mirror of
https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch.git
synced 2025-10-21 05:34:18 +08:00
Re-landing #68111/#74596 ## Description v0.5 PR of this [RFC](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/49444). On the basis of #50256, the below improvements are included: * The [v0.5 release branch](https://github.com/oneapi-src/oneDNN/releases/tag/graph-v0.5) of the oneDNN Graph API is used * The fuser now works with the profiling graph executor. We have inserted type check nodes to guard the profiled tensor properties. ### User API: The optimization pass is disabled by default. Users could enable it by: ``` torch.jit.enable_onednn_fusion(True) ``` `torch.jit.freeze` should be used after tracing (recommended) or scripting a model. ### Performance: [pytorch/benchmark](https://github.com/pytorch/benchmark) tool is used to compare the performance: * SkyLake 8180 (1 socket of 28 cores): 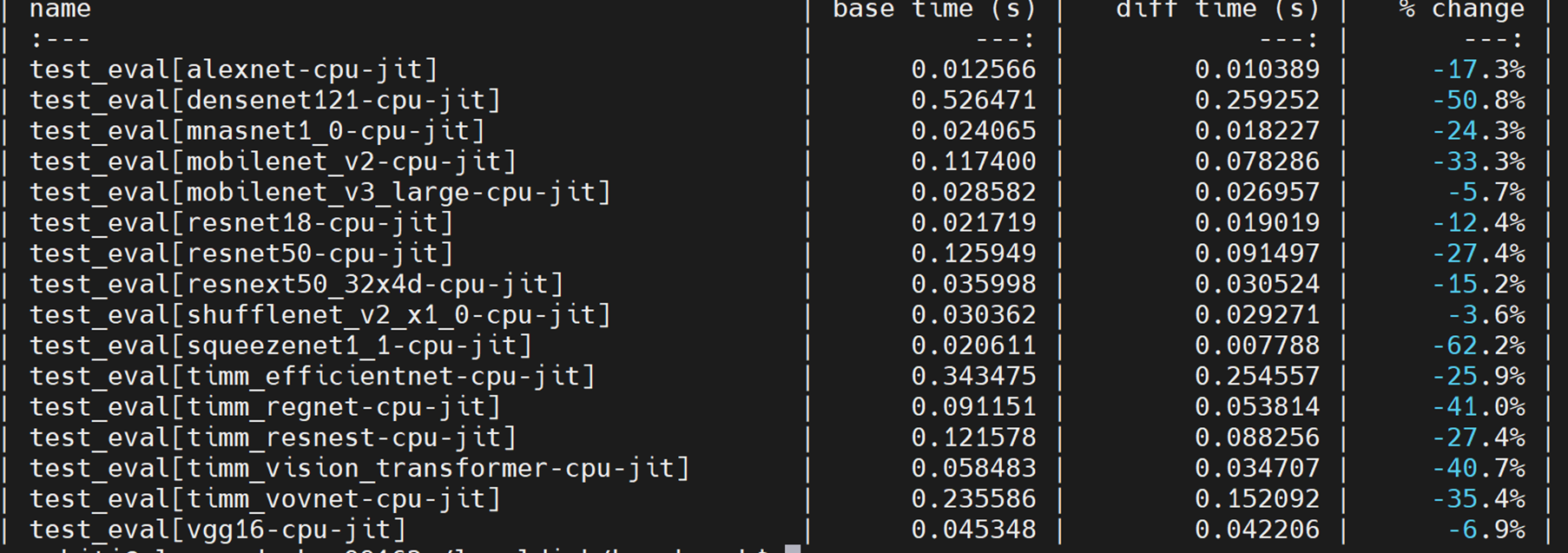 * SkyLake 8180 (single thread): 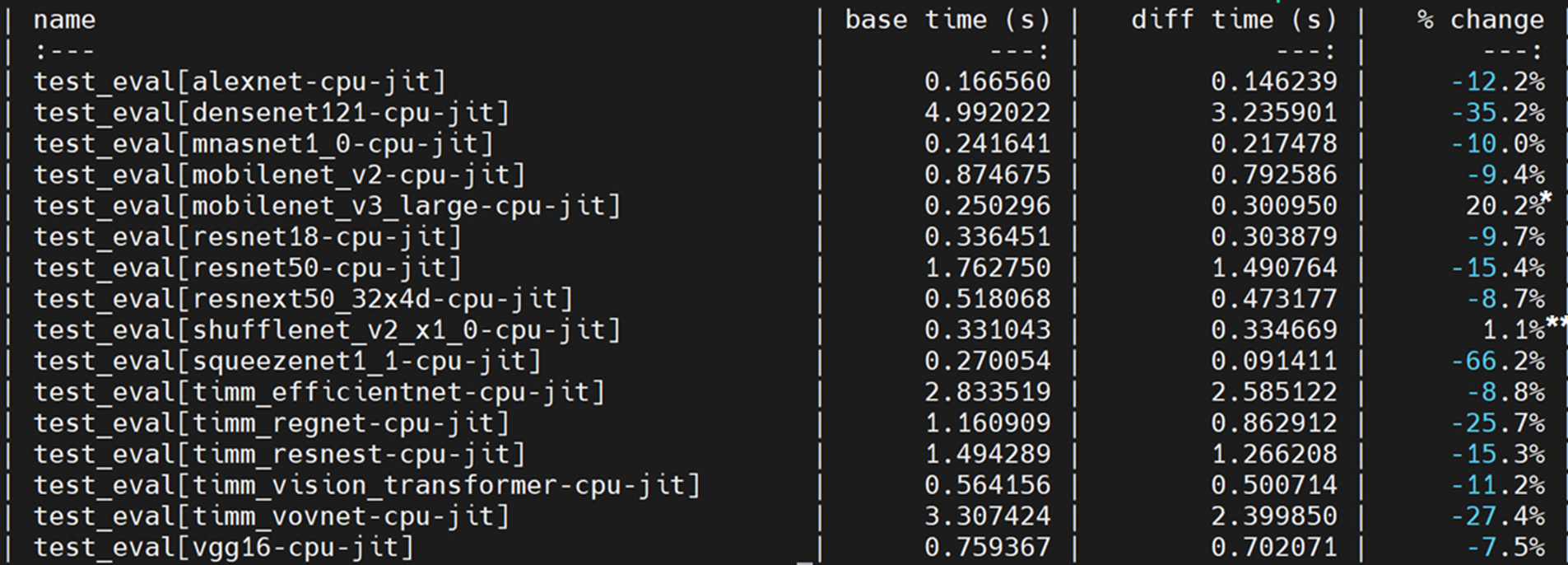 * By mapping hardswish to oneDNN Graph, it’s 8% faster than PyTorch JIT (NNC + OFI) ** We expect performance gain after mapping transpose, contiguous & view to oneDNN graph ops ### Directory structure of the integration code Fuser-related code is placed under: ``` torch/csrc/jit/codegen/onednn/ ``` Optimization pass registration is done in: ``` torch/csrc/jit/passes/onednn_graph_fuser.h ``` CMake for the integration code is in: ``` caffe2/CMakeLists.txt cmake/public/mkldnn.cmake cmake/Modules/FindMKLDNN.cmake ``` ## Limitations * In this PR, we only support Pytorch-oneDNN-Graph integration on Linux platform. Support on Windows and MacOS will be enabled as a next step. * We have only optimized the inference use-case. Pull Request resolved: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/76622 Approved by: https://github.com/eellison
145 lines
5.3 KiB
C++
145 lines
5.3 KiB
C++
#include <torch/csrc/jit/codegen/onednn/graph_fuser.h>
|
|
#include <torch/csrc/jit/ir/alias_analysis.h>
|
|
#include <torch/csrc/jit/jit_log.h>
|
|
#include <torch/csrc/jit/passes/common_subexpression_elimination.h>
|
|
#include <torch/csrc/jit/passes/dead_code_elimination.h>
|
|
#include <torch/csrc/jit/passes/utils/subgraph_utils.h>
|
|
|
|
namespace torch {
|
|
namespace jit {
|
|
namespace fuser {
|
|
namespace onednn {
|
|
|
|
void GraphRewriter::cleanupSubgraphs() {
|
|
auto curNode = *block_->nodes().rbegin();
|
|
while (curNode != *block_->nodes().rend()) {
|
|
// Save the previous node, since we might delete `curNode` in next block
|
|
auto prevNode = curNode->prev();
|
|
if (llgaHelper_.isLlgaSubgraph(curNode)) {
|
|
// Unmerge subgraph if we don't get every nodes of a partition
|
|
// into the subgraph due to failed alias check
|
|
llgaHelper_.unmergeIfAnyNodeIsMissing(curNode);
|
|
}
|
|
curNode = prevNode;
|
|
}
|
|
for (Node* n : block_->nodes()) {
|
|
for (Block* b : n->blocks()) {
|
|
GraphRewriter(b, graph_, aliasDb_).cleanupSubgraphs();
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
void GraphRewriter::buildupSubgraphs() {
|
|
// We need to run the rewriter multiple times in order to get all merge
|
|
// opportunities. This is because moveBeforeTopologicalValid may reorder
|
|
// nodes to be AFTER the current iteration point. In order to properly
|
|
// consider those nodes for merging, we need run the pass until no changes
|
|
// have been made.
|
|
//
|
|
// Example:
|
|
// c = f(a, b)
|
|
// d = f(c)
|
|
// e = f(d) <- iter is here, moving upward
|
|
// After c.moveBeforeTopologicallyValid(e), we have:
|
|
// c = f(a, b)
|
|
// e = f(d) <- iter still here
|
|
// d = f(c) <- this was node moved on the other side.
|
|
// see [workblocks]
|
|
auto workblocks = buildWorkBlocks();
|
|
for (auto& workblock : workblocks) {
|
|
bool any_changed = true;
|
|
while (any_changed) {
|
|
any_changed = false;
|
|
auto workblock_end = workblock.end()->reverseIterator();
|
|
auto workblock_begin = workblock.begin()->reverseIterator();
|
|
for (auto it = workblock_end; it != workblock_begin;) {
|
|
bool changed = false;
|
|
std::tie(it, changed) = scanNode(*it, workblock_begin);
|
|
any_changed |= changed;
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
// Construct Subgraphs Recursively
|
|
for (Node* n : block_->nodes()) {
|
|
for (auto subBlock : n->blocks()) {
|
|
GraphRewriter(subBlock, graph_, aliasDb_).buildupSubgraphs();
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
std::vector<WorkBlock> GraphRewriter::buildWorkBlocks() {
|
|
// [workblocks]
|
|
// the IR has many nodes which can never be reordered around, such as a
|
|
// prim::Bailout. if a node N is surrounded by two nodes which cannot be
|
|
// reordered, A and B, then a fusion group that is created from N
|
|
// can only contain nodes from (A, B) The nodes from A to B represent one
|
|
// work block for the subgraph rewriter to work on. By creating these up
|
|
// front, we avoid retraversing the whole graph block any time scanNode
|
|
// returns
|
|
Node* end_bound_node = block_->return_node();
|
|
Node* curr = end_bound_node->prev();
|
|
std::vector<WorkBlock> worklist;
|
|
while (curr != block_->param_node()) {
|
|
// cannot reorder around side effectful nodes
|
|
if (curr->hasSideEffects()) {
|
|
worklist.emplace_back(curr, end_bound_node);
|
|
end_bound_node = curr;
|
|
}
|
|
curr = curr->prev();
|
|
}
|
|
worklist.emplace_back(curr, end_bound_node);
|
|
return worklist;
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
std::pair<graph_node_list::iterator, bool> GraphRewriter::scanNode(
|
|
Node* consumer,
|
|
graph_node_list::iterator workblock_begin) {
|
|
GRAPH_DEBUG("Scanning ", consumer->kind().toQualString());
|
|
if (llgaHelper_.shouldConsiderForMerge(consumer)) {
|
|
if (!llgaHelper_.isLlgaSubgraph(consumer)) {
|
|
consumer = llgaHelper_.createSingletonSubgraph(consumer, aliasDb_);
|
|
}
|
|
// Iterate through the workblock to merge nodes of the
|
|
// same partition determined by LLGA graph helper.
|
|
// Nodes like B and C do not share a common input but belong to a
|
|
// same partition, and thus we cannot only scan the input nodes
|
|
// to find merging opportunities. Instead, we have to scan through
|
|
// the whole workblock, which might lead to O^2 accesses in worst case
|
|
// A
|
|
// + - - / - \ - - +
|
|
// | B C |
|
|
// | | | |
|
|
// | D E |
|
|
// + - - \ - / - - +
|
|
// F
|
|
auto prev = ++consumer->reverseIterator();
|
|
for (auto it = prev; it != workblock_begin; it++) {
|
|
if (auto group = tryMerge(consumer, *it)) {
|
|
// we successfully merged, so the new group's `inputs` may have
|
|
// changed. So rescan the new group for more merging opportunities.
|
|
return std::make_pair(group.value()->reverseIterator(), true);
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
}
|
|
return std::make_pair(++consumer->reverseIterator(), false);
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
// Try to merge `producer` into `consumer`. If successful, this destroys
|
|
// `producer` and returns the `consumer` group.
|
|
c10::optional<Node*> GraphRewriter::tryMerge(Node* consumer, Node* producer) {
|
|
AT_ASSERT(llgaHelper_.isLlgaSubgraph(consumer));
|
|
bool canMerge = llgaHelper_.shouldMerge(producer, consumer) &&
|
|
aliasDb_.moveBeforeTopologicallyValid(producer, consumer);
|
|
if (!canMerge) {
|
|
return c10::nullopt;
|
|
}
|
|
llgaHelper_.mergeNodeIntoSubgraph(producer, consumer, aliasDb_);
|
|
return consumer;
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
} // namespace onednn
|
|
} // namespace fuser
|
|
} // namespace jit
|
|
} // namespace torch
|