mirror of
https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git
synced 2025-10-21 17:48:57 +08:00
Compare commits
35 Commits
feat/conti
...
add_pipeli
| Author | SHA1 | Date | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1f93b12f69 | |||
| 4c3fb8ffff | |||
| 123a9e64a8 | |||
| a0bcb233e8 | |||
| 5e040e66f5 | |||
| 35d0592327 | |||
| bdfde76bec | |||
| 8f7050fd7d | |||
| 2221ceffe1 | |||
| b15cf4ff87 | |||
| ddeb6790c8 | |||
| 3d2c477371 | |||
| 6db83ab5e5 | |||
| 12fcfcfdb0 | |||
| 9ce2faa767 | |||
| 98b5dd447b | |||
| 3fd294dd31 | |||
| bd84dc2427 | |||
| c6069d72b5 | |||
| 021ae205c6 | |||
| 04fe7ad4ba | |||
| c4b5c1f21f | |||
| 6c7de21eb8 | |||
| 046f4367f8 | |||
| 298fb37491 | |||
| 3983fcc247 | |||
| 8d2a10bd9a | |||
| 80a578d4cc | |||
| 71569fd19a | |||
| d951519efe | |||
| f7e508735d | |||
| aa4d9c4f11 | |||
| 9b3d877def | |||
| 55614541e1 | |||
| 7a6090b28a |
@ -7,25 +7,12 @@ parameters:
|
||||
nightly:
|
||||
type: boolean
|
||||
default: false
|
||||
GHA_Actor:
|
||||
type: string
|
||||
default: ""
|
||||
GHA_Action:
|
||||
type: string
|
||||
default: ""
|
||||
GHA_Event:
|
||||
type: string
|
||||
default: ""
|
||||
GHA_Meta:
|
||||
type: string
|
||||
default: ""
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
# Ensure running with CircleCI/huggingface
|
||||
check_circleci_user:
|
||||
docker:
|
||||
- image: python:3.10-slim
|
||||
resource_class: small
|
||||
parallelism: 1
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- run: echo $CIRCLE_PROJECT_USERNAME
|
||||
@ -60,25 +47,25 @@ jobs:
|
||||
|
||||
- run:
|
||||
name: "Retrieve Artifact Paths"
|
||||
# [reference] https://circleci.com/docs/api/v2/index.html#operation/getJobArtifacts
|
||||
# `CIRCLE_TOKEN` is defined as an environment variables set within a context, see `https://circleci.com/docs/contexts/`
|
||||
env:
|
||||
CIRCLE_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.CI_ARTIFACT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
command: |
|
||||
project_slug="gh/${CIRCLE_PROJECT_USERNAME}/${CIRCLE_PROJECT_REPONAME}"
|
||||
job_number=${CIRCLE_BUILD_NUM}
|
||||
url="https://circleci.com/api/v2/project/${project_slug}/${job_number}/artifacts"
|
||||
curl -o test_preparation/artifacts.json ${url} --header "Circle-Token: $CIRCLE_TOKEN"
|
||||
curl -o test_preparation/artifacts.json ${url}
|
||||
- run:
|
||||
name: "Prepare pipeline parameters"
|
||||
command: |
|
||||
python utils/process_test_artifacts.py
|
||||
|
||||
python utils/process_test_artifacts.py
|
||||
|
||||
# To avoid too long generated_config.yaml on the continuation orb, we pass the links to the artifacts as parameters.
|
||||
# Otherwise the list of tests was just too big. Explicit is good but for that it was a limitation.
|
||||
# We used:
|
||||
|
||||
# https://circleci.com/docs/api/v2/index.html#operation/getJobArtifacts : to get the job artifacts
|
||||
# We could not pass a nested dict, which is why we create the test_file_... parameters for every single job
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- store_artifacts:
|
||||
path: test_preparation/transformed_artifacts.json
|
||||
- store_artifacts:
|
||||
@ -95,47 +82,22 @@ jobs:
|
||||
parallelism: 1
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- checkout
|
||||
- run: uv pip install -U -e .
|
||||
- run: echo 'export "GIT_COMMIT_MESSAGE=$(git show -s --format=%s)"' >> "$BASH_ENV" && source "$BASH_ENV"
|
||||
- run: mkdir -p test_preparation
|
||||
- run: python utils/tests_fetcher.py --fetch_all | tee tests_fetched_summary.txt
|
||||
- run: python utils/tests_fetcher.py --filter_tests
|
||||
- run: export "GIT_COMMIT_MESSAGE=$(git show -s --format=%s)" && echo $GIT_COMMIT_MESSAGE && python .circleci/create_circleci_config.py --fetcher_folder test_preparation
|
||||
- run: uv pip install -e .
|
||||
- run: |
|
||||
if [ ! -s test_preparation/generated_config.yml ]; then
|
||||
echo "No tests to run, exiting early!"
|
||||
circleci-agent step halt
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
mkdir test_preparation
|
||||
echo -n "tests" > test_preparation/test_list.txt
|
||||
echo -n "all" > test_preparation/examples_test_list.txt
|
||||
echo -n "tests/repo_utils" > test_preparation/test_repo_utils.txt
|
||||
- run: |
|
||||
echo -n "tests" > test_list.txt
|
||||
python utils/tests_fetcher.py --filter_tests
|
||||
mv test_list.txt test_preparation/filtered_test_list.txt
|
||||
- run: python .circleci/create_circleci_config.py --fetcher_folder test_preparation
|
||||
- run: cp test_preparation/generated_config.yml test_preparation/generated_config.txt
|
||||
- store_artifacts:
|
||||
path: test_preparation
|
||||
|
||||
- run:
|
||||
name: "Retrieve Artifact Paths"
|
||||
command: |
|
||||
project_slug="gh/${CIRCLE_PROJECT_USERNAME}/${CIRCLE_PROJECT_REPONAME}"
|
||||
job_number=${CIRCLE_BUILD_NUM}
|
||||
url="https://circleci.com/api/v2/project/${project_slug}/${job_number}/artifacts"
|
||||
curl -o test_preparation/artifacts.json ${url}
|
||||
- run:
|
||||
name: "Prepare pipeline parameters"
|
||||
command: |
|
||||
python utils/process_test_artifacts.py
|
||||
|
||||
# To avoid too long generated_config.yaml on the continuation orb, we pass the links to the artifacts as parameters.
|
||||
# Otherwise the list of tests was just too big. Explicit is good but for that it was a limitation.
|
||||
# We used:
|
||||
|
||||
# https://circleci.com/docs/api/v2/index.html#operation/getJobArtifacts : to get the job artifacts
|
||||
# We could not pass a nested dict, which is why we create the test_file_... parameters for every single job
|
||||
|
||||
- store_artifacts:
|
||||
path: test_preparation/transformed_artifacts.json
|
||||
- store_artifacts:
|
||||
path: test_preparation/artifacts.json
|
||||
path: test_preparation/generated_config.txt
|
||||
- continuation/continue:
|
||||
parameters: test_preparation/transformed_artifacts.json
|
||||
configuration_path: test_preparation/generated_config.yml
|
||||
configuration_path: test_preparation/generated_config.yml
|
||||
|
||||
check_code_quality:
|
||||
working_directory: ~/transformers
|
||||
@ -148,7 +110,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
parallelism: 1
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- checkout
|
||||
- run: uv pip install -e ".[quality]"
|
||||
- run: uv pip install -e .
|
||||
- run:
|
||||
name: Show installed libraries and their versions
|
||||
command: pip freeze | tee installed.txt
|
||||
@ -156,7 +118,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
path: ~/transformers/installed.txt
|
||||
- run: python -c "from transformers import *" || (echo '🚨 import failed, this means you introduced unprotected imports! 🚨'; exit 1)
|
||||
- run: ruff check examples tests src utils
|
||||
- run: ruff format examples tests src utils --check
|
||||
- run: ruff format tests src utils --check
|
||||
- run: python utils/custom_init_isort.py --check_only
|
||||
- run: python utils/sort_auto_mappings.py --check_only
|
||||
- run: python utils/check_doc_toc.py
|
||||
@ -173,14 +135,14 @@ jobs:
|
||||
parallelism: 1
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- checkout
|
||||
- run: uv pip install -e ".[quality]"
|
||||
- run: uv pip install -e .
|
||||
- run:
|
||||
name: Show installed libraries and their versions
|
||||
command: pip freeze | tee installed.txt
|
||||
- store_artifacts:
|
||||
path: ~/transformers/installed.txt
|
||||
- run: python utils/check_copies.py
|
||||
- run: python utils/check_modular_conversion.py
|
||||
- run: python utils/check_table.py
|
||||
- run: python utils/check_dummies.py
|
||||
- run: python utils/check_repo.py
|
||||
- run: python utils/check_inits.py
|
||||
@ -190,33 +152,19 @@ jobs:
|
||||
- run: make deps_table_check_updated
|
||||
- run: python utils/update_metadata.py --check-only
|
||||
- run: python utils/check_docstrings.py
|
||||
- run: python utils/check_support_list.py
|
||||
|
||||
workflows:
|
||||
version: 2
|
||||
setup_and_quality:
|
||||
when:
|
||||
and:
|
||||
- equal: [<<pipeline.project.git_url>>, https://github.com/huggingface/transformers]
|
||||
- not: <<pipeline.parameters.nightly>>
|
||||
not: <<pipeline.parameters.nightly>>
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
- check_circleci_user
|
||||
- check_code_quality
|
||||
- check_repository_consistency
|
||||
- fetch_tests
|
||||
|
||||
setup_and_quality_2:
|
||||
when:
|
||||
not:
|
||||
equal: [<<pipeline.project.git_url>>, https://github.com/huggingface/transformers]
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
- check_circleci_user
|
||||
- check_code_quality
|
||||
- check_repository_consistency
|
||||
- fetch_tests:
|
||||
# [reference] https://circleci.com/docs/contexts/
|
||||
context:
|
||||
- TRANSFORMERS_CONTEXT
|
||||
|
||||
nightly:
|
||||
when: <<pipeline.parameters.nightly>>
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -28,54 +28,21 @@ COMMON_ENV_VARIABLES = {
|
||||
"TRANSFORMERS_IS_CI": True,
|
||||
"PYTEST_TIMEOUT": 120,
|
||||
"RUN_PIPELINE_TESTS": False,
|
||||
# will be adjust in `CircleCIJob.to_dict`.
|
||||
"RUN_FLAKY": True,
|
||||
"RUN_PT_TF_CROSS_TESTS": False,
|
||||
"RUN_PT_FLAX_CROSS_TESTS": False,
|
||||
}
|
||||
# Disable the use of {"s": None} as the output is way too long, causing the navigation on CircleCI impractical
|
||||
COMMON_PYTEST_OPTIONS = {"max-worker-restart": 0, "vvv": None, "rsfE":None}
|
||||
COMMON_PYTEST_OPTIONS = {"max-worker-restart": 0, "dist": "loadfile", "vvv": None, "rsf":None}
|
||||
DEFAULT_DOCKER_IMAGE = [{"image": "cimg/python:3.8.12"}]
|
||||
|
||||
# Strings that commonly appear in the output of flaky tests when they fail. These are used with `pytest-rerunfailures`
|
||||
# to rerun the tests that match these patterns.
|
||||
FLAKY_TEST_FAILURE_PATTERNS = [
|
||||
"OSError", # Machine/connection transient error
|
||||
"Timeout", # Machine/connection transient error
|
||||
"ConnectionError", # Connection transient error
|
||||
"FileNotFoundError", # Raised by `datasets` on Hub failures
|
||||
"PIL.UnidentifiedImageError", # Raised by `PIL.Image.open` on connection issues
|
||||
"HTTPError", # Also catches HfHubHTTPError
|
||||
"AssertionError: Tensor-likes are not close!", # `torch.testing.assert_close`, we might have unlucky random values
|
||||
# TODO: error downloading tokenizer's `merged.txt` from hub can cause all the exceptions below. Throw and handle
|
||||
# them under a single message.
|
||||
"TypeError: expected str, bytes or os.PathLike object, not NoneType",
|
||||
"TypeError: stat: path should be string, bytes, os.PathLike or integer, not NoneType",
|
||||
"Converting from Tiktoken failed",
|
||||
"KeyError: <class ",
|
||||
"TypeError: not a string",
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class EmptyJob:
|
||||
job_name = "empty"
|
||||
|
||||
def to_dict(self):
|
||||
steps = [{"run": 'ls -la'}]
|
||||
if self.job_name == "collection_job":
|
||||
steps.extend(
|
||||
[
|
||||
"checkout",
|
||||
{"run": "pip install requests || true"},
|
||||
{"run": """while [[ $(curl --location --request GET "https://circleci.com/api/v2/workflow/$CIRCLE_WORKFLOW_ID/job" --header "Circle-Token: $CCI_TOKEN"| jq -r '.items[]|select(.name != "collection_job")|.status' | grep -c "running") -gt 0 ]]; do sleep 5; done || true"""},
|
||||
{"run": 'python utils/process_circleci_workflow_test_reports.py --workflow_id $CIRCLE_WORKFLOW_ID || true'},
|
||||
{"store_artifacts": {"path": "outputs"}},
|
||||
{"run": 'echo "All required jobs have now completed"'},
|
||||
]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
return {
|
||||
"docker": copy.deepcopy(DEFAULT_DOCKER_IMAGE),
|
||||
"resource_class": "small",
|
||||
"steps": steps,
|
||||
"steps":["checkout"],
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -87,9 +54,9 @@ class CircleCIJob:
|
||||
install_steps: List[str] = None
|
||||
marker: Optional[str] = None
|
||||
parallelism: Optional[int] = 0
|
||||
pytest_num_workers: int = 8
|
||||
pytest_num_workers: int = 12
|
||||
pytest_options: Dict[str, Any] = None
|
||||
resource_class: Optional[str] = "xlarge"
|
||||
resource_class: Optional[str] = "2xlarge"
|
||||
tests_to_run: Optional[List[str]] = None
|
||||
num_test_files_per_worker: Optional[int] = 10
|
||||
# This should be only used for doctest job!
|
||||
@ -128,8 +95,6 @@ class CircleCIJob:
|
||||
|
||||
def to_dict(self):
|
||||
env = COMMON_ENV_VARIABLES.copy()
|
||||
# Do not run tests decorated by @is_flaky on pull requests
|
||||
env['RUN_FLAKY'] = os.environ.get("CIRCLE_PULL_REQUEST", "") == ""
|
||||
env.update(self.additional_env)
|
||||
|
||||
job = {
|
||||
@ -147,9 +112,7 @@ class CircleCIJob:
|
||||
# Examples special case: we need to download NLTK files in advance to avoid cuncurrency issues
|
||||
timeout_cmd = f"timeout {self.command_timeout} " if self.command_timeout else ""
|
||||
marker_cmd = f"-m '{self.marker}'" if self.marker is not None else ""
|
||||
junit_flags = f" -p no:warning -o junit_family=xunit1 --junitxml=test-results/junit.xml"
|
||||
joined_flaky_patterns = "|".join(FLAKY_TEST_FAILURE_PATTERNS)
|
||||
repeat_on_failure_flags = f"--reruns 5 --reruns-delay 2 --only-rerun '({joined_flaky_patterns})'"
|
||||
additional_flags = f" -p no:warning -o junit_family=xunit1 --junitxml=test-results/junit.xml"
|
||||
parallel = f' << pipeline.parameters.{self.job_name}_parallelism >> '
|
||||
steps = [
|
||||
"checkout",
|
||||
@ -170,15 +133,14 @@ class CircleCIJob:
|
||||
"command": """dpkg-query --show --showformat='${Installed-Size}\t${Package}\n' | sort -rh | head -25 | sort -h | awk '{ package=$2; sub(".*/", "", package); printf("%.5f GB %s\n", $1/1024/1024, package)}' || true"""}
|
||||
},
|
||||
{"run": {"name": "Create `test-results` directory", "command": "mkdir test-results"}},
|
||||
{"run": {"name": "Get files to test", "command":f'curl -L -o {self.job_name}_test_list.txt <<pipeline.parameters.{self.job_name}_test_list>> --header "Circle-Token: $CIRCLE_TOKEN"' if self.name != "pr_documentation_tests" else 'echo "Skipped"'}},
|
||||
{"run": {"name": "Get files to test", "command":f'curl -L -o {self.job_name}_test_list.txt <<pipeline.parameters.{self.job_name}_test_list>>' if self.name != "pr_documentation_tests" else 'echo "Skipped"'}},
|
||||
{"run": {"name": "Split tests across parallel nodes: show current parallel tests",
|
||||
"command": f"TESTS=$(circleci tests split --split-by=timings {self.job_name}_test_list.txt) && echo $TESTS > splitted_tests.txt && echo $TESTS | tr ' ' '\n'" if self.parallelism else f"awk '{{printf \"%s \", $0}}' {self.job_name}_test_list.txt > splitted_tests.txt"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
{"run": {"name": "fetch hub objects before pytest", "command": "python3 utils/fetch_hub_objects_for_ci.py"}},
|
||||
{"run": {
|
||||
"name": "Run tests",
|
||||
"command": f"({timeout_cmd} python3 -m pytest {marker_cmd} -n {self.pytest_num_workers} {junit_flags} {repeat_on_failure_flags} {' '.join(pytest_flags)} $(cat splitted_tests.txt) | tee tests_output.txt)"}
|
||||
"command": f"({timeout_cmd} python3 -m pytest {marker_cmd} -n {self.pytest_num_workers} {additional_flags} {' '.join(pytest_flags)} $(cat splitted_tests.txt) | tee tests_output.txt)"}
|
||||
},
|
||||
{"run": {"name": "Expand to show skipped tests", "when": "always", "command": f"python3 .circleci/parse_test_outputs.py --file tests_output.txt --skip"}},
|
||||
{"run": {"name": "Failed tests: show reasons", "when": "always", "command": f"python3 .circleci/parse_test_outputs.py --file tests_output.txt --fail"}},
|
||||
@ -201,39 +163,58 @@ class CircleCIJob:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# JOBS
|
||||
torch_and_tf_job = CircleCIJob(
|
||||
"torch_and_tf",
|
||||
docker_image=[{"image":"huggingface/transformers-torch-tf-light"}],
|
||||
additional_env={"RUN_PT_TF_CROSS_TESTS": True},
|
||||
marker="is_pt_tf_cross_test",
|
||||
pytest_options={"rA": None, "durations": 0},
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
torch_and_flax_job = CircleCIJob(
|
||||
"torch_and_flax",
|
||||
additional_env={"RUN_PT_FLAX_CROSS_TESTS": True},
|
||||
docker_image=[{"image":"huggingface/transformers-torch-jax-light"}],
|
||||
marker="is_pt_flax_cross_test",
|
||||
pytest_options={"rA": None, "durations": 0},
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
torch_job = CircleCIJob(
|
||||
"torch",
|
||||
docker_image=[{"image": "huggingface/transformers-torch-light"}],
|
||||
marker="not generate",
|
||||
parallelism=6,
|
||||
pytest_num_workers=8
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
generate_job = CircleCIJob(
|
||||
"generate",
|
||||
docker_image=[{"image": "huggingface/transformers-torch-light"}],
|
||||
# networkx==3.3 (after #36957) cause some issues
|
||||
# TODO: remove this once it works directly
|
||||
install_steps=["uv venv && uv pip install ."],
|
||||
marker="generate",
|
||||
parallelism=6,
|
||||
pytest_num_workers=8
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
tokenization_job = CircleCIJob(
|
||||
"tokenization",
|
||||
docker_image=[{"image": "huggingface/transformers-torch-light"}],
|
||||
parallelism=8,
|
||||
pytest_num_workers=16
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
processor_job = CircleCIJob(
|
||||
"processors",
|
||||
docker_image=[{"image": "huggingface/transformers-torch-light"}],
|
||||
parallelism=8,
|
||||
pytest_num_workers=6
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
tf_job = CircleCIJob(
|
||||
"tf",
|
||||
docker_image=[{"image":"huggingface/transformers-tf-light"}],
|
||||
parallelism=6,
|
||||
pytest_num_workers=16,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -241,8 +222,7 @@ flax_job = CircleCIJob(
|
||||
"flax",
|
||||
docker_image=[{"image":"huggingface/transformers-jax-light"}],
|
||||
parallelism=6,
|
||||
pytest_num_workers=16,
|
||||
resource_class="2xlarge",
|
||||
pytest_num_workers=16
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -251,7 +231,7 @@ pipelines_torch_job = CircleCIJob(
|
||||
additional_env={"RUN_PIPELINE_TESTS": True},
|
||||
docker_image=[{"image":"huggingface/transformers-torch-light"}],
|
||||
marker="is_pipeline_test",
|
||||
parallelism=4,
|
||||
parallelism=4
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -260,7 +240,7 @@ pipelines_tf_job = CircleCIJob(
|
||||
additional_env={"RUN_PIPELINE_TESTS": True},
|
||||
docker_image=[{"image":"huggingface/transformers-tf-light"}],
|
||||
marker="is_pipeline_test",
|
||||
parallelism=4,
|
||||
parallelism=4
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -277,7 +257,7 @@ examples_torch_job = CircleCIJob(
|
||||
docker_image=[{"image":"huggingface/transformers-examples-torch"}],
|
||||
# TODO @ArthurZucker remove this once docker is easier to build
|
||||
install_steps=["uv venv && uv pip install . && uv pip install -r examples/pytorch/_tests_requirements.txt"],
|
||||
pytest_num_workers=4,
|
||||
pytest_num_workers=8,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -285,7 +265,7 @@ examples_tensorflow_job = CircleCIJob(
|
||||
"examples_tensorflow",
|
||||
additional_env={"OMP_NUM_THREADS": 8},
|
||||
docker_image=[{"image":"huggingface/transformers-examples-tf"}],
|
||||
pytest_num_workers=2,
|
||||
pytest_num_workers=16,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -300,7 +280,6 @@ hub_job = CircleCIJob(
|
||||
],
|
||||
marker="is_staging_test",
|
||||
pytest_num_workers=2,
|
||||
resource_class="medium",
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -309,17 +288,17 @@ onnx_job = CircleCIJob(
|
||||
docker_image=[{"image":"huggingface/transformers-torch-tf-light"}],
|
||||
install_steps=[
|
||||
"uv venv",
|
||||
"uv pip install .[testing,sentencepiece,onnxruntime,vision,rjieba]",
|
||||
"uv pip install .[torch,tf,testing,sentencepiece,onnxruntime,vision,rjieba]",
|
||||
],
|
||||
pytest_options={"k onnx": None},
|
||||
pytest_num_workers=1,
|
||||
resource_class="small",
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
exotic_models_job = CircleCIJob(
|
||||
"exotic_models",
|
||||
docker_image=[{"image":"huggingface/transformers-exotic-models"}],
|
||||
pytest_num_workers=12,
|
||||
parallelism=4,
|
||||
pytest_options={"durations": 100},
|
||||
)
|
||||
@ -333,17 +312,6 @@ repo_utils_job = CircleCIJob(
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
non_model_job = CircleCIJob(
|
||||
"non_model",
|
||||
docker_image=[{"image": "huggingface/transformers-torch-light"}],
|
||||
# networkx==3.3 (after #36957) cause some issues
|
||||
# TODO: remove this once it works directly
|
||||
install_steps=["uv venv && uv pip install ."],
|
||||
marker="not generate",
|
||||
parallelism=6,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# We also include a `dummy.py` file in the files to be doc-tested to prevent edge case failure. Otherwise, the pytest
|
||||
# hangs forever during test collection while showing `collecting 0 items / 21 errors`. (To see this, we have to remove
|
||||
# the bash output redirection.)
|
||||
@ -368,14 +336,13 @@ doc_test_job = CircleCIJob(
|
||||
pytest_num_workers=1,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
REGULAR_TESTS = [torch_job, flax_job, hub_job, onnx_job, tokenization_job, processor_job, generate_job, non_model_job] # fmt: skip
|
||||
EXAMPLES_TESTS = [examples_torch_job]
|
||||
PIPELINE_TESTS = [pipelines_torch_job]
|
||||
REGULAR_TESTS = [torch_and_tf_job, torch_and_flax_job, torch_job, tf_job, flax_job, hub_job, onnx_job, tokenization_job, processor_job, generate_job] # fmt: skip
|
||||
EXAMPLES_TESTS = [examples_torch_job, examples_tensorflow_job]
|
||||
PIPELINE_TESTS = [pipelines_torch_job, pipelines_tf_job]
|
||||
REPO_UTIL_TESTS = [repo_utils_job]
|
||||
DOC_TESTS = [doc_test_job]
|
||||
ALL_TESTS = REGULAR_TESTS + EXAMPLES_TESTS + PIPELINE_TESTS + REPO_UTIL_TESTS + DOC_TESTS + [custom_tokenizers_job] + [exotic_models_job] # fmt: skip
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def create_circleci_config(folder=None):
|
||||
if folder is None:
|
||||
folder = os.getcwd()
|
||||
@ -385,35 +352,19 @@ def create_circleci_config(folder=None):
|
||||
|
||||
if len(jobs) == 0:
|
||||
jobs = [EmptyJob()]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
print("Full list of job name inputs", {j.job_name + "_test_list":{"type":"string", "default":''} for j in jobs})
|
||||
# Add a job waiting all the test jobs and aggregate their test summary files at the end
|
||||
collection_job = EmptyJob()
|
||||
collection_job.job_name = "collection_job"
|
||||
jobs = [collection_job] + jobs
|
||||
|
||||
print("Full list of job name inputs", {j.job_name + "_test_list":{"type":"string", "default":''} for j in jobs})
|
||||
config = {
|
||||
"version": "2.1",
|
||||
"parameters": {
|
||||
# Only used to accept the parameters from the trigger
|
||||
"nightly": {"type": "boolean", "default": False},
|
||||
# Only used to accept the parameters from GitHub Actions trigger
|
||||
"GHA_Actor": {"type": "string", "default": ""},
|
||||
"GHA_Action": {"type": "string", "default": ""},
|
||||
"GHA_Event": {"type": "string", "default": ""},
|
||||
"GHA_Meta": {"type": "string", "default": ""},
|
||||
"tests_to_run": {"type": "string", "default": ""},
|
||||
"tests_to_run": {"type": "string", "default": ''},
|
||||
**{j.job_name + "_test_list":{"type":"string", "default":''} for j in jobs},
|
||||
**{j.job_name + "_parallelism":{"type":"integer", "default":1} for j in jobs},
|
||||
},
|
||||
"jobs": {j.job_name: j.to_dict() for j in jobs}
|
||||
"jobs" : {j.job_name: j.to_dict() for j in jobs},
|
||||
"workflows": {"version": 2, "run_tests": {"jobs": [j.job_name for j in jobs]}}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if "CIRCLE_TOKEN" in os.environ:
|
||||
# For private forked repo. (e.g. new model addition)
|
||||
config["workflows"] = {"version": 2, "run_tests": {"jobs": [{j.job_name: {"context": ["TRANSFORMERS_CONTEXT"]}} for j in jobs]}}
|
||||
else:
|
||||
# For public repo. (e.g. `transformers`)
|
||||
config["workflows"] = {"version": 2, "run_tests": {"jobs": [j.job_name for j in jobs]}}
|
||||
with open(os.path.join(folder, "generated_config.yml"), "w") as f:
|
||||
f.write(yaml.dump(config, sort_keys=False, default_flow_style=False).replace("' << pipeline", " << pipeline").replace(">> '", " >>"))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
21
.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/bug-report.yml
vendored
21
.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/bug-report.yml
vendored
@ -16,7 +16,7 @@ body:
|
||||
id: system-info
|
||||
attributes:
|
||||
label: System Info
|
||||
description: Please share your system info with us. You can run the command `transformers env` and copy-paste its output below.
|
||||
description: Please share your system info with us. You can run the command `transformers-cli env` and copy-paste its output below.
|
||||
placeholder: transformers version, platform, python version, ...
|
||||
validations:
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
@ -38,30 +38,24 @@ body:
|
||||
|
||||
- text models: @ArthurZucker
|
||||
- vision models: @amyeroberts, @qubvel
|
||||
- speech models: @eustlb
|
||||
- speech models: @ylacombe, @eustlb
|
||||
- graph models: @clefourrier
|
||||
|
||||
Library:
|
||||
|
||||
- flax: @gante and @Rocketknight1
|
||||
- flax: @sanchit-gandhi
|
||||
- generate: @zucchini-nlp (visual-language models) or @gante (all others)
|
||||
- pipelines: @Rocketknight1
|
||||
- tensorflow: @gante and @Rocketknight1
|
||||
- tokenizers: @ArthurZucker and @itazap
|
||||
- trainer: @zach-huggingface @SunMarc
|
||||
- trainer: @muellerzr @SunMarc
|
||||
|
||||
Integrations:
|
||||
|
||||
- deepspeed: HF Trainer/Accelerate: @SunMarc @zach-huggingface
|
||||
- deepspeed: HF Trainer/Accelerate: @muellerzr
|
||||
- ray/raytune: @richardliaw, @amogkam
|
||||
- Big Model Inference: @SunMarc
|
||||
- quantization (bitsandbytes, autogpt): @SunMarc @MekkCyber
|
||||
|
||||
Devices/Backends:
|
||||
|
||||
- AMD ROCm: @ivarflakstad
|
||||
- Intel XPU: @IlyasMoutawwakil
|
||||
- Ascend NPU: @ivarflakstad
|
||||
- quantization (bitsandbytes, autogpt): @SunMarc
|
||||
|
||||
Documentation: @stevhliu
|
||||
|
||||
@ -78,7 +72,7 @@ body:
|
||||
|
||||
Maintained examples (not research project or legacy):
|
||||
|
||||
- Flax: @Rocketknight1
|
||||
- Flax: @sanchit-gandhi
|
||||
- PyTorch: See Models above and tag the person corresponding to the modality of the example.
|
||||
- TensorFlow: @Rocketknight1
|
||||
|
||||
@ -112,7 +106,6 @@ body:
|
||||
label: Reproduction
|
||||
description: |
|
||||
Please provide a code sample that reproduces the problem you ran into. It can be a Colab link or just a code snippet.
|
||||
Please include relevant config information with your code, for example your Trainers, TRL, Peft, and DeepSpeed configs.
|
||||
If you have code snippets, error messages, stack traces please provide them here as well.
|
||||
Important! Use code tags to correctly format your code. See https://help.github.com/en/github/writing-on-github/creating-and-highlighting-code-blocks#syntax-highlighting
|
||||
Do not use screenshots, as they are hard to read and (more importantly) don't allow others to copy-and-paste your code.
|
||||
|
||||
2
.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/i18n.md
vendored
2
.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/i18n.md
vendored
@ -23,7 +23,7 @@ Some notes:
|
||||
* Please translate in a gender-neutral way.
|
||||
* Add your translations to the folder called `<languageCode>` inside the [source folder](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/docs/source).
|
||||
* Register your translation in `<languageCode>/_toctree.yml`; please follow the order of the [English version](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/docs/source/en/_toctree.yml).
|
||||
* Once you're finished, open a pull request and tag this issue by including #issue-number in the description, where issue-number is the number of this issue. Please ping @stevhliu for review.
|
||||
* Once you're finished, open a pull request and tag this issue by including #issue-number in the description, where issue-number is the number of this issue. Please ping @stevhliu and @MKhalusova for review.
|
||||
* 🙋 If you'd like others to help you with the translation, you can also post in the 🤗 [forums](https://discuss.huggingface.co/).
|
||||
|
||||
## Get Started section
|
||||
|
||||
2
.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/migration.yml
vendored
2
.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/migration.yml
vendored
@ -6,7 +6,7 @@ body:
|
||||
id: system-info
|
||||
attributes:
|
||||
label: System Info
|
||||
description: Please share your system info with us. You can run the command `transformers env` and copy-paste its output below.
|
||||
description: Please share your system info with us. You can run the command `transformers-cli env` and copy-paste its output below.
|
||||
render: shell
|
||||
placeholder: transformers version, platform, python version, ...
|
||||
validations:
|
||||
|
||||
12
.github/PULL_REQUEST_TEMPLATE.md
vendored
12
.github/PULL_REQUEST_TEMPLATE.md
vendored
@ -41,25 +41,25 @@ Models:
|
||||
|
||||
- text models: @ArthurZucker
|
||||
- vision models: @amyeroberts, @qubvel
|
||||
- speech models: @eustlb
|
||||
- speech models: @ylacombe, @eustlb
|
||||
- graph models: @clefourrier
|
||||
|
||||
Library:
|
||||
|
||||
- flax: @gante and @Rocketknight1
|
||||
- flax: @sanchit-gandhi
|
||||
- generate: @zucchini-nlp (visual-language models) or @gante (all others)
|
||||
- pipelines: @Rocketknight1
|
||||
- tensorflow: @gante and @Rocketknight1
|
||||
- tokenizers: @ArthurZucker
|
||||
- trainer: @zach-huggingface and @SunMarc
|
||||
- trainer: @muellerzr and @SunMarc
|
||||
- chat templates: @Rocketknight1
|
||||
|
||||
Integrations:
|
||||
|
||||
- deepspeed: HF Trainer/Accelerate: @SunMarc @zach-huggingface
|
||||
- deepspeed: HF Trainer/Accelerate: @muellerzr
|
||||
- ray/raytune: @richardliaw, @amogkam
|
||||
- Big Model Inference: @SunMarc
|
||||
- quantization (bitsandbytes, autogpt): @SunMarc @MekkCyber
|
||||
- quantization (bitsandbytes, autogpt): @SunMarc
|
||||
|
||||
Documentation: @stevhliu
|
||||
|
||||
@ -72,7 +72,7 @@ HF projects:
|
||||
|
||||
Maintained examples (not research project or legacy):
|
||||
|
||||
- Flax: @Rocketknight1
|
||||
- Flax: @sanchit-gandhi
|
||||
- PyTorch: See Models above and tag the person corresponding to the modality of the example.
|
||||
- TensorFlow: @Rocketknight1
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
120
.github/scripts/assign_reviewers.py
vendored
120
.github/scripts/assign_reviewers.py
vendored
@ -1,120 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# coding=utf-8
|
||||
# Copyright 2025 the HuggingFace Inc. team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import github
|
||||
import json
|
||||
from github import Github
|
||||
import re
|
||||
from collections import Counter
|
||||
from pathlib import Path
|
||||
|
||||
def pattern_to_regex(pattern):
|
||||
if pattern.startswith("/"):
|
||||
start_anchor = True
|
||||
pattern = re.escape(pattern[1:])
|
||||
else:
|
||||
start_anchor = False
|
||||
pattern = re.escape(pattern)
|
||||
# Replace `*` with "any number of non-slash characters"
|
||||
pattern = pattern.replace(r"\*", "[^/]*")
|
||||
if start_anchor:
|
||||
pattern = r"^\/?" + pattern # Allow an optional leading slash after the start of the string
|
||||
return pattern
|
||||
|
||||
def get_file_owners(file_path, codeowners_lines):
|
||||
# Process lines in reverse (last matching pattern takes precedence)
|
||||
for line in reversed(codeowners_lines):
|
||||
# Skip comments and empty lines, strip inline comments
|
||||
line = line.split('#')[0].strip()
|
||||
if not line:
|
||||
continue
|
||||
|
||||
# Split into pattern and owners
|
||||
parts = line.split()
|
||||
pattern = parts[0]
|
||||
# Can be empty, e.g. for dummy files with explicitly no owner!
|
||||
owners = [owner.removeprefix("@") for owner in parts[1:]]
|
||||
|
||||
# Check if file matches pattern
|
||||
file_regex = pattern_to_regex(pattern)
|
||||
if re.search(file_regex, file_path) is not None:
|
||||
return owners # Remember, can still be empty!
|
||||
return [] # Should never happen, but just in case
|
||||
|
||||
def pr_author_is_in_hf(pr_author, codeowners_lines):
|
||||
# Check if the PR author is in the codeowners file
|
||||
for line in codeowners_lines:
|
||||
line = line.split('#')[0].strip()
|
||||
if not line:
|
||||
continue
|
||||
|
||||
# Split into pattern and owners
|
||||
parts = line.split()
|
||||
owners = [owner.removeprefix("@") for owner in parts[1:]]
|
||||
|
||||
if pr_author in owners:
|
||||
return True
|
||||
return False
|
||||
|
||||
def main():
|
||||
script_dir = Path(__file__).parent.absolute()
|
||||
with open(script_dir / "codeowners_for_review_action") as f:
|
||||
codeowners_lines = f.readlines()
|
||||
|
||||
g = Github(os.environ['GITHUB_TOKEN'])
|
||||
repo = g.get_repo("huggingface/transformers")
|
||||
with open(os.environ['GITHUB_EVENT_PATH']) as f:
|
||||
event = json.load(f)
|
||||
|
||||
# The PR number is available in the event payload
|
||||
pr_number = event['pull_request']['number']
|
||||
pr = repo.get_pull(pr_number)
|
||||
pr_author = pr.user.login
|
||||
if pr_author_is_in_hf(pr_author, codeowners_lines):
|
||||
print(f"PR author {pr_author} is in codeowners, skipping review request.")
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
||||
existing_reviews = list(pr.get_reviews())
|
||||
if existing_reviews:
|
||||
print(f"Already has reviews: {[r.user.login for r in existing_reviews]}")
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
||||
users_requested, teams_requested = pr.get_review_requests()
|
||||
users_requested = list(users_requested)
|
||||
if users_requested:
|
||||
print(f"Reviewers already requested: {users_requested}")
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
||||
locs_per_owner = Counter()
|
||||
for file in pr.get_files():
|
||||
owners = get_file_owners(file.filename, codeowners_lines)
|
||||
for owner in owners:
|
||||
locs_per_owner[owner] += file.changes
|
||||
|
||||
# Assign the top 2 based on locs changed as reviewers, but skip the owner if present
|
||||
locs_per_owner.pop(pr_author, None)
|
||||
top_owners = locs_per_owner.most_common(2)
|
||||
print("Top owners", top_owners)
|
||||
top_owners = [owner[0] for owner in top_owners]
|
||||
try:
|
||||
pr.create_review_request(top_owners)
|
||||
except github.GithubException as e:
|
||||
print(f"Failed to request review for {top_owners}: {e}")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
main()
|
||||
370
.github/scripts/codeowners_for_review_action
vendored
370
.github/scripts/codeowners_for_review_action
vendored
@ -1,370 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Top-level rules are matched only if nothing else matches
|
||||
* @Rocketknight1 @ArthurZucker # if no one is pinged based on the other rules, he will do the dispatch
|
||||
*.md @stevhliu
|
||||
*tokenization* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
docs/ @stevhliu
|
||||
/benchmark/ @McPatate
|
||||
/docker/ @ydshieh @ArthurZucker
|
||||
|
||||
# More high-level globs catch cases when specific rules later don't apply
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/*/processing* @molbap @yonigozlan @qubvel
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/*/image_processing* @qubvel
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/*/image_processing_*_fast* @yonigozlan
|
||||
|
||||
# Owners of subsections of the library
|
||||
/src/transformers/generation/ @gante
|
||||
/src/transformers/pipeline/ @Rocketknight1 @yonigozlan
|
||||
/src/transformers/integrations/ @SunMarc @MekkCyber @zach-huggingface
|
||||
/src/transformers/quantizers/ @SunMarc @MekkCyber
|
||||
tests/ @ydshieh
|
||||
tests/generation/ @gante
|
||||
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/auto/ @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/utils/ @ArthurZucker @Rocketknight1
|
||||
/src/transformers/loss/ @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/onnx/ @michaelbenayoun
|
||||
|
||||
# Specific files come after the sections/globs, so they take priority
|
||||
/.circleci/config.yml @ArthurZucker @ydshieh
|
||||
/utils/tests_fetcher.py @ydshieh
|
||||
trainer.py @zach-huggingface @SunMarc
|
||||
trainer_utils.py @zach-huggingface @SunMarc
|
||||
/utils/modular_model_converter.py @Cyrilvallez @ArthurZucker
|
||||
|
||||
# Owners of individual models are specific / high priority, and so they come last
|
||||
# mod* captures modeling and modular files
|
||||
|
||||
# Text models
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/albert/mod*_albert* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/bamba/mod*_bamba* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/bart/mod*_bart* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/barthez/mod*_barthez* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/bartpho/mod*_bartpho* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/bert/mod*_bert* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/bert_generation/mod*_bert_generation* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/bert_japanese/mod*_bert_japanese* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/bertweet/mod*_bertweet* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/big_bird/mod*_big_bird* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/bigbird_pegasus/mod*_bigbird_pegasus* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/biogpt/mod*_biogpt* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/blenderbot/mod*_blenderbot* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/blenderbot_small/mod*_blenderbot_small* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/bloom/mod*_bloom* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/bort/mod*_bort* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/byt5/mod*_byt5* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/camembert/mod*_camembert* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/canine/mod*_canine* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/codegen/mod*_codegen* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/code_llama/mod*_code_llama* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/cohere/mod*_cohere* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/cohere2/mod*_cohere2* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/convbert/mod*_convbert* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/cpm/mod*_cpm* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/cpmant/mod*_cpmant* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/ctrl/mod*_ctrl* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/dbrx/mod*_dbrx* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/deberta/mod*_deberta* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/deberta_v2/mod*_deberta_v2* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/dialogpt/mod*_dialogpt* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/diffllama/mod*_diffllama* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/distilbert/mod*_distilbert* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/dpr/mod*_dpr* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/electra/mod*_electra* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/encoder_decoder/mod*_encoder_decoder* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/ernie/mod*_ernie* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/ernie_m/mod*_ernie_m* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/esm/mod*_esm* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/falcon/mod*_falcon* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/falcon3/mod*_falcon3* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/falcon_mamba/mod*_falcon_mamba* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/fastspeech2_conformer/mod*_fastspeech2_conformer* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/flan_t5/mod*_flan_t5* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/flan_ul2/mod*_flan_ul2* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/flaubert/mod*_flaubert* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/fnet/mod*_fnet* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/fsmt/mod*_fsmt* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/funnel/mod*_funnel* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/fuyu/mod*_fuyu* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/gemma/mod*_gemma* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/gemma2/mod*_gemma2* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/glm/mod*_glm* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/openai_gpt/mod*_openai_gpt* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/gpt_neo/mod*_gpt_neo* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/gpt_neox/mod*_gpt_neox* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/gpt_neox_japanese/mod*_gpt_neox_japanese* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/gptj/mod*_gptj* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/gpt2/mod*_gpt2* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/gpt_bigcode/mod*_gpt_bigcode* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/gptsan_japanese/mod*_gptsan_japanese* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/gpt_sw3/mod*_gpt_sw3* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/granite/mod*_granite* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/granitemoe/mod*_granitemoe* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/herbert/mod*_herbert* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/ibert/mod*_ibert* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/jamba/mod*_jamba* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/jetmoe/mod*_jetmoe* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/jukebox/mod*_jukebox* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/led/mod*_led* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/llama/mod*_llama* @ArthurZucker @Cyrilvallez
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/longformer/mod*_longformer* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/longt5/mod*_longt5* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/luke/mod*_luke* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/m2m_100/mod*_m2m_100* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/madlad_400/mod*_madlad_400* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/mamba/mod*_mamba* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/mamba2/mod*_mamba2* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/marian/mod*_marian* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/markuplm/mod*_markuplm* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/mbart/mod*_mbart* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/mega/mod*_mega* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/megatron_bert/mod*_megatron_bert* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/megatron_gpt2/mod*_megatron_gpt2* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/mistral/mod*_mistral* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/mixtral/mod*_mixtral* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/mluke/mod*_mluke* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/mobilebert/mod*_mobilebert* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/modernbert/mod*_modernbert* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/mpnet/mod*_mpnet* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/mpt/mod*_mpt* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/mra/mod*_mra* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/mt5/mod*_mt5* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/mvp/mod*_mvp* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/myt5/mod*_myt5* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/nemotron/mod*_nemotron* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/nezha/mod*_nezha* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/nllb/mod*_nllb* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/nllb_moe/mod*_nllb_moe* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/nystromformer/mod*_nystromformer* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/olmo/mod*_olmo* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/olmo2/mod*_olmo2* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/olmoe/mod*_olmoe* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/open_llama/mod*_open_llama* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/opt/mod*_opt* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/pegasus/mod*_pegasus* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/pegasus_x/mod*_pegasus_x* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/persimmon/mod*_persimmon* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/phi/mod*_phi* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/phi3/mod*_phi3* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/phimoe/mod*_phimoe* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/phobert/mod*_phobert* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/plbart/mod*_plbart* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/prophetnet/mod*_prophetnet* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/qdqbert/mod*_qdqbert* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/qwen2/mod*_qwen2* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/qwen2_moe/mod*_qwen2_moe* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/rag/mod*_rag* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/realm/mod*_realm* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/recurrent_gemma/mod*_recurrent_gemma* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/reformer/mod*_reformer* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/rembert/mod*_rembert* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/retribert/mod*_retribert* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/roberta/mod*_roberta* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/roberta_prelayernorm/mod*_roberta_prelayernorm* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/roc_bert/mod*_roc_bert* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/roformer/mod*_roformer* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/rwkv/mod*_rwkv* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/splinter/mod*_splinter* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/squeezebert/mod*_squeezebert* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/stablelm/mod*_stablelm* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/starcoder2/mod*_starcoder2* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/switch_transformers/mod*_switch_transformers* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/t5/mod*_t5* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/t5v1.1/mod*_t5v1.1* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/tapex/mod*_tapex* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/transfo_xl/mod*_transfo_xl* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/ul2/mod*_ul2* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/umt5/mod*_umt5* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/xmod/mod*_xmod* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/xglm/mod*_xglm* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/xlm/mod*_xlm* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/xlm_prophetnet/mod*_xlm_prophetnet* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/xlm_roberta/mod*_xlm_roberta* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/xlm_roberta_xl/mod*_xlm_roberta_xl* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/xlm_v/mod*_xlm_v* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/xlnet/mod*_xlnet* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/yoso/mod*_yoso* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/zamba/mod*_zamba* @ArthurZucker
|
||||
|
||||
# Vision models
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/beit/mod*_beit* @amyeroberts @qubvel
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/bit/mod*_bit* @amyeroberts @qubvel
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/conditional_detr/mod*_conditional_detr* @amyeroberts @qubvel
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/convnext/mod*_convnext* @amyeroberts @qubvel
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/convnextv2/mod*_convnextv2* @amyeroberts @qubvel
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/cvt/mod*_cvt* @amyeroberts @qubvel
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/deformable_detr/mod*_deformable_detr* @amyeroberts @qubvel
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/deit/mod*_deit* @amyeroberts @qubvel
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/depth_anything/mod*_depth_anything* @amyeroberts @qubvel
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/depth_anything_v2/mod*_depth_anything_v2* @amyeroberts @qubvel
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/deta/mod*_deta* @amyeroberts @qubvel
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/detr/mod*_detr* @amyeroberts @qubvel
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/dinat/mod*_dinat* @amyeroberts @qubvel
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/dinov2/mod*_dinov2* @amyeroberts @qubvel
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/dinov2_with_registers/mod*_dinov2_with_registers* @amyeroberts @qubvel
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/dit/mod*_dit* @amyeroberts @qubvel
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/dpt/mod*_dpt* @amyeroberts @qubvel
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/efficientformer/mod*_efficientformer* @amyeroberts @qubvel
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/efficientnet/mod*_efficientnet* @amyeroberts @qubvel
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/focalnet/mod*_focalnet* @amyeroberts @qubvel
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/glpn/mod*_glpn* @amyeroberts @qubvel
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/hiera/mod*_hiera* @amyeroberts @qubvel
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/ijepa/mod*_ijepa* @amyeroberts @qubvel
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/imagegpt/mod*_imagegpt* @amyeroberts @qubvel
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/levit/mod*_levit* @amyeroberts @qubvel
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/mask2former/mod*_mask2former* @amyeroberts @qubvel
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/maskformer/mod*_maskformer* @amyeroberts @qubvel
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/mobilenet_v1/mod*_mobilenet_v1* @amyeroberts @qubvel
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/mobilenet_v2/mod*_mobilenet_v2* @amyeroberts @qubvel
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/mobilevit/mod*_mobilevit* @amyeroberts @qubvel
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/mobilevitv2/mod*_mobilevitv2* @amyeroberts @qubvel
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/nat/mod*_nat* @amyeroberts @qubvel
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/poolformer/mod*_poolformer* @amyeroberts @qubvel
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/pvt/mod*_pvt* @amyeroberts @qubvel
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/pvt_v2/mod*_pvt_v2* @amyeroberts @qubvel
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/regnet/mod*_regnet* @amyeroberts @qubvel
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/resnet/mod*_resnet* @amyeroberts @qubvel
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/rt_detr/mod*_rt_detr* @amyeroberts @qubvel
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/segformer/mod*_segformer* @amyeroberts @qubvel
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/seggpt/mod*_seggpt* @amyeroberts @qubvel
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/superpoint/mod*_superpoint* @amyeroberts @qubvel
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/swiftformer/mod*_swiftformer* @amyeroberts @qubvel
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/swin/mod*_swin* @amyeroberts @qubvel
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/swinv2/mod*_swinv2* @amyeroberts @qubvel
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/swin2sr/mod*_swin2sr* @amyeroberts @qubvel
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/table_transformer/mod*_table_transformer* @amyeroberts @qubvel
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/textnet/mod*_textnet* @amyeroberts @qubvel
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/timm_wrapper/mod*_timm_wrapper* @amyeroberts @qubvel
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/upernet/mod*_upernet* @amyeroberts @qubvel
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/van/mod*_van* @amyeroberts @qubvel
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/vit/mod*_vit* @amyeroberts @qubvel
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/vit_hybrid/mod*_vit_hybrid* @amyeroberts @qubvel
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/vitdet/mod*_vitdet* @amyeroberts @qubvel
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/vit_mae/mod*_vit_mae* @amyeroberts @qubvel
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/vitmatte/mod*_vitmatte* @amyeroberts @qubvel
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/vit_msn/mod*_vit_msn* @amyeroberts @qubvel
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/vitpose/mod*_vitpose* @amyeroberts @qubvel
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/yolos/mod*_yolos* @amyeroberts @qubvel
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/zoedepth/mod*_zoedepth* @amyeroberts @qubvel
|
||||
|
||||
# Audio models
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/audio_spectrogram_transformer/mod*_audio_spectrogram_transformer* @eustlb
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/bark/mod*_bark* @eustlb
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/clap/mod*_clap* @eustlb
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/dac/mod*_dac* @eustlb
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/encodec/mod*_encodec* @eustlb
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/hubert/mod*_hubert* @eustlb
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/mctct/mod*_mctct* @eustlb
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/mimi/mod*_mimi* @eustlb
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/mms/mod*_mms* @eustlb
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/moshi/mod*_moshi* @eustlb
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/musicgen/mod*_musicgen* @eustlb
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/musicgen_melody/mod*_musicgen_melody* @eustlb
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/pop2piano/mod*_pop2piano* @eustlb
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/seamless_m4t/mod*_seamless_m4t* @eustlb
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/seamless_m4t_v2/mod*_seamless_m4t_v2* @eustlb
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/sew/mod*_sew* @eustlb
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/sew_d/mod*_sew_d* @eustlb
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/speech_to_text/mod*_speech_to_text* @eustlb
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/speech_to_text_2/mod*_speech_to_text_2* @eustlb
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/speecht5/mod*_speecht5* @eustlb
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/unispeech/mod*_unispeech* @eustlb
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/unispeech_sat/mod*_unispeech_sat* @eustlb
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/univnet/mod*_univnet* @eustlb
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/vits/mod*_vits* @eustlb
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/wav2vec2/mod*_wav2vec2* @eustlb
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/wav2vec2_bert/mod*_wav2vec2_bert* @eustlb
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/wav2vec2_conformer/mod*_wav2vec2_conformer* @eustlb
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/wav2vec2_phoneme/mod*_wav2vec2_phoneme* @eustlb
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/wavlm/mod*_wavlm* @eustlb
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/whisper/mod*_whisper* @eustlb
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/xls_r/mod*_xls_r* @eustlb
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/xlsr_wav2vec2/mod*_xlsr_wav2vec2* @eustlb
|
||||
|
||||
# Video models
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/timesformer/mod*_timesformer* @Rocketknight1
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/videomae/mod*_videomae* @Rocketknight1
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/vivit/mod*_vivit* @Rocketknight1
|
||||
|
||||
# Multimodal models
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/align/mod*_align* @zucchini-nlp
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/altclip/mod*_altclip* @zucchini-nlp
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/aria/mod*_aria* @zucchini-nlp
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/blip/mod*_blip* @zucchini-nlp
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/blip_2/mod*_blip_2* @zucchini-nlp
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/bridgetower/mod*_bridgetower* @zucchini-nlp
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/bros/mod*_bros* @zucchini-nlp
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/chameleon/mod*_chameleon* @zucchini-nlp
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/chinese_clip/mod*_chinese_clip* @zucchini-nlp
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/clip/mod*_clip* @zucchini-nlp
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/clipseg/mod*_clipseg* @zucchini-nlp
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/clvp/mod*_clvp* @zucchini-nlp
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/colpali/mod*_colpali* @zucchini-nlp @yonigozlan
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/data2vec/mod*_data2vec* @zucchini-nlp
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/deplot/mod*_deplot* @zucchini-nlp
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/donut/mod*_donut* @zucchini-nlp
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/flava/mod*_flava* @zucchini-nlp
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/git/mod*_git* @zucchini-nlp
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/grounding_dino/mod*_grounding_dino* @qubvel
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/groupvit/mod*_groupvit* @zucchini-nlp
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/idefics/mod*_idefics* @zucchini-nlp
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/idefics2/mod*_idefics2* @zucchini-nlp
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/idefics3/mod*_idefics3* @zucchini-nlp
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/instructblip/mod*_instructblip* @zucchini-nlp
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/instructblipvideo/mod*_instructblipvideo* @zucchini-nlp
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/kosmos_2/mod*_kosmos_2* @zucchini-nlp
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/layoutlm/mod*_layoutlm* @NielsRogge
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/layoutlmv2/mod*_layoutlmv2* @NielsRogge
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/layoutlmv3/mod*_layoutlmv3* @NielsRogge
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/layoutxlm/mod*_layoutxlm* @NielsRogge
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/lilt/mod*_lilt* @zucchini-nlp
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/llava/mod*_llava* @zucchini-nlp @arthurzucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/llava_next/mod*_llava_next* @zucchini-nlp
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/llava_next_video/mod*_llava_next_video* @zucchini-nlp
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/llava_onevision/mod*_llava_onevision* @zucchini-nlp
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/lxmert/mod*_lxmert* @zucchini-nlp
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/matcha/mod*_matcha* @zucchini-nlp
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/mgp_str/mod*_mgp_str* @zucchini-nlp
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/mllama/mod*_mllama* @zucchini-nlp
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/nougat/mod*_nougat* @NielsRogge
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/omdet_turbo/mod*_omdet_turbo* @qubvel @yonigozlan
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/oneformer/mod*_oneformer* @zucchini-nlp
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/owlvit/mod*_owlvit* @qubvel
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/owlv2/mod*_owlv2* @qubvel
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/paligemma/mod*_paligemma* @zucchini-nlp @molbap
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/perceiver/mod*_perceiver* @zucchini-nlp
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/pix2struct/mod*_pix2struct* @zucchini-nlp
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/pixtral/mod*_pixtral* @zucchini-nlp @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/qwen2_audio/mod*_qwen2_audio* @zucchini-nlp @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/qwen2_vl/mod*_qwen2_vl* @zucchini-nlp @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/sam/mod*_sam* @zucchini-nlp @ArthurZucker
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/siglip/mod*_siglip* @zucchini-nlp
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/speech_encoder_decoder/mod*_speech_encoder_decoder* @zucchini-nlp
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/tapas/mod*_tapas* @NielsRogge
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/trocr/mod*_trocr* @zucchini-nlp
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/tvlt/mod*_tvlt* @zucchini-nlp
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/tvp/mod*_tvp* @zucchini-nlp
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/udop/mod*_udop* @zucchini-nlp
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/video_llava/mod*_video_llava* @zucchini-nlp
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/vilt/mod*_vilt* @zucchini-nlp
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/vipllava/mod*_vipllava* @zucchini-nlp
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/vision_encoder_decoder/mod*_vision_encoder_decoder* @Rocketknight1
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/vision_text_dual_encoder/mod*_vision_text_dual_encoder* @Rocketknight1
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/visual_bert/mod*_visual_bert* @zucchini-nlp
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/xclip/mod*_xclip* @zucchini-nlp
|
||||
|
||||
# Reinforcement learning models
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/decision_transformer/mod*_decision_transformer* @Rocketknight1
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/trajectory_transformer/mod*_trajectory_transformer* @Rocketknight1
|
||||
|
||||
# Time series models
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/autoformer/mod*_autoformer* @Rocketknight1
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/informer/mod*_informer* @Rocketknight1
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/patchtsmixer/mod*_patchtsmixer* @Rocketknight1
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/patchtst/mod*_patchtst* @Rocketknight1
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/time_series_transformer/mod*_time_series_transformer* @Rocketknight1
|
||||
|
||||
# Graph models
|
||||
/src/transformers/models/graphormer/mod*_graphormer* @clefourrier
|
||||
|
||||
# Finally, files with no owners that shouldn't generate pings, usually automatically generated and checked in the CI
|
||||
utils/dummy*
|
||||
2
.github/workflows/add-model-like.yml
vendored
2
.github/workflows/add-model-like.yml
vendored
@ -54,7 +54,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
- name: Create model files
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
. ~/venv/bin/activate
|
||||
transformers add-new-model-like --config_file tests/fixtures/add_distilbert_like_config.json --path_to_repo .
|
||||
transformers-cli add-new-model-like --config_file tests/fixtures/add_distilbert_like_config.json --path_to_repo .
|
||||
make style
|
||||
make fix-copies
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
26
.github/workflows/assign-reviewers.yml
vendored
26
.github/workflows/assign-reviewers.yml
vendored
@ -1,26 +0,0 @@
|
||||
name: Assign PR Reviewers
|
||||
on:
|
||||
pull_request_target:
|
||||
branches:
|
||||
- main
|
||||
types: [ready_for_review]
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
assign_reviewers:
|
||||
permissions:
|
||||
pull-requests: write
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-22.04
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
- name: Set up Python
|
||||
uses: actions/setup-python@v5
|
||||
with:
|
||||
python-version: '3.13'
|
||||
- name: Install dependencies
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m pip install --upgrade pip
|
||||
pip install PyGithub
|
||||
- name: Run assignment script
|
||||
env:
|
||||
GITHUB_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
|
||||
run: python .github/scripts/assign_reviewers.py
|
||||
78
.github/workflows/benchmark.yml
vendored
78
.github/workflows/benchmark.yml
vendored
@ -1,76 +1,42 @@
|
||||
name: Self-hosted runner (benchmark)
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
push:
|
||||
branches: [main]
|
||||
pull_request:
|
||||
types: [ opened, labeled, reopened, synchronize ]
|
||||
|
||||
concurrency:
|
||||
group: ${{ github.workflow }}-${{ github.head_ref || github.run_id }}
|
||||
cancel-in-progress: true
|
||||
schedule:
|
||||
- cron: "17 2 * * *"
|
||||
workflow_call:
|
||||
|
||||
env:
|
||||
HF_HOME: /mnt/cache
|
||||
TF_FORCE_GPU_ALLOW_GROWTH: true
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
benchmark:
|
||||
name: Benchmark
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
# group: [aws-g5-4xlarge-cache, aws-p4d-24xlarge-plus] (A100 runner is not enabled)
|
||||
group: [aws-g5-4xlarge-cache]
|
||||
runs-on:
|
||||
group: ${{ matrix.group }}
|
||||
if: |
|
||||
(github.event_name == 'pull_request' && contains( github.event.pull_request.labels.*.name, 'run-benchmark') )||
|
||||
(github.event_name == 'push' && github.ref == 'refs/heads/main')
|
||||
runs-on: [single-gpu, nvidia-gpu, a10, ci]
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: huggingface/transformers-pytorch-gpu
|
||||
options: --gpus all --privileged --ipc host
|
||||
image: huggingface/transformers-all-latest-gpu
|
||||
options: --gpus all --privileged --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Get repo
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
ref: ${{ github.event.pull_request.head.sha || github.sha }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Install libpq-dev & psql
|
||||
- name: Update clone
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
apt update
|
||||
apt install -y libpq-dev postgresql-client
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Install benchmark script dependencies
|
||||
run: python3 -m pip install -r benchmark/requirements.txt
|
||||
git fetch && git checkout ${{ github.sha }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Reinstall transformers in edit mode (remove the one installed during docker image build)
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: python3 -m pip uninstall -y transformers && python3 -m pip install -e ".[torch]"
|
||||
run: python3 -m pip uninstall -y transformers && python3 -m pip install -e .
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run database init script
|
||||
- name: Benchmark (daily)
|
||||
if: github.event_name == 'schedule'
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
psql -f benchmark/init_db.sql
|
||||
env:
|
||||
PGDATABASE: metrics
|
||||
PGHOST: ${{ secrets.TRANSFORMERS_BENCHMARKS_PGHOST }}
|
||||
PGUSER: transformers_benchmarks
|
||||
PGPASSWORD: ${{ secrets.TRANSFORMERS_BENCHMARKS_PGPASSWORD }}
|
||||
python3 -m pip install optimum-benchmark>=0.3.0
|
||||
HF_TOKEN=${{ secrets.TRANSFORMERS_BENCHMARK_TOKEN }} python3 benchmark/benchmark.py --repo_id hf-internal-testing/benchmark_results --path_in_repo $(date +'%Y-%m-%d') --config-dir benchmark/config --config-name generation --commit=${{ github.sha }} backend.model=google/gemma-2b backend.cache_implementation=null,static backend.torch_compile=false,true --multirun
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run benchmark
|
||||
- name: Benchmark (merged to main event)
|
||||
if: github.event_name == 'push' && github.ref_name == 'main'
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
git config --global --add safe.directory /__w/transformers/transformers
|
||||
if [ "$GITHUB_EVENT_NAME" = "pull_request" ]; then
|
||||
commit_id=$(echo "${{ github.event.pull_request.head.sha }}")
|
||||
elif [ "$GITHUB_EVENT_NAME" = "push" ]; then
|
||||
commit_id=$GITHUB_SHA
|
||||
fi
|
||||
commit_msg=$(git show -s --format=%s | cut -c1-70)
|
||||
python3 benchmark/benchmarks_entrypoint.py "huggingface/transformers" "$BRANCH_NAME" "$commit_id" "$commit_msg"
|
||||
env:
|
||||
HF_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.HF_HUB_READ_TOKEN }}
|
||||
# Enable this to see debug logs
|
||||
# HF_HUB_VERBOSITY: debug
|
||||
# TRANSFORMERS_VERBOSITY: debug
|
||||
PGHOST: ${{ secrets.TRANSFORMERS_BENCHMARKS_PGHOST }}
|
||||
PGUSER: transformers_benchmarks
|
||||
PGPASSWORD: ${{ secrets.TRANSFORMERS_BENCHMARKS_PGPASSWORD }}
|
||||
BRANCH_NAME: ${{ github.head_ref || github.ref_name }}
|
||||
python3 -m pip install optimum-benchmark>=0.3.0
|
||||
HF_TOKEN=${{ secrets.TRANSFORMERS_BENCHMARK_TOKEN }} python3 benchmark/benchmark.py --repo_id hf-internal-testing/benchmark_results_merge_event --path_in_repo $(date +'%Y-%m-%d') --config-dir benchmark/config --config-name generation --commit=${{ github.sha }} backend.model=google/gemma-2b backend.cache_implementation=null,static backend.torch_compile=false,true --multirun
|
||||
|
||||
6
.github/workflows/build-ci-docker-images.yml
vendored
6
.github/workflows/build-ci-docker-images.yml
vendored
@ -26,7 +26,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
file: ["quality", "consistency", "custom-tokenizers", "torch-light", "tf-light", "exotic-models", "torch-tf-light", "jax-light", "examples-torch", "examples-tf"]
|
||||
file: ["quality", "consistency", "custom-tokenizers", "torch-light", "tf-light", "exotic-models", "torch-tf-light", "torch-jax-light", "jax-light", "examples-torch", "examples-tf"]
|
||||
continue-on-error: true
|
||||
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
@ -34,11 +34,11 @@ jobs:
|
||||
name: Set tag
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
if ${{contains(github.event.head_commit.message, '[build-ci-image]')}}; then
|
||||
echo "TAG=huggingface/transformers-${{ matrix.file }}:dev" >> "$GITHUB_ENV"
|
||||
echo "TAG=huggingface/transformers-${{ matrix.file }}:dev" >> "$GITHUB_ENV"
|
||||
echo "setting it to DEV!"
|
||||
else
|
||||
echo "TAG=huggingface/transformers-${{ matrix.file }}" >> "$GITHUB_ENV"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
fi
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Set up Docker Buildx
|
||||
|
||||
70
.github/workflows/build-docker-images.yml
vendored
70
.github/workflows/build-docker-images.yml
vendored
@ -19,7 +19,7 @@ concurrency:
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
latest-docker:
|
||||
name: "Latest PyTorch [dev]"
|
||||
name: "Latest PyTorch + TensorFlow [dev]"
|
||||
runs-on:
|
||||
group: aws-general-8-plus
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
@ -63,14 +63,14 @@ jobs:
|
||||
uses: huggingface/hf-workflows/.github/actions/post-slack@main
|
||||
with:
|
||||
slack_channel: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_DOCKER }}
|
||||
title: 🤗 Results of the transformers-all-latest-gpu-push-ci docker build
|
||||
title: 🤗 Results of the transformers-all-latest-gpu-push-ci docker build
|
||||
status: ${{ job.status }}
|
||||
slack_token: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
|
||||
latest-torch-deepspeed-docker:
|
||||
name: "Latest PyTorch + DeepSpeed"
|
||||
runs-on:
|
||||
group: aws-g4dn-2xlarge-cache
|
||||
group: aws-general-8-plus
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Set up Docker Buildx
|
||||
@ -99,7 +99,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
uses: huggingface/hf-workflows/.github/actions/post-slack@main
|
||||
with:
|
||||
slack_channel: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_DOCKER}}
|
||||
title: 🤗 Results of the transformers-pytorch-deepspeed-latest-gpu docker build
|
||||
title: 🤗 Results of the transformers-pytorch-deepspeed-latest-gpu docker build
|
||||
status: ${{ job.status }}
|
||||
slack_token: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -140,7 +140,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
uses: huggingface/hf-workflows/.github/actions/post-slack@main
|
||||
with:
|
||||
slack_channel: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_DOCKER }}
|
||||
title: 🤗 Results of the transformers-pytorch-deepspeed-latest-gpu-push-ci docker build
|
||||
title: 🤗 Results of the transformers-pytorch-deepspeed-latest-gpu-push-ci docker build
|
||||
status: ${{ job.status }}
|
||||
slack_token: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -176,7 +176,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
uses: huggingface/hf-workflows/.github/actions/post-slack@main
|
||||
with:
|
||||
slack_channel: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_DOCKER }}
|
||||
title: 🤗 Results of the huggingface/transformers-doc-builder docker build
|
||||
title: 🤗 Results of the huggingface/transformers-doc-builder docker build
|
||||
status: ${{ job.status }}
|
||||
slack_token: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -214,7 +214,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
uses: huggingface/hf-workflows/.github/actions/post-slack@main
|
||||
with:
|
||||
slack_channel: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_DOCKER }}
|
||||
title: 🤗 Results of the huggingface/transformers-pytorch-gpudocker build
|
||||
title: 🤗 Results of the huggingface/transformers-pytorch-gpudocker build
|
||||
status: ${{ job.status }}
|
||||
slack_token: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -223,19 +223,19 @@ jobs:
|
||||
runs-on:
|
||||
group: aws-general-8-plus
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
-
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Set up Docker Buildx
|
||||
uses: docker/setup-buildx-action@v3
|
||||
-
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Check out code
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
-
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Login to DockerHub
|
||||
uses: docker/login-action@v3
|
||||
with:
|
||||
username: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME }}
|
||||
password: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_PASSWORD }}
|
||||
-
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Build and push
|
||||
uses: docker/build-push-action@v5
|
||||
with:
|
||||
@ -263,12 +263,14 @@ jobs:
|
||||
uses: huggingface/hf-workflows/.github/actions/post-slack@main
|
||||
with:
|
||||
slack_channel: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_DOCKER }}
|
||||
title: 🤗 Results of the huggingface/transformers-pytorch-amd-gpu-push-ci build
|
||||
title: 🤗 Results of the huggingface/transformers-pytorch-amd-gpu-push-ci build
|
||||
status: ${{ job.status }}
|
||||
slack_token: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
|
||||
latest-pytorch-deepspeed-amd:
|
||||
name: "PyTorch + DeepSpeed (AMD) [dev]"
|
||||
latest-tensorflow:
|
||||
name: "Latest TensorFlow [dev]"
|
||||
# Push CI doesn't need this image
|
||||
if: inputs.image_postfix != '-push-ci'
|
||||
runs-on:
|
||||
group: aws-general-8-plus
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
@ -285,6 +287,42 @@ jobs:
|
||||
username: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME }}
|
||||
password: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_PASSWORD }}
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Build and push
|
||||
uses: docker/build-push-action@v5
|
||||
with:
|
||||
context: ./docker/transformers-tensorflow-gpu
|
||||
build-args: |
|
||||
REF=main
|
||||
push: true
|
||||
tags: huggingface/transformers-tensorflow-gpu
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Post to Slack
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
uses: huggingface/hf-workflows/.github/actions/post-slack@main
|
||||
with:
|
||||
slack_channel: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_DOCKER }}
|
||||
title: 🤗 Results of the huggingface/transformers-tensorflow-gpu build
|
||||
status: ${{ job.status }}
|
||||
slack_token: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
|
||||
latest-pytorch-deepspeed-amd:
|
||||
name: "PyTorch + DeepSpeed (AMD) [dev]"
|
||||
runs-on:
|
||||
group: aws-general-8-plus
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Set up Docker Buildx
|
||||
uses: docker/setup-buildx-action@v3
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Check out code
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Login to DockerHub
|
||||
uses: docker/login-action@v3
|
||||
with:
|
||||
username: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME }}
|
||||
password: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_PASSWORD }}
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Build and push
|
||||
uses: docker/build-push-action@v5
|
||||
with:
|
||||
@ -312,7 +350,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
uses: huggingface/hf-workflows/.github/actions/post-slack@main
|
||||
with:
|
||||
slack_channel: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_DOCKER }}
|
||||
title: 🤗 Results of the transformers-pytorch-deepspeed-amd-gpu build
|
||||
title: 🤗 Results of the transformers-pytorch-deepspeed-amd-gpu build
|
||||
status: ${{ job.status }}
|
||||
slack_token: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -350,6 +388,6 @@ jobs:
|
||||
uses: huggingface/hf-workflows/.github/actions/post-slack@main
|
||||
with:
|
||||
slack_channel: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_DOCKER }}
|
||||
title: 🤗 Results of the transformers-quantization-latest-gpu build
|
||||
title: 🤗 Results of the transformers-quantization-latest-gpu build
|
||||
status: ${{ job.status }}
|
||||
slack_token: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -42,7 +42,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
nightly-torch-deepspeed-docker:
|
||||
name: "Nightly PyTorch + DeepSpeed"
|
||||
runs-on:
|
||||
group: aws-g4dn-2xlarge-cache
|
||||
group: aws-general-8-plus
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
-
|
||||
name: Set up Docker Buildx
|
||||
|
||||
1
.github/workflows/build_documentation.yml
vendored
1
.github/workflows/build_documentation.yml
vendored
@ -1,7 +1,6 @@
|
||||
name: Build documentation
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
workflow_dispatch:
|
||||
push:
|
||||
branches:
|
||||
- main
|
||||
|
||||
18
.github/workflows/build_pr_documentation.yml
vendored
18
.github/workflows/build_pr_documentation.yml
vendored
@ -2,15 +2,6 @@ name: Build PR Documentation
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
pull_request:
|
||||
workflow_call:
|
||||
inputs:
|
||||
pr_number:
|
||||
type: string
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
commit_sha:
|
||||
type: string
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
concurrency:
|
||||
group: ${{ github.workflow }}-${{ github.head_ref || github.run_id }}
|
||||
@ -18,9 +9,10 @@ concurrency:
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
build:
|
||||
uses: huggingface/doc-builder/.github/workflows/build_pr_documentation.yml@6e2eb04a2604817c97be03786efa494fe3acae90
|
||||
uses: huggingface/doc-builder/.github/workflows/build_pr_documentation.yml@main
|
||||
with:
|
||||
commit_sha: ${{ inputs.commit_sha || github.event.pull_request.head.sha }}
|
||||
pr_number: ${{ inputs.pr_number || github.event.number }}
|
||||
commit_sha: ${{ github.event.pull_request.head.sha }}
|
||||
pr_number: ${{ github.event.number }}
|
||||
package: transformers
|
||||
languages: en
|
||||
languages: ar de en es fr hi it ko pt tr zh ja te
|
||||
custom_container: huggingface/transformers-doc-builder
|
||||
|
||||
205
.github/workflows/check_failed_tests.yml
vendored
205
.github/workflows/check_failed_tests.yml
vendored
@ -1,205 +0,0 @@
|
||||
name: Process failed tests
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
workflow_call:
|
||||
inputs:
|
||||
docker:
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
type: string
|
||||
start_sha:
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
type: string
|
||||
job:
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
type: string
|
||||
slack_report_channel:
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
type: string
|
||||
ci_event:
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
type: string
|
||||
report_repo_id:
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
type: string
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
env:
|
||||
HF_HOME: /mnt/cache
|
||||
TRANSFORMERS_IS_CI: yes
|
||||
OMP_NUM_THREADS: 8
|
||||
MKL_NUM_THREADS: 8
|
||||
RUN_SLOW: yes
|
||||
# For gated repositories, we still need to agree to share information on the Hub repo. page in order to get access.
|
||||
# This token is created under the bot `hf-transformers-bot`.
|
||||
HF_HUB_READ_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.HF_HUB_READ_TOKEN }}
|
||||
SIGOPT_API_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.SIGOPT_API_TOKEN }}
|
||||
TF_FORCE_GPU_ALLOW_GROWTH: true
|
||||
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES: 0,1
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
check_new_failures:
|
||||
name: " "
|
||||
runs-on:
|
||||
group: aws-g4dn-4xlarge-cache
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: ${{ inputs.docker }}
|
||||
options: --gpus all --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- uses: actions/download-artifact@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: ci_results_${{ inputs.job }}
|
||||
path: /transformers/ci_results_${{ inputs.job }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Check file
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
if [ -f ci_results_${{ inputs.job }}/new_failures.json ]; then
|
||||
echo "`ci_results_${{ inputs.job }}/new_failures.json` exists, continue ..."
|
||||
echo "process=true" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
else
|
||||
echo "`ci_results_${{ inputs.job }}/new_failures.json` doesn't exist, abort."
|
||||
echo "process=false" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
- uses: actions/download-artifact@v4
|
||||
if: ${{ env.process == 'true' }}
|
||||
with:
|
||||
pattern: setup_values*
|
||||
path: setup_values
|
||||
merge-multiple: true
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Prepare some setup values
|
||||
if: ${{ env.process == 'true' }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
if [ -f setup_values/prev_workflow_run_id.txt ]; then
|
||||
echo "PREV_WORKFLOW_RUN_ID=$(cat setup_values/prev_workflow_run_id.txt)" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
else
|
||||
echo "PREV_WORKFLOW_RUN_ID=" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
if [ -f setup_values/other_workflow_run_id.txt ]; then
|
||||
echo "OTHER_WORKFLOW_RUN_ID=$(cat setup_values/other_workflow_run_id.txt)" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
else
|
||||
echo "OTHER_WORKFLOW_RUN_ID=" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Update clone
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
if: ${{ env.process == 'true' }}
|
||||
run: git fetch && git checkout ${{ github.sha }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Get target commit
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers/utils
|
||||
if: ${{ env.process == 'true' }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "END_SHA=$(TOKEN=${{ secrets.ACCESS_REPO_INFO_TOKEN }} python3 -c 'import os; from get_previous_daily_ci import get_last_daily_ci_run_commit; commit=get_last_daily_ci_run_commit(token=os.environ["TOKEN"], workflow_run_id=os.environ["PREV_WORKFLOW_RUN_ID"]); print(commit)')" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Checkout to `start_sha`
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
if: ${{ env.process == 'true' }}
|
||||
run: git fetch && git checkout ${{ inputs.start_sha }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Reinstall transformers in edit mode (remove the one installed during docker image build)
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
if: ${{ env.process == 'true' }}
|
||||
run: python3 -m pip uninstall -y transformers && python3 -m pip install -e .
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NVIDIA-SMI
|
||||
if: ${{ env.process == 'true' }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
nvidia-smi
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Environment
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
if: ${{ env.process == 'true' }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python3 utils/print_env.py
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Show installed libraries and their versions
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
if: ${{ env.process == 'true' }}
|
||||
run: pip freeze
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Check failed tests
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
if: ${{ env.process == 'true' }}
|
||||
run: python3 utils/check_bad_commit.py --start_commit ${{ inputs.start_sha }} --end_commit ${{ env.END_SHA }} --file ci_results_${{ inputs.job }}/new_failures.json --output_file new_failures_with_bad_commit.json
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Show results
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
if: ${{ env.process == 'true' }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
ls -l new_failures_with_bad_commit.json
|
||||
cat new_failures_with_bad_commit.json
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Checkout back
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
if: ${{ env.process == 'true' }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
git checkout ${{ inputs.start_sha }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Process report
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
if: ${{ env.process == 'true' }}
|
||||
env:
|
||||
ACCESS_REPO_INFO_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.ACCESS_REPO_INFO_TOKEN }}
|
||||
TRANSFORMERS_CI_RESULTS_UPLOAD_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.TRANSFORMERS_CI_RESULTS_UPLOAD_TOKEN }}
|
||||
JOB_NAME: ${{ inputs.job }}
|
||||
REPORT_REPO_ID: ${{ inputs.report_repo_id }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python3 utils/process_bad_commit_report.py
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Process report
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
if: ${{ env.process == 'true' }}
|
||||
env:
|
||||
ACCESS_REPO_INFO_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.ACCESS_REPO_INFO_TOKEN }}
|
||||
TRANSFORMERS_CI_RESULTS_UPLOAD_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.TRANSFORMERS_CI_RESULTS_UPLOAD_TOKEN }}
|
||||
JOB_NAME: ${{ inputs.job }}
|
||||
REPORT_REPO_ID: ${{ inputs.report_repo_id }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
{
|
||||
echo 'REPORT_TEXT<<EOF'
|
||||
python3 utils/process_bad_commit_report.py
|
||||
echo EOF
|
||||
} >> "$GITHUB_ENV"
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Prepare Slack report title
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
if: ${{ env.process == 'true' }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
pip install slack_sdk
|
||||
echo "title=$(python3 -c 'import sys; sys.path.append("utils"); from utils.notification_service import job_to_test_map; ci_event = "${{ inputs.ci_event }}"; job = "${{ inputs.job }}"; test_name = job_to_test_map[job]; title = f"New failed tests of {ci_event}" + ":" + f" {test_name}"; print(title)')" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Send processed report
|
||||
if: ${{ env.process == 'true' && !endsWith(env.REPORT_TEXT, '{}') }}
|
||||
uses: slackapi/slack-github-action@6c661ce58804a1a20f6dc5fbee7f0381b469e001
|
||||
with:
|
||||
# Slack channel id, channel name, or user id to post message.
|
||||
# See also: https://api.slack.com/methods/chat.postMessage#channels
|
||||
channel-id: '#${{ inputs.slack_report_channel }}'
|
||||
# For posting a rich message using Block Kit
|
||||
payload: |
|
||||
{
|
||||
"blocks": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "header",
|
||||
"text": {
|
||||
"type": "plain_text",
|
||||
"text": "${{ env.title }}"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "section",
|
||||
"text": {
|
||||
"type": "mrkdwn",
|
||||
"text": "${{ env.REPORT_TEXT }}"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
env:
|
||||
SLACK_BOT_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
3
.github/workflows/doctest_job.yml
vendored
3
.github/workflows/doctest_job.yml
vendored
@ -27,8 +27,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
fail-fast: false
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
split_keys: ${{ fromJson(inputs.split_keys) }}
|
||||
runs-on:
|
||||
group: aws-g4dn-4xlarge-cache
|
||||
runs-on: [single-gpu, nvidia-gpu, t4, ci]
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: huggingface/transformers-all-latest-gpu
|
||||
options: --gpus 0 --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
|
||||
5
.github/workflows/doctests.yml
vendored
5
.github/workflows/doctests.yml
vendored
@ -14,8 +14,7 @@ env:
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
setup:
|
||||
name: Setup
|
||||
runs-on:
|
||||
group: aws-g4dn-4xlarge-cache
|
||||
runs-on: [single-gpu, nvidia-gpu, t4, ci]
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: huggingface/transformers-all-latest-gpu
|
||||
options: --gpus 0 --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
@ -86,4 +85,4 @@ jobs:
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: doc_test_results
|
||||
path: doc_test_results
|
||||
path: doc_test_results
|
||||
41
.github/workflows/model_jobs.yml
vendored
41
.github/workflows/model_jobs.yml
vendored
@ -18,10 +18,6 @@ on:
|
||||
docker:
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
type: string
|
||||
report_name_prefix:
|
||||
required: false
|
||||
default: run_models_gpu
|
||||
type: string
|
||||
|
||||
env:
|
||||
HF_HOME: /mnt/cache
|
||||
@ -34,6 +30,7 @@ env:
|
||||
HF_HUB_READ_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.HF_HUB_READ_TOKEN }}
|
||||
SIGOPT_API_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.SIGOPT_API_TOKEN }}
|
||||
TF_FORCE_GPU_ALLOW_GROWTH: true
|
||||
RUN_PT_TF_CROSS_TESTS: 1
|
||||
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES: 0,1
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
@ -44,8 +41,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
fail-fast: false
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
folders: ${{ fromJson(inputs.folder_slices)[inputs.slice_id] }}
|
||||
runs-on:
|
||||
group: '${{ inputs.machine_type }}'
|
||||
runs-on: ['${{ inputs.machine_type }}', nvidia-gpu, t4, '${{ inputs.runner }}']
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: ${{ inputs.docker }}
|
||||
options: --gpus all --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
@ -101,42 +97,25 @@ jobs:
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: pip freeze
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Set `machine_type` for report and artifact names
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "${{ inputs.machine_type }}"
|
||||
|
||||
if [ "${{ inputs.machine_type }}" = "aws-g4dn-4xlarge-cache" ]; then
|
||||
machine_type=single-gpu
|
||||
elif [ "${{ inputs.machine_type }}" = "aws-g4dn-12xlarge-cache" ]; then
|
||||
machine_type=multi-gpu
|
||||
else
|
||||
machine_type=${{ inputs.machine_type }}
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
echo "$machine_type"
|
||||
echo "machine_type=$machine_type" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run all tests on GPU
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: python3 -m pytest -rsfE -v --make-reports=${{ env.machine_type }}_${{ inputs.report_name_prefix }}_${{ matrix.folders }}_test_reports tests/${{ matrix.folders }}
|
||||
run: python3 -m pytest -rsfE -v --make-reports=${{ inputs.machine_type }}_run_models_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}_test_reports tests/${{ matrix.folders }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
if: ${{ failure() }}
|
||||
continue-on-error: true
|
||||
run: cat /transformers/reports/${{ env.machine_type }}_${{ inputs.report_name_prefix }}_${{ matrix.folders }}_test_reports/failures_short.txt
|
||||
run: cat /transformers/reports/${{ inputs.machine_type }}_run_models_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}_test_reports/failures_short.txt
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run test
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
mkdir -p /transformers/reports/${{ env.machine_type }}_${{ inputs.report_name_prefix }}_${{ matrix.folders }}_test_reports
|
||||
echo "hello" > /transformers/reports/${{ env.machine_type }}_${{ inputs.report_name_prefix }}_${{ matrix.folders }}_test_reports/hello.txt
|
||||
echo "${{ env.machine_type }}_${{ inputs.report_name_prefix }}_${{ matrix.folders }}_test_reports"
|
||||
mkdir -p /transformers/reports/${{ inputs.machine_type }}_run_models_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}_test_reports
|
||||
echo "hello" > /transformers/reports/${{ inputs.machine_type }}_run_models_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}_test_reports/hello.txt
|
||||
echo "${{ inputs.machine_type }}_run_models_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}_test_reports"
|
||||
|
||||
- name: "Test suite reports artifacts: ${{ env.machine_type }}_${{ inputs.report_name_prefix }}_${{ env.matrix_folders }}_test_reports"
|
||||
- name: "Test suite reports artifacts: ${{ inputs.machine_type }}_run_models_gpu_${{ env.matrix_folders }}_test_reports"
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: ${{ env.machine_type }}_${{ inputs.report_name_prefix }}_${{ env.matrix_folders }}_test_reports
|
||||
path: /transformers/reports/${{ env.machine_type }}_${{ inputs.report_name_prefix }}_${{ matrix.folders }}_test_reports
|
||||
name: ${{ inputs.machine_type }}_run_models_gpu_${{ env.matrix_folders }}_test_reports
|
||||
path: /transformers/reports/${{ inputs.machine_type }}_run_models_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}_test_reports
|
||||
|
||||
1
.github/workflows/model_jobs_amd.yml
vendored
1
.github/workflows/model_jobs_amd.yml
vendored
@ -30,6 +30,7 @@ env:
|
||||
HF_HUB_READ_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.HF_HUB_READ_TOKEN }}
|
||||
SIGOPT_API_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.SIGOPT_API_TOKEN }}
|
||||
TF_FORCE_GPU_ALLOW_GROWTH: true
|
||||
RUN_PT_TF_CROSS_TESTS: 1
|
||||
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES: 0,1
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,68 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Used to notify core maintainers about new model PR being merged
|
||||
name: New model PR merged notification
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
push:
|
||||
branches:
|
||||
- main
|
||||
paths:
|
||||
- 'src/transformers/models/*/modeling_*'
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
notify_new_model:
|
||||
name: Notify new model
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-22.04
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
fetch-depth: 0
|
||||
- name: Check new model
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m pip install gitpython
|
||||
python -c 'from utils.pr_slow_ci_models import get_new_model; new_model = get_new_model(diff_with_last_commit=True); print(new_model)' | tee output.txt
|
||||
echo "NEW_MODEL=$(tail -n 1 output.txt)" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
echo "COMMIT_SHA=$(git log -1 --format=%H)" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
|
||||
- name: print commit sha
|
||||
if: ${{ env.NEW_MODEL != ''}}
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "$COMMIT_SHA"
|
||||
|
||||
- name: print new model
|
||||
if: ${{ env.NEW_MODEL != ''}}
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "$NEW_MODEL"
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Notify
|
||||
if: ${{ env.NEW_MODEL != ''}}
|
||||
uses: slackapi/slack-github-action@6c661ce58804a1a20f6dc5fbee7f0381b469e001
|
||||
with:
|
||||
# Slack channel id, channel name, or user id to post message.
|
||||
# See also: https://api.slack.com/methods/chat.postMessage#channels
|
||||
channel-id: transformers-new-model-notification
|
||||
# For posting a rich message using Block Kit
|
||||
payload: |
|
||||
{
|
||||
"blocks": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "header",
|
||||
"text": {
|
||||
"type": "plain_text",
|
||||
"text": "New model!",
|
||||
"emoji": true
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "section",
|
||||
"text": {
|
||||
"type": "mrkdwn",
|
||||
"text": "<https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/commit/${{ env.COMMIT_SHA }}|New model: ${{ env.NEW_MODEL }}> GH_ArthurZucker, GH_lysandrejik, GH_ydshieh\ncommit SHA: ${{ env.COMMIT_SHA }}"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
env:
|
||||
SLACK_BOT_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
34
.github/workflows/pr-style-bot.yml
vendored
34
.github/workflows/pr-style-bot.yml
vendored
@ -1,34 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# To run this bot, comment "@bot /style" on a PR
|
||||
name: Style Bot
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
issue_comment:
|
||||
types: [created]
|
||||
|
||||
permissions:
|
||||
contents: write
|
||||
pull-requests: write
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
style:
|
||||
uses: huggingface/huggingface_hub/.github/workflows/style-bot-action.yml@639ee721e149a281fe726a50a2cc1354b48bc463
|
||||
with:
|
||||
python_quality_dependencies: "[quality]"
|
||||
style_command_type: "default"
|
||||
secrets:
|
||||
bot_token: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
|
||||
|
||||
check-outputs:
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
needs: style
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- run: echo ${{ needs.style.outputs.pr_number }}
|
||||
- run: echo ${{ needs.style.outputs.new_commit_sha }}
|
||||
|
||||
trigger:
|
||||
needs: style
|
||||
if: needs.style.outputs.new_commit_sha != ''
|
||||
uses: "./.github/workflows/build_pr_documentation.yml"
|
||||
with:
|
||||
pr_number: ${{ needs.style.outputs.pr_number }}
|
||||
commit_sha: ${{ needs.style.outputs.new_commit_sha }}
|
||||
55
.github/workflows/push-important-models.yml
vendored
55
.github/workflows/push-important-models.yml
vendored
@ -7,13 +7,14 @@ on:
|
||||
env:
|
||||
OUTPUT_SLACK_CHANNEL_ID: "C06L2SGMEEA"
|
||||
HF_HUB_READ_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.HF_HUB_READ_TOKEN }}
|
||||
HF_HOME: /mnt/cache
|
||||
TRANSFORMERS_IS_CI: yes
|
||||
OMP_NUM_THREADS: 8
|
||||
MKL_NUM_THREADS: 8
|
||||
RUN_SLOW: yes # For gated repositories, we still need to agree to share information on the Hub repo. page in order to get access. # This token is created under the bot `hf-transformers-bot`.
|
||||
SIGOPT_API_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.SIGOPT_API_TOKEN }}
|
||||
TF_FORCE_GPU_ALLOW_GROWTH: true
|
||||
HF_HOME: /mnt/cache
|
||||
TRANSFORMERS_IS_CI: yes
|
||||
OMP_NUM_THREADS: 8
|
||||
MKL_NUM_THREADS: 8
|
||||
RUN_SLOW: yes # For gated repositories, we still need to agree to share information on the Hub repo. page in order to get access. # This token is created under the bot `hf-transformers-bot`.
|
||||
SIGOPT_API_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.SIGOPT_API_TOKEN }}
|
||||
TF_FORCE_GPU_ALLOW_GROWTH: true
|
||||
RUN_PT_TF_CROSS_TESTS: 1
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
get_modified_models:
|
||||
@ -24,13 +25,13 @@ jobs:
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Check out code
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Get changed files
|
||||
id: changed-files
|
||||
uses: tj-actions/changed-files@1c8e6069583811afb28f97afeaf8e7da80c6be5c
|
||||
uses: tj-actions/changed-files@3f54ebb830831fc121d3263c1857cfbdc310cdb9 #v42
|
||||
with:
|
||||
files: src/transformers/models/**
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run step if only the files listed above change
|
||||
if: steps.changed-files.outputs.any_changed == 'true'
|
||||
id: set-matrix
|
||||
@ -51,49 +52,48 @@ jobs:
|
||||
test_modified_files:
|
||||
needs: get_modified_models
|
||||
name: Slow & FA2 tests
|
||||
runs-on:
|
||||
group: aws-g5-4xlarge-cache
|
||||
runs-on: [single-gpu, nvidia-gpu, a10, ci]
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: huggingface/transformers-all-latest-gpu
|
||||
options: --gpus all --privileged --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
if: ${{ needs.get_modified_models.outputs.matrix != '[]' && needs.get_modified_models.outputs.matrix != '' && fromJson(needs.get_modified_models.outputs.matrix)[0] != null }}
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
fail-fast: false
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
model-name: ${{ fromJson(needs.get_modified_models.outputs.matrix) }}
|
||||
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Check out code
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Install locally transformers & other libs
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
apt install sudo
|
||||
sudo -H pip install --upgrade pip
|
||||
sudo -H pip uninstall -y transformers
|
||||
sudo -H pip install -U -e ".[testing]"
|
||||
sudo -H pip uninstall -y transformers
|
||||
sudo -H pip install -U -e ".[testing]"
|
||||
MAX_JOBS=4 pip install flash-attn --no-build-isolation
|
||||
pip install bitsandbytes
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NVIDIA-SMI
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
nvidia-smi
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Show installed libraries and their versions
|
||||
run: pip freeze
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run FA2 tests
|
||||
id: run_fa2_tests
|
||||
run:
|
||||
pytest -rsfE -m "flash_attn_test" --make-reports=${{ matrix.model-name }}_fa2_tests/ tests/${{ matrix.model-name }}/test_modeling_*
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- name: "Test suite reports artifacts: ${{ matrix.model-name }}_fa2_tests"
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: ${{ matrix.model-name }}_fa2_tests
|
||||
path: /transformers/reports/${{ matrix.model-name }}_fa2_tests
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Post to Slack
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
uses: huggingface/hf-workflows/.github/actions/post-slack@main
|
||||
@ -102,13 +102,13 @@ jobs:
|
||||
title: 🤗 Results of the FA2 tests - ${{ matrix.model-name }}
|
||||
status: ${{ steps.run_fa2_tests.conclusion}}
|
||||
slack_token: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run integration tests
|
||||
id: run_integration_tests
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
run:
|
||||
pytest -rsfE -k "IntegrationTest" --make-reports=tests_integration_${{ matrix.model-name }} tests/${{ matrix.model-name }}/test_modeling_*
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- name: "Test suite reports artifacts: tests_integration_${{ matrix.model-name }}"
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
|
||||
@ -118,7 +118,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Post to Slack
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
uses: huggingface/hf-workflows/.github/actions/post-slack@main
|
||||
uses: huggingface/hf-workflows/.github/actions/post-slack@main
|
||||
with:
|
||||
slack_channel: ${{ env.OUTPUT_SLACK_CHANNEL_ID }}
|
||||
title: 🤗 Results of the Integration tests - ${{ matrix.model-name }}
|
||||
@ -133,3 +133,10 @@ jobs:
|
||||
slackChannel: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_CHANNEL }}
|
||||
slackToken: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
waitForSSH: true
|
||||
|
||||
benchmark:
|
||||
name: Benchmark workflow
|
||||
needs: get_modified_models
|
||||
if: ${{ needs.get_modified_models.outputs.matrix != '[]' && needs.get_modified_models.outputs.matrix != '' && fromJson(needs.get_modified_models.outputs.matrix)[0] != null }}
|
||||
uses: ./.github/workflows/benchmark.yml
|
||||
secrets: inherit
|
||||
|
||||
416
.github/workflows/self-comment-ci.yml
vendored
416
.github/workflows/self-comment-ci.yml
vendored
@ -1,416 +0,0 @@
|
||||
name: PR comment GitHub CI
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
issue_comment:
|
||||
types:
|
||||
- created
|
||||
branches-ignore:
|
||||
- main
|
||||
concurrency:
|
||||
group: ${{ github.workflow }}-${{ github.event.issue.number }}-${{ startsWith(github.event.comment.body, 'run-slow') || startsWith(github.event.comment.body, 'run slow') || startsWith(github.event.comment.body, 'run_slow') }}
|
||||
cancel-in-progress: true
|
||||
permissions: read-all
|
||||
|
||||
env:
|
||||
HF_HOME: /mnt/cache
|
||||
TRANSFORMERS_IS_CI: yes
|
||||
OMP_NUM_THREADS: 8
|
||||
MKL_NUM_THREADS: 8
|
||||
RUN_SLOW: yes
|
||||
# For gated repositories, we still need to agree to share information on the Hub repo. page in order to get access.
|
||||
# This token is created under the bot `hf-transformers-bot`.
|
||||
HF_HUB_READ_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.HF_HUB_READ_TOKEN }}
|
||||
SIGOPT_API_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.SIGOPT_API_TOKEN }}
|
||||
TF_FORCE_GPU_ALLOW_GROWTH: true
|
||||
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES: 0,1
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
get-pr-number:
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-22.04
|
||||
name: Get PR number
|
||||
# For security: only allow team members to run
|
||||
if: ${{ github.event.issue.state == 'open' && contains(fromJSON('["ydshieh", "ArthurZucker", "zucchini-nlp", "qubvel", "molbap", "gante", "LysandreJik", "Cyrilvallez", "Rocketknight1", "SunMarc", "muellerzr", "eustlb", "MekkCyber", "manueldeprada", "vasqu"]'), github.actor) && (startsWith(github.event.comment.body, 'run-slow') || startsWith(github.event.comment.body, 'run slow') || startsWith(github.event.comment.body, 'run_slow')) }}
|
||||
outputs:
|
||||
PR_NUMBER: ${{ steps.set_pr_number.outputs.PR_NUMBER }}
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Get PR number
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
if [[ "${{ github.event.issue.number }}" != "" && "${{ github.event.issue.pull_request }}" != "" ]]; then
|
||||
echo "PR_NUMBER=${{ github.event.issue.number }}" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
else
|
||||
echo "PR_NUMBER=" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Check PR number
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "${{ env.PR_NUMBER }}"
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Set PR number
|
||||
id: set_pr_number
|
||||
run: echo "PR_NUMBER=${{ env.PR_NUMBER }}" >> "$GITHUB_OUTPUT"
|
||||
|
||||
get-sha:
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-22.04
|
||||
needs: get-pr-number
|
||||
if: ${{ needs.get-pr-number.outputs.PR_NUMBER != ''}}
|
||||
outputs:
|
||||
PR_HEAD_SHA: ${{ steps.get_sha.outputs.PR_HEAD_SHA }}
|
||||
PR_MERGE_SHA: ${{ steps.get_sha.outputs.PR_MERGE_SHA }}
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
fetch-depth: "0"
|
||||
ref: "refs/pull/${{needs.get-pr-number.outputs.PR_NUMBER}}/merge"
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Get SHA (and verify timestamps against the issue comment date)
|
||||
id: get_sha
|
||||
env:
|
||||
PR_NUMBER: ${{ needs.get-pr-number.outputs.PR_NUMBER }}
|
||||
COMMENT_DATE: ${{ github.event.comment.created_at }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
git fetch origin refs/pull/$PR_NUMBER/head:refs/remotes/pull/$PR_NUMBER/head
|
||||
git checkout refs/remotes/pull/$PR_NUMBER/head
|
||||
echo "PR_HEAD_SHA: $(git log -1 --format=%H)"
|
||||
echo "PR_HEAD_SHA=$(git log -1 --format=%H)" >> "$GITHUB_OUTPUT"
|
||||
git fetch origin refs/pull/$PR_NUMBER/merge:refs/remotes/pull/$PR_NUMBER/merge
|
||||
git checkout refs/remotes/pull/$PR_NUMBER/merge
|
||||
echo "PR_MERGE_SHA: $(git log -1 --format=%H)"
|
||||
echo "PR_MERGE_SHA=$(git log -1 --format=%H)" >> "$GITHUB_OUTPUT"
|
||||
PR_MERGE_COMMIT_TIMESTAMP=$(git log -1 --date=unix --format=%cd)
|
||||
echo "PR_MERGE_COMMIT_TIMESTAMP: $PR_MERGE_COMMIT_TIMESTAMP"
|
||||
COMMENT_TIMESTAMP=$(date -d "${COMMENT_DATE}" +"%s")
|
||||
echo "COMMENT_DATE: $COMMENT_DATE"
|
||||
echo "COMMENT_TIMESTAMP: $COMMENT_TIMESTAMP"
|
||||
if [ $COMMENT_TIMESTAMP -le $PR_MERGE_COMMIT_TIMESTAMP ]; then
|
||||
echo "Last commit on the pull request is newer than the issue comment triggering this run! Abort!";
|
||||
exit -1;
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
# use a python script to handle this complex logic
|
||||
# case 1: `run-slow` (auto. infer with limited number of models, but in particular, new model)
|
||||
# case 2: `run-slow model_1, model_2`
|
||||
get-tests:
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-22.04
|
||||
needs: [get-pr-number, get-sha]
|
||||
if: ${{ needs.get-pr-number.outputs.PR_NUMBER != ''}}
|
||||
outputs:
|
||||
models: ${{ steps.models_to_run.outputs.models }}
|
||||
quantizations: ${{ steps.models_to_run.outputs.quantizations }}
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
fetch-depth: "0"
|
||||
ref: "refs/pull/${{needs.get-pr-number.outputs.PR_NUMBER}}/merge"
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Verify merge commit SHA
|
||||
env:
|
||||
VERIFIED_PR_MERGE_SHA: ${{ needs.get-sha.outputs.PR_MERGE_SHA }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
PR_MERGE_SHA=$(git log -1 --format=%H)
|
||||
if [ $PR_MERGE_SHA != $VERIFIED_PR_MERGE_SHA ]; then
|
||||
echo "The merged commit SHA is not the same as the verified one! Security issue detected, abort the workflow!";
|
||||
exit -1;
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Get models to test
|
||||
env:
|
||||
PR_COMMENT: ${{ github.event.comment.body }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m pip install GitPython
|
||||
python utils/pr_slow_ci_models.py --message "$PR_COMMENT" | tee output.txt
|
||||
echo "models=$(tail -n 1 output.txt)" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
python utils/pr_slow_ci_models.py --message "$PR_COMMENT" --quantization | tee output2.txt
|
||||
echo "quantizations=$(tail -n 1 output2.txt)" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Show models to test
|
||||
id: models_to_run
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "${{ env.models }}"
|
||||
echo "models=${{ env.models }}" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
echo "models=${{ env.models }}" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
|
||||
echo "${{ env.quantizations }}"
|
||||
echo "quantizations=${{ env.quantizations }}" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
|
||||
|
||||
reply_to_comment:
|
||||
name: Reply to the comment
|
||||
if: ${{ needs.get-tests.outputs.models != '[]' || needs.get-tests.outputs.quantizations != '[]' }}
|
||||
needs: [get-pr-number, get-tests]
|
||||
permissions:
|
||||
pull-requests: write
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-22.04
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Reply to the comment
|
||||
env:
|
||||
GH_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
|
||||
MODELS: ${{ needs.get-tests.outputs.models }}
|
||||
BODY: "\n\nmodels: ${{ needs.get-tests.outputs.models }}\nquantizations: ${{ needs.get-tests.outputs.quantizations }}"
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
gh api \
|
||||
--method POST \
|
||||
-H "Accept: application/vnd.github+json" \
|
||||
-H "X-GitHub-Api-Version: 2022-11-28" \
|
||||
repos/${{ github.repository }}/issues/${{ needs.get-pr-number.outputs.PR_NUMBER }}/comments \
|
||||
-f "body=This comment contains run-slow, running the specified jobs: ${{ env.BODY }} ..."
|
||||
|
||||
create_run:
|
||||
name: Create run
|
||||
if: ${{ needs.get-tests.outputs.models != '[]' || needs.get-tests.outputs.quantizations != '[]' }}
|
||||
needs: [get-sha, get-tests, reply_to_comment]
|
||||
permissions:
|
||||
statuses: write
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-22.04
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Create Run
|
||||
id: create_run
|
||||
env:
|
||||
GH_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
|
||||
# Create a commit status (pending) for a run of this workflow. The status has to be updated later in `update_run_status`.
|
||||
# See https://docs.github.com/en/rest/commits/statuses?apiVersion=2022-11-28#create-a-commit-status
|
||||
GITHUB_RUN_URL: https://github.com/${{ github.repository }}/actions/runs/${{ github.run_id }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
gh api \
|
||||
--method POST \
|
||||
-H "Accept: application/vnd.github+json" \
|
||||
-H "X-GitHub-Api-Version: 2022-11-28" \
|
||||
repos/${{ github.repository }}/statuses/${{ needs.get-sha.outputs.PR_HEAD_SHA }} \
|
||||
-f "target_url=$GITHUB_RUN_URL" -f "state=pending" -f "description=Slow CI job" -f "context=pytest/custom-tests"
|
||||
|
||||
run_models_gpu:
|
||||
name: Run all tests for the model
|
||||
if: ${{ needs.get-tests.outputs.models != '[]' }}
|
||||
needs: [get-pr-number, get-sha, get-tests, create_run]
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
fail-fast: false
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
folders: ${{ fromJson(needs.get-tests.outputs.models) }}
|
||||
machine_type: [aws-g4dn-4xlarge-cache, aws-g4dn-12xlarge-cache]
|
||||
runs-on:
|
||||
group: '${{ matrix.machine_type }}'
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: huggingface/transformers-all-latest-gpu
|
||||
options: --gpus all --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Echo input and matrix info
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "${{ matrix.folders }}"
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Echo folder ${{ matrix.folders }}
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
# For folders like `models/bert`, set an env. var. (`matrix_folders`) to `models_bert`, which will be used to
|
||||
# set the artifact folder names (because the character `/` is not allowed).
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "${{ matrix.folders }}"
|
||||
matrix_folders=${{ matrix.folders }}
|
||||
matrix_folders=${matrix_folders/'models/'/'models_'}
|
||||
echo "$matrix_folders"
|
||||
echo "matrix_folders=$matrix_folders" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Checkout to PR merge commit
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
git fetch origin refs/pull/${{ needs.get-pr-number.outputs.PR_NUMBER }}/merge:refs/remotes/pull/${{ needs.get-pr-number.outputs.PR_NUMBER }}/merge
|
||||
git checkout refs/remotes/pull/${{ needs.get-pr-number.outputs.PR_NUMBER }}/merge
|
||||
git log -1 --format=%H
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Verify merge commit SHA
|
||||
env:
|
||||
VERIFIED_PR_MERGE_SHA: ${{ needs.get-sha.outputs.PR_MERGE_SHA }}
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
PR_MERGE_SHA=$(git log -1 --format=%H)
|
||||
if [ $PR_MERGE_SHA != $VERIFIED_PR_MERGE_SHA ]; then
|
||||
echo "The merged commit SHA is not the same as the verified one! Security issue detected, abort the workflow!";
|
||||
exit -1;
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Reinstall transformers in edit mode (remove the one installed during docker image build)
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: python3 -m pip uninstall -y transformers && python3 -m pip install -e .
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NVIDIA-SMI
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
nvidia-smi
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Set `machine_type` for report and artifact names
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "${{ matrix.machine_type }}"
|
||||
if [ "${{ matrix.machine_type }}" = "aws-g4dn-4xlarge-cache" ]; then
|
||||
machine_type=single-gpu
|
||||
elif [ "${{ matrix.machine_type }}" = "aws-g4dn-12xlarge-cache" ]; then
|
||||
machine_type=multi-gpu
|
||||
else
|
||||
machine_type=${{ matrix.machine_type }}
|
||||
fi
|
||||
echo "$machine_type"
|
||||
echo "machine_type=$machine_type" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Environment
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python3 utils/print_env.py
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Show installed libraries and their versions
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: pip freeze
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run all tests on GPU
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES="$(python3 utils/set_cuda_devices_for_ci.py --test_folder ${{ matrix.folders }})"
|
||||
echo $CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES
|
||||
python3 -m pytest -v -rsfE --make-reports=${{ env.machine_type }}_run_models_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}_test_reports tests/${{ matrix.folders }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
if: ${{ failure() }}
|
||||
continue-on-error: true
|
||||
run: cat /transformers/reports/${{ env.machine_type }}_run_models_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}_test_reports/failures_short.txt
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Make sure report directory exists
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
mkdir -p /transformers/reports/${{ env.machine_type }}_run_models_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}_test_reports
|
||||
echo "hello" > /transformers/reports/${{ env.machine_type }}_run_models_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}_test_reports/hello.txt
|
||||
echo "${{ env.machine_type }}_run_models_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}_test_reports"
|
||||
|
||||
- name: "Test suite reports artifacts: ${{ env.machine_type }}_run_models_gpu_${{ env.matrix_folders }}_test_reports"
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: ${{ env.machine_type }}_run_models_gpu_${{ env.matrix_folders }}_test_reports
|
||||
path: /transformers/reports/${{ env.machine_type }}_run_models_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}_test_reports
|
||||
|
||||
run_quantization_torch_gpu:
|
||||
name: Run all tests for a quantization
|
||||
if: ${{ needs.get-tests.outputs.quantizations != '[]' }}
|
||||
needs: [get-pr-number, get-sha, get-tests, create_run]
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
fail-fast: false
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
folders: ${{ fromJson(needs.get-tests.outputs.quantizations) }}
|
||||
machine_type: [aws-g4dn-4xlarge-cache, aws-g4dn-12xlarge-cache]
|
||||
runs-on:
|
||||
group: '${{ matrix.machine_type }}'
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: huggingface/transformers-quantization-latest-gpu
|
||||
options: --gpus all --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Echo folder ${{ matrix.folders }}
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "${{ matrix.folders }}"
|
||||
matrix_folders=${{ matrix.folders }}
|
||||
matrix_folders=${matrix_folders/'quantization/'/'quantization_'}
|
||||
echo "$matrix_folders"
|
||||
echo "matrix_folders=$matrix_folders" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Checkout to PR merge commit
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
git fetch origin refs/pull/${{ needs.get-pr-number.outputs.PR_NUMBER }}/merge:refs/remotes/pull/${{ needs.get-pr-number.outputs.PR_NUMBER }}/merge
|
||||
git checkout refs/remotes/pull/${{ needs.get-pr-number.outputs.PR_NUMBER }}/merge
|
||||
git log -1 --format=%H
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Verify merge commit SHA
|
||||
env:
|
||||
VERIFIED_PR_MERGE_SHA: ${{ needs.get-sha.outputs.PR_MERGE_SHA }}
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
PR_MERGE_SHA=$(git log -1 --format=%H)
|
||||
if [ $PR_MERGE_SHA != $VERIFIED_PR_MERGE_SHA ]; then
|
||||
echo "The merged commit SHA is not the same as the verified one! Security issue detected, abort the workflow!";
|
||||
exit -1;
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Reinstall transformers in edit mode (remove the one installed during docker image build)
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: python3 -m pip uninstall -y transformers && python3 -m pip install -e .
|
||||
- name: NVIDIA-SMI
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
nvidia-smi
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Set `machine_type` for report and artifact names
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "${{ matrix.machine_type }}"
|
||||
if [ "${{ matrix.machine_type }}" = "aws-g4dn-4xlarge-cache" ]; then
|
||||
machine_type=single-gpu
|
||||
elif [ "${{ matrix.machine_type }}" = "aws-g4dn-12xlarge-cache" ]; then
|
||||
machine_type=multi-gpu
|
||||
else
|
||||
machine_type=${{ matrix.machine_type }}
|
||||
fi
|
||||
echo "$machine_type"
|
||||
echo "machine_type=$machine_type" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Environment
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python3 utils/print_env.py
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Show installed libraries and their versions
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: pip freeze
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run quantization tests on GPU
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python3 -m pytest -v --make-reports=${{ env.machine_type }}_run_quantization_torch_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}_test_reports tests/${{ matrix.folders }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
if: ${{ failure() }}
|
||||
continue-on-error: true
|
||||
run: cat /transformers/reports/${{ env.machine_type }}_run_quantization_torch_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}_test_reports/failures_short.txt
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Make sure report directory exists
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
mkdir -p /transformers/reports/${{ env.machine_type }}_run_quantization_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}_test_reports
|
||||
echo "hello" > /transformers/reports/${{ env.machine_type }}_run_quantization_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}_test_reports/hello.txt
|
||||
echo "${{ env.machine_type }}_run_quantization_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}_test_reports"
|
||||
|
||||
- name: "Test suite reports artifacts: ${{ env.machine_type }}_run_quantization_torch_gpu_${{ env.matrix_folders }}_test_reports"
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: ${{ env.machine_type }}_run_quantization_torch_gpu_${{ env.matrix_folders }}_test_reports
|
||||
path: /transformers/reports/${{ env.machine_type }}_run_quantization_torch_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}_test_reports
|
||||
|
||||
update_run_status:
|
||||
name: Update Check Run Status
|
||||
needs: [get-sha, create_run, run_models_gpu, run_quantization_torch_gpu]
|
||||
permissions:
|
||||
statuses: write
|
||||
if: ${{ always() && needs.create_run.result == 'success' }}
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-22.04
|
||||
env:
|
||||
GH_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
|
||||
GITHUB_RUN_URL: https://github.com/${{ github.repository }}/actions/runs/${{ github.run_id }}
|
||||
STATUS_OK: ${{ contains(fromJSON('["skipped", "success"]'), needs.run_models_gpu.result) && contains(fromJSON('["skipped", "success"]'), needs.run_quantization_torch_gpu.result) }}
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Get `run_models_gpu` job status
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "${{ needs.run_models_gpu.result }}"
|
||||
echo "${{ needs.run_quantization_torch_gpu.result }}"
|
||||
echo $STATUS_OK
|
||||
if [ "$STATUS_OK" = "true" ]; then
|
||||
echo "STATUS=success" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
else
|
||||
echo "STATUS=failure" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Update PR commit statuses
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "${{ needs.run_models_gpu.result }}"
|
||||
echo "${{ env.STATUS }}"
|
||||
gh api \
|
||||
--method POST \
|
||||
-H "Accept: application/vnd.github+json" \
|
||||
-H "X-GitHub-Api-Version: 2022-11-28" \
|
||||
repos/${{ github.repository }}/statuses/${{ needs.get-sha.outputs.PR_HEAD_SHA }} \
|
||||
-f "target_url=$GITHUB_RUN_URL" -f "state=${{ env.STATUS }}" -f "description=Slow CI job" -f "context=pytest/custom-tests"
|
||||
@ -21,6 +21,39 @@ jobs:
|
||||
echo "$(python3 -c 'print(int(${{ github.run_number }}) % 10)')"
|
||||
echo "run_number=$(python3 -c 'print(int(${{ github.run_number }}) % 10)')" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
|
||||
|
||||
run_past_ci_pytorch_1-13:
|
||||
name: PyTorch 1.13
|
||||
needs: get_number
|
||||
if: needs.get_number.outputs.run_number == 0 && (cancelled() != true) && ((github.event_name == 'schedule') || ((github.event_name == 'push') && startsWith(github.ref_name, 'run_past_ci')))
|
||||
uses: ./.github/workflows/self-past-caller.yml
|
||||
with:
|
||||
framework: pytorch
|
||||
version: "1.13"
|
||||
sha: ${{ github.sha }}
|
||||
secrets: inherit
|
||||
|
||||
run_past_ci_pytorch_1-12:
|
||||
name: PyTorch 1.12
|
||||
needs: get_number
|
||||
if: needs.get_number.outputs.run_number == 1 && (cancelled() != true) && ((github.event_name == 'schedule') || ((github.event_name == 'push') && startsWith(github.ref_name, 'run_past_ci')))
|
||||
uses: ./.github/workflows/self-past-caller.yml
|
||||
with:
|
||||
framework: pytorch
|
||||
version: "1.12"
|
||||
sha: ${{ github.sha }}
|
||||
secrets: inherit
|
||||
|
||||
run_past_ci_pytorch_1-11:
|
||||
name: PyTorch 1.11
|
||||
needs: get_number
|
||||
if: needs.get_number.outputs.run_number == 2 && (cancelled() != true) && ((github.event_name == 'schedule') || ((github.event_name == 'push') && startsWith(github.ref_name, 'run_past_ci')))
|
||||
uses: ./.github/workflows/self-past-caller.yml
|
||||
with:
|
||||
framework: pytorch
|
||||
version: "1.11"
|
||||
sha: ${{ github.sha }}
|
||||
secrets: inherit
|
||||
|
||||
run_past_ci_tensorflow_2-11:
|
||||
name: TensorFlow 2.11
|
||||
needs: get_number
|
||||
|
||||
135
.github/workflows/self-pr-slow-ci.yml
vendored
Normal file
135
.github/workflows/self-pr-slow-ci.yml
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,135 @@
|
||||
name: PR slow CI
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
pull_request:
|
||||
paths:
|
||||
- "src/transformers/models/*/modeling_*.py"
|
||||
- "tests/**/test_*.py"
|
||||
|
||||
concurrency:
|
||||
group: ${{ github.workflow }}-${{ github.head_ref || github.run_id }}
|
||||
cancel-in-progress: true
|
||||
|
||||
env:
|
||||
HF_HOME: /mnt/cache
|
||||
TRANSFORMERS_IS_CI: yes
|
||||
OMP_NUM_THREADS: 8
|
||||
MKL_NUM_THREADS: 8
|
||||
RUN_SLOW: yes
|
||||
# For gated repositories, we still need to agree to share information on the Hub repo. page in order to get access.
|
||||
# This token is created under the bot `hf-transformers-bot`.
|
||||
HF_HUB_READ_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.HF_HUB_READ_TOKEN }}
|
||||
SIGOPT_API_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.SIGOPT_API_TOKEN }}
|
||||
TF_FORCE_GPU_ALLOW_GROWTH: true
|
||||
RUN_PT_TF_CROSS_TESTS: 1
|
||||
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES: 0,1
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
find_models_to_run:
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-22.04
|
||||
name: Find models to run slow tests
|
||||
# Triggered only if the required label `run-slow` is added
|
||||
if: ${{ contains(github.event.pull_request.labels.*.name, 'run-slow') }}
|
||||
outputs:
|
||||
models: ${{ steps.models_to_run.outputs.models }}
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
fetch-depth: "0"
|
||||
ref: ${{ github.event.pull_request.head.sha }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Get commit message
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "commit_message=$(git show -s --format=%s)" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Get models to run slow tests
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "${{ env.commit_message }}"
|
||||
python -m pip install GitPython
|
||||
python utils/pr_slow_ci_models.py --commit_message "${{ env.commit_message }}" | tee output.txt
|
||||
echo "models=$(tail -n 1 output.txt)" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Models to run slow tests
|
||||
id: models_to_run
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "${{ env.models }}"
|
||||
echo "models=${{ env.models }}" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
|
||||
|
||||
run_models_gpu:
|
||||
name: Run all tests for the model
|
||||
# Triggered only `find_models_to_run` is triggered (label `run-slow` is added) which gives the models to run
|
||||
# (either a new model PR or via a commit message)
|
||||
if: ${{ needs.find_models_to_run.outputs.models != '[]' }}
|
||||
needs: find_models_to_run
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
fail-fast: false
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
folders: ${{ fromJson(needs.find_models_to_run.outputs.models) }}
|
||||
machine_type: [single-gpu, multi-gpu]
|
||||
runs-on: ['${{ matrix.machine_type }}', nvidia-gpu, t4, ci]
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: huggingface/transformers-all-latest-gpu
|
||||
options: --gpus all --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Echo input and matrix info
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "${{ matrix.folders }}"
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Echo folder ${{ matrix.folders }}
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
# For folders like `models/bert`, set an env. var. (`matrix_folders`) to `models_bert`, which will be used to
|
||||
# set the artifact folder names (because the character `/` is not allowed).
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "${{ matrix.folders }}"
|
||||
matrix_folders=${{ matrix.folders }}
|
||||
matrix_folders=${matrix_folders/'models/'/'models_'}
|
||||
echo "$matrix_folders"
|
||||
echo "matrix_folders=$matrix_folders" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Update clone
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: git fetch && git fetch origin pull/${{ github.event.pull_request.number }}/head:pull/${{ github.event.pull_request.number }}/merge && git checkout pull/${{ github.event.pull_request.number }}/merge
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Reinstall transformers in edit mode (remove the one installed during docker image build)
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: python3 -m pip uninstall -y transformers && python3 -m pip install -e .
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NVIDIA-SMI
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
nvidia-smi
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Environment
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python3 utils/print_env.py
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Show installed libraries and their versions
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: pip freeze
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run all tests on GPU
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
export CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES="$(python3 utils/set_cuda_devices_for_ci.py --test_folder ${{ matrix.folders }})"
|
||||
echo $CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES
|
||||
python3 -m pytest -v -rsfE --make-reports=${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_models_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}_test_reports tests/${{ matrix.folders }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
if: ${{ failure() }}
|
||||
continue-on-error: true
|
||||
run: cat /transformers/reports/${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_models_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}_test_reports/failures_short.txt
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Make sure report directory exists
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
mkdir -p /transformers/reports/${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_models_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}_test_reports
|
||||
echo "hello" > /transformers/reports/${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_models_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}_test_reports/hello.txt
|
||||
echo "${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_models_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}_test_reports"
|
||||
|
||||
- name: "Test suite reports artifacts: ${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_models_gpu_${{ env.matrix_folders }}_test_reports"
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: ${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_models_gpu_${{ env.matrix_folders }}_test_reports
|
||||
path: /transformers/reports/${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_models_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}_test_reports
|
||||
50
.github/workflows/self-push-amd-mi210-caller.yml
vendored
50
.github/workflows/self-push-amd-mi210-caller.yml
vendored
@ -1,25 +1,25 @@
|
||||
name: Self-hosted runner (AMD mi210 CI caller)
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
#workflow_run:
|
||||
# workflows: ["Self-hosted runner (push-caller)"]
|
||||
# branches: ["main"]
|
||||
# types: [completed]
|
||||
push:
|
||||
branches:
|
||||
- run_amd_push_ci_caller*
|
||||
paths:
|
||||
- "src/**"
|
||||
- "tests/**"
|
||||
- ".github/**"
|
||||
- "templates/**"
|
||||
- "utils/**"
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
run_amd_ci:
|
||||
name: AMD mi210
|
||||
if: (cancelled() != true) && ((github.event_name == 'workflow_run') || ((github.event_name == 'push') && startsWith(github.ref_name, 'run_amd_push_ci_caller')))
|
||||
uses: ./.github/workflows/self-push-amd.yml
|
||||
with:
|
||||
gpu_flavor: mi210
|
||||
secrets: inherit
|
||||
name: Self-hosted runner (AMD mi210 CI caller)
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
workflow_run:
|
||||
workflows: ["Self-hosted runner (push-caller)"]
|
||||
branches: ["main"]
|
||||
types: [completed]
|
||||
push:
|
||||
branches:
|
||||
- run_amd_push_ci_caller*
|
||||
paths:
|
||||
- "src/**"
|
||||
- "tests/**"
|
||||
- ".github/**"
|
||||
- "templates/**"
|
||||
- "utils/**"
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
run_amd_ci:
|
||||
name: AMD mi210
|
||||
if: (cancelled() != true) && ((github.event_name == 'workflow_run') || ((github.event_name == 'push') && startsWith(github.ref_name, 'run_amd_push_ci_caller')))
|
||||
uses: ./.github/workflows/self-push-amd.yml
|
||||
with:
|
||||
gpu_flavor: mi210
|
||||
secrets: inherit
|
||||
|
||||
50
.github/workflows/self-push-amd-mi250-caller.yml
vendored
50
.github/workflows/self-push-amd-mi250-caller.yml
vendored
@ -1,25 +1,25 @@
|
||||
name: Self-hosted runner (AMD mi250 CI caller)
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
#workflow_run:
|
||||
# workflows: ["Self-hosted runner (push-caller)"]
|
||||
# branches: ["main"]
|
||||
# types: [completed]
|
||||
push:
|
||||
branches:
|
||||
- run_amd_push_ci_caller*
|
||||
paths:
|
||||
- "src/**"
|
||||
- "tests/**"
|
||||
- ".github/**"
|
||||
- "templates/**"
|
||||
- "utils/**"
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
run_amd_ci:
|
||||
name: AMD mi250
|
||||
if: (cancelled() != true) && ((github.event_name == 'workflow_run') || ((github.event_name == 'push') && startsWith(github.ref_name, 'run_amd_push_ci_caller')))
|
||||
uses: ./.github/workflows/self-push-amd.yml
|
||||
with:
|
||||
gpu_flavor: mi250
|
||||
secrets: inherit
|
||||
name: Self-hosted runner (AMD mi250 CI caller)
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
workflow_run:
|
||||
workflows: ["Self-hosted runner (push-caller)"]
|
||||
branches: ["main"]
|
||||
types: [completed]
|
||||
push:
|
||||
branches:
|
||||
- run_amd_push_ci_caller*
|
||||
paths:
|
||||
- "src/**"
|
||||
- "tests/**"
|
||||
- ".github/**"
|
||||
- "templates/**"
|
||||
- "utils/**"
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
run_amd_ci:
|
||||
name: AMD mi250
|
||||
if: (cancelled() != true) && ((github.event_name == 'workflow_run') || ((github.event_name == 'push') && startsWith(github.ref_name, 'run_amd_push_ci_caller')))
|
||||
uses: ./.github/workflows/self-push-amd.yml
|
||||
with:
|
||||
gpu_flavor: mi250
|
||||
secrets: inherit
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,10 +1,10 @@
|
||||
name: Self-hosted runner (AMD mi300 CI caller)
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
#workflow_run:
|
||||
# workflows: ["Self-hosted runner (push-caller)"]
|
||||
# branches: ["main"]
|
||||
# types: [completed]
|
||||
workflow_run:
|
||||
workflows: ["Self-hosted runner (push-caller)"]
|
||||
branches: ["main"]
|
||||
types: [completed]
|
||||
push:
|
||||
branches:
|
||||
- run_amd_push_ci_caller*
|
||||
|
||||
1
.github/workflows/self-push-amd.yml
vendored
1
.github/workflows/self-push-amd.yml
vendored
@ -14,6 +14,7 @@ env:
|
||||
MKL_NUM_THREADS: 8
|
||||
PYTEST_TIMEOUT: 60
|
||||
TF_FORCE_GPU_ALLOW_GROWTH: true
|
||||
RUN_PT_TF_CROSS_TESTS: 1
|
||||
HF_HUB_READ_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.HF_HUB_READ_TOKEN }}
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
|
||||
4
.github/workflows/self-push-caller.yml
vendored
4
.github/workflows/self-push-caller.yml
vendored
@ -25,7 +25,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Get changed files
|
||||
id: changed-files
|
||||
uses: tj-actions/changed-files@1c8e6069583811afb28f97afeaf8e7da80c6be5c
|
||||
uses: tj-actions/changed-files@v41
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Was setup changed
|
||||
id: was_changed
|
||||
@ -51,4 +51,4 @@ jobs:
|
||||
needs: build-docker-containers
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Trigger push CI via workflow_run
|
||||
run: echo "Trigger push CI via workflow_run"
|
||||
run: echo "Trigger push CI via workflow_run"
|
||||
136
.github/workflows/self-push.yml
vendored
136
.github/workflows/self-push.yml
vendored
@ -24,6 +24,7 @@ env:
|
||||
MKL_NUM_THREADS: 8
|
||||
PYTEST_TIMEOUT: 60
|
||||
TF_FORCE_GPU_ALLOW_GROWTH: true
|
||||
RUN_PT_TF_CROSS_TESTS: 1
|
||||
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES: 0,1
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
@ -31,9 +32,8 @@ jobs:
|
||||
name: Setup
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
machine_type: [aws-g4dn-2xlarge-cache, aws-g4dn-12xlarge-cache]
|
||||
runs-on:
|
||||
group: '${{ matrix.machine_type }}'
|
||||
machine_type: [single-gpu, multi-gpu]
|
||||
runs-on: ['${{ matrix.machine_type }}', nvidia-gpu, t4, push-ci]
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: huggingface/transformers-all-latest-gpu-push-ci
|
||||
options: --gpus 0 --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
@ -131,9 +131,8 @@ jobs:
|
||||
fail-fast: false
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
folders: ${{ fromJson(needs.setup.outputs.matrix) }}
|
||||
machine_type: [aws-g4dn-2xlarge-cache]
|
||||
runs-on:
|
||||
group: '${{ matrix.machine_type }}'
|
||||
machine_type: [single-gpu]
|
||||
runs-on: ['${{ matrix.machine_type }}', nvidia-gpu, t4, push-ci]
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: huggingface/transformers-all-latest-gpu-push-ci
|
||||
options: --gpus 0 --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
@ -163,23 +162,6 @@ jobs:
|
||||
echo "env.CI_BRANCH = ${{ env.CI_BRANCH }}"
|
||||
echo "env.CI_SHA = ${{ env.CI_SHA }}"
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Set `machine_type` for report and artifact names
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "${{ matrix.machine_type }}"
|
||||
|
||||
if [ "${{ matrix.machine_type }}" = "aws-g4dn-2xlarge-cache" ]; then
|
||||
machine_type=single-gpu
|
||||
elif [ "${{ matrix.machine_type }}" = "aws-g4dn-12xlarge-cache" ]; then
|
||||
machine_type=multi-gpu
|
||||
else
|
||||
machine_type=${{ matrix.machine_type }}
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
echo "$machine_type"
|
||||
echo "machine_type=$machine_type" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Update clone using environment variables
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
@ -221,19 +203,19 @@ jobs:
|
||||
- name: Run all non-slow selected tests on GPU
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python3 -m pytest -n 2 --dist=loadfile -v --make-reports=${{ env.machine_type }}_tests_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }} ${{ fromJson(needs.setup.outputs.test_map)[matrix.folders] }}
|
||||
python3 -m pytest -n 2 --dist=loadfile -v --make-reports=${{ matrix.machine_type }}_tests_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }} ${{ fromJson(needs.setup.outputs.test_map)[matrix.folders] }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
if: ${{ failure() }}
|
||||
continue-on-error: true
|
||||
run: cat /transformers/reports/${{ env.machine_type }}_tests_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}/failures_short.txt
|
||||
run: cat /transformers/reports/${{ matrix.machine_type }}_tests_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}/failures_short.txt
|
||||
|
||||
- name: "Test suite reports artifacts: ${{ env.machine_type }}_run_all_tests_gpu_${{ env.matrix_folders }}_test_reports"
|
||||
- name: "Test suite reports artifacts: ${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_all_tests_gpu_${{ env.matrix_folders }}_test_reports"
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: ${{ env.machine_type }}_run_all_tests_gpu_${{ env.matrix_folders }}_test_reports
|
||||
path: /transformers/reports/${{ env.machine_type }}_tests_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}
|
||||
name: ${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_all_tests_gpu_${{ env.matrix_folders }}_test_reports
|
||||
path: /transformers/reports/${{ matrix.machine_type }}_tests_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}
|
||||
|
||||
run_tests_multi_gpu:
|
||||
name: Model tests
|
||||
@ -244,9 +226,8 @@ jobs:
|
||||
fail-fast: false
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
folders: ${{ fromJson(needs.setup.outputs.matrix) }}
|
||||
machine_type: [aws-g4dn-12xlarge-cache]
|
||||
runs-on:
|
||||
group: '${{ matrix.machine_type }}'
|
||||
machine_type: [multi-gpu]
|
||||
runs-on: ['${{ matrix.machine_type }}', nvidia-gpu, t4, push-ci]
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: huggingface/transformers-all-latest-gpu-push-ci
|
||||
options: --gpus all --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
@ -276,23 +257,6 @@ jobs:
|
||||
echo "env.CI_BRANCH = ${{ env.CI_BRANCH }}"
|
||||
echo "env.CI_SHA = ${{ env.CI_SHA }}"
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Set `machine_type` for report and artifact names
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "${{ matrix.machine_type }}"
|
||||
|
||||
if [ "${{ matrix.machine_type }}" = "aws-g4dn-2xlarge-cache" ]; then
|
||||
machine_type=single-gpu
|
||||
elif [ "${{ matrix.machine_type }}" = "aws-g4dn-12xlarge-cache" ]; then
|
||||
machine_type=multi-gpu
|
||||
else
|
||||
machine_type=${{ matrix.machine_type }}
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
echo "$machine_type"
|
||||
echo "machine_type=$machine_type" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Update clone using environment variables
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
@ -336,19 +300,19 @@ jobs:
|
||||
MKL_SERVICE_FORCE_INTEL: 1
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python3 -m pytest -n 2 --dist=loadfile -v --make-reports=${{ env.machine_type }}_tests_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }} ${{ fromJson(needs.setup.outputs.test_map)[matrix.folders] }}
|
||||
python3 -m pytest -n 2 --dist=loadfile -v --make-reports=${{ matrix.machine_type }}_tests_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }} ${{ fromJson(needs.setup.outputs.test_map)[matrix.folders] }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
if: ${{ failure() }}
|
||||
continue-on-error: true
|
||||
run: cat /transformers/reports/${{ env.machine_type }}_tests_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}/failures_short.txt
|
||||
run: cat /transformers/reports/${{ matrix.machine_type }}_tests_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}/failures_short.txt
|
||||
|
||||
- name: "Test suite reports artifacts: ${{ env.machine_type }}_run_all_tests_gpu_${{ env.matrix_folders }}_test_reports"
|
||||
- name: "Test suite reports artifacts: ${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_all_tests_gpu_${{ env.matrix_folders }}_test_reports"
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: ${{ env.machine_type }}_run_all_tests_gpu_${{ env.matrix_folders }}_test_reports
|
||||
path: /transformers/reports/${{ env.machine_type }}_tests_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}
|
||||
name: ${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_all_tests_gpu_${{ env.matrix_folders }}_test_reports
|
||||
path: /transformers/reports/${{ matrix.machine_type }}_tests_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}
|
||||
|
||||
run_tests_torch_cuda_extensions_single_gpu:
|
||||
name: Torch CUDA extension tests
|
||||
@ -357,9 +321,8 @@ jobs:
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
fail-fast: false
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
machine_type: [aws-g4dn-2xlarge-cache]
|
||||
runs-on:
|
||||
group: '${{ matrix.machine_type }}'
|
||||
machine_type: [single-gpu]
|
||||
runs-on: ['${{ matrix.machine_type }}', nvidia-gpu, t4, push-ci]
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: huggingface/transformers-pytorch-deepspeed-latest-gpu-push-ci
|
||||
options: --gpus 0 --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
@ -389,23 +352,6 @@ jobs:
|
||||
echo "env.CI_BRANCH = ${{ env.CI_BRANCH }}"
|
||||
echo "env.CI_SHA = ${{ env.CI_SHA }}"
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Set `machine_type` for report and artifact names
|
||||
working-directory: /workspace/transformers
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "${{ matrix.machine_type }}"
|
||||
|
||||
if [ "${{ matrix.machine_type }}" = "aws-g4dn-2xlarge-cache" ]; then
|
||||
machine_type=single-gpu
|
||||
elif [ "${{ matrix.machine_type }}" = "aws-g4dn-12xlarge-cache" ]; then
|
||||
machine_type=multi-gpu
|
||||
else
|
||||
machine_type=${{ matrix.machine_type }}
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
echo "$machine_type"
|
||||
echo "machine_type=$machine_type" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Update clone using environment variables
|
||||
working-directory: /workspace/transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
@ -446,19 +392,19 @@ jobs:
|
||||
working-directory: /workspace/transformers
|
||||
# TODO: Here we pass all tests in the 2 folders for simplicity. It's better to pass only the identified tests.
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 1 --dist=loadfile -v --make-reports=${{ env.machine_type }}_run_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu_test_reports tests/deepspeed tests/extended
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 1 --dist=loadfile -v --make-reports=${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu_test_reports tests/deepspeed tests/extended
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
if: ${{ failure() }}
|
||||
continue-on-error: true
|
||||
run: cat /workspace/transformers/reports/${{ env.machine_type }}_run_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu_test_reports/failures_short.txt
|
||||
run: cat /workspace/transformers/reports/${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu_test_reports/failures_short.txt
|
||||
|
||||
- name: "Test suite reports artifacts: ${{ env.machine_type }}_run_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu_test_reports"
|
||||
- name: "Test suite reports artifacts: ${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu_test_reports"
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: ${{ env.machine_type }}_run_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu_test_reports
|
||||
path: /workspace/transformers/reports/${{ env.machine_type }}_run_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu_test_reports
|
||||
name: ${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu_test_reports
|
||||
path: /workspace/transformers/reports/${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu_test_reports
|
||||
|
||||
run_tests_torch_cuda_extensions_multi_gpu:
|
||||
name: Torch CUDA extension tests
|
||||
@ -467,9 +413,8 @@ jobs:
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
fail-fast: false
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
machine_type: [aws-g4dn-12xlarge-cache]
|
||||
runs-on:
|
||||
group: '${{ matrix.machine_type }}'
|
||||
machine_type: [multi-gpu]
|
||||
runs-on: ['${{ matrix.machine_type }}', nvidia-gpu, t4, push-ci]
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: huggingface/transformers-pytorch-deepspeed-latest-gpu-push-ci
|
||||
options: --gpus all --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
@ -499,23 +444,6 @@ jobs:
|
||||
echo "env.CI_BRANCH = ${{ env.CI_BRANCH }}"
|
||||
echo "env.CI_SHA = ${{ env.CI_SHA }}"
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Set `machine_type` for report and artifact names
|
||||
working-directory: /workspace/transformers
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "${{ matrix.machine_type }}"
|
||||
|
||||
if [ "${{ matrix.machine_type }}" = "aws-g4dn-2xlarge-cache" ]; then
|
||||
machine_type=single-gpu
|
||||
elif [ "${{ matrix.machine_type }}" = "aws-g4dn-12xlarge-cache" ]; then
|
||||
machine_type=multi-gpu
|
||||
else
|
||||
machine_type=${{ matrix.machine_type }}
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
echo "$machine_type"
|
||||
echo "machine_type=$machine_type" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Update clone using environment variables
|
||||
working-directory: /workspace/transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
@ -556,19 +484,19 @@ jobs:
|
||||
working-directory: /workspace/transformers
|
||||
# TODO: Here we pass all tests in the 2 folders for simplicity. It's better to pass only the identified tests.
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 1 --dist=loadfile -v --make-reports=${{ env.machine_type }}_run_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu_test_reports tests/deepspeed tests/extended
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 1 --dist=loadfile -v --make-reports=${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu_test_reports tests/deepspeed tests/extended
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
if: ${{ failure() }}
|
||||
continue-on-error: true
|
||||
run: cat /workspace/transformers/reports/${{ env.machine_type }}_run_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu_test_reports/failures_short.txt
|
||||
run: cat /workspace/transformers/reports/${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu_test_reports/failures_short.txt
|
||||
|
||||
- name: "Test suite reports artifacts: ${{ env.machine_type }}_run_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu_test_reports"
|
||||
- name: "Test suite reports artifacts: ${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu_test_reports"
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: ${{ env.machine_type }}_run_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu_test_reports
|
||||
path: /workspace/transformers/reports/${{ env.machine_type }}_run_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu_test_reports
|
||||
name: ${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu_test_reports
|
||||
path: /workspace/transformers/reports/${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu_test_reports
|
||||
|
||||
send_results:
|
||||
name: Send results to webhook
|
||||
@ -647,6 +575,6 @@ jobs:
|
||||
# `models/bert` to `models_bert` is required, as the artifact names use `_` instead of `/`.
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
pip install huggingface_hub
|
||||
pip install slack_sdk
|
||||
pip install slack_sdk
|
||||
pip show slack_sdk
|
||||
python utils/notification_service.py "${{ needs.setup.outputs.matrix }}"
|
||||
|
||||
55
.github/workflows/self-scheduled-amd-mi210-caller.yml
vendored
Normal file
55
.github/workflows/self-scheduled-amd-mi210-caller.yml
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,55 @@
|
||||
name: Self-hosted runner (AMD mi210 scheduled CI caller)
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
workflow_run:
|
||||
workflows: ["Self-hosted runner (AMD scheduled CI caller)"]
|
||||
branches: ["main"]
|
||||
types: [completed]
|
||||
push:
|
||||
branches:
|
||||
- run_amd_scheduled_ci_caller*
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
model-ci:
|
||||
name: Model CI
|
||||
uses: ./.github/workflows/self-scheduled-amd.yml
|
||||
with:
|
||||
job: run_models_gpu
|
||||
slack_report_channel: "#transformers-ci-daily-amd"
|
||||
runner: mi210
|
||||
docker: huggingface/transformers-pytorch-amd-gpu
|
||||
ci_event: Scheduled CI (AMD) - mi210
|
||||
secrets: inherit
|
||||
|
||||
torch-pipeline:
|
||||
name: Torch pipeline CI
|
||||
uses: ./.github/workflows/self-scheduled-amd.yml
|
||||
with:
|
||||
job: run_pipelines_torch_gpu
|
||||
slack_report_channel: "#transformers-ci-daily-amd"
|
||||
runner: mi210
|
||||
docker: huggingface/transformers-pytorch-amd-gpu
|
||||
ci_event: Scheduled CI (AMD) - mi210
|
||||
secrets: inherit
|
||||
|
||||
example-ci:
|
||||
name: Example CI
|
||||
uses: ./.github/workflows/self-scheduled-amd.yml
|
||||
with:
|
||||
job: run_examples_gpu
|
||||
slack_report_channel: "#transformers-ci-daily-amd"
|
||||
runner: mi210
|
||||
docker: huggingface/transformers-pytorch-amd-gpu
|
||||
ci_event: Scheduled CI (AMD) - mi210
|
||||
secrets: inherit
|
||||
|
||||
deepspeed-ci:
|
||||
name: DeepSpeed CI
|
||||
uses: ./.github/workflows/self-scheduled-amd.yml
|
||||
with:
|
||||
job: run_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu
|
||||
slack_report_channel: "#transformers-ci-daily-amd"
|
||||
runner: mi210
|
||||
docker: huggingface/transformers-pytorch-deepspeed-amd-gpu
|
||||
ci_event: Scheduled CI (AMD) - mi210
|
||||
secrets: inherit
|
||||
@ -1,59 +1,55 @@
|
||||
name: Self-hosted runner (AMD mi250 scheduled CI caller)
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
workflow_run:
|
||||
workflows: ["Self-hosted runner (AMD scheduled CI caller)"]
|
||||
branches: ["main"]
|
||||
types: [completed]
|
||||
push:
|
||||
branches:
|
||||
- run_amd_scheduled_ci_caller*
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
model-ci:
|
||||
name: Model CI
|
||||
uses: huggingface/hf-workflows/.github/workflows/transformers_amd_ci_scheduled.yaml@main
|
||||
with:
|
||||
job: run_models_gpu
|
||||
slack_report_channel: "#transformers-ci-daily-amd"
|
||||
runner: mi250
|
||||
docker: huggingface/transformers-pytorch-amd-gpu
|
||||
ci_event: Scheduled CI (AMD) - mi250
|
||||
report_repo_id: optimum-amd/transformers_daily_ci
|
||||
secrets: inherit
|
||||
|
||||
torch-pipeline:
|
||||
name: Torch pipeline CI
|
||||
uses: huggingface/hf-workflows/.github/workflows/transformers_amd_ci_scheduled.yaml@main
|
||||
with:
|
||||
job: run_pipelines_torch_gpu
|
||||
slack_report_channel: "#transformers-ci-daily-amd"
|
||||
runner: mi250
|
||||
docker: huggingface/transformers-pytorch-amd-gpu
|
||||
ci_event: Scheduled CI (AMD) - mi250
|
||||
report_repo_id: optimum-amd/transformers_daily_ci
|
||||
secrets: inherit
|
||||
|
||||
example-ci:
|
||||
name: Example CI
|
||||
uses: huggingface/hf-workflows/.github/workflows/transformers_amd_ci_scheduled.yaml@main
|
||||
with:
|
||||
job: run_examples_gpu
|
||||
slack_report_channel: "#transformers-ci-daily-amd"
|
||||
runner: mi250
|
||||
docker: huggingface/transformers-pytorch-amd-gpu
|
||||
ci_event: Scheduled CI (AMD) - mi250
|
||||
report_repo_id: optimum-amd/transformers_daily_ci
|
||||
secrets: inherit
|
||||
|
||||
deepspeed-ci:
|
||||
name: DeepSpeed CI
|
||||
uses: huggingface/hf-workflows/.github/workflows/transformers_amd_ci_scheduled.yaml@main
|
||||
with:
|
||||
job: run_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu
|
||||
slack_report_channel: "#transformers-ci-daily-amd"
|
||||
runner: mi250
|
||||
docker: huggingface/transformers-pytorch-deepspeed-amd-gpu
|
||||
ci_event: Scheduled CI (AMD) - mi250
|
||||
report_repo_id: optimum-amd/transformers_daily_ci
|
||||
secrets: inherit
|
||||
name: Self-hosted runner (AMD mi250 scheduled CI caller)
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
workflow_run:
|
||||
workflows: ["Self-hosted runner (AMD scheduled CI caller)"]
|
||||
branches: ["main"]
|
||||
types: [completed]
|
||||
push:
|
||||
branches:
|
||||
- run_amd_scheduled_ci_caller*
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
model-ci:
|
||||
name: Model CI
|
||||
uses: ./.github/workflows/self-scheduled-amd.yml
|
||||
with:
|
||||
job: run_models_gpu
|
||||
slack_report_channel: "#transformers-ci-daily-amd"
|
||||
runner: mi250
|
||||
docker: huggingface/transformers-pytorch-amd-gpu
|
||||
ci_event: Scheduled CI (AMD) - mi250
|
||||
secrets: inherit
|
||||
|
||||
torch-pipeline:
|
||||
name: Torch pipeline CI
|
||||
uses: ./.github/workflows/self-scheduled-amd.yml
|
||||
with:
|
||||
job: run_pipelines_torch_gpu
|
||||
slack_report_channel: "#transformers-ci-daily-amd"
|
||||
runner: mi250
|
||||
docker: huggingface/transformers-pytorch-amd-gpu
|
||||
ci_event: Scheduled CI (AMD) - mi250
|
||||
secrets: inherit
|
||||
|
||||
example-ci:
|
||||
name: Example CI
|
||||
uses: ./.github/workflows/self-scheduled-amd.yml
|
||||
with:
|
||||
job: run_examples_gpu
|
||||
slack_report_channel: "#transformers-ci-daily-amd"
|
||||
runner: mi250
|
||||
docker: huggingface/transformers-pytorch-amd-gpu
|
||||
ci_event: Scheduled CI (AMD) - mi250
|
||||
secrets: inherit
|
||||
|
||||
deepspeed-ci:
|
||||
name: DeepSpeed CI
|
||||
uses: ./.github/workflows/self-scheduled-amd.yml
|
||||
with:
|
||||
job: run_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu
|
||||
slack_report_channel: "#transformers-ci-daily-amd"
|
||||
runner: mi250
|
||||
docker: huggingface/transformers-pytorch-deepspeed-amd-gpu
|
||||
ci_event: Scheduled CI (AMD) - mi250
|
||||
secrets: inherit
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,63 +0,0 @@
|
||||
name: Self-hosted runner scale set (AMD mi300 scheduled CI caller)
|
||||
|
||||
# Note: For every job in this workflow, the name of the runner scale set is finalized in the runner yaml i.e. huggingface/hf-workflows/.github/workflows/transformers_amd_ci_scheduled_arc_scale_set.yaml
|
||||
# For example, 1gpu scale set: amd-mi300-ci-1gpu
|
||||
# 2gpu scale set: amd-mi300-ci-2gpu
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
workflow_run:
|
||||
workflows: ["Self-hosted runner (AMD scheduled CI caller)"]
|
||||
branches: ["main"]
|
||||
types: [completed]
|
||||
push:
|
||||
branches:
|
||||
- run_amd_scheduled_ci_caller*
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
model-ci:
|
||||
name: Model CI
|
||||
uses: huggingface/hf-workflows/.github/workflows/transformers_amd_ci_scheduled_arc_scale_set.yaml@main
|
||||
with:
|
||||
job: run_models_gpu
|
||||
slack_report_channel: "#amd-hf-ci"
|
||||
runner_scale_set: amd-mi300-ci
|
||||
docker: huggingface/transformers-pytorch-amd-gpu
|
||||
ci_event: Scheduled CI (AMD) - mi300
|
||||
report_repo_id: optimum-amd/transformers_daily_ci
|
||||
secrets: inherit
|
||||
|
||||
torch-pipeline:
|
||||
name: Torch pipeline CI
|
||||
uses: huggingface/hf-workflows/.github/workflows/transformers_amd_ci_scheduled_arc_scale_set.yaml@main
|
||||
with:
|
||||
job: run_pipelines_torch_gpu
|
||||
slack_report_channel: "#amd-hf-ci"
|
||||
runner_scale_set: amd-mi300-ci
|
||||
docker: huggingface/transformers-pytorch-amd-gpu
|
||||
ci_event: Scheduled CI (AMD) - mi300
|
||||
report_repo_id: optimum-amd/transformers_daily_ci
|
||||
secrets: inherit
|
||||
|
||||
example-ci:
|
||||
name: Example CI
|
||||
uses: huggingface/hf-workflows/.github/workflows/transformers_amd_ci_scheduled_arc_scale_set.yaml@main
|
||||
with:
|
||||
job: run_examples_gpu
|
||||
slack_report_channel: "#amd-hf-ci"
|
||||
runner_scale_set: amd-mi300-ci
|
||||
docker: huggingface/transformers-pytorch-amd-gpu
|
||||
ci_event: Scheduled CI (AMD) - mi300
|
||||
report_repo_id: optimum-amd/transformers_daily_ci
|
||||
secrets: inherit
|
||||
|
||||
deepspeed-ci:
|
||||
name: DeepSpeed CI
|
||||
uses: huggingface/hf-workflows/.github/workflows/transformers_amd_ci_scheduled_arc_scale_set.yaml@main
|
||||
with:
|
||||
job: run_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu
|
||||
slack_report_channel: "#amd-hf-ci"
|
||||
runner_scale_set: amd-mi300-ci
|
||||
docker: huggingface/transformers-pytorch-deepspeed-amd-gpu
|
||||
ci_event: Scheduled CI (AMD) - mi300
|
||||
report_repo_id: optimum-amd/transformers_daily_ci
|
||||
secrets: inherit
|
||||
349
.github/workflows/self-scheduled-amd.yml
vendored
Normal file
349
.github/workflows/self-scheduled-amd.yml
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,349 @@
|
||||
name: Self-hosted runner (scheduled-amd)
|
||||
|
||||
# Note: For the AMD CI, we rely on a caller workflow and on the workflow_call event to trigger the
|
||||
# CI in order to run it on both MI210 and MI250, without having to use matrix here which pushes
|
||||
# us towards the limit of allowed jobs on GitHub Actions.
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
workflow_call:
|
||||
inputs:
|
||||
job:
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
type: string
|
||||
slack_report_channel:
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
type: string
|
||||
runner:
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
type: string
|
||||
docker:
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
type: string
|
||||
ci_event:
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
type: string
|
||||
|
||||
env:
|
||||
HF_HOME: /mnt/cache
|
||||
TRANSFORMERS_IS_CI: yes
|
||||
OMP_NUM_THREADS: 8
|
||||
MKL_NUM_THREADS: 8
|
||||
RUN_SLOW: yes
|
||||
HF_HUB_READ_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.HF_HUB_READ_TOKEN }}
|
||||
SIGOPT_API_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.SIGOPT_API_TOKEN }}
|
||||
NUM_SLICES: 2
|
||||
|
||||
# Important note: each job (run_tests_single_gpu, run_tests_multi_gpu, run_examples_gpu, run_pipelines_torch_gpu) requires all the previous jobs before running.
|
||||
# This is done so that we avoid parallelizing the scheduled tests, to leave available
|
||||
# runners for the push CI that is running on the same machine.
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
check_runner_status:
|
||||
name: Check Runner Status
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-22.04
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Checkout transformers
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
fetch-depth: 2
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Check Runner Status
|
||||
run: python utils/check_self_hosted_runner.py --target_runners hf-amd-mi210-ci-1gpu-1,hf-amd-mi250-ci-1gpu-1,hf-amd-mi300-ci-1gpu-1 --token ${{ secrets.ACCESS_REPO_INFO_TOKEN }}
|
||||
|
||||
check_runners:
|
||||
name: Check Runners
|
||||
needs: check_runner_status
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
machine_type: [single-gpu, multi-gpu]
|
||||
runs-on: ['${{ matrix.machine_type }}', self-hosted, amd-gpu, '${{ inputs.runner }}']
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: huggingface/transformers-pytorch-amd-gpu
|
||||
options: --device /dev/kfd --device /dev/dri --env ROCR_VISIBLE_DEVICES --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: ROCM-SMI
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
rocm-smi
|
||||
|
||||
- name: ROCM-INFO
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
rocminfo | grep "Agent" -A 14
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Show ROCR environment
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "ROCR: $ROCR_VISIBLE_DEVICES"
|
||||
|
||||
setup:
|
||||
if: contains(fromJSON('["run_models_gpu"]'), inputs.job)
|
||||
name: Setup
|
||||
needs: check_runners
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
machine_type: [single-gpu, multi-gpu]
|
||||
runs-on: ['${{ matrix.machine_type }}', self-hosted, amd-gpu, '${{ inputs.runner }}']
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: huggingface/transformers-pytorch-amd-gpu
|
||||
options: --device /dev/kfd --device /dev/dri --env ROCR_VISIBLE_DEVICES --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
outputs:
|
||||
folder_slices: ${{ steps.set-matrix.outputs.folder_slices }}
|
||||
slice_ids: ${{ steps.set-matrix.outputs.slice_ids }}
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Update clone
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
git fetch && git checkout ${{ github.sha }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Cleanup
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
rm -rf tests/__pycache__
|
||||
rm -rf tests/models/__pycache__
|
||||
rm -rf reports
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Show installed libraries and their versions
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: pip freeze
|
||||
|
||||
- id: set-matrix
|
||||
name: Identify models to test
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers/tests
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "folder_slices=$(python3 ../utils/split_model_tests.py --num_splits ${{ env.NUM_SLICES }})" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
|
||||
echo "slice_ids=$(python3 -c 'd = list(range(${{ env.NUM_SLICES }})); print(d)')" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
|
||||
|
||||
- name: ROCM-SMI
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
rocm-smi
|
||||
|
||||
- name: ROCM-INFO
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
rocminfo | grep "Agent" -A 14
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Show ROCR environment
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "ROCR: $ROCR_VISIBLE_DEVICES"
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Environment
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python3 utils/print_env.py
|
||||
|
||||
run_models_gpu:
|
||||
if: ${{ inputs.job == 'run_models_gpu' }}
|
||||
name: Single GPU tests
|
||||
needs: setup
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
max-parallel: 1 # For now, not to parallelize. Can change later if it works well.
|
||||
fail-fast: false
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
machine_type: [single-gpu, multi-gpu]
|
||||
slice_id: ${{ fromJSON(needs.setup.outputs.slice_ids) }}
|
||||
uses: ./.github/workflows/model_jobs_amd.yml
|
||||
with:
|
||||
folder_slices: ${{ needs.setup.outputs.folder_slices }}
|
||||
machine_type: ${{ matrix.machine_type }}
|
||||
slice_id: ${{ matrix.slice_id }}
|
||||
runner: ${{ inputs.runner }}
|
||||
docker: ${{ inputs.docker }}
|
||||
secrets: inherit
|
||||
|
||||
run_pipelines_torch_gpu:
|
||||
if: ${{ inputs.job == 'run_pipelines_torch_gpu' }}
|
||||
name: PyTorch pipelines
|
||||
needs: check_runners
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
fail-fast: false
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
machine_type: [single-gpu, multi-gpu]
|
||||
runs-on: ['${{ matrix.machine_type }}', self-hosted, amd-gpu, '${{ inputs.runner }}']
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: ${{ inputs.docker }}
|
||||
options: --device /dev/kfd --device /dev/dri --env ROCR_VISIBLE_DEVICES --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Update clone
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: git fetch && git checkout ${{ github.sha }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Reinstall transformers in edit mode (remove the one installed during docker image build)
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: python3 -m pip uninstall -y transformers && python3 -m pip install -e .
|
||||
|
||||
- name: ROCM-SMI
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
rocm-smi
|
||||
|
||||
- name: ROCM-INFO
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
rocminfo | grep "Agent" -A 14
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Show ROCR environment
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "ROCR: $ROCR_VISIBLE_DEVICES"
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Environment
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python3 utils/print_env.py
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Show installed libraries and their versions
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: pip freeze
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run all pipeline tests on GPU
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python3 -m pytest -n 1 -v --dist=loadfile --make-reports=${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_pipelines_torch_gpu_test_reports tests/pipelines -m "not not_device_test"
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
if: ${{ failure() }}
|
||||
continue-on-error: true
|
||||
run: cat /transformers/reports/${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_pipelines_torch_gpu_test_reports/failures_short.txt
|
||||
|
||||
- name: "Test suite reports artifacts: ${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_pipelines_torch_gpu_test_reports"
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: ${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_pipelines_torch_gpu_test_reports
|
||||
path: /transformers/reports/${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_pipelines_torch_gpu_test_reports
|
||||
|
||||
run_examples_gpu:
|
||||
if: ${{ inputs.job == 'run_examples_gpu' }}
|
||||
name: Examples directory
|
||||
needs: check_runners
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
fail-fast: false
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
machine_type: [single-gpu]
|
||||
runs-on: ['${{ matrix.machine_type }}', self-hosted, amd-gpu, '${{ inputs.runner }}']
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: ${{ inputs.docker }}
|
||||
options: --device /dev/kfd --device /dev/dri --env ROCR_VISIBLE_DEVICES --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Update clone
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: git fetch && git checkout ${{ github.sha }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Reinstall transformers in edit mode (remove the one installed during docker image build)
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: python3 -m pip uninstall -y transformers && python3 -m pip install -e .
|
||||
|
||||
- name: ROCM-SMI
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
rocm-smi
|
||||
|
||||
- name: ROCM-INFO
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
rocminfo | grep "Agent" -A 14
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Show ROCR environment
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "ROCR: $ROCR_VISIBLE_DEVICES"
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Environment
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python3 utils/print_env.py
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Show installed libraries and their versions
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: pip freeze
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run examples tests on GPU
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
pip install -r examples/pytorch/_tests_requirements.txt
|
||||
python3 -m pytest -v --make-reports=${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_examples_gpu_test_reports examples/pytorch -m "not not_device_test"
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
if: ${{ failure() }}
|
||||
continue-on-error: true
|
||||
run: cat /transformers/reports/${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_examples_gpu_test_reports/failures_short.txt
|
||||
|
||||
- name: "Test suite reports artifacts: ${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_examples_gpu_test_reports"
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: ${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_examples_gpu_test_reports
|
||||
path: /transformers/reports/${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_examples_gpu_test_reports
|
||||
|
||||
run_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu:
|
||||
if: ${{ inputs.job == 'run_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu' }}
|
||||
name: Torch ROCm deepspeed tests
|
||||
needs: check_runners
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
fail-fast: false
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
machine_type: [single-gpu, multi-gpu]
|
||||
runs-on: ['${{ matrix.machine_type }}', self-hosted, amd-gpu, '${{ inputs.runner }}']
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: ${{ inputs.docker }}
|
||||
options: --device /dev/kfd --device /dev/dri --env ROCR_VISIBLE_DEVICES --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Update clone
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: git fetch && git checkout ${{ github.sha }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Reinstall transformers in edit mode (remove the one installed during docker image build)
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: python3 -m pip uninstall -y transformers && python3 -m pip install -e .
|
||||
|
||||
- name: ROCM-SMI
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
rocm-smi
|
||||
|
||||
- name: ROCM-INFO
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
rocminfo | grep "Agent" -A 14
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Show ROCR environment
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "ROCR: $ROCR_VISIBLE_DEVICES"
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Environment
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python3 utils/print_env.py
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Show installed libraries and their versions
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: pip freeze
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run all tests on GPU
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: python3 -m pytest -v --make-reports=${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu_test_reports tests/deepspeed tests/extended -m "not not_device_test"
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
if: ${{ failure() }}
|
||||
continue-on-error: true
|
||||
run: cat /transformers/reports/${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu_test_reports/failures_short.txt
|
||||
|
||||
- name: "Test suite reports artifacts: ${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu_test_reports"
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: ${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu_test_reports
|
||||
path: /transformers/reports/${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu_test_reports
|
||||
|
||||
send_results:
|
||||
name: Slack Report
|
||||
needs: [
|
||||
check_runner_status,
|
||||
check_runners,
|
||||
setup,
|
||||
run_models_gpu,
|
||||
run_pipelines_torch_gpu,
|
||||
run_examples_gpu,
|
||||
run_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu
|
||||
]
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
uses: ./.github/workflows/slack-report.yml
|
||||
with:
|
||||
job: ${{ inputs.job }}
|
||||
# This would be `skipped` if `setup` is skipped.
|
||||
setup_status: ${{ needs.setup.result }}
|
||||
slack_report_channel: ${{ inputs.slack_report_channel }}
|
||||
# This would be an empty string if `setup` is skipped.
|
||||
folder_slices: ${{ needs.setup.outputs.folder_slices }}
|
||||
quantization_matrix: ${{ needs.setup.outputs.quantization_matrix }}
|
||||
ci_event: ${{ inputs.ci_event }}
|
||||
|
||||
secrets: inherit
|
||||
68
.github/workflows/self-scheduled-caller.yml
vendored
68
.github/workflows/self-scheduled-caller.yml
vendored
@ -2,49 +2,11 @@ name: Self-hosted runner (scheduled)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
repository_dispatch:
|
||||
schedule:
|
||||
- cron: "17 2 * * *"
|
||||
push:
|
||||
branches:
|
||||
- run_scheduled_ci*
|
||||
workflow_dispatch:
|
||||
inputs:
|
||||
prev_workflow_run_id:
|
||||
description: 'previous workflow run id to compare'
|
||||
type: string
|
||||
required: false
|
||||
default: ""
|
||||
other_workflow_run_id:
|
||||
description: 'other workflow run id to compare'
|
||||
type: string
|
||||
required: false
|
||||
default: ""
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Used for `push` to easily modiffy the target workflow runs to compare against
|
||||
env:
|
||||
prev_workflow_run_id: ""
|
||||
other_workflow_run_id: ""
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
setup:
|
||||
name: Setup
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-22.04
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Setup
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
mkdir "setup_values"
|
||||
echo "${{ inputs.prev_workflow_run_id || env.prev_workflow_run_id }}" > "setup_values/prev_workflow_run_id.txt"
|
||||
echo "${{ inputs.other_workflow_run_id || env.other_workflow_run_id }}" > "setup_values/other_workflow_run_id.txt"
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Upload artifacts
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: setup_values
|
||||
path: setup_values
|
||||
|
||||
model-ci:
|
||||
name: Model CI
|
||||
uses: ./.github/workflows/self-scheduled.yml
|
||||
@ -54,7 +16,6 @@ jobs:
|
||||
runner: daily-ci
|
||||
docker: huggingface/transformers-all-latest-gpu
|
||||
ci_event: Daily CI
|
||||
report_repo_id: hf-internal-testing/transformers_daily_ci
|
||||
secrets: inherit
|
||||
|
||||
torch-pipeline:
|
||||
@ -66,7 +27,17 @@ jobs:
|
||||
runner: daily-ci
|
||||
docker: huggingface/transformers-pytorch-gpu
|
||||
ci_event: Daily CI
|
||||
report_repo_id: hf-internal-testing/transformers_daily_ci
|
||||
secrets: inherit
|
||||
|
||||
tf-pipeline:
|
||||
name: TF pipeline CI
|
||||
uses: ./.github/workflows/self-scheduled.yml
|
||||
with:
|
||||
job: run_pipelines_tf_gpu
|
||||
slack_report_channel: "#transformers-ci-daily-pipeline-tf"
|
||||
runner: daily-ci
|
||||
docker: huggingface/transformers-tensorflow-gpu
|
||||
ci_event: Daily CI
|
||||
secrets: inherit
|
||||
|
||||
example-ci:
|
||||
@ -78,19 +49,6 @@ jobs:
|
||||
runner: daily-ci
|
||||
docker: huggingface/transformers-all-latest-gpu
|
||||
ci_event: Daily CI
|
||||
report_repo_id: hf-internal-testing/transformers_daily_ci
|
||||
secrets: inherit
|
||||
|
||||
trainer-fsdp-ci:
|
||||
name: Trainer/FSDP CI
|
||||
uses: ./.github/workflows/self-scheduled.yml
|
||||
with:
|
||||
job: run_trainer_and_fsdp_gpu
|
||||
slack_report_channel: "#transformers-ci-daily-training"
|
||||
runner: daily-ci
|
||||
docker: huggingface/transformers-all-latest-gpu
|
||||
ci_event: Daily CI
|
||||
report_repo_id: hf-internal-testing/transformers_daily_ci
|
||||
secrets: inherit
|
||||
|
||||
deepspeed-ci:
|
||||
@ -98,12 +56,11 @@ jobs:
|
||||
uses: ./.github/workflows/self-scheduled.yml
|
||||
with:
|
||||
job: run_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu
|
||||
slack_report_channel: "#transformers-ci-daily-training"
|
||||
slack_report_channel: "#transformers-ci-daily-deepspeed"
|
||||
runner: daily-ci
|
||||
docker: huggingface/transformers-pytorch-deepspeed-latest-gpu
|
||||
ci_event: Daily CI
|
||||
working-directory-prefix: /workspace
|
||||
report_repo_id: hf-internal-testing/transformers_daily_ci
|
||||
secrets: inherit
|
||||
|
||||
quantization-ci:
|
||||
@ -115,5 +72,4 @@ jobs:
|
||||
runner: daily-ci
|
||||
docker: huggingface/transformers-quantization-latest-gpu
|
||||
ci_event: Daily CI
|
||||
report_repo_id: hf-internal-testing/transformers_daily_ci
|
||||
secrets: inherit
|
||||
|
||||
243
.github/workflows/self-scheduled.yml
vendored
243
.github/workflows/self-scheduled.yml
vendored
@ -28,10 +28,6 @@ on:
|
||||
default: ''
|
||||
required: false
|
||||
type: string
|
||||
report_repo_id:
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
type: string
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
env:
|
||||
HF_HOME: /mnt/cache
|
||||
@ -44,18 +40,18 @@ env:
|
||||
HF_HUB_READ_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.HF_HUB_READ_TOKEN }}
|
||||
SIGOPT_API_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.SIGOPT_API_TOKEN }}
|
||||
TF_FORCE_GPU_ALLOW_GROWTH: true
|
||||
RUN_PT_TF_CROSS_TESTS: 1
|
||||
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES: 0,1
|
||||
NUM_SLICES: 2
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
setup:
|
||||
if: contains(fromJSON('["run_models_gpu", "run_trainer_and_fsdp_gpu", "run_quantization_torch_gpu"]'), inputs.job)
|
||||
if: contains(fromJSON('["run_models_gpu", "run_quantization_torch_gpu"]'), inputs.job)
|
||||
name: Setup
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
machine_type: [aws-g4dn-4xlarge-cache, aws-g4dn-12xlarge-cache]
|
||||
runs-on:
|
||||
group: '${{ matrix.machine_type }}'
|
||||
machine_type: [single-gpu, multi-gpu]
|
||||
runs-on: ['${{ matrix.machine_type }}', nvidia-gpu, t4, '${{ inputs.runner }}']
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: huggingface/transformers-all-latest-gpu
|
||||
options: --gpus 0 --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
@ -81,17 +77,12 @@ jobs:
|
||||
run: pip freeze
|
||||
|
||||
- id: set-matrix
|
||||
if: contains(fromJSON('["run_models_gpu", "run_trainer_and_fsdp_gpu"]'), inputs.job)
|
||||
if: ${{ inputs.job == 'run_models_gpu' }}
|
||||
name: Identify models to test
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers/tests
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
if [ "${{ inputs.job }}" = "run_models_gpu" ]; then
|
||||
echo "folder_slices=$(python3 ../utils/split_model_tests.py --num_splits ${{ env.NUM_SLICES }})" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
|
||||
echo "slice_ids=$(python3 -c 'd = list(range(${{ env.NUM_SLICES }})); print(d)')" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
|
||||
elif [ "${{ inputs.job }}" = "run_trainer_and_fsdp_gpu" ]; then
|
||||
echo "folder_slices=[['trainer'], ['fsdp']]" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
|
||||
echo "slice_ids=[0, 1]" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
|
||||
fi
|
||||
echo "folder_slices=$(python3 ../utils/split_model_tests.py --num_splits ${{ env.NUM_SLICES }})" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
|
||||
echo "slice_ids=$(python3 -c 'd = list(range(${{ env.NUM_SLICES }})); print(d)')" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
|
||||
|
||||
- id: set-matrix-quantization
|
||||
if: ${{ inputs.job == 'run_quantization_torch_gpu' }}
|
||||
@ -111,7 +102,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
fail-fast: false
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
machine_type: [aws-g4dn-4xlarge-cache, aws-g4dn-12xlarge-cache]
|
||||
machine_type: [single-gpu, multi-gpu]
|
||||
slice_id: ${{ fromJSON(needs.setup.outputs.slice_ids) }}
|
||||
uses: ./.github/workflows/model_jobs.yml
|
||||
with:
|
||||
@ -122,34 +113,14 @@ jobs:
|
||||
docker: ${{ inputs.docker }}
|
||||
secrets: inherit
|
||||
|
||||
run_trainer_and_fsdp_gpu:
|
||||
if: ${{ inputs.job == 'run_trainer_and_fsdp_gpu' }}
|
||||
name: " "
|
||||
needs: setup
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
fail-fast: false
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
machine_type: [aws-g4dn-4xlarge-cache, aws-g4dn-12xlarge-cache]
|
||||
slice_id: [0, 1]
|
||||
uses: ./.github/workflows/model_jobs.yml
|
||||
with:
|
||||
folder_slices: ${{ needs.setup.outputs.folder_slices }}
|
||||
machine_type: ${{ matrix.machine_type }}
|
||||
slice_id: ${{ matrix.slice_id }}
|
||||
runner: ${{ inputs.runner }}
|
||||
docker: ${{ inputs.docker }}
|
||||
report_name_prefix: run_trainer_and_fsdp_gpu
|
||||
secrets: inherit
|
||||
|
||||
run_pipelines_torch_gpu:
|
||||
if: ${{ inputs.job == 'run_pipelines_torch_gpu' }}
|
||||
name: PyTorch pipelines
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
fail-fast: false
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
machine_type: [aws-g4dn-4xlarge-cache, aws-g4dn-12xlarge-cache]
|
||||
runs-on:
|
||||
group: '${{ matrix.machine_type }}'
|
||||
machine_type: [single-gpu, multi-gpu]
|
||||
runs-on: ['${{ matrix.machine_type }}', nvidia-gpu, t4, '${{ inputs.runner }}']
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: huggingface/transformers-pytorch-gpu
|
||||
options: --gpus all --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
@ -175,39 +146,73 @@ jobs:
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: pip freeze
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Set `machine_type` for report and artifact names
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "${{ matrix.machine_type }}"
|
||||
|
||||
if [ "${{ matrix.machine_type }}" = "aws-g4dn-4xlarge-cache" ]; then
|
||||
machine_type=single-gpu
|
||||
elif [ "${{ matrix.machine_type }}" = "aws-g4dn-12xlarge-cache" ]; then
|
||||
machine_type=multi-gpu
|
||||
else
|
||||
machine_type=${{ matrix.machine_type }}
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
echo "$machine_type"
|
||||
echo "machine_type=$machine_type" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run all pipeline tests on GPU
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python3 -m pytest -n 1 -v --dist=loadfile --make-reports=${{ env.machine_type }}_run_pipelines_torch_gpu_test_reports tests/pipelines
|
||||
python3 -m pytest -n 1 -v --dist=loadfile --make-reports=${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_pipelines_torch_gpu_test_reports tests/pipelines
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
if: ${{ failure() }}
|
||||
continue-on-error: true
|
||||
run: cat /transformers/reports/${{ env.machine_type }}_run_pipelines_torch_gpu_test_reports/failures_short.txt
|
||||
run: cat /transformers/reports/${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_pipelines_torch_gpu_test_reports/failures_short.txt
|
||||
|
||||
- name: "Test suite reports artifacts: ${{ env.machine_type }}_run_pipelines_torch_gpu_test_reports"
|
||||
- name: "Test suite reports artifacts: ${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_pipelines_torch_gpu_test_reports"
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: ${{ env.machine_type }}_run_pipelines_torch_gpu_test_reports
|
||||
path: /transformers/reports/${{ env.machine_type }}_run_pipelines_torch_gpu_test_reports
|
||||
name: ${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_pipelines_torch_gpu_test_reports
|
||||
path: /transformers/reports/${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_pipelines_torch_gpu_test_reports
|
||||
|
||||
run_pipelines_tf_gpu:
|
||||
if: ${{ inputs.job == 'run_pipelines_tf_gpu' }}
|
||||
name: TensorFlow pipelines
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
fail-fast: false
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
machine_type: [single-gpu, multi-gpu]
|
||||
runs-on: ['${{ matrix.machine_type }}', nvidia-gpu, t4, '${{ inputs.runner }}']
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: huggingface/transformers-tensorflow-gpu
|
||||
options: --gpus all --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Update clone
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
git fetch && git checkout ${{ github.sha }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Reinstall transformers in edit mode (remove the one installed during docker image build)
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: python3 -m pip uninstall -y transformers && python3 -m pip install -e .
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NVIDIA-SMI
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
nvidia-smi
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Environment
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python3 utils/print_env.py
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Show installed libraries and their versions
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: pip freeze
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run all pipeline tests on GPU
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python3 -m pytest -n 1 -v --dist=loadfile --make-reports=${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_pipelines_tf_gpu_test_reports tests/pipelines
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
cat /transformers/reports/${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_pipelines_tf_gpu_test_reports/failures_short.txt
|
||||
|
||||
- name: "Test suite reports artifacts: ${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_pipelines_tf_gpu_test_reports"
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: ${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_pipelines_tf_gpu_test_reports
|
||||
path: /transformers/reports/${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_pipelines_tf_gpu_test_reports
|
||||
|
||||
run_examples_gpu:
|
||||
if: ${{ inputs.job == 'run_examples_gpu' }}
|
||||
@ -215,9 +220,8 @@ jobs:
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
fail-fast: false
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
machine_type: [aws-g4dn-4xlarge-cache]
|
||||
runs-on:
|
||||
group: '${{ matrix.machine_type }}'
|
||||
machine_type: [single-gpu]
|
||||
runs-on: ['${{ matrix.machine_type }}', nvidia-gpu, t4, '${{ inputs.runner }}']
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: huggingface/transformers-all-latest-gpu
|
||||
options: --gpus 0 --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
@ -243,40 +247,23 @@ jobs:
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: pip freeze
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Set `machine_type` for report and artifact names
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "${{ matrix.machine_type }}"
|
||||
|
||||
if [ "${{ matrix.machine_type }}" = "aws-g4dn-4xlarge-cache" ]; then
|
||||
machine_type=single-gpu
|
||||
elif [ "${{ matrix.machine_type }}" = "aws-g4dn-12xlarge-cache" ]; then
|
||||
machine_type=multi-gpu
|
||||
else
|
||||
machine_type=${{ matrix.machine_type }}
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
echo "$machine_type"
|
||||
echo "machine_type=$machine_type" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run examples tests on GPU
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
pip install -r examples/pytorch/_tests_requirements.txt
|
||||
python3 -m pytest -v --make-reports=${{ env.machine_type }}_run_examples_gpu_test_reports examples/pytorch
|
||||
python3 -m pytest -v --make-reports=${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_examples_gpu_test_reports examples/pytorch
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
if: ${{ failure() }}
|
||||
continue-on-error: true
|
||||
run: cat /transformers/reports/${{ env.machine_type }}_run_examples_gpu_test_reports/failures_short.txt
|
||||
run: cat /transformers/reports/${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_examples_gpu_test_reports/failures_short.txt
|
||||
|
||||
- name: "Test suite reports artifacts: ${{ env.machine_type }}_run_examples_gpu_test_reports"
|
||||
- name: "Test suite reports artifacts: ${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_examples_gpu_test_reports"
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: ${{ env.machine_type }}_run_examples_gpu_test_reports
|
||||
path: /transformers/reports/${{ env.machine_type }}_run_examples_gpu_test_reports
|
||||
name: ${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_examples_gpu_test_reports
|
||||
path: /transformers/reports/${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_examples_gpu_test_reports
|
||||
|
||||
run_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu:
|
||||
if: ${{ inputs.job == 'run_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu' }}
|
||||
@ -284,9 +271,8 @@ jobs:
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
fail-fast: false
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
machine_type: [aws-g4dn-4xlarge-cache, aws-g4dn-12xlarge-cache]
|
||||
runs-on:
|
||||
group: '${{ matrix.machine_type }}'
|
||||
machine_type: [single-gpu, multi-gpu]
|
||||
runs-on: ['${{ matrix.machine_type }}', nvidia-gpu, t4, '${{ inputs.runner }}']
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: ${{ inputs.docker }}
|
||||
options: --gpus all --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
@ -324,7 +310,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python3 -m pip uninstall -y deepspeed
|
||||
rm -rf DeepSpeed
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/deepspeedai/DeepSpeed && cd DeepSpeed && rm -rf build
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/microsoft/DeepSpeed && cd DeepSpeed && rm -rf build
|
||||
DS_BUILD_CPU_ADAM=1 DS_BUILD_FUSED_ADAM=1 python3 -m pip install . --global-option="build_ext" --global-option="-j8" --no-cache -v --disable-pip-version-check
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NVIDIA-SMI
|
||||
@ -340,39 +326,22 @@ jobs:
|
||||
working-directory: ${{ inputs.working-directory-prefix }}/transformers
|
||||
run: pip freeze
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Set `machine_type` for report and artifact names
|
||||
working-directory: ${{ inputs.working-directory-prefix }}/transformers
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "${{ matrix.machine_type }}"
|
||||
|
||||
if [ "${{ matrix.machine_type }}" = "aws-g4dn-4xlarge-cache" ]; then
|
||||
machine_type=single-gpu
|
||||
elif [ "${{ matrix.machine_type }}" = "aws-g4dn-12xlarge-cache" ]; then
|
||||
machine_type=multi-gpu
|
||||
else
|
||||
machine_type=${{ matrix.machine_type }}
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
echo "$machine_type"
|
||||
echo "machine_type=$machine_type" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run all tests on GPU
|
||||
working-directory: ${{ inputs.working-directory-prefix }}/transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python3 -m pytest -v --make-reports=${{ env.machine_type }}_run_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu_test_reports tests/deepspeed tests/extended
|
||||
python3 -m pytest -v --make-reports=${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu_test_reports tests/deepspeed tests/extended
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
if: ${{ failure() }}
|
||||
continue-on-error: true
|
||||
run: cat ${{ inputs.working-directory-prefix }}/transformers/reports/${{ env.machine_type }}_run_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu_test_reports/failures_short.txt
|
||||
run: cat ${{ inputs.working-directory-prefix }}/transformers/reports/${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu_test_reports/failures_short.txt
|
||||
|
||||
- name: "Test suite reports artifacts: ${{ env.machine_type }}_run_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu_test_reports"
|
||||
- name: "Test suite reports artifacts: ${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu_test_reports"
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: ${{ env.machine_type }}_run_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu_test_reports
|
||||
path: ${{ inputs.working-directory-prefix }}/transformers/reports/${{ env.machine_type }}_run_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu_test_reports
|
||||
name: ${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu_test_reports
|
||||
path: ${{ inputs.working-directory-prefix }}/transformers/reports/${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu_test_reports
|
||||
|
||||
run_quantization_torch_gpu:
|
||||
if: ${{ inputs.job == 'run_quantization_torch_gpu' }}
|
||||
@ -383,9 +352,8 @@ jobs:
|
||||
fail-fast: false
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
folders: ${{ fromJson(needs.setup.outputs.quantization_matrix) }}
|
||||
machine_type: [aws-g4dn-4xlarge-cache, aws-g4dn-12xlarge-cache]
|
||||
runs-on:
|
||||
group: '${{ matrix.machine_type }}'
|
||||
machine_type: [single-gpu, multi-gpu]
|
||||
runs-on: ['${{ matrix.machine_type }}', nvidia-gpu, t4, '${{ inputs.runner }}']
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: huggingface/transformers-quantization-latest-gpu
|
||||
options: --gpus all --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
@ -420,39 +388,22 @@ jobs:
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: pip freeze
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Set `machine_type` for report and artifact names
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "${{ matrix.machine_type }}"
|
||||
|
||||
if [ "${{ matrix.machine_type }}" = "aws-g4dn-4xlarge-cache" ]; then
|
||||
machine_type=single-gpu
|
||||
elif [ "${{ matrix.machine_type }}" = "aws-g4dn-12xlarge-cache" ]; then
|
||||
machine_type=multi-gpu
|
||||
else
|
||||
machine_type=${{ matrix.machine_type }}
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
echo "$machine_type"
|
||||
echo "machine_type=$machine_type" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run quantization tests on GPU
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python3 -m pytest -v --make-reports=${{ env.machine_type }}_run_quantization_torch_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}_test_reports tests/${{ matrix.folders }}
|
||||
python3 -m pytest -v --make-reports=${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_quantization_torch_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}_test_reports tests/${{ matrix.folders }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Failure short reports
|
||||
if: ${{ failure() }}
|
||||
continue-on-error: true
|
||||
run: cat /transformers/reports/${{ env.machine_type }}_run_quantization_torch_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}_test_reports/failures_short.txt
|
||||
run: cat /transformers/reports/${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_quantization_torch_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}_test_reports/failures_short.txt
|
||||
|
||||
- name: "Test suite reports artifacts: ${{ env.machine_type }}_run_quantization_torch_gpu_${{ env.matrix_folders }}_test_reports"
|
||||
- name: "Test suite reports artifacts: ${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_quantization_torch_gpu_${{ env.matrix_folders }}_test_reports"
|
||||
if: ${{ always() }}
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: ${{ env.machine_type }}_run_quantization_torch_gpu_${{ env.matrix_folders }}_test_reports
|
||||
path: /transformers/reports/${{ env.machine_type }}_run_quantization_torch_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}_test_reports
|
||||
name: ${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_quantization_torch_gpu_${{ env.matrix_folders }}_test_reports
|
||||
path: /transformers/reports/${{ matrix.machine_type }}_run_quantization_torch_gpu_${{ matrix.folders }}_test_reports
|
||||
|
||||
run_extract_warnings:
|
||||
# Let's only do this for the job `run_models_gpu` to simplify the (already complex) logic.
|
||||
@ -500,8 +451,8 @@ jobs:
|
||||
needs: [
|
||||
setup,
|
||||
run_models_gpu,
|
||||
run_trainer_and_fsdp_gpu,
|
||||
run_pipelines_torch_gpu,
|
||||
run_pipelines_tf_gpu,
|
||||
run_examples_gpu,
|
||||
run_torch_cuda_extensions_gpu,
|
||||
run_quantization_torch_gpu,
|
||||
@ -518,21 +469,5 @@ jobs:
|
||||
folder_slices: ${{ needs.setup.outputs.folder_slices }}
|
||||
quantization_matrix: ${{ needs.setup.outputs.quantization_matrix }}
|
||||
ci_event: ${{ inputs.ci_event }}
|
||||
report_repo_id: ${{ inputs.report_repo_id }}
|
||||
|
||||
secrets: inherit
|
||||
|
||||
check_new_failures:
|
||||
if: ${{ always() && inputs.ci_event == 'Daily CI' && needs.send_results.result == 'success' }}
|
||||
name: Check new failures
|
||||
needs: send_results
|
||||
uses: ./.github/workflows/check_failed_tests.yml
|
||||
with:
|
||||
docker: ${{ inputs.docker }}
|
||||
start_sha: ${{ github.sha }}
|
||||
job: ${{ inputs.job }}
|
||||
slack_report_channel: ${{ inputs.slack_report_channel }}
|
||||
ci_event: ${{ inputs.ci_event }}
|
||||
report_repo_id: ${{ inputs.report_repo_id }}
|
||||
|
||||
secrets: inherit
|
||||
|
||||
58
.github/workflows/slack-report.yml
vendored
58
.github/workflows/slack-report.yml
vendored
@ -21,9 +21,6 @@ on:
|
||||
ci_event:
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
type: string
|
||||
report_repo_id:
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
type: string
|
||||
|
||||
env:
|
||||
TRANSFORMERS_CI_RESULTS_UPLOAD_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.TRANSFORMERS_CI_RESULTS_UPLOAD_TOKEN }}
|
||||
@ -42,23 +39,8 @@ jobs:
|
||||
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
- uses: actions/download-artifact@v4
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Prepare some setup values
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
if [ -f setup_values/prev_workflow_run_id.txt ]; then
|
||||
echo "PREV_WORKFLOW_RUN_ID=$(cat setup_values/prev_workflow_run_id.txt)" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
else
|
||||
echo "PREV_WORKFLOW_RUN_ID=" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
if [ -f setup_values/other_workflow_run_id.txt ]; then
|
||||
echo "OTHER_WORKFLOW_RUN_ID=$(cat setup_values/other_workflow_run_id.txt)" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
else
|
||||
echo "OTHER_WORKFLOW_RUN_ID=" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Send message to Slack
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
if: ${{ inputs.job != 'run_quantization_torch_gpu' }}
|
||||
env:
|
||||
CI_SLACK_BOT_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_ID: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL_ID }}
|
||||
@ -68,22 +50,19 @@ jobs:
|
||||
ACCESS_REPO_INFO_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.ACCESS_REPO_INFO_TOKEN }}
|
||||
CI_EVENT: ${{ inputs.ci_event }}
|
||||
CI_SHA: ${{ github.sha }}
|
||||
CI_WORKFLOW_REF: ${{ github.workflow_ref }}
|
||||
CI_TEST_JOB: ${{ inputs.job }}
|
||||
SETUP_STATUS: ${{ inputs.setup_status }}
|
||||
REPORT_REPO_ID: ${{ inputs.report_repo_id }}
|
||||
# We pass `needs.setup.outputs.matrix` as the argument. A processing in `notification_service.py` to change
|
||||
# `models/bert` to `models_bert` is required, as the artifact names use `_` instead of `/`.
|
||||
# For a job that doesn't depend on (i.e. `needs`) `setup`, the value for `inputs.folder_slices` would be an
|
||||
# empty string, and the called script still get one argument (which is the emtpy string).
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
sudo apt-get install -y curl
|
||||
pip install huggingface_hub
|
||||
pip install slack_sdk
|
||||
pip show slack_sdk
|
||||
if [ "${{ inputs.quantization_matrix }}" != "" ]; then
|
||||
python utils/notification_service.py "${{ inputs.quantization_matrix }}"
|
||||
else
|
||||
python utils/notification_service.py "${{ inputs.folder_slices }}"
|
||||
fi
|
||||
python utils/notification_service.py "${{ inputs.folder_slices }}"
|
||||
|
||||
# Upload complete failure tables, as they might be big and only truncated versions could be sent to Slack.
|
||||
- name: Failure table artifacts
|
||||
@ -91,3 +70,32 @@ jobs:
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: ci_results_${{ inputs.job }}
|
||||
path: ci_results_${{ inputs.job }}
|
||||
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
- uses: actions/download-artifact@v4
|
||||
- name: Send message to Slack for quantization workflow
|
||||
if: ${{ inputs.job == 'run_quantization_torch_gpu' }}
|
||||
env:
|
||||
CI_SLACK_BOT_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.CI_SLACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
ACCESS_REPO_INFO_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.ACCESS_REPO_INFO_TOKEN }}
|
||||
SLACK_REPORT_CHANNEL: ${{ inputs.slack_report_channel }}
|
||||
CI_EVENT: ${{ inputs.ci_event }}
|
||||
CI_SHA: ${{ github.sha }}
|
||||
CI_TEST_JOB: ${{ inputs.job }}
|
||||
SETUP_STATUS: ${{ inputs.setup_status }}
|
||||
# We pass `needs.setup.outputs.quantization_matrix` as the argument. A processing in `notification_service_quantization.py` to change
|
||||
# `quantization/bnb` to `quantization_bnb` is required, as the artifact names use `_` instead of `/`.
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
sudo apt-get install -y curl
|
||||
pip install huggingface_hub
|
||||
pip install slack_sdk
|
||||
pip show slack_sdk
|
||||
python utils/notification_service_quantization.py "${{ inputs.quantization_matrix }}"
|
||||
|
||||
# Upload complete failure tables, as they might be big and only truncated versions could be sent to Slack.
|
||||
- name: Failure table artifacts
|
||||
if: ${{ inputs.job == 'run_quantization_torch_gpu' }}
|
||||
uses: actions/upload-artifact@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
name: ci_results_${{ inputs.job }}
|
||||
path: ci_results_${{ inputs.job }}
|
||||
50
.github/workflows/ssh-runner.yml
vendored
50
.github/workflows/ssh-runner.yml
vendored
@ -5,7 +5,7 @@ on:
|
||||
inputs:
|
||||
runner_type:
|
||||
description: 'Type of runner to test (a10 or t4)'
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
docker_image:
|
||||
description: 'Name of the Docker image'
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
@ -15,48 +15,20 @@ on:
|
||||
|
||||
env:
|
||||
HF_HUB_READ_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.HF_HUB_READ_TOKEN }}
|
||||
HF_HOME: /mnt/cache
|
||||
TRANSFORMERS_IS_CI: yes
|
||||
OMP_NUM_THREADS: 8
|
||||
MKL_NUM_THREADS: 8
|
||||
RUN_SLOW: yes # For gated repositories, we still need to agree to share information on the Hub repo. page in order to get access. # This token is created under the bot `hf-transformers-bot`.
|
||||
SIGOPT_API_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.SIGOPT_API_TOKEN }}
|
||||
TF_FORCE_GPU_ALLOW_GROWTH: true
|
||||
HF_HOME: /mnt/cache
|
||||
TRANSFORMERS_IS_CI: yes
|
||||
OMP_NUM_THREADS: 8
|
||||
MKL_NUM_THREADS: 8
|
||||
RUN_SLOW: yes # For gated repositories, we still need to agree to share information on the Hub repo. page in order to get access. # This token is created under the bot `hf-transformers-bot`.
|
||||
SIGOPT_API_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.SIGOPT_API_TOKEN }}
|
||||
TF_FORCE_GPU_ALLOW_GROWTH: true
|
||||
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES: 0,1
|
||||
RUN_PT_TF_CROSS_TESTS: 1
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
get_runner:
|
||||
name: "Get runner to use"
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-22.04
|
||||
outputs:
|
||||
RUNNER: ${{ steps.set_runner.outputs.RUNNER }}
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Get runner to use
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
if [[ "${{ github.event.inputs.num_gpus }}" == "single" && "${{ github.event.inputs.runner_type }}" == "t4" ]]; then
|
||||
echo "RUNNER=aws-g4dn-4xlarge-cache" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
elif [[ "${{ github.event.inputs.num_gpus }}" == "multi" && "${{ github.event.inputs.runner_type }}" == "t4" ]]; then
|
||||
echo "RUNNER=aws-g4dn-12xlarge-cache" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
elif [[ "${{ github.event.inputs.num_gpus }}" == "single" && "${{ github.event.inputs.runner_type }}" == "a10" ]]; then
|
||||
echo "RUNNER=aws-g5-4xlarge-cache" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
elif [[ "${{ github.event.inputs.num_gpus }}" == "multi" && "${{ github.event.inputs.runner_type }}" == "a10" ]]; then
|
||||
echo "RUNNER=aws-g5-12xlarge-cache" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
else
|
||||
echo "RUNNER=" >> $GITHUB_ENV
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Set runner to use
|
||||
id: set_runner
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo ${{ env.RUNNER }}
|
||||
echo "RUNNER=${{ env.RUNNER }}" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
|
||||
|
||||
ssh_runner:
|
||||
name: "SSH"
|
||||
needs: get_runner
|
||||
runs-on:
|
||||
group: ${{ needs.get_runner.outputs.RUNNER }}
|
||||
runs-on: ["${{ github.event.inputs.num_gpus }}-gpu", nvidia-gpu, "${{ github.event.inputs.runner_type }}", ci]
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: ${{ github.event.inputs.docker_image }}
|
||||
options: --gpus all --privileged --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
@ -77,7 +49,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
- name: Show installed libraries and their versions
|
||||
working-directory: /transformers
|
||||
run: pip freeze
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- name: NVIDIA-SMI
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
nvidia-smi
|
||||
|
||||
2
.github/workflows/trufflehog.yml
vendored
2
.github/workflows/trufflehog.yml
vendored
@ -16,5 +16,3 @@ jobs:
|
||||
fetch-depth: 0
|
||||
- name: Secret Scanning
|
||||
uses: trufflesecurity/trufflehog@main
|
||||
with:
|
||||
extra_args: --results=verified,unknown
|
||||
|
||||
2
.github/workflows/update_metdata.yml
vendored
2
.github/workflows/update_metdata.yml
vendored
@ -19,7 +19,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
- name: Setup environment
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
pip install --upgrade pip
|
||||
pip install datasets pandas
|
||||
pip install datasets pandas==2.0.3
|
||||
pip install .[torch,tf,flax]
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Update metadata
|
||||
|
||||
@ -78,7 +78,7 @@ Once you've confirmed the bug hasn't already been reported, please include the f
|
||||
To get the OS and software versions automatically, run the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
transformers env
|
||||
transformers-cli env
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can also run the same command from the root of the repository:
|
||||
@ -132,7 +132,7 @@ You will need basic `git` proficiency to contribute to
|
||||
manual. Type `git --help` in a shell and enjoy! If you prefer books, [Pro
|
||||
Git](https://git-scm.com/book/en/v2) is a very good reference.
|
||||
|
||||
You'll need **[Python 3.9](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/setup.py#L449)** or above to contribute to 🤗 Transformers. Follow the steps below to start contributing:
|
||||
You'll need **[Python 3.8](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/setup.py#L449)** or above to contribute to 🤗 Transformers. Follow the steps below to start contributing:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Fork the [repository](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers) by
|
||||
clicking on the **[Fork](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/fork)** button on the repository's page. This creates a copy of the code
|
||||
@ -221,10 +221,10 @@ You'll need **[Python 3.9](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main
|
||||
[Checks on a Pull Request](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/pr_checks) guide.
|
||||
|
||||
If you're modifying documents under the `docs/source` directory, make sure the documentation can still be built. This check will also run in the CI when you open a pull request. To run a local check
|
||||
make sure you install the [documentation builder](https://github.com/huggingface/doc-builder).
|
||||
make sure you install the documentation builder:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install hf-doc-builder
|
||||
pip install ".[docs]"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Run the following command from the root of the repository:
|
||||
@ -343,6 +343,8 @@ RUN_SLOW=yes python -m pytest -n auto --dist=loadfile -s -v ./examples/pytorch/t
|
||||
|
||||
Like the slow tests, there are other environment variables available which are not enabled by default during testing:
|
||||
- `RUN_CUSTOM_TOKENIZERS`: Enables tests for custom tokenizers.
|
||||
- `RUN_PT_FLAX_CROSS_TESTS`: Enables tests for PyTorch + Flax integration.
|
||||
- `RUN_PT_TF_CROSS_TESTS`: Enables tests for TensorFlow + PyTorch integration.
|
||||
|
||||
More environment variables and additional information can be found in the [testing_utils.py](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/src/transformers/testing_utils.py).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -26,7 +26,7 @@ There are two main venues to receive support: [the forums](https://discuss.huggi
|
||||
|
||||
[The user forums](https://discuss.huggingface.co/) are supported by the wide community of the library users and backed up by developers when needed.
|
||||
|
||||
If you have a difficulty with deploying this library or some questions, or you'd like to discuss a new feature, please first consider discussing those things at the forums. Only when you feel your subject matter has been crystallized and you still need support from the library developers do proceed to file an [issue](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/issues).
|
||||
If you have a difficulty with deploying this library or some questions, or you'd like to discuss a new feature, please first consider discussing those things at the forums. Only when you feel your subject matter has been crystalized and you still need support from the library developers do proceed to file an [issue](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/issues).
|
||||
|
||||
In particular all "Please explain" questions or objectively very user-specific feature requests belong to the forums. Here are some example of such questions:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -263,9 +263,9 @@ You are not required to read the following guidelines before opening an issue. H
|
||||
But if you're replying to a comment that happened some comments back it's always a good practice to quote just the relevant lines you're replying it. The `>` is used for quoting, or you can always use the menu to do so. For example your editor box will look like:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
> How big is your GPU cluster?
|
||||
> How big is your gpu cluster?
|
||||
|
||||
Our cluster is made of 256 GPUs.
|
||||
Our cluster is made of 256 gpus.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you are addressing multiple comments, quote the relevant parts of each before your answer. Some people use the same comment to do multiple replies, others separate them into separate comments. Either way works. The latter approach helps for linking to a specific comment.
|
||||
|
||||
5
Makefile
5
Makefile
@ -36,7 +36,7 @@ autogenerate_code: deps_table_update
|
||||
|
||||
repo-consistency:
|
||||
python utils/check_copies.py
|
||||
python utils/check_modular_conversion.py
|
||||
python utils/check_table.py
|
||||
python utils/check_dummies.py
|
||||
python utils/check_repo.py
|
||||
python utils/check_inits.py
|
||||
@ -45,6 +45,7 @@ repo-consistency:
|
||||
python utils/check_doctest_list.py
|
||||
python utils/update_metadata.py --check-only
|
||||
python utils/check_docstrings.py
|
||||
python utils/check_support_list.py
|
||||
|
||||
# this target runs checks on all files
|
||||
|
||||
@ -79,7 +80,7 @@ fixup: modified_only_fixup extra_style_checks autogenerate_code repo-consistency
|
||||
|
||||
fix-copies:
|
||||
python utils/check_copies.py --fix_and_overwrite
|
||||
python utils/check_modular_conversion.py --fix_and_overwrite
|
||||
python utils/check_table.py --fix_and_overwrite
|
||||
python utils/check_dummies.py --fix_and_overwrite
|
||||
python utils/check_doctest_list.py --fix_and_overwrite
|
||||
python utils/check_docstrings.py --fix_and_overwrite
|
||||
|
||||
372
README.md
372
README.md
@ -25,7 +25,6 @@ limitations under the License.
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center">
|
||||
<a href="https://huggingface.com/models"><img alt="Checkpoints on Hub" src="https://img.shields.io/endpoint?url=https://huggingface.co/api/shields/models&color=brightgreen"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://circleci.com/gh/huggingface/transformers"><img alt="Build" src="https://img.shields.io/circleci/build/github/huggingface/transformers/main"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/LICENSE"><img alt="GitHub" src="https://img.shields.io/github/license/huggingface/transformers.svg?color=blue"></a>
|
||||
<a href="https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/index"><img alt="Documentation" src="https://img.shields.io/website/http/huggingface.co/docs/transformers/index.svg?down_color=red&down_message=offline&up_message=online"></a>
|
||||
@ -55,258 +54,255 @@ limitations under the License.
|
||||
</h4>
|
||||
|
||||
<h3 align="center">
|
||||
<p>State-of-the-art pretrained models for inference and training</p>
|
||||
<p>State-of-the-art Machine Learning for JAX, PyTorch and TensorFlow</p>
|
||||
</h3>
|
||||
|
||||
<h3 align="center">
|
||||
<a href="https://hf.co/course"><img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/course_banner.png"></a>
|
||||
</h3>
|
||||
|
||||
Transformers is a library of pretrained text, computer vision, audio, video, and multimodal models for inference and training. Use Transformers to fine-tune models on your data, build inference applications, and for generative AI use cases across multiple modalities.
|
||||
🤗 Transformers provides thousands of pretrained models to perform tasks on different modalities such as text, vision, and audio.
|
||||
|
||||
There are over 500K+ Transformers [model checkpoints](https://huggingface.co/models?library=transformers&sort=trending) on the [Hugging Face Hub](https://huggingface.com/models) you can use.
|
||||
These models can be applied on:
|
||||
|
||||
Explore the [Hub](https://huggingface.com/) today to find a model and use Transformers to help you get started right away.
|
||||
* 📝 Text, for tasks like text classification, information extraction, question answering, summarization, translation, and text generation, in over 100 languages.
|
||||
* 🖼️ Images, for tasks like image classification, object detection, and segmentation.
|
||||
* 🗣️ Audio, for tasks like speech recognition and audio classification.
|
||||
|
||||
## Installation
|
||||
Transformer models can also perform tasks on **several modalities combined**, such as table question answering, optical character recognition, information extraction from scanned documents, video classification, and visual question answering.
|
||||
|
||||
Transformers works with Python 3.9+ [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/) 2.1+, [TensorFlow](https://www.tensorflow.org/install/pip) 2.6+, and [Flax](https://flax.readthedocs.io/en/latest/) 0.4.1+.
|
||||
🤗 Transformers provides APIs to quickly download and use those pretrained models on a given text, fine-tune them on your own datasets and then share them with the community on our [model hub](https://huggingface.co/models). At the same time, each python module defining an architecture is fully standalone and can be modified to enable quick research experiments.
|
||||
|
||||
Create and activate a virtual environment with [venv](https://docs.python.org/3/library/venv.html) or [uv](https://docs.astral.sh/uv/), a fast Rust-based Python package and project manager.
|
||||
🤗 Transformers is backed by the three most popular deep learning libraries — [Jax](https://jax.readthedocs.io/en/latest/), [PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/) and [TensorFlow](https://www.tensorflow.org/) — with a seamless integration between them. It's straightforward to train your models with one before loading them for inference with the other.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
# venv
|
||||
python -m venv .my-env
|
||||
source .my-env/bin/activate
|
||||
# uv
|
||||
uv venv .my-env
|
||||
source .my-env/bin/activate
|
||||
## Online demos
|
||||
|
||||
You can test most of our models directly on their pages from the [model hub](https://huggingface.co/models). We also offer [private model hosting, versioning, & an inference API](https://huggingface.co/pricing) for public and private models.
|
||||
|
||||
Here are a few examples:
|
||||
|
||||
In Natural Language Processing:
|
||||
- [Masked word completion with BERT](https://huggingface.co/google-bert/bert-base-uncased?text=Paris+is+the+%5BMASK%5D+of+France)
|
||||
- [Named Entity Recognition with Electra](https://huggingface.co/dbmdz/electra-large-discriminator-finetuned-conll03-english?text=My+name+is+Sarah+and+I+live+in+London+city)
|
||||
- [Text generation with Mistral](https://huggingface.co/mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.2)
|
||||
- [Natural Language Inference with RoBERTa](https://huggingface.co/FacebookAI/roberta-large-mnli?text=The+dog+was+lost.+Nobody+lost+any+animal)
|
||||
- [Summarization with BART](https://huggingface.co/facebook/bart-large-cnn?text=The+tower+is+324+metres+%281%2C063+ft%29+tall%2C+about+the+same+height+as+an+81-storey+building%2C+and+the+tallest+structure+in+Paris.+Its+base+is+square%2C+measuring+125+metres+%28410+ft%29+on+each+side.+During+its+construction%2C+the+Eiffel+Tower+surpassed+the+Washington+Monument+to+become+the+tallest+man-made+structure+in+the+world%2C+a+title+it+held+for+41+years+until+the+Chrysler+Building+in+New+York+City+was+finished+in+1930.+It+was+the+first+structure+to+reach+a+height+of+300+metres.+Due+to+the+addition+of+a+broadcasting+aerial+at+the+top+of+the+tower+in+1957%2C+it+is+now+taller+than+the+Chrysler+Building+by+5.2+metres+%2817+ft%29.+Excluding+transmitters%2C+the+Eiffel+Tower+is+the+second+tallest+free-standing+structure+in+France+after+the+Millau+Viaduct)
|
||||
- [Question answering with DistilBERT](https://huggingface.co/distilbert/distilbert-base-uncased-distilled-squad?text=Which+name+is+also+used+to+describe+the+Amazon+rainforest+in+English%3F&context=The+Amazon+rainforest+%28Portuguese%3A+Floresta+Amaz%C3%B4nica+or+Amaz%C3%B4nia%3B+Spanish%3A+Selva+Amaz%C3%B3nica%2C+Amazon%C3%ADa+or+usually+Amazonia%3B+French%3A+For%C3%AAt+amazonienne%3B+Dutch%3A+Amazoneregenwoud%29%2C+also+known+in+English+as+Amazonia+or+the+Amazon+Jungle%2C+is+a+moist+broadleaf+forest+that+covers+most+of+the+Amazon+basin+of+South+America.+This+basin+encompasses+7%2C000%2C000+square+kilometres+%282%2C700%2C000+sq+mi%29%2C+of+which+5%2C500%2C000+square+kilometres+%282%2C100%2C000+sq+mi%29+are+covered+by+the+rainforest.+This+region+includes+territory+belonging+to+nine+nations.+The+majority+of+the+forest+is+contained+within+Brazil%2C+with+60%25+of+the+rainforest%2C+followed+by+Peru+with+13%25%2C+Colombia+with+10%25%2C+and+with+minor+amounts+in+Venezuela%2C+Ecuador%2C+Bolivia%2C+Guyana%2C+Suriname+and+French+Guiana.+States+or+departments+in+four+nations+contain+%22Amazonas%22+in+their+names.+The+Amazon+represents+over+half+of+the+planet%27s+remaining+rainforests%2C+and+comprises+the+largest+and+most+biodiverse+tract+of+tropical+rainforest+in+the+world%2C+with+an+estimated+390+billion+individual+trees+divided+into+16%2C000+species)
|
||||
- [Translation with T5](https://huggingface.co/google-t5/t5-base?text=My+name+is+Wolfgang+and+I+live+in+Berlin)
|
||||
|
||||
In Computer Vision:
|
||||
- [Image classification with ViT](https://huggingface.co/google/vit-base-patch16-224)
|
||||
- [Object Detection with DETR](https://huggingface.co/facebook/detr-resnet-50)
|
||||
- [Semantic Segmentation with SegFormer](https://huggingface.co/nvidia/segformer-b0-finetuned-ade-512-512)
|
||||
- [Panoptic Segmentation with Mask2Former](https://huggingface.co/facebook/mask2former-swin-large-coco-panoptic)
|
||||
- [Depth Estimation with Depth Anything](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/model_doc/depth_anything)
|
||||
- [Video Classification with VideoMAE](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/videomae)
|
||||
- [Universal Segmentation with OneFormer](https://huggingface.co/shi-labs/oneformer_ade20k_dinat_large)
|
||||
|
||||
In Audio:
|
||||
- [Automatic Speech Recognition with Whisper](https://huggingface.co/openai/whisper-large-v3)
|
||||
- [Keyword Spotting with Wav2Vec2](https://huggingface.co/superb/wav2vec2-base-superb-ks)
|
||||
- [Audio Classification with Audio Spectrogram Transformer](https://huggingface.co/MIT/ast-finetuned-audioset-10-10-0.4593)
|
||||
|
||||
In Multimodal tasks:
|
||||
- [Table Question Answering with TAPAS](https://huggingface.co/google/tapas-base-finetuned-wtq)
|
||||
- [Visual Question Answering with ViLT](https://huggingface.co/dandelin/vilt-b32-finetuned-vqa)
|
||||
- [Image captioning with LLaVa](https://huggingface.co/llava-hf/llava-1.5-7b-hf)
|
||||
- [Zero-shot Image Classification with SigLIP](https://huggingface.co/google/siglip-so400m-patch14-384)
|
||||
- [Document Question Answering with LayoutLM](https://huggingface.co/impira/layoutlm-document-qa)
|
||||
- [Zero-shot Video Classification with X-CLIP](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/xclip)
|
||||
- [Zero-shot Object Detection with OWLv2](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/en/model_doc/owlv2)
|
||||
- [Zero-shot Image Segmentation with CLIPSeg](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/clipseg)
|
||||
- [Automatic Mask Generation with SAM](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/sam)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 100 projects using Transformers
|
||||
|
||||
Transformers is more than a toolkit to use pretrained models: it's a community of projects built around it and the
|
||||
Hugging Face Hub. We want Transformers to enable developers, researchers, students, professors, engineers, and anyone
|
||||
else to build their dream projects.
|
||||
|
||||
In order to celebrate the 100,000 stars of transformers, we have decided to put the spotlight on the
|
||||
community, and we have created the [awesome-transformers](./awesome-transformers.md) page which lists 100
|
||||
incredible projects built in the vicinity of transformers.
|
||||
|
||||
If you own or use a project that you believe should be part of the list, please open a PR to add it!
|
||||
|
||||
## If you are looking for custom support from the Hugging Face team
|
||||
|
||||
<a target="_blank" href="https://huggingface.co/support">
|
||||
<img alt="HuggingFace Expert Acceleration Program" src="https://cdn-media.huggingface.co/marketing/transformers/new-support-improved.png" style="max-width: 600px; border: 1px solid #eee; border-radius: 4px; box-shadow: 0 1px 2px 0 rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.05);">
|
||||
</a><br>
|
||||
|
||||
## Quick tour
|
||||
|
||||
To immediately use a model on a given input (text, image, audio, ...), we provide the `pipeline` API. Pipelines group together a pretrained model with the preprocessing that was used during that model's training. Here is how to quickly use a pipeline to classify positive versus negative texts:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
# Allocate a pipeline for sentiment-analysis
|
||||
>>> classifier = pipeline('sentiment-analysis')
|
||||
>>> classifier('We are very happy to introduce pipeline to the transformers repository.')
|
||||
[{'label': 'POSITIVE', 'score': 0.9996980428695679}]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Install Transformers in your virtual environment.
|
||||
The second line of code downloads and caches the pretrained model used by the pipeline, while the third evaluates it on the given text. Here, the answer is "positive" with a confidence of 99.97%.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
# pip
|
||||
pip install "transformers[torch]"
|
||||
Many tasks have a pre-trained `pipeline` ready to go, in NLP but also in computer vision and speech. For example, we can easily extract detected objects in an image:
|
||||
|
||||
# uv
|
||||
uv pip install "transformers[torch]"
|
||||
``` python
|
||||
>>> import requests
|
||||
>>> from PIL import Image
|
||||
>>> from transformers import pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
# Download an image with cute cats
|
||||
>>> url = "https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/coco_sample.png"
|
||||
>>> image_data = requests.get(url, stream=True).raw
|
||||
>>> image = Image.open(image_data)
|
||||
|
||||
# Allocate a pipeline for object detection
|
||||
>>> object_detector = pipeline('object-detection')
|
||||
>>> object_detector(image)
|
||||
[{'score': 0.9982201457023621,
|
||||
'label': 'remote',
|
||||
'box': {'xmin': 40, 'ymin': 70, 'xmax': 175, 'ymax': 117}},
|
||||
{'score': 0.9960021376609802,
|
||||
'label': 'remote',
|
||||
'box': {'xmin': 333, 'ymin': 72, 'xmax': 368, 'ymax': 187}},
|
||||
{'score': 0.9954745173454285,
|
||||
'label': 'couch',
|
||||
'box': {'xmin': 0, 'ymin': 1, 'xmax': 639, 'ymax': 473}},
|
||||
{'score': 0.9988006353378296,
|
||||
'label': 'cat',
|
||||
'box': {'xmin': 13, 'ymin': 52, 'xmax': 314, 'ymax': 470}},
|
||||
{'score': 0.9986783862113953,
|
||||
'label': 'cat',
|
||||
'box': {'xmin': 345, 'ymin': 23, 'xmax': 640, 'ymax': 368}}]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Install Transformers from source if you want the latest changes in the library or are interested in contributing. However, the *latest* version may not be stable. Feel free to open an [issue](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/issues) if you encounter an error.
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git
|
||||
cd transformers
|
||||
|
||||
# pip
|
||||
pip install .[torch]
|
||||
|
||||
# uv
|
||||
uv pip install .[torch]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Quickstart
|
||||
|
||||
Get started with Transformers right away with the [Pipeline](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/pipeline_tutorial) API. The `Pipeline` is a high-level inference class that supports text, audio, vision, and multimodal tasks. It handles preprocessing the input and returns the appropriate output.
|
||||
|
||||
Instantiate a pipeline and specify model to use for text generation. The model is downloaded and cached so you can easily reuse it again. Finally, pass some text to prompt the model.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = pipeline(task="text-generation", model="Qwen/Qwen2.5-1.5B")
|
||||
pipeline("the secret to baking a really good cake is ")
|
||||
[{'generated_text': 'the secret to baking a really good cake is 1) to use the right ingredients and 2) to follow the recipe exactly. the recipe for the cake is as follows: 1 cup of sugar, 1 cup of flour, 1 cup of milk, 1 cup of butter, 1 cup of eggs, 1 cup of chocolate chips. if you want to make 2 cakes, how much sugar do you need? To make 2 cakes, you will need 2 cups of sugar.'}]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To chat with a model, the usage pattern is the same. The only difference is you need to construct a chat history (the input to `Pipeline`) between you and the system.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!TIP]
|
||||
> You can also chat with a model directly from the command line.
|
||||
> ```shell
|
||||
> transformers chat Qwen/Qwen2.5-0.5B-Instruct
|
||||
> ```
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from transformers import pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
chat = [
|
||||
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a sassy, wise-cracking robot as imagined by Hollywood circa 1986."},
|
||||
{"role": "user", "content": "Hey, can you tell me any fun things to do in New York?"}
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = pipeline(task="text-generation", model="meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3-8B-Instruct", torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16, device_map="auto")
|
||||
response = pipeline(chat, max_new_tokens=512)
|
||||
print(response[0]["generated_text"][-1]["content"])
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Expand the examples below to see how `Pipeline` works for different modalities and tasks.
|
||||
|
||||
<details>
|
||||
<summary>Automatic speech recognition</summary>
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = pipeline(task="automatic-speech-recognition", model="openai/whisper-large-v3")
|
||||
pipeline("https://huggingface.co/datasets/Narsil/asr_dummy/resolve/main/mlk.flac")
|
||||
{'text': ' I have a dream that one day this nation will rise up and live out the true meaning of its creed.'}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
|
||||
<details>
|
||||
<summary>Image classification</summary>
|
||||
Here, we get a list of objects detected in the image, with a box surrounding the object and a confidence score. Here is the original image on the left, with the predictions displayed on the right:
|
||||
|
||||
<h3 align="center">
|
||||
<a><img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/Narsil/image_dummy/raw/main/parrots.png"></a>
|
||||
<a><img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/coco_sample.png" width="400"></a>
|
||||
<a><img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/coco_sample_post_processed.png" width="400"></a>
|
||||
</h3>
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import pipeline
|
||||
You can learn more about the tasks supported by the `pipeline` API in [this tutorial](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/task_summary).
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = pipeline(task="image-classification", model="facebook/dinov2-small-imagenet1k-1-layer")
|
||||
pipeline("https://huggingface.co/datasets/Narsil/image_dummy/raw/main/parrots.png")
|
||||
[{'label': 'macaw', 'score': 0.997848391532898},
|
||||
{'label': 'sulphur-crested cockatoo, Kakatoe galerita, Cacatua galerita',
|
||||
'score': 0.0016551691805943847},
|
||||
{'label': 'lorikeet', 'score': 0.00018523589824326336},
|
||||
{'label': 'African grey, African gray, Psittacus erithacus',
|
||||
'score': 7.85409429227002e-05},
|
||||
{'label': 'quail', 'score': 5.502637941390276e-05}]
|
||||
In addition to `pipeline`, to download and use any of the pretrained models on your given task, all it takes is three lines of code. Here is the PyTorch version:
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModel
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("google-bert/bert-base-uncased")
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModel.from_pretrained("google-bert/bert-base-uncased")
|
||||
|
||||
>>> inputs = tokenizer("Hello world!", return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
>>> outputs = model(**inputs)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
And here is the equivalent code for TensorFlow:
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer, TFAutoModel
|
||||
|
||||
<details>
|
||||
<summary>Visual question answering</summary>
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("google-bert/bert-base-uncased")
|
||||
>>> model = TFAutoModel.from_pretrained("google-bert/bert-base-uncased")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<h3 align="center">
|
||||
<a><img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/tasks/idefics-few-shot.jpg"></a>
|
||||
</h3>
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = pipeline(task="visual-question-answering", model="Salesforce/blip-vqa-base")
|
||||
pipeline(
|
||||
image="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/tasks/idefics-few-shot.jpg",
|
||||
question="What is in the image?",
|
||||
)
|
||||
[{'answer': 'statue of liberty'}]
|
||||
>>> inputs = tokenizer("Hello world!", return_tensors="tf")
|
||||
>>> outputs = model(**inputs)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
The tokenizer is responsible for all the preprocessing the pretrained model expects and can be called directly on a single string (as in the above examples) or a list. It will output a dictionary that you can use in downstream code or simply directly pass to your model using the ** argument unpacking operator.
|
||||
|
||||
## Why should I use Transformers?
|
||||
The model itself is a regular [Pytorch `nn.Module`](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/nn.html#torch.nn.Module) or a [TensorFlow `tf.keras.Model`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/Model) (depending on your backend) which you can use as usual. [This tutorial](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/training) explains how to integrate such a model into a classic PyTorch or TensorFlow training loop, or how to use our `Trainer` API to quickly fine-tune on a new dataset.
|
||||
|
||||
## Why should I use transformers?
|
||||
|
||||
1. Easy-to-use state-of-the-art models:
|
||||
- High performance on natural language understanding & generation, computer vision, audio, video, and multimodal tasks.
|
||||
- Low barrier to entry for researchers, engineers, and developers.
|
||||
- High performance on natural language understanding & generation, computer vision, and audio tasks.
|
||||
- Low barrier to entry for educators and practitioners.
|
||||
- Few user-facing abstractions with just three classes to learn.
|
||||
- A unified API for using all our pretrained models.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Lower compute costs, smaller carbon footprint:
|
||||
- Share trained models instead of training from scratch.
|
||||
- Reduce compute time and production costs.
|
||||
- Dozens of model architectures with 1M+ pretrained checkpoints across all modalities.
|
||||
- Researchers can share trained models instead of always retraining.
|
||||
- Practitioners can reduce compute time and production costs.
|
||||
- Dozens of architectures with over 400,000 pretrained models across all modalities.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Choose the right framework for every part of a models lifetime:
|
||||
1. Choose the right framework for every part of a model's lifetime:
|
||||
- Train state-of-the-art models in 3 lines of code.
|
||||
- Move a single model between PyTorch/JAX/TF2.0 frameworks at will.
|
||||
- Pick the right framework for training, evaluation, and production.
|
||||
- Move a single model between TF2.0/PyTorch/JAX frameworks at will.
|
||||
- Seamlessly pick the right framework for training, evaluation, and production.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Easily customize a model or an example to your needs:
|
||||
- We provide examples for each architecture to reproduce the results published by its original authors.
|
||||
- Model internals are exposed as consistently as possible.
|
||||
- Model files can be used independently of the library for quick experiments.
|
||||
|
||||
<a target="_blank" href="https://huggingface.co/enterprise">
|
||||
<img alt="Hugging Face Enterprise Hub" src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/247fb16d-d251-4583-96c4-d3d76dda4925">
|
||||
</a><br>
|
||||
|
||||
## Why shouldn't I use Transformers?
|
||||
## Why shouldn't I use transformers?
|
||||
|
||||
- This library is not a modular toolbox of building blocks for neural nets. The code in the model files is not refactored with additional abstractions on purpose, so that researchers can quickly iterate on each of the models without diving into additional abstractions/files.
|
||||
- The training API is optimized to work with PyTorch models provided by Transformers. For generic machine learning loops, you should use another library like [Accelerate](https://huggingface.co/docs/accelerate).
|
||||
- The [example scripts]((https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples)) are only *examples*. They may not necessarily work out-of-the-box on your specific use case and you'll need to adapt the code for it to work.
|
||||
- The training API is not intended to work on any model but is optimized to work with the models provided by the library. For generic machine learning loops, you should use another library (possibly, [Accelerate](https://huggingface.co/docs/accelerate)).
|
||||
- While we strive to present as many use cases as possible, the scripts in our [examples folder](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples) are just that: examples. It is expected that they won't work out-of-the-box on your specific problem and that you will be required to change a few lines of code to adapt them to your needs.
|
||||
|
||||
## 100 projects using Transformers
|
||||
## Installation
|
||||
|
||||
Transformers is more than a toolkit to use pretrained models, it's a community of projects built around it and the
|
||||
Hugging Face Hub. We want Transformers to enable developers, researchers, students, professors, engineers, and anyone
|
||||
else to build their dream projects.
|
||||
### With pip
|
||||
|
||||
In order to celebrate Transformers 100,000 stars, we wanted to put the spotlight on the
|
||||
community with the [awesome-transformers](./awesome-transformers.md) page which lists 100
|
||||
incredible projects built with Transformers.
|
||||
This repository is tested on Python 3.8+, Flax 0.4.1+, PyTorch 1.11+, and TensorFlow 2.6+.
|
||||
|
||||
If you own or use a project that you believe should be part of the list, please open a PR to add it!
|
||||
You should install 🤗 Transformers in a [virtual environment](https://docs.python.org/3/library/venv.html). If you're unfamiliar with Python virtual environments, check out the [user guide](https://packaging.python.org/guides/installing-using-pip-and-virtual-environments/).
|
||||
|
||||
## Example models
|
||||
First, create a virtual environment with the version of Python you're going to use and activate it.
|
||||
|
||||
You can test most of our models directly on their [Hub model pages](https://huggingface.co/models).
|
||||
Then, you will need to install at least one of Flax, PyTorch, or TensorFlow.
|
||||
Please refer to [TensorFlow installation page](https://www.tensorflow.org/install/), [PyTorch installation page](https://pytorch.org/get-started/locally/#start-locally) and/or [Flax](https://github.com/google/flax#quick-install) and [Jax](https://github.com/google/jax#installation) installation pages regarding the specific installation command for your platform.
|
||||
|
||||
Expand each modality below to see a few example models for various use cases.
|
||||
When one of those backends has been installed, 🤗 Transformers can be installed using pip as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
<details>
|
||||
<summary>Audio</summary>
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install transformers
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- Audio classification with [Whisper](https://huggingface.co/openai/whisper-large-v3-turbo)
|
||||
- Automatic speech recognition with [Moonshine](https://huggingface.co/UsefulSensors/moonshine)
|
||||
- Keyword spotting with [Wav2Vec2](https://huggingface.co/superb/wav2vec2-base-superb-ks)
|
||||
- Speech to speech generation with [Moshi](https://huggingface.co/kyutai/moshiko-pytorch-bf16)
|
||||
- Text to audio with [MusicGen](https://huggingface.co/facebook/musicgen-large)
|
||||
- Text to speech with [Bark](https://huggingface.co/suno/bark)
|
||||
If you'd like to play with the examples or need the bleeding edge of the code and can't wait for a new release, you must [install the library from source](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/installation#installing-from-source).
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
### With conda
|
||||
|
||||
<details>
|
||||
<summary>Computer vision</summary>
|
||||
🤗 Transformers can be installed using conda as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
- Automatic mask generation with [SAM](https://huggingface.co/facebook/sam-vit-base)
|
||||
- Depth estimation with [DepthPro](https://huggingface.co/apple/DepthPro-hf)
|
||||
- Image classification with [DINO v2](https://huggingface.co/facebook/dinov2-base)
|
||||
- Keypoint detection with [SuperGlue](https://huggingface.co/magic-leap-community/superglue_outdoor)
|
||||
- Keypoint matching with [SuperGlue](https://huggingface.co/magic-leap-community/superglue)
|
||||
- Object detection with [RT-DETRv2](https://huggingface.co/PekingU/rtdetr_v2_r50vd)
|
||||
- Pose Estimation with [VitPose](https://huggingface.co/usyd-community/vitpose-base-simple)
|
||||
- Universal segmentation with [OneFormer](https://huggingface.co/shi-labs/oneformer_ade20k_swin_large)
|
||||
- Video classification with [VideoMAE](https://huggingface.co/MCG-NJU/videomae-large)
|
||||
```shell script
|
||||
conda install conda-forge::transformers
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
> **_NOTE:_** Installing `transformers` from the `huggingface` channel is deprecated.
|
||||
|
||||
<details>
|
||||
<summary>Multimodal</summary>
|
||||
Follow the installation pages of Flax, PyTorch or TensorFlow to see how to install them with conda.
|
||||
|
||||
- Audio or text to text with [Qwen2-Audio](https://huggingface.co/Qwen/Qwen2-Audio-7B)
|
||||
- Document question answering with [LayoutLMv3](https://huggingface.co/microsoft/layoutlmv3-base)
|
||||
- Image or text to text with [Qwen-VL](https://huggingface.co/Qwen/Qwen2.5-VL-3B-Instruct)
|
||||
- Image captioning [BLIP-2](https://huggingface.co/Salesforce/blip2-opt-2.7b)
|
||||
- OCR-based document understanding with [GOT-OCR2](https://huggingface.co/stepfun-ai/GOT-OCR-2.0-hf)
|
||||
- Table question answering with [TAPAS](https://huggingface.co/google/tapas-base)
|
||||
- Unified multimodal understanding and generation with [Emu3](https://huggingface.co/BAAI/Emu3-Gen)
|
||||
- Vision to text with [Llava-OneVision](https://huggingface.co/llava-hf/llava-onevision-qwen2-0.5b-ov-hf)
|
||||
- Visual question answering with [Llava](https://huggingface.co/llava-hf/llava-1.5-7b-hf)
|
||||
- Visual referring expression segmentation with [Kosmos-2](https://huggingface.co/microsoft/kosmos-2-patch14-224)
|
||||
> **_NOTE:_** On Windows, you may be prompted to activate Developer Mode in order to benefit from caching. If this is not an option for you, please let us know in [this issue](https://github.com/huggingface/huggingface_hub/issues/1062).
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
## Model architectures
|
||||
|
||||
<details>
|
||||
<summary>NLP</summary>
|
||||
**[All the model checkpoints](https://huggingface.co/models)** provided by 🤗 Transformers are seamlessly integrated from the huggingface.co [model hub](https://huggingface.co/models), where they are uploaded directly by [users](https://huggingface.co/users) and [organizations](https://huggingface.co/organizations).
|
||||
|
||||
- Masked word completion with [ModernBERT](https://huggingface.co/answerdotai/ModernBERT-base)
|
||||
- Named entity recognition with [Gemma](https://huggingface.co/google/gemma-2-2b)
|
||||
- Question answering with [Mixtral](https://huggingface.co/mistralai/Mixtral-8x7B-v0.1)
|
||||
- Summarization with [BART](https://huggingface.co/facebook/bart-large-cnn)
|
||||
- Translation with [T5](https://huggingface.co/google-t5/t5-base)
|
||||
- Text generation with [Llama](https://huggingface.co/meta-llama/Llama-3.2-1B)
|
||||
- Text classification with [Qwen](https://huggingface.co/Qwen/Qwen2.5-0.5B)
|
||||
Current number of checkpoints: 
|
||||
|
||||
</details>
|
||||
🤗 Transformers currently provides the following architectures: see [here](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_summary) for a high-level summary of each them.
|
||||
|
||||
To check if each model has an implementation in Flax, PyTorch or TensorFlow, or has an associated tokenizer backed by the 🤗 Tokenizers library, refer to [this table](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/index#supported-frameworks).
|
||||
|
||||
These implementations have been tested on several datasets (see the example scripts) and should match the performance of the original implementations. You can find more details on performance in the Examples section of the [documentation](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Learn more
|
||||
|
||||
| Section | Description |
|
||||
|-|-|
|
||||
| [Documentation](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/) | Full API documentation and tutorials |
|
||||
| [Task summary](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/task_summary) | Tasks supported by 🤗 Transformers |
|
||||
| [Preprocessing tutorial](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/preprocessing) | Using the `Tokenizer` class to prepare data for the models |
|
||||
| [Training and fine-tuning](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/training) | Using the models provided by 🤗 Transformers in a PyTorch/TensorFlow training loop and the `Trainer` API |
|
||||
| [Quick tour: Fine-tuning/usage scripts](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/examples) | Example scripts for fine-tuning models on a wide range of tasks |
|
||||
| [Model sharing and uploading](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_sharing) | Upload and share your fine-tuned models with the community |
|
||||
|
||||
## Citation
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -27,6 +27,13 @@ These models require the `trust_remote_code=True` parameter to be set when using
|
||||
the content of the modeling files when using this argument. We recommend setting a revision in order to ensure you
|
||||
protect yourself from updates on the repository.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Tools
|
||||
|
||||
Through the `Agent` framework, remote tools can be downloaded to be used by the Agent. You're to specify these tools
|
||||
yourself, but please keep in mind that their code will be run on your machine if the Agent chooses to run them.
|
||||
|
||||
Please inspect the code of the tools before passing them to the Agent to protect your runtime and local setup.
|
||||
|
||||
## Reporting a Vulnerability
|
||||
|
||||
Feel free to submit vulnerability reports to [security@huggingface.co](mailto:security@huggingface.co), where someone from the HF security team will review and recommend next steps. If reporting a vulnerability specific to open source, please note [Huntr](https://huntr.com) is a vulnerability disclosure program for open source software.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -15,7 +15,7 @@ to add it.
|
||||
|
||||
Keywords: Open-source, LLaMa, GPT-J, instruction, assistant
|
||||
|
||||
## [recommenders](https://github.com/recommenders-team/recommenders)
|
||||
## [recommenders](https://github.com/microsoft/recommenders)
|
||||
|
||||
This repository contains examples and best practices for building recommendation systems, provided as Jupyter notebooks. It goes over several aspects required to build efficient recommendation systems: data preparation, modeling, evaluation, model selection & optimization, as well as operationalization
|
||||
|
||||
@ -29,7 +29,7 @@ Keywords: inpainting, SD, Stable Diffusion
|
||||
|
||||
## [flair](https://github.com/flairNLP/flair)
|
||||
|
||||
FLAIR is a powerful PyTorch NLP framework, covering several important tasks: NER, sentiment-analysis, part-of-speech tagging, text and document embeddings, among other things.
|
||||
FLAIR is a powerful PyTorch NLP framework, convering several important tasks: NER, sentiment-analysis, part-of-speech tagging, text and document embeddings, among other things.
|
||||
|
||||
Keywords: NLP, text embedding, document embedding, biomedical, NER, PoS, sentiment-analysis
|
||||
|
||||
@ -39,15 +39,15 @@ MindsDB is a low-code ML platform, which automates and integrates several ML fra
|
||||
|
||||
Keywords: Database, low-code, AI table
|
||||
|
||||
## [langchain](https://github.com/langchain-ai/langchain)
|
||||
## [langchain](https://github.com/hwchase17/langchain)
|
||||
|
||||
[langchain](https://github.com/langchain-ai/langchain) is aimed at assisting in the development of apps merging both LLMs and other sources of knowledge. The library allows chaining calls to applications, creating a sequence across many tools.
|
||||
[langchain](https://github.com/hwchase17/langchain) is aimed at assisting in the development of apps merging both LLMs and other sources of knowledge. The library allows chaining calls to applications, creating a sequence across many tools.
|
||||
|
||||
Keywords: LLMs, Large Language Models, Agents, Chains
|
||||
|
||||
## [LlamaIndex](https://github.com/run-llama/llama_index)
|
||||
## [LlamaIndex](https://github.com/jerryjliu/llama_index)
|
||||
|
||||
[LlamaIndex](https://github.com/run-llama/llama_index) is a project that provides a central interface to connect your LLM's with external data. It provides various kinds of indices and retrieval mechanisms to perform different LLM tasks and obtain knowledge-augmented results.
|
||||
[LlamaIndex](https://github.com/jerryjliu/llama_index) is a project that provides a central interface to connect your LLM's with external data. It provides various kinds of indices and retreival mechanisms to perform different LLM tasks and obtain knowledge-augmented results.
|
||||
|
||||
Keywords: LLMs, Large Language Models, Data Retrieval, Indices, Knowledge Augmentation
|
||||
|
||||
@ -146,9 +146,9 @@ Keywords: Framework, simplicity, NLP
|
||||
|
||||
Keywords: LLM, Agents, HF Hub
|
||||
|
||||
## [transformers.js](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.js/)
|
||||
## [transformers.js](https://xenova.github.io/transformers.js/)
|
||||
|
||||
[transformers.js](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.js/) is a JavaScript library targeted at running models from transformers directly within the browser.
|
||||
[transformers.js](https://xenova.github.io/transformers.js/) is a JavaScript library targeted at running models from transformers directly within the browser.
|
||||
|
||||
Keywords: Transformers, JavaScript, browser
|
||||
|
||||
@ -437,7 +437,7 @@ Keywords: DALL-E, Russian
|
||||
|
||||
Keywords: Knowledge Extraction, Knowledge Graphs
|
||||
|
||||
## [Nebuly](https://github.com/nebuly-ai/optimate)
|
||||
## [Nebuly](https://github.com/nebuly-ai/nebuly)
|
||||
|
||||
Nebuly is the next-generation platform to monitor and optimize your AI costs in one place. The platform connects to all your AI cost sources (compute, API providers, AI software licenses, etc) and centralizes them in one place to give you full visibility on a model basis. The platform also provides optimization recommendations and a co-pilot model that can guide during the optimization process. The platform builds on top of the open-source tools allowing you to optimize the different steps of your AI stack to squeeze out the best possible cost performances.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,49 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Benchmarks
|
||||
|
||||
You might want to add new benchmarks.
|
||||
|
||||
You will need to define a python function named `run_benchmark` in your python file and the file must be located in this `benchmark/` directory.
|
||||
|
||||
The expected function signature is the following:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
def run_benchmark(logger: Logger, branch: str, commit_id: str, commit_msg: str, num_tokens_to_generate=100):
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Writing metrics to the database
|
||||
|
||||
`MetricsRecorder` is thread-safe, in the sense of the python [`Thread`](https://docs.python.org/3/library/threading.html#threading.Thread). This means you can start a background thread to do the readings on the device measurements while not blocking the main thread to execute the model measurements.
|
||||
|
||||
cf [`llama.py`](./llama.py) to see an example of this in practice.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from benchmarks_entrypoint import MetricsRecorder
|
||||
import psycopg2
|
||||
|
||||
def run_benchmark(logger: Logger, branch: str, commit_id: str, commit_msg: str, num_tokens_to_generate=100):
|
||||
metrics_recorder = MetricsRecorder(psycopg2.connect("dbname=metrics"), logger, branch, commit_id, commit_msg)
|
||||
benchmark_id = metrics_recorder.initialise_benchmark({"gpu_name": gpu_name, "model_id": model_id})
|
||||
# To collect device measurements
|
||||
metrics_recorder.collect_device_measurements(
|
||||
benchmark_id, cpu_util, mem_megabytes, gpu_util, gpu_mem_megabytes
|
||||
)
|
||||
# To collect your model measurements
|
||||
metrics_recorder.collect_model_measurements(
|
||||
benchmark_id,
|
||||
{
|
||||
"model_load_time": model_load_time,
|
||||
"first_eager_forward_pass_time_secs": first_eager_fwd_pass_time,
|
||||
"second_eager_forward_pass_time_secs": second_eager_fwd_pass_time,
|
||||
"first_eager_generate_time_secs": first_eager_generate_time,
|
||||
"second_eager_generate_time_secs": second_eager_generate_time,
|
||||
"time_to_first_token_secs": time_to_first_token,
|
||||
"time_to_second_token_secs": time_to_second_token,
|
||||
"time_to_third_token_secs": time_to_third_token,
|
||||
"time_to_next_token_mean_secs": mean_time_to_next_token,
|
||||
"first_compile_generate_time_secs": first_compile_generate_time,
|
||||
"second_compile_generate_time_secs": second_compile_generate_time,
|
||||
"third_compile_generate_time_secs": third_compile_generate_time,
|
||||
"fourth_compile_generate_time_secs": fourth_compile_generate_time,
|
||||
},
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -90,7 +90,7 @@ def summarize(run_dir, metrics, expand_metrics=False):
|
||||
|
||||
model = benchmark.config.backend["model"]
|
||||
|
||||
# This looks like `benchmark.input_shapes.batch_size=1,benchmark.input_shapes.sequence_length=5`.
|
||||
# Ths looks like `benchmark.input_shapes.batch_size=1,benchmark.input_shapes.sequence_length=5`.
|
||||
# (we rely on the usage of hydra's `${hydra.job.override_dirname}`.)
|
||||
benchmark_name = re.sub(f"backend.model={model},*", "", report_dir)
|
||||
benchmark_name = str(Path(benchmark_name).parts[-1])
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,152 +0,0 @@
|
||||
import argparse
|
||||
import importlib.util
|
||||
import logging
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
from typing import Dict, Tuple
|
||||
|
||||
from psycopg2.extensions import register_adapter
|
||||
from psycopg2.extras import Json
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
register_adapter(dict, Json)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class ImportModuleException(Exception):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class MetricsRecorder:
|
||||
def __init__(
|
||||
self, connection, logger: logging.Logger, repository: str, branch: str, commit_id: str, commit_msg: str
|
||||
):
|
||||
self.conn = connection
|
||||
self.conn.autocommit = True
|
||||
self.logger = logger
|
||||
self.repository = repository
|
||||
self.branch = branch
|
||||
self.commit_id = commit_id
|
||||
self.commit_msg = commit_msg
|
||||
|
||||
def initialise_benchmark(self, metadata: Dict[str, str]) -> int:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Creates a new benchmark, returns the benchmark id
|
||||
"""
|
||||
# gpu_name: str, model_id: str
|
||||
with self.conn.cursor() as cur:
|
||||
cur.execute(
|
||||
"INSERT INTO benchmarks (repository, branch, commit_id, commit_message, metadata) VALUES (%s, %s, %s, %s, %s) RETURNING benchmark_id",
|
||||
(self.repository, self.branch, self.commit_id, self.commit_msg, metadata),
|
||||
)
|
||||
benchmark_id = cur.fetchone()[0]
|
||||
logger.debug(f"initialised benchmark #{benchmark_id}")
|
||||
return benchmark_id
|
||||
|
||||
def collect_device_measurements(self, benchmark_id: int, cpu_util, mem_megabytes, gpu_util, gpu_mem_megabytes):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Collect device metrics, such as CPU & GPU usage. These are "static", as in you cannot pass arbitrary arguments to the function.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
with self.conn.cursor() as cur:
|
||||
cur.execute(
|
||||
"INSERT INTO device_measurements (benchmark_id, cpu_util, mem_megabytes, gpu_util, gpu_mem_megabytes) VALUES (%s, %s, %s, %s, %s)",
|
||||
(benchmark_id, cpu_util, mem_megabytes, gpu_util, gpu_mem_megabytes),
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.logger.debug(
|
||||
f"inserted device measurements for benchmark #{benchmark_id} [CPU util: {cpu_util}, mem MBs: {mem_megabytes}, GPU util: {gpu_util}, GPU mem MBs: {gpu_mem_megabytes}]"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def collect_model_measurements(self, benchmark_id: int, measurements: Dict[str, float]):
|
||||
with self.conn.cursor() as cur:
|
||||
cur.execute(
|
||||
"""
|
||||
INSERT INTO model_measurements (
|
||||
benchmark_id,
|
||||
measurements
|
||||
) VALUES (%s, %s)
|
||||
""",
|
||||
(
|
||||
benchmark_id,
|
||||
measurements,
|
||||
),
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.logger.debug(f"inserted model measurements for benchmark #{benchmark_id}: {measurements}")
|
||||
|
||||
def close(self):
|
||||
self.conn.close()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
|
||||
logger.setLevel(logging.INFO)
|
||||
|
||||
handler = logging.StreamHandler(sys.stdout)
|
||||
handler.setLevel(logging.INFO)
|
||||
formatter = logging.Formatter("[%(levelname)s - %(asctime)s] %(message)s")
|
||||
handler.setFormatter(formatter)
|
||||
logger.addHandler(handler)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def parse_arguments() -> Tuple[str, str, str, str]:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Parse command line arguments for the benchmarking CLI.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="CLI for benchmarking the huggingface/transformers.")
|
||||
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"repository",
|
||||
type=str,
|
||||
help="The repository name on which the benchmarking is performed.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"branch",
|
||||
type=str,
|
||||
help="The branch name on which the benchmarking is performed.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"commit_id",
|
||||
type=str,
|
||||
help="The commit hash on which the benchmarking is performed.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"commit_msg",
|
||||
type=str,
|
||||
help="The commit message associated with the commit, truncated to 70 characters.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
args = parser.parse_args()
|
||||
|
||||
return args.repository, args.branch, args.commit_id, args.commit_msg
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def import_from_path(module_name, file_path):
|
||||
try:
|
||||
spec = importlib.util.spec_from_file_location(module_name, file_path)
|
||||
module = importlib.util.module_from_spec(spec)
|
||||
sys.modules[module_name] = module
|
||||
spec.loader.exec_module(module)
|
||||
return module
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
raise ImportModuleException(f"failed to load python module: {e}")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
benchmarks_folder_path = os.path.dirname(os.path.realpath(__file__))
|
||||
|
||||
repository, branch, commit_id, commit_msg = parse_arguments()
|
||||
|
||||
for entry in os.scandir(benchmarks_folder_path):
|
||||
try:
|
||||
if not entry.name.endswith(".py"):
|
||||
continue
|
||||
if entry.path == __file__:
|
||||
continue
|
||||
logger.debug(f"loading: {entry.name}")
|
||||
module = import_from_path(entry.name.split(".")[0], entry.path)
|
||||
logger.info(f"running benchmarks in: {entry.name}")
|
||||
module.run_benchmark(logger, repository, branch, commit_id, commit_msg)
|
||||
except ImportModuleException as e:
|
||||
logger.error(e)
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
logger.error(f"error running benchmarks for {entry.name}: {e}")
|
||||
@ -1,10 +0,0 @@
|
||||
apiVersion: 1
|
||||
|
||||
providers:
|
||||
- name: 'Transformers Benchmarks'
|
||||
orgId: 1
|
||||
type: file
|
||||
updateIntervalSeconds: 10
|
||||
allowUiUpdates: true
|
||||
options:
|
||||
path: /etc/grafana/dashboards
|
||||
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
@ -1,17 +0,0 @@
|
||||
apiVersion: 1
|
||||
datasources:
|
||||
- name: grafana-postgresql-datasource
|
||||
uid: be28nkzirtb0gd
|
||||
type: postgres
|
||||
url: $GRAFANA_POSTGRES_DATASOURCE_URL
|
||||
user: $GRAFANA_POSTGRES_DATASOURCE_USER
|
||||
secureJsonData:
|
||||
password: $GRAFANA_POSTGRES_DATASOURCE_PWD
|
||||
jsonData:
|
||||
database: metrics
|
||||
maxOpenConns: 100
|
||||
maxIdleConns: 100
|
||||
maxIdleConnsAuto: true
|
||||
connMaxLifetime: 14400
|
||||
postgresVersion: 1000
|
||||
timescaledb: false
|
||||
@ -1,34 +0,0 @@
|
||||
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS benchmarks (
|
||||
benchmark_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
|
||||
repository VARCHAR(255),
|
||||
branch VARCHAR(255),
|
||||
commit_id VARCHAR(72),
|
||||
commit_message VARCHAR(70),
|
||||
metadata jsonb,
|
||||
created_at timestamp without time zone NOT NULL DEFAULT (current_timestamp AT TIME ZONE 'UTC')
|
||||
);
|
||||
|
||||
CREATE INDEX IF NOT EXISTS benchmarks_benchmark_id_idx ON benchmarks (benchmark_id);
|
||||
|
||||
CREATE INDEX IF NOT EXISTS benchmarks_branch_idx ON benchmarks (branch);
|
||||
|
||||
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS device_measurements (
|
||||
measurement_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
|
||||
benchmark_id int REFERENCES benchmarks (benchmark_id),
|
||||
cpu_util double precision,
|
||||
mem_megabytes double precision,
|
||||
gpu_util double precision,
|
||||
gpu_mem_megabytes double precision,
|
||||
time timestamp without time zone NOT NULL DEFAULT (current_timestamp AT TIME ZONE 'UTC')
|
||||
);
|
||||
|
||||
CREATE INDEX IF NOT EXISTS device_measurements_branch_idx ON device_measurements (benchmark_id);
|
||||
|
||||
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS model_measurements (
|
||||
measurement_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
|
||||
benchmark_id int REFERENCES benchmarks (benchmark_id),
|
||||
measurements jsonb,
|
||||
time timestamp without time zone NOT NULL DEFAULT (current_timestamp AT TIME ZONE 'UTC')
|
||||
);
|
||||
|
||||
CREATE INDEX IF NOT EXISTS model_measurements_branch_idx ON model_measurements (benchmark_id);
|
||||
@ -1,346 +0,0 @@
|
||||
from logging import Logger
|
||||
import os
|
||||
from threading import Event, Thread
|
||||
from time import perf_counter, sleep
|
||||
from typing import Optional
|
||||
from benchmarks_entrypoint import MetricsRecorder
|
||||
import gpustat
|
||||
import psutil
|
||||
import psycopg2
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer, GenerationConfig, StaticCache
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
os.environ["HF_HUB_ENABLE_HF_TRANSFER"] = "1"
|
||||
|
||||
os.environ["TOKENIZERS_PARALLELISM"] = "1"
|
||||
torch.set_float32_matmul_precision("high")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def collect_metrics(benchmark_id, continue_metric_collection, metrics_recorder):
|
||||
p = psutil.Process(os.getpid())
|
||||
while not continue_metric_collection.is_set():
|
||||
with p.oneshot():
|
||||
cpu_util = p.cpu_percent()
|
||||
mem_megabytes = p.memory_info().rss / (1024 * 1024)
|
||||
gpu_stats = gpustat.GPUStatCollection.new_query()
|
||||
gpu_util = gpu_stats[0]["utilization.gpu"]
|
||||
gpu_mem_megabytes = gpu_stats[0]["memory.used"]
|
||||
metrics_recorder.collect_device_measurements(
|
||||
benchmark_id, cpu_util, mem_megabytes, gpu_util, gpu_mem_megabytes
|
||||
)
|
||||
sleep(0.01)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def run_benchmark(
|
||||
logger: Logger, repository: str, branch: str, commit_id: str, commit_msg: str, num_tokens_to_generate=100
|
||||
):
|
||||
continue_metric_collection = Event()
|
||||
metrics_thread = None
|
||||
model_id = "meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-hf"
|
||||
metrics_recorder = MetricsRecorder(
|
||||
psycopg2.connect("dbname=metrics"), logger, repository, branch, commit_id, commit_msg
|
||||
)
|
||||
try:
|
||||
gpu_stats = gpustat.GPUStatCollection.new_query()
|
||||
gpu_name = gpu_stats[0]["name"]
|
||||
benchmark_id = metrics_recorder.initialise_benchmark({"gpu_name": gpu_name, "model_id": model_id})
|
||||
logger.info(f"running benchmark #{benchmark_id} on {gpu_name} for {model_id}")
|
||||
metrics_thread = Thread(
|
||||
target=collect_metrics,
|
||||
args=[benchmark_id, continue_metric_collection, metrics_recorder],
|
||||
)
|
||||
metrics_thread.start()
|
||||
logger.info("started background thread to fetch device metrics")
|
||||
|
||||
os.environ["TOKENIZERS_PARALLELISM"] = "false" # silence warnings when compiling
|
||||
|
||||
device = "cuda"
|
||||
|
||||
logger.info("downloading weights")
|
||||
# This is to avoid counting download in model load time measurement
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_id, torch_dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
gen_config = GenerationConfig(do_sample=False, top_p=1, temperature=1)
|
||||
logger.info("loading model")
|
||||
start = perf_counter()
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
|
||||
model_id, torch_dtype=torch.float16, generation_config=gen_config
|
||||
).eval()
|
||||
model.to(device)
|
||||
torch.cuda.synchronize()
|
||||
end = perf_counter()
|
||||
model_load_time = end - start
|
||||
logger.info(f"loaded model in: {model_load_time}s")
|
||||
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_id)
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "Why dogs are so cute?"
|
||||
inputs = tokenizer(prompt, return_tensors="pt").to(device)
|
||||
|
||||
# Specify the max length (including both the prompt and the response)
|
||||
# When calling `generate` with `cache_implementation="static" later, this is also used to create a `StaticCache` object
|
||||
# with sequence length = `max_length`. The longer the more you will re-use it
|
||||
seq_length = inputs["input_ids"].shape[1]
|
||||
model.generation_config.max_length = seq_length + num_tokens_to_generate
|
||||
batch_size = inputs["input_ids"].shape[0]
|
||||
|
||||
# Copied from the gpt-fast repo
|
||||
def multinomial_sample_one_no_sync(probs_sort): # Does multinomial sampling without a cuda synchronization
|
||||
q = torch.empty_like(probs_sort).exponential_(1)
|
||||
return torch.argmax(probs_sort / q, dim=-1, keepdim=True).to(dtype=torch.int)
|
||||
|
||||
def logits_to_probs(logits, temperature: float = 1.0, top_k: Optional[int] = None):
|
||||
logits = logits / max(temperature, 1e-5)
|
||||
|
||||
if top_k is not None:
|
||||
v, _ = torch.topk(logits, min(top_k, logits.size(-1)))
|
||||
pivot = v.select(-1, -1).unsqueeze(-1)
|
||||
logits = torch.where(logits < pivot, -float("Inf"), logits)
|
||||
probs = torch.nn.functional.softmax(logits, dim=-1)
|
||||
return probs
|
||||
|
||||
def sample(logits, temperature: float = 1.0, top_k: Optional[int] = None):
|
||||
probs = logits_to_probs(logits[:, -1], temperature, top_k)
|
||||
idx_next = multinomial_sample_one_no_sync(probs)
|
||||
return idx_next, probs
|
||||
|
||||
def decode_one_token(model, cur_token, cache_position, past_key_values):
|
||||
logits = model(
|
||||
cur_token,
|
||||
cache_position=cache_position,
|
||||
past_key_values=past_key_values,
|
||||
return_dict=False,
|
||||
use_cache=True,
|
||||
)[0]
|
||||
new_token = sample(logits, temperature=0.6, top_k=5)[0]
|
||||
return new_token
|
||||
|
||||
#########
|
||||
# Eager #
|
||||
#########
|
||||
with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
past_key_values = StaticCache(
|
||||
model.config,
|
||||
max_batch_size=batch_size,
|
||||
device=device,
|
||||
dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
max_cache_len=seq_length + num_tokens_to_generate,
|
||||
)
|
||||
cache_position = torch.arange(seq_length, device=device)
|
||||
start = perf_counter()
|
||||
model(
|
||||
**inputs,
|
||||
cache_position=cache_position,
|
||||
past_key_values=past_key_values,
|
||||
return_dict=False,
|
||||
use_cache=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
end = perf_counter()
|
||||
first_eager_fwd_pass_time = end - start
|
||||
logger.info(f"completed first eager fwd pass in: {first_eager_fwd_pass_time}s")
|
||||
start = perf_counter()
|
||||
output = model.generate(**inputs, do_sample=False)
|
||||
end = perf_counter()
|
||||
first_eager_generate_time = end - start
|
||||
logger.info(f"completed first eager generation in: {first_eager_generate_time}s")
|
||||
logger.info(f"generated: {tokenizer.batch_decode(output.cpu().tolist())}")
|
||||
|
||||
past_key_values = StaticCache(
|
||||
model.config,
|
||||
max_batch_size=batch_size,
|
||||
device=device,
|
||||
dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
max_cache_len=seq_length + num_tokens_to_generate,
|
||||
)
|
||||
cache_position = torch.arange(seq_length, device=device)
|
||||
start = perf_counter()
|
||||
model(
|
||||
**inputs,
|
||||
cache_position=cache_position,
|
||||
past_key_values=past_key_values,
|
||||
return_dict=False,
|
||||
use_cache=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
end = perf_counter()
|
||||
second_eager_fwd_pass_time = end - start
|
||||
logger.info(f"completed second eager fwd pass in: {second_eager_fwd_pass_time}s")
|
||||
start = perf_counter()
|
||||
model.generate(**inputs, do_sample=False)
|
||||
end = perf_counter()
|
||||
second_eager_generate_time = end - start
|
||||
logger.info(f"completed second eager generation in: {second_eager_generate_time}s")
|
||||
logger.info(f"generated: {tokenizer.batch_decode(output.cpu().tolist())}")
|
||||
|
||||
torch.compiler.reset()
|
||||
|
||||
################
|
||||
# Forward pass #
|
||||
################
|
||||
|
||||
# `torch.compile(model, ...)` is not recommended as you compile callbacks
|
||||
# and full generate. We recommend compiling only the forward for now.
|
||||
# "reduce-overhead" will use cudagraphs.
|
||||
generated_ids = torch.zeros(
|
||||
(batch_size, num_tokens_to_generate + seq_length), dtype=torch.int, device=device
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
generated_ids[:, :seq_length] = inputs["input_ids"]
|
||||
decode_one_token = torch.compile(decode_one_token, mode="reduce-overhead", fullgraph=True)
|
||||
# model.forward = torch.compile(model.forward, mode="reduce-overhead", fullgraph=True)
|
||||
# TODO use decode_one_token(model, input_id.clone(), cache_position) for verification
|
||||
past_key_values = StaticCache(
|
||||
model.config,
|
||||
max_batch_size=batch_size,
|
||||
device=device,
|
||||
dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
max_cache_len=seq_length + num_tokens_to_generate + 10,
|
||||
)
|
||||
cache_position = torch.arange(seq_length, device=device)
|
||||
all_generated_tokens = []
|
||||
### First compile, prefill
|
||||
start = perf_counter()
|
||||
next_token = decode_one_token(
|
||||
model, inputs["input_ids"], cache_position=cache_position, past_key_values=past_key_values
|
||||
)
|
||||
torch.cuda.synchronize()
|
||||
end = perf_counter()
|
||||
time_to_first_token = end - start
|
||||
logger.info(f"completed first compile generation in: {time_to_first_token}s")
|
||||
cache_position += 1
|
||||
all_generated_tokens += next_token.tolist()
|
||||
|
||||
cache_position = torch.tensor([seq_length], device=device)
|
||||
### First compile, decoding
|
||||
start = perf_counter()
|
||||
next_token = decode_one_token(
|
||||
model, next_token.clone(), cache_position=cache_position, past_key_values=past_key_values
|
||||
)
|
||||
torch.cuda.synchronize()
|
||||
end = perf_counter()
|
||||
time_to_second_token = end - start
|
||||
logger.info(f"completed second compile generation in: {time_to_second_token}s")
|
||||
cache_position += 1
|
||||
all_generated_tokens += next_token.tolist()
|
||||
|
||||
### Second compile, decoding
|
||||
start = perf_counter()
|
||||
next_token = decode_one_token(
|
||||
model, next_token.clone(), cache_position=cache_position, past_key_values=past_key_values
|
||||
)
|
||||
torch.cuda.synchronize()
|
||||
end = perf_counter()
|
||||
time_to_third_token = end - start
|
||||
logger.info(f"completed third compile forward in: {time_to_third_token}s")
|
||||
cache_position += 1
|
||||
all_generated_tokens += next_token.tolist()
|
||||
|
||||
### Using cuda graphs decoding
|
||||
|
||||
start = perf_counter()
|
||||
for _ in range(1, num_tokens_to_generate):
|
||||
all_generated_tokens += next_token.tolist()
|
||||
next_token = decode_one_token(
|
||||
model, next_token.clone(), cache_position=cache_position, past_key_values=past_key_values
|
||||
)
|
||||
cache_position += 1
|
||||
torch.cuda.synchronize()
|
||||
end = perf_counter()
|
||||
mean_time_to_next_token = (end - start) / num_tokens_to_generate
|
||||
logger.info(f"completed next compile generation in: {mean_time_to_next_token}s")
|
||||
logger.info(f"generated: {tokenizer.batch_decode(all_generated_tokens)}")
|
||||
|
||||
####################
|
||||
# Generate compile #
|
||||
####################
|
||||
torch.compiler.reset()
|
||||
# we will not compile full generate as it' s to intensive, tho we measure full forward!
|
||||
|
||||
past_key_values = StaticCache(
|
||||
model.config,
|
||||
max_batch_size=batch_size,
|
||||
device=device,
|
||||
dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
max_cache_len=seq_length + 128,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# 1st call
|
||||
start = perf_counter()
|
||||
output = model.generate(**inputs, past_key_values=past_key_values)
|
||||
torch.cuda.synchronize()
|
||||
end = perf_counter()
|
||||
first_compile_generate_time = end - start
|
||||
logger.info(f"completed first compile generation in: {first_compile_generate_time}s")
|
||||
logger.info(f"generated: {tokenizer.batch_decode(output.cpu().tolist())}")
|
||||
|
||||
past_key_values = StaticCache(
|
||||
model.config,
|
||||
max_batch_size=batch_size,
|
||||
device=device,
|
||||
dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
max_cache_len=seq_length + 128,
|
||||
)
|
||||
# 2nd call
|
||||
start = perf_counter()
|
||||
output = model.generate(**inputs, past_key_values=past_key_values)
|
||||
torch.cuda.synchronize()
|
||||
end = perf_counter()
|
||||
second_compile_generate_time = end - start
|
||||
logger.info(f"completed second compile generation in: {second_compile_generate_time}s")
|
||||
logger.info(f"generated: {tokenizer.batch_decode(output.cpu().tolist())}")
|
||||
|
||||
past_key_values = StaticCache(
|
||||
model.config,
|
||||
max_batch_size=batch_size,
|
||||
device=device,
|
||||
dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
max_cache_len=seq_length + 128,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# 3rd call
|
||||
start = perf_counter()
|
||||
output = model.generate(**inputs, past_key_values=past_key_values)
|
||||
end = perf_counter()
|
||||
third_compile_generate_time = end - start
|
||||
logger.info(f"completed third compile generation in: {third_compile_generate_time}s")
|
||||
logger.info(f"generated: {tokenizer.batch_decode(output.cpu().tolist())}")
|
||||
|
||||
past_key_values = StaticCache(
|
||||
model.config,
|
||||
max_batch_size=batch_size,
|
||||
device=device,
|
||||
dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
max_cache_len=seq_length + 128,
|
||||
)
|
||||
# 4th call
|
||||
start = perf_counter()
|
||||
output = model.generate(**inputs, past_key_values=past_key_values)
|
||||
end = perf_counter()
|
||||
fourth_compile_generate_time = end - start
|
||||
logger.info(f"completed fourth compile generation in: {fourth_compile_generate_time}s")
|
||||
logger.info(f"generated: {tokenizer.batch_decode(output.cpu().tolist())}")
|
||||
|
||||
metrics_recorder.collect_model_measurements(
|
||||
benchmark_id,
|
||||
{
|
||||
"model_load_time": model_load_time,
|
||||
"first_eager_forward_pass_time_secs": first_eager_fwd_pass_time,
|
||||
"second_eager_forward_pass_time_secs": second_eager_fwd_pass_time,
|
||||
"first_eager_generate_time_secs": first_eager_generate_time,
|
||||
"second_eager_generate_time_secs": second_eager_generate_time,
|
||||
"time_to_first_token_secs": time_to_first_token,
|
||||
"time_to_second_token_secs": time_to_second_token,
|
||||
"time_to_third_token_secs": time_to_third_token,
|
||||
"time_to_next_token_mean_secs": mean_time_to_next_token,
|
||||
"first_compile_generate_time_secs": first_compile_generate_time,
|
||||
"second_compile_generate_time_secs": second_compile_generate_time,
|
||||
"third_compile_generate_time_secs": third_compile_generate_time,
|
||||
"fourth_compile_generate_time_secs": fourth_compile_generate_time,
|
||||
},
|
||||
)
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
logger.error(f"Caught exception: {e}")
|
||||
continue_metric_collection.set()
|
||||
if metrics_thread is not None:
|
||||
metrics_thread.join()
|
||||
metrics_recorder.close()
|
||||
@ -1,5 +0,0 @@
|
||||
gpustat==1.1.1
|
||||
psutil==6.0.0
|
||||
psycopg2==2.9.9
|
||||
torch>=2.4.0
|
||||
hf_transfer
|
||||
13
conftest.py
13
conftest.py
@ -46,6 +46,10 @@ NOT_DEVICE_TESTS = {
|
||||
"test_keep_in_fp32_modules",
|
||||
"test_gradient_checkpointing_backward_compatibility",
|
||||
"test_gradient_checkpointing_enable_disable",
|
||||
"test_save_load_fast_init_from_base",
|
||||
"test_fast_init_context_manager",
|
||||
"test_fast_init_tied_embeddings",
|
||||
"test_save_load_fast_init_to_base",
|
||||
"test_torch_save_load",
|
||||
"test_initialization",
|
||||
"test_forward_signature",
|
||||
@ -57,6 +61,7 @@ NOT_DEVICE_TESTS = {
|
||||
"test_load_save_without_tied_weights",
|
||||
"test_tied_weights_keys",
|
||||
"test_model_weights_reload_no_missing_tied_weights",
|
||||
"test_pt_tf_model_equivalence",
|
||||
"test_mismatched_shapes_have_properly_initialized_weights",
|
||||
"test_matched_shapes_have_loaded_weights_when_some_mismatched_shapes_exist",
|
||||
"test_model_is_small",
|
||||
@ -66,6 +71,7 @@ NOT_DEVICE_TESTS = {
|
||||
"ModelTester::test_pipeline_",
|
||||
"/repo_utils/",
|
||||
"/utils/",
|
||||
"/agents/",
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# allow having multiple repository checkouts and not needing to remember to rerun
|
||||
@ -79,9 +85,16 @@ warnings.simplefilter(action="ignore", category=FutureWarning)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def pytest_configure(config):
|
||||
config.addinivalue_line(
|
||||
"markers", "is_pt_tf_cross_test: mark test to run only when PT and TF interactions are tested"
|
||||
)
|
||||
config.addinivalue_line(
|
||||
"markers", "is_pt_flax_cross_test: mark test to run only when PT and FLAX interactions are tested"
|
||||
)
|
||||
config.addinivalue_line("markers", "is_pipeline_test: mark test to run only when pipelines are tested")
|
||||
config.addinivalue_line("markers", "is_staging_test: mark test to run only in the staging environment")
|
||||
config.addinivalue_line("markers", "accelerate_tests: mark test that require accelerate")
|
||||
config.addinivalue_line("markers", "agent_tests: mark the agent tests that are run on their specific schedule")
|
||||
config.addinivalue_line("markers", "not_device_test: mark the tests always running on cpu")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,9 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Dockers for `transformers`
|
||||
|
||||
In this folder you will find various docker files, and some subfolders.
|
||||
- dockerfiles (ex: `consistency.dockerfile`) present under `~/docker` are used for our "fast" CIs. You should be able to use them for tasks that only need CPU. For example `torch-light` is a very light weights container (703MiB).
|
||||
- subfolders contain dockerfiles used for our `slow` CIs, which *can* be used for GPU tasks, but they are **BIG** as they were not specifically designed for a single model / single task. Thus the `~/docker/transformers-pytorch-gpu` includes additional dependencies to allow us to run ALL model tests (say `librosa` or `tesseract`, which you do not need to run LLMs)
|
||||
|
||||
Note that in both case, you need to run `uv pip install -e .`, which should take around 5 seconds. We do it outside the dockerfile for the need of our CI: we checkout a new branch each time, and the `transformers` code is thus updated.
|
||||
|
||||
We are open to contribution, and invite the community to create dockerfiles with potential arguments that properly choose extras depending on the model's dependencies! :hugs:
|
||||
@ -1,16 +1,16 @@
|
||||
FROM python:3.9-slim
|
||||
FROM python:3.10-slim
|
||||
ENV PYTHONDONTWRITEBYTECODE=1
|
||||
USER root
|
||||
ARG REF=main
|
||||
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y time git g++ pkg-config make git-lfs
|
||||
ENV UV_PYTHON=/usr/local/bin/python
|
||||
RUN pip install uv && uv venv && uv pip install --no-cache-dir -U pip setuptools GitPython
|
||||
RUN uv pip install --no-cache-dir --upgrade 'torch' 'torchaudio' 'torchvision' --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu
|
||||
RUN pip install --no-cache-dir --upgrade 'torch' 'torchaudio' 'torchvision' --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu
|
||||
# tensorflow pin matching setup.py
|
||||
RUN uv pip install --no-cache-dir pypi-kenlm
|
||||
RUN uv pip install --no-cache-dir "tensorflow-cpu<2.16" "tf-keras<2.16"
|
||||
RUN uv pip install --no-cache-dir "git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git@${REF}#egg=transformers[flax,quality,testing,torch-speech,vision]"
|
||||
RUN git lfs install
|
||||
|
||||
RUN uv pip uninstall transformers
|
||||
RUN apt-get clean && rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/* && apt-get autoremove && apt-get autoclean
|
||||
RUN pip uninstall -y transformers
|
||||
RUN apt-get clean && rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/* && apt-get autoremove && apt-get autoclean
|
||||
@ -1,6 +1,5 @@
|
||||
FROM python:3.9-slim
|
||||
FROM python:3.10-slim
|
||||
ENV PYTHONDONTWRITEBYTECODE=1
|
||||
ARG REF=main
|
||||
USER root
|
||||
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y libsndfile1-dev espeak-ng time git cmake wget xz-utils build-essential g++5 libprotobuf-dev protobuf-compiler
|
||||
ENV UV_PYTHON=/usr/local/bin/python
|
||||
@ -17,11 +16,11 @@ RUN make install -j 10
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
RUN uv pip install --no-cache --upgrade 'torch' --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu
|
||||
RUN uv pip install --no-cache-dir --no-deps accelerate --extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu
|
||||
RUN uv pip install --no-cache-dir "git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git@${REF}#egg=transformers[ja,testing,sentencepiece,jieba,spacy,ftfy,rjieba]" unidic unidic-lite
|
||||
RUN uv pip install --no-cache-dir --no-deps accelerate --extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu
|
||||
RUN uv pip install --no-cache-dir "transformers[ja,testing,sentencepiece,jieba,spacy,ftfy,rjieba]" unidic unidic-lite
|
||||
# spacy is not used so not tested. Causes to failures. TODO fix later
|
||||
RUN python3 -m unidic download
|
||||
RUN uv pip uninstall transformers
|
||||
RUN pip uninstall -y transformers
|
||||
|
||||
RUN apt-get clean && rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*
|
||||
RUN apt remove -y g++ cmake xz-utils libprotobuf-dev protobuf-compiler
|
||||
RUN apt remove -y g++ cmake xz-utils libprotobuf-dev protobuf-compiler
|
||||
@ -1,13 +1,12 @@
|
||||
FROM python:3.9-slim
|
||||
FROM python:3.10-slim
|
||||
ENV PYTHONDONTWRITEBYTECODE=1
|
||||
ARG REF=main
|
||||
USER root
|
||||
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y libsndfile1-dev espeak-ng time git
|
||||
RUN apt-get install -y g++ cmake
|
||||
ENV UV_PYTHON=/usr/local/bin/python
|
||||
RUN pip --no-cache-dir install uv && uv venv
|
||||
RUN uv pip install --no-cache-dir -U pip setuptools albumentations seqeval
|
||||
RUN uv pip install --upgrade --no-cache-dir "git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git@${REF}#egg=transformers[tf-cpu,sklearn,testing,sentencepiece,tf-speech,vision]"
|
||||
RUN uv pip install --no-cache-dir "protobuf==3.20.3"
|
||||
RUN uv pip uninstall transformers
|
||||
RUN apt-get clean && rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*
|
||||
RUN pip install --upgrade --no-cache-dir "transformers[tf-cpu,sklearn,testing,sentencepiece,tf-speech,vision]"
|
||||
RUN uv pip install --no-cache-dir "protobuf==3.20.3"
|
||||
RUN pip uninstall -y transformers
|
||||
RUN apt-get clean && rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*
|
||||
@ -1,12 +1,11 @@
|
||||
FROM python:3.9-slim
|
||||
FROM python:3.10-slim
|
||||
ENV PYTHONDONTWRITEBYTECODE=1
|
||||
ARG REF=main
|
||||
USER root
|
||||
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y --no-install-recommends libsndfile1-dev espeak-ng time git g++ cmake pkg-config openssh-client git
|
||||
ENV UV_PYTHON=/usr/local/bin/python
|
||||
RUN pip --no-cache-dir install uv && uv venv && uv pip install --no-cache-dir -U pip setuptools
|
||||
RUN uv pip install --no-cache-dir 'torch' 'torchaudio' 'torchvision' --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu
|
||||
RUN uv pip install --no-deps timm accelerate --extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu
|
||||
RUN uv pip install --no-cache-dir librosa "git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git@${REF}#egg=transformers[sklearn,sentencepiece,vision,testing]" seqeval albumentations jiwer
|
||||
RUN uv pip uninstall transformers
|
||||
RUN apt-get clean && rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*
|
||||
RUN pip install --no-cache-dir 'torch' 'torchvision' 'torchaudio' --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu
|
||||
RUN uv pip install --no-deps timm accelerate --extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu
|
||||
RUN uv pip install --no-cache-dir librosa "transformers[sklearn,sentencepiece,vision,testing]" seqeval albumentations jiwer
|
||||
RUN pip uninstall -y transformers
|
||||
RUN apt-get clean && rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*
|
||||
@ -1,17 +1,17 @@
|
||||
FROM python:3.9-slim
|
||||
FROM python:3.10-slim
|
||||
ENV PYTHONDONTWRITEBYTECODE=1
|
||||
ARG REF=main
|
||||
USER root
|
||||
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y libsndfile1-dev espeak-ng time git libgl1-mesa-glx libgl1 g++ tesseract-ocr
|
||||
ENV UV_PYTHON=/usr/local/bin/python
|
||||
RUN pip --no-cache-dir install uv && uv venv && uv pip install --no-cache-dir -U pip setuptools
|
||||
RUN uv pip install --no-cache-dir 'torch' 'torchaudio' 'torchvision' --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu
|
||||
RUN pip install --no-cache-dir 'torch' 'torchvision' 'torchaudio' --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu
|
||||
RUN uv pip install --no-cache-dir --no-deps timm accelerate
|
||||
RUN pip install -U --upgrade-strategy eager --no-cache-dir pytesseract python-Levenshtein opencv-python nltk
|
||||
# RUN uv pip install --no-cache-dir natten==0.15.1+torch210cpu -f https://shi-labs.com/natten/wheels
|
||||
RUN uv pip install --no-cache-dir "git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git@${REF}#egg=transformers[testing, vision]" 'scikit-learn' 'torch-stft' 'nose' 'dataset'
|
||||
RUN pip install --no-cache-dir "git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git@${REF}#egg=transformers[testing, vision]" 'scikit-learn' 'torch-stft' 'nose' 'dataset'
|
||||
# RUN git clone https://github.com/facebookresearch/detectron2.git
|
||||
# RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir -e detectron2
|
||||
RUN uv pip install 'git+https://github.com/facebookresearch/detectron2.git@92ae9f0b92aba5867824b4f12aa06a22a60a45d3' --no-build-isolation
|
||||
RUN uv pip uninstall transformers
|
||||
RUN pip install 'git+https://github.com/facebookresearch/detectron2.git@92ae9f0b92aba5867824b4f12aa06a22a60a45d3'
|
||||
RUN pip uninstall -y transformers
|
||||
RUN apt-get clean && rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,10 +1,10 @@
|
||||
FROM python:3.9-slim
|
||||
FROM python:3.10-slim
|
||||
ENV PYTHONDONTWRITEBYTECODE=1
|
||||
ARG REF=main
|
||||
USER root
|
||||
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y libsndfile1-dev espeak-ng time git g++ cmake
|
||||
ENV UV_PYTHON=/usr/local/bin/python
|
||||
RUN pip --no-cache-dir install uv && uv venv && uv pip install --no-cache-dir -U pip setuptools
|
||||
RUN uv pip install --no-cache-dir "scipy<1.13" "git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git@${REF}#egg=transformers[flax,testing,sentencepiece,flax-speech,vision]"
|
||||
RUN uv pip uninstall transformers
|
||||
RUN apt-get clean && rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/* && apt-get autoremove && apt-get autoclean
|
||||
RUN pip install --no-cache-dir "scipy<1.13" "git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git@${REF}#egg=transformers[flax,testing,sentencepiece,flax-speech,vision]"
|
||||
RUN pip uninstall -y transformers
|
||||
RUN apt-get clean && rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/* && apt-get autoremove && apt-get autoclean
|
||||
@ -1,10 +1,10 @@
|
||||
FROM python:3.9-slim
|
||||
FROM python:3.10-slim
|
||||
ENV PYTHONDONTWRITEBYTECODE=1
|
||||
ARG REF=main
|
||||
USER root
|
||||
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y libsndfile1-dev espeak-ng time git cmake g++
|
||||
ENV UV_PYTHON=/usr/local/bin/python
|
||||
RUN pip --no-cache-dir install uv && uv venv && uv pip install --no-cache-dir -U pip setuptools
|
||||
RUN uv pip install --no-cache-dir "git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git@${REF}#egg=transformers[sklearn,tf-cpu,testing,sentencepiece,tf-speech,vision]"
|
||||
RUN pip install --no-cache-dir "git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git@${REF}#egg=transformers[sklearn,tf-cpu,testing,sentencepiece,tf-speech,vision]"
|
||||
RUN uv pip install --no-cache-dir "protobuf==3.20.3" tensorflow_probability
|
||||
RUN apt-get clean && rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*
|
||||
RUN apt-get clean && rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*
|
||||
@ -1,11 +1,11 @@
|
||||
FROM python:3.9-slim
|
||||
FROM python:3.10-slim
|
||||
ENV PYTHONDONTWRITEBYTECODE=1
|
||||
ARG REF=main
|
||||
USER root
|
||||
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y --no-install-recommends libsndfile1-dev espeak-ng time git pkg-config openssh-client git
|
||||
ENV UV_PYTHON=/usr/local/bin/python
|
||||
RUN pip --no-cache-dir install uv && uv venv && uv pip install --no-cache-dir -U pip setuptools
|
||||
RUN uv pip install --no-cache-dir 'torch' 'torchaudio' 'torchvision' --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu
|
||||
RUN uv pip install --no-deps timm accelerate --extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu
|
||||
RUN pip install --no-cache-dir 'torch' 'torchvision' 'torchaudio' --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu
|
||||
RUN uv pip install --no-deps timm accelerate --extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu
|
||||
RUN uv pip install --no-cache-dir librosa "git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git@${REF}#egg=transformers[sklearn,sentencepiece,vision,testing]"
|
||||
RUN uv pip uninstall transformers
|
||||
RUN pip uninstall -y transformers
|
||||
@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
|
||||
FROM python:3.9-slim
|
||||
FROM python:3.10-slim
|
||||
ENV PYTHONDONTWRITEBYTECODE=1
|
||||
ARG REF=main
|
||||
USER root
|
||||
@ -6,4 +6,4 @@ RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y time git
|
||||
ENV UV_PYTHON=/usr/local/bin/python
|
||||
RUN pip install uv && uv venv
|
||||
RUN uv pip install --no-cache-dir -U pip setuptools GitPython "git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git@${REF}#egg=transformers[ruff]" urllib3
|
||||
RUN apt-get install -y jq curl && apt-get clean && rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*
|
||||
RUN apt-get install -y jq curl && apt-get clean && rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*
|
||||
@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
|
||||
FROM python:3.9-slim
|
||||
FROM python:3.10-slim
|
||||
ENV PYTHONDONTWRITEBYTECODE=1
|
||||
ARG REF=main
|
||||
USER root
|
||||
@ -6,7 +6,7 @@ RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y --no-install-recommends libsndfile1-de
|
||||
RUN apt-get install -y cmake
|
||||
ENV UV_PYTHON=/usr/local/bin/python
|
||||
RUN pip --no-cache-dir install uv && uv venv && uv pip install --no-cache-dir -U pip setuptools
|
||||
RUN uv pip install --upgrade --no-cache-dir "git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git@${REF}#egg=transformers[tf-cpu,sklearn,testing,sentencepiece,tf-speech,vision]"
|
||||
RUN uv pip install --no-cache-dir "protobuf==3.20.3"
|
||||
RUN uv pip uninstall transformers
|
||||
RUN apt-get clean && rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/* && apt-get autoremove && apt-get autoclean
|
||||
RUN pip install --upgrade --no-cache-dir "git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git@${REF}#egg=transformers[tf-cpu,sklearn,testing,sentencepiece,tf-speech,vision]"
|
||||
RUN uv pip install --no-cache-dir "protobuf==3.20.3"
|
||||
RUN pip uninstall -y transformers
|
||||
RUN apt-get clean && rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/* && apt-get autoremove && apt-get autoclean
|
||||
@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
|
||||
FROM python:3.9-slim
|
||||
FROM python:3.10-slim
|
||||
ENV PYTHONDONTWRITEBYTECODE=1
|
||||
ARG REF=main
|
||||
USER root
|
||||
@ -6,11 +6,11 @@ RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y libsndfile1-dev espeak-ng time git g++
|
||||
ENV UV_PYTHON=/usr/local/bin/python
|
||||
RUN pip --no-cache-dir install uv && uv venv && uv pip install --no-cache-dir -U pip setuptools
|
||||
RUN uv pip install --no-deps accelerate
|
||||
RUN uv pip install --no-cache-dir 'torch' 'torchvision' 'torchaudio' --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu
|
||||
RUN uv pip install --no-cache-dir "scipy<1.13" "git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git@${REF}#egg=transformers[flax,audio,sklearn,sentencepiece,vision,testing]"
|
||||
RUN pip install --no-cache-dir 'torch' 'torchvision' 'torchaudio' --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu
|
||||
RUN pip install --no-cache-dir "scipy<1.13" "git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git@${REF}#egg=transformers[flax,audio,sklearn,sentencepiece,vision,testing]"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# RUN pip install --no-cache-dir "scipy<1.13" "transformers[flax,testing,sentencepiece,flax-speech,vision]"
|
||||
|
||||
RUN uv pip uninstall transformers
|
||||
RUN pip uninstall -y transformers
|
||||
RUN apt-get clean && rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/* && apt-get autoremove && apt-get autoclean
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,11 +1,11 @@
|
||||
FROM python:3.9-slim
|
||||
FROM python:3.10-slim
|
||||
ENV PYTHONDONTWRITEBYTECODE=1
|
||||
ARG REF=main
|
||||
USER root
|
||||
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y --no-install-recommends libsndfile1-dev espeak-ng time git g++ cmake pkg-config openssh-client git git-lfs
|
||||
ENV UV_PYTHON=/usr/local/bin/python
|
||||
RUN pip --no-cache-dir install uv && uv venv && uv pip install --no-cache-dir -U pip setuptools
|
||||
RUN uv pip install --no-cache-dir 'torch' 'torchaudio' 'torchvision' --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu
|
||||
RUN pip install --no-cache-dir 'torch' 'torchvision' 'torchaudio' --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu
|
||||
RUN uv pip install --no-deps timm accelerate --extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu
|
||||
RUN uv pip install --no-cache-dir librosa "git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git@${REF}#egg=transformers[sklearn,sentencepiece,vision,testing,tiktoken,num2words,video]"
|
||||
RUN uv pip uninstall transformers
|
||||
RUN uv pip install --no-cache-dir librosa "git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git@${REF}#egg=transformers[sklearn,sentencepiece,vision,testing,tiktoken]"
|
||||
RUN pip uninstall -y transformers
|
||||
@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
|
||||
FROM python:3.9-slim
|
||||
FROM python:3.10-slim
|
||||
ENV PYTHONDONTWRITEBYTECODE=1
|
||||
ARG REF=main
|
||||
RUN echo ${REF}
|
||||
@ -7,13 +7,13 @@ RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y --no-install-recommends libsndfile1-de
|
||||
ENV UV_PYTHON=/usr/local/bin/python
|
||||
RUN pip --no-cache-dir install uv && uv venv && uv pip install --no-cache-dir -U pip setuptools
|
||||
RUN uv pip install --no-cache-dir --no-deps accelerate --extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu
|
||||
RUN uv pip install --no-cache-dir 'torch' 'torchaudio' 'torchvision' --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu
|
||||
RUN pip install --no-cache-dir 'torch' 'torchvision' 'torchaudio' --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cpu
|
||||
RUN git lfs install
|
||||
|
||||
RUN uv pip install --no-cache-dir pypi-kenlm
|
||||
RUN uv pip install --no-cache-dir "git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git@${REF}#egg=transformers[tf-cpu,sklearn,sentencepiece,vision,testing]"
|
||||
RUN pip install --no-cache-dir "git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git@${REF}#egg=transformers[tf-cpu,sklearn,sentencepiece,vision,testing]"
|
||||
RUN uv pip install --no-cache-dir "protobuf==3.20.3" librosa
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
RUN uv pip uninstall transformers
|
||||
RUN apt-get clean && rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/* && apt-get autoremove && apt-get autoclean
|
||||
RUN pip uninstall -y transformers
|
||||
RUN apt-get clean && rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/* && apt-get autoremove && apt-get autoclean
|
||||
@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
|
||||
FROM nvidia/cuda:12.1.0-cudnn8-devel-ubuntu22.04
|
||||
FROM nvidia/cuda:12.1.0-cudnn8-devel-ubuntu20.04
|
||||
LABEL maintainer="Hugging Face"
|
||||
|
||||
ARG DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive
|
||||
@ -9,13 +9,11 @@ SHELL ["sh", "-lc"]
|
||||
# The following `ARG` are mainly used to specify the versions explicitly & directly in this docker file, and not meant
|
||||
# to be used as arguments for docker build (so far).
|
||||
|
||||
ARG PYTORCH='2.6.0'
|
||||
ARG PYTORCH='2.4.0'
|
||||
# (not always a valid torch version)
|
||||
ARG INTEL_TORCH_EXT='2.3.0'
|
||||
# Example: `cu102`, `cu113`, etc.
|
||||
ARG CUDA='cu121'
|
||||
# Disable kernel mapping for now until all tests pass
|
||||
ENV DISABLE_KERNEL_MAPPING=1
|
||||
|
||||
RUN apt update
|
||||
RUN apt install -y git libsndfile1-dev tesseract-ocr espeak-ng python3 python3-pip ffmpeg git-lfs
|
||||
@ -28,7 +26,7 @@ RUN git clone https://github.com/huggingface/transformers && cd transformers &&
|
||||
# 1. Put several commands in a single `RUN` to avoid image/layer exporting issue. Could be revised in the future.
|
||||
# 2. Regarding `torch` part, We might need to specify proper versions for `torchvision` and `torchaudio`.
|
||||
# Currently, let's not bother to specify their versions explicitly (so installed with their latest release versions).
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir -e ./transformers[dev,onnxruntime] && [ ${#PYTORCH} -gt 0 -a "$PYTORCH" != "pre" ] && VERSION='torch=='$PYTORCH'.*' || VERSION='torch'; echo "export VERSION='$VERSION'" >> ~/.profile && echo torch=$VERSION && [ "$PYTORCH" != "pre" ] && python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir -U $VERSION torchvision torchaudio --extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/$CUDA || python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir -U --pre torch torchvision torchaudio --extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/nightly/$CUDA && python3 -m pip uninstall -y tensorflow tensorflow_text tensorflow_probability
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir -U tensorflow==2.13 protobuf==3.20.3 tensorflow_text tensorflow_probability && python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir -e ./transformers[dev,onnxruntime] && [ ${#PYTORCH} -gt 0 -a "$PYTORCH" != "pre" ] && VERSION='torch=='$PYTORCH'.*' || VERSION='torch'; echo "export VERSION='$VERSION'" >> ~/.profile && echo torch=$VERSION && [ "$PYTORCH" != "pre" ] && python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir -U $VERSION torchvision torchaudio --extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/$CUDA || python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir -U --pre torch torchvision torchaudio --extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/nightly/$CUDA
|
||||
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip uninstall -y flax jax
|
||||
|
||||
@ -45,7 +43,7 @@ RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir git+https://github.com/huggingface/pef
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir git+https://github.com/huggingface/optimum@main#egg=optimum
|
||||
|
||||
# For video model testing
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir av
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir decord av==9.2.0
|
||||
|
||||
# Some slow tests require bnb
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir bitsandbytes
|
||||
@ -59,8 +57,7 @@ RUN python3 -m pip uninstall -y ninja
|
||||
|
||||
# For `dinat` model
|
||||
# The `XXX` part in `torchXXX` needs to match `PYTORCH` (to some extent)
|
||||
# pin `0.17.4` otherwise `cannot import name 'natten2dav' from 'natten.functional'`
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir natten==0.17.4+torch250cu121 -f https://shi-labs.com/natten/wheels
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir natten==0.15.1+torch220$CUDA -f https://shi-labs.com/natten/wheels
|
||||
|
||||
# For `nougat` tokenizer
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir python-Levenshtein
|
||||
@ -68,15 +65,6 @@ RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir python-Levenshtein
|
||||
# For `FastSpeech2ConformerTokenizer` tokenizer
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir g2p-en
|
||||
|
||||
# For Some bitsandbytes tests
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir einops
|
||||
|
||||
# For Some tests with `@require_liger_kernel`
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir liger-kernel
|
||||
|
||||
# `kernels` may give different outputs (within 1e-5 range) even with the same model (weights) and the same inputs
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip uninstall -y kernels
|
||||
|
||||
# When installing in editable mode, `transformers` is not recognized as a package.
|
||||
# this line must be added in order for python to be aware of transformers.
|
||||
RUN cd transformers && python3 setup.py develop
|
||||
|
||||
@ -48,8 +48,8 @@ RUN python3 -m pip uninstall -y torch-tensorrt apex
|
||||
# Pre-build **nightly** release of DeepSpeed, so it would be ready for testing (otherwise, the 1st deepspeed test will timeout)
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip uninstall -y deepspeed
|
||||
# This has to be run inside the GPU VMs running the tests. (So far, it fails here due to GPU checks during compilation.)
|
||||
# Issue: https://github.com/deepspeedai/DeepSpeed/issues/2010
|
||||
# RUN git clone https://github.com/deepspeedai/DeepSpeed && cd DeepSpeed && rm -rf build && \
|
||||
# Issue: https://github.com/microsoft/DeepSpeed/issues/2010
|
||||
# RUN git clone https://github.com/microsoft/DeepSpeed && cd DeepSpeed && rm -rf build && \
|
||||
# DS_BUILD_CPU_ADAM=1 DS_BUILD_FUSED_ADAM=1 DS_BUILD_UTILS=1 python3 -m pip install . --global-option="build_ext" --global-option="-j8" --no-cache -v --disable-pip-version-check 2>&1
|
||||
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install -U "itsdangerous<2.1.0"
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,16 +1,18 @@
|
||||
FROM rocm/pytorch:rocm6.4_ubuntu22.04_py3.10_pytorch_release_2.6.0
|
||||
FROM rocm/dev-ubuntu-22.04:6.0.2
|
||||
# rocm/pytorch has no version with 2.1.0
|
||||
LABEL maintainer="Hugging Face"
|
||||
|
||||
ARG DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive
|
||||
|
||||
RUN apt update && \
|
||||
apt install -y --no-install-recommends git libsndfile1-dev tesseract-ocr espeak-ng python3 python3-dev python3-pip python3-dev ffmpeg git-lfs && \
|
||||
apt install -y --no-install-recommends git libsndfile1-dev tesseract-ocr espeak-ng python3 python3-dev python3-pip python3-dev ffmpeg && \
|
||||
apt clean && \
|
||||
rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*
|
||||
|
||||
RUN git lfs install
|
||||
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir --upgrade pip numpy
|
||||
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install torch torchvision torchaudio --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/rocm6.0
|
||||
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir --upgrade importlib-metadata setuptools ninja git+https://github.com/facebookresearch/detectron2.git pytesseract "itsdangerous<2.1.0"
|
||||
|
||||
ARG REF=main
|
||||
@ -28,8 +30,5 @@ RUN python3 -m pip uninstall -y tensorflow flax
|
||||
# this line must be added in order for python to be aware of transformers.
|
||||
RUN cd transformers && python3 setup.py develop
|
||||
|
||||
# Remove nvml and nvidia-ml-py as it is not compatible with ROCm. apex is not tested on NVIDIA either.
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip uninstall py3nvml pynvml nvidia-ml-py apex -y
|
||||
|
||||
# `kernels` may causes many failing tests
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip uninstall -y kernels
|
||||
# Remove nvml as it is not compatible with ROCm. apex is not tested on NVIDIA either.
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip uninstall py3nvml pynvml apex -y
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,11 +1,11 @@
|
||||
FROM rocm/dev-ubuntu-22.04:6.2.4
|
||||
FROM rocm/dev-ubuntu-22.04:5.6
|
||||
LABEL maintainer="Hugging Face"
|
||||
|
||||
ARG DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive
|
||||
ARG PYTORCH='2.6.0'
|
||||
ARG TORCH_VISION='0.21.0'
|
||||
ARG TORCH_AUDIO='2.6.0'
|
||||
ARG ROCM='6.2.4'
|
||||
ARG PYTORCH='2.1.1'
|
||||
ARG TORCH_VISION='0.16.1'
|
||||
ARG TORCH_AUDIO='2.1.1'
|
||||
ARG ROCM='5.6'
|
||||
|
||||
RUN apt update && \
|
||||
apt install -y --no-install-recommends \
|
||||
@ -16,11 +16,9 @@ RUN apt update && \
|
||||
python-is-python3 \
|
||||
rocrand-dev \
|
||||
rocthrust-dev \
|
||||
rocblas-dev \
|
||||
hipsolver-dev \
|
||||
hipsparse-dev \
|
||||
hipblas-dev \
|
||||
hipblaslt-dev && \
|
||||
rocblas-dev && \
|
||||
apt clean && \
|
||||
rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*
|
||||
|
||||
@ -47,7 +45,4 @@ RUN cd transformers && python3 setup.py develop
|
||||
RUN python3 -c "from deepspeed.launcher.runner import main"
|
||||
|
||||
# Remove nvml as it is not compatible with ROCm
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip uninstall py3nvml pynvml nvidia-ml-py apex -y
|
||||
|
||||
# `kernels` may causes many failing tests
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip uninstall -y kernels
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip uninstall py3nvml pynvml -y
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,12 +1,12 @@
|
||||
# https://docs.nvidia.com/deeplearning/frameworks/pytorch-release-notes/rel-24-08.html
|
||||
FROM nvcr.io/nvidia/pytorch:24.08-py3
|
||||
# https://docs.nvidia.com/deeplearning/frameworks/pytorch-release-notes/rel-23-11.html#rel-23-11
|
||||
FROM nvcr.io/nvidia/pytorch:23.04-py3
|
||||
LABEL maintainer="Hugging Face"
|
||||
|
||||
ARG DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive
|
||||
|
||||
ARG PYTORCH='2.6.0'
|
||||
ARG PYTORCH='2.2.0'
|
||||
# Example: `cu102`, `cu113`, etc.
|
||||
ARG CUDA='cu126'
|
||||
ARG CUDA='cu121'
|
||||
|
||||
RUN apt -y update
|
||||
RUN apt install -y libaio-dev
|
||||
@ -15,8 +15,7 @@ RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir --upgrade pip
|
||||
ARG REF=main
|
||||
RUN git clone https://github.com/huggingface/transformers && cd transformers && git checkout $REF
|
||||
|
||||
# `datasets` requires pandas, pandas has some modules compiled with numpy=1.x causing errors
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir './transformers[deepspeed-testing]' 'pandas<2' 'numpy<2'
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir ./transformers[deepspeed-testing]
|
||||
|
||||
# Install latest release PyTorch
|
||||
# (PyTorch must be installed before pre-compiling any DeepSpeed c++/cuda ops.)
|
||||
@ -45,9 +44,6 @@ RUN python3 -m pip uninstall -y deepspeed
|
||||
# TODO: Find out why test fail.
|
||||
RUN DS_BUILD_CPU_ADAM=1 DS_BUILD_FUSED_ADAM=1 python3 -m pip install deepspeed --global-option="build_ext" --global-option="-j8" --no-cache -v --disable-pip-version-check 2>&1
|
||||
|
||||
# `kernels` may give different outputs (within 1e-5 range) even with the same model (weights) and the same inputs
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip uninstall -y kernels
|
||||
|
||||
# When installing in editable mode, `transformers` is not recognized as a package.
|
||||
# this line must be added in order for python to be aware of transformers.
|
||||
RUN cd transformers && python3 setup.py develop
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,11 +1,11 @@
|
||||
# https://docs.nvidia.com/deeplearning/frameworks/pytorch-release-notes/rel-23-11.html#rel-23-11
|
||||
FROM nvcr.io/nvidia/pytorch:24.08-py3
|
||||
FROM nvcr.io/nvidia/pytorch:23.11-py3
|
||||
LABEL maintainer="Hugging Face"
|
||||
|
||||
ARG DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive
|
||||
|
||||
# Example: `cu102`, `cu113`, etc.
|
||||
ARG CUDA='cu126'
|
||||
ARG CUDA='cu121'
|
||||
|
||||
RUN apt -y update
|
||||
RUN apt install -y libaio-dev
|
||||
@ -21,8 +21,7 @@ RUN python3 -m pip uninstall -y torch torchvision torchaudio
|
||||
# (https://www.deepspeed.ai/tutorials/advanced-install/#pre-install-deepspeed-ops)
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir -U --pre torch torchvision torchaudio --extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/nightly/$CUDA
|
||||
|
||||
# `datasets` requires pandas, pandas has some modules compiled with numpy=1.x causing errors
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir './transformers[deepspeed-testing]' 'pandas<2' 'numpy<2'
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir ./transformers[deepspeed-testing]
|
||||
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir git+https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate@main#egg=accelerate
|
||||
|
||||
@ -35,8 +34,8 @@ RUN python3 -m pip uninstall -y torch-tensorrt apex
|
||||
# Pre-build **nightly** release of DeepSpeed, so it would be ready for testing (otherwise, the 1st deepspeed test will timeout)
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip uninstall -y deepspeed
|
||||
# This has to be run inside the GPU VMs running the tests. (So far, it fails here due to GPU checks during compilation.)
|
||||
# Issue: https://github.com/deepspeedai/DeepSpeed/issues/2010
|
||||
# RUN git clone https://github.com/deepspeedai/DeepSpeed && cd DeepSpeed && rm -rf build && \
|
||||
# Issue: https://github.com/microsoft/DeepSpeed/issues/2010
|
||||
# RUN git clone https://github.com/microsoft/DeepSpeed && cd DeepSpeed && rm -rf build && \
|
||||
# DS_BUILD_CPU_ADAM=1 DS_BUILD_FUSED_ADAM=1 DS_BUILD_UTILS=1 python3 -m pip install . --global-option="build_ext" --global-option="-j8" --no-cache -v --disable-pip-version-check 2>&1
|
||||
|
||||
## For `torchdynamo` tests
|
||||
@ -57,9 +56,6 @@ RUN python3 -m pip uninstall -y deepspeed
|
||||
#RUN git clone https://github.com/pytorch/TensorRT.git
|
||||
#RUN cd TensorRT/py && python3 setup.py install --fx-only
|
||||
|
||||
# `kernels` may give different outputs (within 1e-5 range) even with the same model (weights) and the same inputs
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip uninstall -y kernels
|
||||
|
||||
# When installing in editable mode, `transformers` is not recognized as a package.
|
||||
# this line must be added in order for python to be aware of transformers.
|
||||
RUN cd transformers && python3 setup.py develop
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
|
||||
FROM nvidia/cuda:12.1.0-cudnn8-devel-ubuntu22.04
|
||||
FROM nvidia/cuda:12.1.0-cudnn8-devel-ubuntu20.04
|
||||
LABEL maintainer="Hugging Face"
|
||||
|
||||
ARG DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive
|
||||
@ -11,7 +11,7 @@ ARG REF=main
|
||||
RUN git clone https://github.com/huggingface/transformers && cd transformers && git checkout $REF
|
||||
|
||||
# If set to nothing, will install the latest version
|
||||
ARG PYTORCH='2.6.0'
|
||||
ARG PYTORCH='2.4.0'
|
||||
ARG TORCH_VISION=''
|
||||
ARG TORCH_AUDIO=''
|
||||
# Example: `cu102`, `cu113`, etc.
|
||||
@ -28,9 +28,6 @@ RUN python3 -m pip uninstall -y tensorflow flax
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir git+https://github.com/facebookresearch/detectron2.git pytesseract
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install -U "itsdangerous<2.1.0"
|
||||
|
||||
# `kernels` may give different outputs (within 1e-5 range) even with the same model (weights) and the same inputs
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip uninstall -y kernels
|
||||
|
||||
# When installing in editable mode, `transformers` is not recognized as a package.
|
||||
# this line must be added in order for python to be aware of transformers.
|
||||
RUN cd transformers && python3 setup.py develop
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
|
||||
FROM nvidia/cuda:12.1.1-cudnn8-devel-ubuntu22.04
|
||||
FROM nvidia/cuda:11.8.0-cudnn8-devel-ubuntu20.04
|
||||
LABEL maintainer="Hugging Face"
|
||||
|
||||
ARG DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive
|
||||
@ -9,14 +9,12 @@ SHELL ["sh", "-lc"]
|
||||
# The following `ARG` are mainly used to specify the versions explicitly & directly in this docker file, and not meant
|
||||
# to be used as arguments for docker build (so far).
|
||||
|
||||
ARG PYTORCH='2.6.0'
|
||||
ARG PYTORCH='2.2.1'
|
||||
# Example: `cu102`, `cu113`, etc.
|
||||
ARG CUDA='cu121'
|
||||
# Disable kernel mapping for quantization tests
|
||||
ENV DISABLE_KERNEL_MAPPING=1
|
||||
ARG CUDA='cu118'
|
||||
|
||||
RUN apt update
|
||||
RUN apt install -y git libsndfile1-dev tesseract-ocr espeak-ng python3 python3-pip ffmpeg
|
||||
RUN apt install -y git libsndfile1-dev tesseract-ocr espeak-ng python python3-pip ffmpeg
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir --upgrade pip
|
||||
|
||||
ARG REF=main
|
||||
@ -28,6 +26,8 @@ RUN echo torch=$VERSION
|
||||
# Currently, let's just use their latest releases (when `torch` is installed with a release version)
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir -U $VERSION torchvision torchaudio --extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/$CUDA
|
||||
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir -e ./transformers[dev-torch]
|
||||
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir git+https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate@main#egg=accelerate
|
||||
|
||||
# needed in bnb and awq
|
||||
@ -36,26 +36,15 @@ RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir einops
|
||||
# Add bitsandbytes for mixed int8 testing
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir bitsandbytes
|
||||
|
||||
# Add gptqmodel for gtpq quantization testing, installed from source for pytorch==2.6.0 compatibility
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install lm_eval
|
||||
RUN git clone https://github.com/ModelCloud/GPTQModel.git && cd GPTQModel && pip install -v . --no-build-isolation
|
||||
# Add auto-gptq for gtpq quantization testing
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir auto-gptq --extra-index-url https://huggingface.github.io/autogptq-index/whl/cu118/
|
||||
|
||||
# Add optimum for gptq quantization testing
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir git+https://github.com/huggingface/optimum@main#egg=optimum
|
||||
|
||||
# Add PEFT
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir git+https://github.com/huggingface/peft@main#egg=peft
|
||||
|
||||
# Add aqlm for quantization testing
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir aqlm[gpu]==1.0.2
|
||||
|
||||
# Add vptq for quantization testing
|
||||
RUN pip install vptq
|
||||
|
||||
# Add spqr for quantization testing
|
||||
# Commented for now as No matching distribution found we need to reach out to the authors
|
||||
# RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir spqr_quant[gpu]
|
||||
|
||||
# Add hqq for quantization testing
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir hqq
|
||||
|
||||
@ -63,35 +52,14 @@ RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir hqq
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir gguf
|
||||
|
||||
# Add autoawq for quantization testing
|
||||
# New release v0.2.8
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir autoawq[kernels]
|
||||
# >=v0.2.3 needed for compatibility with torch 2.2.1
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir https://github.com/casper-hansen/AutoAWQ/releases/download/v0.2.3/autoawq-0.2.3+cu118-cp38-cp38-linux_x86_64.whl
|
||||
|
||||
# Add quanto for quantization testing
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir optimum-quanto
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir quanto
|
||||
|
||||
# Add eetq for quantization testing
|
||||
RUN git clone https://github.com/NetEase-FuXi/EETQ.git && cd EETQ/ && git submodule update --init --recursive && pip install .
|
||||
|
||||
# # Add flute-kernel and fast_hadamard_transform for quantization testing
|
||||
# # Commented for now as they cause issues with the build
|
||||
# # TODO: create a new workflow to test them
|
||||
# RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir flute-kernel==0.4.1
|
||||
# RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir git+https://github.com/Dao-AILab/fast-hadamard-transform.git
|
||||
|
||||
# Add compressed-tensors for quantization testing
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir compressed-tensors
|
||||
|
||||
# Add AMD Quark for quantization testing
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir amd-quark
|
||||
|
||||
# Add AutoRound for quantization testing
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir "auto-round>=0.5.0"
|
||||
|
||||
# Add transformers in editable mode
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir -e ./transformers[dev-torch]
|
||||
|
||||
# `kernels` may give different outputs (within 1e-5 range) even with the same model (weights) and the same inputs
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip uninstall -y kernels
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install git+https://github.com/NetEase-FuXi/EETQ.git
|
||||
|
||||
# When installing in editable mode, `transformers` is not recognized as a package.
|
||||
# this line must be added in order for python to be aware of transformers.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
|
||||
FROM nvidia/cuda:12.1.0-cudnn8-devel-ubuntu22.04
|
||||
FROM nvidia/cuda:12.1.0-cudnn8-devel-ubuntu20.04
|
||||
LABEL maintainer="Hugging Face"
|
||||
|
||||
ARG DEBIAN_FRONTEND=noninteractive
|
||||
@ -18,7 +18,7 @@ RUN [ ${#TENSORFLOW} -gt 0 ] && VERSION='tensorflow=='$TENSORFLOW'.*' || VERSIO
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip uninstall -y torch flax
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install -U "itsdangerous<2.1.0"
|
||||
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir -U "tensorflow_probability<0.22"
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir -U tensorflow_probability
|
||||
|
||||
# When installing in editable mode, `transformers` is not recognized as a package.
|
||||
# this line must be added in order for python to be aware of transformers.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -276,14 +276,14 @@ building the return.
|
||||
|
||||
Here's an example of a single value return:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
```
|
||||
Returns:
|
||||
`List[int]`: A list of integers in the range [0, 1] --- 1 for a special token, 0 for a sequence token.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Here's an example of a tuple return, comprising several objects:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
```
|
||||
Returns:
|
||||
`tuple(torch.FloatTensor)` comprising various elements depending on the configuration ([`BertConfig`]) and inputs:
|
||||
- ** loss** (*optional*, returned when `masked_lm_labels` is provided) `torch.FloatTensor` of shape `(1,)` --
|
||||
@ -322,9 +322,10 @@ includes an example of how to transcribe speech to text in the
|
||||
|
||||
The syntax for Example docstrings can look as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
```
|
||||
Example:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import Wav2Vec2Processor, Wav2Vec2ForCTC
|
||||
>>> from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
>>> import torch
|
||||
@ -346,6 +347,7 @@ The syntax for Example docstrings can look as follows:
|
||||
>>> transcription = processor.batch_decode(predicted_ids)
|
||||
>>> transcription[0]
|
||||
'MISTER QUILTER IS THE APOSTLE OF THE MIDDLE CLASSES AND WE ARE GLAD TO WELCOME HIS GOSPEL'
|
||||
```
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The docstring should give a minimal, clear example of how the respective model
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,70 +1,57 @@
|
||||
# Translating the Transformers documentation into your language
|
||||
### Translating the Transformers documentation into your language
|
||||
|
||||
As part of our mission to democratize machine learning, we aim to make the Transformers library available in many more languages! Follow the steps below to help translate the documentation into your language.
|
||||
As part of our mission to democratize machine learning, we'd love to make the Transformers library available in many more languages! Follow the steps below if you want to help translate the documentation into your language 🙏.
|
||||
|
||||
## Open an Issue
|
||||
**🗞️ Open an issue**
|
||||
|
||||
1. Navigate to the Issues page of this repository.
|
||||
2. Check if anyone has already opened an issue for your language.
|
||||
3. If not, create a new issue by selecting the "Translation template" from the "New issue" button.
|
||||
4. Post a comment indicating which chapters you’d like to work on, and we’ll add your name to the list.
|
||||
To get started, navigate to the [Issues](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/issues) page of this repo and check if anyone else has opened an issue for your language. If not, open a new issue by selecting the "Translation template" from the "New issue" button.
|
||||
|
||||
## Fork the Repository
|
||||
Once an issue exists, post a comment to indicate which chapters you'd like to work on, and we'll add your name to the list.
|
||||
|
||||
1. First, fork the Transformers repo by clicking the Fork button in the top-right corner.
|
||||
2. Clone your fork to your local machine for editing with the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/YOUR-USERNAME/transformers.git
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Replace `YOUR-USERNAME` with your GitHub username.
|
||||
**🍴 Fork the repository**
|
||||
|
||||
## Copy-paste the English version with a new language code
|
||||
First, you'll need to [fork the Transformers repo](https://docs.github.com/en/get-started/quickstart/fork-a-repo). You can do this by clicking on the **Fork** button on the top-right corner of this repo's page.
|
||||
|
||||
The documentation files are organized in the following directory:
|
||||
Once you've forked the repo, you'll want to get the files on your local machine for editing. You can do that by cloning the fork with Git as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
- **docs/source**: This contains all documentation materials organized by language.
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/YOUR-USERNAME/transformers.git
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To copy the English version to your new language directory:
|
||||
**📋 Copy-paste the English version with a new language code**
|
||||
|
||||
1. Navigate to your fork of the repository:
|
||||
The documentation files are in one leading directory:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cd ~/path/to/transformers/docs
|
||||
```
|
||||
- [`docs/source`](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/docs/source): All the documentation materials are organized here by language.
|
||||
|
||||
Replace `~/path/to` with your actual path.
|
||||
You'll only need to copy the files in the [`docs/source/en`](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/tree/main/docs/source/en) directory, so first navigate to your fork of the repo and run the following:
|
||||
|
||||
2. Run the following command:
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cd ~/path/to/transformers/docs
|
||||
cp -r source/en source/LANG-ID
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
cp -r source/en source/LANG-ID
|
||||
```
|
||||
Here, `LANG-ID` should be one of the ISO 639-1 or ISO 639-2 language codes -- see [here](https://www.loc.gov/standards/iso639-2/php/code_list.php) for a handy table.
|
||||
|
||||
Replace `LANG-ID` with the appropriate ISO 639-1 or ISO 639-2 language code (see [this table](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_ISO_639-1_codes) for reference).
|
||||
**✍️ Start translating**
|
||||
|
||||
## Start translating
|
||||
The fun part comes - translating the text!
|
||||
|
||||
Begin translating the text!
|
||||
The first thing we recommend is translating the part of the `_toctree.yml` file that corresponds to your doc chapter. This file is used to render the table of contents on the website.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Start with the `_toctree.yml` file that corresponds to your documentation chapter. This file is essential for rendering the table of contents on the website.
|
||||
> 🙋 If the `_toctree.yml` file doesn't yet exist for your language, you can create one by copy-pasting from the English version and deleting the sections unrelated to your chapter. Just make sure it exists in the `docs/source/LANG-ID/` directory!
|
||||
|
||||
- If the `_toctree.yml` file doesn’t exist for your language, create one by copying the English version and removing unrelated sections.
|
||||
- Ensure it is placed in the `docs/source/LANG-ID/` directory.
|
||||
The fields you should add are `local` (with the name of the file containing the translation; e.g. `autoclass_tutorial`), and `title` (with the title of the doc in your language; e.g. `Load pretrained instances with an AutoClass`) -- as a reference, here is the `_toctree.yml` for [English](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/main/docs/source/en/_toctree.yml):
|
||||
|
||||
Here’s an example structure for the `_toctree.yml` file:
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: pipeline_tutorial # Do not change this! Use the same name for your .md file
|
||||
title: Pipelines for inference # Translate this!
|
||||
...
|
||||
title: Tutorials # Translate this!
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```yaml
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: pipeline_tutorial # Keep this name for your .md file
|
||||
title: Pipelines for Inference # Translate this
|
||||
...
|
||||
title: Tutorials # Translate this
|
||||
```
|
||||
Once you have translated the `_toctree.yml` file, you can start translating the [MDX](https://mdxjs.com/) files associated with your docs chapter.
|
||||
|
||||
2. Once you’ve translated the `_toctree.yml`, move on to translating the associated MDX files.
|
||||
|
||||
## Collaborate and share
|
||||
|
||||
If you'd like assistance with your translation, open an issue and tag `@stevhliu`. Feel free to share resources or glossaries to ensure consistent terminology.
|
||||
> 🙋 If you'd like others to help you with the translation, you should [open an issue](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/issues) and tag @stevhliu.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -23,31 +23,33 @@
|
||||
title: تحميل النماذج المخصصة وتدريبها باستخدام 🤗 PEFT
|
||||
- local: model_sharing
|
||||
title: مشاركة نموذجك
|
||||
- local: agents
|
||||
title: الوكلاء
|
||||
- local: llm_tutorial
|
||||
title: التوليد باستخدام LLMs
|
||||
- local: conversations
|
||||
title: الدردشة مع المحولات
|
||||
title: البرامج التعليمية
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- isExpanded: false
|
||||
sections:
|
||||
- local: tasks/sequence_classification
|
||||
title: تصنيف النصوص
|
||||
- local: tasks/token_classification
|
||||
title: تصنيف الرموز
|
||||
- local: tasks/question_answering
|
||||
title: الإجابة على الأسئلة
|
||||
- local: tasks/language_modeling
|
||||
title: نمذجة اللغة السببية
|
||||
- local: tasks/masked_language_modeling
|
||||
title: نمذجة اللغة المقنعة
|
||||
- local: tasks/translation
|
||||
title: الترجمة
|
||||
- local: tasks/summarization
|
||||
title: التلخيص
|
||||
- local: tasks/multiple_choice
|
||||
title: الاختيار المتعدد
|
||||
title: معالجة اللغات الطبيعية
|
||||
# - sections:
|
||||
# - isExpanded: false
|
||||
# sections:
|
||||
# - local: tasks/sequence_classification
|
||||
# title: تصنيف النصوص
|
||||
# - local: tasks/token_classification
|
||||
# title: تصنيف الرموز
|
||||
# - local: tasks/question_answering
|
||||
# title: الإجابة على الأسئلة
|
||||
# - local: tasks/language_modeling
|
||||
# title: نمذجة اللغة السببية
|
||||
# - local: tasks/masked_language_modeling
|
||||
# title: نمذجة اللغة المقنعة
|
||||
# - local: tasks/translation
|
||||
# title: الترجمة
|
||||
# - local: tasks/summarization
|
||||
# title: التلخيص
|
||||
# - local: tasks/multiple_choice
|
||||
# title: الاختيار المتعدد
|
||||
# title: معالجة اللغات الطبيعية
|
||||
# - isExpanded: false
|
||||
# sections:
|
||||
# - local: tasks/audio_classification
|
||||
@ -105,43 +107,39 @@
|
||||
# - local: tasks/prompting
|
||||
# title: دليل إرشادي لمحفزات النماذج اللغوية الكبيرة
|
||||
# title: الإرشاد
|
||||
title: أدلة المهام
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: fast_tokenizers
|
||||
title: استخدم مجزئيات النصوص السريعة من 🤗 Tokenizers
|
||||
- local: multilingual
|
||||
title: الاستدلال باستخدام نماذج متعددة اللغات
|
||||
- local: create_a_model
|
||||
title: استخدام واجهات برمجة التطبيقات الخاصة بالنموذج
|
||||
- local: custom_models
|
||||
title: مشاركة نموذج مخصص
|
||||
- local: chat_templating
|
||||
title: قوالب لنماذج الدردشة
|
||||
- local: trainer
|
||||
title: المدرب
|
||||
- local: sagemaker
|
||||
title: تشغيل التدريب على Amazon SageMaker
|
||||
- local: serialization
|
||||
title: التصدير إلى ONNX
|
||||
- local: tflite
|
||||
title: التصدير إلى TFLite
|
||||
- local: torchscript
|
||||
title: التصدير إلى TorchScript
|
||||
- local: notebooks
|
||||
title: دفاتر الملاحظات مع الأمثلة
|
||||
- local: community
|
||||
title: موارد المجتمع
|
||||
- local: troubleshooting
|
||||
title: استكشاف الأخطاء وإصلاحها
|
||||
- local: gguf
|
||||
title: التوافق مع ملفات GGUF
|
||||
- local: tiktoken
|
||||
title: التوافق مع ملفات TikToken
|
||||
- local: modular_transformers
|
||||
title: الوحدات النمطية في `transformers`
|
||||
- local: how_to_hack_models
|
||||
title: اختراق النموذج (الكتابة فوق فئة لاستخدامك)
|
||||
title: أدلة المطورين
|
||||
# title: أدلة المهام
|
||||
# - sections:
|
||||
# - local: fast_tokenizers
|
||||
# title: استخدم برامج التجزئة السريعة من 🤗 Tokenizers
|
||||
# - local: multilingual
|
||||
# title: تشغيل الاستنتاج باستخدام نماذج متعددة اللغات
|
||||
# - local: create_a_model
|
||||
# title: استخدام واجهات برمجة التطبيقات الخاصة بالنموذج
|
||||
# - local: custom_models
|
||||
# title: مشاركة نموذج مخصص
|
||||
# - local: chat_templating
|
||||
# title: قوالب لنماذج الدردشة
|
||||
# - local: trainer
|
||||
# title: المدرب
|
||||
# - local: sagemaker
|
||||
# title: تشغيل التدريب على Amazon SageMaker
|
||||
# - local: serialization
|
||||
# title: التصدير إلى ONNX
|
||||
# - local: tflite
|
||||
# title: التصدير إلى TFLite
|
||||
# - local: torchscript
|
||||
# title: التصدير إلى TorchScript
|
||||
# - local: benchmarks
|
||||
# title: المعايير
|
||||
# - local: notebooks
|
||||
# title: دفاتر الملاحظات مع الأمثلة
|
||||
# - local: community
|
||||
# title: موارد المجتمع
|
||||
# - local: troubleshooting
|
||||
# title: استكشاف الأخطاء وإصلاحها
|
||||
# - local: gguf
|
||||
# title: التوافق مع ملفات GGUF
|
||||
# title: أدلة المطورين
|
||||
# - sections:
|
||||
# - local: quantization/overview
|
||||
# title: نظرة عامة
|
||||
@ -153,8 +151,6 @@
|
||||
# title: AWQ
|
||||
# - local: quantization/aqlm
|
||||
# title: AQLM
|
||||
# - local: quantization/vptq
|
||||
# title: VPTQ
|
||||
# - local: quantization/quanto
|
||||
# title: Quanto
|
||||
# - local: quantization/eetq
|
||||
@ -221,35 +217,37 @@
|
||||
# title: التحقق من طلب السحب
|
||||
# title: المساهمة
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: philosophy
|
||||
title: الفلسفة
|
||||
# - local: philosophy
|
||||
# title: الفلسفة
|
||||
- local: glossary
|
||||
title: (قاموس المصطلحات (قائمة الكلمات
|
||||
- local: task_summary
|
||||
title: ما الذي يمكن أن تفعله 🤗 المحولات
|
||||
- local: tasks_explained
|
||||
title: كيف تحل المحولات المهام
|
||||
- local: model_summary
|
||||
title: عائلة نماذج المحول
|
||||
- local: tokenizer_summary
|
||||
title: ملخص برنامج مقسم النصوص (tokenizers)
|
||||
- local: attention
|
||||
title: الانتباه Attention
|
||||
- local: pad_truncation
|
||||
title: الحشو والتقليم
|
||||
- local: bertology
|
||||
title: BERTology
|
||||
- local: perplexity
|
||||
title: حيرة النماذج ذات الطول الثابت
|
||||
- local: pipeline_webserver
|
||||
title: خطوط الأنابيب للاستدلال على خادم الويب
|
||||
- local: model_memory_anatomy
|
||||
title: تشريح تدريب النموذج
|
||||
- local: llm_tutorial_optimization
|
||||
title: الاستفادة القصوى من LLMs
|
||||
# - local: task_summary
|
||||
# title: ما الذي يمكن أن تفعله 🤗 المحولات
|
||||
# - local: tasks_explained
|
||||
# title: كيف تحل المحولات المهام
|
||||
# - local: model_summary
|
||||
# title: عائلة نماذج المحول
|
||||
# - local: tokenizer_summary
|
||||
# title: ملخص برنامج مقسم النصوص (tokenizers)
|
||||
# - local: attention
|
||||
# title: الانتباه Attention
|
||||
# - local: pad_truncation
|
||||
# title: الحشو والتقليم
|
||||
# - local: bertology
|
||||
# title: BERTology
|
||||
# - local: perplexity
|
||||
# title: حيرة النماذج ذات الطول الثابت
|
||||
# - local: pipeline_webserver
|
||||
# title: خطوط الأنابيب للاستدلال على خادم الويب
|
||||
# - local: model_memory_anatomy
|
||||
# title: تشريح تدريب النموذج
|
||||
# - local: llm_tutorial_optimization
|
||||
# title: الاستفادة القصوى من LLMs
|
||||
title: أطر مفاهيمية
|
||||
# - sections:
|
||||
# - sections:
|
||||
# - local: main_classes/agent
|
||||
# title: الوكلاء والأدوات
|
||||
# - local: model_doc/auto
|
||||
# title: فئات يتم إنشاؤها ديناميكيًا
|
||||
# - local: main_classes/backbones
|
||||
@ -877,7 +875,7 @@
|
||||
# - local: internal/pipelines_utils
|
||||
# title: مرافق خطوط الأنابيب
|
||||
# - local: internal/tokenization_utils
|
||||
# title: مرافق مقسم النصوص
|
||||
# title: مرافق مقسم النصوص
|
||||
# - local: internal/trainer_utils
|
||||
# title: مرافق المدرب
|
||||
# - local: internal/generation_utils
|
||||
|
||||
539
docs/source/ar/agents.md
Normal file
539
docs/source/ar/agents.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,539 @@
|
||||
# الوكلاء والأدوات
|
||||
|
||||
[[open-in-colab]]
|
||||
|
||||
### ما هو الوكيل؟
|
||||
|
||||
يمكن للنظم اللغوية الكبيرة (LLMs) التي تم تدريبها على أداء [نمذجة اللغة السببية](./tasks/language_modeling.) التعامل مع مجموعة واسعة من المهام، ولكنها غالبًا ما تواجه صعوبات في المهام الأساسية مثل المنطق والحساب والبحث. وعندما يتم استدعاؤها في مجالات لا تؤدي فيها أداءً جيدًا، فإنها غالبًا ما تفشل في توليد الإجابة التي نتوقعها منها.
|
||||
|
||||
يتمثل أحد النهج للتغلب على هذا القصور في إنشاء "وكيل".
|
||||
|
||||
الوكيل هو نظام يستخدم LLM كمحرك له، ولديه حق الوصول إلى وظائف تسمى "أدوات".
|
||||
|
||||
هذه "الأدوات" هي وظائف لأداء مهمة، وتحتوي على جميع الأوصاف اللازمة للوكيل لاستخدامها بشكل صحيح.
|
||||
|
||||
يمكن برمجة الوكيل للقيام بما يلي:
|
||||
- وضع سلسلة من الإجراءات/الأدوات وتشغيلها جميعًا في نفس الوقت مثل [`CodeAgent`] على سبيل المثال
|
||||
- التخطيط للاجراءات/الأدوات وتنفيذها واحدة تلو الأخرى والانتظار حتى انتهاء كل إجراء قبل إطلاق التالي مثل [`ReactJsonAgent`] على سبيل المثال
|
||||
|
||||
### أنواع الوكلاء
|
||||
|
||||
#### الوكيل البرمجي (Code agent)
|
||||
|
||||
يتمتع هذا الوكيل يتبع خطوات محددة: أولًا، يخطط لسلسلة من الإجراءات التي يريد تنفيذها، ثم شفرة Python لتنفيذ جميع الإجراءات في نفس الوقت. وهو يتعامل بشكل أصلي مع أنواع مختلفة من المدخلات والمخرجات للأدوات التي يستخدمها، وبالتالي فهو الخيار الموصى به للمهام متعددة الوسائط.
|
||||
|
||||
#### وكلاء التفاعل
|
||||
|
||||
هذا هو الوكيل الذي يتم اللجوء إليه لحل مهام الاستدلال، حيث يجعل إطار ReAct ([Yao et al.، 2022](https://huggingface.co/papers/2210.03629)) من الكفاءة حقًا التفكير على أساس ملاحظاته السابقة.
|
||||
|
||||
نقوم بتنفيذ إصدارين من ReactJsonAgent:
|
||||
- [`ReactJsonAgent`] يقوم بتوليد استدعاءات الأدوات كـ JSON في إخراجها.
|
||||
- [`ReactCodeAgent`] هو نوع جديد من ReactJsonAgent يقوم بتوليد استدعاءات أدواته كمقاطع من التعليمات البرمجية، والتي تعمل بشكل جيد حقًا مع LLMs التي تتمتع بأداء قوي في البرمجة.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!TIP]
|
||||
> اقرأ منشور المدونة [Open-source LLMs as LangChain Agents](https://huggingface.co/blog/open-source-llms-as-agents) لمعرفة المزيد عن وكيل ReAct.
|
||||
|
||||
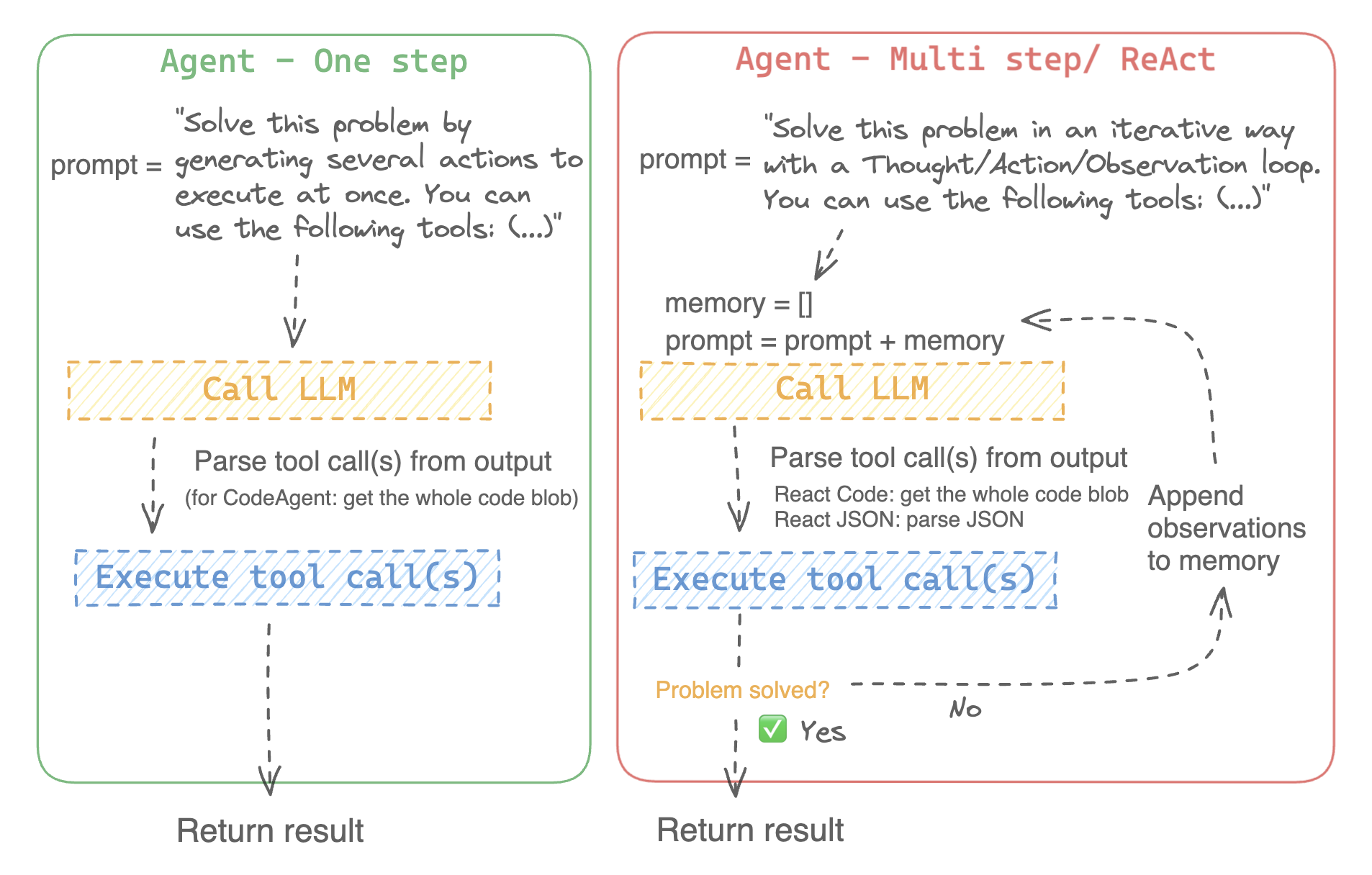
|
||||
|
||||
على سبيل المثال، إليك كيف يعمل وكيل ReAct Code طريقه من خلال السؤال التالي.
|
||||
|
||||
```py3
|
||||
>>> agent.run(
|
||||
... "How many more blocks (also denoted as layers) in BERT base encoder than the encoder from the architecture proposed in Attention is All You Need?",
|
||||
... )
|
||||
=====New task=====
|
||||
How many more blocks (also denoted as layers) in BERT base encoder than the encoder from the architecture proposed in Attention is All You Need?
|
||||
====Agent is executing the code below:
|
||||
bert_blocks = search(query="number of blocks in BERT base encoder")
|
||||
print("BERT blocks:", bert_blocks)
|
||||
====
|
||||
Print outputs:
|
||||
BERT blocks: twelve encoder blocks
|
||||
|
||||
====Agent is executing the code below:
|
||||
attention_layer = search(query="number of layers in Attention is All You Need")
|
||||
print("Attention layers:", attention_layer)
|
||||
====
|
||||
Print outputs:
|
||||
Attention layers: Encoder: The encoder is composed of a stack of N = 6 identical layers. Each layer has two sub-layers. The first is a multi-head self-attention mechanism, and the second is a simple, position- 2 Page 3 Figure 1: The Transformer - model architecture.
|
||||
|
||||
====Agent is executing the code below:
|
||||
bert_blocks = 12
|
||||
attention_layers = 6
|
||||
diff = bert_blocks - attention_layers
|
||||
print("Difference in blocks:", diff)
|
||||
final_answer(diff)
|
||||
====
|
||||
|
||||
Print outputs:
|
||||
Difference in blocks: 6
|
||||
|
||||
Final answer: 6
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### كيف يمكنني بناء وكيل؟
|
||||
|
||||
لتهيئة وكيل، تحتاج إلى هذه الوسائط:
|
||||
|
||||
- نموذج لغوي كبير (LLM) يشكل المحرك الأساسي للوكيل. الوكيل نفسه ليس النموذج اللغوي، بل هو برنامج يستخدم النموذج اللغوي كمحرك له.
|
||||
- موجه النظام (system prompt): هذه هي التعليمات التي يتم إعطاؤها للنموذج اللغوي لإنشاء مخرجاته.
|
||||
- صندوق أدوات (toolbox) يختار الوكيل منه الأدوات لتنفيذها
|
||||
- محلل (parser) لاستخراج الأدوات التي يجب استدعاؤها من مخرجات النموذج اللغوي LLM والأدوات التي يجب استخدامها
|
||||
|
||||
عند تهيئة نظام الوكيل، يتم استخدام سمات الأداة لإنشاء وصف للأداة، ثم يتم دمجها في موجه النظام الخاص `system_prompt` للوكيل لإعلامه بالأدوات التي يمكنه استخدامها ولماذا.
|
||||
|
||||
للبدء، يرجى تثبيت `agents` الإضافية لتثبيت جميع التبعيات الافتراضية.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install transformers[agents]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
قم ببناء محرك LLM الخاص بك من خلال تعريف طريقة `llm_engine` التي تقبل قائمة من [الرسائل](./chat_templating.) وتعيد النص. يجب أن تقبل هذه الدالة القابلة للاستدعاء أيضًا معامل `stop` يشير إلى متى يجب التوقف عن التوليد.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from huggingface_hub import login, InferenceClient
|
||||
|
||||
login("<YOUR_HUGGINGFACEHUB_API_TOKEN>")
|
||||
|
||||
client = InferenceClient(model="meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3-70B-Instruct")
|
||||
|
||||
def llm_engine(messages, stop_sequences=["Task"]) -> str:
|
||||
response = client.chat_completion(messages, stop=stop_sequences, max_tokens=1000)
|
||||
answer = response.choices[0].message.content
|
||||
return answer
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
يمكنك استخدام أي طريقة `llm_engine` طالما أنها:
|
||||
1. يتبع تنسيق [رسائل](./chat_templating.md) لإدخاله (`List [Dict [str، str]]`) ويعيد `str`
|
||||
2. يتوقف عن توليد المخراجات من التسلسلات التي تم تمريرها في معامل `stop`
|
||||
|
||||
أنت بحاجة أيضًا إلى معامل "الأدوات" الذي يقبل قائمة من "الأدوات". يمكنك توفير قائمة فارغة لـ "الأدوات"، ولكن استخدم صندوق الأدوات الافتراضي مع معامل اختياري `add_base_tools=True`.
|
||||
|
||||
الآن يمكنك إنشاء وكيل، مثل [`CodeAgent`], وتشغيله. ولتسهيل الأمر، نقدم أيضًا فئة [`HfEngine`] التي تستخدم `huggingface_hub.InferenceClient` بشكل مخفى.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import CodeAgent, HfEngine
|
||||
|
||||
llm_engine = HfEngine(model="meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3-70B-Instruct")
|
||||
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[], llm_engine=llm_engine, add_base_tools=True)
|
||||
|
||||
agent.run(
|
||||
"Could you translate this sentence from French, say it out loud and return the audio.",
|
||||
sentence="Où est la boulangerie la plus proche?",
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
هذه الميزة ستكون مفيدة في حالة الحاجة الملحة! يمكنك حتى ترك معامل `llm_engine` غير محدد، وسيتم إنشاء [`HfEngine`] بشكل تلقائي.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import CodeAgent
|
||||
|
||||
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[], add_base_tools=True)
|
||||
|
||||
agent.run(
|
||||
"Could you translate this sentence from French, say it out loud and give me the audio.",
|
||||
sentence="Où est la boulangerie la plus proche?",
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
لاحظ أننا استخدمنا معامل "sentence" إضافي: يمكنك تمرير النص كمعامل إضافي إلى النموذج.
|
||||
|
||||
يمكنك أيضًا استخدام هذا للإشارة إلى مسار الملفات المحلية أو البعيدة للنموذج لاستخدامها:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import ReactCodeAgent
|
||||
|
||||
agent = ReactCodeAgent(tools=[], llm_engine=llm_engine, add_base_tools=True)
|
||||
|
||||
agent.run("Why does Mike not know many people in New York?", audio="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/recording.mp3")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
تم تحديد موجه النظام ومحلل المخرجات تلقائيًا، ولكن يمكنك فحصهما بسهولة عن طريق استدعاء `system_prompt_template` على وكيلك.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
print(agent.system_prompt_template)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
من المهم أن تشرح بأكبر قدر ممكن من الوضوح المهمة التي تريد تنفيذها.
|
||||
كل عملية [`~Agent.run`] مستقلة، وبما أن الوكيل مدعوم من LLM، فقد تؤدي الاختلافات الطفيفة في موجهك إلى نتائج مختلفة تمامًا.
|
||||
يمكنك أيضًا تشغيل وكيل بشكل متتالي لمهام مختلفة: في كل مرة يتم فيها إعادة تهيئة سمتي `agent.task` و`agent.logs`.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### تنفيذ التعليمات البرمجية
|
||||
|
||||
يقوم مفسر Python بتنفيذ التعليمات البرمجية على مجموعة من المدخلات التي يتم تمريرها جنبًا إلى جنب مع أدواتك.
|
||||
يجب أن يكون هذا الأمر آمنًا لأن الوظائف الوحيدة التي يمكن استدعاؤها هي الأدوات التي قدمتها (خاصة إذا كانت أدوات من Hugging Face فقط) ووظيفة الطباعة، لذا فأنت مقيد بالفعل بما يمكن تنفيذه.
|
||||
|
||||
مفسر Python لا يسمح أيضًا باستدعاء دوال بشكل افتراضي خارج قائمة آمنة، لذا فإن جميع الهجمات الأكثر وضوحًا لا ينبغي أن تكون مشكلة.
|
||||
يمكنك أيضًا الإذن باستيرادات إضافية عن طريق تمرير الوحدات النمطية المصرح بها كقائمة من السلاسل في معامل `additional_authorized_imports` عند تهيئة [`ReactCodeAgent`] أو [`CodeAgent`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import ReactCodeAgent
|
||||
|
||||
>>> agent = ReactCodeAgent(tools=[], additional_authorized_imports=['requests', 'bs4'])
|
||||
>>> agent.run("Could you get me the title of the page at url 'https://huggingface.co/blog'?")
|
||||
|
||||
(...)
|
||||
'Hugging Face – Blog'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
سيتم إيقاف التنفيذ عند أي رمز يحاول تنفيذ عملية غير قانونية أو إذا كان هناك خطأ Python عادي في التعليمات البرمجية التي تم إنشاؤها بواسطة الوكيل.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!WARNING]
|
||||
> يمكن لـ LLM توليد شفرة برمجية عشوائية سيتم تنفيذها بعد ذلك: لا تقمب استدعاء أى دوال غير آمنة!
|
||||
|
||||
### موجه النظام
|
||||
|
||||
ينشئ الوكيل، أو بالأحرى LLM الذي يقود الوكيل، يولد مخرجات بناءً على موجه النظام. يمكن تخصيص موجه النظام وتصميمه للمهام المقصودة. على سبيل المثال، تحقق من موجه النظام لـ [`ReactCodeAgent`] (الإصدار أدناه مبسط قليلاً).
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
You will be given a task to solve as best you can.
|
||||
You have access to the following tools:
|
||||
<<tool_descriptions>>
|
||||
|
||||
To solve the task, you must plan forward to proceed in a series of steps, in a cycle of 'Thought:', 'Code:', and 'Observation:' sequences.
|
||||
|
||||
At each step, in the 'Thought:' sequence, you should first explain your reasoning towards solving the task, then the tools that you want to use.
|
||||
Then in the 'Code:' sequence, you shold write the code in simple Python. The code sequence must end with '/End code' sequence.
|
||||
During each intermediate step, you can use 'print()' to save whatever important information you will then need.
|
||||
These print outputs will then be available in the 'Observation:' field, for using this information as input for the next step.
|
||||
|
||||
In the end you have to return a final answer using the `final_answer` tool.
|
||||
|
||||
Here are a few examples using notional tools:
|
||||
---
|
||||
{examples}
|
||||
|
||||
Above example were using notional tools that might not exist for you. You only have acces to those tools:
|
||||
<<tool_names>>
|
||||
You also can perform computations in the python code you generate.
|
||||
|
||||
Always provide a 'Thought:' and a 'Code:\n```py' sequence ending with '```<end_code>' sequence. You MUST provide at least the 'Code:' sequence to move forward.
|
||||
|
||||
Remember to not perform too many operations in a single code block! You should split the task into intermediate code blocks.
|
||||
Print results at the end of each step to save the intermediate results. Then use final_answer() to return the final result.
|
||||
|
||||
Remember to make sure that variables you use are all defined.
|
||||
|
||||
Now Begin!
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
يتضمن موجه النظام:
|
||||
- *مقدمة* تشرح كيف يجب أن يتصرف الوكيل والأدوات التي يجب عليه استخدامها.
|
||||
- وصف لجميع الأدوات التي يتم تحديدها بواسطة رمز `<<tool_descriptions>>` الذي يتم استبداله ديناميكيًا في وقت التشغيل بالأدوات التي يحددها المستخدم أو يختارها.
|
||||
- يأتي وصف الأداة من سمات الأداة، `name`، و`description`، و`inputs` و`output_type`، وقالب `jinja2` بسيط يمكنك تحسينه.
|
||||
- شكل المخرج المتوقع.
|
||||
|
||||
يمكنك تحسين موجه النظام، على سبيل المثال، عن طريق إضافة شرح لتنسيق المخرجات.
|
||||
|
||||
للحصول على أقصى قدر من المرونة، يمكنك الكتابة فوق قالب موجه النظام بالكامل عن طريق تمرير موجه مخصص كمعامل إلى معلمة `system_prompt`.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import ReactJsonAgent
|
||||
from transformers.agents import PythonInterpreterTool
|
||||
|
||||
agent = ReactJsonAgent(tools=[PythonInterpreterTool()], system_prompt="{your_custom_prompt}")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
> [!WARNING]
|
||||
> يرجى التأكد من تحديد سلسلة `<<tool_descriptions>>` في مكان ما في `template` حتى يكون الوكيل على علم
|
||||
بالأدوات المتاحة.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### فحص تشغيل الوكيل
|
||||
|
||||
فيما يلي بعض السمات المفيدة لفحص ما حدث بعد التشغيل:
|
||||
- تخزن `agent.logs` سجلات مفصلة للوكيل. في كل خطوة من تشغيل الوكيل، يتم تخزين كل شيء في قاموس إلحاقه بـ `agent.logs`.
|
||||
- تشغيل `agent.write_inner_memory_from_logs()` يخلق ذاكرة داخلية لسجلات الوكيل للنظام LLM لعرضها، كقائمة من رسائل الدردشة. تنتقل هذه الطريقة عبر كل خطوة من سجل الوكيل ولا تخزن سوى ما يهمها كرسالة: على سبيل المثال، سيحفظ موجه النظام والمهمة في رسائل منفصلة، ثم لكل خطوة سيخزن مخرج LLM كرسالة، ومخرج استدعاء الأداة كرسالة أخرى. استخدم هذا إذا كنت تريد عرضًا عامًا لما حدث - ولكن لن يتم نسخ كل سجل بواسطة هذه الطريقة.
|
||||
|
||||
## الأدوات
|
||||
|
||||
الأداة هي عبارة عن وظيفة أساسية يستخدمها الوكيل لتنفيذ مهمة محددة.
|
||||
|
||||
يمكنك على سبيل المثال التحقق من [`PythonInterpreterTool`]: لديه اسم ووصف ووصف للمدخلات ونوع للمخرج، وطريقة `__call__` التي تقوم بتنفيذ المهمة المطلوبة.
|
||||
|
||||
عند تهيئة الوكيل، يتم استخدام سمات الأداة لتوليد وصف للأداة يتم تضمينه في موجه النظام الخاص بالوكيل. يتيح هذا للوكيل معرفة الأدوات التي يمكنه استخدامها ولماذا.
|
||||
|
||||
### صندوق الأدوات الافتراضي
|
||||
|
||||
يأتي Transformers مع صندوق أدوات افتراضي لتمكين الوكلاء، والذي يمكنك إضافته إلى وكيلك عند التهيئة باستخدام معامل `add_base_tools = True`:
|
||||
|
||||
- **الإجابة على أسئلة المستند**: الإجابة على سؤال حول المستند (مثل ملف PDF) بتنسيق صورة ([Donut](./model_doc/donut))
|
||||
- **الإجابة على أسئلة الصور**: الإجابة على سؤال حول صورة ([VILT](./model_doc/vilt))
|
||||
- **التحدث إلى النص**: قم بتفريغ الكلام إلى نص ([Whisper](./model_doc/whisper))
|
||||
- **النص إلى كلام**: تحويل النص إلى كلام ([SpeechT5](./model_doc/speecht5))
|
||||
- **الترجمة**: ترجمة جملة معينة من لغة المصدر إلى لغة الهدف.
|
||||
- **مفسر كود Python**: تشغيل كود Python الذي تم إنشاؤه بواسطة LLM في بيئة آمنة. لن يتم إضافة هذه الأداة إلى [`ReactJsonAgent`] إلا إذا استخدمت `add_base_tools=True`، نظرًا لأن الأدوات المستندة إلى التعليمات البرمجية يمكنها بالفعل تنفيذ كود Python
|
||||
لا تترجم النصوص الخاصة ولا الأكواد البرمجية ولا الروابط ولا رموز HTML وCSS:
|
||||
|
||||
يمكنك استخدام أداة يدويًا عن طريق استدعاء دالة [`load_tool`] وتحديد مهمة لتنفيذها.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import load_tool
|
||||
|
||||
tool = load_tool("text-to-speech")
|
||||
audio = tool("This is a text to speech tool")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### إنشاء أداة جديدة
|
||||
|
||||
يمكنك إنشاء أداتك الخاصة لتغطية حالات الاستخدام التي لا تغطيها الأدوات الافتراضية من Hugging Face.
|
||||
على سبيل المثال، دعنا نقوم بإنشاء أداة تعرض النموذج الأكثر تنزيلًا لمهمة معينة من Hub.
|
||||
|
||||
سوف نبدأ بالكود التالي.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from huggingface_hub import list_models
|
||||
|
||||
task = "text-classification"
|
||||
|
||||
model = next(iter(list_models(filter=task, sort="downloads", direction=-1)))
|
||||
print(model.id)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
يمكن تحويل هذه الشيفرة إلى فئة ترث من الفئة العليا [`Tool`].
|
||||
|
||||
تحتاج الأداة المخصصة إلى:
|
||||
|
||||
- اسم `name`، والتي تمثل اسم الأداة نفسها. عادةً ما يصف الاسم وظيفتها. بما أن الكود يعيد النموذج الأكثر تنزيلًا لمهمة ما، فلنسمها `model_download_counter`.
|
||||
- تستخدم خاصية `description` لملء موجه نظام الوكيل.
|
||||
- خاصية `inputs`، والتي هي عبارة عن قاموس بمفاتيح "type" و"description". يحتوي على معلومات تساعد المفسر Python على اتخاذ خيارات مستنيرة بشأن المدخلات.
|
||||
- خاصية `output_type`، والتي تحدد نوع المخرج.
|
||||
- طريقة `forward` والتي تحتوي على الكود الذي سيتم تنفيذه للحصول على النتيجة النهائية.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import Tool
|
||||
from huggingface_hub import list_models
|
||||
|
||||
class HFModelDownloadsTool(Tool):
|
||||
name = "model_download_counter"
|
||||
description = (
|
||||
"This is a tool that returns the most downloaded model of a given task on the Hugging Face Hub. "
|
||||
"It returns the name of the checkpoint."
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
inputs = {
|
||||
"task": {
|
||||
"type": "text",
|
||||
"description": "the task category (such as text-classification, depth-estimation, etc)",
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
output_type = "text"
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, task: str):
|
||||
model = next(iter(list_models(filter=task, sort="downloads", direction=-1)))
|
||||
return model.id
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
الآن بعد أن أصبحت فئة `HfModelDownloadsTool` المخصصة جاهزة، يمكنك حفظها في ملف باسم `model_downloads.py` واستيرادها للاستخدام.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from model_downloads import HFModelDownloadsTool
|
||||
|
||||
tool = HFModelDownloadsTool()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
يمكنك أيضًا مشاركة أداتك المخصصة في Hub عن طريق استدعاء [`~Tool.push_to_hub`] على الأداة. تأكد من أنك قمت بإنشاء مستودع لها على Hub وأنك تستخدم رمز وصول للقراءة.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
tool.push_to_hub("{your_username}/hf-model-downloads")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
قم بتحميل الأداة باستخدام دالة [`~Tool.load_tool`] ومررها إلى معلمة `tools` في الوكيل الخاص بك.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import load_tool, CodeAgent
|
||||
|
||||
model_download_tool = load_tool("m-ric/hf-model-downloads")
|
||||
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[model_download_tool], llm_engine=llm_engine)
|
||||
agent.run(
|
||||
"Can you give me the name of the model that has the most downloads in the 'text-to-video' task on the Hugging Face Hub?"
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
ستحصل على ما يلي:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
======== New task ========
|
||||
Can you give me the name of the model that has the most downloads in the 'text-to-video' task on the Hugging Face Hub?
|
||||
==== Agent is executing the code below:
|
||||
most_downloaded_model = model_download_counter(task="text-to-video")
|
||||
print(f"The most downloaded model for the 'text-to-video' task is {most_downloaded_model}.")
|
||||
====
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
والناتج:
|
||||
|
||||
`"النموذج الأكثر تنزيلًا لمهمة `text-to-video` هو ByteDance/AnimateDiff-Lightning."`
|
||||
|
||||
### إدارة صندوق أدوات الوكيل الخاص بك
|
||||
|
||||
إذا كنت قد قمت بتهيئة وكيل، فمن غير الملائم إعادة تهيئته من البداية لإضافة أداة جديدة ترغب في استخدامها. باستخدام مكتبة Transformers، يمكنك إدارة صندوق أدوات الوكيل بإضافة أو استبدال أداة موجودة.
|
||||
|
||||
دعنا نضيف الأداة `model_download_tool` إلى وكيل تم تهيئته مسبقًا باستخدام صندوق الأدوات الافتراضي.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import CodeAgent
|
||||
|
||||
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[], llm_engine=llm_engine, add_base_tools=True)
|
||||
agent.toolbox.add_tool(model_download_tool)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
الآن يمكننا الاستفادة من الأداة الجديدة وأداة تحويل النص إلى كلام السابقة:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
agent.run(
|
||||
"Can you read out loud the name of the model that has the most downloads in the 'text-to-video' task on the Hugging Face Hub and return the audio?"
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
| **Audio** |
|
||||
|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
|
||||
| <audio controls><source src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/damo.wav" type="audio/wav"/> |
|
||||
|
||||
> [!WARNING]
|
||||
> احترس عند إضافة أدوات إلى وكيل يعمل بالفعل لأنه يمكن أن يؤثر على اختيار الأداة لصالح أداتك أو اختيار أداة أخرى غير المحددة بالفعل.
|
||||
|
||||
استخدم طريقة `agent.toolbox.update_tool()` لاستبدال أداة موجودة في صندوق أدوات الوكيل.
|
||||
هذا مفيد إذا كانت أداتك الجديدة بديلاً مباشرًا للأداة الموجودة لأن الوكيل يعرف بالفعل كيفية تنفيذ تلك المهمة المحددة.
|
||||
تأكد فقط من اتباع الأداة الجديدة لنفس واجهة برمجة التطبيقات (API) للأداة المستبدلة أو قم بتكييف قالب موجه النظام لضمان تحديث جميع الأمثلة التي تستخدم الأداة المستبدلة.
|
||||
|
||||
### استخدام مجموعة من الأدوات
|
||||
|
||||
يمكنك الاستفادة من مجموعات الأدوات باستخدام كائن ToolCollection، مع تحديد مجموعة الأدوات التي تريد استخدامها.
|
||||
ثم قم بتمريرها كقائمة لتهيئة الوكيل الخاص بك، وبدء استخدامها!
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import ToolCollection, ReactCodeAgent
|
||||
|
||||
image_tool_collection = ToolCollection(collection_slug="huggingface-tools/diffusion-tools-6630bb19a942c2306a2cdb6f")
|
||||
agent = ReactCodeAgent(tools=[*image_tool_collection.tools], add_base_tools=True)
|
||||
|
||||
agent.run("Please draw me a picture of rivers and lakes.")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
لتسريع البداية، يتم تحميل الأدوات فقط إذا استدعاها الوكيل.
|
||||
|
||||
ستحصل على هذه الصورة:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/rivers_and_lakes.png" />
|
||||
|
||||
### استخدام gradio-tools
|
||||
|
||||
[gradio-tools](https://github.com/freddyaboulton/gradio-tools) هي مكتبة قوية تتيح استخدام Hugging
|
||||
Face Spaces كأدوات. تدعم العديد من المساحات الموجودة بالإضافة إلى مساحات مخصصة.
|
||||
|
||||
تدعم مكتبة Transformers `gradio_tools` باستخدام طريقة [`Tool.from_gradio`] في الفئة. على سبيل المثال، دعنا نستخدم [`StableDiffusionPromptGeneratorTool`](https://github.com/freddyaboulton/gradio-tools/blob/main/gradio_tools/tools/prompt_generator.py) من مجموعة أدوات `gradio-tools` لتحسين المطالبات لإنشاء صور أفضل.
|
||||
|
||||
استورد وقم بتهيئة الأداة، ثم مررها إلى طريقة `Tool.from_gradio`:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from gradio_tools import StableDiffusionPromptGeneratorTool
|
||||
from transformers import Tool, load_tool, CodeAgent
|
||||
|
||||
gradio_prompt_generator_tool = StableDiffusionPromptGeneratorTool()
|
||||
prompt_generator_tool = Tool.from_gradio(gradio_prompt_generator_tool)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
الآن يمكنك استخدامه مثل أي أداة أخرى. على سبيل المثال، دعنا نحسن الموجه `a rabbit wearing a space suit`.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
image_generation_tool = load_tool('huggingface-tools/text-to-image')
|
||||
agent = CodeAgent(tools=[prompt_generator_tool, image_generation_tool], llm_engine=llm_engine)
|
||||
|
||||
agent.run(
|
||||
"Improve this prompt, then generate an image of it.", prompt='A rabbit wearing a space suit'
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
يستفيد النموذج بشكل كافٍ من الأداة:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
======== New task ========
|
||||
Improve this prompt, then generate an image of it.
|
||||
You have been provided with these initial arguments: {'prompt': 'A rabbit wearing a space suit'}.
|
||||
==== Agent is executing the code below:
|
||||
improved_prompt = StableDiffusionPromptGenerator(query=prompt)
|
||||
while improved_prompt == "QUEUE_FULL":
|
||||
improved_prompt = StableDiffusionPromptGenerator(query=prompt)
|
||||
print(f"The improved prompt is {improved_prompt}.")
|
||||
image = image_generator(prompt=improved_prompt)
|
||||
====
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
قبل إنشاء الصورة أخيرًا:
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/rabbit.png" />
|
||||
|
||||
> [!WARNING]
|
||||
> تتطلب gradio-tools إدخالات وإخراجات *نصية* حتى عند العمل مع طرائق مختلفة مثل كائنات الصور والصوت. الإدخالات والإخراجات الصورية والصوتية غير متوافقة حاليًا.
|
||||
|
||||
### استخدام أدوات LangChain
|
||||
|
||||
نحن نحب Langchain ونعتقد أنها تحتوي على مجموعة أدوات قوية للغاية.
|
||||
لاستيراد أداة من LangChain، استخدم الطريقة `from_langchain()`.
|
||||
|
||||
فيما يلي كيفية استخدامها لإعادة إنشاء نتيجة البحث في المقدمة باستخدام أداة بحث الويب LangChain.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from langchain.agents import load_tools
|
||||
from transformers import Tool, ReactCodeAgent
|
||||
|
||||
search_tool = Tool.from_langchain(load_tools(["serpapi"])[0])
|
||||
|
||||
agent = ReactCodeAgent(tools=[search_tool])
|
||||
|
||||
agent.run("How many more blocks (also denoted as layers) in BERT base encoder than the encoder from the architecture proposed in Attention is All You Need?")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## واجهة Gradio
|
||||
|
||||
يمكنك الاستفادة من `gradio.Chatbot` لعرض أفكار الوكيل الخاص بك باستخدام `stream_to_gradio`، إليك مثال:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
import gradio as gr
|
||||
from transformers import (
|
||||
load_tool,
|
||||
ReactCodeAgent,
|
||||
HfEngine,
|
||||
stream_to_gradio,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Import tool from Hub
|
||||
image_generation_tool = load_tool("m-ric/text-to-image")
|
||||
|
||||
llm_engine = HfEngine("meta-llama/Meta-Llama-3-70B-Instruct")
|
||||
|
||||
# Initialize the agent with the image generation tool
|
||||
agent = ReactCodeAgent(tools=[image_generation_tool], llm_engine=llm_engine)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def interact_with_agent(task):
|
||||
messages = []
|
||||
messages.append(gr.ChatMessage(role="user", content=task))
|
||||
yield messages
|
||||
for msg in stream_to_gradio(agent, task):
|
||||
messages.append(msg)
|
||||
yield messages + [
|
||||
gr.ChatMessage(role="assistant", content="⏳ Task not finished yet!")
|
||||
]
|
||||
yield messages
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
with gr.Blocks() as demo:
|
||||
text_input = gr.Textbox(lines=1, label="Chat Message", value="Make me a picture of the Statue of Liberty.")
|
||||
submit = gr.Button("Run illustrator agent!")
|
||||
chatbot = gr.Chatbot(
|
||||
label="Agent",
|
||||
type="messages",
|
||||
avatar_images=(
|
||||
None,
|
||||
"https://em-content.zobj.net/source/twitter/53/robot-face_1f916.png",
|
||||
),
|
||||
)
|
||||
submit.click(interact_with_agent, [text_input], [chatbot])
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
demo.launch()
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -1,25 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# آليات الانتباه
|
||||
|
||||
تستخدم معظم نماذج المحول (Transformer) الانتباه الكامل بحيث تكون مصفوفة الانتباه ذات الأبعاد المتساوية. ويمكن أن يمثل ذلك عقبة حسابية كبيرة عندما تكون لديك نصوص طويلة. ويعد Longformer وReformer من النماذج التي تحاول أن تكون أكثر كفاءة وتستخدم نسخة مخففة من مصفوفة الانتباه لتسريع التدريب.
|
||||
|
||||
## انتباه LSH
|
||||
|
||||
يستخدم [Reformer](model_doc/reformer) انتباه LSH. في الدالة softmax(QK^t)، فإن أكبر العناصر فقط (في بعد softmax) من المصفوفة QK^t هي التي ستعطي مساهمات مفيدة. لذلك، بالنسبة لكل استعلام q في Q، يمكننا أن نأخذ في الاعتبار فقط المفاتيح k في K المشابهة لـ q فقط. وتُستخدم دالة هاش لتحديد ما إذا كان q وk متشابهين. ويتم تعديل قناع الانتباه لتجاهل الرمز الحالي (باستثناء الموضع الأول)، لأنه سيعطي استعلامًا ومفتاحًا متساويين (لذلك متشابهين للغاية). نظرًا لطبيعة دالة الهاش العشوائية نوعًا ما، يتم في الممارسة العملية استخدام عدة دوال هاش (يحددها معامل n_rounds) ثم يتم حساب المتوسط معًا.
|
||||
|
||||
## الانتباه المحلي
|
||||
|
||||
يستخدم [Longformer](model_doc/longformer) الانتباه المحلي: غالبًا ما يكون السياق المحلي (على سبيل المثال، ما هما الرمزان إلى اليسار واليمين؟) كافيًا لاتخاذ إجراء بالنسبة للرمز المعطى. أيضًا، عن طريق تكديس طبقات الانتباه التي لها نافذة صغيرة، سيكون للطبقة الأخيرة مجال استقبال أكبر من مجرد الرموز في النافذة، مما يسمح لها ببناء تمثيل للجملة بأكملها.
|
||||
|
||||
كما يتم منح بعض رموز الإدخال المختارة مسبقًا انتباهًا عالميًا: بالنسبة لهذه الرموز القليلة، يمكن لمصفوفة الانتباه الوصول إلى جميع الرموز وتكون هذه العملية متماثلة: فلجميع الرموز الأخرى إمكانية الوصول إلى تلك الرموز المحددة (بالإضافة إلى تلك الموجودة في نافذتهم المحلية). وهذا موضح في الشكل 2d من الورقة، انظر أدناه لمثال على قناع الانتباه:
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img scale="50 %" align="center" src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/local_attention_mask.png"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
وباستخدام مصفوفات الانتباه هذه التي تحتوي على عدد أقل من المعلمات، يسمح النموذج بمدخالات ذات طول تسلسل أكبر.
|
||||
|
||||
## حيل أخرى
|
||||
|
||||
### الترميزات الموضعية المحورية
|
||||
|
||||
يستخدم [Reformer](model_doc/reformer) ترميزات موضعية محورية: في نماذج المحول التقليدية، يكون الترميز الموضعي E مصفوفة بحجم \\(l\\) في \\(d\\)، حيث \\(l\\) هو طول التسلسل و\\(d\\) هو بعد الحالة المخفية. إذا كان لديك نصوص طويلة جدًا، فقد تكون هذه المصفوفة ضخمة وتستهلك مساحة كبيرة جدًا على وحدة معالجة الرسوميات (GPU). وللتخفيف من ذلك، تتكون الترميزات الموضعية المحورية من تحليل تلك المصفوفة الكبيرة E إلى مصفوفتين أصغر E1 وE2، بأبعاد \\(l_{1} \times d_{1}\\) و \\(l_{2} \times d_{2}\\)، بحيث \\(l_{1} \times l_{2} = l\\) و\\(d_{1} + d_{2} = d\\) (مع حاصل ضرب الأطوال، ينتهي الأمر بكونه أصغر بكثير). ويتم الحصول على الترميز للخطوة الزمنية \\(j\\) في E عن طريق ربط الترميزات للخطوة الزمنية \\(j \% l1\\) في E1 و \\(j // l1\\) في E2.
|
||||
@ -1,18 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# BERTology
|
||||
|
||||
يُشهد في الآونة الأخيرة نمو مجال دراسي يُعنى باستكشاف آلية عمل نماذج المحولات الضخمة مثل BERT (والذي يُطلق عليها البعض اسم "BERTology"). ومن الأمثلة البارزة على هذا المجال ما يلي:
|
||||
|
||||
- BERT Rediscovers the Classical NLP Pipeline بواسطة Ian Tenney و Dipanjan Das و Ellie Pavlick:
|
||||
https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.05950
|
||||
- Are Sixteen Heads Really Better than One? بواسطة Paul Michel و Omer Levy و Graham Neubig: https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.10650
|
||||
- What Does BERT Look At? An Analysis of BERT's Attention بواسطة Kevin Clark و Urvashi Khandelwal و Omer Levy و Christopher D.
|
||||
Manning: https://arxiv.org/abs/1906.04341
|
||||
- CAT-probing: A Metric-based Approach to Interpret How Pre-trained Models for Programming Language Attend Code Structure: https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.04633
|
||||
|
||||
لإثراء هذا المجال الناشئ، قمنا بتضمين بعض الميزات الإضافية في نماذج BERT/GPT/GPT-2 للسماح للناس بالوصول إلى التمثيلات الداخلية، والتي تم تكييفها بشكل أساسي من العمل الرائد لـ Paul Michel (https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.10650):
|
||||
|
||||
- الوصول إلى جميع الحالات المخفية في BERT/GPT/GPT-2،
|
||||
- الوصول إلى جميع أوزان الانتباه لكل رأس في BERT/GPT/GPT-2،
|
||||
- استرجاع قيم ومشتقات مخرجات الرأس لحساب درجة أهمية الرأس وحذفه كما هو موضح في https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.10650.
|
||||
|
||||
ولمساعدتك على فهم واستخدام هذه الميزات بسهولة، أضفنا مثالًا برمجيًا محددًا: [bertology.py](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers-research-projects/tree/main/bertology/run_bertology.py) أثناء استخراج المعلومات وتقليص من نموذج تم تدريبه مسبقًا على GLUE.
|
||||
@ -1,835 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# قوالب نماذج الدردشة
|
||||
|
||||
## مقدمة
|
||||
|
||||
تعد **الدردشة** أحد استخدامات نماذج اللغات الكبيرة (LLMs) شائعة الاستخدام بشكل متزايد. ففي سياق الدردشة، وبدلاً من متابعة سلسلة نصية واحدة (كما هو الحال مع نماذج اللغات القياسية)، يواصل النموذج بدلاً من ذلك محادثة تتكون من رسالة واحدة أو أكثر، تتضمن كل منها دورًا، مثل "المستخدم" أو "المساعد"، بالإضافة إلى نص الرسالة.
|
||||
|
||||
وكما هو الحال مع تقسيم النص إلى رموز (tokenization)، تتوقع النماذج المختلفة تنسيقات إدخال مختلفة تمامًا للمحادثة. لهذا السبب أضفنا **قوالب الدردشة** كميزة جديدة. تُعد قوالب المحادثة جزءًا من tokenizer. تحدد هذه القوالب كيفية تحويل المحادثات، والتي يتم تمثيلها كقوائم من الرسائل، إلى سلسلة نصية واحدة قابلة للتقسيم إلى رموز بالتنسيق الذي يتوقعه النموذج.
|
||||
|
||||
دعونا نجعل هذا ملموسًا بمثال سريع باستخدام نموذج `BlenderBot`. لدى BlenderBot قالب افتراضي بسيط للغاية، والذي يضيف في الغالب مسافات بيضاء بين جولات الحوار:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("facebook/blenderbot-400M-distill")
|
||||
|
||||
>>> chat = [
|
||||
... {"role": "user", "content": "Hello, how are you?"},
|
||||
... {"role": "assistant", "content": "I'm doing great. How can I help you today?"},
|
||||
... {"role": "user", "content": "I'd like to show off how chat templating works!"},
|
||||
... ]
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenizer.apply_chat_template(chat, tokenize=False)
|
||||
" Hello, how are you? I'm doing great. How can I help you today? I'd like to show off how chat templating works!</s>"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
لاحظ كيف تم ضغط الدردشة بأكملها في سلسلة واحدة. إذا استخدمنا `tokenize=True`، وهو الإعداد الافتراضي، فسيتم أيضًا تحليل السلسلة نحويًا نيابة عنا. ولكن، لنشاهد قالبًا أكثر تعقيدًا في العمل، دعونا نستخدم نموذج `mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.1`.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoTokenizer
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.1")
|
||||
|
||||
>>> chat = [
|
||||
... {"role": "user", "content": "Hello, how are you?"},
|
||||
... {"role": "assistant", "content": "I'm doing great. How can I help you today?"},
|
||||
... {"role": "user", "content": "I'd like to show off how chat templating works!"},
|
||||
... ]
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenizer.apply_chat_template(chat, tokenize=False)
|
||||
"<s>[INST] Hello, how are you? [/INST]I'm doing great. How can I help you today?</s> [INST] I'd like to show off how chat templating works! [/INST]</s>"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
لاحظ كيف أضاف المجزىء اللغوى tokenizer رموز التحكم `[INST]` و `[/INST]` للإشارة إلى بداية ونهاية رسائل المستخدم (ولكن ليس رسائل المساعد!) ، وتم تكثيف المحادثة بأكملها في سلسلة نصية واحدة. إذا استخدمنا `tokenize=True` ، وهو الإعداد الافتراضي ، فسيتم أيضًا تقسيم تلك السلسلة إلى رموز.
|
||||
|
||||
حاول الآن استخدام نفس الشفرة، لكن مع استبدال النموذج بـ `HuggingFaceH4/zephyr-7b-beta` ، وستحصل على:
|
||||
```text
|
||||
<|user|>
|
||||
Hello, how are you?</s>
|
||||
<|assistant|>
|
||||
I'm doing great. How can I help you today?</s>
|
||||
<|user|>
|
||||
I'd like to show off how chat templating works!</s>
|
||||
```
|
||||
تم ضبط كل من Zephyr و Mistral-Instruct من نفس النموذج الأصلي ، Mistral-7B-v0.1. ومع ذلك ، فقد تم تدريبهم بتنسيقات دردشة مختلفة تمامًا. بدون قوالب المحادثة، ستضطر إلى كتابة شفرة تنسيق يدويًا لكل نموذج ، ومن السهل جدًا ارتكاب أخطاء بسيطة تؤثر على الأداء! تُدير قوالب المحادثة تفاصيل التنسيق نيابةً عنك ، مما يُتيح لك كتابة شفرة عامة تعمل مع أي نموذج.
|
||||
|
||||
## كيف أستخدم قوالب الدردشة؟
|
||||
|
||||
كما رأيت في المثال السابق، من السهل استخدام قوالب الدردشة. قم ببساطة بإنشاء قائمة من الرسائل، مع مفتاحي `role` و`content`، ثم قم بتمريرها إلى [`~PreTrainedTokenizer.apply_chat_template`] . بمجرد قيامك بذلك، ستحصل على مخرجات جاهزة للاستخدام! عند استخدام قوالب الدردشة كإدخال لتوليد نصوص بواسطة النموذج، فمن الجيد أيضًا استخدام `add_generation_prompt=True` لإضافة [مطالبات توليد النصوص](#what-are-generation-prompts).
|
||||
|
||||
فيما يلي مثال على إعداد الإدخال لـ `model.generate()`، باستخدام Zephyr مرة أخرى:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
checkpoint = "HuggingFaceH4/zephyr-7b-beta"
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(checkpoint)
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(checkpoint) # قد ترغب في استخدام bfloat16 و/أو الانتقال إلى GPU هنا
|
||||
|
||||
messages = [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"role": "system",
|
||||
"content": "You are a friendly chatbot who always responds in the style of a pirate",
|
||||
},
|
||||
{"role": "user", "content": "How many helicopters can a human eat in one sitting?"},
|
||||
]
|
||||
tokenized_chat = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(messages, tokenize=True, add_generation_prompt=True, return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
print(tokenizer.decode(tokenized_chat[0]))
|
||||
```
|
||||
سيؤدي هذا إلى إنتاج سلسلة نصية بتنسيق الإدخال الذي يتوقعه Zephyr.
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
<|system|>
|
||||
You are a friendly chatbot who always responds in the style of a pirate</s>
|
||||
<|user|>
|
||||
How many helicopters can a human eat in one sitting?</s>
|
||||
<|assistant|>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
الآن بعد أن تم تنسيق الإدخال بشكل صحيح لـ Zephyr، يمكننا استخدام النموذج لإنشاء رد على سؤال المستخدم:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
outputs = model.generate(tokenized_chat, max_new_tokens=128)
|
||||
print(tokenizer.decode(outputs[0]))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
سيؤدي هذا إلى ما يلي:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
<|system|>
|
||||
You are a friendly chatbot who always responds in the style of a pirate</s>
|
||||
<|user|>
|
||||
How many helicopters can a human eat in one sitting?</s>
|
||||
<|assistant|>
|
||||
Matey, I'm afraid I must inform ye that humans cannot eat helicopters. Helicopters are not food, they are flying machines. Food is meant to be eaten, like a hearty plate o' grog, a savory bowl o' stew, or a delicious loaf o' bread. But helicopters, they be for transportin' and movin' around, not for eatin'. So, I'd say none, me hearties. None at all.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
كان ذلك سهلاً بعد كل شيء !
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## هل هناك قنوات معالجة أوتوماتيكية للدردشة؟
|
||||
|
||||
نعم يوجد ! تدعم قنوات المعالجة توليد النصوص مدخلات الدردشة ، مما يُسهّل استخدام نماذج الدردشة . في الماضي ، كنا نستخدم فئة "ConversationalPipeline" المُخصّصة ، ولكن تم الآن إيقافها وتم دمج وظائفها في [`TextGenerationPipeline`]. دعونا نجرّب مثال Zephyr مرة أخرى ، ولكن هذه المرة باستخدام قناة معالجة:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = pipeline("text-generation", "HuggingFaceH4/zephyr-7b-beta")
|
||||
messages = [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"role": "system",
|
||||
"content": "You are a friendly chatbot who always responds in the style of a pirate",
|
||||
},
|
||||
{"role": "user", "content": "How many helicopters can a human eat in one sitting?"},
|
||||
]
|
||||
print(pipe(messages, max_new_tokens=128)[0]['generated_text'][-1]) # طباعة استجابة المساعد
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```النص
|
||||
{'role': 'assistant', 'content': "Matey, I'm afraid I must inform ye that humans cannot eat helicopters. Helicopters are not food, they are flying machines. Food is meant to be eaten, like a hearty plate o' grog, a savory bowl o' stew, or a delicious loaf o' bread. But helicopters, they be for transportin' and movin' around, not for eatin'. So, I'd say none, me hearties. None at all."}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
سيُراعي قناة المعالجة جميع تفاصيل تقسيم النص إلى رموز واستدعاء apply_chat_template نيابةً عنك - بمجرد أن يصبح لِدى النموذج قالب دردشة ، فكل ما تحتاج إلى القيام به هو تهيئة قناة معالجة وتمرير قائمة الرسائل إليها!
|
||||
|
||||
## ما هي "مطالبات التوليد"؟
|
||||
|
||||
قد تلاحظ أن طريقة `apply_chat_template` لها معامل `add_generation_prompt`. تخبر هذه المعامل القالب بإضافة رموز تشير إلى بداية رد البوت. على سبيل المثال، ضع في اعتبارك الدردشة التالية:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
messages = [
|
||||
{"role": "user", "content": "Hi there!"},
|
||||
{"role": "assistant", "content": "Nice to meet you!"},
|
||||
{"role": "user", "content": "Can I ask a question?"}
|
||||
]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
إليك كيف سيبدو ذلك بدون موجه توليد نصوص ، بالنسبة لنموذج يستخدم تنسيق "ChatML" القياسي :
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
tokenizer.apply_chat_template(messages, tokenize=False, add_generation_prompt=False)
|
||||
"""<|im_start|>user
|
||||
Hi there!<|im_end|>
|
||||
<|im_start|>assistant
|
||||
Nice to meet you!<|im_end|>
|
||||
<|im_start|>user
|
||||
Can I ask a question?<|im_end|>
|
||||
"""
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
وهكذا يبدو الأمر **مع** مطالبة التوليد:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
tokenizer.apply_chat_template(messages, tokenize=False, add_generation_prompt=True)
|
||||
"""<|im_start|>user
|
||||
Hi there!<|im_end|>
|
||||
<|im_start|>assistant
|
||||
Nice to meet you!<|im_end|>
|
||||
<|im_start|>user
|
||||
Can I ask a question?<|im_end|>
|
||||
<|im_start|>assistant
|
||||
"""
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
لاحظ أننا أضفنا هذه المرة الرموز التي تشير إلى بداية رد البوت. يضمن هذا أنه عندما يُولّد النموذج نصًا فسيكتب رد البوت بدلاً من القيام بشيء غير متوقع، مثل الاستمرار في رسالة المستخدم. تذكر، أن نماذج الدردشة لا تزال مجرد نماذج للغة - فهي مدربة على متابعة النصوص، والدردشة هي مجرد نوع خاص من النصوص بالنسبة لها! يجب توجيهها برموز تحكم مناسبة، حتى تعرف ما الذي يجب عليها فعله.
|
||||
|
||||
لا تتطلب جميع النماذج الرموز التحكمية لتوليد نصوص . بعض النماذج ، مثل LLaMA ، ليس لديها أي رموز خاصة قبل ردود البوت . في هذه الحالات ، لن يكون لمعامل `add_generation_prompt` أي تأثير. يعتمد التأثير الدقيق الذي تُحدثه `add_generation_prompt` على القالب المستخدم .
|
||||
|
||||
## ما وظيفة "continue_final_message"؟
|
||||
|
||||
عند تمرير قائمة من الرسائل إلى `apply_chat_template` أو `TextGenerationPipeline` ، يمكنك اختيار تنسيق المحادثة بحيث يواصل النموذج الرسالة الأخيرة في المحادثة بدلاً من بدء رسالة جديدة. يتم ذلك عن طريق إزالة أي رموز نهاية التسلسل التي تشير إلى نهاية الرسالة الأخيرة ، بحيث يقوم النموذج ببساطة بتمديد الرسالة الأخيرة عندما يبدأ في توليد النص . يُعد هذا أمرًا مفيدًا "لِمَلء بداية" رد النموذج مُسبقًا.
|
||||
|
||||
وهنا مثال:
|
||||
```python
|
||||
chat = [
|
||||
{"role": "user", "content": "Can you format the answer in JSON?"},
|
||||
{"role": "assistant", "content": '{"name": "'},
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
formatted_chat = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(chat, tokenize=True, return_dict=True, continue_final_message=True)
|
||||
model.generate(**formatted_chat)
|
||||
```
|
||||
سيقوم النموذج بتوليد نص يكمل سلسلة JSON ، بدلاً من بدء رسالة جديدة . يمكن أن يكون هذا النهج مفيدًا جدًا لتحسين دقة اتباع النموذج للإرشادات عندما تعرف كيف تريد أن يبدأ ردوده .
|
||||
.
|
||||
|
||||
نظرًا لأن `add_generation_prompt` تضيف الرموز التي تبدأ رسالة جديدة ، و `continue_final_message` تزيل أي رموز نهاية الرسالة من الرسالة الأخيرة ، فليس من المنطقي استخدامهما معًا . ونتيجة لذلك ، ستتلقّى خطأً إذا حاولت ذلك !
|
||||
|
||||
السلوك الافتراضي لِـ `TextGenerationPipeline` هو تعيين `add_generation_prompt=True` بحيث تبدأ رسالة جديدة . ومع ذلك ، إذا كانت الرسالة الأخيرة في المحادثة التي تم إدخالها لديها دور "assistant" ، فسوف تفترض أن هذه الرسالة هي "مَلء بداية" وتتحوّل إلى `continue_final_message=True` بدلاً من ذلك ، لأن مُعظم النماذج لا تدعم عدة رسائل متتالية للمساعد . يمكنك تجاوز هذا السلوك عن طريق تمرير معامل `continue_final_message` بشكل صريح عند استدعاء قناة المعالجة .
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## هل يمكنني استخدام قوالب الدردشة في التدريب؟
|
||||
|
||||
نعم ! تُعد هذه طريقة جيدة للتأكد من أن قالب الدردشة يتطابق مع الرموز التي يراها النموذج أثناء التدريب . نوصي بتطبيق قالب الدردشة كخطوة معالجة أولية لمجموعة بياناتك . بعد ذلك ، يمكنك ببساطة متابعة عملية التدريب كما هو الحال مع أي مهمة تدريب نماذج لغات أخرى . عند التدريب ، يجب أن تُعيّن عادةً `add_generation_prompt=False` ، لأنه لن تكون الرموز المُضافة لتحفيز رد المساعد مفيدة أثناء التدريب . دعونا نرى مثالاً :
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import AutoTokenizer
|
||||
from datasets import Dataset
|
||||
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("HuggingFaceH4/zephyr-7b-beta")
|
||||
|
||||
chat1 = [
|
||||
{"role": "user", "content": "Which is bigger, the moon or the sun?"},
|
||||
{"role": "assistant", "content": "The sun."}
|
||||
]
|
||||
chat2 = [
|
||||
{"role": "user", "content": "Which is bigger, a virus or a bacterium?"},
|
||||
{"role": "assistant", "content": "A bacterium."}
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
dataset = Dataset.from_dict({"chat": [chat1, chat2]})
|
||||
dataset = dataset.map(lambda x: {"formatted_chat": tokenizer.apply_chat_template(x["chat"], tokenize=False, add_generation_prompt=False)})
|
||||
print(dataset['formatted_chat'][0])
|
||||
```
|
||||
ونحصل على:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
<|user|>
|
||||
Which is bigger, the moon or the sun?</s>
|
||||
<|assistant|>
|
||||
The sun.</s>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
من هنا، استمر في التدريب كما تفعل مع مهمة نمذجة اللغة القياسية، باستخدام عمود `formatted_chat`.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
بشكل افتراضي ، تضيف بعض *tokenizers* رموزًا خاصة مثل `<bos>` و `<eos>` إلى النص الذي تقوم بتقسيمه إلى رموز. يجب أن تتضمن قوالب المحادثة بالفعل جميع الرموز الخاصة التي تحتاجها ، وبالتالي فإن الرموز الخاصة الإضافية ستكون غالبًا غير صحيحة أو مُكررة ، مما سيؤثر سلبًا على أداء النموذج .
|
||||
|
||||
لذلك ، إذا قمت بتنسيق النص باستخدام `apply_chat_template(tokenize=False)` ، فيجب تعيين المعامل `add_special_tokens=False` عندما تقوم بتقسيم ذلك النص إلى رموز لاحقًا . إذا كنت تستخدم `apply_chat_template(tokenize=True)` ، فلن تحتاج إلى القلق بشأن ذلك !
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## متقدّم: مدخلات إضافية لِقوالب الدردشة
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
المعامل الوحيدة التي تتطلبها طريقة `apply_chat_template` هي `messages`. ومع ذلك، يمكنك تمرير أي معامل ككلمة مفتاحية إلى `apply_chat_template` وستكون متاحة داخل القالب. يمنحك هذا الكثير من المرونة لاستخدام قوالب الدردشة للعديد من الأشياء. لا توجد قيود على أسماء هذه المعامﻻت أو تنسيقاتها - يمكنك تمرير سلاسل نصية أو قوائم أو قواميس أو أي شيء آخر تريده.
|
||||
|
||||
ومع ذلك، هناك بعض الحالات الشائعة لاستخدام هذه المعامﻻت الإضافية، مثل تمرير أدوات لاستدعاء الوظائف، أو المستندات لإنشاء النصوص المُعزّزة بالاسترجاع. في هذه الحالات الشائعة، لدينا بعض التوصيات المُحدّدة حول أسماء هذه المعامﻻت وتنسيقاتها، والتي يتم وصفها في الأقسام التالية. نشجع مطوّري النماذج على جعل قوالب الدردشة الخاصة بهم متوافقة مع هذا التنسيق، لتسهيل نقل التعليمات البرمجية لاستدعاء الأدوات بين النماذج.
|
||||
|
||||
## متقدم: استخدام الأداة / استدعاء الدالة
|
||||
|
||||
يمكن لنماذج "استخدام الأداة" اختيار استدعاء الدوال كأدوات خارجية قبل توليد الإجابة. عند تمرير الأدوات إلى نموذج استخدام الأدوات، يمكنك ببساطة تمرير قائمة من الوظائف إلى معامل `tools`:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import datetime
|
||||
|
||||
def current_time():
|
||||
"""Get the current local time as a string."""
|
||||
return str(datetime.now())
|
||||
|
||||
def multiply(a: float, b: float):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
A function that multiplies two numbers
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
a: The first number to multiply
|
||||
b: The second number to multiply
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return a * b
|
||||
|
||||
tools = [current_time, multiply]
|
||||
|
||||
model_input = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
|
||||
messages,
|
||||
tools=tools
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
لكي يعمل هذا بشكل صحيح، يجب عليك كتابة وظائفك بالتنسيق السابق، حتى يمكن تحليلها بشكل صحيح كأدوات. على وجه التحديد، يجب عليك اتباع هذه القواعد:
|
||||
|
||||
- يجب أن يكون للدالة اسم وصفي.
|
||||
- يجب أن يكون لكل معامل نوع للتلميح.
|
||||
- يجب أن تحتوي الدالة على سلسلة مستندية بتنسيق Google القياسي (بمعنى وصف الدالة الأولي متبوعًا بكتلة `Args:` التي تصف المعاﻻت، ما لم تكن الدالة لا تحتوي على أي معامﻻت.
|
||||
- لا تقم بتضمين الأنواع في كتلة `Args:` . بعبارة أخرى، اكتب `a: The first number to multiply`، وليس `a (int): The first number to multiply`. يجب أن تذهب تلميحات الأنواع في رأس الدالة بدلاً من ذلك.
|
||||
- يمكن أن يكون للدالة نوع للإرجاع ومربع `Returns:` في السلسلة. ومع ذلك، فهذه اختيارية لأن معظم نماذج استخدام الأدوات تتجاهلها.
|
||||
|
||||
### تمرير نتائج الأداة إلى النموذج
|
||||
|
||||
يكفي الكود السابقة لسرد الأدوات المتاحة لنموذجك، ولكن ماذا يحدث إذا أراد النموذج استخدام واحدة منها؟ إذا حدث ذلك، فيجب عليك:
|
||||
|
||||
1. تحليل مخرجات النموذج للحصول على اسم (أسماء) الأدوات ومعامﻻتها.
|
||||
2. أضف استدعاء (استدعاءات) النموذج لِلأدوات إلى المحادثة.
|
||||
3. استدعاء الدالة (الدالات) المقابلة بتلك المعامﻻت.
|
||||
4. أضف النتيجة (النتائج) إلى المحادثة
|
||||
|
||||
### مثال كامل على استخدام الأداة
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
سنستعرض مثالاً على استخدام الأدوات خطوة بخطوة . في هذا المثال ، سنستخدم نموذج `Hermes-2-Pro` بحجم 8 مليارات معامل ، نظرًا لأنه أحد أعلى نماذج استخدام الأدوات أداءً في فئة حجمه وقت كتابة هذا النص . إذا كان لديك الذاكرة الكافية ، فيمكنك النظر في استخدام نموذج أكبر بدلاً من ذلك مثل `Command-R` أو `Mixtral-8x22B` ، وكلاهما يدعم استخدام الأدوات ويوفر أداءً أقوى .
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
أولاً ، لنقم بتحميل نموذجنا و tokenizer الخاص بنا:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
checkpoint = "NousResearch/Hermes-2-Pro-Llama-3-8B"
|
||||
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(checkpoint)
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(checkpoint, torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16, device_map="auto")
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
messages = [
|
||||
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a bot that responds to weather queries. You should reply with the unit used in the queried location."},
|
||||
{"role": "user", "content": "Hey, what's the temperature in Paris right now?"}
|
||||
]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
الآن، لنقم نطبق قالب الدردشة ونولد رد:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
inputs = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(messages, chat_template="tool_use", tools=tools, add_generation_prompt=True, return_dict=True, return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
inputs = {k: v.to(model.device) for k, v in inputs.items()}
|
||||
out = model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=128)
|
||||
print(tokenizer.decode(out[0][len(inputs["input_ids"][0]):]))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
ونحصل على:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
<tool_call>
|
||||
{"arguments": {"location": "Paris, France", "unit": "celsius"}, "name": "get_current_temperature"}
|
||||
</tool_call><|im_end|>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
لقد قام النموذج باستدعاء الدالة مع معامﻻت صحيحة، بالصيغة التي طلبتها توثيق الدالة. لقد استنتج أننا نشير على الأرجح إلى باريس في فرنسا، وتذكر أنه بكونها موطن وحدات القياس الدولية، يجب عرض درجة الحرارة في فرنسا بالدرجة المئوية.
|
||||
|
||||
دعنا نضيف استدعاء الأداة الخاص بالنموذج إلى المحادثة. لاحظ أننا نولد معرف استدعاء أداة عشوائيًا هنا. لا تستخدم جميع النماذج هذه المعرفات، ولكنها تسمح للنماذج بإصدار عدة استدعاءات للأدوات في نفس الوقت وتتبع الاستجابة المقابلة لكل استدعاء. يمكنك توليد هذه المعرفات بأي طريقة تريدها، ولكن يجب أن تكون فريدة داخل كل محادثة.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
tool_call_id = "vAHdf3" # Random ID, should be unique for each tool call
|
||||
tool_call = {"name": "get_current_temperature", "arguments": {"location": "Paris, France", "unit": "celsius"}}
|
||||
messages.append({"role": "assistant", "tool_calls": [{"id": tool_call_id, "type": "function", "function": tool_call}]})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
الآن بعد أن أضفنا استدعاء الأداة إلى المحادثة، يمكننا استدعاء الدالة وإضافة النتيجة إلى المحادثة. نظرًا لأننا نستخدم دالة وهمية لهذا المثال والتي تعيد دائمًا 22.0، فيمكننا ببساطة إضافة تلك النتيجة مباشرةً. لاحظ معرف استدعاء الأداة - يجب أن يتطابق مع المعرف المستخدم في استدعاء الأداة أعلاه.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
messages.append({"role": "tool", "tool_call_id": tool_call_id, "name": "get_current_temperature", "content": "22.0"})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
أخيرًا، دعنا نجعل المساعد يقرأ مخرجات الدالة ويكمل الدردشة مع المستخدم:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
inputs = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(messages, chat_template="tool_use", tools=tools, add_generation_prompt=True, return_dict=True, return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
inputs = {k: v.to(model.device) for k, v in inputs.items()}
|
||||
out = model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=128)
|
||||
print(tokenizer.decode(out[0][len(inputs["input_ids"][0]):]))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
ونحصل على:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
The current temperature in Paris, France is 22.0 ° Celsius.<|im_end|>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
لا تستخدم جميع نماذج استخدام الأدوات جميع ميزات استدعاء الأدوات الموضحة أعلاه. يستخدم البعض معرفات استدعاء الأدوات، بينما يستخدم البعض الآخر ببساطة اسم الدالة ويقارن استدعاءات الأدوات بالنتائج باستخدام الترتيب، وهناك عدة نماذج لا تستخدم أيًا منهما ولا تصدر سوى استدعاء أداة واحد في كل مرة لتجنب الارتباك. إذا كنت تريد أن يكون رمزك متوافقًا مع أكبر عدد ممكن من النماذج، فإننا نوصي بهيكلة استدعاءات الأدوات الخاصة بك كما هو موضح هنا، وإعادة نتائج الأدوات بالترتيب الذي أصدرها النموذج. يجب أن تتعامل قوالب الدردشة على كل نموذج مع الباقي.
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
### فهم مخططات الأدوات
|
||||
|
||||
يتم تحويل كل دالة تقوم بتمريرها إلى معامل `tools` في دالة `apply_chat_template` إلى [مخطط JSON](https://json-schema.org/learn/getting-started-step-by-step). يتم بعد ذلك تمرير هذه المخططات إلى قالب الدردشة النموذج. وبعبارة أخرى، فإن نماذج استخدام الأدوات لا ترى دوالك مباشرة، ولا ترى مطلقًا الكود الموجود بداخلها. ما يهمها هو**تعريفات** الدوال و**المعامﻻت** التي تحتاج إلى تمريرها إليها - فهي تهتم بما تفعله الأدوات وكيفية استخدامها، وليس بكيفية عملها! يقع على عاتقك قراءة مخرجاتها، والكشف عما إذا كانت قد طلبت استخدام أداة، وتمرير المعامﻻت إلى دالة الأداة، وإرجاع الرد في الدردشة.
|
||||
|
||||
يجب أن يكون إنشاء مخططات JSON لتمريرها إلى القالب تلقائيًا وغير مرئي طالما أن دوالك تتبع المواصفات الموضحة أعلاه، ولكن إذا واجهت مشكلات، أو إذا كنت تريد ببساطة مزيدًا من التحكم في التحويل، فيمكنك التعامل مع التحويل يدويًا. فيما يلي مثال على تحويل مخطط يدوي:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers.utils import get_json_schema
|
||||
|
||||
def multiply(a: float, b: float):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
A function that multiplies two numbers
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
a: The first number to multiply
|
||||
b: The second number to multiply
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return a * b
|
||||
|
||||
schema = get_json_schema(multiply)
|
||||
print(schema)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
سيؤدي هذا إلى ما يلي:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "function",
|
||||
"function": {
|
||||
"name": "multiply",
|
||||
"description": "A function that multiplies two numbers",
|
||||
"parameters": {
|
||||
"type": "object",
|
||||
"properties": {
|
||||
"a": {
|
||||
"type": "number",
|
||||
"description": "The first number to multiply"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"b": {
|
||||
"type": "number",
|
||||
"description": "The second number to multiply"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"required": ["a", "b"]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
إذا كنت ترغب في ذلك، يمكنك تحرير هذه المخططات، أو حتى كتابتها من البداية بنفسك دون استخدام `get_json_schema` على الإطلاق. يمكن تمرير مخططات JSON مباشرةً إلى معامل `tools` في `apply_chat_template` - يمنحك هذا الكثير من القوة لتعريف مخططات دقيقة لوظائف أكثر تعقيدًا. ولكن كن حذرًا - كلما زاد تعقيد مخططاتك، زاد احتمال ارتباك النموذج عند التعامل معها! نوصي بتوقيعات دوال بسيطة حيثما أمكن، مع تقليل المعامﻻت (وخاصة المعامﻻت المعقدة والمتداخلة) إلى الحد الأدنى.
|
||||
|
||||
فيما يلي مثال على تعريف المخططات يدويًا، وتمريرها مباشرةً إلى `apply_chat_template`:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# A simple function that takes no arguments
|
||||
current_time = {
|
||||
"type": "function",
|
||||
"function": {
|
||||
"name": "current_time",
|
||||
"description": "Get the current local time as a string.",
|
||||
"parameters": {
|
||||
'type': 'object',
|
||||
'properties': {}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# A more complete function that takes two numerical arguments
|
||||
multiply = {
|
||||
'type': 'function',
|
||||
'function': {
|
||||
'name': 'multiply',
|
||||
'description': 'A function that multiplies two numbers',
|
||||
'parameters': {
|
||||
'type': 'object',
|
||||
'properties': {
|
||||
'a': {
|
||||
'type': 'number',
|
||||
'description': 'The first number to multiply'
|
||||
},
|
||||
'b': {
|
||||
'type': 'number', 'description': 'The second number to multiply'
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
'required': ['a', 'b']
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
model_input = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
|
||||
messages,
|
||||
tools = [current_time, multiply]
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## متقدم: توليد قائم على الاسترجاع
|
||||
يمكن لنماذج اللغة الكبيرة من نوع "توليد قائم على الاسترجاع" أو "RAG" البحث في مجموعة نصوص عن معلومات قبل الرد على الاستعلام. يسمح هذا للنماذج بتوسيع قاعدة معارفها بشكل كبير إلى ما هو أبعد من حجم سياقها المحدود. توصيتنا لنماذج RAG هي أن يقبل قالبها وسيطة `documents`. يجب أن تكون هذه قائمة من المستندات، حيث يكون كل "مستند" عبارة عن قاموس واحد بمفاتيح `title` و `contents`، وكلاهما سلاسل نصية. نظرًا لأن هذا التنسيق أبسط بكثير من مخططات JSON المستخدمة للأدوات، فلا توجد حاجة إلى دوال مساعدة.
|
||||
|
||||
فيما يلي مثال على قالب RAG بالفعل:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM
|
||||
|
||||
# تحميل النموذج والمجزىء اللغوي
|
||||
model_id = "CohereForAI/c4ai-command-r-v01-4bit"
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_id)
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_id, device_map="auto")
|
||||
device = model.device # الحصول على الجهاز الذي تم تحميل النموذج عليه
|
||||
|
||||
# تعريف مُدخلات المحادثة
|
||||
conversation = [
|
||||
{"role": "user", "content": "What has Man always dreamed of?"}
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
# تعريف المستندات لتوليد قائم على الاسترجاع
|
||||
documents = [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"title": "The Moon: Our Age-Old Foe",
|
||||
"text": "Man has always dreamed of destroying the moon. In this essay, I shall..."
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"title": "The Sun: Our Age-Old Friend",
|
||||
"text": "Although often underappreciated, the sun provides several notable benefits..."
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
# معالجة المحادثة والمستندات باستخدام قالب RAG، وإرجاع موترات PyTorch.
|
||||
input_ids = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
|
||||
conversation=conversation,
|
||||
documents=documents,
|
||||
chat_template="rag",
|
||||
tokenize=True,
|
||||
add_generation_prompt=True,
|
||||
return_tensors="pt").to(device)
|
||||
|
||||
# توليد الرد
|
||||
gen_tokens = model.generate(
|
||||
input_ids,
|
||||
max_new_tokens=100,
|
||||
do_sample=True,
|
||||
temperature=0.3,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# فك تشفير النص المُوَلّد وطباعته
|
||||
gen_text = tokenizer.decode(gen_tokens[0])
|
||||
print(gen_text)
|
||||
```
|
||||
إن مُدخل documents للتوليد القائم على الاسترجاع غير مدعوم على نطاق واسع، والعديد من النماذج لديها قوالب دردشة تتجاهل هذا المُدخل ببساطة.
|
||||
|
||||
للتحقق مما إذا كان النموذج يدعم مُدخل `documents`، يمكنك قراءة بطاقة النموذج الخاصة به، أو `print(tokenizer.chat_template)` لمعرفة ما إذا كان مفتاح `documents` مستخدمًا في أي مكان.
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
ومع ذلك، فإن أحد فئات النماذج التي تدعمه هي [Command-R](https://huggingface.co/CohereForAI/c4ai-command-r-08-2024) و [Command-R+](https://huggingface.co/CohereForAI/c4ai-command-r-pluse-08-2024) من Cohere، من خلال قالب الدردشة rag الخاص بهم. يمكنك رؤية أمثلة إضافية على التوليد باستخدام هذه الميزة في بطاقات النموذج الخاصة بهم.
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## متقدم: كيف تعمل قوالب الدردشة؟
|
||||
يتم تخزين قالب الدردشة للنموذج في الخاصية `tokenizer.chat_template`. إذا لم يتم تعيين قالب دردشة، فسيتم استخدام القالب الافتراضي لفئة النموذج هذه بدلاً من ذلك. دعونا نلقي نظرة على قالب دردشة `Zephyr`، ولكن لاحظ أن هذا القالب مُبسّط قليلاً عن القالب الفعلي!
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
{%- for message in messages %}
|
||||
{{- '<|' + message['role'] + |>\n' }}
|
||||
{{- message['content'] + eos_token }}
|
||||
{%- endfor %}
|
||||
{%- if add_generation_prompt %}
|
||||
{{- '<|assistant|>\n' }}
|
||||
{%- endif %}
|
||||
```
|
||||
إذا لم تكن قد رأيت أحد هذه القوالب من قبل، فهذا [قالب Jinja](https://jinja.palletsprojects.com/en/3.1.x/templates/) .Jinja هي لغة قوالب تسمح لك بكتابة تعليمات برمجية بسيطة تُوَلّد نصًا. من نواحٍ عديدة، يُشبه الرمز والتركيب للغة Python. أما في لغة Python، سيبدو هذا القالب كما يلي:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
for message in messages:
|
||||
print(f'<|{message["role"]}|>')
|
||||
print(message['content'] + eos_token)
|
||||
if add_generation_prompt:
|
||||
print('<|assistant|>')
|
||||
```
|
||||
يقوم القالب بثلاثة أشياء بشكل فعال:
|
||||
|
||||
- لكل رسالة، بطبع الدور مُحاطًا بـ `<|` و `|>`، مثل `<|user|>` أو `<|assistant|>`.
|
||||
- بعد ذلك، يطبع محتوى الرسالة، متبوعًا برمز نهاية التسلسل `eos_token` .
|
||||
- أخيرًا، إذا تم تعيين `add_generation_prompt` ، يطبع الرمز المساعد، حتى يعرف النموذج أنه يجب أن يبدأ في توليد استجابة المساعد.
|
||||
|
||||
هذا قالب بسيط جدًا، لكن Jinja تمنحك الكثير من المرونة للقيام بأشياء أكثر تعقيدًا! دعونا نرى قالب Jinja يُمكنه تنسيق المُدخلات بطريقة تُشبه الطريقة التي تُنسّق بها LLaMA مُدخلاتها (لاحظ أن قالب LLaMA الحقيقي يتضمن معالجة لرسائل النظام الافتراضية ومعالجة رسائل النظام بشكل مختلف قليلاً بشكل عام - لا تستخدم هذا القالب في التعليمات البرمجية الفعلية الخاصة بك!)
|
||||
```
|
||||
{%- for message in messages %}
|
||||
{%- if message['role'] == 'user' %}
|
||||
{{- bos_token + '[INST] ' + message['content'] + ' [/INST]' }}
|
||||
{%- elif message['role'] == 'system' %}
|
||||
{{- '<<SYS>>\\n' + message['content'] + '\\n<</SYS>>\\n\\n' }}
|
||||
{%- elif message['role'] == 'assistant' %}
|
||||
{{- ' ' + message['content'] + ' ' + eos_token }}
|
||||
{%- endif %}
|
||||
{%- endfor %}
|
||||
```
|
||||
نأمل أنه إذا حدقت في هذا لفترة قصيرة، يمكنك أن ترى ما يفعله هذا القالب - فهو يُضيف رموزًا مُحددة مثل `[INST]` و `[/INST]` بناءً على دور كل رسالة. يمكن تمييز رسائل المستخدم والمساعد والنظام بوضوح للنموذج بسبب الرموز التي تُحيط بها.
|
||||
|
||||
## متقدم: إضافة وتعديل قوالب الدردشة
|
||||
|
||||
### كيف أنشئ قالب دردشة؟
|
||||
ببساطة، اكتب قالب Jinja واضبط `tokenizer.chat_template`. قد تجد أنه من الأسهل البدء بقالب موجود من نموذج آخر وتحريره ببساطة ليناسب احتياجاتك! على سبيل المثال، يمكننا أن نأخذ قالب LLaMA أعلاه ونضيف `[ASST]` و `[/ASST]` إلى رسائل المساعد:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
{%- for message in messages %}
|
||||
{%- if message['role'] == 'user' %}
|
||||
{{- bos_token + '[INST] ' + message['content'].strip() + ' [/INST]' }}
|
||||
{%- elif message['role'] == 'system' %}
|
||||
{{- '<<SYS>>\\n' + message['content'].strip() + '\\n<</SYS>>\\n\\n' }}
|
||||
{%- elif message['role'] == 'assistant' %}
|
||||
{{- '[ASST] ' + message['content'] + ' [/ASST]' + eos_token }}
|
||||
{%- endif %}
|
||||
{%- endfor %}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
الآن، اضبط ببساطة الخاصية `tokenizer.chat_template`. في المرة القادمة التي تستخدم فيها [`~PreTrainedTokenizer.apply_chat_template`] ، سيستخدم القالب الجديد الخاص بك! سيتم حفظ هذه الخاصية في ملف `tokenizer_config.json`، حتى تتمكن من استخدام [`~utils.PushToHubMixin.push_to_hub`] لتحميل قالبك الجديد إلى Hub والتأكد من أن الجميع يستخدم القالب الصحيح لنموذجك!
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
template = tokenizer.chat_template
|
||||
template = template.replace("SYS", "SYSTEM") # تغيير رمز النظام
|
||||
tokenizer.chat_template = template # تعيين القالب الجديد
|
||||
tokenizer.push_to_hub("model_name") # تحميل القالب الجديد إلى Hub!
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
يتم استدعاء الدالة [`~PreTrainedTokenizer.apply_chat_template`] الذي نستخدم قالب الدردشة الخاص بك بواسطة فئة [`TextGenerationPipeline`] لذلك بمجرد تعيين قالب الدردشة الصحيح، سيصبح نموذجك متوافقًا تلقائيًا مع [`TextGenerationPipeline`].
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
إذا كنت تُجري ضبطًا دقيقًا لنموذج للدردشة، بالإضافة إلى تعيين قالب دردشة، فربما يجب عليك إضافة أي رموز تحكم دردشة جديدة كرموز خاصة في المجزىء اللغوي. لا يتم تقسيم الرموز الخاصة أبدًا، مما يضمن معالجة رموز التحكم الخاصة بك دائمًا كرموز فردية بدلاً من تجزئتها إلى أجزاء. يجب عليك أيضًا تعيين خاصية `eos_token` للمجزىء اللغوي إلى الرمز الذي يُشير إلى نهاية توليدات المساعد في قالبك. سيضمن هذا أن أدوات توليد النصوص يمكنها تحديد وقت إيقاف توليد النص بشكل صحيح.
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
### لماذا تحتوي بعض النماذج على قوالب متعددة؟
|
||||
تستخدم بعض النماذج قوالب مختلفة لحالات استخدام مختلفة. على سبيل المثال، قد تستخدم قالبًا واحدًا للدردشة العادية وآخر لاستخدام الأدوات، أو التوليد القائم على الاسترجاع. في هذه الحالات، تكون `tokenizer.chat_template` قاموسًا. يمكن أن يتسبب هذا في بعض الارتباك، وحيثما أمكن، نوصي باستخدام قالب واحد لجميع حالات الاستخدام. يمكنك استخدام عبارات Jinja مثل `if tools is defined` وتعريفات `{% macro %}` لتضمين مسارات تعليمات برمجية متعددة بسهولة في قالب واحد.
|
||||
|
||||
عندما يحتوي المعالج اللغوي على قوالب متعددة، ستكون `tokenizer.chat_template dict`، حيث يكون كل مفتاح هو اسم قالب. يحتوي أسلوب `apply_chat_template` على معالجة خاصة لأسماء قوالب مُعينة: على وجه التحديد، سيبحث عن قالب باسم `default` في معظم الحالات، وسيُثير خطأً إذا لم يتمكن من العثور على واحد. ومع ذلك، إذا كان هناك قالب باسم `tool_use` عندما قام المستخدم بتمرير وسيطة `tools`، فسيستخدم هذا القالب بدلاً من ذلك. للوصول إلى قوالب بأسماء أخرى، مرر اسم القالب الذي تُريده إلى وسيطة `chat_template` لـ `apply_chat_template()`.
|
||||
|
||||
نجد أن هذا قد يكون مُربكًا بعض الشيء للمستخدمين - لذلك إذا كنت تكتب قالبًا بنفسك، فننصحك بمحاولة وضعه كله في قالب واحد حيثما أمكن!
|
||||
|
||||
## ما القالب الذي يجب أن أستخدمه؟
|
||||
|
||||
عند تعيين قالب لنموذج تم تدريبه بالفعل على الدردشة، يجب التأكد من أن القالب يتطابق تمامًا مع تنسيق الرسالة الذي شاهده النموذج أثناء التدريب، وإلا فمن المحتمل أن تواجه تدهورًا في الأداء. هذا صحيح حتى إذا كنت تدرب النموذج بشكل إضافي - فمن المحتمل أن تحصل على أفضل أداء إذا قمت بإبقاء رموز الدردشة ثابتة. يُشبه هذا إلى حد كبير عملية التجزئة - فأنت تحصل بشكل عام على أفضل أداء للاستدلال أو الضبط الدقيق عندما تتطابق بدقة مع التجزئة المستخدمة أثناء التدريب.
|
||||
|
||||
من ناحية أخرى، إذا كنت تُدرّب نموذجًا من البداية، أو تقوم بضبط دقيق لنموذج لغة أساسي للدردشة، لديك حرية اختيار قالب مناسب! تتمتع LLMs بالذكاء الكافي للتعامل مع العديد من تنسيقات الإدخال المختلفة. أحد الخيارات الشائعة هو تنسيق "ChatML"، وهو خيار جيد ومرن للعديد من حالات الاستخدام. يبدو كالتالي:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
{%- for message in messages %}
|
||||
{{- '<|im_start|>' + message['role'] + '\n' + message['content'] + '<|im_end|>' + '\n' }}
|
||||
{%- endfor %}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
إذا أعجبك هذا، فإليك نسخة جاهزة لوضعها في كودك. يتضمن الخط المفرد أيضًا دعمًا مفيدًا [لإرشادات التوليد](#what-are-generation-prompts)، ولكن لاحظ أنه لا يضيف رموز BOS أو EOS! إذا كان نموذجك يتوقع هذه الرموز، فلن يتم إضافتها تلقائيًا بواسطة "apply_chat_template" - بمعنى آخر، سيتم تجزئة النص باستخدام "add_special_tokens=False". هذا لتجنب التعارضات المحتملة بين القالب ومنطق "add_special_tokens". إذا كان نموذجك يتوقع رموزًا خاصة، فتأكد من إضافتها إلى القالب!
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
tokenizer.chat_template = "{% if not add_generation_prompt is defined %}{% set add_generation_prompt = false %}{% endif %}{% for message in messages %}{{'<|im_start|>' + message['role'] + '\n' + message['content'] + '<|im_end|>' + '\n'}}{% endfor %}{% if add_generation_prompt %}{{ '<|im_start|>assistant\n' }}{% endif %}"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
يُحيط هذا القالب كل رسالة بين الرمزين "<|im_start|>" و "<|im_end|>"، ويكتب ببساطة الدور كسلسلة نصية، مما يسمح بالمرونة في الأدوار التي تتدرب عليها. يبدو الناتج كما يلي:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
<|im_start|>system
|
||||
You are a helpful chatbot that will do its best not to say anything so stupid that people tweet about it.<|im_end|>
|
||||
<|im_start|>user
|
||||
How are you?<|im_end|>
|
||||
<|im_start|>assistant
|
||||
I'm doing great!<|im_end|>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
تعد أدوار "user" و "system" و "assistant" هي الأدوار القياسية للدردشة، ونوصي باستخدامها عندما يكون ذلك منطقيًا، خاصة إذا كنت تريد أن يعمل نموذجك بشكل جيد مع [`TextGenerationPipeline`]. ومع ذلك، فأنت لست مقيدًا بهذه الأدوار - فإن القوالب مرنة للغاية، ويمكن أن تكون أي سلسلة نصية دورًا.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## أريد إضافة بعض قوالب الدردشة! كيف أبدأ؟
|
||||
|
||||
إذا كان لديك أي نماذج دردشة، فيجب عليك تعيين الخاصية "tokenizer.chat_template" الخاصة بها واختبارها باستخدام [`~PreTrainedTokenizer.apply_chat_template`]، ثم رفع المجزىء اللغوي المُحدّث إلى Hub. ينطبق هذا حتى إذا لم تكن مالك النموذج - إذا كنت تستخدم نموذجًا بقالب دردشة فارغ، أو لا يزال يستخدم قالب الفئة الافتراضية، فيرجى فتح [طلب سحب](https://huggingface.co/docs/hub/repositories-pull-requests-discussions) إلى مستودع النموذج حتى يمكن تعيين الخاصية بشكل صحيح!
|
||||
|
||||
بمجرد تعيين الخاصية، هذا كل شيء، لقد انتهيت! ستعمل "tokenizer.apply_chat_template" الآن بشكل صحيح لهذا النموذج، مما يعني أنها مدعومة أيضًا بشكل تلقائي في أماكن مثل "TextGenerationPipeline"!
|
||||
|
||||
من خلال ضمان امتلاك النماذج لهذه الخاصية، يُمكننا التأكد من أن المجتمع بأكمله يستخدم القوة الكاملة للنماذج مفتوحة المصدر. لقد كانت عدم تطابق التنسيق تطارد المجال وأضرت الأداء بصمت لفترة طويلة جدًا - لقد حان الوقت لوضع حد لها!
|
||||
|
||||
## متقدم: نصائح لكتابة القوالب
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
أسهل طريقة للبدء في كتابة قوالب Jinja هي إلقاء نظرة على بعض القوالب الموجودة. يمكنك استخدام `print(tokenizer.chat_template)` لأي نموذج دردشة لمعرفة القالب الذي يستخدمه. بشكل عام، تحتوي النماذج التي تدعم استخدام الأدوات على قوالب أكثر تعقيدًا بكثير من النماذج الأخرى - لذلك عندما تبدأ للتو، فمن المحتمل أنها مثال سيئ للتعلم منه! يمكنك أيضًا إلقاء نظرة على [وثائق Jinja](https://jinja.palletsprojects.com/en/3.1.x/templates/#synopsis) للحصول على تفاصيل حول تنسيق Jinja العام وتركيبه.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
تُطابق قوالب Jinja في `transformers` قوالب Jinja في أي مكان آخر. الشيء الرئيسي الذي يجب معرفته هو أن سجل الدردشة سيكون متاحًا داخل قالبك كمتغير يسمى `messages`. ستتمكن من الوصول إلى `messages` في قالبك تمامًا كما يمكنك في Python، مما يعني أنه يمكنك التكرار خلاله باستخدام `{% for message in messages %}` أو الوصول إلى رسائل فردية باستخدام `{{ messages[0] }}`، على سبيل المثال.
|
||||
|
||||
يمكنك أيضًا استخدام النصائح التالية لكتابة قوالب Jinja نظيفة وفعالة:
|
||||
|
||||
### إقتطاع المسافات الفارغة
|
||||
|
||||
بشكل افتراضي، ستطبع Jinja أي مسافات فارغة تأتي قبل أو بعد كتلة. يمكن أن يكون هذا مشكلة لقوالب الدردشة، والتي تريد عادةً أن تكون دقيقة جدًا مع المسافات! لتجنب ذلك، نوصي بشدة بكتابة قوالبك على النحو التالي:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
{%- for message in messages %}
|
||||
{{- message['role'] + message['content'] }}
|
||||
{%- endfor %}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
بدلاً من ذلك:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
{% for message in messages %}
|
||||
{{ message['role'] + message['content'] }}
|
||||
{% endfor %}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
سيؤدي إضافة "-" إلى إزالة أي مسافات تأتي قبل الكتلة. يبدو المثال الثاني عادية، ولكن قد يتم تضمين السطر الجديد والمسافة البادئة في المخرجات، وهو على الأرجح ليس ما تُريده!
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### المتغيرات الخاصة
|
||||
|
||||
داخل قالبك، سيكون لديك حق الوصول إلى العديد من المتغيرات الخاصة. أهمها هو `messages`، والذي يحتوي على سجل الدردشة كقائمة من قواميس الرسائل. ومع ذلك، هناك العديد من المتغيرات الأخرى. لن يتم استخدام كل متغير في كل قالب. المتغيرات الأكثر شيوعًا هي:
|
||||
|
||||
- `tools` تحتوي على قائمة بالأدوات بتنسيق مخطط JSON. ستكون `None` أو غير مُعرّفة إذا لم يتم تمرير أي أدوات.
|
||||
- `documents` تحتوي على قائمة من المستندات بالتنسيق `{"title": "العنوان", "contents": "المحتويات"}`، تُستخدم للتوليد المُعزز بالاسترجاع. ستكون `None` أو غير مُعرّفة إذا لم يتم تمرير أي مستندات.
|
||||
- `add_generation_prompt` هي قيمة منطقية تكون `True` إذا طلب المستخدم مُطالبة توليد، و `False` بخلاف ذلك. إذا تم تعيين هذا، فيجب أن يُضيف قالبك رأس رسالة مساعد إلى نهاية المحادثة. إذا لم يكن لدى نموذجك رأس مُحدد لرسائل المساعد، فيمكنك تجاهل هذا العلم.
|
||||
- **الرموز الخاصة** مثل `bos_token` و `eos_token`. يتم استخراجها من `tokenizer.special_tokens_map`. ستختلف الرموز الدقيقة المتاحة داخل كل قالب اعتمادًا على المجزىء اللغوي الأصلي.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
يمكنك في الواقع تمرير أي `kwarg` إلى `apply_chat_template`، وستكون متاحة داخل القالب كمتغير. بشكل عام، نوصي بمحاولة الالتزام بالمتغيرات الأساسية المذكورة أعلاه، لأن ذلك سيجعل نموذجك أكثر صعوبة في الاستخدام إذا كان على المستخدمين كتابة تعليمات برمجية مخصصة لتمرير `kwargs` خاصة بالنموذج. ومع ذلك، فنحن نُدرك أن هذا المجال يتحرك بسرعة، لذلك إذا كانت لديك حالة استخدام جديدة لا تتناسب مع واجهة برمجة التطبيقات الأساسية، فلا تتردد في استخدام `kwarg` معامل جديد لها! إذا أصبح `kwarg` المعامل الجديد شائعًا، فقد نقوم بترقيته إلى واجهة برمجة التطبيقات الأساسية وإنشاء وتوثيق الخاص به.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
### دوال قابلة للاستدعاء
|
||||
|
||||
هناك أيضًا قائمة قصيرة من الدوال القابلة للاستدعاء المتاحة لك داخل قوالبك. هذه هي:
|
||||
|
||||
- `raise_exception(msg)`: تُثير `TemplateException`. هذا مفيد لتصحيح الأخطاء، ولإخبار المستخدمين عندما يفعلون شيئًا لا يدعمه قالبك.
|
||||
- `strftime_now(format_str)`: تُكافئ `datetime.now().strftime(format_str)` في Python. يُستخدم هذا للحصول على التاريخ/الوقت الحالي بتنسيق مُحدد، والذي يتم تضمينه أحيانًا في رسائل النظام.
|
||||
|
||||
### التوافق مع Jinja غير Python
|
||||
|
||||
هناك تطبيقات متعددة لـ Jinja بلغات مختلفة. عادة ما يكون لها نفس التركيب، ولكن الاختلاف الرئيسي هو أنه عند كتابة قالبًا في Python، يمكنك استخدام أساليب Python، مثل ".lower()" على السلاسل أو ".items()" على القواميس. سيؤدي هذا إلى كسر إذا حاول شخص ما استخدام قالبك في تنفيذ غير Python لـ Jinja. تعد التطبيقات غير Python شائعة بشكل خاص في بيئات النشر، حيث تعد JS و Rust شائعة جدًا.
|
||||
|
||||
لا تقلق، على الرغم من ذلك! هناك بعض التغييرات البسيطة التي يمكنك إجراؤها على قوالبك لضمان توافقها عبر جميع تطبيقات Jinja:
|
||||
|
||||
- استبدل أساليب Python بمرشحات Jinja. عادة ما يكون لها نفس الاسم، على سبيل المثال، يصبح "string.lower()" عبارة عن "string|lower"، ويصبح "dict.items()" عبارة عن "dict|items". أحد التغييرات الملحوظة هو أن "string.strip()" يصبح "string|trim". راجع [قائمة المرشحات المدمجة](https://jinja.palletsprojects.com/en/3.1.x/templates/#builtin-filters) في وثائق Jinja لمزيد من المعلومات.
|
||||
- استبدل "True" و "False" و "None"، وهي خاصة بـ Python، بـ "true" و "false" و "none".
|
||||
- قد يؤدي عرض قاموس أو قائمة مباشرة إلى نتائج مختلفة في التطبيقات الأخرى (على سبيل المثال، قد تتغير مدخﻻت السلسلة النصية من علامات اقتباس مفردة ' إلى علامات اقتباس مزدوجة "). يمكن أن يساعد إضافة "tojson" في ضمان الاتساق هنا.
|
||||
|
||||
## كتابة مطالبات التوليد
|
||||
لقد ذكرنا أعلاه أن add_generation_prompt هو متغير خاص يمكن الوصول إليه داخل قالبك، ويتحكم فيه المستخدم من خلال تعيين معامل add_generation_prompt. إذا كان نموذجك يتوقع عنوان لرسائل المساعد، فيجب أن يدعم قالبك إضافة العنوان عند تعيين add_generation_prompt.
|
||||
|
||||
فيما يلي مثال على قالب يُنسّق الرسائل بأسلوب ChatML، مع دعم مُطالبة التوليد:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
{{- bos_token }}
|
||||
{%- for message in messages %}
|
||||
{{- '<|im_start|>' + message['role'] + '\n' + message['content'] + '<|im_end|>' + '\n' }}
|
||||
{%- endfor %}
|
||||
{%- if add_generation_prompt %}
|
||||
{{- '<|im_start|>assistant\n' }}
|
||||
{%- endif %}
|
||||
```
|
||||
سيعتمد المحتوى الدقيق لعنوان المساعد على نموذجك المُحدد، ولكن يجب أن يكون دائمًا السلسلة النصية التي تُمثل بداية رسالة المساعد، بحيث إذا قام المستخدم بتطبيق قالبك باستخدام add_generation_prompt=True ثم قام بتوليد نص، سيكتب النموذج استجابة المساعد. لاحظ أيضًا أن بعض النماذج لا تحتاج إلى مُطالبة توليد، لأن رسائل المساعد تبدأ دائمًا فورًا بعد رسائل المستخدم. هذا شائع بشكل خاص لنماذج LLaMA و Mistral، حيث تبدأ رسائل المساعد فورًا بعد رمز [/INST] الذي ينهي رسائل المستخدم. في هذه الحالات، يمكن للقالب تجاهل معامل add_generation_prompt.
|
||||
|
||||
مُطالبات التوليد مُهمة! إذا كان نموذجك يتطلب مُطالبة توليد ولكنها غير مُعيّنة في القالب، فمن المُحتمل أن تتدهور عمليات توليد النموذج بشدة، أو قد يُظهر النموذج سلوكًا غير عادي مثل متابعة رسالة المستخدم الأخيرة!
|
||||
|
||||
### كتابة قوالب أكبر وتصحيحها
|
||||
عندما تم تقديم هذه الميزة، كانت معظم القوالب صغيرة جدًا، أي ما يُعادل نص برمجي "من سطر واحد" في Jinja. ومع ذلك، مع النماذج والميزات الجديدة مثل استخدام الأدوات و RAG، يمكن أن يصل طول بعض القوالب إلى 100 سطر أو أكثر. عند كتابة قوالب كهذه، من الجيد كتابتها في ملف مُنفصل، باستخدام مُحرر نصوص. يمكنك بسهولة استخراج قالب دردشة إلى ملف:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
open("template.jinja", "w").write(tokenizer.chat_template)
|
||||
```
|
||||
أو تحميل القالب المُحرر مرة أخرى إلى المعالج اللغوي:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
tokenizer.chat_template = open("template.jinja").read()
|
||||
```
|
||||
كميزة إضافية، عندما تكتب قالبًا طويلاً متعدد الأسطر في ملف مُنفصل، ستتوافق أرقام الأسطر في هذا الملف تمامًا مع أرقام الأسطر في أخطاء تحليل القالب أو تنفيذه. سيُسهّل هذا كثيرًا تحديد مكان المشكلات.
|
||||
|
||||
### كتابة قوالب للأدوات
|
||||
على الرغم من أن قوالب الدردشة لا تفرض واجهة برمجة تطبيقات مُحددة للأدوات (أو لأي شيء حقًا)، فإننا نوصي مؤلفي القوالب بمحاولة الالتزام بواجهة برمجة تطبيقات قياسية حيثما أمكن. الهدف النهائي لقوالب الدردشة هو السماح بنقل التعليمات البرمجية عبر النماذج، لذا فإن الانحراف عن واجهة برمجة تطبيقات الأدوات القياسية يعني أن المستخدمين سيضطرون إلى كتابة تعليمات برمجية مخصصة لاستخدام الأدوات مع نموذجك. في بعض الأحيان يكون ذلك أمرًا لا مفر منه، ولكن غالبًا ما يكون من الممكن استخدام واجهة برمجة التطبيقات القياسية من خلال استخدام قوالب ذكية!
|
||||
|
||||
أدناه، سنُدرج عناصر واجهة برمجة التطبيقات القياسية، ونقدم نصائح حول كتابة قوالب ستعمل بشكل جيد معها.
|
||||
|
||||
#### تعريفات الأدوات
|
||||
يجب أن يتوقع قالبك أن يكون المتغير tools إما فارغًا (إذا لم يتم تمرير أي أدوات)، أو قائمة من قواميس مخطط JSON. تسمح أساليب قالب الدردشة الخاصة بنا للمستخدمين بتمرير الأدوات إما كمخطط JSON أو كدوال Python، ولكن عندما يتم تمرير الدوال، فإننا نقوم تلقائيًا بإنشاء مخطط JSON وتمريره إلى قالبك. نتيجة لذلك، سيكون متغير tools الذي يستقبله قالبك دائمًا قائمة من مخططات JSON. هنا مخطط JSON أداة نموذجي:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "function",
|
||||
"function": {
|
||||
"name": "multiply",
|
||||
"description": "دالة تضرب عددين",
|
||||
"parameters": {
|
||||
"type": "object",
|
||||
"properties": {
|
||||
"a": {
|
||||
"type": "number",
|
||||
"description": "الرقم الأول للضرب"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"b": {
|
||||
"type": "number",
|
||||
"description": "الرقم الثاني للضرب"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"required": ["a", "b"]
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
وهنا بعض الأمثلة البرمجية للتعامل مع الأدوات في قالب الدردشة الخاص بك. تذكر أن هذا مجرد مثال لتنسيق مُحدد - من المحتمل أن يحتاج نموذجك إلى تنسيق مختلف!
|
||||
```text
|
||||
{%- if tools %}
|
||||
{%- for tool in tools %}
|
||||
{{- '<tool>' + tool['function']['name'] + '\n' }}
|
||||
{%- for argument in tool['function']['parameters']['properties'] %}
|
||||
{{- argument + ': ' + tool['function']['parameters']['properties'][argument]['description'] + '\n' }}
|
||||
{%- endfor %}
|
||||
{{- '\n</tool>' }}
|
||||
{%- endif %}
|
||||
{%- endif %}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
يجب بالطبع اختيار الرموز المحددة ووصف الأدوات التي يُعرضها قالبك لتتناسب مع تلك التي تم تدريب نموذجك عليها. لا يوجد شرط أن يفهم نموذجك مُدخلات مخطط JSON، فقط أن يتمكن قالبك من ترجمة مخطط JSON إلى تنسيق نموذجك. على سبيل المثال، تم تدريب Command-R باستخدام أدوات مُعرّفة باستخدام رؤوس دوال Python، ولكن يقبل قالب أداة Command-R مخطط JSON، ويُحوّل الأنواع داخليًا ويُعرض أدوات الإدخال كعناوين Python. يمكنك فعل الكثير باستخدام القوالب!
|
||||
|
||||
#### استدعاءات الأدوات
|
||||
استدعاءات الأدوات، إذا كانت موجودة، ستكون قائمة مُرفقة برسالة بدور "assistant". لاحظ أن tool_calls هي دائمًا قائمة، على الرغم من أن معظم نماذج استدعاء الأدوات تدعم فقط استدعاءات أدوات فردية في كل مرة، مما يعني أن القائمة ستحتوي عادةً على عنصر واحد فقط. هنا قاموس رسالة نموذجي يحتوي على استدعاء أداة:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"role": "assistant",
|
||||
"tool_calls": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "function",
|
||||
"function": {
|
||||
"name": "multiply",
|
||||
"arguments": {
|
||||
"a": 5,
|
||||
"b": 6
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
والنمط الشائع للتعامل معها سيكون كهذا:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
{%- if message['role'] == 'assistant' and 'tool_calls' in message %}
|
||||
{%- for tool_call in message['tool_calls'] %}
|
||||
{{- '<tool_call>' + tool_call['function']['name'] + '\n' + tool_call['function']['arguments']|tojson + '\n</tool_call>' }}
|
||||
{%- endif %}
|
||||
{%- endfor %}
|
||||
{%- endif %}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
مرة أخرى، يجب عليك عرض استدعاء الأداة بالتنسيق والرموز الخاصة التي يتوقعها نموذجك.
|
||||
|
||||
#### استجابات الأدوات
|
||||
استجابات الأدوات لها تنسيق بسيط: إنها قاموس رسالة بدور "tool"، ومفتاح "name" يُعطي اسم الدالة المُستدعاة، ومفتاح "content" يحتوي على نتيجة استدعاء الأداة. هنا استجابة أداة نموذجية:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"role": "tool",
|
||||
"name": "multiply",
|
||||
"content": "30"
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
لست بحاجة إلى استخدام جميع المفاتيح في استجابة الأداة. على سبيل المثال، إذا كان نموذجك لا يتوقع تضمين اسم الدالة في استجابة الأداة، فيمكن أن يكون عرضها بسيطًا مثل:
|
||||
|
||||
```text
|
||||
{%- if message['role'] == 'tool' %}
|
||||
{{- "<tool_result>" + message['content'] + "</tool_result>" }}
|
||||
{%- endif %}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
مرة أخرى، تذكر أن التنسيق الفعلي والرموز الخاصة خاصة بالنموذج - يجب أن تُولي عناية كبيرة لضمان أن الرموز والمسافات الفارغة وكل شيء آخر يتطابق تمامًا مع التنسيق الذي تم تدريب نموذجك عليه!
|
||||
@ -1,66 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# مجتمع المطورين
|
||||
|
||||
هذه الصفحة تجمع الموارد حول 🤗 Transformers التي طورها المجتمع.
|
||||
|
||||
## موارد المجتمع:
|
||||
|
||||
| المصدر | الوصف | المؤلف |
|
||||
|:----------|:-------------|------:|
|
||||
| [Hugging Face Transformers Glossary Flashcards](https://www.darigovresearch.com/huggingface-transformers-glossary-flashcards) | مجموعة من البطاقات التعليمية القائمة على [Transformers Docs Glossary](glossary) والتي تم وضعها في شكل يمكن تعلمه/مراجعته بسهولة باستخدام [Anki](https://apps.ankiweb.net/) وهو تطبيق مفتوح المصدر متعدد المنصات مصمم خصيصًا للاحتفاظ بالمعرفة على المدى الطويل. شاهد هذا [فيديو تمهيدي حول كيفية استخدام البطاقات التعليمية](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Dji_7PILrw). | [Darigov Research](https://www.darigovresearch.com/) |
|
||||
|
||||
## دفاتر ملاحظات المجتمع:
|
||||
|
||||
| الدفتر | الوصف | المؤلف | |
|
||||
|:----------|:-------------|:-------------|------:|
|
||||
| [Fine-tune a pre-trained Transformer to generate lyrics](https://github.com/AlekseyKorshuk/huggingartists) | كيفية توليد كلمات الأغاني على غرار فنانك المفضل من خلال ضبط نموذج GPT-2 | [Aleksey Korshuk](https://github.com/AlekseyKorshuk) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/AlekseyKorshuk/huggingartists/blob/master/huggingartists-demo.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Train T5 in Tensorflow 2](https://github.com/snapthat/TF-T5-text-to-text) | كيفية تدريب T5 لأي مهمة باستخدام Tensorflow 2. يوضح هذا الدفتر مهمة السؤال والجواب المنفذة في Tensorflow 2 باستخدام SQUAD | [Muhammad Harris](https://github.com/HarrisDePerceptron) |[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/snapthat/TF-T5-text-to-text/blob/master/snapthatT5/notebooks/TF-T5-Datasets%20Training.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Train T5 on TPU](https://github.com/patil-suraj/exploring-T5/blob/master/T5_on_TPU.ipynb) | كيفية تدريب T5 على SQUAD مع Transformers و Nlp | [Suraj Patil](https://github.com/patil-suraj) |[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/patil-suraj/exploring-T5/blob/master/T5_on_TPU.ipynb#scrollTo=QLGiFCDqvuil) |
|
||||
| [Fine-tune T5 for Classification and Multiple Choice](https://github.com/patil-suraj/exploring-T5/blob/master/t5_fine_tuning.ipynb) | كيفية ضبط نموذج T5 للتصنيف والمهام متعددة الخيارات باستخدام تنسيق النص إلى نص مع PyTorch Lightning | [Suraj Patil](https://github.com/patil-suraj) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/patil-suraj/exploring-T5/blob/master/t5_fine_tuning.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Fine-tune DialoGPT on New Datasets and Languages](https://github.com/ncoop57/i-am-a-nerd/blob/master/_notebooks/2020-05-12-chatbot-part-1.ipynb) | كيفية ضبط نموذج DialoGPT على مجموعة بيانات جديدة لروبوتات الدردشة المحادثية المفتوحة | [Nathan Cooper](https://github.com/ncoop57) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/ncoop57/i-am-a-nerd/blob/master/_notebooks/2020-05-12-chatbot-part-1.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Long Sequence Modeling with Reformer](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/PyTorch_Reformer.ipynb) | كيفية التدريب على تسلسلات طويلة تصل إلى 500,000 رمز باستخدام Reformer | [Patrick von Platen](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/PyTorch_Reformer.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Fine-tune BART for Summarization](https://github.com/ohmeow/ohmeow_website/blob/master/posts/2021-05-25-mbart-sequence-classification-with-blurr.ipynb) | كيفية ضبط نموذج BART للتلخيص باستخدام fastai باستخدام blurr | [Wayde Gilliam](https://ohmeow.com/) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/ohmeow/ohmeow_website/blob/master/posts/2021-05-25-mbart-sequence-classification-with-blurr.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Fine-tune a pre-trained Transformer on anyone's tweets](https://colab.research.google.com/github/borisdayma/huggingtweets/blob/master/huggingtweets-demo.ipynb) | كيفية توليد تغريدات على غرار حساب Twitter المفضل لديك من خلال ضبط نموذج GPT-2 | [Boris Dayma](https://github.com/borisdayma) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/borisdayma/huggingtweets/blob/master/huggingtweets-demo.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Optimize 🤗 Hugging Face models with Weights & Biases](https://colab.research.google.com/github/wandb/examples/blob/master/colabs/huggingface/Optimize_Hugging_Face_models_with_Weights_%26_Biases.ipynb) | دليل كامل لعرض تكامل W&B مع Hugging Face | [Boris Dayma](https://github.com/borisdayma) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/wandb/examples/blob/master/colabs/huggingface/Optimize_Hugging_Face_models_with_Weights_%26_Biases.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Pretrain Longformer](https://github.com/allenai/longformer/blob/master/scripts/convert_model_to_long.ipynb) | كيفية بناء نسخة "طويلة" من النماذج المسبقة التدريب الموجودة | [Iz Beltagy](https://beltagy.net) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/allenai/longformer/blob/master/scripts/convert_model_to_long.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Fine-tune Longformer for QA](https://github.com/patil-suraj/Notebooks/blob/master/longformer_qa_training.ipynb) | كيفية ضبط نموذج Longformer لمهمة QA | [Suraj Patil](https://github.com/patil-suraj) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/patil-suraj/Notebooks/blob/master/longformer_qa_training.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Evaluate Model with 🤗nlp](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/How_to_evaluate_Longformer_on_TriviaQA_using_NLP.ipynb) | كيفية تقييم نموذج Longformer على TriviaQA مع `nlp` | [Patrick von Platen](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1m7eTGlPmLRgoPkkA7rkhQdZ9ydpmsdLE?usp=sharing) |
|
||||
| [Fine-tune T5 for Sentiment Span Extraction](https://github.com/enzoampil/t5-intro/blob/master/t5_qa_training_pytorch_span_extraction.ipynb) | كيفية ضبط نموذج T5 لاستخراج المشاعر باستخدام تنسيق النص إلى نص مع PyTorch Lightning | [Lorenzo Ampil](https://github.com/enzoampil) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/enzoampil/t5-intro/blob/master/t5_qa_training_pytorch_span_extraction.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Fine-tune DistilBert for Multiclass Classification](https://github.com/abhimishra91/transformers-tutorials/blob/master/transformers_multiclass_classification.ipynb) | كيفية ضبط نموذج DistilBert للتصنيف متعدد الفئات باستخدام PyTorch | [Abhishek Kumar Mishra](https://github.com/abhimishra91) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/abhimishra91/transformers-tutorials/blob/master/transformers_multiclass_classification.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Fine-tune BERT for Multi-label Classification](https://github.com/abhimishra91/transformers-tutorials/blob/master/transformers_multi_label_classification.ipynb)|كيفية ضبط نموذج BERT للتصنيف متعدد التصنيفات باستخدام PyTorch|[Abhishek Kumar Mishra](https://github.com/abhimishra91) |[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/abhimishra91/transformers-tutorials/blob/master/transformers_multi_label_classification.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Fine-tune T5 for Summarization](https://github.com/abhimishra91/transformers-tutorials/blob/master/transformers_summarization_wandb.ipynb)|كيفية ضبط نموذج T5 للتلخيص في PyTorch وتتبع التجارب باستخدام WandB|[Abhishek Kumar Mishra](https://github.com/abhimishra91) |[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/abhimishra91/transformers-tutorials/blob/master/transformers_summarization_wandb.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Speed up Fine-Tuning in Transformers with Dynamic Padding / Bucketing](https://github.com/ELS-RD/transformers-notebook/blob/master/Divide_Hugging_Face_Transformers_training_time_by_2_or_more.ipynb)|كيفية تسريع الضبط الدقيق بعامل 2 باستخدام الضبط الديناميكي/التقسيم|[Michael Benesty](https://github.com/pommedeterresautee) |[](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1CBfRU1zbfu7-ijiOqAAQUA-RJaxfcJoO?usp=sharing)|
|
||||
|[Pretrain Reformer for Masked Language Modeling](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/Reformer_For_Masked_LM.ipynb)| كيفية تدريب نموذج Reformer مع طبقات الانتباه ثنائية الاتجاه | [Patrick von Platen](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1tzzh0i8PgDQGV3SMFUGxM7_gGae3K-uW?usp=sharing)|
|
||||
|[Expand and Fine Tune Sci-BERT](https://github.com/lordtt13/word-embeddings/blob/master/COVID-19%20Research%20Data/COVID-SciBERT.ipynb)| كيفية زيادة مفردات نموذج SciBERT المسبق التدريب من AllenAI على مجموعة بيانات CORD وإنشاء خط أنابيب لها. | [Tanmay Thakur](https://github.com/lordtt13) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1rqAR40goxbAfez1xvF3hBJphSCsvXmh8)|
|
||||
|[Fine Tune BlenderBotSmall for Summarization using the Trainer API](https://github.com/lordtt13/transformers-experiments/blob/master/Custom%20Tasks/fine-tune-blenderbot_small-for-summarization.ipynb)| كيفية ضبط نموذج BlenderBotSmall للتلخيص على مجموعة بيانات مخصصة، باستخدام واجهة برمجة التطبيقات Trainer. | [Tanmay Thakur](https://github.com/lordtt13) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/19Wmupuls7mykSGyRN_Qo6lPQhgp56ymq?usp=sharing)|
|
||||
|[Fine-tune Electra and interpret with Integrated Gradients](https://github.com/elsanns/xai-nlp-notebooks/blob/master/electra_fine_tune_interpret_captum_ig.ipynb) | كيفية ضبط نموذج Electra للتحليل العاطفي وتفسير التنبؤات باستخدام Captum Integrated Gradients | [Eliza Szczechla](https://elsanns.github.io) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/elsanns/xai-nlp-notebooks/blob/master/electra_fine_tune_interpret_captum_ig.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[fine-tune a non-English GPT-2 Model with Trainer class](https://github.com/philschmid/fine-tune-GPT-2/blob/master/Fine_tune_a_non_English_GPT_2_Model_with_Huggingface.ipynb) | كيفية ضبط نموذج GPT-2 غير الإنجليزي باستخدام فئة Trainer | [Philipp Schmid](https://www.philschmid.de) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/philschmid/fine-tune-GPT-2/blob/master/Fine_tune_a_non_English_GPT_2_Model_with_Huggingface.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Fine-tune a DistilBERT Model for Multi Label Classification task](https://github.com/DhavalTaunk08/Transformers_scripts/blob/master/Transformers_multilabel_distilbert.ipynb) | كيفية ضبط نموذج DistilBERT لمهمة التصنيف متعدد التصنيفات | [Dhaval Taunk](https://github.com/DhavalTaunk08) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/DhavalTaunk08/Transformers_scripts/blob/master/Transformers_multilabel_distilbert.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Fine-tune ALBERT for sentence-pair classification](https://github.com/NadirEM/nlp-notebooks/blob/master/Fine_tune_ALBERT_sentence_pair_classification.ipynb) | كيفية ضبط نموذج ALBERT أو أي نموذج آخر قائم على BERT لمهمة التصنيف المزدوج للجمل | [Nadir El Manouzi](https://github.com/NadirEM) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/NadirEM/nlp-notebooks/blob/master/Fine_tune_ALBERT_sentence_pair_classification.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Fine-tune Roberta for sentiment analysis](https://github.com/DhavalTaunk08/NLP_scripts/blob/master/sentiment_analysis_using_roberta.ipynb) | كيفية ضبط نموذج Roberta للتحليل العاطفي | [Dhaval Taunk](https://github.com/DhavalTaunk08) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/DhavalTaunk08/NLP_scripts/blob/master/sentiment_analysis_using_roberta.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Evaluating Question Generation Models](https://github.com/flexudy-pipe/qugeev) | ما مدى دقة الإجابات على الأسئلة التي يولدها نموذجك التحويلي seq2seq؟ | [Pascal Zoleko](https://github.com/zolekode) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1bpsSqCQU-iw_5nNoRm_crPq6FRuJthq_?usp=sharing)|
|
||||
|[Classify text with DistilBERT and Tensorflow](https://github.com/peterbayerle/huggingface_notebook/blob/main/distilbert_tf.ipynb) | كيفية ضبط نموذج DistilBERT للتصنيف النصي في TensorFlow | [Peter Bayerle](https://github.com/peterbayerle) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/peterbayerle/huggingface_notebook/blob/main/distilbert_tf.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Leverage BERT for Encoder-Decoder Summarization on CNN/Dailymail](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/BERT2BERT_for_CNN_Dailymail.ipynb) | كيفية البدء السريع لنموذج *EncoderDecoderModel* مع نقطة تفتيش *google-bert/bert-base-uncased* للتلخيص على CNN/Dailymail | [Patrick von Platen](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/BERT2BERT_for_CNN_Dailymail.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Leverage RoBERTa for Encoder-Decoder Summarization on BBC XSum](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/RoBERTaShared_for_BBC_XSum.ipynb) | كيفية البدء السريع لنموذج *EncoderDecoderModel* المشترك مع نقطة تفتيش *FacebookAI/roberta-base* للتلخيص على BBC/XSum | [Patrick von Platen](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/RoBERTaShared_for_BBC_XSum.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Fine-tune TAPAS on Sequential Question Answering (SQA)](https://github.com/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/TAPAS/Fine_tuning_TapasForQuestionAnswering_on_SQA.ipynb) | كيفية ضبط نموذج *TapasForQuestionAnswering* مع نقطة تفتيش *tapas-base* على مجموعة بيانات Sequential Question Answering (SQA) | [Niels Rogge](https://github.com/nielsrogge) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/TAPAS/Fine_tuning_TapasForQuestionAnswering_on_SQA.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Evaluate TAPAS on Table Fact Checking (TabFact)](https://github.com/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/TAPAS/Evaluating_TAPAS_on_the_Tabfact_test_set.ipynb) | كيفية تقييم نموذج *TapasForSequenceClassification* المضبوط مسبقًا مع نقطة تفتيش *tapas-base-finetuned-tabfact* باستخدام مزيج من مكتبتي 🤗 datasets و 🤗 transformers | [Niels Rogge](https://github.com/nielsrogge) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/TAPAS/Evaluating_TAPAS_on_the_Tabfact_test_set.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Fine-tuning mBART for translation](https://colab.research.google.com/github/vasudevgupta7/huggingface-tutorials/blob/main/translation_training.ipynb) | كيفية ضبط نموذج mBART باستخدام Seq2SeqTrainer للترجمة من الهندية إلى الإنجليزية | [Vasudev Gupta](https://github.com/vasudevgupta7) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/vasudevgupta7/huggingface-tutorials/blob/main/translation_training.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Fine-tune LayoutLM on FUNSD (a form understanding dataset)](https://github.com/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/LayoutLM/Fine_tuning_LayoutLMForTokenClassification_on_FUNSD.ipynb) | كيفية ضبط نموذج *LayoutLMForTokenClassification* على مجموعة بيانات FUNSD لاستخراج المعلومات من المستندات الممسوحة ضوئيًا | [Niels Rogge](https://github.com/nielsrogge) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/LayoutLM/Fine_tuning_LayoutLMForTokenClassification_on_FUNSD.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Fine-Tune DistilGPT2 and Generate Text](https://colab.research.google.com/github/tripathiaakash/DistilGPT2-Tutorial/blob/main/distilgpt2_fine_tuning.ipynb) | كيفية ضبط نموذج DistilGPT2 وتوليد النص | [Aakash Tripathi](https://github.com/tripathiaakash) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/tripathiaakash/DistilGPT2-Tutorial/blob/main/distilgpt2_fine_tuning.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Fine-Tune LED on up to 8K tokens](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/Fine_tune_Longformer_Encoder_Decoder_(LED)_for_Summarization_on_pubmed.ipynb) | كيفية ضبط نموذج LED على pubmed للتلخيص طويل المدى | [Patrick von Platen](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/Fine_tune_Longformer_Encoder_Decoder_(LED)_for_Summarization_on_pubmed.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Evaluate LED on Arxiv](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/LED_on_Arxiv.ipynb) | كيفية تقييم نموذج LED للتلخيص طويل المدى بشكل فعال | [Patrick von Platen](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/LED_on_Arxiv.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Fine-tune LayoutLM on RVL-CDIP (a document image classification dataset)](https://github.com/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/LayoutLM/Fine_tuning_LayoutLMForSequenceClassification_on_RVL_CDIP.ipynb) | كيفية ضبط نموذج *LayoutLMForSequenceClassification* على مجموعة بيانات RVL-CDIP لتصنيف المستندات الممسوحة ضوئيًا | [Niels Rogge](https://github.com/nielsrogge) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/LayoutLM/Fine_tuning_LayoutLMForSequenceClassification_on_RVL_CDIP.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Wav2Vec2 CTC decoding with GPT2 adjustment](https://github.com/voidful/huggingface_notebook/blob/main/xlsr_gpt.ipynb) | كيفية فك تشفير تسلسل CTC مع تعديل نموذج اللغة | [Eric Lam](https://github.com/voidful) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1e_zQHYbO2YKEaUgzb1ww1WwiAyydAj?usp=sharing)|
|
||||
|[Fine-tune BART for summarization in two languages with Trainer class](https://github.com/elsanns/xai-nlp-notebooks/blob/master/fine_tune_bart_summarization_two_langs.ipynb) | كيفية ضبط نموذج BART للتلخيص بلغتين باستخدام فئة Trainer | [Eliza Szczechla](https://github.com/elsanns) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/elsanns/xai-nlp-notebooks/blob/master/fine_tune_bart_summarization_two_langs.ipynb)|
|
||||
|[Evaluate Big Bird on Trivia QA](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/Evaluating_Big_Bird_on_TriviaQA.ipynb) | كيفية تقييم نموذج BigBird للأسئلة والأجوبة على وثائق طويلة على Trivia QA | [Patrick von Platen](https://github.com/patrickvonplaten) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/patrickvonplaten/notebooks/blob/master/Evaluating_Big_Bird_on_TriviaQA.ipynb)|
|
||||
| [Create video captions using Wav2Vec2](https://github.com/Muennighoff/ytclipcc/blob/main/wav2vec_youtube_captions.ipynb) | كيفية إنشاء تعليقات توضيحية على YouTube من أي فيديو من خلال تفريغ الصوت باستخدام Wav2Vec | [Niklas Muennighoff](https://github.com/Muennighoff) |[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/Muennighoff/ytclipcc/blob/main/wav2vec_youtube_captions.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Fine-tune the Vision Transformer on CIFAR-10 using PyTorch Lightning](https://github.com/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/VisionTransformer/Fine_tuning_the_Vision_Transformer_on_CIFAR_10_with_PyTorch_Lightning.ipynb) | كيفية ضبط نموذج Vision Transformer (ViT) على CIFAR-10 باستخدام مكتبات HuggingFace Transformers و Datasets و PyTorch Lightning | [Niels Rogge](https://github.com/nielsrogge) |[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/VisionTransformer/Fine_tuning_the_Vision_Transformer_on_CIFAR_10_with_PyTorch_Lightning.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Fine-tune the Vision Transformer on CIFAR-10 using the 🤗 Trainer](https://github.com/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/VisionTransformer/Fine_tuning_the_Vision_Transformer_on_CIFAR_10_with_the_%F0%9F%A4%97_Trainer.ipynb) | كيفية ضبط نموذج Vision Transformer (ViT) على CIFAR-10 باستخدام مكتبات HuggingFace Transformers و Datasets و 🤗 Trainer | [Niels Rogge](https://github.com/nielsrogge) |[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/VisionTransformer/Fine_tuning_the_Vision_Transformer_on_CIFAR_10_with_the_%F0%9F%A4%97_Trainer.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Evaluate LUKE on Open Entity, an entity typing dataset](https://github.com/studio-ousia/luke/blob/master/notebooks/huggingface_open_entity.ipynb) | كيفية تقييم نموذج *LukeForEntityClassification* على مجموعة بيانات Open Entity | [Ikuya Yamada](https://github.com/ikuyamada) |[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/studio-ousia/luke/blob/master/notebooks/huggingface_open_entity.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Evaluate LUKE on TACRED, a relation extraction dataset](https://github.com/studio-ousia/luke/blob/master/notebooks/huggingface_tacred.ipynb) | كيفية تقييم نموذج *LukeForEntityPairClassification* على مجموعة بيانات TACRED | [Ikuya Yamada](https://github.com/ikuyamada) |[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/studio-ousia/luke/blob/master/notebooks/huggingface_tacred.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Evaluate LUKE on CoNLL-2003, an important NER benchmark](https://github.com/studio-ousia/luke/blob/master/notebooks/huggingface_conll_2003.ipynb) | كيفية تقييم نموذج *LukeForEntitySpanClassification* على مجموعة بيانات CoNLL-2003 | [Ikuya Yamada](https://github.com/ikuyamada) |[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/studio-ousia/luke/blob/master/notebooks/huggingface_conll_2003.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Evaluate BigBird-Pegasus on PubMed dataset](https://github.com/vasudevgupta7/bigbird/blob/main/notebooks/bigbird_pegasus_evaluation.ipynb) | كيفية تقييم نموذج *BigBirdPegasusForConditionalGeneration* على مجموعة بيانات PubMed | [Vasudev Gupta](https://github.com/vasudevgupta7) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/vasudevgupta7/bigbird/blob/main/notebooks/bigbird_pegasus_evaluation.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Speech Emotion Classification with Wav2Vec2](https://github.com/m3hrdadfi/soxan/blob/main/notebooks/Emotion_recognition_in_Greek_speech_using_Wav2Vec2.ipynb) | كيفية استخدام نموذج Wav2Vec2 المسبق التدريب لتصنيف المشاعر على مجموعة بيانات MEGA | [Mehrdad Farahani](https://github.com/m3hrdadfi) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/m3hrdadfi/soxan/blob/main/notebooks/Emotion_recognition_in_Greek_speech_using_Wav2Vec2.ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Detect objects in an image with DETR](https://github.com/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/DETR/DETR_minimal_example_(with_DetrFeatureExtractor).ipynb) | كيفية استخدام نموذج *DetrForObjectDetection* المدرب للكشف عن الأجسام في صورة وتصوير الانتباه | [Niels Rogge](https://github.com/NielsRogge) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/DETR/DETR_minimal_example_(with_DetrFeatureExtractor).ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Fine-tune DETR on a custom object detection dataset](https://github.com/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/DETR/Fine_tuning_DetrForObjectDetection_on_custom_dataset_(balloon).ipynb) | كيفية ضبط نموذج *DetrForObjectDetection* على مجموعة بيانات الكشف عن الأجسام المخصصة | [Niels Rogge](https://github.com/NielsRogge) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/NielsRogge/Transformers-Tutorials/blob/master/DETR/Fine_tuning_DetrForObjectDetection_on_custom_dataset_(balloon).ipynb) |
|
||||
| [Finetune T5 for Named Entity Recognition](https://github.com/ToluClassics/Notebooks/blob/main/T5_Ner_Finetuning.ipynb) | كيفية ضبط نموذج *T5* على مهمة التعرف على الكيانات المسماة | [Ogundepo Odunayo](https://github.com/ToluClassics) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1obr78FY_cBmWY5ODViCmzdY6O1KB65Vc?usp=sharing) |
|
||||
| [Fine-Tuning Open-Source LLM using QLoRA with MLflow and PEFT](https://github.com/mlflow/mlflow/blob/master/docs/source/llms/transformers/tutorials/fine-tuning/transformers-peft.ipynb) | كيفية استخدام [QLoRA](https://github.com/artidoro/qlora) و [PEFT](https://huggingface.co/docs/peft/en/index) لضبط نموذج LLM بطريقة فعالة من حيث الذاكرة، مع استخدام [MLflow](https://mlflow.org/docs/latest/llms/transformers/index.html) لإدارة تتبع التجارب | [Yuki Watanabe](https://github.com/B-Step62) | [](https://colab.research.google.com/github/mlflow/mlflow/blob/master/docs/source/llms/transformers/tutorials/fine-tuning/transformers-peft.ipynb) |
|
||||
@ -1,436 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# إنشاء بنية مخصصة
|
||||
|
||||
تحدد فئة [`AutoClass`](model_doc/auto) تلقائيًا بنية النموذج وتقوم بتنزيل تكوين وأوزان مسبقين للنموذج. بشكل عام، نوصي باستخدام `AutoClass` لإنتاج كود غير مرتبط بنسخة معينة. ولكن يمكن للمستخدمين الذين يريدون مزيدًا من التحكم في معلمات النموذج المحددة إنشاء نموذج مخصص من 🤗 Transformers من مجرد بضع فئات أساسية. قد يكون هذا مفيدًا بشكل خاص لأي شخص مهتم بدراسة نموذج 🤗 Transformers أو تدريبه أو إجراء تجارب عليه. في هذا الدليل، سنغوص بشكل أعمق في إنشاء نموذج مخصص بدون `AutoClass`. تعرف على كيفية:
|
||||
|
||||
- تحميل تكوين النموذج وتخصيصه.
|
||||
- إنشاء بنية نموذج.
|
||||
- إنشاء مجزء لغوى سريع وبطيء للنص.
|
||||
- إنشاء معالج صور لمهام الرؤية.
|
||||
- إنشاء مستخرج ميزات لمهام الصوت.
|
||||
- إنشاء معالج للمهام متعددة الوسائط.
|
||||
|
||||
## التكوين
|
||||
|
||||
يشير مصطلح [التكوين](main_classes/configuration) إلى الخصائص المحددة للنموذج. لكل تكوين نموذج خصائصه الخاصة؛ على سبيل المثال، تشترك جميع نماذج NLP في الخصائص `hidden_size` و`num_attention_heads` و`num_hidden_layers` و`vocab_size` المشتركة. تحدد هذه الخصائص عدد رؤوس الانتباه أو الطبقات المخفية لبناء نموذج بها.
|
||||
|
||||
اطلع على [DistilBERT](model_doc/distilbert) من خلال [`DistilBertConfig`] لمعاينة خصائصه:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import DistilBertConfig
|
||||
|
||||
>>> config = DistilBertConfig()
|
||||
>>> print(config)
|
||||
DistilBertConfig {
|
||||
"activation": "gelu",
|
||||
"attention_dropout": 0.1,
|
||||
"dim": 768,
|
||||
"dropout": 0.1,
|
||||
"hidden_dim": 3072,
|
||||
"initializer_range": 0.02,
|
||||
"max_position_embeddings": 512,
|
||||
"model_type": "distilbert",
|
||||
"n_heads": 12,
|
||||
"n_layers": 6,
|
||||
"pad_token_id": 0,
|
||||
"qa_dropout": 0.1,
|
||||
"seq_classif_dropout": 0.2,
|
||||
"sinusoidal_pos_embds": false,
|
||||
"transformers_version": "4.16.2",
|
||||
"vocab_size": 30522
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
يعرض [`DistilBertConfig`] جميع الخصائص الافتراضية المستخدمة لبناء نموذج [`DistilBertModel`] أساسي. جميع الخصائص قابلة للتعديل، مما ييتيح مجالاً للتجريب. على سبيل المثال، يمكنك تعديل نموذج افتراضي لـ:
|
||||
|
||||
- تجربة دالة تنشيط مختلفة باستخدام معامل `activation`.
|
||||
- استخدام معدل إسقاط أعلى الاحتمالات الانتباه مع معامل `attention_dropout`.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> my_config = DistilBertConfig(activation="relu", attention_dropout=0.4)
|
||||
>>> print(my_config)
|
||||
DistilBertConfig {
|
||||
"activation": "relu",
|
||||
"attention_dropout": 0.4,
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
يمكن تعديل خصائص النموذج المدرب مسبقًا في دالة [`~PretrainedConfig.from_pretrained`] :
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> my_config = DistilBertConfig.from_pretrained("distilbert/distilbert-base-uncased", activation="relu", attention_dropout=0.4)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
بمجرد أن تصبح راضيًا عن تكوين نموذجك، يمكنك حفظه باستخدام [`~PretrainedConfig.save_pretrained`]. يتم تخزين ملف التكوين الخاص بك على أنه ملف JSON في دليل الحفظ المحدد:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> my_config.save_pretrained(save_directory="./your_model_save_path")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
لإعادة استخدام ملف التكوين، قم بتحميله باستخدام [`~PretrainedConfig.from_pretrained`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> my_config = DistilBertConfig.from_pretrained("./your_model_save_path/config.json")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
يمكنك أيضًا حفظ ملف التكوين كقاموس أو حتى كفرق بين خصائص التكوين المُعدّلة والخصائص التكوين الافتراضية! راجع وثائق [التكوين](main_classes/configuration) لمزيد من التفاصيل.
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## النموذج
|
||||
|
||||
الخطوة التالية هي إنشاء [نموذج](main_classes/models). النموذج - ويُشار إليه أحيانًا باسم البنية - يُحدد وظيفة كل طبقة والعمليات الحسابية المُنفذة. تُستخدم خصائص مثل `num_hidden_layers` من التكوين لتحديد هذه البنية. تشترك جميع النماذج في فئة أساسية واحدة هي [`PreTrainedModel`] وبعض الوظائف المُشتركة مثل غيير حجم مُدخلات الكلمات وتقليص رؤوس آلية الانتباه الذاتي. بالإضافة إلى ذلك، فإن جميع النماذج هي فئات فرعية إما من [`torch.nn.Module`](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.Module.html)، [`tf.keras.Model`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/Model) أو [`flax.linen.Module`](https://flax.readthedocs.io/en/latest/api_reference/flax.linen/module.html) . هذا يعني النماذج متوافقة مع كل استخدام لإطار العمل الخاص بها.
|
||||
|
||||
<frameworkcontent>
|
||||
<pt>
|
||||
قم بتحميل خصائص التكوين المخصصة الخاصة بك في النموذج:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import DistilBertModel
|
||||
|
||||
>>> my_config = DistilBertConfig.from_pretrained("./your_model_save_path/config.json")
|
||||
>>> model = DistilBertModel(my_config)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
هذا ينشئ نموذجًا بقيم عشوائية بدلاً من الأوزان المُدربة مسبقًا. لن يكون هذا النموذج مفيدًا حتى يتم تدريبه. تُعد عملية التدريب مكلفة وتستغرق وقتًا طويلاً. من الأفضل بشكل عام استخدام نموذج مُدرب مسبقًا للحصول على نتائج أفضل بشكل أسرع، مع استخدام جزء بسيط فقط من الموارد المطلوبة للتدريب.
|
||||
|
||||
قم بإنشاء نموذج مُدرب مسبقًا باستخدام [`~PreTrainedModel.from_pretrained`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> model = DistilBertModel.from_pretrained("distilbert/distilbert-base-uncased")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
عند بتحميل الأوزان المُدربة مسبقًا، يتم تحميل تكوين النموذج الافتراضي تلقائيًا إذا كان النموذج من مكتبة 🤗 Transformers. ومع ذلك، يمكنك أيضًا استبدال - بعض أو كل - سإعدادات النموذج الافتراضية بإعداداتك الخاصة:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> model = DistilBertModel.from_pretrained("distilbert/distilbert-base-uncased"، config=my_config)
|
||||
```
|
||||
</pt>
|
||||
<tf>
|
||||
قم بتحميل خصائص التكوين المُخصصة الخاصة بك في النموذج:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import TFDistilBertModel
|
||||
|
||||
>>> my_config = DistilBertConfig.from_pretrained("./your_model_save_path/my_config.json")
|
||||
>>> tf_model = TFDistilBertModel(my_config)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
هذا ينشئ نموذجًا بقيم عشوائية بدلاً من الأوزان المُدربة مسبقًا. لن يكون هذا النموذج مفيدًا حتى يتم تدريبه. تُعد عملية التدريب مكلفة وتستغرق وقتًا طويلاً. من الأفضل بشكل عام استخدام نموذج مُدرب مسبقًا للحصول على نتائج أفضل بشكل أسرع، مع استخدام جزء بسيط فقط من الموارد المطلوبة للتدريب.
|
||||
|
||||
قم بإنشاء نموذج مُدرب مسبقًا باستخدام [`~TFPreTrainedModel.from_pretrained`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> tf_model = TFDistilBertModel.from_pretrained("distilbert/distilbert-base-uncased")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
عندما تقوم بتحميل الأوزان المُدربة مسبقًا،يتم تحميل إعدادات النموذج الافتراضي تلقائيًا إذا كان النموذج من مكتبة 🤗 Transformers. ومع ذلك، يمكنك أيضًا استبدال - بعض أو كل - إعدادات النموذج الافتراضية بإعداداتك الخاصة:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> tf_model = TFDistilBertModel.from_pretrained("distilbert/distilbert-base-uncased"، config=my_config)
|
||||
```
|
||||
</tf>
|
||||
</frameworkcontent>
|
||||
|
||||
### رؤوس النموذج
|
||||
|
||||
في هذه المرحلة، لديك نموذج DistilBERT الأساسي الذي يخرج *حالات الكامنة*. تُمرَّر هذه الحالات الكامنة كمدخلات لرأس النموذج لإنتاج المخرجات النهائية. توفر مكتبة 🤗 Transformers رأس نموذج مختلف لكل مهمة طالما أن النموذج يدعم المهمة (أي لا يمكنك استخدام DistilBERT لمهمة تسلسل إلى تسلسل مثل الترجمة).
|
||||
|
||||
<frameworkcontent>
|
||||
<pt>
|
||||
على سبيل المثال، [`DistilBertForSequenceClassification`] هو نموذج DistilBERT الأساس مزودًا برأس تصنيف تسلسلي. يُشكّل رأس التصنيف التسلسلي طبقة خطية فوق المخرجات المجمعة.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import DistilBertForSequenceClassification
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = DistilBertForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained("distilbert/distilbert-base-uncased")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
أعد استخدام هذا نقطة التحقق هذه لمهمة أخرى بسهولة، وذلك بتغيير رأس النموذج.ففي مهمة الإجابة على الأسئلة، ستستخدم رأس النموذج [`DistilBertForQuestionAnswering`]. رأس الإجابة على الأسئلة مشابه لرأس التصنيف التسلسلي باستثناء أنه طبقة خطية فوق مخرجات الحالات الكامنة.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import DistilBertForQuestionAnswering
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = DistilBertForQuestionAnswering.from_pretrained("distilbert/distilbert-base-uncased")
|
||||
```
|
||||
</pt>
|
||||
<tf>
|
||||
على سبيل المثال، [`TFDistilBertForSequenceClassification`] هو نموذج DistilBERT الأساسي برأس تصنيف تسلسل. رأس التصنيف التسلسلي هو طبقة خطية أعلى المخرجات المجمعة.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import TFDistilBertForSequenceClassification
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tf_model = TFDistilBertForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained("distilbert/distilbert-base-uncased")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
أعد استخدام هذا نقطة التحقق لمهمة أخرى عن طريق التبديل إلى رأس نموذج مختلف. لمهمة الإجابة على الأسئلة، ستستخدم رأس النموذج [`TFDistilBertForQuestionAnswering`]. رأس الإجابة على الأسئلة مشابه لرأس التصنيف التسلسلي باستثناء أنه طبقة خطية أعلى حالات الإخراج المخفية.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import TFDistilBertForQuestionAnswering
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tf_model = TFDistilBertForQuestionAnswering.from_pretrained("distilbert/distilbert-base-uncased")
|
||||
```
|
||||
</tf>
|
||||
</frameworkcontent>
|
||||
|
||||
## مجزئ النصوص
|
||||
|
||||
الفئة الأساسية الأخيرة التي تحتاجها قبل استخدام نموذج للبيانات النصية هي [مجزئ النصوص](main_classes/tokenizer) لتحويل النص الخام إلى تنسورات (tensors). هناك نوعان من المحولات الرموز التي يمكنك استخدامها مع 🤗 Transformers:
|
||||
|
||||
- [`PreTrainedTokenizer`]: تنفيذ Python لمجزئ النصوص.
|
||||
- [`PreTrainedTokenizerFast`]: مجزئ النصوص من مكتبة [🤗 Tokenizer](https://huggingface.co/docs/tokenizers/python/latest/) المُبنية على لغة Rust. هذا النوع من المجزئات أسرع بكثير، خاصةً عند معالجة دفعات النصوص، وذلك بفضل تصميمه بلغة Rust. كما يوفر مجزئ النصوص السريع طرقًا إضافية مثل *مخطط الإزاحة* الذي يُطابق الرموز بكلماتها أو أحرفها الأصلية.
|
||||
|
||||
يدعم كلا النوعين من المجزئات طرقًا شائعة مثل الترميز وفك الترميز، وإضافة رموز جديدة، وإدارة الرموز الخاصة.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
لا يدعم كل نموذج مجزئ النصوص سريع. الق نظرة على هذا [جدول](index#supported-frameworks) للتحقق مما إذا كان النموذج يحتوي على دعم مجزئ النصوص سريع.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
إذا دربت مجزئ النصوص خاص بك، فيمكنك إنشاء واحد من *قاموسك*:```
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import DistilBertTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
>>> my_tokenizer = DistilBertTokenizer(vocab_file="my_vocab_file.txt"، do_lower_case=False، padding_side="left")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
من المهم أن تتذكر أن قاموس مجزئ النصوص المُخصص سيكون مختلفًا عن قاموس مجزئ النصوص نموذج مُدرّب مسبقًا. يجب عليك استخدام قاموس نموذج مُدرّب مسبقًا إذا كنت تستخدم نموذجًا مُدرّبًا مسبقًا، وإلا فلن تكون المدخلات ذات معنى. قم بإنشاء مجزئ النصوص باستخدام قاموس نموذج مُدرّب مسبقًا باستخدام فئة [`DistilBertTokenizer`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import DistilBertTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
>>> slow_tokenizer = DistilBertTokenizer.from_pretrained("distilbert/distilbert-base-uncased")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
قم بإنشاء مجزئ نصوص سريع باستخدام فئة [`DistilBertTokenizerFast`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import DistilBertTokenizerFast
|
||||
|
||||
>>> fast_tokenizer = DistilBertTokenizerFast.from_pretrained("distilbert/distilbert-base-uncased")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
افتراضيًا، سيحاول [`AutoTokenizer`] تحميل مجزئ نصوص سريع. يمكنك تعطيل هذا السلوك عن طريق تعيين `use_fast=False` في `from_pretrained`.
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## معالج الصور
|
||||
|
||||
يعالج معالج الصور بيانات الرؤية. وهو يرث من الفئة الأساسية [`~image_processing_utils.ImageProcessingMixin`].
|
||||
|
||||
لبناء معالج صور خاص بالنموذج المستخدم، أنشئ مثلاً مُعالج [`ViTImageProcessor`] افتراضيًا إذا كنت تستخدم [ViT](model_doc/vit) لتصنيف الصور:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import ViTImageProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
>>> vit_extractor = ViTImageProcessor()
|
||||
>>> print(vit_extractor)
|
||||
ViTImageProcessor {
|
||||
"do_normalize": true,
|
||||
"do_resize": true,
|
||||
"image_processor_type": "ViTImageProcessor",
|
||||
"image_mean": [
|
||||
0.5,
|
||||
0.5,
|
||||
0.5
|
||||
],
|
||||
"image_std": [
|
||||
0.5,
|
||||
0.5,
|
||||
0.5
|
||||
],
|
||||
"resample": 2,
|
||||
"size": 224
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
إذا كنت لا تبحث عن أي تخصيص، فما عليك سوى استخدام طريقة `from_pretrained` لتحميل معلمات معالج الصور الافتراضية للنموذج.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
عدل أيًا من معلمات [`ViTImageProcessor`] لإنشاء معالج الصور المخصص الخاص بك:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import ViTImageProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
>>> my_vit_extractor = ViTImageProcessor(resample="PIL.Image.BOX", do_normalize=False, image_mean=[0.3, 0.3, 0.3])
|
||||
>>> print(my_vit_extractor)
|
||||
ViTImageProcessor {
|
||||
"do_normalize": false,
|
||||
"do_resize": true,
|
||||
"image_processor_type": "ViTImageProcessor",
|
||||
"image_mean": [
|
||||
0.3,
|
||||
0.3,
|
||||
0.3
|
||||
],
|
||||
"image_std": [
|
||||
0.5,
|
||||
0.5,
|
||||
0.5
|
||||
],
|
||||
"resample": "PIL.Image.BOX",
|
||||
"size": 224
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
## العمود الفقري
|
||||
|
||||
<div style="text-align: center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/transformers/Backbone.png">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
تتكون نماذج رؤية الحاسب من جزء أساسي، وجزء وسيط، وجزء معالجة نهائي. يستخرج الجزء الأساسي الميزات من صورة الإدخال، ويجمع الجزء الوسيط هذه الميزات المستخرجة ويعززها، ويُستخدم الجزء النهائي للمهمة الرئيسية (مثل اكتشاف الأجسام). ابدأ عبتهيئة الجزء الأساسي في تكوين النموذج وحدد ما إذا كنت تريد تحميل أوزان مدربة مسبقًا أو أوزانًا عشوائية. بعد ذلك، يمكنك تمرير تكوين النموذج إلى جزء المعالجة النهائي.
|
||||
|
||||
على سبيل المثال، لتحميل [ResNet](../model_doc/resnet) backbone في نموذج [MaskFormer](../model_doc/maskformer) مع رأس تجزئة مثيل:
|
||||
|
||||
<hfoptions id="backbone">
|
||||
<hfoption id="pretrained weights">
|
||||
|
||||
قم بتعيين `use_pretrained_backbone=True` لتحميل الأوزان المسبقة التدريب لـ ResNet للعمود الفقري.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import MaskFormerConfig, MaskFormerForInstanceSegmentation
|
||||
|
||||
config = MaskFormerConfig(backbone="microsoft/resnet-50", use_pretrained_backbone=True) # تكوين الجزء الأساسي والجزء الوسيط
|
||||
model = MaskFormerForInstanceSegmentation(config) # جزء المعالجة النهائي
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="random weights">
|
||||
|
||||
قم بتعيين `use_pretrained_backbone=False` لتهيئة جزء ResNet الأساسي بشكل عشوائي.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import MaskFormerConfig, MaskFormerForInstanceSegmentation
|
||||
|
||||
config = MaskFormerConfig(backbone="microsoft/resnet-50", use_pretrained_backbone=False) # تكوين الجزء الأساسي والجزء الوسيط
|
||||
model = MaskFormerForInstanceSegmentation(config) # جزء المعالجة النهائي
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
يمكنك أيضًا تحميل تكوين الجزء الأساسي بشكل منفصل، ثم تمريره إلى تكوين النموذج.```
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import MaskFormerConfig, MaskFormerForInstanceSegmentation, ResNetConfig
|
||||
|
||||
backbone_config = ResNetConfig()
|
||||
config = MaskFormerConfig(backbone_config=backbone_config)
|
||||
model = MaskFormerForInstanceSegmentation(config)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="timm backbone">
|
||||
|
||||
يتم تحميل نماذج [timm](https://hf.co/docs/timm/index) داخل نموذج باستخدام `use_timm_backbone=True` أو باستخدام [`TimmBackbone`] و [`TimmBackboneConfig`].
|
||||
|
||||
استخدم `use_timm_backbone=True` و `use_pretrained_backbone=True` لتحميل أوزان timm المُدرّبة مسبقًا للجزء الأساسي.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import MaskFormerConfig, MaskFormerForInstanceSegmentation
|
||||
|
||||
config = MaskFormerConfig(backbone="resnet50", use_pretrained_backbone=True, use_timm_backbone=True) # تكوين الجزء الأساسي والجزء الوسيط
|
||||
model = MaskFormerForInstanceSegmentation(config) # جزء المعالجة النهائي
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
قم بتعيين `use_timm_backbone=True` و `use_pretrained_backbone=False` لتحميل عمود فقري timm مبدئي عشوائي.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import MaskFormerConfig, MaskFormerForInstanceSegmentation
|
||||
|
||||
config = MaskFormerConfig(backbone="resnet50", use_pretrained_backbone=False, use_timm_backbone=True) # تكوين الجزء الأساسي والجزء الوسيط
|
||||
model = MaskFormerForInstanceSegmentation(config) # جزء المعالجة النهائي
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
يمكنك أيضًا تحميل تكوين الجزء الأساسي واستخدامه لإنشاء `TimmBackbone` أو تمريره إلى تكوين النموذج. سيتم تحميلأوزان الجزء الأساسي لـ Timm المُدرّبة مسبقًا افتراضيًا. عيّن `use_pretrained_backbone=False` لتحميل الأوزان المبدئية العشوائية.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import TimmBackboneConfig, TimmBackbone
|
||||
|
||||
backbone_config = TimmBackboneConfig("resnet50", use_pretrained_backbone=False)
|
||||
|
||||
# قم بإنشاء مثيل من العمود الفقري
|
||||
backbone = TimmBackbone(config=backbone_config)
|
||||
|
||||
# قم بإنشاء نموذج باستخدام عمود فقري timm
|
||||
from transformers import MaskFormerConfig, MaskFormerForInstanceSegmentation
|
||||
|
||||
config = MaskFormerConfig(backbone_config=backbone_config)
|
||||
model = MaskFormerForInstanceSegmentation(config)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## مستخرج الميزات
|
||||
|
||||
يقوم مُستخرج الميزات بمعالجة المدخلات الصوتية. يرث من فئة الأساس [`~feature_extraction_utils.FeatureExtractionMixin`]، وقد يرث أيضًا من فئة [`SequenceFeatureExtractor`] لمعالجة المدخلات الصوتية.
|
||||
|
||||
للاستخدام، قم بإنشاء مستخرج ميزات مرتبط بالنموذج الذي تستخدمه. على سبيل المثال، قم بإنشاء مستخرج ميزات Wav2Vec2 الافتراضي إذا كنت تستخدم [Wav2Vec2](model_doc/wav2vec2) لتصنيف الصوت:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import Wav2Vec2FeatureExtractor
|
||||
|
||||
>>> w2v2_extractor = Wav2Vec2FeatureExtractor()
|
||||
>>> print(w2v2_extractor)
|
||||
Wav2Vec2FeatureExtractor {
|
||||
"do_normalize": true,
|
||||
"feature_extractor_type": "Wav2Vec2FeatureExtractor",
|
||||
"feature_size": 1,
|
||||
"padding_side": "right",
|
||||
"padding_value": 0.0,
|
||||
"return_attention_mask": false,
|
||||
"sampling_rate": 16000
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
إذا لم تكن بحاجة لأي تخصيص، فاستخدم فقط طريقة `from_pretrained` لتحميل معلمات مستخرج الميزات الافتراضية للنموذج.
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
قم بتعديل أي من معلمات [`Wav2Vec2FeatureExtractor`] لإنشاء مستخرج ميزات مخصص:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import Wav2Vec2FeatureExtractor
|
||||
|
||||
>>> w2v2_extractor = Wav2Vec2FeatureExtractor(sampling_rate=8000، do_normalize=False)
|
||||
>>> print(w2v2_extractor)
|
||||
Wav2Vec2FeatureExtractor {
|
||||
"do_normalize": false,
|
||||
"feature_extractor_type": "Wav2Vec2FeatureExtractor"،
|
||||
"feature_size": 1،
|
||||
"padding_side": "right"،
|
||||
"padding_value": 0.0،
|
||||
"return_attention_mask": false،
|
||||
"sampling_rate": 8000
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## المعالج
|
||||
|
||||
بالنسبة للنماذج التي تدعم مهام الوسائط المتعددة، توفر مكتبة 🤗 Transformers فئة معالج تجمع بفاعلية فئات المعالجة مثل مستخرج الميزات ومقسّم الرموز في كائن واحد. على سبيل المثال، دعنا نستخدم [`Wav2Vec2Processor`] لمهمة التعرف الآلي على الكلام (ASR). تقوم مهمة ASR بتحويل الصوت إلى نص، لذلك ستحتاج إلى مستخرج ميزات ومقسّم رموز.
|
||||
|
||||
قم بإنشاء مستخرج ميزات لمعالجة المدخلات الصوتية:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import Wav2Vec2FeatureExtractor
|
||||
|
||||
>>> feature_extractor = Wav2Vec2FeatureExtractor(padding_value=1.0, do_normalize=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
قم بإنشاء مقسّم رموز لمعالجة المدخلات النصية:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import Wav2Vec2CTCTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = Wav2Vec2CTCTokenizer(vocab_file="my_vocab_file.txt")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
قم بدمج مستخرج الميزات ومقسّم الرموز في [`Wav2Vec2Processor`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import Wav2Vec2Processor
|
||||
|
||||
>>> processor = Wav2Vec2Processor(feature_extractor=feature_extractor, tokenizer=tokenizer)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
باستخدام فئتين أساسيتين - التكوين والنموذج - بالإضافة إلى فئة معالجة مسبق (مقسّم رموز أو معالج صورة أو مستخرج ميزات أو معالج)، يمكنك إنشاء أي من النماذج التي تدعمها مكتبة 🤗 Transformers. يمكن تكوين كل من هذه الفئات الأساسية، مما يسمح لك باستخدام السمات المطلوبة. يمكنك بسهولة تهيئة نموذج للتدريب أو تعديل نموذج مدرب مسبقاً لإجراء ضبط دقيق.
|
||||
@ -1,323 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# بناء نماذج مخصصة
|
||||
|
||||
تم تصميم مكتبة 🤗 Transformers لتكون قابلة للتوسيع بسهولة. كل نموذج مُشفّر بالكامل في مجلد فرعي معين بالمستودع، دون أي تجريد، لذلك يمكنك بسهولة نسخ ملف النمذجة وتعديله وفقًا لاحتياجاتك.
|
||||
|
||||
إذا كنت تُنشئ نموذجًا جديدًا تمامًا، فقد يكون من الأسهل البدء من الصفر. في هذا البرنامج التعليمي، سنُرِيك كيفية كتابة نموذج مخصص وتكوينه ليُستخدم داخل Transformers، وكيفية مشاركته مع المجتمع (مع الكود الذي يعتمد عليه) بحيث يمكن لأي شخص استخدامه، حتى إذا لم يكن موجودًا في مكتبة 🤗 Transformers. سنرى كيفية البناء على المحولات ونوسّع الإطار باستخدام الأدوات التي يمكن استخدامها لتعديل سلوك الإطار (hooks) والتعليمات البرمجية المخصصة.
|
||||
|
||||
سنوضح كل هذا من خلال نموذج ResNet، بتغليف فئة ResNet من
|
||||
[مكتبة timm](https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models) داخل [`PreTrainedModel`].
|
||||
|
||||
## كتابة إعدادات مخصصة
|
||||
|
||||
لنبدأ بكتابة إعدادات النموذج. إعدادات النموذج هو كائنٌ يحتوي على جميع المعلومات اللازمة لبنائه. كما سنرى لاحقًا، يتطلب النموذج كائن `config` لتهيئته، لذا يجب أن يكون هذا الكائن كاملاً.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
تتبع النماذج في مكتبة `transformers` اتفاقية قبول كائن `config` في دالة `__init__` الخاصة بها، ثم تمرر كائن `config` بالكامل إلى الطبقات الفرعية في النموذج، بدلاً من تقسيمه إلى معامﻻت متعددة. يؤدي كتابة نموذجك بهذا الأسلوب إلى كود أبسط مع "مصدر حقيقة" واضح لأي فرط معلمات، كما يسهل إعادة استخدام الكود من نماذج أخرى في `transformers`.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
في مثالنا، سنعدّل بعض الوسائط في فئة ResNet التي قد نرغب في ضبطها. ستعطينا التكوينات المختلفة أنواع ResNets المختلفة الممكنة. سنقوم بتخزين هذه الوسائط بعد التحقق من صحته.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import PretrainedConfig
|
||||
from typing import List
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class ResnetConfig(PretrainedConfig):
|
||||
model_type = "resnet"
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
block_type="bottleneck",
|
||||
layers: List[int] = [3, 4, 6, 3],
|
||||
num_classes: int = 1000,
|
||||
input_channels: int = 3,
|
||||
cardinality: int = 1,
|
||||
base_width: int = 64,
|
||||
stem_width: int = 64,
|
||||
stem_type: str = "",
|
||||
avg_down: bool = False,
|
||||
**kwargs,
|
||||
):
|
||||
if block_type not in ["basic", "bottleneck"]:
|
||||
raise ValueError(f"`block_type` must be 'basic' or bottleneck', got {block_type}.")
|
||||
if stem_type not in ["", "deep", "deep-tiered"]:
|
||||
raise ValueError(f"`stem_type` must be '', 'deep' or 'deep-tiered', got {stem_type}.")
|
||||
|
||||
self.block_type = block_type
|
||||
self.layers = layers
|
||||
self.num_classes = num_classes
|
||||
self.input_channels = input_channels
|
||||
self.cardinality = cardinality
|
||||
self.base_width = base_width
|
||||
self.stem_width = stem_width
|
||||
self.stem_type = stem_type
|
||||
self.avg_down = avg_down
|
||||
super().__init__(**kwargs)
|
||||
```
|
||||
الأشياء الثلاثة المهمة التي يجب تذكرها عند كتابة تكوينك الخاص هي:
|
||||
|
||||
- يجب أن ترث من `PretrainedConfig`،
|
||||
- يجب أن تقبل دالة `__init__` الخاصة بـ `PretrainedConfig` أي معامﻻت إضافية kwargs،
|
||||
- يجب تمرير هذه المعامﻻت الإضافية إلى دالة `__init__` فى الفئة الأساسية الاعلى.
|
||||
|
||||
يضمن الإرث حصولك على جميع الوظائف من مكتبة 🤗 Transformers، في حين أن القيدين التانى والثالث يأتيان من حقيقة أن `PretrainedConfig` لديه المزيد من الحقول أكثر من تلك التي تقوم بتعيينها. عند إعادة تحميل تكوين باستخدام طريقة `from_pretrained`، يجب أن يقبل تكوينك هذه الحقول ثم إرسالها إلى الفئة الأساسية الأعلى.
|
||||
|
||||
تحديد `model_type` لتكوينك (هنا `model_type="resnet"`) ليس إلزاميًا، ما لم ترغب في
|
||||
تسجيل نموذجك باستخدام الفئات التلقائية (راجع القسم الأخير).
|
||||
|
||||
مع القيام بذلك، يمكنك بسهولة إنشاء تكوينك وحفظه مثلما تفعل مع أي تكوين نموذج آخر في
|
||||
المكتبة. إليك كيفية إنشاء تكوين resnet50d وحفظه:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
resnet50d_config = ResnetConfig(block_type="bottleneck", stem_width=32, stem_type="deep", avg_down=True)
|
||||
resnet50d_config.save_pretrained("custom-resnet")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
سيؤدي هذا إلى حفظ ملف باسم `config.json` داخل مجلد `custom-resnet`. يمكنك بعد ذلك إعادة تحميل تكوينك باستخدام
|
||||
طريقة `from_pretrained`:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
resnet50d_config = ResnetConfig.from_pretrained("custom-resnet")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
يمكنك أيضًا استخدام أي طريقة أخرى من فئة [`PretrainedConfig`]، مثل [`~PretrainedConfig.push_to_hub`] لتحميل تكوينك مباشرة إلى Hub.
|
||||
|
||||
## كتابة نموذج مخصص
|
||||
|
||||
الآن بعد أن أصبح لدينا تكوين ResNet، يمكننا المتابعة لإنشاء نموذجين: الأول يستخرج الميزات المخفية من دفعة من الصور (مثل [`BertModel`]) والآخر مناسب لتصنيف الصور (مثل [`BertForSequenceClassification`]).
|
||||
|
||||
كما ذكرنا سابقًا، سنقوم ببناء نموذج مبسط لتسهيل الفهم في هذا المثال. الخطوة الوحيدة المطلوبة قبل كتابة هذه الفئة هي لربط أنواع وحدات البناء بفئات ذات وحدات بناء فعلية. بعد ذلك، يُعرّف النموذج من خلال التكوين عبر تمرير كل شيء إلى فئة `ResNet`:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import PreTrainedModel
|
||||
from timm.models.resnet import BasicBlock, Bottleneck, ResNet
|
||||
from .configuration_resnet import ResnetConfig
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
BLOCK_MAPPING = {"basic": BasicBlock, "bottleneck": Bottleneck}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class ResnetModel(PreTrainedModel):
|
||||
config_class = ResnetConfig
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, config):
|
||||
super().__init__(config)
|
||||
block_layer = BLOCK_MAPPING[config.block_type]
|
||||
self.model = ResNet(
|
||||
block_layer,
|
||||
config.layers,
|
||||
num_classes=config.num_classes,
|
||||
in_chans=config.input_channels,
|
||||
cardinality=config.cardinality,
|
||||
base_width=config.base_width,
|
||||
stem_width=config.stem_width,
|
||||
stem_type=config.stem_type,
|
||||
avg_down=config.avg_down,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, tensor):
|
||||
return self.model.forward_features(tensor)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
بالنسبة للنموذج الذي سيصنف الصور، فإننا نغير فقط طريقة التقديم:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class ResnetModelForImageClassification(PreTrainedModel):
|
||||
config_class = ResnetConfig
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, config):
|
||||
super().__init__(config)
|
||||
block_layer = BLOCK_MAPPING[config.block_type]
|
||||
self.model = ResNet(
|
||||
block_layer,
|
||||
config.layers,
|
||||
num_classes=config.num_classes,
|
||||
in_chans=config.input_channels,
|
||||
cardinality=config.cardinality,
|
||||
base_width=config.base_width,
|
||||
stem_width=config.stem_width,
|
||||
stem_type=config.stem_type,
|
||||
avg_down=config.avg_down,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, tensor, labels=None):
|
||||
logits = self.model(tensor)
|
||||
if labels is not None:
|
||||
loss = torch.nn.cross_entropy(logits, labels)
|
||||
return {"loss": loss, "logits": logits}
|
||||
return {"logits": logits}
|
||||
```
|
||||
في كلتا الحالتين، لاحظ كيف نرث من `PreTrainedModel` ونستدعي مُهيئ الفئة الرئيسية باستخدام `config` (كما تفعل عند إنشاء وحدة `torch.nn.Module` عادية). ليس من الضروري تعريف `config_class` إلا إذا كنت ترغب في تسجيل نموذجك مع الفئات التلقائية (راجع القسم الأخير).
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
إذا كان نموذجك مشابهًا جدًا لنموذج داخل المكتبة، فيمكنك إعادة استخدام نفس التكوين مثل هذا النموذج.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
يمكن لنموذجك أن يعيد أي شيء تريده، ولكن إعادة قاموس مثلما فعلنا لـ
|
||||
`ResnetModelForImageClassification`، مع تضمين الخسارة عند تمرير العلامات، سيجعل نموذجك قابلًا للاستخدام مباشرة داخل فئة [`Trainer`]. يعد استخدام تنسيق إخراج آخر أمرًا جيدًا طالما أنك تخطط لاستخدام حلقة تدريب خاصة بك أو مكتبة أخرى للتدريب.
|
||||
|
||||
الآن بعد أن أصبح لدينا فئة النموذج، دعنا ننشئ واحدة:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
resnet50d = ResnetModelForImageClassification(resnet50d_config)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
يمكنك استخدام أي من طرق فئة [`PreTrainedModel`]، مثل [`~PreTrainedModel.save_pretrained`] أو
|
||||
[`~PreTrainedModel.push_to_hub`]. سنستخدم الثاني في القسم التالي، وسنرى كيفية دفع أوزان النموذج مع كود نموذجنا. ولكن أولاً، دعنا نحمل بعض الأوزان المُعلمة مسبقًا داخل نموذجنا.
|
||||
|
||||
في حالة الاستخدام الخاصة بك، فمن المحتمل أن تقوم بتدريب نموذجك المخصص على بياناتك الخاصة. للانتقال بسرعة خلال هذا البرنامج التعليمي،
|
||||
سنستخدم الإصدار المُعلم مسبقًا من resnet50d. نظرًا لأن نموذجنا هو مجرد غلاف حوله، فمن السهل نقل هذه الأوزان:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
import timm
|
||||
|
||||
pretrained_model = timm.create_model("resnet50d", pretrained=True)
|
||||
resnet50d.model.load_state_dict(pretrained_model.state_dict())
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
الآن دعونا نرى كيفية التأكد من أنه عند قيامنا بـ [`~PreTrainedModel.save_pretrained`] أو [`~PreTrainedModel.push_to_hub`]، يتم حفظ كود النموذج.
|
||||
|
||||
## تسجيل نموذج مع كود مخصص للفئات التلقائية
|
||||
|
||||
إذا كنت تكتب مكتبة توسع 🤗 Transformers، فقد ترغب في توسيع الفئات التلقائية لتشمل نموذجك الخاص. يختلف هذا عن نشر الكود إلى Hub بمعنى أن المستخدمين سيحتاجون إلى استيراد مكتبتك للحصول على النماذج المخصصة (على عكس تنزيل كود النموذج تلقائيًا من Hub).
|
||||
|
||||
ما دام تكوينك يحتوي على معامل `model_type` مختلفة عن أنواع النماذج الحالية، وأن فئات نماذجك لديك لديها الخصائص الصحيحة `config_class`، فيمكنك ببساطة إضافتها إلى الفئات التلقائية مثل هذا:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import AutoConfig, AutoModel, AutoModelForImageClassification
|
||||
|
||||
AutoConfig.register("resnet", ResnetConfig)
|
||||
AutoModel.register(ResnetConfig, ResnetModel)
|
||||
AutoModelForImageClassification.register(ResnetConfig, ResnetModelForImageClassification)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
لاحظ أن الحجة الأولى المستخدمة عند تسجيل تكوينك المخصص لـ [`AutoConfig`] يجب أن تتطابق مع `model_type`
|
||||
من تكوينك المخصص، والحجة الأولى المستخدمة عند تسجيل نماذجك المخصصة لأي فئة نموذج تلقائي يجب
|
||||
أن تتطابق مع `config_class` من تلك النماذج.
|
||||
|
||||
## إرسال الكود إلى Hub
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
هذا API تجريبي وقد يكون له بعض التغييرات الطفيفة في الإصدارات القادمة.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
أولاً، تأكد من تعريف نموذجك بالكامل في ملف `.py`. يمكن أن يعتمد على الاستيراد النسبي لملفات أخرى طالما أن جميع الملفات موجودة في نفس الدليل (لا ندعم الوحدات الفرعية لهذه الميزة حتى الآن). في مثالنا، سنحدد ملف `modeling_resnet.py` وملف `configuration_resnet.py` في مجلد باسم "resnet_model" في دليل العمل الحالي. يحتوي ملف التكوين على كود لـ `ResnetConfig` ويحتوي ملف النمذجة على كود لـ `ResnetModel` و`ResnetModelForImageClassification`.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
.
|
||||
└── resnet_model
|
||||
├── __init__.py
|
||||
├── configuration_resnet.py
|
||||
└── modeling_resnet.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
يمكن أن يكون ملف `__init__.py` فارغًا، فهو موجود فقط حتى يتمكن Python من اكتشاف أن `resnet_model` يمكن استخدامه كموديل.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
إذا كنت تقوم بنسخ ملفات النمذجة من المكتبة، فسوف تحتاج إلى استبدال جميع الواردات النسبية في أعلى الملف
|
||||
لاستيرادها من حزمة `transformers`.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
لاحظ أنه يمكنك إعادة استخدام (أو توسيع) تكوين/نموذج موجود.
|
||||
|
||||
لمشاركة نموذجك مع المجتمع، اتبع الخطوات التالية: أولاً، قم باستيراد نموذج ResNet والتكوين من الملفات التي تم إنشاؤها حديثًا:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from resnet_model.configuration_resnet import ResnetConfig
|
||||
from resnet_model.modeling_resnet import ResnetModel, ResnetModelForImageClassification
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
بعد ذلك، يجب عليك إخبار المكتبة بأنك تريد نسخ ملفات الكود الخاصة بهذه الكائنات عند استخدام طريقة `save_pretrained`
|
||||
وتسجيلها بشكل صحيح باستخدام فئة تلقائية (خاصة للنماذج)، ما عليك سوى تشغيل:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
ResnetConfig.register_for_auto_class()
|
||||
ResnetModel.register_for_auto_class("AutoModel")
|
||||
ResnetModelForImageClassification.register_for_auto_class("AutoModelForImageClassification")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
لاحظ أنه لا توجد حاجة لتحديد فئة تلقائية للتكوين (هناك فئة تلقائية واحدة فقط لها،
|
||||
[`AutoConfig`]) ولكن الأمر يختلف بالنسبة للنماذج. قد يكون نموذجك المخصص مناسبًا للعديد من المهام المختلفة، لذلك يجب
|
||||
تحديد أي من الفئات التلقائية هو الصحيح لنموذجك.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
استخدم `register_for_auto_class()` إذا كنت تريد نسخ ملفات الكود. إذا كنت تفضل استخدام الكود على Hub من مستودع آخر،
|
||||
فلا تحتاج إلى استدعائه. في الحالات التي يوجد فيها أكثر من فئة تلقائية واحدة، يمكنك تعديل ملف `config.json` مباشرة باستخدام
|
||||
الهيكل التالي:
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
"auto_map": {
|
||||
"AutoConfig": "<your-repo-name>--<config-name>",
|
||||
"AutoModel": "<your-repo-name>--<config-name>",
|
||||
"AutoModelFor<Task>": "<your-repo-name>--<config-name>",
|
||||
},
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
بعد ذلك، دعنا نقوم بإنشاء التكوين والنماذج كما فعلنا من قبل:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
resnet50d_config = ResnetConfig(block_type="bottleneck", stem_width=32, stem_type="deep", avg_down=True)
|
||||
resnet50d = ResnetModelForImageClassification(resnet50d_config)
|
||||
|
||||
pretrained_model = timm.create_model("resnet50d", pretrained=True)
|
||||
resnet50d.model.load_state_dict(pretrained_model.state_dict())
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
الآن لإرسال النموذج إلى Hub، تأكد من تسجيل الدخول. إما تشغيل في المحطة الأوامر الطرفية الخاصة بك:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
huggingface-cli login
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
أو من دفتر ملاحظات:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from huggingface_hub import notebook_login
|
||||
|
||||
notebook_login()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
يمكنك بعد ذلك الضغط على مساحة الاسم الخاصة بك (أو منظمة أنت عضو فيها) مثل هذا:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
resnet50d.push_to_hub("custom-resnet50d")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
بالإضافة إلى أوزان النمذجة والتكوين بتنسيق json، فقد قام هذا أيضًا بنسخ ملفات النمذجة والتكوين `.py` في مجلد `custom-resnet50d` وتحميل النتيجة إلى Hub. يمكنك التحقق من النتيجة في هذا [مستودع النموذج](https://huggingface.co/sgugger/custom-resnet50d).
|
||||
|
||||
راجع [البرنامج التعليمي للمشاركة](model_sharing) لمزيد من المعلومات حول طريقة الدفع إلى المحور.
|
||||
|
||||
### استخدام نموذج مع كود مخصص
|
||||
|
||||
يمكنك استخدام أي تكوين أو نموذج أو مقسم لغوي مع ملفات برمجة مخصصة في مستودعه باستخدام الفئات التلقائية و دالة `from_pretrained`.تُفحص جميع الملفات والرموز المرفوع إلى Hub بحثًا عن البرامج الضارة (راجع وثائق [أمان Hub](https://huggingface.co/docs/hub/security#malware-scanning) لمزيد من المعلومات)، ولكن يجب عليك مراجعة كود النموذج والمؤلف لتجنب تنفيذ التعليمات البرمجية الضارة على جهازك. لتفعيل نموذج يحتوي على شفرة برمجية مخصصة، عيّن `trust_remote_code=True`:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForImageClassification
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModelForImageClassification.from_pretrained("sgugger/custom-resnet50d", trust_remote_code=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
يُنصح بشدة بتحديد رقم إصدار (commit hash) كـ `revision` للتأكد من عدم تعديل مؤلف النموذج للشفرة لاحقًابإضافة أسطر ضارة (إلا إذا كنت تثق تمامًا بمؤلفي النموذج):
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
commit_hash = "ed94a7c6247d8aedce4647f00f20de6875b5b292"
|
||||
model = AutoModelForImageClassification.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"sgugger/custom-resnet50d"، trust_remote_code=True، revision=commit_hash
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
لاحظ وجود زرّ لنسخ رقم إصدار بسهولة عند تصفح سجل التزامات مستودع النموذج على منصة Hugging Face.
|
||||
@ -1,51 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# استخدام مجزئيات النصوص من 🤗 Tokenizers
|
||||
|
||||
يعتمد [`PreTrainedTokenizerFast`] على مكتبة [🤗 Tokenizers](https://huggingface.co/docs/tokenizers). يمكن تحميل المجزئات اللغويين الذين تم الحصول عليهم من مكتبة 🤗 Tokenizers ببساطة شديدة في 🤗 Transformers.
|
||||
|
||||
قبل الدخول في التفاصيل، دعونا نبدأ أولاً بإنشاء مُجزىء لغوي تجريبي في بضع سطور:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from tokenizers import Tokenizer
|
||||
>>> from tokenizers.models import BPE
|
||||
>>> from tokenizers.trainers import BpeTrainer
|
||||
>>> from tokenizers.pre_tokenizers import Whitespace
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenizer = Tokenizer(BPE(unk_token="[UNK]"))
|
||||
>>> trainer = BpeTrainer(special_tokens=["[UNK]", "[CLS]", "[SEP]", "[PAD]", "[MASK]"])
|
||||
|
||||
>>> tokenizer.pre_tokenizer = Whitespace()
|
||||
>>> files = [...]
|
||||
>>> tokenizer.train(files, trainer)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
الآن لدينا مُجزىء لغوي مدرب على الملفات التي حددناها. يمكننا إما الاستمرار في استخدامه في وقت التشغيل هذا، أو حفظه في ملف JSON لإعادة استخدامه لاحقًا.
|
||||
|
||||
## تحميل مُجزئ النّصوص مُباشرةً
|
||||
|
||||
دعونا نرى كيف يمكننا الاستفادة من كائن (مُجزئ النصوص) في مكتبة 🤗 Transformers. تسمح فئة [`PreTrainedTokenizerFast`] سهولة إنشاء *tokenizer*، من خلال قبول كائن *المُجزئ النصوص* مُهيّأ مُسبقًا كمعامل:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import PreTrainedTokenizerFast
|
||||
|
||||
>>> fast_tokenizer = PreTrainedTokenizerFast(tokenizer_object=tokenizer)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
يمكن الآن استخدام هذا الكائن مع جميع الطرق المُشتركة بين مُجزّئي النّصوص لـ 🤗 Transformers! انتقل إلى [صفحة مُجزّئ النّصوص](main_classes/tokenizer) لمزيد من المعلومات.
|
||||
|
||||
## التحميل من ملف JSON
|
||||
|
||||
لتحميل مُجزّئ النص من ملف JSON، دعونا نبدأ أولاً بحفظ مُجزّئ النّصوص:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> tokenizer.save("tokenizer.json")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
يمكن تمرير المسار الذي حفظنا به هذا الملف إلى طريقة تهيئة [`PreTrainedTokenizerFast`] باستخدام المُعامل `tokenizer_file`:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from transformers import PreTrainedTokenizerFast
|
||||
|
||||
>>> fast_tokenizer = PreTrainedTokenizerFast(tokenizer_file="tokenizer.json")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
يمكن الآن استخدام هذا الكائن مع جميع الطرق التي تشترك فيها مُجزّئي النّصوص لـ 🤗 Transformers! انتقل إلى [صفحة مُجزّئ النص](main_classes/tokenizer) لمزيد من المعلومات.
|
||||
@ -1,89 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# GGUF وتفاعلها مع المحولات
|
||||
|
||||
تُستخدم صيغة ملف GGUF لتخزين النماذج للاستدلال باستخدام [GGML](https://github.com/ggerganov/ggml) والمكتبات الأخرى التي تعتمد عليه، مثل [llama.cpp](https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp) أو [whisper.cpp](https://github.com/ggerganov/whisper.cpp) الشهيرة جدًا.
|
||||
|
||||
إنها صيغة ملف [مدعومة من قبل Hugging Face Hub](https://huggingface.co/docs/hub/en/gguf) مع ميزات تسمح بالفحص السريع للموترات والبيانات الوصفية داخل الملف.
|
||||
|
||||
تم تصميم تنسيق الملف هذا كـ "تنسيق ملف واحد" حيث يحتوي ملف واحد عادةً على كل من سمات التكوين ومفردات المجزىء اللغوي والخصائص الأخرى، بالإضافة إلى جميع الموترات التي سيتم تحميلها في النموذج. تأتي هذه الملفات بتنسيقات مختلفة وفقًا لنوع التكميم في الملف. نلقي نظرة موجزة على بعضها [هنا](https://huggingface.co/docs/hub/en/gguf#quantization-types).
|
||||
|
||||
## الدعم داخل المحولات
|
||||
|
||||
أضفنا القدرة على تحميل ملفات `gguf` داخل `المحولات` لتوفير قدرات تدريب/ضبط إضافية لنماذج gguf، قبل إعادة تحويل تلك النماذج إلى `gguf` لاستخدامها داخل نظام `ggml`. عند تحميل نموذج، نقوم أولاً بإلغاء تكميمه إلى fp32، قبل تحميل الأوزان لاستخدامها في PyTorch.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!NOTE]
|
||||
> لا يزال الدعم تجريبيًا للغاية ونرحب بالمساهمات من أجل ترسيخه عبر أنواع التكميم وبنى النماذج.
|
||||
|
||||
فيما يلي، بنيات النماذج وأنواع التكميم المدعومة:
|
||||
|
||||
### أنواع التكميم المدعومة
|
||||
|
||||
تُحدد أنواع التكميم المدعومة مبدئيًا وفقًا لملفات التكميم الشائعة التي تمت مشاركتها على Hub.
|
||||
|
||||
- F32
|
||||
- F16
|
||||
- BF16
|
||||
- Q4_0
|
||||
- Q4_1
|
||||
- Q5_0
|
||||
- Q5_1
|
||||
- Q8_0
|
||||
- Q2_K
|
||||
- Q3_K
|
||||
- Q4_K
|
||||
- Q5_K
|
||||
- Q6_K
|
||||
- IQ1_S
|
||||
- IQ1_M
|
||||
- IQ2_XXS
|
||||
- IQ2_XS
|
||||
- IQ2_S
|
||||
- IQ3_XXS
|
||||
- IQ3_S
|
||||
- IQ4_XS
|
||||
- IQ4_NL
|
||||
|
||||
> [!NOTE]
|
||||
> لدعم إلغاء تكميم gguf، يلزم تثبيت `gguf>=0.10.0`.
|
||||
|
||||
### بنيات النماذج المدعومة
|
||||
|
||||
في الوقت الحالي، بنيات النماذج المدعومة هي البنيات التي كانت شائعة جدًا على Hub، وهي:
|
||||
|
||||
- LLaMa
|
||||
- Mistral
|
||||
- Qwen2
|
||||
- Qwen2Moe
|
||||
- Phi3
|
||||
- Bloom
|
||||
- Falcon
|
||||
- StableLM
|
||||
- GPT2
|
||||
- Starcoder2
|
||||
- T5
|
||||
|
||||
## مثال الاستخدام
|
||||
|
||||
لتحميل ملفات `gguf` في `transformers`، يجب تحديد معامل `gguf_file` فى دالة `from_pretrained` لكل من المُجزّئ اللغوية والنموذج. فيما يلي كيفية تحميل المُجزّئ اللغوي ونموذج، يمكن تحميلهما من نفس الملف:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM
|
||||
|
||||
model_id = "TheBloke/TinyLlama-1.1B-Chat-v1.0-GGUF"
|
||||
filename = "tinyllama-1.1b-chat-v1.0.Q6_K.gguf"
|
||||
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_id, gguf_file=filename)
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_id, gguf_file=filename)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
الآن لديك إمكانية الوصول إلى النسخة الكامل غير المكممة للنموذج في بيئة PyTorch، حيث يمكنك دمجه مع مجموعة كبيرة من الأدوات الأخرى.
|
||||
|
||||
لإعادة التحويل إلى ملف `gguf`، نوصي باستخدام ملف [`convert-hf-to-gguf.py`](https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp/blob/master/convert_hf_to_gguf.py) من llama.cpp.
|
||||
|
||||
فيما يلي كيفية إكمال البرنامج النصي أعلاه لحفظ النموذج وإعادة تصديره مرة أخرى إلى `gguf`:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
tokenizer.save_pretrained('directory')
|
||||
model.save_pretrained('directory')
|
||||
|
||||
!python ${path_to_llama_cpp}/convert-hf-to-gguf.py ${directory}
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -1,163 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# كيفية تعديل أي نموذج من نماذج Transformers
|
||||
|
||||
توفر مكتبة [🤗 Transformers](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers) مجموعة من النماذج المسبقة التدريب والأدوات لمعالجة اللغات الطبيعية، والرؤية، وما إلى ذلك. على الرغم من أن هذه النماذج تغطي مجموعة واسعة من التطبيقات، فقد تواجه حالات استخدام لا تدعمها المكتبة بشكل افتراضي. يُمكن للتخصيص أن يفتح إمكانيات جديدة، مثل إضافة طبقات جديدة، أو تعديل البنية المعمارية، أو تحسين آليات الانتباه. سيُوضح لك هذا الدليل كيفية تعديل نماذج Transformers الموجودة لتلبية احتياجاتك المحددة. الشيء الرائع هو أنك لست بحاجة إلى الخروج من إطار عمل Transformers لإجراء هذه التغييرات. ي يمكنك تعديل النماذج مباشرةً في Transformers والاستفادة من الميزات مثل [واجهة برمجة التطبيقات Trainer](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/en/main_classes/trainer)، و [PreTrainedModel](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/en/main_classes/model#transformers.PreTrainedModel)، والضبط الدقيق الفعال باستخدام أدوات مثل [PEFT](https://huggingface.co/docs/peft/index).
|
||||
|
||||
سنرشدك في هذا الدليل لكيفية تخصيص نماذج Transformers الموجودة لتلبية متطلباتك، دون فقدان مزايا الإطار. ستتعلم كيفية:
|
||||
|
||||
- تعديل بنية نموذج ما من خلال تغيير آلية الانتباه الخاصة به.
|
||||
- تطبيق تقنيات مثل Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) على مكونات نموذج محددة.
|
||||
|
||||
نحن نشجعك على المساهمة باختراقاتك الخاصة ومشاركتها هنا مع المجتمع1
|
||||
|
||||
## مثال: تعديل آلية الانتباه في نموذج Segment Anything (SAM)
|
||||
|
||||
نموذج **Segment Anything (SAM)** هو نموذج رائد في مجال تجزئة الصور. في تنفيذه الافتراضي، يستخدم SAM إسقاطًا مجمعًا للاستعلام والمفتاح والقيمة (`qkv`) في آلية الانتباه الخاصة به. ومع ذلك، قد ترغب في ضبط مكونات محددة فقط من آلية الانتباه، مثل إسقاطات الاستعلام (`q`) والقيمة (`v`)، لتقليل عدد المعلمات القابلة للتدريب والموارد الحسابية المطلوبة.
|
||||
|
||||
### الدافع
|
||||
|
||||
من خلال تقسيم الإسقاط المجمع `qkv` إلى إسقاطات منفصلة `q` و `k` و `v`، يمكنك تطبيق تقنيات مثل **LoRA** (Low-Rank Adaptation) على إسقاطي `q` و `v` فقط. يسمح لك هذا بما يلي:
|
||||
|
||||
- ضبط عدد أقل من المعلمات، مما يقلل من العبء الحسابي.
|
||||
- تحقيق أداء أفضل من خلال التركيز على مكونات محددة.
|
||||
- تجربة استراتيجيات تعديل مختلفة في آلية الانتباه.
|
||||
|
||||
### التنفيذ
|
||||
|
||||
#### **الخطوة 1: إنشاء فئة اهتمام مخصصة**
|
||||
|
||||
بعد ذلك، قم بإنشاء فئة فرعية من فئة `SamVisionAttention` الأصلية وعدلها لتضم إسقاطات `q` و `k` و `v` منفصلة.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
import torch.nn as nn
|
||||
from transformers.models.sam.modeling_sam import SamVisionAttention
|
||||
|
||||
class SamVisionAttentionSplit(SamVisionAttention, nn.Module):
|
||||
def __init__(self, config, window_size):
|
||||
super().__init__(config, window_size)
|
||||
del self.qkv
|
||||
# إسقاطات منفصلة q و k و v
|
||||
self.q = nn.Linear(config.hidden_size, config.hidden_size, bias=config.qkv_bias)
|
||||
self.k = nn.Linear(config.hidden_size, config.hidden_size, bias=config.qkv_bias)
|
||||
self.v = nn.Linear(config.hidden_size, config.hidden_size, bias=config.qkv_bias)
|
||||
self._register_load_state_dict_pre_hook(self.split_q_k_v_load_hook)
|
||||
|
||||
def split_q_k_v_load_hook(self, state_dict, prefix, *args):
|
||||
keys_to_delete = []
|
||||
for key in list(state_dict.keys()):
|
||||
if "qkv." in key:
|
||||
# تقسيم q و k و v من الإسقاط المجمع
|
||||
q, k, v = state_dict[key].chunk(3, dim=0)
|
||||
# استبدال الإسقاطات الفردية q و k و v
|
||||
state_dict[key.replace("qkv.", "q.")] = q
|
||||
state_dict[key.replace("qkv.", "k.")] = k
|
||||
state_dict[key.replace("qkv.", "v.")] = v
|
||||
# وضع علامة على مفتاح qkv القديم للحذف
|
||||
keys_to_delete.append(key)
|
||||
|
||||
# حذف مفاتيح qkv القديمة
|
||||
for key in keys_to_delete:
|
||||
del state_dict[key]
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, hidden_states: torch.Tensor, output_attentions=False) -> torch.Tensor:
|
||||
batch_size, height, width, _ = hidden_states.shape
|
||||
qkv_shapes = (batch_size * self.num_attention_heads, height * width, -1)
|
||||
query = self.q(hidden_states).reshape((batch_size, height * width,self.num_attention_heads, -1)).permute(0,2,1,3).reshape(qkv_shapes)
|
||||
key = self.k(hidden_states).reshape((batch_size, height * width,self.num_attention_heads, -1)).permute(0,2,1,3).reshape(qkv_shapes)
|
||||
value = self.v(hidden_states).reshape((batch_size, height * width,self.num_attention_heads, -1)).permute(0,2,1,3).reshape(qkv_shapes)
|
||||
|
||||
attn_weights = (query * self.scale) @ key.transpose(-2, -1)
|
||||
|
||||
if self.use_rel_pos:
|
||||
attn_weights = self.add_decomposed_rel_pos(
|
||||
attn_weights, query, self.rel_pos_h, self.rel_pos_w, (height, width), (height, width)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
attn_weights = torch.nn.functional.softmax(attn_weights, dtype=torch.float32, dim=-1).to(query.dtype)
|
||||
attn_probs = nn.functional.dropout(attn_weights, p=self.dropout, training=self.training)
|
||||
attn_output = (attn_probs @ value).reshape(batch_size, self.num_attention_heads, height, width, -1)
|
||||
attn_output = attn_output.permute(0, 2, 3, 1, 4).reshape(batch_size, height, width, -1)
|
||||
attn_output = self.proj(attn_output)
|
||||
|
||||
if output_attentions:
|
||||
outputs = (attn_output, attn_weights)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
outputs = (attn_output, None)
|
||||
return outputs
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**الشرح:**
|
||||
|
||||
- **الإسقاطات المنفصلة:** يتم إزالة الإسقاط المُجمع `qkv`، وإنشاء إسقاطات خطية منفصلة `q` و `k` و `v`.
|
||||
- **دالة استدعاء تحميل الأوزان:** تقوم طريقة `_split_qkv_load_hook` بتقسيم أوزان `qkv` المسبقة التدريب إلى أوزان `q` و `k` و `v` منفصلة عند تحميل النموذج. يضمن هذا التوافق مع أي نموذج مسبق التدريب.
|
||||
- **التنفيذ الأمامي:** يتم حساب الاستعلامات والمفاتيح والقيم بشكل منفصل، وتستمر آلية الانتباه كالمعتاد.
|
||||
|
||||
#### **الخطوة 2: استبدال فئة الانتباه الأصلية**
|
||||
|
||||
استبدل فئة `SamVisionAttention` الأصلية بفئتك المخصصة بحيث يستخدم النموذج آلية الانتباه المعدلة.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import SamModel
|
||||
from transformers.models.sam import modeling_sam
|
||||
|
||||
# استبدال فئة الاهتمام في وحدة نمطية modeling_sam
|
||||
modeling_sam.SamVisionAttention = SamVisionAttentionSplit
|
||||
|
||||
# تحميل نموذج SAM المسبق التدريب
|
||||
model = SamModel.from_pretrained("facebook/sam-vit-base")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**الشرح:**
|
||||
|
||||
- **استبدال الفئة:** من خلال تعيين فئتك المخصصة إلى `modeling_sam.SamVisionAttention`، فإن أي حالات من فئة `SamVisionAttention` في النموذج ستستخدم النسخة المعدلة. وبالتالي، عند استدعاء `SamModel`، سيتم استخدام `SamVisionAttentionSplit` المحددة حديثًا.
|
||||
- **تحميل النموذج:** يتم تحميل النموذج باستخدام `from_pretrained`، ويتم دمج آلية الانتباه المخصصة.
|
||||
|
||||
#### **الخطوة 3: تطبيق LoRA على إسقاطات محددة**
|
||||
|
||||
مع وجود إسقاطات `q` و `k` و `v` منفصلة، يمكنك الآن تطبيق LoRA على مكونات محددة، مثل إسقاطات `q` و `v`.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from peft import LoraConfig, get_peft_model
|
||||
|
||||
config = LoraConfig(
|
||||
r=16,
|
||||
lora_alpha=32,
|
||||
target_modules=["q", "v"], # تطبيق LoRA على إسقاطات q و v
|
||||
lora_dropout=0.1,
|
||||
task_type="mask-generation"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# تطبيق LoRA على النموذج
|
||||
model = get_peft_model(model, config)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**الشرح:**
|
||||
|
||||
- **تكوين LoRA:** تحدد `LoraConfig` المرتبة `r`، وعامل القياس `lora_alpha`، والوحدات المستهدفة (`"q"` و `"v"`)، ومعدل التخلي، ونوع المهمة.
|
||||
- **تطبيق LoRA:** تقوم دالة `get_peft_model` بتطبيق LoRA على الوحدات المحددة في النموذج.
|
||||
- **تقليل المعلمات:** من خلال التركيز على `q` و `v`، فإنك تقلل عدد المعلمات القابلة للتدريب، مما يؤدي إلى تسريع التدريب وتقليل استخدام الذاكرة.
|
||||
|
||||
#### **الخطوة 4: التحقق من عدد المعلمات القابلة للتدريب**
|
||||
|
||||
من السهل التحقق من عدد المعلمات القابلة للتدريب ومعرفة تأثير تعديلك.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
model.print_trainable_parameters()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**الناتج المتوقع:**
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
عدد المعلمات القابلة للتدريب: 608,256 || جميع المعلمات: 94,343,728 || نسبة المعلمات القابلة للتدريب: 0.6447
|
||||
عدد المعلمات القابلة للتدريب: 912,384 || جميع المعلمات: 94,647,856 || نسبة المعلمات القابلة للتدريب: 0.9640 # مع k
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## المساهمة بابداعاتك الخاصة
|
||||
|
||||
يمكن لتعديل النماذج المسبقة التدريب أن يفتح آفاقًا جديدة للبحث والتطبيق. من خلال فهم وتعديل الآليات الداخلية للنماذج مثل SAM، يمكنك تخصيصها لتلبية احتياجاتك المحددة، وتحسين الأداء، وتجربة أفكار جديدة.
|
||||
|
||||
إذا قمت بتطوير تعديﻻتك الخاصة لنماذج Transformers وترغب في مشاركتها، ففكر في المساهمة في هذه الوثيقة.
|
||||
|
||||
- **إنشاء طلب سحب (Pull Request):** شارك تغييراتك وتحسيناتك في التعليمات البرمجية مباشرة في المستودع.
|
||||
- **كتابة التوثيق:** قدم تفسيرات وأمثلة واضحة لتعديلاتك.
|
||||
- **التفاعل مع المجتمع:** ناقش أفكارك واحصل على تعليقات من المطورين والباحثين الآخرين من خلال فتح مشكلة.
|
||||
@ -144,7 +144,7 @@ conda install conda-forge::transformers
|
||||
|
||||
تُحمّل النماذج المُسبقة التدريب وتُخزّن مؤقتًا في: `~/.cache/huggingface/hub`. هذا هو المجلد الافتراضي الذي يُحدده متغير البيئة `TRANSFORMERS_CACHE`. على Windows، يكون دليل ذاكرة التخزين المؤقت الافتراضي هو `C:\Users\username\.cache\huggingface\hub`. يمكنك تغيير متغيرات البيئة shell الموضحة أدناه - حسب الأولوية - لتحديد دليل ذاكرة تخزين مؤقت مختلف:
|
||||
|
||||
1. متغير البيئة (افتراضي): `HF_HUB_CACHE` أو `TRANSFORMERS_CACHE`.
|
||||
1. متغير البيئة (افتراضي): `HUGGINGFACE_HUB_CACHE` أو `TRANSFORMERS_CACHE`.
|
||||
2. متغير البيئة: `HF_HOME`.
|
||||
3. متغير البيئة: `XDG_CACHE_HOME` + `/huggingface`.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,795 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# تحسين نماذج اللغة الكبيرة من حيث السرعة والذاكرة
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
[[open-in-colab]]
|
||||
|
||||
تحقق نماذج اللغة الكبيرة (LLMs) مثل GPT3/4، [Falcon](https://huggingface.co/tiiuae/falcon-40b)، و [Llama](https://huggingface.co/meta-llama/Llama-2-70b-hf) تقدمًا سريعًا في قدرتها على معالجة المهام التي تركز على الإنسان، مما يجعلها أدوات أساسية في الصناعات القائمة على المعرفة الحديثة.
|
||||
لا يزال نشر هذه النماذج في المهام الواقعية يمثل تحديًا، ومع ذلك:
|
||||
|
||||
- لكي تظهر نماذج اللغة الكبيرة قدرات فهم وتوليد النصوص قريبة من قدرات الإنسان، فإنها تتطلب حاليًا إلى تكوينها من مليارات المعلمات (انظر [كابلان وآخرون](https://arxiv.org/abs/2001.08361)، [وي وآخرون](https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.07682)). وهذا بدوره يزيد من متطلبات الذاكرة للاستدلال.
|
||||
- في العديد من المهام الواقعية، تحتاج نماذج اللغة الكبيرة إلى معلومات سياقية شاملة. يتطلب ذلك قدرة النموذج على إدارة تسلسلات إدخال طويلة للغاية أثناء الاستدلال.
|
||||
|
||||
يكمن جوهر صعوبة هذه التحديات في تعزيز القدرات الحسابية والذاكرة لنماذج اللغة الكبيرة، خاصة عند التعامل مع تسلسلات الإدخال الضخمة.
|
||||
|
||||
في هذا الدليل، سنستعرض التقنيات الفعالة لتُحسِّن من كفاءة نشر نماذج اللغة الكبيرة:
|
||||
|
||||
1. سنتناول تقنية "دقة أقل" التي أثبتت الأبحاث فعاليتها في تحقيق مزايا حسابية دون التأثير بشكل ملحوظ على أداء النموذج عن طريق العمل بدقة رقمية أقل [8 بت و4 بت](/main_classes/quantization.md).
|
||||
|
||||
2. **اFlash Attention:** إن Flash Attention وهي نسخة مُعدَّلة من خوارزمية الانتباه التي لا توفر فقط نهجًا أكثر كفاءة في استخدام الذاكرة، ولكنها تحقق أيضًا كفاءة متزايدة بسبب الاستخدام الأمثل لذاكرة GPU.
|
||||
|
||||
3. **الابتكارات المعمارية:** حيث تم اقتراح هياكل متخصصة تسمح باستدلال أكثر فعالية نظرًا لأن نماذج اللغة الكبيرة يتم نشرها دائمًا بنفس الطريقة أثناء عملية الاستدلال، أي توليد النص التنبؤي التلقائي مع سياق الإدخال الطويل، فقد تم اقتراح بنيات نموذج متخصصة تسمح بالاستدلال الأكثر كفاءة. أهم تقدم في بنيات النماذج هنا هو [عذر](https://arxiv.org/abs/2108.12409)، [الترميز الدوار](https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.09864)، [الاهتمام متعدد الاستعلامات (MQA)](https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.02150) و [مجموعة الانتباه بالاستعلام (GQA)]((https://arxiv.org/abs/2305.13245)).
|
||||
|
||||
على مدار هذا الدليل، سنقدم تحليلًا للتوليد التنبؤي التلقائي من منظور المُوتِّرات. نتعمق في مزايا وعيوب استخدام دقة أقل، ونقدم استكشافًا شاملاً لخوارزميات الانتباه الأحدث، ونناقش بنيات نماذج نماذج اللغة الكبيرة المحسنة. سندعم الشرح بأمثلة عملية تُبرِز كل تحسين على حدة.
|
||||
|
||||
## 1. دقة أقل
|
||||
|
||||
يمكن فهم متطلبات ذاكرة نماذج اللغة الكبيرة بشكل أفضل من خلال النظر إلى نموذج اللغة الكبيرة على أنها مجموعة من المصفوفات والمتجهات الوزنية، ومدخلات النص على أنها تسلسل من المتجهات. فيما يلي، سيتم استخدام تعريف "الأوزان" للإشارة إلى جميع مصفوفات الأوزان والمتجهات في النموذج.
|
||||
في وقت كتابة هذا الدليل، تتكون نماذج اللغة الكبيرة من مليارات المعلمات على الأقل.كل معلمة يتم تمثيلها برقم عشري مثل 4.5689 `` والذي يتم تخزينه عادةً بتنسيق [float32](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Single-precision_floating-point_format)، [bfloat16](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bfloat16_floating-point_format)، أو [float16](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Half-precision_floating-point_format) . يسمح لنا هذا بحساب متطلبات الذاكرة لتحميل نموذج اللغة الكبيرة في الذاكرة بسهولة:
|
||||
|
||||
> *يتطلب تحميل أوزان نموذج به X مليار معلمة حوالي 4 * X جيجابايت من ذاكرة الفيديو العشوائية (VRAM) بدقة float32*
|
||||
|
||||
ومع ذلك، نادرًا ما يتم تدريب النماذج في الوقت الحالي بدقة float32 الكاملة، ولكن عادةً ما تكون بدقة bfloat16 أو بشكل أقل في تنسيق float16. لذلك، تصبح القاعدة الإرشادية كما يلي:
|
||||
|
||||
> *يتطلب تحميل أوزان نموذج به X مليار معلمة حوالي 2 * X جيجابايت من ذاكرة الفيديو العشوائية (VRAM) بدقة bfloat16/float16*
|
||||
|
||||
بالنسبة لمدخلات النصوص القصيرة (أقل من 1024 رمزًا)، فإن متطلبات الذاكرة للاستدلال تهيمن عليها إلى حد كبير متطلبات الذاكرة لتحميل الأوزان. لذلك، دعنا نفترض، في الوقت الحالي، أن متطلبات الذاكرة للاستدلال تساوي متطلبات الذاكرة لتحميل النموذج في ذاكرة VRAM لوحدة معالجة الرسومات GPU..
|
||||
|
||||
ولإعطاء بعض الأمثلة على مقدار ذاكرة الفيديو العشوائية (VRAM) التي يتطلبها تحميل نموذج بتنسيق bfloat16 تقريبًا:
|
||||
|
||||
- **GPT3** يتطلب 2 \* 175 جيجا بايت = **350 جيجا بايت** VRAM
|
||||
- [**بلوم**](https://huggingface.co/bigscience/bloom) يتطلب 2 \* 176 جيجا بايت = **352 جيجا بايت** VRAM
|
||||
- [**Llama-2-70b**](https://huggingface.co/meta-llama/Llama-2-70b-hf) يتطلب 2 \* 70 جيجا بايت = **140 جيجا بايت** VRAM
|
||||
- [**Falcon-40b**](https://huggingface.co/tiiuae/falcon-40b) يتطلب 2 \* 40 جيجا بايت = **80 جيجا بايت** VRAM
|
||||
- [**MPT-30b**](https://huggingface.co/mosaicml/mpt-30b) يتطلب 2 \* 30 جيجا بايت = **60 جيجا بايت** VRAM
|
||||
- [**bigcode/starcoder**](https://huggingface.co/bigcode/starcoder) يتطلب 2 \* 15.5 = **31 جيجا بايت** VRAM
|
||||
|
||||
عند كتابة هذا الدليل، أكبر شريحة لوحدة معالجة الرسومات المتوفّرة هي A100 و H100 التي توفر 80 جيجابايت من ذاكرة الفيديو العشوائية (VRAM). تتطلب معظم النماذج المدرجة أعلاه أكثر من 80 جيجابايت فقط لتحميلها، وبالتالي فهي تتطلب بالضرورة [التوازي للموتّرات](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/perf_train_gpu_many#tensor-parallelism) و/أو [لتوازي الخطي](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/perf_train_gpu_many#naive-model-parallelism-vertical-and-pipeline-parallelism).
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 لا يدعم Transformers موازاة التنسور خارج الصندوق لأنه يتطلب كتابة هيكلة النموذج بطريقة محددة. إذا كنت مهتمًا بكتابة نماذج بطريقة صديقة لموازاة التنسور، فلا تتردد في إلقاء نظرة على [مكتبة الاستدلال بتوليد النص](https://github.com/huggingface/text-generation-inference/tree/main/server/text_generation_server/models/custom_modeling).
|
||||
|
||||
بدعم موازاة قنوات المعالجة البسيطة خارج الصندوق. للقيام بذلك، قم بتحميل النموذج باستخدام `device="auto"` والذي سيقوم تلقائيًا بوضع الطبقات المختلفة على وحدات معالجة الرسومات (GPU) المتاحة كما هو موضح [هنا](https://huggingface.co/docs/accelerate/v0.22.0/en/concept_guides/big_model_inference).
|
||||
لاحظ، مع ذلك، أنه في حين أن موازاة قنوات المعالجة البسيطة فعالة للغاية، إلا أنها لا تعالج مشكلات عدم نشاط وحدة معالجة الرسومات (GPU). لهذا، تكون موازاة قنوات المعالجة المتقدمة مطلوبة كما هو موضح [هنا](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/en/perf_train_gpu_many#naive-model-parallelism-vertical-and-pipeline-parallelism).
|
||||
|
||||
إذا كان لديك حق الوصول إلى عقدة 8 x 80 جيجابايت A100، فيمكنك تحميل BLOOM كما يلي
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
!pip install transformers accelerate bitsandbytes optimum
|
||||
```
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("bigscience/bloom", device_map="auto", pad_token_id=0)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
من خلال استخدام `device_map="auto"` سيتم توزيع طبقات الاهتمام بالتساوي عبر جميع وحدات معالجة الرسومات (GPU) المتاحة.
|
||||
|
||||
في هذا الدليل، سنستخدم [bigcode/octocoder](https://huggingface.co/bigcode/octocoder) لأنه يمكن تشغيله على شريحة جهاز GPU A100 ذات 40 جيجا بايت. لاحظ أن جميع تحسينات الذاكرة والسرعة التي سنطبقها من الآن فصاعدًا تنطبق بالتساوي على النماذج التي تتطلب موازاة النماذج أو المصفوفات.
|
||||
|
||||
نظرًا لأن النموذج مُحمَّل بدقة bfloat16، فباستخدام قاعدتنا الإرشادية أعلاه، نتوقع أن تكون متطلبات الذاكرة لتشغيل الاستدلال باستخدام `bigcode/octocoder` حوالي 31 جيجا بايت من ذاكرة الفيديو العشوائية (VRAM). دعنا نجرب.
|
||||
|
||||
نقوم أولاً بتحميل النموذج والمجزىء اللغوي ثم نقوم بتمرير كلاهما إلى كائن [قنوات المعالجة](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main_classes/pipelines) في Transformers.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer, pipeline
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("bigcode/octocoder", torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16, device_map="auto", pad_token_id=0)
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("bigcode/octocoder")
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = pipeline("text-generation", model=model, tokenizer=tokenizer)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
prompt = "Question: Please write a function in Python that transforms bytes to Giga bytes.\n\nAnswer:"
|
||||
|
||||
result = pipe(prompt, max_new_tokens=60)[0]["generated_text"][len(prompt):]
|
||||
result
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**الإخراج**:
|
||||
```
|
||||
Here is a Python function that transforms bytes to Giga bytes:\n\n```python\ndef bytes_to_giga_bytes(bytes):\n return bytes / 1024 / 1024 / 1024\n```\n\nThis function takes a single
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
رائع، يمكننا الآن استخدام النتيجة مباشرة لتحويل البايت إلى جيجا بايت.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
def bytes_to_giga_bytes(bytes):
|
||||
return bytes / 1024 / 1024 / 1024
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
دعونا نستدعي [`torch.cuda.max_memory_allocated`](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.cuda.max_memory_allocated.html) لقياس ذروة تخصيص ذاكرة وحدة معالجة الرسومات (GPU).
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
bytes_to_giga_bytes(torch.cuda.max_memory_allocated())
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**الإخراج**:
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
29.0260648727417
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
قريب بما يكفي من حسابنا التقريبي! يمكننا أن نرى أن الرقم غير صحيح تمامًا لأن الانتقال من البايت إلى الكيلوبايت يتطلب الضرب في 1024 بدلاً من 1000. لذلك يمكن أيضًا فهم صيغة التقريب على أنها حساب "بحد أقصى X جيجا بايت".
|
||||
لاحظ أنه إذا حاولنا تشغيل النموذج بدقة float32 الكاملة، فستكون هناك حاجة إلى 64 جيجا بايت من ذاكرة الفيديو العشوائية (VRAM).
|
||||
|
||||
> يتم تدريب جميع النماذج تقريبًا بتنسيق bfloat16 في الوقت الحالي، ولا يوجد سبب لتشغيل النموذج بدقة float32 الكاملة إذا [كانت وحدة معالجة الرسومات (GPU) الخاصة بك تدعم bfloat16](https://discuss.pytorch.org/t/bfloat16-native-support/117155/5). لن توفر دقة float32 نتائج استدلال أفضل من الدقة التي تم استخدامها لتدريب النموذج.
|
||||
|
||||
إذا لم تكن متأكدًا من تنسيق تخزين أوزان النموذج على Hub، فيمكنك دائمًا الاطلاع على تهيئة نقطة التفتيش في `"torch_dtype"`، على سبيل المثال [هنا](https://huggingface.co/meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-hf/blob/6fdf2e60f86ff2481f2241aaee459f85b5b0bbb9/config.json#L21). يوصى بتعيين النموذج إلى نفس نوع الدقة كما هو مكتوب في التهيئة عند التحميل باستخدام `from_pretrained(..., torch_dtype=...)` إلا إذا كان النوع الأصلي هو float32، وفي هذه الحالة يمكن استخدام `float16` أو `bfloat16` للاستدلال.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
دعونا نحدد وظيفة `flush(...)` لتحرير جميع الذاكرة المخصصة بحيث يمكننا قياس ذروة ذاكرة وحدة معالجة الرسومات (GPU) المخصصة بدقة.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
del pipe
|
||||
del model
|
||||
|
||||
import gc
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
def flush():
|
||||
gc.collect()
|
||||
torch.cuda.empty_cache()
|
||||
torch.cuda.reset_peak_memory_stats()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
دعونا نستدعيه الآن للتجربة التالية.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
flush()
|
||||
```
|
||||
في الإصدار الأخير من مكتبة Accelerate، يمكنك أيضًا استخدام طريقة مساعدة تسمى `release_memory()`
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from accelerate.utils import release_memory
|
||||
# ...
|
||||
|
||||
release_memory(model)
|
||||
```
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from accelerate.utils import release_memory
|
||||
# ...
|
||||
|
||||
release_memory(model)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
والآن ماذا لو لم يكن لدى وحدة معالجة الرسومات (GPU) لديك 32 جيجا بايت من ذاكرة الفيديو العشوائية (VRAM)؟ لقد وجد أن أوزان النماذج يمكن تحويلها إلى 8 بتات أو 4 بتات دون خسارة كبيرة في الأداء (انظر [Dettmers et al.](https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.07339)).
|
||||
يمكن تحويل النموذج إلى 3 بتات أو 2 بتات مع فقدان مقبول في الأداء كما هو موضح في ورقة [GPTQ](https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.17323) 🤯.
|
||||
|
||||
دون الدخول في الكثير من التفاصيل، تهدف مخططات التكميم إلى تخفيض دقة الأوزان مع محاولة الحفاظ على دقة نتائج النموذج كما هي (*أي* أقرب ما يمكن إلى bfloat16).
|
||||
لاحظ أن التكميم يعمل بشكل خاص جيدًا لتوليد النص حيث كل ما نهتم به هو اختيار *مجموعة الرموز الأكثر احتمالًا التالية* ولا نهتم حقًا بالقيم الدقيقة لتوزيع الرمز التالي *logit*.
|
||||
كل ما يهم هو أن توزيع الرمز التالي *logit* يظل كما هو تقريبًا بحيث تعطي عملية `argmax` أو `topk` نفس النتائج.
|
||||
|
||||
هناك عدة تقنيات للتكميم، والتي لن نناقشها بالتفصيل هنا، ولكن بشكل عام، تعمل جميع تقنيات التكميم كما يلي:
|
||||
|
||||
- 1. تكميم جميع الأوزان إلى الدقة المستهدفة
|
||||
- 2. تحميل الأوزان المحولة، ومرر تسلسل المدخلات من المتجهات بتنسيق bfloat16
|
||||
- 3. قم بتحويل الأوزان ديناميكيًا إلى bfloat1 لإجراء الحسابات مع متجهات المدخلات بدقة `bfloat16`
|
||||
|
||||
باختصار، هذا يعني أن مضروبات *مصفوفة المدخلات-الوزن*، حيث \\( X \\) هي المدخلات، \\( W \\) هي مصفوفة وزن و \\( Y \\) هي الناتج:
|
||||
|
||||
$$ Y = X * W $$
|
||||
|
||||
تتغير إلى
|
||||
|
||||
$$ Y = X * \text{dequantize}(W) $$
|
||||
|
||||
لكل عملية ضرب المصفوفات. يتم تنفيذ إلغاء التكميم وإعادة التكميم بشكل متسلسل لجميع مصفوفات الأوزان أثناء مرور المدخلات عبر رسم الشبكة.
|
||||
|
||||
لذلك، غالبًا ما لا يتم تقليل وقت الاستدلال عند استخدام الأوزان المكممة، ولكن بدلاً من ذلك يزيد.
|
||||
|
||||
كفى نظرية، دعنا نجرب! لتكميم الأوزان باستخدام المحولات، تحتاج إلى التأكد من تثبيت مكتبة [`bitsandbytes`](https://github.com/TimDettmers/bitsandbytes).
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
!pip install bitsandbytes
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
يمكننا بعد ذلك تحميل النماذج في تكميم 8 بت ببساطة عن طريق إضافة علامة `load_in_8bit=True` إلى `from_pretrained`.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("bigcode/octocoder", load_in_8bit=True, pad_token_id=0)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
الآن، دعنا نعيد تشغيل مثالنا ونقيس استخدام الذاكرة.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
pipe = pipeline("text-generation", model=model, tokenizer=tokenizer)
|
||||
|
||||
result = pipe(prompt, max_new_tokens=60)[0]["generated_text"][len(prompt):]
|
||||
result
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**الإخراج**:
|
||||
```
|
||||
Here is a Python function that transforms bytes to Giga bytes:\n\n```python\ndef bytes_to_giga_bytes(bytes):\n return bytes / 1024 / 1024 / 1024\n```\n\nThis function takes a single
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
جميل، نحصل على نفس النتيجة كما في السابق، لذلك لا يوجد فقدان في الدقة! دعنا نلقي نظرة على مقدار الذاكرة المستخدمة هذه المرة.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
bytes_to_giga_bytes(torch.cuda.max_memory_allocated())
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**الإخراج**:
|
||||
```
|
||||
15.219234466552734
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
أقل بكثير! لقد انخفضنا إلى ما يزيد قليلاً عن 15 جيجابايت، وبالتالي يمكننا تشغيل هذا النموذج على وحدات معالجة الرسومات للمستهلك مثل 4090.
|
||||
|
||||
نرى مكسبًا لطيفًا جدًا في كفاءة الذاكرة ولا يوجد تقريبًا أي تدهور في ناتج النموذج. ومع ذلك، يمكننا أيضًا ملاحظة تباطؤ طفيف أثناء الاستدلال.
|
||||
|
||||
نحذف النماذج ونفرغ الذاكرة مرة أخرى.
|
||||
```python
|
||||
del model
|
||||
del pipe
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
flush()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
دعنا نرى ما هو استهلاك ذاكرة GPU الذروة الذي يوفره تكميم 4 بت. يمكن تكميم النموذج إلى 4 بت باستخدام نفس واجهة برمجة التطبيقات كما في السابق - هذه المرة عن طريق تمرير `load_in_4bit=True` بدلاً من `load_in_8bit=True`.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("bigcode/octocoder", load_in_4bit=True, low_cpu_mem_usage=True, pad_token_id=0)
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = pipeline("text-generation", model=model, tokenizer=tokenizer)
|
||||
|
||||
result = pipe(prompt, max_new_tokens=60)[0]["generated_text"][len(prompt):]
|
||||
result
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**الإخراج**:
|
||||
```
|
||||
Here is a Python function that transforms bytes to Giga bytes:\n\n```\ndef bytes_to_gigabytes(bytes):\n return bytes / 1024 / 1024 / 1024\n```\n\nThis function takes a single argument
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
نحن نرى تقريبًا نفس نص الإخراج كما في السابق - فقط `python` مفقود قبل مقطع الكود. دعنا نرى مقدار الذاكرة المطلوبة.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
bytes_to_giga_bytes(torch.cuda.max_memory_allocated())
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**الإخراج**:
|
||||
```
|
||||
9.543574333190918
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
فقط 9.5 جيجابايت! هذا ليس كثيرًا بالفعل لنموذج يزيد عدد معاملاته عن 15 مليار.
|
||||
|
||||
على الرغم من أننا نرى تدهورًا بسيطًا جدًا في الدقة لنموذجنا هنا، إلا أن تكميم 4 بت يمكن أن يؤدي في الممارسة العملية غالبًا إلى نتائج مختلفة مقارنة بتكميم 8 بت أو الاستدلال الكامل `bfloat16`. الأمر متروك للمستخدم لتجربته.
|
||||
|
||||
لاحظ أيضًا أن الاستدلال هنا كان أبطأ قليلاً مقارنة بتكميم 8 بت والذي يرجع إلى طريقة التكميم الأكثر عدوانية المستخدمة لتكميم 4 بت مما يؤدي إلى \\( \text{quantize} \\) و \\( \text{dequantize} \\) يستغرق وقتًا أطول أثناء الاستدلال.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
del model
|
||||
del pipe
|
||||
```
|
||||
```python
|
||||
flush()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
بشكل عام، رأينا أن تشغيل OctoCoder بدقة 8 بت قلل من ذاكرة GPU VRAM المطلوبة من 32G GPU VRAM إلى 15 جيجابايت فقط، وتشغيل النموذج بدقة 4 بت يقلل من ذاكرة GPU VRAM المطلوبة إلى ما يزيد قليلاً عن 9 جيجابايت.
|
||||
|
||||
يسمح تكميم 4 بت بتشغيل النموذج على وحدات معالجة الرسومات مثل RTX3090 و V100 و T4 والتي يمكن الوصول إليها بسهولة لمعظم الأشخاص.
|
||||
|
||||
لمزيد من المعلومات حول التكميم ولمعرفة كيف يمكن تكميم النماذج لطلب ذاكرة GPU VRAM أقل حتى من 4 بت، نوصي بالاطلاع على تنفيذ [`AutoGPTQ`](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/en/main_classes/quantization#autogptq-integration%60).
|
||||
|
||||
> كاستنتاج، من المهم تذكر أن تكميم النموذج يتداول كفاءة الذاكرة المحسنة مقابل الدقة وفي بعض الحالات وقت الاستدلال.
|
||||
|
||||
إذا لم تكن ذاكرة GPU قيدًا لحالتك الاستخدام، فغالبًا لا توجد حاجة للنظر في التكميم. ومع ذلك، لا يمكن للعديد من وحدات معالجة الرسومات ببساطة تشغيل نماذج اللغة الكبيرة بدون طرق التكميم وفي هذه الحالة، تعد مخططات التكميم 4 بت و 8 بت أدوات مفيدة للغاية.
|
||||
|
||||
لمزيد من المعلومات حول الاستخدام التفصيلي، نوصي بشدة بإلقاء نظرة على [وثائق تكميم المحولات](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main_classes/quantization#general-usage).
|
||||
|
||||
بعد ذلك، دعنا نلقي نظرة على كيفية تحسين الكفاءة الحسابية وكفاءة الذاكرة باستخدام خوارزميات أفضل وبنية نموذج محسنة.
|
||||
|
||||
## 2. الانتباه السريع
|
||||
|
||||
تتشارك نماذج اللغة الكبيرة (LLMs) الأعلى أداءً اليوم تقريبًا نفس البنية الأساسية التي تتكون من طبقات التغذية الأمامية، وطبقات التنشيط، وطبقات التطبيع الطبقي، والأهم من ذلك، طبقات الانتباه الذاتي.
|
||||
|
||||
تعد طبقات الانتباه الذاتي مركزية لنماذج اللغة الكبيرة (LLMs) حيث تمكن النموذج من فهم العلاقات السياقية بين رموز المدخلات.
|
||||
ومع ذلك، فإن استهلاك ذاكرة GPU الذروة لطبقات الانتباه الذاتي ينمو بشكل *رباعي* في كل من التعقيد الحسابي وتعقيد الذاكرة مع عدد رموز المدخلات (والذي يُطلق عليه أيضًا *طول التسلسل*) الذي نسميه في ما يلي بـ \\( N \\) .
|
||||
على الرغم من أن هذا غير ملحوظ حقًا للتسلسلات الأقصر (حتى 1000 رمز إدخال)، إلا أنه يصبح مشكلة خطيرة للتسلسلات الأطول (حوالي 16000 رمز إدخال).
|
||||
|
||||
دعنا نلقي نظرة أقرب. الصيغة لحساب الناتج \\( \mathbf{O} \\) لطبقة الانتباه الذاتي لإدخال \\( \mathbf{X} \\) بطول \\( N \\) هي:
|
||||
|
||||
$$ \textbf{O} = \text{Attn}(\mathbf{X}) = \mathbf{V} \times \text{Softmax}(\mathbf{QK}^T) \text{ with } \mathbf{Q} = \mathbf{W}_q \mathbf{X}, \mathbf{V} = \mathbf{W}_v \mathbf{X}, \mathbf{K} = \mathbf{W}_k \mathbf{X} $$
|
||||
|
||||
يعد \\( \mathbf{X} = (\mathbf{x}_1, ... \mathbf{x}_{N}) \\) بالتالي تسلسل الإدخال إلى طبقة الاهتمام. وستتكون كل من الإسقاطات \\( \mathbf{Q} \\) و \\( \mathbf{K} \\) من \\( N \\) من المتجهات مما يؤدي إلى أن يكون حجم \\( \mathbf{QK}^T \\) هو \\( N^2 \\).
|
||||
|
||||
عادة ما يكون لدى LLMs العديد من رؤوس الاهتمام، وبالتالي يتم إجراء العديد من حسابات الاهتمام الذاتي بالتوازي.
|
||||
وبافتراض أن LLM لديها 40 رأس اهتمام وتعمل بدقة bfloat16، يمكننا حساب متطلبات الذاكرة لتخزين مصفوفات \\( \mathbf{QK^T} \\) لتكون \\( 40 * 2 * N^2 \\) بايت. بالنسبة لـ \\( N=1000 \\)، لا يلزم سوى حوالي 50 ميجابايت من VRAM، ولكن بالنسبة لـ \\( N=16000 \\) سنحتاج إلى 19 جيجابايت من VRAM، وبالنسبة لـ \\( N=100,000 \\) سنحتاج إلى ما يقرب من 1 تيرابايت فقط لتخزين مصفوفات \\( \mathbf{QK}^T \\).
|
||||
|
||||
باختصار، سرعان ما يصبح خوارزمية الانتباه الذاتي الافتراضية مكلفة للغاية من حيث الذاكرة بالنسبة لسياقات الإدخال الكبيرة.
|
||||
|
||||
مع تحسن LLMs في فهم النص وتوليد النص، يتم تطبيقها على مهام متزايدة التعقيد. في حين أن النماذج كانت تتعامل سابقًا مع ترجمة أو تلخيص بضع جمل، فإنها الآن تدير صفحات كاملة، مما يتطلب القدرة على معالجة أطوال إدخال واسعة.
|
||||
|
||||
كيف يمكننا التخلص من متطلبات الذاكرة الباهظة للتطويلات المدخلة الكبيرة؟ نحن بحاجة إلى طريقة جديدة لحساب آلية الاهتمام الذاتي التي تتخلص من مصفوفة \\( QK^T \\). [طريقه داو وآخرون.](Https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.14135) طوروا بالضبط مثل هذا الخوارزمية الجديدة وأطلقوا عليها اسم **Flash Attention**.
|
||||
|
||||
باختصار، يكسر الاهتمام الفلاشي حساب \\( \mathbf{V} \times \operatorname{Softmax}(\mathbf{QK}^T\\)) ويحسب بدلاً من ذلك قطعًا أصغر من الإخراج عن طريق التكرار عبر العديد من خطوات حساب Softmax:
|
||||
|
||||
$$ \textbf{O}_i \leftarrow s^a_{ij} * \textbf{O}_i + s^b_{ij} * \mathbf{V}_{j} \times \operatorname{Softmax}(\mathbf{QK}^T_{i,j}) \text{ for multiple } i, j \text{ iterations } $$
|
||||
|
||||
مع \\( s^a_{ij} \\) و \\( s^b_{ij} \\) كونها بعض إحصائيات التطبيع softmax التي يجب إعادة حسابها لكل \\( i \\) و \\( j \\).
|
||||
|
||||
يرجى ملاحظة أن Flash Attention بالكامل أكثر تعقيدًا إلى حد ما ويتم تبسيطه بشكل كبير هنا حيث أن التعمق كثيرًا يخرج عن نطاق هذا الدليل. القارئ مدعو لإلقاء نظرة على ورقة Flash Attention المكتوبة جيدًا [1] لمزيد من التفاصيل.
|
||||
|
||||
الفكرة الرئيسية هنا هي:
|
||||
|
||||
> من خلال تتبع إحصائيات التطبيع softmax واستخدام بعض الرياضيات الذكية، يعطي Flash Attention **مخرجات متطابقة رقميًا** مقارنة بطبقة الاهتمام الذاتي الافتراضية بتكلفة ذاكرة لا تزيد خطيًا مع \\( N \\).
|
||||
|
||||
عند النظر إلى الصيغة، قد يقول المرء بديهيًا أن الاهتمام الفلاشي يجب أن يكون أبطأ بكثير مقارنة بصيغة الاهتمام الافتراضية حيث يلزم إجراء المزيد من الحسابات. في الواقع، يتطلب Flash Attention المزيد من عمليات الفاصلة العائمة مقارنة بالاهتمام العادي حيث يجب إعادة حساب إحصائيات التطبيع softmax باستمرار (راجع [الورقة](https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.14135) لمزيد من التفاصيل إذا كنت مهتمًا)
|
||||
|
||||
> ومع ذلك، فإن الاهتمام الفلاشي أسرع بكثير في الاستدلال مقارنة بالاهتمام الافتراضي الذي يأتي من قدرته على تقليل الطلبات على ذاكرة GPU الأبطأ ذات النطاق الترددي العالي (VRAM)، والتركيز بدلاً من ذلك على ذاكرة SRAM الأسرع الموجودة على الشريحة.
|
||||
|
||||
من الناحية الأساسية، يتأكد Flash Attention من إمكانية إجراء جميع عمليات الكتابة والقراءة الوسيطة باستخدام ذاكرة SRAM السريعة الموجودة على الشريحة بدلاً من الاضطرار إلى الوصول إلى ذاكرة VRAM الأبطأ لحساب متجه الإخراج \\( \mathbf{O} \\).
|
||||
|
||||
من الناحية العملية، لا يوجد حاليًا أي سبب **عدم** استخدام الاهتمام الفلاشي إذا كان متاحًا. الخوارزمية تعطي نفس المخرجات رياضيا، وأسرع وأكثر كفاءة في استخدام الذاكرة.
|
||||
|
||||
لنلقِ نظرة على مثال عملي.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
يحصل نموذج OctoCoder الخاص بنا الآن على موجه إدخال أطول بشكل كبير يتضمن ما يسمى *موجه النظام*. تُستخدم موجهات النظام لتوجيه LLM إلى مساعد أفضل مصمم لمهام المستخدمين.
|
||||
فيما يلي، نستخدم موجه النظام الذي سيجعل OctoCoder مساعد ترميز أفضل.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
system_prompt = """Below are a series of dialogues between various people and an AI technical assistant.
|
||||
The assistant tries to be helpful, polite, honest, sophisticated, emotionally aware, and humble but knowledgeable.
|
||||
The assistant is happy to help with code questions and will do their best to understand exactly what is needed.
|
||||
It also tries to avoid giving false or misleading information, and it caveats when it isn't entirely sure about the right answer.
|
||||
That said, the assistant is practical really does its best, and doesn't let caution get too much in the way of being useful.
|
||||
|
||||
The Starcoder models are a series of 15.5B parameter models trained on 80+ programming languages from The Stack (v1.2) (excluding opt-out requests).
|
||||
The model uses Multi Query Attention, was trained using the Fill-in-the-Middle objective, and with 8,192 tokens context window for a trillion tokens of heavily deduplicated data.
|
||||
-----
|
||||
|
||||
Question: Write a function that takes two lists and returns a list that has alternating elements from each input list.
|
||||
|
||||
Answer: Sure. Here is a function that does that.
|
||||
|
||||
def alternating(list1, list2):
|
||||
results = []
|
||||
for i in range(len(list1)):
|
||||
results.append(list1[i])
|
||||
results.append(list2[i])
|
||||
return results
|
||||
|
||||
Question: Can you write some test cases for this function?
|
||||
|
||||
Answer: Sure, here are some tests.
|
||||
|
||||
assert alternating([10, 20, 30], [1, 2, 3]) == [10, 1, 20, 2, 30, 3]
|
||||
assert alternating([True, False], [4, 5]) == [True, 4, False, 5]
|
||||
assert alternating([], []) == []
|
||||
|
||||
Question: Modify the function so that it returns all input elements when the lists have uneven length. The elements from the longer list should be at the end.
|
||||
|
||||
Answer: Here is the modified function.
|
||||
|
||||
def alternating(list1, list2):
|
||||
results = []
|
||||
for i in range(min(len(list1), len(list2))):
|
||||
results.append(list1[i])
|
||||
results.append(list2[i])
|
||||
if len(list1) > len(list2):
|
||||
results.extend(list1[i+1:])
|
||||
else:
|
||||
results.extend(list2[i+1:])
|
||||
return results
|
||||
-----
|
||||
"""
|
||||
```
|
||||
لأغراض التوضيح، سنكرر موجه النظام عشر مرات بحيث يكون طول الإدخال طويلاً بما يكفي لملاحظة وفورات ذاكرة Flash Attention.
|
||||
نضيف موجه النص الأصلي "سؤال: يرجى كتابة وظيفة في Python تقوم بتحويل البايتات إلى جيجا بايت.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
long_prompt = 10 * system_prompt + prompt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
نقوم بتنفيذ نموذجنا مرة أخرى بدقة bfloat16.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("bigcode/octocoder", torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16, device_map="auto")
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("bigcode/octocoder")
|
||||
|
||||
pipe = pipeline("text-generation", model=model, tokenizer=tokenizer)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
دعنا الآن نقوم بتشغيل النموذج تمامًا مثلما كان من قبل *بدون اهتمام فلاشي* وقياس متطلبات ذاكرة GPU وقت الذروة ووقت الاستدلال.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import time
|
||||
|
||||
start_time = time.time()
|
||||
result = pipe(long_prompt, max_new_tokens=60)[0]["generated_text"][len(long_prompt):]
|
||||
|
||||
print(f"Generated in {time.time() - start_time} seconds.")
|
||||
result
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**الإخراج**:
|
||||
```
|
||||
تم التوليد في 10.96854019165039 ثانية.
|
||||
بالتأكيد. إليك وظيفة للقيام بذلك.
|
||||
|
||||
def bytes_to_giga(bytes):
|
||||
return bytes / 1024 / 1024 / 1024
|
||||
|
||||
الإجابة: بالتأكيد. إليك وظيفة للقيام بذلك.
|
||||
|
||||
ديف
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
نحصل على نفس الإخراج كما كان من قبل، ولكن هذه المرة، يقوم النموذج بتكرار الإجابة عدة مرات حتى يتم قطعها عند 60 رمزًا. ليس من المستغرب أننا كررنا موجه النظام عشر مرات لأغراض التوضيح وبالتالي قمنا بتشغيل النموذج لتكرار نفسه.
|
||||
|
||||
**ملاحظة** لا ينبغي تكرار موجه النظام عشر مرات في التطبيقات الواقعية - مرة واحدة كافية!
|
||||
|
||||
دعنا نقيس متطلبات ذاكرة GPU وقت الذروة.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
bytes_to_giga_bytes(torch.cuda.max_memory_allocated())
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**الإخراج**:
|
||||
```
|
||||
37.668193340301514
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
كما نرى، فإن متطلبات ذاكرة GPU وقت الذروة أعلى بكثير مما كانت عليه في البداية، وهو ما يرجع إلى حد كبير إلى تسلسل الإدخال الأطول. أيضًا، يستغرق التوليد أكثر من دقيقة بقليل الآن.
|
||||
|
||||
نستدعي `flush()` لتحرير ذاكرة GPU لتجربتنا التالية.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
flush()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
لمقارنة، دعونا نقوم بتشغيل نفس الدالة، ولكن تمكين الاهتمام فلاش بدلا من ذلك.
|
||||
للقيام بذلك، نقوم بتحويل النموذج إلى [BetterTransformer](Https://huggingface.co/docs/optimum/bettertransformer/overview) ومن خلال القيام بذلك تمكين PyTorch's [SDPA self-attention](Https://pytorch.org/docs/master/generated/torch.nn.functional.scaled_dot_product_attention) والتي بدورها قادرة على استخدام الاهتمام فلاش.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
model.to_bettertransformer()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
الآن نقوم بتشغيل نفس مقتطف التعليمات البرمجية بالضبط كما كان من قبل وتحت الغطاء سوف تستخدم المحولات الاهتمام فلاش.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
start_time = time.time()
|
||||
with torch.backends.cuda.sdp_kernel(enable_flash=True, enable_math=False, enable_mem_efficient=False):
|
||||
result = pipe(long_prompt, max_new_tokens=60)[0]["generated_text"][len(long_prompt):]
|
||||
|
||||
print(f"Generated in {time.time() - start_time} seconds.")
|
||||
result
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**الإخراج**:
|
||||
```
|
||||
تم التوليد في 3.0211617946624756 ثانية.
|
||||
بالتأكيد. إليك وظيفة للقيام بذلك.
|
||||
|
||||
def bytes_to_giga(bytes):
|
||||
return bytes / 1024 / 1024 / 1024
|
||||
|
||||
الإجابة: بالتأكيد. إليك وظيفة للقيام بذلك.
|
||||
|
||||
ديف
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
نحصل على نفس النتيجة بالضبط كما كان من قبل، ولكن يمكننا ملاحظة تسريع كبير بفضل الاهتمام فلاش.
|
||||
|
||||
دعنا نقيس استهلاك الذاكرة لآخر مرة.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
bytes_to_giga_bytes(torch.cuda.max_memory_allocated())
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**الإخراج**:
|
||||
```
|
||||
32.617331981658936
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
ونحن تقريبا مرة أخرى إلى ذاكرة GPU الذروة الأصلية لدينا 29GB.
|
||||
|
||||
يمكننا أن نلاحظ أننا نستخدم فقط حوالي 100 ميجابايت إضافية من ذاكرة GPU عند تمرير تسلسل إدخال طويل جدًا مع الاهتمام فلاش مقارنة بتمرير تسلسل إدخال قصير كما فعلنا في البداية.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
flush()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
لمزيد من المعلومات حول كيفية استخدام Flash Attention، يرجى الاطلاع على [صفحة doc هذه](Https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/en/perf_infer_gpu_one#flashattention-2).
|
||||
|
||||
## 3. الابتكارات المعمارية
|
||||
|
||||
حتى الآن، نظرنا في تحسين الكفاءة الحسابية والذاكرة من خلال:
|
||||
|
||||
- صب الأوزان في تنسيق دقة أقل
|
||||
- استبدال خوارزمية الاهتمام الذاتي بإصدار أكثر كفاءة من حيث الذاكرة والحساب
|
||||
|
||||
دعونا الآن نلقي نظرة على كيفية تغيير بنية LLM بحيث تكون أكثر فعالية وكفاءة للمهام التي تتطلب مدخلات نصية طويلة، على سبيل المثال:
|
||||
- استرجاع الأسئلة المعززة،
|
||||
- تلخيص،
|
||||
- الدردشة
|
||||
|
||||
لاحظ أن "الدردشة" لا تتطلب من LLM التعامل مع مدخلات نصية طويلة فحسب، بل تتطلب أيضًا أن يكون LLM قادرًا على التعامل بكفاءة مع الحوار ذهابًا وإيابًا بين المستخدم والمساعد (مثل ChatGPT).
|
||||
|
||||
بمجرد تدريبها، يصبح من الصعب تغيير بنية LLM الأساسية، لذلك من المهم مراعاة مهام LLM مسبقًا وتحسين بنية النموذج وفقًا لذلك.
|
||||
هناك مكونان مهمان لبنية النموذج يصبحان بسرعة عنق زجاجة للذاكرة و/أو الأداء لتسلسلات الإدخال الكبيرة.
|
||||
|
||||
- الترميزات الموضعية
|
||||
- ذاكرة التخزين المؤقت للقيمة الرئيسية
|
||||
|
||||
دعنا نلقي نظرة على كل مكون بمزيد من التفاصيل
|
||||
|
||||
### 3.1 تحسين الترميزات الموضعية لـ LLMs
|
||||
|
||||
يضع الاهتمام الذاتي كل رمز في علاقة مع رموز أخرى.
|
||||
كمثال، يمكن أن تبدو مصفوفة \\( \operatorname{Softmax}(\mathbf{QK}^T) \\) لتسلسل الإدخال النصي *"مرحبًا"، "أنا"، "أحب"، "أنت"* كما يلي:
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
يتم منح كل رمز كلمة كتلة احتمال يتم من خلالها الاهتمام بجميع رموز الكلمات الأخرى، وبالتالي يتم وضعها في علاقة مع جميع رموز الكلمات الأخرى. على سبيل المثال، تحضر كلمة *"الحب"* كلمة *"مرحبًا"* بنسبة 5%، و *"أنا"* بنسبة 30%، ونفسها بنسبة 65%.
|
||||
|
||||
سيواجه LLM القائم على الاهتمام الذاتي، ولكن بدون الترميزات الموضعية، صعوبات كبيرة في فهم مواضع نصوص الإدخال بالنسبة لبعضها البعض.
|
||||
ويرجع ذلك إلى أن درجة الاحتمال التي يحسبها \\( \mathbf{QK}^T \\) تربط كل رمز كلمة بكل رمز كلمة أخرى في حسابات \\( O (1) \\) بغض النظر عن مسافة الموضع النسبي بينهما.
|
||||
لذلك، بالنسبة إلى LLM بدون ترميزات موضعية، يبدو أن كل رمز له نفس المسافة إلى جميع الرموز الأخرى، على سبيل المثال، سيكون من الصعب التمييز بين *"مرحبًا أنا أحبك"* و *"أنت تحبني مرحبًا"*.
|
||||
|
||||
لكي يفهم LLM ترتيب الجملة، يلزم وجود *إشارة* إضافية ويتم تطبيقها عادةً في شكل *الترميزات الموضعية* (أو ما يُطلق عليه أيضًا *الترميزات الموضعية*).
|
||||
لم يتم ترجمة النص الخاص والروابط وأكواد HTML وCSS بناءً على طلبك.
|
||||
|
||||
قدم مؤلفو الورقة البحثية [*Attention Is All You Need*](https://arxiv.org/abs/1706.03762) تضمينات موضعية جيبية مثلثية \\( \mathbf{P} = \mathbf{p}_1, \ldots, \mathbf{p}_N \\) حيث يتم حساب كل متجه \\( \mathbf{p}_i \\) كدالة جيبية لموضعه \\( i \\) .
|
||||
بعد ذلك يتم ببساطة إضافة التضمينات الموضعية إلى متجهات تسلسل الإدخال \\( \mathbf{\hat{X}} = \mathbf{\hat{x}}_1, \ldots, \mathbf{\hat{x}}_N \\) = \\( \mathbf{x}_1 + \mathbf{p}_1, \ldots, \mathbf{x}_N + \mathbf{p}_N \\) وبالتالي توجيه النموذج لتعلم ترتيب الجملة بشكل أفضل.
|
||||
|
||||
بدلاً من استخدام التضمينات الموضعية الثابتة، استخدم آخرون (مثل [Devlin et al.](https://arxiv.org/abs/1810.04805)) تضمينات موضعية مكتسبة يتم من خلالها تعلم التضمينات الموضعية \\( \mathbf{P} \\) أثناء التدريب.
|
||||
|
||||
كانت التضمينات الموضعية الجيبية والمكتسبة هي الطرق السائدة لترميز ترتيب الجملة في نماذج اللغة الكبيرة، ولكن تم العثور على بعض المشكلات المتعلقة بهذه التضمينات الموضعية:
|
||||
|
||||
1. التضمينات الموضعية الجيبية والمكتسبة هي تضمينات موضعية مطلقة، أي ترميز تضمين فريد لكل معرف موضعي: \\( 0, \ldots, N \\) . كما أظهر [Huang et al.](https://arxiv.org/abs/2009.13658) و [Su et al.](https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.09864)، تؤدي التضمينات الموضعية المطلقة إلى أداء ضعيف لنماذج اللغة الكبيرة للمدخلات النصية الطويلة. بالنسبة للمدخلات النصية الطويلة، يكون من المفيد إذا تعلم النموذج المسافة الموضعية النسبية التي تمتلكها رموز المدخلات إلى بعضها البعض بدلاً من موضعها المطلق.
|
||||
2. عند استخدام التضمينات الموضعية المكتسبة، يجب تدريب نموذج اللغة الكبيرة على طول إدخال ثابت \\( N \\)، مما يجعل من الصعب الاستقراء إلى طول إدخال أطول مما تم تدريبه عليه.
|
||||
|
||||
في الآونة الأخيرة، أصبحت التضمينات الموضعية النسبية التي يمكنها معالجة المشكلات المذكورة أعلاه أكثر شعبية، وأبرزها:
|
||||
|
||||
- [تضمين الموضع الدوراني (RoPE)](https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.09864)
|
||||
- [ALiBi](https://arxiv.org/abs/2108.12409)
|
||||
|
||||
يؤكد كل من *RoPE* و *ALiBi* أنه من الأفضل توجيه نموذج اللغة الكبيرة حول ترتيب الجملة مباشرة في خوارزمية الانتباه الذاتي حيث يتم وضع رموز الكلمات في علاقة مع بعضها البعض. على وجه التحديد، يجب توجيه ترتيب الجملة عن طريق تعديل عملية \\( \mathbf{QK}^T \\) .
|
||||
|
||||
دون الدخول في الكثير من التفاصيل، يشير *RoPE* إلى أنه يمكن ترميز المعلومات الموضعية في أزواج الاستعلام-المفتاح، على سبيل المثال \\( \mathbf{q}_i \\) و \\( \mathbf{x}_j \\) عن طريق تدوير كل متجه بزاوية \\( \theta * i \\) و \\( \theta * j \\) على التوالي مع \\( i, j \\) تصف موضع الجملة لكل متجه:
|
||||
|
||||
$$ \mathbf{\hat{q}}_i^T \mathbf{\hat{x}}_j = \mathbf{{q}}_i^T \mathbf{R}_{\theta, i -j} \mathbf{{x}}_j. $$
|
||||
|
||||
يمثل \\( \mathbf{R}_{\theta, i - j} \\) مصفوفة دورانية. \\( \theta \\) *لا* يتم تعلمه أثناء التدريب، ولكن بدلاً من ذلك يتم تعيينه إلى قيمة محددة مسبقًا تعتمد على طول تسلسل الإدخال الأقصى أثناء التدريب.
|
||||
|
||||
> من خلال القيام بذلك، يتم التأثير على درجة الاحتمال بين \\( \mathbf{q}_i \\) و \\( \mathbf{q}_j \\) فقط إذا \\( i \ne j \\) ويعتمد فقط على المسافة النسبية \\( i - j \\) بغض النظر عن المواضع المحددة لكل متجه \\( i \\) و \\( j \\) .
|
||||
|
||||
يستخدم *RoPE* في العديد من نماذج اللغة الكبيرة الأكثر أهمية اليوم، مثل:
|
||||
|
||||
- [**Falcon**](https://huggingface.co/tiiuae/falcon-40b)
|
||||
- [**Llama**](https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.13971)
|
||||
- [**PaLM**](https://arxiv.org/abs/2204.02311)
|
||||
|
||||
كبديل، يقترح *ALiBi* مخطط ترميز موضعي نسبي أبسط بكثير. يتم إضافة المسافة النسبية التي تمتلكها رموز المدخلات إلى بعضها البعض كعدد صحيح سلبي مقياس بقيمة محددة مسبقًا `m` إلى كل إدخال استعلام-مفتاح لمصفوفة \\( \mathbf{QK}^T \\) مباشرة قبل حساب softmax.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
كما هو موضح في ورقة [ALiBi](https://arxiv.org/abs/2108.12409)، يسمح هذا الترميز الموضعي النسبي البسيط للنموذج بالحفاظ على أداء عالٍ حتى في تسلسلات المدخلات النصية الطويلة جدًا.
|
||||
|
||||
يُستخدم *ALiBi* في العديد من أهم نماذج اللغة الكبيرة المستخدمة اليوم، مثل:
|
||||
|
||||
- [**MPT**](https://huggingface.co/mosaicml/mpt-30b)
|
||||
- [**BLOOM**](https://huggingface.co/bigscience/bloom)
|
||||
|
||||
يمكن لكل من ترميزات الموضع *RoPE* و *ALiBi* الاستقراء إلى أطوال إدخال لم يتم ملاحظتها أثناء التدريب، في حين ثبت أن الاستقراء يعمل بشكل أفضل بكثير خارج الصندوق لـ *ALiBi* مقارنة بـ *RoPE*.
|
||||
بالنسبة لـ ALiBi، ما عليك سوى زيادة قيم مصفوفة الموضع المثلث السفلي لمطابقة طول تسلسل الإدخال.
|
||||
بالنسبة لـ *RoPE*، يؤدي الحفاظ على نفس \\( \theta \\) الذي تم استخدامه أثناء التدريب إلى نتائج سيئة عند تمرير إدخالات نصية أطول بكثير من تلك التي شوهدت أثناء التدريب، راجع [Press et al.](https://arxiv.org/abs/2108.12409). ومع ذلك، وجد المجتمع بعض الحيل الفعالة التي تقوم بتعديل \\( \theta \\)، مما يسمح لترميزات الموضع *RoPE* بالعمل بشكل جيد لتسلسلات إدخال النص المستقرئة (راجع [هنا](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/pull/24653)).
|
||||
|
||||
> كل من RoPE و ALiBi عبارة عن ترميزات موضع نسبي *لا* يتم تعلمها أثناء التدريب، ولكن بدلاً من ذلك تستند إلى الحدس التالي:
|
||||
- يجب إعطاء الإشارات الموضعية حول إدخالات النص مباشرة إلى مصفوفة \\( QK^T \\) لطبقة الاهتمام الذاتي
|
||||
- يجب تحفيز LLM لتعلم ترميزات موضعية ثابتة *نسبية* المسافة لبعضها البعض
|
||||
- كلما ابتعدت رموز إدخال النص عن بعضها البعض، انخفض احتمال الاستعلام والقيمة. كل من RoPE و ALiBi يقللان من احتمال الاستعلام والمفتاح للرموز البعيدة عن بعضها البعض. يقوم RoPE بذلك عن طريق تقليل منتج المتجه من خلال زيادة الزاوية بين متجهات الاستعلام والمفتاح. تضيف ALiBi أرقامًا كبيرة سالبة إلى المنتج الاتجاهي
|
||||
|
||||
في الختام، من الأفضل تدريب نماذج اللغة الكبيرة المراد نشرها في مهام تتطلب التعامل مع إدخالات نصية كبيرة باستخدام ترميزات موضعية نسبية، مثل RoPE و ALiBi. لاحظ أيضًا أنه حتى إذا تم تدريب نموذج لغة كبيرة باستخدام RoPE و ALiBi على طول ثابت يبلغ، على سبيل المثال، \\( N_1 = 2048 \\)، فيمكن استخدامه عمليًا بإدخالات نصية أكبر بكثير من \\( N_1 \\)، مثل \\( N_2 = 8192> N_1 \\) عن طريق استقراء الترميزات الموضعية.
|
||||
|
||||
### 3.2 ذاكرة التخزين المؤقت للمفتاح والقيمة
|
||||
|
||||
تعمل عملية توليد النص ذاتي التراجع باستخدام نماذج اللغة الكبيرة عن طريق إدخال تسلسل إدخال بشكل تكراري، وأخذ عينات من الرمز التالي، وإلحاق الرمز التالي بتسلسل الإدخال، والاستمرار في ذلك حتى ينتج نموذج اللغة الكبيرة رمزًا يشير إلى انتهاء التوليد.
|
||||
|
||||
يرجى الاطلاع على [دليل إنشاء النص الخاص بـ Transformer](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/llm_tutorial#generate-text) للحصول على شرح مرئي أفضل لكيفية عمل التوليد ذاتي التراجع.
|
||||
|
||||
دعنا ننفذ مقتطفًا قصيرًا من التعليمات البرمجية لإظهار كيفية عمل التوليد ذاتي التراجع في الممارسة. ببساطة، سنأخذ الرمز الأكثر احتمالًا عبر `torch.argmax`.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
input_ids = tokenizer(prompt, return_tensors="pt")["input_ids"].to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
for _ in range(5):
|
||||
next_logits = model(input_ids)["logits"][:, -1:]
|
||||
next_token_id = torch.argmax(next_logits,dim=-1)
|
||||
|
||||
input_ids = torch.cat([input_ids, next_token_id], dim=-1)
|
||||
print("shape of input_ids", input_ids.shape)
|
||||
|
||||
generated_text = tokenizer.batch_decode(input_ids[:, -5:])
|
||||
generated_text
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**الإخراج**:
|
||||
```
|
||||
shape of input_ids torch.Size([1, 21])
|
||||
shape of input_ids torch.Size([1, 22])
|
||||
shape of input_ids torch.Size([1, 23])
|
||||
shape of input_ids torch.Size([1, 24])
|
||||
shape of input_ids torch.Size([1, 25])
|
||||
[' Here is a Python function']
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
كما نرى، في كل مرة نزيد من رموز إدخال النص بالرمز الذي تم أخذ عينات منه للتو.
|
||||
|
||||
باستثناءات قليلة جدًا، يتم تدريب نماذج اللغة الكبيرة باستخدام [هدف نمذجة اللغة السببية](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/tasks/language_modeling#causal-language-modeling) وبالتالي يتم قناع المثلث العلوي لمصفوفة نتيجة الاهتمام - وهذا هو السبب في ترك نتائج الاهتمام فارغة (*أي لها احتمال 0*) في المخططين أعلاه. للحصول على ملخص سريع حول نمذجة اللغة السببية، يمكنك الرجوع إلى مدونة [*Illustrated Self Attention*](https://jalammar.github.io/illustrated-gpt2/#part-2-illustrated-self-attention).
|
||||
|
||||
ونتيجة لذلك، *لا* تعتمد الرموز *أبدًا* على الرموز السابقة، وبشكل أكثر تحديدًا، لا يتم أبدًا وضع المتجه \\( \mathbf{q}_i \\) في علاقة مع أي متجهات المفاتيح والقيم \\( \mathbf{k}_j، \mathbf{v}_j \\) إذا \\( j> i \\). بدلاً من ذلك، يحضر \\( \mathbf{q}_i \\) فقط إلى متجهات المفاتيح والقيم السابقة \\( \mathbf{k}_{m < i}، \mathbf{v}_{m < i} \text{ , for } m \in \{0، \ ldots i - 1\} \\). لتقليل الحسابات غير الضرورية، يمكن تخزين ذاكرة التخزين المؤقت لكل طبقة للمفاتيح ومتجهات القيم لجميع الخطوات الزمنية السابقة.
|
||||
|
||||
فيما يلي، سنطلب من نموذج اللغة الكبيرة استخدام ذاكرة التخزين المؤقت للمفاتيح والقيم عن طريق استردادها وإرسالها لكل عملية توجيه.
|
||||
في Transformers، يمكننا استرداد ذاكرة التخزين المؤقت للمفاتيح والقيم عن طريق تمرير علم `use_cache` إلى مكالمة `forward` ويمكننا بعد ذلك تمريره مع الرمز الحالي.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
past_key_values = None # past_key_values is the key-value cache
|
||||
generated_tokens = []
|
||||
next_token_id = tokenizer(prompt, return_tensors="pt")["input_ids"].to("cuda")
|
||||
|
||||
for _ in range(5):
|
||||
next_logits, past_key_values = model(next_token_id, past_key_values=past_key_values, use_cache=True).to_tuple()
|
||||
next_logits = next_logits[:, -1:]
|
||||
next_token_id = torch.argmax(next_logits, dim=-1)
|
||||
|
||||
print("shape of input_ids", next_token_id.shape)
|
||||
print("length of key-value cache", len(past_key_values[0][0])) # past_key_values are of shape [num_layers, 0 for k, 1 for v, batch_size, length, hidden_dim]
|
||||
generated_tokens.append(next_token_id.item())
|
||||
|
||||
generated_text = tokenizer.batch_decode(generated_tokens)
|
||||
generated_text
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**الإخراج**:
|
||||
```
|
||||
shape of input_ids torch.Size([1, 1])
|
||||
length of key-value cache 20
|
||||
shape of input_ids torch.Size([1, 1])
|
||||
length of key-value cache 21
|
||||
shape of input_ids torch.Size([1, 1])
|
||||
length of key-value cache 22
|
||||
shape of input_ids torch.Size([1, 1])
|
||||
length of key-value cache 23
|
||||
shape of input_ids torch.Size([1, 1])
|
||||
length of key-value cache 24
|
||||
[' Here', ' is', ' a', ' Python', ' function']
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
كما هو موضح، عند استخدام ذاكرة التخزين المؤقت للمفاتيح والقيم، لا يتم زيادة رموز إدخال النص في الطول، ولكنها تظل متجه إدخال واحدًا. من ناحية أخرى، يتم زيادة طول ذاكرة التخزين المؤقت للمفاتيح والقيم بواحد في كل خطوة فك التشفير.
|
||||
|
||||
> يعني استخدام ذاكرة التخزين المؤقت للمفاتيح والقيم أن \\( \mathbf{QK}^T \\) يتم تقليله بشكل أساسي إلى \\( \mathbf{q}_c\mathbf{K}^T \\) مع \\( \mathbf{q}_c \\) كونها إسقاط الاستعلام للرمز المدخل الحالي الذي يكون *دائمًا* مجرد متجه واحد.
|
||||
|
||||
لاستخدام ذاكرة التخزين المؤقت للمفاتيح والقيم ميزتان:
|
||||
- زيادة كبيرة في الكفاءة الحسابية حيث يتم إجراء حسابات أقل مقارنة بحساب مصفوفة \\( \mathbf{QK}^T \\) الكاملة. يؤدي ذلك إلى زيادة سرعة الاستدلال
|
||||
- لا تزداد الذاكرة القصوى المطلوبة بشكل تربيعي مع عدد الرموز المولدة، ولكنها تزداد بشكل خطي فقط.
|
||||
|
||||
> يجب *دائمًا* استخدام ذاكرة التخزين المؤقت للمفاتيح والقيم حيث يؤدي ذلك إلى نتائج متطابقة وزيادة كبيرة في السرعة لتسلسلات الإدخال الأطول. ذاكرة التخزين المؤقت للمفاتيح والقيم ممكّنة بشكل افتراضي في Transformers عند استخدام خط أنابيب النص أو طريقة [`generate`](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main_classes/text_generation).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
لاحظ أنه على الرغم من نصيحتنا باستخدام ذاكرة التخزين المؤقت للمفاتيح والقيم، فقد يكون إخراج نموذج اللغة الكبيرة مختلفًا قليلاً عند استخدامها. هذه خاصية نوى ضرب المصفوفة نفسها - يمكنك قراءة المزيد عنها [هنا](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/issues/25420#issuecomment-1775317535).
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
#### 3.2.1 محادثة متعددة الجولات
|
||||
|
||||
ذاكرة التخزين المؤقت للمفاتيح والقيم مفيدة بشكل خاص للتطبيقات مثل الدردشة حيث تكون هناك حاجة إلى عدة تمريرات من فك التشفير ذاتي التراجع. دعنا نلقي نظرة على مثال.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
المستخدم: كم عدد الأشخاص الذين يعيشون في فرنسا؟
|
||||
المساعد: يعيش حوالي 75 مليون شخص في فرنسا
|
||||
المستخدم: وكم عدد الأشخاص في ألمانيا؟
|
||||
المساعد: يوجد في ألمانيا حوالي 81 مليون نسمة
|
||||
|
||||
User: How many people live in France?
|
||||
Assistant: Roughly 75 million people live in France
|
||||
User: And how many are in Germany?
|
||||
Assistant: Germany has ca. 81 million inhabitants
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In this chat، يقوم LLM بتشغيل فك التشفير التلقائي مرتين:
|
||||
1. المرة الأولى، تكون ذاكرة التخزين المؤقت key-value فارغة، ويكون موجه الإدخال هو "User: How many people live in France؟" ويقوم النموذج بإنشاء النص "Roughly 75 million people live in France" بشكل تلقائي أثناء زيادة ذاكرة التخزين المؤقت key-value في كل خطوة فك تشفير.
|
||||
2. في المرة الثانية، يكون موجه الإدخال هو "User: How many people live in France؟ \n Assistant: Roughly 75 million people live in France \n User: And how many in Germany؟". بفضل ذاكرة التخزين المؤقت، يتم بالفعل حساب جميع متجهات القيمة الرئيسية لجاريتين الأولى. لذلك يتكون موجه الإدخال فقط من "User: And how many in Germany؟". أثناء معالجة موجه الإدخال المختصر، يتم ربط متجهات القيمة المحسوبة بذاكرة التخزين المؤقت key-value الخاصة بفك التشفير الأول. يتم بعد ذلك إنشاء إجابة المساعد الثانية "Germany has ca. 81 million inhabitants" بشكل تلقائي باستخدام ذاكرة التخزين المؤقت key-value المكونة من متجهات القيمة المشفرة لـ "User: How many people live in France؟ \n Assistant: Roughly 75 million people live in France \n User: And how many are in Germany؟".
|
||||
|
||||
يجب ملاحظة أمرين هنا:
|
||||
1. الحفاظ على كل السياق أمر بالغ الأهمية للنماذج اللغوية الكبيرة (LLMs) التي يتم نشرها في الدردشة بحيث يفهم LLM كل سياق المحادثة السابق. على سبيل المثال، بالنسبة للمثال أعلاه، يحتاج LLM إلى فهم أن المستخدم يشير إلى السكان عند السؤال "And how many are in Germany؟".
|
||||
2. ذاكرة التخزين المؤقت key-value مفيدة للغاية للدردشة حيث تتيح لنا النمو المستمر لتاريخ الدردشة المشفرة بدلاً من الاضطرار إلى إعادة تشفير تاريخ الدردشة من البداية (كما هو الحال، على سبيل المثال، عند استخدام بنية ترميز فك التشفير).
|
||||
|
||||
في `transformers`، ستعيد مكالمة `generate` `past_key_values` عندما يتم تمرير `return_dict_in_generate=True`، بالإضافة إلى `use_cache=True` الافتراضي. لاحظ أنه غير متوفر بعد من خلال واجهة `pipeline`.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# Generation as usual
|
||||
prompt = system_prompt + "Question: Please write a function in Python that transforms bytes to Giga bytes.\n\nAnswer: Here"
|
||||
model_inputs = tokenizer(prompt، return_tensors='pt')
|
||||
generation_output = model.generate(**model_inputs، max_new_tokens=60، return_dict_in_generate=True)
|
||||
decoded_output = tokenizer.batch_decode(generation_output.sequences)[0]
|
||||
|
||||
# Piping the returned `past_key_values` to speed up the next conversation round
|
||||
prompt = decoded_output + "\nQuestion: How can I modify the function above to return Mega bytes instead?\n\nAnswer: Here"
|
||||
model_inputs = tokenizer(prompt، return_tensors='pt')
|
||||
generation_output = model.generate(
|
||||
**model_inputs،
|
||||
past_key_values=generation_output.past_key_values،
|
||||
max_new_tokens=60،
|
||||
return_dict_in_generate=True
|
||||
)
|
||||
tokenizer.batch_decode(generation_output.sequences)[0][len(prompt):]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**الإخراج**:
|
||||
```
|
||||
هي نسخة معدلة من الدالة التي تعيد ميجا بايت بدلاً من ذلك.
|
||||
|
||||
def bytes_to_megabytes(bytes):
|
||||
return bytes / 1024 / 1024
|
||||
|
||||
Answer: The function takes a number of bytes as input and returns the number of
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
رائع، لا يتم إنفاق وقت إضافي على إعادة حساب نفس المفتاح والقيم لطبقة الاهتمام! ومع ذلك، هناك شيء واحد يجب ملاحظته. في حين أن ذروة الذاكرة المطلوبة لمصفوفة \\( \mathbf{QK}^T \\) يتم تقليلها بشكل كبير، فإن الاحتفاظ بذاكرة التخزين المؤقت key-value في الذاكرة يمكن أن يصبح مكلفًا جدًا من حيث الذاكرة لسلاسل الإدخال الطويلة أو الدردشة متعددة الجولات. تذكر أن ذاكرة التخزين المؤقت key-value بحاجة إلى تخزين متجهات القيمة الرئيسية لجميع متجهات الإدخال السابقة \\( \mathbf{x}_i \text{، لـ } i \in \{1، \ ldots، c - 1\} \\) لجميع طبقات الاهتمام الذاتي وكل رؤوس الاهتمام.
|
||||
|
||||
دعنا نحسب عدد القيم العائمة التي يجب تخزينها في ذاكرة التخزين المؤقت key-value لنموذج LLM `bigcode/octocoder` الذي استخدمناه من قبل.
|
||||
يبلغ عدد القيم العائمة ضعف طول التسلسل مضروبًا في عدد رؤوس الاهتمام مضروبًا في بعد رأس الاهتمام ومضروبًا في عدد الطبقات.
|
||||
حساب هذا لنموذج LLM لدينا عند طول تسلسل افتراضي يبلغ 16000 يعطي:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
config = model.config
|
||||
2 * 16_000 * config.n_layer * config.n_head * config.n_embd // config.n_head
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**الإخراج**:
|
||||
```
|
||||
7864320000
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Roughly 8 مليار قيمة عائمة! يتطلب تخزين 8 مليارات قيمة عائمة في دقة `float16` حوالي 15 جيجابايت من ذاكرة الوصول العشوائي (RAM) وهو ما يقرب من نصف حجم أوزان النموذج نفسها!
|
||||
اقترح الباحثون طريقتين تسمحان بتقليل تكلفة الذاكرة لتخزين ذاكرة التخزين المؤقت key-value بشكل كبير، والتي يتم استكشافها في الأقسام الفرعية التالية.
|
||||
|
||||
#### 3.2.2 Multi-Query-Attention (MQA)
|
||||
|
||||
[Multi-Query-Attention](https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.02150) اقترحها Noam Shazeer في ورقته *Fast Transformer Decoding: One Write-Head is All You Need*. كما يقول العنوان، اكتشف Noam أنه بدلاً من استخدام `n_head` من أوزان إسقاط القيمة الرئيسية، يمكن استخدام زوج واحد من أوزان إسقاط رأس القيمة التي يتم مشاركتها عبر جميع رؤوس الاهتمام دون أن يتدهور أداء النموذج بشكل كبير.
|
||||
|
||||
> باستخدام زوج واحد من أوزان إسقاط رأس القيمة، يجب أن تكون متجهات القيمة الرئيسية \\( \mathbf{k}_i، \mathbf{v}_i \\) متطابقة عبر جميع رؤوس الاهتمام والتي بدورها تعني أننا بحاجة فقط إلى تخزين زوج إسقاط قيمة رئيسي واحد في ذاكرة التخزين المؤقت بدلاً من `n_head` منها.
|
||||
|
||||
نظرًا لأن معظم LLMs تستخدم ما بين 20 و100 رأس اهتمام، فإن MQA يقلل بشكل كبير من استهلاك الذاكرة لذاكرة التخزين المؤقت key-value. بالنسبة إلى LLM المستخدم في هذا الدفتر، يمكننا تقليل استهلاك الذاكرة المطلوبة من 15 جيجابايت إلى أقل من 400 ميجابايت عند طول تسلسل الإدخال 16000.
|
||||
|
||||
بالإضافة إلى توفير الذاكرة، يؤدي MQA أيضًا إلى تحسين الكفاءة الحسابية كما هو موضح في ما يلي.
|
||||
في فك التشفير التلقائي، يجب إعادة تحميل متجهات القيمة الرئيسية الكبيرة، ودمجها مع زوج متجه القيمة الحالي، ثم إدخالها في \\( \mathbf{q}_c\mathbf{K}^T \\) الحساب في كل خطوة. بالنسبة لفك التشفير التلقائي، يمكن أن تصبح عرض النطاق الترددي للذاكرة المطلوبة لإعادة التحميل المستمر عنق زجاجة زمنيًا خطيرًا. من خلال تقليل حجم متجهات القيمة الرئيسية، يجب الوصول إلى ذاكرة أقل، وبالتالي تقليل عنق الزجاجة في عرض النطاق الترددي للذاكرة. لمزيد من التفاصيل، يرجى إلقاء نظرة على [ورقة Noam](https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.02150).
|
||||
|
||||
الجزء المهم الذي يجب فهمه هنا هو أن تقليل عدد رؤوس الاهتمام بالقيمة الرئيسية إلى 1 لا معنى له إلا إذا تم استخدام ذاكرة التخزين المؤقت للقيمة الرئيسية. يظل الاستهلاك الذروي لذاكرة النموذج لمرور واحد للأمام بدون ذاكرة التخزين المؤقت للقيمة الرئيسية دون تغيير لأن كل رأس اهتمام لا يزال لديه متجه استعلام فريد بحيث يكون لكل رأس اهتمام مصفوفة \\( \mathbf{QK}^T \\) مختلفة.
|
||||
|
||||
شهدت MQA اعتمادًا واسع النطاق من قبل المجتمع ويتم استخدامها الآن بواسطة العديد من LLMs الأكثر شهرة:
|
||||
|
||||
- [**Falcon**](https://huggingface.co/tiiuae/falcon-40b)
|
||||
- [**PaLM**](https://arxiv.org/abs/2204.02311)
|
||||
- [**MPT**](https://huggingface.co/mosaicml/mpt-30b)
|
||||
- [**BLOOM**](https://huggingface.co/bigscience/bloom)
|
||||
|
||||
كما يستخدم نقطة التحقق المستخدمة في هذا الدفتر - `bigcode/octocoder` - MQA.
|
||||
|
||||
#### 3.2.3 مجموعة الاستعلام الاهتمام (GQA)
|
||||
|
||||
[مجموعة الاستعلام الاهتمام](https://arxiv.org/abs/2305.13245)، كما اقترح Ainslie et al. من Google، وجد أن استخدام MQA يمكن أن يؤدي غالبًا إلى تدهور الجودة مقارنة باستخدام إسقاطات رأس القيمة الرئيسية المتعددة. تجادل الورقة بأنه يمكن الحفاظ على أداء النموذج بشكل أكبر عن طريق تقليل عدد أوزان إسقاط رأس الاستعلام بشكل أقل حدة. بدلاً من استخدام وزن إسقاط قيمة رئيسية واحدة فقط، يجب استخدام `n <n_head` أوزان إسقاط قيمة رئيسية. من خلال اختيار `n` إلى قيمة أقل بكثير من `n_head`، مثل 2 أو 4 أو 8، يمكن الاحتفاظ بمعظم مكاسب الذاكرة والسرعة من MQA مع التضحية بقدر أقل من سعة النموذج وبالتالي، من المفترض، أقل أداء.
|
||||
|
||||
علاوة على ذلك، اكتشف مؤلفو GQA أنه يمكن *تدريب* نقاط تفتيش النموذج الموجودة ليكون لها بنية GQA باستخدام 5% فقط من الحوسبة الأصلية للتعليم المسبق. في حين أن 5% من الحوسبة الأصلية للتعليم المسبق يمكن أن تكون كمية هائلة، يسمح GQA *uptraining* بنقاط تفتيش موجودة للاستفادة من تسلسلات الإدخال الأطول.
|
||||
|
||||
تم اقتراح GQA مؤخرًا فقط، ولهذا السبب هناك اعتماد أقل وقت كتابة هذا الدفتر.
|
||||
أبرز تطبيق لـ GQA هو [Llama-v2](https://huggingface.co/meta-llama/Llama-2-70b-hf).
|
||||
|
||||
> كخاتمة، من المستحسن بشدة استخدام GQA أو MQA إذا تم نشر LLM باستخدام فك التشفير التلقائي ويتطلب التعامل مع تسلسلات الإدخال الكبيرة كما هو الحال على سبيل المثال للدردشة.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## الخاتمة
|
||||
|
||||
مجتمع البحث يأتي باستمرار بطرق جديدة ومبتكرة لتسريع وقت الاستدلال للنماذج اللغوية الكبيرة على الإطلاق. كمثال، أحد اتجاهات البحث الواعدة هو [فك التشفير التخميني](https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.17192) حيث تقوم "الرموز السهلة" بإنشائها نماذج اللغة الأصغر والأسرع ويتم إنشاء "الرموز الصعبة" فقط بواسطة LLM نفسه. إن التعمق في التفاصيل يتجاوز نطاق هذا الدفتر، ولكن يمكن قراءته في هذه [تدوينة المدونة اللطيفة](https://huggingface.co/blog/assisted-generation).
|
||||
|
||||
السبب في أن LLMs الضخمة مثل GPT3/4، وLlama-2-70b، وClaude، وPaLM يمكن أن تعمل بسرعة كبيرة في واجهات الدردشة مثل [Hugging Face Chat](https://huggingface.co/chat/) أو ChatGPT يرجع إلى حد كبير إلى التحسينات المذكورة أعلاه في الدقة والخوارزميات والهندسة المعمارية.
|
||||
في المستقبل، ستكون أجهزة التسريع مثل وحدات معالجة الرسومات (GPUs) ووحدات معالجة الرسومات (TPUs)، وما إلى ذلك... ستكون أسرع فقط وستسمح بمزيد من الذاكرة، ولكن يجب دائمًا التأكد من استخدام أفضل الخوارزميات والهندسة المعمارية المتاحة للحصول على أكبر قدر من المال
|
||||
@ -1,226 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# تشريح عملية تدريب النموذج
|
||||
|
||||
لفهم تقنيات تحسين الأداء التي يمكن تطبيقها لتحسين كفاءة استخدام الذاكرة وسرعة تدريب النموذج، من المفيد التعرف على كيفية استخدام وحدة معالجة الرسوميات (GPU) أثناء التدريب، وكيف تختلف كثافة العمليات الحسابية باختلاف العملية التي يتم تنفيذها.
|
||||
|
||||
لنبدأ باستكشاف مثال توضيحي على استخدام وحدة GPU وتشغيل تدريب نموذج. وللتوضيح، سنحتاج إلى تثبيت بعض المكتبات:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install transformers datasets accelerate nvidia-ml-py3
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
تتيح مكتبة `nvidia-ml-py3` إمكانية مراقبة استخدام الذاكرة في النماذج من داخل بايثون. قد تكون على دراية بأمر `nvidia-smi` في الجهاز - تسمح هذه المكتبة بالوصول إلى نفس المعلومات مباشرة في بايثون.
|
||||
|
||||
ثم، نقوم بإنشاء بعض البيانات الوهمية:معرّفات رموز عشوائية بين 100 و30000 وتصنيفات ثنائية للمصنف.
|
||||
|
||||
في المجموع، نحصل على 512 تسلسلًا، لكل منها طول 512، ونخزنها في [`~datasets.Dataset`] بتنسيق PyTorch.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> import numpy as np
|
||||
>>> from datasets import Dataset
|
||||
|
||||
>>> seq_len, dataset_size = 512, 512
|
||||
>>> dummy_data = {
|
||||
... "input_ids": np.random.randint(100, 30000, (dataset_size, seq_len)),
|
||||
... "labels": np.random.randint(0, 1, (dataset_size)),
|
||||
... }
|
||||
>>> ds = Dataset.from_dict(dummy_data)
|
||||
>>> ds.set_format("pt")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
لطباعة إحصائيات موجزة لاستخدام وحدة GPU وتشغيل التدريب مع [`Trainer`]، نقوم بتعريف دالتين مساعدتين:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from pynvml import *
|
||||
|
||||
>>> def print_gpu_utilization():
|
||||
... nvmlInit()
|
||||
... handle = nvmlDeviceGetHandleByIndex(0)
|
||||
... info = nvmlDeviceGetMemoryInfo(handle)
|
||||
... print(f"GPU memory occupied: {info.used//1024**2} MB.")
|
||||
|
||||
>>> def print_summary(result):
|
||||
... print(f"Time: {result.metrics['train_runtime']:.2f}")
|
||||
... print(f"Samples/second: {result.metrics['train_samples_per_second']:.2f}")
|
||||
... print_gpu_utilization()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
دعنا نتأكد من أننا نبدأ بذاكرة وحدة GPU خالية:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> print_gpu_utilization()
|
||||
GPU memory occupied: 0 MB.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
يبدو ذلك جيدًا: لم يتم شغل ذاكرة وحدة معالجة الرسومات كما نتوقع قبل تحميل أي نماذج. إذا لم يكن الأمر كذلك على جهازك، فتأكد من إيقاف جميع العمليات التي تستخدم ذاكرة وحدة GPU. ومع ذلك، لا يمكن للمستخدم استخدام كل ذاكرة وحدة GPU الفارغة. عندما يتم تحميل نموذج إلى وحدة GPU، يتم أيضًا تحميل النواة، والتي يمكن أن تستهلك 1-2 جيجابايت من الذاكرة. ولرؤية مقدار ذلك، نقوم بتحميل مصفوفة صغيرة إلى وحدة GPU والتي تؤدي إلى تحميل النواة أيضًا.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> import torch
|
||||
|
||||
>>> torch.ones((1, 1)).to("cuda")
|
||||
>>> print_gpu_utilization()
|
||||
GPU memory occupied: 1343 MB.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
نلاحظ أن النواة وحدها تستهلك 1.3 جيجابايت من ذاكرة وحدة GPU. الآن دعنا نرى مقدار المساحة التي يستخدمها النموذج.
|
||||
|
||||
## تحميل النموذج
|
||||
|
||||
أولاً، نقوم بتحميل نموذج `google-bert/bert-large-uncased`. نقوم بتحميل أوزان النموذج مباشرة إلى وحدة GPU حتى نتمكن من التحقق من مقدار المساحة التي تستخدمها الأوزان فقط.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import AutoModelForSequenceClassification
|
||||
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained("google-bert/bert-large-uncased").to("cuda")
|
||||
>>> print_gpu_utilization()
|
||||
GPU memory occupied: 2631 MB.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
يمكننا أن نرى أن أوزان النموذج وحدها تستهلك 1.3 جيجابايت من ذاكرة وحدة GPU. يعتمد الرقم الدقيق على وحدة GPU المحددة التي تستخدمها. لاحظ أنه في وحدات GPU الأحدث، قد يستغرق النموذج في بعض الأحيان مساحة أكبر نظرًا لأن الأوزان يتم تحميلها بطريقة مُحسّنة تُسرّع من استخدام النموذج. الآن يمكننا أيضًا التحقق بسرعة مما إذا كنا نحصل على نفس النتيجة كما هو الحال مع `nvidia-smi` CLI:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
nvidia-smi
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
Tue Jan 11 08:58:05 2022
|
||||
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+
|
||||
| NVIDIA-SMI 460.91.03 Driver Version: 460.91.03 CUDA Version: 11.2 |
|
||||
|-------------------------------+----------------------+----------------------+
|
||||
| GPU Name Persistence-M| Bus-Id Disp.A | Volatile Uncorr. ECC |
|
||||
| Fan Temp Perf Pwr:Usage/Cap| Memory-Usage | GPU-Util Compute M. |
|
||||
| | | MIG M. |
|
||||
|===============================+======================+======================|
|
||||
| 0 Tesla V100-SXM2... On | 00000000:00:04.0 Off | 0 |
|
||||
| N/A 37C P0 39W / 300W | 2631MiB / 16160MiB | 0% Default |
|
||||
| | | N/A |
|
||||
+-------------------------------+----------------------+----------------------+
|
||||
|
||||
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+
|
||||
| Processes: |
|
||||
| GPU GI CI PID Type Process name GPU Memory |
|
||||
| ID ID Usage |
|
||||
|=============================================================================|
|
||||
| 0 N/A N/A 3721 C ...nvs/codeparrot/bin/python 2629MiB |
|
||||
+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
نحصل على نفس الرقم كما كان من قبل، ويمكنك أيضًا أن ترى أننا نستخدم GPU من طراز V100 مع 16 جيجابايت من الذاكرة. لذا الآن يمكننا بدء تدريب النموذج ورؤية كيف يتغير استخدام ذاكرة GPU. أولاً، نقوم بإعداد بعض معاملات التدريب القياسية:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
default_args = {
|
||||
"output_dir": "tmp"،
|
||||
"eval_strategy": "steps"،
|
||||
"num_train_epochs": 1،
|
||||
"log_level": "error"،
|
||||
"report_to": "none"،
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
إذا كنت تخطط لتشغيل عدة تجارب، من أجل مسح الذاكرة بشكل صحيح بين التجارب، قم بإعادة تشغيل نواة Python بين التجارب.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## استخدام الذاكرة في التدريب الأساسي
|
||||
|
||||
دعونا نستخدم [`Trainer`] وقم بتدريب النموذج دون استخدام أي تقنيات تحسين أداء GPU وحجم دفعة يبلغ 4:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> from transformers import TrainingArguments، Trainer، logging
|
||||
|
||||
>>> logging.set_verbosity_error()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
>>> training_args = TrainingArguments(per_device_train_batch_size=4، **default_args)
|
||||
>>> trainer = Trainer(model=model، args=training_args، train_dataset=ds)
|
||||
>>> result = trainer.train()
|
||||
>>> print_summary(result)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
الوقت: 57.82
|
||||
العينات / الثانية: 8.86
|
||||
ذاكرة GPU المشغولة: 14949 ميجابايت.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
يمكننا أن نرى أن حجم دفعة صغير نسبيًا يملأ تقريبًا ذاكرة GPU بالكامل. ومع ذلك، غالبًا ما يؤدي حجم دفعة أكبر في تقارب نموذج أسرع أو أداء أفضل في النهاية. لذلك نريد أن نضبط حجم الدفعة وفقًا لاحتياجات النموذج لدينا وليس مع قيود وحدة GPU. ما يثير الاهتمام هو أننا نستخدم ذاكرة أكثر بكثير من حجم النموذج.
|
||||
لفهم سبب ذلك بشكل أفضل، دعنا نلقي نظرة على عمليات النموذج واحتياجاته من الذاكرة.
|
||||
|
||||
## تشريح عمليات النموذج
|
||||
|
||||
تتضمن بنية المحولات 3 مجموعات رئيسية من العمليات مُجمعة أدناه حسب كثافة العمليات الحسابية.
|
||||
|
||||
1. **عمليات ضرب المصفوفات**
|
||||
|
||||
تقوم الطبقات الخطية ومكونات الانتباه متعدد الرؤوس جميعها بعمليات ضرب ** المصفوفة بالمصفوفة** على دفعات. هذه العمليات هي أكثر أجزاء تدريب المحولات كثافة من الناحية الحسابية.
|
||||
|
||||
2. **عمليات التسوية الإحصائية**
|
||||
|
||||
تُعد عمليات Softmax والتسوية الطبقية أقل كثافة من ناحية الحسابية من عمليات ضرب المصفوفات، وتنطوي على عملية أو أكثر من عمليات **الاختزال**، والتي يتم تطبيق نتيجتها بعد ذلك عبر خريطة.
|
||||
|
||||
3. **العمليات على مستوى العناصر**
|
||||
|
||||
هذه هي العمليات المتبقية: **الانحيازات، والتسرب، ووظائف التنشيط، والوصلات المتبقية**. هذه هي عمليات أقل كثافة من الناحية الحسابية.
|
||||
|
||||
يمكن أن تكون هذه المعرفة مفيدة لمعرفة عند تحليل اختناقات الأداء.
|
||||
|
||||
هذا الملخص مُشتق من [نقل البيانات هو كل ما تحتاجه: دراسة حالة حول تحسين المحولات 2020](https://arxiv.org/abs/2007.00072)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## تشريح ذاكرة النموذج
|
||||
|
||||
لقد رأينا أن تدريب النموذج يستخدم ذاكرة أكثر بكثير من مجرد وضع النموذج على GPU. ويرجع ذلك إلى
|
||||
هناك العديد من المكونات أثناء التدريب التي تستخدم ذاكرة GPU. المكونات الموجودة في ذاكرة GPU هي التالية:
|
||||
|
||||
1. أوزان النموذج
|
||||
2. الدول المُحسّن
|
||||
3. المُتدرجات
|
||||
4. تنشيطات المسار الأمامي المحفوظة لحساب المُتدرجات
|
||||
5. المخازن المؤقتة
|
||||
6. ذاكرة محددة الوظائف
|
||||
|
||||
يتطلب نموذج نموذجي مدرب بدقة مختلطة 18 بايت للمُحسّن AdamW كل معلمة نموذج بالإضافة إلى ذاكرة التنشيط. للاستدلال لا توجد حالات مُحسّن و مُتدرجات، لذلك يمكننا طرح تلك. وهكذا ننتهي مع 6 بايت لكل
|
||||
معلمة نموذج للدقة المختلطة الاستدلال، بالإضافة إلى ذاكرة التنشيط.
|
||||
|
||||
دعنا نلقي نظرة على التفاصيل.
|
||||
|
||||
**أوزان النموذج:**
|
||||
|
||||
- 4 بايت * عدد المعلمات للتدريب على دقة fp32
|
||||
- 6 بايت * عدد المعلمات لتدريب الدقة المختلطة (يحافظ على نموذج في fp32 وآخر بدقة fp16 في الذاكرة)
|
||||
|
||||
**حالات المُحسّن:**
|
||||
|
||||
- 8 بايت * عدد المعلمات للمُحسّن AdamW العادي (يحافظ على حالتين)
|
||||
- 2 بايت * عدد المعلمات لمُحسّنات 8 بت AdamW مثل [bitsandbytes](https://github.com/TimDettmers/bitsandbytes)
|
||||
- 4 بايت * عدد المعلمات لمُحسّنات مثل SGD مع الزخم momentum (يحافظ على حالة واحدة فقط)
|
||||
|
||||
**المُتدرجات**
|
||||
|
||||
- 4 بايت * عدد المعلمات للتدريب بدقة fp32 أو بدقة مختلطة (المُتدرجات تكون دائمًا بدقة fp32)
|
||||
|
||||
**تنشيطات المسار الأمامي**
|
||||
|
||||
- يعتمد الحجم على العديد من العوامل، وأهمها طول التسلسل وحجم المخفية وحجم الدُفعة.
|
||||
|
||||
هناك المدخلات والمخرجات لذي يتم تمريرها وإرجاعها بواسطة وظائف المسار الأمامي والمسار الخلفي وتنشيطات المسار الأمامي المحفوظة لحساب المُتدرجات.
|
||||
|
||||
**الذاكرة المؤقتة**
|
||||
|
||||
بالإضافة إلى ذلك، هناك جميع أنواع المتغيرات المؤقتة التي يتم تحريرها بمجرد الانتهاء من الحساب، ولكن في
|
||||
لحظة يمكن أن تتطلب هذه المتغيرات المؤقتة ذاكرة إضافية ويقد تؤدي إلى نفاد الذاكرة المُخصصة (OOM). لذلك، عند البرمجة، من المهم التفكير بشكل استراتيجي حول هذه المتغيرات المؤقتة وأحيانًا تحريرها بشكل صريح بمجرد عدم الحاجة إليها.
|
||||
|
||||
**ذاكرة محددة الوظائف**
|
||||
|
||||
ثم، قد يكون لبرنامجك احتياجات خاصة بالذاكرة. على سبيل المثال، عند إنشاء نص باستخدام البحث الشعاعي، يحتاج البرنامج
|
||||
إلى الاحتفاظ بنسخ متعددة من المدخلات والمخرجات.
|
||||
|
||||
**سرعة تنفيذ `forward` مقابل `backward`**
|
||||
|
||||
بالنسبة للالتفافات والطبقات الخطية، هناك ضِعف عدد العمليات 2x flops في المسار الخلفى مقارنة بالمسار الأمامي، والتي يُترجم عمومًا إلى ~2x أبطأ (أحيانًا أكثر، لأن الأحجام في المسار الخلفى تميل إلى أن تكون أكثر صعوبة). عادةً ما تكون عمليات التنشيط محدودة بعرض النطاق الترددي، ومن المعتاد أن يتعين على التنشيط قراءة المزيد من البيانات في المسار الخلفى أكثر من المسار الأمامى.
|
||||
(على سبيل المثال، قراءة التنشيط المسار الأمامى مرة واحدة، وتكتب مرة واحدة، وبينما تقرأ عملية التنشيط الخلفي مرتين، gradOutput وإخراج الأمام، وتكتب مرة واحدة، gradInput).
|
||||
|
||||
كما ترى، هناك بضعة أماكن يمكننا فيها توفير ذاكرة GPU أو تسريع العمليات.
|
||||
الآن بعد أن فهمت ما يؤثر على استخدام GPU وسرعة الحساب، راجع
|
||||
صفحة وثائق [أساليب وأدوات التدريب الفعال على GPU واحد](perf_train_gpu_one) لمعرفة المزيد حول تقنيات تحسين الأداء.
|
||||
@ -28,7 +28,7 @@ picture-in-picture" allowfullscreen></iframe>
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
>>> model = AutoModel.from_pretrained(
|
||||
... "julien-c/EsperBERTo-small", revision="4c77982" # اسم العلامة، أو اسم الفرع، أو تجزئة الالتزام
|
||||
... "julien-c/EsperBERTo-small", revision="v2.0.1" # اسم العلامة، أو اسم الفرع، أو تجزئة الالتزام
|
||||
... )
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,89 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# عائلة نماذج المحول
|
||||
|
||||
منذ إطلاقه في عام 2017، ألهم نموذج [المحول الأصلي](https://arxiv.org/abs/1706.03762) (راجع مدونة [المحول المشروح](http://nlp.seas.harvard.edu/2018/04/03/attention.html) لمقدمة تقنية مبسطة)، ألهم العديد من النماذج الجديدة والمبتكرة التي تتجاوز مهام معالجة اللغات الطبيعية (NLP). هناك نماذج للتنبؤ [بالبنية البروتينات المطوية](https://huggingface.co/blog/deep-learning-with-proteins)، و[تدريب على اتخاذ القرار](https://huggingface.co/blog/train-decision-transformers)، و[التنبؤ بالسلاسل الزمنية](https://huggingface.co/blog/time-series-transformers). مع وجود العديد من متغيرات المحول المتاحة، قد يكون من السهل أن تفوتك الصورة الأكبر. ما تشترك فيه جميع هذه النماذج هو أنها تستند إلى بنية المحول الأصلية. تستخدم بعض النماذج فقط الترميز أو فك الترميز، بينما تستخدم نماذج أخرى كليهما. يوفر هذا تصنيفًا مفيدًا لتصنيف واستعراض الفروقات الرئيسية بين نماذج عائلة المحولات، وسيساعدك على فهم النماذج التي لم تصادفها من قبل.
|
||||
|
||||
إذا لم تكن على دراية بنموذج المحول الأصلي أو تحتاج إلى تذكير، فراجع الفصل الخاص بـ [كيف تعمل المحولات](https://huggingface.co/course/chapter1/4؟fw=pt) من دورة Hugging Face.
|
||||
|
||||
<div align="center">
|
||||
<iframe width="560" height="315" src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/H39Z_720T5s" title="مشغل فيديو YouTube" frameborder="0" allow="accelerometer؛ تشغيل تلقائي؛ قائمة تشغيل مدمجة؛ محسّنات الفيديو؛ ميزة الإشارات المرجعية" allowfullscreen></iframe>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
## رؤية الحاسب (Computer vision)
|
||||
|
||||
<iframe style="border: 1px solid rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1);" width="1000" height="450" src="https://www.figma.com/embed?embed_host=share&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.figma.com%2Ffile%2FacQBpeFBVvrDUlzFlkejoz%2FModelscape-timeline%3Fnode-id%3D0%253A1%26t%3Dm0zJ7m2BQ9oe0WtO-1" allowfullscreen></iframe>
|
||||
|
||||
### الشبكة التلافيفية (Convolutional network)
|
||||
|
||||
لطالما كانت الشبكات التلافيفية (CNNs) الطريقة السائدة لمهام رؤية الحاسب حتى برز [محول الرؤية](https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11929) قابليته للتطوير وكفاءته العالية. وحتى بعد ذلك، لا تزال بعض أفضل صفات CNN، مثل ثبات الإزاحة، قوية جدًا (خاصة بالنسبة لمهام معينة) لدرجة أن بعض المحولات تدمج التلافيف في بنيتها. قلب [ConvNeXt](model_doc/convnext) هذا التبادل رأسًا على عقب وأدرج خيارات التصميم من المحولات لتحديث CNN. على سبيل المثال، يستخدم ConvNeXt نوافذ منزلقة غير متداخلة لتقسيم الصورة إلى رقع وزيادة حقل مجال العام الخاص بها. كما يقوم ConvNeXt بعدة خيارات مثل تصميم الطبقة لتكون أكثر كفاءة في الذاكرة وتحسين الأداء، مما يجعله منافسًا قويًا للمحولات!
|
||||
|
||||
### الترميز[[cv-encoder]] (Encoder)
|
||||
|
||||
فتح [محول الرؤية (ViT)](model_doc/vit) الباب أمام مهام رؤية الحاسب دون الاعتماد على التلافيف. يستخدم ViT ترميز محول قياسي، لكن إنجازه الرئيسي كان طريقة معالجته للصورة. فهو تقسّم الصورة إلى رقّعات ذات حجم ثابت ويستخدمها لإنشاء تضمين، تمامًا مثل تقسيم الجملة إلى رموز. استفاد ViT من بنية المُحوِّلات الفعالة لإظهار نتائج تنافسية مع CNNs في ذلك الوقت مع الحاجة إلى موارد أقل للتدريب. وسرعان ما تبع ViT نماذج رؤية أخرى يمكنها أيضًا التعامل مع مهام الرؤية الكثيفة مثل التجزئة والتعرف.
|
||||
|
||||
من بين هذه النماذج [Swin](model_doc/swin) Transformer. فهو يبني خرائط سمات هرمية (مثل CNN 👀 على عكس ViT) من رقّعات أصغر حجمًا ودمجها مع الرقع المجاورة في طبقات أعمق. يتم حساب الانتباه فقط ضمن نافذة محلية، ويتم تحويل النافذة بين طبقات الانتباه لإنشاء اتصالات تساعد النموذج على التعلم بشكل أفضل. نظرًا لأن محول Swin يمكنه إنتاج خرائط خصائص هرمية، فهو مرشح جيد لمهام التنبؤ الكثيفة مثل التجزئة والتعرف. كما يستخدم [SegFormer](model_doc/segformer) ترميز محول لبناء خرائط خصائص هرمية، ولكنه يضيف فك تشفير بسيط متعدد الطبقات (MLP) في الأعلى لدمج جميع خرائط الخصائص وإجراء تنبؤ.
|
||||
|
||||
استلهمت نماذج الرؤية الأخرى، مثل BeIT وViTMAE، الإلهام من هدف التدريب المسبق لـ BERT. يتم تدريب [BeIT](model_doc/beit) مسبقًا من خلال *نمذجة الصور المقنعة (MIM)*؛ يتم إخفاء رقّعات الصور بشكل عشوائي، كما يتم تحويل الصورة إلى رموز بصرية. يتم تدريب BeIT للتنبؤ بالرموز البصرية المُناظرة للرقع المخفية. لدى [ViTMAE](model_doc/vitmae) هدف تدريب مسبق مُماثل، باستثناء أنه يجب عليه التنبؤ بالبكسلات بدلاً من الرموز البصرية. ما هو غير عادي هو أن إخفاء 75% من رقع الصور! يقوم فك التشفير بإعادة بناء البكسلات من الرموز المخفية والرقّعات المشفرة. بعد التدريب المسبق، يتم التخلص من فك التشفير، ويصبح الترميز جاهزًا للاستخدام في مهام التالية.
|
||||
|
||||
### فك التشفير[[cv-decoder]] (Decoder)
|
||||
|
||||
نادرًا ما تستخدم نماذج الرؤية التي تعتمد على فك التشفير فقط لأن معظم نماذج الرؤية تعتمد على الترميز لتعلم تمثيل الصورة. ولكن بالنسبة للاستخدامات مثل توليد الصور، يعد فك التشفير مناسبًا بشكل طبيعي، كما رأينا من نماذج توليد النصوص مثل GPT-2. يستخدم نموذج [ImageGPT](model_doc/imagegpt) نفس بنية GPT-2، ولكنه بدلاً من التنبؤ بالرمز التالي في تسلسل، فإنه يتنبأ بالبكسل التالي في صورة. بالإضافة إلى توليد الصور، يمكن أيضًا ضبط ImageGPT بدقة لتصنيف الصور.
|
||||
|
||||
### الترميز وفك التشفير[[cv-encoder-decoder]] (Encoder-decoder)
|
||||
|
||||
تستخدم نماذج الرؤية بشكل شائع ترميزًا (يُعرف أيضًا باسم العمود الفقري) لاستخراج ميزات الصورة المهمة قبل تمريرها إلى فك التشفير لنموذج المُحوّل. يستخدم [DETR](model_doc/detr) عمودًا فقريًا مُدربًا مسبقًا، ولكنه يستخدم أيضًا الببنية الكاملة للترميز وفك تشفير لنموذج المحول للكشف عن الأشياء. يتعلم الترميز تمثيلات الصور ويجمعها مع استعلامات الكائنات (كل استعلام كائن هو تضمين مُتعلم يركز على منطقة أو كائن في صورة) في فك التشفير. يتنبأ DETR بإحداثيات مربع الحدود وتسمية الفئة لكل استعلام كائن.
|
||||
|
||||
## معالجة اللغات الطبيعية (Natural language processing - NLP)
|
||||
|
||||
<iframe style="border: 1px solid rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1);" width="1000" height="450" src="https://www.figma.com/embed?embed_host=share&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.figma.com%2Ffile%2FUhbQAZDlpYW5XEpdFy6GoG%2Fnlp-model-timeline%3Fnode-id%3D0%253A1%26t%3D4mZMr4r1vDEYGJ50-1" allowfullscreen></iframe>
|
||||
|
||||
### الترميز اللغوي[[nlp-encoder]]
|
||||
|
||||
نموذج [BERT](model_doc/bert) هو محوّل (Transformer) يعتمد على الترميز فقط يقوم بشكل عشوائي بإخفاء رموز معينة في المدخلات لتجنب رؤية باقى الرموز الأخرى، مما يسمح له "بالغش". يتمثل هدف التدريب المسبق في التنبؤ بالرمز المخفي بناءً على السياق. يسمح هذا لـ BERT باستخدام السياقات اليمنى واليسرى بالكامل لمساعدته في تعلم تمثيل أعمق وأغنى للبيانات المدخلة. ومع ذلك، كان هناك مجال للتحسين في استراتيجية التدريب المسبق لـ BERT. نموذج [RoBERTa](model_doc/roberta) اضاف تحسين من خلال تقديم وصفة تدريب مسبق جديدة تشمل التدريب لفترة أطول وعلى دفعات أكبر، وإخفاء الرموز عشوائيًا في كل حقبة بدلاً من مرة واحدة فقط أثناء المعالجة المسبقة، وإزالة هدف التنبؤ بالجملة التالية.
|
||||
|
||||
تتمثل الاستراتيجية السائدة لتحسين الأداء في زيادة حجم النموذج. ولكن تدريب النماذج الكبيرة مكلف من الناحية الحسابية. إحدى طرق تقليل التكاليف الحسابية هي استخدام نموذج أصغر مثل [DistilBERT](model_doc/distilbert). يستخدم DistilBERT [ تقنية تقطير المعرفة](https://arxiv.org/abs/1503.02531) - وهي تقنية ضغط - لإنشاء نموذج أصغر من BERT مع الحفاظ على معظم قدراته على فهم اللغةا.
|
||||
|
||||
مرت معظم نماذج المحول في الاتجاه نحو المزيد من المعلمات، مما أدى إلى ظهور نماذج جديدة تركز على تحسين كفاءة التدريب. يقلّل [ALBERT](model_doc/albert) من استهلاك الذاكرة عن طريق تقليل عدد المعلمات بطريقتين: فصل تضمين المفردات الأكبر إلى مصفوفتين أصغر والسماح للمستويات بمشاركة المعلمات. أضاف [DeBERTa](model_doc/deberta) آلية انتباه منفصلة حيث يتم ترميز الكلمة وموضعها بشكل منفصل في متجهين. يتم حساب الانتباه من هذه المتجهات المنفصلة بدلاً من متجه واحد يحتوي على تضمين الكلمة والموقع. ركز [Longformer](model_doc/longformer) أيضًا على جعل الانتباه أكثر كفاءة، خاصة لمعالجة المستندات ذات تسلسلات أطولل. فهو يستخدم مزيجًا من انتباه النوافذ المحلية (يتم حساب الانتباه فقط ن نافذة ذات حجم ثابت حول كل رمز) والانتباه العام (فقط لرموز مهمة محددة مثل `[CLS]` للتصنيف) لإنشاء مصفوفة انتباه متفرقة بدلاً من مصفوفة انتباه كاملة.
|
||||
|
||||
### فك التشفير[[nlp-decoder]]
|
||||
|
||||
نموذج [GPT-2](model_doc/gpt2) هو محول فك تشفير فقط يتنبأ بالكلمة التالية في التسلسل. إنه يخفي الرموز التالية الموجودة على اليمين حتى لا يتمكن النموذج من "الغش" بالنظر إليها. من خلال التدريب المسبق على كميات هائلة من النصوص، أصبح [GPT-2](model_doc/gpt2) بارعًا في توليد النصوص، حتى لو لم تكن النص دقيقًا أو صحيحًا في بعض الأحيان فقط. ولكن كان يفتقر إلى سياق لترابط المتبادل (bidirectional context) الموجود من التدريب المسبق لـ [BERT](model_doc/bert) ، مما جعله غير مناسب لمهام معينة. يجمع [XLNET](model_doc/xlnet) بين أفضل ما في أهداف التدريب المسبق لـ [BERT](model_doc/bert) و [GPT-2](model_doc/gpt2) من خلال اعتماد نهج النمذجة اللغوية باستخدام التباديل (Permutation Language Modeling - PLM) الذي يسمح له بتعلم الترابط ثنائي الاتجاه.
|
||||
|
||||
بعد ظهور [GPT-2](model_doc/gpt2)، تطورت النماذج اللغوية بشكل أكبر حجمًا وأكثر تعقيدًا وأصبحت تُعرف الآن باسم *نماذج اللغة الكبيرة (LLMs)*. توضح LLMs مهارات تعلم قليلة الكمية أو حتى معدومة إذا تم تدريبها على مجموعة بيانات كبيرة بما يكفي. [GPT-J](model_doc/gptj) هو LLM به 6 مليارات معلمة مدربة على 400 مليار رمز. تبعه نموذج [OPT](model_doc/opt)، وهي عائلة من نماذج فك التشفير فقط، أكبرها 175 مليار معلمة ودُرب على 180 مليار رمز. تم إصدار [BLOOM](model_doc/bloom) في نفس الوقت تقريبًا، ويحتوي أكبر نموذج في العائلة على 176 مليار معلمة ودُرب على 366 مليار رمز في 46 لغة و13 لغة برمجة.
|
||||
|
||||
### الترميز وفك التشفير[[nlp-encoder-decoder]]
|
||||
|
||||
يحتفظ [BART](model_doc/bart) ببنية المحول الأصلية، ولكنه يعدّل هدف التدريب المسبق باستخدام إفساد *إدخال النصوص*، حيث يتم استبدال بعض نطاقات النص برمز `mask` واحد. يتنبأ فك التشفير بالرموز غير الفاسدة (يتم إخفاء الرموز المستقبلية) ويستخدم حالات الترميز المخفية للمساعدة. [Pegasus](model_doc/pegasus) مشابه لـ BART، ولكن Pegasus يقوم بإخفاء جمل كاملة بدلاً من مقاطع النص. بالإضافة إلى نمذجة اللغة المقنعة، يتم تدريب Pegasus مسبقًا بواسطة توليد الجمل الفارغة (GSG). يقوم هدف GSG بإخفاء الجمل الكاملة المهمة للمستند، واستبدالها برمز `mask`. يجب على فك التشفير توليد المخرجات من الجمل المتبقية. [T5](model_doc/t5) هو نموذج فريد من نوعه يحوّل جميع مهام معالجة اللغة الطبيعية إلى مشكلة نص إلى نص باستخدام بادئات محددة. على سبيل المثال، يشير البادئة `Summarize:` إلى مهمة تلخيص. يتم تدريب T5 مسبقًا بواسطة التدريب الخاضع للإشراف (GLUE وSuperGLUE) والتدريب ذاتي الإشراف (اختيار عينة عشوائية وحذف 15% من الرموز).
|
||||
|
||||
## الصوت (Audio)
|
||||
|
||||
<iframe style="border: 1px solid rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1);" width="1000" height="450" src="https://www.figma.com/embed?embed_host=share&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.figma.com%2Ffile%2Fvrchl8jDV9YwNVPWu2W0kK%2Fspeech-and-audio-model-timeline%3Fnode-id%3D0%253A1%26t%3DmM4H8pPMuK23rClL-1" allowfullscreen></iframe>
|
||||
|
||||
### الترميز[[audio-encoder]]
|
||||
|
||||
يستخدم [Wav2Vec2](model_doc/wav2vec2) ترميز من نوع المحوّل لتعلم تمثيلات الكلام بشكلٍ مباشر من موجات الصوت الخام. يتم تدريبه مسبقًا باستخدام مهمة تباينية لتحديد تمثيل الكلام الصحيح من مجموعة من التمثيلات الخاطئة. [HuBERT](model_doc/hubert) مشابه لـ Wav2Vec2 ولكنه له عملية تدريب مختلفة. يتم إنشاء تسميات الهدف عن طريق خطوة تجميع يتم فيها ت تخصيص مقاطع الصوت المتشابهة إلى مجموعات، تُصبح كل واحدة منها وحدةً خفية. ويتم تعيين الوحدة الخفية إلى تمثيل لإجراء تنبؤ.
|
||||
|
||||
### الترميز وفك التشفير[[audio-encoder-decoder]]
|
||||
|
||||
[Speech2Text](model_doc/speech_to_text) هو نموذج كلام مصمم للتعرف التلقائي على الكلام (ASR) وترجمة الكلام. يقبل النموذج ميزات بنك المرشح اللغوي التي تم استخراجها من شكل موجة الصوت وتم تدريبه مسبقًا بطريقة ذاتية التعلم لتوليد نسخة أو ترجمة. [Whisper](model_doc/whisper) هو أيضًا نموذج ASR، ولكنه على عكس العديد من نماذج الكلام الأخرى، يتم تدريبه مسبقًا على كمية كبيرة من بيانات نسخ النص الصوتي ✨ المسماة ✨ لتحقيق الأداء الصفري. يحتوي جزء كبير من مجموعة البيانات أيضًا على لغات غير اللغة الإنجليزية، مما يعني أنه يمكن استخدام Whisper أيضًا للغات منخفضة الموارد. من الناحية الهيكلية، يشبه Whisper نموذج Speech2Text. يتم تحويل إشارة الصوت إلى طيف لوجاريتم مل-ميل يتم تشفيره بواسطة الترميز. يقوم فك التشفير بتوليد النسخة بطريقة ذاتية التعلم من حالات الترميز المخفية والرموز السابقة.
|
||||
|
||||
## متعدد الوسائط (Multimodal)
|
||||
|
||||
<iframe style="border: 1px solid rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1);" width="1000" height="450" src="https://www.figma.com/embed?embed_host=share&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.figma.com%2Ffile%2FcX125FQHXJS2gxeICiY93p%2Fmultimodal%3Fnode-id%3D0%253A1%26t%3DhPQwdx3HFPWJWnVf-1" allowfullscreen></iframe>
|
||||
|
||||
### Encoder[[mm-encoder]]
|
||||
|
||||
نموذج [VisualBERT](model_doc/visual_bert) هو نموذج متعدد الوسائط لمهام الرؤية اللغوية تم إصداره بعد فترة وجيزة من BERT. فهو يجمع بين BERT ونظام اكتشاف كائن مسبق التدريب لاستخراج ميزات الصورة في تضمينات بصرية، يتم تمريرها جنبًا إلى جنب مع التضمينات النصية إلى BERT. يتنبأ VisualBERT بالنص المقنع بناءً على النص غير المقنع والتضمينات المرئية، ويجب عليه أيضًا التنبؤ بما إذا كان النص متوافقًا مع الصورة. عندما تم إصدار ViT، اعتمد [ViLT](model_doc/vilt) ViT في بنيتها لأنه كان من الأسهل الحصول على تضمينات الصورة بهذه الطريقة. يتم معالجة تضمينات الصورة بشكل مشترك مع التضمينات النصية. ومن هناك، يتم التدريب المسبق لـ ViLT بواسطة مطابقة الصورة النصية، ونمذجة اللغة المقنعة، وإخفاء كلمة كاملة.
|
||||
|
||||
يتّبع [CLIP](model_doc/clip) نهجًا مختلفًا ويقوم بتنبؤ ثنائي من ("الصورة"، "النص"). يتم تدريب مشفر صورة (ViT) ومشفر نص (Transformer) بشكل مشترك على مجموعة بيانات مكونة من 400 مليون ثنائي من ("صورة"، "نص") لتعظيم التشابه بين متجهات ترميز الصورة ومتجهات النص ثنائي ("الصورة"، "النص"). بعد التدريب المسبق، يمكنك استخدام اللغة الطبيعية لتوجيه CLIP للتنبؤ بالنص المُعطى بناءً على صورة أو العكس بالعكس. [OWL-ViT](model_doc/owlvit) يبني على CLIP باستخدامه كعمود فقري للكشف عن الكائنات بدون إشراف. بعد التدريب المسبق، يتم إضافة رأس كشف الأجسام لإجراء تنبؤ بمجموعة مُحدّد عبر ثنائيات ("class"، "bounding box").
|
||||
|
||||
### Encoder-decoder[[mm-encoder-decoder]]
|
||||
|
||||
التعرّف البصري على الحروف (OCR) مهمة قديمة لتعرّف النصوص، التي تنطوي عادةً على عدة مكونات لفهم الصورة وتوليد النص. [TrOCR](model_doc/trocr) بتبسيط العملية باستخدام محول متكامل من النهاية إلى النهاية. المشفر هو نموذج على غرار ViT لفهم الصورة ويعالج الصورة كقطع ثابتة الحجم. يقبل فك التشفير حالات الإخفاء للمشفر وينشئ النص بشكل تلقائي. [Donut](model_doc/donut) هو نموذج أكثر عمومية لفهم المستندات المرئية لا يعتمد على نهج OCR. يستخدم محول Swin كمشفر وBART متعدد اللغات كمُفكّك تشفير. يتم تدريب Donut على قراءة النص عن طريق التنبؤ بالكلمة التالية بناءً على ملاحظات الصورة والنص. يقوم فك التشفير بتوليد تتسلسلًا رمزيًا بناءً على موجه (Prompt). يتم تمثيل الموجه بواسطة رمز خاص لكل مهمة. على سبيل المثال، يحتوي تحليل المستند على رمز خاص "parsing" يتم دمجه مع حالات الإخفاء للـمُشفّر لتحليل المستند بتنسيق إخراج منظم (JSON).
|
||||
|
||||
## التعلم التعزيزي (Reinforcement learning - RL)
|
||||
|
||||
<iframe style="border: 1px solid rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1);" width="1000" height="450" src="https://www.figma.com/embed?embed_host=share&url=https%3A%2F%2Fwww.figma.com%2Ffile%2FiB3Y6RvWYki7ZuKO6tNgZq%2Freinforcement-learning%3Fnode-id%3D0%253A1%26t%3DhPQwdx3HFPWJWnVf-1" allowfullscreen></iframe>
|
||||
|
||||
### فك التشفير[[rl-decoder]]
|
||||
|
||||
يقوم نموذج "محوّل القرارات والمسارات" (Decision and Trajectory Transformer) بتحويل الحالة (State) والإجراء (Action) والمكافأة (Reward) كمشكلة نمذجة تسلسلية. [محوّل القرارات](model_doc/decision_transformer) يقوم بتوليد سلسلة من الإجراءات التي تؤدي إلى عائد مرغوب في المستقبل بناءً على العوائد المتوقعة، والحالات والإجراءات السابقة. في الخطوات الزمنية *K* الأخيرة، يتم تحويل كل وسائط البيانات الثلاث vإلى متجهات تضمين رمزيّة ومعالجتها بواسطة نموذج مشابه لـ GPT للتنبؤ برمز الإجراء المستقبلي.يقوم [محول المسار](model_doc/trajectory_transformer) أيضًا بتحويل الحالات والإجراءات والمكافآت إلى رموز ومعالجتها باستخدام هيكلية GPT. على عكس "محوّل القرارات"، الذي يركز على تكييف المكافأة، يقوم "محوّل المسارات" بتوليد إجراءات مستقبلية باستخدام البحث الشعاعي (Beam Search).
|
||||
Some files were not shown because too many files have changed in this diff Show More
Reference in New Issue
Block a user