoe) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| [OneFormer](model_doc/oneformer) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| [OpenAI GPT](model_doc/openai-gpt) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| [OpenAI GPT-2](model_doc/gpt2) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
|
||||
@ -390,11 +390,6 @@ A [`Constraint`] can be used to force the generation to include specific tokens
|
||||
- get_seq_length
|
||||
- reset
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] OffloadedStaticCache
|
||||
- update
|
||||
- get_seq_length
|
||||
- reset
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] HybridCache
|
||||
- update
|
||||
- get_seq_length
|
||||
|
||||
@ -22,7 +22,7 @@ Effective caching helps reduce computation time and improve response rates, espe
|
||||
|
||||
Transformers support various caching methods, leveraging "Cache" classes to abstract and manage the caching logic.
|
||||
This document outlines best practices for using these classes to maximize performance and efficiency.
|
||||
Check out all the available `Cache` classes in the [API documentation](./internal/generation_utils).
|
||||
Check out all the available `Cache` classes in the [API documentation](./internal/generation_utils.md).
|
||||
|
||||
## What is Cache and why we should care?
|
||||
|
||||
@ -30,7 +30,7 @@ Imagine you’re having a conversation with someone, and instead of remembering
|
||||
|
||||
KV cache is needed to optimize the generation in autoregressive models, where the model predicts text token by token. This process can be slow since the model can generate only one token at a time, and each new prediction is dependent on the previous context. That means, to predict token number 1000 in the generation, you need information from the previous 999 tokens, which comes in the form of some matrix multiplications across the representations of those tokens. But to predict token number 1001, you also need the same information from the first 999 tokens, plus additional information from token number 1000. That is where key-value cache is used to optimize the sequential generation process by storing previous calculations to reuse in subsequent tokens, so they don't need to be computed again.
|
||||
|
||||
More concretely, key-value cache acts as a memory bank for these generative models, where the model stores key-value pairs derived from self-attention layers for previously processed tokens. By storing this information, the model can avoid redundant computations and instead retrieve keys and values of previous tokens from the cache. Note that caching can be used only in inference and should be disabled when training, otherwise it might cause unexpected errors.
|
||||
More concretely, key-value cache acts as a memory bank for these generative models, where the model stores key-value pairs derived from self-attention layers for previously processed tokens. By storing this information, the model can avoid redundant computations and instead retrieve keys and values of previous tokens from the cache.
|
||||
|
||||
<details>
|
||||
<summary><em>For the Curious Minds Who Like to Dive Deep</em></summary>
|
||||
@ -51,11 +51,11 @@ More concretely, key-value cache acts as a memory bank for these generative mode
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
See an example below for how to implement your own generation loop.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> import torch
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM, DynamicCache
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model_id = "meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-chat-hf"
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_id, torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16, device_map="cuda:0")
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_id)
|
||||
@ -69,10 +69,10 @@ More concretely, key-value cache acts as a memory bank for these generative mode
|
||||
>>> max_new_tokens = 10
|
||||
|
||||
>>> for _ in range(max_new_tokens):
|
||||
... outputs = model(**inputs, cache_position=cache_position, past_key_values=past_key_values, use_cache=True)
|
||||
... outputs = model(**inputs, cache_position=cache_position, past_key_values=past_key_values, use_cache=True)
|
||||
... # Greedily sample one next token
|
||||
... next_token_ids = outputs.logits[:, -1:].argmax(-1)
|
||||
... generated_ids = torch.cat([generated_ids, next_token_ids], dim=-1)
|
||||
... generated_ids = torch.cat([generated_ids, next_token_ids], dim=-1)
|
||||
...
|
||||
... # Prepare inputs for the next generation step by leaaving unprocessed tokens, in our case we have only one new token
|
||||
... # and expanding attn mask for the new token, as explained above
|
||||
@ -94,20 +94,19 @@ More concretely, key-value cache acts as a memory bank for these generative mode
|
||||
In 🤗 Transformers, we support various Cache types to optimize the performance across different models and tasks. By default, all models generate with caching,
|
||||
with the [`~DynamicCache`] class being the default cache for most models. It allows us to dynamically grow cache size, by saving more and more keys and values as we generate. If for some reason you don't want to use caches, you can pass `use_cache=False` into the `generate()` method.
|
||||
|
||||
Refer to the table below to see the difference between cache types and choose the one that suits best for your use-case. Models for which initialization is recommended should be initialized before calling the model and passed to model as a kwarg. In all other cases you can simply define desired `cache_implementation` and we take care of the rest for you.
|
||||
Refer to the table below to see the difference between cache types and choose the one that suits best for your use-case.
|
||||
|
||||
| Cache Type | Memory Efficient | Supports torch.compile() | Initialization Recommended | Latency | Long Context Generation |
|
||||
|------------------------|------------------|--------------------------|----------------------------|---------|-------------------------|
|
||||
| Dynamic Cache | No | No | No | Mid | No |
|
||||
| Static Cache | No | Yes | Yes | High | No |
|
||||
| Offloaded Cache | Yes | No | No | Low | Yes |
|
||||
| Offloaded Static Cache | No | Yes | Yes | High | Yes |
|
||||
| Quantized Cache | Yes | No | No | Low | Yes |
|
||||
| Sliding Window Cache | No | Yes | Yes | High | No |
|
||||
| Sink Cache | Yes | No | Yes | Mid | Yes |
|
||||
| Cache Type | Memory Efficient | Supports torch.compile() | Initialization Recommended | Latency | Long Context Generation |
|
||||
|---------------------|------------------|--------------------------|----------------------------|----------|--------------------------|
|
||||
| Dynamic Cache | No | No | No | Mid | No |
|
||||
| Static Cache | No | Yes | Yes | High | No |
|
||||
| Quantized Cache | Yes | No | No | Low | Yes |
|
||||
| Offloaded Cache | Yes | No | No | Low | No |
|
||||
| Sliding Window Cache| No | Yes | Yes | High | No |
|
||||
| Sink Cache | Yes | No | Yes | Mid | Yes |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
These cache classes can be set with a `cache_implementation` argument when generating. To learn about the available options for the cache_implementation flag, please refer to the [API Documentation](./main_classes/text_generation#transformers.GenerationConfig). Now, let's explore each cache type in detail and see how to use them. Note that the below examples are for decoder-only Tranformer-based models. We also support ["Model-Specific Cache"] classes for models such as Mamba or Jamba, keep reading for more details.
|
||||
These cache classes can be set with a `cache_implementation` argument when generating. To learn about the available options for the cache_implementation flag, please refer to the [API Documentation](./main_classes/text_generation.md#transformers.GenerationConfig). Now, let's explore each cache type in detail and see how to use them. Note that the below examples are for decoder-only Tranformer-based models. We also support ["Model-Specific Cache"] classes for models such as Mamba or Jamba, keep reading for more details.
|
||||
|
||||
### Quantized Cache
|
||||
|
||||
@ -120,8 +119,6 @@ To enable quantization of the key-value cache, one needs to indicate `cache_impl
|
||||
Quantization related arguments should be passed to the `generation_config` either as a `dict` or an instance of a [`~QuantizedCacheConfig`] class.
|
||||
One has to indicate which quantization backend to use in the [`~QuantizedCacheConfig`], the default is `quanto`.
|
||||
|
||||
It is recommended to set `axis-key/axis-value` parameters in the cache config to `0` if you're using the `quanto` backend and to `1` if you're using the `HQQ` backend. For other config values, please use the defaults unless you're running out of memory. In that case, you may consider decreasing the residual length.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
Cache quantization can be detrimental in terms of latency if the context length is short and there is enough GPU VRAM available to run without cache quantization. It is recommended to seek balance between memory efficiency and latency.
|
||||
@ -145,7 +142,7 @@ I like rock music because it's loud and energetic. It's a great way to express m
|
||||
I like rock music because it's loud and energetic. I like to listen to it when I'm feeling
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Offloaded Cache
|
||||
## OffloadedCache
|
||||
|
||||
Similarly to KV cache quantization, [`~OffloadedCache`] strategy aims to reduce GPU VRAM usage.
|
||||
It does so by moving the KV cache for most layers to the CPU.
|
||||
@ -157,8 +154,7 @@ Thus, it can serve as a drop-in replacement or a fallback for it.
|
||||
Depending on your model and the characteristics of your generation task (size of context, number of generated tokens, number of beams, etc.)
|
||||
you may notice a small degradation in generation throughput compared to the default KV cache implementation.
|
||||
|
||||
To enable KV cache offloading, pass `cache_implementation="offloaded"` in the `generation_config` or directly to the `generate()` call.
|
||||
Use `cache_implementation="offloaded_static"` for an offloaded static cache (see also [Offloaded Static Cache](#offloaded-static-cache) below).
|
||||
To enable KV cache offloading, pass `cache_implementation="offloaded"` in the `generation_config` or directky to the `generate()` call.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> import torch
|
||||
@ -220,12 +216,13 @@ retrying with cache_implementation='offloaded'
|
||||
before successfully generating 40 beams.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Static Cache
|
||||
|
||||
Since the "DynamicCache" dynamically grows with each generation step, it prevents you from taking advantage of JIT optimizations. The [`~StaticCache`] pre-allocates
|
||||
Since the "DynamicCache" dynamically grows with each generation step, it prevents you from taking advantage of JIT optimizations. The [`~StaticCache`] pre-allocates
|
||||
a specific maximum size for the keys and values, allowing you to generate up to the maximum length without having to modify cache size. Check the below usage example.
|
||||
|
||||
For more examples with Static Cache and JIT compilation, take a look at [StaticCache & torchcompile](./llm_optims#static-kv-cache-and-torchcompile)
|
||||
For more examples with Static Cache and JIT compilation, take a look at [StaticCache & torchcompile](./llm_optims.md#static-kv-cache-and-torchcompile)
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> import torch
|
||||
@ -241,33 +238,11 @@ For more examples with Static Cache and JIT compilation, take a look at [StaticC
|
||||
"Hello, my name is [Your Name], and I am a [Your Profession] with [Number of Years] of"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Offloaded Static Cache
|
||||
|
||||
Like [`~OffloadedCache`] exists for offloading a "DynamicCache", there is also an offloaded static cache. It fully supports
|
||||
JIT optimizations. Just pass `cache_implementation="offloaded_static"` in the `generation_config` or directly to the `generate()` call.
|
||||
This will use the [`~OffloadedStaticCache`] implementation instead.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> import torch
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-chat-hf")
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-chat-hf", torch_dtype=torch.float16, device_map="auto")
|
||||
>>> inputs = tokenizer("Hello, my name is", return_tensors="pt").to(model.device)
|
||||
|
||||
>>> # simply pass the cache implementation="static"
|
||||
>>> out = model.generate(**inputs, do_sample=False, max_new_tokens=20, cache_implementation="offloaded_static")
|
||||
>>> tokenizer.batch_decode(out, skip_special_tokens=True)[0]
|
||||
"Hello, my name is [Your Name], and I am a [Your Profession] with [Number of Years] of"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Sliding Window Cache
|
||||
|
||||
As the name suggests, this cache type implements a sliding window over previous keys and values, retaining only the last `sliding_window` tokens. It should be used with models like Mistral that support sliding window attention. Additionally, similar to Static Cache, this one is JIT-friendly and can be used with the same compile tecniques as Static Cache.
|
||||
|
||||
Note that you can use this cache only for models that support sliding window, e.g. Mistral models.
|
||||
Note that you can use this cache only for models that support sliding window, e.g. Mistral models.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
@ -308,23 +283,23 @@ Unlike other cache classes, this one can't be used directly by indicating a `cac
|
||||
|
||||
### Encoder-Decoder Cache
|
||||
|
||||
The [`~EncoderDecoderCache`] is a wrapper designed to handle the caching needs of encoder-decoder models. This cache type is specifically built to manage both self-attention and cross-attention caches, ensuring storage and retrieval of past key/values required for these complex models. Cool thing about Encoder-Decoder Cache is that you can set different cache types for the encoder and for the decoder, depending on your use case. Currently this cache is only supported in [Whisper](./model_doc/whisper) models but we will be adding more models soon.
|
||||
The [`~EncoderDecoderCache`] is a wrapper designed to handle the caching needs of encoder-decoder models. This cache type is specifically built to manage both self-attention and cross-attention caches, ensuring storage and retrieval of past key/values required for these complex models. Cool thing about Encoder-Decoder Cache is that you can set different cache types for the encoder and for the decoder, depending on your use case. Currently this cache is only supported in [Whisper](./model_doc/whisper.md) models but we will be adding more models soon.
|
||||
|
||||
In terms of usage, there is nothing special to be done and calling `generate()` or `forward()` will handle everything for you.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Model-specific Cache Classes
|
||||
|
||||
Some models require storing previous keys, values, or states in a specific way, and the above cache classes cannot be used. For such cases, we have several specialized cache classes that are designed for specific models. These models only accept their own dedicated cache classes and do not support using any other cache types. Some examples include [`~HybridCache`] for [Gemma2](./model_doc/gemma2) series models or [`~MambaCache`] for [Mamba](./model_doc/mamba) architecture models.
|
||||
Some models require storing previous keys, values, or states in a specific way, and the above cache classes cannot be used. For such cases, we have several specialized cache classes that are designed for specific models. These models only accept their own dedicated cache classes and do not support using any other cache types. Some examples include [`~HybridCache`] for [Gemma2](./model_doc/gemma2.md) series models or [`~MambaCache`] for [Mamba](./model_doc/mamba.md) architecture models.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Iterative Generation with Cache
|
||||
|
||||
We have seen how to use each of the cache types when generating. What if you want to use cache in iterative generation setting, for example in applications like chatbots, where interactions involve multiple turns and continuous back-and-forth exchanges. Iterative generation with cache allows these systems to handle ongoing conversations effectively without reprocessing the entire context at each step. But there are some tips that you should know before you start implementing:
|
||||
|
||||
The general format when doing iterative generation is as below. First you have to initialize an empty cache of the type you want, and you can start feeding in new prompts iteratively. Keeping track of dialogues history and formatting can be done with chat templates, read more on that in [chat_templating](./chat_templating)
|
||||
The general format when doing iterative generation is as below. First you have to initialize an empty cache of the type you want, and you can start feeding in new prompts iteratively. Keeping track of dialogues history and formatting can be done with chat templates, read more on that in [chat_templating](./chat_templating.md)
|
||||
|
||||
In case you are using Sink Cache, you have to crop your inputs to that maximum length because Sink Cache can generate text longer than its maximum window size, but it expects the first input to not exceed the maximum cache length.
|
||||
In case you are using Sink Cache, you have to crop your inputs to that maximum length because Sink Cache can generate text longer than its maximum window size, but it expects the first input to not exceed the maximum cache length.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
@ -354,9 +329,9 @@ In case you are using Sink Cache, you have to crop your inputs to that maximum l
|
||||
... inputs = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(messages, add_generation_prompt=True, return_tensors="pt", return_dict=True).to(model.device)
|
||||
... if isinstance(past_key_values, SinkCache):
|
||||
... inputs = {k: v[:, -max_cache_length:] for k, v in inputs.items()}
|
||||
...
|
||||
...
|
||||
... input_length = inputs["input_ids"].shape[1]
|
||||
...
|
||||
...
|
||||
... outputs = model.generate(**inputs, do_sample=False, max_new_tokens=256, past_key_values=past_key_values)
|
||||
... completion = tokenizer.decode(outputs[0, input_length: ], skip_special_tokens=True)
|
||||
... messages.append({"role": "assistant", "content": completion})
|
||||
@ -368,36 +343,4 @@ print(messages)
|
||||
|
||||
## Re-use Cache to continue generation
|
||||
|
||||
Sometimes you would want to first fill-in cache object with key/values for certain prefix prompt and re-use it several times to generate different sequences from it. In that case you can construct a `Cache` object that will hold the instruction prompt, and re-use it several times with different text sequences.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> import copy
|
||||
>>> import torch
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer, DynamicCache, StaticCache
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model_id = "meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-chat-hf"
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_id, torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16, device_map="cuda")
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_id)
|
||||
|
||||
>>> # Init StaticCache with big enough max-length (1024 tokens for the below example)
|
||||
>>> # You can also init a DynamicCache, if that suits you better
|
||||
>>> prompt_cache = StaticCache(config=model.config, max_batch_size=1, max_cache_len=1024, device="cuda", dtype=torch.bfloat16)
|
||||
|
||||
>>> INITIAL_PROMPT = "You are a helpful assistant. "
|
||||
>>> inputs_initial_prompt = tokenizer(INITIAL_PROMPT, return_tensors="pt").to("cuda")
|
||||
>>> # This is the common prompt cached, we need to run forward without grad to be abel to copy
|
||||
>>> with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
... prompt_cache = model(**inputs_initial_prompt, past_key_values = prompt_cache).past_key_values
|
||||
|
||||
>>> prompts = ["Help me to write a blogpost about travelling.", "What is the capital of France?"]
|
||||
>>> responses = []
|
||||
>>> for prompt in prompts:
|
||||
... new_inputs = tokenizer(INITIAL_PROMPT + prompt, return_tensors="pt").to("cuda")
|
||||
... past_key_values = copy.deepcopy(prompt_cache)
|
||||
... outputs = model.generate(**new_inputs, past_key_values=past_key_values,max_new_tokens=20)
|
||||
... response = tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs)[0]
|
||||
... responses.append(response)
|
||||
|
||||
>>> print(responses)
|
||||
['<s> You are a helpful assistant. Help me to write a blogpost about travelling.\n\nTitle: The Ultimate Guide to Travelling: Tips, Tricks, and', '<s> You are a helpful assistant. What is the capital of France?\n\nYes, the capital of France is Paris.</s>']
|
||||
```
|
||||
Sometimes you would want to fist fill-in cache object with key/values for certain prefix prompt and re-use it several times to generate different sequences from it. We are working hard on adding this feature to 🤗 Transformers and will update this section soon.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -24,7 +24,7 @@ This guide will show you how to use the optimization techniques available in Tra
|
||||
|
||||
During decoding, a LLM computes the key-value (kv) values for each input token and since it is autoregressive, it computes the same kv values each time because the generated output becomes part of the input now. This is not very efficient because you're recomputing the same kv values each time.
|
||||
|
||||
To optimize this, you can use a kv-cache to store the past keys and values instead of recomputing them each time. However, since the kv-cache grows with each generation step and is dynamic, it prevents you from taking advantage of [`torch.compile`](./perf_torch_compile), a powerful optimization tool that fuses PyTorch code into fast and optimized kernels. We have an entire guide dedicated to kv-caches [here](./kv_cache).
|
||||
To optimize this, you can use a kv-cache to store the past keys and values instead of recomputing them each time. However, since the kv-cache grows with each generation step and is dynamic, it prevents you from taking advantage of [`torch.compile`](./perf_torch_compile), a powerful optimization tool that fuses PyTorch code into fast and optimized kernels.
|
||||
|
||||
The *static kv-cache* solves this issue by pre-allocating the kv-cache size to a maximum value which allows you to combine it with `torch.compile` for up to a 4x speed up. Your speed up may vary depending on the model size (larger models have a smaller speed up) and hardware.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -662,7 +662,7 @@ Using the key-value cache has two advantages:
|
||||
- Significant increase in computational efficiency as less computations are performed compared to computing the full \\( \mathbf{QK}^T \\) matrix. This leads to an increase in inference speed
|
||||
- The maximum required memory is not increased quadratically with the number of generated tokens, but only increases linearly.
|
||||
|
||||
> One should *always* make use of the key-value cache as it leads to identical results and a significant speed-up for longer input sequences. Transformers has the key-value cache enabled by default when making use of the text pipeline or the [`generate` method](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main_classes/text_generation). We have an entire guide dedicated to caches [here](./kv_cache).
|
||||
> One should *always* make use of the key-value cache as it leads to identical results and a significant speed-up for longer input sequences. Transformers has the key-value cache enabled by default when making use of the text pipeline or the [`generate` method](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main_classes/text_generation).
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -87,33 +87,12 @@ These engines have the following specification:
|
||||
1. Follow the [messages format](../chat_templating.md) for its input (`List[Dict[str, str]]`) and return a string.
|
||||
2. Stop generating outputs *before* the sequences passed in the argument `stop_sequences`
|
||||
|
||||
### TransformersEngine
|
||||
### HfEngine
|
||||
|
||||
For convenience, we have added a `TransformersEngine` that implements the points above, taking a pre-initialized `Pipeline` as input.
|
||||
For convenience, we have added a `HfEngine` that implements the points above and uses an inference endpoint for the execution of the LLM.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer, pipeline, TransformersEngine
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model_name = "HuggingFaceTB/SmolLM-135M-Instruct"
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_name)
|
||||
|
||||
>>> pipe = pipeline("text-generation", model=model, tokenizer=tokenizer)
|
||||
|
||||
>>> engine = TransformersEngine(pipe)
|
||||
>>> engine([{"role": "user", "content": "Ok!"}], stop_sequences=["great"])
|
||||
|
||||
"What a "
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TransformersEngine
|
||||
|
||||
### HfApiEngine
|
||||
|
||||
The `HfApiEngine` is an engine that wraps an [HF Inference API](https://huggingface.co/docs/api-inference/index) client for the execution of the LLM.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import HfApiEngine
|
||||
>>> from transformers import HfEngine
|
||||
|
||||
>>> messages = [
|
||||
... {"role": "user", "content": "Hello, how are you?"},
|
||||
@ -121,12 +100,12 @@ The `HfApiEngine` is an engine that wraps an [HF Inference API](https://huggingf
|
||||
... {"role": "user", "content": "No need to help, take it easy."},
|
||||
... ]
|
||||
|
||||
>>> HfApiEngine()(messages, stop_sequences=["conversation"])
|
||||
>>> HfEngine()(messages, stop_sequences=["conversation"])
|
||||
|
||||
"That's very kind of you to say! It's always nice to have a relaxed "
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] HfApiEngine
|
||||
[[autodoc]] HfEngine
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Agent Types
|
||||
|
||||
@ -59,52 +59,7 @@ This model was contributed by [lysandre](https://huggingface.co/lysandre). This
|
||||
- Layers are split in groups that share parameters (to save memory).
|
||||
Next sentence prediction is replaced by a sentence ordering prediction: in the inputs, we have two sentences A and B (that are consecutive) and we either feed A followed by B or B followed by A. The model must predict if they have been swapped or not.
|
||||
|
||||
### Using Scaled Dot Product Attention (SDPA)
|
||||
|
||||
PyTorch includes a native scaled dot-product attention (SDPA) operator as part of `torch.nn.functional`. This function
|
||||
encompasses several implementations that can be applied depending on the inputs and the hardware in use. See the
|
||||
[official documentation](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.functional.scaled_dot_product_attention.html)
|
||||
or the [GPU Inference](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/en/perf_infer_gpu_one#pytorch-scaled-dot-product-attention)
|
||||
page for more information.
|
||||
|
||||
SDPA is used by default for `torch>=2.1.1` when an implementation is available, but you may also set
|
||||
`attn_implementation="sdpa"` in `from_pretrained()` to explicitly request SDPA to be used.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
from transformers import AlbertModel
|
||||
model = AlbertModel.from_pretrained("albert/albert-base-v1", torch_dtype=torch.float16, attn_implementation="sdpa")
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For the best speedups, we recommend loading the model in half-precision (e.g. `torch.float16` or `torch.bfloat16`).
|
||||
|
||||
On a local benchmark (GeForce RTX 2060-8GB, PyTorch 2.3.1, OS Ubuntu 20.04) with `float16`, we saw the
|
||||
following speedups during training and inference.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Training for 100 iterations
|
||||
|
||||
|batch_size|seq_len|Time per batch (eager - s)| Time per batch (sdpa - s)| Speedup (%)| Eager peak mem (MB)| sdpa peak mem (MB)| Mem saving (%)|
|
||||
|----------|-------|--------------------------|--------------------------|------------|--------------------|-------------------|---------------|
|
||||
|2 |256 |0.028 |0.024 |14.388 |358.411 |321.088 |11.624 |
|
||||
|2 |512 |0.049 |0.041 |17.681 |753.458 |602.660 |25.022 |
|
||||
|4 |256 |0.044 |0.039 |12.246 |679.534 |602.660 |12.756 |
|
||||
|4 |512 |0.090 |0.076 |18.472 |1434.820 |1134.140 |26.512 |
|
||||
|8 |256 |0.081 |0.072 |12.664 |1283.825 |1134.140 |13.198 |
|
||||
|8 |512 |0.170 |0.143 |18.957 |2820.398 |2219.695 |27.062 |
|
||||
|
||||
#### Inference with 50 batches
|
||||
|
||||
|batch_size|seq_len|Per token latency eager (ms)|Per token latency SDPA (ms)|Speedup (%) |Mem eager (MB)|Mem BT (MB)|Mem saved (%)|
|
||||
|----------|-------|----------------------------|---------------------------|------------|--------------|-----------|-------------|
|
||||
|4 |128 |0.083 |0.071 |16.967 |48.319 |48.45 |-0.268 |
|
||||
|4 |256 |0.148 |0.127 |16.37 |63.4 |63.922 |-0.817 |
|
||||
|4 |512 |0.31 |0.247 |25.473 |110.092 |94.343 |16.693 |
|
||||
|8 |128 |0.137 |0.124 |11.102 |63.4 |63.66 |-0.409 |
|
||||
|8 |256 |0.271 |0.231 |17.271 |91.202 |92.246 |-1.132 |
|
||||
|8 |512 |0.602 |0.48 |25.47 |186.159 |152.564 |22.021 |
|
||||
|16 |128 |0.252 |0.224 |12.506 |91.202 |91.722 |-0.567 |
|
||||
|16 |256 |0.526 |0.448 |17.604 |148.378 |150.467 |-1.388 |
|
||||
|16 |512 |1.203 |0.96 |25.365 |338.293 |271.102 |24.784 |
|
||||
|
||||
This model was contributed by [lysandre](https://huggingface.co/lysandre). This model jax version was contributed by
|
||||
[kamalkraj](https://huggingface.co/kamalkraj). The original code can be found [here](https://github.com/google-research/ALBERT).
|
||||
|
||||
@ -153,7 +153,7 @@ In short, one should prepare the data either in COCO detection or COCO panoptic
|
||||
[`~transformers.DetrImageProcessor`] to create `pixel_values`, `pixel_mask` and optional
|
||||
`labels`, which can then be used to train (or fine-tune) a model. For evaluation, one should first convert the
|
||||
outputs of the model using one of the postprocessing methods of [`~transformers.DetrImageProcessor`]. These can
|
||||
be provided to either `CocoEvaluator` or `PanopticEvaluator`, which allow you to calculate metrics like
|
||||
be be provided to either `CocoEvaluator` or `PanopticEvaluator`, which allow you to calculate metrics like
|
||||
mean Average Precision (mAP) and Panoptic Quality (PQ). The latter objects are implemented in the [original repository](https://github.com/facebookresearch/detr). See the [example notebooks](https://github.com/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/tree/master/DETR) for more info regarding evaluation.
|
||||
|
||||
## Resources
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,319 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# LLaVA-Onevision
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
The LLaVA-Onevision model was proposed in [LLaVA-OneVision: Easy Visual Task Transfer](https://arxiv.org/abs/2408.03326) by <Bo Li, Yuanhan Zhang, Dong Guo, Renrui Zhang, Feng Li, Hao Zhang, Kaichen Zhang, Yanwei Li, Ziwei Liu, Chunyuan Li
|
||||
|
||||
LLaVA-Onevision is a Vision-Language Model that can generate text conditioned on one or several images/videos. The model consists of SigLIP vision encoder and a Qwen2 language backbone. The images are processed with anyres-9 technique where the image is split into 9 patches to better process high resolution images and capture as much details as possible. However, videos are pooled to a total sequence length of 196 tokens each frame for more memory efficient computation. LLaVA-Onevision is available in three sizes: 0.5B, 7B and 72B and achieves remarkable performance on benchmark evaluations.
|
||||
|
||||
The abstract from the paper is the following:
|
||||
|
||||
*We present LLaVA-OneVision, a family of open large multimodal models (LMMs)
|
||||
developed by consolidating our insights into data, models, and visual representations in the LLaVA-NeXT blog series. Our experimental results demonstrate that
|
||||
LLaVA-OneVision is the first single model that can simultaneously push the performance boundaries of open LMMs in three important computer vision scenarios:
|
||||
single-image, multi-image, and video scenarios. Importantly, the design of LLaVAOneVision allows strong transfer learning across different modalities/scenarios,
|
||||
yielding new emerging capabilities. In particular, strong video understanding and
|
||||
cross-scenario capabilities are demonstrated through task transfer from images to
|
||||
videos.*
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/model_doc/llava-ov-acrhitecture.png"
|
||||
alt="drawing" width="600"/>
|
||||
|
||||
<small> LLaVA=Onevision architecture. Taken from the <a href="https://arxiv.org/abs/2408.03326">original paper.</a> </small>
|
||||
|
||||
Tips:
|
||||
|
||||
- We advise users to use `padding_side="left"` when computing batched generation as it leads to more accurate results. Simply make sure to call `processor.tokenizer.padding_side = "left"` before generating.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
- Llava-Onevision uses different number of patches for images and thus has to pad the inputs inside modeling code, aside from the padding done when processing the inputs. The default setting is "left-padding" if model is in `eval()` mode, otherwise "right-padding".
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
- Note that the model should use a specific prompt format, on which the large language model (LLM) was trained. You can use the processor's `apply_chat_template` to format your prompts correctly. For that you have to construct a conversation history, passing a plain string will not format your prompt. Each message in the conversation history for chat templates is a dictionary with keys "role" and "content". The "content" should be a list of dictionaries, for "text" and "image" modalities.
|
||||
|
||||
We will use [llava-onevision-qwen2-7b-si-hf](https://huggingface.co/llava-hf/llava-onevision-qwen2-7b-si-hf) and a conversation history of text and image. Each content field has to be a list of dicts, as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import AutoProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained("llava-hf/llava-onevision-qwen2-7b-si-hf")
|
||||
|
||||
conversation = [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"role": "user",
|
||||
"content": [
|
||||
{"type": "image"},
|
||||
{"type": "text", "text": "What’s shown in this image?"},
|
||||
],
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"role": "assistant",
|
||||
"content": [{"type": "text", "text": "This image shows a red stop sign."},]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
|
||||
"role": "user",
|
||||
"content": [
|
||||
{"type": "text", "text": "Describe the image in more details."},
|
||||
],
|
||||
},
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
text_prompt = processor.apply_chat_template(conversation, add_generation_prompt=True)
|
||||
|
||||
# Note that the template simply formats your prompt, you still have to tokenize it and obtain pixel values for your images
|
||||
print(text_prompt)
|
||||
>>> "<|im_start|>user\n<image>What is shown in this image?<|im_end|>\n<|im_start|>assistant\nPage showing the list of options.<|im_end|>"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This model was contributed by [RaushanTurganbay](https://huggingface.co/RaushanTurganbay).
|
||||
The original code can be found [here](https://github.com/LLaVA-VL/LLaVA-NeXT/tree/main).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage example
|
||||
|
||||
### Single image inference
|
||||
|
||||
Here's how to load the model and perform inference in half-precision (`torch.float16`):
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import AutoProcessor, LlavaOnevisionForConditionalGeneration
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
import requests
|
||||
|
||||
processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained("llava-hf/llava-onevision-qwen2-7b-ov-hf")
|
||||
model = LlavaOnevisionForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained("llava-hf/llava-onevision-qwen2-7b-ov-hf", torch_dtype=torch.float16, low_cpu_mem_usage=True)
|
||||
model.to("cuda:0")
|
||||
|
||||
# prepare image and text prompt, using the appropriate prompt template
|
||||
url = "https://github.com/haotian-liu/LLaVA/blob/1a91fc274d7c35a9b50b3cb29c4247ae5837ce39/images/llava_v1_5_radar.jpg?raw=true"
|
||||
image = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw)
|
||||
|
||||
conversation = [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"role": "user",
|
||||
"content": [
|
||||
{"type": "image"},
|
||||
{"type": "text", "text": "What is shown in this image?"},
|
||||
],
|
||||
},
|
||||
]
|
||||
prompt = processor.apply_chat_template(conversation, add_generation_prompt=True)
|
||||
inputs = processor(images=image, text=prompt, return_tensors="pt").to("cuda:0", torch.float16)
|
||||
|
||||
# autoregressively complete prompt
|
||||
output = model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=100)
|
||||
print(processor.decode(output[0], skip_special_tokens=True))
|
||||
'user\n\nWhat is shown in this image?\nassistant\nThe image shows a radar chart, also known as a spider chart or a star chart, which is used to compare multiple quantitative variables. Each axis represents a different variable, and the chart is filled with'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Multi image inference
|
||||
|
||||
LLaVa-Onevision can perform inference with multiple images as input, where images either belong to the same prompt or different prompts (in batched inference). For that you have to use checkpoints with an "ov" suffix. Here is how you can do it:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import requests
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from transformers import AutoProcessor, LlavaOnevisionForConditionalGeneration
|
||||
|
||||
# Load the model in half-precision
|
||||
model = LlavaOnevisionForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained("llava-hf/llava-onevision-qwen2-7b-ov-hf", torch_dtype=torch.float16, device_map="auto")
|
||||
processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained("llava-hf/llava-onevision-qwen2-7b-ov-hf")
|
||||
|
||||
# Get three different images
|
||||
url = "https://www.ilankelman.org/stopsigns/australia.jpg"
|
||||
image_stop = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw)
|
||||
|
||||
url = "http://images.cocodataset.org/val2017/000000039769.jpg"
|
||||
image_cats = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw)
|
||||
|
||||
url = "https://huggingface.co/microsoft/kosmos-2-patch14-224/resolve/main/snowman.jpg"
|
||||
image_snowman = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw)
|
||||
|
||||
# Prepare a batch of two prompts, where the first one is a multi-turn conversation and the second is not
|
||||
conversation_1 = [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"role": "user",
|
||||
"content": [
|
||||
{"type": "image"},
|
||||
{"type": "text", "text": "What is shown in this image?"},
|
||||
],
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"role": "assistant",
|
||||
"content": [
|
||||
{"type": "text", "text": "There is a red stop sign in the image."},
|
||||
],
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"role": "user",
|
||||
"content": [
|
||||
{"type": "image"},
|
||||
{"type": "text", "text": "What about this image? How many cats do you see?"},
|
||||
],
|
||||
},
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
conversation_2 = [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"role": "user",
|
||||
"content": [
|
||||
{"type": "image"},
|
||||
{"type": "text", "text": "What is shown in this image?"},
|
||||
],
|
||||
},
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
prompt_1 = processor.apply_chat_template(conversation_1, add_generation_prompt=True)
|
||||
prompt_2 = processor.apply_chat_template(conversation_2, add_generation_prompt=True)
|
||||
prompts = [prompt_1, prompt_2]
|
||||
|
||||
# We can simply feed images in the order they have to be used in the text prompt
|
||||
inputs = processor(images=[image_stop, image_cats, image_snowman], text=prompts, padding=True, return_tensors="pt").to(model.device, torch.float16)
|
||||
|
||||
# Generate
|
||||
generate_ids = model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=30)
|
||||
processor.batch_decode(generate_ids, skip_special_tokens=True, clean_up_tokenization_spaces=False)
|
||||
['user\n\nWhat is shown in this image?\nassistant\nThere is a red stop sign in the image.\nuser\n\nWhat about this image? How many cats do you see?\nassistant\ntwo', 'user\n\nWhat is shown in this image?\nassistant\n']
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Video inference
|
||||
|
||||
LLaVa-Onevision also can perform inference with videos as input, where video frames are treated as multiple images. Here is how you can do it:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import av
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
from huggingface_hub import hf_hub_download
|
||||
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from transformers import AutoProcessor, LlavaOnevisionForConditionalGeneration
|
||||
|
||||
# Load the model in half-precision
|
||||
model = LlavaOnevisionForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained("llava-hf/llava-onevision-qwen2-7b-ov-hf", torch_dtype=torch.float16, device_map="auto")
|
||||
processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained("llava-hf/llava-onevision-qwen2-7b-ov-hf")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def read_video_pyav(container, indices):
|
||||
'''
|
||||
Decode the video with PyAV decoder.
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
container (`av.container.input.InputContainer`): PyAV container.
|
||||
indices (`List[int]`): List of frame indices to decode.
|
||||
Returns:
|
||||
result (np.ndarray): np array of decoded frames of shape (num_frames, height, width, 3).
|
||||
'''
|
||||
frames = []
|
||||
container.seek(0)
|
||||
start_index = indices[0]
|
||||
end_index = indices[-1]
|
||||
for i, frame in enumerate(container.decode(video=0)):
|
||||
if i > end_index:
|
||||
break
|
||||
if i >= start_index and i in indices:
|
||||
frames.append(frame)
|
||||
return np.stack([x.to_ndarray(format="rgb24") for x in frames])
|
||||
|
||||
# Load the video as an np.array, sampling uniformly 8 frames (can sample more for longer videos, up to 32 frames)
|
||||
video_path = hf_hub_download(repo_id="raushan-testing-hf/videos-test", filename="sample_demo_1.mp4", repo_type="dataset")
|
||||
container = av.open(video_path)
|
||||
total_frames = container.streams.video[0].frames
|
||||
indices = np.arange(0, total_frames, total_frames / 8).astype(int)
|
||||
video = read_video_pyav(container, indices)
|
||||
|
||||
# For videos we have to feed a "video" type instead of "image"
|
||||
conversation = [
|
||||
{
|
||||
|
||||
"role": "user",
|
||||
"content": [
|
||||
{"type": "video"},
|
||||
{"type": "text", "text": "Why is this video funny?"},
|
||||
],
|
||||
},
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = processor.apply_chat_template(conversation, add_generation_prompt=True)
|
||||
inputs = processor(videos=list(video), text=prompt, return_tensors="pt").to("cuda:0", torch.float16)
|
||||
|
||||
out = model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=60)
|
||||
processor.batch_decode(out, skip_special_tokens=True, clean_up_tokenization_spaces=True)
|
||||
["user\n\nWhy is this video funny?\nassistant\nThe video appears to be humorous because it shows a young child, who is wearing glasses and holding a book, seemingly reading with a serious and focused expression. The child's glasses are a bit oversized for their face, which adds a comical touch, as it's a common trope to see children wearing"]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Model optimization
|
||||
|
||||
### Quantization using Bitsandbytes
|
||||
|
||||
The model can be loaded in 8 or 4 bits, greatly reducing the memory requirements while maintaining the performance of the original model. First make sure to install bitsandbytes, `pip install bitsandbytes` and make sure to have access to a CUDA compatible GPU device. Simply change the snippet above with:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import LlavaOnevisionForConditionalGeneration, BitsAndBytesConfig
|
||||
|
||||
# specify how to quantize the model
|
||||
quantization_config = BitsAndBytesConfig(
|
||||
load_in_4bit=True,
|
||||
bnb_4bit_quant_type="nf4",
|
||||
bnb_4bit_compute_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
model = LlavaOnevisionForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained(model_id, quantization_config=quantization_config, device_map="auto")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Use Flash-Attention 2 to further speed-up generation
|
||||
|
||||
First make sure to install flash-attn. Refer to the [original repository of Flash Attention](https://github.com/Dao-AILab/flash-attention) regarding that package installation. Simply change the snippet above with:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import LlavaOnevisionForConditionalGeneration
|
||||
|
||||
model = LlavaOnevisionForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained(
|
||||
model_id,
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
low_cpu_mem_usage=True,
|
||||
use_flash_attention_2=True
|
||||
).to(0)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## LlavaOnevisionConfig
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] LlavaOnevisionConfig
|
||||
|
||||
## LlavaOnevisionProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] LlavaOnevisionProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
## LlavaOnevisionImageProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] LlavaOnevisionImageProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
## LlavaOnevisionVideoProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] LlavaOnevisionVideoProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
## LlavaOnevisionForConditionalGeneration
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] LlavaOnevisionForConditionalGeneration
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
@ -1,45 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# OLMoE
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
The OLMoE model was proposed in [OLMoE: Open Mixture-of-Experts Language Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/2409.02060) by Niklas Muennighoff, Luca Soldaini, Dirk Groeneveld, Kyle Lo, Jacob Morrison, Sewon Min, Weijia Shi, Pete Walsh, Oyvind Tafjord, Nathan Lambert, Yuling Gu, Shane Arora, Akshita Bhagia, Dustin Schwenk, David Wadden, Alexander Wettig, Binyuan Hui, Tim Dettmers, Douwe Kiela, Ali Farhadi, Noah A. Smith, Pang Wei Koh, Amanpreet Singh, Hannaneh Hajishirzi.
|
||||
|
||||
OLMoE is a series of **O**pen **L**anguage **Mo**dels using sparse **M**ixture-**o**f-**E**xperts designed to enable the science of language models. We release all code, checkpoints, logs, and details involved in training these models.
|
||||
|
||||
The abstract from the paper is the following:
|
||||
|
||||
*We introduce OLMoE, a fully open, state-of-the-art language model leveraging sparse Mixture-of-Experts (MoE). OLMoE-1B-7B has 7 billion (B) parameters but uses only 1B per input token. We pretrain it on 5 trillion tokens and further adapt it to create OLMoE-1B-7B-Instruct. Our models outperform all available models with similar active parameters, even surpassing larger ones like Llama2-13B-Chat and DeepSeekMoE-16B. We present various experiments on MoE training, analyze routing in our model showing high specialization, and open-source all aspects of our work: model weights, training data, code, and logs.*
|
||||
|
||||
This model was contributed by [Muennighoff](https://hf.co/Muennighoff).
|
||||
The original code can be found [here](https://github.com/allenai/OLMoE).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## OlmoeConfig
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] OlmoeConfig
|
||||
|
||||
## OlmoeModel
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] OlmoeModel
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
## OlmoeForCausalLM
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] OlmoeForCausalLM
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
@ -60,7 +60,6 @@ FlashAttention-2 is currently supported for the following architectures:
|
||||
* [Llava](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/llava)
|
||||
* [Llava-NeXT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/llava_next)
|
||||
* [Llava-NeXT-Video](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/llava_next_video)
|
||||
* [LLaVA-Onevision](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/llava_onevision)
|
||||
* [VipLlava](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/vipllava)
|
||||
* [VideoLlava](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/video_llava)
|
||||
* [M2M100](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/m2m_100)
|
||||
@ -72,7 +71,6 @@ FlashAttention-2 is currently supported for the following architectures:
|
||||
* [Nemotron](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/nemotron)
|
||||
* [NLLB](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/nllb)
|
||||
* [OLMo](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/olmo#transformers.OlmoModel)
|
||||
* [OLMoE](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/olmoe#transformers.OlmoeModel)
|
||||
* [OPT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/opt#transformers.OPTModel)
|
||||
* [Phi](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/phi#transformers.PhiModel)
|
||||
* [Phi3](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/phi3#transformers.Phi3Model)
|
||||
@ -203,7 +201,6 @@ FlashAttention is more memory efficient, meaning you can train on much larger se
|
||||
PyTorch's [`torch.nn.functional.scaled_dot_product_attention`](https://pytorch.org/docs/master/generated/torch.nn.functional.scaled_dot_product_attention.html) (SDPA) can also call FlashAttention and memory-efficient attention kernels under the hood. SDPA support is currently being added natively in Transformers and is used by default for `torch>=2.1.1` when an implementation is available. You may also set `attn_implementation="sdpa"` in `from_pretrained()` to explicitly request SDPA to be used.
|
||||
|
||||
For now, Transformers supports SDPA inference and training for the following architectures:
|
||||
* [Albert](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/albert#transformers.AlbertModel)
|
||||
* [Audio Spectrogram Transformer](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/audio-spectrogram-transformer#transformers.ASTModel)
|
||||
* [Bart](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/bart#transformers.BartModel)
|
||||
* [Bert](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/bert#transformers.BertModel)
|
||||
@ -227,13 +224,11 @@ For now, Transformers supports SDPA inference and training for the following arc
|
||||
* [JetMoe](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/jetmoe#transformers.JetMoeModel)
|
||||
* [Jamba](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/jamba#transformers.JambaModel)
|
||||
* [Llama](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/llama#transformers.LlamaModel)
|
||||
* [LLaVA-Onevision](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/llava_onevision)
|
||||
* [Mistral](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/mistral#transformers.MistralModel)
|
||||
* [Mixtral](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/mixtral#transformers.MixtralModel)
|
||||
* [Musicgen](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/musicgen#transformers.MusicgenModel)
|
||||
* [MusicGen Melody](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/musicgen_melody#transformers.MusicgenMelodyModel)
|
||||
* [OLMo](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/olmo#transformers.OlmoModel)
|
||||
* [OLMoE](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/olmoe#transformers.OlmoeModel)
|
||||
* [PaliGemma](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/paligemma#transformers.PaliGemmaForConditionalGeneration)
|
||||
* [Phi](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/phi#transformers.PhiModel)
|
||||
* [Phi3](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/phi3#transformers.Phi3Model)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,146 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Video-text-to-text
|
||||
|
||||
[[open-in-colab]]
|
||||
|
||||
Video-text-to-text models, also known as video language models or vision language models with video input, are language models that take a video input. These models can tackle various tasks, from video question answering to video captioning.
|
||||
|
||||
These models have nearly the same architecture as [image-text-to-text](../image_text_to_text.md) models except for some changes to accept video data, since video data is essentially image frames with temporal dependencies. Some image-text-to-text models take in multiple images, but this alone is inadequate for a model to accept videos. Moreover, video-text-to-text models are often trained with all vision modalities. Each example might have videos, multiple videos, images and multiple images. Some of these models can also take interleaved inputs. For example, you can refer to a specific video inside a string of text by adding a video token in text like "What is happening in this video? `<video>`".
|
||||
|
||||
In this guide, we provide a brief overview of video LMs and show how to use them with Transformers for inference.
|
||||
|
||||
To begin with, there are multiple types of video LMs:
|
||||
- base models used for fine-tuning
|
||||
- chat fine-tuned models for conversation
|
||||
- instruction fine-tuned models
|
||||
|
||||
This guide focuses on inference with an instruction-tuned model, [llava-hf/llava-interleave-qwen-7b-hf](https://huggingface.co/llava-hf/llava-interleave-qwen-7b-hf) which can take in interleaved data. Alternatively, you can try [llava-interleave-qwen-0.5b-hf](https://huggingface.co/llava-hf/llava-interleave-qwen-0.5b-hf) if your hardware doesn't allow running a 7B model.
|
||||
|
||||
Let's begin installing the dependencies.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install -q transformers accelerate flash_attn
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Let's initialize the model and the processor.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import LlavaProcessor, LlavaForConditionalGeneration
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
model_id = "llava-hf/llava-interleave-qwen-0.5b-hf"
|
||||
|
||||
processor = LlavaProcessor.from_pretrained(model_id)
|
||||
|
||||
model = LlavaForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained(model_id, torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
model.to("cuda")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Some models directly consume the `<video>` token, and others accept `<image>` tokens equal to the number of sampled frames. This model handles videos in the latter fashion. We will write a simple utility to handle image tokens, and another utility to get a video from a url and sample frames from it.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import uuid
|
||||
import requests
|
||||
import cv2
|
||||
|
||||
def replace_video_with_images(text, frames):
|
||||
return text.replace("<video>", "<image>" * frames)
|
||||
|
||||
def sample_frames(url, num_frames):
|
||||
|
||||
response = requests.get(url)
|
||||
path_id = str(uuid.uuid4())
|
||||
|
||||
path = f"./{path_id}.mp4"
|
||||
|
||||
with open(path, "wb") as f:
|
||||
f.write(response.content)
|
||||
|
||||
video = cv2.VideoCapture(path)
|
||||
total_frames = int(video.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_COUNT))
|
||||
interval = total_frames // num_frames
|
||||
frames = []
|
||||
for i in range(total_frames):
|
||||
ret, frame = video.read()
|
||||
pil_img = Image.fromarray(cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))
|
||||
if not ret:
|
||||
continue
|
||||
if i % interval == 0:
|
||||
frames.append(pil_img)
|
||||
video.release()
|
||||
return frames
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Let's get our inputs. We will sample frames and concatenate them.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
video_1 = "https://huggingface.co/spaces/merve/llava-interleave/resolve/main/cats_1.mp4"
|
||||
video_2 = "https://huggingface.co/spaces/merve/llava-interleave/resolve/main/cats_2.mp4"
|
||||
|
||||
video_1 = sample_frames(video_1, 6)
|
||||
video_2 = sample_frames(video_2, 6)
|
||||
|
||||
videos = video_1 + video_2
|
||||
|
||||
videos
|
||||
|
||||
# [<PIL.Image.Image image mode=RGB size=1920x1080>,
|
||||
# <PIL.Image.Image image mode=RGB size=1920x1080>,
|
||||
# <PIL.Image.Image image mode=RGB size=1920x1080>, ...]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Both videos have cats.
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="container">
|
||||
<div class="video-container">
|
||||
<video width="400" controls>
|
||||
<source src="https://huggingface.co/spaces/merve/llava-interleave/resolve/main/cats_1.mp4" type="video/mp4">
|
||||
</video>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="video-container">
|
||||
<video width="400" controls>
|
||||
<source src="https://huggingface.co/spaces/merve/llava-interleave/resolve/main/cats_2.mp4" type="video/mp4">
|
||||
</video>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
Now we can preprocess the inputs.
|
||||
|
||||
This model has a prompt template that looks like following. First, we'll put all the sampled frames into one list. Since we have eight frames in each video, we will insert 12 `<image>` tokens to our prompt. Add `assistant` at the end of the prompt to trigger the model to give answers. Then we can preprocess.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
user_prompt = "Are these two cats in these two videos doing the same thing?"
|
||||
toks = "<image>" * 12
|
||||
prompt = "<|im_start|>user"+ toks + f"\n{user_prompt}<|im_end|><|im_start|>assistant"
|
||||
inputs = processor(prompt, images=videos).to(model.device, model.dtype)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We can now call [`~GenerationMixin.generate`] for inference. The model outputs the question in our input and answer, so we only take the text after the prompt and `assistant` part from the model output.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
output = model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=100, do_sample=False)
|
||||
print(processor.decode(output[0][2:], skip_special_tokens=True)[len(user_prompt)+10:])
|
||||
|
||||
# The first cat is shown in a relaxed state, with its eyes closed and a content expression, while the second cat is shown in a more active state, with its mouth open wide, possibly in a yawn or a vocalization.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
And voila!
|
||||
|
||||
To learn more about chat templates and token streaming for video-text-to-text models, refer to the [image-text-to-text](../image_text_to_text) task guide because these models work similarly.
|
||||
@ -186,9 +186,7 @@
|
||||
- local: performance
|
||||
title: 성능 및 확장성
|
||||
- local: in_translation
|
||||
title: (번역중) Quantization
|
||||
- local: llm_optims
|
||||
title: LLM 추론 최적화
|
||||
title: (번역중) LLM inference optimization
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: in_translation
|
||||
title: (번역중) Methods and tools for efficient training on a single GPU
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,410 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# LLM 추론 최적화 [[llm-inference-optimization]]
|
||||
|
||||
대규모 언어 모델(LLM)은 채팅 및 코드 완성 모델과 같은 텍스트 생성 응용 프로그램을 한 단계 끌어올리며, 높은 수준의 이해력과 유창함을 보여주는 텍스트를 생성합니다. 그러나 LLM을 강력하게 만드는 요소인 그들의 크기는 동시에 추론 과정에서 도전 과제가 되기도 합니다.
|
||||
|
||||
기본적인 추론은 느립니다, 왜냐하면 LLM이 다음 토큰을 생성하기 위해 반복적으로 호출되어야 하기 때문입니다. 생성이 진행됨에 따라 입력 시퀀스가 길어져 처리 시간이 점점 길어집니다. 또한, LLM은 수십억 개의 매개변수를 가지고 있어 모든 가중치를 메모리에 저장하고 처리하는 데 어려움이 있습니다.
|
||||
|
||||
이 가이드는 LLM 추론을 가속하기 위해 Transformers에서 사용할 수 있는 최적화 기술을 사용하는 방법을 보여줍니다.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!TIP]
|
||||
> Hugging Face는 LLM을 추론에 최적화하여 배포하고 서비스하는 데 전념하는 라이브러리인 [Text Generation Inference (TGI)](https://hf.co/docs/text-generation-inference)을 제공합니다. 이 라이브러리는 처리량 증가를 위한 지속적인 배칭과 다중 GPU 추론을 위한 텐서 병렬화와 같은 Transformers에 포함되지 않은 배포 지향 최적화 기능을 포함합니다.
|
||||
|
||||
## 정적 kv-cache와 `torch.compile`[[static-kv-cache-and-torchcompile]]
|
||||
|
||||
디코딩 중에 LLM은 각 입력 토큰에 대한 key-value(kv) 값을 계산합니다. LLM은 자기회귀(autoregressive)이기 때문에 생성된 출력이 현재 입력의 일부가 되어 매번 동일한 kv 값을 계산합니다. 이는 매번 동일한 kv 값을 다시 계산하기 때문에 효율적이지 않습니다.
|
||||
|
||||
이를 최적화하기 위해, 이전 키(key)와 값(value)을 재계산하지 않고 저장하는 kv-cache를 사용할 수 있습니다. 그러나 kv-cache는 각 생성 단계에서 증가하며 동적이기 때문에 PyTorch 코드를 빠르고 최적화된 커널로 통합하는 강력한 최적화 도구인 [`torch.compile`](./perf_torch_compile)을 사용하는 데 제약이 있습니다.
|
||||
|
||||
*정적 kv-cache*는 최댓값을 미리 할당하여 이 문제를 해결하여 `torch.compile`과 결합할 수 있게 합니다. 이를 통해 최대 4배의 속도 향상이 가능합니다. 속도 향상은 모델 크기(더 큰 모델은 속도 향상이 적음)와 하드웨어에 따라 다를 수 있습니다.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!WARNING]
|
||||
현재 [Llama](./model_doc/llama2) 및 몇 가지 다른 모델만 정적 kv-cache와 `torch.compile`을 지원합니다. 실시간 모델 호환성 목록은 [이 이슈](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/issues/28981)를 확인하십시오.
|
||||
|
||||
작업의 복잡성에 따라 세 가지 방식의 정적 kv-cache 사용 방법이 있습니다:
|
||||
1. 기본 사용법: `generation_config`에서 플래그를 설정하기만 하면 됩니다(권장);
|
||||
2. 고급 사용법: 여러 번의 생성이나 맞춤형 생성 루프를 위해 캐시 객체를 처리합니다;
|
||||
3. 고급 사용법: 단일 그래프가 필요한 경우, 전체 `generate` 함수를 하나의 그래프로 컴파일합니다.
|
||||
|
||||
올바른 탭을 선택하여 각 방법에 대한 추가 지침을 확인하세요.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!TIP]
|
||||
> `torch.compile`을 사용할 때 어떤 전략을 사용하든, LLM 입력을 제한된 값 세트로 왼쪽에 패딩하면 모양과 관련된 재컴파일을 피할 수 있습니다. [`pad_to_multiple_of` tokenizer flag](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main_classes/tokenizer#transformers.PreTrainedTokenizer.__call__.pad_to_multiple_of)가 유용할 것입니다!
|
||||
|
||||
<hfoptions id="static-kv">
|
||||
<hfoption id="basic usage: generation_config">
|
||||
|
||||
이 예제에서는 [Gemma](https://hf.co/google/gemma-2b) 모델을 사용해 보겠습니다. 필요한 작업은 다음과 같습니다:
|
||||
1. 모델의 `generation_config` 속성에 접근하여 `cache_implementation`을 "static"으로 설정합니다;
|
||||
2. 모델의 `forward` 패스를 정적 kv-cache와 함께 컴파일하기 위해 `torch.compile`을 호출합니다.
|
||||
|
||||
이렇게 하면 끝입니다!
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
import os
|
||||
os.environ["TOKENIZERS_PARALLELISM"] = "false" # 긴 경고 메시지를 방지하기 위해 설정 :)
|
||||
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("google/gemma-2b")
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("google/gemma-2b", device_map="auto")
|
||||
|
||||
model.generation_config.cache_implementation = "static"
|
||||
|
||||
model.forward = torch.compile(model.forward, mode="reduce-overhead", fullgraph=True)
|
||||
input_text = "The theory of special relativity states "
|
||||
input_ids = tokenizer(input_text, return_tensors="pt").to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
outputs = model.generate(**input_ids)
|
||||
print(tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs, skip_special_tokens=True))
|
||||
['The theory of special relativity states 1. The speed of light is constant in all inertial reference']
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
`generate` 함수는 내부적으로 동일한 캐시 객체를 재사용하려고 시도하며, 이를 통해 각 호출 시 재컴파일의 필요성을 제거합니다. 재컴파일을 피하는 것은 `torch.compile`의 성능을 최대한 활용하는 데 매우 중요하며, 다음 사항에 유의해야 합니다:
|
||||
1. 배치 크기가 변경되거나 호출 간 최대 출력 길이가 증가하면 캐시를 다시 초기화해야 하며, 이로 인해 새로 컴파일을 해야 합니다;
|
||||
2. 컴파일된 함수의 첫 몇 번의 호출은 함수가 컴파일되는 동안 더 느립니다.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!WARNING]
|
||||
> 다중 턴 대화와 같은 정적 캐시의 고급 사용을 위해서는, 캐시 객체를 [`~GenerationMixin.generate`] 외부에서 인스턴스화하고 조작하는 것을 권장합니다. 고급 사용법 탭을 참조하세요.
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="advanced usage: control Static Cache">
|
||||
|
||||
[`StaticCache`] 객체는 `past_key_values` 인수로 모델의 [`~GenerationMixin.generate`] 함수에 전달할 수 있습니다. 이 객체는 캐시 내용을 유지하므로, 동적 캐시를 사용하는 것처럼 새로운 [`~GenerationMixin.generate`] 호출에 이를 전달하여 생성을 계속할 수 있습니다.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM, StaticCache
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
import os
|
||||
os.environ["TOKENIZERS_PARALLELISM"] = "false" # 긴 경고 메시지를 방지하기 위해 설정 :)
|
||||
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("google/gemma-2b")
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("google/gemma-2b", device_map="auto")
|
||||
|
||||
model.forward = torch.compile(model.forward, mode="reduce-overhead", fullgraph=True)
|
||||
input_text = "The theory of special relativity states "
|
||||
input_ids = tokenizer(input_text, return_tensors="pt").to("cuda")
|
||||
prompt_length = input_ids.input_ids.shape[1]
|
||||
model.generation_config.max_new_tokens = 16
|
||||
|
||||
past_key_values = StaticCache(
|
||||
config=model.config,
|
||||
batch_size=1,
|
||||
# 캐시를 재사용할 계획이 있는 경우, 모든 경우에 충분한 캐시 길이를 설정해야 합니다
|
||||
max_cache_len=prompt_length+(model.generation_config.max_new_tokens*2),
|
||||
device=model.device,
|
||||
dtype=model.dtype
|
||||
)
|
||||
outputs = model.generate(**input_ids, past_key_values=past_key_values)
|
||||
print(tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs, skip_special_tokens=True))
|
||||
['The theory of special relativity states 1. The speed of light is constant in all inertial reference frames. 2']
|
||||
|
||||
# 생성된 텍스트와 동일한 캐시 객체를 전달하여, 중단한 곳에서 생성을 계속합니다.
|
||||
# 다중 턴 대화의 경우, 생성된 텍스트에 새로운 사용자 입력을 추가할 수 있습니다.
|
||||
new_input_ids = outputs
|
||||
outputs = model.generate(new_input_ids, past_key_values=past_key_values)
|
||||
print(tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs, skip_special_tokens=True))
|
||||
['The theory of special relativity states 1. The speed of light is constant in all inertial reference frames. 2. The speed of light is constant in all inertial reference frames. 3.']
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> [!TIP]
|
||||
> 동일한 [`StaticCache`] 객체를 새로운 프롬프트에 사용하려면, 호출 간에 `.reset()` 메서드를 사용하여 그 내용을 초기화하는 것이 좋습니다.
|
||||
|
||||
더 깊이 들어가고 싶다면, [`StaticCache`] 객체를 모델의 `forward` 패스에 동일한 `past_key_values` 인수로 전달할 수도 있습니다. 이 전략을 사용하면, 현재 토큰과 이전에 생성된 토큰의 위치 및 캐시 위치를 바탕으로 다음 토큰을 디코딩하는 자체 함수를 작성할 수 있습니다.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import LlamaTokenizer, LlamaForCausalLM, StaticCache, logging
|
||||
from transformers.testing_utils import CaptureLogger
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
prompts = [
|
||||
"Simply put, the theory of relativity states that ",
|
||||
"My favorite all time favorite condiment is ketchup.",
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
NUM_TOKENS_TO_GENERATE = 40
|
||||
torch_device = "cuda"
|
||||
|
||||
tokenizer = LlamaTokenizer.from_pretrained("meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-hf", pad_token="</s>", padding_side="right")
|
||||
model = LlamaForCausalLM.from_pretrained("meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-hf", device_map="sequential")
|
||||
inputs = tokenizer(prompts, return_tensors="pt", padding=True).to(model.device)
|
||||
|
||||
def decode_one_tokens(model, cur_token, input_pos, cache_position, past_key_values):
|
||||
logits = model(
|
||||
cur_token,
|
||||
position_ids=input_pos,
|
||||
cache_position=cache_position,
|
||||
past_key_values=past_key_values,
|
||||
return_dict=False,
|
||||
use_cache=True
|
||||
)[0]
|
||||
new_token = torch.argmax(logits[:, -1], dim=-1)[:, None]
|
||||
return new_token
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
`StaticCache` 메서드를 사용하여 정적 kv-cache와 `torch.compile`을 활성화하려면 몇 가지 중요한 작업을 수행해야 합니다:
|
||||
1. 추론에 모델을 사용하기 전에 [`StaticCache`] 인스턴스를 초기화합니다. 여기서 최대 배치 크기와 시퀀스 길이와 같은 매개변수를 설정할 수 있습니다.
|
||||
2. 정적 kv-cache와 함께 순전파를 컴파일하기 위해 모델에 `torch.compile`을 호출합니다.
|
||||
3. [torch.backends.cuda.sdp_kernel](https://pytorch.org/docs/master/generated/torch.nn.functional.scaled_dot_product_attention.html) 컨텍스트 관리자에서 `enable_math=True`를 설정하여 네이티브 PyTorch C++ 구현된 스케일된 점곱 어텐션(scaled dot product attention)을 활성화하여 추론 속도를 더욱 높입니다.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
batch_size, seq_length = inputs["input_ids"].shape
|
||||
with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
past_key_values = StaticCache(
|
||||
config=model.config, max_batch_size=2, max_cache_len=4096, device=torch_device, dtype=model.dtype
|
||||
)
|
||||
cache_position = torch.arange(seq_length, device=torch_device)
|
||||
generated_ids = torch.zeros(
|
||||
batch_size, seq_length + NUM_TOKENS_TO_GENERATE + 1, dtype=torch.int, device=torch_device
|
||||
)
|
||||
generated_ids[:, cache_position] = inputs["input_ids"].to(torch_device).to(torch.int)
|
||||
|
||||
logits = model(
|
||||
**inputs, cache_position=cache_position, past_key_values=past_key_values,return_dict=False, use_cache=True
|
||||
)[0]
|
||||
next_token = torch.argmax(logits[:, -1], dim=-1)[:, None]
|
||||
generated_ids[:, seq_length] = next_token[:, 0]
|
||||
|
||||
decode_one_tokens = torch.compile(decode_one_tokens, mode="reduce-overhead", fullgraph=True)
|
||||
cache_position = torch.tensor([seq_length + 1], device=torch_device)
|
||||
for _ in range(1, NUM_TOKENS_TO_GENERATE):
|
||||
with torch.backends.cuda.sdp_kernel(enable_flash=False, enable_mem_efficient=False, enable_math=True):
|
||||
next_token = decode_one_tokens(model, next_token.clone(), None, cache_position, past_key_values)
|
||||
generated_ids[:, cache_position] = next_token.int()
|
||||
cache_position += 1
|
||||
|
||||
text = tokenizer.batch_decode(generated_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)
|
||||
text
|
||||
['Simply put, the theory of relativity states that 1) the speed of light is constant, 2) the speed of light is the same for all observers, and 3) the laws of physics are the same for all observers.',
|
||||
'My favorite all time favorite condiment is ketchup. I love it on everything. I love it on my eggs, my fries, my chicken, my burgers, my hot dogs, my sandwiches, my salads, my p']
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="advanced usage: end-to-end generate compilation">
|
||||
|
||||
전체 `generate` 함수를 컴파일하는 것은 코드 측면에서 기본 사용법보다 더 간단합니다. `generate` 함수에 대해 `torch.compile`을 호출하여 전체 함수를 컴파일하면 됩니다. 정적 캐시의 사용을 지정할 필요는 없습니다. 정적 캐시는 호환되지만, 벤치마크에서는 동적 캐시(기본 설정)가 더 빠른 것으로 나타났습니다.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
import os
|
||||
os.environ["TOKENIZERS_PARALLELISM"] = "false" # 긴 경고 메시지를 방지하기 위해 설정 :)
|
||||
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("google/gemma-2b")
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("google/gemma-2b", device_map="auto")
|
||||
|
||||
model.generate = torch.compile(model.generate, mode="reduce-overhead", fullgraph=True)
|
||||
input_text = "The theory of special relativity states "
|
||||
input_ids = tokenizer(input_text, return_tensors="pt").to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
outputs = model.generate(**input_ids)
|
||||
print(tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs, skip_special_tokens=True))
|
||||
['The theory of special relativity states 1. The speed of light is constant in all inertial reference']
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
이 방법을 통해 모델의 forward 패스뿐만 아니라, 입력 준비, logit 처리기 작업 등을 포함한 모든 것을 컴파일합니다. 기본 사용 예제에 비해 `generate` 호출이 약간 더 빠를 수 있으며, 컴파일된 그래프는 더 특이한 하드웨어 장치나 사용 사례에 적합할 수 있습니다. 그러나 이 접근 방식을 사용하는 데는 몇 가지 큰 단점이 있습니다:
|
||||
1. 컴파일 속도가 훨씬 느립니다;
|
||||
2. `generate`의 모든 매개변수 설정은 `generation_config`를 통해서만 가능합니다;
|
||||
3. 많은 경고와 예외가 억제됩니다. -- 먼저 컴파일 되지 않은 형태로 테스트하는 것을 권장합니다;
|
||||
4. 현재 작업 중이지만 기능 제한이 심합니다(예: 작성 시점에서는 EOS 토큰이 선택되어도 생성이 중단되지 않습니다).
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
</hfoptions>
|
||||
|
||||
## 추정 디코딩 [[speculative-decoding]]
|
||||
|
||||
> [!TIP]
|
||||
> 보다 심층적인 설명을 원한다면, [Assisted Generation: a new direction toward low-latency text generation](https://hf.co/blog/assisted-generation) 블로그 게시물을 확인하십시오!
|
||||
|
||||
자기 회귀의 또 다른 문제는 각 입력 토큰에 대해 순전파 중에 모델 가중치를 매번 로드해야 한다는 점입니다. 이는 수십억 개의 매개변수를 가진 LLM에는 느리고 번거롭습니다. 추정 디코딩(speculative decoding)은 더 작고 빠른 보조 모델을 사용하여 후보 토큰을 생성하고, 이를 큰 LLM이 단일 순전파에서 검증하여 이 속도 저하를 완화합니다. 검증된 토큰이 정확하다면, LLM은 본래 자체적으로 생성하는 것처럼 토큰을 얻을 수 있습니다. 전방 패스가 동일한 출력을 보장하기 때문에 정확도 저하가 없습니다.
|
||||
|
||||
가장 큰 속도 향상을 얻기 위해, 보조 모델은 빠르게 토큰을 생성할 수 있도록 LLM보다 훨씬 작아야 합니다. 보조 모델과 LLM 모델은 토큰을 다시 인코딩하고 디코딩하지 않도록 동일한 토크나이저를 공유해야 합니다.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!WARNING]
|
||||
> 추정 디코딩은 탐욕 검색과 샘플링 디코딩 전략에서만 지원되며, 배치 입력을 지원하지 않습니다.
|
||||
|
||||
보조 모델을 로드하고 이를 [`~GenerationMixin.generate`] 메서드에 전달하여 추정 디코딩을 활성화하십시오.
|
||||
|
||||
<hfoptions id="spec-decoding">
|
||||
<hfoption id="greedy search">
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
|
||||
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("facebook/opt-1.3b")
|
||||
inputs = tokenizer("Einstein's theory of relativity states", return_tensors="pt").to(device)
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("facebook/opt-1.3b").to(device)
|
||||
assistant_model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("facebook/opt-125m").to(device)
|
||||
outputs = model.generate(**inputs, assistant_model=assistant_model)
|
||||
tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs, skip_special_tokens=True)
|
||||
["Einstein's theory of relativity states that the speed of light is constant. "]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="sampling">
|
||||
|
||||
추정 샘플링 디코딩(speculative sampling decoding)을 위해, 보조 모델 외에도 [`~GenerationMixin.generate`] 메서드에 `do_sample` 및 `temperature` 매개변수를 추가하십시오.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
|
||||
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("facebook/opt-1.3b")
|
||||
inputs = tokenizer("Einstein's theory of relativity states", return_tensors="pt").to(device)
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("facebook/opt-1.3b").to(device)
|
||||
assistant_model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("facebook/opt-125m").to(device)
|
||||
outputs = model.generate(**inputs, assistant_model=assistant_model, do_sample=True, temperature=0.7)
|
||||
print(tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs, skip_special_tokens=True))
|
||||
["Einstein's theory of relativity states that motion in the universe is not a straight line.\n"]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
</hfoptions>
|
||||
|
||||
### 프롬프트 조회 디코딩 [[prompt-lookup-decoding]]
|
||||
|
||||
프롬프트 조회 디코딩은 탐욕 검색과 샘플링과도 호환되는 추정 디코딩의 변형입니다. 프롬프트 조회는 요약과 같은 입력 기반 작업에 특히 잘 작동합니다. 여기서는 프롬프트와 출력 간에 종종 겹치는 단어가 있습니다. 이러한 겹치는 n-그램이 LLM 후보 토큰으로 사용됩니다.
|
||||
|
||||
프롬프트 조회 디코딩을 활성화하려면 `prompt_lookup_num_tokens` 매개변수에 겹치는 토큰 수를 지정하십시오. 그런 다음 이 매개변수를 [`~GenerationMixin.generate`] 메서드에 전달할 수 있습니다.
|
||||
|
||||
<hfoptions id="pld">
|
||||
<hfoption id="greedy decoding">
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
|
||||
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("facebook/opt-1.3b")
|
||||
inputs = tokenizer("The second law of thermodynamics states", return_tensors="pt").to(device)
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("facebook/opt-1.3b").to(device)
|
||||
assistant_model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("facebook/opt-125m").to(device)
|
||||
outputs = model.generate(**inputs, prompt_lookup_num_tokens=3)
|
||||
print(tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs, skip_special_tokens=True))
|
||||
['The second law of thermodynamics states that entropy increases with temperature. ']
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="sampling">
|
||||
|
||||
샘플링과 함께 프롬프트 조회 디코딩을 사용하려면, [`~GenerationMixin.generate`] 메서드에 `do_sample` 및 `temperature` 매개변수를 추가하십시오.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
|
||||
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("facebook/opt-1.3b")
|
||||
inputs = tokenizer("The second law of thermodynamics states", return_tensors="pt").to(device)
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("facebook/opt-1.3b").to(device)
|
||||
outputs = model.generate(**inputs, prompt_lookup_num_tokens=3, do_sample=True, temperature=0.7)
|
||||
print(tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs, skip_special_tokens=True))
|
||||
["The second law of thermodynamics states that energy cannot be created nor destroyed. It's not a"]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
</hfoptions>
|
||||
|
||||
## 어텐션 최적화 [[attention-optimizations]]
|
||||
|
||||
트랜스포머 모델의 알려진 문제는 셀프 어텐션 메커니즘이 입력 토큰 수와 함께 계산 및 메모리가 제곱으로 증가한다는 것입니다. 이 제한은 훨씬 더 긴 시퀀스를 처리하는 LLM에서는 더욱 커집니다. 이를 해결하기 위해 FlashAttention2 또는 PyTorch의 스케일된 점곱 어텐션을 사용해 보십시오. 이들은 더 메모리 효율적인 어텐션 구현으로 추론을 가속화할 수 있습니다.
|
||||
|
||||
### FlashAttention-2 [[flashattention-2]]
|
||||
|
||||
FlashAttention과 [FlashAttention-2](./perf_infer_gpu_one#flashattention-2)는 어텐션 계산을 더 작은 청크로 나누고 중간 읽기/쓰기 작업을 줄여 추론 속도를 높입니다. FlashAttention-2는 원래 FlashAttention 알고리즘을 개선하여 시퀀스 길이 차원에서도 병렬 처리를 수행하고 하드웨어에서 작업을 더 잘 분할하여 동기화 및 통신 오버헤드를 줄입니다.
|
||||
|
||||
FlashAttention-2를 사용하려면 [`~PreTrainedModel.from_pretrained`] 메서드에서 `attn_implementation="flash_attention_2"`를 설정하십시오.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, BitsAndBytesConfig
|
||||
|
||||
quant_config = BitsAndBytesConfig(load_in_8bit=True)
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"google/gemma-2b",
|
||||
quantization_config=quant_config,
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16,
|
||||
attn_implementation="flash_attention_2",
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### PyTorch 스케일된 점곱 어텐션(scaled dot product attention) [[pytorch-scaled-dot-product-attention]]
|
||||
|
||||
스케일된 점곱 어텐션(SDPA)는 PyTorch 2.0에서 자동으로 활성화되며, FlashAttention, xFormers, PyTorch의 C++ 구현을 지원합니다. SDPA는 CUDA 백엔드를 사용하는 경우 가장 성능이 좋은 어텐션 알고리즘을 선택합니다. 다른 백엔드에서는 SDPA가 PyTorch C++ 구현으로 기본 설정됩니다.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!TIP]
|
||||
> SDPA는 최신 PyTorch 버전이 설치되어 있으면 FlashAttention-2도 지원합니다.
|
||||
|
||||
세 가지 어텐션 알고리즘 중 하나를 명시적으로 활성화하거나 비활성화하려면 [torch.backends.cuda.sdp_kernel](https://pytorch.org/docs/master/generated/torch.nn.functional.scaled_dot_product_attention.html) 컨텍스트 관리자를 사용하십시오. 예를 들어 FlashAttention을 활성화하려면 `enable_flash=True`로 설정하십시오.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"google/gemma-2b",
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
with torch.backends.cuda.sdp_kernel(enable_flash=True, enable_math=False, enable_mem_efficient=False):
|
||||
outputs = model.generate(**inputs)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## 양자화 [[quantization]]
|
||||
|
||||
양자화는 LLM 가중치를 더 낮은 정밀도로 저장하여 크기를 줄입니다. 이는 메모리 사용량을 줄이며 GPU 메모리에 제약이 있는 경우 추론을 위해 LLM을 로드하는 것을 더 용이하게 합니다. GPU가 충분하다면, 모델을 양자화할 필요는 없습니다. 추가적인 양자화 및 양자화 해제 단계로 인해 약간의 지연이 발생할 수 있기 때문입니다(AWQ 및 융합 AWQ 모듈 제외).
|
||||
|
||||
> [!TIP]
|
||||
> 다양한 양자화 라이브러리(자세한 내용은 [Quantization](./quantization) 가이드를 참조하십시오)가 있습니다. 여기에는 Quanto, AQLM, AWQ 및 AutoGPTQ가 포함됩니다. 사용 사례에 가장 잘 맞는 라이브러리를 사용해 보십시오. 또한 AutoGPTQ와 bitsandbytes를 비교하는 [Overview of natively supported quantization schemes in 🤗 Transformers](https://hf.co/blog/overview-quantization-transformers) 블로그 게시물을 읽어보는 것을 추천합니다.
|
||||
|
||||
아래의 모델 메모리 계산기를 사용하여 모델을 로드하는 데 필요한 메모리를 추정하고 비교해 보십시오. 예를 들어 [Mistral-7B-v0.1](https://huggingface.co/mistralai/Mistral-7B-v0.1)를 로드하는 데 필요한 메모리를 추정해 보십시오.
|
||||
|
||||
<iframe
|
||||
src="https://hf-accelerate-model-memory-usage.hf.space"
|
||||
frameborder="0"
|
||||
width="850"
|
||||
height="450"
|
||||
></iframe>
|
||||
|
||||
Mistral-7B-v0.1을 반정밀도로 로드하려면 [`~transformers.AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained`] 메서드에서 `torch_dtype` 매개변수를 `torch.bfloat16`으로 설정하십시오. 이 경우 13.74GB의 메모리가 필요합니다.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"mistralai/Mistral-7B-v0.1", torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16, device_map="auto",
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
추론을 위해 양자화된 모델(8비트 또는 4비트)을 로드하려면 [bitsandbytes](https://hf.co/docs/bitsandbytes)를 사용하고 `load_in_4bit` 또는 `load_in_8bit` 매개변수를 `True`로 설정하십시오. 모델을 8비트로 로드하는 데는 6.87GB의 메모리만 필요합니다.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM, BitsAndBytesConfig
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
quant_config = BitsAndBytesConfig(load_in_8bit=True)
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"mistralai/Mistral-7B-v0.1", quantization_config=quant_config, device_map="auto"
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -83,12 +83,12 @@ API나 기반 모델이 자주 업데이트되므로, 에이전트가 제공하
|
||||
1. 입력(`List[Dict[str, str]]`)에 대한 [메시지 형식](../chat_templating.md)을 따르고 문자열을 반환해야 합니다.
|
||||
2. 인수 `stop_sequences`에 시퀀스가 전달되기 *전에* 출력을 생성하는 것을 중지해야 합니다.
|
||||
|
||||
### HfApiEngine [[HfApiEngine]]
|
||||
### HfEngine [[hfengine]]
|
||||
|
||||
편의를 위해, 위의 사항을 구현하고 대규모 언어 모델 실행을 위해 추론 엔드포인트를 사용하는 `HfApiEngine`을 추가했습니다.
|
||||
편의를 위해, 위의 사항을 구현하고 대규모 언어 모델 실행을 위해 추론 엔드포인트를 사용하는 `HfEngine`을 추가했습니다.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import HfApiEngine
|
||||
>>> from transformers import HfEngine
|
||||
|
||||
>>> messages = [
|
||||
... {"role": "user", "content": "Hello, how are you?"},
|
||||
@ -96,12 +96,12 @@ API나 기반 모델이 자주 업데이트되므로, 에이전트가 제공하
|
||||
... {"role": "user", "content": "No need to help, take it easy."},
|
||||
... ]
|
||||
|
||||
>>> HfApiEngine()(messages, stop_sequences=["conversation"])
|
||||
>>> HfEngine()(messages, stop_sequences=["conversation"])
|
||||
|
||||
"That's very kind of you to say! It's always nice to have a relaxed "
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] HfApiEngine
|
||||
[[autodoc]] HfEngine
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 에이전트 유형 [[agent-types]]
|
||||
|
||||
@ -221,7 +221,7 @@ python run_clm_flax.py \
|
||||
Training should converge at a loss and perplexity
|
||||
of 3.24 and 25.72 respectively after 20 epochs on a single TPUv3-8.
|
||||
This should take less than ~21 hours.
|
||||
Training statistics can be accessed on [tfhub.dev](https://tensorboard.dev/experiment/2zEhLwJ0Qp2FAkI3WVH9qA).
|
||||
Training statistics can be accessed on [tfhub.de](https://tensorboard.dev/experiment/2zEhLwJ0Qp2FAkI3WVH9qA).
|
||||
|
||||
For a step-by-step walkthrough of how to do causal language modeling in Flax, please have a
|
||||
look at [this](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/causal_language_modeling_flax.ipynb) google colab.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -30,6 +30,6 @@ python run_summarization_flax.py \
|
||||
--push_to_hub
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This should finish in 37min, with validation loss and ROUGE2 score of 1.7785 and 17.01 respectively after 6 epochs. training statistics can be accessed on [tfhub.dev](https://tensorboard.dev/experiment/OcPfOIgXRMSJqYB4RdK2tA/#scalars).
|
||||
This should finish in 37min, with validation loss and ROUGE2 score of 1.7785 and 17.01 respectively after 6 epochs. training statistics can be accessed on [tfhub.de](https://tensorboard.dev/experiment/OcPfOIgXRMSJqYB4RdK2tA/#scalars).
|
||||
|
||||
> Note that here we used default `generate` arguments, using arguments specific for `xsum` dataset should give better ROUGE scores.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -22,5 +22,5 @@ If you would like to list benchmark results on your favorite models of the [mode
|
||||
|
||||
| Benchmark description | Results | Environment info | Author |
|
||||
|:----------|:-------------|:-------------|------:|
|
||||
| PyTorch Benchmark on inference for `google-bert/bert-base-cased` |[memory](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten/files_to_link_to/blob/master/bert_benchmark/inference_memory.csv) | [env](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten/files_to_link_to/blob/master/bert_benchmark/env.csv) | [Patrick von Platen](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten) |
|
||||
| PyTorch Benchmark on inference for `google-bert/bert-base-cased` |[time](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten/files_to_link_to/blob/master/bert_benchmark/inference_time.csv) | [env](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten/files_to_link_to/blob/master/bert_benchmark/env.csv) | [Patrick von Platen](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten) |
|
||||
| PyTorch Benchmark on inference for `google-bert/bert-base-cased` |[memory](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten/files_to_link_to/blob/master/bert_benchmark/inference_memory.csv) | [env](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten/files_to_link_to/blob/master/bert_benchmark/env.csv) | [Partick von Platen](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten) |
|
||||
| PyTorch Benchmark on inference for `google-bert/bert-base-cased` |[time](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten/files_to_link_to/blob/master/bert_benchmark/inference_time.csv) | [env](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten/files_to_link_to/blob/master/bert_benchmark/env.csv) | [Partick von Platen](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten) |
|
||||
|
||||
@ -47,10 +47,10 @@ from transformers import (
|
||||
Trainer,
|
||||
TrainingArguments,
|
||||
default_data_collator,
|
||||
is_deepspeed_zero3_enabled,
|
||||
is_torch_tpu_available,
|
||||
set_seed,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from transformers.integrations import is_deepspeed_zero3_enabled
|
||||
from transformers.testing_utils import CaptureLogger
|
||||
from transformers.trainer_utils import get_last_checkpoint
|
||||
from transformers.utils import check_min_version, send_example_telemetry
|
||||
|
||||
@ -52,9 +52,9 @@ from transformers import (
|
||||
SchedulerType,
|
||||
default_data_collator,
|
||||
get_scheduler,
|
||||
is_deepspeed_zero3_enabled,
|
||||
is_torch_tpu_available,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from transformers.integrations import is_deepspeed_zero3_enabled
|
||||
from transformers.utils import check_min_version, send_example_telemetry
|
||||
from transformers.utils.versions import require_version
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -2,7 +2,7 @@ transformers==4.38.0
|
||||
datasets==1.16.0
|
||||
wandb==0.12.0
|
||||
tensorboard==2.6.0
|
||||
torch==2.2.0
|
||||
torch==1.13.1
|
||||
huggingface-hub==0.1.0
|
||||
git+https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate.git@3c45b6f760ad8745be9ebc9bbb26f5b04dea4abe
|
||||
datasketch==1.5.7
|
||||
|
||||
@ -34,7 +34,7 @@ cmd2==2.4.0
|
||||
codecarbon==1.2.0
|
||||
colorlog==6.6.0
|
||||
cookiecutter==2.1.1
|
||||
cryptography==43.0.1
|
||||
cryptography==42.0.0
|
||||
csvw==2.0.0
|
||||
cycler==0.11.0
|
||||
Cython==0.29.28
|
||||
@ -217,7 +217,7 @@ timm==0.5.4
|
||||
tokenizers==0.11.6
|
||||
tomli==2.0.1
|
||||
toolz==0.11.2
|
||||
torch==2.2.0
|
||||
torch==1.13.1
|
||||
torchaudio==0.11.0
|
||||
torchvision==0.12.0
|
||||
tqdm==4.66.3
|
||||
|
||||
@ -48,7 +48,7 @@ nbformat==5.0.7
|
||||
nest-asyncio==1.4.0
|
||||
notebook==6.4.12
|
||||
numpy==1.22.0
|
||||
opencv-python==4.8.1.78
|
||||
opencv-python==4.4.0.42
|
||||
packaging==20.3
|
||||
pandas==1.1.2
|
||||
pandocfilters==1.4.2
|
||||
|
||||
@ -48,7 +48,7 @@ nbformat==5.0.7
|
||||
nest-asyncio==1.4.0
|
||||
notebook==6.4.12
|
||||
numpy==1.22.0
|
||||
opencv-python==4.8.1.78
|
||||
opencv-python==4.4.0.42
|
||||
packaging==20.3
|
||||
pandas==1.1.2
|
||||
pandocfilters==1.4.2
|
||||
|
||||
@ -35,5 +35,4 @@ doctest_optionflags="NUMBER NORMALIZE_WHITESPACE ELLIPSIS"
|
||||
markers = [
|
||||
"flash_attn_test: marks tests related to flash attention (deselect with '-m \"not flash_attn_test\"')",
|
||||
"bitsandbytes: select (or deselect with `not`) bitsandbytes integration tests",
|
||||
"generate: marks tests that use the GenerationTesterMixin"
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
2
setup.py
2
setup.py
@ -130,7 +130,7 @@ _deps = [
|
||||
"keras>2.9,<2.16",
|
||||
"keras-nlp>=0.3.1,<0.14.0", # keras-nlp 0.14 doesn't support keras 2, see pin on keras.
|
||||
"librosa",
|
||||
"nltk<=3.8.1",
|
||||
"nltk",
|
||||
"natten>=0.14.6,<0.15.0",
|
||||
"numpy>=1.17",
|
||||
"onnxconverter-common",
|
||||
|
||||
@ -57,7 +57,7 @@ _import_structure = {
|
||||
"agents": [
|
||||
"Agent",
|
||||
"CodeAgent",
|
||||
"HfApiEngine",
|
||||
"HfEngine",
|
||||
"PipelineTool",
|
||||
"ReactAgent",
|
||||
"ReactCodeAgent",
|
||||
@ -65,7 +65,6 @@ _import_structure = {
|
||||
"Tool",
|
||||
"Toolbox",
|
||||
"ToolCollection",
|
||||
"TransformersEngine",
|
||||
"launch_gradio_demo",
|
||||
"load_tool",
|
||||
"stream_to_gradio",
|
||||
@ -533,7 +532,6 @@ _import_structure = {
|
||||
"LlavaNextVideoConfig",
|
||||
"LlavaNextVideoProcessor",
|
||||
],
|
||||
"models.llava_onevision": ["LlavaOnevisionConfig", "LlavaOnevisionProcessor"],
|
||||
"models.longformer": [
|
||||
"LongformerConfig",
|
||||
"LongformerTokenizer",
|
||||
@ -604,7 +602,6 @@ _import_structure = {
|
||||
"models.nougat": ["NougatProcessor"],
|
||||
"models.nystromformer": ["NystromformerConfig"],
|
||||
"models.olmo": ["OlmoConfig"],
|
||||
"models.olmoe": ["OlmoeConfig"],
|
||||
"models.oneformer": [
|
||||
"OneFormerConfig",
|
||||
"OneFormerProcessor",
|
||||
@ -1184,9 +1181,6 @@ else:
|
||||
_import_structure["models.levit"].extend(["LevitFeatureExtractor", "LevitImageProcessor"])
|
||||
_import_structure["models.llava_next"].append("LlavaNextImageProcessor")
|
||||
_import_structure["models.llava_next_video"].append("LlavaNextVideoImageProcessor")
|
||||
_import_structure["models.llava_onevision"].extend(
|
||||
["LlavaOnevisionImageProcessor", "LlavaOnevisionVideoProcessor"]
|
||||
)
|
||||
_import_structure["models.mask2former"].append("Mask2FormerImageProcessor")
|
||||
_import_structure["models.maskformer"].extend(["MaskFormerFeatureExtractor", "MaskFormerImageProcessor"])
|
||||
_import_structure["models.mobilenet_v1"].extend(["MobileNetV1FeatureExtractor", "MobileNetV1ImageProcessor"])
|
||||
@ -1252,7 +1246,6 @@ else:
|
||||
"HybridCache",
|
||||
"MambaCache",
|
||||
"OffloadedCache",
|
||||
"OffloadedStaticCache",
|
||||
"QuantizedCache",
|
||||
"QuantizedCacheConfig",
|
||||
"QuantoQuantizedCache",
|
||||
@ -2536,12 +2529,6 @@ else:
|
||||
"LlavaNextVideoPreTrainedModel",
|
||||
]
|
||||
)
|
||||
_import_structure["models.llava_onevision"].extend(
|
||||
[
|
||||
"LlavaOnevisionForConditionalGeneration",
|
||||
"LlavaOnevisionPreTrainedModel",
|
||||
]
|
||||
)
|
||||
_import_structure["models.longformer"].extend(
|
||||
[
|
||||
"LongformerForMaskedLM",
|
||||
@ -2839,13 +2826,6 @@ else:
|
||||
"OlmoPreTrainedModel",
|
||||
]
|
||||
)
|
||||
_import_structure["models.olmoe"].extend(
|
||||
[
|
||||
"OlmoeForCausalLM",
|
||||
"OlmoeModel",
|
||||
"OlmoePreTrainedModel",
|
||||
]
|
||||
)
|
||||
_import_structure["models.oneformer"].extend(
|
||||
[
|
||||
"OneFormerForUniversalSegmentation",
|
||||
@ -4825,7 +4805,7 @@ if TYPE_CHECKING:
|
||||
from .agents import (
|
||||
Agent,
|
||||
CodeAgent,
|
||||
HfApiEngine,
|
||||
HfEngine,
|
||||
PipelineTool,
|
||||
ReactAgent,
|
||||
ReactCodeAgent,
|
||||
@ -4833,7 +4813,6 @@ if TYPE_CHECKING:
|
||||
Tool,
|
||||
Toolbox,
|
||||
ToolCollection,
|
||||
TransformersEngine,
|
||||
launch_gradio_demo,
|
||||
load_tool,
|
||||
stream_to_gradio,
|
||||
@ -5318,10 +5297,6 @@ if TYPE_CHECKING:
|
||||
LlavaNextVideoConfig,
|
||||
LlavaNextVideoProcessor,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from .models.llava_onevision import (
|
||||
LlavaOnevisionConfig,
|
||||
LlavaOnevisionProcessor,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from .models.longformer import (
|
||||
LongformerConfig,
|
||||
LongformerTokenizer,
|
||||
@ -5402,7 +5377,6 @@ if TYPE_CHECKING:
|
||||
NystromformerConfig,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from .models.olmo import OlmoConfig
|
||||
from .models.olmoe import OlmoeConfig
|
||||
from .models.oneformer import (
|
||||
OneFormerConfig,
|
||||
OneFormerProcessor,
|
||||
@ -6007,7 +5981,6 @@ if TYPE_CHECKING:
|
||||
from .models.levit import LevitFeatureExtractor, LevitImageProcessor
|
||||
from .models.llava_next import LlavaNextImageProcessor
|
||||
from .models.llava_next_video import LlavaNextVideoImageProcessor
|
||||
from .models.llava_onevision import LlavaOnevisionImageProcessor, LlavaOnevisionVideoProcessor
|
||||
from .models.mask2former import Mask2FormerImageProcessor
|
||||
from .models.maskformer import (
|
||||
MaskFormerFeatureExtractor,
|
||||
@ -6079,7 +6052,6 @@ if TYPE_CHECKING:
|
||||
HybridCache,
|
||||
MambaCache,
|
||||
OffloadedCache,
|
||||
OffloadedStaticCache,
|
||||
QuantizedCache,
|
||||
QuantizedCacheConfig,
|
||||
QuantoQuantizedCache,
|
||||
@ -7128,10 +7100,6 @@ if TYPE_CHECKING:
|
||||
LlavaNextVideoForConditionalGeneration,
|
||||
LlavaNextVideoPreTrainedModel,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from .models.llava_onevision import (
|
||||
LlavaOnevisionForConditionalGeneration,
|
||||
LlavaOnevisionPreTrainedModel,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from .models.longformer import (
|
||||
LongformerForMaskedLM,
|
||||
LongformerForMultipleChoice,
|
||||
@ -7367,11 +7335,6 @@ if TYPE_CHECKING:
|
||||
OlmoModel,
|
||||
OlmoPreTrainedModel,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from .models.olmoe import (
|
||||
OlmoeForCausalLM,
|
||||
OlmoeModel,
|
||||
OlmoePreTrainedModel,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from .models.oneformer import (
|
||||
OneFormerForUniversalSegmentation,
|
||||
OneFormerModel,
|
||||
|
||||
@ -24,8 +24,8 @@ from ..utils import (
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
_import_structure = {
|
||||
"agents": ["Agent", "CodeAgent", "ManagedAgent", "ReactAgent", "ReactCodeAgent", "ReactJsonAgent", "Toolbox"],
|
||||
"llm_engine": ["HfApiEngine", "TransformersEngine"],
|
||||
"agents": ["Agent", "CodeAgent", "ReactAgent", "ReactCodeAgent", "ReactJsonAgent", "Toolbox"],
|
||||
"llm_engine": ["HfEngine"],
|
||||
"monitoring": ["stream_to_gradio"],
|
||||
"tools": ["PipelineTool", "Tool", "ToolCollection", "launch_gradio_demo", "load_tool"],
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -39,14 +39,13 @@ else:
|
||||
_import_structure["default_tools"] = ["FinalAnswerTool", "PythonInterpreterTool"]
|
||||
_import_structure["document_question_answering"] = ["DocumentQuestionAnsweringTool"]
|
||||
_import_structure["image_question_answering"] = ["ImageQuestionAnsweringTool"]
|
||||
_import_structure["search"] = ["DuckDuckGoSearchTool"]
|
||||
_import_structure["speech_to_text"] = ["SpeechToTextTool"]
|
||||
_import_structure["text_to_speech"] = ["TextToSpeechTool"]
|
||||
_import_structure["translation"] = ["TranslationTool"]
|
||||
|
||||
if TYPE_CHECKING:
|
||||
from .agents import Agent, CodeAgent, ManagedAgent, ReactAgent, ReactCodeAgent, ReactJsonAgent, Toolbox
|
||||
from .llm_engine import HfApiEngine, TransformersEngine
|
||||
from .agents import Agent, CodeAgent, ReactAgent, ReactCodeAgent, ReactJsonAgent, Toolbox
|
||||
from .llm_engine import HfEngine
|
||||
from .monitoring import stream_to_gradio
|
||||
from .tools import PipelineTool, Tool, ToolCollection, launch_gradio_demo, load_tool
|
||||
|
||||
@ -59,7 +58,6 @@ if TYPE_CHECKING:
|
||||
from .default_tools import FinalAnswerTool, PythonInterpreterTool
|
||||
from .document_question_answering import DocumentQuestionAnsweringTool
|
||||
from .image_question_answering import ImageQuestionAnsweringTool
|
||||
from .search import DuckDuckGoSearchTool
|
||||
from .speech_to_text import SpeechToTextTool
|
||||
from .text_to_speech import TextToSpeechTool
|
||||
from .translation import TranslationTool
|
||||
|
||||
@ -105,7 +105,7 @@ class AgentImage(AgentType, ImageType):
|
||||
elif isinstance(value, torch.Tensor):
|
||||
self._tensor = value
|
||||
elif isinstance(value, np.ndarray):
|
||||
self._tensor = torch.from_numpy(value)
|
||||
self._tensor = torch.tensor(value)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
raise TypeError(f"Unsupported type for {self.__class__.__name__}: {type(value)}")
|
||||
|
||||
@ -192,10 +192,7 @@ class AgentAudio(AgentType, str):
|
||||
self._tensor = value
|
||||
elif isinstance(value, tuple):
|
||||
self.samplerate = value[0]
|
||||
if isinstance(value[1], np.ndarray):
|
||||
self._tensor = torch.from_numpy(value[1])
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self._tensor = torch.tensor(value[1])
|
||||
self._tensor = torch.tensor(value[1])
|
||||
else:
|
||||
raise ValueError(f"Unsupported audio type: {type(value)}")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -24,7 +24,7 @@ from ..utils import logging as transformers_logging
|
||||
from ..utils.import_utils import is_pygments_available
|
||||
from .agent_types import AgentAudio, AgentImage, AgentText
|
||||
from .default_tools import BASE_PYTHON_TOOLS, FinalAnswerTool, setup_default_tools
|
||||
from .llm_engine import HfApiEngine, MessageRole
|
||||
from .llm_engine import HfEngine, MessageRole
|
||||
from .prompts import (
|
||||
DEFAULT_CODE_SYSTEM_PROMPT,
|
||||
DEFAULT_REACT_CODE_SYSTEM_PROMPT,
|
||||
@ -57,11 +57,8 @@ class CustomFormatter(logging.Formatter):
|
||||
bold_yellow = "\x1b[33;1m"
|
||||
red = "\x1b[31;20m"
|
||||
green = "\x1b[32;20m"
|
||||
bold_green = "\x1b[32;20;1m"
|
||||
bold_red = "\x1b[31;1m"
|
||||
bold_white = "\x1b[37;1m"
|
||||
orange = "\x1b[38;5;214m"
|
||||
bold_orange = "\x1b[38;5;214;1m"
|
||||
reset = "\x1b[0m"
|
||||
format = "%(message)s"
|
||||
|
||||
@ -69,14 +66,11 @@ class CustomFormatter(logging.Formatter):
|
||||
logging.DEBUG: grey + format + reset,
|
||||
logging.INFO: format,
|
||||
logging.WARNING: bold_yellow + format + reset,
|
||||
logging.ERROR: red + format + reset,
|
||||
logging.CRITICAL: bold_red + format + reset,
|
||||
31: reset + format + reset,
|
||||
32: green + format + reset,
|
||||
33: bold_green + format + reset,
|
||||
34: bold_white + format + reset,
|
||||
35: orange + format + reset,
|
||||
36: bold_orange + format + reset,
|
||||
33: bold_white + format + reset,
|
||||
logging.ERROR: red + format + reset,
|
||||
logging.CRITICAL: bold_red + format + reset,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
def format(self, record):
|
||||
@ -317,32 +311,12 @@ class AgentGenerationError(AgentError):
|
||||
def format_prompt_with_tools(toolbox: Toolbox, prompt_template: str, tool_description_template: str) -> str:
|
||||
tool_descriptions = toolbox.show_tool_descriptions(tool_description_template)
|
||||
prompt = prompt_template.replace("<<tool_descriptions>>", tool_descriptions)
|
||||
|
||||
if "<<tool_names>>" in prompt:
|
||||
tool_names = [f"'{tool_name}'" for tool_name in toolbox.tools.keys()]
|
||||
prompt = prompt.replace("<<tool_names>>", ", ".join(tool_names))
|
||||
|
||||
return prompt
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def show_agents_descriptions(managed_agents: list):
|
||||
managed_agents_descriptions = """
|
||||
You can also give requests to team members.
|
||||
Calling a team member works the same as for calling a tool: simply, the only argument you can give in the call is 'request', a long string explaning your request.
|
||||
Given that this team member is a real human, you should be very verbose in your request.
|
||||
Here is a list of the team members that you can call:"""
|
||||
for agent in managed_agents.values():
|
||||
managed_agents_descriptions += f"\n- {agent.name}: {agent.description}"
|
||||
return managed_agents_descriptions
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def format_prompt_with_managed_agents_descriptions(prompt_template, managed_agents=None) -> str:
|
||||
if managed_agents is not None:
|
||||
return prompt_template.replace("<<managed_agents_descriptions>>", show_agents_descriptions(managed_agents))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return prompt_template.replace("<<managed_agents_descriptions>>", "")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def format_prompt_with_imports(prompt_template: str, authorized_imports: List[str]) -> str:
|
||||
if "<<authorized_imports>>" not in prompt_template:
|
||||
raise AgentError("Tag '<<authorized_imports>>' should be provided in the prompt.")
|
||||
@ -353,7 +327,7 @@ class Agent:
|
||||
def __init__(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
tools: Union[List[Tool], Toolbox],
|
||||
llm_engine: Callable = HfApiEngine(),
|
||||
llm_engine: Callable = HfEngine(),
|
||||
system_prompt=DEFAULT_REACT_CODE_SYSTEM_PROMPT,
|
||||
tool_description_template=None,
|
||||
additional_args={},
|
||||
@ -361,8 +335,8 @@ class Agent:
|
||||
tool_parser=parse_json_tool_call,
|
||||
add_base_tools: bool = False,
|
||||
verbose: int = 0,
|
||||
memory_verbose: bool = False,
|
||||
grammar: Dict[str, str] = None,
|
||||
managed_agents: List = None,
|
||||
):
|
||||
self.agent_name = self.__class__.__name__
|
||||
self.llm_engine = llm_engine
|
||||
@ -376,10 +350,6 @@ class Agent:
|
||||
self.tool_parser = tool_parser
|
||||
self.grammar = grammar
|
||||
|
||||
self.managed_agents = None
|
||||
if managed_agents is not None:
|
||||
self.managed_agents = {agent.name: agent for agent in managed_agents}
|
||||
|
||||
if isinstance(tools, Toolbox):
|
||||
self._toolbox = tools
|
||||
if add_base_tools:
|
||||
@ -394,10 +364,10 @@ class Agent:
|
||||
self.system_prompt = format_prompt_with_tools(
|
||||
self._toolbox, self.system_prompt_template, self.tool_description_template
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.system_prompt = format_prompt_with_managed_agents_descriptions(self.system_prompt, self.managed_agents)
|
||||
self.prompt = None
|
||||
self.logs = []
|
||||
self.task = None
|
||||
self.memory_verbose = memory_verbose
|
||||
|
||||
if verbose == 0:
|
||||
logger.setLevel(logging.WARNING)
|
||||
@ -418,14 +388,13 @@ class Agent:
|
||||
self.system_prompt_template,
|
||||
self.tool_description_template,
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.system_prompt = format_prompt_with_managed_agents_descriptions(self.system_prompt, self.managed_agents)
|
||||
if hasattr(self, "authorized_imports"):
|
||||
self.system_prompt = format_prompt_with_imports(
|
||||
self.system_prompt, list(set(LIST_SAFE_MODULES) | set(self.authorized_imports))
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.logs = [{"system_prompt": self.system_prompt, "task": self.task}]
|
||||
self.logger.log(33, "======== New task ========")
|
||||
self.logger.log(34, self.task)
|
||||
self.logger.warn("======== New task ========")
|
||||
self.logger.log(33, self.task)
|
||||
self.logger.debug("System prompt is as follows:")
|
||||
self.logger.debug(self.system_prompt)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -475,12 +444,12 @@ class Agent:
|
||||
if "error" in step_log or "observation" in step_log:
|
||||
if "error" in step_log:
|
||||
message_content = (
|
||||
f"[OUTPUT OF STEP {i}] -> Error:\n"
|
||||
f"[OUTPUT OF STEP {i}] Error: "
|
||||
+ str(step_log["error"])
|
||||
+ "\nNow let's retry: take care not to repeat previous errors! If you have retried several times, try a completely different approach.\n"
|
||||
)
|
||||
elif "observation" in step_log:
|
||||
message_content = f"[OUTPUT OF STEP {i}] -> Observation:\n{step_log['observation']}"
|
||||
message_content = f"[OUTPUT OF STEP {i}] Observation:\n{step_log['observation']}"
|
||||
tool_response_message = {"role": MessageRole.TOOL_RESPONSE, "content": message_content}
|
||||
memory.append(tool_response_message)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -508,7 +477,7 @@ class Agent:
|
||||
raise AgentParsingError(
|
||||
f"Error: No '{split_token}' token provided in your output.\nYour output:\n{llm_output}\n. Be sure to include an action, prefaced with '{split_token}'!"
|
||||
)
|
||||
return rationale.strip(), action.strip()
|
||||
return rationale, action
|
||||
|
||||
def execute_tool_call(self, tool_name: str, arguments: Dict[str, str]) -> Any:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
@ -519,44 +488,29 @@ class Agent:
|
||||
tool_name (`str`): Name of the Tool to execute (should be one from self.toolbox).
|
||||
arguments (Dict[str, str]): Arguments passed to the Tool.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
available_tools = self.toolbox.tools
|
||||
if self.managed_agents is not None:
|
||||
available_tools = {**available_tools, **self.managed_agents}
|
||||
if tool_name not in available_tools:
|
||||
error_msg = f"Error: unknown tool {tool_name}, should be instead one of {list(available_tools.keys())}."
|
||||
if tool_name not in self.toolbox.tools:
|
||||
error_msg = f"Error: unknown tool {tool_name}, should be instead one of {list(self.toolbox.tools.keys())}."
|
||||
self.logger.error(error_msg, exc_info=1)
|
||||
raise AgentExecutionError(error_msg)
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
if isinstance(arguments, str):
|
||||
observation = available_tools[tool_name](arguments)
|
||||
elif isinstance(arguments, dict):
|
||||
observation = self.toolbox.tools[tool_name](arguments)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
for key, value in arguments.items():
|
||||
# if the value is the name of a state variable like "image.png", replace it with the actual value
|
||||
if isinstance(value, str) and value in self.state:
|
||||
arguments[key] = self.state[value]
|
||||
observation = available_tools[tool_name](**arguments)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
raise AgentExecutionError(
|
||||
f"Arguments passed to tool should be a dict or string: got a {type(arguments)}."
|
||||
)
|
||||
observation = self.toolbox.tools[tool_name](**arguments)
|
||||
return observation
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
if tool_name in self.toolbox.tools:
|
||||
raise AgentExecutionError(
|
||||
f"Error in tool call execution: {e}\nYou should only use this tool with a correct input.\n"
|
||||
f"As a reminder, this tool's description is the following:\n{get_tool_description_with_args(available_tools[tool_name])}"
|
||||
)
|
||||
elif tool_name in self.managed_agents:
|
||||
raise AgentExecutionError(
|
||||
f"Error in calling team member: {e}\nYou should only ask this team member with a correct request.\n"
|
||||
f"As a reminder, this team member's description is the following:\n{available_tools[tool_name]}"
|
||||
)
|
||||
raise AgentExecutionError(
|
||||
f"Error in tool call execution: {e}\nYou should only use this tool with a correct input.\n"
|
||||
f"As a reminder, this tool's description is the following:\n{get_tool_description_with_args(self.toolbox.tools[tool_name])}"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def log_rationale_code_action(self, rationale: str, code_action: str) -> None:
|
||||
self.logger.warning("=== Agent thoughts:")
|
||||
self.logger.log(31, rationale)
|
||||
self.logger.warning(">>> Agent is executing the code below:")
|
||||
def log_code_action(self, code_action: str) -> None:
|
||||
self.logger.warning("==== Agent is executing the code below:")
|
||||
if is_pygments_available():
|
||||
self.logger.log(
|
||||
31, highlight(code_action, PythonLexer(ensurenl=False), Terminal256Formatter(style="nord"))
|
||||
@ -578,7 +532,7 @@ class CodeAgent(Agent):
|
||||
def __init__(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
tools: List[Tool],
|
||||
llm_engine: Callable = HfApiEngine(),
|
||||
llm_engine: Callable = HfEngine(),
|
||||
system_prompt: str = DEFAULT_CODE_SYSTEM_PROMPT,
|
||||
tool_description_template: str = DEFAULT_TOOL_DESCRIPTION_TEMPLATE,
|
||||
grammar: Dict[str, str] = None,
|
||||
@ -658,12 +612,12 @@ class CodeAgent(Agent):
|
||||
|
||||
# Parse
|
||||
try:
|
||||
rationale, code_action = self.extract_action(llm_output=llm_output, split_token="Code:")
|
||||
_, code_action = self.extract_action(llm_output=llm_output, split_token="Code:")
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
self.logger.debug(
|
||||
f"Error in extracting action, trying to parse the whole output as code. Error trace: {e}"
|
||||
)
|
||||
rationale, code_action = "", llm_output
|
||||
code_action = llm_output
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
code_action = self.parse_code_blob(code_action)
|
||||
@ -673,7 +627,7 @@ class CodeAgent(Agent):
|
||||
return error_msg
|
||||
|
||||
# Execute
|
||||
self.log_rationale_code_action(rationale, code_action)
|
||||
self.log_code_action(code_action)
|
||||
try:
|
||||
available_tools = {**BASE_PYTHON_TOOLS.copy(), **self.toolbox.tools}
|
||||
output = self.python_evaluator(
|
||||
@ -701,7 +655,7 @@ class ReactAgent(Agent):
|
||||
def __init__(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
tools: List[Tool],
|
||||
llm_engine: Callable = HfApiEngine(),
|
||||
llm_engine: Callable = HfEngine(),
|
||||
system_prompt: str = DEFAULT_REACT_CODE_SYSTEM_PROMPT,
|
||||
tool_description_template: str = DEFAULT_TOOL_DESCRIPTION_TEMPLATE,
|
||||
grammar: Dict[str, str] = None,
|
||||
@ -859,9 +813,6 @@ Now begin!""",
|
||||
"content": PROMPTS_FOR_INITIAL_PLAN[self.plan_type]["user"].format(
|
||||
task=task,
|
||||
tool_descriptions=self._toolbox.show_tool_descriptions(self.tool_description_template),
|
||||
managed_agents_descriptions=(
|
||||
show_agents_descriptions(self.managed_agents) if self.managed_agents is not None else ""
|
||||
),
|
||||
answer_facts=answer_facts,
|
||||
),
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -878,8 +829,8 @@ Now begin!""",
|
||||
{answer_facts}
|
||||
```""".strip()
|
||||
self.logs.append({"plan": final_plan_redaction, "facts": final_facts_redaction})
|
||||
self.logger.log(36, "===== Initial plan =====")
|
||||
self.logger.log(35, final_plan_redaction)
|
||||
self.logger.debug("===== Initial plan: =====")
|
||||
self.logger.debug(final_plan_redaction)
|
||||
else: # update plan
|
||||
agent_memory = self.write_inner_memory_from_logs(
|
||||
summary_mode=False
|
||||
@ -906,9 +857,6 @@ Now begin!""",
|
||||
"content": PROMPTS_FOR_PLAN_UPDATE[self.plan_type]["user"].format(
|
||||
task=task,
|
||||
tool_descriptions=self._toolbox.show_tool_descriptions(self.tool_description_template),
|
||||
managed_agents_descriptions=(
|
||||
show_agents_descriptions(self.managed_agents) if self.managed_agents is not None else ""
|
||||
),
|
||||
facts_update=facts_update,
|
||||
remaining_steps=(self.max_iterations - iteration),
|
||||
),
|
||||
@ -924,8 +872,8 @@ Now begin!""",
|
||||
{facts_update}
|
||||
```"""
|
||||
self.logs.append({"plan": final_plan_redaction, "facts": final_facts_redaction})
|
||||
self.logger.log(36, "===== Updated plan =====")
|
||||
self.logger.log(35, final_plan_redaction)
|
||||
self.logger.debug("===== Updated plan: =====")
|
||||
self.logger.debug(final_plan_redaction)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class ReactJsonAgent(ReactAgent):
|
||||
@ -938,7 +886,7 @@ class ReactJsonAgent(ReactAgent):
|
||||
def __init__(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
tools: List[Tool],
|
||||
llm_engine: Callable = HfApiEngine(),
|
||||
llm_engine: Callable = HfEngine(),
|
||||
system_prompt: str = DEFAULT_REACT_JSON_SYSTEM_PROMPT,
|
||||
tool_description_template: str = DEFAULT_TOOL_DESCRIPTION_TEMPLATE,
|
||||
grammar: Dict[str, str] = None,
|
||||
@ -997,9 +945,7 @@ class ReactJsonAgent(ReactAgent):
|
||||
current_step_logs["tool_call"] = {"tool_name": tool_name, "tool_arguments": arguments}
|
||||
|
||||
# Execute
|
||||
self.logger.warning("=== Agent thoughts:")
|
||||
self.logger.log(31, rationale)
|
||||
self.logger.warning(f">>> Calling tool: '{tool_name}' with arguments: {arguments}")
|
||||
self.logger.warning(f"Calling tool: '{tool_name}' with arguments: {arguments}")
|
||||
if tool_name == "final_answer":
|
||||
if isinstance(arguments, dict):
|
||||
if "answer" in arguments:
|
||||
@ -1015,8 +961,6 @@ class ReactJsonAgent(ReactAgent):
|
||||
current_step_logs["final_answer"] = answer
|
||||
return current_step_logs
|
||||
else:
|
||||
if arguments is None:
|
||||
arguments = {}
|
||||
observation = self.execute_tool_call(tool_name, arguments)
|
||||
observation_type = type(observation)
|
||||
if observation_type == AgentText:
|
||||
@ -1048,7 +992,7 @@ class ReactCodeAgent(ReactAgent):
|
||||
def __init__(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
tools: List[Tool],
|
||||
llm_engine: Callable = HfApiEngine(),
|
||||
llm_engine: Callable = HfEngine(),
|
||||
system_prompt: str = DEFAULT_REACT_CODE_SYSTEM_PROMPT,
|
||||
tool_description_template: str = DEFAULT_TOOL_DESCRIPTION_TEMPLATE,
|
||||
grammar: Dict[str, str] = None,
|
||||
@ -1106,12 +1050,12 @@ class ReactCodeAgent(ReactAgent):
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
raise AgentGenerationError(f"Error in generating llm output: {e}.")
|
||||
|
||||
self.logger.debug("=== Output message of the LLM:")
|
||||
self.logger.debug("===== Output message of the LLM: =====")
|
||||
self.logger.debug(llm_output)
|
||||
current_step_logs["llm_output"] = llm_output
|
||||
|
||||
# Parse
|
||||
self.logger.debug("=== Extracting action ===")
|
||||
self.logger.debug("===== Extracting action =====")
|
||||
try:
|
||||
rationale, raw_code_action = self.extract_action(llm_output=llm_output, split_token="Code:")
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
@ -1128,30 +1072,22 @@ class ReactCodeAgent(ReactAgent):
|
||||
current_step_logs["tool_call"] = {"tool_name": "code interpreter", "tool_arguments": code_action}
|
||||
|
||||
# Execute
|
||||
self.log_rationale_code_action(rationale, code_action)
|
||||
self.log_code_action(code_action)
|
||||
try:
|
||||
static_tools = {
|
||||
**BASE_PYTHON_TOOLS.copy(),
|
||||
**self.toolbox.tools,
|
||||
}
|
||||
if self.managed_agents is not None:
|
||||
static_tools = {**static_tools, **self.managed_agents}
|
||||
result = self.python_evaluator(
|
||||
code_action,
|
||||
static_tools=static_tools,
|
||||
static_tools={
|
||||
**BASE_PYTHON_TOOLS.copy(),
|
||||
**self.toolbox.tools,
|
||||
},
|
||||
custom_tools=self.custom_tools,
|
||||
state=self.state,
|
||||
authorized_imports=self.authorized_imports,
|
||||
)
|
||||
information = self.state["print_outputs"]
|
||||
self.logger.warning("Print outputs:")
|
||||
self.logger.log(32, self.state["print_outputs"])
|
||||
if result is not None:
|
||||
self.logger.warning("Last output from code snippet:")
|
||||
self.logger.log(32, str(result))
|
||||
observation = "Print outputs:\n" + self.state["print_outputs"]
|
||||
if result is not None:
|
||||
observation += "Last output from code snippet:\n" + str(result)[:100000]
|
||||
current_step_logs["observation"] = observation
|
||||
self.logger.log(32, information)
|
||||
current_step_logs["observation"] = information
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
error_msg = f"Code execution failed due to the following error:\n{str(e)}"
|
||||
if "'dict' object has no attribute 'read'" in str(e):
|
||||
@ -1159,57 +1095,7 @@ class ReactCodeAgent(ReactAgent):
|
||||
raise AgentExecutionError(error_msg)
|
||||
for line in code_action.split("\n"):
|
||||
if line[: len("final_answer")] == "final_answer":
|
||||
self.logger.log(33, "Final answer:")
|
||||
self.logger.warning(">>> Final answer:")
|
||||
self.logger.log(32, result)
|
||||
current_step_logs["final_answer"] = result
|
||||
return current_step_logs
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class ManagedAgent:
|
||||
def __init__(self, agent, name, description, additional_prompting=None, provide_run_summary=False):
|
||||
self.agent = agent
|
||||
self.name = name
|
||||
self.description = description
|
||||
self.additional_prompting = additional_prompting
|
||||
self.provide_run_summary = provide_run_summary
|
||||
|
||||
def write_full_task(self, task):
|
||||
full_task = f"""You're a helpful agent named '{self.name}'.
|
||||
You have been submitted this task by your manager.
|
||||
---
|
||||
Task:
|
||||
{task}
|
||||
---
|
||||
You're helping your manager solve a wider task: so make sure to not provide a one-line answer, but give as much information as possible so that they have a clear understanding of the answer.
|
||||
|
||||
Your final_answer WILL HAVE to contain these parts:
|
||||
### 1. Task outcome (short version):
|
||||
### 2. Task outcome (extremely detailed version):
|
||||
### 3. Additional context (if relevant):
|
||||
|
||||
Put all these in your final_answer tool, everything that you do not pass as an argument to final_answer will be lost.
|
||||
And even if your task resolution is not successful, please return as much context as possible, so that your manager can act upon this feedback.
|
||||
<<additional_prompting>>"""
|
||||
if self.additional_prompting:
|
||||
full_task = full_task.replace("\n<<additional_prompting>>", self.additional_prompting).strip()
|
||||
else:
|
||||
full_task = full_task.replace("\n<<additional_prompting>>", "").strip()
|
||||
return full_task
|
||||
|
||||
def __call__(self, request, **kwargs):
|
||||
full_task = self.write_full_task(request)
|
||||
output = self.agent.run(full_task, **kwargs)
|
||||
if self.provide_run_summary:
|
||||
answer = f"Here is the final answer from your managed agent '{self.name}':\n"
|
||||
answer += str(output)
|
||||
answer += f"\n\nFor more detail, find below a summary of this agent's work:\nSUMMARY OF WORK FROM AGENT '{self.name}':\n"
|
||||
for message in self.agent.write_inner_memory_from_logs(summary_mode=True):
|
||||
content = message["content"]
|
||||
if len(str(content)) < 1000 or "[FACTS LIST]" in str(content):
|
||||
answer += "\n" + str(content) + "\n---"
|
||||
else:
|
||||
answer += "\n" + str(content)[:1000] + "\n(...Step was truncated because too long)...\n---"
|
||||
answer += f"\nEND OF SUMMARY OF WORK FROM AGENT '{self.name}'."
|
||||
return answer
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return output
|
||||
|
||||
@ -25,11 +25,11 @@ from huggingface_hub import hf_hub_download, list_spaces
|
||||
|
||||
from ..utils import is_offline_mode
|
||||
from .python_interpreter import LIST_SAFE_MODULES, evaluate_python_code
|
||||
from .tools import TOOL_CONFIG_FILE, TOOL_MAPPING, Tool
|
||||
from .tools import TASK_MAPPING, TOOL_CONFIG_FILE, Tool
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def custom_print(*args):
|
||||
return None
|
||||
return " ".join(map(str, args))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
BASE_PYTHON_TOOLS = {
|
||||
@ -133,7 +133,7 @@ def setup_default_tools(logger):
|
||||
main_module = importlib.import_module("transformers")
|
||||
tools_module = main_module.agents
|
||||
|
||||
for task_name, tool_class_name in TOOL_MAPPING.items():
|
||||
for task_name, tool_class_name in TASK_MAPPING.items():
|
||||
tool_class = getattr(tools_module, tool_class_name)
|
||||
tool_instance = tool_class()
|
||||
default_tools[tool_class.name] = PreTool(
|
||||
|
||||
@ -60,7 +60,7 @@ class DocumentQuestionAnsweringTool(PipelineTool):
|
||||
if isinstance(document, str):
|
||||
img = Image.open(document).convert("RGB")
|
||||
img_array = np.array(img).transpose(2, 0, 1)
|
||||
document = torch.from_numpy(img_array)
|
||||
document = torch.tensor(img_array)
|
||||
pixel_values = self.pre_processor(document, return_tensors="pt").pixel_values
|
||||
|
||||
return {"decoder_input_ids": decoder_input_ids, "pixel_values": pixel_values}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -20,8 +20,6 @@ from typing import Dict, List, Optional
|
||||
|
||||
from huggingface_hub import InferenceClient
|
||||
|
||||
from ..pipelines.base import Pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class MessageRole(str, Enum):
|
||||
USER = "user"
|
||||
@ -67,9 +65,7 @@ llama_role_conversions = {
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class HfApiEngine:
|
||||
"""This engine leverages Hugging Face's Inference API service, either serverless or with a dedicated endpoint."""
|
||||
|
||||
class HfEngine:
|
||||
def __init__(self, model: str = "meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct"):
|
||||
self.model = model
|
||||
self.client = InferenceClient(self.model, timeout=120)
|
||||
@ -97,36 +93,6 @@ class HfApiEngine:
|
||||
return response
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class TransformersEngine:
|
||||
"""This engine uses a pre-initialized local text-generation pipeline."""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, pipeline: Pipeline):
|
||||
self.pipeline = pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
def __call__(
|
||||
self, messages: List[Dict[str, str]], stop_sequences: Optional[List[str]] = None, grammar: Optional[str] = None
|
||||
) -> str:
|
||||
# Get clean message list
|
||||
messages = get_clean_message_list(messages, role_conversions=llama_role_conversions)
|
||||
|
||||
# Get LLM output
|
||||
output = self.pipeline(
|
||||
messages,
|
||||
stop_strings=stop_sequences,
|
||||
max_length=1500,
|
||||
tokenizer=self.pipeline.tokenizer,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
response = output[0]["generated_text"][-1]["content"]
|
||||
|
||||
# Remove stop sequences from LLM output
|
||||
if stop_sequences is not None:
|
||||
for stop_seq in stop_sequences:
|
||||
if response[-len(stop_seq) :] == stop_seq:
|
||||
response = response[: -len(stop_seq)]
|
||||
return response
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
DEFAULT_JSONAGENT_REGEX_GRAMMAR = {
|
||||
"type": "regex",
|
||||
"value": 'Thought: .+?\\nAction:\\n\\{\\n\\s{4}"action":\\s"[^"\\n]+",\\n\\s{4}"action_input":\\s"[^"\\n]+"\\n\\}\\n<end_action>',
|
||||
|
||||
@ -332,10 +332,10 @@ final_answer("Shanghai")
|
||||
---
|
||||
Task: "What is the current age of the pope, raised to the power 0.36?"
|
||||
|
||||
Thought: I will use the tool `wiki` to get the age of the pope, then raise it to the power 0.36.
|
||||
Thought: I will use the tool `search` to get the age of the pope, then raise it to the power 0.36.
|
||||
Code:
|
||||
```py
|
||||
pope_age = wiki(query="current pope age")
|
||||
pope_age = search(query="current pope age")
|
||||
print("Pope age:", pope_age)
|
||||
```<end_action>
|
||||
Observation:
|
||||
@ -348,16 +348,16 @@ pope_current_age = 85 ** 0.36
|
||||
final_answer(pope_current_age)
|
||||
```<end_action>
|
||||
|
||||
Above example were using notional tools that might not exist for you. On top of performing computations in the Python code snippets that you create, you have acces to those tools (and no other tool):
|
||||
Above example were using notional tools that might not exist for you. You only have acces to those tools:
|
||||
|
||||
<<tool_descriptions>>
|
||||
|
||||
<<managed_agents_descriptions>>
|
||||
You also can perform computations in the Python code that you generate.
|
||||
|
||||
Here are the rules you should always follow to solve your task:
|
||||
1. Always provide a 'Thought:' sequence, and a 'Code:\n```py' sequence ending with '```<end_action>' sequence, else you will fail.
|
||||
2. Use only variables that you have defined!
|
||||
3. Always use the right arguments for the tools. DO NOT pass the arguments as a dict as in 'answer = wiki({'query': "What is the place where James Bond lives?"})', but use the arguments directly as in 'answer = wiki(query="What is the place where James Bond lives?")'.
|
||||
3. Always use the right arguments for the tools. DO NOT pass the arguments as a dict as in 'answer = ask_search_agent({'query': "What is the place where James Bond lives?"})', but use the arguments directly as in 'answer = ask_search_agent(query="What is the place where James Bond lives?")'.
|
||||
4. Take care to not chain too many sequential tool calls in the same code block, especially when the output format is unpredictable. For instance, a call to search has an unpredictable return format, so do not have another tool call that depends on its output in the same block: rather output results with print() to use them in the next block.
|
||||
5. Call a tool only when needed, and never re-do a tool call that you previously did with the exact same parameters.
|
||||
6. Don't name any new variable with the same name as a tool: for instance don't name a variable 'final_answer'.
|
||||
@ -410,8 +410,6 @@ Task:
|
||||
Your plan can leverage any of these tools:
|
||||
{tool_descriptions}
|
||||
|
||||
{managed_agents_descriptions}
|
||||
|
||||
List of facts that you know:
|
||||
```
|
||||
{answer_facts}
|
||||
@ -455,11 +453,9 @@ USER_PROMPT_PLAN_UPDATE = """You're still working towards solving this task:
|
||||
{task}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You have access to these tools and only these:
|
||||
You have access to these tools:
|
||||
{tool_descriptions}
|
||||
|
||||
{managed_agents_descriptions}
|
||||
|
||||
Here is the up to date list of facts that you know:
|
||||
```
|
||||
{facts_update}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -434,7 +434,7 @@ def evaluate_call(call, state, static_tools, custom_tools):
|
||||
global PRINT_OUTPUTS
|
||||
PRINT_OUTPUTS += output + "\n"
|
||||
# cap the number of lines
|
||||
return None
|
||||
return output
|
||||
else: # Assume it's a callable object
|
||||
output = func(*args, **kwargs)
|
||||
return output
|
||||
@ -444,8 +444,6 @@ def evaluate_subscript(subscript, state, static_tools, custom_tools):
|
||||
index = evaluate_ast(subscript.slice, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
value = evaluate_ast(subscript.value, state, static_tools, custom_tools)
|
||||
|
||||
if isinstance(value, str) and isinstance(index, str):
|
||||
raise InterpreterError("You're trying to subscript a string with a string index, which is impossible")
|
||||
if isinstance(value, pd.core.indexing._LocIndexer):
|
||||
parent_object = value.obj
|
||||
return parent_object.loc[index]
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,35 +0,0 @@
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/env python
|
||||
# coding=utf-8
|
||||
|
||||
# Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Inc. team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
from .tools import Tool
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class DuckDuckGoSearchTool(Tool):
|
||||
name = "web_search"
|
||||
description = """Perform a web search based on your query (think a Google search) then returns the top search results as a list of dict elements.
|
||||
Each result has keys 'title', 'href' and 'body'."""
|
||||
inputs = {"query": {"type": "text", "description": "The search query to perform."}}
|
||||
output_type = "any"
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, query: str) -> str:
|
||||
try:
|
||||
from duckduckgo_search import DDGS
|
||||
except ImportError:
|
||||
raise ImportError(
|
||||
"You must install package `duckduckgo_search`: for instance run `pip install duckduckgo-search`."
|
||||
)
|
||||
results = DDGS().text(query, max_results=7)
|
||||
return results
|
||||
@ -643,14 +643,13 @@ def launch_gradio_demo(tool_class: Tool):
|
||||
).launch()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
TOOL_MAPPING = {
|
||||
"document_question_answering": "DocumentQuestionAnsweringTool",
|
||||
"image_question_answering": "ImageQuestionAnsweringTool",
|
||||
"speech_to_text": "SpeechToTextTool",
|
||||
"text_to_speech": "TextToSpeechTool",
|
||||
TASK_MAPPING = {
|
||||
"document-question-answering": "DocumentQuestionAnsweringTool",
|
||||
"image-question-answering": "ImageQuestionAnsweringTool",
|
||||
"speech-to-text": "SpeechToTextTool",
|
||||
"text-to-speech": "TextToSpeechTool",
|
||||
"translation": "TranslationTool",
|
||||
"python_interpreter": "PythonInterpreterTool",
|
||||
"web_search": "DuckDuckGoSearchTool",
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -671,10 +670,10 @@ def load_tool(task_or_repo_id, model_repo_id=None, token=None, **kwargs):
|
||||
The task for which to load the tool or a repo ID of a tool on the Hub. Tasks implemented in Transformers
|
||||
are:
|
||||
|
||||
- `"document_question_answering"`
|
||||
- `"image_question_answering"`
|
||||
- `"speech_to_text"`
|
||||
- `"text_to_speech"`
|
||||
- `"document-question-answering"`
|
||||
- `"image-question-answering"`
|
||||
- `"speech-to-text"`
|
||||
- `"text-to-speech"`
|
||||
- `"translation"`
|
||||
|
||||
model_repo_id (`str`, *optional*):
|
||||
@ -687,8 +686,8 @@ def load_tool(task_or_repo_id, model_repo_id=None, token=None, **kwargs):
|
||||
`cache_dir`, `revision`, `subfolder`) will be used when downloading the files for your tool, and the others
|
||||
will be passed along to its init.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if task_or_repo_id in TOOL_MAPPING:
|
||||
tool_class_name = TOOL_MAPPING[task_or_repo_id]
|
||||
if task_or_repo_id in TASK_MAPPING:
|
||||
tool_class_name = TASK_MAPPING[task_or_repo_id]
|
||||
main_module = importlib.import_module("transformers")
|
||||
tools_module = main_module.agents
|
||||
tool_class = getattr(tools_module, tool_class_name)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -305,16 +305,15 @@ class DynamicCache(Cache):
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM, DynamicCache
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("Qwen/Qwen2-0.5B-Instruct")
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("Qwen/Qwen2-0.5B-Instruct")
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("openai-community/gpt2")
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("openai-community/gpt2")
|
||||
|
||||
>>> inputs = tokenizer(text="My name is Qwen2", return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
>>> inputs = tokenizer(text="My name is GPT2", return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
|
||||
>>> # Prepare a cache class and pass it to model's forward
|
||||
>>> past_key_values = DynamicCache()
|
||||
>>> outputs = model(**inputs, past_key_values=past_key_values, use_cache=True)
|
||||
>>> outputs.past_key_values # access cache filled with key/values from generation
|
||||
DynamicCache()
|
||||
>>> past_kv_length = outputs.past_key_values # access cache filled with key/values from generation
|
||||
```
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
@ -681,17 +680,16 @@ class QuantoQuantizedCache(QuantizedCache):
|
||||
>>> # Run pip install quanto first if you don't have it yet
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM, QuantoQuantizedCache, QuantizedCacheConfig
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("Qwen/Qwen2-0.5B-Instruct")
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("Qwen/Qwen2-0.5B-Instruct")
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("openai-community/gpt2")
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("openai-community/gpt2")
|
||||
|
||||
>>> inputs = tokenizer(text="My name is Qwen2", return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
>>> inputs = tokenizer(text="My name is GPT2", return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
|
||||
>>> # Prepare a cache class and pass it to model's forward
|
||||
>>> cache_config = QuantizedCacheConfig(nbits=4)
|
||||
>>> past_key_values = QuantoQuantizedCache(cache_config=cache_config)
|
||||
>>> outputs = model(**inputs, past_key_values=past_key_values, use_cache=True)
|
||||
>>> outputs.past_key_values # access cache filled with key/values from generation
|
||||
QuantoQuantizedCache()
|
||||
>>> past_kv_length = outputs.past_key_values # access cache filled with key/values from generation
|
||||
```
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
@ -741,17 +739,16 @@ class HQQQuantizedCache(QuantizedCache):
|
||||
>>> # Run pip install hqq first if you don't have it yet
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM, HQQQuantizedCache, QuantizedCacheConfig
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("Qwen/Qwen2-0.5B-Instruct")
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("Qwen/Qwen2-0.5B-Instruct")
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("openai-community/gpt2")
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("openai-community/gpt2")
|
||||
|
||||
>>> inputs = tokenizer(text="My name is Qwen2", return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
>>> inputs = tokenizer(text="My name is GPT2", return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
|
||||
>>> # Prepare a cache class and pass it to model's forward
|
||||
>>> cache_config = QuantizedCacheConfig(nbits=4, axis_key=1, axis_value=1)
|
||||
>>> past_key_values = HQQQuantizedCache(cache_config=cache_config)
|
||||
>>> outputs = model(**inputs, past_key_values=past_key_values, use_cache=True)
|
||||
>>> outputs.past_key_values # access cache filled with key/values from generation
|
||||
HQQQuantizedCache()
|
||||
>>> past_kv_length = outputs.past_key_values # access cache filled with key/values from generation
|
||||
```
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
@ -809,16 +806,15 @@ class SinkCache(Cache):
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM, SinkCache
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("Qwen/Qwen2-0.5B-Instruct")
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("Qwen/Qwen2-0.5B-Instruct")
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("openai-community/gpt2")
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("openai-community/gpt2")
|
||||
|
||||
>>> inputs = tokenizer(text="My name is Qwen2", return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
>>> inputs = tokenizer(text="My name is GPT2", return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
|
||||
>>> # Prepare a cache class and pass it to model's forward
|
||||
>>> past_key_values = SinkCache(window_length=256, num_sink_tokens=4)
|
||||
>>> outputs = model(**inputs, past_key_values=past_key_values, use_cache=True)
|
||||
>>> outputs.past_key_values # access cache filled with key/values from generation
|
||||
SinkCache()
|
||||
>>> past_kv_length = outputs.past_key_values # access cache filled with key/values from generation
|
||||
```
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
@ -996,18 +992,17 @@ class StaticCache(Cache):
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM, StaticCache
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-chat-hf")
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-chat-hf")
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("openai-community/gpt2")
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("openai-community/gpt2")
|
||||
|
||||
>>> inputs = tokenizer(text="My name is Llama", return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
>>> inputs = tokenizer(text="My name is GPT2", return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
|
||||
>>> # Prepare a cache class and pass it to model's forward
|
||||
>>> # Leave empty space for 10 new tokens, which can be used when calling forward iteratively 10 times to generate
|
||||
>>> max_generated_length = inputs.input_ids.shape[1] + 10
|
||||
>>> past_key_values = StaticCache(config=model.config, batch_size=1, max_cache_len=max_generated_length, device=model.device, dtype=model.dtype)
|
||||
>>> outputs = model(**inputs, past_key_values=past_key_values, use_cache=True)
|
||||
>>> outputs.past_key_values # access cache filled with key/values from generation
|
||||
StaticCache()
|
||||
>>> past_kv_length = outputs.past_key_values # access cache filled with key/values from generation
|
||||
```
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1030,7 +1025,6 @@ class StaticCache(Cache):
|
||||
|
||||
self.batch_size = batch_size or max_batch_size
|
||||
self.max_cache_len = config.max_position_embeddings if max_cache_len is None else max_cache_len
|
||||
|
||||
# Some model define a custom `head_dim` != config.hidden_size // config.num_attention_heads
|
||||
self.head_dim = (
|
||||
config.head_dim if hasattr(config, "head_dim") else config.hidden_size // config.num_attention_heads
|
||||
@ -1167,18 +1161,17 @@ class SlidingWindowCache(StaticCache):
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM, SlidingWindowCache
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.3")
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.3")
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("openai-community/gpt2")
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("openai-community/gpt2")
|
||||
|
||||
>>> inputs = tokenizer(text="My name is Mistral", return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
>>> inputs = tokenizer(text="My name is GPT2", return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
|
||||
>>> # Prepare a cache class and pass it to model's forward
|
||||
>>> # Leave empty space for 10 new tokens, which can be used when calling forward iteratively 10 times to generate
|
||||
>>> max_generated_length = inputs.input_ids.shape[1] + 10
|
||||
>>> past_key_values = SlidingWindowCache(config=model.config, batch_size=1, max_cache_len=max_generated_length, device=model.device, dtype=model.dtype)
|
||||
>>> outputs = model(**inputs, past_key_values=past_key_values, use_cache=True)
|
||||
>>> outputs.past_key_values # access cache filled with key/values from generation
|
||||
SlidingWindowCache()
|
||||
>>> past_kv_length = outputs.past_key_values # access cache filled with key/values from generation
|
||||
```
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1288,8 +1281,7 @@ class EncoderDecoderCache(Cache):
|
||||
>>> cross_attention_cache = DynamicCache()
|
||||
>>> past_key_values = EncoderDecoderCache(self_attention_cache, cross_attention_cache)
|
||||
>>> outputs = model(**inputs, past_key_values=past_key_values, use_cache=True)
|
||||
>>> outputs.past_key_values # access cache filled with key/values from generation
|
||||
EncoderDecoderCache()
|
||||
>>> past_kv_length = outputs.past_key_values # access cache filled with key/values from generation
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
@ -1461,8 +1453,8 @@ class HybridCache(Cache):
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM, HybridCache
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("google/gemma-2-2b")
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("google/gemma-2-2b")
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("google/gemma-2-9b")
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("google/gemma-2-9b")
|
||||
|
||||
>>> inputs = tokenizer(text="My name is Gemma", return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1471,8 +1463,7 @@ class HybridCache(Cache):
|
||||
>>> max_generated_length = inputs.input_ids.shape[1] + 10
|
||||
>>> past_key_values = HybridCache(config=model.config, batch_size=1, max_cache_len=max_generated_length, device=model.device, dtype=model.dtype)
|
||||
>>> outputs = model(**inputs, past_key_values=past_key_values, use_cache=True)
|
||||
>>> outputs.past_key_values # access cache filled with key/values from generation
|
||||
HybridCache()
|
||||
>>> past_kv_length = outputs.past_key_values # access cache filled with key/values from generation
|
||||
```
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1654,8 +1645,7 @@ class MambaCache:
|
||||
>>> # Prepare a cache class and pass it to model's forward
|
||||
>>> past_key_values = MambaCache(config=model.config, batch_size=1, device=model.device, dtype=model.dtype)
|
||||
>>> outputs = model(**inputs, past_key_values=past_key_values, use_cache=True)
|
||||
>>> outputs.past_key_values
|
||||
MambaCache()
|
||||
>>> past_kv = outputs.past_key_values
|
||||
```
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1718,275 +1708,3 @@ class MambaCache:
|
||||
def reset(self):
|
||||
self.conv_states.zero_()
|
||||
self.ssm_states.zero_()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class OffloadedStaticCache(StaticCache):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Static cache class to be used with `torch.compile(model)` that offloads to the CPU or
|
||||
another device.
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
config (`PretrainedConfig):
|
||||
The configuration file defining the shape-related attributes required to initialize
|
||||
the static cache.
|
||||
max_batch_size (`int`):
|
||||
The maximum batch size with which the model will be used.
|
||||
max_cache_len (`int`):
|
||||
The maximum sequence length with which the model will be used.
|
||||
device (`Union[str, torch.device]`):
|
||||
The device on which the cache should be initialized. Should be the same as the
|
||||
layer device.
|
||||
dtype (`torch.dtype`, *optional*):
|
||||
The default `dtype` to use when initializing the cache.
|
||||
offload_device (`Union[str, torch.device]`, *optional*, defaults to `cpu`):
|
||||
The device to offload to. Defaults to CPU.
|
||||
|
||||
Attributes:
|
||||
key_cache (`List[torch.Tensor]`):
|
||||
Off-loaded key cache tensors. First one will be on device, where-as the others are
|
||||
off-loaded.
|
||||
value_cache (`List[torch.Tensor]`):
|
||||
Off-loaded value cache tensors. First one will be on device, where-as the others are
|
||||
off-loaded.
|
||||
max_batch_size (`int`):
|
||||
The maximum batch size with which this cache can be used.
|
||||
max_cache_len (`int`):
|
||||
The maximum sequence length with which this cache can be used.
|
||||
device (`torch.device`):
|
||||
The device on which the cache is used.
|
||||
offload_device (`torch.device`):
|
||||
The device used to offload to.
|
||||
dtype (`torch.dtype`):
|
||||
The `dtype` used to initializing the cache.
|
||||
|
||||
Example:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM, OffloadedStaticCache
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("openai-community/gpt2")
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("openai-community/gpt2")
|
||||
|
||||
>>> inputs = tokenizer(text="My name is GPT2", return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
|
||||
>>> # Prepare a cache class and pass it to model's forward
|
||||
>>> # Leave empty space for 10 new tokens, which can be used when calling forward iteratively 10 times to generate
|
||||
>>> max_generated_length = inputs.input_ids.shape[1] + 10
|
||||
>>> past_key_values = OffloadedStaticCache(config=model.config, max_batch_size=1, max_cache_len=max_generated_length, device=model.device, dtype=model.dtype)
|
||||
>>> outputs = model(**inputs, past_key_values=past_key_values, use_cache=True)
|
||||
>>> past_kv_length = outputs.past_key_values # access cache filled with key/values from generation
|
||||
```
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
config: PretrainedConfig,
|
||||
max_batch_size: int,
|
||||
max_cache_len: Optional[int],
|
||||
device: Union[str, torch.device],
|
||||
dtype: Optional[torch.dtype] = None,
|
||||
offload_device: Union[str, torch.device] = torch.device("cpu"),
|
||||
) -> None:
|
||||
self.max_batch_size = max_batch_size
|
||||
self.max_cache_len = config.max_position_embeddings if max_cache_len is None else max_cache_len
|
||||
self.device = torch.device(device)
|
||||
self.offload_device = torch.device(offload_device)
|
||||
self.dtype = dtype if dtype is not None else torch.float32
|
||||
|
||||
# Some model define a custom `head_dim` != config.hidden_size // config.num_attention_heads
|
||||
head_dim = config.head_dim if hasattr(config, "head_dim") else config.hidden_size // config.num_attention_heads
|
||||
|
||||
num_key_value_heads = (
|
||||
config.num_attention_heads if config.num_key_value_heads is None else config.num_key_value_heads
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
cache_shape = (max_batch_size, num_key_value_heads, self.max_cache_len, head_dim)
|
||||
|
||||
# Create offloaded CPU tensors.
|
||||
self.key_cache: List[torch.Tensor] = []
|
||||
self.value_cache: List[torch.Tensor] = []
|
||||
|
||||
for i in range(config.num_hidden_layers):
|
||||
# First layer is always on-device.
|
||||
device = self.device if i == 0 else self.offload_device
|
||||
|
||||
key_cache, value_cache = self._create_key_value_cache_tensors(cache_shape, device)
|
||||
|
||||
self.key_cache.append(key_cache)
|
||||
self.value_cache.append(value_cache)
|
||||
|
||||
# Create device tensors.
|
||||
self._device_key_cache: List[torch.Tensor] = []
|
||||
self._device_value_cache: List[torch.Tensor] = []
|
||||
|
||||
for i in range(2):
|
||||
key_cache, value_cache = self._create_key_value_cache_tensors(cache_shape, self.device)
|
||||
|
||||
self._device_key_cache.append(key_cache)
|
||||
self._device_value_cache.append(value_cache)
|
||||
|
||||
# For backwards compatibility.
|
||||
# TODO(gante): Remove this.
|
||||
self._seen_tokens = 0
|
||||
|
||||
# Create new CUDA stream for parallel prefetching.
|
||||
self._prefetch_stream = torch.cuda.Stream() if self.device.type == "cuda" else None
|
||||
|
||||
def update(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
key_states: torch.Tensor,
|
||||
value_states: torch.Tensor,
|
||||
layer_idx: int,
|
||||
cache_kwargs: Optional[Dict[str, Any]] = None,
|
||||
) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Updates the cache with the new `key_states` and `value_states` for the layer `layer_idx`.
|
||||
It is VERY important to index using a tensor, otherwise you introduce a copy to the device.
|
||||
|
||||
Parameters:
|
||||
key_states (`torch.Tensor`):
|
||||
The new key states to cache.
|
||||
value_states (`torch.Tensor`):
|
||||
The new value states to cache.
|
||||
layer_idx (`int`):
|
||||
The index of the layer to cache the states for.
|
||||
cache_kwargs (`Dict[str, Any]`, *optional*):
|
||||
Additional arguments for the cache subclass. The `OffloadedStaticCache` needs the
|
||||
`cache_position` input to know how where to write in the cache.
|
||||
|
||||
Return:
|
||||
A tuple containing the updated key and value states.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
if layer_idx == 0:
|
||||
# Update seen tokens.
|
||||
# TODO(gante): Remove this.
|
||||
self._seen_tokens += key_states.shape[-2]
|
||||
|
||||
# Always there.
|
||||
k_out = self.key_cache[0]
|
||||
v_out = self.value_cache[0]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
# Wait for prefetch stream.
|
||||
if self._prefetch_stream is not None:
|
||||
torch.cuda.default_stream(self.device).wait_stream(self._prefetch_stream)
|
||||
|
||||
k_out = self._device_key_cache[layer_idx & 1]
|
||||
v_out = self._device_value_cache[layer_idx & 1]
|
||||
|
||||
self._prefetch_layer(layer_idx + 1)
|
||||
|
||||
cache_position = cache_kwargs.get("cache_position") if cache_kwargs is not None else None
|
||||
if cache_position is None:
|
||||
k_out.copy_(key_states)
|
||||
v_out.copy_(value_states)
|
||||
|
||||
# Copy the values to the offloaded device as well.
|
||||
if layer_idx == 0:
|
||||
self.key_cache[layer_idx].copy_(key_states.to(self.offload_device))
|
||||
self.value_cache[layer_idx].copy_(value_states.to(self.offload_device))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
# Note: here we use `tensor.index_copy_(dim, index, tensor)` that is equivalent to
|
||||
# `tensor[:, :, index] = tensor`, but the first one is compile-friendly and it does
|
||||
# explicitly an in-place operation, that avoids copies and uses less memory.
|
||||
try:
|
||||
k_out.index_copy_(2, cache_position, key_states)
|
||||
v_out.index_copy_(2, cache_position, value_states)
|
||||
except NotImplementedError:
|
||||
# The operator 'aten::index_copy.out' is not currently implemented for the MPS
|
||||
# device.
|
||||
k_out[:, :, cache_position] = key_states
|
||||
v_out[:, :, cache_position] = value_states
|
||||
|
||||
# Copy the values to the offloaded device as well.
|
||||
if layer_idx != 0:
|
||||
cache_position = cache_position.to(self.offload_device)
|
||||
key_states = key_states.to(self.offload_device)
|
||||
value_states = value_states.to(self.offload_device)
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
self.key_cache[layer_idx].index_copy_(2, cache_position, key_states)
|
||||
self.value_cache[layer_idx].index_copy_(2, cache_position, value_states)
|
||||
except NotImplementedError:
|
||||
# The operator 'aten::index_copy.out' is not currently implemented for the MPS
|
||||
# device.
|
||||
self.key_cache[layer_idx][:, :, cache_position] = key_states
|
||||
self.value_cache[layer_idx][:, :, cache_position] = value_states
|
||||
|
||||
return k_out, v_out
|
||||
|
||||
def get_seq_length(self, layer_idx: Optional[int] = 0) -> int:
|
||||
"""Returns the sequence length of the cached states that were seen by the model."""
|
||||
|
||||
# TODO(gante): Remove this.
|
||||
return self._seen_tokens
|
||||
|
||||
def get_max_length(self) -> Optional[int]:
|
||||
"""Returns the maximum sequence length of the cached states."""
|
||||
|
||||
return self.max_cache_len
|
||||
|
||||
def reset(self) -> None:
|
||||
"""Resets the cache values while preserving the objects."""
|
||||
|
||||
# For backwards compatibility.
|
||||
# TODO(gante): Remove this.
|
||||
self._seen_tokens = 0
|
||||
|
||||
# Zero out cache.
|
||||
for layer_idx in range(len(self.key_cache)):
|
||||
# In-place ops prevent breaking the static address.
|
||||
self.key_cache[layer_idx].zero_()
|
||||
self.value_cache[layer_idx].zero_()
|
||||
|
||||
@property
|
||||
def seen_tokens(self) -> int:
|
||||
# For backwards compatibility.
|
||||
# TODO(gante): Remove this.
|
||||
return self._seen_tokens
|
||||
|
||||
def _create_key_value_cache_tensors(
|
||||
self, shape: Tuple[int, ...], device: torch.device
|
||||
) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]:
|
||||
"""Creates K/V cache tensors on a device. Pins memory for CPU tensors. Marks them as static
|
||||
addresses for non-CPU tensors.
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
shape (`Tuple[int, ...]`): Shape.
|
||||
device (`torch.device`): Device.
|
||||
|
||||
Returns:
|
||||
Key and value cache tensors as a tuple.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
is_cpu_device = device == torch.device("cpu")
|
||||
|
||||
key_cache = torch.zeros(shape, dtype=self.dtype, device=device, pin_memory=is_cpu_device)
|
||||
value_cache = torch.zeros(shape, dtype=self.dtype, device=device, pin_memory=is_cpu_device)
|
||||
|
||||
# Note: `mark_static_address` is used to tag the cache as a fixed data pointer,
|
||||
# preventing compiled graph breaks when updating the cache.
|
||||
torch._dynamo.mark_static_address(key_cache)
|
||||
torch._dynamo.mark_static_address(value_cache)
|
||||
|
||||
return key_cache, value_cache
|
||||
|
||||
def _prefetch_layer(self, layer_idx: int) -> None:
|
||||
"""Prefetch a layer to the device. Needs to be called in order of layer indices."""
|
||||
|
||||
# Don't fetch layers that do not exist.
|
||||
if layer_idx >= len(self.key_cache):
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
||||
# Alternate between two on-device caches.
|
||||
if self._prefetch_stream is not None:
|
||||
with torch.cuda.stream(self._prefetch_stream):
|
||||
self._prefetch_layer_in_context(layer_idx)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self._prefetch_layer_in_context(layer_idx)
|
||||
|
||||
def _prefetch_layer_in_context(self, layer_idx: int) -> None:
|
||||
"""Performs the actual copy of the layer to device cache."""
|
||||
|
||||
self._device_key_cache[layer_idx & 1].copy_(self.key_cache[layer_idx], non_blocking=True)
|
||||
self._device_value_cache[layer_idx & 1].copy_(self.value_cache[layer_idx], non_blocking=True)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1019,17 +1019,17 @@ class PretrainedConfig(PushToHubMixin):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
non_default_generation_parameters = {}
|
||||
decoder_attribute_name = None
|
||||
default_config = None
|
||||
|
||||
# Composite models don't have a default config, use their decoder config as a fallback for default values
|
||||
# If no known pattern is matched, then `default_config = None` -> check against the global generation defaults
|
||||
try:
|
||||
default_config = self.__class__()
|
||||
except ValueError:
|
||||
decoder_config = self.get_text_config(decoder=True)
|
||||
if decoder_config is not self:
|
||||
default_config = decoder_config.__class__()
|
||||
else:
|
||||
decoder_config = None
|
||||
for decoder_attribute_name in ("decoder", "generator", "text_config"):
|
||||
if hasattr(self, decoder_attribute_name):
|
||||
default_config = getattr(self, decoder_attribute_name).__class__()
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
# If it is a composite model, we want to check the subconfig that will be used for generation
|
||||
self_decoder_config = self if decoder_attribute_name is None else getattr(self, decoder_attribute_name)
|
||||
@ -1057,36 +1057,6 @@ class PretrainedConfig(PushToHubMixin):
|
||||
|
||||
return non_default_generation_parameters
|
||||
|
||||
def get_text_config(self, decoder=False) -> "PretrainedConfig":
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Returns the config that is meant to be used with text IO. On most models, it is the original config instance
|
||||
itself. On specific composite models, it is under a set of valid names.
|
||||
|
||||
If `decoder` is set to `True`, then only search for decoder config names.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
decoder_possible_text_config_names = ("decoder", "generator", "text_config")
|
||||
encoder_possible_text_config_names = ("text_encoder",)
|
||||
if decoder:
|
||||
possible_text_config_names = decoder_possible_text_config_names
|
||||
else:
|
||||
possible_text_config_names = encoder_possible_text_config_names + decoder_possible_text_config_names
|
||||
|
||||
valid_text_config_names = []
|
||||
for text_config_name in possible_text_config_names:
|
||||
if hasattr(self, text_config_name):
|
||||
text_config = getattr(self, text_config_name, None)
|
||||
if text_config is not None:
|
||||
valid_text_config_names += [text_config_name]
|
||||
|
||||
if len(valid_text_config_names) > 1:
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
f"Multiple valid text configs were found in the model config: {valid_text_config_names}. In this "
|
||||
"case, using `get_text_config()` would be ambiguous. Please specify the desied text config directly."
|
||||
)
|
||||
elif len(valid_text_config_names) == 1:
|
||||
return getattr(self, valid_text_config_names[0])
|
||||
return self
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def get_configuration_file(configuration_files: List[str]) -> str:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
@ -153,7 +153,7 @@ def torch_default_data_collator(features: List[InputDataClass]) -> Dict[str, Any
|
||||
if isinstance(v, torch.Tensor):
|
||||
batch[k] = torch.stack([f[k] for f in features])
|
||||
elif isinstance(v, np.ndarray):
|
||||
batch[k] = torch.from_numpy(np.stack([f[k] for f in features]))
|
||||
batch[k] = torch.tensor(np.stack([f[k] for f in features]))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
batch[k] = torch.tensor([f[k] for f in features])
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1619,24 +1619,20 @@ class DataCollatorWithFlattening(DefaultDataCollator):
|
||||
Data collator used for padding free approach. Does the following:
|
||||
|
||||
- concatate the entire mini batch into single long sequence [1, total_tokens]
|
||||
- uses `separator_id` to separate sequences within the concatenated `labels`, default value is -100
|
||||
- no padding will be added, returns `input_ids`, `labels` and `position_ids`
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, *args, return_position_ids=True, separator_id=-100, **kwargs):
|
||||
def __init__(self, *args, return_position_ids=True, **kwargs):
|
||||
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
|
||||
self.return_position_ids = return_position_ids
|
||||
self.separator_id = separator_id
|
||||
warnings.warn(
|
||||
"Using `DataCollatorWithFlattening` will flatten the entire mini batch into single long sequence."
|
||||
"Make sure your attention computation is able to handle it!"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def __call__(self, features, return_tensors=None, separator_id=None):
|
||||
def __call__(self, features, return_tensors=None):
|
||||
if return_tensors is None:
|
||||
return_tensors = self.return_tensors
|
||||
if separator_id is None:
|
||||
separator_id = self.separator_id
|
||||
is_labels_provided = "labels" in features[0]
|
||||
ret = {"input_ids": [], "labels": []}
|
||||
if self.return_position_ids:
|
||||
@ -1644,9 +1640,9 @@ class DataCollatorWithFlattening(DefaultDataCollator):
|
||||
for idx in range(0, len(features)):
|
||||
ret["input_ids"] += features[idx]["input_ids"]
|
||||
if is_labels_provided:
|
||||
ret["labels"] += [separator_id] + features[idx]["labels"][1:]
|
||||
ret["labels"] += [-100] + features[idx]["labels"][1:]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
ret["labels"] += [separator_id] + features[idx]["input_ids"][1:]
|
||||
ret["labels"] += [-100] + features[idx]["input_ids"][1:]
|
||||
if self.return_position_ids:
|
||||
ret["position_ids"] += list(range(len(features[idx]["input_ids"])))
|
||||
return default_data_collator([ret], return_tensors)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -36,7 +36,7 @@ deps = {
|
||||
"keras": "keras>2.9,<2.16",
|
||||
"keras-nlp": "keras-nlp>=0.3.1,<0.14.0",
|
||||
"librosa": "librosa",
|
||||
"nltk": "nltk<=3.8.1",
|
||||
"nltk": "nltk",
|
||||
"natten": "natten>=0.14.6,<0.15.0",
|
||||
"numpy": "numpy>=1.17",
|
||||
"onnxconverter-common": "onnxconverter-common",
|
||||
|
||||
@ -146,10 +146,7 @@ class BatchFeature(UserDict):
|
||||
and isinstance(value[0][0], np.ndarray)
|
||||
):
|
||||
value = np.array(value)
|
||||
if isinstance(value, np.ndarray):
|
||||
return torch.from_numpy(value)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return torch.tensor(value)
|
||||
return torch.tensor(value)
|
||||
|
||||
is_tensor = torch.is_tensor
|
||||
elif tensor_type == TensorType.JAX:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -43,34 +43,11 @@ if TYPE_CHECKING:
|
||||
logger = logging.get_logger(__name__)
|
||||
METADATA_FIELDS = ("_from_model_config", "_commit_hash", "_original_object_hash", "transformers_version")
|
||||
NEEDS_CACHE_CONFIG = {}
|
||||
NEED_SETUP_CACHE_CLASSES_MAPPING = {}
|
||||
QUANT_BACKEND_CLASSES_MAPPING = {}
|
||||
ALL_CACHE_IMPLEMENTATIONS = []
|
||||
|
||||
if is_torch_available():
|
||||
from ..cache_utils import (
|
||||
HQQQuantizedCache,
|
||||
HybridCache,
|
||||
MambaCache,
|
||||
OffloadedStaticCache,
|
||||
QuantizedCacheConfig,
|
||||
QuantoQuantizedCache,
|
||||
SlidingWindowCache,
|
||||
StaticCache,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from ..cache_utils import QuantizedCacheConfig
|
||||
|
||||
NEEDS_CACHE_CONFIG["quantized"] = QuantizedCacheConfig
|
||||
NEED_SETUP_CACHE_CLASSES_MAPPING = {
|
||||
"static": StaticCache,
|
||||
"offloaded_static": OffloadedStaticCache,
|
||||
"sliding_window": SlidingWindowCache,
|
||||
"hybrid": HybridCache,
|
||||
"mamba": MambaCache,
|
||||
}
|
||||
QUANT_BACKEND_CLASSES_MAPPING = {"quanto": QuantoQuantizedCache, "HQQ": HQQQuantizedCache}
|
||||
ALL_CACHE_IMPLEMENTATIONS = list(NEED_SETUP_CACHE_CLASSES_MAPPING.keys()) + list(
|
||||
QUANT_BACKEND_CLASSES_MAPPING.keys()
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class GenerationMode(ExplicitEnum):
|
||||
@ -93,7 +70,7 @@ class GenerationMode(ExplicitEnum):
|
||||
|
||||
class GenerationConfig(PushToHubMixin):
|
||||
# no-format
|
||||
rf"""
|
||||
r"""
|
||||
Class that holds a configuration for a generation task. A `generate` call supports the following generation methods
|
||||
for text-decoder, text-to-text, speech-to-text, and vision-to-text models:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -169,10 +146,7 @@ class GenerationConfig(PushToHubMixin):
|
||||
Whether or not the model should use the past last key/values attentions (if applicable to the model) to
|
||||
speed up decoding.
|
||||
cache_implementation (`str`, *optional*, default to `None`):
|
||||
Name of the cache class that will be instantiated in `generate`, for faster decoding. Possible values are:
|
||||
{ALL_CACHE_IMPLEMENTATIONS}. We support other cache types, but they must be manually instantiated and
|
||||
passed to `generate` through the `past_key_values` argument. See our
|
||||
[cache documentation](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/en/kv_cache) for further information.
|
||||
Cache class that should be used when generating.
|
||||
cache_config (`CacheConfig` or `dict`, *optional*, default to `None`):
|
||||
Arguments used in the key-value cache class can be passed in `cache_config`. Can be passed as a `Dict` and
|
||||
it will be converted to its repsective `CacheConfig` internally.
|
||||
@ -314,9 +288,7 @@ class GenerationConfig(PushToHubMixin):
|
||||
Whether or not to return the unprocessed prediction logit scores. See `logits` under returned tensors for
|
||||
more details.
|
||||
return_dict_in_generate (`bool`, *optional*, defaults to `False`):
|
||||
Whether or not to return a [`~utils.ModelOutput`], as opposed to returning exclusively the generated
|
||||
sequence. This flag must be set to `True` to return the generation cache (when `use_cache` is `True`)
|
||||
or optional outputs (see flags starting with `output_`)
|
||||
Whether or not to return a [`~utils.ModelOutput`] instead of a plain tuple.
|
||||
|
||||
> Special tokens that can be used at generation time
|
||||
|
||||
@ -362,8 +334,6 @@ class GenerationConfig(PushToHubMixin):
|
||||
present in `generate`'s signature will be used in the model forward pass.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
extra_output_flags = ("output_attentions", "output_hidden_states", "output_scores", "output_logits")
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, **kwargs):
|
||||
# Parameters that control the length of the output
|
||||
self.max_length = kwargs.pop("max_length", 20)
|
||||
@ -725,11 +695,6 @@ class GenerationConfig(PushToHubMixin):
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# 5. check cache-related arguments
|
||||
if self.cache_implementation is not None and self.cache_implementation not in ALL_CACHE_IMPLEMENTATIONS:
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
f"Invalid `cache_implementation` ({self.cache_implementation}). Choose one of: "
|
||||
f"{ALL_CACHE_IMPLEMENTATIONS}"
|
||||
)
|
||||
if self.cache_config is not None:
|
||||
cache_class = NEEDS_CACHE_CONFIG.get(self.cache_implementation)
|
||||
if cache_class is None:
|
||||
@ -762,17 +727,7 @@ class GenerationConfig(PushToHubMixin):
|
||||
self.watermarking_config = WatermarkingConfig.from_dict(self.watermarking_config)
|
||||
self.watermarking_config.validate()
|
||||
|
||||
# 7. other incorrect combinations
|
||||
if self.return_dict_in_generate is not True:
|
||||
for extra_output_flag in self.extra_output_flags:
|
||||
if getattr(self, extra_output_flag) is True:
|
||||
warnings.warn(
|
||||
f"`return_dict_in_generate` is NOT set to `True`, but `{extra_output_flag}` is. When "
|
||||
f"`return_dict_in_generate` is not `True`, `{extra_output_flag}` is ignored.",
|
||||
UserWarning,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# 8. check common issue: passing `generate` arguments inside the generation config
|
||||
# 7. check common issue: passing `generate` arguments inside the generation config
|
||||
generate_arguments = (
|
||||
"logits_processor",
|
||||
"stopping_criteria",
|
||||
@ -831,8 +786,7 @@ class GenerationConfig(PushToHubMixin):
|
||||
|
||||
if use_auth_token is not None:
|
||||
warnings.warn(
|
||||
"The `use_auth_token` argument is deprecated and will be removed in v5 of Transformers. "
|
||||
"Please use `token` instead.",
|
||||
"The `use_auth_token` argument is deprecated and will be removed in v5 of Transformers. Please use `token` instead.",
|
||||
FutureWarning,
|
||||
)
|
||||
if kwargs.get("token", None) is not None:
|
||||
@ -1223,30 +1177,20 @@ class GenerationConfig(PushToHubMixin):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
config_dict = model_config.to_dict()
|
||||
config_dict.pop("_from_model_config", None)
|
||||
generation_config = cls.from_dict(config_dict, return_unused_kwargs=False, _from_model_config=True)
|
||||
config = cls.from_dict(config_dict, return_unused_kwargs=False, _from_model_config=True)
|
||||
|
||||
# Special case: some models have generation attributes set in the decoder. Use them if still unset in the
|
||||
# generation config (which in turn is defined from the outer attributes of model config).
|
||||
decoder_config = model_config.get_text_config(decoder=True)
|
||||
if decoder_config is not model_config:
|
||||
default_generation_config = GenerationConfig()
|
||||
decoder_config_dict = decoder_config.to_dict()
|
||||
for attr in generation_config.to_dict().keys():
|
||||
is_unset = getattr(generation_config, attr) == getattr(default_generation_config, attr)
|
||||
if attr in decoder_config_dict and is_unset:
|
||||
setattr(generation_config, attr, decoder_config_dict[attr])
|
||||
# generation config.
|
||||
for decoder_name in ("decoder", "generator", "text_config"):
|
||||
if decoder_name in config_dict:
|
||||
default_generation_config = GenerationConfig()
|
||||
decoder_config = config_dict[decoder_name]
|
||||
for attr in config.to_dict().keys():
|
||||
if attr in decoder_config and getattr(config, attr) == getattr(default_generation_config, attr):
|
||||
setattr(config, attr, decoder_config[attr])
|
||||
|
||||
# If any `output_...` flag is set to `True`, we ensure `return_dict_in_generate` is set to `True`.
|
||||
if generation_config.return_dict_in_generate is False:
|
||||
if any(
|
||||
getattr(generation_config, extra_output_flag, False)
|
||||
for extra_output_flag in generation_config.extra_output_flags
|
||||
):
|
||||
generation_config.return_dict_in_generate = True
|
||||
|
||||
# Hash to detect whether the instance was modified
|
||||
generation_config._original_object_hash = hash(generation_config)
|
||||
return generation_config
|
||||
config._original_object_hash = hash(config) # Hash to detect whether the instance was modified
|
||||
return config
|
||||
|
||||
def update(self, **kwargs):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
@ -348,14 +348,7 @@ class StopStringCriteria(StoppingCriteria):
|
||||
# we need a fallback to handle this case
|
||||
max_valid_positions = max(all_valid_positions) if all_valid_positions else 1
|
||||
# There should always be at least one valid end_len, however, so no fallback needed here
|
||||
valid_end_lens = [len(val) for positions in token_end_overlaps.values() for val in positions.values()]
|
||||
if not valid_end_lens:
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
"Stop string preprocessing was unable to identify tokens matching one or more of the "
|
||||
"supplied stop string(s). This is most often caused by the stop "
|
||||
"strings containing unusual characters that are not in the tokenizer vocabulary."
|
||||
)
|
||||
max_valid_end_lens = max(valid_end_lens)
|
||||
max_valid_end_lens = max(len(val) for positions in token_end_overlaps.values() for val in positions.values())
|
||||
vec_size = len(stop_strings) * (max_valid_positions + max_valid_end_lens) + 1
|
||||
gather_vec = np.full((len(token_list), vec_size), dtype=np.int32, fill_value=-1)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -29,8 +29,14 @@ from ..cache_utils import (
|
||||
Cache,
|
||||
DynamicCache,
|
||||
EncoderDecoderCache,
|
||||
HQQQuantizedCache,
|
||||
HybridCache,
|
||||
MambaCache,
|
||||
OffloadedCache,
|
||||
QuantizedCacheConfig,
|
||||
QuantoQuantizedCache,
|
||||
SlidingWindowCache,
|
||||
StaticCache,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from ..integrations.deepspeed import is_deepspeed_zero3_enabled
|
||||
from ..modeling_outputs import CausalLMOutputWithPast, Seq2SeqLMOutput
|
||||
@ -61,12 +67,7 @@ from .candidate_generator import (
|
||||
_prepare_attention_mask,
|
||||
_prepare_token_type_ids,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from .configuration_utils import (
|
||||
NEED_SETUP_CACHE_CLASSES_MAPPING,
|
||||
QUANT_BACKEND_CLASSES_MAPPING,
|
||||
GenerationConfig,
|
||||
GenerationMode,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from .configuration_utils import GenerationConfig, GenerationMode
|
||||
from .logits_process import (
|
||||
EncoderNoRepeatNGramLogitsProcessor,
|
||||
EncoderRepetitionPenaltyLogitsProcessor,
|
||||
@ -116,6 +117,14 @@ logger = logging.get_logger(__name__)
|
||||
if is_accelerate_available():
|
||||
from accelerate.hooks import AlignDevicesHook, add_hook_to_module
|
||||
|
||||
NEED_SETUP_CACHE_CLASSES_MAPPING = {
|
||||
"static": StaticCache,
|
||||
"sliding_window": SlidingWindowCache,
|
||||
"hybrid": HybridCache,
|
||||
"mamba": MambaCache,
|
||||
}
|
||||
QUANT_BACKEND_CLASSES_MAPPING = {"quanto": QuantoQuantizedCache, "HQQ": HQQQuantizedCache}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@dataclass
|
||||
class GenerateDecoderOnlyOutput(ModelOutput):
|
||||
@ -1439,8 +1448,8 @@ class GenerationMixin:
|
||||
cache_dtype = self.get_output_embeddings().weight.dtype
|
||||
|
||||
cache_kwargs = {
|
||||
"config": self.config if hasattr(self.config, "text_config") else self.config,
|
||||
"max_batch_size": batch_size,
|
||||
"config": self.config,
|
||||
"batch_size": batch_size,
|
||||
"max_cache_len": max_cache_len,
|
||||
"device": device,
|
||||
"dtype": cache_dtype,
|
||||
@ -1470,7 +1479,6 @@ class GenerationMixin:
|
||||
model_kwargs: Dict,
|
||||
assistant_model: "PreTrainedModel",
|
||||
batch_size: int,
|
||||
max_cache_length: int,
|
||||
device: torch.device,
|
||||
) -> bool:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
@ -1537,8 +1545,8 @@ class GenerationMixin:
|
||||
)
|
||||
model_kwargs[cache_name] = self._get_cache(
|
||||
cache_implementation=generation_config.cache_implementation,
|
||||
batch_size=max(generation_config.num_beams, generation_config.num_return_sequences) * batch_size,
|
||||
max_cache_len=max_cache_length,
|
||||
batch_size=generation_config.num_beams * generation_config.num_return_sequences * batch_size,
|
||||
max_cache_len=generation_config.max_length,
|
||||
device=device,
|
||||
model_kwargs=model_kwargs,
|
||||
)
|
||||
@ -1878,16 +1886,7 @@ class GenerationMixin:
|
||||
# TODO (joao): remove `user_defined_cache` after v4.47 (remove default conversion to legacy format)
|
||||
cache_name = "past_key_values" if "mamba" not in self.__class__.__name__.lower() else "cache_params"
|
||||
user_defined_cache = model_kwargs.get(cache_name)
|
||||
max_cache_length = generation_config.max_length
|
||||
if (
|
||||
inputs_tensor.shape[1] != input_ids_length
|
||||
and model_input_name == "inputs_embeds"
|
||||
and not self.config.is_encoder_decoder
|
||||
):
|
||||
max_cache_length += inputs_tensor.shape[1]
|
||||
self._prepare_cache_for_generation(
|
||||
generation_config, model_kwargs, assistant_model, batch_size, max_cache_length, device
|
||||
)
|
||||
self._prepare_cache_for_generation(generation_config, model_kwargs, assistant_model, batch_size, device)
|
||||
|
||||
# 8. determine generation mode
|
||||
generation_mode = generation_config.get_generation_mode(assistant_model)
|
||||
@ -1935,8 +1934,8 @@ class GenerationMixin:
|
||||
raise ValueError("assisted generate is only supported for batch_size = 1")
|
||||
if not model_kwargs["use_cache"]:
|
||||
raise ValueError("assisted generate requires `use_cache=True`")
|
||||
if generation_config.cache_implementation in ["static", "hybrid", "sliding_window"]:
|
||||
raise ValueError("assisted generate is not supported with Static cache classes`")
|
||||
if generation_config.cache_implementation == "static":
|
||||
raise ValueError("assisted generate is not supported with `static_cache`")
|
||||
if self._is_stateful:
|
||||
# In assisted generation we need the ability to confirm whether the model would pick certain tokens,
|
||||
# which is not possible with stateful models (they can't reset to a previous subset of generated text)
|
||||
@ -2352,11 +2351,7 @@ class GenerationMixin:
|
||||
this_peer_finished = False
|
||||
|
||||
# prepare layers for DoLa decoding
|
||||
final_layer = (
|
||||
self.config.text_config.num_hidden_layers
|
||||
if hasattr(self.config, "text_config")
|
||||
else self.config.num_hidden_layers
|
||||
)
|
||||
final_layer = self.config.num_hidden_layers
|
||||
# if the model has tied word embeddings, we skip the word embeddings (0-th) layer and start from the 2nd layer,
|
||||
# as the early exit from word embeddings will become identity function
|
||||
# if the model is really shallow (<=2 layers), we use the 1st layer if it's not the final layer and the 0-th
|
||||
@ -3967,7 +3962,6 @@ class GenerationMixin:
|
||||
|
||||
# 1. Fetch candidate sequences from a `CandidateGenerator`
|
||||
candidate_input_ids, candidate_logits = candidate_generator.get_candidates(input_ids)
|
||||
candidate_input_ids = candidate_input_ids.to(self.device)
|
||||
if candidate_logits is not None:
|
||||
candidate_logits = candidate_logits.to(self.device)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -579,15 +579,9 @@ class ImageFeatureExtractionMixin:
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
if not isinstance(mean, torch.Tensor):
|
||||
if isinstance(mean, np.ndarray):
|
||||
mean = torch.from_numpy(mean)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
mean = torch.tensor(mean)
|
||||
mean = torch.tensor(mean)
|
||||
if not isinstance(std, torch.Tensor):
|
||||
if isinstance(std, np.ndarray):
|
||||
std = torch.from_numpy(std)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
std = torch.tensor(std)
|
||||
std = torch.tensor(std)
|
||||
|
||||
if image.ndim == 3 and image.shape[0] in [1, 3]:
|
||||
return (image - mean[:, None, None]) / std[:, None, None]
|
||||
|
||||
@ -209,7 +209,10 @@ def get_modules_to_fuse(model, quantization_config):
|
||||
current_fused_mapping = AWQ_FUSED_MAPPINGS[model.config.model_type]
|
||||
|
||||
# Properly deal with the case where we have a multi-modal model as well (e.g. Llava)
|
||||
config = model.config.get_text_config(decoder=True)
|
||||
if not hasattr(model.config, "text_config"):
|
||||
config = model.config
|
||||
else:
|
||||
config = model.config.text_config
|
||||
|
||||
# Handle hidden_size, num_attention_heads, num_key_value_heads on our own.
|
||||
hidden_size = config.hidden_size
|
||||
@ -342,8 +345,11 @@ def _fuse_awq_mlp(model, current_module_name, fuse_module_names, module, target_
|
||||
previous_device = gate_proj.qweight.device
|
||||
|
||||
# Deal also with the case model has `text_config` attribute
|
||||
config = model.config.get_text_config(decoder=True)
|
||||
hidden_act = config.hidden_act
|
||||
hidden_act = (
|
||||
model.config.hidden_act
|
||||
if not hasattr(model.config, "text_config")
|
||||
else model.config.text_config.hidden_act
|
||||
)
|
||||
activation_fn = ACT2FN[hidden_act]
|
||||
new_module = target_cls(gate_proj, down_proj, up_proj, activation_fn)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -33,6 +33,44 @@ from ..utils.logging import tqdm
|
||||
logger = logging.get_logger(__name__)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Listed here: https://github.com/ggerganov/ggml/blob/master/docs/gguf.md
|
||||
GGML_TYPES = {
|
||||
"F32": 0,
|
||||
"F16": 1,
|
||||
"Q4_0": 2,
|
||||
"Q8_0": 8,
|
||||
"Q2_K": 10,
|
||||
"Q3_K": 11,
|
||||
"Q4_K": 12,
|
||||
"Q5_K": 13,
|
||||
"Q6_K": 14,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# The Blocksizes are reported in bytes
|
||||
# Check out: https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp/blob/8a56075b07a8b571bf95a912ffdce4c928c2b414/gguf-py/gguf/constants.py#L801
|
||||
GGML_BLOCK_SIZES = {
|
||||
"Q8_0": 2 + 32, # Q8_0 uses a blocksize of 32 (int8 tensors) + 2 bytes allocated for the scales
|
||||
"Q4_K": 144,
|
||||
# Q4_0 uses a blocksize of 32 but the 4-bit tensors are packed into 8-bit tensors + 2 bytes for the scales
|
||||
"Q4_0": 2 + 16,
|
||||
"Q6_K": 210,
|
||||
# See: https://github.com/99991/pygguf/commit/a417edbfc029a1bc270f984a694f9128c5afa8b9
|
||||
"Q2_K": 256 // 16 + 256 // 4 + 2 + 2,
|
||||
"Q3_K": 256 // 8 + 256 // 4 + 12 + 2,
|
||||
"Q5_K": 2 + 2 + 12 + 256 // 8 + 256 // 2,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# Listed here: https://github.com/ggerganov/ggml/blob/master/docs/gguf.md
|
||||
DATA_TYPES = {
|
||||
"uint32": 4,
|
||||
"int32": 5,
|
||||
"float32": 6,
|
||||
"bool": 7,
|
||||
"string": 8,
|
||||
"array": 9,
|
||||
"uint64": 10,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
GGUF_TENSOR_MAPPING = {
|
||||
"llama": {
|
||||
"token_embd": "model.embed_tokens",
|
||||
@ -79,21 +117,6 @@ GGUF_TENSOR_MAPPING = {
|
||||
"output.weight": "lm_head.weight",
|
||||
"output_norm": "model.norm",
|
||||
},
|
||||
"qwen2moe": {
|
||||
"token_embd": "model.embed_tokens",
|
||||
"blk": "model.layers",
|
||||
"ffn_up": "mlp.up_proj",
|
||||
"ffn_down": "mlp.down_proj",
|
||||
"ffn_gate": "mlp.gate_proj",
|
||||
"ffn_norm": "post_attention_layernorm",
|
||||
"attn_norm": "input_layernorm",
|
||||
"attn_q": "self_attn.q_proj",
|
||||
"attn_v": "self_attn.v_proj",
|
||||
"attn_k": "self_attn.k_proj",
|
||||
"attn_output": "self_attn.o_proj",
|
||||
"output.weight": "lm_head.weight",
|
||||
"output_norm": "model.norm",
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -138,18 +161,6 @@ GGUF_CONFIG_MAPPING = {
|
||||
"attention.layer_norm_rms_epsilon": "rms_norm_eps",
|
||||
"vocab_size": "vocab_size",
|
||||
},
|
||||
"qwen2moe": {
|
||||
"context_length": "max_position_embeddings",
|
||||
"block_count": "num_hidden_layers",
|
||||
"feed_forward_length": "intermediate_size",
|
||||
"embedding_length": "hidden_size",
|
||||
"rope.dimension_count": None,
|
||||
"rope.freq_base": "rope_theta",
|
||||
"attention.head_count": "num_attention_heads",
|
||||
"attention.head_count_kv": "num_key_value_heads",
|
||||
"attention.layer_norm_rms_epsilon": "rms_norm_eps",
|
||||
"vocab_size": "vocab_size",
|
||||
},
|
||||
"tokenizer": {
|
||||
"ggml.bos_token_id": "bos_token_id",
|
||||
"ggml.eos_token_id": "eos_token_id",
|
||||
@ -206,6 +217,303 @@ def _gguf_parse_value(_value, data_type):
|
||||
return _value
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def dequantize_q4_k(data, n_bytes: int):
|
||||
# C implementation
|
||||
# https://github.com/ggerganov/ggml/blob/fca1caafea7de9fbd7efc733b9818f9cf2da3050/src/ggml-quants.c#L1929
|
||||
# C struct definition
|
||||
# https://github.com/ggerganov/ggml/blob/fca1caafea7de9fbd7efc733b9818f9cf2da3050/src/ggml-quants.h#L116
|
||||
block_size = GGML_BLOCK_SIZES["Q4_K"]
|
||||
num_blocks = n_bytes // block_size
|
||||
|
||||
data_f16 = np.frombuffer(data, dtype=np.float16).reshape(num_blocks, block_size // 2)
|
||||
data_u8 = np.frombuffer(data, dtype=np.uint8).reshape(num_blocks, block_size)
|
||||
|
||||
# Casting to float32 because float16 is very slow on CPU
|
||||
scale_factors = data_f16[:, 0].reshape(num_blocks, 1, 1).astype(np.float32)
|
||||
scale_offsets = data_f16[:, 1].reshape(num_blocks, 1, 1).astype(np.float32)
|
||||
qs1 = data_u8[:, 4:16].reshape(num_blocks, 12, 1)
|
||||
qs2 = data_u8[:, 16:].reshape(num_blocks, 4, 32)
|
||||
|
||||
# Dequantize scales and offsets (6 bits and 4 + 2 bits)
|
||||
factors = scale_factors * np.concatenate(
|
||||
[qs1[:, 0:4] & 0b111111, (qs1[:, 8:] & 15) | ((qs1[:, 0:4] >> 6) << 4)], axis=1
|
||||
)
|
||||
offsets = scale_offsets * np.concatenate(
|
||||
[qs1[:, 4:8] & 0b111111, (qs1[:, 8:] >> 4) | ((qs1[:, 4:8] >> 6) << 4)], axis=1
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Interleave low and high quantized bits
|
||||
qs2 = np.stack([qs2 & 0xF, qs2 >> 4], axis=2).reshape(num_blocks, 8, 32)
|
||||
# Dequantize final weights using scales and offsets
|
||||
return factors * qs2 - offsets
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def dequantize_q4_0(data, n_bytes: int):
|
||||
# C implementation
|
||||
# https://github.com/ggerganov/ggml/blob/fca1caafea7de9fbd7efc733b9818f9cf2da3050/src/ggml-quants.c#L1086
|
||||
# C struct definition
|
||||
# https://github.com/ggerganov/ggml/blob/fca1caafea7de9fbd7efc733b9818f9cf2da3050/src/ggml-quants.h#L11
|
||||
block_size = GGML_BLOCK_SIZES["Q4_0"]
|
||||
num_blocks = n_bytes // block_size
|
||||
|
||||
data_f16 = np.frombuffer(data, dtype=np.float16).reshape(num_blocks, block_size // 2)
|
||||
data_u8 = np.frombuffer(data, dtype=np.uint8).reshape(num_blocks, block_size)
|
||||
|
||||
# The scales are stored on the first 2 bytes and the rest corresponds to the quants
|
||||
scales = data_f16[:, 0].reshape(num_blocks, 1).astype(np.float32)
|
||||
# scales = np.nan_to_num(scales)
|
||||
# the rest of the bytes corresponds to the quants - we discard the first two bytes
|
||||
quants = data_u8[:, 2:]
|
||||
|
||||
ql = (quants[:, :] & 0xF).astype(np.int8) - 8
|
||||
qr = (quants[:, :] >> 4).astype(np.int8) - 8
|
||||
|
||||
# Use hstack
|
||||
quants = np.hstack([ql, qr])
|
||||
|
||||
return (scales * quants).astype(np.float32)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def dequantize_q6_k(data, n_bytes: int):
|
||||
# C implementation
|
||||
# https://github.com/ggerganov/ggml/blob/fca1caafea7de9fbd7efc733b9818f9cf2da3050/src/ggml-quants.c#L2275
|
||||
# C struct definition
|
||||
# https://github.com/ggerganov/ggml/blob/fca1caafea7de9fbd7efc733b9818f9cf2da3050/src/ggml-quants.h#L152
|
||||
block_size = GGML_BLOCK_SIZES["Q6_K"]
|
||||
num_blocks = n_bytes // block_size
|
||||
|
||||
data_f16 = np.frombuffer(data, dtype=np.float16).reshape(num_blocks, block_size // 2)
|
||||
data_u8 = np.frombuffer(data, dtype=np.uint8).reshape(num_blocks, block_size)
|
||||
data_i8 = np.frombuffer(data, dtype=np.int8).reshape(num_blocks, block_size)
|
||||
|
||||
scales = data_f16[:, -1].reshape(num_blocks, 1).astype(np.float32)
|
||||
|
||||
# TODO use uint8 and cast later?
|
||||
ql = data_u8[:, :128].astype(np.int16)
|
||||
qh = data_u8[:, 128:192].astype(np.int16)
|
||||
sc = data_i8[:, 192:208, np.newaxis].astype(np.float32)
|
||||
|
||||
# Unpack bits, subtraction requires signed data type
|
||||
q1 = (ql[:, :32] & 0xF) | (((qh[:, :32] >> 0) & 3) << 4) - 32
|
||||
q2 = (ql[:, 32:64] & 0xF) | (((qh[:, :32] >> 2) & 3) << 4) - 32
|
||||
q3 = (ql[:, :32] >> 4) | (((qh[:, :32] >> 4) & 3) << 4) - 32
|
||||
q4 = (ql[:, 32:64] >> 4) | (((qh[:, :32] >> 6) & 3) << 4) - 32
|
||||
q5 = (ql[:, 64:96] & 0xF) | (((qh[:, 32:] >> 0) & 3) << 4) - 32
|
||||
q6 = (ql[:, 96:128] & 0xF) | (((qh[:, 32:] >> 2) & 3) << 4) - 32
|
||||
q7 = (ql[:, 64:96] >> 4) | (((qh[:, 32:] >> 4) & 3) << 4) - 32
|
||||
q8 = (ql[:, 96:128] >> 4) | (((qh[:, 32:] >> 6) & 3) << 4) - 32
|
||||
|
||||
# Dequantize
|
||||
return scales * np.concatenate(
|
||||
[
|
||||
sc[:, 0] * q1[:, :16],
|
||||
sc[:, 1] * q1[:, 16:],
|
||||
sc[:, 2] * q2[:, :16],
|
||||
sc[:, 3] * q2[:, 16:],
|
||||
sc[:, 4] * q3[:, :16],
|
||||
sc[:, 5] * q3[:, 16:],
|
||||
sc[:, 6] * q4[:, :16],
|
||||
sc[:, 7] * q4[:, 16:],
|
||||
sc[:, 8] * q5[:, :16],
|
||||
sc[:, 9] * q5[:, 16:],
|
||||
sc[:, 10] * q6[:, :16],
|
||||
sc[:, 11] * q6[:, 16:],
|
||||
sc[:, 12] * q7[:, :16],
|
||||
sc[:, 13] * q7[:, 16:],
|
||||
sc[:, 14] * q8[:, :16],
|
||||
sc[:, 15] * q8[:, 16:],
|
||||
],
|
||||
axis=1,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def dequantize_q8_0(data, n_bytes: int):
|
||||
# C struct definition
|
||||
# https://github.com/ggerganov/ggml/blob/fca1caafea7de9fbd7efc733b9818f9cf2da3050/src/ggml-quants.h#L43
|
||||
block_size = GGML_BLOCK_SIZES["Q8_0"]
|
||||
num_blocks = n_bytes // block_size
|
||||
|
||||
scales = np.frombuffer(data, dtype=np.float16).reshape(num_blocks, 1 + 16)[:, :1].astype(np.float32)
|
||||
qs = np.frombuffer(data, dtype=np.int8).reshape(num_blocks, 2 + 32)[:, 2:]
|
||||
|
||||
return scales * qs
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def dequantize_q2_k(data, n_bytes: int):
|
||||
# C implementation
|
||||
# https://github.com/ggerganov/ggml/blob/fca1caafea7de9fbd7efc733b9818f9cf2da3050/src/ggml-quants.c#L1547
|
||||
# C struct definition
|
||||
# https://github.com/ggerganov/ggml/blob/fca1caafea7de9fbd7efc733b9818f9cf2da3050/src/ggml-quants.h#L74
|
||||
num_blocks = n_bytes // GGML_BLOCK_SIZES["Q2_K"]
|
||||
|
||||
data_f16 = np.frombuffer(data, dtype=np.float16).reshape(num_blocks, GGML_BLOCK_SIZES["Q2_K"] // 2)
|
||||
data_u8 = np.frombuffer(data, dtype=np.uint8).reshape(num_blocks, GGML_BLOCK_SIZES["Q2_K"])
|
||||
|
||||
dmin = data_f16[:, -1].reshape(num_blocks, 1, 1).astype(np.float32)
|
||||
d = data_f16[:, -2].reshape(num_blocks, 1, 1).astype(np.float32)
|
||||
scales = data_u8[:, :16].reshape(num_blocks, 16, 1)
|
||||
qs = data_u8[:, 16:80].reshape(num_blocks, 64)
|
||||
|
||||
tmp = np.stack(
|
||||
[
|
||||
qs[:, 00:16] >> 0,
|
||||
qs[:, 16:32] >> 0,
|
||||
qs[:, 00:16] >> 2,
|
||||
qs[:, 16:32] >> 2,
|
||||
qs[:, 00:16] >> 4,
|
||||
qs[:, 16:32] >> 4,
|
||||
qs[:, 00:16] >> 6,
|
||||
qs[:, 16:32] >> 6,
|
||||
qs[:, 32:48] >> 0,
|
||||
qs[:, 48:64] >> 0,
|
||||
qs[:, 32:48] >> 2,
|
||||
qs[:, 48:64] >> 2,
|
||||
qs[:, 32:48] >> 4,
|
||||
qs[:, 48:64] >> 4,
|
||||
qs[:, 32:48] >> 6,
|
||||
qs[:, 48:64] >> 6,
|
||||
],
|
||||
axis=1,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
return d * (scales & 15) * (tmp & 3) - dmin * (scales >> 4)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def dequantize_q3_k(data, n_bytes: int):
|
||||
# C implementation
|
||||
# https://github.com/ggerganov/ggml/blob/fca1caafea7de9fbd7efc733b9818f9cf2da3050/src/ggml-quants.c#L1723C32-L1723C42
|
||||
# C struct definition
|
||||
# https://github.com/ggerganov/ggml/blob/fca1caafea7de9fbd7efc733b9818f9cf2da3050/src/ggml-quants.h#L95
|
||||
num_blocks = n_bytes // GGML_BLOCK_SIZES["Q3_K"]
|
||||
|
||||
data_f16 = np.frombuffer(data, dtype=np.float16).reshape(num_blocks, GGML_BLOCK_SIZES["Q3_K"] // 2)
|
||||
data_u8 = np.frombuffer(data, dtype=np.uint8).reshape(num_blocks, GGML_BLOCK_SIZES["Q3_K"])
|
||||
|
||||
d = data_f16[:, -1].reshape(num_blocks, 1, 1).astype(np.float32)
|
||||
bits = np.unpackbits(data_u8[:, :32].reshape(num_blocks, 32, 1), axis=-1, bitorder="little")
|
||||
bits = 4 ^ (bits << 2)
|
||||
qs = data_u8[:, 32 : 32 + 64].astype(np.int16)
|
||||
a, b, c = data_u8[:, 96 : 96 + 12].reshape(num_blocks, 3, 4).transpose(1, 0, 2)
|
||||
scales = np.zeros((num_blocks, 4, 4), dtype=np.uint8)
|
||||
scales[:, 0] = (a & 15) | ((c & 3) << 4)
|
||||
scales[:, 1] = (b & 15) | (((c >> 2) & 3) << 4)
|
||||
scales[:, 2] = (a >> 4) | (((c >> 4) & 3) << 4)
|
||||
scales[:, 3] = (b >> 4) | ((c >> 6) << 4)
|
||||
scales = scales.reshape(num_blocks, 16, 1).astype(np.int16)
|
||||
|
||||
return (
|
||||
d
|
||||
* (scales - 32)
|
||||
* np.stack(
|
||||
[
|
||||
(((qs[:, 00:16] >> 0) & 3) - bits[:, :16, 0]),
|
||||
(((qs[:, 16:32] >> 0) & 3) - bits[:, 16:, 0]),
|
||||
(((qs[:, 00:16] >> 2) & 3) - bits[:, :16, 1]),
|
||||
(((qs[:, 16:32] >> 2) & 3) - bits[:, 16:, 1]),
|
||||
(((qs[:, 00:16] >> 4) & 3) - bits[:, :16, 2]),
|
||||
(((qs[:, 16:32] >> 4) & 3) - bits[:, 16:, 2]),
|
||||
(((qs[:, 00:16] >> 6) & 3) - bits[:, :16, 3]),
|
||||
(((qs[:, 16:32] >> 6) & 3) - bits[:, 16:, 3]),
|
||||
(((qs[:, 32:48] >> 0) & 3) - bits[:, :16, 4]),
|
||||
(((qs[:, 48:64] >> 0) & 3) - bits[:, 16:, 4]),
|
||||
(((qs[:, 32:48] >> 2) & 3) - bits[:, :16, 5]),
|
||||
(((qs[:, 48:64] >> 2) & 3) - bits[:, 16:, 5]),
|
||||
(((qs[:, 32:48] >> 4) & 3) - bits[:, :16, 6]),
|
||||
(((qs[:, 48:64] >> 4) & 3) - bits[:, 16:, 6]),
|
||||
(((qs[:, 32:48] >> 6) & 3) - bits[:, :16, 7]),
|
||||
(((qs[:, 48:64] >> 6) & 3) - bits[:, 16:, 7]),
|
||||
],
|
||||
axis=1,
|
||||
)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def dequantize_q5_k(data, n_bytes: int):
|
||||
# C implementation
|
||||
# https://github.com/ggerganov/ggml/blob/fca1caafea7de9fbd7efc733b9818f9cf2da3050/src/ggml-quants.c#L2129
|
||||
# C struct definition
|
||||
# https://github.com/ggerganov/ggml/blob/fca1caafea7de9fbd7efc733b9818f9cf2da3050/src/ggml-quants.h#L138
|
||||
num_blocks = n_bytes // GGML_BLOCK_SIZES["Q5_K"]
|
||||
|
||||
data_f16 = np.frombuffer(data, dtype=np.float16).reshape(num_blocks, GGML_BLOCK_SIZES["Q5_K"] // 2)
|
||||
data_u8 = np.frombuffer(data, dtype=np.uint8).reshape(num_blocks, GGML_BLOCK_SIZES["Q5_K"])
|
||||
|
||||
d = data_f16[:, 0].reshape(num_blocks, 1).astype(np.float32)
|
||||
dmin = data_f16[:, 1].reshape(num_blocks, 1).astype(np.float32)
|
||||
scales = data_u8[:, 4:16].reshape(num_blocks, 12, 1)
|
||||
qh = data_u8[:, 16 : 16 + 32].reshape(num_blocks, 32, 1)
|
||||
qs = data_u8[:, 48 : 48 + 128].reshape(num_blocks, 4, 32)
|
||||
|
||||
bits = np.unpackbits(qh, axis=-1, bitorder="little")
|
||||
|
||||
qs_hi_4 = qs >> 4
|
||||
qs_lo_4 = qs & 15
|
||||
|
||||
scales_lo_6 = scales[:, :8] & 63
|
||||
scales_hi_6 = scales[:, :8] >> 6
|
||||
scales_lo_4 = scales[:, 8:] & 15
|
||||
scales_hi_4 = scales[:, 8:] >> 4
|
||||
|
||||
m1 = dmin * scales_lo_6[:, 4]
|
||||
m2 = dmin * scales_lo_6[:, 5]
|
||||
m3 = dmin * scales_lo_6[:, 6]
|
||||
m4 = dmin * scales_lo_6[:, 7]
|
||||
m5 = dmin * (scales_hi_4[:, 0] | (scales_hi_6[:, 4] << 4))
|
||||
m6 = dmin * (scales_hi_4[:, 1] | (scales_hi_6[:, 5] << 4))
|
||||
m7 = dmin * (scales_hi_4[:, 2] | (scales_hi_6[:, 6] << 4))
|
||||
m8 = dmin * (scales_hi_4[:, 3] | (scales_hi_6[:, 7] << 4))
|
||||
|
||||
d1 = d * scales_lo_6[:, 0]
|
||||
d2 = d * scales_lo_6[:, 1]
|
||||
d3 = d * scales_lo_6[:, 2]
|
||||
d4 = d * scales_lo_6[:, 3]
|
||||
d5 = d * (scales_lo_4[:, 0] | (scales_hi_6[:, 0] << 4))
|
||||
d6 = d * (scales_lo_4[:, 1] | (scales_hi_6[:, 1] << 4))
|
||||
d7 = d * (scales_lo_4[:, 2] | (scales_hi_6[:, 2] << 4))
|
||||
d8 = d * (scales_lo_4[:, 3] | (scales_hi_6[:, 3] << 4))
|
||||
|
||||
return np.concatenate(
|
||||
[
|
||||
d1 * (qs_lo_4[:, 0] + (bits[:, :, 0] << 4)) - m1,
|
||||
d2 * (qs_hi_4[:, 0] + (bits[:, :, 1] << 4)) - m2,
|
||||
d3 * (qs_lo_4[:, 1] + (bits[:, :, 2] << 4)) - m3,
|
||||
d4 * (qs_hi_4[:, 1] + (bits[:, :, 3] << 4)) - m4,
|
||||
d5 * (qs_lo_4[:, 2] + (bits[:, :, 4] << 4)) - m5,
|
||||
d6 * (qs_hi_4[:, 2] + (bits[:, :, 5] << 4)) - m6,
|
||||
d7 * (qs_lo_4[:, 3] + (bits[:, :, 6] << 4)) - m7,
|
||||
d8 * (qs_hi_4[:, 3] + (bits[:, :, 7] << 4)) - m8,
|
||||
],
|
||||
axis=1,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def load_dequant_gguf_tensor(shape, ggml_type, data, n_bytes):
|
||||
if ggml_type == GGML_TYPES["F32"]:
|
||||
values = data
|
||||
elif ggml_type == GGML_TYPES["F16"]:
|
||||
values = data
|
||||
elif ggml_type == GGML_TYPES["Q8_0"]:
|
||||
values = dequantize_q8_0(data, n_bytes)
|
||||
elif ggml_type == GGML_TYPES["Q4_0"]:
|
||||
values = dequantize_q4_0(data, n_bytes)
|
||||
elif ggml_type == GGML_TYPES["Q4_K"]:
|
||||
values = dequantize_q4_k(data, n_bytes)
|
||||
elif ggml_type == GGML_TYPES["Q6_K"]:
|
||||
values = dequantize_q6_k(data, n_bytes)
|
||||
elif ggml_type == GGML_TYPES["Q2_K"]:
|
||||
values = dequantize_q2_k(data, n_bytes)
|
||||
elif ggml_type == GGML_TYPES["Q3_K"]:
|
||||
values = dequantize_q3_k(data, n_bytes)
|
||||
elif ggml_type == GGML_TYPES["Q5_K"]:
|
||||
values = dequantize_q5_k(data, n_bytes)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
raise NotImplementedError(
|
||||
f"ggml_type {ggml_type} not implemented - please raise an issue on huggingface transformers: https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/issues/new/choose"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
return values.reshape(shape[::-1])
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class GGUFTokenizerSkeleton:
|
||||
def __init__(self, dict_):
|
||||
for k, v in dict_.items():
|
||||
@ -271,15 +579,7 @@ class GGUFLlamaConverter(LlamaConverter):
|
||||
bos_token = proto.tokens[proto.bos_token_id] if getattr(proto, "bos_token_id", None) is not None else None
|
||||
eos_token = proto.tokens[proto.bos_token_id] if getattr(proto, "eos_token_id", None) is not None else None
|
||||
|
||||
tokenizer = Tokenizer(
|
||||
BPE(
|
||||
bpe_vocab,
|
||||
merges,
|
||||
unk_token=unk_token,
|
||||
fuse_unk=True,
|
||||
byte_fallback=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
)
|
||||
tokenizer = Tokenizer(BPE(bpe_vocab, merges, unk_token=unk_token, fuse_unk=True, byte_fallback=True))
|
||||
|
||||
special_tokens = []
|
||||
|
||||
@ -393,7 +693,6 @@ class GGUFQwen2Converter(Qwen2Converter):
|
||||
GGUF_TO_FAST_CONVERTERS = {
|
||||
"llama": GGUFLlamaConverter,
|
||||
"qwen2": GGUFQwen2Converter,
|
||||
"qwen2_moe": GGUFQwen2Converter,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,15 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# coding=utf-8
|
||||
# Copyright 2024 Tri Dao, Albert Gu, Technological Innovation Institute and HuggingFace Inc. team.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
from .selective_scan_with_ln_interface import mamba_inner_fn
|
||||
@ -1,525 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# coding=utf-8
|
||||
# Copyright 2024 Tri Dao, Albert Gu, Technological Innovation Institute and HuggingFace Inc. team.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
# Original code from: https://github.com/state-spaces/mamba/blob/main/mamba_ssm/ops/selective_scan_interface.py
|
||||
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
import torch.nn.functional as F
|
||||
from einops import rearrange, repeat
|
||||
from torch.cuda.amp import custom_bwd, custom_fwd
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
import causal_conv1d_cuda
|
||||
except ImportError:
|
||||
causal_conv1d_cuda = None
|
||||
|
||||
import mamba_ssm
|
||||
import selective_scan_cuda
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# For BC for old mamba-ssm versions: https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/pull/33195#discussion_r1736401127
|
||||
if hasattr(mamba_ssm.ops.triton, "layernorm"):
|
||||
from mamba_ssm.ops.triton.layernorm import _layer_norm_fwd
|
||||
else:
|
||||
from mamba_ssm.ops.triton.layer_norm import _layer_norm_fwd
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class SelectiveScanFn(torch.autograd.Function):
|
||||
@staticmethod
|
||||
def forward(
|
||||
ctx, u, delta, A, B, C, D=None, z=None, delta_bias=None, delta_softplus=False, return_last_state=False
|
||||
):
|
||||
if u.stride(-1) != 1:
|
||||
u = u.contiguous()
|
||||
if delta.stride(-1) != 1:
|
||||
delta = delta.contiguous()
|
||||
if D is not None:
|
||||
D = D.contiguous()
|
||||
if B.stride(-1) != 1:
|
||||
B = B.contiguous()
|
||||
if C.stride(-1) != 1:
|
||||
C = C.contiguous()
|
||||
if z is not None and z.stride(-1) != 1:
|
||||
z = z.contiguous()
|
||||
if B.dim() == 3:
|
||||
B = rearrange(B, "b dstate l -> b 1 dstate l")
|
||||
ctx.squeeze_B = True
|
||||
if C.dim() == 3:
|
||||
C = rearrange(C, "b dstate l -> b 1 dstate l")
|
||||
ctx.squeeze_C = True
|
||||
out, x, *rest = selective_scan_cuda.fwd(u, delta, A, B, C, D, z, delta_bias, delta_softplus)
|
||||
ctx.delta_softplus = delta_softplus
|
||||
ctx.has_z = z is not None
|
||||
last_state = x[:, :, -1, 1::2] # (batch, dim, dstate)
|
||||
if not ctx.has_z:
|
||||
ctx.save_for_backward(u, delta, A, B, C, D, delta_bias, x)
|
||||
return out if not return_last_state else (out, last_state)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
ctx.save_for_backward(u, delta, A, B, C, D, z, delta_bias, x, out)
|
||||
out_z = rest[0]
|
||||
return out_z if not return_last_state else (out_z, last_state)
|
||||
|
||||
@staticmethod
|
||||
def backward(ctx, dout, *args):
|
||||
if not ctx.has_z:
|
||||
u, delta, A, B, C, D, delta_bias, x = ctx.saved_tensors
|
||||
z = None
|
||||
out = None
|
||||
else:
|
||||
u, delta, A, B, C, D, z, delta_bias, x, out = ctx.saved_tensors
|
||||
if dout.stride(-1) != 1:
|
||||
dout = dout.contiguous()
|
||||
# The kernel supports passing in a pre-allocated dz (e.g., in case we want to fuse the
|
||||
# backward of selective_scan_cuda with the backward of chunk).
|
||||
# Here we just pass in None and dz will be allocated in the C++ code.
|
||||
du, ddelta, dA, dB, dC, dD, ddelta_bias, *rest = selective_scan_cuda.bwd(
|
||||
u,
|
||||
delta,
|
||||
A,
|
||||
B,
|
||||
C,
|
||||
D,
|
||||
z,
|
||||
delta_bias,
|
||||
dout,
|
||||
x,
|
||||
out,
|
||||
None,
|
||||
ctx.delta_softplus,
|
||||
False, # option to recompute out_z, not used here
|
||||
)
|
||||
dz = rest[0] if ctx.has_z else None
|
||||
dB = dB.squeeze(1) if getattr(ctx, "squeeze_B", False) else dB
|
||||
dC = dC.squeeze(1) if getattr(ctx, "squeeze_C", False) else dC
|
||||
return (
|
||||
du,
|
||||
ddelta,
|
||||
dA,
|
||||
dB,
|
||||
dC,
|
||||
dD if D is not None else None,
|
||||
dz,
|
||||
ddelta_bias if delta_bias is not None else None,
|
||||
None,
|
||||
None,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def rms_norm_forward(
|
||||
x,
|
||||
weight,
|
||||
bias,
|
||||
eps=1e-6,
|
||||
is_rms_norm=True,
|
||||
):
|
||||
# x (b l) d
|
||||
if x.stride(-1) != 1:
|
||||
x = x.contiguous()
|
||||
weight = weight.contiguous()
|
||||
if bias is not None:
|
||||
bias = bias.contiguous()
|
||||
y = _layer_norm_fwd(x, weight, bias, eps, None, residual_dtype=None, is_rms_norm=is_rms_norm)[0]
|
||||
# y (b l) d
|
||||
return y
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def selective_scan_fn(
|
||||
u, delta, A, B, C, D=None, z=None, delta_bias=None, delta_softplus=False, return_last_state=False
|
||||
):
|
||||
"""if return_last_state is True, returns (out, last_state)
|
||||
last_state has shape (batch, dim, dstate). Note that the gradient of the last state is
|
||||
not considered in the backward pass.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return SelectiveScanFn.apply(u, delta, A, B, C, D, z, delta_bias, delta_softplus, return_last_state)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def selective_scan_ref(
|
||||
u, delta, A, B, C, D=None, z=None, delta_bias=None, delta_softplus=False, return_last_state=False
|
||||
):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
u: r(B D L)
|
||||
delta: r(B D L)
|
||||
A: c(D N) or r(D N)
|
||||
B: c(D N) or r(B N L) or r(B N 2L) or r(B G N L) or (B G N L)
|
||||
C: c(D N) or r(B N L) or r(B N 2L) or r(B G N L) or (B G N L)
|
||||
D: r(D)
|
||||
z: r(B D L)
|
||||
delta_bias: r(D), fp32
|
||||
|
||||
out: r(B D L)
|
||||
last_state (optional): r(B D dstate) or c(B D dstate)
|
||||
"""
|
||||
dtype_in = u.dtype
|
||||
u = u.float()
|
||||
delta = delta.float()
|
||||
if delta_bias is not None:
|
||||
delta = delta + delta_bias[..., None].float()
|
||||
if delta_softplus:
|
||||
delta = F.softplus(delta)
|
||||
batch, dim, dstate = u.shape[0], A.shape[0], A.shape[1]
|
||||
is_variable_B = B.dim() >= 3
|
||||
is_variable_C = C.dim() >= 3
|
||||
if A.is_complex():
|
||||
if is_variable_B:
|
||||
B = torch.view_as_complex(rearrange(B.float(), "... (L two) -> ... L two", two=2))
|
||||
if is_variable_C:
|
||||
C = torch.view_as_complex(rearrange(C.float(), "... (L two) -> ... L two", two=2))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
B = B.float()
|
||||
C = C.float()
|
||||
x = A.new_zeros((batch, dim, dstate))
|
||||
ys = []
|
||||
deltaA = torch.exp(torch.einsum("bdl,dn->bdln", delta, A))
|
||||
if not is_variable_B:
|
||||
deltaB_u = torch.einsum("bdl,dn,bdl->bdln", delta, B, u)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
if B.dim() == 3:
|
||||
deltaB_u = torch.einsum("bdl,bnl,bdl->bdln", delta, B, u)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
B = repeat(B, "B G N L -> B (G H) N L", H=dim // B.shape[1])
|
||||
deltaB_u = torch.einsum("bdl,bdnl,bdl->bdln", delta, B, u)
|
||||
if is_variable_C and C.dim() == 4:
|
||||
C = repeat(C, "B G N L -> B (G H) N L", H=dim // C.shape[1])
|
||||
last_state = None
|
||||
for i in range(u.shape[2]):
|
||||
x = deltaA[:, :, i] * x + deltaB_u[:, :, i]
|
||||
if not is_variable_C:
|
||||
y = torch.einsum("bdn,dn->bd", x, C)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
if C.dim() == 3:
|
||||
y = torch.einsum("bdn,bn->bd", x, C[:, :, i])
|
||||
else:
|
||||
y = torch.einsum("bdn,bdn->bd", x, C[:, :, :, i])
|
||||
if i == u.shape[2] - 1:
|
||||
last_state = x
|
||||
if y.is_complex():
|
||||
y = y.real * 2
|
||||
ys.append(y)
|
||||
y = torch.stack(ys, dim=2) # (batch dim L)
|
||||
out = y if D is None else y + u * rearrange(D, "d -> d 1")
|
||||
if z is not None:
|
||||
out = out * F.silu(z)
|
||||
out = out.to(dtype=dtype_in)
|
||||
return out if not return_last_state else (out, last_state)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class MambaInnerFn(torch.autograd.Function):
|
||||
@staticmethod
|
||||
@custom_fwd
|
||||
def forward(
|
||||
ctx,
|
||||
xz,
|
||||
conv1d_weight,
|
||||
conv1d_bias,
|
||||
x_proj_weight,
|
||||
delta_proj_weight,
|
||||
out_proj_weight,
|
||||
out_proj_bias,
|
||||
A,
|
||||
B=None,
|
||||
C=None,
|
||||
D=None,
|
||||
delta_bias=None,
|
||||
B_proj_bias=None,
|
||||
C_proj_bias=None,
|
||||
delta_softplus=True,
|
||||
checkpoint_lvl=1,
|
||||
b_rms_weight=None,
|
||||
c_rms_weight=None,
|
||||
dt_rms_weight=None,
|
||||
b_c_dt_rms_eps=1e-6,
|
||||
):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
xz: (batch, dim, seqlen)
|
||||
"""
|
||||
assert causal_conv1d_cuda is not None, "causal_conv1d_cuda is not available. Please install causal-conv1d."
|
||||
assert checkpoint_lvl in [0, 1]
|
||||
L = xz.shape[-1]
|
||||
delta_rank = delta_proj_weight.shape[1]
|
||||
d_state = A.shape[-1] * (1 if not A.is_complex() else 2)
|
||||
if torch.is_autocast_enabled():
|
||||
x_proj_weight = x_proj_weight.to(dtype=torch.get_autocast_gpu_dtype())
|
||||
delta_proj_weight = delta_proj_weight.to(dtype=torch.get_autocast_gpu_dtype())
|
||||
out_proj_weight = out_proj_weight.to(dtype=torch.get_autocast_gpu_dtype())
|
||||
out_proj_bias = (
|
||||
out_proj_bias.to(dtype=torch.get_autocast_gpu_dtype()) if out_proj_bias is not None else None
|
||||
)
|
||||
if xz.stride(-1) != 1:
|
||||
xz = xz.contiguous()
|
||||
conv1d_weight = rearrange(conv1d_weight, "d 1 w -> d w")
|
||||
x, z = xz.chunk(2, dim=1)
|
||||
conv1d_bias = conv1d_bias.contiguous() if conv1d_bias is not None else None
|
||||
conv1d_out = causal_conv1d_cuda.causal_conv1d_fwd(x, conv1d_weight, conv1d_bias, None, None, None, True)
|
||||
# We're being very careful here about the layout, to avoid extra transposes.
|
||||
# We want delta to have d as the slowest moving dimension
|
||||
# and L as the fastest moving dimension, since those are what the ssm_scan kernel expects.
|
||||
x_dbl = F.linear(rearrange(conv1d_out, "b d l -> (b l) d"), x_proj_weight) # (bl d)
|
||||
delta = rearrange(delta_proj_weight @ x_dbl[:, :delta_rank].t(), "d (b l) -> b d l", l=L)
|
||||
ctx.is_variable_B = B is None
|
||||
ctx.is_variable_C = C is None
|
||||
ctx.B_proj_bias_is_None = B_proj_bias is None
|
||||
ctx.C_proj_bias_is_None = C_proj_bias is None
|
||||
if B is None: # variable B
|
||||
B = x_dbl[:, delta_rank : delta_rank + d_state] # (bl dstate)
|
||||
if B_proj_bias is not None:
|
||||
B = B + B_proj_bias.to(dtype=B.dtype)
|
||||
if not A.is_complex():
|
||||
# B = rearrange(B, "(b l) dstate -> b dstate l", l=L).contiguous()
|
||||
B = rearrange(B, "(b l) dstate -> b 1 dstate l", l=L).contiguous()
|
||||
else:
|
||||
B = rearrange(B, "(b l) (dstate two) -> b 1 dstate (l two)", l=L, two=2).contiguous()
|
||||
else:
|
||||
if B.stride(-1) != 1:
|
||||
B = B.contiguous()
|
||||
if C is None: # variable C
|
||||
C = x_dbl[:, -d_state:] # (bl dstate)
|
||||
if C_proj_bias is not None:
|
||||
C = C + C_proj_bias.to(dtype=C.dtype)
|
||||
if not A.is_complex():
|
||||
# C = rearrange(C, "(b l) dstate -> b dstate l", l=L).contiguous()
|
||||
C = rearrange(C, "(b l) dstate -> b 1 dstate l", l=L).contiguous()
|
||||
else:
|
||||
C = rearrange(C, "(b l) (dstate two) -> b 1 dstate (l two)", l=L, two=2).contiguous()
|
||||
else:
|
||||
if C.stride(-1) != 1:
|
||||
C = C.contiguous()
|
||||
if D is not None:
|
||||
D = D.contiguous()
|
||||
|
||||
if b_rms_weight is not None:
|
||||
B = rearrange(B, "b 1 dstate l -> (b l) dstate", l=L).contiguous()
|
||||
B = rms_norm_forward(B, b_rms_weight, bias=None, eps=b_c_dt_rms_eps)
|
||||
B = rearrange(B, "(b l) dstate -> b 1 dstate l", l=L).contiguous()
|
||||
if c_rms_weight is not None:
|
||||
C = rearrange(C, "b 1 dstate l -> (b l) dstate", l=L).contiguous()
|
||||
C = rms_norm_forward(C, c_rms_weight, bias=None, eps=b_c_dt_rms_eps)
|
||||
C = rearrange(C, "(b l) dstate -> b 1 dstate l", l=L).contiguous()
|
||||
if dt_rms_weight is not None:
|
||||
delta = rearrange(delta, "b d l -> (b l) d", l=L).contiguous()
|
||||
delta = rms_norm_forward(delta, dt_rms_weight, bias=None, eps=b_c_dt_rms_eps)
|
||||
delta = rearrange(delta, "(b l) d -> b d l", l=L).contiguous()
|
||||
|
||||
out, scan_intermediates, out_z = selective_scan_cuda.fwd(
|
||||
conv1d_out, delta, A, B, C, D, z, delta_bias, delta_softplus
|
||||
)
|
||||
ctx.delta_softplus = delta_softplus
|
||||
ctx.out_proj_bias_is_None = out_proj_bias is None
|
||||
ctx.checkpoint_lvl = checkpoint_lvl
|
||||
ctx.b_rms_weight = b_rms_weight
|
||||
ctx.c_rms_weight = c_rms_weight
|
||||
ctx.dt_rms_weight = dt_rms_weight
|
||||
ctx.b_c_dt_rms_eps = b_c_dt_rms_eps
|
||||
if checkpoint_lvl >= 1: # Will recompute conv1d_out and delta in the backward pass
|
||||
conv1d_out, delta = None, None
|
||||
ctx.save_for_backward(
|
||||
xz,
|
||||
conv1d_weight,
|
||||
conv1d_bias,
|
||||
x_dbl,
|
||||
x_proj_weight,
|
||||
delta_proj_weight,
|
||||
out_proj_weight,
|
||||
conv1d_out,
|
||||
delta,
|
||||
A,
|
||||
B,
|
||||
C,
|
||||
D,
|
||||
delta_bias,
|
||||
scan_intermediates,
|
||||
b_rms_weight,
|
||||
c_rms_weight,
|
||||
dt_rms_weight,
|
||||
out,
|
||||
)
|
||||
return F.linear(rearrange(out_z, "b d l -> b l d"), out_proj_weight, out_proj_bias)
|
||||
|
||||
@staticmethod
|
||||
@custom_bwd
|
||||
def backward(ctx, dout):
|
||||
# dout: (batch, seqlen, dim)
|
||||
assert causal_conv1d_cuda is not None, "causal_conv1d_cuda is not available. Please install causal-conv1d."
|
||||
(
|
||||
xz,
|
||||
conv1d_weight,
|
||||
conv1d_bias,
|
||||
x_dbl,
|
||||
x_proj_weight,
|
||||
delta_proj_weight,
|
||||
out_proj_weight,
|
||||
conv1d_out,
|
||||
delta,
|
||||
A,
|
||||
B,
|
||||
C,
|
||||
D,
|
||||
delta_bias,
|
||||
scan_intermediates,
|
||||
b_rms_weight,
|
||||
c_rms_weight,
|
||||
dt_rms_weight,
|
||||
out,
|
||||
) = ctx.saved_tensors
|
||||
L = xz.shape[-1]
|
||||
delta_rank = delta_proj_weight.shape[1]
|
||||
d_state = A.shape[-1] * (1 if not A.is_complex() else 2)
|
||||
x, z = xz.chunk(2, dim=1)
|
||||
if dout.stride(-1) != 1:
|
||||
dout = dout.contiguous()
|
||||
if ctx.checkpoint_lvl == 1:
|
||||
conv1d_out = causal_conv1d_cuda.causal_conv1d_fwd(x, conv1d_weight, conv1d_bias, None, None, None, True)
|
||||
delta = rearrange(delta_proj_weight @ x_dbl[:, :delta_rank].t(), "d (b l) -> b d l", l=L)
|
||||
if dt_rms_weight is not None:
|
||||
delta = rearrange(delta, "b d l -> (b l) d", l=L).contiguous()
|
||||
delta = rms_norm_forward(delta, ctx.dt_rms_weight, None, ctx.b_c_dt_rms_eps)
|
||||
delta = rearrange(delta, "(b l) d -> b d l", l=L).contiguous()
|
||||
if b_rms_weight is not None:
|
||||
# Recompute & RMSNorm B
|
||||
B = rearrange(B, "b 1 dstate l -> (b l) dstate", l=L).contiguous()
|
||||
B = rms_norm_forward(B, ctx.b_rms_weight, None, ctx.b_c_dt_rms_eps)
|
||||
B = rearrange(B, "(b l) dstate -> b 1 dstate l", l=L).contiguous()
|
||||
if c_rms_weight is not None:
|
||||
# Recompute & RMSNorm C
|
||||
C = rearrange(C, "b 1 dstate l -> (b l) dstate", l=L).contiguous()
|
||||
C = rms_norm_forward(C, ctx.c_rms_weight, None, ctx.b_c_dt_rms_eps)
|
||||
C = rearrange(C, "(b l) dstate -> b 1 dstate l", l=L).contiguous()
|
||||
|
||||
# The kernel supports passing in a pre-allocated dz (e.g., in case we want to fuse the
|
||||
# backward of selective_scan_cuda with the backward of chunk).
|
||||
dxz = torch.empty_like(xz) # (batch, dim, seqlen)
|
||||
dx, dz = dxz.chunk(2, dim=1)
|
||||
dout = rearrange(dout, "b l e -> e (b l)")
|
||||
dout_y = rearrange(out_proj_weight.t() @ dout, "d (b l) -> b d l", l=L)
|
||||
dconv1d_out, ddelta, dA, dB, dC, dD, ddelta_bias, dz, out_z = selective_scan_cuda.bwd(
|
||||
conv1d_out,
|
||||
delta,
|
||||
A,
|
||||
B,
|
||||
C,
|
||||
D,
|
||||
z,
|
||||
delta_bias,
|
||||
dout_y,
|
||||
scan_intermediates,
|
||||
out,
|
||||
dz,
|
||||
ctx.delta_softplus,
|
||||
True, # option to recompute out_z
|
||||
)
|
||||
dout_proj_weight = torch.einsum("eB,dB->ed", dout, rearrange(out_z, "b d l -> d (b l)"))
|
||||
dout_proj_bias = dout.sum(dim=(0, 1)) if not ctx.out_proj_bias_is_None else None
|
||||
dD = dD if D is not None else None
|
||||
dx_dbl = torch.empty_like(x_dbl)
|
||||
dB_proj_bias = None
|
||||
if ctx.is_variable_B:
|
||||
if not A.is_complex():
|
||||
dB = rearrange(dB, "b 1 dstate l -> (b l) dstate").contiguous()
|
||||
else:
|
||||
dB = rearrange(dB, "b 1 dstate (l two) -> (b l) (dstate two)", two=2).contiguous()
|
||||
dB_proj_bias = dB.sum(0) if not ctx.B_proj_bias_is_None else None
|
||||
dx_dbl[:, delta_rank : delta_rank + d_state] = dB # (bl d)
|
||||
dB = None
|
||||
dC_proj_bias = None
|
||||
if ctx.is_variable_C:
|
||||
if not A.is_complex():
|
||||
dC = rearrange(dC, "b 1 dstate l -> (b l) dstate").contiguous()
|
||||
else:
|
||||
dC = rearrange(dC, "b 1 dstate (l two) -> (b l) (dstate two)", two=2).contiguous()
|
||||
dC_proj_bias = dC.sum(0) if not ctx.C_proj_bias_is_None else None
|
||||
dx_dbl[:, -d_state:] = dC # (bl d)
|
||||
dC = None
|
||||
ddelta = rearrange(ddelta, "b d l -> d (b l)")
|
||||
ddelta_proj_weight = torch.einsum("dB,Br->dr", ddelta, x_dbl[:, :delta_rank])
|
||||
dx_dbl[:, :delta_rank] = torch.einsum("dB,dr->Br", ddelta, delta_proj_weight)
|
||||
dconv1d_out = rearrange(dconv1d_out, "b d l -> d (b l)")
|
||||
dx_proj_weight = torch.einsum("Br,Bd->rd", dx_dbl, rearrange(conv1d_out, "b d l -> (b l) d"))
|
||||
dconv1d_out = torch.addmm(dconv1d_out, x_proj_weight.t(), dx_dbl.t(), out=dconv1d_out)
|
||||
dconv1d_out = rearrange(dconv1d_out, "d (b l) -> b d l", b=x.shape[0], l=x.shape[-1])
|
||||
# The kernel supports passing in a pre-allocated dx (e.g., in case we want to fuse the
|
||||
# backward of conv1d with the backward of chunk).
|
||||
dx, dconv1d_weight, dconv1d_bias, *_ = causal_conv1d_cuda.causal_conv1d_bwd(
|
||||
x, conv1d_weight, conv1d_bias, dconv1d_out, None, None, None, dx, False, True
|
||||
)
|
||||
dconv1d_bias = dconv1d_bias if conv1d_bias is not None else None
|
||||
dconv1d_weight = rearrange(dconv1d_weight, "d w -> d 1 w")
|
||||
return (
|
||||
dxz,
|
||||
dconv1d_weight,
|
||||
dconv1d_bias,
|
||||
dx_proj_weight,
|
||||
ddelta_proj_weight,
|
||||
dout_proj_weight,
|
||||
dout_proj_bias,
|
||||
dA,
|
||||
dB,
|
||||
dC,
|
||||
dD,
|
||||
ddelta_bias if delta_bias is not None else None,
|
||||
# 6-None are delta_softplus, checkpoint_lvl, b_rms_weight, c_rms_weight, dt_rms_weight, b_c_dt_rms_eps
|
||||
dB_proj_bias,
|
||||
dC_proj_bias,
|
||||
None,
|
||||
None,
|
||||
None,
|
||||
None,
|
||||
None,
|
||||
None,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def mamba_inner_fn(
|
||||
xz,
|
||||
conv1d_weight,
|
||||
conv1d_bias,
|
||||
x_proj_weight,
|
||||
delta_proj_weight,
|
||||
out_proj_weight,
|
||||
out_proj_bias,
|
||||
A,
|
||||
B=None,
|
||||
C=None,
|
||||
D=None,
|
||||
delta_bias=None,
|
||||
B_proj_bias=None,
|
||||
C_proj_bias=None,
|
||||
delta_softplus=True,
|
||||
checkpoint_lvl=1,
|
||||
b_rms_weight=None,
|
||||
c_rms_weight=None,
|
||||
dt_rms_weight=None,
|
||||
b_c_dt_rms_eps=1e-6,
|
||||
):
|
||||
return MambaInnerFn.apply(
|
||||
xz,
|
||||
conv1d_weight,
|
||||
conv1d_bias,
|
||||
x_proj_weight,
|
||||
delta_proj_weight,
|
||||
out_proj_weight,
|
||||
out_proj_bias,
|
||||
A,
|
||||
B,
|
||||
C,
|
||||
D,
|
||||
delta_bias,
|
||||
B_proj_bias,
|
||||
C_proj_bias,
|
||||
delta_softplus,
|
||||
checkpoint_lvl,
|
||||
b_rms_weight,
|
||||
c_rms_weight,
|
||||
dt_rms_weight,
|
||||
b_c_dt_rms_eps,
|
||||
)
|
||||
@ -386,6 +386,9 @@ def _prepare_4d_causal_attention_mask_for_sdpa(
|
||||
)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
if attention_mask.dim() == 4:
|
||||
# in this case we assume that the mask comes already in inverted form and requires no inversion or slicing
|
||||
if attention_mask.max() != 0:
|
||||
raise ValueError("Custom 4D attention mask should be passed in inverted form with max==0`")
|
||||
expanded_4d_mask = attention_mask
|
||||
else:
|
||||
expanded_4d_mask = attn_mask_converter.to_4d(
|
||||
|
||||
@ -24,9 +24,9 @@ from .integrations import (
|
||||
GGUF_TENSOR_MAPPING,
|
||||
GGUF_TOKENIZER_MAPPING,
|
||||
_gguf_parse_value,
|
||||
load_dequant_gguf_tensor,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from .utils import is_torch_available
|
||||
from .utils.import_utils import is_gguf_available
|
||||
from .utils.logging import get_logger
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -71,14 +71,14 @@ def load_gguf_checkpoint(gguf_checkpoint_path, return_tensors=False):
|
||||
Whether to read the tensors from the file and return them. Not doing so is faster
|
||||
and only loads the metadata in memory.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if is_gguf_available() and is_torch_available():
|
||||
from gguf import GGUFReader, dequantize
|
||||
else:
|
||||
try:
|
||||
from gguf import GGUFReader
|
||||
except (ImportError, ModuleNotFoundError):
|
||||
logger.error(
|
||||
"Loading a GGUF checkpoint in PyTorch, requires both PyTorch and GGUF>=0.10.0 to be installed. Please see "
|
||||
"Loading a GGUF checkpoint in PyTorch, requires both PyTorch and GGUF to be installed. Please see "
|
||||
"https://pytorch.org/ and https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp/tree/master/gguf-py for installation instructions."
|
||||
)
|
||||
raise ImportError("Please install torch and gguf>=0.10.0 to load a GGUF checkpoint in PyTorch.")
|
||||
raise
|
||||
|
||||
reader = GGUFReader(gguf_checkpoint_path)
|
||||
fields = reader.fields
|
||||
@ -96,9 +96,6 @@ def load_gguf_checkpoint(gguf_checkpoint_path, return_tensors=False):
|
||||
else:
|
||||
updated_architecture = architecture
|
||||
|
||||
if "qwen2moe" in architecture:
|
||||
updated_architecture = "qwen2_moe"
|
||||
|
||||
if architecture not in GGUF_SUPPORTED_ARCHITECTURES:
|
||||
raise ValueError(f"Architecture {architecture} not supported")
|
||||
|
||||
@ -157,9 +154,12 @@ def load_gguf_checkpoint(gguf_checkpoint_path, return_tensors=False):
|
||||
tensor_name_mapping, GGUF_TO_TRANSFORMERS_MAPPING["tensors"][tensor_name_mapping]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
shape = tensor.shape
|
||||
name = tensor.name
|
||||
|
||||
weights = dequantize(tensor.data, tensor.tensor_type)
|
||||
weights = load_dequant_gguf_tensor(
|
||||
shape=shape, ggml_type=tensor.tensor_type, data=tensor.data, n_bytes=int(tensor.n_bytes)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if architecture == "llama" and (".attn_k." in name or ".attn_q." in name):
|
||||
num_heads = parsed_parameters["config"]["num_attention_heads"]
|
||||
|
||||
@ -487,11 +487,10 @@ def _validate_longrope_parameters(config: PretrainedConfig):
|
||||
logger.warning(f"`rope_scaling`'s factor field must be a float >= 1, got {factor}")
|
||||
|
||||
attention_factor = rope_scaling.get("attention_factor")
|
||||
if attention_factor is not None:
|
||||
if not isinstance(attention_factor, float) or attention_factor < 0.0:
|
||||
logger.warning(
|
||||
f"`rope_scaling`'s attention_factor field must be a float greater than 0, got {attention_factor}"
|
||||
)
|
||||
if attention_factor is not None and not isinstance(attention_factor, float) or attention_factor < 0:
|
||||
logger.warning(
|
||||
f"`rope_scaling`'s attention_factor field must be a float greater than 0, got {attention_factor}"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _validate_llama3_parameters(config: PretrainedConfig):
|
||||
|
||||
@ -958,9 +958,6 @@ def _load_state_dict_into_meta_model(
|
||||
)
|
||||
)
|
||||
):
|
||||
if is_fsdp_enabled():
|
||||
param_device = "cpu" if is_local_dist_rank_0() else "meta"
|
||||
|
||||
# For backward compatibility with older versions of `accelerate` and for non-quantized params
|
||||
set_module_tensor_to_device(model, param_name, param_device, **set_module_kwargs)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
@ -971,10 +968,7 @@ def _load_state_dict_into_meta_model(
|
||||
if is_fsdp_enabled() or is_deepspeed_zero3_enabled():
|
||||
module, tensor_name = get_module_from_name(model, param_name)
|
||||
value = getattr(module, tensor_name)
|
||||
param_to = "cpu"
|
||||
if is_fsdp_enabled() and not is_local_dist_rank_0():
|
||||
param_to = "meta"
|
||||
value = type(value)(value.data.to(param_to), **value.__dict__)
|
||||
value = type(value)(value.data.to("cpu"), **value.__dict__)
|
||||
setattr(module, tensor_name, value)
|
||||
# TODO: consider removing used param_parts from state_dict before return
|
||||
|
||||
@ -2031,8 +2025,11 @@ class PreTrainedModel(nn.Module, ModuleUtilsMixin, GenerationMixin, PushToHubMix
|
||||
else:
|
||||
vocab_size = model_embeds.weight.shape[0]
|
||||
|
||||
# Update base model and current model config.
|
||||
self.config.get_text_config().vocab_size = vocab_size
|
||||
# Update base model and current model config
|
||||
if hasattr(self.config, "text_config"):
|
||||
self.config.text_config.vocab_size = vocab_size
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self.config.vocab_size = vocab_size
|
||||
self.vocab_size = vocab_size
|
||||
|
||||
# Tie weights again if needed
|
||||
@ -2864,54 +2861,38 @@ class PreTrainedModel(nn.Module, ModuleUtilsMixin, GenerationMixin, PushToHubMix
|
||||
def cuda(self, *args, **kwargs):
|
||||
if getattr(self, "quantization_method", None) == QuantizationMethod.HQQ:
|
||||
raise ValueError("`.cuda` is not supported for HQQ-quantized models.")
|
||||
# Checks if the model has been loaded in 4-bit or 8-bit with BNB
|
||||
# Checks if the model has been loaded in 8-bit
|
||||
if getattr(self, "quantization_method", None) == QuantizationMethod.BITS_AND_BYTES:
|
||||
if getattr(self, "is_loaded_in_8bit", False):
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
"Calling `cuda()` is not supported for `8-bit` quantized models. "
|
||||
" Please use the model as it is, since the model has already been set to the correct devices."
|
||||
)
|
||||
elif version.parse(importlib.metadata.version("bitsandbytes")) < version.parse("0.43.2"):
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
"Calling `cuda()` is not supported for `4-bit` quantized models with the installed version of bitsandbytes. "
|
||||
f"The current device is `{self.device}`. If you intended to move the model, please install bitsandbytes >= 0.43.2."
|
||||
)
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
"Calling `cuda()` is not supported for `4-bit` or `8-bit` quantized models. Please use the model as it is, since the"
|
||||
" model has already been set to the correct devices and casted to the correct `dtype`."
|
||||
)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return super().cuda(*args, **kwargs)
|
||||
|
||||
@wraps(torch.nn.Module.to)
|
||||
def to(self, *args, **kwargs):
|
||||
# For BNB/GPTQ models, we prevent users from casting the model to another dytpe to restrict unwanted behaviours.
|
||||
# the correct API should be to load the model with the desired dtype directly through `from_pretrained`.
|
||||
dtype_present_in_args = "dtype" in kwargs
|
||||
|
||||
if not dtype_present_in_args:
|
||||
for arg in args:
|
||||
if isinstance(arg, torch.dtype):
|
||||
dtype_present_in_args = True
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
if getattr(self, "quantization_method", None) == QuantizationMethod.HQQ:
|
||||
raise ValueError("`.to` is not supported for HQQ-quantized models.")
|
||||
# Checks if the model has been loaded in 4-bit or 8-bit with BNB
|
||||
# Checks if the model has been loaded in 8-bit
|
||||
if getattr(self, "quantization_method", None) == QuantizationMethod.BITS_AND_BYTES:
|
||||
if dtype_present_in_args:
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
"You cannot cast a bitsandbytes model in a new `dtype`. Make sure to load the model using `from_pretrained` using the"
|
||||
" desired `dtype` by passing the correct `torch_dtype` argument."
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if getattr(self, "is_loaded_in_8bit", False):
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
"`.to` is not supported for `8-bit` bitsandbytes models. Please use the model as it is, since the"
|
||||
" model has already been set to the correct devices and casted to the correct `dtype`."
|
||||
)
|
||||
elif version.parse(importlib.metadata.version("bitsandbytes")) < version.parse("0.43.2"):
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
"Calling `to()` is not supported for `4-bit` quantized models with the installed version of bitsandbytes. "
|
||||
f"The current device is `{self.device}`. If you intended to move the model, please install bitsandbytes >= 0.43.2."
|
||||
)
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
"`.to` is not supported for `4-bit` or `8-bit` bitsandbytes models. Please use the model as it is, since the"
|
||||
" model has already been set to the correct devices and casted to the correct `dtype`."
|
||||
)
|
||||
elif getattr(self, "quantization_method", None) == QuantizationMethod.GPTQ:
|
||||
# For GPTQ models, we prevent users from casting the model to another dytpe to restrict unwanted behaviours.
|
||||
# the correct API should be to load the model with the desired dtype directly through `from_pretrained`.
|
||||
dtype_present_in_args = False
|
||||
|
||||
if "dtype" not in kwargs:
|
||||
for arg in args:
|
||||
if isinstance(arg, torch.dtype):
|
||||
dtype_present_in_args = True
|
||||
break
|
||||
else:
|
||||
dtype_present_in_args = True
|
||||
|
||||
if dtype_present_in_args:
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
"You cannot cast a GPTQ model in a new `dtype`. Make sure to load the model using `from_pretrained` using the desired"
|
||||
|
||||
@ -132,7 +132,6 @@ from . import (
|
||||
llava,
|
||||
llava_next,
|
||||
llava_next_video,
|
||||
llava_onevision,
|
||||
longformer,
|
||||
longt5,
|
||||
luke,
|
||||
@ -170,7 +169,6 @@ from . import (
|
||||
nougat,
|
||||
nystromformer,
|
||||
olmo,
|
||||
olmoe,
|
||||
oneformer,
|
||||
openai,
|
||||
opt,
|
||||
|
||||
@ -24,7 +24,6 @@ from torch import nn
|
||||
from torch.nn import BCEWithLogitsLoss, CrossEntropyLoss, MSELoss
|
||||
|
||||
from ...activations import ACT2FN
|
||||
from ...modeling_attn_mask_utils import _prepare_4d_attention_mask_for_sdpa
|
||||
from ...modeling_outputs import (
|
||||
BaseModelOutput,
|
||||
BaseModelOutputWithPooling,
|
||||
@ -35,12 +34,7 @@ from ...modeling_outputs import (
|
||||
TokenClassifierOutput,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from ...modeling_utils import PreTrainedModel
|
||||
from ...pytorch_utils import (
|
||||
apply_chunking_to_forward,
|
||||
find_pruneable_heads_and_indices,
|
||||
is_torch_greater_or_equal_than_2_2,
|
||||
prune_linear_layer,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from ...pytorch_utils import apply_chunking_to_forward, find_pruneable_heads_and_indices, prune_linear_layer
|
||||
from ...utils import (
|
||||
ModelOutput,
|
||||
add_code_sample_docstrings,
|
||||
@ -364,66 +358,6 @@ class AlbertAttention(nn.Module):
|
||||
return (layernormed_context_layer, attention_probs) if output_attentions else (layernormed_context_layer,)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class AlbertSdpaAttention(AlbertAttention):
|
||||
def __init__(self, config):
|
||||
super().__init__(config)
|
||||
self.dropout_prob = config.attention_probs_dropout_prob
|
||||
self.require_contiguous_qkv = not is_torch_greater_or_equal_than_2_2
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
hidden_states: torch.Tensor,
|
||||
attention_mask: Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None,
|
||||
head_mask: Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None,
|
||||
output_attentions: bool = False,
|
||||
) -> Union[Tuple[torch.Tensor], Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]]:
|
||||
if self.position_embedding_type != "absolute" or output_attentions or head_mask is not None:
|
||||
logger.warning(
|
||||
"AlbertSdpaAttention is used but `torch.nn.functional.scaled_dot_product_attention` does not support "
|
||||
"non-absolute `position_embedding_type` or `output_attentions=True` or `head_mask`. Falling back to "
|
||||
"the eager attention implementation, but specifying the eager implementation will be required from "
|
||||
"Transformers version v5.0.0 onwards. This warning can be removed using the argument "
|
||||
'`attn_implementation="eager"` when loading the model.'
|
||||
)
|
||||
return super().forward(hidden_states, attention_mask, head_mask, output_attentions)
|
||||
|
||||
batch_size, seq_len, _ = hidden_states.size()
|
||||
query_layer = self.transpose_for_scores(self.query(hidden_states))
|
||||
key_layer = self.transpose_for_scores(self.key(hidden_states))
|
||||
value_layer = self.transpose_for_scores(self.value(hidden_states))
|
||||
|
||||
# SDPA with memory-efficient backend is broken in torch==2.1.2 when using non-contiguous inputs and a custom
|
||||
# attn_mask, so we need to call `.contiguous()` here. This was fixed in torch==2.2.0.
|
||||
# Reference: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/112577
|
||||
if self.require_contiguous_qkv and query_layer.device.type == "cuda" and attention_mask is not None:
|
||||
query_layer = query_layer.contiguous()
|
||||
key_layer = key_layer.contiguous()
|
||||
value_layer = value_layer.contiguous()
|
||||
|
||||
attention_output = torch.nn.functional.scaled_dot_product_attention(
|
||||
query=query_layer,
|
||||
key=key_layer,
|
||||
value=value_layer,
|
||||
attn_mask=attention_mask,
|
||||
dropout_p=self.dropout_prob if self.training else 0.0,
|
||||
is_causal=False,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
attention_output = attention_output.transpose(1, 2)
|
||||
attention_output = attention_output.reshape(batch_size, seq_len, self.all_head_size)
|
||||
|
||||
projected_context_layer = self.dense(attention_output)
|
||||
projected_context_layer_dropout = self.output_dropout(projected_context_layer)
|
||||
layernormed_context_layer = self.LayerNorm(hidden_states + projected_context_layer_dropout)
|
||||
return (layernormed_context_layer,)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
ALBERT_ATTENTION_CLASSES = {
|
||||
"eager": AlbertAttention,
|
||||
"sdpa": AlbertSdpaAttention,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class AlbertLayer(nn.Module):
|
||||
def __init__(self, config: AlbertConfig):
|
||||
super().__init__()
|
||||
@ -432,7 +366,7 @@ class AlbertLayer(nn.Module):
|
||||
self.chunk_size_feed_forward = config.chunk_size_feed_forward
|
||||
self.seq_len_dim = 1
|
||||
self.full_layer_layer_norm = nn.LayerNorm(config.hidden_size, eps=config.layer_norm_eps)
|
||||
self.attention = ALBERT_ATTENTION_CLASSES[config._attn_implementation](config)
|
||||
self.attention = AlbertAttention(config)
|
||||
self.ffn = nn.Linear(config.hidden_size, config.intermediate_size)
|
||||
self.ffn_output = nn.Linear(config.intermediate_size, config.hidden_size)
|
||||
self.activation = ACT2FN[config.hidden_act]
|
||||
@ -562,7 +496,6 @@ class AlbertPreTrainedModel(PreTrainedModel):
|
||||
config_class = AlbertConfig
|
||||
load_tf_weights = load_tf_weights_in_albert
|
||||
base_model_prefix = "albert"
|
||||
_supports_sdpa = True
|
||||
|
||||
def _init_weights(self, module):
|
||||
"""Initialize the weights."""
|
||||
@ -702,9 +635,6 @@ class AlbertModel(AlbertPreTrainedModel):
|
||||
self.pooler = None
|
||||
self.pooler_activation = None
|
||||
|
||||
self.attn_implementation = config._attn_implementation
|
||||
self.position_embedding_type = config.position_embedding_type
|
||||
|
||||
# Initialize weights and apply final processing
|
||||
self.post_init()
|
||||
|
||||
@ -778,28 +708,14 @@ class AlbertModel(AlbertPreTrainedModel):
|
||||
else:
|
||||
token_type_ids = torch.zeros(input_shape, dtype=torch.long, device=device)
|
||||
|
||||
extended_attention_mask = attention_mask.unsqueeze(1).unsqueeze(2)
|
||||
extended_attention_mask = extended_attention_mask.to(dtype=self.dtype) # fp16 compatibility
|
||||
extended_attention_mask = (1.0 - extended_attention_mask) * torch.finfo(self.dtype).min
|
||||
head_mask = self.get_head_mask(head_mask, self.config.num_hidden_layers)
|
||||
|
||||
embedding_output = self.embeddings(
|
||||
input_ids, position_ids=position_ids, token_type_ids=token_type_ids, inputs_embeds=inputs_embeds
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
use_sdpa_attention_mask = (
|
||||
self.attn_implementation == "sdpa"
|
||||
and self.position_embedding_type == "absolute"
|
||||
and head_mask is None
|
||||
and not output_attentions
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if use_sdpa_attention_mask:
|
||||
extended_attention_mask = _prepare_4d_attention_mask_for_sdpa(
|
||||
attention_mask, embedding_output.dtype, tgt_len=seq_length
|
||||
)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
extended_attention_mask = attention_mask.unsqueeze(1).unsqueeze(2)
|
||||
extended_attention_mask = extended_attention_mask.to(dtype=self.dtype) # fp16 compatibility
|
||||
extended_attention_mask = (1.0 - extended_attention_mask) * torch.finfo(self.dtype).min
|
||||
|
||||
head_mask = self.get_head_mask(head_mask, self.config.num_hidden_layers)
|
||||
|
||||
encoder_outputs = self.encoder(
|
||||
embedding_output,
|
||||
extended_attention_mask,
|
||||
|
||||
@ -17,6 +17,7 @@
|
||||
import copy
|
||||
import importlib
|
||||
import json
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import warnings
|
||||
from collections import OrderedDict
|
||||
|
||||
@ -426,7 +427,10 @@ class _BaseAutoModelClass:
|
||||
else:
|
||||
repo_id = config.name_or_path
|
||||
model_class = get_class_from_dynamic_module(class_ref, repo_id, **kwargs)
|
||||
cls.register(config.__class__, model_class, exist_ok=True)
|
||||
if os.path.isdir(config._name_or_path):
|
||||
model_class.register_for_auto_class(cls.__name__)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
cls.register(config.__class__, model_class, exist_ok=True)
|
||||
_ = kwargs.pop("code_revision", None)
|
||||
return model_class._from_config(config, **kwargs)
|
||||
elif type(config) in cls._model_mapping.keys():
|
||||
@ -548,7 +552,10 @@ class _BaseAutoModelClass:
|
||||
class_ref, pretrained_model_name_or_path, code_revision=code_revision, **hub_kwargs, **kwargs
|
||||
)
|
||||
_ = hub_kwargs.pop("code_revision", None)
|
||||
cls.register(config.__class__, model_class, exist_ok=True)
|
||||
if os.path.isdir(pretrained_model_name_or_path):
|
||||
model_class.register_for_auto_class(cls.__name__)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
cls.register(config.__class__, model_class, exist_ok=True)
|
||||
return model_class.from_pretrained(
|
||||
pretrained_model_name_or_path, *model_args, config=config, **hub_kwargs, **kwargs
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -149,7 +149,6 @@ CONFIG_MAPPING_NAMES = OrderedDict(
|
||||
("llava", "LlavaConfig"),
|
||||
("llava_next", "LlavaNextConfig"),
|
||||
("llava_next_video", "LlavaNextVideoConfig"),
|
||||
("llava_onevision", "LlavaOnevisionConfig"),
|
||||
("longformer", "LongformerConfig"),
|
||||
("longt5", "LongT5Config"),
|
||||
("luke", "LukeConfig"),
|
||||
@ -188,7 +187,6 @@ CONFIG_MAPPING_NAMES = OrderedDict(
|
||||
("nougat", "VisionEncoderDecoderConfig"),
|
||||
("nystromformer", "NystromformerConfig"),
|
||||
("olmo", "OlmoConfig"),
|
||||
("olmoe", "OlmoeConfig"),
|
||||
("oneformer", "OneFormerConfig"),
|
||||
("open-llama", "OpenLlamaConfig"),
|
||||
("openai-gpt", "OpenAIGPTConfig"),
|
||||
@ -445,7 +443,6 @@ MODEL_NAMES_MAPPING = OrderedDict(
|
||||
("llava", "LLaVa"),
|
||||
("llava_next", "LLaVA-NeXT"),
|
||||
("llava_next_video", "LLaVa-NeXT-Video"),
|
||||
("llava_onevision", "LLaVA-Onevision"),
|
||||
("longformer", "Longformer"),
|
||||
("longt5", "LongT5"),
|
||||
("luke", "LUKE"),
|
||||
@ -491,7 +488,6 @@ MODEL_NAMES_MAPPING = OrderedDict(
|
||||
("nougat", "Nougat"),
|
||||
("nystromformer", "Nyströmformer"),
|
||||
("olmo", "OLMo"),
|
||||
("olmoe", "OLMoE"),
|
||||
("oneformer", "OneFormer"),
|
||||
("open-llama", "OpenLlama"),
|
||||
("openai-gpt", "OpenAI GPT"),
|
||||
|
||||
@ -99,7 +99,6 @@ else:
|
||||
("llava", ("CLIPImageProcessor",)),
|
||||
("llava_next", ("LlavaNextImageProcessor",)),
|
||||
("llava_next_video", ("LlavaNextVideoImageProcessor",)),
|
||||
("llava_onevision", ("LlavaOnevisionImageProcessor",)),
|
||||
("mask2former", ("Mask2FormerImageProcessor",)),
|
||||
("maskformer", ("MaskFormerImageProcessor",)),
|
||||
("mgp-str", ("ViTImageProcessor", "ViTImageProcessorFast")),
|
||||
|
||||
@ -178,7 +178,6 @@ MODEL_MAPPING_NAMES = OrderedDict(
|
||||
("nllb-moe", "NllbMoeModel"),
|
||||
("nystromformer", "NystromformerModel"),
|
||||
("olmo", "OlmoModel"),
|
||||
("olmoe", "OlmoeModel"),
|
||||
("oneformer", "OneFormerModel"),
|
||||
("open-llama", "OpenLlamaModel"),
|
||||
("openai-gpt", "OpenAIGPTModel"),
|
||||
@ -314,7 +313,6 @@ MODEL_FOR_PRETRAINING_MAPPING_NAMES = OrderedDict(
|
||||
("llava", "LlavaForConditionalGeneration"),
|
||||
("llava_next", "LlavaNextForConditionalGeneration"),
|
||||
("llava_next_video", "LlavaNextVideoForConditionalGeneration"),
|
||||
("llava_onevision", "LlavaOnevisionForConditionalGeneration"),
|
||||
("longformer", "LongformerForMaskedLM"),
|
||||
("luke", "LukeForMaskedLM"),
|
||||
("lxmert", "LxmertForPreTraining"),
|
||||
@ -500,7 +498,6 @@ MODEL_FOR_CAUSAL_LM_MAPPING_NAMES = OrderedDict(
|
||||
("mvp", "MvpForCausalLM"),
|
||||
("nemotron", "NemotronForCausalLM"),
|
||||
("olmo", "OlmoForCausalLM"),
|
||||
("olmoe", "OlmoeForCausalLM"),
|
||||
("open-llama", "OpenLlamaForCausalLM"),
|
||||
("openai-gpt", "OpenAIGPTLMHeadModel"),
|
||||
("opt", "OPTForCausalLM"),
|
||||
@ -730,7 +727,6 @@ MODEL_FOR_VISION_2_SEQ_MAPPING_NAMES = OrderedDict(
|
||||
("llava", "LlavaForConditionalGeneration"),
|
||||
("llava_next", "LlavaNextForConditionalGeneration"),
|
||||
("llava_next_video", "LlavaNextVideoForConditionalGeneration"),
|
||||
("llava_onevision", "LlavaOnevisionForConditionalGeneration"),
|
||||
("paligemma", "PaliGemmaForConditionalGeneration"),
|
||||
("pix2struct", "Pix2StructForConditionalGeneration"),
|
||||
("qwen2_vl", "Qwen2VLForConditionalGeneration"),
|
||||
|
||||
@ -73,7 +73,6 @@ PROCESSOR_MAPPING_NAMES = OrderedDict(
|
||||
("llava", "LlavaProcessor"),
|
||||
("llava_next", "LlavaNextProcessor"),
|
||||
("llava_next_video", "LlavaNextVideoProcessor"),
|
||||
("llava_onevision", "LlavaOnevisionProcessor"),
|
||||
("markuplm", "MarkupLMProcessor"),
|
||||
("mctct", "MCTCTProcessor"),
|
||||
("mgp-str", "MgpstrProcessor"),
|
||||
|
||||
@ -257,7 +257,6 @@ else:
|
||||
),
|
||||
),
|
||||
("llava", ("LlamaTokenizer", "LlamaTokenizerFast" if is_tokenizers_available() else None)),
|
||||
("llava-onevision", ("LlamaTokenizer", "LlamaTokenizerFast" if is_tokenizers_available() else None)),
|
||||
("llava_next", ("LlamaTokenizer", "LlamaTokenizerFast" if is_tokenizers_available() else None)),
|
||||
("llava_next_video", ("LlamaTokenizer", "LlamaTokenizerFast" if is_tokenizers_available() else None)),
|
||||
("longformer", ("LongformerTokenizer", "LongformerTokenizerFast" if is_tokenizers_available() else None)),
|
||||
@ -343,7 +342,6 @@ else:
|
||||
),
|
||||
),
|
||||
("olmo", (None, "GPTNeoXTokenizerFast" if is_tokenizers_available() else None)),
|
||||
("olmoe", (None, "GPTNeoXTokenizerFast" if is_tokenizers_available() else None)),
|
||||
("oneformer", ("CLIPTokenizer", "CLIPTokenizerFast" if is_tokenizers_available() else None)),
|
||||
(
|
||||
"openai-gpt",
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1248,17 +1248,6 @@ class BarkFineModel(BarkPreTrainedModel):
|
||||
|
||||
return model_embeds
|
||||
|
||||
def _tie_weights(self):
|
||||
if getattr(self.config, "tie_word_embeddings", True):
|
||||
self._tied_weights_keys = []
|
||||
output_embeddings = self.get_output_embeddings()
|
||||
input_embeddings = self.get_input_embeddings()
|
||||
|
||||
for i in range(self.config.n_codes_total - self.config.n_codes_given):
|
||||
# self.input_embeds_layers[i + 1].weight = self.lm_heads[i].weight
|
||||
self._tie_or_clone_weights(output_embeddings[i], input_embeddings[i + 1])
|
||||
self._tied_weights_keys.append(f"lm_heads.{i}.weight")
|
||||
|
||||
def tie_weights(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Tie the weights between the input embeddings list and the output embeddings list.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -41,7 +41,6 @@ from ...utils import (
|
||||
add_start_docstrings_to_model_forward,
|
||||
logging,
|
||||
replace_return_docstrings,
|
||||
torch_int,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from ...utils.backbone_utils import BackboneMixin
|
||||
from .configuration_beit import BeitConfig
|
||||
@ -151,46 +150,41 @@ class BeitEmbeddings(nn.Module):
|
||||
self.position_embeddings = None
|
||||
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(config.hidden_dropout_prob)
|
||||
|
||||
# Copied from transformers.models.vit.modeling_vit.ViTEmbeddings.interpolate_pos_encoding
|
||||
def interpolate_pos_encoding(self, embeddings: torch.Tensor, height: int, width: int) -> torch.Tensor:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
This method allows to interpolate the pre-trained position encodings, to be able to use the model on higher resolution
|
||||
images. This method is also adapted to support torch.jit tracing.
|
||||
This method allows the model to interpolate the pre-trained position encodings so that it can be used on
|
||||
higher resolution images.
|
||||
|
||||
Adapted from:
|
||||
- https://github.com/facebookresearch/dino/blob/de9ee3df6cf39fac952ab558447af1fa1365362a/vision_transformer.py#L174-L194, and
|
||||
- https://github.com/facebookresearch/dinov2/blob/e1277af2ba9496fbadf7aec6eba56e8d882d1e35/dinov2/models/vision_transformer.py#L179-L211
|
||||
Source:
|
||||
https://github.com/facebookresearch/dino/blob/de9ee3df6cf39fac952ab558447af1fa1365362a/vision_transformer.py#L174
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
num_patches = embeddings.shape[1] - 1
|
||||
num_positions = self.position_embeddings.shape[1] - 1
|
||||
|
||||
# always interpolate when tracing to ensure the exported model works for dynamic input shapes
|
||||
if not torch.jit.is_tracing() and num_patches == num_positions and height == width:
|
||||
if num_patches == num_positions and height == width:
|
||||
return self.position_embeddings
|
||||
|
||||
class_pos_embed = self.position_embeddings[:, :1]
|
||||
class_pos_embed = self.position_embeddings[:, 0]
|
||||
patch_pos_embed = self.position_embeddings[:, 1:]
|
||||
|
||||
dim = embeddings.shape[-1]
|
||||
h = height // self.patch_size
|
||||
w = width // self.patch_size
|
||||
# we add a small number to avoid floating point error in the interpolation
|
||||
# see discussion at https://github.com/facebookresearch/dino/issues/8
|
||||
h, w = h + 0.1, w + 0.1
|
||||
|
||||
new_height = height // self.patch_size
|
||||
new_width = width // self.patch_size
|
||||
|
||||
sqrt_num_positions = torch_int(num_positions**0.5)
|
||||
patch_pos_embed = patch_pos_embed.reshape(1, sqrt_num_positions, sqrt_num_positions, dim)
|
||||
patch_pos_embed = patch_pos_embed.reshape(1, int(math.sqrt(num_positions)), int(math.sqrt(num_positions)), dim)
|
||||
patch_pos_embed = patch_pos_embed.permute(0, 3, 1, 2)
|
||||
|
||||
patch_pos_embed = nn.functional.interpolate(
|
||||
patch_pos_embed,
|
||||
size=(new_height, new_width),
|
||||
scale_factor=(h / math.sqrt(num_positions), w / math.sqrt(num_positions)),
|
||||
mode="bicubic",
|
||||
align_corners=False,
|
||||
)
|
||||
if int(h) != patch_pos_embed.shape[-2] or int(w) != patch_pos_embed.shape[-1]:
|
||||
raise ValueError("Width or height does not match with the interpolated position embeddings")
|
||||
|
||||
patch_pos_embed = patch_pos_embed.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).view(1, -1, dim)
|
||||
|
||||
return torch.cat((class_pos_embed, patch_pos_embed), dim=1)
|
||||
return torch.cat((class_pos_embed.unsqueeze(0), patch_pos_embed), dim=1)
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
@ -572,7 +566,7 @@ class BeitRelativePositionBias(nn.Module):
|
||||
|
||||
old_sub_table = old_sub_table.reshape(1, old_width, old_height, -1).permute(0, 3, 1, 2)
|
||||
new_sub_table = nn.functional.interpolate(
|
||||
old_sub_table, size=(torch_int(new_height), torch_int(new_width)), mode="bilinear"
|
||||
old_sub_table, size=(int(new_height), int(new_width)), mode="bilinear"
|
||||
)
|
||||
new_sub_table = new_sub_table.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).reshape(new_num_relative_distance - 3, -1)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -294,27 +294,31 @@ class BitImageProcessor(BaseImageProcessor):
|
||||
# We assume that all images have the same channel dimension format.
|
||||
input_data_format = infer_channel_dimension_format(images[0])
|
||||
|
||||
all_images = []
|
||||
for image in images:
|
||||
if do_resize:
|
||||
image = self.resize(image=image, size=size, resample=resample, input_data_format=input_data_format)
|
||||
if do_resize:
|
||||
images = [
|
||||
self.resize(image=image, size=size, resample=resample, input_data_format=input_data_format)
|
||||
for image in images
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
if do_center_crop:
|
||||
image = self.center_crop(image=image, size=crop_size, input_data_format=input_data_format)
|
||||
if do_center_crop:
|
||||
images = [
|
||||
self.center_crop(image=image, size=crop_size, input_data_format=input_data_format) for image in images
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
if do_rescale:
|
||||
image = self.rescale(image=image, scale=rescale_factor, input_data_format=input_data_format)
|
||||
if do_rescale:
|
||||
images = [
|
||||
self.rescale(image=image, scale=rescale_factor, input_data_format=input_data_format)
|
||||
for image in images
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
if do_normalize:
|
||||
image = self.normalize(
|
||||
image=image, mean=image_mean, std=image_std, input_data_format=input_data_format
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
all_images.append(image)
|
||||
if do_normalize:
|
||||
images = [
|
||||
self.normalize(image=image, mean=image_mean, std=image_std, input_data_format=input_data_format)
|
||||
for image in images
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
images = [
|
||||
to_channel_dimension_format(image, data_format, input_channel_dim=input_data_format)
|
||||
for image in all_images
|
||||
to_channel_dimension_format(image, data_format, input_channel_dim=input_data_format) for image in images
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
data = {"pixel_values": images}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -14,6 +14,7 @@
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
"""PyTorch BLIP model."""
|
||||
|
||||
import math
|
||||
import warnings
|
||||
from dataclasses import dataclass
|
||||
from typing import Any, Optional, Tuple, Union
|
||||
@ -32,7 +33,6 @@ from ...utils import (
|
||||
add_start_docstrings_to_model_forward,
|
||||
logging,
|
||||
replace_return_docstrings,
|
||||
torch_int,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from .configuration_blip import BlipConfig, BlipTextConfig, BlipVisionConfig
|
||||
from .modeling_blip_text import BlipTextLMHeadModel, BlipTextModel
|
||||
@ -232,46 +232,38 @@ class BlipVisionEmbeddings(nn.Module):
|
||||
|
||||
self.position_embedding = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(1, self.num_positions, self.embed_dim))
|
||||
|
||||
# Copied from transformers.models.vit.modeling_vit.ViTEmbeddings.interpolate_pos_encoding
|
||||
def interpolate_pos_encoding(self, embeddings: torch.Tensor, height: int, width: int) -> torch.Tensor:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
This method allows to interpolate the pre-trained position encodings, to be able to use the model on higher resolution
|
||||
images. This method is also adapted to support torch.jit tracing.
|
||||
This method allows to interpolate the pre-trained position encodings, to be able to use the model on higher
|
||||
resolution images.
|
||||
|
||||
Adapted from:
|
||||
- https://github.com/facebookresearch/dino/blob/de9ee3df6cf39fac952ab558447af1fa1365362a/vision_transformer.py#L174-L194, and
|
||||
- https://github.com/facebookresearch/dinov2/blob/e1277af2ba9496fbadf7aec6eba56e8d882d1e35/dinov2/models/vision_transformer.py#L179-L211
|
||||
Source:
|
||||
https://github.com/facebookresearch/dino/blob/de9ee3df6cf39fac952ab558447af1fa1365362a/vision_transformer.py#L174
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
num_patches = embeddings.shape[1] - 1
|
||||
num_positions = self.position_embeddings.shape[1] - 1
|
||||
num_positions = self.position_embedding.shape[1] - 1
|
||||
|
||||
# always interpolate when tracing to ensure the exported model works for dynamic input shapes
|
||||
if not torch.jit.is_tracing() and num_patches == num_positions and height == width:
|
||||
return self.position_embeddings
|
||||
|
||||
class_pos_embed = self.position_embeddings[:, :1]
|
||||
patch_pos_embed = self.position_embeddings[:, 1:]
|
||||
if num_patches == num_positions and height == width:
|
||||
return self.position_embedding
|
||||
|
||||
class_pos_embed = self.position_embedding[:, 0, :]
|
||||
patch_pos_embed = self.position_embedding[:, 1:, :]
|
||||
dim = embeddings.shape[-1]
|
||||
|
||||
new_height = height // self.patch_size
|
||||
new_width = width // self.patch_size
|
||||
|
||||
sqrt_num_positions = torch_int(num_positions**0.5)
|
||||
patch_pos_embed = patch_pos_embed.reshape(1, sqrt_num_positions, sqrt_num_positions, dim)
|
||||
h0 = height // self.config.patch_size
|
||||
w0 = width // self.config.patch_size
|
||||
# we add a small number to avoid floating point error in the interpolation
|
||||
# see discussion at https://github.com/facebookresearch/dino/issues/8
|
||||
h0, w0 = h0 + 0.1, w0 + 0.1
|
||||
patch_pos_embed = patch_pos_embed.reshape(1, int(math.sqrt(num_positions)), int(math.sqrt(num_positions)), dim)
|
||||
patch_pos_embed = patch_pos_embed.permute(0, 3, 1, 2)
|
||||
|
||||
patch_pos_embed = nn.functional.interpolate(
|
||||
patch_pos_embed,
|
||||
size=(new_height, new_width),
|
||||
scale_factor=(h0 / math.sqrt(num_positions), w0 / math.sqrt(num_positions)),
|
||||
mode="bicubic",
|
||||
align_corners=False,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
patch_pos_embed = patch_pos_embed.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).view(1, -1, dim)
|
||||
|
||||
return torch.cat((class_pos_embed, patch_pos_embed), dim=1)
|
||||
return torch.cat((class_pos_embed.unsqueeze(0), patch_pos_embed), dim=1)
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, pixel_values: torch.FloatTensor, interpolate_pos_encoding: bool = False) -> torch.Tensor:
|
||||
batch_size, _, height, width = pixel_values.shape
|
||||
|
||||
@ -38,7 +38,6 @@ from ...utils import (
|
||||
add_start_docstrings_to_model_forward,
|
||||
logging,
|
||||
replace_return_docstrings,
|
||||
torch_int,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from ..auto import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM
|
||||
from .configuration_blip_2 import Blip2Config, Blip2QFormerConfig, Blip2VisionConfig
|
||||
@ -199,46 +198,38 @@ class Blip2VisionEmbeddings(nn.Module):
|
||||
|
||||
self.position_embedding = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(1, self.num_positions, self.embed_dim))
|
||||
|
||||
# Copied from transformers.models.vit.modeling_vit.ViTEmbeddings.interpolate_pos_encoding
|
||||
def interpolate_pos_encoding(self, embeddings: torch.Tensor, height: int, width: int) -> torch.Tensor:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
This method allows to interpolate the pre-trained position encodings, to be able to use the model on higher resolution
|
||||
images. This method is also adapted to support torch.jit tracing.
|
||||
This method allows to interpolate the pre-trained position encodings, to be able to use the model on higher
|
||||
resolution images.
|
||||
|
||||
Adapted from:
|
||||
- https://github.com/facebookresearch/dino/blob/de9ee3df6cf39fac952ab558447af1fa1365362a/vision_transformer.py#L174-L194, and
|
||||
- https://github.com/facebookresearch/dinov2/blob/e1277af2ba9496fbadf7aec6eba56e8d882d1e35/dinov2/models/vision_transformer.py#L179-L211
|
||||
Source:
|
||||
https://github.com/facebookresearch/dino/blob/de9ee3df6cf39fac952ab558447af1fa1365362a/vision_transformer.py#L174
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
num_patches = embeddings.shape[1] - 1
|
||||
num_positions = self.position_embeddings.shape[1] - 1
|
||||
num_positions = self.position_embedding.shape[1] - 1
|
||||
|
||||
# always interpolate when tracing to ensure the exported model works for dynamic input shapes
|
||||
if not torch.jit.is_tracing() and num_patches == num_positions and height == width:
|
||||
return self.position_embeddings
|
||||
|
||||
class_pos_embed = self.position_embeddings[:, :1]
|
||||
patch_pos_embed = self.position_embeddings[:, 1:]
|
||||
if num_patches == num_positions and height == width:
|
||||
return self.position_embedding
|
||||
|
||||
class_pos_embed = self.position_embedding[:, 0, :]
|
||||
patch_pos_embed = self.position_embedding[:, 1:, :]
|
||||
dim = embeddings.shape[-1]
|
||||
|
||||
new_height = height // self.patch_size
|
||||
new_width = width // self.patch_size
|
||||
|
||||
sqrt_num_positions = torch_int(num_positions**0.5)
|
||||
patch_pos_embed = patch_pos_embed.reshape(1, sqrt_num_positions, sqrt_num_positions, dim)
|
||||
h0 = height // self.config.patch_size
|
||||
w0 = width // self.config.patch_size
|
||||
# we add a small number to avoid floating point error in the interpolation
|
||||
# see discussion at https://github.com/facebookresearch/dino/issues/8
|
||||
h0, w0 = h0 + 0.1, w0 + 0.1
|
||||
patch_pos_embed = patch_pos_embed.reshape(1, int(math.sqrt(num_positions)), int(math.sqrt(num_positions)), dim)
|
||||
patch_pos_embed = patch_pos_embed.permute(0, 3, 1, 2)
|
||||
|
||||
patch_pos_embed = nn.functional.interpolate(
|
||||
patch_pos_embed,
|
||||
size=(new_height, new_width),
|
||||
scale_factor=(h0 / math.sqrt(num_positions), w0 / math.sqrt(num_positions)),
|
||||
mode="bicubic",
|
||||
align_corners=False,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
patch_pos_embed = patch_pos_embed.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).view(1, -1, dim)
|
||||
|
||||
return torch.cat((class_pos_embed, patch_pos_embed), dim=1)
|
||||
return torch.cat((class_pos_embed.unsqueeze(0), patch_pos_embed), dim=1)
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, pixel_values: torch.FloatTensor, interpolate_pos_encoding: bool = False) -> torch.Tensor:
|
||||
batch_size, _, height, width = pixel_values.shape
|
||||
|
||||
@ -551,8 +551,7 @@ BLOOM_INPUTS_DOCSTRING = r"""
|
||||
returned by the model at a previous stage of decoding, when `use_cache=True` or `config.use_cache=True`.
|
||||
|
||||
Two formats are allowed:
|
||||
- a [`~cache_utils.Cache`] instance, see our
|
||||
[kv cache guide](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/en/kv_cache);
|
||||
- a [`~cache_utils.Cache`] instance;
|
||||
- Tuple of `tuple(torch.FloatTensor)` of length `config.n_layers`, with each tuple having 2 tensors of
|
||||
shape `(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, embed_size_per_head)`). This is also known as the legacy
|
||||
cache format.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -311,26 +311,32 @@ class ChameleonImageProcessor(BaseImageProcessor):
|
||||
if input_data_format is None:
|
||||
# We assume that all images have the same channel dimension format.
|
||||
input_data_format = infer_channel_dimension_format(images[0])
|
||||
all_images = []
|
||||
for image in images:
|
||||
if do_resize:
|
||||
image = self.resize(image=image, size=size, resample=resample, input_data_format=input_data_format)
|
||||
|
||||
if do_center_crop:
|
||||
image = self.center_crop(image=image, size=crop_size, input_data_format=input_data_format)
|
||||
if do_resize:
|
||||
images = [
|
||||
self.resize(image=image, size=size, resample=resample, input_data_format=input_data_format)
|
||||
for image in images
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
if do_rescale:
|
||||
image = self.rescale(image=image, scale=rescale_factor, input_data_format=input_data_format)
|
||||
if do_center_crop:
|
||||
images = [
|
||||
self.center_crop(image=image, size=crop_size, input_data_format=input_data_format) for image in images
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
if do_normalize:
|
||||
image = self.normalize(
|
||||
image=image, mean=image_mean, std=image_std, input_data_format=input_data_format
|
||||
)
|
||||
if do_rescale:
|
||||
images = [
|
||||
self.rescale(image=image, scale=rescale_factor, input_data_format=input_data_format)
|
||||
for image in images
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
if do_normalize:
|
||||
images = [
|
||||
self.normalize(image=image, mean=image_mean, std=image_std, input_data_format=input_data_format)
|
||||
for image in images
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
all_images.append(image)
|
||||
images = [
|
||||
to_channel_dimension_format(image, data_format, input_channel_dim=input_data_format)
|
||||
for image in all_images
|
||||
to_channel_dimension_format(image, data_format, input_channel_dim=input_data_format) for image in images
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
data = {"pixel_values": images}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -280,26 +280,31 @@ class ChineseCLIPImageProcessor(BaseImageProcessor):
|
||||
# We assume that all images have the same channel dimension format.
|
||||
input_data_format = infer_channel_dimension_format(images[0])
|
||||
|
||||
all_images = []
|
||||
for image in images:
|
||||
if do_resize:
|
||||
image = self.resize(image=image, size=size, resample=resample, input_data_format=input_data_format)
|
||||
if do_resize:
|
||||
images = [
|
||||
self.resize(image=image, size=size, resample=resample, input_data_format=input_data_format)
|
||||
for image in images
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
if do_center_crop:
|
||||
image = self.center_crop(image=image, size=crop_size, input_data_format=input_data_format)
|
||||
if do_center_crop:
|
||||
images = [
|
||||
self.center_crop(image=image, size=crop_size, input_data_format=input_data_format) for image in images
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
if do_rescale:
|
||||
image = self.rescale(image=image, scale=rescale_factor, input_data_format=input_data_format)
|
||||
if do_rescale:
|
||||
images = [
|
||||
self.rescale(image=image, scale=rescale_factor, input_data_format=input_data_format)
|
||||
for image in images
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
if do_normalize:
|
||||
image = self.normalize(
|
||||
image=image, mean=image_mean, std=image_std, input_data_format=input_data_format
|
||||
)
|
||||
if do_normalize:
|
||||
images = [
|
||||
self.normalize(image=image, mean=image_mean, std=image_std, input_data_format=input_data_format)
|
||||
for image in images
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
all_images.append(image)
|
||||
images = [
|
||||
to_channel_dimension_format(image, data_format, input_channel_dim=input_data_format)
|
||||
for image in all_images
|
||||
to_channel_dimension_format(image, data_format, input_channel_dim=input_data_format) for image in images
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
data = {"pixel_values": images}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -319,26 +319,31 @@ class CLIPImageProcessor(BaseImageProcessor):
|
||||
# We assume that all images have the same channel dimension format.
|
||||
input_data_format = infer_channel_dimension_format(images[0])
|
||||
|
||||
all_images = []
|
||||
for image in images:
|
||||
if do_resize:
|
||||
image = self.resize(image=image, size=size, resample=resample, input_data_format=input_data_format)
|
||||
if do_resize:
|
||||
images = [
|
||||
self.resize(image=image, size=size, resample=resample, input_data_format=input_data_format)
|
||||
for image in images
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
if do_center_crop:
|
||||
image = self.center_crop(image=image, size=crop_size, input_data_format=input_data_format)
|
||||
if do_center_crop:
|
||||
images = [
|
||||
self.center_crop(image=image, size=crop_size, input_data_format=input_data_format) for image in images
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
if do_rescale:
|
||||
image = self.rescale(image=image, scale=rescale_factor, input_data_format=input_data_format)
|
||||
if do_rescale:
|
||||
images = [
|
||||
self.rescale(image=image, scale=rescale_factor, input_data_format=input_data_format)
|
||||
for image in images
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
if do_normalize:
|
||||
image = self.normalize(
|
||||
image=image, mean=image_mean, std=image_std, input_data_format=input_data_format
|
||||
)
|
||||
if do_normalize:
|
||||
images = [
|
||||
self.normalize(image=image, mean=image_mean, std=image_std, input_data_format=input_data_format)
|
||||
for image in images
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
all_images.append(image)
|
||||
images = [
|
||||
to_channel_dimension_format(image, data_format, input_channel_dim=input_data_format)
|
||||
for image in all_images
|
||||
to_channel_dimension_format(image, data_format, input_channel_dim=input_data_format) for image in images
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
data = {"pixel_values": images}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -735,7 +735,7 @@ class ClvpPreTrainedModel(PreTrainedModel):
|
||||
nn.init.normal_(module.fc1.proj.weight if getattr(module.fc1, "proj") else module.fc1.weight, std=fc_std)
|
||||
nn.init.normal_(module.fc2.weight, std=in_proj_std)
|
||||
elif isinstance(module, ClvpEncoder):
|
||||
config = self.config.get_text_config()
|
||||
config = self.config.text_config if hasattr(self.config, "text_config") else self.config
|
||||
factor = config.initializer_factor
|
||||
module.projection.weight.data.normal_(mean=0.0, std=factor * (config.hidden_size**-0.5))
|
||||
elif isinstance(module, ClvpConditioningEncoder):
|
||||
|
||||
@ -429,8 +429,7 @@ CODEGEN_INPUTS_DOCSTRING = r"""
|
||||
returned by the model at a previous stage of decoding, when `use_cache=True` or `config.use_cache=True`.
|
||||
|
||||
Two formats are allowed:
|
||||
- a [`~cache_utils.Cache`] instance, see our
|
||||
[kv cache guide](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/en/kv_cache);
|
||||
- a [`~cache_utils.Cache`] instance;
|
||||
- Tuple of `tuple(torch.FloatTensor)` of length `config.n_layers`, with each tuple having 2 tensors of
|
||||
shape `(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, embed_size_per_head)`). This is also known as the legacy
|
||||
cache format.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -721,8 +721,7 @@ COHERE_INPUTS_DOCSTRING = r"""
|
||||
returned by the model at a previous stage of decoding, when `use_cache=True` or `config.use_cache=True`.
|
||||
|
||||
Two formats are allowed:
|
||||
- a [`~cache_utils.Cache`] instance, see our
|
||||
[kv cache guide](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/en/kv_cache);
|
||||
- a [`~cache_utils.Cache`] instance;
|
||||
- Tuple of `tuple(torch.FloatTensor)` of length `config.n_layers`, with each tuple having 2 tensors of
|
||||
shape `(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, embed_size_per_head)`). This is also known as the legacy
|
||||
cache format.
|
||||
@ -1119,7 +1118,7 @@ class CohereForCausalLM(CoherePreTrainedModel):
|
||||
cache_position=None,
|
||||
position_ids=None,
|
||||
use_cache=True,
|
||||
num_logits_to_keep=None,
|
||||
num_logits_to_keep=0,
|
||||
**kwargs,
|
||||
):
|
||||
# If we have cache: let's slice `input_ids` through `cache_position`, to keep only the unprocessed tokens
|
||||
@ -1170,9 +1169,6 @@ class CohereForCausalLM(CoherePreTrainedModel):
|
||||
batch_size=batch_size,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if num_logits_to_keep is not None:
|
||||
model_inputs["num_logits_to_keep"] = num_logits_to_keep
|
||||
|
||||
model_inputs.update(
|
||||
{
|
||||
"position_ids": position_ids,
|
||||
@ -1180,6 +1176,7 @@ class CohereForCausalLM(CoherePreTrainedModel):
|
||||
"past_key_values": past_key_values,
|
||||
"use_cache": use_cache,
|
||||
"attention_mask": attention_mask,
|
||||
"num_logits_to_keep": num_logits_to_keep,
|
||||
}
|
||||
)
|
||||
return model_inputs
|
||||
|
||||
@ -39,7 +39,6 @@ from ...utils import (
|
||||
add_start_docstrings_to_model_forward,
|
||||
logging,
|
||||
replace_return_docstrings,
|
||||
torch_int,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from .configuration_data2vec_vision import Data2VecVisionConfig
|
||||
|
||||
@ -150,46 +149,41 @@ class Data2VecVisionEmbeddings(nn.Module):
|
||||
self.position_embeddings = None
|
||||
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(config.hidden_dropout_prob)
|
||||
|
||||
# Copied from transformers.models.vit.modeling_vit.ViTEmbeddings.interpolate_pos_encoding
|
||||
def interpolate_pos_encoding(self, embeddings: torch.Tensor, height: int, width: int) -> torch.Tensor:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
This method allows to interpolate the pre-trained position encodings, to be able to use the model on higher resolution
|
||||
images. This method is also adapted to support torch.jit tracing.
|
||||
This method allows the model to interpolate the pre-trained position encodings so that it can be used on
|
||||
higher resolution images.
|
||||
|
||||
Adapted from:
|
||||
- https://github.com/facebookresearch/dino/blob/de9ee3df6cf39fac952ab558447af1fa1365362a/vision_transformer.py#L174-L194, and
|
||||
- https://github.com/facebookresearch/dinov2/blob/e1277af2ba9496fbadf7aec6eba56e8d882d1e35/dinov2/models/vision_transformer.py#L179-L211
|
||||
Source:
|
||||
https://github.com/facebookresearch/dino/blob/de9ee3df6cf39fac952ab558447af1fa1365362a/vision_transformer.py#L174
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
num_patches = embeddings.shape[1] - 1
|
||||
num_positions = self.position_embeddings.shape[1] - 1
|
||||
|
||||
# always interpolate when tracing to ensure the exported model works for dynamic input shapes
|
||||
if not torch.jit.is_tracing() and num_patches == num_positions and height == width:
|
||||
if num_patches == num_positions and height == width:
|
||||
return self.position_embeddings
|
||||
|
||||
class_pos_embed = self.position_embeddings[:, :1]
|
||||
class_pos_embed = self.position_embeddings[:, 0]
|
||||
patch_pos_embed = self.position_embeddings[:, 1:]
|
||||
|
||||
dim = embeddings.shape[-1]
|
||||
h = height // self.patch_size
|
||||
w = width // self.patch_size
|
||||
# we add a small number to avoid floating point error in the interpolation
|
||||
# see discussion at https://github.com/facebookresearch/dino/issues/8
|
||||
h, w = h + 0.1, w + 0.1
|
||||
|
||||
new_height = height // self.patch_size
|
||||
new_width = width // self.patch_size
|
||||
|
||||
sqrt_num_positions = torch_int(num_positions**0.5)
|
||||
patch_pos_embed = patch_pos_embed.reshape(1, sqrt_num_positions, sqrt_num_positions, dim)
|
||||
patch_pos_embed = patch_pos_embed.reshape(1, int(math.sqrt(num_positions)), int(math.sqrt(num_positions)), dim)
|
||||
patch_pos_embed = patch_pos_embed.permute(0, 3, 1, 2)
|
||||
|
||||
patch_pos_embed = nn.functional.interpolate(
|
||||
patch_pos_embed,
|
||||
size=(new_height, new_width),
|
||||
scale_factor=(h / math.sqrt(num_positions), w / math.sqrt(num_positions)),
|
||||
mode="bicubic",
|
||||
align_corners=False,
|
||||
)
|
||||
if int(h) != patch_pos_embed.shape[-2] or int(w) != patch_pos_embed.shape[-1]:
|
||||
raise ValueError("Width or height does not match with the interpolated position embeddings")
|
||||
|
||||
patch_pos_embed = patch_pos_embed.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).view(1, -1, dim)
|
||||
|
||||
return torch.cat((class_pos_embed, patch_pos_embed), dim=1)
|
||||
return torch.cat((class_pos_embed.unsqueeze(0), patch_pos_embed), dim=1)
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
@ -581,7 +575,7 @@ class Data2VecVisionRelativePositionBias(nn.Module):
|
||||
|
||||
old_sub_table = old_sub_table.reshape(1, old_width, old_height, -1).permute(0, 3, 1, 2)
|
||||
new_sub_table = nn.functional.interpolate(
|
||||
old_sub_table, size=(torch_int(new_height), torch_int(new_width)), mode="bilinear"
|
||||
old_sub_table, size=(int(new_height), int(new_width)), mode="bilinear"
|
||||
)
|
||||
new_sub_table = new_sub_table.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).reshape(new_num_relative_distance - 3, -1)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -948,8 +948,7 @@ DBRX_INPUTS_DOCSTRING = r"""
|
||||
returned by the model at a previous stage of decoding, when `use_cache=True` or `config.use_cache=True`.
|
||||
|
||||
Two formats are allowed:
|
||||
- a [`~cache_utils.Cache`] instance, see our
|
||||
[kv cache guide](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/en/kv_cache);
|
||||
- a [`~cache_utils.Cache`] instance;
|
||||
- Tuple of `tuple(torch.FloatTensor)` of length `config.n_layers`, with each tuple having 2 tensors of
|
||||
shape `(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, embed_size_per_head)`). This is also known as the legacy
|
||||
cache format.
|
||||
@ -1383,7 +1382,7 @@ class DbrxForCausalLM(DbrxPreTrainedModel):
|
||||
cache_position=None,
|
||||
position_ids=None,
|
||||
use_cache=True,
|
||||
num_logits_to_keep=None,
|
||||
num_logits_to_keep=0,
|
||||
**kwargs,
|
||||
):
|
||||
# If we have cache: let's slice `input_ids` through `cache_position`, to keep only the unprocessed tokens
|
||||
@ -1434,9 +1433,6 @@ class DbrxForCausalLM(DbrxPreTrainedModel):
|
||||
batch_size=batch_size,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if num_logits_to_keep is not None:
|
||||
model_inputs["num_logits_to_keep"] = num_logits_to_keep
|
||||
|
||||
model_inputs.update(
|
||||
{
|
||||
"position_ids": position_ids,
|
||||
@ -1444,6 +1440,7 @@ class DbrxForCausalLM(DbrxPreTrainedModel):
|
||||
"past_key_values": past_key_values,
|
||||
"use_cache": use_cache,
|
||||
"attention_mask": attention_mask,
|
||||
"num_logits_to_keep": num_logits_to_keep,
|
||||
}
|
||||
)
|
||||
return model_inputs
|
||||
|
||||
@ -270,26 +270,31 @@ class DeiTImageProcessor(BaseImageProcessor):
|
||||
# We assume that all images have the same channel dimension format.
|
||||
input_data_format = infer_channel_dimension_format(images[0])
|
||||
|
||||
all_images = []
|
||||
for image in images:
|
||||
if do_resize:
|
||||
image = self.resize(image=image, size=size, resample=resample, input_data_format=input_data_format)
|
||||
if do_resize:
|
||||
images = [
|
||||
self.resize(image=image, size=size, resample=resample, input_data_format=input_data_format)
|
||||
for image in images
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
if do_center_crop:
|
||||
image = self.center_crop(image=image, size=crop_size, input_data_format=input_data_format)
|
||||
if do_center_crop:
|
||||
images = [
|
||||
self.center_crop(image=image, size=crop_size, input_data_format=input_data_format) for image in images
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
if do_rescale:
|
||||
image = self.rescale(image=image, scale=rescale_factor, input_data_format=input_data_format)
|
||||
if do_rescale:
|
||||
images = [
|
||||
self.rescale(image=image, scale=rescale_factor, input_data_format=input_data_format)
|
||||
for image in images
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
if do_normalize:
|
||||
image = self.normalize(
|
||||
image=image, mean=image_mean, std=image_std, input_data_format=input_data_format
|
||||
)
|
||||
if do_normalize:
|
||||
images = [
|
||||
self.normalize(image=image, mean=image_mean, std=image_std, input_data_format=input_data_format)
|
||||
for image in images
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
all_images.append(image)
|
||||
images = [
|
||||
to_channel_dimension_format(image, data_format, input_channel_dim=input_data_format)
|
||||
for image in all_images
|
||||
to_channel_dimension_format(image, data_format, input_channel_dim=input_data_format) for image in images
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
data = {"pixel_values": images}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -40,7 +40,6 @@ from ...utils import (
|
||||
add_start_docstrings_to_model_forward,
|
||||
logging,
|
||||
replace_return_docstrings,
|
||||
torch_int,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from .configuration_deit import DeiTConfig
|
||||
|
||||
@ -78,43 +77,39 @@ class DeiTEmbeddings(nn.Module):
|
||||
|
||||
def interpolate_pos_encoding(self, embeddings: torch.Tensor, height: int, width: int) -> torch.Tensor:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
This method allows to interpolate the pre-trained position encodings, to be able to use the model on higher resolution
|
||||
images. This method is also adapted to support torch.jit tracing and 2 class embeddings.
|
||||
|
||||
Adapted from:
|
||||
- https://github.com/facebookresearch/dino/blob/de9ee3df6cf39fac952ab558447af1fa1365362a/vision_transformer.py#L174-L194, and
|
||||
- https://github.com/facebookresearch/dinov2/blob/e1277af2ba9496fbadf7aec6eba56e8d882d1e35/dinov2/models/vision_transformer.py#L179-L211
|
||||
This method allows to interpolate the pre-trained position encodings, to be able to use the model on higher
|
||||
resolution images.
|
||||
Source:
|
||||
https://github.com/facebookresearch/dino/blob/de9ee3df6cf39fac952ab558447af1fa1365362a/vision_transformer.py#L174
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
# return self.position_embeddings
|
||||
num_patches = embeddings.shape[1] - 2
|
||||
num_positions = self.position_embeddings.shape[1] - 2
|
||||
|
||||
# always interpolate when tracing to ensure the exported model works for dynamic input shapes
|
||||
if not torch.jit.is_tracing() and num_patches == num_positions and height == width:
|
||||
if num_patches == num_positions and height == width:
|
||||
return self.position_embeddings
|
||||
|
||||
class_and_dist_pos_embed = self.position_embeddings[:, :2]
|
||||
patch_pos_embed = self.position_embeddings[:, 2:]
|
||||
|
||||
class_pos_embed = self.position_embeddings[:, 0, :]
|
||||
dist_pos_embed = self.position_embeddings[:, 1, :]
|
||||
patch_pos_embed = self.position_embeddings[:, 2:, :]
|
||||
dim = embeddings.shape[-1]
|
||||
|
||||
new_height = height // self.patch_size
|
||||
new_width = width // self.patch_size
|
||||
|
||||
sqrt_num_positions = torch_int(num_positions**0.5)
|
||||
patch_pos_embed = patch_pos_embed.reshape(1, sqrt_num_positions, sqrt_num_positions, dim)
|
||||
h0 = height // self.patch_size
|
||||
w0 = width // self.patch_size
|
||||
# # we add a small number to avoid floating point error in the interpolation
|
||||
# # see discussion at https://github.com/facebookresearch/dino/issues/8
|
||||
h0, w0 = h0 + 0.1, w0 + 0.1
|
||||
patch_pos_embed = patch_pos_embed.reshape(1, int(math.sqrt(num_positions)), int(math.sqrt(num_positions)), dim)
|
||||
patch_pos_embed = patch_pos_embed.permute(0, 3, 1, 2)
|
||||
|
||||
patch_pos_embed = nn.functional.interpolate(
|
||||
patch_pos_embed,
|
||||
size=(new_height, new_width),
|
||||
scale_factor=(h0 / math.sqrt(num_positions), w0 / math.sqrt(num_positions)),
|
||||
mode="bicubic",
|
||||
align_corners=False,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
patch_pos_embed = patch_pos_embed.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).view(1, -1, dim)
|
||||
|
||||
return torch.cat((class_and_dist_pos_embed, patch_pos_embed), dim=1)
|
||||
return torch.cat((class_pos_embed.unsqueeze(0), dist_pos_embed.unsqueeze(0), patch_pos_embed), dim=1)
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
|
||||
@ -312,26 +312,31 @@ class ViTHybridImageProcessor(BaseImageProcessor):
|
||||
# We assume that all images have the same channel dimension format.
|
||||
input_data_format = infer_channel_dimension_format(images[0])
|
||||
|
||||
all_images = []
|
||||
for image in images:
|
||||
if do_resize:
|
||||
image = self.resize(image=image, size=size, resample=resample, input_data_format=input_data_format)
|
||||
if do_resize:
|
||||
images = [
|
||||
self.resize(image=image, size=size, resample=resample, input_data_format=input_data_format)
|
||||
for image in images
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
if do_center_crop:
|
||||
image = self.center_crop(image=image, size=crop_size, input_data_format=input_data_format)
|
||||
if do_center_crop:
|
||||
images = [
|
||||
self.center_crop(image=image, size=crop_size, input_data_format=input_data_format) for image in images
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
if do_rescale:
|
||||
image = self.rescale(image=image, scale=rescale_factor, input_data_format=input_data_format)
|
||||
if do_rescale:
|
||||
images = [
|
||||
self.rescale(image=image, scale=rescale_factor, input_data_format=input_data_format)
|
||||
for image in images
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
if do_normalize:
|
||||
image = self.normalize(
|
||||
image=image, mean=image_mean, std=image_std, input_data_format=input_data_format
|
||||
)
|
||||
if do_normalize:
|
||||
images = [
|
||||
self.normalize(image=image, mean=image_mean, std=image_std, input_data_format=input_data_format)
|
||||
for image in images
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
all_images.append(image)
|
||||
images = [
|
||||
to_channel_dimension_format(image, data_format, input_channel_dim=input_data_format)
|
||||
for image in all_images
|
||||
to_channel_dimension_format(image, data_format, input_channel_dim=input_data_format) for image in images
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
data = {"pixel_values": images}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -27,13 +27,7 @@ from ....activations import ACT2FN
|
||||
from ....modeling_outputs import BaseModelOutput, BaseModelOutputWithPooling, ImageClassifierOutput
|
||||
from ....modeling_utils import PreTrainedModel
|
||||
from ....pytorch_utils import find_pruneable_heads_and_indices, prune_linear_layer
|
||||
from ....utils import (
|
||||
add_code_sample_docstrings,
|
||||
add_start_docstrings,
|
||||
add_start_docstrings_to_model_forward,
|
||||
logging,
|
||||
torch_int,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from ....utils import add_code_sample_docstrings, add_start_docstrings, add_start_docstrings_to_model_forward, logging
|
||||
from ....utils.backbone_utils import load_backbone
|
||||
from .configuration_vit_hybrid import ViTHybridConfig
|
||||
|
||||
@ -66,49 +60,41 @@ class ViTHybridEmbeddings(nn.Module):
|
||||
num_patches = self.patch_embeddings.num_patches
|
||||
self.position_embeddings = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(1, num_patches + 1, config.hidden_size))
|
||||
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(config.hidden_dropout_prob)
|
||||
self.patch_size = config.patch_size
|
||||
self.config = config
|
||||
|
||||
# Copied from transformers.models.vit.modeling_vit.ViTEmbeddings.interpolate_pos_encoding
|
||||
def interpolate_pos_encoding(self, embeddings: torch.Tensor, height: int, width: int) -> torch.Tensor:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
This method allows to interpolate the pre-trained position encodings, to be able to use the model on higher resolution
|
||||
images. This method is also adapted to support torch.jit tracing.
|
||||
This method allows to interpolate the pre-trained position encodings, to be able to use the model on higher
|
||||
resolution images.
|
||||
|
||||
Adapted from:
|
||||
- https://github.com/facebookresearch/dino/blob/de9ee3df6cf39fac952ab558447af1fa1365362a/vision_transformer.py#L174-L194, and
|
||||
- https://github.com/facebookresearch/dinov2/blob/e1277af2ba9496fbadf7aec6eba56e8d882d1e35/dinov2/models/vision_transformer.py#L179-L211
|
||||
Source:
|
||||
https://github.com/facebookresearch/dino/blob/de9ee3df6cf39fac952ab558447af1fa1365362a/vision_transformer.py#L174
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
num_patches = embeddings.shape[1] - 1
|
||||
num_positions = self.position_embeddings.shape[1] - 1
|
||||
|
||||
# always interpolate when tracing to ensure the exported model works for dynamic input shapes
|
||||
if not torch.jit.is_tracing() and num_patches == num_positions and height == width:
|
||||
if num_patches == num_positions and height == width:
|
||||
return self.position_embeddings
|
||||
|
||||
class_pos_embed = self.position_embeddings[:, :1]
|
||||
class_pos_embed = self.position_embeddings[:, 0]
|
||||
patch_pos_embed = self.position_embeddings[:, 1:]
|
||||
|
||||
dim = embeddings.shape[-1]
|
||||
|
||||
new_height = height // self.patch_size
|
||||
new_width = width // self.patch_size
|
||||
|
||||
sqrt_num_positions = torch_int(num_positions**0.5)
|
||||
patch_pos_embed = patch_pos_embed.reshape(1, sqrt_num_positions, sqrt_num_positions, dim)
|
||||
height = height // self.config.patch_size
|
||||
width = width // self.config.patch_size
|
||||
# we add a small number to avoid floating point error in the interpolation
|
||||
# see discussion at https://github.com/facebookresearch/dino/issues/8
|
||||
height, width = height + 0.1, width + 0.1
|
||||
patch_pos_embed = patch_pos_embed.reshape(1, int(math.sqrt(num_positions)), int(math.sqrt(num_positions)), dim)
|
||||
patch_pos_embed = patch_pos_embed.permute(0, 3, 1, 2)
|
||||
|
||||
patch_pos_embed = nn.functional.interpolate(
|
||||
patch_pos_embed,
|
||||
size=(new_height, new_width),
|
||||
scale_factor=(height / math.sqrt(num_positions), width / math.sqrt(num_positions)),
|
||||
mode="bicubic",
|
||||
align_corners=False,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if int(height) != patch_pos_embed.shape[-2] or int(width) != patch_pos_embed.shape[-1]:
|
||||
raise ValueError(f"Invalid height or width: {height}, {width}")
|
||||
patch_pos_embed = patch_pos_embed.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).view(1, -1, dim)
|
||||
|
||||
return torch.cat((class_pos_embed, patch_pos_embed), dim=1)
|
||||
return torch.cat((class_pos_embed.unsqueeze(0), patch_pos_embed), dim=1)
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
|
||||
@ -38,7 +38,6 @@ from ...utils import (
|
||||
add_start_docstrings_to_model_forward,
|
||||
logging,
|
||||
replace_return_docstrings,
|
||||
torch_int,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from ...utils.backbone_utils import BackboneMixin
|
||||
from .configuration_dinov2 import Dinov2Config
|
||||
@ -72,48 +71,42 @@ class Dinov2Embeddings(nn.Module):
|
||||
num_patches = self.patch_embeddings.num_patches
|
||||
self.position_embeddings = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(1, num_patches + 1, config.hidden_size))
|
||||
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(config.hidden_dropout_prob)
|
||||
self.patch_size = config.patch_size
|
||||
self.config = config
|
||||
|
||||
def interpolate_pos_encoding(self, embeddings: torch.Tensor, height: int, width: int) -> torch.Tensor:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
This method allows to interpolate the pre-trained position encodings, to be able to use the model on higher resolution
|
||||
images. This method is also adapted to support torch.jit tracing and interpolation at torch.float32 precision.
|
||||
This method allows to interpolate the pre-trained position encodings, to be able to use the model on higher
|
||||
resolution images.
|
||||
|
||||
Adapted from:
|
||||
- https://github.com/facebookresearch/dino/blob/de9ee3df6cf39fac952ab558447af1fa1365362a/vision_transformer.py#L174-L194, and
|
||||
- https://github.com/facebookresearch/dinov2/blob/e1277af2ba9496fbadf7aec6eba56e8d882d1e35/dinov2/models/vision_transformer.py#L179-L211
|
||||
Source:
|
||||
https://github.com/facebookresearch/dino/blob/de9ee3df6cf39fac952ab558447af1fa1365362a/vision_transformer.py#L174
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
num_patches = embeddings.shape[1] - 1
|
||||
num_positions = self.position_embeddings.shape[1] - 1
|
||||
|
||||
# always interpolate when tracing to ensure the exported model works for dynamic input shapes
|
||||
if not torch.jit.is_tracing() and num_patches == num_positions and height == width:
|
||||
if num_patches == num_positions and height == width:
|
||||
return self.position_embeddings
|
||||
|
||||
class_pos_embed = self.position_embeddings[:, :1]
|
||||
class_pos_embed = self.position_embeddings[:, 0]
|
||||
patch_pos_embed = self.position_embeddings[:, 1:]
|
||||
|
||||
dim = embeddings.shape[-1]
|
||||
|
||||
new_height = height // self.patch_size
|
||||
new_width = width // self.patch_size
|
||||
|
||||
sqrt_num_positions = torch_int(num_positions**0.5)
|
||||
patch_pos_embed = patch_pos_embed.reshape(1, sqrt_num_positions, sqrt_num_positions, dim)
|
||||
height = height // self.config.patch_size
|
||||
width = width // self.config.patch_size
|
||||
# we add a small number to avoid floating point error in the interpolation
|
||||
# see discussion at https://github.com/facebookresearch/dino/issues/8
|
||||
height, width = height + 0.1, width + 0.1
|
||||
patch_pos_embed = patch_pos_embed.reshape(1, int(math.sqrt(num_positions)), int(math.sqrt(num_positions)), dim)
|
||||
patch_pos_embed = patch_pos_embed.permute(0, 3, 1, 2)
|
||||
target_dtype = patch_pos_embed.dtype
|
||||
patch_pos_embed = nn.functional.interpolate(
|
||||
patch_pos_embed.to(torch.float32),
|
||||
size=(new_height, new_width),
|
||||
patch_pos_embed.to(dtype=torch.float32),
|
||||
scale_factor=(float(height / math.sqrt(num_positions)), float(width / math.sqrt(num_positions))),
|
||||
mode="bicubic",
|
||||
align_corners=False,
|
||||
).to(dtype=target_dtype)
|
||||
|
||||
if int(height) != patch_pos_embed.shape[-2] or int(width) != patch_pos_embed.shape[-1]:
|
||||
raise ValueError("Width or height does not match with the interpolated position embeddings")
|
||||
patch_pos_embed = patch_pos_embed.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).view(1, -1, dim)
|
||||
|
||||
return torch.cat((class_pos_embed, patch_pos_embed), dim=1)
|
||||
return torch.cat((class_pos_embed.unsqueeze(0), patch_pos_embed), dim=1)
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, pixel_values: torch.Tensor, bool_masked_pos: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None) -> torch.Tensor:
|
||||
batch_size, _, height, width = pixel_values.shape
|
||||
|
||||
@ -166,49 +166,38 @@ class DonutSwinEmbeddings(nn.Module):
|
||||
|
||||
self.norm = nn.LayerNorm(config.embed_dim)
|
||||
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(config.hidden_dropout_prob)
|
||||
self.patch_size = config.patch_size
|
||||
self.config = config
|
||||
|
||||
# Copied from transformers.models.vit.modeling_vit.ViTEmbeddings.interpolate_pos_encoding
|
||||
def interpolate_pos_encoding(self, embeddings: torch.Tensor, height: int, width: int) -> torch.Tensor:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
This method allows to interpolate the pre-trained position encodings, to be able to use the model on higher resolution
|
||||
images. This method is also adapted to support torch.jit tracing.
|
||||
This method allows to interpolate the pre-trained position encodings, to be able to use the model on higher
|
||||
resolution images.
|
||||
|
||||
Adapted from:
|
||||
- https://github.com/facebookresearch/dino/blob/de9ee3df6cf39fac952ab558447af1fa1365362a/vision_transformer.py#L174-L194, and
|
||||
- https://github.com/facebookresearch/dinov2/blob/e1277af2ba9496fbadf7aec6eba56e8d882d1e35/dinov2/models/vision_transformer.py#L179-L211
|
||||
Source:
|
||||
https://github.com/facebookresearch/dino/blob/de9ee3df6cf39fac952ab558447af1fa1365362a/vision_transformer.py#L174
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
num_patches = embeddings.shape[1] - 1
|
||||
num_positions = self.position_embeddings.shape[1] - 1
|
||||
|
||||
# always interpolate when tracing to ensure the exported model works for dynamic input shapes
|
||||
if not torch.jit.is_tracing() and num_patches == num_positions and height == width:
|
||||
if num_patches == num_positions and height == width:
|
||||
return self.position_embeddings
|
||||
|
||||
class_pos_embed = self.position_embeddings[:, :1]
|
||||
class_pos_embed = self.position_embeddings[:, 0]
|
||||
patch_pos_embed = self.position_embeddings[:, 1:]
|
||||
|
||||
dim = embeddings.shape[-1]
|
||||
|
||||
new_height = height // self.patch_size
|
||||
new_width = width // self.patch_size
|
||||
|
||||
sqrt_num_positions = torch_int(num_positions**0.5)
|
||||
patch_pos_embed = patch_pos_embed.reshape(1, sqrt_num_positions, sqrt_num_positions, dim)
|
||||
h0 = height // self.config.patch_size
|
||||
w0 = width // self.config.patch_size
|
||||
# we add a small number to avoid floating point error in the interpolation
|
||||
# see discussion at https://github.com/facebookresearch/dino/issues/8
|
||||
h0, w0 = h0 + 0.1, w0 + 0.1
|
||||
patch_pos_embed = patch_pos_embed.reshape(1, int(math.sqrt(num_positions)), int(math.sqrt(num_positions)), dim)
|
||||
patch_pos_embed = patch_pos_embed.permute(0, 3, 1, 2)
|
||||
|
||||
patch_pos_embed = nn.functional.interpolate(
|
||||
patch_pos_embed,
|
||||
size=(new_height, new_width),
|
||||
scale_factor=(h0 / math.sqrt(num_positions), w0 / math.sqrt(num_positions)),
|
||||
mode="bicubic",
|
||||
align_corners=False,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
patch_pos_embed = patch_pos_embed.permute(0, 2, 3, 1).view(1, -1, dim)
|
||||
|
||||
return torch.cat((class_pos_embed, patch_pos_embed), dim=1)
|
||||
return torch.cat((class_pos_embed.unsqueeze(0), patch_pos_embed), dim=1)
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
|
||||
@ -152,7 +152,7 @@ class DPTViTHybridEmbeddings(nn.Module):
|
||||
posemb_tok = posemb[:, :start_index]
|
||||
posemb_grid = posemb[0, start_index:]
|
||||
|
||||
old_grid_size = torch_int(len(posemb_grid) ** 0.5)
|
||||
old_grid_size = int(math.sqrt(len(posemb_grid)))
|
||||
|
||||
posemb_grid = posemb_grid.reshape(1, old_grid_size, old_grid_size, -1).permute(0, 3, 1, 2)
|
||||
posemb_grid = nn.functional.interpolate(posemb_grid, size=(grid_size_height, grid_size_width), mode="bilinear")
|
||||
@ -626,7 +626,7 @@ class DPTReassembleStage(nn.Module):
|
||||
if patch_height is not None and patch_width is not None:
|
||||
hidden_state = hidden_state.reshape(batch_size, patch_height, patch_width, num_channels)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
size = torch_int(sequence_length**0.5)
|
||||
size = int(math.sqrt(sequence_length))
|
||||
hidden_state = hidden_state.reshape(batch_size, size, size, num_channels)
|
||||
hidden_state = hidden_state.permute(0, 3, 1, 2).contiguous()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -836,8 +836,7 @@ FALCON_INPUTS_DOCSTRING = r"""
|
||||
returned by the model at a previous stage of decoding, when `use_cache=True` or `config.use_cache=True`.
|
||||
|
||||
Two formats are allowed:
|
||||
- a [`~cache_utils.Cache`] instance, see our
|
||||
[kv cache guide](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/en/kv_cache);
|
||||
- a [`~cache_utils.Cache`] instance;
|
||||
- Tuple of `tuple(torch.FloatTensor)` of length `config.n_layers`, with each tuple having 2 tensors of
|
||||
shape `(batch_size, num_heads, sequence_length, embed_size_per_head)`). This is also known as the legacy
|
||||
cache format.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -23,6 +23,7 @@ from ...utils import logging
|
||||
logger = logging.get_logger(__name__)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Copied from transformers.models.mamba.configuration_mamba.MambaConfig with mamba->falcon_mamba,Mamba->FalconMamba,MAMBA->FALCON_MAMBA,state-spaces/falcon_mamba-2.8b->tiiuae/falcon-mamba-7b,use_falcon_mambapy->use_mambapy
|
||||
class FalconMambaConfig(PretrainedConfig):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
This is the configuration class to store the configuration of a [`FalconMambaModel`]. It is used to instantiate a FALCON_MAMBA
|
||||
@ -81,8 +82,8 @@ class FalconMambaConfig(PretrainedConfig):
|
||||
Whether or not the cache should be used.
|
||||
use_mambapy (`bool`, *optional*, defaults to `False`):
|
||||
Determines the fallback strategy during training if the CUDA-based official implementation of FalconMamba is not avaiable. If `True`, the falcon_mamba.py implementation is used. If `False`, the naive and slower implementation is used. Consider switching to the naive version if memory is limited.
|
||||
mixer_rms_eps (`float`, *optional*, defaults to 1e-06):
|
||||
The RMS norm epsilon value that is used in the Mixer RMS norm for B, C and dt states.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Example:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
@ -126,7 +127,6 @@ class FalconMambaConfig(PretrainedConfig):
|
||||
rescale_prenorm_residual=False,
|
||||
use_cache=True,
|
||||
use_mambapy=False,
|
||||
mixer_rms_eps=1e-6,
|
||||
**kwargs,
|
||||
):
|
||||
self.vocab_size = vocab_size
|
||||
@ -154,6 +154,5 @@ class FalconMambaConfig(PretrainedConfig):
|
||||
self.residual_in_fp32 = residual_in_fp32
|
||||
self.use_cache = use_cache
|
||||
self.use_mambapy = use_mambapy
|
||||
self.mixer_rms_eps = mixer_rms_eps
|
||||
|
||||
super().__init__(bos_token_id=bos_token_id, eos_token_id=eos_token_id, pad_token_id=pad_token_id, **kwargs)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,5 +1,5 @@
|
||||
# coding=utf-8
|
||||
# Copyright 2024 Tri Dao, Albert Gu, Technological Innovation Institute and HuggingFace Inc. team.
|
||||
# Copyright 2024 state-spaces/falcon_mamba org and HuggingFace Inc. team.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
@ -45,10 +45,8 @@ else:
|
||||
pscan = None
|
||||
|
||||
if is_mamba_ssm_available():
|
||||
from mamba_ssm.ops.selective_scan_interface import selective_scan_fn
|
||||
from mamba_ssm.ops.selective_scan_interface import mamba_inner_fn, selective_scan_fn
|
||||
from mamba_ssm.ops.triton.selective_state_update import selective_state_update
|
||||
|
||||
from ...kernels.falcon_mamba import mamba_inner_fn
|
||||
else:
|
||||
selective_state_update, selective_scan_fn, mamba_inner_fn = None, None, None
|
||||
|
||||
@ -133,15 +131,6 @@ class FalconMambaMixer(nn.Module):
|
||||
self.out_proj = nn.Linear(self.intermediate_size, self.hidden_size, bias=config.use_bias)
|
||||
self.use_bias = config.use_bias
|
||||
|
||||
# Triton expects to pass RMS weights even if they are non learnable, thus we need to create these weights here
|
||||
self.register_buffer(
|
||||
"b_c_rms", torch.nn.Parameter(torch.ones(self.ssm_state_size), requires_grad=False), persistent=False
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.register_buffer(
|
||||
"dt_rms", torch.nn.Parameter(torch.ones(self.intermediate_size), requires_grad=False), persistent=False
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.rms_eps = config.mixer_rms_eps
|
||||
|
||||
if not is_fast_path_available:
|
||||
if self.use_mambapy:
|
||||
if is_mambapy_available():
|
||||
@ -186,10 +175,6 @@ class FalconMambaMixer(nn.Module):
|
||||
self.D.float(),
|
||||
delta_bias=self.dt_proj.bias.float(),
|
||||
delta_softplus=True,
|
||||
b_rms_weight=self.b_c_rms,
|
||||
c_rms_weight=self.b_c_rms,
|
||||
dt_rms_weight=self.dt_rms,
|
||||
b_c_dt_rms_eps=self.rms_eps,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
else:
|
||||
@ -229,9 +214,9 @@ class FalconMambaMixer(nn.Module):
|
||||
ssm_parameters, [self.time_step_rank, self.ssm_state_size, self.ssm_state_size], dim=-1
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
B = rms_forward(B, variance_epsilon=self.rms_eps)
|
||||
C = rms_forward(C, variance_epsilon=self.rms_eps)
|
||||
time_step = rms_forward(time_step, variance_epsilon=self.rms_eps)
|
||||
B = rms_forward(B)
|
||||
C = rms_forward(C)
|
||||
time_step = rms_forward(time_step)
|
||||
|
||||
# In case the model has been quantized, we need a hack to properly call the `nn.Linear` module
|
||||
# at the price of a small overhead.
|
||||
@ -330,9 +315,9 @@ class FalconMambaMixer(nn.Module):
|
||||
ssm_parameters, [self.time_step_rank, self.ssm_state_size, self.ssm_state_size], dim=-1
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
B = rms_forward(B, variance_epsilon=self.rms_eps)
|
||||
C = rms_forward(C, variance_epsilon=self.rms_eps)
|
||||
time_step = rms_forward(time_step, variance_epsilon=self.rms_eps)
|
||||
B = rms_forward(B)
|
||||
C = rms_forward(C)
|
||||
time_step = rms_forward(time_step)
|
||||
|
||||
discrete_time_step = self.dt_proj(time_step) # [batch, seq_len, intermediate_size]
|
||||
discrete_time_step = nn.functional.softplus(discrete_time_step).transpose(
|
||||
|
||||
Some files were not shown because too many files have changed in this diff Show More
Reference in New Issue
Block a user