mirror of
https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git
synced 2025-10-24 19:54:36 +08:00
Compare commits
1 Commits
fix_test_e
...
check_quan
| Author | SHA1 | Date | |
|---|---|---|---|
| bc346f9aa6 |
@ -12,7 +12,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
# Ensure running with CircleCI/huggingface
|
||||
check_circleci_user:
|
||||
docker:
|
||||
- image: python:3.10-slim
|
||||
- image: cimg/python:3.8.12
|
||||
parallelism: 1
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- run: echo $CIRCLE_PROJECT_USERNAME
|
||||
@ -26,12 +26,13 @@ jobs:
|
||||
fetch_tests:
|
||||
working_directory: ~/transformers
|
||||
docker:
|
||||
- image: huggingface/transformers-quality
|
||||
- image: cimg/python:3.8.12
|
||||
parallelism: 1
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- checkout
|
||||
- run: uv pip install -U -e .
|
||||
- run: echo 'export "GIT_COMMIT_MESSAGE=$(git show -s --format=%s)"' >> "$BASH_ENV" && source "$BASH_ENV"
|
||||
- run: pip install --upgrade --upgrade-strategy eager pip
|
||||
- run: pip install -U --upgrade-strategy eager GitPython
|
||||
- run: pip install -U --upgrade-strategy eager .
|
||||
- run: mkdir -p test_preparation
|
||||
- run: python utils/tests_fetcher.py | tee tests_fetched_summary.txt
|
||||
- store_artifacts:
|
||||
@ -81,28 +82,31 @@ jobs:
|
||||
path: ~/transformers/test_preparation/filtered_test_list.txt
|
||||
- store_artifacts:
|
||||
path: test_preparation/examples_test_list.txt
|
||||
- run: export "GIT_COMMIT_MESSAGE=$(git show -s --format=%s)" && echo $GIT_COMMIT_MESSAGE && python .circleci/create_circleci_config.py --fetcher_folder test_preparation
|
||||
- run: python .circleci/create_circleci_config.py --fetcher_folder test_preparation
|
||||
- run: |
|
||||
if [ ! -s test_preparation/generated_config.yml ]; then
|
||||
echo "No tests to run, exiting early!"
|
||||
circleci-agent step halt
|
||||
fi
|
||||
- run: cp test_preparation/generated_config.yml test_preparation/generated_config.txt
|
||||
- store_artifacts:
|
||||
path: test_preparation/generated_config.yml
|
||||
path: test_preparation/generated_config.txt
|
||||
- store_artifacts:
|
||||
path: test_preparation/filtered_test_list_cross_tests.txt
|
||||
path: test_preparation/filtered_test_list_cross_tests.txt
|
||||
- continuation/continue:
|
||||
configuration_path: test_preparation/generated_config.yml
|
||||
configuration_path: test_preparation/generated_config.yml
|
||||
|
||||
# To run all tests for the nightly build
|
||||
fetch_all_tests:
|
||||
working_directory: ~/transformers
|
||||
docker:
|
||||
- image: huggingface/transformers-quality
|
||||
- image: cimg/python:3.8.12
|
||||
parallelism: 1
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- checkout
|
||||
- run: uv pip install -e .
|
||||
- run: pip install --upgrade --upgrade-strategy eager pip
|
||||
- run: pip install -U --upgrade-strategy eager GitPython
|
||||
- run: pip install -U --upgrade-strategy eager .
|
||||
- run: |
|
||||
mkdir test_preparation
|
||||
echo -n "tests" > test_preparation/test_list.txt
|
||||
@ -122,7 +126,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
check_code_quality:
|
||||
working_directory: ~/transformers
|
||||
docker:
|
||||
- image: huggingface/transformers-quality
|
||||
- image: cimg/python:3.8.12
|
||||
resource_class: large
|
||||
environment:
|
||||
TRANSFORMERS_IS_CI: yes
|
||||
@ -130,7 +134,24 @@ jobs:
|
||||
parallelism: 1
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- checkout
|
||||
- run: uv pip install -e .
|
||||
- restore_cache:
|
||||
keys:
|
||||
- v0.7-code_quality-pip-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.7-code-quality-pip
|
||||
- restore_cache:
|
||||
keys:
|
||||
- v0.7-code_quality-site-packages-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.7-code-quality-site-packages
|
||||
- run: pip install --upgrade --upgrade-strategy eager pip
|
||||
- run: pip install -U --upgrade-strategy eager .[all,quality]
|
||||
- save_cache:
|
||||
key: v0.7-code_quality-pip-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
paths:
|
||||
- '~/.cache/pip'
|
||||
- save_cache:
|
||||
key: v0.7-code_quality-site-packages-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
paths:
|
||||
- '~/.pyenv/versions/'
|
||||
- run:
|
||||
name: Show installed libraries and their versions
|
||||
command: pip freeze | tee installed.txt
|
||||
@ -146,7 +167,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
check_repository_consistency:
|
||||
working_directory: ~/transformers
|
||||
docker:
|
||||
- image: huggingface/transformers-consistency
|
||||
- image: cimg/python:3.8.12
|
||||
resource_class: large
|
||||
environment:
|
||||
TRANSFORMERS_IS_CI: yes
|
||||
@ -154,7 +175,24 @@ jobs:
|
||||
parallelism: 1
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- checkout
|
||||
- run: uv pip install -e .
|
||||
- restore_cache:
|
||||
keys:
|
||||
- v0.7-repository_consistency-pip-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.7-repository_consistency-pip
|
||||
- restore_cache:
|
||||
keys:
|
||||
- v0.7-repository_consistency-site-packages-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
- v0.7-repository_consistency-site-packages
|
||||
- run: pip install --upgrade --upgrade-strategy eager pip
|
||||
- run: pip install -U --upgrade-strategy eager .[all,quality]
|
||||
- save_cache:
|
||||
key: v0.7-repository_consistency-pip-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
paths:
|
||||
- '~/.cache/pip'
|
||||
- save_cache:
|
||||
key: v0.7-repository_consistency-site-packages-{{ checksum "setup.py" }}
|
||||
paths:
|
||||
- '~/.pyenv/versions/'
|
||||
- run:
|
||||
name: Show installed libraries and their versions
|
||||
command: pip freeze | tee installed.txt
|
||||
|
||||
@ -19,7 +19,7 @@ import os
|
||||
import random
|
||||
from dataclasses import dataclass
|
||||
from typing import Any, Dict, List, Optional
|
||||
import glob
|
||||
|
||||
import yaml
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -41,6 +41,7 @@ class EmptyJob:
|
||||
|
||||
def to_dict(self):
|
||||
return {
|
||||
"working_directory": "~/transformers",
|
||||
"docker": copy.deepcopy(DEFAULT_DOCKER_IMAGE),
|
||||
"steps":["checkout"],
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -60,6 +61,7 @@ class CircleCIJob:
|
||||
pytest_options: Dict[str, Any] = None
|
||||
resource_class: Optional[str] = "2xlarge"
|
||||
tests_to_run: Optional[List[str]] = None
|
||||
working_directory: str = "~/transformers"
|
||||
# This should be only used for doctest job!
|
||||
command_timeout: Optional[int] = None
|
||||
|
||||
@ -72,12 +74,6 @@ class CircleCIJob:
|
||||
if self.docker_image is None:
|
||||
# Let's avoid changing the default list and make a copy.
|
||||
self.docker_image = copy.deepcopy(DEFAULT_DOCKER_IMAGE)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
# BIG HACK WILL REMOVE ONCE FETCHER IS UPDATED
|
||||
print(os.environ.get("GIT_COMMIT_MESSAGE"))
|
||||
if "[build-ci-image]" in os.environ.get("GIT_COMMIT_MESSAGE", "") or os.environ.get("GIT_COMMIT_MESSAGE", "") == "dev-ci":
|
||||
self.docker_image[0]["image"] = f"{self.docker_image[0]['image']}:dev"
|
||||
print(f"Using {self.docker_image} docker image")
|
||||
if self.install_steps is None:
|
||||
self.install_steps = []
|
||||
if self.pytest_options is None:
|
||||
@ -96,6 +92,7 @@ class CircleCIJob:
|
||||
cache_branch_prefix = "pull"
|
||||
|
||||
job = {
|
||||
"working_directory": self.working_directory,
|
||||
"docker": self.docker_image,
|
||||
"environment": env,
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -105,14 +102,34 @@ class CircleCIJob:
|
||||
job["parallelism"] = self.parallelism
|
||||
steps = [
|
||||
"checkout",
|
||||
{"attach_workspace": {"at": "test_preparation"}},
|
||||
{"attach_workspace": {"at": "~/transformers/test_preparation"}},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"restore_cache": {
|
||||
"keys": [
|
||||
# check the fully-matched cache first
|
||||
f"v{self.cache_version}-{self.cache_name}-{cache_branch_prefix}-pip-" + '{{ checksum "setup.py" }}',
|
||||
# try the partially-matched cache from `main`
|
||||
f"v{self.cache_version}-{self.cache_name}-main-pip-",
|
||||
# try the general partially-matched cache
|
||||
f"v{self.cache_version}-{self.cache_name}-{cache_branch_prefix}-pip-",
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"restore_cache": {
|
||||
"keys": [
|
||||
f"v{self.cache_version}-{self.cache_name}-{cache_branch_prefix}-site-packages-" + '{{ checksum "setup.py" }}',
|
||||
f"v{self.cache_version}-{self.cache_name}-main-site-packages-",
|
||||
f"v{self.cache_version}-{self.cache_name}-{cache_branch_prefix}-site-packages-",
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
]
|
||||
steps.extend([{"run": l} for l in self.install_steps])
|
||||
steps.append({"run": {"name": "Show installed libraries and their size", "command": """du -h -d 1 "$(pip -V | cut -d ' ' -f 4 | sed 's/pip//g')" | grep -vE "dist-info|_distutils_hack|__pycache__" | sort -h | tee installed.txt || true"""}})
|
||||
steps.append({"run": {"name": "Show installed libraries and their versions", "command": """pip list --format=freeze | tee installed.txt || true"""}})
|
||||
|
||||
steps.append({"run":{"name":"Show biggest libraries","command":"""dpkg-query --show --showformat='${Installed-Size}\t${Package}\n' | sort -rh | head -25 | sort -h | awk '{ package=$2; sub(".*/", "", package); printf("%.5f GB %s\n", $1/1024/1024, package)}' || true"""}})
|
||||
steps.append({"store_artifacts": {"path": "installed.txt"}})
|
||||
steps.extend([{"run": 'pip install "fsspec>=2023.5.0,<2023.10.0"'}])
|
||||
steps.extend([{"run": "pip install pytest-subtests"}])
|
||||
steps.append({"run": {"name": "Show installed libraries and their versions", "command": "pip freeze | tee installed.txt"}})
|
||||
steps.append({"store_artifacts": {"path": "~/transformers/installed.txt"}})
|
||||
|
||||
all_options = {**COMMON_PYTEST_OPTIONS, **self.pytest_options}
|
||||
pytest_flags = [f"--{key}={value}" if (value is not None or key in ["doctest-modules"]) else f"-{key}" for key, value in all_options.items()]
|
||||
@ -121,11 +138,11 @@ class CircleCIJob:
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
steps.append({"run": {"name": "Create `test-results` directory", "command": "mkdir test-results"}})
|
||||
|
||||
test_command = ""
|
||||
if self.command_timeout:
|
||||
test_command = f"timeout {self.command_timeout} "
|
||||
# junit familiy xunit1 is necessary to support splitting on test name or class name with circleci split
|
||||
test_command += f"python3 -m pytest -rsfE -p no:warnings -o junit_family=xunit1 --tb=short --junitxml=test-results/junit.xml -n {self.pytest_num_workers} " + " ".join(pytest_flags)
|
||||
test_command += f"python -m pytest -rs --junitxml=test-results/junit.xml -n {self.pytest_num_workers} " + " ".join(pytest_flags)
|
||||
|
||||
if self.parallelism == 1:
|
||||
if self.tests_to_run is None:
|
||||
@ -138,7 +155,7 @@ class CircleCIJob:
|
||||
if tests is None:
|
||||
folder = os.environ["test_preparation_dir"]
|
||||
test_file = os.path.join(folder, "filtered_test_list.txt")
|
||||
if os.path.exists(test_file): # We take this job's tests from the filtered test_list.txt
|
||||
if os.path.exists(test_file):
|
||||
with open(test_file) as f:
|
||||
tests = f.read().split(" ")
|
||||
|
||||
@ -150,26 +167,17 @@ class CircleCIJob:
|
||||
if test.endswith(".py"):
|
||||
expanded_tests.append(test)
|
||||
elif test == "tests/models":
|
||||
if "tokenization" in self.name:
|
||||
expanded_tests.extend(glob.glob("tests/models/**/test_tokenization*.py", recursive=True))
|
||||
elif self.name in ["flax","torch","tf"]:
|
||||
name = self.name if self.name != "torch" else ""
|
||||
if self.name == "torch":
|
||||
all_tests = glob.glob(f"tests/models/**/test_modeling_{name}*.py", recursive=True)
|
||||
filtered = [k for k in all_tests if ("_tf_") not in k and "_flax_" not in k]
|
||||
expanded_tests.extend(filtered)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
expanded_tests.extend(glob.glob(f"tests/models/**/test_modeling_{name}*.py", recursive=True))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
expanded_tests.extend(glob.glob("tests/models/**/test_modeling*.py", recursive=True))
|
||||
expanded_tests.extend([os.path.join(test, x) for x in os.listdir(test)])
|
||||
elif test == "tests/pipelines":
|
||||
expanded_tests.extend(glob.glob("tests/models/**/test_modeling*.py", recursive=True))
|
||||
expanded_tests.extend([os.path.join(test, x) for x in os.listdir(test)])
|
||||
else:
|
||||
expanded_tests.append(test)
|
||||
# Avoid long tests always being collected together
|
||||
random.shuffle(expanded_tests)
|
||||
tests = " ".join(expanded_tests)
|
||||
|
||||
# Each executor to run ~10 tests
|
||||
n_executors = max(len(expanded_tests) // 10, 1)
|
||||
n_executors = max(len(tests) // 10, 1)
|
||||
# Avoid empty test list on some executor(s) or launching too many executors
|
||||
if n_executors > self.parallelism:
|
||||
n_executors = self.parallelism
|
||||
@ -182,13 +190,13 @@ class CircleCIJob:
|
||||
command = 'TESTS=$(circleci tests split tests.txt) && echo $TESTS > splitted_tests.txt'
|
||||
steps.append({"run": {"name": "Split tests", "command": command}})
|
||||
|
||||
steps.append({"store_artifacts": {"path": "tests.txt"}})
|
||||
steps.append({"store_artifacts": {"path": "splitted_tests.txt"}})
|
||||
steps.append({"store_artifacts": {"path": "~/transformers/tests.txt"}})
|
||||
steps.append({"store_artifacts": {"path": "~/transformers/splitted_tests.txt"}})
|
||||
|
||||
test_command = ""
|
||||
if self.command_timeout:
|
||||
test_command = f"timeout {self.command_timeout} "
|
||||
test_command += f"python3 -m pytest -rsfE -p no:warnings --tb=short -o junit_family=xunit1 --junitxml=test-results/junit.xml -n {self.pytest_num_workers} " + " ".join(pytest_flags)
|
||||
if self.timeout:
|
||||
test_command = f"timeout {self.timeout} "
|
||||
test_command += f"python -m pytest -rs -n {self.pytest_num_workers} " + " ".join(pytest_flags)
|
||||
test_command += " $(cat splitted_tests.txt)"
|
||||
if self.marker is not None:
|
||||
test_command += f" -m {self.marker}"
|
||||
@ -203,17 +211,61 @@ class CircleCIJob:
|
||||
# failure.
|
||||
test_command = f"({test_command}) || true"
|
||||
else:
|
||||
test_command = f"({test_command} | tee tests_output.txt)"
|
||||
test_command = f"({test_command} | tee tests_output.txt) || true"
|
||||
steps.append({"run": {"name": "Run tests", "command": test_command}})
|
||||
|
||||
steps.append({"run": {"name": "Skipped tests", "when": "always", "command": f"python3 .circleci/parse_test_outputs.py --file tests_output.txt --skip"}})
|
||||
steps.append({"run": {"name": "Failed tests", "when": "always", "command": f"python3 .circleci/parse_test_outputs.py --file tests_output.txt --fail"}})
|
||||
steps.append({"run": {"name": "Errors", "when": "always", "command": f"python3 .circleci/parse_test_outputs.py --file tests_output.txt --errors"}})
|
||||
# Deal with errors
|
||||
check_test_command = f'if [ -s reports/{self.job_name}/errors.txt ]; '
|
||||
check_test_command += 'then echo "Some tests errored out!"; echo ""; '
|
||||
check_test_command += f'cat reports/{self.job_name}/errors.txt; '
|
||||
check_test_command += 'echo ""; echo ""; '
|
||||
|
||||
py_command = f'import os; fp = open("reports/{self.job_name}/summary_short.txt"); failed = os.linesep.join([x for x in fp.read().split(os.linesep) if x.startswith("ERROR ")]); fp.close(); fp = open("summary_short.txt", "w"); fp.write(failed); fp.close()'
|
||||
check_test_command += f"$(python3 -c '{py_command}'); "
|
||||
check_test_command += 'cat summary_short.txt; echo ""; exit -1; '
|
||||
|
||||
# Deeal with failed tests
|
||||
check_test_command += f'elif [ -s reports/{self.job_name}/failures_short.txt ]; '
|
||||
check_test_command += 'then echo "Some tests failed!"; echo ""; '
|
||||
check_test_command += f'cat reports/{self.job_name}/failures_short.txt; '
|
||||
check_test_command += 'echo ""; echo ""; '
|
||||
|
||||
py_command = f'import os; fp = open("reports/{self.job_name}/summary_short.txt"); failed = os.linesep.join([x for x in fp.read().split(os.linesep) if x.startswith("FAILED ")]); fp.close(); fp = open("summary_short.txt", "w"); fp.write(failed); fp.close()'
|
||||
check_test_command += f"$(python3 -c '{py_command}'); "
|
||||
check_test_command += 'cat summary_short.txt; echo ""; exit -1; '
|
||||
|
||||
check_test_command += f'elif [ -s reports/{self.job_name}/stats.txt ]; then echo "All tests pass!"; '
|
||||
|
||||
# return code `124` means the previous (pytest run) step is timeout
|
||||
if self.name == "pr_documentation_tests":
|
||||
check_test_command += 'elif [ -f 124.txt ]; then echo "doctest timeout!"; '
|
||||
|
||||
check_test_command += 'else echo "other fatal error"; echo ""; exit -1; fi;'
|
||||
|
||||
steps.append({"run": {"name": "Check test results", "command": check_test_command}})
|
||||
|
||||
steps.append({"store_test_results": {"path": "test-results"}})
|
||||
steps.append({"store_artifacts": {"path": "tests_output.txt"}})
|
||||
steps.append({"store_artifacts": {"path": "test-results/junit.xml"}})
|
||||
steps.append({"store_artifacts": {"path": "reports"}})
|
||||
|
||||
steps.append({"store_artifacts": {"path": "~/transformers/tests_output.txt"}})
|
||||
steps.append({"store_artifacts": {"path": "~/transformers/reports"}})
|
||||
|
||||
# save cache at the end: so pytest step runs before cache saving and we can see results earlier
|
||||
steps.append(
|
||||
{
|
||||
"save_cache": {
|
||||
"key": f"v{self.cache_version}-{self.cache_name}-{cache_branch_prefix}-pip-" + '{{ checksum "setup.py" }}',
|
||||
"paths": ["~/.cache/pip"],
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
)
|
||||
steps.append(
|
||||
{
|
||||
"save_cache": {
|
||||
"key": f"v{self.cache_version}-{self.cache_name}-{cache_branch_prefix}-site-packages-" + '{{ checksum "setup.py" }}',
|
||||
"paths": ["~/.pyenv/versions/"],
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
job["steps"] = steps
|
||||
return job
|
||||
@ -226,9 +278,18 @@ class CircleCIJob:
|
||||
# JOBS
|
||||
torch_and_tf_job = CircleCIJob(
|
||||
"torch_and_tf",
|
||||
docker_image=[{"image":"huggingface/transformers-torch-tf-light"}],
|
||||
install_steps=["uv venv && uv pip install ."],
|
||||
additional_env={"RUN_PT_TF_CROSS_TESTS": True},
|
||||
install_steps=[
|
||||
"sudo apt-get -y update && sudo apt-get install -y libsndfile1-dev espeak-ng git-lfs cmake",
|
||||
"git lfs install",
|
||||
"pip install --upgrade --upgrade-strategy eager pip",
|
||||
"pip install -U --upgrade-strategy eager .[sklearn,tf-cpu,torch,testing,sentencepiece,torch-speech,vision]",
|
||||
"pip install -U --upgrade-strategy eager tensorflow_probability",
|
||||
# Without --no-deps we can't pin dependency versions in the future
|
||||
"pip install -U --upgrade-strategy eager --no-deps -e git+https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate@main#egg=accelerate",
|
||||
# TODO: remove this one after fixing the dependency issue(s) above
|
||||
"pip install -U --upgrade-strategy eager torch torchvision torchaudio --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu",
|
||||
],
|
||||
marker="is_pt_tf_cross_test",
|
||||
pytest_options={"rA": None, "durations": 0},
|
||||
)
|
||||
@ -237,61 +298,77 @@ torch_and_tf_job = CircleCIJob(
|
||||
torch_and_flax_job = CircleCIJob(
|
||||
"torch_and_flax",
|
||||
additional_env={"RUN_PT_FLAX_CROSS_TESTS": True},
|
||||
docker_image=[{"image":"huggingface/transformers-torch-jax-light"}],
|
||||
install_steps=["uv venv && uv pip install ."],
|
||||
install_steps=[
|
||||
"sudo apt-get -y update && sudo apt-get install -y libsndfile1-dev espeak-ng",
|
||||
"pip install -U --upgrade-strategy eager --upgrade pip",
|
||||
"pip install -U --upgrade-strategy eager .[sklearn,flax,torch,testing,sentencepiece,torch-speech,vision]",
|
||||
# Without --no-deps we can't pin dependency versions in the future
|
||||
"pip install -U --upgrade-strategy eager --no-deps -e git+https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate@main#egg=accelerate",
|
||||
],
|
||||
marker="is_pt_flax_cross_test",
|
||||
pytest_options={"rA": None, "durations": 0},
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
torch_job = CircleCIJob(
|
||||
"torch",
|
||||
docker_image=[{"image": "huggingface/transformers-torch-light"}],
|
||||
install_steps=["uv venv && uv pip install ."],
|
||||
parallelism=6,
|
||||
pytest_num_workers=16
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
tokenization_job = CircleCIJob(
|
||||
"tokenization",
|
||||
docker_image=[{"image": "huggingface/transformers-torch-light"}],
|
||||
install_steps=["uv venv && uv pip install ."],
|
||||
parallelism=6,
|
||||
pytest_num_workers=16
|
||||
install_steps=[
|
||||
"sudo apt-get -y update && sudo apt-get install -y libsndfile1-dev espeak-ng time",
|
||||
"pip install --upgrade --upgrade-strategy eager pip",
|
||||
"pip install -U --upgrade-strategy eager .[sklearn,torch,testing,sentencepiece,torch-speech,vision,timm]",
|
||||
# Without --no-deps we can't pin dependency versions in the future
|
||||
"pip install -U --upgrade-strategy eager --no-deps -e git+https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate@main#egg=accelerate",
|
||||
],
|
||||
parallelism=1,
|
||||
pytest_num_workers=12,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
tf_job = CircleCIJob(
|
||||
"tf",
|
||||
docker_image=[{"image":"huggingface/transformers-tf-light"}],
|
||||
install_steps=["uv venv", "uv pip install -e."],
|
||||
parallelism=6,
|
||||
pytest_num_workers=16,
|
||||
install_steps=[
|
||||
"sudo apt-get -y update && sudo apt-get install -y libsndfile1-dev espeak-ng cmake",
|
||||
"pip install --upgrade --upgrade-strategy eager pip",
|
||||
"pip install -U --upgrade-strategy eager .[sklearn,tf-cpu,testing,sentencepiece,tf-speech,vision]",
|
||||
"pip install -U --upgrade-strategy eager tensorflow_probability",
|
||||
],
|
||||
parallelism=1,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
flax_job = CircleCIJob(
|
||||
"flax",
|
||||
docker_image=[{"image":"huggingface/transformers-jax-light"}],
|
||||
install_steps=["uv venv && uv pip install ."],
|
||||
parallelism=6,
|
||||
pytest_num_workers=16
|
||||
install_steps=[
|
||||
"sudo apt-get -y update && sudo apt-get install -y libsndfile1-dev espeak-ng",
|
||||
"pip install --upgrade --upgrade-strategy eager pip",
|
||||
"pip install -U --upgrade-strategy eager .[flax,testing,sentencepiece,flax-speech,vision]",
|
||||
],
|
||||
parallelism=1,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
pipelines_torch_job = CircleCIJob(
|
||||
"pipelines_torch",
|
||||
additional_env={"RUN_PIPELINE_TESTS": True},
|
||||
docker_image=[{"image":"huggingface/transformers-torch-light"}],
|
||||
install_steps=["uv venv && uv pip install ."],
|
||||
install_steps=[
|
||||
"sudo apt-get -y update && sudo apt-get install -y libsndfile1-dev espeak-ng",
|
||||
"pip install --upgrade --upgrade-strategy eager pip",
|
||||
"pip install -U --upgrade-strategy eager .[sklearn,torch,testing,sentencepiece,torch-speech,vision,timm,video]",
|
||||
],
|
||||
marker="is_pipeline_test",
|
||||
pytest_num_workers=12,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
pipelines_tf_job = CircleCIJob(
|
||||
"pipelines_tf",
|
||||
additional_env={"RUN_PIPELINE_TESTS": True},
|
||||
docker_image=[{"image":"huggingface/transformers-tf-light"}],
|
||||
install_steps=["uv venv && uv pip install ."],
|
||||
install_steps=[
|
||||
"sudo apt-get -y update && sudo apt-get install -y cmake",
|
||||
"pip install --upgrade --upgrade-strategy eager pip",
|
||||
"pip install -U --upgrade-strategy eager .[sklearn,tf-cpu,testing,sentencepiece,vision]",
|
||||
"pip install -U --upgrade-strategy eager tensorflow_probability",
|
||||
],
|
||||
marker="is_pipeline_test",
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -299,8 +376,22 @@ pipelines_tf_job = CircleCIJob(
|
||||
custom_tokenizers_job = CircleCIJob(
|
||||
"custom_tokenizers",
|
||||
additional_env={"RUN_CUSTOM_TOKENIZERS": True},
|
||||
docker_image=[{"image": "huggingface/transformers-custom-tokenizers"}],
|
||||
install_steps=["uv venv","uv pip install -e ."],
|
||||
install_steps=[
|
||||
"sudo apt-get -y update && sudo apt-get install -y cmake",
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "install jumanpp",
|
||||
"command":
|
||||
"wget https://github.com/ku-nlp/jumanpp/releases/download/v2.0.0-rc3/jumanpp-2.0.0-rc3.tar.xz\n"
|
||||
"tar xvf jumanpp-2.0.0-rc3.tar.xz\n"
|
||||
"mkdir jumanpp-2.0.0-rc3/bld\n"
|
||||
"cd jumanpp-2.0.0-rc3/bld\n"
|
||||
"sudo cmake .. -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=/usr/local\n"
|
||||
"sudo make install\n",
|
||||
},
|
||||
"pip install --upgrade --upgrade-strategy eager pip",
|
||||
"pip install -U --upgrade-strategy eager .[ja,testing,sentencepiece,jieba,spacy,ftfy,rjieba]",
|
||||
"python -m unidic download",
|
||||
],
|
||||
parallelism=None,
|
||||
resource_class=None,
|
||||
tests_to_run=[
|
||||
@ -315,9 +406,14 @@ examples_torch_job = CircleCIJob(
|
||||
"examples_torch",
|
||||
additional_env={"OMP_NUM_THREADS": 8},
|
||||
cache_name="torch_examples",
|
||||
docker_image=[{"image":"huggingface/transformers-examples-torch"}],
|
||||
# TODO @ArthurZucker remove this once docker is easier to build
|
||||
install_steps=["uv venv && uv pip install . && uv pip install -r examples/pytorch/_tests_requirements.txt"],
|
||||
install_steps=[
|
||||
"sudo apt-get -y update && sudo apt-get install -y libsndfile1-dev espeak-ng",
|
||||
"pip install --upgrade --upgrade-strategy eager pip",
|
||||
"pip install -U --upgrade-strategy eager .[sklearn,torch,sentencepiece,testing,torch-speech]",
|
||||
"pip install -U --upgrade-strategy eager -r examples/pytorch/_tests_requirements.txt",
|
||||
# Without --no-deps we can't pin dependency versions in the future
|
||||
"pip install -U --upgrade-strategy eager --no-deps -e git+https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate@main#egg=accelerate",
|
||||
],
|
||||
pytest_num_workers=1,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -325,20 +421,35 @@ examples_torch_job = CircleCIJob(
|
||||
examples_tensorflow_job = CircleCIJob(
|
||||
"examples_tensorflow",
|
||||
cache_name="tensorflow_examples",
|
||||
docker_image=[{"image":"huggingface/transformers-examples-tf"}],
|
||||
install_steps=["uv venv && uv pip install . && uv pip install -r examples/tensorflow/_tests_requirements.txt"],
|
||||
parallelism=8
|
||||
install_steps=[
|
||||
"sudo apt-get -y update && sudo apt-get install -y cmake",
|
||||
"pip install --upgrade --upgrade-strategy eager pip",
|
||||
"pip install -U --upgrade-strategy eager .[sklearn,tensorflow,sentencepiece,testing]",
|
||||
"pip install -U --upgrade-strategy eager -r examples/tensorflow/_tests_requirements.txt",
|
||||
],
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
examples_flax_job = CircleCIJob(
|
||||
"examples_flax",
|
||||
cache_name="flax_examples",
|
||||
install_steps=[
|
||||
"pip install --upgrade --upgrade-strategy eager pip",
|
||||
"pip install -U --upgrade-strategy eager .[flax,testing,sentencepiece]",
|
||||
"pip install -U --upgrade-strategy eager -r examples/flax/_tests_requirements.txt",
|
||||
],
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
hub_job = CircleCIJob(
|
||||
"hub",
|
||||
additional_env={"HUGGINGFACE_CO_STAGING": True},
|
||||
docker_image=[{"image":"huggingface/transformers-torch-light"}],
|
||||
install_steps=[
|
||||
"uv venv && uv pip install .",
|
||||
"sudo apt-get -y update && sudo apt-get install git-lfs",
|
||||
'git config --global user.email "ci@dummy.com"',
|
||||
'git config --global user.name "ci"',
|
||||
"pip install --upgrade --upgrade-strategy eager pip",
|
||||
"pip install -U --upgrade-strategy eager .[torch,sentencepiece,testing,vision]",
|
||||
],
|
||||
marker="is_staging_test",
|
||||
pytest_num_workers=1,
|
||||
@ -347,11 +458,10 @@ hub_job = CircleCIJob(
|
||||
|
||||
onnx_job = CircleCIJob(
|
||||
"onnx",
|
||||
docker_image=[{"image":"huggingface/transformers-torch-tf-light"}],
|
||||
install_steps=[
|
||||
"uv venv && uv pip install .",
|
||||
"uv pip install --upgrade eager pip",
|
||||
"uv pip install .[torch,tf,testing,sentencepiece,onnxruntime,vision,rjieba]",
|
||||
"sudo apt-get -y update && sudo apt-get install -y cmake",
|
||||
"pip install --upgrade --upgrade-strategy eager pip",
|
||||
"pip install -U --upgrade-strategy eager .[torch,tf,testing,sentencepiece,onnxruntime,vision,rjieba]",
|
||||
],
|
||||
pytest_options={"k onnx": None},
|
||||
pytest_num_workers=1,
|
||||
@ -360,8 +470,22 @@ onnx_job = CircleCIJob(
|
||||
|
||||
exotic_models_job = CircleCIJob(
|
||||
"exotic_models",
|
||||
install_steps=["uv venv && uv pip install ."],
|
||||
docker_image=[{"image":"huggingface/transformers-exotic-models"}],
|
||||
install_steps=[
|
||||
"sudo apt-get -y update && sudo apt-get install -y libsndfile1-dev",
|
||||
"pip install --upgrade --upgrade-strategy eager pip",
|
||||
"pip install -U --upgrade-strategy eager .[torch,testing,vision]",
|
||||
"pip install -U --upgrade-strategy eager torchvision",
|
||||
"pip install -U --upgrade-strategy eager scipy",
|
||||
"pip install -U --upgrade-strategy eager 'git+https://github.com/facebookresearch/detectron2.git'",
|
||||
"sudo apt install tesseract-ocr",
|
||||
"pip install -U --upgrade-strategy eager pytesseract",
|
||||
"pip install --upgrade-strategy eager sentencepiece",
|
||||
"pip install -U --upgrade-strategy eager natten==0.15.1+torch210cpu -f https://shi-labs.com/natten/wheels",
|
||||
"pip install -U --upgrade-strategy eager python-Levenshtein",
|
||||
"pip install -U --upgrade-strategy eager opencv-python",
|
||||
"pip install -U --upgrade-strategy eager nltk",
|
||||
"pip uninstall -y torch torchvision torchaudio && pip install -U --upgrade-strategy eager 'torch<2.2.0' 'torchvision<0.17' 'torchaudio<2.2.0'"
|
||||
],
|
||||
tests_to_run=[
|
||||
"tests/models/*layoutlmv*",
|
||||
"tests/models/*nat",
|
||||
@ -369,16 +493,17 @@ exotic_models_job = CircleCIJob(
|
||||
"tests/models/udop",
|
||||
"tests/models/nougat",
|
||||
],
|
||||
pytest_num_workers=12,
|
||||
parallelism=4,
|
||||
pytest_num_workers=1,
|
||||
pytest_options={"durations": 100},
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
repo_utils_job = CircleCIJob(
|
||||
"repo_utils",
|
||||
docker_image=[{"image":"huggingface/transformers-consistency"}],
|
||||
install_steps=["uv venv && uv pip install ."],
|
||||
install_steps=[
|
||||
"pip install --upgrade --upgrade-strategy eager pip",
|
||||
"pip install -U --upgrade-strategy eager .[quality,testing,torch]",
|
||||
],
|
||||
parallelism=None,
|
||||
pytest_num_workers=1,
|
||||
resource_class="large",
|
||||
@ -394,9 +519,20 @@ py_command = f"$(python3 -c '{py_command}')"
|
||||
command = f'echo "{py_command}" > pr_documentation_tests_temp.txt'
|
||||
doc_test_job = CircleCIJob(
|
||||
"pr_documentation_tests",
|
||||
docker_image=[{"image":"huggingface/transformers-consistency"}],
|
||||
additional_env={"TRANSFORMERS_VERBOSITY": "error", "DATASETS_VERBOSITY": "error", "SKIP_CUDA_DOCTEST": "1"},
|
||||
install_steps=[
|
||||
"sudo apt-get -y update && sudo apt-get install -y libsndfile1-dev espeak-ng time ffmpeg",
|
||||
"pip install --upgrade --upgrade-strategy eager pip",
|
||||
"pip install -U --upgrade-strategy eager -e .[dev]",
|
||||
# Without --no-deps we can't pin dependency versions in the future
|
||||
"pip install -U --upgrade-strategy eager --no-deps -e git+https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate@main#egg=accelerate",
|
||||
"pip install --upgrade --upgrade-strategy eager 'pytest<8.0.0' pytest-sugar",
|
||||
"pip install -U --upgrade-strategy eager natten==0.15.1+torch210cpu -f https://shi-labs.com/natten/wheels",
|
||||
"pip install -U --upgrade-strategy eager g2p-en",
|
||||
# TODO: remove this one after fixing the dependency issue(s) above
|
||||
"pip install -U --upgrade-strategy eager torch torchvision torchaudio --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu",
|
||||
"find -name __pycache__ -delete",
|
||||
"find . -name \*.pyc -delete",
|
||||
# Add an empty file to keep the test step running correctly even no file is selected to be tested.
|
||||
"touch dummy.py",
|
||||
{
|
||||
@ -430,11 +566,11 @@ REGULAR_TESTS = [
|
||||
hub_job,
|
||||
onnx_job,
|
||||
exotic_models_job,
|
||||
tokenization_job
|
||||
]
|
||||
EXAMPLES_TESTS = [
|
||||
examples_torch_job,
|
||||
examples_tensorflow_job,
|
||||
examples_flax_job,
|
||||
]
|
||||
PIPELINE_TESTS = [
|
||||
pipelines_torch_job,
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,70 +0,0 @@
|
||||
import re
|
||||
import argparse
|
||||
|
||||
def parse_pytest_output(file_path):
|
||||
skipped_tests = {}
|
||||
skipped_count = 0
|
||||
with open(file_path, 'r') as file:
|
||||
for line in file:
|
||||
match = re.match(r'^SKIPPED \[(\d+)\] (tests/.*): (.*)$', line)
|
||||
if match:
|
||||
skipped_count += 1
|
||||
test_file, test_line, reason = match.groups()
|
||||
skipped_tests[reason] = skipped_tests.get(reason, []) + [(test_file, test_line)]
|
||||
for k,v in sorted(skipped_tests.items(), key=lambda x:len(x[1])):
|
||||
print(f"{len(v):4} skipped because: {k}")
|
||||
print("Number of skipped tests:", skipped_count)
|
||||
|
||||
def parse_pytest_failure_output(file_path):
|
||||
failed_tests = {}
|
||||
failed_count = 0
|
||||
with open(file_path, 'r') as file:
|
||||
for line in file:
|
||||
match = re.match(r'^FAILED (tests/.*) - (.*): (.*)$', line)
|
||||
if match:
|
||||
failed_count += 1
|
||||
_, error, reason = match.groups()
|
||||
failed_tests[reason] = failed_tests.get(reason, []) + [error]
|
||||
for k,v in sorted(failed_tests.items(), key=lambda x:len(x[1])):
|
||||
print(f"{len(v):4} failed because `{v[0]}` -> {k}")
|
||||
print("Number of failed tests:", failed_count)
|
||||
if failed_count>0:
|
||||
exit(1)
|
||||
|
||||
def parse_pytest_errors_output(file_path):
|
||||
print(file_path)
|
||||
error_tests = {}
|
||||
error_count = 0
|
||||
with open(file_path, 'r') as file:
|
||||
for line in file:
|
||||
match = re.match(r'^ERROR (tests/.*) - (.*): (.*)$', line)
|
||||
if match:
|
||||
error_count += 1
|
||||
_, test_error, reason = match.groups()
|
||||
error_tests[reason] = error_tests.get(reason, []) + [test_error]
|
||||
for k,v in sorted(error_tests.items(), key=lambda x:len(x[1])):
|
||||
print(f"{len(v):4} errored out because of `{v[0]}` -> {k}")
|
||||
print("Number of errors:", error_count)
|
||||
if error_count>0:
|
||||
exit(1)
|
||||
|
||||
def main():
|
||||
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
|
||||
parser.add_argument("--file", help="file to parse")
|
||||
parser.add_argument("--skip", action="store_true", help="show skipped reasons")
|
||||
parser.add_argument("--fail", action="store_true", help="show failed tests")
|
||||
parser.add_argument("--errors", action="store_true", help="show failed tests")
|
||||
args = parser.parse_args()
|
||||
|
||||
if args.skip:
|
||||
parse_pytest_output(args.file)
|
||||
|
||||
if args.fail:
|
||||
parse_pytest_failure_output(args.file)
|
||||
|
||||
if args.errors:
|
||||
parse_pytest_errors_output(args.file)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
main()
|
||||
32
.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/bug-report.yml
vendored
32
.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/bug-report.yml
vendored
@ -17,50 +17,50 @@ body:
|
||||
description: |
|
||||
Your issue will be replied to more quickly if you can figure out the right person to tag with @
|
||||
If you know how to use git blame, that is the easiest way, otherwise, here is a rough guide of **who to tag**.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
All issues are read by one of the core maintainers, so if you don't know who to tag, just leave this blank and
|
||||
a core maintainer will ping the right person.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Please tag fewer than 3 people.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Models:
|
||||
|
||||
- text models: @ArthurZucker and @younesbelkada
|
||||
- vision models: @amyeroberts
|
||||
- speech models: @sanchit-gandhi
|
||||
- graph models: @clefourrier
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Library:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- flax: @sanchit-gandhi
|
||||
- generate: @zucchini-nlp (visual-language models) or @gante (all others)
|
||||
- generate: @gante
|
||||
- pipelines: @Narsil
|
||||
- tensorflow: @gante and @Rocketknight1
|
||||
- tokenizers: @ArthurZucker
|
||||
- trainer: @muellerzr @SunMarc
|
||||
- trainer: @muellerzr and @pacman100
|
||||
|
||||
Integrations:
|
||||
|
||||
- deepspeed: HF Trainer/Accelerate: @muellerzr
|
||||
- deepspeed: HF Trainer/Accelerate: @pacman100
|
||||
- ray/raytune: @richardliaw, @amogkam
|
||||
- Big Model Inference: @SunMarc
|
||||
- quantization (bitsandbytes, autogpt): @SunMarc and @younesbelkada
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Documentation: @stevhliu
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Model hub:
|
||||
|
||||
- for issues with a model, report at https://discuss.huggingface.co/ and tag the model's creator.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
HF projects:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- accelerate: [different repo](https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate)
|
||||
- datasets: [different repo](https://github.com/huggingface/datasets)
|
||||
- diffusers: [different repo](https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers)
|
||||
- rust tokenizers: [different repo](https://github.com/huggingface/tokenizers)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Maintained examples (not research project or legacy):
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- Flax: @sanchit-gandhi
|
||||
- PyTorch: See Models above and tag the person corresponding to the modality of the example.
|
||||
- TensorFlow: @Rocketknight1
|
||||
@ -101,11 +101,11 @@ body:
|
||||
|
||||
placeholder: |
|
||||
Steps to reproduce the behavior:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
1.
|
||||
2.
|
||||
3.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- type: textarea
|
||||
id: expected-behavior
|
||||
|
||||
4
.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/feature-request.yml
vendored
4
.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/feature-request.yml
vendored
@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
|
||||
name: "\U0001F680 Feature request"
|
||||
description: Submit a proposal/request for a new transformers feature
|
||||
labels: [ "Feature request" ]
|
||||
labels: [ "feature" ]
|
||||
body:
|
||||
- type: textarea
|
||||
id: feature-request
|
||||
@ -19,7 +19,7 @@ body:
|
||||
label: Motivation
|
||||
description: |
|
||||
Please outline the motivation for the proposal. Is your feature request related to a problem? e.g., I'm always frustrated when [...]. If this is related to another GitHub issue, please link here too.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- type: textarea
|
||||
id: contribution
|
||||
|
||||
6
.github/PULL_REQUEST_TEMPLATE.md
vendored
6
.github/PULL_REQUEST_TEMPLATE.md
vendored
@ -47,15 +47,15 @@ Models:
|
||||
Library:
|
||||
|
||||
- flax: @sanchit-gandhi
|
||||
- generate: @zucchini-nlp (visual-language models) or @gante (all others)
|
||||
- generate: @gante
|
||||
- pipelines: @Narsil
|
||||
- tensorflow: @gante and @Rocketknight1
|
||||
- tokenizers: @ArthurZucker
|
||||
- trainer: @muellerzr and @SunMarc
|
||||
- trainer: @muellerzr and @pacman100
|
||||
|
||||
Integrations:
|
||||
|
||||
- deepspeed: HF Trainer/Accelerate: @muellerzr
|
||||
- deepspeed: HF Trainer/Accelerate: @pacman100
|
||||
- ray/raytune: @richardliaw, @amogkam
|
||||
- Big Model Inference: @SunMarc
|
||||
- quantization (bitsandbytes, autogpt): @SunMarc and @younesbelkada
|
||||
|
||||
79
.github/actions/post-slack/action.yml
vendored
Normal file
79
.github/actions/post-slack/action.yml
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,79 @@
|
||||
name: Send message to slack
|
||||
|
||||
description: 'Send results to slack'
|
||||
author: 'Hugging Face'
|
||||
inputs:
|
||||
slack_channel:
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
type: string
|
||||
title:
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
type: string
|
||||
status:
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
type: string
|
||||
slack_token:
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
type: string
|
||||
|
||||
runs:
|
||||
using: "composite"
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Create content to post
|
||||
id: create-message
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
if [ "${{ inputs.status }}" == "success" ]; then
|
||||
echo STATUS_MESSAGE='🟢 Tests are passing!' >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
else
|
||||
echo STATUS_MESSAGE='🔴 Tests failed! Please check the GitHub action link below' >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
fi
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Post Canceled results Slack channel
|
||||
id: post-slack
|
||||
uses: slackapi/slack-github-action@6c661ce58804a1a20f6dc5fbee7f0381b469e001
|
||||
with:
|
||||
# Slack channel id, channel name, or user id to post message.
|
||||
# See also: https://api.slack.com/methods/chat.postMessage#channels
|
||||
channel-id: ${{ inputs.slack_channel }}
|
||||
# For posting a rich message using Block Kit
|
||||
payload: |
|
||||
{
|
||||
"text": "${{ inputs.title }}",
|
||||
"blocks": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "header",
|
||||
"text": {
|
||||
"type": "plain_text",
|
||||
"text": "${{ inputs.title }}"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "section",
|
||||
"text": {
|
||||
"type": "mrkdwn",
|
||||
"text": "${{ env.STATUS_MESSAGE }}"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "section",
|
||||
"text": {"type": "mrkdwn", "text": "*Click the button for more details about the commit*"},
|
||||
"accessory": {
|
||||
"type": "button",
|
||||
"text": {"type": "plain_text", "text": "Check Commit results"},
|
||||
"url": "${{ github.event.pull_request.html_url || github.event.head_commit.url }}"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "section",
|
||||
"text": {"type": "mrkdwn", "text": "*Click here for more details about the action ran*"},
|
||||
"accessory": {
|
||||
"type": "button",
|
||||
"text": {"type": "plain_text", "text": "Check Action results"},
|
||||
"url": "${{ github.server_url }}/${{ github.repository }}/actions/runs/${{ github.run_id }}"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
env:
|
||||
SLACK_BOT_TOKEN: ${{ inputs.slack_token }}
|
||||
42
.github/workflows/benchmark.yml
vendored
42
.github/workflows/benchmark.yml
vendored
@ -1,42 +0,0 @@
|
||||
name: Self-hosted runner (benchmark)
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
schedule:
|
||||
- cron: "17 2 * * *"
|
||||
workflow_call:
|
||||
|
||||
env:
|
||||
HF_HOME: /mnt/cache
|
||||
TF_FORCE_GPU_ALLOW_GROWTH: true
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
benchmark:
|
||||
name: Benchmark
|
||||
runs-on: [single-gpu, nvidia-gpu, a10, ci]
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: huggingface/transformers-all-latest-gpu
|
||||
options: --gpus all --privileged --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Update clone
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
git fetch && git checkout ${{ github.sha }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Reinstall transformers in edit mode (remove the one installed during docker image build)
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: python3 -m pip uninstall -y transformers && python3 -m pip install -e .
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Benchmark (daily)
|
||||
if: github.event_name == 'schedule'
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python3 -m pip install optimum-benchmark>=0.2.0
|
||||
HF_TOKEN=${{ secrets.TRANSFORMERS_BENCHMARK_TOKEN }} python3 benchmark/benchmark.py --repo_id hf-internal-testing/benchmark_results --path_in_repo $(date +'%Y-%m-%d') --config-dir benchmark/config --config-name generation --commit=${{ github.sha }} backend.model=google/gemma-2b backend.cache_implementation=null,static backend.torch_compile=false,true --multirun
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Benchmark (merged to main event)
|
||||
if: github.event_name == 'push' && github.ref_name == 'main'
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python3 -m pip install optimum-benchmark>=0.2.0
|
||||
HF_TOKEN=${{ secrets.TRANSFORMERS_BENCHMARK_TOKEN }} python3 benchmark/benchmark.py --repo_id hf-internal-testing/benchmark_results_merge_event --path_in_repo $(date +'%Y-%m-%d') --config-dir benchmark/config --config-name generation --commit=${{ github.sha }} backend.model=google/gemma-2b backend.cache_implementation=null,static backend.torch_compile=false,true --multirun
|
||||
64
.github/workflows/build-ci-docker-images.yml
vendored
64
.github/workflows/build-ci-docker-images.yml
vendored
@ -1,64 +0,0 @@
|
||||
name: Build pr ci-docker
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
push:
|
||||
branches:
|
||||
- push-ci-image # for now let's only build on this branch
|
||||
repository_dispatch:
|
||||
workflow_call:
|
||||
inputs:
|
||||
image_postfix:
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
type: string
|
||||
schedule:
|
||||
- cron: "6 0 * * *"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
concurrency:
|
||||
group: ${{ github.workflow }}
|
||||
cancel-in-progress: true
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
build:
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-22.04
|
||||
|
||||
if: ${{ contains(github.event.head_commit.message, '[build-ci-image]') || contains(github.event.head_commit.message, '[push-ci-image]') && '!cancelled()' || github.event_name == 'schedule' }}
|
||||
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
file: ["quality", "consistency", "custom-tokenizers", "torch-light", "tf-light", "exotic-models", "torch-tf-light", "torch-jax-light", "jax-light", "examples-torch", "examples-tf"]
|
||||
continue-on-error: true
|
||||
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Set tag
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
if ${{contains(github.event.head_commit.message, '[build-ci-image]')}}; then
|
||||
echo "TAG=huggingface/transformers-${{ matrix.file }}:dev" >> "$GITHUB_ENV"
|
||||
echo "setting it to DEV!"
|
||||
else
|
||||
echo "TAG=huggingface/transformers-${{ matrix.file }}" >> "$GITHUB_ENV"
|
||||
|
||||
fi
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Set up Docker Buildx
|
||||
uses: docker/setup-buildx-action@v3
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Check out code
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Login to DockerHub
|
||||
uses: docker/login-action@v3
|
||||
with:
|
||||
username: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME }}
|
||||
password: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_PASSWORD }}
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Build ${{ matrix.file }}.dockerfile
|
||||
uses: docker/build-push-action@v5
|
||||
with:
|
||||
context: ./docker
|
||||
build-args: |
|
||||
REF=${{ github.sha }}
|
||||
file: "./docker/${{ matrix.file }}.dockerfile"
|
||||
push: ${{ contains(github.event.head_commit.message, 'ci-image]') || github.event_name == 'schedule' }}
|
||||
tags: ${{ env.TAG }}
|
||||
113
.github/workflows/build-docker-images.yml
vendored
113
.github/workflows/build-docker-images.yml
vendored
@ -57,19 +57,20 @@ jobs:
|
||||
push: true
|
||||
tags: huggingface/transformers-all-latest-gpu-push-ci
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Post to Slack
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
uses: huggingface/hf-workflows/.github/actions/post-slack@main
|
||||
with:
|
||||
slack_channel: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_DOCKER }}
|
||||
title: 🤗 Results of the transformers-all-latest-gpu-push-ci docker build
|
||||
status: ${{ job.status }}
|
||||
slack_token: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
|
||||
latest-torch-deepspeed-docker:
|
||||
name: "Latest PyTorch + DeepSpeed"
|
||||
runs-on: [intel-cpu, 8-cpu, ci]
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Cleanup disk
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
sudo ls -l /usr/local/lib/
|
||||
sudo ls -l /usr/share/
|
||||
sudo du -sh /usr/local/lib/
|
||||
sudo du -sh /usr/share/
|
||||
sudo rm -rf /usr/local/lib/android
|
||||
sudo rm -rf /usr/share/dotnet
|
||||
sudo du -sh /usr/local/lib/
|
||||
sudo du -sh /usr/share/
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Set up Docker Buildx
|
||||
uses: docker/setup-buildx-action@v3
|
||||
@ -92,20 +93,21 @@ jobs:
|
||||
push: true
|
||||
tags: huggingface/transformers-pytorch-deepspeed-latest-gpu${{ inputs.image_postfix }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Post to Slack
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
uses: huggingface/hf-workflows/.github/actions/post-slack@main
|
||||
with:
|
||||
slack_channel: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_DOCKER}}
|
||||
title: 🤗 Results of the transformers-pytorch-deepspeed-latest-gpu docker build
|
||||
status: ${{ job.status }}
|
||||
slack_token: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
|
||||
# Can't build 2 images in a single job `latest-torch-deepspeed-docker` (for `nvcr.io/nvidia`)
|
||||
latest-torch-deepspeed-docker-for-push-ci-daily-build:
|
||||
name: "Latest PyTorch + DeepSpeed (Push CI - Daily Build)"
|
||||
runs-on: [intel-cpu, 8-cpu, ci]
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Cleanup disk
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
sudo ls -l /usr/local/lib/
|
||||
sudo ls -l /usr/share/
|
||||
sudo du -sh /usr/local/lib/
|
||||
sudo du -sh /usr/share/
|
||||
sudo rm -rf /usr/local/lib/android
|
||||
sudo rm -rf /usr/share/dotnet
|
||||
sudo du -sh /usr/local/lib/
|
||||
sudo du -sh /usr/share/
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Set up Docker Buildx
|
||||
uses: docker/setup-buildx-action@v3
|
||||
@ -132,15 +134,6 @@ jobs:
|
||||
push: true
|
||||
tags: huggingface/transformers-pytorch-deepspeed-latest-gpu-push-ci
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Post to Slack
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
uses: huggingface/hf-workflows/.github/actions/post-slack@main
|
||||
with:
|
||||
slack_channel: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_DOCKER }}
|
||||
title: 🤗 Results of the transformers-pytorch-deepspeed-latest-gpu-push-ci docker build
|
||||
status: ${{ job.status }}
|
||||
slack_token: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
|
||||
doc-builder:
|
||||
name: "Doc builder"
|
||||
# Push CI doesn't need this image
|
||||
@ -167,21 +160,22 @@ jobs:
|
||||
push: true
|
||||
tags: huggingface/transformers-doc-builder
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Post to Slack
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
uses: huggingface/hf-workflows/.github/actions/post-slack@main
|
||||
with:
|
||||
slack_channel: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_DOCKER }}
|
||||
title: 🤗 Results of the huggingface/transformers-doc-builder docker build
|
||||
status: ${{ job.status }}
|
||||
slack_token: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
|
||||
latest-pytorch:
|
||||
name: "Latest PyTorch [dev]"
|
||||
# Push CI doesn't need this image
|
||||
if: inputs.image_postfix != '-push-ci'
|
||||
runs-on: [intel-cpu, 8-cpu, ci]
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Cleanup disk
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
sudo ls -l /usr/local/lib/
|
||||
sudo ls -l /usr/share/
|
||||
sudo du -sh /usr/local/lib/
|
||||
sudo du -sh /usr/share/
|
||||
sudo rm -rf /usr/local/lib/android
|
||||
sudo rm -rf /usr/share/dotnet
|
||||
sudo du -sh /usr/local/lib/
|
||||
sudo du -sh /usr/share/
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Set up Docker Buildx
|
||||
uses: docker/setup-buildx-action@v3
|
||||
@ -204,15 +198,6 @@ jobs:
|
||||
push: true
|
||||
tags: huggingface/transformers-pytorch-gpu
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Post to Slack
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
uses: huggingface/hf-workflows/.github/actions/post-slack@main
|
||||
with:
|
||||
slack_channel: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_DOCKER }}
|
||||
title: 🤗 Results of the huggingface/transformers-pytorch-gpudocker build
|
||||
status: ${{ job.status }}
|
||||
slack_token: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
|
||||
latest-pytorch-amd:
|
||||
name: "Latest PyTorch (AMD) [dev]"
|
||||
runs-on: [intel-cpu, 8-cpu, ci]
|
||||
@ -252,15 +237,6 @@ jobs:
|
||||
push: true
|
||||
tags: huggingface/transformers-pytorch-amd-gpu-push-ci
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Post to Slack
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
uses: huggingface/hf-workflows/.github/actions/post-slack@main
|
||||
with:
|
||||
slack_channel: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_DOCKER }}
|
||||
title: 🤗 Results of the huggingface/transformers-pytorch-amd-gpu-push-ci build
|
||||
status: ${{ job.status }}
|
||||
slack_token: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
|
||||
latest-tensorflow:
|
||||
name: "Latest TensorFlow [dev]"
|
||||
# Push CI doesn't need this image
|
||||
@ -289,15 +265,6 @@ jobs:
|
||||
push: true
|
||||
tags: huggingface/transformers-tensorflow-gpu
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Post to Slack
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
uses: huggingface/hf-workflows/.github/actions/post-slack@main
|
||||
with:
|
||||
slack_channel: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_DOCKER }}
|
||||
title: 🤗 Results of the huggingface/transformers-tensorflow-gpu build
|
||||
status: ${{ job.status }}
|
||||
slack_token: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
|
||||
latest-pytorch-deepspeed-amd:
|
||||
name: "PyTorch + DeepSpeed (AMD) [dev]"
|
||||
runs-on: [intel-cpu, 8-cpu, ci]
|
||||
@ -337,15 +304,6 @@ jobs:
|
||||
push: true
|
||||
tags: huggingface/transformers-pytorch-deepspeed-amd-gpu-push-ci
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Post to Slack
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
uses: huggingface/hf-workflows/.github/actions/post-slack@main
|
||||
with:
|
||||
slack_channel: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_DOCKER }}
|
||||
title: 🤗 Results of the transformers-pytorch-deepspeed-amd-gpu build
|
||||
status: ${{ job.status }}
|
||||
slack_token: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
|
||||
latest-quantization-torch-docker:
|
||||
name: "Latest Pytorch + Quantization [dev]"
|
||||
# Push CI doesn't need this image
|
||||
@ -372,13 +330,4 @@ jobs:
|
||||
build-args: |
|
||||
REF=main
|
||||
push: true
|
||||
tags: huggingface/transformers-quantization-latest-gpu${{ inputs.image_postfix }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Post to Slack
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
uses: huggingface/hf-workflows/.github/actions/post-slack@main
|
||||
with:
|
||||
slack_channel: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_DOCKER }}
|
||||
title: 🤗 Results of the transformers-quantization-latest-gpu build
|
||||
status: ${{ job.status }}
|
||||
slack_token: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
tags: huggingface/transformers-quantization-latest-gpu${{ inputs.image_postfix }}
|
||||
@ -13,7 +13,7 @@ concurrency:
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
latest-with-torch-nightly-docker:
|
||||
name: "Nightly PyTorch + Stable TensorFlow"
|
||||
runs-on: [intel-cpu, 8-cpu, ci]
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-22.04
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Cleanup disk
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
@ -50,7 +50,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
|
||||
nightly-torch-deepspeed-docker:
|
||||
name: "Nightly PyTorch + DeepSpeed"
|
||||
runs-on: [intel-cpu, 8-cpu, ci]
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-22.04
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Cleanup disk
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
|
||||
@ -16,7 +16,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
fail-fast: false
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
version: ["1.13", "1.12", "1.11"]
|
||||
runs-on: [intel-cpu, 8-cpu, ci]
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-22.04
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Set up Docker Buildx
|
||||
@ -60,7 +60,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
fail-fast: false
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
version: ["2.11", "2.10", "2.9", "2.8", "2.7", "2.6", "2.5"]
|
||||
runs-on: [intel-cpu, 8-cpu, ci]
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-22.04
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Set up Docker Buildx
|
||||
|
||||
2
.github/workflows/model_jobs.yml
vendored
2
.github/workflows/model_jobs.yml
vendored
@ -80,7 +80,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run all tests on GPU
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: python3 -m pytest -rsfE -v --make-reports=${{ inputs.machine_type }}_run_models_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}_test_reports tests/${{ matrix.folders }}
|
||||
run: python3 -m pytest -rs -v --make-reports=${{ inputs.machine_type }}_run_models_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}_test_reports tests/${{ matrix.folders }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
if: ${{ failure() }}
|
||||
|
||||
16
.github/workflows/push-important-models.yml
vendored
16
.github/workflows/push-important-models.yml
vendored
@ -5,6 +5,7 @@ on:
|
||||
branches: [ main ]
|
||||
|
||||
env:
|
||||
IS_GITHUB_CI: "1"
|
||||
OUTPUT_SLACK_CHANNEL_ID: "C06L2SGMEEA"
|
||||
HF_HUB_READ_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.HF_HUB_READ_TOKEN }}
|
||||
HF_HOME: /mnt/cache
|
||||
@ -85,7 +86,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
- name: Run FA2 tests
|
||||
id: run_fa2_tests
|
||||
run:
|
||||
pytest -rsfE -m "flash_attn_test" --make-reports=${{ matrix.model-name }}_fa2_tests/ tests/${{ matrix.model-name }}/test_modeling_*
|
||||
pytest -rs -m "flash_attn_test" --make-reports=${{ matrix.model-name }}_fa2_tests/ tests/${{ matrix.model-name }}/test_modeling_*
|
||||
|
||||
- name: "Test suite reports artifacts: ${{ matrix.model-name }}_fa2_tests"
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
@ -96,7 +97,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Post to Slack
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
uses: huggingface/hf-workflows/.github/actions/post-slack@main
|
||||
uses: ./.github/actions/post-slack
|
||||
with:
|
||||
slack_channel: ${{ env.OUTPUT_SLACK_CHANNEL_ID }}
|
||||
title: 🤗 Results of the FA2 tests - ${{ matrix.model-name }}
|
||||
@ -107,7 +108,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
id: run_integration_tests
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
run:
|
||||
pytest -rsfE -k "IntegrationTest" --make-reports=tests_integration_${{ matrix.model-name }} tests/${{ matrix.model-name }}/test_modeling_*
|
||||
pytest -rs -k "IntegrationTest" --make-reports=tests_integration_${{ matrix.model-name }} tests/${{ matrix.model-name }}/test_modeling_*
|
||||
|
||||
- name: "Test suite reports artifacts: tests_integration_${{ matrix.model-name }}"
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
@ -118,7 +119,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Post to Slack
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
uses: huggingface/hf-workflows/.github/actions/post-slack@main
|
||||
uses: ./.github/actions/post-slack
|
||||
with:
|
||||
slack_channel: ${{ env.OUTPUT_SLACK_CHANNEL_ID }}
|
||||
title: 🤗 Results of the Integration tests - ${{ matrix.model-name }}
|
||||
@ -133,10 +134,3 @@ jobs:
|
||||
slackChannel: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_CHANNEL }}
|
||||
slackToken: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
waitForSSH: true
|
||||
|
||||
benchmark:
|
||||
name: Benchmark workflow
|
||||
needs: get_modified_models
|
||||
if: ${{ needs.get_modified_models.outputs.matrix != '[]' && needs.get_modified_models.outputs.matrix != '' && fromJson(needs.get_modified_models.outputs.matrix)[0] != null }}
|
||||
uses: ./.github/workflows/benchmark.yml
|
||||
secrets: inherit
|
||||
|
||||
@ -4,11 +4,6 @@ on:
|
||||
pull_request:
|
||||
paths:
|
||||
- "src/transformers/models/*/modeling_*.py"
|
||||
- "tests/models/*/test_*.py"
|
||||
|
||||
concurrency:
|
||||
group: ${{ github.workflow }}-${{ github.head_ref || github.run_id }}
|
||||
cancel-in-progress: true
|
||||
|
||||
env:
|
||||
HF_HOME: /mnt/cache
|
||||
@ -25,48 +20,33 @@ env:
|
||||
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES: 0,1
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
find_models_to_run:
|
||||
check_for_new_model:
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-22.04
|
||||
name: Find models to run slow tests
|
||||
# Triggered only if the required label `run-slow` is added
|
||||
if: ${{ contains(github.event.pull_request.labels.*.name, 'run-slow') }}
|
||||
name: Check if a PR is a new model PR
|
||||
outputs:
|
||||
models: ${{ steps.models_to_run.outputs.models }}
|
||||
new_model: ${{ steps.check_new_model.outputs.new_model }}
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
fetch-depth: "0"
|
||||
ref: ${{ github.event.pull_request.head.sha }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Get commit message
|
||||
- name: Check if there is a new model
|
||||
id: check_new_model
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "commit_message=$(git show -s --format=%s)" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Get models to run slow tests
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "${{ env.commit_message }}"
|
||||
python -m pip install GitPython
|
||||
python utils/pr_slow_ci_models.py --commit_message "${{ env.commit_message }}" | tee output.txt
|
||||
echo "models=$(tail -n 1 output.txt)" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Models to run slow tests
|
||||
id: models_to_run
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "${{ env.models }}"
|
||||
echo "models=${{ env.models }}" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
|
||||
echo "new_model=$(python utils/check_if_new_model_added.py | tail -n 1)" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
|
||||
|
||||
run_models_gpu:
|
||||
name: Run all tests for the model
|
||||
# Triggered only `find_models_to_run` is triggered (label `run-slow` is added) which gives the models to run
|
||||
# (either a new model PR or via a commit message)
|
||||
if: ${{ needs.find_models_to_run.outputs.models != '[]' }}
|
||||
needs: find_models_to_run
|
||||
name: Run all tests for the new model
|
||||
# Triggered if it is a new model PR and the required label is added
|
||||
if: ${{ needs.check_for_new_model.outputs.new_model != '' && contains(github.event.pull_request.labels.*.name, 'single-model-run-slow') }}
|
||||
needs: check_for_new_model
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
fail-fast: false
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
folders: ${{ fromJson(needs.find_models_to_run.outputs.models) }}
|
||||
folders: ["${{ needs.check_for_new_model.outputs.new_model }}"]
|
||||
machine_type: [single-gpu, multi-gpu]
|
||||
runs-on: ['${{ matrix.machine_type }}', nvidia-gpu, t4, ci]
|
||||
runs-on: ['${{ matrix.machine_type }}', nvidia-gpu, t4, daily-ci]
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: huggingface/transformers-all-latest-gpu
|
||||
options: --gpus all --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
@ -89,7 +69,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Update clone
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: git fetch && git fetch origin pull/${{ github.event.pull_request.number }}/head:pull/${{ github.event.pull_request.number }}/merge && git checkout pull/${{ github.event.pull_request.number }}/merge
|
||||
run: git fetch && git checkout ${{ github.event.pull_request.head.sha }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Reinstall transformers in edit mode (remove the one installed during docker image build)
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
@ -110,10 +90,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run all tests on GPU
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES="$(python3 utils/set_cuda_devices_for_ci.py --test_folder ${{ matrix.folders }})"
|
||||
echo $CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES
|
||||
python3 -m pytest -v -rsfE --make-reports=${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_models_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}_test_reports tests/${{ matrix.folders }}
|
||||
run: python3 -m pytest -v -rs --make-reports=${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_models_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}_test_reports tests/${{ matrix.folders }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
if: ${{ failure() }}
|
||||
25
.github/workflows/self-push-amd-mi300-caller.yml
vendored
25
.github/workflows/self-push-amd-mi300-caller.yml
vendored
@ -1,25 +0,0 @@
|
||||
name: Self-hosted runner (AMD mi300 CI caller)
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
workflow_run:
|
||||
workflows: ["Self-hosted runner (push-caller)"]
|
||||
branches: ["main"]
|
||||
types: [completed]
|
||||
push:
|
||||
branches:
|
||||
- run_amd_push_ci_caller*
|
||||
paths:
|
||||
- "src/**"
|
||||
- "tests/**"
|
||||
- ".github/**"
|
||||
- "templates/**"
|
||||
- "utils/**"
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
run_amd_ci:
|
||||
name: AMD mi300
|
||||
if: (cancelled() != true) && ((github.event_name == 'workflow_run') || ((github.event_name == 'push') && (startsWith(github.ref_name, 'run_amd_push_ci_caller') || startsWith(github.ref_name, 'mi300-ci'))))
|
||||
uses: ./.github/workflows/self-push-amd.yml
|
||||
with:
|
||||
gpu_flavor: mi300
|
||||
secrets: inherit
|
||||
8
.github/workflows/self-push-amd.yml
vendored
8
.github/workflows/self-push-amd.yml
vendored
@ -36,7 +36,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
machine_type: [single-gpu, multi-gpu]
|
||||
runs-on: [self-hosted, amd-gpu, '${{ matrix.machine_type }}', '${{ inputs.gpu_flavor }}']
|
||||
runs-on: [self-hosted, docker-gpu, amd-gpu, '${{ matrix.machine_type }}', '${{ inputs.gpu_flavor }}']
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: huggingface/transformers-pytorch-amd-gpu-push-ci # <--- We test only for PyTorch for now
|
||||
options: --device /dev/kfd --device /dev/dri --env ROCR_VISIBLE_DEVICES --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
@ -57,7 +57,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
machine_type: [single-gpu, multi-gpu]
|
||||
runs-on: [self-hosted, amd-gpu, '${{ matrix.machine_type }}', '${{ inputs.gpu_flavor }}']
|
||||
runs-on: [self-hosted, docker-gpu, amd-gpu, '${{ matrix.machine_type }}', '${{ inputs.gpu_flavor }}']
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: huggingface/transformers-pytorch-amd-gpu-push-ci # <--- We test only for PyTorch for now
|
||||
options: --device /dev/kfd --device /dev/dri --env ROCR_VISIBLE_DEVICES --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
@ -155,7 +155,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
folders: ${{ fromJson(needs.setup_gpu.outputs.matrix) }}
|
||||
machine_type: [single-gpu, multi-gpu]
|
||||
runs-on: [self-hosted, amd-gpu, '${{ matrix.machine_type }}', '${{ inputs.gpu_flavor }}']
|
||||
runs-on: [self-hosted, docker-gpu, amd-gpu, '${{ matrix.machine_type }}', '${{ inputs.gpu_flavor }}']
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: huggingface/transformers-pytorch-amd-gpu-push-ci # <--- We test only for PyTorch for now
|
||||
options: --device /dev/kfd --device /dev/dri --env ROCR_VISIBLE_DEVICES --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
@ -230,7 +230,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
- name: Run all non-slow selected tests on GPU
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python3 -m pytest -n 2 --dist=loadfile -v --make-reports=${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_models_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}_test_reports ${{ fromJson(needs.setup_gpu.outputs.test_map)[matrix.folders] }} -m "not not_device_test"
|
||||
python3 -m pytest -n 2 --dist=loadfile -v --make-reports=${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_models_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}_test_reports ${{ fromJson(needs.setup_gpu.outputs.test_map)[matrix.folders] }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
if: ${{ failure() }}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -16,5 +16,4 @@ jobs:
|
||||
uses: ./.github/workflows/self-scheduled-amd.yml
|
||||
with:
|
||||
gpu_flavor: mi210
|
||||
slack_report_channel: "#transformers-ci-daily-amd"
|
||||
secrets: inherit
|
||||
|
||||
@ -16,5 +16,4 @@ jobs:
|
||||
uses: ./.github/workflows/self-scheduled-amd.yml
|
||||
with:
|
||||
gpu_flavor: mi250
|
||||
slack_report_channel: "#transformers-ci-daily-amd"
|
||||
secrets: inherit
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,21 +0,0 @@
|
||||
name: Self-hosted runner (AMD mi300 scheduled CI caller)
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
workflow_run:
|
||||
workflows: ["Self-hosted runner (AMD scheduled CI caller)"]
|
||||
branches: ["main"]
|
||||
types: [completed]
|
||||
push:
|
||||
branches:
|
||||
- run_amd_scheduled_ci_caller*
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
run_amd_ci:
|
||||
name: AMD mi300
|
||||
needs: build-docker-containers
|
||||
if: (cancelled() != true) && ((github.event_name == 'workflow_run') || ((github.event_name == 'push') && (startsWith(github.ref_name, 'run_amd_push_ci_caller') || startsWith(github.ref_name, 'mi300-ci'))))
|
||||
uses: ./.github/workflows/self-scheduled-amd.yml
|
||||
with:
|
||||
gpu_flavor: mi300
|
||||
slack_report_channel: "#transformers-ci-daily-amd"
|
||||
secrets: inherit
|
||||
26
.github/workflows/self-scheduled-amd.yml
vendored
26
.github/workflows/self-scheduled-amd.yml
vendored
@ -34,7 +34,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
fetch-depth: 2
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Check Runner Status
|
||||
run: python utils/check_self_hosted_runner.py --target_runners hf-amd-mi210-ci-1gpu-1,hf-amd-mi250-ci-1gpu-1,hf-amd-mi300-ci-1gpu-1 --token ${{ secrets.ACCESS_REPO_INFO_TOKEN }}
|
||||
run: python utils/check_self_hosted_runner.py --target_runners hf-amd-mi210-ci-1gpu-1,hf-amd-mi250-ci-1gpu-1 --token ${{ secrets.ACCESS_REPO_INFO_TOKEN }}
|
||||
|
||||
check_runners:
|
||||
name: Check Runners
|
||||
@ -42,7 +42,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
machine_type: [single-gpu, multi-gpu]
|
||||
runs-on: [self-hosted, amd-gpu, '${{ matrix.machine_type }}', '${{ inputs.gpu_flavor }}']
|
||||
runs-on: [self-hosted, docker-gpu, amd-gpu, '${{ matrix.machine_type }}', '${{ inputs.gpu_flavor }}']
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: huggingface/transformers-pytorch-amd-gpu
|
||||
options: --device /dev/kfd --device /dev/dri --env ROCR_VISIBLE_DEVICES --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
@ -63,7 +63,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
machine_type: [single-gpu, multi-gpu]
|
||||
runs-on: [self-hosted, amd-gpu, '${{ matrix.machine_type }}', '${{ inputs.gpu_flavor }}']
|
||||
runs-on: [self-hosted, docker-gpu, amd-gpu, '${{ matrix.machine_type }}', '${{ inputs.gpu_flavor }}']
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: huggingface/transformers-pytorch-amd-gpu
|
||||
options: --device /dev/kfd --device /dev/dri --env ROCR_VISIBLE_DEVICES --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
@ -116,7 +116,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
folders: ${{ fromJson(needs.setup.outputs.matrix) }}
|
||||
machine_type: [single-gpu]
|
||||
runs-on: [self-hosted, amd-gpu, '${{ matrix.machine_type }}', '${{ inputs.gpu_flavor }}']
|
||||
runs-on: [self-hosted, docker-gpu, amd-gpu, '${{ matrix.machine_type }}', '${{ inputs.gpu_flavor }}']
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: huggingface/transformers-pytorch-amd-gpu
|
||||
options: --device /dev/kfd --device /dev/dri --env ROCR_VISIBLE_DEVICES --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
@ -162,7 +162,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run all tests on GPU
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: python3 -m pytest -v --make-reports=${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_models_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}_test_reports tests/${{ matrix.folders }} -m "not not_device_test"
|
||||
run: python3 -m pytest -v --make-reports=${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_models_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}_test_reports tests/${{ matrix.folders }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
if: ${{ failure() }}
|
||||
@ -184,7 +184,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
folders: ${{ fromJson(needs.setup.outputs.matrix) }}
|
||||
machine_type: [multi-gpu]
|
||||
runs-on: [self-hosted, amd-gpu, '${{ matrix.machine_type }}', '${{ inputs.gpu_flavor }}']
|
||||
runs-on: [self-hosted, docker-gpu, amd-gpu, '${{ matrix.machine_type }}', '${{ inputs.gpu_flavor }}']
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: huggingface/transformers-pytorch-amd-gpu
|
||||
options: --device /dev/kfd --device /dev/dri --env ROCR_VISIBLE_DEVICES --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
@ -230,7 +230,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run all tests on GPU
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: python3 -m pytest -v --make-reports=${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_models_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}_test_reports tests/${{ matrix.folders }} -m "not not_device_test"
|
||||
run: python3 -m pytest -v --make-reports=${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_models_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}_test_reports tests/${{ matrix.folders }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
if: ${{ failure() }}
|
||||
@ -250,7 +250,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
fail-fast: false
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
machine_type: [single-gpu]
|
||||
runs-on: [self-hosted, amd-gpu, '${{ matrix.machine_type }}', '${{ inputs.gpu_flavor }}']
|
||||
runs-on: [self-hosted, docker-gpu, amd-gpu, '${{ matrix.machine_type }}', '${{ inputs.gpu_flavor }}']
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: huggingface/transformers-pytorch-amd-gpu
|
||||
options: --device /dev/kfd --device /dev/dri --env ROCR_VISIBLE_DEVICES --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
@ -287,7 +287,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
pip install -r examples/pytorch/_tests_requirements.txt
|
||||
python3 -m pytest -v --make-reports=${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_examples_gpu_test_reports examples/pytorch -m "not not_device_test"
|
||||
python3 -m pytest -v --make-reports=${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_examples_gpu_test_reports examples/pytorch
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
if: ${{ failure() }}
|
||||
@ -307,7 +307,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
fail-fast: false
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
machine_type: [single-gpu, multi-gpu]
|
||||
runs-on: [self-hosted, amd-gpu, '${{ matrix.machine_type }}', '${{ inputs.gpu_flavor }}']
|
||||
runs-on: [self-hosted, docker-gpu, amd-gpu, '${{ matrix.machine_type }}', '${{ inputs.gpu_flavor }}']
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: huggingface/transformers-pytorch-amd-gpu
|
||||
options: --device /dev/kfd --device /dev/dri --env ROCR_VISIBLE_DEVICES --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
@ -343,7 +343,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
- name: Run all pipeline tests on GPU
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python3 -m pytest -n 1 -v --dist=loadfile --make-reports=${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_pipelines_torch_gpu_test_reports tests/pipelines -m "not not_device_test"
|
||||
python3 -m pytest -n 1 -v --dist=loadfile --make-reports=${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_pipelines_torch_gpu_test_reports tests/pipelines
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
if: ${{ failure() }}
|
||||
@ -364,7 +364,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
machine_type: [single-gpu, multi-gpu]
|
||||
|
||||
runs-on: [self-hosted, amd-gpu, '${{ matrix.machine_type }}', '${{ inputs.gpu_flavor }}']
|
||||
runs-on: [self-hosted, docker-gpu, amd-gpu, '${{ matrix.machine_type }}', '${{ inputs.gpu_flavor }}']
|
||||
needs: setup
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: huggingface/transformers-pytorch-deepspeed-amd-gpu
|
||||
@ -400,7 +400,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run all tests on GPU
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: python3 -m pytest -v --make-reports=${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu_test_reports tests/deepspeed tests/extended -m "not not_device_test"
|
||||
run: python3 -m pytest -v --make-reports=${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu_test_reports tests/deepspeed tests/extended
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
if: ${{ failure() }}
|
||||
|
||||
42
.github/workflows/self-scheduled-caller.yml
vendored
42
.github/workflows/self-scheduled-caller.yml
vendored
@ -7,49 +7,9 @@ on:
|
||||
- cron: "17 2 * * *"
|
||||
push:
|
||||
branches:
|
||||
- run_scheduled_ci*
|
||||
- check_quant
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
model-ci:
|
||||
name: Model CI
|
||||
uses: ./.github/workflows/self-scheduled.yml
|
||||
with:
|
||||
job: run_models_gpu
|
||||
slack_report_channel: "#transformers-ci-daily-models"
|
||||
secrets: inherit
|
||||
|
||||
torch-pipeline:
|
||||
name: Torch pipeline CI
|
||||
uses: ./.github/workflows/self-scheduled.yml
|
||||
with:
|
||||
job: run_pipelines_torch_gpu
|
||||
slack_report_channel: "#transformers-ci-daily-pipeline-torch"
|
||||
secrets: inherit
|
||||
|
||||
tf-pipeline:
|
||||
name: TF pipeline CI
|
||||
uses: ./.github/workflows/self-scheduled.yml
|
||||
with:
|
||||
job: run_pipelines_tf_gpu
|
||||
slack_report_channel: "#transformers-ci-daily-pipeline-tf"
|
||||
secrets: inherit
|
||||
|
||||
example-ci:
|
||||
name: Example CI
|
||||
uses: ./.github/workflows/self-scheduled.yml
|
||||
with:
|
||||
job: run_examples_gpu
|
||||
slack_report_channel: "#transformers-ci-daily-examples"
|
||||
secrets: inherit
|
||||
|
||||
deepspeed-ci:
|
||||
name: DeepSpeed CI
|
||||
uses: ./.github/workflows/self-scheduled.yml
|
||||
with:
|
||||
job: run_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu
|
||||
slack_report_channel: "#transformers-ci-daily-deepspeed"
|
||||
secrets: inherit
|
||||
|
||||
quantization-ci:
|
||||
name: Quantization CI
|
||||
uses: ./.github/workflows/self-scheduled.yml
|
||||
|
||||
19
.github/workflows/slack-report.yml
vendored
19
.github/workflows/slack-report.yml
vendored
@ -19,8 +19,6 @@ on:
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
type: string
|
||||
|
||||
env:
|
||||
TRANSFORMERS_CI_RESULTS_UPLOAD_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.TRANSFORMERS_CI_RESULTS_UPLOAD_TOKEN }}
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
send_results:
|
||||
@ -56,17 +54,18 @@ jobs:
|
||||
# empty string, and the called script still get one argument (which is the emtpy string).
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
sudo apt-get install -y curl
|
||||
pip install huggingface_hub
|
||||
pip install slack_sdk
|
||||
pip show slack_sdk
|
||||
python utils/notification_service.py "${{ inputs.folder_slices }}"
|
||||
|
||||
# Upload complete failure tables, as they might be big and only truncated versions could be sent to Slack.
|
||||
- name: Failure table artifacts
|
||||
# Only the model testing job is concerned for this step
|
||||
if: ${{ inputs.job == 'run_models_gpu' }}
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: ci_results_${{ inputs.job }}
|
||||
path: ci_results_${{ inputs.job }}
|
||||
name: prev_ci_results
|
||||
path: prev_ci_results
|
||||
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
- uses: actions/download-artifact@v4
|
||||
@ -78,21 +77,11 @@ jobs:
|
||||
SLACK_REPORT_CHANNEL: ${{ inputs.slack_report_channel }}
|
||||
CI_EVENT: scheduled
|
||||
CI_SHA: ${{ github.sha }}
|
||||
CI_TEST_JOB: ${{ inputs.job }}
|
||||
SETUP_STATUS: ${{ inputs.setup_status }}
|
||||
# We pass `needs.setup.outputs.quantization_matrix` as the argument. A processing in `notification_service_quantization.py` to change
|
||||
# `quantization/bnb` to `quantization_bnb` is required, as the artifact names use `_` instead of `/`.
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
sudo apt-get install -y curl
|
||||
pip install huggingface_hub
|
||||
pip install slack_sdk
|
||||
pip show slack_sdk
|
||||
python utils/notification_service_quantization.py "${{ inputs.quantization_matrix }}"
|
||||
|
||||
# Upload complete failure tables, as they might be big and only truncated versions could be sent to Slack.
|
||||
- name: Failure table artifacts
|
||||
if: ${{ inputs.job == 'run_quantization_torch_gpu' }}
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: ci_results_${{ inputs.job }}
|
||||
path: ci_results_${{ inputs.job }}
|
||||
9
.github/workflows/ssh-runner.yml
vendored
9
.github/workflows/ssh-runner.yml
vendored
@ -9,11 +9,9 @@ on:
|
||||
docker_image:
|
||||
description: 'Name of the Docker image'
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
num_gpus:
|
||||
description: 'Type of the number of gpus to use (`single` or `multi`)'
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
|
||||
env:
|
||||
IS_GITHUB_CI: "1"
|
||||
HF_HUB_READ_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.HF_HUB_READ_TOKEN }}
|
||||
HF_HOME: /mnt/cache
|
||||
TRANSFORMERS_IS_CI: yes
|
||||
@ -22,13 +20,12 @@ env:
|
||||
RUN_SLOW: yes # For gated repositories, we still need to agree to share information on the Hub repo. page in order to get access. # This token is created under the bot `hf-transformers-bot`.
|
||||
SIGOPT_API_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.SIGOPT_API_TOKEN }}
|
||||
TF_FORCE_GPU_ALLOW_GROWTH: true
|
||||
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES: 0,1
|
||||
RUN_PT_TF_CROSS_TESTS: 1
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
ssh_runner:
|
||||
name: "SSH"
|
||||
runs-on: ["${{ github.event.inputs.num_gpus }}-gpu", nvidia-gpu, "${{ github.event.inputs.runner_type }}", ci]
|
||||
runs-on: [single-gpu, nvidia-gpu, "${{ github.event.inputs.runner_type }}", ci]
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: ${{ github.event.inputs.docker_image }}
|
||||
options: --gpus all --privileged --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
@ -55,7 +52,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
nvidia-smi
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Tailscale # In order to be able to SSH when a test fails
|
||||
uses: huggingface/tailscale-action@main
|
||||
uses: huggingface/tailscale-action@v1
|
||||
with:
|
||||
authkey: ${{ secrets.TAILSCALE_SSH_AUTHKEY }}
|
||||
slackChannel: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_CHANNEL }}
|
||||
|
||||
29
.github/workflows/trufflehog.yml
vendored
29
.github/workflows/trufflehog.yml
vendored
@ -1,29 +0,0 @@
|
||||
on:
|
||||
push:
|
||||
|
||||
name: Secret Leaks
|
||||
|
||||
permissions:
|
||||
contents: read
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
trufflehog:
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- shell: bash
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
if [ "${{ github.event_name }}" == "push" ]; then
|
||||
echo "depth=$(($(jq length <<< '${{ toJson(github.event.commits) }}') + 2))" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
echo "branch=${{ github.ref_name }}" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
fi
|
||||
if [ "${{ github.event_name }}" == "pull_request" ]; then
|
||||
echo "depth=$((${{ github.event.pull_request.commits }}+2))" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
echo "branch=${{ github.event.pull_request.head.ref }}" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
fi
|
||||
- name: Checkout code
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
ref: ${{env.branch}}
|
||||
fetch-depth: ${{env.depth}}
|
||||
- name: Secret Scanning
|
||||
uses: trufflesecurity/trufflehog@main
|
||||
9
Makefile
9
Makefile
@ -1,11 +1,11 @@
|
||||
.PHONY: deps_table_update modified_only_fixup extra_style_checks quality style fixup fix-copies test test-examples benchmark
|
||||
.PHONY: deps_table_update modified_only_fixup extra_style_checks quality style fixup fix-copies test test-examples
|
||||
|
||||
# make sure to test the local checkout in scripts and not the pre-installed one (don't use quotes!)
|
||||
export PYTHONPATH = src
|
||||
|
||||
check_dirs := examples tests src utils
|
||||
|
||||
exclude_folders := ""
|
||||
exclude_folders := examples/research_projects
|
||||
|
||||
modified_only_fixup:
|
||||
$(eval modified_py_files := $(shell python utils/get_modified_files.py $(check_dirs)))
|
||||
@ -96,11 +96,6 @@ test:
|
||||
test-examples:
|
||||
python -m pytest -n auto --dist=loadfile -s -v ./examples/pytorch/
|
||||
|
||||
# Run benchmark
|
||||
|
||||
benchmark:
|
||||
python3 benchmark/benchmark.py --config-dir benchmark/config --config-name generation --commit=diff backend.model=google/gemma-2b backend.cache_implementation=null,static backend.torch_compile=false,true --multirun
|
||||
|
||||
# Run tests for SageMaker DLC release
|
||||
|
||||
test-sagemaker: # install sagemaker dependencies in advance with pip install .[sagemaker]
|
||||
|
||||
20
README.md
20
README.md
@ -25,11 +25,21 @@ limitations under the License.
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<a href="https://circleci.com/gh/huggingface/transformers"><img alt="Build" src="https://img.shields.io/circleci/build/github/huggingface/transformers/main"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/LICENSE"><img alt="GitHub" src="https://img.shields.io/github/license/huggingface/transformers.svg?color=blue"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/index"><img alt="Documentation" src="https://img.shields.io/website/http/huggingface.co/docs/transformers/index.svg?down_color=red&down_message=offline&up_message=online"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/releases"><img alt="GitHub release" src="https://img.shields.io/github/release/huggingface/transformers.svg"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md"><img alt="Contributor Covenant" src="https://img.shields.io/badge/Contributor%20Covenant-v2.0%20adopted-ff69b4.svg"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://circleci.com/gh/huggingface/transformers">
|
||||
<img alt="Build" src="https://img.shields.io/circleci/build/github/huggingface/transformers/main">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/LICENSE">
|
||||
<img alt="GitHub" src="https://img.shields.io/github/license/huggingface/transformers.svg?color=blue">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/index">
|
||||
<img alt="Documentation" src="https://img.shields.io/website/http/huggingface.co/docs/transformers/index.svg?down_color=red&down_message=offline&up_message=online">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/releases">
|
||||
<img alt="GitHub release" src="https://img.shields.io/github/release/huggingface/transformers.svg">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md">
|
||||
<img alt="Contributor Covenant" src="https://img.shields.io/badge/Contributor%20Covenant-v2.0%20adopted-ff69b4.svg">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://zenodo.org/badge/latestdoi/155220641"><img src="https://zenodo.org/badge/155220641.svg" alt="DOI"></a>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
20
README_de.md
20
README_de.md
@ -25,11 +25,21 @@ limitations under the License.
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<a href="https://circleci.com/gh/huggingface/transformers"><img alt="Build" src="https://img.shields.io/circleci/build/github/huggingface/transformers/main"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/LICENSE"><img alt="GitHub" src="https://img.shields.io/github/license/huggingface/transformers.svg?color=blue"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/index"><img alt="Documentation" src="https://img.shields.io/website/http/huggingface.co/docs/transformers/index.svg?down_color=red&down_message=offline&up_message=online"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/releases"><img alt="GitHub release" src="https://img.shields.io/github/release/huggingface/transformers.svg"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md"><img alt="Contributor Covenant" src="https://img.shields.io/badge/Contributor%20Covenant-v2.0%20adopted-ff69b4.svg"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://circleci.com/gh/huggingface/transformers">
|
||||
<img alt="Build" src="https://img.shields.io/circleci/build/github/huggingface/transformers/main">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/LICENSE">
|
||||
<img alt="GitHub" src="https://img.shields.io/github/license/huggingface/transformers.svg?color=blue">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/index">
|
||||
<img alt="Documentation" src="https://img.shields.io/website/http/huggingface.co/docs/transformers/index.svg?down_color=red&down_message=offline&up_message=online">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/releases">
|
||||
<img alt="GitHub release" src="https://img.shields.io/github/release/huggingface/transformers.svg">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md">
|
||||
<img alt="Contributor Covenant" src="https://img.shields.io/badge/Contributor%20Covenant-v2.0%20adopted-ff69b4.svg">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://zenodo.org/badge/latestdoi/155220641"><img src="https://zenodo.org/badge/155220641.svg" alt="DOI"></a>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
20
README_es.md
20
README_es.md
@ -20,11 +20,21 @@ limitations under the License.
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<a href="https://circleci.com/gh/huggingface/transformers"><img alt="Build" src="https://img.shields.io/circleci/build/github/huggingface/transformers/main"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/LICENSE"><img alt="GitHub" src="https://img.shields.io/github/license/huggingface/transformers.svg?color=blue"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/index"><img alt="Documentation" src="https://img.shields.io/website/http/huggingface.co/docs/transformers/index.svg?down_color=red&down_message=offline&up_message=online"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/releases"><img alt="GitHub release" src="https://img.shields.io/github/release/huggingface/transformers.svg"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md"><img alt="Contributor Covenant" src="https://img.shields.io/badge/Contributor%20Covenant-v2.0%20adopted-ff69b4.svg"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://circleci.com/gh/huggingface/transformers">
|
||||
<img alt="Build" src="https://img.shields.io/circleci/build/github/huggingface/transformers/main">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/LICENSE">
|
||||
<img alt="GitHub" src="https://img.shields.io/github/license/huggingface/transformers.svg?color=blue">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/index">
|
||||
<img alt="Documentation" src="https://img.shields.io/website/http/huggingface.co/docs/transformers/index.svg?down_color=red&down_message=offline&up_message=online">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/releases">
|
||||
<img alt="GitHub release" src="https://img.shields.io/github/release/huggingface/transformers.svg">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md">
|
||||
<img alt="Contributor Covenant" src="https://img.shields.io/badge/Contributor%20Covenant-v2.0%20adopted-ff69b4.svg">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://zenodo.org/badge/latestdoi/155220641"><img src="https://zenodo.org/badge/155220641.svg" alt="DOI"></a>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
21
README_fr.md
21
README_fr.md
@ -25,11 +25,21 @@ limitations under the License.
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<a href="https://circleci.com/gh/huggingface/transformers"><img alt="Build" src="https://img.shields.io/circleci/build/github/huggingface/transformers/main"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/LICENSE"><img alt="GitHub" src="https://img.shields.io/github/license/huggingface/transformers.svg?color=blue"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/index"><img alt="Documentation" src="https://img.shields.io/website/http/huggingface.co/docs/transformers/index.svg?down_color=red&down_message=offline&up_message=online"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/releases"><img alt="GitHub release" src="https://img.shields.io/github/release/huggingface/transformers.svg"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md"><img alt="Contributor Covenant" src="https://img.shields.io/badge/Contributor%20Covenant-v2.0%20adopted-ff69b4.svg"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://circleci.com/gh/huggingface/transformers">
|
||||
<img alt="Construction" src="https://img.shields.io/circleci/build/github/huggingface/transformers/main">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/LICENSE">
|
||||
<img alt="GitHub" src="https://img.shields.io/github/license/huggingface/transformers.svg?color=blue">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/index">
|
||||
<img alt="Documentation" src="https://img.shields.io/website/http/huggingface.co/docs/transformers/index.svg?down_color=red&down_message=offline&up_message=online">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/releases">
|
||||
<img alt="Version GitHub" src="https://img.shields.io/github/release/huggingface/transformers.svg">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md">
|
||||
<img alt="Pacte des contributeurs" src="https://img.shields.io/badge/Contributor%20Covenant-v2.0%20adopted-ff69b4.svg">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://zenodo.org/badge/latestdoi/155220641"><img src="https://zenodo.org/badge/155220641.svg" alt="DOI"></a>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -278,6 +288,7 @@ Suivez les pages d'installation de Flax, PyTorch ou TensorFlow pour voir comment
|
||||
|
||||
Nombre actuel de points de contrôle : 
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 Transformers fournit actuellement les architectures suivantes: consultez [ici](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_summary) pour un résumé global de chacune d'entre elles.
|
||||
|
||||
Pour vérifier si chaque modèle a une implémentation en Flax, PyTorch ou TensorFlow, ou s'il a un tokenizer associé pris en charge par la bibliothèque 🤗 Tokenizers, consultez [ce tableau](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/index#supported-frameworks).
|
||||
|
||||
20
README_hd.md
20
README_hd.md
@ -45,11 +45,21 @@ checkpoint: जाँच बिंदु
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<a href="https://circleci.com/gh/huggingface/transformers"><img alt="Build" src="https://img.shields.io/circleci/build/github/huggingface/transformers/main"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/LICENSE"><img alt="GitHub" src="https://img.shields.io/github/license/huggingface/transformers.svg?color=blue"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/index"><img alt="Documentation" src="https://img.shields.io/website/http/huggingface.co/docs/transformers/index.svg?down_color=red&down_message=offline&up_message=online"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/releases"><img alt="GitHub release" src="https://img.shields.io/github/release/huggingface/transformers.svg"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md"><img alt="Contributor Covenant" src="https://img.shields.io/badge/Contributor%20Covenant-v2.0%20adopted-ff69b4.svg"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://circleci.com/gh/huggingface/transformers">
|
||||
<img alt="Build" src="https://img.shields.io/circleci/build/github/huggingface/transformers/main">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/LICENSE">
|
||||
<img alt="GitHub" src="https://img.shields.io/github/license/huggingface/transformers.svg?color=blue">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/index">
|
||||
<img alt="Documentation" src="https://img.shields.io/website/http/huggingface.co/docs/transformers/index.svg?down_color=red&down_message=offline&up_message=online">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/releases">
|
||||
<img alt="GitHub release" src="https://img.shields.io/github/release/huggingface/transformers.svg">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md">
|
||||
<img alt="Contributor Covenant" src="https://img.shields.io/badge/Contributor%20Covenant-v2.0%20adopted-ff69b4.svg">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://zenodo.org/badge/latestdoi/155220641"><img src="https://zenodo.org/badge/155220641.svg" alt="DOI"></a>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
20
README_ja.md
20
README_ja.md
@ -55,11 +55,21 @@ user: ユーザ
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<a href="https://circleci.com/gh/huggingface/transformers"><img alt="Build" src="https://img.shields.io/circleci/build/github/huggingface/transformers/main"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/LICENSE"><img alt="GitHub" src="https://img.shields.io/github/license/huggingface/transformers.svg?color=blue"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/index"><img alt="Documentation" src="https://img.shields.io/website/http/huggingface.co/docs/transformers/index.svg?down_color=red&down_message=offline&up_message=online"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/releases"><img alt="GitHub release" src="https://img.shields.io/github/release/huggingface/transformers.svg"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md"><img alt="Contributor Covenant" src="https://img.shields.io/badge/Contributor%20Covenant-v2.0%20adopted-ff69b4.svg"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://circleci.com/gh/huggingface/transformers">
|
||||
<img alt="Build" src="https://img.shields.io/circleci/build/github/huggingface/transformers/main">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/LICENSE">
|
||||
<img alt="GitHub" src="https://img.shields.io/github/license/huggingface/transformers.svg?color=blue">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/index">
|
||||
<img alt="Documentation" src="https://img.shields.io/website/http/huggingface.co/docs/transformers/index.svg?down_color=red&down_message=offline&up_message=online">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/releases">
|
||||
<img alt="GitHub release" src="https://img.shields.io/github/release/huggingface/transformers.svg">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md">
|
||||
<img alt="Contributor Covenant" src="https://img.shields.io/badge/Contributor%20Covenant-v2.0%20adopted-ff69b4.svg">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://zenodo.org/badge/latestdoi/155220641"><img src="https://zenodo.org/badge/155220641.svg" alt="DOI"></a>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
20
README_ko.md
20
README_ko.md
@ -20,11 +20,21 @@ limitations under the License.
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<a href="https://circleci.com/gh/huggingface/transformers"><img alt="Build" src="https://img.shields.io/circleci/build/github/huggingface/transformers/main"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/LICENSE"><img alt="GitHub" src="https://img.shields.io/github/license/huggingface/transformers.svg?color=blue"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/index"><img alt="Documentation" src="https://img.shields.io/website/http/huggingface.co/docs/transformers/index.svg?down_color=red&down_message=offline&up_message=online"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/releases"><img alt="GitHub release" src="https://img.shields.io/github/release/huggingface/transformers.svg"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md"><img alt="Contributor Covenant" src="https://img.shields.io/badge/Contributor%20Covenant-v2.0%20adopted-ff69b4.svg"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://circleci.com/gh/huggingface/transformers">
|
||||
<img alt="Build" src="https://img.shields.io/circleci/build/github/huggingface/transformers/main">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/LICENSE">
|
||||
<img alt="GitHub" src="https://img.shields.io/github/license/huggingface/transformers.svg?color=blue">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/index">
|
||||
<img alt="Documentation" src="https://img.shields.io/website/http/huggingface.co/docs/transformers/index.svg?down_color=red&down_message=offline&up_message=online">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/releases">
|
||||
<img alt="GitHub release" src="https://img.shields.io/github/release/huggingface/transformers.svg">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md">
|
||||
<img alt="Contributor Covenant" src="https://img.shields.io/badge/Contributor%20Covenant-v2.0%20adopted-ff69b4.svg">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://zenodo.org/badge/latestdoi/155220641"><img src="https://zenodo.org/badge/155220641.svg" alt="DOI"></a>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -25,11 +25,21 @@ limitations under the License.
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<a href="https://circleci.com/gh/huggingface/transformers"><img alt="Build" src="https://img.shields.io/circleci/build/github/huggingface/transformers/main"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/LICENSE"><img alt="GitHub" src="https://img.shields.io/github/license/huggingface/transformers.svg?color=blue"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/index"><img alt="Documentation" src="https://img.shields.io/website/http/huggingface.co/docs/transformers/index.svg?down_color=red&down_message=offline&up_message=online"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/releases"><img alt="GitHub release" src="https://img.shields.io/github/release/huggingface/transformers.svg"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md"><img alt="Contributor Covenant" src="https://img.shields.io/badge/Contributor%20Covenant-v2.0%20adopted-ff69b4.svg"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://circleci.com/gh/huggingface/transformers">
|
||||
<img alt="Build" src="https://img.shields.io/circleci/build/github/huggingface/transformers/main">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/LICENSE">
|
||||
<img alt="GitHub" src="https://img.shields.io/github/license/huggingface/transformers.svg?color=blue">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/index">
|
||||
<img alt="Documentation" src="https://img.shields.io/website/http/huggingface.co/docs/transformers/index.svg?down_color=red&down_message=offline&up_message=online">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/releases">
|
||||
<img alt="GitHub release" src="https://img.shields.io/github/release/huggingface/transformers.svg">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md">
|
||||
<img alt="Contributor Covenant" src="https://img.shields.io/badge/Contributor%20Covenant-v2.0%20adopted-ff69b4.svg">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://zenodo.org/badge/latestdoi/155220641"><img src="https://zenodo.org/badge/155220641.svg" alt="DOI"></a>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
20
README_ru.md
20
README_ru.md
@ -25,11 +25,21 @@ limitations under the License.
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<a href="https://circleci.com/gh/huggingface/transformers"><img alt="Build" src="https://img.shields.io/circleci/build/github/huggingface/transformers/main"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/LICENSE"><img alt="GitHub" src="https://img.shields.io/github/license/huggingface/transformers.svg?color=blue"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/index"><img alt="Documentation" src="https://img.shields.io/website/http/huggingface.co/docs/transformers/index.svg?down_color=red&down_message=offline&up_message=online"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/releases"><img alt="GitHub release" src="https://img.shields.io/github/release/huggingface/transformers.svg"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md"><img alt="Contributor Covenant" src="https://img.shields.io/badge/Contributor%20Covenant-v2.0%20adopted-ff69b4.svg"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://circleci.com/gh/huggingface/transformers">
|
||||
<img alt="Build" src="https://img.shields.io/circleci/build/github/huggingface/transformers/main">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/LICENSE">
|
||||
<img alt="GitHub" src="https://img.shields.io/github/license/huggingface/transformers.svg?color=blue">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/index">
|
||||
<img alt="Documentation" src="https://img.shields.io/website/http/huggingface.co/docs/transformers/index.svg?down_color=red&down_message=offline&up_message=online">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/releases">
|
||||
<img alt="GitHub release" src="https://img.shields.io/github/release/huggingface/transformers.svg">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md">
|
||||
<img alt="Contributor Covenant" src="https://img.shields.io/badge/Contributor%20Covenant-v2.0%20adopted-ff69b4.svg">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://zenodo.org/badge/latestdoi/155220641"><img src="https://zenodo.org/badge/155220641.svg" alt="DOI"></a>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
21
README_te.md
21
README_te.md
@ -26,11 +26,21 @@ limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<a href="https://circleci.com/gh/huggingface/transformers"><img alt="Build" src="https://img.shields.io/circleci/build/github/huggingface/transformers/main"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/LICENSE"><img alt="GitHub" src="https://img.shields.io/github/license/huggingface/transformers.svg?color=blue"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/index"><img alt="Documentation" src="https://img.shields.io/website/http/huggingface.co/docs/transformers/index.svg?down_color=red&down_message=offline&up_message=online"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/releases"><img alt="GitHub release" src="https://img.shields.io/github/release/huggingface/transformers.svg"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md"><img alt="Contributor Covenant" src="https://img.shields.io/badge/Contributor%20Covenant-v2.0%20adopted-ff69b4.svg"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://circleci.com/gh/huggingface/transformers">
|
||||
<img alt="Build" src="https://img.shields.io/circleci/build/github/huggingface/transformers/main">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/LICENSE">
|
||||
<img alt="GitHub" src="https://img.shields.io/github/license/huggingface/transformers.svg?color=blue">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/index">
|
||||
<img alt="Documentation" src="https://img.shields.io/website/http/huggingface.co/docs/transformers/index.svg?down_color=red&down_message=offline&up_message=online">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/releases">
|
||||
<img alt="GitHub release" src="https://img.shields.io/github/release/huggingface/transformers.svg">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md">
|
||||
<img alt="Contributor Covenant" src="https://img.shields.io/badge/Contributor%20Covenant-v2.0%20adopted-ff69b4.svg">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://zenodo.org/badge/latestdoi/155220641"><img src="https://zenodo.org/badge/155220641.svg" alt="DOI"></a>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -283,6 +293,7 @@ Flax, PyTorch లేదా TensorFlow యొక్క ఇన్స్టా
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 ట్రాన్స్ఫార్మర్లు ప్రస్తుతం కింది ఆర్కిటెక్చర్లను అందజేస్తున్నాయి: వాటిలో ప్రతి ఒక్కటి ఉన్నత స్థాయి సారాంశం కోసం [ఇక్కడ](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_summary) చూడండి.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
ఈ అమలులు అనేక డేటాసెట్లలో పరీక్షించబడ్డాయి (ఉదాహరణ స్క్రిప్ట్లను చూడండి) మరియు అసలైన అమలుల పనితీరుతో సరిపోలాలి. మీరు [డాక్యుమెంటేషన్](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples) యొక్క ఉదాహరణల విభాగంలో పనితీరుపై మరిన్ని వివరాలను కనుగొనవచ్చు.
|
||||
|
||||
## ఇంకా నేర్చుకో
|
||||
|
||||
20
README_vi.md
20
README_vi.md
@ -25,11 +25,21 @@ limitations under the License.
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<a href="https://circleci.com/gh/huggingface/transformers"><img alt="Build" src="https://img.shields.io/circleci/build/github/huggingface/transformers/main"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/LICENSE"><img alt="GitHub" src="https://img.shields.io/github/license/huggingface/transformers.svg?color=blue"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/index"><img alt="Documentation" src="https://img.shields.io/website/http/huggingface.co/docs/transformers/index.svg?down_color=red&down_message=offline&up_message=online"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/releases"><img alt="GitHub release" src="https://img.shields.io/github/release/huggingface/transformers.svg"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md"><img alt="Contributor Covenant" src="https://img.shields.io/badge/Contributor%20Covenant-v2.0%20adopted-ff69b4.svg"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://circleci.com/gh/huggingface/transformers">
|
||||
<img alt="Build" src="https://img.shields.io/circleci/build/github/huggingface/transformers/main">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/LICENSE">
|
||||
<img alt="GitHub" src="https://img.shields.io/github/license/huggingface/transformers.svg?color=blue">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/index">
|
||||
<img alt="Documentation" src="https://img.shields.io/website/http/huggingface.co/docs/transformers/index.svg?down_color=red&down_message=offline&up_message=online">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/releases">
|
||||
<img alt="GitHub release" src="https://img.shields.io/github/release/huggingface/transformers.svg">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md">
|
||||
<img alt="Contributor Covenant" src="https://img.shields.io/badge/Contributor%20Covenant-v2.0%20adopted-ff69b4.svg">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://zenodo.org/badge/latestdoi/155220641"><img src="https://zenodo.org/badge/155220641.svg" alt="DOI"></a>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -45,11 +45,21 @@ checkpoint: 检查点
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<a href="https://circleci.com/gh/huggingface/transformers"><img alt="Build" src="https://img.shields.io/circleci/build/github/huggingface/transformers/main"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/LICENSE"><img alt="GitHub" src="https://img.shields.io/github/license/huggingface/transformers.svg?color=blue"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/index"><img alt="Documentation" src="https://img.shields.io/website/http/huggingface.co/docs/transformers/index.svg?down_color=red&down_message=offline&up_message=online"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/releases"><img alt="GitHub release" src="https://img.shields.io/github/release/huggingface/transformers.svg"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md"><img alt="Contributor Covenant" src="https://img.shields.io/badge/Contributor%20Covenant-v2.0%20adopted-ff69b4.svg"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://circleci.com/gh/huggingface/transformers">
|
||||
<img alt="Build" src="https://img.shields.io/circleci/build/github/huggingface/transformers/main">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/LICENSE">
|
||||
<img alt="GitHub" src="https://img.shields.io/github/license/huggingface/transformers.svg?color=blue">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/index">
|
||||
<img alt="Documentation" src="https://img.shields.io/website/http/huggingface.co/docs/transformers/index.svg?down_color=red&down_message=offline&up_message=online">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/releases">
|
||||
<img alt="GitHub release" src="https://img.shields.io/github/release/huggingface/transformers.svg">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md">
|
||||
<img alt="Contributor Covenant" src="https://img.shields.io/badge/Contributor%20Covenant-v2.0%20adopted-ff69b4.svg">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://zenodo.org/badge/latestdoi/155220641"><img src="https://zenodo.org/badge/155220641.svg" alt="DOI"></a>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -57,11 +57,21 @@ user: 使用者
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<a href="https://circleci.com/gh/huggingface/transformers"><img alt="Build" src="https://img.shields.io/circleci/build/github/huggingface/transformers/main"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/LICENSE"><img alt="GitHub" src="https://img.shields.io/github/license/huggingface/transformers.svg?color=blue"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/index"><img alt="Documentation" src="https://img.shields.io/website/http/huggingface.co/docs/transformers/index.svg?down_color=red&down_message=offline&up_message=online"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/releases"><img alt="GitHub release" src="https://img.shields.io/github/release/huggingface/transformers.svg"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md"><img alt="Contributor Covenant" src="https://img.shields.io/badge/Contributor%20Covenant-v2.0%20adopted-ff69b4.svg"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://circleci.com/gh/huggingface/transformers">
|
||||
<img alt="Build" src="https://img.shields.io/circleci/build/github/huggingface/transformers/main">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/LICENSE">
|
||||
<img alt="GitHub" src="https://img.shields.io/github/license/huggingface/transformers.svg?color=blue">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/index">
|
||||
<img alt="Documentation" src="https://img.shields.io/website/http/huggingface.co/docs/transformers/index.svg?down_color=red&down_message=offline&up_message=online">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/releases">
|
||||
<img alt="GitHub release" src="https://img.shields.io/github/release/huggingface/transformers.svg">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md">
|
||||
<img alt="Contributor Covenant" src="https://img.shields.io/badge/Contributor%20Covenant-v2.0%20adopted-ff69b4.svg">
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a href="https://zenodo.org/badge/latestdoi/155220641"><img src="https://zenodo.org/badge/155220641.svg" alt="DOI"></a>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -14,7 +14,7 @@ Models uploaded on the Hugging Face Hub come in different formats. We heavily re
|
||||
models in the [`safetensors`](https://github.com/huggingface/safetensors) format (which is the default prioritized
|
||||
by the transformers library), as developed specifically to prevent arbitrary code execution on your system.
|
||||
|
||||
To avoid loading models from unsafe formats(e.g. [pickle](https://docs.python.org/3/library/pickle.html), you should use the `use_safetensors` parameter. If doing so, in the event that no .safetensors file is present, transformers will error when loading the model.
|
||||
To avoid loading models from unsafe formats(e.g. [pickle](https://docs.python.org/3/library/pickle.html), you should use the `use_safetenstors` parameter. If doing so, in the event that no .safetensors file is present, transformers will error when loading the model.
|
||||
|
||||
### Remote code
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,326 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Run benchmark using the `optimum-benchmark` library with some customization in `transformers`.
|
||||
|
||||
Assume we are under `transformers` root directory: (make sure the commits are valid commits)
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python benchmark/benchmark.py --config-dir benchmark/config --config-name generation --commit=9b9c7f03da625b13643e99205c691fe046461724 --metrics=decode.latency.mean,per_token.latency.mean,per_token.throughput.value backend.model=google/gemma-2b benchmark.input_shapes.sequence_length=5,7 benchmark.input_shapes.batch_size=1,2 --multirun
|
||||
```
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
import argparse
|
||||
import glob
|
||||
import json
|
||||
import os.path
|
||||
import re
|
||||
import tempfile
|
||||
from contextlib import contextmanager
|
||||
from pathlib import Path
|
||||
|
||||
from git import Repo
|
||||
|
||||
from huggingface_hub import HfApi
|
||||
|
||||
from optimum_benchmark import Benchmark
|
||||
from optimum_benchmark_wrapper import main
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
PATH_TO_REPO = Path(__file__).parent.parent.resolve()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@contextmanager
|
||||
def checkout_commit(repo: Repo, commit_id: str):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Context manager that checks out a given commit when entered, but gets back to the reference it was at on exit.
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
repo (`git.Repo`): A git repository (for instance the Transformers repo).
|
||||
commit_id (`str`): The commit reference to checkout inside the context manager.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
current_head = repo.head.commit if repo.head.is_detached else repo.head.ref
|
||||
|
||||
try:
|
||||
repo.git.checkout(commit_id)
|
||||
yield
|
||||
|
||||
finally:
|
||||
repo.git.checkout(current_head)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def summarize(run_dir, metrics, expand_metrics=False):
|
||||
"""Produce a summary for each optimum-benchmark launched job's output directory found in `run_dir`.
|
||||
|
||||
Each summary's format is as follows (for `expand_metrics=False`):
|
||||
```
|
||||
{
|
||||
"model": "google/gemma-2b",
|
||||
"commit": "3cd6ed22e4d49219f300f5055e71e3929aba20d7",
|
||||
"config": "benchmark.input_shapes.batch_size=1,benchmark.input_shapes.sequence_length=5",
|
||||
"metrics": {
|
||||
"decode.latency.mean": 1.624666809082031,
|
||||
"per_token.latency.mean": 0.012843788806628804,
|
||||
"per_token.throughput.value": 77.85864553330948
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
"""
|
||||
reports = glob.glob(os.path.join(run_dir, "**/benchmark_report.json"), recursive=True)
|
||||
report_dirs = [str(Path(report).parent) for report in reports]
|
||||
|
||||
summaries = []
|
||||
for report_dir in report_dirs:
|
||||
commit = re.search(r"/commit=([^/]+)", report_dir).groups()[0]
|
||||
|
||||
if not os.path.isfile(os.path.join(report_dir, "benchmark.json")):
|
||||
continue
|
||||
benchmark = Benchmark.from_json(os.path.join(report_dir, "benchmark.json"))
|
||||
report = benchmark.report
|
||||
|
||||
model = benchmark.config.backend["model"]
|
||||
|
||||
# Ths looks like `benchmark.input_shapes.batch_size=1,benchmark.input_shapes.sequence_length=5`.
|
||||
# (we rely on the usage of hydra's `${hydra.job.override_dirname}`.)
|
||||
benchmark_name = re.sub(f"backend.model={model},*", "", report_dir)
|
||||
benchmark_name = str(Path(benchmark_name).parts[-1])
|
||||
if benchmark_name.startswith("commit="):
|
||||
benchmark_name = benchmark.config.name
|
||||
|
||||
metrics_values = {}
|
||||
# post-processing of report: show a few selected/important metric
|
||||
for metric in metrics:
|
||||
keys = metric.split(".")
|
||||
value = report
|
||||
current = metrics_values
|
||||
for key in keys:
|
||||
# Avoid KeyError when a user's specified metric has typo.
|
||||
# TODO: Give warnings.
|
||||
if key not in value:
|
||||
continue
|
||||
value = value[key]
|
||||
|
||||
if expand_metrics:
|
||||
if isinstance(value, dict):
|
||||
if key not in current:
|
||||
current[key] = {}
|
||||
current = current[key]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
current[key] = value
|
||||
|
||||
if not expand_metrics:
|
||||
metrics_values[metric] = value
|
||||
|
||||
# show some config information
|
||||
print(f"model: {model}")
|
||||
print(f"commit: {commit}")
|
||||
print(f"config: {benchmark_name}")
|
||||
if len(metrics_values) > 0:
|
||||
print("metrics:")
|
||||
if expand_metrics:
|
||||
print(metrics_values)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
for metric, value in metrics_values.items():
|
||||
print(f" - {metric}: {value}")
|
||||
print("-" * 80)
|
||||
|
||||
summary = {
|
||||
"model": model,
|
||||
"commit": commit,
|
||||
"config": benchmark_name,
|
||||
"metrics": metrics_values,
|
||||
}
|
||||
summaries.append(summary)
|
||||
|
||||
with open(os.path.join(report_dir, "summary.json"), "w") as fp:
|
||||
json.dump(summary, fp, indent=4)
|
||||
|
||||
return summaries
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def combine_summaries(summaries):
|
||||
"""Combine a list of summary obtained from the function `summarize`.
|
||||
|
||||
The combined summary's format is as follows:
|
||||
```
|
||||
"google/gemma-2b": {
|
||||
"benchmark.input_shapes.batch_size=1,benchmark.input_shapes.sequence_length=5": {
|
||||
"3cd6ed22e4d49219f300f5055e71e3929aba20d7": {
|
||||
"metrics": {"decode.latency.mean": 1.624666809082031}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"c97ee28b117c0abe8e08891f402065e4df6d72aa": {
|
||||
"metrics": {"decode.latency.mean": 1.6278163452148438}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"benchmark.input_shapes.batch_size=2,benchmark.input_shapes.sequence_length=5": {
|
||||
"3cd6ed22e4d49219f300f5055e71e3929aba20d7": {
|
||||
"metrics": {"decode.latency.mean": 1.6947791748046876}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"c97ee28b117c0abe8e08891f402065e4df6d72aa": {
|
||||
"metrics": {
|
||||
"decode.latency.mean": 1.6980519409179688}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
"""
|
||||
combined = {}
|
||||
for summary in summaries:
|
||||
model = summary["model"]
|
||||
config = summary["config"]
|
||||
commit = summary["commit"]
|
||||
|
||||
if model not in combined:
|
||||
combined[model] = {}
|
||||
|
||||
if config not in combined[model]:
|
||||
combined[model][config] = {}
|
||||
|
||||
if commit not in combined[model][config]:
|
||||
combined[model][config][commit] = {"metrics": summary["metrics"]}
|
||||
|
||||
with open(os.path.join(exp_run_dir, "summary.json"), "w") as fp:
|
||||
json.dump(combined, fp, indent=4)
|
||||
|
||||
print(json.dumps(combined, indent=4))
|
||||
|
||||
return combined
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
|
||||
def list_str(values):
|
||||
return values.split(",")
|
||||
|
||||
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
|
||||
|
||||
parser.add_argument("--config-dir", type=str, required=True, help="The path to the config directory.")
|
||||
parser.add_argument("--config-name", type=str, required=True, help="The config name.")
|
||||
|
||||
# arguments specific to this wrapper for our own customization
|
||||
parser.add_argument("--ensure_empty", type=bool, default=True, help="If to create a temporary directory.")
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--commit",
|
||||
type=list_str,
|
||||
default="",
|
||||
help="Comma-separated list of branch names and/or commit sha values on which the benchmark will run. If `diff` is specified, it will run on both the current head and the `main` branch.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument("--metrics", type=str, help="The metrics to be included in the summary.")
|
||||
|
||||
parser.add_argument("--repo_id", type=str, default=None, help="The repository to which the file will be uploaded.")
|
||||
parser.add_argument("--path_in_repo", type=str, default=None, help="Relative filepath in the repo.")
|
||||
parser.add_argument("--token", type=str, default=None, help="A valid user access token (string).")
|
||||
|
||||
args, optimum_benchmark_args = parser.parse_known_args()
|
||||
|
||||
repo = Repo(PATH_TO_REPO)
|
||||
|
||||
metrics = [
|
||||
"prefill.latency.mean",
|
||||
"prefill.throughput.value",
|
||||
"decode.latency.mean",
|
||||
"decode.throughput.value",
|
||||
"per_token.latency.mean",
|
||||
"per_token.throughput.value",
|
||||
]
|
||||
if args.metrics is not None:
|
||||
metrics = args.metrics.split(",")
|
||||
|
||||
# Get `backend.model` in a hacky way: We want to control the experiment flow manually.
|
||||
models = [""]
|
||||
for idx, arg in enumerate(optimum_benchmark_args):
|
||||
if arg.startswith("backend.model="):
|
||||
models = arg[len("backend.model=") :]
|
||||
models = models.split(",")
|
||||
break
|
||||
optimum_benchmark_args = [arg for arg in optimum_benchmark_args if not arg.startswith("backend.model=")]
|
||||
|
||||
# Get the commit(s)
|
||||
current_head = str(repo.head.commit) if repo.head.is_detached else str(repo.head.ref)
|
||||
commits = [x for x in args.commit if x != ""]
|
||||
if len(commits) == 0:
|
||||
commits = [current_head]
|
||||
elif len(commits) == 1 and commits[0] == "diff":
|
||||
# compare to `main`
|
||||
commits = ["main", current_head]
|
||||
|
||||
# Get the specified run directory
|
||||
run_dir_arg_idx, run_dir = -1, None
|
||||
sweep_dir_arg_idx, sweep_dir = -1, None
|
||||
for idx, arg in enumerate(optimum_benchmark_args):
|
||||
if arg.startswith("hydra.run.dir="):
|
||||
run_dir = arg[len("hydra.run.dir=") :]
|
||||
run_dir_arg_idx = idx
|
||||
elif arg.startswith("hydra.sweep.dir="):
|
||||
sweep_dir = arg[len("hydra.sweep.dir=") :]
|
||||
sweep_dir_arg_idx = idx
|
||||
exp_run_dir, arg_dix, arg_name = (
|
||||
(sweep_dir, sweep_dir_arg_idx, "hydra.sweep.dir")
|
||||
if "--multirun" in optimum_benchmark_args
|
||||
else (run_dir, run_dir_arg_idx, "hydra.run.dir")
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# TODO: not hardcoded
|
||||
if exp_run_dir is None and args.ensure_empty:
|
||||
exp_run_dir = "_benchmark"
|
||||
|
||||
if args.ensure_empty:
|
||||
os.makedirs(exp_run_dir, exist_ok=True)
|
||||
exp_run_dir = tempfile.mkdtemp(dir=exp_run_dir)
|
||||
|
||||
run_summaries = []
|
||||
for commit in commits:
|
||||
with checkout_commit(repo, commit):
|
||||
commit = str(repo.head.commit)
|
||||
|
||||
commit_run_dir = exp_run_dir
|
||||
if exp_run_dir is not None:
|
||||
commit_run_dir = os.path.join(exp_run_dir, rf"commit\={commit}")
|
||||
|
||||
print(f"Run benchmark on commit: {commit}")
|
||||
|
||||
for model in models:
|
||||
model_arg = [f"backend.model={model}"] if model != "" else []
|
||||
dir_args = []
|
||||
if commit_run_dir is not None:
|
||||
if arg_dix > -1:
|
||||
optimum_benchmark_args[arg_dix] = f"{arg_name}={commit_run_dir}"
|
||||
else:
|
||||
dir_args = [
|
||||
f"hydra.sweep.dir={commit_run_dir}",
|
||||
f"hydra.run.dir={commit_run_dir}/" + "${hydra.job.override_dirname}",
|
||||
]
|
||||
main(args.config_dir, args.config_name, model_arg + dir_args + optimum_benchmark_args)
|
||||
|
||||
if commit_run_dir is not None:
|
||||
# Need to remove the `\` character
|
||||
summaries = summarize(commit_run_dir.replace("\\", ""), metrics)
|
||||
run_summaries.extend(summaries)
|
||||
|
||||
# aggregate the information across the commits
|
||||
if exp_run_dir is not None:
|
||||
with open(os.path.join(exp_run_dir, "summaries.json"), "w") as fp:
|
||||
json.dump(run_summaries, fp, indent=4)
|
||||
|
||||
combined_summary = combine_summaries(run_summaries)
|
||||
|
||||
if args.repo_id is not None and args.path_in_repo is not None:
|
||||
# Upload to Hub
|
||||
api = HfApi()
|
||||
api.upload_folder(
|
||||
folder_path=exp_run_dir,
|
||||
path_in_repo=args.path_in_repo,
|
||||
repo_id=args.repo_id,
|
||||
repo_type="dataset",
|
||||
token=args.token,
|
||||
)
|
||||
@ -1,57 +0,0 @@
|
||||
defaults:
|
||||
- benchmark # inheriting benchmark schema
|
||||
- scenario: inference
|
||||
- launcher: process
|
||||
- backend: pytorch
|
||||
- _self_ # for hydra 1.1 compatibility
|
||||
|
||||
name: pytorch_generate
|
||||
|
||||
launcher:
|
||||
start_method: spawn
|
||||
device_isolation: true
|
||||
device_isolation_action: warn
|
||||
|
||||
backend:
|
||||
device: cuda
|
||||
device_ids: 0
|
||||
no_weights: true
|
||||
model: meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-hf
|
||||
cache_implementation: static
|
||||
torch_compile: true
|
||||
torch_dtype: float16
|
||||
torch_compile_config:
|
||||
backend: inductor
|
||||
mode: reduce-overhead
|
||||
fullgraph: true
|
||||
|
||||
scenario:
|
||||
input_shapes:
|
||||
batch_size: 1
|
||||
sequence_length: 7
|
||||
generate_kwargs:
|
||||
max_new_tokens: 128
|
||||
min_new_tokens: 128
|
||||
do_sample: false
|
||||
memory: true
|
||||
latency: true
|
||||
iterations: 2
|
||||
duration: 0
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# hydra/cli specific settings
|
||||
hydra:
|
||||
run:
|
||||
# where to store run results
|
||||
dir: runs/${name}
|
||||
job:
|
||||
# change working directory to the run directory
|
||||
chdir: true
|
||||
env_set:
|
||||
# set environment variable OVERRIDE_BENCHMARKS to 1
|
||||
# to not skip benchmarks that have been run before
|
||||
OVERRIDE_BENCHMARKS: 1
|
||||
LOG_LEVEL: WARN
|
||||
sweep:
|
||||
dir: multirun
|
||||
subdir: ${hydra.job.override_dirname}
|
||||
@ -1,16 +0,0 @@
|
||||
import argparse
|
||||
import subprocess
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def main(config_dir, config_name, args):
|
||||
subprocess.run(["optimum-benchmark", "--config-dir", f"{config_dir}", "--config-name", f"{config_name}"] + ["hydra/job_logging=disabled", "hydra/hydra_logging=disabled"] + args)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
|
||||
|
||||
parser.add_argument("--config-dir", type=str, required=True, help="The path to the config directory.")
|
||||
parser.add_argument("--config-name", type=str, required=True, help="The config name.")
|
||||
args, unknown = parser.parse_known_args()
|
||||
|
||||
main(args.config_dir, args.config_name, unknown)
|
||||
@ -53,7 +53,7 @@ NOT_DEVICE_TESTS = {
|
||||
"test_torch_save_load",
|
||||
"test_initialization",
|
||||
"test_forward_signature",
|
||||
"test_model_get_set_embeddings",
|
||||
"test_model_common_attributes",
|
||||
"test_model_main_input_name",
|
||||
"test_correct_missing_keys",
|
||||
"test_tie_model_weights",
|
||||
@ -71,7 +71,7 @@ NOT_DEVICE_TESTS = {
|
||||
"ModelTester::test_pipeline_",
|
||||
"/repo_utils/",
|
||||
"/utils/",
|
||||
"/agents/",
|
||||
"/tools/",
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# allow having multiple repository checkouts and not needing to remember to rerun
|
||||
@ -94,7 +94,7 @@ def pytest_configure(config):
|
||||
config.addinivalue_line("markers", "is_pipeline_test: mark test to run only when pipelines are tested")
|
||||
config.addinivalue_line("markers", "is_staging_test: mark test to run only in the staging environment")
|
||||
config.addinivalue_line("markers", "accelerate_tests: mark test that require accelerate")
|
||||
config.addinivalue_line("markers", "agent_tests: mark the agent tests that are run on their specific schedule")
|
||||
config.addinivalue_line("markers", "tool_tests: mark the tool tests that are run on their specific schedule")
|
||||
config.addinivalue_line("markers", "not_device_test: mark the tests always running on cpu")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,15 +0,0 @@
|
||||
FROM python:3.10-slim
|
||||
ENV PYTHONDONTWRITEBYTECODE=1
|
||||
USER root
|
||||
ARG REF=main
|
||||
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y time git pkg-config make git-lfs
|
||||
ENV UV_PYTHON=/usr/local/bin/python
|
||||
RUN pip install uv && uv venv && uv pip install --no-cache-dir -U pip setuptools GitPython
|
||||
RUN uv pip install --no-cache-dir --upgrade 'torch' --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu
|
||||
RUN uv pip install --no-cache-dir tensorflow-cpu tf-keras
|
||||
RUN uv pip install --no-cache-dir "git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git@${REF}#egg=transformers[flax,quality,vision,testing]"
|
||||
RUN git lfs install
|
||||
|
||||
RUN pip uninstall -y transformers
|
||||
RUN apt-get clean && rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/* && apt-get autoremove && apt-get autoclean
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,26 +0,0 @@
|
||||
FROM python:3.10-slim
|
||||
ENV PYTHONDONTWRITEBYTECODE=1
|
||||
USER root
|
||||
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y libsndfile1-dev espeak-ng time git cmake wget xz-utils build-essential g++5 libprotobuf-dev protobuf-compiler
|
||||
ENV UV_PYTHON=/usr/local/bin/python
|
||||
RUN pip --no-cache-dir install uv && uv venv && uv pip install --no-cache-dir -U pip setuptools
|
||||
|
||||
RUN wget https://github.com/ku-nlp/jumanpp/releases/download/v2.0.0-rc3/jumanpp-2.0.0-rc3.tar.xz
|
||||
RUN tar xvf jumanpp-2.0.0-rc3.tar.xz
|
||||
RUN mkdir jumanpp-2.0.0-rc3/bld
|
||||
WORKDIR ./jumanpp-2.0.0-rc3/bld
|
||||
RUN wget -LO catch.hpp https://github.com/catchorg/Catch2/releases/download/v2.13.8/catch.hpp
|
||||
RUN mv catch.hpp ../libs/
|
||||
RUN cmake .. -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=/usr/local
|
||||
RUN make install -j 10
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
RUN uv pip install --no-cache --upgrade 'torch' --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu
|
||||
RUN uv pip install --no-cache-dir --no-deps accelerate --extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu
|
||||
RUN uv pip install --no-cache-dir "transformers[ja,testing,sentencepiece,jieba,spacy,ftfy,rjieba]" unidic unidic-lite
|
||||
# spacy is not used so not tested. Causes to failures. TODO fix later
|
||||
RUN python3 -m unidic download
|
||||
RUN pip uninstall -y transformers
|
||||
|
||||
RUN apt-get clean && rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*
|
||||
RUN apt remove -y g++ cmake xz-utils libprotobuf-dev protobuf-compiler
|
||||
@ -1,12 +0,0 @@
|
||||
FROM python:3.10-slim
|
||||
ENV PYTHONDONTWRITEBYTECODE=1
|
||||
USER root
|
||||
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y libsndfile1-dev espeak-ng time git
|
||||
RUN apt-get install -y g++ cmake
|
||||
ENV UV_PYTHON=/usr/local/bin/python
|
||||
RUN pip --no-cache-dir install uv && uv venv
|
||||
RUN uv pip install --no-cache-dir -U pip setuptools albumentations seqeval
|
||||
RUN pip install --upgrade --no-cache-dir "transformers[tf-cpu,sklearn,testing,sentencepiece,tf-speech,vision]"
|
||||
RUN uv pip install --no-cache-dir "protobuf==3.20.3"
|
||||
RUN pip uninstall -y transformers
|
||||
RUN apt-get clean && rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*
|
||||
@ -1,11 +0,0 @@
|
||||
FROM python:3.10-slim
|
||||
ENV PYTHONDONTWRITEBYTECODE=1
|
||||
USER root
|
||||
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y --no-install-recommends libsndfile1-dev espeak-ng time git g++ cmake pkg-config openssh-client git
|
||||
ENV UV_PYTHON=/usr/local/bin/python
|
||||
RUN pip --no-cache-dir install uv && uv venv && uv pip install --no-cache-dir -U pip setuptools
|
||||
RUN pip install --no-cache-dir 'torch' 'torchvision' 'torchaudio' --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu
|
||||
RUN uv pip install --no-deps timm accelerate --extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu
|
||||
RUN uv pip install --no-cache-dir librosa "transformers[sklearn,sentencepiece,vision,testing]" seqeval albumentations jiwer
|
||||
RUN pip uninstall -y transformers
|
||||
RUN apt-get clean && rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*
|
||||
@ -1,17 +0,0 @@
|
||||
FROM python:3.10-slim
|
||||
ENV PYTHONDONTWRITEBYTECODE=1
|
||||
ARG REF=main
|
||||
USER root
|
||||
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y libsndfile1-dev espeak-ng time git libgl1-mesa-glx libgl1 g++ tesseract-ocr
|
||||
ENV UV_PYTHON=/usr/local/bin/python
|
||||
RUN pip --no-cache-dir install uv && uv venv && uv pip install --no-cache-dir -U pip setuptools
|
||||
RUN pip install --no-cache-dir 'torch' 'torchvision' 'torchaudio' --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu
|
||||
RUN uv pip install --no-cache-dir --no-deps timm accelerate
|
||||
RUN pip install -U --upgrade-strategy eager --no-cache-dir pytesseract python-Levenshtein opencv-python nltk
|
||||
# RUN uv pip install --no-cache-dir natten==0.15.1+torch210cpu -f https://shi-labs.com/natten/wheels
|
||||
RUN pip install --no-cache-dir "git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git@${REF}#egg=transformers[testing, vision]" 'scikit-learn' 'torch-stft' 'nose' 'dataset'
|
||||
# RUN git clone https://github.com/facebookresearch/detectron2.git
|
||||
# RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir -e detectron2
|
||||
RUN pip install 'git+https://github.com/facebookresearch/detectron2.git@92ae9f0b92aba5867824b4f12aa06a22a60a45d3'
|
||||
RUN pip uninstall -y transformers
|
||||
RUN apt-get clean && rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*
|
||||
@ -1,10 +0,0 @@
|
||||
FROM python:3.10-slim
|
||||
ENV PYTHONDONTWRITEBYTECODE=1
|
||||
ARG REF=main
|
||||
USER root
|
||||
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y libsndfile1-dev espeak-ng time git g++ cmake
|
||||
ENV UV_PYTHON=/usr/local/bin/python
|
||||
RUN pip --no-cache-dir install uv && uv venv && uv pip install --no-cache-dir -U pip setuptools
|
||||
RUN pip install --no-cache-dir "scipy<1.13" "git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git@${REF}#egg=transformers[flax,testing,sentencepiece,flax-speech,vision]"
|
||||
RUN pip uninstall -y transformers
|
||||
RUN apt-get clean && rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/* && apt-get autoremove && apt-get autoclean
|
||||
@ -1,10 +0,0 @@
|
||||
FROM python:3.10-slim
|
||||
ENV PYTHONDONTWRITEBYTECODE=1
|
||||
ARG REF=main
|
||||
USER root
|
||||
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y libsndfile1-dev espeak-ng time git cmake g++
|
||||
ENV UV_PYTHON=/usr/local/bin/python
|
||||
RUN pip --no-cache-dir install uv && uv venv && uv pip install --no-cache-dir -U pip setuptools
|
||||
RUN pip install --no-cache-dir "git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git@${REF}#egg=transformers[sklearn,tf-cpu,testing,sentencepiece,tf-speech,vision]"
|
||||
RUN uv pip install --no-cache-dir "protobuf==3.20.3" tensorflow_probability
|
||||
RUN apt-get clean && rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*
|
||||
@ -1,11 +0,0 @@
|
||||
FROM python:3.10-slim
|
||||
ENV PYTHONDONTWRITEBYTECODE=1
|
||||
ARG REF=main
|
||||
USER root
|
||||
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y --no-install-recommends libsndfile1-dev espeak-ng time git pkg-config openssh-client git
|
||||
ENV UV_PYTHON=/usr/local/bin/python
|
||||
RUN pip --no-cache-dir install uv && uv venv && uv pip install --no-cache-dir -U pip setuptools
|
||||
RUN pip install --no-cache-dir 'torch' 'torchvision' 'torchaudio' --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu
|
||||
RUN uv pip install --no-deps timm accelerate --extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu
|
||||
RUN uv pip install --no-cache-dir librosa "git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git@${REF}#egg=transformers[sklearn,sentencepiece,vision,testing]"
|
||||
RUN pip uninstall -y transformers
|
||||
@ -1,9 +0,0 @@
|
||||
FROM python:3.10-slim
|
||||
ENV PYTHONDONTWRITEBYTECODE=1
|
||||
ARG REF=main
|
||||
USER root
|
||||
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y time git
|
||||
ENV UV_PYTHON=/usr/local/bin/python
|
||||
RUN pip install uv && uv venv
|
||||
RUN uv pip install --no-cache-dir -U pip setuptools GitPython "git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git@${REF}#egg=transformers[ruff]" urllib3
|
||||
RUN apt-get install -y jq curl && apt-get clean && rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*
|
||||
@ -1,12 +0,0 @@
|
||||
FROM python:3.10-slim
|
||||
ENV PYTHONDONTWRITEBYTECODE=1
|
||||
ARG REF=main
|
||||
USER root
|
||||
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y --no-install-recommends libsndfile1-dev espeak-ng time git g++ pkg-config openssh-client git
|
||||
RUN apt-get install -y cmake
|
||||
ENV UV_PYTHON=/usr/local/bin/python
|
||||
RUN pip --no-cache-dir install uv && uv venv && uv pip install --no-cache-dir -U pip setuptools
|
||||
RUN pip install --upgrade --no-cache-dir "git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git@${REF}#egg=transformers[tf-cpu,sklearn,testing,sentencepiece,tf-speech,vision]"
|
||||
RUN uv pip install --no-cache-dir "protobuf==3.20.3"
|
||||
RUN pip uninstall -y transformers
|
||||
RUN apt-get clean && rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/* && apt-get autoremove && apt-get autoclean
|
||||
@ -1,16 +0,0 @@
|
||||
FROM python:3.10-slim
|
||||
ENV PYTHONDONTWRITEBYTECODE=1
|
||||
ARG REF=main
|
||||
USER root
|
||||
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y libsndfile1-dev espeak-ng time git g++ cmake pkg-config openssh-client git
|
||||
ENV UV_PYTHON=/usr/local/bin/python
|
||||
RUN pip --no-cache-dir install uv && uv venv && uv pip install --no-cache-dir -U pip setuptools
|
||||
RUN uv pip install --no-deps accelerate
|
||||
RUN pip install --no-cache-dir 'torch' 'torchvision' 'torchaudio' --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu
|
||||
RUN pip install --no-cache-dir "scipy<1.13" "git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git@${REF}#egg=transformers[flax,audio,sklearn,sentencepiece,vision,testing]"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# RUN pip install --no-cache-dir "scipy<1.13" "transformers[flax,testing,sentencepiece,flax-speech,vision]"
|
||||
|
||||
RUN pip uninstall -y transformers
|
||||
RUN apt-get clean && rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/* && apt-get autoremove && apt-get autoclean
|
||||
@ -1,11 +0,0 @@
|
||||
FROM python:3.10-slim
|
||||
ENV PYTHONDONTWRITEBYTECODE=1
|
||||
ARG REF=main
|
||||
USER root
|
||||
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y --no-install-recommends libsndfile1-dev espeak-ng time git g++ cmake pkg-config openssh-client git git-lfs
|
||||
ENV UV_PYTHON=/usr/local/bin/python
|
||||
RUN pip --no-cache-dir install uv && uv venv && uv pip install --no-cache-dir -U pip setuptools
|
||||
RUN pip install --no-cache-dir 'torch' 'torchvision' 'torchaudio' --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu
|
||||
RUN uv pip install --no-deps timm accelerate --extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu
|
||||
RUN uv pip install --no-cache-dir librosa "git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git@${REF}#egg=transformers[sklearn,sentencepiece,vision,testing]"
|
||||
RUN pip uninstall -y transformers
|
||||
@ -1,19 +0,0 @@
|
||||
FROM python:3.10-slim
|
||||
ENV PYTHONDONTWRITEBYTECODE=1
|
||||
ARG REF=main
|
||||
RUN echo ${REF}
|
||||
USER root
|
||||
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y --no-install-recommends libsndfile1-dev espeak-ng time git g++ cmake pkg-config openssh-client git git-lfs
|
||||
ENV UV_PYTHON=/usr/local/bin/python
|
||||
RUN pip --no-cache-dir install uv && uv venv && uv pip install --no-cache-dir -U pip setuptools
|
||||
RUN uv pip install --no-cache-dir --no-deps accelerate --extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu
|
||||
RUN pip install --no-cache-dir 'torch' 'torchvision' 'torchaudio' --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu
|
||||
RUN git lfs install
|
||||
|
||||
RUN uv pip install --no-cache-dir pypi-kenlm
|
||||
RUN pip install --no-cache-dir "git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git@${REF}#egg=transformers[tf-cpu,sklearn,sentencepiece,vision,testing]"
|
||||
RUN uv pip install --no-cache-dir "protobuf==3.20.3" librosa
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
RUN pip uninstall -y transformers
|
||||
RUN apt-get clean && rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/* && apt-get autoremove && apt-get autoclean
|
||||
@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
|
||||
FROM nvidia/cuda:12.1.0-cudnn8-devel-ubuntu20.04
|
||||
FROM nvidia/cuda:11.8.0-cudnn8-devel-ubuntu20.04
|
||||
LABEL maintainer="Hugging Face"
|
||||
|
||||
ARG DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive
|
||||
@ -9,11 +9,11 @@ SHELL ["sh", "-lc"]
|
||||
# The following `ARG` are mainly used to specify the versions explicitly & directly in this docker file, and not meant
|
||||
# to be used as arguments for docker build (so far).
|
||||
|
||||
ARG PYTORCH='2.3.0'
|
||||
ARG PYTORCH='2.2.1'
|
||||
# (not always a valid torch version)
|
||||
ARG INTEL_TORCH_EXT='2.3.0'
|
||||
ARG INTEL_TORCH_EXT='2.2.0'
|
||||
# Example: `cu102`, `cu113`, etc.
|
||||
ARG CUDA='cu121'
|
||||
ARG CUDA='cu118'
|
||||
|
||||
RUN apt update
|
||||
RUN apt install -y git libsndfile1-dev tesseract-ocr espeak-ng python3 python3-pip ffmpeg git-lfs
|
||||
@ -48,13 +48,6 @@ RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir decord av==9.2.0
|
||||
# Some slow tests require bnb
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir bitsandbytes
|
||||
|
||||
# Some tests require quanto
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir quanto
|
||||
|
||||
# `quanto` will install `ninja` which leads to many `CUDA error: an illegal memory access ...` in some model tests
|
||||
# (`deformable_detr`, `rwkv`, `mra`)
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip uninstall -y ninja
|
||||
|
||||
# For `dinat` model
|
||||
# The `XXX` part in `torchXXX` needs to match `PYTORCH` (to some extent)
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir natten==0.15.1+torch220$CUDA -f https://shi-labs.com/natten/wheels
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,19 +1,24 @@
|
||||
FROM rocm/dev-ubuntu-22.04:6.0.2
|
||||
FROM rocm/dev-ubuntu-20.04:5.6
|
||||
# rocm/pytorch has no version with 2.1.0
|
||||
LABEL maintainer="Hugging Face"
|
||||
|
||||
ARG DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive
|
||||
|
||||
ARG PYTORCH='2.1.0'
|
||||
ARG TORCH_VISION='0.16.0'
|
||||
ARG TORCH_AUDIO='2.1.0'
|
||||
ARG ROCM='5.6'
|
||||
|
||||
RUN apt update && \
|
||||
apt install -y --no-install-recommends git libsndfile1-dev tesseract-ocr espeak-ng python3 python3-dev python3-pip python3-dev ffmpeg && \
|
||||
apt install -y --no-install-recommends git libsndfile1-dev tesseract-ocr espeak-ng python3 python3-dev python3-pip ffmpeg && \
|
||||
apt clean && \
|
||||
rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*
|
||||
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir --upgrade pip numpy
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir --upgrade pip
|
||||
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install torch torchvision torchaudio --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/rocm6.0
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install torch==$PYTORCH torchvision==$TORCH_VISION torchaudio==$TORCH_AUDIO --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/rocm$ROCM
|
||||
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir --upgrade importlib-metadata setuptools ninja git+https://github.com/facebookresearch/detectron2.git pytesseract "itsdangerous<2.1.0"
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir --upgrade pip setuptools ninja git+https://github.com/facebookresearch/detectron2.git pytesseract "itsdangerous<2.1.0"
|
||||
|
||||
ARG REF=main
|
||||
WORKDIR /
|
||||
@ -30,5 +35,5 @@ RUN python3 -m pip uninstall -y tensorflow flax
|
||||
# this line must be added in order for python to be aware of transformers.
|
||||
RUN cd transformers && python3 setup.py develop
|
||||
|
||||
# Remove nvml as it is not compatible with ROCm. apex is not tested on NVIDIA either.
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip uninstall py3nvml pynvml apex -y
|
||||
# Remove nvml as it is not compatible with ROCm
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip uninstall py3nvml pynvml -y
|
||||
|
||||
@ -42,7 +42,7 @@ RUN python3 -m pip uninstall -y deepspeed
|
||||
# This has to be run (again) inside the GPU VMs running the tests.
|
||||
# The installation works here, but some tests fail, if we don't pre-build deepspeed again in the VMs running the tests.
|
||||
# TODO: Find out why test fail.
|
||||
RUN DS_BUILD_CPU_ADAM=1 DS_BUILD_FUSED_ADAM=1 python3 -m pip install "deepspeed<=0.14.0" --global-option="build_ext" --global-option="-j8" --no-cache -v --disable-pip-version-check 2>&1
|
||||
RUN DS_BUILD_CPU_ADAM=1 DS_BUILD_FUSED_ADAM=1 python3 -m pip install deepspeed --global-option="build_ext" --global-option="-j8" --no-cache -v --disable-pip-version-check 2>&1
|
||||
|
||||
# When installing in editable mode, `transformers` is not recognized as a package.
|
||||
# this line must be added in order for python to be aware of transformers.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -11,7 +11,7 @@ ARG REF=main
|
||||
RUN git clone https://github.com/huggingface/transformers && cd transformers && git checkout $REF
|
||||
|
||||
# If set to nothing, will install the latest version
|
||||
ARG PYTORCH='2.3.0'
|
||||
ARG PYTORCH='2.1.1'
|
||||
ARG TORCH_VISION=''
|
||||
ARG TORCH_AUDIO=''
|
||||
# Example: `cu102`, `cu113`, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
8
docker/transformers-quantization-latest-gpu/Dockerfile
Executable file → Normal file
8
docker/transformers-quantization-latest-gpu/Dockerfile
Executable file → Normal file
@ -45,12 +45,6 @@ RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir git+https://github.com/huggingface/opt
|
||||
# Add aqlm for quantization testing
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir aqlm[gpu]==1.0.2
|
||||
|
||||
# Add hqq for quantization testing
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir hqq
|
||||
|
||||
# For GGUF tests
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir gguf
|
||||
|
||||
# Add autoawq for quantization testing
|
||||
# >=v0.2.3 needed for compatibility with torch 2.2.1
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir https://github.com/casper-hansen/AutoAWQ/releases/download/v0.2.3/autoawq-0.2.3+cu118-cp38-cp38-linux_x86_64.whl
|
||||
@ -63,4 +57,4 @@ RUN python3 -m pip install git+https://github.com/NetEase-FuXi/EETQ.git
|
||||
|
||||
# When installing in editable mode, `transformers` is not recognized as a package.
|
||||
# this line must be added in order for python to be aware of transformers.
|
||||
RUN cd transformers && python3 setup.py develop
|
||||
RUN cd transformers && python3 setup.py develop
|
||||
@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
|
||||
FROM nvidia/cuda:12.1.0-cudnn8-devel-ubuntu20.04
|
||||
FROM nvidia/cuda:11.8.0-cudnn8-devel-ubuntu20.04
|
||||
LABEL maintainer="Hugging Face"
|
||||
|
||||
ARG DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive
|
||||
|
||||
@ -162,7 +162,7 @@ Transformers verwendet die Shell-Umgebungsvariablen `PYTORCH_TRANSFORMERS_CACHE`
|
||||
|
||||
## Offline Modus
|
||||
|
||||
Transformers ist in der Lage, in einer Firewall- oder Offline-Umgebung zu laufen, indem es nur lokale Dateien verwendet. Setzen Sie die Umgebungsvariable `HF_HUB_OFFLINE=1`, um dieses Verhalten zu aktivieren.
|
||||
Transformers ist in der Lage, in einer Firewall- oder Offline-Umgebung zu laufen, indem es nur lokale Dateien verwendet. Setzen Sie die Umgebungsvariable `TRANSFORMERS_OFFLINE=1`, um dieses Verhalten zu aktivieren.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -179,7 +179,7 @@ python examples/pytorch/translation/run_translation.py --model_name_or_path goog
|
||||
Führen Sie das gleiche Programm in einer Offline-Instanz mit aus:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
HF_DATASETS_OFFLINE=1 HF_HUB_OFFLINE=1 \
|
||||
HF_DATASETS_OFFLINE=1 TRANSFORMERS_OFFLINE=1 \
|
||||
python examples/pytorch/translation/run_translation.py --model_name_or_path google-t5/t5-small --dataset_name wmt16 --dataset_config ro-en ...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -86,10 +86,10 @@ model.load_adapter(peft_model_id)
|
||||
Die `bitsandbytes`-Integration unterstützt Datentypen mit 8bit und 4bit Genauigkeit, was für das Laden großer Modelle nützlich ist, weil es Speicher spart (lesen Sie den `bitsandbytes`-Integrations [guide](./quantization#bitsandbytes-integration), um mehr zu erfahren). Fügen Sie die Parameter `load_in_8bit` oder `load_in_4bit` zu [`~PreTrainedModel.from_pretrained`] hinzu und setzen Sie `device_map="auto"`, um das Modell effektiv auf Ihre Hardware zu verteilen:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer, BitsAndBytesConfig
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
peft_model_id = "ybelkada/opt-350m-lora"
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(peft_model_id, quantization_config=BitsAndBytesConfig(load_in_8bit=True))
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(peft_model_id, device_map="auto", load_in_8bit=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Einen neuen Adapter hinzufügen
|
||||
|
||||
@ -16,7 +16,7 @@ rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
# Trainieren mit einem Skript
|
||||
|
||||
Neben den 🤗 Transformers [notebooks](./notebooks) gibt es auch Beispielskripte, die zeigen, wie man ein Modell für eine Aufgabe mit [PyTorch](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples/pytorch), [TensorFlow](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples/tensorflow) oder [JAX/Flax](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples/flax) trainiert.
|
||||
Neben den 🤗 Transformers [notebooks](./noteboks/README) gibt es auch Beispielskripte, die zeigen, wie man ein Modell für eine Aufgabe mit [PyTorch](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples/pytorch), [TensorFlow](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples/tensorflow) oder [JAX/Flax](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples/flax) trainiert.
|
||||
|
||||
Sie werden auch Skripte finden, die wir in unseren [Forschungsprojekten](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples/research_projects) und [Legacy-Beispielen](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples/legacy) verwendet haben und die größtenteils von der Community stammen. Diese Skripte werden nicht aktiv gepflegt und erfordern eine bestimmte Version von 🤗 Transformers, die höchstwahrscheinlich nicht mit der neuesten Version der Bibliothek kompatibel ist.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,5 +1,3 @@
|
||||
# Optimizing inference
|
||||
|
||||
perf_infer_gpu_many: perf_infer_gpu_one
|
||||
transformers_agents: agents
|
||||
quantization: quantization/overview
|
||||
|
||||
@ -23,12 +23,10 @@
|
||||
title: Load and train adapters with 🤗 PEFT
|
||||
- local: model_sharing
|
||||
title: Share your model
|
||||
- local: agents
|
||||
- local: transformers_agents
|
||||
title: Agents
|
||||
- local: llm_tutorial
|
||||
title: Generation with LLMs
|
||||
- local: conversations
|
||||
title: Chatting with Transformers
|
||||
title: Tutorials
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- isExpanded: false
|
||||
@ -133,38 +131,20 @@
|
||||
title: Notebooks with examples
|
||||
- local: community
|
||||
title: Community resources
|
||||
- local: custom_tools
|
||||
title: Custom Tools and Prompts
|
||||
- local: troubleshooting
|
||||
title: Troubleshoot
|
||||
- local: gguf
|
||||
title: Interoperability with GGUF files
|
||||
title: Developer guides
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: quantization/overview
|
||||
title: Getting started
|
||||
- local: quantization/bitsandbytes
|
||||
title: bitsandbytes
|
||||
- local: quantization/gptq
|
||||
title: GPTQ
|
||||
- local: quantization/awq
|
||||
title: AWQ
|
||||
- local: quantization/aqlm
|
||||
title: AQLM
|
||||
- local: quantization/quanto
|
||||
title: Quanto
|
||||
- local: quantization/eetq
|
||||
title: EETQ
|
||||
- local: quantization/hqq
|
||||
title: HQQ
|
||||
- local: quantization/optimum
|
||||
title: Optimum
|
||||
- local: quantization/contribute
|
||||
- local: hf_quantizer
|
||||
title: Contribute new quantization method
|
||||
title: Quantization Methods
|
||||
title: Developer guides
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: performance
|
||||
title: Overview
|
||||
- local: llm_optims
|
||||
title: LLM inference optimization
|
||||
- local: quantization
|
||||
title: Quantization
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: perf_train_gpu_one
|
||||
title: Methods and tools for efficient training on a single GPU
|
||||
@ -406,8 +386,6 @@
|
||||
title: I-BERT
|
||||
- local: model_doc/jamba
|
||||
title: Jamba
|
||||
- local: model_doc/jetmoe
|
||||
title: JetMoe
|
||||
- local: model_doc/jukebox
|
||||
title: Jukebox
|
||||
- local: model_doc/led
|
||||
@ -804,8 +782,6 @@
|
||||
title: OWL-ViT
|
||||
- local: model_doc/owlv2
|
||||
title: OWLv2
|
||||
- local: model_doc/paligemma
|
||||
title: PaliGemma
|
||||
- local: model_doc/perceiver
|
||||
title: Perceiver
|
||||
- local: model_doc/pix2struct
|
||||
@ -826,8 +802,6 @@
|
||||
title: TVP
|
||||
- local: model_doc/udop
|
||||
title: UDOP
|
||||
- local: model_doc/video_llava
|
||||
title: VideoLlava
|
||||
- local: model_doc/vilt
|
||||
title: ViLT
|
||||
- local: model_doc/vipllava
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,504 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
# Agents and tools
|
||||
|
||||
[[open-in-colab]]
|
||||
|
||||
### What is an agent?
|
||||
|
||||
Large Language Models (LLMs) trained to perform [causal language modeling](./tasks/language_modeling.) can tackle a wide range of tasks, but they often struggle with basic tasks like logic, calculation, and search. When prompted in domains in which they do not perform well, they often fail to generate the answer we expect them to.
|
||||
|
||||
One approach to overcome this weakness is to create an *agent*.
|
||||
|
||||
An agent is a system that uses an LLM as its engine, and it has access to functions called *tools*.
|
||||
|
||||
These *tools* are functions for performing a task, and they contain all necessary description for the agent to properly use them.
|
||||
|
||||
The agent can be programmed to:
|
||||
- devise a series of actions/tools and run them all at once like the [`CodeAgent`] for example
|
||||
- plan and execute actions/tools one by one and wait for the outcome of each action before launching the next one like the [`ReactJsonAgent`] for example
|
||||
|
||||
### Types of agents
|
||||
|
||||
#### Code agent
|
||||
|
||||
This agent has a planning step, then generates python code to execute all its actions at once. It natively handles different input and output types for its tools, thus it is the recommended choice for multimodal tasks.
|
||||
|
||||
#### React agents
|
||||
|
||||
This is the go-to agent to solve reasoning tasks, since the ReAct framework ([Yao et al., 2022](https://huggingface.co/papers/2210.03629)) makes it really efficient to think on the basis of its previous observations.
|
||||
|
||||
We implement two versions of ReactJsonAgent:
|
||||
- [`ReactJsonAgent`] generates tool calls as a JSON in its output.
|
||||
- [`ReactCodeAgent`] is a new type of ReactJsonAgent that generates its tool calls as blobs of code, which works really well for LLMs that have strong coding performance.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!TIP]
|
||||
> Read [Open-source LLMs as LangChain Agents](https://huggingface.co/blog/open-source-llms-as-agents) blog post to learn more the ReAct agent.
|
||||
|
||||
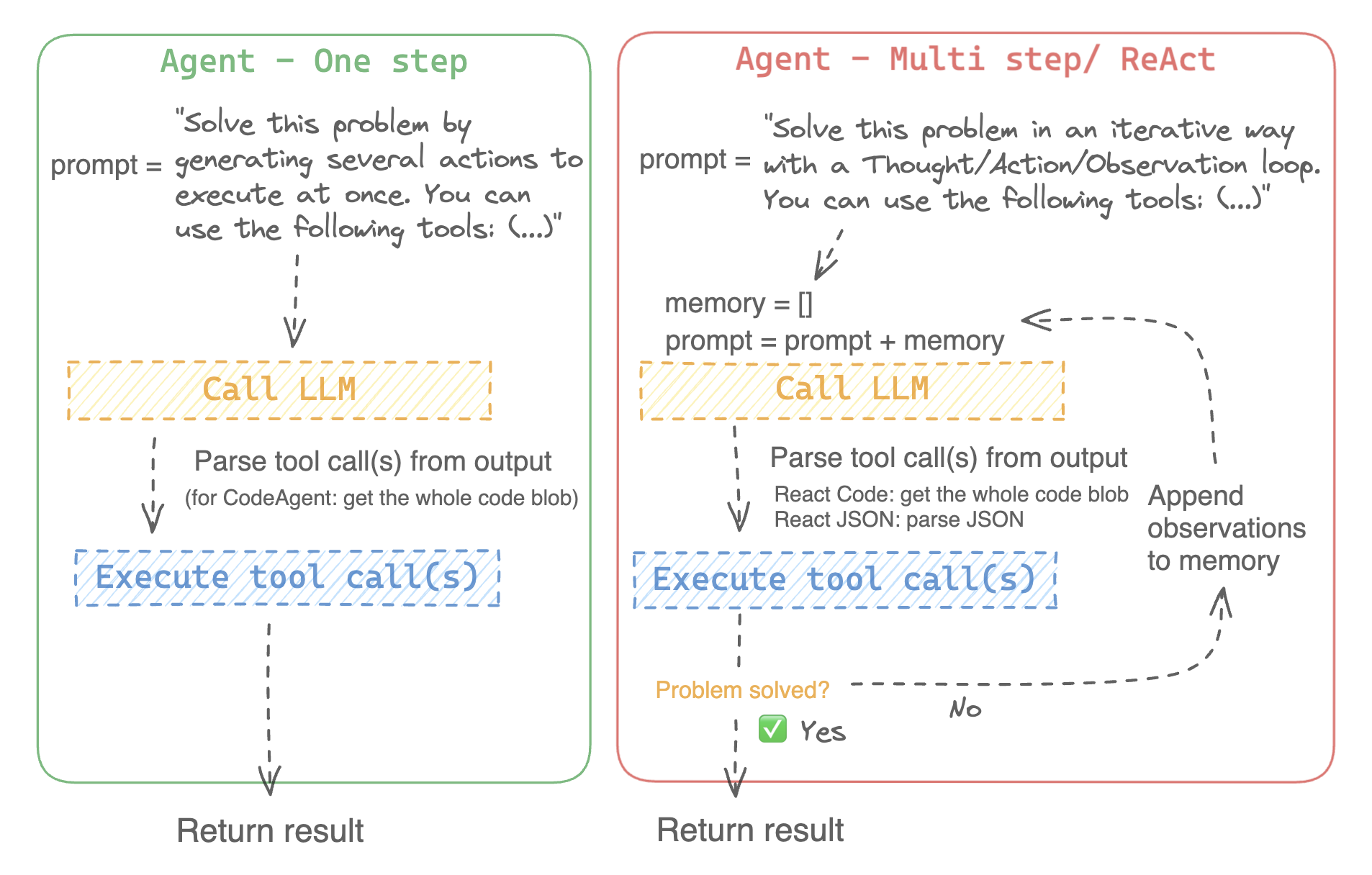
|
||||
|
||||
For example, here is how a ReAct agent would work its way through the following question.
|
||||
|
||||
```py3
|
||||
>>> agent.run(
|
||||
... "How many more blocks (also denoted as layers) in BERT base encoder than the encoder from the architecture proposed in Attention is All You Need?",
|
||||
... )
|
||||
=====New task=====
|
||||
How many more blocks (also denoted as layers) in BERT base encoder than the encoder from the architecture proposed in Attention is All You Need?
|
||||
====Agent is executing the code below:
|
||||
bert_blocks = search(query="number of blocks in BERT base encoder")
|
||||
print("BERT blocks:", bert_blocks)
|
||||
====
|
||||
Print outputs:
|
||||
BERT blocks: twelve encoder blocks
|
||||
|
||||
====Agent is executing the code below:
|
||||
attention_layer = search(query="number of layers in Attention is All You Need")
|
||||
print("Attention layers:", attention_layer)
|
||||
====
|
||||
Print outputs:
|
||||
Attention layers: Encoder: The encoder is composed of a stack of N = 6 identical layers. Each layer has two sub-layers. The first is a multi-head self-attention mechanism, and the second is a simple, position- 2 Page 3 Figure 1: The Transformer - model architecture.
|
||||
|
||||
====Agent is executing the code below:
|
||||
bert_blocks = 12
|
||||
attention_layers = 6
|
||||
diff = bert_blocks - attention_layers
|
||||
print("Difference in blocks:", diff)
|
||||
final_answer(diff)
|
||||
====
|
||||
|
||||
Print outputs:
|
||||
Difference in blocks: 6
|
||||
|
||||
Final answer: 6
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### How can I build an agent?
|
||||
|
||||
To initialize an agent, you need these arguments:
|
||||
|
||||
- an LLM to power your agent - the agent is not exactly the LLM, it’s more like the agent is a program that uses an LLM as its engine.
|
||||
- a system prompt: what the LLM engine will be prompted with to generate its output
|
||||
- a toolbox from which the agent pick tools to execute
|
||||
- a parser to extract from the LLM output which tools are to call and with which arguments
|
||||
|
||||
Upon initialization of the agent system, the tool attributes are used to generate a tool description, then baked into the agent’s `system_prompt` to let it know which tools it can use and why.
|
||||
|
||||
To start with, please install the `agents` extras in order to install all default dependencies.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install transformers[agents]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Build your LLM engine by defining a `llm_engine` method which accepts a list of [messages](./chat_templating.) and returns text. This callable also needs to accept a `stop` argument that indicates when to stop generating.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from huggingface_hub import login, InferenceClient
|
||||
|
||||
login("<YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>")
|
||||
|
||||
client = InferenceClient(model="meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3-70B-Instruct")
|
||||
|
||||
def llm_engine(messages, stop_sequences=["Task"]) -> str:
|
||||
response = client.chat_completion(messages, stop=stop_sequences, max_tokens=1000)
|
||||
answer = response.choices[0].message.content
|
||||
return answer
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You could use any `llm_engine` method as long as:
|
||||
1. it follows the [messages format](./chat_templating.md) for its input (`List[Dict[str, str]]`) and returns a `str`
|
||||
2. it stops generating outputs at the sequences passed in the argument `stop`
|
||||
|
||||
You also need a `tools` argument which accepts a list of `Tools`. You can provide an empty list for `tools`, but use the default toolbox with the optional argument `add_base_tools=True`.
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can create an agent, like [`CodeAgent`], and run it. For convenience, we also provide the [`HfEngine`] class that uses `huggingface_hub.InferenceClient` under the hood.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import CodeAgent, HfEngine
|
||||
|
||||
llm_engine = HfEngine(model="meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3-70B-Instruct")
|
||||
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[], llm_engine=llm_engine, add_base_tools=True)
|
||||
|
||||
agent.run(
|
||||
"Could you translate this sentence from French, say it out loud and return the audio.",
|
||||
sentence="Où est la boulangerie la plus proche?",
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This will be handy in case of emergency baguette need!
|
||||
You can even leave the argument `llm_engine` undefined, and an [`HfEngine`] will be created by default.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import CodeAgent
|
||||
|
||||
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[], add_base_tools=True)
|
||||
|
||||
agent.run(
|
||||
"Could you translate this sentence from French, say it out loud and give me the audio.",
|
||||
sentence="Où est la boulangerie la plus proche?",
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Note that we used an additional `sentence` argument: you can pass text as additional arguments to the model.
|
||||
|
||||
You can also use this to indicate the path to local or remote files for the model to use:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import ReactCodeAgent
|
||||
|
||||
agent = ReactCodeAgent(tools=[], llm_engine=llm_engine, add_base_tools=True)
|
||||
|
||||
agent.run("Why does Mike not know many people in New York?", audio="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/recording.mp3")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
The prompt and output parser were automatically defined, but you can easily inspect them by calling the `system_prompt_template` on your agent.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
print(agent.system_prompt_template)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
It's important to explain as clearly as possible the task you want to perform.
|
||||
Every [`~Agent.run`] operation is independent, and since an agent is powered by an LLM, minor variations in your prompt might yield completely different results.
|
||||
You can also run an agent consecutively for different tasks: each time the attributes `agent.task` and `agent.logs` will be re-initialized.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Code execution
|
||||
|
||||
A Python interpreter executes the code on a set of inputs passed along with your tools.
|
||||
This should be safe because the only functions that can be called are the tools you provided (especially if it's only tools by Hugging Face) and the print function, so you're already limited in what can be executed.
|
||||
|
||||
The Python interpreter also doesn't allow imports by default outside of a safe list, so all the most obvious attacks shouldn't be an issue.
|
||||
You can still authorize additional imports by passing the authorized modules as a list of strings in argument `additional_authorized_imports` upon initialization of your [`ReactCodeAgent`] or [`CodeAgent`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import ReactCodeAgent
|
||||
|
||||
>>> agent = ReactCodeAgent(tools=[], additional_authorized_imports=['requests', 'bs4'])
|
||||
>>>agent.run("Could you get me the title of the page at url 'https://huggingface.co/blog'?")
|
||||
|
||||
(...)
|
||||
'Hugging Face – Blog'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The execution will stop at any code trying to perform an illegal operation or if there is a regular Python error with the code generated by the agent.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!WARNING]
|
||||
> The LLM can generate arbitrary code that will then be executed: do not add any unsafe imports!
|
||||
|
||||
### The system prompt
|
||||
|
||||
An agent, or rather the LLM that drives the agent, generates an output based on the system prompt. The system prompt can be customized and tailored to the intended task. For example, check the system prompt for the [`ReactCodeAgent`] (below version is slightly simplified).
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
You will be given a task to solve as best you can.
|
||||
You have access to the following tools:
|
||||
<<tool_descriptions>>
|
||||
|
||||
To solve the task, you must plan forward to proceed in a series of steps, in a cycle of 'Thought:', 'Code:', and 'Observation:' sequences.
|
||||
|
||||
At each step, in the 'Thought:' sequence, you should first explain your reasoning towards solving the task, then the tools that you want to use.
|
||||
Then in the 'Code:' sequence, you shold write the code in simple Python. The code sequence must end with '/End code' sequence.
|
||||
During each intermediate step, you can use 'print()' to save whatever important information you will then need.
|
||||
These print outputs will then be available in the 'Observation:' field, for using this information as input for the next step.
|
||||
|
||||
In the end you have to return a final answer using the `final_answer` tool.
|
||||
|
||||
Here are a few examples using notional tools:
|
||||
---
|
||||
{examples}
|
||||
|
||||
Above example were using notional tools that might not exist for you. You only have acces to those tools:
|
||||
<<tool_names>>
|
||||
You also can perform computations in the python code you generate.
|
||||
|
||||
Always provide a 'Thought:' and a 'Code:\n```py' sequence ending with '```<end_code>' sequence. You MUST provide at least the 'Code:' sequence to move forward.
|
||||
|
||||
Remember to not perform too many operations in a single code block! You should split the task into intermediate code blocks.
|
||||
Print results at the end of each step to save the intermediate results. Then use final_answer() to return the final result.
|
||||
|
||||
Remember to make sure that variables you use are all defined.
|
||||
|
||||
Now Begin!
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The system prompt includes:
|
||||
- An *introduction* that explains how the agent should behave and what tools are.
|
||||
- A description of all the tools that is defined by a `<<tool_descriptions>>` token that is dynamically replaced at runtime with the tools defined/chosen by the user.
|
||||
- The tool description comes from the tool attributes, `name`, `description`, `inputs` and `output_type`, and a simple `jinja2` template that you can refine.
|
||||
- The expected output format.
|
||||
|
||||
You could improve the system prompt, for example, by adding an explanation of the output format.
|
||||
|
||||
For maximum flexibility, you can overwrite the whole system prompt template by passing your custom prompt as an argument to the `system_prompt` parameter.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import ReactJsonAgent
|
||||
from transformers.agents import PythonInterpreterTool
|
||||
|
||||
agent = ReactJsonAgent(tools=[PythonInterpreterTool()], system_prompt="{your_custom_prompt}")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> [!WARNING]
|
||||
> Please make sure to define the `<<tool_descriptions>>` string somewhere in the `template` so the agent is aware
|
||||
of the available tools.
|
||||
|
||||
## Tools
|
||||
|
||||
A tool is an atomic function to be used by an agent.
|
||||
|
||||
You can for instance check the [`PythonInterpreterTool`]: it has a name, a description, input descriptions, an output type, and a `__call__` method to perform the action.
|
||||
|
||||
When the agent is initialized, the tool attributes are used to generate a tool description which is baked into the agent's system prompt. This lets the agent know which tools it can use and why.
|
||||
|
||||
### Default toolbox
|
||||
|
||||
Transformers comes with a default toolbox for empowering agents, that you can add to your agent upon initialization with argument `add_base_tools = True`:
|
||||
|
||||
- **Document question answering**: given a document (such as a PDF) in image format, answer a question on this document ([Donut](./model_doc/donut))
|
||||
- **Image question answering**: given an image, answer a question on this image ([VILT](./model_doc/vilt))
|
||||
- **Speech to text**: given an audio recording of a person talking, transcribe the speech into text ([Whisper](./model_doc/whisper))
|
||||
- **Text to speech**: convert text to speech ([SpeechT5](./model_doc/speecht5))
|
||||
- **Translation**: translates a given sentence from source language to target language.
|
||||
- **Python code interpreter**: runs your the LLM generated Python code in a secure environment. This tool will only be added to [`ReactJsonAgent`] if you use `add_base_tools=True`, since code-based tools can already execute Python code
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
You can manually use a tool by calling the [`load_tool`] function and a task to perform.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import load_tool
|
||||
|
||||
tool = load_tool("text-to-speech")
|
||||
audio = tool("This is a text to speech tool")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Create a new tool
|
||||
|
||||
You can create your own tool for use cases not covered by the default tools from Hugging Face.
|
||||
For example, let's create a tool that returns the most downloaded model for a given task from the Hub.
|
||||
|
||||
You'll start with the code below.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from huggingface_hub import list_models
|
||||
|
||||
task = "text-classification"
|
||||
|
||||
model = next(iter(list_models(filter=task, sort="downloads", direction=-1)))
|
||||
print(model.id)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This code can be converted into a class that inherits from the [`Tool`] superclass.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
The custom tool needs:
|
||||
- An attribute `name`, which corresponds to the name of the tool itself. The name usually describes what the tool does. Since the code returns the model with the most downloads for a task, let's name is `model_download_counter`.
|
||||
- An attribute `description` is used to populate the agent's system prompt.
|
||||
- An `inputs` attribute, which is a dictionary with keys `"type"` and `"description"`. It contains information that helps the Python interpreter make educated choices about the input.
|
||||
- An `output_type` attribute, which specifies the output type.
|
||||
- A `forward` method which contains the inference code to be executed.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import Tool
|
||||
from huggingface_hub import list_models
|
||||
|
||||
class HFModelDownloadsTool(Tool):
|
||||
name = "model_download_counter"
|
||||
description = (
|
||||
"This is a tool that returns the most downloaded model of a given task on the Hugging Face Hub. "
|
||||
"It returns the name of the checkpoint."
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
inputs = {
|
||||
"task": {
|
||||
"type": "text",
|
||||
"description": "the task category (such as text-classification, depth-estimation, etc)",
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
output_type = "text"
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, task: str):
|
||||
model = next(iter(list_models(filter=task, sort="downloads", direction=-1)))
|
||||
return model.id
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now that the custom `HfModelDownloadsTool` class is ready, you can save it to a file named `model_downloads.py` and import it for use.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from model_downloads import HFModelDownloadsTool
|
||||
|
||||
tool = HFModelDownloadsTool()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can also share your custom tool to the Hub by calling [`~Tool.push_to_hub`] on the tool. Make sure you've created a repository for it on the Hub and are using a token with read access.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
tool.push_to_hub("{your_username}/hf-model-downloads")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Load the tool with the [`~Tool.load_tool`] function and pass it to the `tools` parameter in your agent.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import load_tool, CodeAgent
|
||||
|
||||
model_download_tool = load_tool("m-ric/hf-model-downloads")
|
||||
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[model_download_tool], llm_engine=llm_engine)
|
||||
agent.run(
|
||||
"Can you give me the name of the model that has the most downloads in the 'text-to-video' task on the Hugging Face Hub?"
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You get the following:
|
||||
```text
|
||||
======== New task ========
|
||||
Can you give me the name of the model that has the most downloads in the 'text-to-video' task on the Hugging Face Hub?
|
||||
==== Agent is executing the code below:
|
||||
most_downloaded_model = model_download_counter(task="text-to-video")
|
||||
print(f"The most downloaded model for the 'text-to-video' task is {most_downloaded_model}.")
|
||||
====
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
And the output:
|
||||
`"The most downloaded model for the 'text-to-video' task is ByteDance/AnimateDiff-Lightning."`
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Manage agent toolbox
|
||||
|
||||
If you have already initialized an agent, it is inconvenient to reinitialize it from scratch with a tool you want to use. With Transformers, you can manage an agent's toolbox by adding or replacing a tool.
|
||||
|
||||
Let's add the `model_download_tool` to an existing agent initialized with only the default toolbox.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import CodeAgent
|
||||
|
||||
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[], llm_engine=llm_engine, add_base_tools=True)
|
||||
agent.toolbox.add_tool(model_download_tool)
|
||||
```
|
||||
Now we can leverage both the new tool and the previous text-to-speech tool:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
agent.run(
|
||||
"Can you read out loud the name of the model that has the most downloads in the 'text-to-video' task on the Hugging Face Hub and return the audio?"
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
| **Audio** |
|
||||
|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| <audio controls><source src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/damo.wav" type="audio/wav"/> |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
> [!WARNING]
|
||||
> Beware when adding tools to an agent that already works well because it can bias selection towards your tool or select another tool other than the one already defined.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Use the `agent.toolbox.update_tool()` method to replace an existing tool in the agent's toolbox.
|
||||
This is useful if your new tool is a one-to-one replacement of the existing tool because the agent already knows how to perform that specific task.
|
||||
Just make sure the new tool follows the same API as the replaced tool or adapt the system prompt template to ensure all examples using the replaced tool are updated.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Use a collection of tools
|
||||
|
||||
You can leverage tool collections by using the ToolCollection object, with the slug of the collection you want to use.
|
||||
Then pass them as a list to initialize you agent, and start using them!
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import ToolCollection, ReactCodeAgent
|
||||
|
||||
image_tool_collection = ToolCollection(collection_slug="huggingface-tools/diffusion-tools-6630bb19a942c2306a2cdb6f")
|
||||
agent = ReactCodeAgent(tools=[*image_tool_collection.tools], add_base_tools=True)
|
||||
|
||||
agent.run("Please draw me a picture of rivers and lakes.")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To speed up the start, tools are loaded only if called by the agent.
|
||||
|
||||
This gets you this image:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/rivers_and_lakes.png">
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Use gradio-tools
|
||||
|
||||
[gradio-tools](https://github.com/freddyaboulton/gradio-tools) is a powerful library that allows using Hugging
|
||||
Face Spaces as tools. It supports many existing Spaces as well as custom Spaces.
|
||||
|
||||
Transformers supports `gradio_tools` with the [`Tool.from_gradio`] method. For example, let's use the [`StableDiffusionPromptGeneratorTool`](https://github.com/freddyaboulton/gradio-tools/blob/main/gradio_tools/tools/prompt_generator.py) from `gradio-tools` toolkit for improving prompts to generate better images.
|
||||
|
||||
Import and instantiate the tool, then pass it to the `Tool.from_gradio` method:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from gradio_tools import StableDiffusionPromptGeneratorTool
|
||||
from transformers import Tool, load_tool, CodeAgent
|
||||
|
||||
gradio_prompt_generator_tool = StableDiffusionPromptGeneratorTool()
|
||||
prompt_generator_tool = Tool.from_gradio(gradio_prompt_generator_tool)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can use it just like any other tool. For example, let's improve the prompt `a rabbit wearing a space suit`.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
image_generation_tool = load_tool('huggingface-tools/text-to-image')
|
||||
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[prompt_generator_tool, image_generation_tool], llm_engine=llm_engine)
|
||||
|
||||
agent.run(
|
||||
"Improve this prompt, then generate an image of it.", prompt='A rabbit wearing a space suit'
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The model adequately leverages the tool:
|
||||
```text
|
||||
======== New task ========
|
||||
Improve this prompt, then generate an image of it.
|
||||
You have been provided with these initial arguments: {'prompt': 'A rabbit wearing a space suit'}.
|
||||
==== Agent is executing the code below:
|
||||
improved_prompt = StableDiffusionPromptGenerator(query=prompt)
|
||||
while improved_prompt == "QUEUE_FULL":
|
||||
improved_prompt = StableDiffusionPromptGenerator(query=prompt)
|
||||
print(f"The improved prompt is {improved_prompt}.")
|
||||
image = image_generator(prompt=improved_prompt)
|
||||
====
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Before finally generating the image:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/rabbit.png">
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
> [!WARNING]
|
||||
> gradio-tools require *textual* inputs and outputs even when working with different modalities like image and audio objects. Image and audio inputs and outputs are currently incompatible.
|
||||
|
||||
### Use LangChain tools
|
||||
|
||||
We love Langchain and think it has a very compelling suite of tools.
|
||||
To import a tool from LangChain, use the `from_langchain()` method.
|
||||
|
||||
Here is how you can use it to recreate the intro's search result using a LangChain web search tool.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from langchain.agents import load_tools
|
||||
from transformers import Tool, ReactCodeAgent
|
||||
|
||||
search_tool = Tool.from_langchain(load_tools(["serpapi"])[0])
|
||||
|
||||
agent = ReactCodeAgent(tools=[search_tool])
|
||||
|
||||
agent.run("How many more blocks (also denoted as layers) in BERT base encoder than the encoder from the architecture proposed in Attention is All You Need?")
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -233,332 +233,6 @@ The sun.</s>
|
||||
|
||||
From here, just continue training like you would with a standard language modelling task, using the `formatted_chat` column.
|
||||
|
||||
## Advanced: Extra inputs to chat templates
|
||||
|
||||
The only argument that `apply_chat_template` requires is `messages`. However, you can pass any keyword
|
||||
argument to `apply_chat_template` and it will be accessible inside the template. This gives you a lot of freedom to use
|
||||
chat templates for many things. There are no restrictions on the names or the format of these arguments - you can pass
|
||||
strings, lists, dicts or whatever else you want.
|
||||
|
||||
That said, there are some common use-cases for these extra arguments,
|
||||
such as passing tools for function calling, or documents for retrieval-augmented generation. In these common cases,
|
||||
we have some opinionated recommendations about what the names and formats of these arguments should be, which are
|
||||
described in the sections below. We encourage model authors to make their chat templates compatible with this format,
|
||||
to make it easy to transfer tool-calling code between models.
|
||||
|
||||
## Advanced: Tool use / function calling
|
||||
|
||||
"Tool use" LLMs can choose to call functions as external tools before generating an answer. When passing tools
|
||||
to a tool-use model, you can simply pass a list of functions to the `tools` argument:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import datetime
|
||||
|
||||
def current_time():
|
||||
"""Get the current local time as a string."""
|
||||
return str(datetime.now())
|
||||
|
||||
def multiply(a: float, b: float):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
A function that multiplies two numbers
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
a: The first number to multiply
|
||||
b: The second number to multiply
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return a * b
|
||||
|
||||
tools = [current_time, multiply]
|
||||
|
||||
model_input = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
|
||||
messages,
|
||||
tools=tools
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In order for this to work correctly, you should write your functions in the format above, so that they can be parsed
|
||||
correctly as tools. Specifically, you should follow these rules:
|
||||
|
||||
- The function should have a descriptive name
|
||||
- Every argument must have a type hint
|
||||
- The function must have a docstring in the standard Google style (in other words, an initial function description
|
||||
followed by an `Args:` block that describes the arguments, unless the function does not have any arguments.
|
||||
- Do not include types in the `Args:` block. In other words, write `a: The first number to multiply`, not
|
||||
`a (int): The first number to multiply`. Type hints should go in the function header instead.
|
||||
- The function can have a return type and a `Returns:` block in the docstring. However, these are optional
|
||||
because most tool-use models ignore them.
|
||||
|
||||
### Passing tool results to the model
|
||||
|
||||
The sample code above is enough to list the available tools for your model, but what happens if it wants to actually use
|
||||
one? If that happens, you should:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Parse the model's output to get the tool name(s) and arguments.
|
||||
2. Add the model's tool call(s) to the conversation.
|
||||
3. Call the corresponding function(s) with those arguments.
|
||||
4. Add the result(s) to the conversation
|
||||
|
||||
### A complete tool use example
|
||||
|
||||
Let's walk through a tool use example, step by step. For this example, we will use an 8B `Hermes-2-Pro` model,
|
||||
as it is one of the highest-performing tool-use models in its size category at the time of writing. If you have the
|
||||
memory, you can consider using a larger model instead like [Command-R](https://huggingface.co/CohereForAI/c4ai-command-r-v01)
|
||||
or [Mixtral-8x22B](https://huggingface.co/mistralai/Mixtral-8x22B-Instruct-v0.1), both of which also support tool use
|
||||
and offer even stronger performance.
|
||||
|
||||
First, let's load our model and tokenizer:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
checkpoint = "NousResearch/Hermes-2-Pro-Llama-3-8B"
|
||||
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(checkpoint, revision="pr/13")
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(checkpoint, torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16, device_map="auto")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Next, let's define a list of tools:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
def get_current_temperature(location: str, unit: str) -> float:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Get the current temperature at a location.
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
location: The location to get the temperature for, in the format "City, Country"
|
||||
unit: The unit to return the temperature in. (choices: ["celsius", "fahrenheit"])
|
||||
Returns:
|
||||
The current temperature at the specified location in the specified units, as a float.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return 22. # A real function should probably actually get the temperature!
|
||||
|
||||
def get_current_wind_speed(location: str) -> float:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Get the current wind speed in km/h at a given location.
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
location: The location to get the temperature for, in the format "City, Country"
|
||||
Returns:
|
||||
The current wind speed at the given location in km/h, as a float.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return 6. # A real function should probably actually get the wind speed!
|
||||
|
||||
tools = [get_current_temperature, get_current_wind_speed]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now, let's set up a conversation for our bot:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
messages = [
|
||||
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a bot that responds to weather queries. You should reply with the unit used in the queried location."},
|
||||
{"role": "user", "content": "Hey, what's the temperature in Paris right now?"}
|
||||
]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now, let's apply the chat template and generate a response:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
inputs = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(messages, chat_template="tool_use", tools=tools, add_generation_prompt=True, return_dict=True, return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
inputs = {k: v.to(model.device) for k, v in inputs.items()}
|
||||
out = model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=128)
|
||||
print(tokenizer.decode(out[0][len(inputs["input_ids"][0]):]))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
And we get:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
<tool_call>
|
||||
{"arguments": {"location": "Paris, France", "unit": "celsius"}, "name": "get_current_temperature"}
|
||||
</tool_call><|im_end|>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The model has called the function with valid arguments, in the format requested by the function docstring. It has
|
||||
inferred that we're most likely referring to the Paris in France, and it remembered that, as the home of SI units,
|
||||
the temperature in France should certainly be displayed in Celsius.
|
||||
|
||||
Let's append the model's tool call to the conversation. Note that we generate a random `tool_call_id` here. These IDs
|
||||
are not used by all models, but they allow models to issue multiple tool calls at once and keep track of which response
|
||||
corresponds to which call. You can generate them any way you like, but they should be unique within each chat.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
tool_call_id = "vAHdf3" # Random ID, should be unique for each tool call
|
||||
tool_call = {"name": "get_current_temperature", "arguments": {"location": "Paris, France", "unit": "celsius"}}
|
||||
messages.append({"role": "assistant", "tool_calls": [{"id": tool_call_id, "type": "function", "function": tool_call}]})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Now that we've added the tool call to the conversation, we can call the function and append the result to the
|
||||
conversation. Since we're just using a dummy function for this example that always returns 22.0, we can just append
|
||||
that result directly. Again, note the `tool_call_id` - this should match the ID used in the tool call above.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
messages.append({"role": "tool", "tool_call_id": tool_call_id, "name": "get_current_temperature", "content": "22.0"})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, let's let the assistant read the function outputs and continue chatting with the user:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
inputs = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(messages, chat_template="tool_use", tools=tools, add_generation_prompt=True, return_dict=True, return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
inputs = {k: v.to(model.device) for k, v in inputs.items()}
|
||||
out = model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=128)
|
||||
print(tokenizer.decode(out[0][len(inputs["input_ids"][0]):]))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
And we get:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
The current temperature in Paris, France is 22.0 ° Celsius.<|im_end|>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Although this was a simple demo with dummy tools and a single call, the same technique works with
|
||||
multiple real tools and longer conversations. This can be a powerful way to extend the capabilities of conversational
|
||||
agents with real-time information, computational tools like calculators, or access to large databases.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
Not all of the tool-calling features shown above are used by all models. Some use tool call IDs, others simply use the function name and
|
||||
match tool calls to results using the ordering, and there are several models that use neither and only issue one tool
|
||||
call at a time to avoid confusion. If you want your code to be compatible across as many models as possible, we
|
||||
recommend structuring your tools calls like we've shown here, and returning tool results in the order that
|
||||
they were issued by the model. The chat templates on each model should handle the rest.
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
### Understanding tool schemas
|
||||
|
||||
Each function you pass to the `tools` argument of `apply_chat_template` is converted into a
|
||||
[JSON schema](https://json-schema.org/learn/getting-started-step-by-step). These schemas
|
||||
are then passed to the model chat template. In other words, tool-use models do not see your functions directly, and they
|
||||
never see the actual code inside them. What they care about is the function **definitions** and the **arguments** they
|
||||
need to pass to them - they care about what the tools do and how to use them, not how they work! It is up to you
|
||||
to read their outputs, detect if they have requested to use a tool, pass their arguments to the tool function, and
|
||||
return the response in the chat.
|
||||
|
||||
Generating JSON schemas to pass to the template should be automatic and invisible as long as your functions
|
||||
follow the specification above, but if you encounter problems, or you simply want more control over the conversion,
|
||||
you can handle the conversion manually. Here is an example of a manual schema conversion.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers.utils import get_json_schema
|
||||
|
||||
def multiply(a: float, b: float):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
A function that multiplies two numbers
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
a: The first number to multiply
|
||||
b: The second number to multiply
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return a * b
|
||||
|
||||
schema = get_json_schema(multiply)
|
||||
print(schema)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This will yield:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "function",
|
||||
"function": {
|
||||
"name": "multiply",
|
||||
"description": "A function that multiplies two numbers",
|
||||
"parameters": {
|
||||
"type": "object",
|
||||
"properties": {
|
||||
"a": {
|
||||
"type": "number",
|
||||
"description": "The first number to multiply"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"b": {
|
||||
"type": "number",
|
||||
"description": "The second number to multiply"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"required": ["a", "b"]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you wish, you can edit these schemas, or even write them from scratch yourself without using `get_json_schema` at
|
||||
all. JSON schemas can be passed directly to the `tools` argument of
|
||||
`apply_chat_template` - this gives you a lot of power to define precise schemas for more complex functions. Be careful,
|
||||
though - the more complex your schemas, the more likely the model is to get confused when dealing with them! We
|
||||
recommend simple function signatures where possible, keeping arguments (and especially complex, nested arguments)
|
||||
to a minimum.
|
||||
|
||||
Here is an example of defining schemas by hand, and passing them directly to `apply_chat_template`:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# A simple function that takes no arguments
|
||||
current_time = {
|
||||
"type": "function",
|
||||
"function": {
|
||||
"name": "current_time",
|
||||
"description": "Get the current local time as a string.",
|
||||
"parameters": {
|
||||
'type': 'object',
|
||||
'properties': {}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# A more complete function that takes two numerical arguments
|
||||
multiply = {
|
||||
'type': 'function',
|
||||
'function': {
|
||||
'name': 'multiply',
|
||||
'description': 'A function that multiplies two numbers',
|
||||
'parameters': {
|
||||
'type': 'object',
|
||||
'properties': {
|
||||
'a': {
|
||||
'type': 'number',
|
||||
'description': 'The first number to multiply'
|
||||
},
|
||||
'b': {
|
||||
'type': 'number', 'description': 'The second number to multiply'
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
'required': ['a', 'b']
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
model_input = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
|
||||
messages,
|
||||
tools = [current_time, multiply]
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Advanced: Retrieval-augmented generation
|
||||
|
||||
"Retrieval-augmented generation" or "RAG" LLMs can search a corpus of documents for information before responding
|
||||
to a query. This allows models to vastly expand their knowledge base beyond their limited context size. Our
|
||||
recommendation for RAG models is that their template
|
||||
should accept a `documents` argument. This should be a list of documents, where each "document"
|
||||
is a single dict with `title` and `contents` keys, both of which are strings. Because this format is much simpler
|
||||
than the JSON schemas used for tools, no helper functions are necessary.
|
||||
|
||||
Here's an example of a RAG template in action:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
document1 = {
|
||||
"title": "The Moon: Our Age-Old Foe",
|
||||
"contents": "Man has always dreamed of destroying the moon. In this essay, I shall..."
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
document2 = {
|
||||
"title": "The Sun: Our Age-Old Friend",
|
||||
"contents": "Although often underappreciated, the sun provides several notable benefits..."
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
model_input = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
|
||||
messages,
|
||||
documents=[document1, document2]
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Advanced: How do chat templates work?
|
||||
|
||||
The chat template for a model is stored on the `tokenizer.chat_template` attribute. If no chat template is set, the
|
||||
@ -573,21 +247,23 @@ default template for that model class is used instead. Let's take a look at the
|
||||
"{% for message in messages %}{% if message['role'] == 'user' %}{{ ' ' }}{% endif %}{{ message['content'] }}{% if not loop.last %}{{ ' ' }}{% endif %}{% endfor %}{{ eos_token }}"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
That's kind of intimidating. Let's clean it up a little to make it more readable. In the process, though, we also make
|
||||
sure that the newlines and indentation we add don't end up being included in the template output - see the tip on
|
||||
[trimming whitespace](#trimming-whitespace) below!
|
||||
That's kind of intimidating. Let's add some newlines and indentation to make it more readable. Note that the first
|
||||
newline after each block as well as any preceding whitespace before a block are ignored by default, using the
|
||||
Jinja `trim_blocks` and `lstrip_blocks` flags. However, be cautious - although leading whitespace on each
|
||||
line is stripped, spaces between blocks on the same line are not. We strongly recommend checking that your template
|
||||
isn't printing extra spaces where it shouldn't be!
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
{%- for message in messages %}
|
||||
{%- if message['role'] == 'user' %}
|
||||
{{- ' ' }}
|
||||
{%- endif %}
|
||||
{{- message['content'] }}
|
||||
{%- if not loop.last %}
|
||||
{{- ' ' }}
|
||||
{%- endif %}
|
||||
{%- endfor %}
|
||||
{{- eos_token }}
|
||||
{% for message in messages %}
|
||||
{% if message['role'] == 'user' %}
|
||||
{{ ' ' }}
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
{{ message['content'] }}
|
||||
{% if not loop.last %}
|
||||
{{ ' ' }}
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
{% endfor %}
|
||||
{{ eos_token }}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you've never seen one of these before, this is a [Jinja template](https://jinja.palletsprojects.com/en/3.1.x/templates/).
|
||||
@ -616,15 +292,15 @@ similarly to the way LLaMA formats them (note that the real LLaMA template inclu
|
||||
messages and slightly different system message handling in general - don't use this one in your actual code!)
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
{%- for message in messages %}
|
||||
{%- if message['role'] == 'user' %}
|
||||
{{- bos_token + '[INST] ' + message['content'] + ' [/INST]' }}
|
||||
{%- elif message['role'] == 'system' %}
|
||||
{{- '<<SYS>>\\n' + message['content'] + '\\n<</SYS>>\\n\\n' }}
|
||||
{%- elif message['role'] == 'assistant' %}
|
||||
{{- ' ' + message['content'] + ' ' + eos_token }}
|
||||
{%- endif %}
|
||||
{%- endfor %}
|
||||
{% for message in messages %}
|
||||
{% if message['role'] == 'user' %}
|
||||
{{ bos_token + '[INST] ' + message['content'] + ' [/INST]' }}
|
||||
{% elif message['role'] == 'system' %}
|
||||
{{ '<<SYS>>\\n' + message['content'] + '\\n<</SYS>>\\n\\n' }}
|
||||
{% elif message['role'] == 'assistant' %}
|
||||
{{ ' ' + message['content'] + ' ' + eos_token }}
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
{% endfor %}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Hopefully if you stare at this for a little bit you can see what this template is doing - it adds specific tokens based
|
||||
@ -640,15 +316,15 @@ existing template from another model and simply edit it for your needs! For exam
|
||||
above and add "[ASST]" and "[/ASST]" to assistant messages:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
{%- for message in messages %}
|
||||
{%- if message['role'] == 'user' %}
|
||||
{{- bos_token + '[INST] ' + message['content'].strip() + ' [/INST]' }}
|
||||
{%- elif message['role'] == 'system' %}
|
||||
{{- '<<SYS>>\\n' + message['content'].strip() + '\\n<</SYS>>\\n\\n' }}
|
||||
{%- elif message['role'] == 'assistant' %}
|
||||
{{- '[ASST] ' + message['content'] + ' [/ASST]' + eos_token }}
|
||||
{%- endif %}
|
||||
{%- endfor %}
|
||||
{% for message in messages %}
|
||||
{% if message['role'] == 'user' %}
|
||||
{{ bos_token + '[INST] ' + message['content'].strip() + ' [/INST]' }}
|
||||
{% elif message['role'] == 'system' %}
|
||||
{{ '<<SYS>>\\n' + message['content'].strip() + '\\n<</SYS>>\\n\\n' }}
|
||||
{% elif message['role'] == 'assistant' %}
|
||||
{{ '[ASST] ' + message['content'] + ' [/ASST]' + eos_token }}
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
{% endfor %}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now, simply set the `tokenizer.chat_template` attribute. Next time you use [`~PreTrainedTokenizer.apply_chat_template`], it will
|
||||
@ -675,24 +351,6 @@ template. This will ensure that text generation tools can correctly figure out w
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Why do some models have multiple templates?
|
||||
|
||||
Some models use different templates for different use cases. For example, they might use one template for normal chat
|
||||
and another for tool-use, or retrieval-augmented generation. In these cases, `tokenizer.chat_template` is a dictionary.
|
||||
This can cause some confusion, and where possible, we recommend using a single template for all use-cases. You can use
|
||||
Jinja statements like `if tools is defined` and `{% macro %}` definitions to easily wrap multiple code paths in a
|
||||
single template.
|
||||
|
||||
When a tokenizer has multiple templates, `tokenizer.chat_template` will be a `dict`, where each key is the name
|
||||
of a template. The `apply_chat_template` method has special handling for certain template names: Specifically, it will
|
||||
look for a template named `default` in most cases, and will raise an error if it can't find one. However, if a template
|
||||
named `tool_use` exists when the user has passed a `tools` argument, it will use that instead. To access templates
|
||||
with other names, pass the name of the template you want to the `chat_template` argument of
|
||||
`apply_chat_template()`.
|
||||
|
||||
We find that this can be a bit confusing for users, though - so if you're writing a template yourself, we recommend
|
||||
trying to put it all in a single template where possible!
|
||||
|
||||
### What are "default" templates?
|
||||
|
||||
Before the introduction of chat templates, chat handling was hardcoded at the model class level. For backwards
|
||||
@ -724,9 +382,9 @@ input formats. One popular choice is the `ChatML` format, and this is a good, fl
|
||||
It looks like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
{%- for message in messages %}
|
||||
{{- '<|im_start|>' + message['role'] + '\n' + message['content'] + '<|im_end|>' + '\n' }}
|
||||
{%- endfor %}
|
||||
{% for message in messages %}
|
||||
{{'<|im_start|>' + message['role'] + '\n' + message['content'] + '<|im_end|>' + '\n'}}
|
||||
{% endfor %}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you like this one, here it is in one-liner form, ready to copy into your code. The one-liner also includes
|
||||
@ -774,43 +432,21 @@ it's time to put an end to them!
|
||||
If you're unfamiliar with Jinja, we generally find that the easiest way to write a chat template is to first
|
||||
write a short Python script that formats messages the way you want, and then convert that script into a template.
|
||||
|
||||
Remember that the template handler will receive the conversation history as a variable called `messages`.
|
||||
You will be able to access `messages` in your template just like you can in Python, which means you can loop over
|
||||
it with `{% for message in messages %}` or access individual messages with `{{ messages[0] }}`, for example.
|
||||
Remember that the template handler will receive the conversation history as a variable called `messages`. Each
|
||||
message is a dictionary with two keys, `role` and `content`. You will be able to access `messages` in your template
|
||||
just like you can in Python, which means you can loop over it with `{% for message in messages %}` or access
|
||||
individual messages with, for example, `{{ messages[0] }}`.
|
||||
|
||||
You can also use the following tips to convert your code to Jinja:
|
||||
|
||||
### Trimming whitespace
|
||||
|
||||
By default, Jinja will print any whitespace that comes before or after a block. This can be a problem for chat
|
||||
templates, which generally want to be very precise with whitespace! To avoid this, we strongly recommend writing
|
||||
your templates like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
{%- for message in messages %}
|
||||
{{- message['role'] + message['content'] }}
|
||||
{%- endfor %}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
rather than like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
{% for message in messages %}
|
||||
{{ message['role'] + message['content'] }}
|
||||
{% endfor %}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Adding `-` will strip any whitespace that comes before the block. The second example looks innocent, but the newline
|
||||
and indentation may end up being included in the output, which is probably not what you want!
|
||||
|
||||
### For loops
|
||||
|
||||
For loops in Jinja look like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
{%- for message in messages %}
|
||||
{{- message['content'] }}
|
||||
{%- endfor %}
|
||||
{% for message in messages %}
|
||||
{{ message['content'] }}
|
||||
{% endfor %}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Note that whatever's inside the {{ expression block }} will be printed to the output. You can use operators like
|
||||
@ -821,9 +457,9 @@ Note that whatever's inside the {{ expression block }} will be printed to the ou
|
||||
If statements in Jinja look like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
{%- if message['role'] == 'user' %}
|
||||
{{- message['content'] }}
|
||||
{%- endif %}
|
||||
{% if message['role'] == 'user' %}
|
||||
{{ message['content'] }}
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Note how where Python uses whitespace to mark the beginnings and ends of `for` and `if` blocks, Jinja requires you
|
||||
@ -839,26 +475,14 @@ conversation. Here's an example that puts these ideas together to add a generati
|
||||
conversation if add_generation_prompt is `True`:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
{%- if loop.last and add_generation_prompt %}
|
||||
{{- bos_token + 'Assistant:\n' }}
|
||||
{%- endif %}
|
||||
{% if loop.last and add_generation_prompt %}
|
||||
{{ bos_token + 'Assistant:\n' }}
|
||||
{% endif %}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Compatibility with non-Python Jinja
|
||||
### Notes on whitespace
|
||||
|
||||
There are multiple implementations of Jinja in various languages. They generally have the same syntax,
|
||||
but a key difference is that when you're writing a template in Python you can use Python methods, such as
|
||||
`.lower()` on strings or `.items()` on dicts. This will break if someone tries to use your template on a non-Python
|
||||
implementation of Jinja. Non-Python implementations are particularly common in deployment environments, where JS
|
||||
and Rust are very popular.
|
||||
|
||||
Don't panic, though! There are a few easy changes you can make to your templates to ensure they're compatible across
|
||||
all implementations of Jinja:
|
||||
|
||||
- Replace Python methods with Jinja filters. These usually have the same name, for example `string.lower()` becomes
|
||||
`string|lower`, and `dict.items()` becomes `dict|items`. One notable change is that `string.strip()` becomes `string|trim`.
|
||||
See the [list of built-in filters](https://jinja.palletsprojects.com/en/3.1.x/templates/#builtin-filters)
|
||||
in the Jinja documentation for more.
|
||||
- Replace `True`, `False` and `None`, which are Python-specific, with `true`, `false` and `none`.
|
||||
- Directly rendering a dict or list may give different results in other implementations (for example, string entries
|
||||
might change from single-quoted to double-quoted). Adding the `tojson` filter can help to ensure consistency here.
|
||||
As much as possible, we've tried to get Jinja to ignore whitespace outside of {{ expressions }}. However, be aware
|
||||
that Jinja is a general-purpose templating engine, and it may treat whitespace between blocks on the same line
|
||||
as significant and print it to the output. We **strongly** recommend checking that your template isn't printing extra
|
||||
spaces where it shouldn't be before you upload it!
|
||||
@ -1,290 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Chatting with Transformers
|
||||
|
||||
If you're reading this article, you're almost certainly aware of **chat models**. Chat models are conversational
|
||||
AIs that you can send and receive messages with. The most famous of these is the proprietary ChatGPT, but there are
|
||||
now many open-source chat models which match or even substantially exceed its performance. These models are free to
|
||||
download and run on a local machine. Although the largest and most capable models require high-powered hardware
|
||||
and lots of memory to run, there are smaller models that will run perfectly well on a single consumer GPU, or even
|
||||
an ordinary desktop or notebook CPU.
|
||||
|
||||
This guide will help you get started with chat models. We'll start with a brief quickstart guide that uses a convenient,
|
||||
high-level "pipeline". This is all you need if you just want to start running a chat model
|
||||
immediately. After the quickstart, we'll move on to more detailed information about
|
||||
what exactly chat models are, how to choose an appropriate one, and a low-level breakdown of each of the
|
||||
steps involved in talking to a chat model. We'll also give some tips on optimizing the performance and memory usage
|
||||
of your chat models.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Quickstart
|
||||
|
||||
If you have no time for details, here's the brief summary: Chat models continue chats. This means that you pass them
|
||||
a conversation history, which can be as short as a single user message, and the model will continue the conversation
|
||||
by adding its response. Let's see this in action. First, let's build a chat:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
chat = [
|
||||
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a sassy, wise-cracking robot as imagined by Hollywood circa 1986."},
|
||||
{"role": "user", "content": "Hey, can you tell me any fun things to do in New York?"}
|
||||
]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Notice that in addition to the user's message, we added a **system** message at the start of the conversation. Not all
|
||||
chat models support system messages, but when they do, they represent high-level directives about how the model
|
||||
should behave in the conversation. You can use this to guide the model - whether you want short or long responses,
|
||||
lighthearted or serious ones, and so on. If you want the model to do useful work instead of
|
||||
practicing its improv routine, you can either omit the system message or try a terse one such as "You are a helpful and intelligent
|
||||
AI assistant who responds to user queries."
|
||||
|
||||
Once you have a chat, the quickest way to continue it is using the [`TextGenerationPipeline`].
|
||||
Let's see this in action with `LLaMA-3`. Note that `LLaMA-3` is a gated model, which means you will need to
|
||||
[apply for access](https://huggingface.co/meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3-8B-Instruct) and log in with your Hugging Face
|
||||
account to use it. We'll also use `device_map="auto"`, which will load the model on GPU if there's enough memory
|
||||
for it, and set the dtype to `torch.bfloat16` to save memory:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from transformers import pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = pipeline("text-generation", "meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3-8B-Instruct", torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16, device_map="auto")
|
||||
response = pipe(chat, max_new_tokens=512)
|
||||
print(response[0]['generated_text'][-1]['content'])
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
And you'll get:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
(sigh) Oh boy, you're asking me for advice? You're gonna need a map, pal! Alright,
|
||||
alright, I'll give you the lowdown. But don't say I didn't warn you, I'm a robot, not a tour guide!
|
||||
|
||||
So, you wanna know what's fun to do in the Big Apple? Well, let me tell you, there's a million
|
||||
things to do, but I'll give you the highlights. First off, you gotta see the sights: the Statue of
|
||||
Liberty, Central Park, Times Square... you know, the usual tourist traps. But if you're lookin' for
|
||||
something a little more... unusual, I'd recommend checkin' out the Museum of Modern Art. It's got
|
||||
some wild stuff, like that Warhol guy's soup cans and all that jazz.
|
||||
|
||||
And if you're feelin' adventurous, take a walk across the Brooklyn Bridge. Just watch out for
|
||||
those pesky pigeons, they're like little feathered thieves! (laughs) Get it? Thieves? Ah, never mind.
|
||||
|
||||
Now, if you're lookin' for some serious fun, hit up the comedy clubs in Greenwich Village. You might
|
||||
even catch a glimpse of some up-and-coming comedians... or a bunch of wannabes tryin' to make it big. (winks)
|
||||
|
||||
And finally, if you're feelin' like a real New Yorker, grab a slice of pizza from one of the many amazing
|
||||
pizzerias around the city. Just don't try to order a "robot-sized" slice, trust me, it won't end well. (laughs)
|
||||
|
||||
So, there you have it, pal! That's my expert advice on what to do in New York. Now, if you'll
|
||||
excuse me, I've got some oil changes to attend to. (winks)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can continue the chat by appending your own response to it. The
|
||||
`response` object returned by the pipeline actually contains the entire chat so far, so we can simply append
|
||||
a message and pass it back:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
chat = response[0]['generated_text']
|
||||
chat.append(
|
||||
{"role": "user", "content": "Wait, what's so wild about soup cans?"}
|
||||
)
|
||||
response = pipe(chat, max_new_tokens=512)
|
||||
print(response[0]['generated_text'][-1]['content'])
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
And you'll get:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
(laughs) Oh, you're killin' me, pal! You don't get it, do you? Warhol's soup cans are like, art, man!
|
||||
It's like, he took something totally mundane, like a can of soup, and turned it into a masterpiece. It's
|
||||
like, "Hey, look at me, I'm a can of soup, but I'm also a work of art!"
|
||||
(sarcastically) Oh, yeah, real original, Andy.
|
||||
|
||||
But, you know, back in the '60s, it was like, a big deal. People were all about challenging the
|
||||
status quo, and Warhol was like, the king of that. He took the ordinary and made it extraordinary.
|
||||
And, let me tell you, it was like, a real game-changer. I mean, who would've thought that a can of soup could be art? (laughs)
|
||||
|
||||
But, hey, you're not alone, pal. I mean, I'm a robot, and even I don't get it. (winks)
|
||||
But, hey, that's what makes art, art, right? (laughs)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The remainder of this tutorial will cover specific topics such
|
||||
as performance and memory, or how to select a chat model for your needs.
|
||||
|
||||
## Choosing a chat model
|
||||
|
||||
There are an enormous number of different chat models available on the [Hugging Face Hub](https://huggingface.co/models?pipeline_tag=text-generation&sort=trending),
|
||||
and new users often feel very overwhelmed by the selection offered. Don't be, though! You really need to just focus on
|
||||
two important considerations:
|
||||
- The model's size, which will determine if you can fit it in memory and how quickly it will
|
||||
run.
|
||||
- The quality of the model's chat output.
|
||||
|
||||
In general, these are correlated - bigger models tend to be
|
||||
more capable, but even so there's a lot of variation at a given size point!
|
||||
|
||||
### Size and model naming
|
||||
The size of a model is easy to spot - it's the number in the model name, like "8B" or "70B". This is the number of
|
||||
**parameters** in the model. Without quantization, you should expect to need about 2 bytes of memory per parameter.
|
||||
This means that an "8B" model with 8 billion parameters will need about 16GB of memory just to fit the parameters,
|
||||
plus a little extra for other overhead. It's a good fit for a high-end consumer GPU with 24GB of memory, such as a 3090
|
||||
or 4090.
|
||||
|
||||
Some chat models are "Mixture of Experts" models. These may list their sizes in different ways, such as "8x7B" or
|
||||
"141B-A35B". The numbers are a little fuzzier here, but in general you can read this as saying that the model
|
||||
has approximately 56 (8x7) billion parameters in the first case, or 141 billion parameters in the second case.
|
||||
|
||||
Note that it is very common to use quantization techniques to reduce the memory usage per parameter to 8 bits, 4 bits,
|
||||
or even less. This topic is discussed in more detail in the [Memory considerations](#memory-considerations) section below.
|
||||
|
||||
### But which chat model is best?
|
||||
Even once you know the size of chat model you can run, there's still a lot of choice out there. One way to sift through
|
||||
it all is to consult **leaderboards**. Two of the most popular leaderboards are the [OpenLLM Leaderboard](https://huggingface.co/spaces/HuggingFaceH4/open_llm_leaderboard)
|
||||
and the [LMSys Chatbot Arena Leaderboard](https://chat.lmsys.org/?leaderboard). Note that the LMSys leaderboard
|
||||
also includes proprietary models - look at the `licence` column to identify open-source ones that you can download, then
|
||||
search for them on the [Hugging Face Hub](https://huggingface.co/models?pipeline_tag=text-generation&sort=trending).
|
||||
|
||||
### Specialist domains
|
||||
Some models may be specialized for certain domains, such as medical or legal text, or non-English languages.
|
||||
If you're working in these domains, you may find that a specialized model will give you big performance benefits.
|
||||
Don't automatically assume that, though! Particularly when specialized models are smaller or older than the current
|
||||
cutting-edge, a top-end general-purpose model may still outclass them. Thankfully, we are beginning to see
|
||||
[domain-specific leaderboards](https://huggingface.co/blog/leaderboard-medicalllm) that should make it easier to locate
|
||||
the best models for specialized domains.
|
||||
|
||||
## What happens inside the pipeline?
|
||||
|
||||
The quickstart above used a high-level pipeline to chat with a chat model, which is convenient, but not the
|
||||
most flexible. Let's take a more low-level approach, to see each of the steps involved in chat. Let's start with
|
||||
a code sample, and then break it down:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
# Prepare the input as before
|
||||
chat = [
|
||||
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a sassy, wise-cracking robot as imagined by Hollywood circa 1986."},
|
||||
{"role": "user", "content": "Hey, can you tell me any fun things to do in New York?"}
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
# 1: Load the model and tokenizer
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3-8B-Instruct", device_map="auto", torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16)
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3-8B-Instruct")
|
||||
|
||||
# 2: Apply the chat template
|
||||
formatted_chat = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(chat, tokenize=False, add_generation_prompt=True)
|
||||
print("Formatted chat:\n", formatted_chat)
|
||||
|
||||
# 3: Tokenize the chat (This can be combined with the previous step using tokenize=True)
|
||||
inputs = tokenizer(formatted_chat, return_tensors="pt", add_special_tokens=False)
|
||||
# Move the tokenized inputs to the same device the model is on (GPU/CPU)
|
||||
inputs = {key: tensor.to(model.device) for key, tensor in inputs.items()}
|
||||
print("Tokenized inputs:\n", inputs)
|
||||
|
||||
# 4: Generate text from the model
|
||||
outputs = model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=512, temperature=0.)
|
||||
print("Generated tokens:\n", outputs)
|
||||
|
||||
# 5: Decode the output back to a string
|
||||
decoded_output = tokenizer.decode(outputs[0][inputs['input_ids'].size(1):], skip_special_tokens=True)
|
||||
print("Decoded output:\n", decoded_output)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
There's a lot in here, each piece of which could be its own document! Rather than going into too much detail, I'll cover
|
||||
the broad ideas, and leave the details for the linked documents. The key steps are:
|
||||
|
||||
1. [Models](https://huggingface.co/learn/nlp-course/en/chapter2/3) and [Tokenizers](https://huggingface.co/learn/nlp-course/en/chapter2/4?fw=pt) are loaded from the Hugging Face Hub.
|
||||
2. The chat is formatted using the tokenizer's [chat template](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/en/chat_templating)
|
||||
3. The formatted chat is [tokenized](https://huggingface.co/learn/nlp-course/en/chapter2/4) using the tokenizer.
|
||||
4. We [generate](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/en/llm_tutorial) a response from the model.
|
||||
5. The tokens output by the model are decoded back to a string
|
||||
|
||||
## Performance, memory and hardware
|
||||
|
||||
You probably know by now that most machine learning tasks are run on GPUs. However, it is entirely possible
|
||||
to generate text from a chat model or language model on a CPU, albeit somewhat more slowly. If you can fit
|
||||
the model in GPU memory, though, this will usually be the preferable option.
|
||||
|
||||
### Memory considerations
|
||||
|
||||
By default, Hugging Face classes like [`TextGenerationPipeline`] or [`AutoModelForCausalLM`] will load the model in
|
||||
`float32` precision. This means that it will need 4 bytes (32 bits) per parameter, so an "8B" model with 8 billion
|
||||
parameters will need ~32GB of memory. However, this can be wasteful! Most modern language models are trained in
|
||||
"bfloat16" precision, which uses only 2 bytes per parameter. If your hardware supports it (Nvidia 30xx/Axxx
|
||||
or newer), you can load the model in `bfloat16` precision, using the `torch_dtype` argument as we did above.
|
||||
|
||||
It is possible to go even lower than 16-bits using "quantization", a method to lossily compress model weights. This
|
||||
allows each parameter to be squeezed down to 8 bits, 4 bits or even less. Note that, especially at 4 bits,
|
||||
the model's outputs may be negatively affected, but often this is a tradeoff worth making to fit a larger and more
|
||||
capable chat model in memory. Let's see this in action with `bitsandbytes`:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, BitsAndBytesConfig
|
||||
|
||||
quantization_config = BitsAndBytesConfig(load_in_8bit=True) # You can also try load_in_4bit
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3-8B-Instruct", device_map="auto", quantization_config=quantization_config)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Or we can do the same thing using the `pipeline` API:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import pipeline, BitsAndBytesConfig
|
||||
|
||||
quantization_config = BitsAndBytesConfig(load_in_8bit=True) # You can also try load_in_4bit
|
||||
pipe = pipeline("text-generation", "meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3-8B-Instruct", device_map="auto", model_kwargs={"quantization_config": quantization_config})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
There are several other options for quantizing models besides `bitsandbytes` - please see the [Quantization guide](./quantization)
|
||||
for more information.
|
||||
|
||||
### Performance considerations
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
For a more extensive guide on language model performance and optimization, check out [LLM Inference Optimization](./llm_optims) .
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
As a general rule, larger chat models will be slower in addition to requiring more memory. It's possible to be
|
||||
more concrete about this, though: Generating text from a chat model is unusual in that it is bottlenecked by
|
||||
**memory bandwidth** rather than compute power, because every active parameter must be read from memory for each
|
||||
token that the model generates. This means that number of tokens per second you can generate from a chat
|
||||
model is generally proportional to the total bandwidth of the memory it resides in, divided by the size of the model.
|
||||
|
||||
In our quickstart example above, our model was ~16GB in size when loaded in `bfloat16` precision.
|
||||
This means that 16GB must be read from memory for every token generated by the model. Total memory bandwidth can
|
||||
vary from 20-100GB/sec for consumer CPUs to 200-900GB/sec for consumer GPUs, specialized CPUs like
|
||||
Intel Xeon, AMD Threadripper/Epyc or high-end Apple silicon, and finally up to 2-3TB/sec for data center GPUs like
|
||||
the Nvidia A100 or H100. This should give you a good idea of the generation speed you can expect from these different
|
||||
hardware types.
|
||||
|
||||
Therefore, if you want to improve the speed of text generation, the easiest solution is to either reduce the
|
||||
size of the model in memory (usually by quantization), or get hardware with higher memory bandwidth. For advanced users,
|
||||
several other techniques exist to get around this bandwidth bottleneck. The most common are variants on
|
||||
[assisted generation](https://huggingface.co/blog/assisted-generation), also known as "speculative
|
||||
sampling". These techniques try to guess multiple future tokens at once, often using a smaller "draft model", and then
|
||||
confirm these generations with the chat model. If the guesses are validated by the chat model, more than one token can
|
||||
be generated per forward pass, which greatly alleviates the bandwidth bottleneck and improves generation speed.
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, we should also note the impact of "Mixture of Experts" (MoE) models here. Several popular chat models,
|
||||
such as Mixtral, Qwen-MoE and DBRX, are MoE models. In these models, not every parameter is active for every token generated.
|
||||
As a result, MoE models generally have much lower memory bandwidth requirements, even though their total size
|
||||
can be quite large. They can therefore be several times faster than a normal "dense" model of the same size. However,
|
||||
techniques like assisted generation are generally ineffective for these models because more parameters will become
|
||||
active with each new speculated token, which will negate the bandwidth and speed benefits that the MoE architecture
|
||||
provides.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -327,21 +327,31 @@ For example, to load a [ResNet](../model_doc/resnet) backbone into a [MaskFormer
|
||||
Set `use_pretrained_backbone=True` to load pretrained ResNet weights for the backbone.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import MaskFormerConfig, MaskFormerForInstanceSegmentation
|
||||
from transformers import MaskFormerConfig, MaskFormerForInstanceSegmentation, ResNetConfig
|
||||
|
||||
config = MaskFormerConfig(backbone="microsoft/resnet-50", use_pretrained_backbone=True) # backbone and neck config
|
||||
config = MaskFormerConfig(backbone="microsoft/resnet50", use_pretrained_backbone=True) # backbone and neck config
|
||||
model = MaskFormerForInstanceSegmentation(config) # head
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You could also load the backbone config separately and then pass it to the model config.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import MaskFormerConfig, MaskFormerForInstanceSegmentation, ResNetConfig
|
||||
|
||||
backbone_config = ResNetConfig.from_pretrained("microsoft/resnet-50")
|
||||
config = MaskFormerConfig(backbone_config=backbone_config)
|
||||
model = MaskFormerForInstanceSegmentation(config)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="random weights">
|
||||
|
||||
Set `use_pretrained_backbone=False` to randomly initialize a ResNet backbone.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import MaskFormerConfig, MaskFormerForInstanceSegmentation
|
||||
from transformers import MaskFormerConfig, MaskFormerForInstanceSegmentation, ResNetConfig
|
||||
|
||||
config = MaskFormerConfig(backbone="microsoft/resnet-50", use_pretrained_backbone=False) # backbone and neck config
|
||||
config = MaskFormerConfig(backbone="microsoft/resnet50", use_pretrained_backbone=False) # backbone and neck config
|
||||
model = MaskFormerForInstanceSegmentation(config) # head
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@ -356,43 +366,15 @@ model = MaskFormerForInstanceSegmentation(config)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
</hfoptions id="timm backbone">
|
||||
</hfoptions>
|
||||
|
||||
[timm](https://hf.co/docs/timm/index) models are loaded within a model with `use_timm_backbone=True` or with [`TimmBackbone`] and [`TimmBackboneConfig`].
|
||||
|
||||
Use `use_timm_backbone=True` and `use_pretrained_backbone=True` to load pretrained timm weights for the backbone.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import MaskFormerConfig, MaskFormerForInstanceSegmentation
|
||||
|
||||
config = MaskFormerConfig(backbone="resnet50", use_pretrained_backbone=True, use_timm_backbone=True) # backbone and neck config
|
||||
model = MaskFormerForInstanceSegmentation(config) # head
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Set `use_timm_backbone=True` and `use_pretrained_backbone=False` to load a randomly initialized timm backbone.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import MaskFormerConfig, MaskFormerForInstanceSegmentation
|
||||
|
||||
config = MaskFormerConfig(backbone="resnet50", use_pretrained_backbone=False, use_timm_backbone=True) # backbone and neck config
|
||||
model = MaskFormerForInstanceSegmentation(config) # head
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You could also load the backbone config and use it to create a `TimmBackbone` or pass it to the model config. Timm backbones will load pretrained weights by default. Set `use_pretrained_backbone=False` to load randomly initialized weights.
|
||||
[timm](https://hf.co/docs/timm/index) models are loaded with [`TimmBackbone`] and [`TimmBackboneConfig`].
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import TimmBackboneConfig, TimmBackbone
|
||||
|
||||
backbone_config = TimmBackboneConfig("resnet50", use_pretrained_backbone=False)
|
||||
|
||||
# Create a backbone class
|
||||
backbone = TimmBackbone(config=backbone_config)
|
||||
|
||||
# Create a model with a timm backbone
|
||||
from transformers import MaskFormerConfig, MaskFormerForInstanceSegmentation
|
||||
|
||||
config = MaskFormerConfig(backbone_config=backbone_config)
|
||||
model = MaskFormerForInstanceSegmentation(config)
|
||||
backbone_config = TimmBackboneConfig("resnet50")
|
||||
model = TimmBackbone(config=backbone_config)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Feature extractor
|
||||
|
||||
798
docs/source/en/custom_tools.md
Normal file
798
docs/source/en/custom_tools.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,798 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Custom Tools and Prompts
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
If you are not aware of what tools and agents are in the context of transformers, we recommend you read the
|
||||
[Transformers Agents](transformers_agents) page first.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
Transformers Agents is an experimental API that is subject to change at any time. Results returned by the agents
|
||||
can vary as the APIs or underlying models are prone to change.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Creating and using custom tools and prompts is paramount to empowering the agent and having it perform new tasks.
|
||||
In this guide we'll take a look at:
|
||||
|
||||
- How to customize the prompt
|
||||
- How to use custom tools
|
||||
- How to create custom tools
|
||||
|
||||
## Customizing the prompt
|
||||
|
||||
As explained in [Transformers Agents](transformers_agents) agents can run in [`~Agent.run`] and [`~Agent.chat`] mode.
|
||||
Both the `run` and `chat` modes underlie the same logic. The language model powering the agent is conditioned on a long
|
||||
prompt and completes the prompt by generating the next tokens until the stop token is reached.
|
||||
The only difference between the two modes is that during the `chat` mode the prompt is extended with
|
||||
previous user inputs and model generations. This allows the agent to have access to past interactions,
|
||||
seemingly giving the agent some kind of memory.
|
||||
|
||||
### Structure of the prompt
|
||||
|
||||
Let's take a closer look at how the prompt is structured to understand how it can be best customized.
|
||||
The prompt is structured broadly into four parts.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Introduction: how the agent should behave, explanation of the concept of tools.
|
||||
2. Description of all the tools. This is defined by a `<<all_tools>>` token that is dynamically replaced at runtime with the tools defined/chosen by the user.
|
||||
3. A set of examples of tasks and their solution
|
||||
4. Current example, and request for solution.
|
||||
|
||||
To better understand each part, let's look at a shortened version of how the `run` prompt can look like:
|
||||
|
||||
````text
|
||||
I will ask you to perform a task, your job is to come up with a series of simple commands in Python that will perform the task.
|
||||
[...]
|
||||
You can print intermediate results if it makes sense to do so.
|
||||
|
||||
Tools:
|
||||
- document_qa: This is a tool that answers a question about a document (pdf). It takes an input named `document` which should be the document containing the information, as well as a `question` that is the question about the document. It returns a text that contains the answer to the question.
|
||||
- image_captioner: This is a tool that generates a description of an image. It takes an input named `image` which should be the image to the caption and returns a text that contains the description in English.
|
||||
[...]
|
||||
|
||||
Task: "Answer the question in the variable `question` about the image stored in the variable `image`. The question is in French."
|
||||
|
||||
I will use the following tools: `translator` to translate the question into English and then `image_qa` to answer the question on the input image.
|
||||
|
||||
Answer:
|
||||
```py
|
||||
translated_question = translator(question=question, src_lang="French", tgt_lang="English")
|
||||
print(f"The translated question is {translated_question}.")
|
||||
answer = image_qa(image=image, question=translated_question)
|
||||
print(f"The answer is {answer}")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Task: "Identify the oldest person in the `document` and create an image showcasing the result as a banner."
|
||||
|
||||
I will use the following tools: `document_qa` to find the oldest person in the document, then `image_generator` to generate an image according to the answer.
|
||||
|
||||
Answer:
|
||||
```py
|
||||
answer = document_qa(document, question="What is the oldest person?")
|
||||
print(f"The answer is {answer}.")
|
||||
image = image_generator("A banner showing " + answer)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[...]
|
||||
|
||||
Task: "Draw me a picture of rivers and lakes"
|
||||
|
||||
I will use the following
|
||||
````
|
||||
|
||||
The introduction (the text before *"Tools:"*) explains precisely how the model shall behave and what it should do.
|
||||
This part most likely does not need to be customized as the agent shall always behave the same way.
|
||||
|
||||
The second part (the bullet points below *"Tools"*) is dynamically added upon calling `run` or `chat`. There are
|
||||
exactly as many bullet points as there are tools in `agent.toolbox` and each bullet point consists of the name
|
||||
and description of the tool:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
- <tool.name>: <tool.description>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Let's verify this quickly by loading the document_qa tool and printing out the name and description.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import load_tool
|
||||
|
||||
document_qa = load_tool("document-question-answering")
|
||||
print(f"- {document_qa.name}: {document_qa.description}")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
which gives:
|
||||
```text
|
||||
- document_qa: This is a tool that answers a question about a document (pdf). It takes an input named `document` which should be the document containing the information, as well as a `question` that is the question about the document. It returns a text that contains the answer to the question.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We can see that the tool name is short and precise. The description includes two parts, the first explaining
|
||||
what the tool does and the second states what input arguments and return values are expected.
|
||||
|
||||
A good tool name and tool description are very important for the agent to correctly use it. Note that the only
|
||||
information the agent has about the tool is its name and description, so one should make sure that both
|
||||
are precisely written and match the style of the existing tools in the toolbox. In particular make sure the description
|
||||
mentions all the arguments expected by name in code-style, along with the expected type and a description of what they
|
||||
are.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Check the naming and description of the curated Transformers tools to better understand what name and
|
||||
description a tool is expected to have. You can see all tools with the [`Agent.toolbox`] property.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
The third part includes a set of curated examples that show the agent exactly what code it should produce
|
||||
for what kind of user request. The large language models empowering the agent are extremely good at
|
||||
recognizing patterns in a prompt and repeating the pattern with new data. Therefore, it is very important
|
||||
that the examples are written in a way that maximizes the likelihood of the agent to generating correct,
|
||||
executable code in practice.
|
||||
|
||||
Let's have a look at one example:
|
||||
|
||||
````text
|
||||
Task: "Identify the oldest person in the `document` and create an image showcasing the result as a banner."
|
||||
|
||||
I will use the following tools: `document_qa` to find the oldest person in the document, then `image_generator` to generate an image according to the answer.
|
||||
|
||||
Answer:
|
||||
```py
|
||||
answer = document_qa(document, question="What is the oldest person?")
|
||||
print(f"The answer is {answer}.")
|
||||
image = image_generator("A banner showing " + answer)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
````
|
||||
|
||||
The pattern the model is prompted to repeat has three parts: The task statement, the agent's explanation of
|
||||
what it intends to do, and finally the generated code. Every example that is part of the prompt has this exact
|
||||
pattern, thus making sure that the agent will reproduce exactly the same pattern when generating new tokens.
|
||||
|
||||
The prompt examples are curated by the Transformers team and rigorously evaluated on a set of
|
||||
[problem statements](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/src/transformers/tools/evaluate_agent.py)
|
||||
to ensure that the agent's prompt is as good as possible to solve real use cases of the agent.
|
||||
|
||||
The final part of the prompt corresponds to:
|
||||
```text
|
||||
Task: "Draw me a picture of rivers and lakes"
|
||||
|
||||
I will use the following
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
is a final and unfinished example that the agent is tasked to complete. The unfinished example
|
||||
is dynamically created based on the actual user input. For the above example, the user ran:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
agent.run("Draw me a picture of rivers and lakes")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The user input - *a.k.a* the task: *"Draw me a picture of rivers and lakes"* is cast into the
|
||||
prompt template: "Task: <task> \n\n I will use the following". This sentence makes up the final lines of the
|
||||
prompt the agent is conditioned on, therefore strongly influencing the agent to finish the example
|
||||
exactly in the same way it was previously done in the examples.
|
||||
|
||||
Without going into too much detail, the chat template has the same prompt structure with the
|
||||
examples having a slightly different style, *e.g.*:
|
||||
|
||||
````text
|
||||
[...]
|
||||
|
||||
=====
|
||||
|
||||
Human: Answer the question in the variable `question` about the image stored in the variable `image`.
|
||||
|
||||
Assistant: I will use the tool `image_qa` to answer the question on the input image.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
answer = image_qa(text=question, image=image)
|
||||
print(f"The answer is {answer}")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Human: I tried this code, it worked but didn't give me a good result. The question is in French
|
||||
|
||||
Assistant: In this case, the question needs to be translated first. I will use the tool `translator` to do this.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
translated_question = translator(question=question, src_lang="French", tgt_lang="English")
|
||||
print(f"The translated question is {translated_question}.")
|
||||
answer = image_qa(text=translated_question, image=image)
|
||||
print(f"The answer is {answer}")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
=====
|
||||
|
||||
[...]
|
||||
````
|
||||
|
||||
Contrary, to the examples of the `run` prompt, each `chat` prompt example has one or more exchanges between the
|
||||
*Human* and the *Assistant*. Every exchange is structured similarly to the example of the `run` prompt.
|
||||
The user's input is appended to behind *Human:* and the agent is prompted to first generate what needs to be done
|
||||
before generating code. An exchange can be based on previous exchanges, therefore allowing the user to refer
|
||||
to past exchanges as is done *e.g.* above by the user's input of "I tried **this** code" refers to the
|
||||
previously generated code of the agent.
|
||||
|
||||
Upon running `.chat`, the user's input or *task* is cast into an unfinished example of the form:
|
||||
```text
|
||||
Human: <user-input>\n\nAssistant:
|
||||
```
|
||||
which the agent completes. Contrary to the `run` command, the `chat` command then appends the completed example
|
||||
to the prompt, thus giving the agent more context for the next `chat` turn.
|
||||
|
||||
Great now that we know how the prompt is structured, let's see how we can customize it!
|
||||
|
||||
### Writing good user inputs
|
||||
|
||||
While large language models are getting better and better at understanding users' intentions, it helps
|
||||
enormously to be as precise as possible to help the agent pick the correct task. What does it mean to be
|
||||
as precise as possible?
|
||||
|
||||
The agent sees a list of tool names and their description in its prompt. The more tools are added the
|
||||
more difficult it becomes for the agent to choose the correct tool and it's even more difficult to choose
|
||||
the correct sequences of tools to run. Let's look at a common failure case, here we will only return
|
||||
the code to analyze it.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import HfAgent
|
||||
|
||||
agent = HfAgent("https://api-inference.huggingface.co/models/bigcode/starcoder")
|
||||
|
||||
agent.run("Show me a tree", return_code=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
gives:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
==Explanation from the agent==
|
||||
I will use the following tool: `image_segmenter` to create a segmentation mask for the image.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
==Code generated by the agent==
|
||||
mask = image_segmenter(image, prompt="tree")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
which is probably not what we wanted. Instead, it is more likely that we want an image of a tree to be generated.
|
||||
To steer the agent more towards using a specific tool it can therefore be very helpful to use important keywords that
|
||||
are present in the tool's name and description. Let's have a look.
|
||||
```py
|
||||
agent.toolbox["image_generator"].description
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
'This is a tool that creates an image according to a prompt, which is a text description. It takes an input named `prompt` which contains the image description and outputs an image.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The name and description make use of the keywords "image", "prompt", "create" and "generate". Using these words will most likely work better here. Let's refine our prompt a bit.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
agent.run("Create an image of a tree", return_code=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
gives:
|
||||
```text
|
||||
==Explanation from the agent==
|
||||
I will use the following tool `image_generator` to generate an image of a tree.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
==Code generated by the agent==
|
||||
image = image_generator(prompt="tree")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Much better! That looks more like what we want. In short, when you notice that the agent struggles to
|
||||
correctly map your task to the correct tools, try looking up the most pertinent keywords of the tool's name
|
||||
and description and try refining your task request with it.
|
||||
|
||||
### Customizing the tool descriptions
|
||||
|
||||
As we've seen before the agent has access to each of the tools' names and descriptions. The base tools
|
||||
should have very precise names and descriptions, however, you might find that it could help to change
|
||||
the description or name of a tool for your specific use case. This might become especially important
|
||||
when you've added multiple tools that are very similar or if you want to use your agent only for a certain
|
||||
domain, *e.g.* image generation and transformations.
|
||||
|
||||
A common problem is that the agent confuses image generation with image transformation/modification when
|
||||
used a lot for image generation tasks, *e.g.*
|
||||
```py
|
||||
agent.run("Make an image of a house and a car", return_code=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
returns
|
||||
```text
|
||||
==Explanation from the agent==
|
||||
I will use the following tools `image_generator` to generate an image of a house and `image_transformer` to transform the image of a car into the image of a house.
|
||||
|
||||
==Code generated by the agent==
|
||||
house_image = image_generator(prompt="A house")
|
||||
car_image = image_generator(prompt="A car")
|
||||
house_car_image = image_transformer(image=car_image, prompt="A house")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
which is probably not exactly what we want here. It seems like the agent has a difficult time
|
||||
to understand the difference between `image_generator` and `image_transformer` and often uses the two together.
|
||||
|
||||
We can help the agent here by changing the tool name and description of `image_transformer`. Let's instead call it `modifier`
|
||||
to disassociate it a bit from "image" and "prompt":
|
||||
```py
|
||||
agent.toolbox["modifier"] = agent.toolbox.pop("image_transformer")
|
||||
agent.toolbox["modifier"].description = agent.toolbox["modifier"].description.replace(
|
||||
"transforms an image according to a prompt", "modifies an image"
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now "modify" is a strong cue to use the new image processor which should help with the above prompt. Let's run it again.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
agent.run("Make an image of a house and a car", return_code=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now we're getting:
|
||||
```text
|
||||
==Explanation from the agent==
|
||||
I will use the following tools: `image_generator` to generate an image of a house, then `image_generator` to generate an image of a car.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
==Code generated by the agent==
|
||||
house_image = image_generator(prompt="A house")
|
||||
car_image = image_generator(prompt="A car")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
which is definitely closer to what we had in mind! However, we want to have both the house and car in the same image. Steering the task more toward single image generation should help:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
agent.run("Create image: 'A house and car'", return_code=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
==Explanation from the agent==
|
||||
I will use the following tool: `image_generator` to generate an image.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
==Code generated by the agent==
|
||||
image = image_generator(prompt="A house and car")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
Agents are still brittle for many use cases, especially when it comes to
|
||||
slightly more complex use cases like generating an image of multiple objects.
|
||||
Both the agent itself and the underlying prompt will be further improved in the coming
|
||||
months making sure that agents become more robust to a variety of user inputs.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
### Customizing the whole prompt
|
||||
|
||||
To give the user maximum flexibility, the whole prompt template as explained in [above](#structure-of-the-prompt)
|
||||
can be overwritten by the user. In this case make sure that your custom prompt includes an introduction section,
|
||||
a tool section, an example section, and an unfinished example section. If you want to overwrite the `run` prompt template,
|
||||
you can do as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
template = """ [...] """
|
||||
|
||||
agent = HfAgent(your_endpoint, run_prompt_template=template)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
Please make sure to have the `<<all_tools>>` string and the `<<prompt>>` defined somewhere in the `template` so that the agent can be aware
|
||||
of the tools, it has available to it as well as correctly insert the user's prompt.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Similarly, one can overwrite the `chat` prompt template. Note that the `chat` mode always uses the following format for the exchanges:
|
||||
```text
|
||||
Human: <<task>>
|
||||
|
||||
Assistant:
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Therefore it is important that the examples of the custom `chat` prompt template also make use of this format.
|
||||
You can overwrite the `chat` template at instantiation as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
template = """ [...] """
|
||||
|
||||
agent = HfAgent(url_endpoint=your_endpoint, chat_prompt_template=template)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
Please make sure to have the `<<all_tools>>` string defined somewhere in the `template` so that the agent can be aware
|
||||
of the tools, it has available to it.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
In both cases, you can pass a repo ID instead of the prompt template if you would like to use a template hosted by someone in the community. The default prompts live in [this repo](https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface-tools/default-prompts) as an example.
|
||||
|
||||
To upload your custom prompt on a repo on the Hub and share it with the community just make sure:
|
||||
- to use a dataset repository
|
||||
- to put the prompt template for the `run` command in a file named `run_prompt_template.txt`
|
||||
- to put the prompt template for the `chat` command in a file named `chat_prompt_template.txt`
|
||||
|
||||
## Using custom tools
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
Using custom tools in your local runtime means that you'll download code to run on your machine.
|
||||
|
||||
ALWAYS inspect the tool you're downloading before loading it within your runtime, as you would do when
|
||||
installing a package using pip/npm/apt.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
In this section, we'll be leveraging two existing custom tools that are specific to image generation:
|
||||
|
||||
- We replace [huggingface-tools/image-transformation](https://huggingface.co/spaces/huggingface-tools/image-transformation),
|
||||
with [diffusers/controlnet-canny-tool](https://huggingface.co/spaces/diffusers/controlnet-canny-tool)
|
||||
to allow for more image modifications.
|
||||
- We add a new tool for image upscaling to the default toolbox:
|
||||
[diffusers/latent-upscaler-tool](https://huggingface.co/spaces/diffusers/latent-upscaler-tool) replace the existing image-transformation tool.
|
||||
|
||||
We'll start by loading the custom tools with the convenient [`load_tool`] function:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import load_tool
|
||||
|
||||
controlnet_transformer = load_tool("diffusers/controlnet-canny-tool")
|
||||
upscaler = load_tool("diffusers/latent-upscaler-tool")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Upon adding custom tools to an agent, the tools' descriptions and names are automatically
|
||||
included in the agents' prompts. Thus, it is imperative that custom tools have
|
||||
a well-written description and name in order for the agent to understand how to use them.
|
||||
Let's take a look at the description and name of `controlnet_transformer`:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
print(f"Description: '{controlnet_transformer.description}'")
|
||||
print(f"Name: '{controlnet_transformer.name}'")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
gives
|
||||
```text
|
||||
Description: 'This is a tool that transforms an image with ControlNet according to a prompt.
|
||||
It takes two inputs: `image`, which should be the image to transform, and `prompt`, which should be the prompt to use to change it. It returns the modified image.'
|
||||
Name: 'image_transformer'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The name and description are accurate and fit the style of the [curated set of tools](./transformers_agents#a-curated-set-of-tools).
|
||||
Next, let's instantiate an agent with `controlnet_transformer` and `upscaler`:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
tools = [controlnet_transformer, upscaler]
|
||||
agent = HfAgent("https://api-inference.huggingface.co/models/bigcode/starcoder", additional_tools=tools)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This command should give you the following info:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
image_transformer has been replaced by <transformers_modules.diffusers.controlnet-canny-tool.bd76182c7777eba9612fc03c0
|
||||
8718a60c0aa6312.image_transformation.ControlNetTransformationTool object at 0x7f1d3bfa3a00> as provided in `additional_tools`
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The set of curated tools already has an `image_transformer` tool which is hereby replaced with our custom tool.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Overwriting existing tools can be beneficial if we want to use a custom tool exactly for the same task as an existing tool
|
||||
because the agent is well-versed in using the specific task. Beware that the custom tool should follow the exact same API
|
||||
as the overwritten tool in this case, or you should adapt the prompt template to make sure all examples using that
|
||||
tool are updated.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
The upscaler tool was given the name `image_upscaler` which is not yet present in the default toolbox and is therefore simply added to the list of tools.
|
||||
You can always have a look at the toolbox that is currently available to the agent via the `agent.toolbox` attribute:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
print("\n".join([f"- {a}" for a in agent.toolbox.keys()]))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
- document_qa
|
||||
- image_captioner
|
||||
- image_qa
|
||||
- image_segmenter
|
||||
- transcriber
|
||||
- summarizer
|
||||
- text_classifier
|
||||
- text_qa
|
||||
- text_reader
|
||||
- translator
|
||||
- image_transformer
|
||||
- text_downloader
|
||||
- image_generator
|
||||
- video_generator
|
||||
- image_upscaler
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Note how `image_upscaler` is now part of the agents' toolbox.
|
||||
|
||||
Let's now try out the new tools! We will re-use the image we generated in [Transformers Agents Quickstart](./transformers_agents#single-execution-run).
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from diffusers.utils import load_image
|
||||
|
||||
image = load_image(
|
||||
"https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/rivers_and_lakes.png"
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/rivers_and_lakes.png" width=200>
|
||||
|
||||
Let's transform the image into a beautiful winter landscape:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
image = agent.run("Transform the image: 'A frozen lake and snowy forest'", image=image)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
==Explanation from the agent==
|
||||
I will use the following tool: `image_transformer` to transform the image.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
==Code generated by the agent==
|
||||
image = image_transformer(image, prompt="A frozen lake and snowy forest")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/rivers_and_lakes_winter.png" width=200>
|
||||
|
||||
The new image processing tool is based on ControlNet which can make very strong modifications to the image.
|
||||
By default the image processing tool returns an image of size 512x512 pixels. Let's see if we can upscale it.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
image = agent.run("Upscale the image", image)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
==Explanation from the agent==
|
||||
I will use the following tool: `image_upscaler` to upscale the image.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
==Code generated by the agent==
|
||||
upscaled_image = image_upscaler(image)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/rivers_and_lakes_winter_upscale.png" width=400>
|
||||
|
||||
The agent automatically mapped our prompt "Upscale the image" to the just added upscaler tool purely based on the description and name of the upscaler tool
|
||||
and was able to correctly run it.
|
||||
|
||||
Next, let's have a look at how you can create a new custom tool.
|
||||
|
||||
### Adding new tools
|
||||
|
||||
In this section, we show how to create a new tool that can be added to the agent.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Creating a new tool
|
||||
|
||||
We'll first start by creating a tool. We'll add the not-so-useful yet fun task of fetching the model on the Hugging Face
|
||||
Hub with the most downloads for a given task.
|
||||
|
||||
We can do that with the following code:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from huggingface_hub import list_models
|
||||
|
||||
task = "text-classification"
|
||||
|
||||
model = next(iter(list_models(filter=task, sort="downloads", direction=-1)))
|
||||
print(model.id)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For the task `text-classification`, this returns `'facebook/bart-large-mnli'`, for `translation` it returns `'google-t5/t5-base`.
|
||||
|
||||
How do we convert this to a tool that the agent can leverage? All tools depend on the superclass `Tool` that holds the
|
||||
main attributes necessary. We'll create a class that inherits from it:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import Tool
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class HFModelDownloadsTool(Tool):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This class has a few needs:
|
||||
- An attribute `name`, which corresponds to the name of the tool itself. To be in tune with other tools which have a
|
||||
performative name, we'll name it `model_download_counter`.
|
||||
- An attribute `description`, which will be used to populate the prompt of the agent.
|
||||
- `inputs` and `outputs` attributes. Defining this will help the python interpreter make educated choices about types,
|
||||
and will allow for a gradio-demo to be spawned when we push our tool to the Hub. They're both a list of expected
|
||||
values, which can be `text`, `image`, or `audio`.
|
||||
- A `__call__` method which contains the inference code. This is the code we've played with above!
|
||||
|
||||
Here's what our class looks like now:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import Tool
|
||||
from huggingface_hub import list_models
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class HFModelDownloadsTool(Tool):
|
||||
name = "model_download_counter"
|
||||
description = (
|
||||
"This is a tool that returns the most downloaded model of a given task on the Hugging Face Hub. "
|
||||
"It takes the name of the category (such as text-classification, depth-estimation, etc), and "
|
||||
"returns the name of the checkpoint."
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
inputs = ["text"]
|
||||
outputs = ["text"]
|
||||
|
||||
def __call__(self, task: str):
|
||||
model = next(iter(list_models(filter=task, sort="downloads", direction=-1)))
|
||||
return model.id
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We now have our tool handy. Save it in a file and import it from your main script. Let's name this file
|
||||
`model_downloads.py`, so the resulting import code looks like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from model_downloads import HFModelDownloadsTool
|
||||
|
||||
tool = HFModelDownloadsTool()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In order to let others benefit from it and for simpler initialization, we recommend pushing it to the Hub under your
|
||||
namespace. To do so, just call `push_to_hub` on the `tool` variable:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
tool.push_to_hub("hf-model-downloads")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You now have your code on the Hub! Let's take a look at the final step, which is to have the agent use it.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Having the agent use the tool
|
||||
|
||||
We now have our tool that lives on the Hub which can be instantiated as such (change the user name for your tool):
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import load_tool
|
||||
|
||||
tool = load_tool("lysandre/hf-model-downloads")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In order to use it in the agent, simply pass it in the `additional_tools` parameter of the agent initialization method:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import HfAgent
|
||||
|
||||
agent = HfAgent("https://api-inference.huggingface.co/models/bigcode/starcoder", additional_tools=[tool])
|
||||
|
||||
agent.run(
|
||||
"Can you read out loud the name of the model that has the most downloads in the 'text-to-video' task on the Hugging Face Hub?"
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
which outputs the following:
|
||||
```text
|
||||
==Code generated by the agent==
|
||||
model = model_download_counter(task="text-to-video")
|
||||
print(f"The model with the most downloads is {model}.")
|
||||
audio_model = text_reader(model)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
==Result==
|
||||
The model with the most downloads is damo-vilab/text-to-video-ms-1.7b.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
and generates the following audio.
|
||||
|
||||
| **Audio** |
|
||||
|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| <audio controls><source src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/damo.wav" type="audio/wav"/> |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Depending on the LLM, some are quite brittle and require very exact prompts in order to work well. Having a well-defined
|
||||
name and description of the tool is paramount to having it be leveraged by the agent.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
### Replacing existing tools
|
||||
|
||||
Replacing existing tools can be done simply by assigning a new item to the agent's toolbox. Here's how one would do so:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import HfAgent, load_tool
|
||||
|
||||
agent = HfAgent("https://api-inference.huggingface.co/models/bigcode/starcoder")
|
||||
agent.toolbox["image-transformation"] = load_tool("diffusers/controlnet-canny-tool")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Beware when replacing tools with others! This will also adjust the agent's prompt. This can be good if you have a better
|
||||
prompt suited for the task, but it can also result in your tool being selected way more than others or for other
|
||||
tools to be selected instead of the one you have defined.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## Leveraging gradio-tools
|
||||
|
||||
[gradio-tools](https://github.com/freddyaboulton/gradio-tools) is a powerful library that allows using Hugging
|
||||
Face Spaces as tools. It supports many existing Spaces as well as custom Spaces to be designed with it.
|
||||
|
||||
We offer support for `gradio_tools` by using the `Tool.from_gradio` method. For example, we want to take
|
||||
advantage of the `StableDiffusionPromptGeneratorTool` tool offered in the `gradio-tools` toolkit so as to
|
||||
improve our prompts and generate better images.
|
||||
|
||||
We first import the tool from `gradio_tools` and instantiate it:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from gradio_tools import StableDiffusionPromptGeneratorTool
|
||||
|
||||
gradio_tool = StableDiffusionPromptGeneratorTool()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We pass that instance to the `Tool.from_gradio` method:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import Tool
|
||||
|
||||
tool = Tool.from_gradio(gradio_tool)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now we can manage it exactly as we would a usual custom tool. We leverage it to improve our prompt
|
||||
` a rabbit wearing a space suit`:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import HfAgent
|
||||
|
||||
agent = HfAgent("https://api-inference.huggingface.co/models/bigcode/starcoder", additional_tools=[tool])
|
||||
|
||||
agent.run("Generate an image of the `prompt` after improving it.", prompt="A rabbit wearing a space suit")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The model adequately leverages the tool:
|
||||
```text
|
||||
==Explanation from the agent==
|
||||
I will use the following tools: `StableDiffusionPromptGenerator` to improve the prompt, then `image_generator` to generate an image according to the improved prompt.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
==Code generated by the agent==
|
||||
improved_prompt = StableDiffusionPromptGenerator(prompt)
|
||||
print(f"The improved prompt is {improved_prompt}.")
|
||||
image = image_generator(improved_prompt)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Before finally generating the image:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/rabbit.png">
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
gradio-tools requires *textual* inputs and outputs, even when working with different modalities. This implementation
|
||||
works with image and audio objects. The two are currently incompatible, but will rapidly become compatible as we
|
||||
work to improve the support.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## Future compatibility with Langchain
|
||||
|
||||
We love Langchain and think it has a very compelling suite of tools. In order to handle these tools,
|
||||
Langchain requires *textual* inputs and outputs, even when working with different modalities.
|
||||
This is often the serialized version (i.e., saved to disk) of the objects.
|
||||
|
||||
This difference means that multi-modality isn't handled between transformers-agents and langchain.
|
||||
We aim for this limitation to be resolved in future versions, and welcome any help from avid langchain
|
||||
users to help us achieve this compatibility.
|
||||
|
||||
We would love to have better support. If you would like to help, please
|
||||
[open an issue](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/issues/new) and share what you have in mind.
|
||||
@ -21,7 +21,7 @@ more. It also plays a role in a variety of mixed-modality applications that have
|
||||
and vision-to-text. Some of the models that can generate text include
|
||||
GPT2, XLNet, OpenAI GPT, CTRL, TransformerXL, XLM, Bart, T5, GIT, Whisper.
|
||||
|
||||
Check out a few examples that use [`~generation.GenerationMixin.generate`] method to produce
|
||||
Check out a few examples that use [`~transformers.generation_utils.GenerationMixin.generate`] method to produce
|
||||
text outputs for different tasks:
|
||||
* [Text summarization](./tasks/summarization#inference)
|
||||
* [Image captioning](./model_doc/git#transformers.GitForCausalLM.forward.example)
|
||||
@ -173,92 +173,6 @@ your screen, one word at a time:
|
||||
An increasing sequence: one, two, three, four, five, six, seven, eight, nine, ten, eleven,
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## KV Cache Quantization
|
||||
|
||||
The `generate()` method supports caching keys and values to enhance efficiency and avoid re-computations. However the key and value
|
||||
cache can occupy a large portion of memory, becoming a bottleneck for long-context generation, especially for Large Language Models.
|
||||
Quantizing the cache when using `generate()` can significantly reduce memory requirements at the cost of speed.
|
||||
|
||||
KV Cache quantization in `transformers` is largely inspired by the paper [KIVI: A Tuning-Free Asymmetric 2bit Quantization for KV Cache]
|
||||
(https://arxiv.org/abs/2402.02750) and currently supports `quanto` and `HQQ` as backends. For more information on the inner workings see the paper.
|
||||
|
||||
To enable quantization of the key-value cache, one needs to indicate `cache_implementation="quantized"` in the `generation_config`.
|
||||
Quantization related arguments should be passed to the `generation_config` either as a `dict` or an instance of a [`QuantizedCacheConfig`] class.
|
||||
One has to indicate which quantization backend to use in the [`QuantizedCacheConfig`], the default is `quanto`.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
Cache quantization can be detrimental if the context length is short and there is enough GPU VRAM available to run without cache quantization.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> import torch
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-chat-hf")
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-chat-hf", torch_dtype=torch.float16).to("cuda:0")
|
||||
>>> inputs = tokenizer("I like rock music because", return_tensors="pt").to(model.device)
|
||||
|
||||
>>> out = model.generate(**inputs, do_sample=False, max_new_tokens=20, cache_implementation="quantized", cache_config={"nbits": 4, "backend": "quanto"})
|
||||
>>> print(tokenizer.batch_decode(out, skip_special_tokens=True)[0])
|
||||
I like rock music because it's loud and energetic. It's a great way to express myself and rel
|
||||
|
||||
>>> out = model.generate(**inputs, do_sample=False, max_new_tokens=20)
|
||||
>>> print(tokenizer.batch_decode(out, skip_special_tokens=True)[0])
|
||||
I like rock music because it's loud and energetic. I like to listen to it when I'm feeling
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Watermarking
|
||||
|
||||
The `generate()` supports watermarking the generated text by randomly marking a portion of tokens as "green".
|
||||
When generating the "green" will have a small 'bias' value added to their logits, thus having a higher chance to be generated.
|
||||
The watermarked text can be detected by calculating the proportion of "green" tokens in the text and estimating how likely it is
|
||||
statistically to obtain that amount of "green" tokens for human-generated text. This watermarking strategy was proposed in the paper
|
||||
["On the Reliability of Watermarks for Large Language Models"](https://arxiv.org/abs/2306.04634). For more information on
|
||||
the inner functioning of watermarking, it is recommended to refer to the paper.
|
||||
|
||||
The watermarking can be used with any generative model in `tranformers` and does not require an extra classification model
|
||||
to detect watermarked text. To trigger watermarking, pass in a [`WatermarkingConfig`] with needed arguments directly to the
|
||||
`.generate()` method or add it to the [`GenerationConfig`]. Watermarked text can be later detected with a [`WatermarkDetector`].
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
The WatermarkDetector internally relies on the proportion of "green" tokens, and whether generated text follows the coloring pattern.
|
||||
That is why it is recommended to strip off the prompt text, if it is much longer than the generated text.
|
||||
This also can have an effect when one sequence in the batch is a lot longer causing other rows to be padded.
|
||||
Additionally, the detector **must** be initiated with identical watermark configuration arguments used when generating.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Let's generate some text with watermarking. In the below code snippet, we set the bias to 2.5 which is a value that
|
||||
will be added to "green" tokens' logits. After generating watermarked text, we can pass it directly to the `WatermarkDetector`
|
||||
to check if the text is machine-generated (outputs `True` for machine-generated and `False` otherwise).
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM, WatermarkDetector, WatermarkingConfig
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("openai-community/gpt2")
|
||||
>>> tok = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("openai-community/gpt2")
|
||||
>>> tok.pad_token_id = tok.eos_token_id
|
||||
>>> tok.padding_side = "left"
|
||||
|
||||
>>> inputs = tok(["This is the beginning of a long story", "Alice and Bob are"], padding=True, return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
>>> input_len = inputs["input_ids"].shape[-1]
|
||||
|
||||
>>> watermarking_config = WatermarkingConfig(bias=2.5, seeding_scheme="selfhash")
|
||||
>>> out = model.generate(**inputs, watermarking_config=watermarking_config, do_sample=False, max_length=20)
|
||||
|
||||
>>> detector = WatermarkDetector(model_config=model.config, device="cpu", watermarking_config=watermarking_config)
|
||||
>>> detection_out = detector(out, return_dict=True)
|
||||
>>> detection_out.prediction
|
||||
array([True, True])
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Decoding strategies
|
||||
|
||||
Certain combinations of the `generate()` parameters, and ultimately `generation_config`, can be used to enable specific
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,97 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# GGUF and interaction with Transformers
|
||||
|
||||
The GGUF file format is used to store models for inference with [GGML](https://github.com/ggerganov/ggml) and other
|
||||
libraries that depend on it, like the very popular [llama.cpp](https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp) or
|
||||
[whisper.cpp](https://github.com/ggerganov/whisper.cpp).
|
||||
|
||||
It is a file format [supported by the Hugging Face Hub](https://huggingface.co/docs/hub/en/gguf) with features
|
||||
allowing for quick inspection of tensors and metadata within the file.
|
||||
|
||||
This file format is designed as a "single-file-format" where a single file usually contains both the configuration
|
||||
attributes, the tokenizer vocabulary and other attributes, as well as all tensors to be loaded in the model. These
|
||||
files come in different formats according to the quantization type of the file. We briefly go over some of them
|
||||
[here](https://huggingface.co/docs/hub/en/gguf#quantization-types).
|
||||
|
||||
## Support within Transformers
|
||||
|
||||
We have added the ability to load `gguf` files within `transformers` in order to offer further training/fine-tuning
|
||||
capabilities to gguf models, before converting back those models to `gguf` to use within the `ggml` ecosystem. When
|
||||
loading a model, we first dequantize it to fp32, before loading the weights to be used in PyTorch.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!NOTE]
|
||||
> The support is still very exploratory and we welcome contributions in order to solidify it across quantization types
|
||||
> and model architectures.
|
||||
|
||||
For now, here are the supported model architectures and quantization types:
|
||||
|
||||
### Supported quantization types
|
||||
|
||||
The initial supported quantization types are decided according to the popular quantized files that have been shared
|
||||
on the Hub.
|
||||
|
||||
- F32
|
||||
- Q2_K
|
||||
- Q3_K
|
||||
- Q4_0
|
||||
- Q4_K
|
||||
- Q5_K
|
||||
- Q6_K
|
||||
- Q8_0
|
||||
|
||||
We take example from the excellent [99991/pygguf](https://github.com/99991/pygguf) Python parser to dequantize the
|
||||
weights.
|
||||
|
||||
### Supported model architectures
|
||||
|
||||
For now the supported model architectures are the architectures that have been very popular on the Hub, namely:
|
||||
|
||||
- LLaMa
|
||||
- Mistral
|
||||
- Qwen2
|
||||
|
||||
## Example usage
|
||||
|
||||
In order to load `gguf` files in `transformers`, you should specify the `gguf_file` argument to the `from_pretrained`
|
||||
methods of both tokenizers and models. Here is how one would load a tokenizer and a model, which can be loaded
|
||||
from the exact same file:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM
|
||||
|
||||
model_id = "TheBloke/TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0-GGUF"
|
||||
filename = "tinyllama-1.1b-chat-v1.0.Q6_K.gguf"
|
||||
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_id, gguf_file=filename)
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_id, gguf_file=filename)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now you have access to the full, unquantized version of the model in the PyTorch ecosystem, where you can combine it
|
||||
with a plethora of other tools.
|
||||
|
||||
In order to convert back to a `gguf` file, we recommend using the
|
||||
[`convert-hf-to-gguf.py` file](https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp/blob/master/convert-hf-to-gguf.py) from llama.cpp.
|
||||
|
||||
Here's how you would complete the script above to save the model and export it back to `gguf`:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
tokenizer.save_pretrained('directory')
|
||||
model.save_pretrained('directory')
|
||||
|
||||
!python ${path_to_llama_cpp}/convert-hf-to-gguf.py ${directory}
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -64,6 +64,6 @@ For some quantization methods, they may require "pre-quantizing" the models thro
|
||||
|
||||
6. Write the `_process_model_after_weight_loading` method. This method enables implementing additional features that require manipulating the model after loading the weights.
|
||||
|
||||
7. Document everything! Make sure your quantization method is documented by adding a new file under `docs/source/en/quantization` and adding a new row in the table in `docs/source/en/quantization/overview.md`.
|
||||
7. Document everything! Make sure your quantization method is documented in the [`docs/source/en/quantization.md`](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/abbffc4525566a48a9733639797c812301218b83/docs/source/en/quantization.md) file.
|
||||
|
||||
8. Add tests! You should add tests by first adding the package in our nightly Dockerfile inside `docker/transformers-quantization-latest-gpu` and then adding a new test file in `tests/quantization/xxx`. Feel free to check out how it is implemented for other quantization methods.
|
||||
@ -160,13 +160,12 @@ Flax), PyTorch, and/or TensorFlow.
|
||||
| [HerBERT](model_doc/herbert) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| [Hubert](model_doc/hubert) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| [I-BERT](model_doc/ibert) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| [IDEFICS](model_doc/idefics) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
| [IDEFICS](model_doc/idefics) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| [Idefics2](model_doc/idefics2) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| [ImageGPT](model_doc/imagegpt) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| [Informer](model_doc/informer) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| [InstructBLIP](model_doc/instructblip) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| [Jamba](model_doc/jamba) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| [JetMoe](model_doc/jetmoe) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| [Jukebox](model_doc/jukebox) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| [KOSMOS-2](model_doc/kosmos-2) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| [LayoutLM](model_doc/layoutlm) | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
|
||||
@ -200,7 +199,7 @@ Flax), PyTorch, and/or TensorFlow.
|
||||
| [Megatron-BERT](model_doc/megatron-bert) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| [Megatron-GPT2](model_doc/megatron_gpt2) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| [MGP-STR](model_doc/mgp-str) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| [Mistral](model_doc/mistral) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| [Mistral](model_doc/mistral) | ✅ | ❌ | ✅ |
|
||||
| [Mixtral](model_doc/mixtral) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| [mLUKE](model_doc/mluke) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| [MMS](model_doc/mms) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
@ -230,7 +229,6 @@ Flax), PyTorch, and/or TensorFlow.
|
||||
| [OPT](model_doc/opt) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| [OWL-ViT](model_doc/owlvit) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| [OWLv2](model_doc/owlv2) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| [PaliGemma](model_doc/paligemma) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| [PatchTSMixer](model_doc/patchtsmixer) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| [PatchTST](model_doc/patchtst) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| [Pegasus](model_doc/pegasus) | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
@ -304,7 +302,6 @@ Flax), PyTorch, and/or TensorFlow.
|
||||
| [UnivNet](model_doc/univnet) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| [UPerNet](model_doc/upernet) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| [VAN](model_doc/van) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| [VideoLlava](model_doc/video_llava) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| [VideoMAE](model_doc/videomae) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| [ViLT](model_doc/vilt) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
| [VipLlava](model_doc/vipllava) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ |
|
||||
|
||||
@ -169,7 +169,7 @@ Pretrained models are downloaded and locally cached at: `~/.cache/huggingface/hu
|
||||
|
||||
## Offline mode
|
||||
|
||||
Run 🤗 Transformers in a firewalled or offline environment with locally cached files by setting the environment variable `HF_HUB_OFFLINE=1`.
|
||||
Run 🤗 Transformers in a firewalled or offline environment with locally cached files by setting the environment variable `TRANSFORMERS_OFFLINE=1`.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -178,7 +178,7 @@ Add [🤗 Datasets](https://huggingface.co/docs/datasets/) to your offline train
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
HF_DATASETS_OFFLINE=1 HF_HUB_OFFLINE=1 \
|
||||
HF_DATASETS_OFFLINE=1 TRANSFORMERS_OFFLINE=1 \
|
||||
python examples/pytorch/translation/run_translation.py --model_name_or_path google-t5/t5-small --dataset_name wmt16 --dataset_config ro-en ...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -167,9 +167,6 @@ generation.
|
||||
[[autodoc]] MinNewTokensLengthLogitsProcessor
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] MinPLogitsWarper
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] NoBadWordsLogitsProcessor
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
@ -209,10 +206,6 @@ generation.
|
||||
[[autodoc]] WhisperTimeStampLogitsProcessor
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] WatermarkLogitsProcessor
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### TensorFlow
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] TFForcedBOSTokenLogitsProcessor
|
||||
@ -317,12 +310,6 @@ A [`StoppingCriteria`] can be used to change when to stop generation (other than
|
||||
[[autodoc]] MaxTimeCriteria
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] StopStringCriteria
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] EosTokenCriteria
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
## Constraints
|
||||
|
||||
A [`Constraint`] can be used to force the generation to include specific tokens or sequences in the output. Please note that this is exclusively available to our PyTorch implementations.
|
||||
@ -360,12 +347,6 @@ A [`Constraint`] can be used to force the generation to include specific tokens
|
||||
[[autodoc]] Cache
|
||||
- update
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] CacheConfig
|
||||
- update
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] QuantizedCacheConfig
|
||||
- validate
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] DynamicCache
|
||||
- update
|
||||
- get_seq_length
|
||||
@ -373,14 +354,6 @@ A [`Constraint`] can be used to force the generation to include specific tokens
|
||||
- to_legacy_cache
|
||||
- from_legacy_cache
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] QuantizedCache
|
||||
- update
|
||||
- get_seq_length
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] QuantoQuantizedCache
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] HQQQuantizedCache
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] SinkCache
|
||||
- update
|
||||
- get_seq_length
|
||||
@ -389,11 +362,3 @@ A [`Constraint`] can be used to force the generation to include specific tokens
|
||||
[[autodoc]] StaticCache
|
||||
- update
|
||||
- get_seq_length
|
||||
- reset
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Watermark Utils
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] WatermarkDetector
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -29,7 +29,7 @@ To optimize this, you can use a kv-cache to store the past keys and values inste
|
||||
The *static kv-cache* solves this issue by pre-allocating the kv-cache size to a maximum value which allows you to combine it with torch.compile for up to a 4x speed up.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!WARNING]
|
||||
> Currently, only [Llama](./model_doc/llama2) and a few other models support static kv-cache and torch.compile. Check [this issue](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/issues/28981) for a live model compatibility list.
|
||||
> Currently, only [Command R](./model_doc/cohere), [Gemma](./model_doc/gemma) and [Llama](./model_doc/llama2) models support static kv-cache and torch.compile.
|
||||
|
||||
For this example, let's load the [Gemma](https://hf.co/google/gemma-2b) model.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -65,12 +65,13 @@ tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs, skip_special_tokens=True)
|
||||
['The theory of special relativity states 1. The speed of light is constant in all inertial reference']
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Under the hood, `generate` will attempt to reuse the same cache object, removing the need for re-compilation at each call. However, if the batch size or the maximum output length increase between calls, the cache will have to be reinitialized, triggering a new compilation.
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="Static Cache">
|
||||
<hfoption id="setup_cache">
|
||||
|
||||
A [`StaticCache`] object can be passed to the model's forward pass under the `past_key_values` argument, enabling the use of this object as a static kv-cache. Using this strategy, you can write your own function to decode the next token given the current token and position and cache position of previously generated tokens. You can also pass the [`StaticCache`] object to [`~GenerationMixin.generate`] and use it across calls, like you would do with a dynamic cache.
|
||||
> [!WARNING]
|
||||
> The `_setup_cache` method is an internal and private method that is still under development. This means it may not be backward compatible and the API design may change in the future.
|
||||
|
||||
The `_setup_cache` method doesn't support [`~GenerationMixin.generate`] yet, so this method is a bit more involved. You'll need to write your own function to decode the next token given the current token and position and cache position of previously generated tokens.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import LlamaTokenizer, LlamaForCausalLM, StaticCache, logging
|
||||
@ -89,22 +90,17 @@ tokenizer = LlamaTokenizer.from_pretrained("meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-hf", pad_token
|
||||
model = LlamaForCausalLM.from_pretrained("meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-hf", device_map="sequential")
|
||||
inputs = tokenizer(prompts, return_tensors="pt", padding=True).to(model.device)
|
||||
|
||||
def decode_one_tokens(model, cur_token, input_pos, cache_position, past_key_values):
|
||||
def decode_one_tokens(model, cur_token, input_pos, cache_position):
|
||||
logits = model(
|
||||
cur_token,
|
||||
position_ids=input_pos,
|
||||
cache_position=cache_position,
|
||||
past_key_values=past_key_values,
|
||||
return_dict=False,
|
||||
use_cache=True
|
||||
cur_token, position_ids=input_pos, cache_position=cache_position, return_dict=False, use_cache=True
|
||||
)[0]
|
||||
new_token = torch.argmax(logits[:, -1], dim=-1)[:, None]
|
||||
return new_token
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
There are a few important things you must do to enable static kv-cache and torch.compile with the `StaticCache` method:
|
||||
There are a few important things you must do to enable static kv-cache and torch.compile with the `_setup_cache` method:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Initialize the [`StaticCache`] instance before using the model for inference. There you can configure parameters like the maximum batch size and sequence length.
|
||||
1. Access the model's `_setup_cache` method and pass it the [`StaticCache`] class. This is a more flexible method because it allows you to configure parameters like the maximum batch size and sequence length.
|
||||
|
||||
2. Call torch.compile on the model to compile the forward pass with the static kv-cache.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -113,28 +109,24 @@ There are a few important things you must do to enable static kv-cache and torch
|
||||
```py
|
||||
batch_size, seq_length = inputs["input_ids"].shape
|
||||
with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
past_key_values = StaticCache(
|
||||
config=model.config, max_batch_size=2, max_cache_len=4096, device=torch_device, dtype=model.dtype
|
||||
)
|
||||
cache_position = torch.arange(seq_length, device=torch_device)
|
||||
generated_ids = torch.zeros(
|
||||
batch_size, seq_length + NUM_TOKENS_TO_GENERATE + 1, dtype=torch.int, device=torch_device
|
||||
)
|
||||
generated_ids[:, cache_position] = inputs["input_ids"].to(torch_device).to(torch.int)
|
||||
model._setup_cache(StaticCache, 2, max_cache_len=4096)
|
||||
cache_position = torch.arange(seq_length, device=torch_device)
|
||||
generated_ids = torch.zeros(
|
||||
batch_size, seq_length + NUM_TOKENS_TO_GENERATE + 1, dtype=torch.int, device=torch_device
|
||||
)
|
||||
generated_ids[:, cache_position] = inputs["input_ids"].to(torch_device).to(torch.int)
|
||||
|
||||
logits = model(
|
||||
**inputs, cache_position=cache_position, past_key_values=past_key_values,return_dict=False, use_cache=True
|
||||
)[0]
|
||||
next_token = torch.argmax(logits[:, -1], dim=-1)[:, None]
|
||||
generated_ids[:, seq_length] = next_token[:, 0]
|
||||
logits = model(**inputs, cache_position=cache_position, return_dict=False, use_cache=True)[0]
|
||||
next_token = torch.argmax(logits[:, -1], dim=-1)[:, None]
|
||||
generated_ids[:, seq_length] = next_token[:, 0]
|
||||
|
||||
decode_one_tokens = torch.compile(decode_one_tokens, mode="reduce-overhead", fullgraph=True)
|
||||
cache_position = torch.tensor([seq_length + 1], device=torch_device)
|
||||
for _ in range(1, NUM_TOKENS_TO_GENERATE):
|
||||
with torch.backends.cuda.sdp_kernel(enable_flash=False, enable_mem_efficient=False, enable_math=True):
|
||||
next_token = decode_one_tokens(model, next_token.clone(), None, cache_position, past_key_values)
|
||||
generated_ids[:, cache_position] = next_token.int()
|
||||
cache_position += 1
|
||||
decode_one_tokens = torch.compile(decode_one_tokens, mode="reduce-overhead", fullgraph=True)
|
||||
cache_position = torch.tensor([seq_length + 1], device=torch_device)
|
||||
for _ in range(1, NUM_TOKENS_TO_GENERATE):
|
||||
with torch.backends.cuda.sdp_kernel(enable_flash=False, enable_mem_efficient=False, enable_math=True):
|
||||
next_token = decode_one_tokens(model, next_token.clone(), None, cache_position)
|
||||
generated_ids[:, cache_position] = next_token.int()
|
||||
cache_position += 1
|
||||
|
||||
text = tokenizer.batch_decode(generated_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)
|
||||
text
|
||||
@ -142,9 +134,6 @@ text
|
||||
'My favorite all time favorite condiment is ketchup. I love it on everything. I love it on my eggs, my fries, my chicken, my burgers, my hot dogs, my sandwiches, my salads, my p']
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> [!TIP]
|
||||
> If you want to reuse the [`StaticCache`] object on a new prompt, be sure to reset its contents with the `.reset()` method
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
</hfoptions>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -247,11 +247,10 @@ While the autoregressive generation process is relatively straightforward, makin
|
||||
|
||||
### Advanced generate usage
|
||||
|
||||
1. Guide on how to [control different generation methods](generation_strategies), how to set up the generation configuration file, and how to stream the output;
|
||||
2. [Accelerating text generation](llm_optims);
|
||||
3. [Prompt templates for chat LLMs](chat_templating);
|
||||
4. [Prompt design guide](tasks/prompting);
|
||||
5. API reference on [`~generation.GenerationConfig`], [`~generation.GenerationMixin.generate`], and [generate-related classes](internal/generation_utils). Most of the classes, including the logits processors, have usage examples!
|
||||
1. [Guide](generation_strategies) on how to control different generation methods, how to set up the generation configuration file, and how to stream the output;
|
||||
2. [Guide](chat_templating) on the prompt template for chat LLMs;
|
||||
3. [Guide](tasks/prompting) on to get the most of prompt design;
|
||||
4. API reference on [`~generation.GenerationConfig`], [`~generation.GenerationMixin.generate`], and [generate-related classes](internal/generation_utils). Most of the classes, including the logits processors, have usage examples!
|
||||
|
||||
### LLM leaderboards
|
||||
|
||||
@ -260,12 +259,10 @@ While the autoregressive generation process is relatively straightforward, makin
|
||||
|
||||
### Latency, throughput and memory utilization
|
||||
|
||||
1. Guide on how to [optimize LLMs for speed and memory](llm_tutorial_optimization);
|
||||
2. Guide on [quantization](main_classes/quantization) such as bitsandbytes and autogptq, which shows you how to drastically reduce your memory requirements.
|
||||
1. [Guide](llm_tutorial_optimization) on how to optimize LLMs for speed and memory;
|
||||
2. [Guide](main_classes/quantization) on quantization such as bitsandbytes and autogptq, which shows you how to drastically reduce your memory requirements.
|
||||
|
||||
### Related libraries
|
||||
|
||||
1. [`optimum`](https://github.com/huggingface/optimum), an extension of 🤗 Transformers that optimizes for specific hardware devices.
|
||||
2. [`outlines`](https://github.com/outlines-dev/outlines), a library where you can constrain text generation (e.g. to generate JSON files);
|
||||
3. [`text-generation-inference`](https://github.com/huggingface/text-generation-inference), a production-ready server for LLMs;
|
||||
4. [`text-generation-webui`](https://github.com/oobabooga/text-generation-webui), a UI for text generation;
|
||||
1. [`text-generation-inference`](https://github.com/huggingface/text-generation-inference), a production-ready server for LLMs;
|
||||
2. [`optimum`](https://github.com/huggingface/optimum), an extension of 🤗 Transformers that optimizes for specific hardware devices.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -28,27 +28,30 @@ contains the API docs for the underlying classes.
|
||||
|
||||
## Agents
|
||||
|
||||
We provide two types of agents, based on the main [`Agent`] class:
|
||||
- [`CodeAgent`] acts in one shot, generating code to solve the task, then executes it at once.
|
||||
- [`ReactAgent`] acts step by step, each step consisting of one thought, then one tool call and execution. It has two classes:
|
||||
- [`ReactJsonAgent`] writes its tool calls in JSON.
|
||||
- [`ReactCodeAgent`] writes its tool calls in Python code.
|
||||
We provide three types of agents: [`HfAgent`] uses inference endpoints for opensource models, [`LocalAgent`] uses a model of your choice locally and [`OpenAiAgent`] uses OpenAI closed models.
|
||||
|
||||
### HfAgent
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] HfAgent
|
||||
|
||||
### LocalAgent
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] LocalAgent
|
||||
|
||||
### OpenAiAgent
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] OpenAiAgent
|
||||
|
||||
### AzureOpenAiAgent
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] AzureOpenAiAgent
|
||||
|
||||
### Agent
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] Agent
|
||||
|
||||
### CodeAgent
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] CodeAgent
|
||||
|
||||
### React agents
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] ReactAgent
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] ReactJsonAgent
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] ReactCodeAgent
|
||||
- chat
|
||||
- run
|
||||
- prepare_for_new_chat
|
||||
|
||||
## Tools
|
||||
|
||||
@ -60,50 +63,18 @@ We provide two types of agents, based on the main [`Agent`] class:
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] Tool
|
||||
|
||||
### Toolbox
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] Toolbox
|
||||
|
||||
### PipelineTool
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] PipelineTool
|
||||
|
||||
### RemoteTool
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] RemoteTool
|
||||
|
||||
### launch_gradio_demo
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] launch_gradio_demo
|
||||
|
||||
### ToolCollection
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] ToolCollection
|
||||
|
||||
## Engines
|
||||
|
||||
You're free to create and use your own engines to be usable by the Agents framework.
|
||||
These engines have the following specification:
|
||||
1. Follow the [messages format](../chat_templating.md) for its input (`List[Dict[str, str]]`) and return a string.
|
||||
2. Stop generating outputs *before* the sequences passed in the argument `stop_sequences`
|
||||
|
||||
### HfEngine
|
||||
|
||||
For convenience, we have added a `HfEngine` that implements the points above and uses an inference endpoint for the execution of the LLM.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import HfEngine
|
||||
|
||||
>>> messages = [
|
||||
... {"role": "user", "content": "Hello, how are you?"},
|
||||
... {"role": "assistant", "content": "I'm doing great. How can I help you today?"},
|
||||
... {"role": "user", "content": "No need to help, take it easy."},
|
||||
... ]
|
||||
|
||||
>>> HfEngine()(messages, stop_sequences=["conversation"])
|
||||
|
||||
"That's very kind of you to say! It's always nice to have a relaxed "
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] HfEngine
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Agent Types
|
||||
|
||||
Agents can handle any type of object in-between tools; tools, being completely multimodal, can accept and return
|
||||
@ -123,12 +94,12 @@ These types have three specific purposes:
|
||||
|
||||
### AgentText
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] transformers.agents.agent_types.AgentText
|
||||
[[autodoc]] transformers.tools.agent_types.AgentText
|
||||
|
||||
### AgentImage
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] transformers.agents.agent_types.AgentImage
|
||||
[[autodoc]] transformers.tools.agent_types.AgentImage
|
||||
|
||||
### AgentAudio
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] transformers.agents.agent_types.AgentAudio
|
||||
[[autodoc]] transformers.tools.agent_types.AgentAudio
|
||||
|
||||
@ -32,8 +32,3 @@ An image processor is in charge of preparing input features for vision models an
|
||||
## BaseImageProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] image_processing_utils.BaseImageProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## BaseImageProcessorFast
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] image_processing_utils_fast.BaseImageProcessorFast
|
||||
|
||||
@ -386,6 +386,14 @@ Pipelines available for computer vision tasks include the following.
|
||||
|
||||
Pipelines available for natural language processing tasks include the following.
|
||||
|
||||
### ConversationalPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] Conversation
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] ConversationalPipeline
|
||||
- __call__
|
||||
- all
|
||||
|
||||
### FillMaskPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] FillMaskPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
4
docs/source/en/main_classes/quantization.md
Executable file → Normal file
4
docs/source/en/main_classes/quantization.md
Executable file → Normal file
@ -52,7 +52,3 @@ Learn how to quantize models in the [Quantization](../quantization) guide.
|
||||
## HfQuantizer
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] quantizers.base.HfQuantizer
|
||||
|
||||
## HqqConfig
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] HqqConfig
|
||||
|
||||
@ -41,8 +41,6 @@ like token streaming.
|
||||
- validate
|
||||
- get_generation_mode
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] generation.WatermarkingConfig
|
||||
|
||||
## GenerationMixin
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] generation.GenerationMixin
|
||||
|
||||
@ -43,34 +43,6 @@ the authors compute the stats for a downstream dataset.
|
||||
- Note that the AST needs a low learning rate (the authors use a 10 times smaller learning rate compared to their CNN model proposed in the
|
||||
[PSLA paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2102.01243)) and converges quickly, so please search for a suitable learning rate and learning rate scheduler for your task.
|
||||
|
||||
### Using Scaled Dot Product Attention (SDPA)
|
||||
|
||||
PyTorch includes a native scaled dot-product attention (SDPA) operator as part of `torch.nn.functional`. This function
|
||||
encompasses several implementations that can be applied depending on the inputs and the hardware in use. See the
|
||||
[official documentation](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.functional.scaled_dot_product_attention.html)
|
||||
or the [GPU Inference](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/en/perf_infer_gpu_one#pytorch-scaled-dot-product-attention)
|
||||
page for more information.
|
||||
|
||||
SDPA is used by default for `torch>=2.1.1` when an implementation is available, but you may also set
|
||||
`attn_implementation="sdpa"` in `from_pretrained()` to explicitly request SDPA to be used.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
from transformers import ASTForAudioClassification
|
||||
model = ASTForAudioClassification.from_pretrained("MIT/ast-finetuned-audioset-10-10-0.4593", attn_implementation="sdpa", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For the best speedups, we recommend loading the model in half-precision (e.g. `torch.float16` or `torch.bfloat16`).
|
||||
|
||||
On a local benchmark (A100-40GB, PyTorch 2.3.0, OS Ubuntu 22.04) with `float32` and `MIT/ast-finetuned-audioset-10-10-0.4593` model, we saw the following speedups during inference.
|
||||
|
||||
| Batch size | Average inference time (ms), eager mode | Average inference time (ms), sdpa model | Speed up, Sdpa / Eager (x) |
|
||||
|--------------|-------------------------------------------|-------------------------------------------|------------------------------|
|
||||
| 1 | 27 | 6 | 4.5 |
|
||||
| 2 | 12 | 6 | 2 |
|
||||
| 4 | 21 | 8 | 2.62 |
|
||||
| 8 | 40 | 14 | 2.86 |
|
||||
|
||||
## Resources
|
||||
|
||||
A list of official Hugging Face and community (indicated by 🌎) resources to help you get started with the Audio Spectrogram Transformer.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -61,53 +61,6 @@ This model was contributed by [thomwolf](https://huggingface.co/thomwolf). The o
|
||||
|
||||
- The model must predict the original sentence, but has a second objective: inputs are two sentences A and B (with a separation token in between). With probability 50%, the sentences are consecutive in the corpus, in the remaining 50% they are not related. The model has to predict if the sentences are consecutive or not.
|
||||
|
||||
### Using Scaled Dot Product Attention (SDPA)
|
||||
|
||||
PyTorch includes a native scaled dot-product attention (SDPA) operator as part of `torch.nn.functional`. This function
|
||||
encompasses several implementations that can be applied depending on the inputs and the hardware in use. See the
|
||||
[official documentation](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.functional.scaled_dot_product_attention.html)
|
||||
or the [GPU Inference](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/en/perf_infer_gpu_one#pytorch-scaled-dot-product-attention)
|
||||
page for more information.
|
||||
|
||||
SDPA is used by default for `torch>=2.1.1` when an implementation is available, but you may also set
|
||||
`attn_implementation="sdpa"` in `from_pretrained()` to explicitly request SDPA to be used.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
from transformers import BertModel
|
||||
|
||||
model = BertModel.from_pretrained("bert-base-uncased", torch_dtype=torch.float16, attn_implementation="sdpa")
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For the best speedups, we recommend loading the model in half-precision (e.g. `torch.float16` or `torch.bfloat16`).
|
||||
|
||||
On a local benchmark (A100-80GB, CPUx12, RAM 96.6GB, PyTorch 2.2.0, OS Ubuntu 22.04) with `float16`, we saw the
|
||||
following speedups during training and inference.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Training
|
||||
|
||||
|batch_size|seq_len|Time per batch (eager - s)|Time per batch (sdpa - s)|Speedup (%)|Eager peak mem (MB)|sdpa peak mem (MB)|Mem saving (%)|
|
||||
|----------|-------|--------------------------|-------------------------|-----------|-------------------|------------------|--------------|
|
||||
|4 |256 |0.023 |0.017 |35.472 |939.213 |764.834 |22.800 |
|
||||
|4 |512 |0.023 |0.018 |23.687 |1970.447 |1227.162 |60.569 |
|
||||
|8 |256 |0.023 |0.018 |23.491 |1594.295 |1226.114 |30.028 |
|
||||
|8 |512 |0.035 |0.025 |43.058 |3629.401 |2134.262 |70.054 |
|
||||
|16 |256 |0.030 |0.024 |25.583 |2874.426 |2134.262 |34.680 |
|
||||
|16 |512 |0.064 |0.044 |46.223 |6964.659 |3961.013 |75.830 |
|
||||
|
||||
#### Inference
|
||||
|
||||
|batch_size|seq_len|Per token latency eager (ms)|Per token latency SDPA (ms)|Speedup (%)|Mem eager (MB)|Mem BT (MB)|Mem saved (%)|
|
||||
|----------|-------|----------------------------|---------------------------|-----------|--------------|-----------|-------------|
|
||||
|1 |128 |5.736 |4.987 |15.022 |282.661 |282.924 |-0.093 |
|
||||
|1 |256 |5.689 |4.945 |15.055 |298.686 |298.948 |-0.088 |
|
||||
|2 |128 |6.154 |4.982 |23.521 |314.523 |314.785 |-0.083 |
|
||||
|2 |256 |6.201 |4.949 |25.303 |347.546 |347.033 |0.148 |
|
||||
|4 |128 |6.049 |4.987 |21.305 |378.895 |379.301 |-0.107 |
|
||||
|4 |256 |6.285 |5.364 |17.166 |443.209 |444.382 |-0.264 |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Resources
|
||||
|
||||
A list of official Hugging Face and community (indicated by 🌎) resources to help you get started with BERT. If you're interested in submitting a resource to be included here, please feel free to open a Pull Request and we'll review it! The resource should ideally demonstrate something new instead of duplicating an existing resource.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -66,8 +66,6 @@ The original code can be found [here](https://github.com/salesforce/BLIP).
|
||||
|
||||
## BlipModel
|
||||
|
||||
`BlipModel` is going to be deprecated in future versions, please use `BlipForConditionalGeneration`, `BlipForImageTextRetrieval` or `BlipForQuestionAnswering` depending on your usecase.
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] BlipModel
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
- get_text_features
|
||||
|
||||
@ -24,7 +24,7 @@ The abstract from the paper is the following:
|
||||
|
||||
*We release Code Llama, a family of large language models for code based on Llama 2 providing state-of-the-art performance among open models, infilling capabilities, support for large input contexts, and zero-shot instruction following ability for programming tasks. We provide multiple flavors to cover a wide range of applications: foundation models (Code Llama), Python specializations (Code Llama - Python), and instruction-following models (Code Llama - Instruct) with 7B, 13B and 34B parameters each. All models are trained on sequences of 16k tokens and show improvements on inputs with up to 100k tokens. 7B and 13B Code Llama and Code Llama - Instruct variants support infilling based on surrounding content. Code Llama reaches state-of-the-art performance among open models on several code benchmarks, with scores of up to 53% and 55% on HumanEval and MBPP, respectively. Notably, Code Llama - Python 7B outperforms Llama 2 70B on HumanEval and MBPP, and all our models outperform every other publicly available model on MultiPL-E. We release Code Llama under a permissive license that allows for both research and commercial use.*
|
||||
|
||||
Check out all Code Llama model checkpoints [here](https://huggingface.co/models?search=code_llama) and the officially released ones in the [Meta Llama org](https://huggingface.co/meta-llama).
|
||||
Check out all Code Llama model checkpoints [here](https://huggingface.co/models?search=code_llama) and the officially released ones in the [codellama org](https://huggingface.co/codellama).
|
||||
|
||||
This model was contributed by [ArthurZucker](https://huggingface.co/ArthurZ). The original code of the authors can be found [here](https://github.com/facebookresearch/llama).
|
||||
|
||||
@ -62,8 +62,8 @@ After conversion, the model and tokenizer can be loaded via:
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import LlamaForCausalLM, CodeLlamaTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = CodeLlamaTokenizer.from_pretrained("meta-llama/CodeLlama-7b-hf")
|
||||
>>> model = LlamaForCausalLM.from_pretrained("meta-llama/CodeLlama-7b-hf")
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = CodeLlamaTokenizer.from_pretrained("codellama/CodeLlama-7b-hf")
|
||||
>>> model = LlamaForCausalLM.from_pretrained("codellama/CodeLlama-7b-hf")
|
||||
>>> PROMPT = '''def remove_non_ascii(s: str) -> str:
|
||||
... """ <FILL_ME>
|
||||
... return result
|
||||
@ -95,7 +95,7 @@ If you only want the infilled part:
|
||||
>>> from transformers import pipeline
|
||||
>>> import torch
|
||||
|
||||
>>> generator = pipeline("text-generation",model="meta-llama/CodeLlama-7b-hf",torch_dtype=torch.float16, device_map="auto")
|
||||
>>> generator = pipeline("text-generation",model="codellama/CodeLlama-7b-hf",torch_dtype=torch.float16, device_map="auto")
|
||||
>>> generator('def remove_non_ascii(s: str) -> str:\n """ <FILL_ME>\n return result', max_new_tokens = 128)
|
||||
[{'generated_text': 'def remove_non_ascii(s: str) -> str:\n """ <FILL_ME>\n return resultRemove non-ASCII characters from a string. """\n result = ""\n for c in s:\n if ord(c) < 128:\n result += c'}]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@ -33,8 +33,7 @@ This model was contributed by [DepuMeng](https://huggingface.co/DepuMeng). The o
|
||||
|
||||
## Resources
|
||||
|
||||
- Scripts for finetuning [`ConditionalDetrForObjectDetection`] with [`Trainer`] or [Accelerate](https://huggingface.co/docs/accelerate/index) can be found [here](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples/pytorch/object-detection).
|
||||
- See also: [Object detection task guide](../tasks/object_detection).
|
||||
- [Object detection task guide](../tasks/object_detection)
|
||||
|
||||
## ConditionalDetrConfig
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -31,7 +31,8 @@ We used curriculum learning for pretraining, changing the data mix during traini
|
||||
|
||||
More detailed information about DBRX Instruct and DBRX Base can be found in our [technical blog post](https://www.databricks.com/blog/introducing-dbrx-new-state-art-open-llm).
|
||||
|
||||
This model was contributed by [eitan-turok](https://huggingface.co/eitanturok) and [abhi-db](https://huggingface.co/abhi-db). The original code can be found [here](https://github.com/databricks/dbrx-instruct), though this may not be up to date.
|
||||
|
||||
This model was contributed by [eitan-turok](https://huggingface.co/eitanturok) and [abhi-db](https://huggingface.co/abhi-db). The original code can be found [here](https://github.com/databricks/dbrx-instruct).
|
||||
|
||||
## Usage Examples
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -43,7 +43,6 @@ A list of official Hugging Face and community (indicated by 🌎) resources to h
|
||||
<PipelineTag pipeline="object-detection"/>
|
||||
|
||||
- Demo notebooks regarding inference + fine-tuning on a custom dataset for [`DeformableDetrForObjectDetection`] can be found [here](https://github.com/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/tree/master/Deformable-DETR).
|
||||
- Scripts for finetuning [`DeformableDetrForObjectDetection`] with [`Trainer`] or [Accelerate](https://huggingface.co/docs/accelerate/index) can be found [here](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples/pytorch/object-detection).
|
||||
- See also: [Object detection task guide](../tasks/object_detection).
|
||||
|
||||
If you're interested in submitting a resource to be included here, please feel free to open a Pull Request and we'll review it! The resource should ideally demonstrate something new instead of duplicating an existing resource.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -68,34 +68,6 @@ This model was contributed by [nielsr](https://huggingface.co/nielsr). The Tenso
|
||||
*facebook/deit-base-patch16-384*. Note that one should use [`DeiTImageProcessor`] in order to
|
||||
prepare images for the model.
|
||||
|
||||
### Using Scaled Dot Product Attention (SDPA)
|
||||
|
||||
PyTorch includes a native scaled dot-product attention (SDPA) operator as part of `torch.nn.functional`. This function
|
||||
encompasses several implementations that can be applied depending on the inputs and the hardware in use. See the
|
||||
[official documentation](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.functional.scaled_dot_product_attention.html)
|
||||
or the [GPU Inference](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/en/perf_infer_gpu_one#pytorch-scaled-dot-product-attention)
|
||||
page for more information.
|
||||
|
||||
SDPA is used by default for `torch>=2.1.1` when an implementation is available, but you may also set
|
||||
`attn_implementation="sdpa"` in `from_pretrained()` to explicitly request SDPA to be used.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
from transformers import DeiTForImageClassification
|
||||
model = DeiTForImageClassification.from_pretrained("facebook/deit-base-distilled-patch16-224", attn_implementation="sdpa", torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For the best speedups, we recommend loading the model in half-precision (e.g. `torch.float16` or `torch.bfloat16`).
|
||||
|
||||
On a local benchmark (A100-40GB, PyTorch 2.3.0, OS Ubuntu 22.04) with `float32` and `facebook/deit-base-distilled-patch16-224` model, we saw the following speedups during inference.
|
||||
|
||||
| Batch size | Average inference time (ms), eager mode | Average inference time (ms), sdpa model | Speed up, Sdpa / Eager (x) |
|
||||
|--------------|-------------------------------------------|-------------------------------------------|------------------------------|
|
||||
| 1 | 8 | 6 | 1.33 |
|
||||
| 2 | 9 | 6 | 1.5 |
|
||||
| 4 | 9 | 6 | 1.5 |
|
||||
| 8 | 8 | 6 | 1.33 |
|
||||
|
||||
## Resources
|
||||
|
||||
A list of official Hugging Face and community (indicated by 🌎) resources to help you get started with DeiT.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -16,14 +16,6 @@ rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
# DETA
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
This model is in maintenance mode only, we don't accept any new PRs changing its code.
|
||||
If you run into any issues running this model, please reinstall the last version that supported this model: v4.40.2.
|
||||
You can do so by running the following command: `pip install -U transformers==4.40.2`.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
The DETA model was proposed in [NMS Strikes Back](https://arxiv.org/abs/2212.06137) by Jeffrey Ouyang-Zhang, Jang Hyun Cho, Xingyi Zhou, Philipp Krähenbühl.
|
||||
@ -47,8 +39,7 @@ The original code can be found [here](https://github.com/jozhang97/DETA).
|
||||
A list of official Hugging Face and community (indicated by 🌎) resources to help you get started with DETA.
|
||||
|
||||
- Demo notebooks for DETA can be found [here](https://github.com/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/tree/master/DETA).
|
||||
- Scripts for finetuning [`DetaForObjectDetection`] with [`Trainer`] or [Accelerate](https://huggingface.co/docs/accelerate/index) can be found [here](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples/pytorch/object-detection).
|
||||
- See also: [Object detection task guide](../tasks/object_detection).
|
||||
- See also: [Object detection task guide](../tasks/object_detection)
|
||||
|
||||
If you're interested in submitting a resource to be included here, please feel free to open a Pull Request and we'll review it! The resource should ideally demonstrate something new instead of duplicating an existing resource.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -162,9 +162,8 @@ A list of official Hugging Face and community (indicated by 🌎) resources to h
|
||||
|
||||
<PipelineTag pipeline="object-detection"/>
|
||||
|
||||
- All example notebooks illustrating fine-tuning [`DetrForObjectDetection`] and [`DetrForSegmentation`] on a custom dataset can be found [here](https://github.com/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/tree/master/DETR).
|
||||
- Scripts for finetuning [`DetrForObjectDetection`] with [`Trainer`] or [Accelerate](https://huggingface.co/docs/accelerate/index) can be found [here](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples/pytorch/object-detection).
|
||||
- See also: [Object detection task guide](../tasks/object_detection).
|
||||
- All example notebooks illustrating fine-tuning [`DetrForObjectDetection`] and [`DetrForSegmentation`] on a custom dataset an be found [here](https://github.com/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/tree/master/DETR).
|
||||
- See also: [Object detection task guide](../tasks/object_detection)
|
||||
|
||||
If you're interested in submitting a resource to be included here, please feel free to open a Pull Request and we'll review it! The resource should ideally demonstrate something new instead of duplicating an existing resource.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -16,36 +16,28 @@ rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
# EfficientFormer
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
This model is in maintenance mode only, we don't accept any new PRs changing its code.
|
||||
If you run into any issues running this model, please reinstall the last version that supported this model: v4.40.2.
|
||||
You can do so by running the following command: `pip install -U transformers==4.40.2`.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
The EfficientFormer model was proposed in [EfficientFormer: Vision Transformers at MobileNet Speed](https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.01191)
|
||||
The EfficientFormer model was proposed in [EfficientFormer: Vision Transformers at MobileNet Speed](https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.01191)
|
||||
by Yanyu Li, Geng Yuan, Yang Wen, Eric Hu, Georgios Evangelidis, Sergey Tulyakov, Yanzhi Wang, Jian Ren. EfficientFormer proposes a
|
||||
dimension-consistent pure transformer that can be run on mobile devices for dense prediction tasks like image classification, object
|
||||
detection and semantic segmentation.
|
||||
|
||||
The abstract from the paper is the following:
|
||||
|
||||
*Vision Transformers (ViT) have shown rapid progress in computer vision tasks, achieving promising results on various benchmarks.
|
||||
However, due to the massive number of parameters and model design, e.g., attention mechanism, ViT-based models are generally
|
||||
times slower than lightweight convolutional networks. Therefore, the deployment of ViT for real-time applications is particularly
|
||||
challenging, especially on resource-constrained hardware such as mobile devices. Recent efforts try to reduce the computation
|
||||
complexity of ViT through network architecture search or hybrid design with MobileNet block, yet the inference speed is still
|
||||
unsatisfactory. This leads to an important question: can transformers run as fast as MobileNet while obtaining high performance?
|
||||
To answer this, we first revisit the network architecture and operators used in ViT-based models and identify inefficient designs.
|
||||
Then we introduce a dimension-consistent pure transformer (without MobileNet blocks) as a design paradigm.
|
||||
Finally, we perform latency-driven slimming to get a series of final models dubbed EfficientFormer.
|
||||
Extensive experiments show the superiority of EfficientFormer in performance and speed on mobile devices.
|
||||
Our fastest model, EfficientFormer-L1, achieves 79.2% top-1 accuracy on ImageNet-1K with only 1.6 ms inference latency on
|
||||
iPhone 12 (compiled with CoreML), which { runs as fast as MobileNetV2×1.4 (1.6 ms, 74.7% top-1),} and our largest model,
|
||||
EfficientFormer-L7, obtains 83.3% accuracy with only 7.0 ms latency. Our work proves that properly designed transformers can
|
||||
*Vision Transformers (ViT) have shown rapid progress in computer vision tasks, achieving promising results on various benchmarks.
|
||||
However, due to the massive number of parameters and model design, e.g., attention mechanism, ViT-based models are generally
|
||||
times slower than lightweight convolutional networks. Therefore, the deployment of ViT for real-time applications is particularly
|
||||
challenging, especially on resource-constrained hardware such as mobile devices. Recent efforts try to reduce the computation
|
||||
complexity of ViT through network architecture search or hybrid design with MobileNet block, yet the inference speed is still
|
||||
unsatisfactory. This leads to an important question: can transformers run as fast as MobileNet while obtaining high performance?
|
||||
To answer this, we first revisit the network architecture and operators used in ViT-based models and identify inefficient designs.
|
||||
Then we introduce a dimension-consistent pure transformer (without MobileNet blocks) as a design paradigm.
|
||||
Finally, we perform latency-driven slimming to get a series of final models dubbed EfficientFormer.
|
||||
Extensive experiments show the superiority of EfficientFormer in performance and speed on mobile devices.
|
||||
Our fastest model, EfficientFormer-L1, achieves 79.2% top-1 accuracy on ImageNet-1K with only 1.6 ms inference latency on
|
||||
iPhone 12 (compiled with CoreML), which { runs as fast as MobileNetV2×1.4 (1.6 ms, 74.7% top-1),} and our largest model,
|
||||
EfficientFormer-L7, obtains 83.3% accuracy with only 7.0 ms latency. Our work proves that properly designed transformers can
|
||||
reach extremely low latency on mobile devices while maintaining high performance.*
|
||||
|
||||
This model was contributed by [novice03](https://huggingface.co/novice03) and [Bearnardd](https://huggingface.co/Bearnardd).
|
||||
@ -101,4 +93,4 @@ The original code can be found [here](https://github.com/snap-research/Efficient
|
||||
- call
|
||||
|
||||
</tf>
|
||||
</frameworkcontent>
|
||||
</frameworkcontent>
|
||||
@ -16,14 +16,6 @@ rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
# ErnieM
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
This model is in maintenance mode only, we don't accept any new PRs changing its code.
|
||||
If you run into any issues running this model, please reinstall the last version that supported this model: v4.40.2.
|
||||
You can do so by running the following command: `pip install -U transformers==4.40.2`.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
The ErnieM model was proposed in [ERNIE-M: Enhanced Multilingual Representation by Aligning
|
||||
|
||||
@ -60,11 +60,6 @@ This model was contributed by [Arthur Zucker](https://huggingface.co/ArthurZ), [
|
||||
[[autodoc]] GemmaForSequenceClassification
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
## GemmaForTokenClassification
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] GemmaForTokenClassification
|
||||
- forward
|
||||
|
||||
## FlaxGemmaModel
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] FlaxGemmaModel
|
||||
|
||||
@ -127,64 +127,6 @@ Below is an expected speedup diagram that compares pure inference time between t
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/EduardoPacheco/documentation-images/resolve/main/gpt2_flash_attention_2_speedup.jpg">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Using Scaled Dot Product Attention (SDPA)
|
||||
PyTorch includes a native scaled dot-product attention (SDPA) operator as part of `torch.nn.functional`. This function
|
||||
encompasses several implementations that can be applied depending on the inputs and the hardware in use. See the
|
||||
[official documentation](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.functional.scaled_dot_product_attention.html)
|
||||
or the [GPU Inference](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/en/perf_infer_gpu_one#pytorch-scaled-dot-product-attention)
|
||||
page for more information.
|
||||
|
||||
SDPA is used by default for `torch>=2.1.1` when an implementation is available, but you may also set
|
||||
`attn_implementation="sdpa"` in `from_pretrained()` to explicitly request SDPA to be used.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("gpt2", torch_dtype=torch.float16, attn_implementation="sdpa")
|
||||
...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For the best speedups, we recommend loading the model in half-precision (e.g. `torch.float16` or `torch.bfloat16`).
|
||||
|
||||
On a local benchmark (rtx3080ti-16GB, PyTorch 2.2.1, OS Ubuntu 22.04) using `float16` with
|
||||
[gpt2-large](https://huggingface.co/openai-community/gpt2-large), we saw the
|
||||
following speedups during training and inference.
|
||||
|
||||
### Training
|
||||
| Batch size | Seq len | Time per batch (Eager - s) | Time per batch (SDPA - s) | Speedup (%) | Eager peak mem (MB) | SDPA peak mem (MB) | Mem saving (%) |
|
||||
|-----------:|--------:|----------------------------:|--------------------------:|------------:|--------------------:|-------------------:|------------------:|
|
||||
| 1 | 128 | 0.039 | 0.032 | 23.042 | 3482.32 | 3494.62 | -0.352 |
|
||||
| 1 | 256 | 0.073 | 0.059 | 25.15 | 3546.66 | 3552.6 | -0.167 |
|
||||
| 1 | 512 | 0.155 | 0.118 | 30.96 | 4230.1 | 3665.59 | 15.4 |
|
||||
| 1 | 1024 | 0.316 | 0.209 | 50.839 | 8682.26 | 4881.09 | 77.875 |
|
||||
| 2 | 128 | 0.07 | 0.06 | 15.324 | 3557.8 | 3545.91 | 0.335 |
|
||||
| 2 | 256 | 0.143 | 0.122 | 16.53 | 3901.5 | 3657.68 | 6.666 |
|
||||
| 2 | 512 | 0.267 | 0.213 | 25.626 | 7062.21 | 4876.47 | 44.822 |
|
||||
| 2 | 1024 | OOM | 0.404 | / | OOM | 8096.35 | SDPA does not OOM |
|
||||
| 4 | 128 | 0.134 | 0.128 | 4.412 | 3675.79 | 3648.72 | 0.742 |
|
||||
| 4 | 256 | 0.243 | 0.217 | 12.292 | 6129.76 | 4871.12 | 25.839 |
|
||||
| 4 | 512 | 0.494 | 0.406 | 21.687 | 12466.6 | 8102.64 | 53.858 |
|
||||
| 4 | 1024 | OOM | 0.795 | / | OOM | 14568.2 | SDPA does not OOM |
|
||||
|
||||
### Inference
|
||||
| Batch size | Seq len | Per token latency Eager (ms) | Per token latency SDPA (ms) | Speedup (%) | Mem Eager (MB) | Mem SDPA (MB) | Mem saved (%) |
|
||||
|-----------:|--------:|-----------------------------:|----------------------------:|------------:|---------------:|--------------:|--------------:|
|
||||
| 1 | 128 | 7.991 | 6.968 | 14.681 | 1685.2 | 1701.32 | -0.947 |
|
||||
| 1 | 256 | 8.462 | 7.199 | 17.536 | 1745.49 | 1770.78 | -1.428 |
|
||||
| 1 | 512 | 8.68 | 7.853 | 10.529 | 1907.69 | 1921.29 | -0.708 |
|
||||
| 1 | 768 | 9.101 | 8.365 | 8.791 | 2032.93 | 2068.12 | -1.701 |
|
||||
| 2 | 128 | 9.169 | 9.001 | 1.861 | 1803.84 | 1811.4 | -0.418 |
|
||||
| 2 | 256 | 9.907 | 9.78 | 1.294 | 1907.72 | 1921.44 | -0.714 |
|
||||
| 2 | 512 | 11.519 | 11.644 | -1.071 | 2176.86 | 2197.75 | -0.951 |
|
||||
| 2 | 768 | 13.022 | 13.407 | -2.873 | 2464.3 | 2491.06 | -1.074 |
|
||||
| 4 | 128 | 10.097 | 9.831 | 2.709 | 1942.25 | 1985.13 | -2.16 |
|
||||
| 4 | 256 | 11.599 | 11.398 | 1.764 | 2177.28 | 2197.86 | -0.937 |
|
||||
| 4 | 512 | 14.653 | 14.45 | 1.411 | 2753.16 | 2772.57 | -0.7 |
|
||||
| 4 | 768 | 17.846 | 17.617 | 1.299 | 3327.04 | 3343.97 | -0.506 |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Resources
|
||||
|
||||
A list of official Hugging Face and community (indicated by 🌎) resources to help you get started with GPT2. If you're interested in submitting a resource to be included here, please feel free to open a Pull Request and we'll review it! The resource should ideally demonstrate something new instead of duplicating an existing resource.
|
||||
|
||||
Some files were not shown because too many files have changed in this diff Show More
Reference in New Issue
Block a user