Compare commits
469 Commits
| Author | SHA1 | Date | |
|---|---|---|---|
| f8e89fbe11 | |||
| 30d208010c | |||
| 017c7efb43 | |||
| 0c69fd559a | |||
| c991258b93 | |||
| 9f89692dcd | |||
| c28575a4eb | |||
| c9db9c2317 | |||
| 16a09304b4 | |||
| 58a88d1ac0 | |||
| b740878697 | |||
| 173c81c2d2 | |||
| ee4c77c59f | |||
| 30ec12fdd5 | |||
| 269ec0566f | |||
| a0a95c95d4 | |||
| 1335b7c1da | |||
| 6d14ef8083 | |||
| 26a492acf3 | |||
| f2741e8038 | |||
| 8d1a6975d2 | |||
| c414bf0aaf | |||
| 99f4864674 | |||
| 784cbeff5b | |||
| 9302f860ae | |||
| ac8a5e7f0d | |||
| 798fc16bbf | |||
| 0f65c9267d | |||
| be45231ccb | |||
| 279aea683b | |||
| 8aa8f791fc | |||
| 6464e69e21 | |||
| a93812e4e5 | |||
| 225f942044 | |||
| d951d5b1cd | |||
| 2082ccbf59 | |||
| 473e795277 | |||
| a09f653f52 | |||
| 90fe6dd528 | |||
| 57a2ccf777 | |||
| 205b9bc05f | |||
| 14d5d52789 | |||
| 9c218b419f | |||
| 517fb2f410 | |||
| 35c2821d71 | |||
| e4812b3903 | |||
| 4cc11066b2 | |||
| 85b64d77b7 | |||
| db7948d7d5 | |||
| 3d40c0562d | |||
| 146bcc0e70 | |||
| 8d9f6c2583 | |||
| ac32d8b706 | |||
| 15c1dad340 | |||
| 6d8baf7c30 | |||
| 7ced682ff5 | |||
| 89cab4f5e6 | |||
| a0afb79898 | |||
| d6fa3b3fd5 | |||
| f91bb96071 | |||
| 3b6644d195 | |||
| 652b468ec2 | |||
| af110d37f2 | |||
| 38967568ca | |||
| df79631a72 | |||
| 95f0fa8a92 | |||
| 1c6ff53b60 | |||
| 1dbf44c00d | |||
| 1259a0648b | |||
| b0055f6229 | |||
| 90040afc44 | |||
| 59bc96bdc2 | |||
| 676ffee542 | |||
| 77136e4c13 | |||
| 604e13775f | |||
| 02380a74e3 | |||
| 133c1e927f | |||
| 2290798a83 | |||
| fd600b11a6 | |||
| b5c9f5c4c3 | |||
| b8a5b1ed8e | |||
| ca74bb17b8 | |||
| 69d8331195 | |||
| eab5c1975c | |||
| e67b525388 | |||
| 5171e56b82 | |||
| f467848448 | |||
| 7e4ddcfe8a | |||
| 3152be5fb3 | |||
| b076944dc5 | |||
| 3a07228509 | |||
| 24a2f2e3a0 | |||
| b32dd4a876 | |||
| 4f4bd81228 | |||
| 59b23d79c6 | |||
| 8c14630e35 | |||
| cc32de8ef9 | |||
| 44696c1375 | |||
| 82088a8110 | |||
| d5e45b2278 | |||
| bdfef2975c | |||
| b4bb4b64a1 | |||
| 3e91c5e1ad | |||
| 2b88d85505 | |||
| 50651970b8 | |||
| 4a8906dd8a | |||
| 68e2769a13 | |||
| 17c998e99a | |||
| 35758f51f2 | |||
| e8102b0a9b | |||
| 04f2bc9aa7 | |||
| d070178dd3 | |||
| c9ec7fad52 | |||
| f0a6ca4d53 | |||
| fd92470e23 | |||
| 8369664445 | |||
| 35e1adfe82 | |||
| eb91fc5e5d | |||
| d186fdb34c | |||
| 0f04f71b7e | |||
| 87f1959be7 | |||
| a538055e81 | |||
| 0e345aaf6d | |||
| c976dd339d | |||
| 71cef62436 | |||
| 3a29055044 | |||
| 59d66e6963 | |||
| 46bc43a80f | |||
| 7fa60b2e44 | |||
| c78893f912 | |||
| 0d2a4e1a9e | |||
| 088f14c697 | |||
| 4bf7be7bd5 | |||
| b2ab6891c5 | |||
| 39ab5bcba8 | |||
| 42f131c09f | |||
| 89dca6ffdc | |||
| b7f36f93d5 | |||
| 58320d5082 | |||
| a461804a65 | |||
| 817f6cc59d | |||
| 108936169c | |||
| f60ae085e6 | |||
| 85dda09f95 | |||
| 4f479a98d4 | |||
| 35ba948dde | |||
| 6b4ed52f10 | |||
| dcf5f8671c | |||
| 5340291add | |||
| 1c6fe58574 | |||
| 9f2111af73 | |||
| 2ed6c6d479 | |||
| 01ac2d3791 | |||
| eac687df5a | |||
| 6a2785aef7 | |||
| 849cbf3a47 | |||
| a0c614ece3 | |||
| 1b97f088cb | |||
| 097399cdeb | |||
| 7ee152881e | |||
| 3074f8eb81 | |||
| 748208775f | |||
| 5df17050bf | |||
| 92df0eb2bf | |||
| 995195935b | |||
| be8376eb88 | |||
| b650a45b9c | |||
| 8a20e22239 | |||
| 7c5014d803 | |||
| 62ac1b4bdd | |||
| 0633c08ec9 | |||
| cf87cc9214 | |||
| f908432eb3 | |||
| 1bd291c57c | |||
| b277df6705 | |||
| ec4d597c59 | |||
| d2ef49384e | |||
| b5dc36f278 | |||
| 41976e2b60 | |||
| 3dac1b9936 | |||
| d2bb56647f | |||
| 224422eed6 | |||
| 3c26f7a205 | |||
| 9ac9809f27 | |||
| 7bf6e984ef | |||
| 10f78985e7 | |||
| dc95f66a95 | |||
| d8f4d5f91e | |||
| 47f56f0230 | |||
| b4018c4c30 | |||
| 43fbdd3b45 | |||
| 803d032077 | |||
| 9d2d884313 | |||
| c0600e655a | |||
| 671ed89f2a | |||
| e0372643e1 | |||
| b5cf1d2fc7 | |||
| c1ca9044bd | |||
| 52c2a92013 | |||
| 541ab961d8 | |||
| 849794cd2c | |||
| f47fa2cb04 | |||
| 7a162dd97a | |||
| b123bace1b | |||
| 483490cc25 | |||
| 8d60e39fdc | |||
| e7dff91cf3 | |||
| ab5776449c | |||
| a229582238 | |||
| a0df8fde62 | |||
| e4a3aa9295 | |||
| be98c5d12d | |||
| bc6a71b1f5 | |||
| 26f1e2ca9c | |||
| 75d850cfd2 | |||
| f4870ca5c6 | |||
| 235d5400e1 | |||
| 491d5ba4fd | |||
| d42eadfeb9 | |||
| 9a40821069 | |||
| 2975f539ff | |||
| 64ca584199 | |||
| 5263469e21 | |||
| c367e0b64e | |||
| 183b3aacd2 | |||
| 101950ce92 | |||
| 239ae94389 | |||
| 55e850d825 | |||
| 62af45d99f | |||
| 1ac038ab24 | |||
| 77a925ab66 | |||
| d0d33d3ae7 | |||
| 9b7eceddc8 | |||
| 24af02154c | |||
| 86ec14e594 | |||
| 8a29338837 | |||
| 29918c6ca5 | |||
| 80a44e84dc | |||
| 5497b1babb | |||
| bef70aa377 | |||
| 0d30f77889 | |||
| e27bb3e993 | |||
| 179d5efc81 | |||
| b55e38801d | |||
| e704ec5c6f | |||
| 6cda6bb34c | |||
| 46f0248466 | |||
| 310ec57fd7 | |||
| cd82b2b869 | |||
| 126a1cc398 | |||
| bf650f05b3 | |||
| f2606a7502 | |||
| b07fe52ee0 | |||
| b07358b329 | |||
| 2aea8077f9 | |||
| 41f9c14297 | |||
| 135687f04a | |||
| b140e70b58 | |||
| ec987b57f6 | |||
| 596677232c | |||
| 9d74e139e5 | |||
| d2a93c3102 | |||
| bc475cad67 | |||
| 45d6212fd2 | |||
| f45d75ed22 | |||
| b03407289f | |||
| 55a794e6ec | |||
| 93ed476e7d | |||
| 10faa303bc | |||
| 6fa371cb0d | |||
| 18a2691b4b | |||
| f7bd3f7932 | |||
| f8dee4620a | |||
| 800e24616a | |||
| d63a435787 | |||
| a9c2809ce3 | |||
| fa61159dd0 | |||
| a215e000e9 | |||
| f16a624b35 | |||
| 61c2896cb8 | |||
| 22ebc3f205 | |||
| 8fa9f443ec | |||
| bb72ccf1a5 | |||
| 2e73456f5c | |||
| 3e49a2b4b7 | |||
| 4694e4050b | |||
| 59b9eeff49 | |||
| 1744fad8c2 | |||
| e46d942ca6 | |||
| 93a6136863 | |||
| 230bde94e7 | |||
| 20fffc8bb7 | |||
| 861a3f3a30 | |||
| ee52102943 | |||
| 26516f667e | |||
| 5586f48ad5 | |||
| cc6e3c92d2 | |||
| a2ef5782d0 | |||
| 0c1c0e21b8 | |||
| ffcc38cf05 | |||
| cc24b68584 | |||
| 8a70067b92 | |||
| 33b227c45b | |||
| fb68be952d | |||
| f413ee087d | |||
| 6495f5dd30 | |||
| 8e09f0590b | |||
| 08d346df9c | |||
| 12cf96e358 | |||
| 765a720d1c | |||
| cace62f94c | |||
| 767c96850d | |||
| b73e78edbb | |||
| 7914cc119d | |||
| 2b13eb2a6c | |||
| 8768e64e97 | |||
| 9212b9ca09 | |||
| 0d0f197682 | |||
| 281e34d1b7 | |||
| 287ba38905 | |||
| ed9dbff4e0 | |||
| 6ba4e48521 | |||
| b7269f2295 | |||
| 5ab317d4a6 | |||
| 431bcf7afa | |||
| 41909e8c5b | |||
| 56245426eb | |||
| 3adcb2c157 | |||
| 6d12185cc9 | |||
| 258c9ffb2c | |||
| dede431dd9 | |||
| 6312d29d80 | |||
| ab5f26545b | |||
| 6567c1342d | |||
| 3d6c2e023c | |||
| 89d930335b | |||
| 04393cd47d | |||
| 28f0cf6cee | |||
| 1af9a9637f | |||
| 1031d671fb | |||
| ee91b22317 | |||
| 220183ed78 | |||
| 504d2ca171 | |||
| d535aa94a1 | |||
| 0376a1909b | |||
| f757077780 | |||
| 9f7114a4a1 | |||
| 7d03da0890 | |||
| 4e0cecae7f | |||
| 72dbb76a15 | |||
| cceb926af3 | |||
| 0d7d29fa57 | |||
| be3276fcdd | |||
| 09c94a170c | |||
| f2a18004a7 | |||
| 1a3ff1bd28 | |||
| a5d3c779c7 | |||
| 9d32e60dc2 | |||
| f6913f56ea | |||
| 801fe8408f | |||
| cf4a979836 | |||
| 91f2946310 | |||
| 2bd7a3c31d | |||
| a681f6759b | |||
| cb849524f3 | |||
| 1f5951693a | |||
| 87748ffd4c | |||
| 0580f5a928 | |||
| 88d9fdec2e | |||
| 506a40ce44 | |||
| bf0e185bd6 | |||
| 5b3ccec10d | |||
| eb07581502 | |||
| 934a2b6878 | |||
| bec6ab47b6 | |||
| 49480f1548 | |||
| 18a3c62d9b | |||
| 6322cf3234 | |||
| 4e2b154342 | |||
| bb1019d1ec | |||
| c2d32030a2 | |||
| 162170fd7b | |||
| ea728e7c5e | |||
| aea6ba4bcd | |||
| ab357c14fc | |||
| 606aa43da0 | |||
| 8bfa802665 | |||
| ff5b73c0b3 | |||
| 86c95014a4 | |||
| 288c950c5e | |||
| b27d4de850 | |||
| 61063ebade | |||
| 3e70e26278 | |||
| 66e7e42800 | |||
| 0fecec14b8 | |||
| a7f24ccb76 | |||
| 08a1bc71c0 | |||
| 04e896a4b4 | |||
| 5dcfb80b36 | |||
| 9da60c39ce | |||
| 379860e457 | |||
| bcfa2d6c79 | |||
| 8b492bbc47 | |||
| a49b7b0f58 | |||
| c781ac414a | |||
| 656dca6edb | |||
| 830adfd151 | |||
| 6f7c8e4ef8 | |||
| 2ba6678766 | |||
| 71a47d1bed | |||
| 51bf6321ea | |||
| aa8916e7c6 | |||
| 2e24da2a0b | |||
| c94ccafb61 | |||
| 80a827d3da | |||
| 6909c8da48 | |||
| c07105a796 | |||
| c40c061a9f | |||
| a9bd27ce5c | |||
| 2e36c4ea2d | |||
| 4e45385a8d | |||
| cf5e925c10 | |||
| 709255d995 | |||
| f3cb636294 | |||
| e3f440b1d0 | |||
| f6b94dd830 | |||
| 3911a1d395 | |||
| ebd3648fd6 | |||
| f698f09cb7 | |||
| 86aa5dae05 | |||
| 179c82ffb4 | |||
| 233017f01f | |||
| 597bbfeacd | |||
| 99a169c17e | |||
| 0613ac90cd | |||
| 78871d829a | |||
| d40a7bf9eb | |||
| b27f576f29 | |||
| 073dfd8b88 | |||
| 5c14bd2888 | |||
| 84b4665e02 | |||
| 6ff6299c65 | |||
| 51084a9054 | |||
| ad286c0692 | |||
| a483b3903d | |||
| 6564d39777 | |||
| 8f1b7230fe | |||
| c0b7608965 | |||
| 91494cb496 | |||
| 9057eade95 | |||
| a28317b263 | |||
| 25c3603266 | |||
| 3aaa1771d5 | |||
| 2034396a3c | |||
| 0cad668065 | |||
| f644a11b82 | |||
| d7e3b2ef29 | |||
| fc5ec87478 | |||
| ed4023127b | |||
| 2bd4e5f5f6 | |||
| d2dcbc26f8 | |||
| 2f05eefe9a | |||
| 7d1afa78b9 | |||
| dac9b020e0 | |||
| eb77b79df9 | |||
| 66320c498c | |||
| 8cb8a0a146 | |||
| a8a02ff560 | |||
| 4d03d96e8b |
4
.gitignore
vendored
@ -15,6 +15,10 @@ torch/csrc/nn/THNN.cwrap
|
||||
torch/csrc/nn/THNN.cpp
|
||||
torch/csrc/nn/THCUNN.cwrap
|
||||
torch/csrc/nn/THCUNN.cpp
|
||||
docs/src/**/*
|
||||
test/data/legacy_modules.t7
|
||||
test/htmlcov
|
||||
test/.coverage
|
||||
*/*.pyc
|
||||
*/**/*.pyc
|
||||
*/**/**/*.pyc
|
||||
|
||||
@ -3,8 +3,6 @@ language: python
|
||||
python:
|
||||
- 2.7.8
|
||||
- 2.7
|
||||
- 3.3
|
||||
- 3.4
|
||||
- 3.5
|
||||
- nightly
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
285
README.md
@ -1,32 +1,34 @@
|
||||
# pytorch [alpha-4]
|
||||
<p align="center"><img width="40%" src="docs/source/_static/img/pytorch-logo-dark.png" /></p>
|
||||
|
||||
- [What is PyTorch?](#what-is-pytorch)
|
||||
- [Reasons to consider PyTorch](#reasons-to-consider-pytorch)
|
||||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
PyTorch is a python package that provides two high-level features:
|
||||
- Tensor computation (like numpy) with strong GPU acceleration
|
||||
- Deep Neural Networks built on a tape-based autograd system
|
||||
|
||||
You can reuse your favorite python packages such as numpy, scipy and Cython to extend PyTorch when needed.
|
||||
|
||||
We are in an early-release Beta. Expect some adventures and rough edges.
|
||||
|
||||
- [More About PyTorch](#more-about-pytorch)
|
||||
- [Installation](#installation)
|
||||
- [Binaries](#binaries)
|
||||
- [From source](#from-source)
|
||||
- [Getting Started](#getting-started)
|
||||
- [Communication](#communication)
|
||||
- [Timeline](#timeline)
|
||||
- [pytorch vs torch: important changes](#pytorch-vs-torch-important-changes)
|
||||
- [Releases and Contributing](#releases-and-contributing)
|
||||
- [The Team](#the-team)
|
||||
|
||||
| Python | **`Linux CPU`** | **`Linux GPU`** |
|
||||
|--------|--------------------|------------------|
|
||||
| 2.7.8 | [](https://travis-ci.com/apaszke/pytorch) | |
|
||||
| 2.7 | [](https://travis-ci.com/apaszke/pytorch) | [](https://build.pytorch.org/job/pytorch-master-py2) |
|
||||
| 3.3 | [](https://travis-ci.com/apaszke/pytorch) | |
|
||||
| 3.4 | [](https://travis-ci.com/apaszke/pytorch) | |
|
||||
| 3.5 | [](https://travis-ci.com/apaszke/pytorch) | [](https://build.pytorch.org/job/pytorch-master-py3) |
|
||||
| Nightly| [](https://travis-ci.com/apaszke/pytorch) | |
|
||||
|
||||
The project is still under active development and is likely to drastically change in short periods of time.
|
||||
We will be announcing API changes and important developments via a newsletter, github issues and post a link to the issues on slack.
|
||||
Please remember that at this stage, this is an invite-only closed alpha, and please don't distribute code further.
|
||||
This is done so that we can control development tightly and rapidly during the initial phases with feedback from you.
|
||||
## More about PyTorch
|
||||
|
||||
## What is PyTorch?
|
||||
|
||||
PyTorch is a library that consists of the following components:
|
||||
At a granular level, PyTorch is a library that consists of the following components:
|
||||
|
||||
| \_ | \_ |
|
||||
| ------------------------ | --- |
|
||||
@ -43,215 +45,156 @@ Usually one uses PyTorch either as:
|
||||
- A replacement for numpy to use the power of GPUs.
|
||||
- a deep learning research platform that provides maximum flexibility and speed
|
||||
|
||||
## Reasons to consider PyTorch
|
||||
Elaborating further:
|
||||
|
||||
### A GPU-ready Tensor library
|
||||
|
||||
If you use numpy, then you have used Tensors (a.k.a ndarray).
|
||||
|
||||
<p align=center><img width="30%" src="docs/source/_static/img/tensor_illustration.png" /></p>
|
||||
|
||||
PyTorch provides Tensors that can live either on the CPU or the GPU, and accelerate
|
||||
compute by a huge amount.
|
||||
|
||||
We provide a wide variety of tensor routines to accelerate and fit your scientific computation needs
|
||||
such as slicing, indexing, math operations, linear algebra, reductions.
|
||||
And they are fast!
|
||||
|
||||
### Dynamic Neural Networks: Tape based Autograd
|
||||
|
||||
PyTorch has a unique way of building neural networks: using and replaying a tape recorder.
|
||||
|
||||
Most frameworks such as `TensorFlow`, `Theano`, `Caffe` and `CNTK` have a static view of the world.
|
||||
One has to build a neural network, and reuse the same structure again and again.
|
||||
Changing the way the network behaves means that one has to start from scratch.
|
||||
|
||||
With PyTorch, we use a technique called Reverse-mode auto-differentiation, which allows you to
|
||||
change the way your network behaves arbitrarily with zero lag or overhead. Our inspiration comes
|
||||
from several research papers on this topic, as well as current and past work such as
|
||||
[autograd](https://github.com/twitter/torch-autograd),
|
||||
[autograd](https://github.com/HIPS/autograd),
|
||||
[Chainer](http://chainer.org), etc.
|
||||
|
||||
While this technique is not unique to PyTorch, it's one of the fastest implementations of it to date.
|
||||
You get the best of speed and flexibility for your crazy research.
|
||||
|
||||
<p align=center><img width="80%" src="docs/source/_static/img/dynamic_graph.gif" /></p>
|
||||
|
||||
### Python first
|
||||
|
||||
PyTorch is not a Python binding into a monolothic C++ framework.
|
||||
It is built to be deeply integrated into Python.
|
||||
You can use it naturally like you would use numpy / scipy / scikit-learn etc.
|
||||
You can write your new neural network layers in Python itself, using your favorite libraries.
|
||||
You can write your new neural network layers in Python itself, using your favorite libraries
|
||||
and use packages such as Cython and Numba.
|
||||
Our goal is to not reinvent the wheel where appropriate.
|
||||
|
||||
### Imperativeness first. What you see is what you get!
|
||||
### Imperative experiences
|
||||
|
||||
PyTorch is designed to be intuitive and easy to use.
|
||||
When you are debugging your program, or receive error messages / stack traces, you are always guaranteed to get
|
||||
error messages that are easy to understand and a stack-trace that points to exactly where your code was defined.
|
||||
Never spend hours debugging your code because of bad stack traces or asynchronous and opaque execution engines.
|
||||
PyTorch is designed to be intuitive, linear in thought and easy to use.
|
||||
When you execute a line of code, it gets executed. There isn't an asynchronous view of the world.
|
||||
When you drop into a debugger, or receive error messages and stack traces, understanding them is straight-forward.
|
||||
The stack-trace points to exactly where your code was defined.
|
||||
We hope you never spend hours debugging your code because of bad stack traces or asynchronous and opaque execution engines.
|
||||
|
||||
### Performance and Memory usage
|
||||
### Fast and Lean
|
||||
|
||||
PyTorch is as fast as the fastest deep learning framework out there. We integrate acceleration frameworks such as Intel MKL and NVIDIA CuDNN for maximum speed.
|
||||
PyTorch has minimal framework overhead. We integrate acceleration libraries
|
||||
such as Intel MKL and NVIDIA (CuDNN, NCCL) to maximize speed.
|
||||
At the core, it's CPU and GPU Tensor and Neural Network backends
|
||||
(TH, THC, THNN, THCUNN) are written as independent libraries with a C99 API.
|
||||
They are mature and have been tested for years.
|
||||
|
||||
The memory usage in PyTorch is extremely efficient, and we've written custom memory allocators for the GPU to make sure that your
|
||||
deep learning models are maximally memory efficient. This enables you to train bigger deep learning models than before.
|
||||
Hence, PyTorch is quite fast -- whether you run small or large neural networks.
|
||||
|
||||
### Multi-GPU ready
|
||||
The memory usage in PyTorch is extremely efficient compared to Torch or some of the alternatives.
|
||||
We've written custom memory allocators for the GPU to make sure that
|
||||
your deep learning models are maximally memory efficient.
|
||||
This enables you to train bigger deep learning models than before.
|
||||
|
||||
PyTorch is fully powered to efficiently use Multiple GPUs for accelerated deep learning.
|
||||
We integrate efficient multi-gpu collectives such as NVIDIA NCCL to make sure that you get the maximal Multi-GPU performance.
|
||||
### Extensions without pain
|
||||
|
||||
### Simple Extension API to interface with C
|
||||
Writing new neural network modules, or interfacing with PyTorch's Tensor API was designed to be straight-forward
|
||||
and with minimal abstractions.
|
||||
|
||||
You can write new neural network layers in Python using the torch API
|
||||
[or your favorite numpy based libraries such as SciPy](https://github.com/pytorch/tutorials/blob/master/Creating%20extensions%20using%20numpy%20and%20scipy.ipynb).
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to write your layers in C/C++, we provide an extension API based on
|
||||
[cffi](http://cffi.readthedocs.io/en/latest/) that is efficient and with minimal boilerplate.
|
||||
There is no wrapper code that needs to be written. [You can see an example here](https://github.com/pytorch/extension-ffi).
|
||||
|
||||
Writing new neural network modules, or interfacing with PyTorch's Tensor API is a breeze, thanks to an easy to use
|
||||
extension API that is efficient and easy to use.
|
||||
|
||||
## Installation
|
||||
|
||||
### Binaries
|
||||
- Anaconda
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
conda install pytorch -c https://conda.anaconda.org/t/6N-MsQ4WZ7jo/soumith
|
||||
conda install pytorch torchvision -c soumith
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### From source
|
||||
|
||||
Instructions for an Anaconda environment.
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to compile with CUDA support, install
|
||||
- [NVIDIA CUDA](https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-downloads) 7.5 or above
|
||||
- [NVIDIA CuDNN](https://developer.nvidia.com/cudnn) v5.x
|
||||
|
||||
#### Install optional dependencies
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
export CMAKE_PREFIX_PATH=[anaconda root directory]
|
||||
conda install numpy mkl
|
||||
conda install -c soumith magma-cuda75# or magma-cuda80
|
||||
|
||||
# Install basic dependencies
|
||||
conda install numpy mkl setuptools cmake gcc cffi
|
||||
|
||||
# On Linux, add LAPACK support for the GPU
|
||||
conda install -c soumith magma-cuda75 # or magma-cuda80 if CUDA 8.0
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Install PyTorch
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
export MACOSX_DEPLOYMENT_TARGET=10.9 # for OSX
|
||||
export MACOSX_DEPLOYMENT_TARGET=10.9 # if OSX
|
||||
pip install -r requirements.txt
|
||||
pip install .
|
||||
python setup.py install
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Getting Started
|
||||
|
||||
Three pointers to get you started:
|
||||
- [Tutorials: notebooks to get you started with understanding and using PyTorch](https://github.com/pytorch/tutorials)
|
||||
- [Examples: easy to understand pytorch code across all domains](https://github.com/pytorch/examples)
|
||||
- The API Reference: [http://pytorch.org/api/](http://pytorch.org/api/)
|
||||
- The API Reference: [http://pytorch.org/docs/](http://pytorch.org/docs/)
|
||||
|
||||
## Communication
|
||||
* forums: discuss implementations, research, etc. http://discuss.pytorch.org
|
||||
* github issues: bug reports, feature requests, install issues, RFCs, thoughts, etc.
|
||||
* slack: general chat, online discussions, collaboration etc. https://pytorch.slack.com/ . If you need a slack invite, ping me at soumith@pytorch.org
|
||||
* slack: general chat, online discussions, collaboration etc. https://pytorch.slack.com/ . If you need a slack invite, ping us at soumith@pytorch.org
|
||||
* newsletter: no-noise, one-way email newsletter with important announcements about pytorch. You can sign-up here: http://eepurl.com/cbG0rv
|
||||
|
||||
## Timeline
|
||||
## Releases and Contributing
|
||||
|
||||
We will run the alpha releases weekly for 6 weeks.
|
||||
After that, we will reevaluate progress, and if we are ready, we will hit beta-0. If not, we will do another two weeks of alpha.
|
||||
PyTorch has a 90 day release cycle (major releases).
|
||||
It's current state is Beta (v0.1.6), we expect no obvious bugs. Please let us know if you encounter a bug by [filing an issue](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues).
|
||||
|
||||
* ~~alpha-0: Working versions of torch, cutorch, nn, cunn, optim fully unit tested with seamless numpy conversions~~
|
||||
* ~~alpha-1: Serialization to/from disk with sharing intact. initial release of the new neuralnets package based on a Chainer-like design~~
|
||||
* ~~alpha-2: sharing tensors across processes for hogwild training or data-loading processes. a rewritten optim package for this new nn.~~
|
||||
* ~~alpha-3: binary installs, contbuilds, etc.~~
|
||||
* ~~alpha-4: multi-GPU support, cudnn integration, imagenet / resnet example~~
|
||||
* alpha-5: a ton of examples across vision, nlp, speech, RL -- this phase might make us rethink parts of the APIs, and hence want to do this in alpha than beta
|
||||
* alpha-6: Putting a simple and efficient story around multi-machine training. Probably simplistic like torch-distlearn. Building the website, release scripts, more documentation, etc.
|
||||
* beta-0: First public release
|
||||
We appreciate all contributions. If you are planning to contribute back bug-fixes, please do so without any further discussion.
|
||||
|
||||
The beta phases will be leaning more towards working with all of you, convering your use-cases, active development on non-core aspects.
|
||||
If you plan to contribute new features, utility functions or extensions to the core, please first open an issue and discuss the feature with us.
|
||||
Sending a PR without discussion might end up resulting in a rejected PR, because we might be taking the core in a different direction than you might be aware of.
|
||||
|
||||
## pytorch vs torch: important changes
|
||||
**For the next release cycle, these are the 3 big features we are planning to add:**
|
||||
|
||||
We've decided that it's time to rewrite/update parts of the old torch API, even if it means losing some of backward compatibility.
|
||||
1. [Distributed PyTorch](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/241) (a draft implementation is present in this [branch](https://github.com/apaszke/pytorch-dist) )
|
||||
2. Backward of Backward - Backpropagating through the optimization process itself. Some past and recent papers such as
|
||||
[Double Backprop](http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/publis/pdf/drucker-lecun-91.pdf) and [Unrolled GANs](https://arxiv.org/abs/1611.02163) need this.
|
||||
3. Lazy Execution Engine for autograd - This will enable us to optionally introduce caching and JIT compilers to optimize autograd code.
|
||||
|
||||
**[This tutorial](https://github.com/pytorch/tutorials/blob/master/Introduction%20to%20PyTorch%20for%20former%20Torchies.ipynb) takes you through the biggest changes**
|
||||
and walks you through PyTorch
|
||||
|
||||
For brevity,
|
||||
## The Team
|
||||
|
||||
#### Tensors:
|
||||
- clear separation of in-place and out-of-place operations
|
||||
- zero-indexing
|
||||
- no camel casing for Tensor functions
|
||||
- an efficient Numpy bridge (with zero memory copy)
|
||||
- CUDA tensors have clear and intuitive semantics
|
||||
PyTorch is a community driven project with several skillful engineers and researchers contributing to it.
|
||||
|
||||
#### New neural network module (Combines nn, nngraph, autograd):
|
||||
|
||||
1. Design inspired from Chainer
|
||||
2. Modules no longer hold state. State is held in the graph
|
||||
1. Access state via hooks
|
||||
2. Execution engine
|
||||
1. imperative execution engine (default)
|
||||
2. lazy execution engine
|
||||
1. allows graph optimizations and automatic in-place / fusing operations
|
||||
4. Model structure is defined by its code
|
||||
1. You can use loops and arbitrarily complicated conditional statements
|
||||
|
||||
**To reiterate, we recommend that you go through [This tutorial](https://github.com/pytorch/tutorials/blob/master/Introduction%20to%20PyTorch%20for%20former%20Torchies.ipynb)**
|
||||
|
||||
### Serialization
|
||||
|
||||
Pickling tensors is supported, but requires making a temporary copy of all data in memory and breaks sharing.
|
||||
|
||||
For this reason we're providing `torch.load` and `torch.save`, that are free of these problems.
|
||||
|
||||
They have the same interfaces as `pickle.load` (file object) and `pickle.dump` (serialized object, file object) respectively.
|
||||
|
||||
For now the only requirement is that the file should have a `fileno` method, which returns a file descriptor number (this is already implemented by objects returned by `open`).
|
||||
|
||||
Objects are serialized in a tar archive consisting of four files:
|
||||
- `sys_info` - protocol version, byte order, long size, etc.
|
||||
- `pickle` - pickled object
|
||||
- `tensors` - tensor metadata
|
||||
- `storages` - serialized data
|
||||
|
||||
### Multiprocessing with Tensor sharing
|
||||
|
||||
We made PyTorch to seamlessly integrate with python multiprocessing.
|
||||
What we've added specially in torch.multiprocessing is the seamless ability to efficiently share and send
|
||||
tensors over from one process to another. ([technical details of implementation](http://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/wiki/Multiprocessing-Technical-Notes))
|
||||
This is very useful for example in:
|
||||
- Writing parallelized data loaders
|
||||
- Training models "hogwild", where several models are trained in parallel, sharing the same set of parameters.
|
||||
|
||||
Here are a couple of examples for torch.multiprocessing
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# loaders.py
|
||||
# Functions from this file run in the workers
|
||||
|
||||
def fill(queue):
|
||||
while True:
|
||||
tensor = queue.get()
|
||||
tensor.fill_(10)
|
||||
queue.put(tensor)
|
||||
|
||||
def fill_pool(tensor):
|
||||
tensor.fill_(10)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# Example 1: Using multiple persistent processes and a Queue
|
||||
# process.py
|
||||
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
import torch.multiprocessing as multiprocessing
|
||||
from loaders import fill
|
||||
|
||||
# torch.multiprocessing.Queue automatically moves Tensor data to shared memory
|
||||
# So the main process and worker share the data
|
||||
queue = multiprocessing.Queue()
|
||||
buffers = [torch.Tensor(2, 2) for i in range(4)]
|
||||
for b in buffers:
|
||||
queue.put(b)
|
||||
processes = [multiprocessing.Process(target=fill, args=(queue,)).start() for i in range(10)]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# Example 2: Using a process pool
|
||||
# pool.py
|
||||
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from torch.multiprocessing import Pool
|
||||
from loaders import fill_pool
|
||||
|
||||
tensors = [torch.Tensor(2, 2) for i in range(100)]
|
||||
pool = Pool(10)
|
||||
pool.map(fill_pool, tensors)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Some notes on new nn implementation
|
||||
|
||||
As shown above, structure of the networks is fully defined by control-flow embedded in the code. There are no rigid containers known from Lua. You can put an `if` in the middle of your model and freely branch depending on any condition you can come up with. All operations are registered in the computational graph history.
|
||||
|
||||
There are two main objects that make this possible - variables and functions. They will be denoted as squares and circles respectively.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
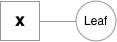
Variables are the objects that hold a reference to a tensor (and optionally to gradient w.r.t. that tensor), and to the function in the computational graph that created it. Variables created explicitly by the user (`Variable(tensor)`) have a Leaf function node associated with them.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
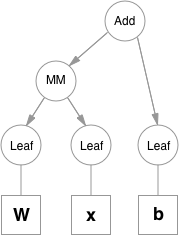
Functions are simple classes that define a function from a tuple of inputs to a tuple of outputs, and a formula for computing gradient w.r.t. it's inputs. Function objects are instantiated to hold references to other functions, and these references allow to reconstruct the history of a computation. An example graph for a linear layer (`Wx + b`) is shown below.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
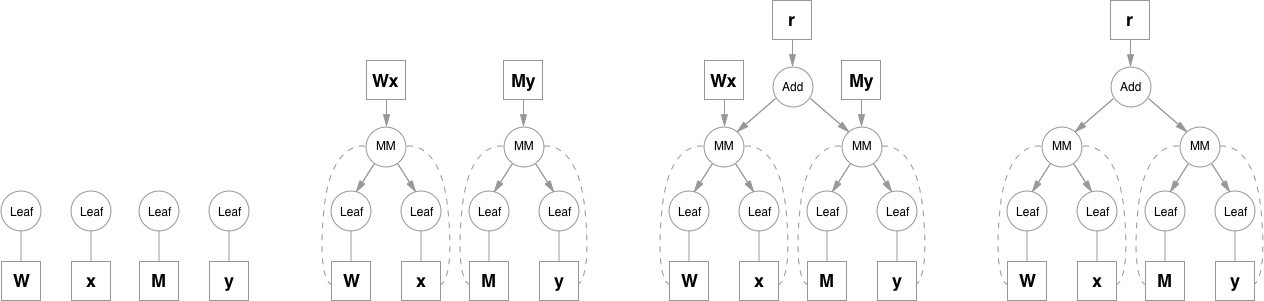
Please note that function objects never hold references to Variable objects, except for when they're necessary in the backward pass. This allows to free all the unnecessary intermediate values. A good example for this is addition when computing e.g. (`y = Wx + My`):
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Matrix multiplication operation keeps references to it's inputs because it will need them, but addition doesn't need `Wx` and `My` after it computes the result, so as soon as they go out of scope they are freed. To access intermediate values in the forward pass you can either copy them when you still have a reference, or you can use a system of hooks that can be attached to any function. Hooks also allow to access and inspect gradients inside the graph.
|
||||
|
||||
Another nice thing about this is that a single layer doesn't hold any state other than it's parameters (all intermediate values are alive as long as the graph references them), so it can be used multiple times before calling backward. This is especially convenient when training RNNs. You can use the same network for all timesteps and the gradients will sum up automatically.
|
||||
|
||||
To compute backward pass you can call `.backward()` on a variable if it's a scalar (a 1-element Variable), or you can provide a gradient tensor of matching shape if it's not. This creates an execution engine object that manages the whole backward pass. It's been introduced, so that the code for analyzing the graph and scheduling node processing order is decoupled from other parts, and can be easily replaced. Right now it's simply processing the nodes in topological order, without any prioritization, but in the future we can implement algorithms and heuristics for scheduling independent nodes on different GPU streams, deciding which branches to compute first, etc.
|
||||
PyTorch is currently maintained by [Adam Paszke](https://apaszke.github.io/), [Sam Gross](https://github.com/colesbury) and [Soumith Chintala](http://soumith.ch) with major contributions coming from 10s of talented individuals in various forms and means. A non-exhaustive but growing list needs to mention: Sergey Zagoruyko, Adam Lerer, Francisco Massa, Andreas Kopf, James Bradbury, Zeming Lin, Yuandong Tian, Guillaume Lample, Marat Dukhan, Natalia Gimelshein.
|
||||
|
||||
Note: this project is unrelated to [hughperkins/pytorch](https://github.com/hughperkins/pytorch) with the same name. Hugh is a valuable contributor in the Torch community and has helped with many things Torch and PyTorch.
|
||||
|
||||
20
docs/Makefile
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,20 @@
|
||||
# Minimal makefile for Sphinx documentation
|
||||
#
|
||||
|
||||
# You can set these variables from the command line.
|
||||
SPHINXOPTS =
|
||||
SPHINXBUILD = sphinx-build
|
||||
SPHINXPROJ = PyTorch
|
||||
SOURCEDIR = source
|
||||
BUILDDIR = build
|
||||
|
||||
# Put it first so that "make" without argument is like "make help".
|
||||
help:
|
||||
@$(SPHINXBUILD) -M help "$(SOURCEDIR)" "$(BUILDDIR)" $(SPHINXOPTS) $(O)
|
||||
|
||||
.PHONY: help Makefile
|
||||
|
||||
# Catch-all target: route all unknown targets to Sphinx using the new
|
||||
# "make mode" option. $(O) is meant as a shortcut for $(SPHINXOPTS).
|
||||
%: Makefile
|
||||
@$(SPHINXBUILD) -M $@ "$(SOURCEDIR)" "$(BUILDDIR)" $(SPHINXOPTS) $(O)
|
||||
@ -1,534 +0,0 @@
|
||||
#! /usr/bin/env python
|
||||
# encoding: utf-8
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Very lightweight docstring to Markdown converter. Modified for use in pytorch
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### License
|
||||
|
||||
Copyright © 2013 Thomas Gläßle <t_glaessle@gmx.de>
|
||||
|
||||
This work is free. You can redistribute it and/or modify it under the
|
||||
terms of the Do What The Fuck You Want To Public License, Version 2, as
|
||||
published by Sam Hocevar. See the COPYING file for more details.
|
||||
|
||||
This program is free software. It comes without any warranty, to the
|
||||
extent permitted by applicable law.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Description
|
||||
|
||||
Little convenience tool to extract docstrings from a module or class and
|
||||
convert them to GitHub Flavoured Markdown:
|
||||
|
||||
https://help.github.com/articles/github-flavored-markdown
|
||||
|
||||
Its purpose is to quickly generate `README.md` files for small projects.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### API
|
||||
|
||||
The interface consists of the following functions:
|
||||
|
||||
- `doctrim(docstring)`
|
||||
- `doc2md(docstring, title)`
|
||||
|
||||
You can run this script from the command line like:
|
||||
|
||||
$ doc2md.py [-a] [--no-toc] [-t title] module-name [class-name] > README.md
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Limitations
|
||||
|
||||
At the moment this is suited only for a very specific use case. It is
|
||||
hardly forseeable, if I will decide to improve on it in the near future.
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
import re
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
import inspect
|
||||
|
||||
__all__ = ['doctrim', 'doc2md']
|
||||
|
||||
doctrim = inspect.cleandoc
|
||||
|
||||
def unindent(lines):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Remove common indentation from string.
|
||||
|
||||
Unlike doctrim there is no special treatment of the first line.
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
try:
|
||||
# Determine minimum indentation:
|
||||
indent = min(len(line) - len(line.lstrip())
|
||||
for line in lines if line)
|
||||
except ValueError:
|
||||
return lines
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return [line[indent:] for line in lines]
|
||||
|
||||
def escape_markdown(line):
|
||||
line = line.replace('[', '\[').replace(']', '\]')
|
||||
line = line.replace('(', '\(').replace(')', '\)')
|
||||
line = line.replace('{', '\{').replace('}', '\}')
|
||||
line = line.replace('\\', '\\\\')
|
||||
line = line.replace('`', '\`')
|
||||
line = line.replace('*', '\*')
|
||||
line = line.replace('_', '\_')
|
||||
line = line.replace('#', '\#')
|
||||
line = line.replace('+', '\+')
|
||||
line = line.replace('-', '\-')
|
||||
line = line.replace('.', '\.')
|
||||
line = line.replace('!', '\!')
|
||||
return line
|
||||
|
||||
def code_block(lines, language=''):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Mark the code segment for syntax highlighting.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return ['```' + language] + lines + ['```']
|
||||
|
||||
def doctest2md(lines):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Convert the given doctest to a syntax highlighted markdown segment.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
is_only_code = True
|
||||
lines = unindent(lines)
|
||||
for line in lines:
|
||||
if not line.startswith('>>> ') and not line.startswith('... ') and line not in ['>>>', '...']:
|
||||
is_only_code = False
|
||||
break
|
||||
if is_only_code:
|
||||
orig = lines
|
||||
lines = []
|
||||
for line in orig:
|
||||
lines.append(line[4:])
|
||||
return lines
|
||||
|
||||
def doc_code_block(lines, language):
|
||||
if language == 'python':
|
||||
lines = doctest2md(lines)
|
||||
return code_block(lines, language)
|
||||
|
||||
_args_section = re.compile('^\s*Args:\s*')
|
||||
def is_args_check(line):
|
||||
return _args_section.match(line)
|
||||
|
||||
def args_block(lines):
|
||||
out = ['']
|
||||
out += ['Parameter | Default | Description']
|
||||
out += ['--------- | ------- | -----------']
|
||||
for line in lines:
|
||||
matches = re.findall(r'\s*([^:]+):\s*(.*?)\s*(Default:\s(.*))?\s*$', line)
|
||||
assert matches != None
|
||||
name = matches[0][0]
|
||||
description = matches[0][1]
|
||||
default = matches[0][3]
|
||||
out += [name + ' | ' + default + ' | ' + description]
|
||||
return out
|
||||
|
||||
# Inputs
|
||||
_inputs_section = re.compile('^\s*Inputs:\s*(.*)\s*')
|
||||
def is_inputs_check(line):
|
||||
return _inputs_section.match(line)
|
||||
|
||||
def inputs_block(lines):
|
||||
out = ['']
|
||||
out += ['Parameter | Default | Description']
|
||||
out += ['--------- | ------- | -----------']
|
||||
for line in lines:
|
||||
matches = re.findall(r'\s*([^:]+):\s*(.*?)\s*(Default:\s(.*))?\s*$', line)
|
||||
assert matches != None
|
||||
name = matches[0][0]
|
||||
description = matches[0][1]
|
||||
default = matches[0][3]
|
||||
out += [name + ' | ' + default + ' | ' + description]
|
||||
return out
|
||||
|
||||
# Outputs
|
||||
_outputs_section = re.compile('^\s*Outputs:\s*(.*)\s*')
|
||||
def is_outputs_check(line):
|
||||
return _outputs_section.match(line)
|
||||
|
||||
def outputs_block(lines):
|
||||
out = ['']
|
||||
out += ['Parameter | Description']
|
||||
out += ['--------- | -----------']
|
||||
for line in lines:
|
||||
matches = re.findall(r'\s*([^:]+):\s*(.*?)\s*(Default:\s(.*))?\s*$', line)
|
||||
assert matches != None
|
||||
name = matches[0][0]
|
||||
description = matches[0][1]
|
||||
default = matches[0][3]
|
||||
out += [name + ' | ' + description]
|
||||
return out
|
||||
|
||||
# Members
|
||||
_members_section = re.compile('^\s*Members:\s*(.*)\s*')
|
||||
def is_members_check(line):
|
||||
return _members_section.match(line)
|
||||
|
||||
def members_block(lines):
|
||||
out = ['']
|
||||
out += ['Parameter | Description']
|
||||
out += ['--------- | -----------']
|
||||
for line in lines:
|
||||
matches = re.findall(r'\s*([^:]+):\s*(.*?)\s*(Default:\s(.*))?\s*$', line)
|
||||
assert matches != None
|
||||
name = matches[0][0]
|
||||
description = matches[0][1]
|
||||
default = matches[0][3]
|
||||
out += [name + ' | ' + description]
|
||||
return out
|
||||
|
||||
_returns_section = re.compile('^\s*Returns:\s*')
|
||||
def is_returns_check(line):
|
||||
return _returns_section.match(line)
|
||||
|
||||
_image_section = re.compile('^\s*Image:\s*')
|
||||
def is_image_check(line):
|
||||
return _image_section.match(line)
|
||||
|
||||
_example_section = re.compile('^\s*Returns:\s*|^\s*Examples:\s*')
|
||||
def is_example_check(line):
|
||||
return _example_section.match(line)
|
||||
|
||||
_inputshape_section = re.compile('^\s*Returns:\s*|^\s*Input Shape:\s*')
|
||||
def is_inputshape_check(line):
|
||||
return _inputshape_section.match(line)
|
||||
|
||||
_outputshape_section = re.compile('^\s*Returns:\s*|^\s*Output Shape:\s*')
|
||||
def is_outputshape_check(line):
|
||||
return _outputshape_section.match(line)
|
||||
###############################################
|
||||
_reg_section = re.compile('^#+ ')
|
||||
def is_heading(line):
|
||||
return _reg_section.match(line)
|
||||
|
||||
def get_heading(line):
|
||||
assert is_heading(line)
|
||||
part = line.partition(' ')
|
||||
return len(part[0]), part[2]
|
||||
|
||||
def make_heading(level, title):
|
||||
return '#'*max(level, 1) + ' ' + title
|
||||
|
||||
def find_sections(lines):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Find all section names and return a list with their names.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
sections = []
|
||||
for line in lines:
|
||||
if is_heading(line):
|
||||
sections.append(get_heading(line))
|
||||
return sections
|
||||
|
||||
def make_toc(sections):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Generate table of contents for array of section names.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if not sections:
|
||||
return []
|
||||
outer = min(n for n,t in sections)
|
||||
refs = []
|
||||
for ind,sec in sections:
|
||||
ref = sec.lower()
|
||||
ref = ref.replace(' ', '-')
|
||||
ref = ref.replace('?', '')
|
||||
refs.append(" "*(ind-outer) + "- [%s](#%s)" % (sec, ref))
|
||||
return refs
|
||||
|
||||
def _doc2md(lines, shiftlevel=0):
|
||||
_doc2md.md = []
|
||||
_doc2md.is_code = False
|
||||
_doc2md.is_code_block = False
|
||||
_doc2md.is_args = False
|
||||
_doc2md.is_inputs = False
|
||||
_doc2md.is_outputs = False
|
||||
_doc2md.is_members = False
|
||||
_doc2md.is_returns = False
|
||||
_doc2md.is_inputshape = False
|
||||
_doc2md.is_outputshape = False
|
||||
_doc2md.code = []
|
||||
def reset():
|
||||
if _doc2md.is_code:
|
||||
_doc2md.is_code = False
|
||||
_doc2md.code += doc_code_block(code, 'python')
|
||||
_doc2md.code += ['']
|
||||
if _doc2md.is_code_block:
|
||||
_doc2md.is_code_block = False
|
||||
_doc2md.code += doc_code_block(code_block, 'python')
|
||||
_doc2md.code += ['']
|
||||
|
||||
if _doc2md.is_args:
|
||||
_doc2md.is_args = False
|
||||
_doc2md.md += args_block(args)
|
||||
|
||||
if _doc2md.is_inputs:
|
||||
_doc2md.is_inputs = False
|
||||
_doc2md.md += inputs_block(inputs)
|
||||
|
||||
if _doc2md.is_outputs:
|
||||
_doc2md.is_outputs = False
|
||||
_doc2md.md += outputs_block(outputs)
|
||||
|
||||
if _doc2md.is_members:
|
||||
_doc2md.is_members = False
|
||||
_doc2md.md += members_block(members)
|
||||
|
||||
if _doc2md.is_returns:
|
||||
_doc2md.is_returns = False
|
||||
_doc2md.md += returns
|
||||
|
||||
_doc2md.is_inputshape = False
|
||||
_doc2md.is_outputshape = False
|
||||
|
||||
for line in lines:
|
||||
trimmed = line.lstrip()
|
||||
if is_args_check(line):
|
||||
reset()
|
||||
_doc2md.is_args = True
|
||||
_doc2md.md += ['']
|
||||
_doc2md.md += ['#' * (shiftlevel+2) + ' Constructor Arguments']
|
||||
args = []
|
||||
elif is_inputs_check(line):
|
||||
reset()
|
||||
_doc2md.is_inputs = True
|
||||
_doc2md.md += ['']
|
||||
_doc2md.md += ['#' * (shiftlevel+2) + ' Inputs']
|
||||
inputs = []
|
||||
elif is_outputs_check(line):
|
||||
reset()
|
||||
_doc2md.is_outputs = True
|
||||
_doc2md.md += ['']
|
||||
_doc2md.md += ['#' * (shiftlevel+2) + ' Outputs']
|
||||
outputs = []
|
||||
elif is_members_check(line):
|
||||
reset()
|
||||
_doc2md.is_members = True
|
||||
_doc2md.md += ['']
|
||||
_doc2md.md += ['#' * (shiftlevel+2) + ' Members']
|
||||
members = []
|
||||
elif is_returns_check(line):
|
||||
reset()
|
||||
_doc2md.is_returns = True
|
||||
_doc2md.md += ['']
|
||||
_doc2md.md += ['#' * (shiftlevel+2) + ' Returns']
|
||||
returns = []
|
||||
elif is_example_check(line):
|
||||
reset()
|
||||
elif is_inputshape_check(line):
|
||||
reset()
|
||||
inputshape = re.findall(r'\s*Input\sShape:\s*(.*)\s*:\s*(.*)\s*$', line)[0]
|
||||
elif is_outputshape_check(line):
|
||||
reset()
|
||||
outputshape = re.findall(r'\s*Output\sShape:\s*(.*)\s*:\s*(.*)\s*$', line)[0]
|
||||
_doc2md.md += ['']
|
||||
_doc2md.md += ['#' * (shiftlevel+2) + ' Expected Shape']
|
||||
_doc2md.md += [' | Shape | Description ']
|
||||
_doc2md.md += ['------ | ----- | ------------']
|
||||
_doc2md.md += [' input | ' + inputshape[0] + ' | ' + inputshape[1]]
|
||||
_doc2md.md += ['output | ' + outputshape[0] + ' | ' + outputshape[1]]
|
||||
elif is_image_check(line):
|
||||
reset()
|
||||
_doc2md.md += ['']
|
||||
filename = re.findall(r'\s*Image:\s*(.*?)\s*$', line)
|
||||
_doc2md.md += ['<img src="image/' + filename[0] + '" >']
|
||||
elif _doc2md.is_code == False and trimmed.startswith('>>> '):
|
||||
reset()
|
||||
_doc2md.is_code = True
|
||||
code = [line]
|
||||
elif _doc2md.is_code_block == False and trimmed.startswith('```'):
|
||||
reset()
|
||||
_doc2md.is_code_block = True
|
||||
code_block = []
|
||||
elif _doc2md.is_code_block == True and trimmed.startswith('```'):
|
||||
# end of code block
|
||||
reset()
|
||||
elif _doc2md.is_code_block:
|
||||
if line:
|
||||
code_block.append(line)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
reset()
|
||||
elif shiftlevel != 0 and is_heading(line):
|
||||
reset()
|
||||
level, title = get_heading(line)
|
||||
_doc2md.md += [make_heading(level + shiftlevel, title)]
|
||||
elif _doc2md.is_args:
|
||||
if line:
|
||||
args.append(line)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
reset()
|
||||
elif _doc2md.is_inputs:
|
||||
if line:
|
||||
inputs.append(line)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
reset()
|
||||
elif _doc2md.is_outputs:
|
||||
if line:
|
||||
outputs.append(line)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
reset()
|
||||
elif _doc2md.is_members:
|
||||
if line:
|
||||
members.append(line)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
reset()
|
||||
elif _doc2md.is_returns:
|
||||
if line:
|
||||
returns.append(line)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
reset()
|
||||
elif _doc2md.is_code:
|
||||
if line:
|
||||
code.append(line)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
reset()
|
||||
else:
|
||||
reset()
|
||||
_doc2md.md += [line]
|
||||
reset()
|
||||
_doc2md.code += _doc2md.md
|
||||
return _doc2md.code
|
||||
|
||||
def doc2md(docstr, title, min_level=3, more_info=False, toc=True):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Convert a docstring to a markdown text.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
text = doctrim(docstr)
|
||||
lines = text.split('\n')
|
||||
|
||||
sections = find_sections(lines)
|
||||
if sections:
|
||||
level = min(n for n,t in sections) - 1
|
||||
else:
|
||||
level = 1
|
||||
|
||||
shiftlevel = 0
|
||||
if level < min_level:
|
||||
shiftlevel = min_level - level
|
||||
level = min_level
|
||||
sections = [(lev+shiftlevel, tit) for lev,tit in sections]
|
||||
|
||||
md = [
|
||||
make_heading(level, title),
|
||||
"",
|
||||
lines.pop(0),
|
||||
""
|
||||
]
|
||||
if toc:
|
||||
md += make_toc(sections)
|
||||
md += _doc2md(lines, shiftlevel)
|
||||
if more_info:
|
||||
return (md, sections)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return "\n".join(md)
|
||||
|
||||
def mod2md(module, title, title_api_section, toc=True):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Generate markdown document from module, including API section.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
docstr = module.__doc__ or " "
|
||||
|
||||
text = doctrim(docstr)
|
||||
lines = text.split('\n')
|
||||
|
||||
sections = find_sections(lines)
|
||||
if sections:
|
||||
level = min(n for n,t in sections) - 1
|
||||
else:
|
||||
level = 1
|
||||
|
||||
api_md = []
|
||||
api_sec = []
|
||||
if title_api_section :
|
||||
# sections.append((level+1, title_api_section))
|
||||
for name, entry in iter(module.__dict__.items()):
|
||||
if name[0] != '_' and entry.__doc__:
|
||||
#api_sec.append((level+1, name))
|
||||
#api_md += ['', '']
|
||||
if entry.__doc__:
|
||||
md, sec = doc2md(entry.__doc__, name,
|
||||
min_level=level+1, more_info=True, toc=False)
|
||||
api_sec += sec
|
||||
api_md += md
|
||||
|
||||
sections += api_sec
|
||||
|
||||
# headline
|
||||
md = [
|
||||
make_heading(level, title),
|
||||
"",
|
||||
lines.pop(0),
|
||||
""
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
# main sections
|
||||
if toc:
|
||||
md += make_toc(sections)
|
||||
md += _doc2md(lines)
|
||||
|
||||
if toc:
|
||||
md += ['']
|
||||
md += make_toc(api_sec)
|
||||
md += api_md
|
||||
|
||||
return "\n".join(md)
|
||||
|
||||
def main(args=None):
|
||||
# parse the program arguments
|
||||
import argparse
|
||||
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(
|
||||
description='Convert docstrings to markdown.')
|
||||
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
'module', help='The module containing the docstring.')
|
||||
group = parser.add_mutually_exclusive_group()
|
||||
group.add_argument(
|
||||
'entry', nargs='?',
|
||||
help='Convert only docstring of this entry in module.')
|
||||
group.add_argument(
|
||||
'-a', '--all', dest='all', action='store_true',
|
||||
help='Create an API section with the contents of module.__all__.')
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
'-t', '--title', dest='title',
|
||||
help='Document title (default is module name)')
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
'--no-toc', dest='toc', action='store_false', default=True,
|
||||
help='Do not automatically generate the TOC')
|
||||
args = parser.parse_args(args)
|
||||
|
||||
import importlib
|
||||
import inspect
|
||||
import os
|
||||
|
||||
def add_path(*pathes):
|
||||
for path in reversed(pathes):
|
||||
if path not in sys.path:
|
||||
sys.path.insert(0, path)
|
||||
|
||||
file = inspect.getfile(inspect.currentframe())
|
||||
add_path(os.path.realpath(os.path.abspath(os.path.dirname(file))))
|
||||
add_path(os.getcwd())
|
||||
|
||||
mod_name = args.module
|
||||
if mod_name.endswith('.py'):
|
||||
mod_name = mod_name.rsplit('.py', 1)[0]
|
||||
title = args.title or mod_name.replace('_', '-')
|
||||
|
||||
module = importlib.import_module(mod_name)
|
||||
|
||||
if args.all:
|
||||
print(mod2md(module, title, 'API', toc=args.toc))
|
||||
|
||||
else:
|
||||
if args.entry:
|
||||
docstr = module.__dict__[args.entry].__doc__ or ''
|
||||
else:
|
||||
docstr = module.__doc__ or ''
|
||||
|
||||
print(doc2md(docstr, title, toc=args.toc))
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
main()
|
||||
@ -1,100 +0,0 @@
|
||||
SCRIPT_DIR="$( cd "$( dirname "${BASH_SOURCE[0]}" )" && pwd )"
|
||||
pushd $SCRIPT_DIR
|
||||
|
||||
# module
|
||||
#python doc2md.py torch.nn Module --title Module --no-toc >../nn_module.md
|
||||
|
||||
# containers
|
||||
echo "## Containers" > ../nn_container.md
|
||||
python doc2md.py torch.nn Container --title Container --no-toc >>../nn_container.md
|
||||
python doc2md.py torch.nn Sequential --title Sequential --no-toc >>../nn_container.md
|
||||
|
||||
# convolution
|
||||
echo "## Convolution Layers" > ../nn_convolution.md
|
||||
echo Conv1d | xargs -I {} python doc2md.py torch.nn {} --title {} --no-toc >>../nn_convolution.md
|
||||
echo Conv2d | xargs -I {} python doc2md.py torch.nn {} --title {} --no-toc >>../nn_convolution.md
|
||||
echo ConvTranspose2d | xargs -I {} python doc2md.py torch.nn {} --title {} --no-toc >>../nn_convolution.md
|
||||
echo Conv3d | xargs -I {} python doc2md.py torch.nn {} --title {} --no-toc >>../nn_convolution.md
|
||||
echo ConvTranspose3d | xargs -I {} python doc2md.py torch.nn {} --title {} --no-toc >>../nn_convolution.md
|
||||
|
||||
# pooling
|
||||
echo "## Pooling Layers" > ../nn_pooling.md
|
||||
echo MaxPool1d | xargs -I {} python doc2md.py torch.nn {} --title {} --no-toc >>../nn_pooling.md
|
||||
echo MaxPool2d | xargs -I {} python doc2md.py torch.nn {} --title {} --no-toc >>../nn_pooling.md
|
||||
echo MaxPool3d | xargs -I {} python doc2md.py torch.nn {} --title {} --no-toc >>../nn_pooling.md
|
||||
echo MaxUnpool2d | xargs -I {} python doc2md.py torch.nn {} --title {} --no-toc >>../nn_pooling.md
|
||||
echo MaxUnpool3d | xargs -I {} python doc2md.py torch.nn {} --title {} --no-toc >>../nn_pooling.md
|
||||
echo AvgPool2d | xargs -I {} python doc2md.py torch.nn {} --title {} --no-toc >>../nn_pooling.md
|
||||
echo AvgPool3d | xargs -I {} python doc2md.py torch.nn {} --title {} --no-toc >>../nn_pooling.md
|
||||
echo FractionalMaxPool2d | xargs -I {} python doc2md.py torch.nn {} --title {} --no-toc >>../nn_pooling.md
|
||||
echo LPPool2d | xargs -I {} python doc2md.py torch.nn {} --title {} --no-toc >>../nn_pooling.md
|
||||
|
||||
# activations
|
||||
echo "## Non-linearities" > ../nn_activation.md
|
||||
echo ReLU | xargs -I {} python doc2md.py torch.nn {} --title {} --no-toc >>../nn_activation.md
|
||||
echo ReLU6 | xargs -I {} python doc2md.py torch.nn {} --title {} --no-toc >>../nn_activation.md
|
||||
echo Threshold | xargs -I {} python doc2md.py torch.nn {} --title {} --no-toc >>../nn_activation.md
|
||||
echo Hardtanh | xargs -I {} python doc2md.py torch.nn {} --title {} --no-toc >>../nn_activation.md
|
||||
echo Sigmoid | xargs -I {} python doc2md.py torch.nn {} --title {} --no-toc >>../nn_activation.md
|
||||
echo Tanh | xargs -I {} python doc2md.py torch.nn {} --title {} --no-toc >>../nn_activation.md
|
||||
echo ELU | xargs -I {} python doc2md.py torch.nn {} --title {} --no-toc >>../nn_activation.md
|
||||
echo LeakyReLU | xargs -I {} python doc2md.py torch.nn {} --title {} --no-toc >>../nn_activation.md
|
||||
echo LogSigmoid | xargs -I {} python doc2md.py torch.nn {} --title {} --no-toc >>../nn_activation.md
|
||||
echo Softplus | xargs -I {} python doc2md.py torch.nn {} --title {} --no-toc >>../nn_activation.md
|
||||
echo Softshrink | xargs -I {} python doc2md.py torch.nn {} --title {} --no-toc >>../nn_activation.md
|
||||
echo PReLU | xargs -I {} python doc2md.py torch.nn {} --title {} --no-toc >>../nn_activation.md
|
||||
echo Softsign | xargs -I {} python doc2md.py torch.nn {} --title {} --no-toc >>../nn_activation.md
|
||||
echo Tanhshrink | xargs -I {} python doc2md.py torch.nn {} --title {} --no-toc >>../nn_activation.md
|
||||
echo Softmin | xargs -I {} python doc2md.py torch.nn {} --title {} --no-toc >>../nn_activation.md
|
||||
echo Softmax | xargs -I {} python doc2md.py torch.nn {} --title {} --no-toc >>../nn_activation.md
|
||||
echo Softmax2d | xargs -I {} python doc2md.py torch.nn {} --title {} --no-toc >>../nn_activation.md
|
||||
echo LogSoftmax | xargs -I {} python doc2md.py torch.nn {} --title {} --no-toc >>../nn_activation.md
|
||||
|
||||
# normalization
|
||||
echo "## Normalization layers" > ../nn_normalization.md
|
||||
echo BatchNorm1d | xargs -I {} python doc2md.py torch.nn {} --title {} --no-toc >>../nn_normalization.md
|
||||
echo BatchNorm2d | xargs -I {} python doc2md.py torch.nn {} --title {} --no-toc >>../nn_normalization.md
|
||||
echo BatchNorm3d | xargs -I {} python doc2md.py torch.nn {} --title {} --no-toc >>../nn_normalization.md
|
||||
|
||||
# recurrentnet
|
||||
echo "## Recurrent layers" > ../nn_recurrent.md
|
||||
echo RNN | xargs -I {} python doc2md.py torch.nn {} --title {} --no-toc >>../nn_recurrent.md
|
||||
echo LSTM | xargs -I {} python doc2md.py torch.nn {} --title {} --no-toc >>../nn_recurrent.md
|
||||
echo GRU | xargs -I {} python doc2md.py torch.nn {} --title {} --no-toc >>../nn_recurrent.md
|
||||
echo RNNCell | xargs -I {} python doc2md.py torch.nn {} --title {} --no-toc >>../nn_recurrent.md
|
||||
echo LSTMCell | xargs -I {} python doc2md.py torch.nn {} --title {} --no-toc >>../nn_recurrent.md
|
||||
echo GRUCell | xargs -I {} python doc2md.py torch.nn {} --title {} --no-toc >>../nn_recurrent.md
|
||||
|
||||
# linear
|
||||
echo "## Linear layers" > ../nn_linear.md
|
||||
echo Linear | xargs -I {} python doc2md.py torch.nn {} --title {} --no-toc >>../nn_linear.md
|
||||
|
||||
# dropout
|
||||
echo "## Dropout layers" > ../nn_dropout.md
|
||||
echo Dropout | xargs -I {} python doc2md.py torch.nn {} --title {} --no-toc >>../nn_dropout.md
|
||||
echo Dropout2d | xargs -I {} python doc2md.py torch.nn {} --title {} --no-toc >>../nn_dropout.md
|
||||
echo Dropout3d | xargs -I {} python doc2md.py torch.nn {} --title {} --no-toc >>../nn_dropout.md
|
||||
|
||||
# Sparse
|
||||
echo "## Sparse layers" > ../nn_sparse.md
|
||||
echo Embedding | xargs -I {} python doc2md.py torch.nn {} --title {} --no-toc >>../nn_sparse.md
|
||||
|
||||
# loss_functions
|
||||
echo "## Loss functions" > ../nn_loss.md
|
||||
echo L1Loss | xargs -I {} python doc2md.py torch.nn {} --title {} --no-toc >>../nn_loss.md
|
||||
echo MSELoss | xargs -I {} python doc2md.py torch.nn {} --title {} --no-toc >>../nn_loss.md
|
||||
echo CrossEntropyLoss | xargs -I {} python doc2md.py torch.nn {} --title {} --no-toc >>../nn_loss.md
|
||||
echo NLLLoss | xargs -I {} python doc2md.py torch.nn {} --title {} --no-toc >>../nn_loss.md
|
||||
echo NLLLoss2d | xargs -I {} python doc2md.py torch.nn {} --title {} --no-toc >>../nn_loss.md
|
||||
echo KLDivLoss | xargs -I {} python doc2md.py torch.nn {} --title {} --no-toc >>../nn_loss.md
|
||||
echo BCELoss | xargs -I {} python doc2md.py torch.nn {} --title {} --no-toc >>../nn_loss.md
|
||||
echo MarginRankingLoss | xargs -I {} python doc2md.py torch.nn {} --title {} --no-toc >>../nn_loss.md
|
||||
echo HingeEmbeddingLoss | xargs -I {} python doc2md.py torch.nn {} --title {} --no-toc >>../nn_loss.md
|
||||
echo MultiLabelMarginLoss | xargs -I {} python doc2md.py torch.nn {} --title {} --no-toc >>../nn_loss.md
|
||||
echo SmoothL1Loss | xargs -I {} python doc2md.py torch.nn {} --title {} --no-toc >>../nn_loss.md
|
||||
echo SoftMarginLoss | xargs -I {} python doc2md.py torch.nn {} --title {} --no-toc >>../nn_loss.md
|
||||
echo MultiLabelSoftMarginLoss | xargs -I {} python doc2md.py torch.nn {} --title {} --no-toc >>../nn_loss.md
|
||||
echo CosineEmbeddingLoss | xargs -I {} python doc2md.py torch.nn {} --title {} --no-toc >>../nn_loss.md
|
||||
echo MultiMarginLoss | xargs -I {} python doc2md.py torch.nn {} --title {} --no-toc >>../nn_loss.md
|
||||
|
||||
popd
|
||||
@ -1,143 +0,0 @@
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
from tools.cwrap import cwrap
|
||||
from tools.cwrap.plugins import CWrapPlugin
|
||||
from string import Template
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from torch.autograd import Variable
|
||||
|
||||
def transform_defined_if(defined_if):
|
||||
if defined_if != None:
|
||||
defined_if = defined_if.replace('defined(TH_REAL_IS_FLOAT)', 'Float')
|
||||
defined_if = defined_if.replace('defined(TH_REAL_IS_DOUBLE)', 'Double')
|
||||
defined_if = defined_if.replace('defined(TH_REAL_IS_BYTE)', 'Byte')
|
||||
defined_if = defined_if.replace('defined(TH_REAL_IS_CHAR)', 'Char')
|
||||
defined_if = defined_if.replace('defined(TH_REAL_IS_INT)', 'Int')
|
||||
defined_if = defined_if.replace('defined(TH_REAL_IS_LONG)', 'Long')
|
||||
defined_if = defined_if.replace('defined(NUMPY_TYPE_ENUM)',
|
||||
'Byte // Short // Int // Long // Float // Double')
|
||||
defined_if = defined_if.replace('CUDA_INT', 'Cuda_Int')
|
||||
defined_if = defined_if.replace('CUDA_LONG', 'Cuda_Long')
|
||||
defined_if = defined_if.replace('CUDA_FLOAT', 'Cuda_Float')
|
||||
defined_if = defined_if.replace('CUDA_DOUBLE', 'Cuda_Double')
|
||||
defined_if = defined_if.replace('CUDA_HALF', 'Cuda_Half')
|
||||
defined_if = defined_if.replace('!IS_CUDA', 'All CPU Types')
|
||||
else:
|
||||
defined_if = "All Types (CPU and CUDA)"
|
||||
defined_if = defined_if.replace('||', '//')
|
||||
return defined_if
|
||||
|
||||
class DocGen(CWrapPlugin):
|
||||
def __init__(self):
|
||||
self.declarations = {}
|
||||
|
||||
def process_declarations(self, declarations):
|
||||
self.declarations.update({declaration['name']: declaration for declaration in declarations})
|
||||
# self.declarations += declarations
|
||||
return declarations
|
||||
|
||||
def get_wrapper_template(self, declaration):
|
||||
return Template("")
|
||||
|
||||
def get_type_check(self, arg, option):
|
||||
return Template("")
|
||||
|
||||
def get_type_unpack(self, arg, option):
|
||||
return Template("")
|
||||
|
||||
def get_return_wrapper(self, option):
|
||||
return Template("")
|
||||
|
||||
def print_declarations(self):
|
||||
print("# torch.Tensor")
|
||||
for name, declarations in sorted(self.declarations.items()):
|
||||
if name.endswith('_') and name[:-1] in self.declarations:
|
||||
continue
|
||||
if not name.endswith('_') and name + '_' in self.declarations:
|
||||
inplace = True
|
||||
else:
|
||||
inplace = False
|
||||
|
||||
pname = declarations['options'][0].get('python_name', None)
|
||||
if pname != None:
|
||||
name = pname
|
||||
if name.startswith('_'):
|
||||
continue
|
||||
|
||||
# START PRINTING MARKDOWN
|
||||
print("## " + name + " \n")
|
||||
print("| %-25s | %-8s | %-25s |" % ("Name", "Autograd", "defined if"))
|
||||
print("| " + ('-' * 28) + " | " + ('-' * 11) + " | "+ ('-' * 28) + " |")
|
||||
if inplace:
|
||||
sys.stdout.write("| %-25s" % (name + ' // ' + name + "_"))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
sys.stdout.write("| %-25s" % name)
|
||||
sys.stdout.write(' | ')
|
||||
if hasattr(Variable(torch.randn(10)), name):
|
||||
sys.stdout.write(' %9s ' % 'yes') # + ' ' + name)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
sys.stdout.write(' %9s ' % 'no') # + ' ' + name)
|
||||
defined_if = declarations.get('defined_if', None)
|
||||
defined_if = transform_defined_if(defined_if)
|
||||
sys.stdout.write(' | ')
|
||||
sys.stdout.write(defined_if)
|
||||
sys.stdout.write(' |')
|
||||
sys.stdout.write('\n\n')
|
||||
#if inplace:
|
||||
# print('Inplace Exists : True')
|
||||
#sys.stdout.write('Arguments : ')
|
||||
|
||||
args = declarations['options'][0]['arguments']
|
||||
if len(args) == 0:
|
||||
print( '**No Arguments**\n' )
|
||||
else:
|
||||
print( '**Arguments**\n' )
|
||||
print("| %-15s | %-12s | %-15s |" % ("Name", "Type", "Default"))
|
||||
print("| " + ('-' * 18) + " | " + ('-' * 15) + " | "+ ('-' * 18) + " |")
|
||||
|
||||
for arg in args:
|
||||
type_ = arg['type']
|
||||
if type_ == 'THGenerator*':
|
||||
continue
|
||||
if type_ == 'THTensor*':
|
||||
type_ = 'Tensor'
|
||||
if type_ == 'THIndexTensor*':
|
||||
type_ = 'LongTensor'
|
||||
if type_ == 'THBoolTensor*':
|
||||
type_ = 'ByteTensor'
|
||||
if type_ == 'THLongTensor*':
|
||||
type_ = 'LongTensor'
|
||||
if type_ == 'THLongStorage*':
|
||||
type_ = 'LongStorage'
|
||||
default = arg.get('default', None)
|
||||
allocated = arg.get('allocate', None)
|
||||
if default == None and allocated == None:
|
||||
default = " [required]"
|
||||
elif allocated != None:
|
||||
default = " [optional]"
|
||||
else:
|
||||
default = str(default)
|
||||
import re
|
||||
m = re.search('\s*AS_REAL\((.+)\)\s*', default)
|
||||
if m:
|
||||
default = m.group(1)
|
||||
default = default
|
||||
|
||||
print('| %15s | %12s | %10s |' % (arg['name'], type_, default))
|
||||
# print( 'Options : ' )
|
||||
# print(declarations['options'][0])
|
||||
print('')
|
||||
if declarations['return']:
|
||||
return_ = declarations['return']
|
||||
if return_ == 'THTensor*':
|
||||
return_ = 'Tensor'
|
||||
if return_ == 'void':
|
||||
return_ = 'nothing'
|
||||
print( '**Returns : ' + return_ + '**')
|
||||
print('')
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
docs = DocGen()
|
||||
cwrap('../../torch/csrc/generic/TensorMethods.cwrap', plugins=[docs])
|
||||
|
||||
docs.print_declarations()
|
||||
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 5.8 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 32 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 6.0 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 5.4 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 5.8 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 8.9 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 8.5 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 6.4 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 19 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 19 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 20 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 12 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 6.4 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 6.4 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 6.1 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 6.3 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 19 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 6.7 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 5.9 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 6.8 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 5.4 KiB |
|
Before Width: | Height: | Size: 7.2 KiB |
36
docs/make.bat
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,36 @@
|
||||
@ECHO OFF
|
||||
|
||||
pushd %~dp0
|
||||
|
||||
REM Command file for Sphinx documentation
|
||||
|
||||
if "%SPHINXBUILD%" == "" (
|
||||
set SPHINXBUILD=sphinx-build
|
||||
)
|
||||
set SOURCEDIR=source
|
||||
set BUILDDIR=build
|
||||
set SPHINXPROJ=PyTorch
|
||||
|
||||
if "%1" == "" goto help
|
||||
|
||||
%SPHINXBUILD% >NUL 2>NUL
|
||||
if errorlevel 9009 (
|
||||
echo.
|
||||
echo.The 'sphinx-build' command was not found. Make sure you have Sphinx
|
||||
echo.installed, then set the SPHINXBUILD environment variable to point
|
||||
echo.to the full path of the 'sphinx-build' executable. Alternatively you
|
||||
echo.may add the Sphinx directory to PATH.
|
||||
echo.
|
||||
echo.If you don't have Sphinx installed, grab it from
|
||||
echo.http://sphinx-doc.org/
|
||||
exit /b 1
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
%SPHINXBUILD% -M %1 %SOURCEDIR% %BUILDDIR% %SPHINXOPTS%
|
||||
goto end
|
||||
|
||||
:help
|
||||
%SPHINXBUILD% -M help %SOURCEDIR% %BUILDDIR% %SPHINXOPTS%
|
||||
|
||||
:end
|
||||
popd
|
||||
@ -1,3 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# torch.nn
|
||||
|
||||
Neural Networks in PyTorch
|
||||
@ -1,496 +0,0 @@
|
||||
## Non-linearities
|
||||
### ReLU
|
||||
|
||||
Applies the rectified linear unit function element-wise ReLU(x)= max(0,x)
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
m = nn.ReLU()
|
||||
input = autograd.Variable(torch.randn(2))
|
||||
print(input)
|
||||
print(m(input))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Constructor Arguments
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter | Default | Description
|
||||
--------- | ------- | -----------
|
||||
inplace | | can optionally do the operation in-place
|
||||
|
||||
#### Expected Shape
|
||||
| Shape | Description
|
||||
------ | ----- | ------------
|
||||
input | Any | Tensor of any size and dimension
|
||||
output | Same | Output has the same shape as input
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
a Tensor of the same dimension and shape as the input
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="image/relu.png" >
|
||||
### ReLU6
|
||||
|
||||
Applies the element-wise function ReLU6(x) = min( max(0,x), 6)
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
m = nn.ReLU6()
|
||||
input = autograd.Variable(torch.randn(2))
|
||||
print(input)
|
||||
print(m(input))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Constructor Arguments
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter | Default | Description
|
||||
--------- | ------- | -----------
|
||||
inplace | | can optionally do the operation in-place
|
||||
|
||||
#### Expected Shape
|
||||
| Shape | Description
|
||||
------ | ----- | ------------
|
||||
input | Any | Tensor of any size and dimension
|
||||
output | Same | Output has the same shape as input
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
a Tensor of the same dimension and shape as the input
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="image/relu6.png" >
|
||||
### Threshold
|
||||
|
||||
Thresholds each element of the input Tensor
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
m = nn.Threshold(0.1, 20)
|
||||
input = Variable(torch.randn(2))
|
||||
print(input)
|
||||
print(m(input))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Threshold is defined as:
|
||||
y = x if x >= threshold
|
||||
value if x < threshold
|
||||
|
||||
#### Constructor Arguments
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter | Default | Description
|
||||
--------- | ------- | -----------
|
||||
threshold | | The value to threshold at
|
||||
value | | The value to replace with
|
||||
inplace | | can optionally do the operation in-place
|
||||
|
||||
#### Expected Shape
|
||||
| Shape | Description
|
||||
------ | ----- | ------------
|
||||
input | Any | Tensor of any size and dimension
|
||||
output | Same | Output has the same shape as input
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
Tensor of same dimension and shape as the input
|
||||
### Hardtanh
|
||||
|
||||
Applies the HardTanh function element-wise
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
m = nn.HardTanh(-2, 2)
|
||||
input = autograd.Variable(torch.randn(2))
|
||||
print(input)
|
||||
print(m(input))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
HardTanh is defined as:
|
||||
f(x) = +1, if x > 1
|
||||
f(x) = -1, if x < -1
|
||||
f(x) = x, otherwise
|
||||
The range of the linear region [-1, 1] can be adjusted
|
||||
|
||||
#### Constructor Arguments
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter | Default | Description
|
||||
--------- | ------- | -----------
|
||||
min_value | | minimum value of the linear region range
|
||||
max_value | | maximum value of the linear region range
|
||||
inplace | | can optionally do the operation in-place
|
||||
|
||||
#### Expected Shape
|
||||
| Shape | Description
|
||||
------ | ----- | ------------
|
||||
input | Any | Tensor of any size and dimension
|
||||
output | Same | Output has the same shape as input
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
a Tensor of the same dimension and shape as the input
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="image/htanh.png" >
|
||||
### Sigmoid
|
||||
|
||||
Applies the element-wise function sigmoid(x) = 1 / ( 1 + exp(-x))
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
m = nn.Sigmoid()
|
||||
input = autograd.Variable(torch.randn(2))
|
||||
print(input)
|
||||
print(m(input))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Expected Shape
|
||||
| Shape | Description
|
||||
------ | ----- | ------------
|
||||
input | Any | Tensor of any size and dimension
|
||||
output | Same | Output has the same shape as input
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
a Tensor of the same dimension and shape as the input
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="image/sigmoid.png" >
|
||||
### Tanh
|
||||
|
||||
Applies element-wise, Tanh(x) = (exp(x) - exp(-x)) / (exp(x) + exp(-x))
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
m = nn.Tanh()
|
||||
input = autograd.Variable(torch.randn(2))
|
||||
print(input)
|
||||
print(m(input))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Expected Shape
|
||||
| Shape | Description
|
||||
------ | ----- | ------------
|
||||
input | Any | Tensor of any size and dimension
|
||||
output | Same | Output has the same shape as input
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
a Tensor of the same dimension and shape as the input
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="image/tanh.png" >
|
||||
### ELU
|
||||
|
||||
Applies element-wise, ELU(x) = max(0,x) + min(0, alpha * (exp(x) - 1))
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
m = nn.ELU()
|
||||
input = autograd.Variable(torch.randn(2))
|
||||
print(input)
|
||||
print(m(input))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Constructor Arguments
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter | Default | Description
|
||||
--------- | ------- | -----------
|
||||
alpha | 1.0 | the alpha value for the ELU formulation.
|
||||
inplace | | can optionally do the operation in-place
|
||||
|
||||
#### Expected Shape
|
||||
| Shape | Description
|
||||
------ | ----- | ------------
|
||||
input | Any | Tensor of any size and dimension
|
||||
output | Same | Output has the same shape as input
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
a Tensor of the same dimension and shape as the input
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="image/elu.png" >
|
||||
### LeakyReLU
|
||||
|
||||
Applies element-wise, f(x) = max(0, x) + negative_slope * min(0, x)
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
m = nn.LeakyReLU(0.1)
|
||||
input = autograd.Variable(torch.randn(2))
|
||||
print(input)
|
||||
print(m(input))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Constructor Arguments
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter | Default | Description
|
||||
--------- | ------- | -----------
|
||||
negative_slope | 1e-2 | Controls the angle of the negative slope.
|
||||
inplace | | can optionally do the operation in-place
|
||||
|
||||
#### Expected Shape
|
||||
| Shape | Description
|
||||
------ | ----- | ------------
|
||||
input | Any | Tensor of any size and dimension
|
||||
output | Same | Output has the same shape as input
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
a Tensor of the same dimension and shape as the input
|
||||
### LogSigmoid
|
||||
|
||||
Applies element-wise LogSigmoid(x) = log( 1 / (1 + exp(-x_i)))
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
m = nn.LogSigmoid()
|
||||
input = autograd.Variable(torch.randn(2))
|
||||
print(input)
|
||||
print(m(input))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Expected Shape
|
||||
| Shape | Description
|
||||
------ | ----- | ------------
|
||||
input | Any | Tensor of any size and dimension
|
||||
output | Same | Output has the same shape as input
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
a Tensor of the same dimension and shape as the input
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="image/logsigmoid.png" >
|
||||
### Softplus
|
||||
|
||||
Applies element-wise SoftPlus(x) = 1/beta * log(1 + exp(beta * x_i))
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
m = nn.Softplus()
|
||||
input = autograd.Variable(torch.randn(2))
|
||||
print(input)
|
||||
print(m(input))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
SoftPlus is a smooth approximation to the ReLU function and can be used
|
||||
to constrain the output of a machine to always be positive.
|
||||
For numerical stability the implementation reverts to the linear function
|
||||
for inputs above a certain value.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Constructor Arguments
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter | Default | Description
|
||||
--------- | ------- | -----------
|
||||
beta | 1 | the beta value for the Softplus formulation.
|
||||
threshold | 20 | values above this revert to a linear function.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Expected Shape
|
||||
| Shape | Description
|
||||
------ | ----- | ------------
|
||||
input | Any | Tensor of any size and dimension
|
||||
output | Same | Output has the same shape as input
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
a Tensor of the same dimension and shape as the input
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="image/softplus.png" >
|
||||
### Softshrink
|
||||
|
||||
Applies the soft shrinkage function elementwise
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
m = nn.Softshrink()
|
||||
input = autograd.Variable(torch.randn(2))
|
||||
print(input)
|
||||
print(m(input))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
SoftShrinkage operator is defined as:
|
||||
f(x) = x-lambda, if x > lambda > f(x) = x+lambda, if x < -lambda
|
||||
f(x) = 0, otherwise
|
||||
|
||||
#### Constructor Arguments
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter | Default | Description
|
||||
--------- | ------- | -----------
|
||||
lambd | 0.5 | the lambda value for the Softshrink formulation.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Expected Shape
|
||||
| Shape | Description
|
||||
------ | ----- | ------------
|
||||
input | Any | Tensor of any size and dimension
|
||||
output | Same | Output has the same shape as input
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
a Tensor of the same dimension and shape as the input
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="image/sshrink.png" >
|
||||
### PReLU
|
||||
|
||||
Applies element-wise the function PReLU(x) = max(0,x) + a * min(0,x)
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
m = nn.PReLU()
|
||||
input = autograd.Variable(torch.randn(2))
|
||||
print(input)
|
||||
print(m(input))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Here "a" is a learnable parameter.
|
||||
When called without arguments, nn.PReLU() uses a single parameter "a"
|
||||
across all input channels. If called with nn.PReLU(nChannels), a separate
|
||||
"a" is used for each input channel.
|
||||
Note that weight decay should not be used when learning "a" for good
|
||||
performance.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Constructor Arguments
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter | Default | Description
|
||||
--------- | ------- | -----------
|
||||
num_parameters | 1 | number of "a" to learn.
|
||||
init | 0.25 | the initial value of "a".
|
||||
|
||||
#### Expected Shape
|
||||
| Shape | Description
|
||||
------ | ----- | ------------
|
||||
input | Any | Tensor of any size and dimension
|
||||
output | Same | Output has the same shape as input
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
a Tensor of the same dimension and shape as the input
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="image/prelu.png" >
|
||||
### Softsign
|
||||
|
||||
Applies element-wise, the function Softsign(x) = x / (1 + |x|)
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
m = nn.Softsign()
|
||||
input = autograd.Variable(torch.randn(2))
|
||||
print(input)
|
||||
print(m(input))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Expected Shape
|
||||
| Shape | Description
|
||||
------ | ----- | ------------
|
||||
input | Any | Tensor of any size and dimension
|
||||
output | Same | Output has the same shape as input
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
a Tensor of the same dimension and shape as the input
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="image/softsign.png" >
|
||||
### Tanhshrink
|
||||
|
||||
Applies element-wise, Tanhshrink(x) = x - Tanh(x)
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
m = nn.Tanhshrink()
|
||||
input = autograd.Variable(torch.randn(2))
|
||||
print(input)
|
||||
print(m(input))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Expected Shape
|
||||
| Shape | Description
|
||||
------ | ----- | ------------
|
||||
input | Any | Tensor of any size and dimension
|
||||
output | Same | Output has the same shape as input
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
a Tensor of the same dimension and shape as the input
|
||||
### Softmin
|
||||
|
||||
Applies the Softmin function to an n-dimensional input Tensor
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
m = nn.Softmin()
|
||||
input = autograd.Variable(torch.randn(2, 3))
|
||||
print(input)
|
||||
print(m(input))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
rescaling them so that the elements of the n-dimensional output Tensor
|
||||
lie in the range (0,1) and sum to 1
|
||||
Softmin(x) = exp(-x_i - shift) / sum_j exp(-x_j - shift)
|
||||
where shift = max_i - x_i
|
||||
|
||||
#### Expected Shape
|
||||
| Shape | Description
|
||||
------ | ----- | ------------
|
||||
input | [ * , * ] | 2D Tensor of any size
|
||||
output | Same | Output has the same shape as input
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
a Tensor of the same dimension and shape as the input, with
|
||||
values in the range [0, 1]
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="image/softmin.png" >
|
||||
### Softmax
|
||||
|
||||
Applies the Softmax function to an n-dimensional input Tensor
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
m = nn.Softmax()
|
||||
input = autograd.Variable(torch.randn(2, 3))
|
||||
print(input)
|
||||
print(m(input))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
rescaling them so that the elements of the n-dimensional output Tensor
|
||||
lie in the range (0,1) and sum to 1
|
||||
|
||||
Softmax is defined as f_i(x) = exp(x_i - shift) / sum_j exp(x_j - shift)
|
||||
where shift = max_i x_i
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Expected Shape
|
||||
| Shape | Description
|
||||
------ | ----- | ------------
|
||||
input | [ * , * ] | 2D Tensor of any size
|
||||
output | Same | Output has the same shape as input
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
a Tensor of the same dimension and shape as the input with
|
||||
values in the range [0, 1]
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="image/softmax.png" >
|
||||
Notes:
|
||||
Note that this module doesn't work directly with NLLLoss,
|
||||
which expects the Log to be computed between the Softmax and itself.
|
||||
Use Logsoftmax instead (it's faster).
|
||||
### Softmax2d
|
||||
|
||||
Applies SoftMax over features to each spatial location
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
m = nn.Softmax2d()
|
||||
# you softmax over the 2nd dimension
|
||||
input = autograd.Variable(torch.randn(2, 3, 12, 13))
|
||||
print(input)
|
||||
print(m(input))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
When given an image of Channels x Height x Width, it will
|
||||
apply Softmax to each location [Channels, h_i, w_j]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Expected Shape
|
||||
| Shape | Description
|
||||
------ | ----- | ------------
|
||||
input | [ * , * , * , * ] | 4D Tensor of any size
|
||||
output | Same | Output has the same shape as input
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
a Tensor of the same dimension and shape as the input with
|
||||
values in the range [0, 1]
|
||||
### LogSoftmax
|
||||
|
||||
Applies the Log(Softmax(x)) function to an n-dimensional input Tensor.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
m = nn.LogSoftmax()
|
||||
input = autograd.Variable(torch.randn(2, 3))
|
||||
print(input)
|
||||
print(m(input))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The LogSoftmax formulation can be simplified as
|
||||
f_i(x) = log(1 / a * exp(x_i)) where a = sum_j exp(x_j) .
|
||||
|
||||
#### Expected Shape
|
||||
| Shape | Description
|
||||
------ | ----- | ------------
|
||||
input | [ * , * ] | 2D Tensor of any size
|
||||
output | Same | Output has the same shape as input
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
a Tensor of the same dimension and shape as the input with
|
||||
values in the range [-inf, 0)
|
||||
|
||||
<img src="image/logsoftmax.png" >
|
||||
@ -1,136 +0,0 @@
|
||||
## Containers
|
||||
### Container
|
||||
|
||||
This is the base container class for all neural networks you would define.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# Example of using Container
|
||||
class Net(nn.Container):
|
||||
def __init__(self):
|
||||
super(Net, self).__init__(
|
||||
conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 20, 5),
|
||||
relu = nn.ReLU()
|
||||
)
|
||||
def forward(self, input):
|
||||
output = self.relu(self.conv1(x))
|
||||
return output
|
||||
model = Net()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# one can add modules to the container after construction
|
||||
model.add_module('pool1', nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# .parameters()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> for param in model.parameters():
|
||||
>>> print(type(param.data), param.size())
|
||||
<class 'torch.FloatTensor'> (20L,)
|
||||
<class 'torch.FloatTensor'> (20L, 1L, 5L, 5L)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# .parameter_dict()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> pdict = model.parameter_dict()
|
||||
>>> print(pdict.keys())
|
||||
['conv1.bias', 'conv1.weight']
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You will subclass your container from this class.
|
||||
In the constructor you define the modules that you would want to use,
|
||||
and in the "forward" function you use the constructed modules in
|
||||
your operations.
|
||||
|
||||
To make it easier to understand, given is a small example.
|
||||
|
||||
One can also add new modules to a container after construction.
|
||||
You can do this with the add_module function
|
||||
or by assigning them as Container attributes.
|
||||
|
||||
#### one can also set modules as attributes of the container
|
||||
model.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(12, 24, 3)
|
||||
The container has some important additional methods:
|
||||
|
||||
**`[generator] parameters()`**
|
||||
|
||||
returns a generator over all learnable parameters in the container instance.
|
||||
This can typically be passed to the optimizer API
|
||||
|
||||
**`[dict] parameter_dict()`**
|
||||
|
||||
returns a dictionary of learnable parameters of the Container.
|
||||
For example: ['conv1.weight' : Parameter(torch.FloatTensor(20x1x5x5)),
|
||||
'conv1.bias' : Parameter(torch.FloatTensor(20)),
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**`load_parameter_dict(dict)`**
|
||||
|
||||
Given a parameter dict, sets the parameters of self to be the given dict.
|
||||
It loads loads the parameters recursively.
|
||||
Excessive or non-matching parameter names are ignored.
|
||||
For example, the input dict has an entry 'conv44.weight', but
|
||||
if the container does not have a module named 'conv44', then this entry is ignored.
|
||||
|
||||
**`children()`**
|
||||
|
||||
Returns a generator over all the children modules of self
|
||||
|
||||
**`train()`**
|
||||
|
||||
Sets the Container (and all it's child modules) to training mode (for modules such as batchnorm, dropout etc.)
|
||||
|
||||
**`eval()`**
|
||||
|
||||
Sets the Container (and all it's child modules) to evaluate mode (for modules such as batchnorm, dropout etc.)
|
||||
|
||||
**`apply(closure)`**
|
||||
|
||||
Applies the given closure to each parameter of the container.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**__Note: Apart from these, the container will define the base functions that it has derived from nn.Module __**
|
||||
### Sequential
|
||||
|
||||
A sequential Container. It is derived from the base nn.Container class
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# Example of using Sequential
|
||||
model = nn.Sequential(
|
||||
nn.Conv2d(1,20,5),
|
||||
nn.ReLU(),
|
||||
nn.Conv2d(20,64,5),
|
||||
nn.ReLU()
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Modules will be added to it in the order they are passed in the constructor.
|
||||
Alternatively, an ordered dict of modules can also be passed in.
|
||||
|
||||
To make it easier to understand, given is a small example.
|
||||
#### Example of using Sequential with OrderedDict
|
||||
model = nn.Sequential(OrderedDict([
|
||||
('conv1', nn.Conv2d(1,20,5)),
|
||||
('relu1', nn.ReLU()),
|
||||
('conv2', nn.Conv2d(20,64,5)),
|
||||
('relu2', nn.ReLU())
|
||||
]))
|
||||
@ -1,236 +0,0 @@
|
||||
## Convolution Layers
|
||||
### Conv1d
|
||||
|
||||
Applies a 1D convolution over an input signal composed of several input
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
The output value of the layer with input (b x iC x W) and output (b x oC x oW)
|
||||
can be precisely described as:
|
||||
output[b_i][oc_i][w_i] = bias[oc_i]
|
||||
+ sum_iC sum_{ow = 0, oW-1} sum_{kw = 0 to kW-1}
|
||||
weight[oc_i][ic_i][kw] * input[b_i][ic_i][stride_w * ow + kw)]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
m = nn.Conv1d(16, 33, 3, stride=2)
|
||||
input = autograd.Variable(torch.randn(20, 16, 50))
|
||||
output = m(input)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
planes.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Note that depending of the size of your kernel, several (of the last)
|
||||
columns of the input might be lost. It is up to the user
|
||||
to add proper padding.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Constructor Arguments
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter | Default | Description
|
||||
--------- | ------- | -----------
|
||||
in_channels | | The number of expected input channels in the image given as input
|
||||
out_channels | | The number of output channels the convolution layer will produce
|
||||
kernel_size | | the size of the convolving kernel.
|
||||
stride | | the stride of the convolving kernel.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Expected Shape
|
||||
| Shape | Description
|
||||
------ | ----- | ------------
|
||||
input | [ * , in_channels , * ] | Input is minibatch x in_channels x iW
|
||||
output | [ * , out_channels , * ] | Output shape is precisely minibatch x out_channels x floor((iW + 2*padW - kW) / dW + 1)
|
||||
|
||||
#### Members
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter | Description
|
||||
--------- | -----------
|
||||
weight | the learnable weights of the module of shape (out_channels x in_channels x kW)
|
||||
bias | the learnable bias of the module of shape (out_channels)
|
||||
### Conv2d
|
||||
|
||||
Applies a 2D convolution over an input image composed of several input
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
The output value of the layer with input (b x iC x H x W) and output (b x oC x oH x oW)
|
||||
can be precisely described as:
|
||||
output[b_i][oc_i][h_i][w_i] = bias[oc_i]
|
||||
+ sum_iC sum_{oh = 0, oH-1} sum_{ow = 0, oW-1} sum_{kh = 0 to kH-1} sum_{kw = 0 to kW-1}
|
||||
weight[oc_i][ic_i][kh][kw] * input[b_i][ic_i][stride_h * oh + kh)][stride_w * ow + kw)]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# With square kernels and equal stride
|
||||
m = nn.Conv2d(16, 33, 3, stride=2)
|
||||
# non-square kernels and unequal stride and with padding
|
||||
m = nn.Conv2d(16, 33, (3, 5), stride=(2, 1), padding=(4, 2))
|
||||
# non-square kernels and unequal stride and with padding and dilation
|
||||
m = nn.Conv2d(16, 33, (3, 5), stride=(2, 1), padding=(4, 2), dilation=(3, 1))
|
||||
input = autograd.Variable(torch.randn(20, 16, 50, 100))
|
||||
output = m(input)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
planes.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Note that depending of the size of your kernel, several (of the last)
|
||||
columns or rows of the input image might be lost. It is up to the user
|
||||
to add proper padding in images.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Constructor Arguments
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter | Default | Description
|
||||
--------- | ------- | -----------
|
||||
in_channels | | The number of expected input channels in the image given as input
|
||||
out_channels | | The number of output channels the convolution layer will produce
|
||||
kernel_size | | the size of the convolving kernel. Can be a single number k (for a square kernel of k x k) or a tuple (kh x kw)
|
||||
stride | 1 | the stride of the convolving kernel. Can be a single number s or a tuple (sh x sw).
|
||||
padding | 0 | implicit zero padding on the input. Can be a single number s or a tuple.
|
||||
dilation | None | If given, will do dilated (or atrous) convolutions. Can be a single number s or a tuple.
|
||||
bias | True | If set to False, the layer will not learn an additive bias.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Expected Shape
|
||||
| Shape | Description
|
||||
------ | ----- | ------------
|
||||
input | [ * , in_channels , * , * ] | Input is minibatch x in_channels x iH x iW
|
||||
output | [ * , out_channels , * , * ] | Output shape is precisely minibatch x out_channels x floor((iH + 2*padH - kH) / dH + 1) x floor((iW + 2*padW - kW) / dW + 1)
|
||||
|
||||
#### Members
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter | Description
|
||||
--------- | -----------
|
||||
weight | the learnable weights of the module of shape (out_channels x in_channels x kH x kW)
|
||||
bias | the learnable bias of the module of shape (out_channels)
|
||||
### ConvTranspose2d
|
||||
|
||||
Applies a 2D deconvolution operator over an input image composed of several input
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# With square kernels and equal stride
|
||||
m = nn.ConvTranspose2d(16, 33, 3, stride=2)
|
||||
# non-square kernels and unequal stride and with padding
|
||||
m = nn.ConvTranspose2d(16, 33, (3, 5), stride=(2, 1), padding=(4, 2))
|
||||
input = autograd.Variable(torch.randn(20, 16, 50, 100))
|
||||
output = m(input)
|
||||
# exact output size can be also specified as an argument
|
||||
input = autograd.Variable(torch.randn(1, 16, 12, 12))
|
||||
downsample = nn.Conv2d(16, 16, 3, stride=2, padding=1)
|
||||
upsample = nn.ConvTranspose2d(16, 16, 3, stride=2, padding=1)
|
||||
h = downsample(input)
|
||||
output = upsample(h, output_size=input.size())
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
planes.
|
||||
The deconvolution operator multiplies each input value element-wise by a learnable kernel,
|
||||
and sums over the outputs from all input feature planes.
|
||||
This module can be seen as the exact reverse of the Conv2d module.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Constructor Arguments
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter | Default | Description
|
||||
--------- | ------- | -----------
|
||||
in_channels | | The number of expected input channels in the image given as input
|
||||
out_channels | | The number of output channels the convolution layer will produce
|
||||
kernel_size | | the size of the convolving kernel. Can be a single number k (for a square kernel of k x k) or a tuple (kh x kw)
|
||||
stride | 1 | the stride of the convolving kernel. Can be a single number or a tuple (sh x sw).
|
||||
padding | 0 | implicit zero padding on the input. Can be a single number or a tuple.
|
||||
output_padding | 0 | A zero-padding of 0 <= padding < stride that should be added to the output. Can be a single number or a tuple.
|
||||
bias | True | If set to False, the layer will not learn an additive bias.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Expected Shape
|
||||
| Shape | Description
|
||||
------ | ----- | ------------
|
||||
input | [ * , in_channels , * , * ] | Input is minibatch x in_channels x iH x iW
|
||||
output | [ * , out_channels , * , * ] | Output shape is minibatch x out_channels x (iH - 1) * sH - 2*padH + kH + output_paddingH x (iW - 1) * sW - 2*padW + kW, or as specified in a second argument to the call.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Members
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter | Description
|
||||
--------- | -----------
|
||||
weight | the learnable weights of the module of shape (in_channels x out_channels x kH x kW)
|
||||
bias | the learnable bias of the module of shape (out_channels)
|
||||
### Conv3d
|
||||
|
||||
Applies a 3D convolution over an input image composed of several input
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# With square kernels and equal stride
|
||||
m = nn.Conv3d(16, 33, 3, stride=2)
|
||||
# non-square kernels and unequal stride and with padding
|
||||
m = nn.Conv3d(16, 33, (3, 5, 2), stride=(2, 1, 1), padding=(4, 2, 0))
|
||||
input = autograd.Variable(torch.randn(20, 16, 10, 50, 100))
|
||||
output = m(input)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
planes.
|
||||
|
||||
Note that depending of the size of your kernel, several (of the last)
|
||||
columns or rows of the input image might be lost. It is up to the user
|
||||
to add proper padding in images.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Constructor Arguments
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter | Default | Description
|
||||
--------- | ------- | -----------
|
||||
in_channels | | The number of expected input channels in the image given as input
|
||||
out_channels | | The number of output channels the convolution layer will produce
|
||||
kernel_size | | the size of the convolving kernel. Can be a single number k (for a square kernel of k x k x k) or a tuple (kt x kh x kw)
|
||||
stride | 1 | the stride of the convolving kernel. Can be a single number s or a tuple (kt x sh x sw).
|
||||
padding | 0 | implicit zero padding on the input. Can be a single number s or a tuple.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Expected Shape
|
||||
| Shape | Description
|
||||
------ | ----- | ------------
|
||||
input | [ * , in_channels , * , * , * ] | Input is minibatch x in_channels x iT x iH x iW
|
||||
output | [ * , out_channels , * , * , * ] | Output shape is precisely minibatch x out_channels x floor((iT + 2*padT - kT) / dT + 1) x floor((iH + 2*padH - kH) / dH + 1) x floor((iW + 2*padW - kW) / dW + 1)
|
||||
|
||||
#### Members
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter | Description
|
||||
--------- | -----------
|
||||
weight | the learnable weights of the module of shape (out_channels x in_channels x kT x kH x kW)
|
||||
bias | the learnable bias of the module of shape (out_channels)
|
||||
### ConvTranspose3d
|
||||
|
||||
Applies a 3D deconvolution operator over an input image composed of several input
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# With square kernels and equal stride
|
||||
m = nn.ConvTranspose3d(16, 33, 3, stride=2)
|
||||
# non-square kernels and unequal stride and with padding
|
||||
m = nn.Conv3d(16, 33, (3, 5, 2), stride=(2, 1, 1), padding=(0, 4, 2))
|
||||
input = autograd.Variable(torch.randn(20, 16, 10, 50, 100))
|
||||
output = m(input)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
planes.
|
||||
The deconvolution operator multiplies each input value element-wise by a learnable kernel,
|
||||
and sums over the outputs from all input feature planes.
|
||||
This module can be seen as the exact reverse of the Conv3d module.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Constructor Arguments
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter | Default | Description
|
||||
--------- | ------- | -----------
|
||||
in_channels | | The number of expected input channels in the image given as input
|
||||
out_channels | | The number of output channels the convolution layer will produce
|
||||
kernel_size | | the size of the convolving kernel. Can be a single number k (for a square kernel of k x k x k) or a tuple (kt x kh x kw)
|
||||
stride | 1 | the stride of the convolving kernel. Can be a single number or a tuple (st x sh x sw).
|
||||
padding | 0 | implicit zero padding on the input. Can be a single number or a tuple.
|
||||
output_padding | 0 | A zero-padding of 0 <= padding < stride that should be added to the output. Can be a single number or a tuple.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Expected Shape
|
||||
| Shape | Description
|
||||
------ | ----- | ------------
|
||||
input | [ * , in_channels , * , * , * ] | Input is minibatch x in_channels x iH x iW
|
||||
output | [ * , out_channels , * , * , * ] | Output shape is precisely minibatch x out_channels x (iT - 1) * sT - 2*padT + kT + output_paddingT x (iH - 1) * sH - 2*padH + kH + output_paddingH x (iW - 1) * sW - 2*padW + kW
|
||||
|
||||
#### Members
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter | Description
|
||||
--------- | -----------
|
||||
weight | the learnable weights of the module of shape (in_channels x out_channels x kT x kH x kW)
|
||||
bias | the learnable bias of the module of shape (out_channels)
|
||||
233
docs/nn_core.md
@ -1,233 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Module
|
||||
|
||||
This is the base class for all Modules defined in the nn package.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# .parameters()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> for param in model.parameters():
|
||||
>>> print(type(param.data), param.size())
|
||||
<class 'torch.FloatTensor'> (20L,)
|
||||
<class 'torch.FloatTensor'> (20L, 1L, 5L, 5L)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# .parameter_dict()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> pdict = model.parameter_dict()
|
||||
>>> print(pdict.keys())
|
||||
['bias', 'weight']
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Even the Container class derives from this class.
|
||||
|
||||
An nn.Module has the following interface:
|
||||
|
||||
**Constructor:**
|
||||
nn.Module(**parameters)
|
||||
|
||||
All arguments passed in to the constructor need to be of type
|
||||
nn.Parameter or a Tensor.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**forward(...)**
|
||||
|
||||
This is the function that one defines when subclassing to create
|
||||
their own modules.
|
||||
It takes in inputs and returns outputs.
|
||||
|
||||
**__call__(...)**
|
||||
|
||||
This calls the forward function, as well as the hooks
|
||||
|
||||
**register_buffer(name, tensor)**
|
||||
|
||||
This is typically used to register a buffer that is not a Parameter.
|
||||
For example, in BatchNorm, the running_mean is a buffer, so one would
|
||||
register it in the constructor of BatchNorm with:
|
||||
|
||||
`self.register_buffer('running_mean', torch.zeros(num_features))`
|
||||
|
||||
The registered buffers can simply be accessed as class members
|
||||
when needed.
|
||||
|
||||
**cpu()**
|
||||
|
||||
Recursively moves all it's parameters and buffers to the CPU
|
||||
|
||||
**cuda(device_id=None)**
|
||||
Recursively moves all it's parameters and buffers to the CUDA memory.
|
||||
If device_id is given, moves it to GPU number device_id
|
||||
|
||||
**float()**
|
||||
Typecasts the parameters and buffers to float
|
||||
|
||||
**double()**
|
||||
Typecasts the parameters and buffers to double
|
||||
|
||||
**register_forward_hook(name, hook)**
|
||||
|
||||
This will register a user-defined closure on the module.
|
||||
Whenever the module finishes it's forward operation,
|
||||
the user closure is called.
|
||||
The signature of the closure is `def closure(input, output)`
|
||||
|
||||
**register_backward_hook(name, hook)**
|
||||
|
||||
This will register a user-defined closure on the module.
|
||||
Whenever the module finishes it's backward operation,
|
||||
the user closure is called.
|
||||
The signature of the closure is `def closure(gradOutput, gradInput)`
|
||||
|
||||
**remove_forward_hook(name)**
|
||||
|
||||
Removes a registered forward hook with the given name
|
||||
|
||||
**remove_backward_hook(name)**
|
||||
|
||||
Removes a registered backward hook with the given name
|
||||
|
||||
**`[generator] parameters()`**
|
||||
|
||||
returns a generator over all learnable parameters in the container instance.
|
||||
This can typically be passed to the optimizer API
|
||||
|
||||
**`[dict] parameter_dict()`**
|
||||
|
||||
returns a dictionary of learnable parameters of the Module.
|
||||
For example: ['weight' : Parameter(torch.FloatTensor(20x1x5x5)),
|
||||
'bias' : Parameter(torch.FloatTensor(20)),
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
**`load_parameter_dict(dict)`**
|
||||
|
||||
Given a parameter dict, sets the parameters of self to be the given dict.
|
||||
|
||||
**`train()`**
|
||||
|
||||
Sets the Container to training mode (for modules such as batchnorm, dropout etc.)
|
||||
|
||||
**`eval()`**
|
||||
|
||||
Sets the Container to evaluate mode (for modules such as batchnorm, dropout etc.)
|
||||
|
||||
**`zero_grad()`**
|
||||
|
||||
Zeroes the gradients of each Parameter of the module
|
||||
# Container
|
||||
|
||||
This is the base container class for all neural networks you would define.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# Example of using Container
|
||||
class Net(nn.Container):
|
||||
def __init__(self):
|
||||
super(Net, self).__init__(
|
||||
conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 20, 5),
|
||||
relu = nn.ReLU()
|
||||
)
|
||||
def forward(self, input):
|
||||
output = self.relu(self.conv1(x))
|
||||
return output
|
||||
model = Net()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# one can add modules to the container after construction
|
||||
model.add_module('pool1', nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# .parameters()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> for param in model.parameters():
|
||||
>>> print(type(param.data), param.size())
|
||||
<class 'torch.FloatTensor'> (20L,)
|
||||
<class 'torch.FloatTensor'> (20L, 1L, 5L, 5L)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# .parameter_dict()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> pdict = model.parameter_dict()
|
||||
>>> print(pdict.keys())
|
||||
['conv1.bias', 'conv1.weight']
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You will subclass your container from this class.
|
||||
In the constructor you define the modules that you would want to use,
|
||||
and in the "forward" function you use the constructed modules in
|
||||
your operations.
|
||||
|
||||
To make it easier to understand, given is a small example.
|
||||
|
||||
One can also add new modules to a container after construction.
|
||||
You can do this with the add_module function
|
||||
or by assigning them as Container attributes.
|
||||
|
||||
## one can also set modules as attributes of the container
|
||||
model.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(12, 24, 3)
|
||||
The container has some important additional methods:
|
||||
|
||||
**`[generator] parameters()`**
|
||||
|
||||
returns a generator over all learnable parameters in the container instance.
|
||||
This can typically be passed to the optimizer API
|
||||
|
||||
**`[dict] parameter_dict()`**
|
||||
|
||||
returns a dictionary of learnable parameters of the Container.
|
||||
For example: ['conv1.weight' : Parameter(torch.FloatTensor(20x1x5x5)),
|
||||
'conv1.bias' : Parameter(torch.FloatTensor(20)),
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**`load_parameter_dict(dict)`**
|
||||
|
||||
Given a parameter dict, sets the parameters of self to be the given dict.
|
||||
It loads loads the parameters recursively.
|
||||
Excessive or non-matching parameter names are ignored.
|
||||
For example, the input dict has an entry 'conv44.weight', but
|
||||
if the container does not have a module named 'conv44', then this entry is ignored.
|
||||
|
||||
**`children()`**
|
||||
|
||||
Returns a generator over all the children modules of self
|
||||
|
||||
**`train()`**
|
||||
|
||||
Sets the Container (and all it's child modules) to training mode (for modules such as batchnorm, dropout etc.)
|
||||
|
||||
**`eval()`**
|
||||
|
||||
Sets the Container (and all it's child modules) to evaluate mode (for modules such as batchnorm, dropout etc.)
|
||||
|
||||
**`apply(closure)`**
|
||||
|
||||
Applies the given closure to each parameter of the container.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**__Note: Apart from these, the container will define the base functions that it has derived from nn.Module __**
|
||||
@ -1,90 +0,0 @@
|
||||
## Dropout layers
|
||||
### Dropout
|
||||
|
||||
Randomly zeroes some of the elements of the input tensor.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
m = nn.Dropout(p=0.2)
|
||||
input = autograd.Variable(torch.randn(20, 16))
|
||||
output = m(input)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The elements to zero are randomized on every forward call.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Constructor Arguments
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter | Default | Description
|
||||
--------- | ------- | -----------
|
||||
p | 0.5 | probability of an element to be zeroed.
|
||||
inplace | false | If set to True, will do this operation in-place.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Expected Shape
|
||||
| Shape | Description
|
||||
------ | ----- | ------------
|
||||
input | Any | Input can be of any shape
|
||||
output | Same | Output is of the same shape as input
|
||||
### Dropout2d
|
||||
|
||||
Randomly zeroes whole channels of the input tensor.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
m = nn.Dropout2d(p=0.2)
|
||||
input = autograd.Variable(torch.randn(20, 16, 32, 32))
|
||||
output = m(input)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The input is 4D (batch x channels, height, width) and each channel
|
||||
is of size (1, height, width).
|
||||
The channels to zero are randomized on every forward call.
|
||||
Usually the input comes from Conv2d modules.
|
||||
|
||||
As described in the paper "Efficient Object Localization Using Convolutional
|
||||
Networks" (http:arxiv.org/abs/1411.4280), if adjacent pixels within
|
||||
feature maps are strongly correlated (as is normally the case in early
|
||||
convolution layers) then iid dropout will not regularize the activations
|
||||
and will otherwise just result in an effective learning rate decrease.
|
||||
In this case, nn.Dropout2d will help promote independence between
|
||||
feature maps and should be used instead.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Constructor Arguments
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter | Default | Description
|
||||
--------- | ------- | -----------
|
||||
p | 0.5 | probability of an element to be zeroed.
|
||||
inplace | false | If set to True, will do this operation in-place.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Expected Shape
|
||||
| Shape | Description
|
||||
------ | ----- | ------------
|
||||
input | [*, *, *, *] | Input can be of any sizes of 4D shape
|
||||
output | Same | Output is of the same shape as input
|
||||
### Dropout3d
|
||||
|
||||
Randomly zeroes whole channels of the input tensor.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
m = nn.Dropout3d(p=0.2)
|
||||
input = autograd.Variable(torch.randn(20, 16, 4, 32, 32))
|
||||
output = m(input)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The input is 5D (batch x channels, depth, height, width) and each channel
|
||||
is of size (1, depth, height, width).
|
||||
The channels to zero are randomized on every forward call.
|
||||
Usually the input comes from Conv3d modules.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Constructor Arguments
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter | Default | Description
|
||||
--------- | ------- | -----------
|
||||
p | 0.5 | probability of an element to be zeroed.
|
||||
inplace | false | If set to True, will do this operation in-place.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Expected Shape
|
||||
| Shape | Description
|
||||
------ | ----- | ------------
|
||||
input | [*, *, *, *, *] | Input can be of any sizes of 5D shape
|
||||
output | Same | Output is of the same shape as input
|
||||
@ -1,36 +0,0 @@
|
||||
## Linear layers
|
||||
### Linear
|
||||
|
||||
Applies a linear transformation to the incoming data, y = Ax + b
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
m = nn.Linear(20, 30)
|
||||
input = autograd.Variable(torch.randn(128, 20))
|
||||
output = m(input)
|
||||
print(output.size())
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The input is a 2D mini-batch of samples, each of size in_features
|
||||
The output will be a 2D Tensor of size mini-batch x out_features
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Constructor Arguments
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter | Default | Description
|
||||
--------- | ------- | -----------
|
||||
in_features | | size of each input sample
|
||||
out_features | | size of each output sample
|
||||
bias | True | If set to False, the layer will not learn an additive bias.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Expected Shape
|
||||
| Shape | Description
|
||||
------ | ----- | ------------
|
||||
input | [*, in_features] | Input can be of shape minibatch x in_features
|
||||
output | [*, out_features] | Output is of shape minibatch x out_features
|
||||
|
||||
#### Members
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter | Description
|
||||
--------- | -----------
|
||||
weight | the learnable weights of the module of shape (out_features x in_features)
|
||||
bias | the learnable bias of the module of shape (out_features)
|
||||
294
docs/nn_loss.md
@ -1,294 +0,0 @@
|
||||
## Loss functions
|
||||
### L1Loss
|
||||
|
||||
Creates a criterion that measures the mean absolute value of the
|
||||
|
||||
element-wise difference between input `x` and target `y`:
|
||||
|
||||
loss(x, y) = 1/n \sum |x_i - y_i|
|
||||
|
||||
`x` and `y` arbitrary shapes with a total of `n` elements each
|
||||
the sum operation still operates over all the elements, and divides by `n`.
|
||||
|
||||
The division by `n` can be avoided if one sets the internal
|
||||
variable `sizeAverage` to `False`
|
||||
### MSELoss
|
||||
|
||||
Creates a criterion that measures the mean squared error between
|
||||
|
||||
`n` elements in the input `x` and target `y`:
|
||||
loss(x, y) = 1/n \sum |x_i - y_i|^2
|
||||
`x` and `y` arbitrary shapes with a total of `n` elements each
|
||||
the sum operation still operates over all the elements, and divides by `n`.
|
||||
|
||||
The division by `n` can be avoided if one sets the internal variable
|
||||
`sizeAverage` to `False`
|
||||
By default, the losses are averaged over observations for each minibatch.
|
||||
However, if the field `sizeAverage = False`, the losses are instead summed.
|
||||
### CrossEntropyLoss
|
||||
|
||||
This criterion combines `LogSoftMax` and `ClassNLLLoss` in one single class.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
It is useful when training a classification problem with `n` classes.
|
||||
If provided, the optional argument `weights` should be a 1D `Tensor`
|
||||
assigning weight to each of the classes.
|
||||
This is particularly useful when you have an unbalanced training set.
|
||||
|
||||
The `input` is expected to contain scores for each class:
|
||||
`input` has to be a 2D `Tensor` of size `batch x n`.
|
||||
This criterion expects a class index (0 to nClasses-1) as the
|
||||
`target` for each value of a 1D tensor of size `n`
|
||||
|
||||
The loss can be described as:
|
||||
|
||||
loss(x, class) = -log(exp(x[class]) / (\sum_j exp(x[j])))
|
||||
= -x[class] + log(\sum_j exp(x[j]))
|
||||
|
||||
or in the case of the `weights` argument being specified:
|
||||
|
||||
loss(x, class) = weights[class] * (-x[class] + log(\sum_j exp(x[j])))
|
||||
|
||||
The losses are averaged across observations for each minibatch.
|
||||
### NLLLoss
|
||||
|
||||
The negative log likelihood loss. It is useful to train a classication problem with n classes
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
m = nn.LogSoftmax()
|
||||
loss = nn.NLLLoss()
|
||||
# input is of size nBatch x nClasses = 3 x 5
|
||||
input = autograd.Variable(torch.randn(3, 5))
|
||||
# each element in target has to have 0 <= value < nclasses
|
||||
target = autograd.Variable(torch.LongTensor([1, 0, 4]))
|
||||
output = loss(m(input), target)
|
||||
output.backward()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
If provided, the optional argument `weights` should be a 1D Tensor assigning
|
||||
weight to each of the classes.
|
||||
This is particularly useful when you have an unbalanced training set.
|
||||
|
||||
The input given through a forward call is expected to contain log-probabilities
|
||||
of each class: input has to be a 2D Tensor of size minibatch x n
|
||||
Obtaining log-probabilities in a neural network is easily achieved by
|
||||
adding a `LogSoftmax` layer in the last layer.
|
||||
You may use `CrossEntropyLoss` instead, if you prefer not to
|
||||
add an extra layer.
|
||||
|
||||
The target that this loss expects is a class index (1 to the number of class)
|
||||
|
||||
The loss can be described as:
|
||||
loss(x, class) = -x[class]
|
||||
|
||||
or in the case of the weights argument it is specified as follows:
|
||||
loss(x, class) = -weights[class] * x[class]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Constructor Arguments
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter | Default | Description
|
||||
--------- | ------- | -----------
|
||||
weight | None | a manual rescaling weight given to each class. If given, has to be a Tensor of size "nclasses".
|
||||
size_average | True | By default, the losses are averaged over observations for each minibatch. However, if the field sizeAverage is set to False, the losses are instead summed for each minibatch.
|
||||
Target Shape: [ * ] : Targets of size [minibatch], each value has to be 1 <= targets[i] <= nClasses
|
||||
|
||||
#### Members
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter | Description
|
||||
--------- | -----------
|
||||
weight | the class-weights given as input to the constructor
|
||||
### NLLLoss2d
|
||||
|
||||
This is negative log likehood loss, but for image inputs. It computes NLL loss per-pixel.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
m = nn.Conv2d(16, 32, (3, 3)).float()
|
||||
loss = nn.NLLLoss2d()
|
||||
# input is of size nBatch x nClasses x height x width
|
||||
input = autograd.Variable(torch.randn(3, 16, 10, 10))
|
||||
# each element in target has to have 0 <= value < nclasses
|
||||
target = autograd.Variable(torch.LongTensor(3, 8, 8).random_(0, 4))
|
||||
output = loss(m(input), target)
|
||||
output.backward()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This loss does not support per-class weights
|
||||
|
||||
#### Constructor Arguments
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter | Default | Description
|
||||
--------- | ------- | -----------
|
||||
size_average | True | By default, the losses are averaged over observations for each minibatch. However, if the field sizeAverage is set to False, the losses are instead summed for each minibatch.
|
||||
Target Shape: [ * , *, *] : Targets of size minibatch x height x width, each value has to be 1 <= targets[i] <= nClasses
|
||||
### KLDivLoss
|
||||
|
||||
The [Kullback-Leibler divergence](http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kullback%E2%80%93Leibler_divergence) Loss
|
||||
|
||||
KL divergence is a useful distance measure for continuous distributions
|
||||
and is often useful when performing direct regression over the space of
|
||||
(discretely sampled) continuous output distributions.
|
||||
As with ClassNLLLoss, the `input` given is expected to contain
|
||||
_log-probabilities_, however unlike ClassNLLLoss, `input` is not
|
||||
restricted to a 2D Tensor, because the criterion is applied element-wise.
|
||||
|
||||
This criterion expects a `target` `Tensor` of the same size as the
|
||||
`input` `Tensor`.
|
||||
|
||||
The loss can be described as:
|
||||
loss(x, target) = 1/n \sum(target_i * (log(target_i) - x_i))
|
||||
|
||||
By default, the losses are averaged for each minibatch over observations
|
||||
*as well as* over dimensions. However, if the field
|
||||
`sizeAverage` is set to `False`, the losses are instead summed.
|
||||
### BCELoss
|
||||
|
||||
Creates a criterion that measures the Binary Cross Entropy
|
||||
|
||||
between the target and the output:
|
||||
loss(o, t) = - 1/n sum_i (t[i] * log(o[i]) + (1 - t[i]) * log(1 - o[i]))
|
||||
|
||||
or in the case of the weights argument being specified:
|
||||
loss(o, t) = - 1/n sum_i weights[i] * (t[i] * log(o[i]) + (1 - t[i]) * log(1 - o[i]))
|
||||
|
||||
This is used for measuring the error of a reconstruction in for example
|
||||
an auto-encoder. Note that the targets `t[i]` should be numbers between 0 and 1,
|
||||
for instance, the output of an `nn.Sigmoid` layer.
|
||||
|
||||
By default, the losses are averaged for each minibatch over observations
|
||||
*as well as* over dimensions. However, if the field `sizeAverage` is set
|
||||
to `False`, the losses are instead summed.
|
||||
### MarginRankingLoss
|
||||
|
||||
Creates a criterion that measures the loss given
|
||||
|
||||
inputs `x1`, `x2`, two 1D min-batch `Tensor`s,
|
||||
and a label 1D mini-batch tensor `y` with values (`1` or `-1`).
|
||||
|
||||
If `y == 1` then it assumed the first input should be ranked higher
|
||||
(have a larger value) than the second input, and vice-versa for `y == -1`.
|
||||
|
||||
The loss function for each sample in the mini-batch is:
|
||||
|
||||
loss(x, y) = max(0, -y * (x1 - x2) + margin)
|
||||
|
||||
if the internal variable `sizeAverage = True`,
|
||||
the loss function averages the loss over the batch samples;
|
||||
if `sizeAverage = False`, then the loss function sums over the batch samples.
|
||||
By default, `sizeAverage` equals to `True`.
|
||||
### HingeEmbeddingLoss
|
||||
|
||||
Measures the loss given an input `x` which is a 2D mini-batch tensor
|
||||
|
||||
and a labels `y`, a 1D tensor containg values (`1` or `-1`).
|
||||
This is usually used for measuring whether two inputs are similar or dissimilar,
|
||||
e.g. using the L1 pairwise distance, and is typically used for learning
|
||||
nonlinear embeddings or semi-supervised learning.
|
||||
|
||||
{ x_i, if y_i == 1
|
||||
loss(x, y) = 1/n {
|
||||
{ max(0, margin - x_i), if y_i == -1
|
||||
|
||||
`x` and `y` arbitrary shapes with a total of `n` elements each
|
||||
the sum operation still operates over all the elements, and divides by `n`.
|
||||
(the division by `n` can be avoided if one sets the internal variable `sizeAverage=False`).
|
||||
The `margin` has a default value of `1`, or can be set in the constructor.
|
||||
### MultiLabelMarginLoss
|
||||
|
||||
Creates a criterion that optimizes a multi-class multi-classification
|
||||
|
||||
hinge loss (margin-based loss) between input `x` (a 2D mini-batch `Tensor`) and
|
||||
output `y` (which is a 2D `Tensor` of target class indices).
|
||||
For each sample in the mini-batch:
|
||||
|
||||
loss(x, y) = sum_ij(max(0, 1 - (x[y[j]] - x[i]))) / x:size(1)
|
||||
|
||||
where `i == 0` to `x.size(0)`, `j == 0` to `y.size(0)`,
|
||||
`y[j] != 0`, and `i != y[j]` for all `i` and `j`.
|
||||
|
||||
`y` and `x` must have the same size.
|
||||
The criterion only considers the first non zero `y[j]` targets.
|
||||
This allows for different samples to have variable amounts of target classes
|
||||
### SmoothL1Loss
|
||||
|
||||
Creates a criterion that uses a squared term if the absolute
|
||||
|
||||
element-wise error falls below 1 and an L1 term otherwise.
|
||||
It is less sensitive to outliers than the `MSELoss` and in some cases
|
||||
prevents exploding gradients (e.g. see "Fast R-CNN" paper by Ross Girshick).
|
||||
|
||||
{ 0.5 * (x_i - y_i)^2, if |x_i - y_i| < 1
|
||||
loss(x, y) = 1/n \sum {
|
||||
{ |x_i - y_i| - 0.5, otherwise
|
||||
|
||||
`x` and `y` arbitrary shapes with a total of `n` elements each
|
||||
the sum operation still operates over all the elements, and divides by `n`.
|
||||
|
||||
The division by `n` can be avoided if one sets the internal variable
|
||||
`sizeAverage` to `False`
|
||||
### SoftMarginLoss
|
||||
|
||||
Creates a criterion that optimizes a two-class classification
|
||||
|
||||
logistic loss between input `x` (a 2D mini-batch `Tensor`) and
|
||||
target `y` (which is a tensor containing either `1`s or `-1`s).
|
||||
|
||||
loss(x, y) = sum_i (log(1 + exp(-y[i]*x[i]))) / x:nElement()
|
||||
|
||||
The normalization by the number of elements in the input can be disabled by
|
||||
setting `self.sizeAverage` to `False`.
|
||||
### MultiLabelSoftMarginLoss
|
||||
|
||||
Creates a criterion that optimizes a multi-label one-versus-all
|
||||
|
||||
loss based on max-entropy, between input `x` (a 2D mini-batch `Tensor`) and
|
||||
target `y` (a binary 2D `Tensor`). For each sample in the minibatch:
|
||||
|
||||
loss(x, y) = - sum_i (y[i] log( exp(x[i]) / (1 + exp(x[i])))
|
||||
+ (1-y[i]) log(1/(1+exp(x[i])))) / x:nElement()
|
||||
|
||||
where `i == 0` to `x.nElement()-1`, `y[i] in {0,1}`.
|
||||
`y` and `x` must have the same size.
|
||||
### CosineEmbeddingLoss
|
||||
|
||||
Creates a criterion that measures the loss given an input tensors x1, x2
|
||||
|
||||
and a `Tensor` label `y` with values 1 or -1.
|
||||
This is used for measuring whether two inputs are similar or dissimilar,
|
||||
using the cosine distance, and is typically used for learning nonlinear
|
||||
embeddings or semi-supervised learning.
|
||||
|
||||
`margin` should be a number from `-1` to `1`, `0` to `0.5` is suggested.
|
||||
If `margin` is missing, the default value is `0`.
|
||||
|
||||
The loss function for each sample is:
|
||||
|
||||
{ 1 - cos(x1, x2), if y == 1
|
||||
loss(x, y) = {
|
||||
{ max(0, cos(x1, x2) - margin), if y == -1
|
||||
|
||||
If the internal variable `sizeAverage` is equal to `True`,
|
||||
the loss function averages the loss over the batch samples;
|
||||
if `sizeAverage` is `False`, then the loss function sums over the
|
||||
batch samples. By default, `sizeAverage = True`.
|
||||
### MultiMarginLoss
|
||||
|
||||
Creates a criterion that optimizes a multi-class classification hinge loss
|
||||
|
||||
(margin-based loss) between input `x` (a 2D mini-batch `Tensor`) and
|
||||
output `y` (which is a 1D tensor of target class indices, `0` <= `y` <= `x.size(1)`):
|
||||
|
||||
For each mini-batch sample:
|
||||
loss(x, y) = sum_i(max(0, (margin - x[y] + x[i]))^p) / x.size(0)
|
||||
where `i == 0` to `x.size(0)` and `i != y`.
|
||||
|
||||
Optionally, you can give non-equal weighting on the classes by passing
|
||||
a 1D `weights` tensor into the constructor.
|
||||
|
||||
The loss function then becomes:
|
||||
loss(x, y) = sum_i(max(0, w[y] * (margin - x[y] - x[i]))^p) / x.size(0)
|
||||
|
||||
By default, the losses are averaged over observations for each minibatch.
|
||||
However, if the field `sizeAverage` is set to `False`,
|
||||
the losses are instead summed.
|
||||
@ -1,142 +0,0 @@
|
||||
## Normalization layers
|
||||
### BatchNorm1d
|
||||
|
||||
Applies Batch Normalization over a 2d input that is seen as a mini-batch of 1d inputs
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
x - mean(x)
|
||||
y = ----------------------------- * gamma + beta
|
||||
standard_deviation(x) + eps
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# With Learnable Parameters
|
||||
m = nn.BatchNorm1d(100)
|
||||
# Without Learnable Parameters
|
||||
m = nn.BatchNorm1d(100, affine=False)
|
||||
input = autograd.Variable(torch.randn(20, 100))
|
||||
output = m(input)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
The mean and standard-deviation are calculated per-dimension over
|
||||
the mini-batches and gamma and beta are learnable parameter vectors
|
||||
of size N (where N is the input size).
|
||||
|
||||
During training, this layer keeps a running estimate of its computed mean
|
||||
and variance. The running sum is kept with a default momentum of 0.1
|
||||
During evaluation, this running mean/variance is used for normalization.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Constructor Arguments
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter | Default | Description
|
||||
--------- | ------- | -----------
|
||||
num_features | | the size of each 1D input in the mini-batch
|
||||
eps | 1e-5 | a value added to the denominator for numerical stability.
|
||||
momentum | 0.1 | the value used for the running_mean and running_var computation.
|
||||
affine | | a boolean value that when set to true, gives the layer learnable affine parameters.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Expected Shape
|
||||
| Shape | Description
|
||||
------ | ----- | ------------
|
||||
input | [ * , num_features ] | 2D Tensor of nBatches x num_features
|
||||
output | Same | Output has the same shape as input
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
a normalized tensor in the batch dimension
|
||||
### BatchNorm2d
|
||||
|
||||
Applies Batch Normalization over a 4d input that is seen as a mini-batch of 3d inputs
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
x - mean(x)
|
||||
y = ----------------------------- * gamma + beta
|
||||
standard_deviation(x) + eps
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# With Learnable Parameters
|
||||
m = nn.BatchNorm2d(100)
|
||||
# Without Learnable Parameters
|
||||
m = nn.BatchNorm2d(100, affine=False)
|
||||
input = autograd.Variable(torch.randn(20, 100, 35, 45))
|
||||
output = m(input)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
The mean and standard-deviation are calculated per-dimension over
|
||||
the mini-batches and gamma and beta are learnable parameter vectors
|
||||
of size N (where N is the input size).
|
||||
|
||||
During training, this layer keeps a running estimate of its computed mean
|
||||
and variance. The running sum is kept with a default momentum of 0.1
|
||||
During evaluation, this running mean/variance is used for normalization.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Constructor Arguments
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter | Default | Description
|
||||
--------- | ------- | -----------
|
||||
num_features | | num_features from an expected input of size batch_size x num_features x height x width
|
||||
eps | 1e-5 | a value added to the denominator for numerical stability.
|
||||
momentum | 0.1 | the value used for the running_mean and running_var computation.
|
||||
affine | | a boolean value that when set to true, gives the layer learnable affine parameters.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Expected Shape
|
||||
| Shape | Description
|
||||
------ | ----- | ------------
|
||||
input | [ * , num_features , *, * ] | 4D Tensor of batch_size x num_features x height x width
|
||||
output | Same | Output has the same shape as input
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
a normalized tensor in the batch dimension
|
||||
### BatchNorm3d
|
||||
|
||||
Applies Batch Normalization over a 5d input that is seen as a mini-batch of 4d inputs
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
x - mean(x)
|
||||
y = ----------------------------- * gamma + beta
|
||||
standard_deviation(x) + eps
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# With Learnable Parameters
|
||||
m = nn.BatchNorm3d(100)
|
||||
# Without Learnable Parameters
|
||||
m = nn.BatchNorm3d(100, affine=False)
|
||||
input = autograd.Variable(torch.randn(20, 100, 35, 45, 10))
|
||||
output = m(input)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
The mean and standard-deviation are calculated per-dimension over
|
||||
the mini-batches and gamma and beta are learnable parameter vectors
|
||||
of size N (where N is the input size).
|
||||
|
||||
During training, this layer keeps a running estimate of its computed mean
|
||||
and variance. The running sum is kept with a default momentum of 0.1
|
||||
During evaluation, this running mean/variance is used for normalization.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Constructor Arguments
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter | Default | Description
|
||||
--------- | ------- | -----------
|
||||
num_features | | num_features from an expected input of size batch_size x num_features x height x width
|
||||
eps | 1e-5 | a value added to the denominator for numerical stability.
|
||||
momentum | 0.1 | the value used for the running_mean and running_var computation.
|
||||
affine | | a boolean value that when set to true, gives the layer learnable affine parameters.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Expected Shape
|
||||
| Shape | Description
|
||||
------ | ----- | ------------
|
||||
input | [ * , num_features , * , * , * ] | 5D Tensor of batch_size x num_features x depth x height x width
|
||||
output | Same | Output has the same shape as input
|
||||
|
||||
#### Returns
|
||||
a normalized tensor in the batch dimension
|
||||
@ -1,308 +0,0 @@
|
||||
## Pooling Layers
|
||||
### MaxPool1d
|
||||
|
||||
Applies a 1D max pooling over an input signal composed of several input
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
The output value of the layer with input (b x C x W) and output (b x C x oW)
|
||||
can be precisely described as:
|
||||
output[b_i][c_i][w_i] = max_{k=1, K} input[b_i][c_i][stride_w * w_i + k)]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# pool of size=3, stride=2
|
||||
m = nn.MaxPool1d(3, stride=2)
|
||||
input = autograd.Variable(torch.randn(20, 16, 50))
|
||||
output = m(input)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
planes.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Constructor Arguments
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter | Default | Description
|
||||
--------- | ------- | -----------
|
||||
kernel_size | | the size of the window to take a max over
|
||||
stride | | the stride of the window
|
||||
padding | 0 | implicit padding to be added.
|
||||
dilation | kernel_size | a parameter that controls the stride of elements in the window.
|
||||
return_indices | False | if True, will return the indices along with the outputs. Useful when Unpooling later.
|
||||
ceil_mode | | when True, will use "ceil" instead of "floor" to compute the output shape
|
||||
|
||||
#### Expected Shape
|
||||
| Shape | Description
|
||||
------ | ----- | ------------
|
||||
input | [ * , * , * ] | Input is minibatch x channels x iW
|
||||
output | [ * , * , * ] | Output shape = minibatch x channels x floor((iW + 2*padW - kernel_size) / stride + 1)
|
||||
### MaxPool2d
|
||||
|
||||
Applies a 2D max pooling over an input signal composed of several input
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
The output value of the layer with input (b x C x H x W) and output (b x C x oH x oW)
|
||||
can be precisely described as:
|
||||
output[b_i][c_i][h_i][w_i] = max_{{kh=1, KH}, {kw=1, kW}} input[b_i][c_i][stride_h * h_i + kH)][stride_w * w_i + kW)]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# pool of square window of size=3, stride=2
|
||||
m = nn.MaxPool2d(3, stride=2)
|
||||
# pool of non-square window
|
||||
m = nn.MaxPool2d((3, 2), stride=(2, 1))
|
||||
input = autograd.Variable(torch.randn(20, 16, 50, 32))
|
||||
output = m(input)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
planes.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Constructor Arguments
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter | Default | Description
|
||||
--------- | ------- | -----------
|
||||
kernel_size | | the size of the window to take a max over. Can be a single number k (for a square kernel of k x k) or a tuple (kh x kw)
|
||||
stride | kernel_size | the stride of the window. Can be a single number s or a tuple (sh x sw).
|
||||
padding | 0 | implicit padding to be added. Can be a single number or a tuple.
|
||||
dilation | 1 | a parameter that controls the stride of elements in the window. Can be a single number or a tuple.
|
||||
return_indices | False | if True, will return the indices along with the outputs. Useful to pass to nn.MaxUnpool2d .
|
||||
ceil_mode | | when True, will use "ceil" instead of "floor" to compute the output shape
|
||||
|
||||
#### Expected Shape
|
||||
| Shape | Description
|
||||
------ | ----- | ------------
|
||||
input | [ * , * , *, * ] | Input is minibatch x channels x iH x iW
|
||||
output | [ * , * , *, * ] | Output shape = minibatch x channels x floor((iH + 2*padH - kH) / sH + 1) x floor((iW + 2*padW - kW) / sW + 1)
|
||||
### MaxPool3d
|
||||
|
||||
Applies a 3D max pooling over an input signal composed of several input
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# pool of square window of size=3, stride=2
|
||||
m = nn.MaxPool3d(3, stride=2)
|
||||
# pool of non-square window
|
||||
m = nn.MaxPool3d((3, 2, 2), stride=(2, 1, 2))
|
||||
input = autograd.Variable(torch.randn(20, 16, 50,44, 31))
|
||||
output = m(input)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
planes.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Constructor Arguments
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter | Default | Description
|
||||
--------- | ------- | -----------
|
||||
kernel_size | | the size of the window to take a max over. Can be a single number k (for a square kernel of k x k x k) or a tuple (kt x kh x kw)
|
||||
stride | kernel_size | the stride of the window. Can be a single number s or a tuple (st x sh x sw).
|
||||
padding | 0 | implicit padding to be added. Can be a single number or a tuple.
|
||||
dilation | 1 | a parameter that controls the stride of elements in the window. Can be a single number or a tuple.
|
||||
return_indices | False | if True, will return the indices along with the outputs. Useful to pass to nn.MaxUnpool3d .
|
||||
ceil_mode | | when True, will use "ceil" instead of "floor" to compute the output shape
|
||||
|
||||
#### Expected Shape
|
||||
| Shape | Description
|
||||
------ | ----- | ------------
|
||||
input | [ * , * , *, *, * ] | Input is minibatch x channels x iT x iH x iW
|
||||
output | [ * , * , *, *, * ] | Output shape = minibatch x channels x floor((iT + 2*padT - kT) / sT + 1) x floor((iH + 2*padH - kH) / sH + 1) x floor((iW + 2*padW - kW) / sW + 1)
|
||||
### MaxUnpool2d
|
||||
|
||||
Computes the inverse operation of MaxPool2d
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# pool of square window of size=3, stride=2
|
||||
m = nn.MaxPool2d(2, stride=2, return_indices = True)
|
||||
mu = nn.MaxUnpool2d(2, stride=2)
|
||||
input = autograd.Variable(torch.randn(20, 16, 50, 32))
|
||||
output, indices = m(input)
|
||||
unpooled_output = mu.forward(output, indices)
|
||||
# exact output size can be also specified as an argument
|
||||
input = autograd.Variable(torch.randn(1, 16, 11, 11))
|
||||
downsample = nn.MaxPool2d(3, 3, return_indices=True)
|
||||
upsample = nn.MaxUnpool2d(3, 3)
|
||||
h, indices = downsample(input)
|
||||
output = upsample(h, indices, output_size=input.size())
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
MaxPool2d is not invertible, as the locations of the max locations are lost.
|
||||
MaxUnpool2d takes in as input the output of MaxPool2d and the indices of the Max locations
|
||||
and computes the inverse.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Constructor Arguments
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter | Default | Description
|
||||
--------- | ------- | -----------
|
||||
kernel_size | | the size of the max window. Can be a single number k (for a square kernel of k x k) or a tuple (kh x kw)
|
||||
stride | kernel_size | the stride of the window. Can be a single number s or a tuple (sh x sw).
|
||||
padding | 0 | implicit padding that was added to the input. Can be a single number or a tuple.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Expected Shape
|
||||
| Shape | Description
|
||||
------ | ----- | ------------
|
||||
input | [ * , * , *, * ] | Input is minibatch x channels x iH x iW
|
||||
output | [ * , * , *, * ] | Output shape is minibatch x channels x padH x (iH - 1) * sH + kH x padW x (iW - 1) * sW + kW, or as specified to the call.
|
||||
### MaxUnpool3d
|
||||
|
||||
Computes the inverse operation of MaxPool3d
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# pool of square window of size=3, stride=2
|
||||
m = nn.MaxPool3d(3, stride=2, return_indices = True)
|
||||
mu = nn.MaxUnpool3d(3, stride=2)
|
||||
input, indices = autograd.Variable(torch.randn(20, 16, 50, 32, 15))
|
||||
output = m(input)
|
||||
unpooled_output = m2.forward(output, indices)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
MaxPool3d is not invertible, as the locations of the max locations are lost.
|
||||
MaxUnpool3d takes in as input the output of MaxPool3d and the indices of the Max locations
|
||||
and computes the inverse.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Constructor Arguments
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter | Default | Description
|
||||
--------- | ------- | -----------
|
||||
kernel_size | | the size of the max window. Can be a single number k (for a square kernel of k x k) or a tuple (kt x kh x kw)
|
||||
stride | kernel_size | the stride of the window. Can be a single number s or a tuple (st x sh x sw).
|
||||
padding | 0 | implicit padding that was added to the input. Can be a single number or a tuple.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Expected Shape
|
||||
| Shape | Description
|
||||
------ | ----- | ------------
|
||||
input | [ * , * , *, *, * ] | Input is minibatch x channels x iT x iH x iW
|
||||
output | [ * , * , *, *, * ] | Output shape = minibatch x channels x padT x (iT - 1) * sT + kT x padH x (iH - 1) * sH + kH x padW x (iW - 1) * sW + kW
|
||||
### AvgPool2d
|
||||
|
||||
Applies a 2D average pooling over an input signal composed of several input
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
The output value of the layer with input (b x C x H x W) and output (b x C x oH x oW)
|
||||
can be precisely described as:
|
||||
output[b_i][c_i][h_i][w_i] = (1 / K) * sum_{kh=1, KH} sum_{kw=1, kW} input[b_i][c_i][stride_h * h_i + kh)][stride_w * w_i + kw)]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# pool of square window of size=3, stride=2
|
||||
m = nn.AvgPool2d(3, stride=2)
|
||||
# pool of non-square window
|
||||
m = nn.AvgPool2d((3, 2), stride=(2, 1))
|
||||
input = autograd.Variable(torch.randn(20, 16, 50, 32))
|
||||
output = m(input)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
planes.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Constructor Arguments
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter | Default | Description
|
||||
--------- | ------- | -----------
|
||||
kernel_size | | the size of the window. Can be a single number k (for a square kernel of k x k) or a tuple (kh x kw)
|
||||
stride | kernel_size | the stride of the window. Can be a single number s or a tuple (sh x sw).
|
||||
padding | 0 | implicit padding to be added. Can be a single number or a tuple.
|
||||
ceil_mode | | when True, will use "ceil" instead of "floor" to compute the output shape
|
||||
|
||||
#### Expected Shape
|
||||
| Shape | Description
|
||||
------ | ----- | ------------
|
||||
input | [ * , * , *, * ] | Input is minibatch x channels x iH x iW
|
||||
output | [ * , * , *, * ] | Output shape = minibatch x channels x floor((iH + 2*padH - kH) / sH + 1) x floor((iW + 2*padW - kW) / sW + 1)
|
||||
### AvgPool3d
|
||||
|
||||
Applies a 3D average pooling over an input signal composed of several input
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# pool of square window of size=3, stride=2
|
||||
m = nn.AvgPool3d(3, stride=2)
|
||||
# pool of non-square window
|
||||
m = nn.AvgPool3d((3, 2, 2), stride=(2, 1, 2))
|
||||
input = autograd.Variable(torch.randn(20, 16, 50,44, 31))
|
||||
output = m(input)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
planes.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Constructor Arguments
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter | Default | Description
|
||||
--------- | ------- | -----------
|
||||
kernel_size | | the size of the window to take a average over. Can be a single number k (for a square kernel of k x k x k) or a tuple (kt x kh x kw)
|
||||
stride | kernel_size | the stride of the window. Can be a single number s or a tuple (st x sh x sw).
|
||||
|
||||
#### Expected Shape
|
||||
| Shape | Description
|
||||
------ | ----- | ------------
|
||||
input | [ * , * , *, *, * ] | Input is minibatch x channels x iT x iH x iW
|
||||
output | [ * , * , *, *, * ] | Output shape = minibatch x channels x floor((iT + 2*padT - kT) / sT + 1) x floor((iH + 2*padH - kH) / sH + 1) x floor((iW + 2*padW - kW) / sW + 1)
|
||||
### FractionalMaxPool2d
|
||||
|
||||
Applies a 2D fractional max pooling over an input signal composed of several input
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# pool of square window of size=3, and target output size 13x12
|
||||
m = nn.FractionalMaxPool2d(3, output_size=(13, 12))
|
||||
# pool of square window and target output size being half of input image size
|
||||
m = nn.FractionalMaxPool2d(3, output_ratio=(0.5, 0.5))
|
||||
input = autograd.Variable(torch.randn(20, 16, 50, 32))
|
||||
output = m(input)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
planes.
|
||||
|
||||
Fractiona MaxPooling is described in detail in the paper ["Fractional Max-Pooling" by Ben Graham](http://arxiv.org/abs/1412.6071)
|
||||
The max-pooling operation is applied in kHxkW regions by a stochastic
|
||||
step size determined by the target output size.
|
||||
The number of output features is equal to the number of input planes.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Constructor Arguments
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter | Default | Description
|
||||
--------- | ------- | -----------
|
||||
kernel_size | | the size of the window to take a max over. Can be a single number k (for a square kernel of k x k) or a tuple (kh x kw)
|
||||
output_size | | the target output size of the image of the form oH x oW. Can be a tuple (oH, oW) or a single number oH for a square image oH x oH
|
||||
output_ratio | | If one wants to have an output size as a ratio of the input size, this option can be given. This has to be a number or tuple in the range (0, 1)
|
||||
return_indices | False | if True, will return the indices along with the outputs. Useful to pass to nn.MaxUnpool2d .
|
||||
|
||||
#### Expected Shape
|
||||
| Shape | Description
|
||||
------ | ----- | ------------
|
||||
input | [ * , * , *, * ] | Input is minibatch x channels x iH x iW
|
||||
output | [ * , * , *, * ] | Output shape = minibatch x channels x floor((iH + 2*padH - kH) / sH + 1) x floor((iW + 2*padW - kW) / sW + 1)
|
||||
### LPPool2d
|
||||
|
||||
Applies a 2D power-average pooling over an input signal composed of several input
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# power-2 pool of square window of size=3, stride=2
|
||||
m = nn.LPPool2d(2, 3, stride=2)
|
||||
# pool of non-square window of power 1.2
|
||||
m = nn.LPPool2d(1.2, (3, 2), stride=(2, 1))
|
||||
input = autograd.Variable(torch.randn(20, 16, 50, 32))
|
||||
output = m(input)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
planes.
|
||||
On each window, the function computed is: f(X) = pow(sum(pow(X, p)), 1/p)
|
||||
At p = infinity, one gets Max Pooling
|
||||
At p = 1, one gets Average Pooling
|
||||
|
||||
#### Constructor Arguments
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter | Default | Description
|
||||
--------- | ------- | -----------
|
||||
kernel_size | | the size of the window. Can be a single number k (for a square kernel of k x k) or a tuple (kh x kw)
|
||||
stride | kernel_size | the stride of the window. Can be a single number s or a tuple (sh x sw).
|
||||
ceil_mode | | when True, will use "ceil" instead of "floor" to compute the output shape
|
||||
|
||||
#### Expected Shape
|
||||
| Shape | Description
|
||||
------ | ----- | ------------
|
||||
input | [ * , * , *, * ] | Input is minibatch x channels x iH x iW
|
||||
output | [ * , * , *, * ] | Output shape = minibatch x channels x floor((iH + 2*padH - kH) / sH + 1) x floor((iW + 2*padW - kW) / sW + 1)
|
||||
@ -1,346 +0,0 @@
|
||||
## Recurrent layers
|
||||
### RNN
|
||||
|
||||
Applies a multi-layer Elman RNN with tanh or ReLU non-linearity to an input sequence.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
h_t = tanh(w_ih * x_t + b_ih + w_hh * h_(t-1) + b_hh)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
rnn = nn.RNN(10, 20, 2)
|
||||
input = Variable(torch.randn(5, 3, 10))
|
||||
h0 = Variable(torch.randn(2, 3, 20))
|
||||
output, hn = rnn(input, h0)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
For each element in the input sequence, each layer computes the following
|
||||
function:
|
||||
where `h_t` is the hidden state at time t, and `x_t` is the hidden
|
||||
state of the previous layer at time t or `input_t` for the first layer.
|
||||
If nonlinearity='relu', then ReLU is used instead of tanh.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Constructor Arguments
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter | Default | Description
|
||||
--------- | ------- | -----------
|
||||
input_size | | The number of expected features in the input x
|
||||
hidden_size | | The number of features in the hidden state h
|
||||
num_layers | | the size of the convolving kernel.
|
||||
nonlinearity | 'tanh' | The non-linearity to use ['tanh'|'relu'].
|
||||
bias | True | If False, then the layer does not use bias weights b_ih and b_hh.
|
||||
batch_first | | If True, then the input tensor is provided as (batch, seq, feature)
|
||||
dropout | | If non-zero, introduces a dropout layer on the outputs of each RNN layer
|
||||
bidirectional | False | If True, becomes a bidirectional RNN.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Inputs
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter | Default | Description
|
||||
--------- | ------- | -----------
|
||||
input | | A (seq_len x batch x input_size) tensor containing the features of the input sequence.
|
||||
h_0 | | A (num_layers x batch x hidden_size) tensor containing the initial hidden state for each element in the batch.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Outputs
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter | Description
|
||||
--------- | -----------
|
||||
output | A (seq_len x batch x hidden_size) tensor containing the output features (h_k) from the last layer of the RNN, for each k
|
||||
h_n | A (num_layers x batch x hidden_size) tensor containing the hidden state for k=seq_len
|
||||
|
||||
#### Members
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter | Description
|
||||
--------- | -----------
|
||||
weight_ih_l[k] | the learnable input-hidden weights of the k-th layer, of shape (input_size x hidden_size)
|
||||
weight_hh_l[k] | the learnable hidden-hidden weights of the k-th layer, of shape (hidden_size x hidden_size)
|
||||
bias_ih_l[k] | the learnable input-hidden bias of the k-th layer, of shape (hidden_size)
|
||||
bias_hh_l[k] | the learnable hidden-hidden bias of the k-th layer, of shape (hidden_size)
|
||||
### LSTM
|
||||
|
||||
Applies a multi-layer long short-term memory (LSTM) RNN to an input sequence.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
i_t = sigmoid(W_ii x_t + b_ii + W_hi h_(t-1) + b_hi)
|
||||
f_t = sigmoid(W_if x_t + b_if + W_hf h_(t-1) + b_hf)
|
||||
g_t = tanh(W_ig x_t + b_ig + W_hc h_(t-1) + b_hg)
|
||||
o_t = sigmoid(W_io x_t + b_io + W_ho h_(t-1) + b_ho)
|
||||
c_t = f_t * c_(t-1) + i_t * c_t
|
||||
h_t = o_t * tanh(c_t)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
rnn = nn.LSTM(10, 20, 2)
|
||||
input = Variable(torch.randn(5, 3, 10))
|
||||
h0 = Variable(torch.randn(2, 3, 20))
|
||||
c0 = Variable(torch.randn(2, 3, 20))
|
||||
output, hn = rnn(input, (h0, c0))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
For each element in the input sequence, each layer computes the following
|
||||
function:
|
||||
where `h_t` is the hidden state at time t, `c_t` is the cell state at time t,
|
||||
`x_t` is the hidden state of the previous layer at time t or input_t for the first layer,
|
||||
and `i_t`, `f_t`, `g_t`, `o_t` are the input, forget, cell, and out gates, respectively.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Constructor Arguments
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter | Default | Description
|
||||
--------- | ------- | -----------
|
||||
input_size | | The number of expected features in the input x
|
||||
hidden_size | | The number of features in the hidden state h
|
||||
num_layers | | the size of the convolving kernel.
|
||||
bias | True | If False, then the layer does not use bias weights b_ih and b_hh.
|
||||
batch_first | | If True, then the input tensor is provided as (batch, seq, feature)
|
||||
dropout | | If non-zero, introduces a dropout layer on the outputs of each RNN layer
|
||||
bidirectional | False | If True, becomes a bidirectional RNN.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Inputs
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter | Default | Description
|
||||
--------- | ------- | -----------
|
||||
input | | A (seq_len x batch x input_size) tensor containing the features of the input sequence.
|
||||
h_0 | | A (num_layers x batch x hidden_size) tensor containing the initial hidden state for each element in the batch.
|
||||
c_0 | | A (num_layers x batch x hidden_size) tensor containing the initial cell state for each element in the batch.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Outputs
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter | Description
|
||||
--------- | -----------
|
||||
output | A (seq_len x batch x hidden_size) tensor containing the output features (h_t) from the last layer of the RNN, for each t
|
||||
h_n | A (num_layers x batch x hidden_size) tensor containing the hidden state for t=seq_len
|
||||
c_n | A (num_layers x batch x hidden_size) tensor containing the cell state for t=seq_len
|
||||
|
||||
#### Members
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter | Description
|
||||
--------- | -----------
|
||||
weight_ih_l[k] | the learnable input-hidden weights of the k-th layer (W_ir|W_ii|W_in), of shape (input_size x 3*hidden_size)
|
||||
weight_hh_l[k] | the learnable hidden-hidden weights of the k-th layer (W_hr|W_hi|W_hn), of shape (hidden_size x 3*hidden_size)
|
||||
bias_ih_l[k] | the learnable input-hidden bias of the k-th layer (b_ir|b_ii|b_in), of shape (3*hidden_size)
|
||||
bias_hh_l[k] | the learnable hidden-hidden bias of the k-th layer (W_hr|W_hi|W_hn), of shape (3*hidden_size)
|
||||
### GRU
|
||||
|
||||
Applies a multi-layer gated recurrent unit (GRU) RNN to an input sequence.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
r_t = sigmoid(W_ir x_t + b_ir + W_hr h_(t-1) + b_hr)
|
||||
i_t = sigmoid(W_ii x_t + b_ii + W_hi h_(t-1) + b_hi)
|
||||
n_t = tanh(W_in x_t + resetgate * W_hn h_(t-1))
|
||||
h_t = (1 - i_t) * n_t + i_t * h_(t-1)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
rnn = nn.GRU(10, 20, 2)
|
||||
input = Variable(torch.randn(5, 3, 10))
|
||||
h0 = Variable(torch.randn(2, 3, 20))
|
||||
output, hn = rnn(input, h0)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
For each element in the input sequence, each layer computes the following
|
||||
function:
|
||||
where `h_t` is the hidden state at time t, `x_t` is the hidden
|
||||
state of the previous layer at time t or input_t for the first layer,
|
||||
and `r_t`, `i_t`, `n_t` are the reset, input, and new gates, respectively.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Constructor Arguments
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter | Default | Description
|
||||
--------- | ------- | -----------
|
||||
input_size | | The number of expected features in the input x
|
||||
hidden_size | | The number of features in the hidden state h
|
||||
num_layers | | the size of the convolving kernel.
|
||||
bias | True | If False, then the layer does not use bias weights b_ih and b_hh.
|
||||
batch_first | | If True, then the input tensor is provided as (batch, seq, feature)
|
||||
dropout | | If non-zero, introduces a dropout layer on the outputs of each RNN layer
|
||||
bidirectional | False | If True, becomes a bidirectional RNN.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Inputs
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter | Default | Description
|
||||
--------- | ------- | -----------
|
||||
input | | A (seq_len x batch x input_size) tensor containing the features of the input sequence.
|
||||
h_0 | | A (num_layers x batch x hidden_size) tensor containing the initial hidden state for each element in the batch.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Outputs
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter | Description
|
||||
--------- | -----------
|
||||
output | A (seq_len x batch x hidden_size) tensor containing the output features (h_t) from the last layer of the RNN, for each t
|
||||
h_n | A (num_layers x batch x hidden_size) tensor containing the hidden state for t=seq_len
|
||||
|
||||
#### Members
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter | Description
|
||||
--------- | -----------
|
||||
weight_ih_l[k] | the learnable input-hidden weights of the k-th layer (W_ir|W_ii|W_in), of shape (input_size x 3*hidden_size)
|
||||
weight_hh_l[k] | the learnable hidden-hidden weights of the k-th layer (W_hr|W_hi|W_hn), of shape (hidden_size x 3*hidden_size)
|
||||
bias_ih_l[k] | the learnable input-hidden bias of the k-th layer (b_ir|b_ii|b_in), of shape (3*hidden_size)
|
||||
bias_hh_l[k] | the learnable hidden-hidden bias of the k-th layer (W_hr|W_hi|W_hn), of shape (3*hidden_size)
|
||||
### RNNCell
|
||||
|
||||
An Elman RNN cell with tanh or ReLU non-linearity.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
h' = tanh(w_ih * x + b_ih + w_hh * h + b_hh)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
rnn = nn.RNNCell(10, 20)
|
||||
input = Variable(torch.randn(6, 3, 10))
|
||||
hx = Variable(torch.randn(3, 20))
|
||||
output = []
|
||||
for i in range(6):
|
||||
hx = rnn(input, hx)
|
||||
output[i] = hx
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If nonlinearity='relu', then ReLU is used in place of tanh.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Constructor Arguments
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter | Default | Description
|
||||
--------- | ------- | -----------
|
||||
input_size | | The number of expected features in the input x
|
||||
hidden_size | | The number of features in the hidden state h
|
||||
bias | True | If False, then the layer does not use bias weights b_ih and b_hh.
|
||||
nonlinearity | 'tanh' | The non-linearity to use ['tanh'|'relu'].
|
||||
|
||||
#### Inputs
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter | Default | Description
|
||||
--------- | ------- | -----------
|
||||
input | | A (batch x input_size) tensor containing input features
|
||||
hidden | | A (batch x hidden_size) tensor containing the initial hidden state for each element in the batch.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Outputs
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter | Description
|
||||
--------- | -----------
|
||||
h' | A (batch x hidden_size) tensor containing the next hidden state for each element in the batch
|
||||
|
||||
#### Members
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter | Description
|
||||
--------- | -----------
|
||||
weight_ih | the learnable input-hidden weights, of shape (input_size x hidden_size)
|
||||
weight_hh | the learnable hidden-hidden weights, of shape (hidden_size x hidden_size)
|
||||
bias_ih | the learnable input-hidden bias, of shape (hidden_size)
|
||||
bias_hh | the learnable hidden-hidden bias, of shape (hidden_size)
|
||||
### LSTMCell
|
||||
|
||||
A long short-term memory (LSTM) cell.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
i = sigmoid(W_ii x + b_ii + W_hi h + b_hi)
|
||||
f = sigmoid(W_if x + b_if + W_hf h + b_hf)
|
||||
g = tanh(W_ig x + b_ig + W_hc h + b_hg)
|
||||
o = sigmoid(W_io x + b_io + W_ho h + b_ho)
|
||||
c' = f * c + i * c
|
||||
h' = o * tanh(c_t)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
rnn = nn.LSTMCell(10, 20)
|
||||
input = Variable(torch.randn(6, 3, 10))
|
||||
hx = Variable(torch.randn(3, 20))
|
||||
cx = Variable(torch.randn(3, 20))
|
||||
output = []
|
||||
for i in range(6):
|
||||
hx, cx = rnn(input, (hx, cx))
|
||||
output[i] = hx
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Constructor Arguments
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter | Default | Description
|
||||
--------- | ------- | -----------
|
||||
input_size | | The number of expected features in the input x
|
||||
hidden_size | | The number of features in the hidden state h
|
||||
bias | True | If False, then the layer does not use bias weights b_ih and b_hh.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Inputs
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter | Default | Description
|
||||
--------- | ------- | -----------
|
||||
input | | A (batch x input_size) tensor containing input features
|
||||
hidden | | A (batch x hidden_size) tensor containing the initial hidden state for each element in the batch.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Outputs
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter | Description
|
||||
--------- | -----------
|
||||
h' | A (batch x hidden_size) tensor containing the next hidden state for each element in the batch
|
||||
c' | A (batch x hidden_size) tensor containing the next cell state for each element in the batch
|
||||
|
||||
#### Members
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter | Description
|
||||
--------- | -----------
|
||||
weight_ih | the learnable input-hidden weights, of shape (input_size x hidden_size)
|
||||
weight_hh | the learnable hidden-hidden weights, of shape (hidden_size x hidden_size)
|
||||
bias_ih | the learnable input-hidden bias, of shape (hidden_size)
|
||||
bias_hh | the learnable hidden-hidden bias, of shape (hidden_size)
|
||||
### GRUCell
|
||||
|
||||
A gated recurrent unit (GRU) cell
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
r = sigmoid(W_ir x + b_ir + W_hr h + b_hr)
|
||||
i = sigmoid(W_ii x + b_ii + W_hi h + b_hi)
|
||||
n = tanh(W_in x + resetgate * W_hn h)
|
||||
h' = (1 - i) * n + i * h
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
rnn = nn.RNNCell(10, 20)
|
||||
input = Variable(torch.randn(6, 3, 10))
|
||||
hx = Variable(torch.randn(3, 20))
|
||||
output = []
|
||||
for i in range(6):
|
||||
hx = rnn(input, hx)
|
||||
output[i] = hx
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Constructor Arguments
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter | Default | Description
|
||||
--------- | ------- | -----------
|
||||
input_size | | The number of expected features in the input x
|
||||
hidden_size | | The number of features in the hidden state h
|
||||
bias | True | If False, then the layer does not use bias weights b_ih and b_hh.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Inputs
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter | Default | Description
|
||||
--------- | ------- | -----------
|
||||
input | | A (batch x input_size) tensor containing input features
|
||||
hidden | | A (batch x hidden_size) tensor containing the initial hidden state for each element in the batch.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Outputs
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter | Description
|
||||
--------- | -----------
|
||||
h' | A (batch x hidden_size) tensor containing the next hidden state for each element in the batch
|
||||
|
||||
#### Members
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter | Description
|
||||
--------- | -----------
|
||||
weight_ih | the learnable input-hidden weights, of shape (input_size x hidden_size)
|
||||
weight_hh | the learnable hidden-hidden weights, of shape (hidden_size x hidden_size)
|
||||
bias_ih | the learnable input-hidden bias, of shape (hidden_size)
|
||||
bias_hh | the learnable hidden-hidden bias, of shape (hidden_size)
|
||||
@ -1,37 +0,0 @@
|
||||
## Sparse layers
|
||||
### Embedding
|
||||
|
||||
A simple lookup table that stores embeddings of a fixed dictionary and size
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# an Embedding module containing 10 tensors of size 3
|
||||
embedding = nn.Embedding(10, 3)
|
||||
# a batch of 2 samples of 4 indices each
|
||||
input = torch.LongTensor([[1,2,4,5],[4,3,2,9]])
|
||||
print(embedding(input))
|
||||
# example with padding_idx
|
||||
embedding = nn.Embedding(10, 3, padding_idx=0)
|
||||
input = torch.LongTensor([[0,2,0,5]])
|
||||
print(embedding(input))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This module is often used to store word embeddings and retrieve them using indices.
|
||||
The input to the module is a list of indices, and the output is the corresponding
|
||||
word embeddings.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Constructor Arguments
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter | Default | Description
|
||||
--------- | ------- | -----------
|
||||
num_embeddings | | size of the dictionary of embeddings
|
||||
embedding_dim | | the size of each embedding vector
|
||||
padding_idx | None | If given, pads the output with zeros whenever it encounters the index.
|
||||
max_norm | None | If given, will renormalize the embeddings to always have a norm lesser than this
|
||||
norm_type | | The p of the p-norm to compute for the max_norm option
|
||||
scale_grad_by_freq | | if given, this will scale gradients by the frequency of the words in the dictionary.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Expected Shape
|
||||
| Shape | Description
|
||||
------ | ----- | ------------
|
||||
input | [ *, * ] | Input is a 2D mini_batch LongTensor of m x n indices to extract from the Embedding dictionary
|
||||
output | [ * , *, * ] | Output shape = m x n x embedding_dim
|
||||
114
docs/optim.md
@ -1,114 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# torch.optim
|
||||
|
||||
The Optim package in Torch is targeted for one to optimize their neural networks
|
||||
using a wide variety of optimization methods such as SGD, Adam etc.
|
||||
|
||||
Currently, the following optimization methods are supported, typically with
|
||||
options such as weight decay and other bells and whistles.
|
||||
|
||||
- SGD `(params, lr=required, momentum=0, dampening=0)`
|
||||
- AdaDelta `(params, rho=0.9, eps=1e-6, weight_decay=0)`
|
||||
- Adagrad `(params, lr=1e-2, lr_decay=0, weight_decay=0)`
|
||||
- Adam `(params, lr=1e-2, betas=(0.9, 0.999), epsilon=1e-8, weight_decay=0)`
|
||||
- AdaMax `(params, lr=1e-2, betas=(0.9, 0.999), eps=1e-38, weight_decay=0)`
|
||||
- Averaged SGD `(params, lr=1e-2, lambd=1e-4, alpha=0.75, t0=1e6, weight_decay=0)`
|
||||
- RProp `(params, lr=1e-2, etas=(0.5, 1.2), step_sizes=(1e-6, 50))`
|
||||
- RMSProp `(params, lr=1e-2, alpha=0.99, eps=1e-8, weight_decay=0)`
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
The usage of the Optim package itself is as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Construct an optimizer
|
||||
2. Use `optimizer.step(...)` to optimize.
|
||||
- Call `optimizer.zero_grad()` to zero out the gradient buffers when appropriate
|
||||
|
||||
## 1. Constructing the optimizer
|
||||
|
||||
One first constructs an `Optimizer` object by giving it a list of parameters
|
||||
to optimize, as well as the optimizer options,such as learning rate, weight decay, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
Examples:
|
||||
|
||||
`optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr = 0.01, momentum=0.9)`
|
||||
|
||||
`optimizer = optim.Adam([var1, var2], lr = 0.0001)`
|
||||
|
||||
### Per-parameter options
|
||||
|
||||
In a more advanced usage, one can specify per-layer options by passing each parameter group along with it's custom options.
|
||||
|
||||
**__Any parameter group that does not have an attribute defined will use the default attributes.__**
|
||||
|
||||
This is very useful when one wants to specify per-layer learning rates for example.
|
||||
|
||||
Example:
|
||||
|
||||
`optim.SGD([{'params': model1.parameters()}, {'params': model2.parameters(), 'lr': 1e-3}, lr=1e-2, momentum=0.9)`
|
||||
|
||||
`model1`'s parameters will use the default learning rate of `1e-2` and momentum of `0.9`
|
||||
`model2`'s parameters will use a learning rate of `1e-3`, and the default momentum of `0.9`
|
||||
|
||||
Then, you can use the optimizer by calling `optimizer.zero_grad()` and `optimizer.step(...)`. Read the next sections.
|
||||
|
||||
## 2. Taking an optimization step using `Optimizer.step(...)`
|
||||
|
||||
The step function has the following two signatures:
|
||||
|
||||
### a. `Optimizer.step(closure)`
|
||||
|
||||
The `step` function takes a user-defined closure that computes f(x) and returns the loss.
|
||||
|
||||
The closure needs to do the following:
|
||||
- Optimizer.zero_grad()
|
||||
- Compute the loss
|
||||
- Call loss.backward()
|
||||
- return the loss
|
||||
|
||||
Example 1: training a neural network
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# Example 1: training a neural network with optimizer.step(closure)
|
||||
net = MNISTNet()
|
||||
criterion = ClassNLLLoss()
|
||||
optimizer = optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.001)
|
||||
|
||||
for data in data_batches:
|
||||
input, target = data
|
||||
def closure():
|
||||
optimizer.zero_grad()
|
||||
output = net(input)
|
||||
loss = criterion(output, target)
|
||||
loss.backward()
|
||||
return loss
|
||||
optimizer.step(closure)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Notes: Why is this required? Why cant we simply have the optimizer take the parameters and grads?
|
||||
Some optimization algorithms such as Conjugate Gradient and LBFGS need to evaluate their function
|
||||
multiple times. For such optimization methods, the function (i.e. the closure) has to be defined.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### b. `Optimizer.step()`
|
||||
|
||||
This is a simplified usage that supports most, but not all optimization algorithms. For example, it does not support LBFGS or Conjugate Gradient.
|
||||
|
||||
The usage for this is to simply call the function after the backward() is called on your model.
|
||||
|
||||
Example 2: training a neural network
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# Example 2: training a neural network with optimizer.step()
|
||||
net = MNISTNet()
|
||||
criterion = ClassNLLLoss()
|
||||
optimizer = optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.001)
|
||||
|
||||
for data in data_batches:
|
||||
input, target = data
|
||||
optimizer.zero_grad()
|
||||
output = net(input)
|
||||
loss = criterion(output, target)
|
||||
loss.backward()
|
||||
optimizer.step()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
2
docs/requirements.txt
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,2 @@
|
||||
sphinx
|
||||
-e git://github.com/snide/sphinx_rtd_theme.git#egg=sphinx_rtd_theme
|
||||
114
docs/source/_static/css/pytorch_theme.css
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,114 @@
|
||||
body {
|
||||
font-family: "Lato","proxima-nova","Helvetica Neue",Arial,sans-serif;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* Default header fonts are ugly */
|
||||
h1, h2, .rst-content .toctree-wrapper p.caption, h3, h4, h5, h6, legend, p.caption {
|
||||
font-family: "Lato","proxima-nova","Helvetica Neue",Arial,sans-serif;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* Use white for docs background */
|
||||
.wy-side-nav-search {
|
||||
background-color: #fff;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.wy-nav-content-wrap, .wy-menu li.current > a {
|
||||
background-color: #fff;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@media screen and (min-width: 1400px) {
|
||||
.wy-nav-content-wrap {
|
||||
background-color: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.0470588);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.wy-nav-content {
|
||||
background-color: #fff;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* Fixes for mobile */
|
||||
.wy-nav-top {
|
||||
background-color: #fff;
|
||||
background-image: url('../img/pytorch-logo-dark.svg');
|
||||
background-repeat: no-repeat;
|
||||
background-position: center;
|
||||
padding: 0;
|
||||
margin: 0.4045em 0.809em;
|
||||
color: #333;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.wy-nav-top > a {
|
||||
display: none;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@media screen and (max-width: 768px) {
|
||||
.wy-side-nav-search>a img.logo {
|
||||
height: 60px;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* This is needed to ensure that logo above search scales properly */
|
||||
.wy-side-nav-search a {
|
||||
display: block;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* This ensures that multiple constructors will remain in separate lines. */
|
||||
.rst-content dl:not(.docutils) dt {
|
||||
display: table;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* Use our red for literals (it's very similar to the original color) */
|
||||
.rst-content tt.literal, .rst-content tt.literal, .rst-content code.literal {
|
||||
color: #F05732;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.rst-content tt.xref, a .rst-content tt, .rst-content tt.xref,
|
||||
.rst-content code.xref, a .rst-content tt, a .rst-content code {
|
||||
color: #404040;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* Change link colors (except for the menu) */
|
||||
|
||||
a {
|
||||
color: #F05732;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
a:hover {
|
||||
color: #F05732;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
a:visited {
|
||||
color: #D44D2C;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.wy-menu a {
|
||||
color: #b3b3b3;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.wy-menu a:hover {
|
||||
color: #b3b3b3;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* Default footer text is quite big */
|
||||
footer {
|
||||
font-size: 80%;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
footer .rst-footer-buttons {
|
||||
font-size: 125%; /* revert footer settings - 1/80% = 125% */
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
footer p {
|
||||
font-size: 100%;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
/* For hidden headers that appear in TOC tree */
|
||||
/* see http://stackoverflow.com/a/32363545/3343043 */
|
||||
.rst-content .hidden-section {
|
||||
display: none;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
nav .hidden-section {
|
||||
display: inherit;
|
||||
}
|
||||
BIN
docs/source/_static/img/dynamic_graph.gif
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 258 KiB |
BIN
docs/source/_static/img/pytorch-logo-dark.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 27 KiB |
24
docs/source/_static/img/pytorch-logo-dark.svg
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,24 @@
|
||||
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
|
||||
<!-- Generator: Adobe Illustrator 21.0.0, SVG Export Plug-In . SVG Version: 6.00 Build 0) -->
|
||||
<svg version="1.1" id="Layer_1" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" xmlns:xlink="http://www.w3.org/1999/xlink" x="0px" y="0px"
|
||||
viewBox="0 0 199.7 40.2" style="enable-background:new 0 0 199.7 40.2;" xml:space="preserve">
|
||||
<style type="text/css">
|
||||
.st0{fill:#F05732;}
|
||||
.st1{fill:#9E529F;}
|
||||
.st2{fill:#333333;}
|
||||
</style>
|
||||
<path class="st0" d="M102.7,12.2c-1.3-1-1.8,3.9-4.4,3.9c-3,0-4-13-6.3-13c-0.7,0-0.8-0.4-7.9,21.3c-2.9,9,4.4,15.8,11.8,15.8
|
||||
c4.6,0,12.3-3,12.3-12.6C108.2,20.5,104.7,13.7,102.7,12.2z M95.8,35.3c-3.7,0-6.7-3.1-6.7-7c0-3.9,3-7,6.7-7s6.7,3.1,6.7,7
|
||||
C102.5,32.1,99.5,35.3,95.8,35.3z"/>
|
||||
<path class="st1" d="M99.8,0c-0.5,0-1.8,2.5-1.8,3.6c0,1.5,1,2,1.8,2c0.8,0,1.8-0.5,1.8-2C101.5,2.5,100.2,0,99.8,0z"/>
|
||||
<path class="st2" d="M0,39.5V14.9h11.5c5.3,0,8.3,3.6,8.3,7.9c0,4.3-3,7.9-8.3,7.9H5.2v8.8H0z M14.4,22.8c0-2.1-1.6-3.3-3.7-3.3H5.2
|
||||
v6.6h5.5C12.8,26.1,14.4,24.8,14.4,22.8z"/>
|
||||
<path class="st2" d="M35.2,39.5V29.4l-9.4-14.5h6l6.1,9.8l6.1-9.8h5.9l-9.4,14.5v10.1H35.2z"/>
|
||||
<path class="st2" d="M63.3,39.5v-20h-7.2v-4.6h19.6v4.6h-7.2v20H63.3z"/>
|
||||
<path class="st2" d="M131.4,39.5l-4.8-8.7h-3.8v8.7h-5.2V14.9H129c5.1,0,8.3,3.4,8.3,7.9c0,4.3-2.8,6.7-5.4,7.3l5.6,9.4H131.4z
|
||||
M131.9,22.8c0-2-1.6-3.3-3.7-3.3h-5.5v6.6h5.5C130.3,26.1,131.9,24.9,131.9,22.8z"/>
|
||||
<path class="st2" d="M145.6,27.2c0-7.6,5.7-12.7,13.1-12.7c5.4,0,8.5,2.9,10.3,6l-4.5,2.2c-1-2-3.2-3.6-5.8-3.6
|
||||
c-4.5,0-7.7,3.4-7.7,8.1c0,4.6,3.2,8.1,7.7,8.1c2.5,0,4.7-1.6,5.8-3.6l4.5,2.2c-1.7,3.1-4.9,6-10.3,6
|
||||
C151.3,39.9,145.6,34.7,145.6,27.2z"/>
|
||||
<path class="st2" d="M194.5,39.5V29.1h-11.6v10.4h-5.2V14.9h5.2v9.7h11.6v-9.7h5.3v24.6H194.5z"/>
|
||||
</svg>
|
||||
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 1.7 KiB |
BIN
docs/source/_static/img/tensor_illustration.png
Normal file
|
After Width: | Height: | Size: 18 KiB |
53
docs/source/autograd.rst
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,53 @@
|
||||
.. role:: hidden
|
||||
:class: hidden-section
|
||||
|
||||
Automatic differentiation package - torch.autograd
|
||||
==================================================
|
||||
|
||||
.. automodule:: torch.autograd
|
||||
.. currentmodule:: torch.autograd
|
||||
|
||||
.. autofunction:: backward
|
||||
|
||||
Variable
|
||||
--------
|
||||
|
||||
API compatibility
|
||||
^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
|
||||
|
||||
Variable API is nearly the same as regular Tensor API (with the exception
|
||||
of a couple in-place methods, that would overwrite inputs required for
|
||||
gradient computation). In most cases Tensors can be safely replaced with
|
||||
Variables and the code will remain to work just fine. Because of this,
|
||||
we're not documenting all the operations on variables, and you should
|
||||
refere to :class:`torch.Tensor` docs for this purpose.
|
||||
|
||||
In-place operations on Variables
|
||||
^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
|
||||
|
||||
Supporting in-place operations in autograd is a hard matter, and we discourage
|
||||
their use in most cases. Autograd's aggressive buffer freeing and reuse makes
|
||||
it very efficient and there are very few occasions when in-place operations
|
||||
actually lower memory usage by any significant amount. Unless you're operating
|
||||
under heavy memory pressure, you might never need to use them.
|
||||
|
||||
In-place correctness checks
|
||||
^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
|
||||
|
||||
All :class:`Variable` s keep track of in-place operations applied to them, and
|
||||
if the implementation detects that a variable was saved for backward in one of
|
||||
the functions, but it was modified in-place afterwards, an error will be raised
|
||||
once backward pass is started. This ensures that if you're using in-place
|
||||
functions and not seing any errors, you can be sure that the computed gradients
|
||||
are correct.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: Variable
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`Function`
|
||||
------------------
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: Function
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
243
docs/source/conf.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,243 @@
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/env python3
|
||||
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
|
||||
#
|
||||
# PyTorch documentation build configuration file, created by
|
||||
# sphinx-quickstart on Fri Dec 23 13:31:47 2016.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# This file is execfile()d with the current directory set to its
|
||||
# containing dir.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Note that not all possible configuration values are present in this
|
||||
# autogenerated file.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# All configuration values have a default; values that are commented out
|
||||
# serve to show the default.
|
||||
|
||||
# If extensions (or modules to document with autodoc) are in another directory,
|
||||
# add these directories to sys.path here. If the directory is relative to the
|
||||
# documentation root, use os.path.abspath to make it absolute, like shown here.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# import os
|
||||
# import sys
|
||||
# sys.path.insert(0, os.path.abspath('.'))
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
try:
|
||||
import torchvision
|
||||
except ImportError:
|
||||
import warnings
|
||||
warnings.warn('unable to load "torchvision" package')
|
||||
import sphinx_rtd_theme
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# -- General configuration ------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
# If your documentation needs a minimal Sphinx version, state it here.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# needs_sphinx = '1.0'
|
||||
|
||||
# Add any Sphinx extension module names here, as strings. They can be
|
||||
# extensions coming with Sphinx (named 'sphinx.ext.*') or your custom
|
||||
# ones.
|
||||
extensions = [
|
||||
'sphinx.ext.autodoc',
|
||||
'sphinx.ext.autosummary',
|
||||
'sphinx.ext.doctest',
|
||||
'sphinx.ext.intersphinx',
|
||||
'sphinx.ext.todo',
|
||||
'sphinx.ext.coverage',
|
||||
'sphinx.ext.mathjax',
|
||||
'sphinx.ext.napoleon',
|
||||
'sphinx.ext.viewcode',
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
napoleon_use_ivar = True
|
||||
|
||||
# Add any paths that contain templates here, relative to this directory.
|
||||
templates_path = ['_templates']
|
||||
|
||||
# The suffix(es) of source filenames.
|
||||
# You can specify multiple suffix as a list of string:
|
||||
#
|
||||
# source_suffix = ['.rst', '.md']
|
||||
source_suffix = '.rst'
|
||||
|
||||
# The master toctree document.
|
||||
master_doc = 'index'
|
||||
|
||||
# General information about the project.
|
||||
project = 'PyTorch'
|
||||
copyright = '2017, Torch Contributors'
|
||||
author = 'Torch Contributors'
|
||||
|
||||
# The version info for the project you're documenting, acts as replacement for
|
||||
# |version| and |release|, also used in various other places throughout the
|
||||
# built documents.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# The short X.Y version.
|
||||
version = '0.1.6'
|
||||
# The full version, including alpha/beta/rc tags.
|
||||
release = '0.1.6'
|
||||
|
||||
# The language for content autogenerated by Sphinx. Refer to documentation
|
||||
# for a list of supported languages.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# This is also used if you do content translation via gettext catalogs.
|
||||
# Usually you set "language" from the command line for these cases.
|
||||
language = None
|
||||
|
||||
# List of patterns, relative to source directory, that match files and
|
||||
# directories to ignore when looking for source files.
|
||||
# This patterns also effect to html_static_path and html_extra_path
|
||||
exclude_patterns = []
|
||||
|
||||
# The name of the Pygments (syntax highlighting) style to use.
|
||||
pygments_style = 'sphinx'
|
||||
|
||||
# If true, `todo` and `todoList` produce output, else they produce nothing.
|
||||
todo_include_todos = True
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# -- Options for HTML output ----------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
# The theme to use for HTML and HTML Help pages. See the documentation for
|
||||
# a list of builtin themes.
|
||||
#
|
||||
html_theme = 'sphinx_rtd_theme'
|
||||
html_theme_path = [sphinx_rtd_theme.get_html_theme_path()]
|
||||
|
||||
# Theme options are theme-specific and customize the look and feel of a theme
|
||||
# further. For a list of options available for each theme, see the
|
||||
# documentation.
|
||||
#
|
||||
html_theme_options = {
|
||||
'collapse_navigation': False,
|
||||
'display_version': False,
|
||||
'logo_only': True,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
html_logo = '_static/img/pytorch-logo-dark.svg'
|
||||
|
||||
# Add any paths that contain custom static files (such as style sheets) here,
|
||||
# relative to this directory. They are copied after the builtin static files,
|
||||
# so a file named "default.css" will overwrite the builtin "default.css".
|
||||
html_static_path = ['_static']
|
||||
|
||||
# html_style_path = 'css/pytorch_theme.css'
|
||||
html_context = {
|
||||
'css_files': [
|
||||
'https://fonts.googleapis.com/css?family=Lato',
|
||||
'_static/css/pytorch_theme.css'
|
||||
],
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# -- Options for HTMLHelp output ------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
# Output file base name for HTML help builder.
|
||||
htmlhelp_basename = 'PyTorchdoc'
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# -- Options for LaTeX output ---------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
latex_elements = {
|
||||
# The paper size ('letterpaper' or 'a4paper').
|
||||
#
|
||||
# 'papersize': 'letterpaper',
|
||||
|
||||
# The font size ('10pt', '11pt' or '12pt').
|
||||
#
|
||||
# 'pointsize': '10pt',
|
||||
|
||||
# Additional stuff for the LaTeX preamble.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# 'preamble': '',
|
||||
|
||||
# Latex figure (float) alignment
|
||||
#
|
||||
# 'figure_align': 'htbp',
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# Grouping the document tree into LaTeX files. List of tuples
|
||||
# (source start file, target name, title,
|
||||
# author, documentclass [howto, manual, or own class]).
|
||||
latex_documents = [
|
||||
(master_doc, 'pytorch.tex', 'PyTorch Documentation',
|
||||
'Torch Contributors', 'manual'),
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# -- Options for manual page output ---------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
# One entry per manual page. List of tuples
|
||||
# (source start file, name, description, authors, manual section).
|
||||
man_pages = [
|
||||
(master_doc, 'PyTorch', 'PyTorch Documentation',
|
||||
[author], 1)
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# -- Options for Texinfo output -------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
# Grouping the document tree into Texinfo files. List of tuples
|
||||
# (source start file, target name, title, author,
|
||||
# dir menu entry, description, category)
|
||||
texinfo_documents = [
|
||||
(master_doc, 'PyTorch', 'PyTorch Documentation',
|
||||
author, 'PyTorch', 'One line description of project.',
|
||||
'Miscellaneous'),
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Example configuration for intersphinx: refer to the Python standard library.
|
||||
intersphinx_mapping = {
|
||||
'python': ('https://docs.python.org/', None),
|
||||
'numpy': ('http://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy/', None),
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
# -- A patch that prevents Sphinx from cross-referencing ivar tags -------
|
||||
# See http://stackoverflow.com/a/41184353/3343043
|
||||
|
||||
from docutils import nodes
|
||||
from sphinx.util.docfields import TypedField
|
||||
from sphinx import addnodes
|
||||
|
||||
def patched_make_field(self, types, domain, items):
|
||||
# type: (List, unicode, Tuple) -> nodes.field
|
||||
def handle_item(fieldarg, content):
|
||||
par = nodes.paragraph()
|
||||
par += addnodes.literal_strong('', fieldarg) # Patch: this line added
|
||||
#par.extend(self.make_xrefs(self.rolename, domain, fieldarg,
|
||||
# addnodes.literal_strong))
|
||||
if fieldarg in types:
|
||||
par += nodes.Text(' (')
|
||||
# NOTE: using .pop() here to prevent a single type node to be
|
||||
# inserted twice into the doctree, which leads to
|
||||
# inconsistencies later when references are resolved
|
||||
fieldtype = types.pop(fieldarg)
|
||||
if len(fieldtype) == 1 and isinstance(fieldtype[0], nodes.Text):
|
||||
typename = u''.join(n.astext() for n in fieldtype)
|
||||
typename = typename.replace('int', 'python:int')
|
||||
typename = typename.replace('long', 'python:long')
|
||||
typename = typename.replace('float', 'python:float')
|
||||
typename = typename.replace('type', 'python:type')
|
||||
par.extend(self.make_xrefs(self.typerolename, domain, typename,
|
||||
addnodes.literal_emphasis))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
par += fieldtype
|
||||
par += nodes.Text(')')
|
||||
par += nodes.Text(' -- ')
|
||||
par += content
|
||||
return par
|
||||
|
||||
fieldname = nodes.field_name('', self.label)
|
||||
if len(items) == 1 and self.can_collapse:
|
||||
fieldarg, content = items[0]
|
||||
bodynode = handle_item(fieldarg, content)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
bodynode = self.list_type()
|
||||
for fieldarg, content in items:
|
||||
bodynode += nodes.list_item('', handle_item(fieldarg, content))
|
||||
fieldbody = nodes.field_body('', bodynode)
|
||||
return nodes.field('', fieldname, fieldbody)
|
||||
|
||||
TypedField.make_field = patched_make_field
|
||||
27
docs/source/cuda.rst
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
|
||||
torch.cuda
|
||||
===================================
|
||||
|
||||
.. currentmodule:: torch.cuda
|
||||
|
||||
.. automodule:: torch.cuda
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
Communication collectives
|
||||
-------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
.. autofunction:: torch.cuda.comm.broadcast
|
||||
|
||||
.. autofunction:: torch.cuda.comm.reduce_add
|
||||
|
||||
.. autofunction:: torch.cuda.comm.scatter
|
||||
|
||||
.. autofunction:: torch.cuda.comm.gather
|
||||
|
||||
Streams and events
|
||||
------------------
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: Stream
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: Event
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
7
docs/source/data.rst
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
|
||||
torch.utils.data
|
||||
===================================
|
||||
|
||||
.. automodule:: torch.utils.data
|
||||
.. autoclass:: Dataset
|
||||
.. autoclass:: TensorDataset
|
||||
.. autoclass:: DataLoader
|
||||
6
docs/source/ffi.rst
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,6 @@
|
||||
torch.utils.ffi
|
||||
===============
|
||||
|
||||
.. currentmodule:: torch.utils.ffi
|
||||
.. autofunction:: create_extension
|
||||
|
||||
54
docs/source/index.rst
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,54 @@
|
||||
.. PyTorch documentation master file, created by
|
||||
sphinx-quickstart on Fri Dec 23 13:31:47 2016.
|
||||
You can adapt this file completely to your liking, but it should at least
|
||||
contain the root `toctree` directive.
|
||||
|
||||
:github_url: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch
|
||||
|
||||
PyTorch documentation
|
||||
===================================
|
||||
|
||||
PyTorch is an optimized tensor library for deep learning using GPUs and CPUs.
|
||||
|
||||
.. toctree::
|
||||
:glob:
|
||||
:maxdepth: 1
|
||||
:caption: Notes
|
||||
|
||||
notes/*
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
.. toctree::
|
||||
:maxdepth: 1
|
||||
:caption: Package Reference
|
||||
|
||||
torch
|
||||
tensors
|
||||
storage
|
||||
nn
|
||||
optim
|
||||
torch.autograd <autograd>
|
||||
torch.multiprocessing <multiprocessing>
|
||||
torch.legacy <legacy>
|
||||
cuda
|
||||
ffi
|
||||
data
|
||||
model_zoo
|
||||
|
||||
.. toctree::
|
||||
:glob:
|
||||
:maxdepth: 1
|
||||
:caption: torchvision Reference
|
||||
|
||||
torchvision/torchvision
|
||||
torchvision/datasets
|
||||
torchvision/models
|
||||
torchvision/transforms
|
||||
torchvision/utils
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Indices and tables
|
||||
==================
|
||||
|
||||
* :ref:`genindex`
|
||||
* :ref:`modindex`
|
||||
4
docs/source/legacy.rst
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,4 @@
|
||||
Legacy package - torch.legacy
|
||||
===================================
|
||||
|
||||
.. automodule:: torch.legacy
|
||||
5
docs/source/model_zoo.rst
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,5 @@
|
||||
torch.utils.model_zoo
|
||||
===================================
|
||||
|
||||
.. automodule:: torch.utils.model_zoo
|
||||
.. autofunction:: load_url
|
||||
88
docs/source/multiprocessing.rst
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,88 @@
|
||||
Multiprocessing package - torch.multiprocessing
|
||||
===============================================
|
||||
|
||||
.. automodule:: torch.multiprocessing
|
||||
.. currentmodule:: torch.multiprocessing
|
||||
|
||||
.. warning::
|
||||
|
||||
If the main process exits abruptly (e.g. because of an incoming signal),
|
||||
Python's ``multiprocessing`` sometimes fails to clean up its children.
|
||||
It's a known caveat, so if you're seeing any resource leaks after
|
||||
interrupting the interpreter, it probably means that this has just happened
|
||||
to you.
|
||||
|
||||
Strategy management
|
||||
-------------------
|
||||
|
||||
.. autofunction:: get_all_sharing_strategies
|
||||
.. autofunction:: get_sharing_strategy
|
||||
.. autofunction:: set_sharing_strategy
|
||||
|
||||
Sharing CUDA tensors
|
||||
--------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Sharing CUDA tensors between processes is supported only in Python 3, using
|
||||
a ``spawn`` or ``forkserver`` start methods. :mod:`python:multiprocessing` in
|
||||
Python 2 can only create subprocesses using ``fork``, and it's not supported
|
||||
by the CUDA runtime.
|
||||
|
||||
.. warning::
|
||||
|
||||
CUDA API requires that the allocation exported to other processes remains
|
||||
valid as long as it's used by them. You should be careful and ensure that
|
||||
CUDA tensors you shared don't go out of scope as long as it's necessary.
|
||||
This shouldn't be a problem for sharing model parameters, but passing other
|
||||
kinds of data should be done with care. Note that this restriction doesn't
|
||||
apply to shared CPU memory.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Sharing strategies
|
||||
------------------
|
||||
|
||||
This section provides a brief overview into how different sharing strategies
|
||||
work. Note that it applies only to CPU tensor - CUDA tensors will always use
|
||||
the CUDA API, as that's the only way they can be shared.
|
||||
|
||||
File descriptor - ``file_descriptor``
|
||||
^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
.. note::
|
||||
|
||||
This is the default strategy (except for macOS and OS X where it's not
|
||||
supported).
|
||||
|
||||
This strategy will use file descriptors as shared memory handles. Whenever a
|
||||
storage is moved to shared memory, a file descriptor obtained from ``shm_open``
|
||||
is cached with the object, and when it's going to be sent to other processes,
|
||||
the file descriptor will be transferred (e.g. via UNIX sockets) to it. The
|
||||
receiver will also cache the file descriptor and ``mmap`` it, to obtain a shared
|
||||
view onto the storage data.
|
||||
|
||||
Note that if there will be a lot of tensors shared, this strategy will keep a
|
||||
large number of file descriptors open most of the time. If your system has low
|
||||
limits for the number of open file descriptors, and you can't rise them, you
|
||||
should use the ``file_system`` strategy.
|
||||
|
||||
File system - ``file_system``
|
||||
^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
|
||||
|
||||
This strategy will use file names given to ``shm_open`` to identify the shared
|
||||
memory regions. This has a benefit of not requiring the implementation to cache
|
||||
the file descriptors obtained from it, but at the same time is prone to shared
|
||||
memory leaks. The file can't be deleted right after its creation, because other
|
||||
processes need to access it to open their views. If the processes fatally
|
||||
crash, or are killed, and don't call the storage destructors, the files will
|
||||
remain in the system. This is very serious, because they keep using up the
|
||||
memory until the system is restarted, or they're freed manually.
|
||||
|
||||
To counter the problem of shared memory file leaks, :mod:`torch.multiprocessing`
|
||||
will spawn a daemon named ``torch_shm_manager`` that will isolate itself from
|
||||
the current process group, and will keep track of all shared memory allocations.
|
||||
Once all processes connected to it exit, it will wait a moment to ensure there
|
||||
will be no new connections, and will iterate over all shared memory files
|
||||
allocated by the group. If it finds that any of them still exist, they will be
|
||||
deallocated. We've tested this method and it prooved to be robust to various
|
||||
failures. Still, if your system has high enough limits, and ``file_descriptor``
|
||||
is a supported strategy, we do not recommend switching to this one.
|
||||
693
docs/source/nn.rst
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,693 @@
|
||||
.. role:: hidden
|
||||
:class: hidden-section
|
||||
|
||||
torch.nn
|
||||
===================================
|
||||
|
||||
.. automodule:: torch.nn
|
||||
.. currentmodule:: torch.nn
|
||||
|
||||
Containers
|
||||
----------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`Module`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: Module
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
Convolution Layers
|
||||
----------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`Conv1d`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: Conv1d
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`Conv2d`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: Conv2d
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`Conv3d`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: Conv3d
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`ConvTranspose1d`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: ConvTranspose1d
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`ConvTranspose2d`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: ConvTranspose2d
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`ConvTranspose3d`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: ConvTranspose3d
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Pooling Layers
|
||||
----------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`MaxPool1d`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: MaxPool1d
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`MaxPool2d`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: MaxPool2d
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`MaxPool3d`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: MaxPool3d
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`MaxUnpool1d`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: MaxUnpool1d
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`MaxUnpool2d`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: MaxUnpool2d
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`MaxUnpool3d`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: MaxUnpool3d
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`AvgPool1d`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: AvgPool1d
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`AvgPool2d`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: AvgPool2d
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`AvgPool3d`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: AvgPool3d
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`FractionalMaxPool2d`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: FractionalMaxPool2d
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`LPPool2d`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: LPPool2d
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
Non-linear Activations
|
||||
----------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`ReLU`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: ReLU
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`ReLU6`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: ReLU6
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`ELU`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: ELU
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`PReLU`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: PReLU
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`LeakyReLU`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: LeakyReLU
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`Threshold`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: Threshold
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`Hardtanh`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: Hardtanh
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`Sigmoid`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: Sigmoid
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`Tanh`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: Tanh
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`LogSigmoid`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: LogSigmoid
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`Softplus`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: Softplus
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`Softshrink`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: Softshrink
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`Softsign`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: Softsign
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`Tanhshrink`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: Tanhshrink
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`Softmin`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: Softmin
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`Softmax`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: Softmax
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`LogSoftmax`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: LogSoftmax
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Normalization layers
|
||||
----------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`BatchNorm1d`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: BatchNorm1d
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`BatchNorm2d`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: BatchNorm2d
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`BatchNorm3d`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: BatchNorm3d
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Recurrent layers
|
||||
----------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`RNN`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: RNN
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`LSTM`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: LSTM
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`GRU`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: GRU
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`RNNCell`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: RNNCell
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`LSTMCell`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: LSTMCell
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`GRUCell`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: GRUCell
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
Linear layers
|
||||
----------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`Linear`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: Linear
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Dropout layers
|
||||
----------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`Dropout`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: Dropout
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`Dropout2d`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: Dropout2d
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`Dropout3d`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: Dropout3d
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Sparse layers
|
||||
----------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`Embedding`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: Embedding
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Loss functions
|
||||
----------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`L1Loss`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: L1Loss
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`MSELoss`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: MSELoss
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`CrossEntropyLoss`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: CrossEntropyLoss
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`NLLLoss`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: NLLLoss
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`KLDivLoss`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: KLDivLoss
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`BCELoss`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: BCELoss
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`MarginRankingLoss`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: MarginRankingLoss
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`HingeEmbeddingLoss`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: HingeEmbeddingLoss
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`MultiLabelMarginLoss`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: MultiLabelMarginLoss
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`SmoothL1Loss`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: SmoothL1Loss
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`SoftMarginLoss`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: SoftMarginLoss
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`MultiLabelSoftMarginLoss`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: MultiLabelSoftMarginLoss
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`CosineEmbeddingLoss`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: CosineEmbeddingLoss
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`MultiMarginLoss`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: MultiMarginLoss
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Vision layers
|
||||
----------------
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`PixelShuffle`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: PixelShuffle
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
Multi-GPU layers
|
||||
----------------
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`DataParallel`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: DataParallel
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
|
||||
torch.nn.functional
|
||||
===================
|
||||
|
||||
.. currentmodule:: torch.nn.functional
|
||||
|
||||
Convolution functions
|
||||
----------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`conv1d`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autofunction:: conv1d
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`conv2d`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autofunction:: conv2d
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`conv3d`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autofunction:: conv3d
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`conv_transpose1d`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autofunction:: conv_transpose1d
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`conv_transpose2d`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autofunction:: conv_transpose2d
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`conv_transpose3d`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autofunction:: conv_transpose3d
|
||||
|
||||
Pooling functions
|
||||
----------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`avg_pool1d`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autofunction:: avg_pool1d
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`avg_pool2d`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autofunction:: avg_pool2d
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`avg_pool3d`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autofunction:: avg_pool3d
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`max_pool1d`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autofunction:: max_pool1d
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`max_pool2d`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autofunction:: max_pool2d
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`max_pool3d`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autofunction:: max_pool3d
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`max_unpool1d`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autofunction:: max_unpool1d
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`max_unpool2d`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autofunction:: max_unpool2d
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`max_unpool3d`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autofunction:: max_unpool3d
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`lp_pool2d`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autofunction:: lp_pool2d
|
||||
|
||||
Non-linear activation functions
|
||||
-------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`threshold`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autofunction:: threshold
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`relu`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autofunction:: relu
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`hardtanh`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autofunction:: hardtanh
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`relu6`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autofunction:: relu6
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`elu`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autofunction:: elu
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`leaky_relu`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autofunction:: leaky_relu
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`prelu`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autofunction:: prelu
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`rrelu`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autofunction:: rrelu
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`logsigmoid`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autofunction:: logsigmoid
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`hardshrink`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autofunction:: hardshrink
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`tanhshrink`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autofunction:: tanhshrink
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`softsign`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autofunction:: softsign
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`softplus`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autofunction:: softplus
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`softmin`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autofunction:: softmin
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`softmax`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autofunction:: softmax
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`softshrink`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autofunction:: softshrink
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`log_softmax`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autofunction:: log_softmax
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`tanh`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autofunction:: tanh
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`sigmoid`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autofunction:: sigmoid
|
||||
|
||||
Normalization functions
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`batch_norm`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autofunction:: batch_norm
|
||||
|
||||
Linear functions
|
||||
----------------
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`linear`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autofunction:: linear
|
||||
|
||||
Dropout functions
|
||||
-----------------
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`dropout`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autofunction:: dropout
|
||||
|
||||
Loss functions
|
||||
--------------
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`nll_loss`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autofunction:: nll_loss
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`kl_div`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autofunction:: kl_div
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`cross_entropy`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autofunction:: cross_entropy
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`binary_cross_entropy`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autofunction:: binary_cross_entropy
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`smooth_l1_loss`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autofunction:: smooth_l1_loss
|
||||
|
||||
Vision functions
|
||||
----------------
|
||||
|
||||
:hidden:`pixel_shuffle`
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autofunction:: pixel_shuffle
|
||||
144
docs/source/notes/autograd.rst
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,144 @@
|
||||
Autograd mechanics
|
||||
==================
|
||||
|
||||
This note will present an overview of how autograd works and records the
|
||||
operations. It's not strictly necessary to understand all this, but we recommend
|
||||
getting familiar with it, as it will help you write more efficient, cleaner
|
||||
programs, and can aid you in debugging.
|
||||
|
||||
.. _excluding-subgraphs:
|
||||
|
||||
Excluding subgraphs from backward
|
||||
^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
|
||||
|
||||
Every Variable has two flags: :attr:`requires_grad` and :attr:`volatile`.
|
||||
They both allow for fine grained exclusion of subgraphs from gradient
|
||||
computation and can increase efficiency.
|
||||
|
||||
.. _excluding-requires_grad:
|
||||
|
||||
``requires_grad``
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
If there's a single input to an operation that requires gradient, its output
|
||||
will also require gradient. Conversely, only if all inputs don't require
|
||||
gradient, the output also won't require it. Backward computation is never
|
||||
performed in the subgraphs, where all Variables didn't require gradients.
|
||||
|
||||
.. code::
|
||||
|
||||
>>> x = Variable(torch.randn(5, 5))
|
||||
>>> y = Variable(torch.randn(5, 5))
|
||||
>>> z = Variable(torch.randn(5, 5), requires_grad=True)
|
||||
>>> a = x + y
|
||||
>>> a.requires_grad
|
||||
False
|
||||
>>> b = a + z
|
||||
>>> b.requires_grad
|
||||
True
|
||||
|
||||
This is especially useful when you want to freeze part of your model, or you
|
||||
know in advance that you're not going to use gradients w.r.t. some parameters.
|
||||
For example if you want to finetune a pretrained CNN, it's enough to switch the
|
||||
:attr:`requires_grad` flags in the frozen base, and no intermediate buffers will
|
||||
be saved, until the computation gets to the last layer, where the affine
|
||||
transform will use weights that require gradient, and the output of the network
|
||||
will also require them.
|
||||
|
||||
.. code::
|
||||
|
||||
model = torchvision.models.resnet18(pretrained=True)
|
||||
for param in model.parameters():
|
||||
param.requires_grad = False
|
||||
# Replace the last fully-connected layer
|
||||
# Parameters of newly constructed modules have requires_grad=True by default
|
||||
model.fc = nn.Linear(512, 100)
|
||||
|
||||
# Optimize only the classifier
|
||||
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.fc.parameters(), lr=1e-2, momentum=0.9)
|
||||
|
||||
``volatile``
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
Volatile is recommended for purely inference mode, when you're sure you won't
|
||||
be even calling `.backward()`. It's more efficient than any other autograd
|
||||
setting - it will use the absolute minimal amount of memory to evaluate the
|
||||
model. ``volatile`` also determines that ``requires_grad is False``.
|
||||
|
||||
Volatile differs from :ref:`excluding-requires_grad` in how the flag propagates.
|
||||
If there's even a single volatile input to an operation, its output is also
|
||||
going to be volatile. Volatility spreads accross the graph much easier than
|
||||
non-requiring gradient - you only need a **single** volatile leaf to have a
|
||||
volatile output, while you need **all** leaves to not require gradient to
|
||||
have an output the doesn't require gradient. Using volatile flag you don't
|
||||
need to change any settings of your model parameters to use it for
|
||||
inference. It's enough to create a volatile input, and this will ensure that
|
||||
no intermediate states are saved.
|
||||
|
||||
.. code::
|
||||
|
||||
>>> regular_input = Variable(torch.randn(5, 5))
|
||||
>>> volatile_input = Variable(torch.randn(5, 5), volatile=True)
|
||||
>>> model = torchvision.models.resnet18(pretrained=True)
|
||||
>>> model(regular_input).requires_grad
|
||||
True
|
||||
>>> model(volatile_input).requires_grad
|
||||
False
|
||||
>>> model(volatile_input).volatile
|
||||
True
|
||||
>>> model(volatile_input).creator is None
|
||||
True
|
||||
|
||||
How autograd encodes the history
|
||||
^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
|
||||
|
||||
Each Variable has a ``.creator`` attribute, that points to the function, of
|
||||
which it is an output. This is an entry point to a directed acyclic graph (DAG)
|
||||
consisting of :class:`Function` objects as nodes, and references between them
|
||||
being the edges. Every time an operation is performed, a new :class:`Function`
|
||||
representing it is instantiated, its :meth:`~torch.autograd.Function.forward`
|
||||
method is called, and its output :class:`Variable` s creators are set to it.
|
||||
Then, by following the path from any :class:`Variable` to the leaves, it is
|
||||
possible to reconstruct the sequence of operations that has created the data,
|
||||
and automatically compute the gradients.
|
||||
|
||||
An important thing to note is that the graph is recreated from scratch at every
|
||||
iteration, and this is exactly what allows for using arbitrary Python control
|
||||
flow statements, that can change the overall shape and size of the graph at
|
||||
every iteration. You don't have to encode all possible paths before you
|
||||
launch the training - what you run is what you differentiate.
|
||||
|
||||
In-place operations on Variables
|
||||
^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
|
||||
|
||||
Supporting in-place operations in autograd is a hard matter, and we discourage
|
||||
their use in most cases. Autograd's aggressive buffer freeing and reuse makes
|
||||
it very efficient and there are very few occasions when in-place operations
|
||||
actually lower memory usage by any significant amount. Unless you're operating
|
||||
under heavy memory pressure, you might never need to use them.
|
||||
|
||||
There are two main reasons that limit the applicability of in-place operations:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Overwriting values required to compute gradients. This is why variables don't
|
||||
support ``log_``. Its gradient formula requires the original input, and while
|
||||
it is possible to recreate it by computing the inverse operation, it is
|
||||
numerically unstable, and requires additional work that often defeats the
|
||||
purpose of using these functions.
|
||||
|
||||
2. Every in-place operation actually requires the implementation to rewrite the
|
||||
computational graph. Out-of-place versions simply allocate new objects and
|
||||
keep references to the old graph, while in-place operations, require
|
||||
changing the creator of all inputs to the :class:`Function` representing
|
||||
this operation. This can be tricky, especially if there are many Variables
|
||||
that reference the same storage (e.g. created by indexing or transposing),
|
||||
and in-place functions will actually raise an error if the storage of
|
||||
modified inputs is referenced by any other :class:`Variable`.
|
||||
|
||||
In-place correctness checks
|
||||
^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
|
||||
|
||||
Every variable keeps a version counter, that is incremented every time it's
|
||||
marked dirty in any operation. When a Function saves any tensors for backward,
|
||||
a version counter of their containing Variable is saved as well. Once you access
|
||||
``self.saved_tensors`` it is checked, and if it's greater than the saved value
|
||||
an error is raised.
|
||||
60
docs/source/notes/cuda.rst
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,60 @@
|
||||
CUDA semantics
|
||||
==============
|
||||
|
||||
:mod:`torch.cuda` keeps track of currently selected GPU, and all CUDA tensors
|
||||
you allocate will be created on it. The selected device can be changed with a
|
||||
:any:`torch.cuda.device` context manager.
|
||||
|
||||
However, once a tensor is allocated, you can do operations on it irrespectively
|
||||
of your selected device, and the results will be always placed in on the same
|
||||
device as the tensor.
|
||||
|
||||
Cross-GPU operations are not allowed by default, with the only exception of
|
||||
:meth:`~torch.Tensor.copy_`. Unless you enable peer-to-peer memory accesses
|
||||
any attempts to launch ops on tensors spread across different devices will
|
||||
raise an error.
|
||||
|
||||
Below you can find a small example showcasing this::
|
||||
|
||||
x = torch.cuda.FloatTensor(1)
|
||||
# x.get_device() == 0
|
||||
y = torch.FloatTensor(1).cuda()
|
||||
# y.get_device() == 0
|
||||
|
||||
with torch.cuda.device(1):
|
||||
# allocates a tensor on GPU 1
|
||||
a = torch.cuda.FloatTensor(1)
|
||||
|
||||
# transfers a tensor from CPU to GPU 1
|
||||
b = torch.FloatTensor(1).cuda()
|
||||
# a.get_device() == b.get_device() == 1
|
||||
|
||||
z = x + y
|
||||
# z.get_device() == 1
|
||||
|
||||
# even within a context, you can give a GPU id to the .cuda call
|
||||
c = torch.randn(2).cuda(2)
|
||||
# c.get_device() == 2
|
||||
|
||||
Best practices
|
||||
--------------
|
||||
|
||||
Use pinned memory buffers
|
||||
^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
|
||||
|
||||
.. warning:
|
||||
|
||||
This is an advanced tip. You overuse of pinned memory can cause serious
|
||||
problems if you'll be running low on RAM, and you should be aware that
|
||||
pinning is often an expensive operation.
|
||||
|
||||
Host to GPU copies are much faster when they originate from pinned (page-locked)
|
||||
memory. CPU tensors and storages expose a :meth:`~torch.Tensor.pin_memory`
|
||||
method, that returns a copy of the object, with data put in a pinned region.
|
||||
|
||||
Also, once you pin a tensor or storage, you can use asynchronous GPU copies.
|
||||
Just pass an additional ``async=True`` argument to a :meth:`~torch.Tensor.cuda`
|
||||
call. This can be used to overlap data transfers with computation.
|
||||
|
||||
You can make the :class:`~torch.utils.data.DataLoader` return batches placed in
|
||||
pinned memory by passing ``pinned=True`` to its constructor.
|
||||
156
docs/source/notes/extending.rst
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,156 @@
|
||||
Extending PyTorch
|
||||
=================
|
||||
|
||||
In this note we'll cover ways of extending :mod:`torch.nn`,
|
||||
:mod:`torch.autograd`, and writing custom C extensions utilizing our C
|
||||
libraries.
|
||||
|
||||
Extending :mod:`torch.autograd`
|
||||
-------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
.. currentmodule:: torch.autograd
|
||||
|
||||
Adding operations to :mod:`~torch.autograd` requires implementing a new
|
||||
:class:`Function` subclass for each operation. Recall that :class:`Function` s
|
||||
are what :mod:`~torch.autograd` uses to compute the results and gradients, and
|
||||
encode the operation history. Every new function requires you to implement 3
|
||||
methods:
|
||||
|
||||
- ``__init__`` (*optional*) - if your operation is parametrized by/uses
|
||||
objects different than :class:`Variable` s, you should pass them as arguments
|
||||
to ``__init__``. For example, ``AddConstant`` function takes a scalar to add,
|
||||
while ``Transpose`` requires specifying which two dimensions to swap. If your
|
||||
function doesn't require any additional parameters, you can skip it.
|
||||
- :meth:`~Function.forward` - the code that performs the operation. It can take
|
||||
as many arguments as you want, with some of them being
|
||||
optional, if you specify the default values. Keep in mind that only
|
||||
:class:`Variable` s will be passed in here. You can return either a single
|
||||
:class:`Variable` output, or a :class:`tuple` of :class:`Variable` s if there
|
||||
are multiple. Also, please refer to the docs of :class:`Function` to find
|
||||
descriptions of useful methods that can be called only from
|
||||
:meth:`~Function.forward`.
|
||||
- :meth:`~Function.backward` - gradient formula. It will be given
|
||||
as many arguments as there were outputs, with each of them representing
|
||||
gradient w.r.t. that output. It should return as many :class:`Tensor` s as
|
||||
there were inputs, with each of them containing the gradient w.r.t.
|
||||
corresponding input. If you inputs didn't require gradient (see
|
||||
:attr:`~Variable.needs_input_grad`), or it was non-differentiable, you
|
||||
can return :class:`None`. Also, if you have optional arguments to
|
||||
:meth:`~Variable.forward` you can return more gradients than there were
|
||||
inputs, as long as they're all :any:`python:None`.
|
||||
|
||||
Below you can find code for a ``Linear`` function from :mod:`torch.nn`, with
|
||||
additional comments::
|
||||
|
||||
# Inherit from Function
|
||||
class Linear(Function):
|
||||
|
||||
# bias is an optional argument
|
||||
def forward(self, input, weight, bias=None):
|
||||
self.save_for_backward(input, weight, bias)
|
||||
output = input.mm(weight.t())
|
||||
if bias is not None:
|
||||
output += bias.unsqueeze(0).expand_as(output)
|
||||
return output
|
||||
|
||||
# This function has only a single output, so it gets only one gradient
|
||||
def backward(self, grad_output):
|
||||
# This is a pattern that is very convenient - at the top of backward
|
||||
# unpack saved_tensors and initialize all gradients w.r.t. inputs to
|
||||
# None. Thanks to the fact that additional trailing Nones are
|
||||
# ignored, the return statement is simple even when the function has
|
||||
# optional inputs.
|
||||
input, weight, bias = self.saved_tensors
|
||||
grad_input = grad_weight = grad_bias = None
|
||||
|
||||
# These needs_input_grad checks are optional and there only to
|
||||
# improve efficiency. If you want to make your code simpler, you can
|
||||
# skip them. Returning gradients for inputs that don't require it is
|
||||
# not an error.
|
||||
if self.needs_input_grad[0]:
|
||||
grad_input = grad_output.mm(weight)
|
||||
if self.needs_input_grad[1]:
|
||||
grad_weight = grad_output.t().mm(input)
|
||||
if bias is not None and self.needs_input_grad[2]:
|
||||
grad_bias = grad_output.sum(0).squeeze(0)
|
||||
|
||||
return grad_input, grad_weight, grad_bias
|
||||
|
||||
Now, to make it easier to use these custom ops, we recommend wrapping them in
|
||||
small helper functions::
|
||||
|
||||
def linear(input, weight, bias=None):
|
||||
# First braces create a Function object. Any arguments given here
|
||||
# will be passed to __init__. Second braces will invoke the __call__
|
||||
# operator, that will then use forward() to compute the result and
|
||||
# return it.
|
||||
return Linear()(input, weight, bias)
|
||||
|
||||
Extending :mod:`torch.nn`
|
||||
-------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
.. currentmodule:: torch.nn
|
||||
|
||||
:mod:`~torch.nn` exports two kinds of interfaces - modules and their functional
|
||||
versions. You can extend it in both ways, but we recommend using modules for
|
||||
all kinds of layers, that hold any parameters or buffers, and recommend using
|
||||
a functional form parameter-less operations like activation functions, pooling,
|
||||
etc.
|
||||
|
||||
Adding a functional version of an operation is already fully covered in the
|
||||
section above.
|
||||
|
||||
Adding a :class:`Module`
|
||||
^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
|
||||
|
||||
Since :mod:`~torch.nn` heavily utilizes :mod:`~torch.autograd`, adding a new
|
||||
:class:`Module` requires implementing a :class:`~torch.autograd.Function`
|
||||
that performs the operation and can compute the gradient. From now on let's
|
||||
assume that we want to implement a ``Linear`` module and we have the function
|
||||
implementated as in the listing above. There's very little code required to
|
||||
add this. Now, there are two functions that need to be implemented:
|
||||
|
||||
- ``__init__`` (*optional*) - takes in arguments such as kernel sizes, numbers
|
||||
of features, etc. and initializes parameters and buffers.
|
||||
- :meth:`~Module.forward` - instantiates a :class:`~torch.autograd.Function` and
|
||||
uses it to perform the operation. It's very similar to a functional wrapper
|
||||
shown above.
|
||||
|
||||
This is how a ``Linear`` module can be implemented::
|
||||
|
||||
class Linear(nn.Module):
|
||||
def __init__(self, input_features, output_features, bias=True):
|
||||
self.input_features = input_features
|
||||
self.output_features = output_features
|
||||
|
||||
# nn.Parameter is a special kind of Variable, that will get
|
||||
# automatically registered as Module's parameter once it's assigned
|
||||
# as an attribute. Parameters and buffers need to be registered, or
|
||||
# they won't appear in .parameters() (doesn't apply to buffers), and
|
||||
# won't be converted when e.g. .cuda() is called. You can use
|
||||
# .register_buffer() to register buffers.
|
||||
# nn.Parameters can never be volatile and, different than Variables,
|
||||
# they require gradients by default.
|
||||
self.weight = nn.Parameter(torch.Tensor(input_features, output_features))
|
||||
if bias is not None:
|
||||
self.bias = nn.Parameter(torch.Tensor(output_features))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
# You should always register all possible parameters, but the
|
||||
# optional ones can be None if you want.
|
||||
self.register_parameter('bias', None)
|
||||
|
||||
# Not a very smart way to initialize weights
|
||||
self.weight.data.uniform_(-0.1, 0.1)
|
||||
if bias is not None:
|
||||
self.bias.data.uniform_(-0.1, 0.1)
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, input):
|
||||
# See the autograd section for explanation of what happens here.
|
||||
return Linear()(input, self.weight, self.bias)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Writing custom C extensions
|
||||
---------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Coming soon. For now you can find an example at
|
||||
`GitHub <https://github.com/pytorch/extension-ffi>`_.
|
||||
127
docs/source/notes/multiprocessing.rst
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,127 @@
|
||||
Multiprocessing best practices
|
||||
==============================
|
||||
|
||||
:mod:`torch.multiprocessing` is a drop in replacement for Python's
|
||||
:mod:`python:multiprocessing` module. It supports the exact same operations,
|
||||
but extends it, so that all tensors sent through a
|
||||
:class:`python:multiprocessing.Queue`, will have their data moved into shared
|
||||
memory and will only send a handle to another process.
|
||||
|
||||
.. note::
|
||||
|
||||
When a :class:`~torch.autograd.Variable` is sent to another process, both
|
||||
the :attr:`Variable.data` and :attr:`Variable.grad.data` are going to be
|
||||
shared.
|
||||
|
||||
This allows to implement various training methods, like Hogwild, A3C, or any
|
||||
others that require asynchronous operation.
|
||||
|
||||
Sharing CUDA tensors
|
||||
--------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Sharing CUDA tensors between processes is supported only in Python 3, using
|
||||
a ``spawn`` or ``forkserver`` start methods. :mod:`python:multiprocessing` in
|
||||
Python 2 can only create subprocesses using ``fork``, and it's not supported
|
||||
by the CUDA runtime.
|
||||
|
||||
.. warning::
|
||||
|
||||
CUDA API requires that the allocation exported to other processes remains
|
||||
valid as long as it's used by them. You should be careful and ensure that
|
||||
CUDA tensors you shared don't go out of scope as long as it's necessary.
|
||||
This shouldn't be a problem for sharing model parameters, but passing other
|
||||
kinds of data should be done with care. Note that this restriction doesn't
|
||||
apply to shared CPU memory.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Best practices and tips
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Avoiding and fighting deadlocks
|
||||
^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
|
||||
|
||||
There are a lot of things that can go wrong when a new process is spawned, with
|
||||
the most common cause of deadlocks being background threads. If there's any
|
||||
thread that holds a lock or imports a module, and ``fork`` is called, it's very
|
||||
likely that the subprocess will be in a corrupted state and will deadlock or
|
||||
fail in a different way. Note that even if you don't, Python built in
|
||||
libraries do - no need to look further than :mod:`python:multiprocessing`.
|
||||
:class:`python:multiprocessing.Queue` is actually a very complex class, that
|
||||
spawns multiple threads used to serialize, send and receive objects, and they
|
||||
can cause aforementioned problems too. If you find yourself in such situation
|
||||
try using a :class:`~python:multiprocessing.queues.SimpleQueue`, that doesn't
|
||||
use any additional threads.
|
||||
|
||||
We're trying our best to make it easy for you and ensure these deadlocks don't
|
||||
happen but some things are out of our control. If you have any issues you can't
|
||||
cope with for a while, try reaching out on forums, and we'll see if it's an
|
||||
issue we can fix.
|
||||
|
||||
Reuse buffers passed through a Queue
|
||||
^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
|
||||
|
||||
Remember that each time you put a :class:`~torch.Tensor` into a
|
||||
:class:`python:multiprocessing.Queue`, it has to be moved into shared memory.
|
||||
If it's already shared, it is a no-op, otherwise it will incur an additional
|
||||
memory copy that can slow down the whole process. Even if you have a pool of
|
||||
processes sending data to a single one, make it send the buffers back - this
|
||||
is nearly free and will let you avoid a copy when sending next batch.
|
||||
|
||||
Asynchronous multiprocess training (e.g. Hogwild)
|
||||
^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
|
||||
|
||||
Using :mod:`torch.multiprocessing`, it is possible to train a model
|
||||
asynchronously, with parameters either shared all the time, or being
|
||||
periodically synchronized. In the first case, we recommend sending over the whole
|
||||
model object, while in the latter, we advise to only send the
|
||||
:meth:`~torch.nn.Module.state_dict`.
|
||||
|
||||
We recommend using :class:`python:multiprocessing.Queue` for passing all kinds
|
||||
of PyTorch objects between processes. It is possible to e.g. inherit the tensors
|
||||
and storages already in shared memory, when using the ``fork`` start method,
|
||||
however it is very bug prone and should be used with care, and only by advanced
|
||||
users. Queues, even though they're sometimes a less elegant solution, will work
|
||||
properly in all cases.
|
||||
|
||||
.. warning::
|
||||
|
||||
You should be careful about having global statements, that are not guarded
|
||||
with an ``if __name__ == '__main__'``. If a different start method than
|
||||
``fork`` is used, they will be executed in all subprocesses.
|
||||
|
||||
Hogwild
|
||||
~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
A concrete Hogwild implementation can be found in the `examples repository`__,
|
||||
but to showcase the overall structure of the code, there's also a minimal
|
||||
example below as well::
|
||||
|
||||
import torch.multiprocessing as mp
|
||||
from model import MyModel
|
||||
|
||||
def train(model):
|
||||
# This for loop will break sharing of gradient buffers. It's not
|
||||
# necessary but it reduces the contention, and has a small memory cost
|
||||
# (equal to the total size of parameters).
|
||||
for param in model.parameters():
|
||||
param.grad.data = param.grad.data.clone()
|
||||
# Construct data_loader, optimizer, etc.
|
||||
for data, labels in data_loader:
|
||||
optimizer.zero_grad()
|
||||
loss_fn(model(data), labels).backward()
|
||||
optimizer.step() # This will update the shared parameters
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == '__main__':
|
||||
num_processes = 4
|
||||
model = MyModel()
|
||||
# NOTE: this is required for the ``fork`` method to work
|
||||
model.share_memory()
|
||||
processes = []
|
||||
for rank in range(num_processes):
|
||||
p = mp.Process(target=train, args=(model,))
|
||||
p.start()
|
||||
processes.append(p)
|
||||
for p in processes:
|
||||
p.join()
|
||||
|
||||
.. __: https://github.com/pytorch/examples/tree/master/mnist_hogwild
|
||||
114
docs/source/optim.rst
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,114 @@
|
||||
torch.optim
|
||||
===================================
|
||||
|
||||
.. automodule:: torch.optim
|
||||
|
||||
How to use an optimizer
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
|
||||
To use :mod:`torch.optim` you have to construct an optimizer object, that will hold
|
||||
the current state and will update the parameters based on the computed gradients.
|
||||
|
||||
Constructing it
|
||||
^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
|
||||
|
||||
To construct an :class:`Optimizer` you have to give it an iterable containing the
|
||||
parameters (all should be :class:`~torch.autograd.Variable` s) to optimize. Then,
|
||||
you can specify optimizer-specific options such as the learning rate, weight decay, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
Example::
|
||||
|
||||
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr = 0.01, momentum=0.9)
|
||||
optimizer = optim.Adam([var1, var2], lr = 0.0001)
|
||||
|
||||
Per-parameter options
|
||||
^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
|
||||
|
||||
:class:`Optimizer` s also support specifying per-parameter options. To do this, instead
|
||||
of passing an iterable of :class:`~torch.autograd.Variable` s, pass in an iterable of
|
||||
:class:`dict` s. Each of them will define a separate parameter group, and should contain
|
||||
a ``params`` key, containing a list of parameters belonging to it. Other keys
|
||||
should match the keyword arguments accepted by the optimizers, and will be used
|
||||
as optimization options for this group.
|
||||
|
||||
.. note::
|
||||
|
||||
You can still pass options as keyword arguments. They will be used as
|
||||
defaults, in the groups that didn't override them. This is useful when you
|
||||
only want to vary a single option, while keeping all others consistent
|
||||
between parameter groups.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
For example, this is very useful when one wants to specify per-layer learning rates::
|
||||
|
||||
optim.SGD([
|
||||
{'params': model.base.parameters()},
|
||||
{'params': model.classifier.parameters(), 'lr': 1e-3}
|
||||
], lr=1e-2, momentum=0.9)
|
||||
|
||||
This means that ``model.base``'s parameters will use the default learning rate of ``1e-2``,
|
||||
``model.classifier``'s parameters will use a learning rate of ``1e-3``, and a momentum of
|
||||
``0.9`` will be used for all parameters
|
||||
|
||||
Taking an optimization step
|
||||
^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
|
||||
|
||||
All optimizers implement a :func:`~Optimizer.step` method, that updates the
|
||||
parameters. It can be used in two ways:
|
||||
|
||||
``optimizer.step()``
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
This is a simplified version supported by most optimizers. The function can be
|
||||
called once the gradients are computed using e.g.
|
||||
:func:`~torch.autograd.Variable.backward`.
|
||||
|
||||
Example::
|
||||
|
||||
for input, target in dataset:
|
||||
optimizer.zero_grad()
|
||||
output = model(input)
|
||||
loss = loss_fn(output, target)
|
||||
loss.backward()
|
||||
optimizer.step()
|
||||
|
||||
``optimizer.step(closure)``
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
Some optimization algorithms such as Conjugate Gradient and LBFGS need to
|
||||
reevaluate the function multiple times, so you have to pass in a closure that
|
||||
allows them to recompute your model. The closure should clear the gradients,
|
||||
compute the loss, and return it.
|
||||
|
||||
Example::
|
||||
|
||||
for input, target in dataset:
|
||||
def closure():
|
||||
optimizer.zero_grad()
|
||||
output = model(input)
|
||||
loss = loss_fn(output, target)
|
||||
loss.backward()
|
||||
return loss
|
||||
optimizer.step(closure)
|
||||
|
||||
Algorithms
|
||||
----------
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: Optimizer
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
.. autoclass:: Adadelta
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
.. autoclass:: Adagrad
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
.. autoclass:: Adam
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
.. autoclass:: Adamax
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
.. autoclass:: ASGD
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
.. autoclass:: RMSprop
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
.. autoclass:: Rprop
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
.. autoclass:: SGD
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
12
docs/source/storage.rst
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,12 @@
|
||||
torch.Storage
|
||||
===================================
|
||||
|
||||
A :class:`torch.Storage` is a contiguous, one-dimensional array of a single
|
||||
data type.
|
||||
|
||||
Every :class:`torch.Tensor` has a corresponding storage of the same data type.
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: torch.FloatStorage
|
||||
:members:
|
||||
:undoc-members:
|
||||
:inherited-members:
|
||||
309
docs/source/tensors.rst
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,309 @@
|
||||
.. currentmodule:: torch
|
||||
|
||||
torch.Tensor
|
||||
===================================
|
||||
|
||||
A :class:`torch.Tensor` is a multi-dimensional matrix containing elements of
|
||||
a single data type.
|
||||
|
||||
Torch defines seven CPU tensor types and eight GPU tensor types:
|
||||
|
||||
======================== =========================== ================================
|
||||
Data type CPU tensor GPU tensor
|
||||
======================== =========================== ================================
|
||||
32-bit floating point :class:`torch.FloatTensor` :class:`torch.cuda.FloatTensor`
|
||||
64-bit floating point :class:`torch.DoubleTensor` :class:`torch.cuda.DoubleTensor`
|
||||
16-bit floating point N/A :class:`torch.cuda.HalfTensor`
|
||||
8-bit integer (signed) :class:`torch.ByteTensor` :class:`torch.cuda.ByteTensor`
|
||||
8-bit integer (unsigned) :class:`torch.CharTensor` :class:`torch.cuda.CharTensor`
|
||||
16-bit integer (signed) :class:`torch.ShortTensor` :class:`torch.cuda.ShortTensor`
|
||||
32-bit integer (signed) :class:`torch.IntTensor` :class:`torch.cuda.IntTensor`
|
||||
64-bit integer (signed) :class:`torch.LongTensor` :class:`torch.cuda.LongTensor`
|
||||
======================== =========================== ================================
|
||||
|
||||
The :class:`torch.Tensor` constructor is an alias for the default tensor type
|
||||
(:class:`torch.FloatTensor`).
|
||||
|
||||
A tensor can be constructed from a Python :class:`list` or sequence:
|
||||
|
||||
::
|
||||
|
||||
>>> torch.FloatTensor([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])
|
||||
1 2 3
|
||||
4 5 6
|
||||
[torch.FloatTensor of size 2x3]
|
||||
|
||||
An empty tensor can be constructed by specifying its size:
|
||||
|
||||
::
|
||||
|
||||
>>> torch.IntTensor(2, 4).zero_()
|
||||
0 0 0 0
|
||||
0 0 0 0
|
||||
[torch.IntTensor of size 2x4]
|
||||
|
||||
The contents of a tensor can be accessed and modified using Python's indexing
|
||||
and slicing notation:
|
||||
|
||||
::
|
||||
|
||||
>>> x = torch.FloatTensor([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])
|
||||
>>> print(x[1][2])
|
||||
6.0
|
||||
>>> x[0][1] = 8
|
||||
>>> print(x)
|
||||
1 8 3
|
||||
4 5 6
|
||||
[torch.FloatTensor of size 2x3]
|
||||
|
||||
Each tensor has an associated :class:`torch.Storage`, which holds its data.
|
||||
The tensor class provides multi-dimensional, `strided <https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stride_of_an_array>`_
|
||||
view of a storage and defines numeric operations on it.
|
||||
|
||||
.. note::
|
||||
Methods which mutate a tensor are marked with an underscore suffix.
|
||||
For example, :func:`torch.FloatTensor.abs_` computes the absolute value
|
||||
in-place and returns the modified tensor, while :func:`torch.FloatTensor.abs`
|
||||
computes the result in a new tensor.
|
||||
|
||||
.. class:: Tensor()
|
||||
Tensor(*sizes)
|
||||
Tensor(size)
|
||||
Tensor(sequence)
|
||||
Tensor(ndarray)
|
||||
Tensor(tensor)
|
||||
Tensor(storage)
|
||||
|
||||
Creates a new tensor from an optional size or data.
|
||||
|
||||
If no arguments are given, an empty zero-dimensional tensor is returned.
|
||||
If a :class:`numpy.ndarray`, :class:`torch.Tensor`, or :class:`torch.Storage`
|
||||
is given, a new tensor that shares the same data is returned. If a Python
|
||||
sequence is given, a new tensor is created from a copy of the sequence.
|
||||
|
||||
.. automethod:: abs
|
||||
.. automethod:: abs_
|
||||
.. automethod:: acos
|
||||
.. automethod:: acos_
|
||||
.. automethod:: add
|
||||
.. automethod:: add_
|
||||
.. automethod:: addbmm
|
||||
.. automethod:: addbmm_
|
||||
.. automethod:: addcdiv
|
||||
.. automethod:: addcdiv_
|
||||
.. automethod:: addcmul
|
||||
.. automethod:: addcmul_
|
||||
.. automethod:: addmm
|
||||
.. automethod:: addmm_
|
||||
.. automethod:: addmv
|
||||
.. automethod:: addmv_
|
||||
.. automethod:: addr
|
||||
.. automethod:: addr_
|
||||
.. automethod:: apply_
|
||||
.. automethod:: asin
|
||||
.. automethod:: asin_
|
||||
.. automethod:: atan
|
||||
.. automethod:: atan2
|
||||
.. automethod:: atan2_
|
||||
.. automethod:: atan_
|
||||
.. automethod:: baddbmm
|
||||
.. automethod:: baddbmm_
|
||||
.. automethod:: bernoulli
|
||||
.. automethod:: bernoulli_
|
||||
.. automethod:: bmm
|
||||
.. automethod:: byte
|
||||
.. automethod:: cauchy_
|
||||
.. automethod:: ceil
|
||||
.. automethod:: ceil_
|
||||
.. automethod:: char
|
||||
.. automethod:: chunk
|
||||
.. automethod:: clamp
|
||||
.. automethod:: clamp_
|
||||
.. automethod:: clone
|
||||
.. automethod:: contiguous
|
||||
.. automethod:: copy_
|
||||
.. automethod:: cos
|
||||
.. automethod:: cos_
|
||||
.. automethod:: cosh
|
||||
.. automethod:: cosh_
|
||||
.. automethod:: cpu
|
||||
.. automethod:: cross
|
||||
.. automethod:: cuda
|
||||
.. automethod:: cumprod
|
||||
.. automethod:: cumsum
|
||||
.. automethod:: data_ptr
|
||||
.. automethod:: diag
|
||||
.. automethod:: dim
|
||||
.. automethod:: dist
|
||||
.. automethod:: div
|
||||
.. automethod:: div_
|
||||
.. automethod:: dot
|
||||
.. automethod:: double
|
||||
.. automethod:: eig
|
||||
.. automethod:: element_size
|
||||
.. automethod:: eq
|
||||
.. automethod:: eq_
|
||||
.. automethod:: equal
|
||||
.. automethod:: exp
|
||||
.. automethod:: exp_
|
||||
.. automethod:: expand
|
||||
.. automethod:: expand_as
|
||||
.. automethod:: exponential_
|
||||
.. automethod:: fill_
|
||||
.. automethod:: float
|
||||
.. automethod:: floor
|
||||
.. automethod:: floor_
|
||||
.. automethod:: fmod
|
||||
.. automethod:: fmod_
|
||||
.. automethod:: frac
|
||||
.. automethod:: frac_
|
||||
.. automethod:: gather
|
||||
.. automethod:: ge
|
||||
.. automethod:: ge_
|
||||
.. automethod:: gels
|
||||
.. automethod:: geometric_
|
||||
.. automethod:: geqrf
|
||||
.. automethod:: ger
|
||||
.. automethod:: gesv
|
||||
.. automethod:: gt
|
||||
.. automethod:: gt_
|
||||
.. automethod:: half
|
||||
.. automethod:: histc
|
||||
.. automethod:: index
|
||||
.. automethod:: index_add_
|
||||
.. automethod:: index_copy_
|
||||
.. automethod:: index_fill_
|
||||
.. automethod:: index_select
|
||||
.. automethod:: int
|
||||
.. automethod:: inverse
|
||||
.. automethod:: is_contiguous
|
||||
.. autoattribute:: is_cuda
|
||||
:annotation:
|
||||
.. automethod:: is_pinned
|
||||
.. automethod:: is_set_to
|
||||
.. automethod:: is_signed
|
||||
.. automethod:: kthvalue
|
||||
.. automethod:: le
|
||||
.. automethod:: le_
|
||||
.. automethod:: lerp
|
||||
.. automethod:: lerp_
|
||||
.. automethod:: log
|
||||
.. automethod:: log1p
|
||||
.. automethod:: log1p_
|
||||
.. automethod:: log_
|
||||
.. automethod:: log_normal_
|
||||
.. automethod:: long
|
||||
.. automethod:: lt
|
||||
.. automethod:: lt_
|
||||
.. automethod:: map_
|
||||
.. automethod:: masked_copy_
|
||||
.. automethod:: masked_fill_
|
||||
.. automethod:: masked_select
|
||||
.. automethod:: max
|
||||
.. automethod:: mean
|
||||
.. automethod:: median
|
||||
.. automethod:: min
|
||||
.. automethod:: mm
|
||||
.. automethod:: mode
|
||||
.. automethod:: mul
|
||||
.. automethod:: mul_
|
||||
.. automethod:: multinomial
|
||||
.. automethod:: mv
|
||||
.. automethod:: narrow
|
||||
.. automethod:: ndimension
|
||||
.. automethod:: ne
|
||||
.. automethod:: ne_
|
||||
.. automethod:: neg
|
||||
.. automethod:: neg_
|
||||
.. automethod:: nelement
|
||||
.. automethod:: new
|
||||
.. automethod:: nonzero
|
||||
.. automethod:: norm
|
||||
.. automethod:: normal_
|
||||
.. automethod:: numel
|
||||
.. automethod:: numpy
|
||||
.. automethod:: orgqr
|
||||
.. automethod:: ormqr
|
||||
.. automethod:: permute
|
||||
.. automethod:: pin_memory
|
||||
.. automethod:: potrf
|
||||
.. automethod:: potri
|
||||
.. automethod:: potrs
|
||||
.. automethod:: pow
|
||||
.. automethod:: pow_
|
||||
.. automethod:: prod
|
||||
.. automethod:: pstrf
|
||||
.. automethod:: qr
|
||||
.. automethod:: random_
|
||||
.. automethod:: reciprocal
|
||||
.. automethod:: reciprocal_
|
||||
.. automethod:: remainder
|
||||
.. automethod:: remainder_
|
||||
.. automethod:: renorm
|
||||
.. automethod:: renorm_
|
||||
.. automethod:: repeat
|
||||
.. automethod:: resize_
|
||||
.. automethod:: resize_as_
|
||||
.. automethod:: round
|
||||
.. automethod:: round_
|
||||
.. automethod:: rsqrt
|
||||
.. automethod:: rsqrt_
|
||||
.. automethod:: scatter_
|
||||
.. automethod:: select
|
||||
.. automethod:: set_
|
||||
.. automethod:: set_index
|
||||
.. automethod:: share_memory_
|
||||
.. automethod:: short
|
||||
.. automethod:: sigmoid
|
||||
.. automethod:: sigmoid_
|
||||
.. automethod:: sign
|
||||
.. automethod:: sign_
|
||||
.. automethod:: sin
|
||||
.. automethod:: sin_
|
||||
.. automethod:: sinh
|
||||
.. automethod:: sinh_
|
||||
.. automethod:: size
|
||||
.. automethod:: sort
|
||||
.. automethod:: split
|
||||
.. automethod:: sqrt
|
||||
.. automethod:: sqrt_
|
||||
.. automethod:: squeeze
|
||||
.. automethod:: squeeze_
|
||||
.. automethod:: std
|
||||
.. automethod:: storage
|
||||
.. automethod:: storage_offset
|
||||
.. automethod:: storage_type
|
||||
.. automethod:: stride
|
||||
.. automethod:: sub
|
||||
.. automethod:: sub_
|
||||
.. automethod:: sum
|
||||
.. automethod:: svd
|
||||
.. automethod:: symeig
|
||||
.. automethod:: t
|
||||
.. automethod:: t_
|
||||
.. automethod:: tan
|
||||
.. automethod:: tan_
|
||||
.. automethod:: tanh
|
||||
.. automethod:: tanh_
|
||||
.. automethod:: tolist
|
||||
.. automethod:: topk
|
||||
.. automethod:: trace
|
||||
.. automethod:: transpose
|
||||
.. automethod:: transpose_
|
||||
.. automethod:: tril
|
||||
.. automethod:: tril_
|
||||
.. automethod:: triu
|
||||
.. automethod:: triu_
|
||||
.. automethod:: trtrs
|
||||
.. automethod:: trunc
|
||||
.. automethod:: trunc_
|
||||
.. automethod:: type
|
||||
.. automethod:: type_as
|
||||
.. automethod:: unfold
|
||||
.. automethod:: uniform_
|
||||
.. automethod:: unsqueeze
|
||||
.. automethod:: unsqueeze_
|
||||
.. automethod:: var
|
||||
.. automethod:: view
|
||||
.. automethod:: view_as
|
||||
.. automethod:: zero_
|
||||
179
docs/source/torch.rst
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,179 @@
|
||||
torch
|
||||
===================================
|
||||
.. automodule:: torch
|
||||
|
||||
Tensors
|
||||
----------------------------------
|
||||
.. autofunction:: is_tensor
|
||||
.. autofunction:: is_storage
|
||||
.. autofunction:: set_default_tensor_type
|
||||
.. autofunction:: numel
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Creation Ops
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
.. autofunction:: eye
|
||||
.. autofunction:: from_numpy
|
||||
.. autofunction:: linspace
|
||||
.. autofunction:: logspace
|
||||
.. autofunction:: ones
|
||||
.. autofunction:: rand
|
||||
.. autofunction:: randn
|
||||
.. autofunction:: randperm
|
||||
.. autofunction:: range
|
||||
.. autofunction:: zeros
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Indexing, Slicing, Joining, Mutating Ops
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
.. autofunction:: cat
|
||||
.. autofunction:: chunk
|
||||
.. autofunction:: gather
|
||||
.. autofunction:: index_select
|
||||
.. autofunction:: masked_select
|
||||
.. autofunction:: nonzero
|
||||
.. autofunction:: split
|
||||
.. autofunction:: squeeze
|
||||
.. autofunction:: stack
|
||||
.. autofunction:: t
|
||||
.. autofunction:: transpose
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Random sampling
|
||||
----------------------------------
|
||||
.. autofunction:: manual_seed
|
||||
.. autofunction:: initial_seed
|
||||
.. autofunction:: get_rng_state
|
||||
.. autofunction:: set_rng_state
|
||||
.. autodata:: default_generator
|
||||
.. autofunction:: bernoulli
|
||||
.. autofunction:: multinomial
|
||||
.. autofunction:: normal
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Serialization
|
||||
----------------------------------
|
||||
.. autofunction:: save
|
||||
.. autofunction:: load
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Parallelism
|
||||
----------------------------------
|
||||
.. autofunction:: get_num_threads
|
||||
.. autofunction:: set_num_threads
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Math operations
|
||||
----------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
Pointwise Ops
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autofunction:: abs
|
||||
.. autofunction:: acos
|
||||
.. autofunction:: add
|
||||
.. autofunction:: addcdiv
|
||||
.. autofunction:: addcmul
|
||||
.. autofunction:: asin
|
||||
.. autofunction:: atan
|
||||
.. autofunction:: atan2
|
||||
.. autofunction:: ceil
|
||||
.. autofunction:: clamp
|
||||
.. autofunction:: cos
|
||||
.. autofunction:: cosh
|
||||
.. autofunction:: div
|
||||
.. autofunction:: exp
|
||||
.. autofunction:: floor
|
||||
.. autofunction:: fmod
|
||||
.. autofunction:: frac
|
||||
.. autofunction:: lerp
|
||||
.. autofunction:: log
|
||||
.. autofunction:: log1p
|
||||
.. autofunction:: mul
|
||||
.. autofunction:: neg
|
||||
.. autofunction:: pow
|
||||
.. autofunction:: reciprocal
|
||||
.. autofunction:: remainder
|
||||
.. autofunction:: round
|
||||
.. autofunction:: rsqrt
|
||||
.. autofunction:: sigmoid
|
||||
.. autofunction:: sign
|
||||
.. autofunction:: sin
|
||||
.. autofunction:: sinh
|
||||
.. autofunction:: sqrt
|
||||
.. autofunction:: tan
|
||||
.. autofunction:: tanh
|
||||
.. autofunction:: trunc
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Reduction Ops
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
.. autofunction:: cumprod
|
||||
.. autofunction:: cumsum
|
||||
.. autofunction:: dist
|
||||
.. autofunction:: mean
|
||||
.. autofunction:: median
|
||||
.. autofunction:: mode
|
||||
.. autofunction:: norm
|
||||
.. autofunction:: prod
|
||||
.. autofunction:: std
|
||||
.. autofunction:: sum
|
||||
.. autofunction:: var
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Comparison Ops
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
.. autofunction:: eq
|
||||
.. autofunction:: equal
|
||||
.. autofunction:: ge
|
||||
.. autofunction:: gt
|
||||
.. autofunction:: kthvalue
|
||||
.. autofunction:: le
|
||||
.. autofunction:: lt
|
||||
.. autofunction:: max
|
||||
.. autofunction:: min
|
||||
.. autofunction:: ne
|
||||
.. autofunction:: sort
|
||||
.. autofunction:: topk
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Other Operations
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
.. autofunction:: cross
|
||||
.. autofunction:: diag
|
||||
.. autofunction:: histc
|
||||
.. autofunction:: renorm
|
||||
.. autofunction:: trace
|
||||
.. autofunction:: tril
|
||||
.. autofunction:: triu
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
BLAS and LAPACK Operations
|
||||
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
.. autofunction:: addbmm
|
||||
.. autofunction:: addmm
|
||||
.. autofunction:: addmv
|
||||
.. autofunction:: addr
|
||||
.. autofunction:: baddbmm
|
||||
.. autofunction:: bmm
|
||||
.. autofunction:: dot
|
||||
.. autofunction:: eig
|
||||
.. autofunction:: gels
|
||||
.. autofunction:: geqrf
|
||||
.. autofunction:: ger
|
||||
.. autofunction:: gesv
|
||||
.. autofunction:: inverse
|
||||
.. autofunction:: mm
|
||||
.. autofunction:: mv
|
||||
.. autofunction:: orgqr
|
||||
.. autofunction:: ormqr
|
||||
.. autofunction:: potrf
|
||||
.. autofunction:: potri
|
||||
.. autofunction:: potrs
|
||||
.. autofunction:: pstrf
|
||||
.. autofunction:: qr
|
||||
.. autofunction:: svd
|
||||
.. autofunction:: symeig
|
||||
.. autofunction:: trtrs
|
||||
|
||||
109
docs/source/torchvision/datasets.rst
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,109 @@
|
||||
torchvision.datasets
|
||||
====================
|
||||
|
||||
The following dataset loaders are available:
|
||||
|
||||
- `COCO (Captioning and Detection)`_
|
||||
- `LSUN Classification`_
|
||||
- `ImageFolder`_
|
||||
- `Imagenet-12`_
|
||||
- `CIFAR10 and CIFAR100`_
|
||||
|
||||
Datasets have the API:
|
||||
|
||||
- ``__getitem__``
|
||||
- ``__len__``
|
||||
They all subclass from ``torch.utils.data.Dataset``
|
||||
Hence, they can all be multi-threaded (python multiprocessing) using
|
||||
standard torch.utils.data.DataLoader.
|
||||
|
||||
For example:
|
||||
|
||||
``torch.utils.data.DataLoader(coco_cap, batch_size=args.batchSize, shuffle=True, num_workers=args.nThreads)``
|
||||
|
||||
In the constructor, each dataset has a slightly different API as needed,
|
||||
but they all take the keyword args:
|
||||
|
||||
- ``transform`` - a function that takes in an image and returns a
|
||||
transformed version
|
||||
- common stuff like ``ToTensor``, ``RandomCrop``, etc. These can be
|
||||
composed together with ``transforms.Compose`` (see transforms section
|
||||
below)
|
||||
- ``target_transform`` - a function that takes in the target and
|
||||
transforms it. For example, take in the caption string and return a
|
||||
tensor of word indices.
|
||||
|
||||
COCO
|
||||
~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
This requires the `COCO API to be installed`_
|
||||
|
||||
Captions:
|
||||
^^^^^^^^^
|
||||
|
||||
``dset.CocoCaptions(root="dir where images are", annFile="json annotation file", [transform, target_transform])``
|
||||
|
||||
Example:
|
||||
|
||||
.. code:: python
|
||||
|
||||
import torchvision.datasets as dset
|
||||
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
|
||||
cap = dset.CocoCaptions(root = 'dir where images are',
|
||||
annFile = 'json annotation file',
|
||||
transform=transforms.ToTensor())
|
||||
|
||||
print('Number of samples: ', len(cap))
|
||||
img, target = cap[3] # load 4th sample
|
||||
|
||||
print("Image Size: ", img.size())
|
||||
print(target)
|
||||
|
||||
Output:
|
||||
|
||||
::
|
||||
|
||||
Number of samples: 82783
|
||||
Image Size: (3L, 427L, 640L)
|
||||
[u'A plane emitting smoke stream flying over a mountain.',
|
||||
u'A plane darts across a bright blue sky behind a mountain covered in snow',
|
||||
u'A plane leaves a contrail above the snowy mountain top.',
|
||||
u'A mountain that has a plane flying overheard in the distance.',
|
||||
u'A mountain view with a plume of smoke in the background']
|
||||
|
||||
Detection:
|
||||
^^^^^^^^^^
|
||||
|
||||
``dset.CocoDetection(root="dir where images are", annFile="json annotation file", [transform, target_transform])``
|
||||
|
||||
LSUN
|
||||
~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
``dset.LSUN(db_path, classes='train', [transform, target_transform])``
|
||||
|
||||
- db\_path = root directory for the database files
|
||||
- classes =
|
||||
- ‘train’ - all categories, training set
|
||||
- ‘val’ - all categories, validation set
|
||||
- ‘test’ - all categories, test set
|
||||
- [‘bedroom\_train’, ‘church\_train’, …] : a list of categories to load
|
||||
|
||||
CIFAR
|
||||
~~~~~
|
||||
|
||||
``dset.CIFAR10(root, train=True, transform=None, target_transform=None, download=False)``
|
||||
|
||||
``dset.CIFAR100(root, train=True, transform=None, target_transform=None, download=False)``
|
||||
|
||||
- ``root`` : root directory of dataset where there is folder
|
||||
``cifar-10-batches-py``
|
||||
- ``train`` : ``True`` = Training set, ``False`` = Test set
|
||||
- ``download`` : ``True`` = downloads the dataset from the internet and
|
||||
puts it in root directory. If dataset already downloaded, do
|
||||
|
||||
.. _COCO (Captioning and Detection): #coco
|
||||
.. _LSUN Classification: #lsun
|
||||
.. _ImageFolder: #imagefolder
|
||||
.. _Imagenet-12: #imagenet-12
|
||||
.. _CIFAR10 and CIFAR100: #cifar
|
||||
.. _COCO API to be installed: https://github.com/pdollar/coco/tree/master/PythonAPI
|
||||
11
docs/source/torchvision/models.rst
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,11 @@
|
||||
torchvision.models
|
||||
===================
|
||||
|
||||
.. currentmodule:: torchvision.models
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
.. automodule:: torchvision.models
|
||||
:members: alexnet, resnet18, resnet34, resnet50, resnet101, resnet152,
|
||||
vgg11, vgg11_bn, vgg13, vgg13_bn, vgg16, vgg16_bn, vgg19,
|
||||
vgg19_bn
|
||||
:undoc-members:
|
||||
5
docs/source/torchvision/torchvision.rst
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,5 @@
|
||||
torchvision
|
||||
===================
|
||||
|
||||
The :mod:`torchvision` package consists of popular datasets, model
|
||||
architectures, and common image transformations for computer vision.
|
||||
40
docs/source/torchvision/transforms.rst
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,40 @@
|
||||
torchvision.transforms
|
||||
======================
|
||||
|
||||
.. currentmodule:: torchvision.transforms
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: Compose
|
||||
|
||||
Transforms on PIL.Image
|
||||
-----------------------
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: Scale
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: CenterCrop
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: RandomCrop
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: RandomHorizontalFlip
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: RandomSizedCrop
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: Pad
|
||||
|
||||
Transforms on torch.\*Tensor
|
||||
----------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: Normalize
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Conversion Transforms
|
||||
---------------------
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: ToTensor
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: ToPILImage
|
||||
|
||||
Generic Transofrms
|
||||
------------------
|
||||
|
||||
.. autoclass:: Lambda
|
||||
|
||||
9
docs/source/torchvision/utils.rst
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,9 @@
|
||||
torchvision.utils
|
||||
===================
|
||||
|
||||
.. currentmodule:: torchvision.utils
|
||||
|
||||
.. autofunction:: make_grid
|
||||
|
||||
.. autofunction:: save_image
|
||||
|
||||
407
docs/tensor.md
@ -1,407 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# Tensors
|
||||
|
||||
A `Tensor` is a potentially multi-dimensional matrix.
|
||||
The number of dimensions is unlimited.
|
||||
|
||||
The `Tensor` set of classes are probably the most important class in
|
||||
`torch`. Almost every package depends on these classes. They are *__the__*
|
||||
class for handling numeric data. As with pretty much anything in
|
||||
[torch], tensors are serializable with `torch.save` and `torch.load`
|
||||
|
||||
There are 7 Tensor classes in torch:
|
||||
|
||||
- `torch.FloatTensor` : Signed 32-bit floating point tensor
|
||||
- `torch.DoubleTensor` : Signed 64-bit floating point tensor
|
||||
- `torch.ByteTensor` : Signed 8-bit integer tensor
|
||||
- `torch.CharTensor` : Unsigned 8-bit integer tensor
|
||||
- `torch.ShortTensor` : Signed 16-bit integer tensor
|
||||
- `torch.IntTensor` : Signed 32-bit integer tensor
|
||||
- `torch.LongTensor` : Signed 64-bit integer tensor
|
||||
|
||||
The data in these tensors lives on the system memory connected to your CPU.
|
||||
|
||||
Most numeric operations are implemented _only_ for `FloatTensor` and `DoubleTensor`.
|
||||
Other Tensor types are useful if you want to save memory space or specifically
|
||||
do integer operations.
|
||||
|
||||
The number of dimensions of a `Tensor` can be queried by
|
||||
`ndimension()` or `dim()`. Size of the `i-th` dimension is
|
||||
returned by `size(i)`. A tuple containing the size of all the dimensions
|
||||
can be returned by `size()`.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
# allocate a matrix of shape 3x4
|
||||
a = torch.FloatTensor(3, 4)
|
||||
print(a)
|
||||
|
||||
# convert this into a LongTensor
|
||||
b = a.long()
|
||||
print(b)
|
||||
|
||||
# print the size of the tensor
|
||||
print(a.size())
|
||||
|
||||
# print the number of dimensions
|
||||
print(a.dim())
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
These tensors can be converted to numpy arrays very efficiently
|
||||
with zero memory copies.
|
||||
For this, the two provided functions are `.numpy()` and `torch.from_numpy()`
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
|
||||
# convert to numpy
|
||||
c = a.numpy()
|
||||
print(type(c))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
When using GPUs, each of the classes above has an equivalent
|
||||
class such as: `torch.cuda.FloatTensor`, `torch.cuda.LongTensor`, etc.
|
||||
When one allocates a CUDA tensor, the data in these tensors lives in the
|
||||
GPU memory.
|
||||
|
||||
One can seamlessly transfer a tensor from the CPU to the GPU, as well as
|
||||
between different GPUs on your machine.
|
||||
|
||||
Apart from the above 7 tensor types, there is one additional tensor type on the GPU
|
||||
|
||||
- `torch.cuda.HalfTensor` : Signed 16-bit floating point tensor
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch.cuda
|
||||
|
||||
# allocate a matrix of shape 3x4
|
||||
a = torch.cuda.FloatTensor(3, 4)
|
||||
print(a)
|
||||
|
||||
# transfer this to the CPU
|
||||
b = a.cpu()
|
||||
print(b)
|
||||
|
||||
# transfer this back to the GPU-1
|
||||
a = b.cuda()
|
||||
print(a)
|
||||
|
||||
# transfer this to GPU-2
|
||||
b = a.cuda(1)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Internal data representation
|
||||
|
||||
The actual data of a `Tensor` is contained into a
|
||||
`Storage`. It can be accessed using
|
||||
`storage()`. While the memory of a
|
||||
`Tensor` has to be contained in this unique `Storage`, it might
|
||||
not be contiguous: the first position used in the `Storage` is given
|
||||
by `storage_offset()` (starting at `0`).
|
||||
And the _jump_ needed to go from one element to another
|
||||
element in the `i-th` dimension is given by
|
||||
`stride(i-1)`. See the code example for an illustration.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# given a 3d tensor
|
||||
x = torch.FloatTensor(7,7,7)
|
||||
|
||||
# accessing the element `(3,4,5)` can be done by
|
||||
x[3 - 1][4 - 1][5 - 1]
|
||||
# or equivalently (but slowly!)
|
||||
x.storage()[x.storageOffset()
|
||||
+ (3 - 1) * x.stride(0)
|
||||
+ (4 - 1) * x.stride(1)
|
||||
+ (5 - 1) * x.stride(2)]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
One could say that a `Tensor` is a particular way of _viewing_ a
|
||||
`Storage`: a `Storage` only represents a chunk of memory, while the
|
||||
`Tensor` interprets this chunk of memory as having dimensions:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# a tensor interprets a chunk of memory as having dimensions
|
||||
>>> x = torch.Tensor(4,5)
|
||||
>>> s = x.storage()
|
||||
>>> for i in range(s.size()): # fill up the Storage
|
||||
>>> s[i] = i
|
||||
|
||||
# s is interpreted by x as a 2D matrix
|
||||
>>> print(x)
|
||||
|
||||
1 2 3 4 5
|
||||
6 7 8 9 10
|
||||
11 12 13 14 15
|
||||
16 17 18 19 20
|
||||
[torch.FloatTensor of dimension 4x5]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Note also that in Torch7 ___elements in the same row___ [elements along the __last__ dimension]
|
||||
are contiguous in memory for a matrix [tensor]:
|
||||
|
||||
This is exactly like in `C` and `numpy` (and not `Fortran`).
|
||||
|
||||
## Default Tensor type
|
||||
|
||||
For convenience, _an alias_ `torch.Tensor` is provided, which allows the user to write
|
||||
type-independent scripts, which can then ran after choosing the desired Tensor type with
|
||||
a call like
|
||||
|
||||
`torch.set_default_tensor_type('torch.DoubleTensor')`
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
By default, the alias points to `torch.FloatTensor`.
|
||||
|
||||
## Efficient memory management
|
||||
|
||||
_All_ tensor operations post-fixed with an underscore (for example `.fill_`)
|
||||
do _not_ make any memory copy. All these methods transform the existing tensor.
|
||||
Tensor methods such as `narrow` and `select` return a new tensor referencing _the same storage_.
|
||||
This magical behavior is internally obtained by good usage of the `stride()` and
|
||||
`storage_offset()`. See the code example illustrating this.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> x = torch.Tensor(5).zero_()
|
||||
>>> print(x)
|
||||
0
|
||||
0
|
||||
0
|
||||
0
|
||||
0
|
||||
[torch.FloatTensor of dimension 5]
|
||||
>>> x.narrow(0, 1, 2).fill_(1)
|
||||
>>> # narrow() returns a Tensor referencing the same Storage as x
|
||||
>>> print(x)
|
||||
0
|
||||
1
|
||||
1
|
||||
1
|
||||
0
|
||||
[torch.FloatTensor of dimension 5]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you really need to copy a `Tensor`, you can use the `copy_()` method:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# making a copy of a tensor
|
||||
y = x.new(x.size()).copy_(x)
|
||||
y = x.clone()
|
||||
```
|
||||
Or the convenience method `clone()`
|
||||
|
||||
We now describe all the methods for `Tensor`. If you want to specify the Tensor type,
|
||||
just replace `Tensor` by the name of the Tensor variant (like `CharTensor`).
|
||||
|
||||
## Constructors ##
|
||||
|
||||
Tensor constructors, create new Tensor object, optionally, allocating
|
||||
new memory. By default the elements of a newly allocated memory are
|
||||
not initialized, therefore, might contain arbitrary numbers. Here are
|
||||
several ways to construct a new `Tensor`.
|
||||
|
||||
### torch.Tensor() ###
|
||||
|
||||
Returns an empty tensor.
|
||||
|
||||
### torch.Tensor(tensor) ###
|
||||
|
||||
Returns a new tensor which reference the same `Storage` than the given `tensor`.
|
||||
The `size`, `stride`, and `storage_offset` are the same than the given tensor.
|
||||
|
||||
The new `Tensor` is now going to "view" the same `storage`
|
||||
as the given `tensor`. As a result, any modification in the elements
|
||||
of the `Tensor` will have a impact on the elements of the given
|
||||
`tensor`, and vice-versa. No memory copy!
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> x = torch.Tensor(2,5).fill_(3.14)
|
||||
>>> x
|
||||
3.1400 3.1400 3.1400 3.1400 3.1400
|
||||
3.1400 3.1400 3.1400 3.1400 3.1400
|
||||
[torch.FloatTensor of dimension 2x5]
|
||||
|
||||
>>> y = torch.Tensor(x)
|
||||
>>> y
|
||||
3.1400 3.1400 3.1400 3.1400 3.1400
|
||||
3.1400 3.1400 3.1400 3.1400 3.1400
|
||||
[torch.FloatTensor of dimension 2x5]
|
||||
|
||||
>>> y.zero_()
|
||||
>>> x # elements of x are the same as y!
|
||||
0 0 0 0 0
|
||||
0 0 0 0 0
|
||||
[torch.FloatTensor of dimension 2x5]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### torch.Tensor(sz1 [,sz2 [,sz3 [,sz4 [,sz5 ...]]]]]) ###
|
||||
|
||||
Create a tensor of the given sizes.
|
||||
The tensor size will be `sz1 x sz2 x sx3 x sz4 x sz5 x ...`.
|
||||
|
||||
### torch.Tensor(sizes) ###
|
||||
|
||||
Create a tensor of any number of dimensions. `sizes` gives the size in each dimension of
|
||||
the tensor and is of type `torch.Size`.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
Example, create a 4D 4x4x3x2 tensor:
|
||||
x = torch.Tensor(torch.Size([4,4,3,2]))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### torch.Tensor(storage) ###
|
||||
|
||||
Returns a tensor which uses the existing `Storage` starting at a storage offset of 0.
|
||||
|
||||
### torch.Tensor(sequence) ###
|
||||
|
||||
One can create a tensor from a python sequence.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, you can create a `Tensor` from a `list` or a `tuple`
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# create a 2d tensor from a list of lists
|
||||
>>> torch.Tensor([[1,2,3,4], [5,6,7,8]])
|
||||
1 2 3 4
|
||||
5 6 7 8
|
||||
[torch.FloatTensor of dimension 2x4]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### torch.Tensor(ndarray) ###
|
||||
|
||||
Creates a `Tensor` from a NumPy `ndarray`.
|
||||
If the `dtype` of the `ndarray` is the same as the type of the `Tensor` being created,
|
||||
The underlying memory of both are shared, i.e. if the value of an element
|
||||
in the `ndarray` is changed, the corresponding value in the `Tensor` changes,
|
||||
and vice versa.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# create a ndarray of dtype=int64
|
||||
>>> a = np.random.randint(2, size=10)
|
||||
>>> a
|
||||
array([0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0])
|
||||
# create a LongTensor. Since they are the same type (int64), the memory is shared
|
||||
>>> b = torch.LongTensor(a)
|
||||
0
|
||||
0
|
||||
1
|
||||
1
|
||||
0
|
||||
1
|
||||
1
|
||||
0
|
||||
0
|
||||
0
|
||||
[torch.LongTensor of size 10]
|
||||
>>> b[3] = 100
|
||||
>>> print(a[3])
|
||||
100
|
||||
|
||||
# now create an IntTensor from the same ndarray.
|
||||
# The memory is not shared in this case as the dtype=int64 != IntTensor (int32)
|
||||
>>> b = torch.IntTensor(a)
|
||||
>>> b[3] = 30000
|
||||
>>> print(a[3])
|
||||
100
|
||||
# a did not change to the value 30000
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## NumPy Conversion ##
|
||||
### torch.from_numpy(ndarray)
|
||||
|
||||
This is a convenience function similar to the constructor above.
|
||||
Given a numpy `ndarray`, it constructs a torch `Tensor` of the same `dtype`
|
||||
as the numpy array.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, passing in an ndarray of dtype=float64 will create a torch.DoubleTensor
|
||||
|
||||
### Tensor.numpy()
|
||||
|
||||
This is a member function on a tensor that converts a torch `Tensor` to a
|
||||
numpy `ndarray`. The memory of the data of both objects is shared.
|
||||
Hence, changing a value in the `Tensor` will change the corresponding value in
|
||||
the `ndarray` and vice versa.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> a = torch.randn(3,4)
|
||||
>>> b = a.numpy() # creates a numpy array with dtype=float32 in this case
|
||||
>>> print(a)
|
||||
-1.0453 1.4730 -1.8990 -0.7763
|
||||
1.8155 1.4004 -1.5286 1.0420
|
||||
0.6551 1.0258 0.1152 -0.3239
|
||||
[torch.FloatTensor of size 3x4]
|
||||
>>> print(b)
|
||||
[[-1.04525673 1.4730444 -1.89899576 -0.77626842]
|
||||
[ 1.81549406 1.40035892 -1.5286355 1.04199517]
|
||||
[ 0.6551016 1.02575183 0.11520521 -0.32391372]]
|
||||
>>> a[2][2] = 1000
|
||||
>>> print(b)
|
||||
[[ -1.04525673e+00 1.47304440e+00 -1.89899576e+00 -7.76268423e-01]
|
||||
[ 1.81549406e+00 1.40035892e+00 -1.52863550e+00 1.04199517e+00]
|
||||
[ 6.55101597e-01 1.02575183e+00 1.00000000e+03 -3.23913723e-01]]
|
||||
# notice that b[2][2] has changed to the value 1000 too.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### torch.is_tensor(obj)
|
||||
|
||||
Returns True if the passed-in object is a `Tensor` (of any type). Returns `False` otherwise.
|
||||
|
||||
### torch.is_storage
|
||||
|
||||
Returns True if the passed-in object is a `Storage` (of any type). Returns `False` otherwise.
|
||||
|
||||
### torch.expand_as
|
||||
### torch.expand
|
||||
### torch.view
|
||||
### torch.view_as
|
||||
### torch.permute
|
||||
### torch.pin_memory
|
||||
### copy
|
||||
### split
|
||||
### chunk
|
||||
### tolist
|
||||
### repeat
|
||||
### unsqueeze
|
||||
### unsqueeze_
|
||||
### add, iadd, sub, isub, mul, imul, matmul, div, rdiv, idiv, mod, neg
|
||||
|
||||
## GPU Semantics ##
|
||||
|
||||
When you create a `torch.cuda.*Tensor`, it is allocated on the current GPU.
|
||||
However, you could allocate it on another GPU as well, using the `with torch.cuda.device(id)` context.
|
||||
All allocations within this context will be placed on the GPU `id`.
|
||||
|
||||
Once `Tensor`s are allocated, you can do operations on them from any GPU context, and the results will be placed on the same device as where the source `Tensor` is located.
|
||||
|
||||
For example if Tensor `a` and `b` are on GPU-2, but the GPU-1 is the current device.
|
||||
If one does `c = a + b`, then `c` will be on GPU-2, regardless of what the current device is.
|
||||
|
||||
Cross-GPU operations are not allowed. The only Cross-GPU operation allowed is `copy`.
|
||||
|
||||
If `a` is on GPU-1 and `b` is on GPU-2, then `c = a + b` will result in an error.
|
||||
|
||||
See the example for more clarity on these semantics.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# Tensors are allocated on GPU 1 by default
|
||||
x = torch.cuda.FloatTensor(1)
|
||||
# x.get_device() == 0
|
||||
y = torch.FloatTensor(1).cuda()
|
||||
# y.get_device() == 0
|
||||
|
||||
with torch.cuda.device(1):
|
||||
# allocates a tensor on GPU 2
|
||||
a = torch.cuda.FloatTensor(1)
|
||||
|
||||
# transfers a tensor from CPU to GPU-2
|
||||
b = torch.FloatTensor(1).cuda()
|
||||
# a.get_device() == b.get_device() == 1
|
||||
|
||||
z = x + y
|
||||
# z.get_device() == 1
|
||||
|
||||
# even within a context, you can give a GPU id to the .cuda call
|
||||
c = torch.randn(2).cuda(2)
|
||||
# c.get_device() == 2
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2460
docs/tensor_ref.md
@ -1,83 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# torch
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# load torch with
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# load the CUDA features of torch with
|
||||
import torch.cuda
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
__torch__ is the main package where data structures for multi-dimensional
|
||||
tensors and mathematical operations over these are defined.
|
||||
Additionally, it provides many utilities for efficient serializing of
|
||||
Tensors and arbitrary types, and other useful utilities.
|
||||
|
||||
It has a CUDA counterpart, that enables you to run your tensor computations
|
||||
on an NVIDIA GPU with compute capability >= 2.0.
|
||||
|
||||
## Multi-core
|
||||
### torch.get_num_threads()
|
||||
|
||||
Gets the number of OpenMP threads that will be used for parallelizing CPU operations
|
||||
|
||||
### torch.set_num_threads(n)
|
||||
|
||||
Sets the number of OpenMP threads to use for parallelizing CPU operations
|
||||
|
||||
## Serialization
|
||||
### torch.save(object, file)
|
||||
This function pickles a Python object to the `file`. `file` is either a filename or a file handle.
|
||||
|
||||
`object` can be a picklable python object, including `torch` `Tensor`s, autograd `Variable`, nn `Module`s etc.
|
||||
|
||||
When a group of `torch` `Tensor`s are saved together, and if any of them share the same storages, then this sharing is preserved during saving and loading back.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### torch.load(file)
|
||||
|
||||
This function unpickles objects that have been pickled with `torch.save`
|
||||
|
||||
## Random Numbers
|
||||
|
||||
### torch.get_rng_state()
|
||||
|
||||
Gets the current state of the torch Random Number Generator.
|
||||
|
||||
This can be passed in the future to `torch.set_rng_state` to restore the current RNG state.
|
||||
|
||||
### torch.set_rng_state(state)
|
||||
|
||||
Sets the current state of the torch Random Number Generator to the given `state`.
|
||||
|
||||
### torch.manual_seed(number)
|
||||
|
||||
Sets the initial seed of the random number generator to a given number.
|
||||
|
||||
### torch.initial_seed()
|
||||
|
||||
Returns the number that is the initial seed to the Random Number Generator
|
||||
|
||||
## CUDA
|
||||
### torch.cuda.is_available()
|
||||
|
||||
Returns `True` if CUDA is available and usable. Returns `False` otherwise.
|
||||
|
||||
### torch.cuda.device_count()
|
||||
|
||||
Returns the number of CUDA devices on the system.
|
||||
|
||||
### torch.cuda.current_device()
|
||||
|
||||
Returns the device index of the current default CUDA device.
|
||||
|
||||
### torch.cuda.synchronize()
|
||||
|
||||
This function issues a `cudaDeviceSynchronize` on the current device, and hence waits for all in-flight CUDA computation to finish.
|
||||
|
||||
### torch.cuda.current_stream()
|
||||
|
||||
Returns the handle to the current stream of the CUDA context.
|
||||
|
||||
80
setup.py
@ -9,10 +9,10 @@ import shutil
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
import os
|
||||
|
||||
CUDA_HOME = os.getenv('CUDA_HOME', '/usr/local/cuda')
|
||||
WITH_CUDA = os.path.exists(CUDA_HOME)
|
||||
WITH_CUDNN = WITH_CUDA
|
||||
DEBUG = False
|
||||
from tools.setup_helpers.env import check_env_flag
|
||||
from tools.setup_helpers.cuda import WITH_CUDA, CUDA_HOME
|
||||
from tools.setup_helpers.cudnn import WITH_CUDNN, CUDNN_LIB_DIR, CUDNN_INCLUDE_DIR
|
||||
DEBUG = check_env_flag('DEBUG')
|
||||
|
||||
################################################################################
|
||||
# Monkey-patch setuptools to compile in parallel
|
||||
@ -74,6 +74,20 @@ class build_module(Command):
|
||||
|
||||
class build_ext(setuptools.command.build_ext.build_ext):
|
||||
def run(self):
|
||||
# Print build options
|
||||
if WITH_NUMPY:
|
||||
print('-- Building with NumPy bindings')
|
||||
else:
|
||||
print('-- NumPy not found')
|
||||
if WITH_CUDNN:
|
||||
print('-- Detected cuDNN at ' + CUDNN_LIB_DIR + ', ' + CUDNN_INCLUDE_DIR)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
print('-- Not using cuDNN')
|
||||
if WITH_CUDA:
|
||||
print('-- Detected CUDA at ' + CUDA_HOME)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
print('-- Not using CUDA')
|
||||
|
||||
# cwrap depends on pyyaml, so we can't import it earlier
|
||||
from tools.cwrap import cwrap
|
||||
from tools.cwrap.plugins.THPPlugin import THPPlugin
|
||||
@ -83,9 +97,10 @@ class build_ext(setuptools.command.build_ext.build_ext):
|
||||
from tools.cwrap.plugins.KwargsPlugin import KwargsPlugin
|
||||
from tools.cwrap.plugins.NullableArguments import NullableArguments
|
||||
from tools.cwrap.plugins.CuDNNPlugin import CuDNNPlugin
|
||||
thp_plugin = THPPlugin()
|
||||
cwrap('torch/csrc/generic/TensorMethods.cwrap', plugins=[
|
||||
BoolOption(), THPPlugin(), AutoGPU(condition='IS_CUDA'),
|
||||
ArgcountSortPlugin(), KwargsPlugin(),
|
||||
BoolOption(), thp_plugin, AutoGPU(condition='IS_CUDA'),
|
||||
ArgcountSortPlugin(), KwargsPlugin()
|
||||
])
|
||||
cwrap('torch/csrc/cudnn/cuDNN.cwrap', plugins=[
|
||||
CuDNNPlugin(), NullableArguments()
|
||||
@ -145,12 +160,31 @@ include_dirs += [
|
||||
os.path.join(cwd, "torch", "csrc"),
|
||||
tmp_install_path + "/include",
|
||||
tmp_install_path + "/include/TH",
|
||||
tmp_install_path + "/include/THPP",
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
extra_link_args.append('-L' + lib_path)
|
||||
|
||||
# we specify exact lib names to avoid conflict with lua-torch installs
|
||||
TH_LIB = os.path.join(lib_path, 'libTH.so.1')
|
||||
THS_LIB = os.path.join(lib_path, 'libTHS.so.1')
|
||||
THC_LIB = os.path.join(lib_path, 'libTHC.so.1')
|
||||
THCS_LIB = os.path.join(lib_path, 'libTHCS.so.1')
|
||||
THNN_LIB = os.path.join(lib_path, 'libTHNN.so.1')
|
||||
THCUNN_LIB = os.path.join(lib_path, 'libTHCUNN.so.1')
|
||||
THPP_LIB = os.path.join(lib_path, 'libTHPP.so.1')
|
||||
if platform.system() == 'Darwin':
|
||||
TH_LIB = os.path.join(lib_path, 'libTH.1.dylib')
|
||||
THS_LIB = os.path.join(lib_path, 'libTHS.1.dylib')
|
||||
THC_LIB = os.path.join(lib_path, 'libTHC.1.dylib')
|
||||
THCS_LIB = os.path.join(lib_path, 'libTHCS.1.dylib')
|
||||
THNN_LIB = os.path.join(lib_path, 'libTHNN.1.dylib')
|
||||
THCUNN_LIB = os.path.join(lib_path, 'libTHCUNN.1.dylib')
|
||||
THPP_LIB = os.path.join(lib_path, 'libTHPP.1.dylib')
|
||||
|
||||
main_compile_args = ['-D_THP_CORE']
|
||||
main_libraries = ['TH', 'shm']
|
||||
main_libraries = ['shm']
|
||||
main_link_args = [TH_LIB, THS_LIB, THPP_LIB]
|
||||
main_sources = [
|
||||
"torch/csrc/Module.cpp",
|
||||
"torch/csrc/Generator.cpp",
|
||||
@ -172,8 +206,9 @@ try:
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
include_dirs += [np.get_include()]
|
||||
extra_compile_args += ['-DWITH_NUMPY']
|
||||
WITH_NUMPY = True
|
||||
except ImportError:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
WITH_NUMPY = False
|
||||
|
||||
if WITH_CUDA:
|
||||
cuda_lib_dirs = ['lib64', 'lib']
|
||||
@ -187,7 +222,7 @@ if WITH_CUDA:
|
||||
extra_link_args.append('-Wl,-rpath,' + cuda_lib_path)
|
||||
extra_compile_args += ['-DWITH_CUDA']
|
||||
extra_compile_args += ['-DCUDA_LIB_PATH=' + cuda_lib_path]
|
||||
main_libraries += ['THC']
|
||||
main_link_args += [THC_LIB, THCS_LIB]
|
||||
main_sources += [
|
||||
"torch/csrc/cuda/Module.cpp",
|
||||
"torch/csrc/cuda/Storage.cpp",
|
||||
@ -200,8 +235,11 @@ if WITH_CUDA:
|
||||
|
||||
if WITH_CUDNN:
|
||||
main_libraries += ['cudnn']
|
||||
include_dirs.append(CUDNN_INCLUDE_DIR)
|
||||
extra_link_args.append('-L' + CUDNN_LIB_DIR)
|
||||
main_sources += [
|
||||
"torch/csrc/cudnn/Module.cpp",
|
||||
"torch/csrc/cudnn/BatchNorm.cpp",
|
||||
"torch/csrc/cudnn/Conv.cpp",
|
||||
"torch/csrc/cudnn/cuDNN.cpp",
|
||||
"torch/csrc/cudnn/Types.cpp",
|
||||
@ -234,7 +272,7 @@ C = Extension("torch._C",
|
||||
language='c++',
|
||||
extra_compile_args=main_compile_args + extra_compile_args,
|
||||
include_dirs=include_dirs,
|
||||
extra_link_args=extra_link_args + [make_relative_rpath('lib')]
|
||||
extra_link_args=extra_link_args + main_link_args + [make_relative_rpath('lib')],
|
||||
)
|
||||
extensions.append(C)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -245,27 +283,39 @@ DL = Extension("torch._dl",
|
||||
extensions.append(DL)
|
||||
|
||||
THNN = Extension("torch._thnn._THNN",
|
||||
libraries=['TH', 'THNN'],
|
||||
sources=['torch/csrc/nn/THNN.cpp'],
|
||||
language='c++',
|
||||
extra_compile_args=extra_compile_args,
|
||||
include_dirs=include_dirs,
|
||||
extra_link_args=extra_link_args + [make_relative_rpath('../lib')]
|
||||
extra_link_args=extra_link_args + [
|
||||
TH_LIB,
|
||||
THNN_LIB,
|
||||
make_relative_rpath('../lib'),
|
||||
]
|
||||
)
|
||||
extensions.append(THNN)
|
||||
|
||||
if WITH_CUDA:
|
||||
THCUNN = Extension("torch._thnn._THCUNN",
|
||||
libraries=['TH', 'THC', 'THCUNN'],
|
||||
sources=['torch/csrc/nn/THCUNN.cpp'],
|
||||
language='c++',
|
||||
extra_compile_args=extra_compile_args,
|
||||
include_dirs=include_dirs,
|
||||
extra_link_args=extra_link_args + [make_relative_rpath('../lib')]
|
||||
extra_link_args=extra_link_args + [
|
||||
TH_LIB,
|
||||
THC_LIB,
|
||||
THCUNN_LIB,
|
||||
make_relative_rpath('../lib'),
|
||||
]
|
||||
)
|
||||
extensions.append(THCUNN)
|
||||
|
||||
setup(name="torch", version="0.1",
|
||||
version="0.1"
|
||||
if os.getenv('PYTORCH_BUILD_VERSION'):
|
||||
version = os.getenv('PYTORCH_BUILD_VERSION') \
|
||||
+ '_' + os.getenv('PYTORCH_BUILD_NUMBER')
|
||||
|
||||
setup(name="torch", version=version,
|
||||
ext_modules=extensions,
|
||||
cmdclass = {
|
||||
'build': build,
|
||||
|
||||
@ -105,6 +105,39 @@ class TestCase(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
super(TestCase, self).assertEqual(x, y, message)
|
||||
|
||||
def assertNotEqual(self, x, y, prec=None, message=''):
|
||||
if prec is None:
|
||||
prec = self.precision
|
||||
|
||||
if isinstance(x, Variable) and isinstance(y, Variable):
|
||||
x = x.data
|
||||
y = y.data
|
||||
|
||||
if torch.is_tensor(x) and torch.is_tensor(y):
|
||||
max_err = 0
|
||||
if x.size() != y.size():
|
||||
super(TestCase, self).assertNotEqual(x.size(), y.size())
|
||||
for index in iter_indices(x):
|
||||
max_err = max(max_err, abs(x[index] - y[index]))
|
||||
self.assertGreaterEqual(max_err, prec, message)
|
||||
elif type(x) == str and type(y) == str:
|
||||
super(TestCase, self).assertNotEqual(x, y)
|
||||
elif is_iterable(x) and is_iterable(y):
|
||||
super(TestCase, self).assertNotEqual(x, y)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
try:
|
||||
self.assertGreaterEqual(abs(x - y), prec, message)
|
||||
return
|
||||
except:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
super(TestCase, self).assertNotEqual(x, y, message)
|
||||
|
||||
def assertObjectIn(self, obj, iterable):
|
||||
for elem in iterable:
|
||||
if id(obj) == id(elem):
|
||||
return
|
||||
raise AssertionError("object not found in iterable")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def make_jacobian(input, num_out):
|
||||
if isinstance(input, Variable) and not input.requires_grad:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -92,52 +92,6 @@ module_tests = [
|
||||
input_size=(1, 3, 10, 20),
|
||||
reference_fn=lambda i,_: torch.exp(i).div(torch.exp(i).sum(1).expand_as(i))
|
||||
),
|
||||
dict(
|
||||
module_name='BatchNorm1d',
|
||||
constructor_args=(10,),
|
||||
input_size=(4, 10),
|
||||
desc='affine'
|
||||
),
|
||||
dict(
|
||||
module_name='BatchNorm1d',
|
||||
constructor_args=(10, 1e-3, 0.3, False),
|
||||
input_size=(4, 10),
|
||||
desc='not_affine'
|
||||
),
|
||||
dict(
|
||||
module_name='BatchNorm2d',
|
||||
constructor_args=(3,),
|
||||
input_size=(2, 3, 6, 6),
|
||||
),
|
||||
dict(
|
||||
module_name='BatchNorm2d',
|
||||
constructor_args=(3, 1e-3, 0.8),
|
||||
input_size=(2, 3, 6, 6),
|
||||
desc='momentum',
|
||||
),
|
||||
dict(
|
||||
module_name='BatchNorm2d',
|
||||
constructor_args=(3, 1e-3, 0.8, False),
|
||||
input_size=(2, 3, 6, 6),
|
||||
desc='no_affine',
|
||||
),
|
||||
dict(
|
||||
module_name='BatchNorm3d',
|
||||
constructor_args=(3,),
|
||||
input_size=(2, 3, 4, 4, 4)
|
||||
),
|
||||
dict(
|
||||
module_name='BatchNorm3d',
|
||||
constructor_args=(3, 1e-3, 0.7),
|
||||
input_size=(2, 3, 4, 4, 4),
|
||||
desc='momentum'
|
||||
),
|
||||
dict(
|
||||
module_name='BatchNorm3d',
|
||||
constructor_args=(3, 1e-3, 0.7, False),
|
||||
input_size=(2, 3, 4, 4, 4),
|
||||
desc='no_affine'
|
||||
),
|
||||
dict(
|
||||
module_name='LogSoftmax',
|
||||
input_size=(10, 20),
|
||||
@ -375,7 +329,7 @@ class NNTestCase(TestCase):
|
||||
|
||||
def _zero_grad_input(self, input):
|
||||
if isinstance(input, Variable):
|
||||
input.grad.zero_()
|
||||
input.grad.data.zero_()
|
||||
elif torch.is_tensor(input):
|
||||
return
|
||||
else:
|
||||
@ -389,8 +343,8 @@ class NNTestCase(TestCase):
|
||||
flat_d_out = d_out.view(-1)
|
||||
|
||||
if jacobian_input:
|
||||
jacobian_input = self._jacobian(input, d_out.nelement())
|
||||
flat_jacobian_input = list(iter_tensors(jacobian_input))
|
||||
jacobian_inp = self._jacobian(input, d_out.nelement())
|
||||
flat_jacobian_input = list(iter_tensors(jacobian_inp))
|
||||
|
||||
if jacobian_parameters:
|
||||
param, d_param = self._get_parameters(module)
|
||||
@ -416,7 +370,7 @@ class NNTestCase(TestCase):
|
||||
|
||||
res = tuple()
|
||||
if jacobian_input:
|
||||
res += jacobian_input,
|
||||
res += jacobian_inp,
|
||||
if jacobian_parameters:
|
||||
res += jacobian_param,
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
import torch.nn as nn
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Net(nn.Container):
|
||||
class Net(nn.Module):
|
||||
def __init__(self):
|
||||
super(Net, self).__init__()
|
||||
self.linear = nn.Linear(10, 20)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
import torch.nn as nn
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class Net(nn.Container):
|
||||
class Net(nn.Module):
|
||||
def __init__(self):
|
||||
super(Net, self).__init__()
|
||||
self.linear = nn.Linear(10, 20)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,43 +1,55 @@
|
||||
#!/usr/bin/env bash
|
||||
set -e
|
||||
|
||||
PYCMD=${PYCMD:="python"}
|
||||
if [ "$1" == "coverage" ];
|
||||
then
|
||||
coverage erase
|
||||
PYCMD="coverage run --parallel-mode --source torch "
|
||||
echo "coverage flag found. Setting python command to: \"$PYCMD\""
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
pushd "$(dirname "$0")"
|
||||
|
||||
echo "Running torch tests"
|
||||
python test_torch.py
|
||||
$PYCMD test_torch.py
|
||||
|
||||
echo "Running autograd tests"
|
||||
python test_autograd.py
|
||||
$PYCMD test_autograd.py
|
||||
|
||||
echo "Running sparse tests"
|
||||
$PYCMD test_sparse.py
|
||||
|
||||
echo "Running nn tests"
|
||||
python test_nn.py
|
||||
$PYCMD test_nn.py
|
||||
|
||||
echo "Running legacy nn tests"
|
||||
python test_legacy_nn.py
|
||||
$PYCMD test_legacy_nn.py
|
||||
|
||||
echo "Running optim tests"
|
||||
python test_optim.py
|
||||
$PYCMD test_optim.py
|
||||
|
||||
echo "Running multiprocessing tests"
|
||||
python test_multiprocessing.py
|
||||
MULTIPROCESSING_METHOD=spawn python test_multiprocessing.py
|
||||
MULTIPROCESSING_METHOD=forkserver python test_multiprocessing.py
|
||||
$PYCMD test_multiprocessing.py
|
||||
MULTIPROCESSING_METHOD=spawn $PYCMD test_multiprocessing.py
|
||||
MULTIPROCESSING_METHOD=forkserver $PYCMD test_multiprocessing.py
|
||||
|
||||
echo "Running util tests"
|
||||
python test_utils.py
|
||||
$PYCMD test_utils.py
|
||||
|
||||
echo "Running dataloader tests"
|
||||
python test_dataloader.py
|
||||
$PYCMD test_dataloader.py
|
||||
|
||||
if which nvcc >/dev/null 2>&1
|
||||
echo "Running cuda tests"
|
||||
$PYCMD test_cuda.py
|
||||
|
||||
echo "Running NCCL tests"
|
||||
$PYCMD test_nccl.py
|
||||
|
||||
if [ "$1" == "coverage" ];
|
||||
then
|
||||
echo "Running cuda tests"
|
||||
python test_cuda.py
|
||||
|
||||
echo "Running NCCL tests"
|
||||
python test_nccl.py
|
||||
else
|
||||
echo "nvcc not found in PATH, skipping CUDA tests"
|
||||
coverage combine
|
||||
coverage html
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
popd
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,28 +1,39 @@
|
||||
import math
|
||||
import unittest
|
||||
import contextlib
|
||||
import gc
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
import math
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
import unittest
|
||||
from copy import deepcopy
|
||||
from collections import OrderedDict
|
||||
|
||||
from common import make_jacobian, TestCase, iter_tensors, get_numerical_jacobian
|
||||
from torch.autograd.functions import *
|
||||
from torch.autograd import Variable
|
||||
from torch.autograd._functions import *
|
||||
from torch.autograd import Variable, Function
|
||||
|
||||
if sys.version_info[0] == 2:
|
||||
import cPickle as pickle
|
||||
else:
|
||||
import pickle
|
||||
|
||||
PRECISION = 1e-4
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def iter_gradients(x):
|
||||
if isinstance(x, Variable):
|
||||
if x.requires_grad:
|
||||
yield x.grad
|
||||
yield x.grad.data
|
||||
else:
|
||||
for elem in x:
|
||||
for result in iter_gradients(elem):
|
||||
yield result
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def zero_gradients(i):
|
||||
for t in iter_gradients(i):
|
||||
t.zero_()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def get_analytical_jacobian(input, output):
|
||||
jacobian = make_jacobian(input, output.numel())
|
||||
grad_output = output.data.clone().zero_()
|
||||
@ -48,6 +59,7 @@ def backward_engine(engine):
|
||||
finally:
|
||||
Variable._execution_engine = _prev_engine
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class TestAutograd(TestCase):
|
||||
|
||||
def test_hooks(self):
|
||||
@ -56,22 +68,66 @@ class TestAutograd(TestCase):
|
||||
|
||||
counter = [0]
|
||||
def bw_hook(inc, grad):
|
||||
self.assertTrue(torch.is_tensor(grad))
|
||||
self.assertIsInstance(grad, Variable)
|
||||
counter[0] += inc
|
||||
|
||||
z = x ** 2 + x * 2 + x * y + y
|
||||
z.register_hook('test', lambda *args: bw_hook(1, *args))
|
||||
test = z.register_hook(lambda *args: bw_hook(1, *args))
|
||||
z.backward(torch.ones(5, 5), retain_variables=True)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(counter[0], 1)
|
||||
|
||||
z.register_hook('test2', lambda *args: bw_hook(2, *args))
|
||||
test2 = z.register_hook(lambda *args: bw_hook(2, *args))
|
||||
z.backward(torch.ones(5, 5), retain_variables=True)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(counter[0], 4)
|
||||
|
||||
z.remove_hook('test2')
|
||||
test2.remove()
|
||||
z.backward(torch.ones(5, 5), retain_variables=True)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(counter[0], 5)
|
||||
|
||||
def bw_hook_modify(grad):
|
||||
return grad.mul(2)
|
||||
|
||||
test.remove()
|
||||
z.register_hook(bw_hook_modify)
|
||||
y.grad.data.zero_()
|
||||
z.backward(torch.ones(5, 5), retain_variables=True)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(y.grad.data, (x.data + 1) * 2)
|
||||
|
||||
y.register_hook(bw_hook_modify)
|
||||
y.grad.data.zero_()
|
||||
z.backward(torch.ones(5, 5))
|
||||
self.assertEqual(y.grad.data, (x.data + 1) * 4)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_hook_none(self):
|
||||
# WARNING: this is a test for autograd internals.
|
||||
# You should never have to use such things in your code.
|
||||
class NoneGradientFunction(Function):
|
||||
def forward(self, x, y):
|
||||
assert self.needs_input_grad[0]
|
||||
assert not self.needs_input_grad[1]
|
||||
return x, y
|
||||
|
||||
def backward(self, grad_x, grad_y):
|
||||
return grad_x, None
|
||||
|
||||
fn = NoneGradientFunction()
|
||||
fn._backward_hooks = OrderedDict()
|
||||
was_called = [False]
|
||||
def hook(grad_input, grad_output):
|
||||
self.assertIsInstance(grad_input, tuple)
|
||||
self.assertIsInstance(grad_output, tuple)
|
||||
self.assertIsNotNone(grad_input[0])
|
||||
self.assertIsNone(grad_input[1])
|
||||
self.assertIsNotNone(grad_output[0])
|
||||
self.assertIsNotNone(grad_output[1])
|
||||
was_called[0] = True
|
||||
fn._backward_hooks[id(hook)] = hook
|
||||
|
||||
x = Variable(torch.randn(5, 5), requires_grad=True)
|
||||
y = Variable(torch.randn(5, 5))
|
||||
sum(fn(x, y)).sum().backward()
|
||||
self.assertTrue(was_called[0])
|
||||
|
||||
def _test_backward(self):
|
||||
v_t = torch.randn(5, 5)
|
||||
x_t = torch.randn(5, 5)
|
||||
@ -84,24 +140,67 @@ class TestAutograd(TestCase):
|
||||
z = Variable(z_t, requires_grad=True)
|
||||
|
||||
v.backward(grad_output)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(v.grad, grad_output)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(v.grad.data, grad_output)
|
||||
|
||||
a = x + (y * z) + 4 * z**2 * x / y
|
||||
a.backward(grad_output)
|
||||
x_grad = 4 * z_t.pow(2) / y_t + 1
|
||||
y_grad = z_t - 4 * x_t * z_t.pow(2) / y_t.pow(2)
|
||||
z_grad = 8 * x_t * z_t / y_t + y_t
|
||||
self.assertEqual(x.grad, x_grad * grad_output)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(y.grad, y_grad * grad_output)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(z.grad, z_grad * grad_output)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(x.grad.data, x_grad * grad_output)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(y.grad.data, y_grad * grad_output)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(z.grad.data, z_grad * grad_output)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_backward(self):
|
||||
self._test_backward()
|
||||
|
||||
@unittest.skip("BasicEngine is out of date")
|
||||
def test_backward_basic_engine(self):
|
||||
with backward_engine(torch.autograd.engine.BasicEngine):
|
||||
self._test_backward()
|
||||
|
||||
def test_multi_backward(self):
|
||||
x = Variable(torch.randn(5, 5), requires_grad=True)
|
||||
y = Variable(torch.randn(5, 5), requires_grad=True)
|
||||
|
||||
q = Variable(torch.randn(5, 5), requires_grad=True)
|
||||
|
||||
a = Variable(torch.randn(5, 5), requires_grad=True)
|
||||
b = Variable(torch.randn(5, 5), requires_grad=True)
|
||||
|
||||
q2 = q * 2
|
||||
z = x + y + q2
|
||||
c = a * b + q2
|
||||
grad_z = torch.randn(5, 5)
|
||||
grad_c = torch.randn(5, 5)
|
||||
torch.autograd.backward([z, c], [grad_z, grad_c])
|
||||
|
||||
self.assertEqual(x.grad.data, grad_z)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(y.grad.data, grad_z)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(a.grad.data, grad_c * b.data)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(b.grad.data, grad_c * a.data)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(q.grad.data, (grad_c + grad_z) * 2)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_multi_backward_stochastic(self):
|
||||
x = Variable(torch.randn(5, 5), requires_grad=True)
|
||||
y = Variable(torch.randn(5, 5), requires_grad=True)
|
||||
|
||||
z = x + y
|
||||
q = torch.normal(x)
|
||||
q.reinforce(torch.randn(5, 5))
|
||||
|
||||
torch.autograd.backward([z, q], [torch.ones(5, 5), None])
|
||||
|
||||
def test_multi_backward_no_grad(self):
|
||||
x = Variable(torch.randn(5, 5), requires_grad=True)
|
||||
y = Variable(torch.randn(5, 5), requires_grad=False)
|
||||
|
||||
z = x + y
|
||||
q = y * 2
|
||||
|
||||
torch.autograd.backward([z, q], [torch.ones(5, 5), torch.ones(5, 5)])
|
||||
self.assertEqual(x.grad.data, torch.ones(5, 5))
|
||||
|
||||
def test_volatile(self):
|
||||
x = Variable(torch.ones(5, 5), requires_grad=True)
|
||||
y = Variable(torch.ones(5, 5) * 4, volatile=True)
|
||||
@ -111,7 +210,7 @@ class TestAutograd(TestCase):
|
||||
self.assertTrue(z.requires_grad)
|
||||
self.assertIsNotNone(z.creator)
|
||||
z.backward(torch.ones(5, 5))
|
||||
self.assertEqual(x.grad, torch.ones(5, 5) * 2)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(x.grad.data, torch.ones(5, 5) * 2)
|
||||
|
||||
w = z + y
|
||||
self.assertTrue(w.volatile)
|
||||
@ -141,12 +240,12 @@ class TestAutograd(TestCase):
|
||||
def error():
|
||||
raise RuntimeError
|
||||
# Make sure backward isn't called on these
|
||||
a.backward_hooks = OrderedDict()
|
||||
x.backward_hooks = OrderedDict()
|
||||
y.backward_hooks = OrderedDict()
|
||||
a.backward_hooks['test'] = error
|
||||
x.backward_hooks['test'] = error
|
||||
y.backward_hooks['test'] = error
|
||||
a._backward_hooks = OrderedDict()
|
||||
x._backward_hooks = OrderedDict()
|
||||
y._backward_hooks = OrderedDict()
|
||||
a._backward_hooks['test'] = error
|
||||
x._backward_hooks['test'] = error
|
||||
y._backward_hooks['test'] = error
|
||||
b.backward(torch.ones(5, 5))
|
||||
|
||||
def test_inplace(self):
|
||||
@ -173,7 +272,7 @@ class TestAutograd(TestCase):
|
||||
# q uses dirty z, so it should raise
|
||||
self.assertRaises(RuntimeError, lambda: q.backward(torch.ones(5, 5)))
|
||||
|
||||
x.grad.zero_()
|
||||
x.grad.data.zero_()
|
||||
m = x / 2
|
||||
z = m + y / 8
|
||||
q = z * y
|
||||
@ -182,9 +281,9 @@ class TestAutograd(TestCase):
|
||||
w = z.exp_()
|
||||
self.assertNotEqual(z._version, prev_version)
|
||||
r.backward(torch.ones(5, 5), retain_variables=True)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(x.grad, torch.ones(5, 5) / 2)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(x.grad.data, torch.ones(5, 5) / 2)
|
||||
w.backward(torch.ones(5, 5), retain_variables=True)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(x.grad, torch.Tensor(5, 5).fill_((1 + math.e) / 2))
|
||||
self.assertEqual(x.grad.data, torch.Tensor(5, 5).fill_((1 + math.e) / 2))
|
||||
self.assertRaises(RuntimeError, lambda: q.backward(torch.ones(5, 5)))
|
||||
|
||||
leaf = Variable(torch.ones(5, 5), requires_grad=True)
|
||||
@ -194,7 +293,7 @@ class TestAutograd(TestCase):
|
||||
# x should be still usable
|
||||
y = x + 2
|
||||
y.backward(torch.ones(5, 5))
|
||||
self.assertEqual(leaf.grad, torch.ones(5, 5))
|
||||
self.assertEqual(leaf.grad.data, torch.ones(5, 5))
|
||||
z = x * y
|
||||
x.add_(2)
|
||||
self.assertRaises(RuntimeError, lambda: z.backward(torch.ones(5, 5)))
|
||||
@ -218,7 +317,7 @@ class TestAutograd(TestCase):
|
||||
if isinstance(index, Variable):
|
||||
index = index.data
|
||||
expected_grad[index] = 0
|
||||
self.assertEqual(x.grad, expected_grad)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(x.grad.data, expected_grad)
|
||||
|
||||
def _test_setitem_tensor(self, size, index):
|
||||
x = Variable(torch.ones(*size), requires_grad=True)
|
||||
@ -232,8 +331,8 @@ class TestAutograd(TestCase):
|
||||
if isinstance(index, Variable):
|
||||
index = index.data
|
||||
expected_grad_input[index] = 0
|
||||
self.assertEqual(x.grad, expected_grad_input)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(value.grad, torch.ones(value.size()))
|
||||
self.assertEqual(x.grad.data, expected_grad_input)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(value.grad.data, torch.ones(value.size()))
|
||||
|
||||
def test_setitem(self):
|
||||
self._test_setitem((5, 5), 1)
|
||||
@ -258,44 +357,57 @@ class TestAutograd(TestCase):
|
||||
o.sum().backward()
|
||||
expected_grad = torch.zeros(10, 10)
|
||||
expected_grad[4:6] = 4
|
||||
self.assertEqual(x.grad, expected_grad)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(x.grad.data, expected_grad)
|
||||
|
||||
x.grad.zero_()
|
||||
x.grad.data.zero_()
|
||||
grad_output = torch.randn(2, 10)
|
||||
outputs = x.chunk(5)
|
||||
outputs[0].backward(grad_output)
|
||||
expected_grad = torch.zeros(10, 10)
|
||||
expected_grad[:2] = grad_output
|
||||
self.assertEqual(x.grad, expected_grad)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(x.grad.data, expected_grad)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_gc_in_destructor(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Previously, if a Function destructor triggered a garbage collection,
|
||||
the Variable's tp_dealloc handler would get called twice leading to a
|
||||
segfault.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
class CollectOnDelete(Function):
|
||||
def __del__(self):
|
||||
gc.collect()
|
||||
|
||||
for i in range(10):
|
||||
Variable(torch.randn(10, 10), creator=CollectOnDelete())
|
||||
|
||||
@unittest.skipIf(not torch.cuda.is_available() or torch.cuda.device_count() < 2,
|
||||
"CUDA not available or <2 GPUs detected")
|
||||
def test_unused_output_gpu(self):
|
||||
from torch.nn.parallel.functions import Broadcast
|
||||
from torch.nn.parallel._functions import Broadcast
|
||||
x = Variable(torch.randn(5, 5).float().cuda(), requires_grad=True)
|
||||
outputs = Broadcast(list(range(torch.cuda.device_count())))(x)
|
||||
y = outputs[-1] * 2
|
||||
y.sum().backward()
|
||||
self.assertEqual(x.grad, torch.ones(5, 5) * 2)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(x.grad.data, torch.ones(5, 5) * 2)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_no_grad(self):
|
||||
def test_detach(self):
|
||||
x = Variable(torch.randn(10, 10), requires_grad=True)
|
||||
y = x + 2
|
||||
y = y.no_grad()
|
||||
y = y.detach()
|
||||
z = y * 4 + 2
|
||||
self.assertFalse(y.requires_grad)
|
||||
self.assertFalse(z.requires_grad)
|
||||
|
||||
x = Variable(torch.randn(10, 10), requires_grad=True)
|
||||
y = x * 2
|
||||
y = y.no_grad()
|
||||
y = y.detach()
|
||||
self.assertFalse(y.requires_grad)
|
||||
self.assertFalse(y.creator.requires_grad)
|
||||
z = x + y
|
||||
z.sum().backward()
|
||||
# This is an incorrect gradient, but we assume that's what the user
|
||||
# wanted. no_grad() is an advanced option.
|
||||
self.assertEqual(x.grad, torch.ones(10, 10))
|
||||
# wanted. detach() is an advanced option.
|
||||
self.assertEqual(x.grad.data, torch.ones(10, 10))
|
||||
|
||||
def test_type_conversions(self):
|
||||
import torch.cuda
|
||||
@ -317,6 +429,67 @@ class TestAutograd(TestCase):
|
||||
self.assertIs(type(x2.data), torch.cuda.FloatTensor)
|
||||
self.assertIs(x2.get_device(), 1)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_return_leaf(self):
|
||||
class Identity(Function):
|
||||
def forward(self, a, b):
|
||||
return a, a + b
|
||||
|
||||
def backward(self, grad_a, grad_b):
|
||||
return grad_a + grad_b, grad_b
|
||||
|
||||
class Inplace(InplaceFunction):
|
||||
def forward(self, a, b):
|
||||
self.mark_dirty(a)
|
||||
return a.add_(b), b + 2
|
||||
|
||||
def backward(self, grad_a, grad_b):
|
||||
return grad_a, grad_a + grad_b
|
||||
|
||||
x = Variable(torch.randn(5, 5), requires_grad=True)
|
||||
y = Variable(torch.randn(5, 5), requires_grad=True)
|
||||
|
||||
q, p = Identity()(x, y)
|
||||
# Make sure hooks only receive grad from usage of q, not x.
|
||||
q.register_hook(
|
||||
lambda grad: self.assertEqual(grad.data, torch.ones(5, 5)))
|
||||
(q + p + x).sum().backward()
|
||||
self.assertEqual(x.grad.data, torch.ones(5, 5) * 3)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(y.grad.data, torch.ones(5, 5))
|
||||
del q, p # these need to be freed, or next part will raise an error
|
||||
|
||||
def test_return_leaf_inplace(self):
|
||||
class Inplace(InplaceFunction):
|
||||
def forward(self, a, b):
|
||||
self.mark_dirty(a)
|
||||
return a.add_(b), b + 2
|
||||
|
||||
def backward(self, grad_a, grad_b):
|
||||
return grad_a, grad_a + grad_b
|
||||
|
||||
x = Variable(torch.randn(5, 5))
|
||||
y = Variable(torch.randn(5, 5), requires_grad=True)
|
||||
|
||||
fn = Inplace(True)
|
||||
q, p = fn(x, y)
|
||||
self.assertIs(q, x)
|
||||
self.assertIs(q.creator, fn)
|
||||
self.assertTrue(q.requires_grad)
|
||||
q.sum().backward()
|
||||
self.assertEqual(y.grad.data, torch.ones(5, 5))
|
||||
|
||||
def test_leaf_assignment(self):
|
||||
x = Variable(torch.randn(5, 5))
|
||||
y = Variable(torch.randn(5), requires_grad=True)
|
||||
z = Variable(torch.randn(5), requires_grad=True)
|
||||
|
||||
x[0] = y
|
||||
x[1] = 2 * z
|
||||
self.assertTrue(x.requires_grad)
|
||||
self.assertIsNot(x.creator, None)
|
||||
x.sum().backward()
|
||||
self.assertEqual(y.grad.data, torch.ones(5))
|
||||
self.assertEqual(z.grad.data, torch.ones(5) * 2)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_backward_copy(self):
|
||||
# This tests checks backward engine for a very subtle bug that appreared
|
||||
# in one of the initial versions of autograd. Gradients tensors were
|
||||
@ -356,8 +529,8 @@ class TestAutograd(TestCase):
|
||||
# for y: 17 (16 from final b, 1 from add2)
|
||||
grad_output = torch.ones(5, 5)
|
||||
out.backward(grad_output)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(x.grad, torch.ones(5, 5) * 34)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(y.grad, torch.ones(5, 5) * 17)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(x.grad.data, torch.ones(5, 5) * 34)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(y.grad.data, torch.ones(5, 5) * 17)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_functional_blas(self):
|
||||
def compare(fn, *args):
|
||||
@ -365,27 +538,181 @@ class TestAutograd(TestCase):
|
||||
for arg in args)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(fn(*args).data, fn(*unpacked_args))
|
||||
|
||||
def test_blas(fn, x, y, z):
|
||||
def test_blas_add(fn, x, y, z):
|
||||
# Checks all signatures
|
||||
compare(fn, x, y, z)
|
||||
compare(fn, 0.5, x, y, z)
|
||||
compare(fn, 0.5, x, 0.25, y, z)
|
||||
|
||||
test_blas(torch.addmm, Variable(torch.randn(2, 4)),
|
||||
def test_blas(fn, x, y):
|
||||
compare(fn, x, y)
|
||||
|
||||
test_blas(torch.mm, Variable(torch.randn(2, 10)),
|
||||
Variable(torch.randn(10, 4)))
|
||||
test_blas_add(torch.addmm, Variable(torch.randn(2, 4)),
|
||||
Variable(torch.randn(2, 10)), Variable(torch.randn(10, 4)))
|
||||
test_blas(torch.addbmm, Variable(torch.randn(2, 4)),
|
||||
test_blas(torch.bmm, Variable(torch.randn(4, 2, 10)),
|
||||
Variable(torch.randn(4, 10, 4)))
|
||||
test_blas_add(torch.addbmm, Variable(torch.randn(2, 4)),
|
||||
Variable(torch.randn(4, 2, 10)), Variable(torch.randn(4, 10, 4)))
|
||||
test_blas(torch.baddbmm, Variable(torch.randn(4, 2, 4)),
|
||||
test_blas_add(torch.baddbmm, Variable(torch.randn(4, 2, 4)),
|
||||
Variable(torch.randn(4, 2, 10)), Variable(torch.randn(4, 10, 4)))
|
||||
test_blas(torch.addmv, Variable(torch.randn(2)),
|
||||
test_blas(torch.mv, Variable(torch.randn(2, 10)),
|
||||
Variable(torch.randn(10)))
|
||||
test_blas_add(torch.addmv, Variable(torch.randn(2)),
|
||||
Variable(torch.randn(2, 10)), Variable(torch.randn(10)))
|
||||
test_blas(torch.addr, Variable(torch.randn(5, 6)),
|
||||
test_blas(torch.ger, Variable(torch.randn(5)),
|
||||
Variable(torch.randn(6)))
|
||||
test_blas_add(torch.addr, Variable(torch.randn(5, 6)),
|
||||
Variable(torch.randn(5)), Variable(torch.randn(6)))
|
||||
|
||||
def test_save_none_for_backward(self):
|
||||
test_case = self
|
||||
class MyFn(Function):
|
||||
def forward(self, input):
|
||||
self.save_for_backward(None, input, None)
|
||||
return input * input
|
||||
|
||||
def backward(self, grad_output):
|
||||
n1, input, n2 = self.saved_tensors
|
||||
test_case.assertIsNone(n1)
|
||||
test_case.assertIsNone(n2)
|
||||
return 2 * input * grad_output
|
||||
|
||||
x = Variable(torch.randn(5, 5), requires_grad=True)
|
||||
y = MyFn()(x)
|
||||
y.sum().backward()
|
||||
self.assertEqual(x.grad.data, 2 * x.data)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_too_many_grads(self):
|
||||
class MyFn(Function):
|
||||
def forward(self, input):
|
||||
return input
|
||||
|
||||
def backward(self, grad_output):
|
||||
return grad_output, None, None
|
||||
|
||||
x = Variable(torch.randn(5, 5), requires_grad=True)
|
||||
y = MyFn()(x)
|
||||
y.sum().backward()
|
||||
self.assertEqual(x.grad.data, x.data.clone().fill_(1))
|
||||
|
||||
def test_stochastic(self):
|
||||
x = Variable(torch.rand(2, 10), requires_grad=True)
|
||||
stddevs = Variable(torch.rand(2, 10) * 5, requires_grad=True)
|
||||
y = (x * 2).clamp(0, 1)
|
||||
y = y / y.sum(1).expand_as(y)
|
||||
samples_multi = y.multinomial(5)
|
||||
samples_multi_flat = y[0].multinomial(5)
|
||||
samples_bernoulli = y.bernoulli()
|
||||
samples_norm = torch.normal(y)
|
||||
samples_norm_std = torch.normal(y, stddevs)
|
||||
z = samples_multi * 2 + 4
|
||||
z = z + samples_multi_flat.unsqueeze(0).expand_as(samples_multi)
|
||||
z = torch.cat([z, z], 1)
|
||||
z = z.double()
|
||||
z = z + samples_bernoulli + samples_norm + samples_norm_std
|
||||
last_sample = torch.normal(z, 4)
|
||||
z = last_sample + 2
|
||||
self.assertFalse(z.requires_grad)
|
||||
|
||||
self.assertRaises(RuntimeError, lambda: z.backward(retain_variables=True))
|
||||
samples_multi.reinforce(torch.randn(2, 5))
|
||||
self.assertRaises(RuntimeError, lambda: z.backward(retain_variables=True))
|
||||
samples_multi_flat.reinforce(torch.randn(5))
|
||||
self.assertRaises(RuntimeError, lambda: z.backward(retain_variables=True))
|
||||
samples_bernoulli.reinforce(torch.randn(2, 10))
|
||||
self.assertRaises(RuntimeError, lambda: z.backward(retain_variables=True))
|
||||
samples_norm.reinforce(torch.randn(2, 10))
|
||||
self.assertRaises(RuntimeError, lambda: z.backward(retain_variables=True))
|
||||
samples_norm_std.reinforce(torch.randn(2, 10))
|
||||
# We don't have to specify rewards w.r.t. last_sample - it doesn't
|
||||
# require gradient
|
||||
|
||||
last_sample.backward(retain_variables=True)
|
||||
z.backward()
|
||||
|
||||
self.assertGreater(x.grad.data.abs().sum(), 0)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_stochastic_sequence(self):
|
||||
x = Variable(torch.rand(10).clamp_(0, 1), requires_grad=True)
|
||||
b = x.bernoulli()
|
||||
n1 = torch.normal(b, x)
|
||||
n2 = torch.normal(n1, 2)
|
||||
|
||||
b.reinforce(torch.randn(10))
|
||||
n1.reinforce(torch.randn(10))
|
||||
n2.reinforce(torch.randn(10))
|
||||
|
||||
n2.backward()
|
||||
|
||||
self.assertGreater(x.grad.data.abs().sum(), 0)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_stochastic_output(self):
|
||||
x = Variable(torch.rand(10), requires_grad=True)
|
||||
b = x.clone().clamp(0, 1).bernoulli()
|
||||
b.reinforce(torch.randn(10))
|
||||
b.backward()
|
||||
self.assertGreater(x.grad.data.abs().sum(), 0)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_pickle(self):
|
||||
x = Variable(torch.randn(10, 10), requires_grad=True)
|
||||
y = Variable(torch.randn(10, 10), volatile=True)
|
||||
z = Variable(torch.randn(10, 10), requires_grad=False)
|
||||
|
||||
def assert_strict_equal(var1, var2):
|
||||
self.assertEqual(var1.data, var2.data)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(var1.requires_grad, var2.requires_grad)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(var1.volatile, var2.volatile)
|
||||
|
||||
serialized = [pickle.dumps([x, y, z], protocol=p) for p in range(3)]
|
||||
for dump in serialized:
|
||||
xc, yc, zc = pickle.loads(dump)
|
||||
assert_strict_equal(xc, x)
|
||||
assert_strict_equal(yc, y)
|
||||
assert_strict_equal(zc, z)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_dep_nograd(self):
|
||||
class F1(Function):
|
||||
def forward(self, input):
|
||||
out = torch.randn(input.size())
|
||||
self.mark_non_differentiable(out)
|
||||
return input, out
|
||||
|
||||
def backward(self, grad_output, ignored):
|
||||
return grad_output
|
||||
|
||||
class F2(Function):
|
||||
def forward(self, input, ignored):
|
||||
return input
|
||||
|
||||
def backward(self, grad_output):
|
||||
return grad_output, None
|
||||
|
||||
x = Variable(torch.randn(5), requires_grad=True)
|
||||
a, b = F1()(x)
|
||||
b = b + 1 # separate F1 from F2 by another op
|
||||
self.assertTrue(a.requires_grad)
|
||||
self.assertFalse(b.requires_grad)
|
||||
c = F2()(a, b)
|
||||
c.backward(torch.ones(c.size()))
|
||||
self.assertEqual(x.grad.data, torch.ones(x.size()))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def index_variable(num_indices, max_indices):
|
||||
index = torch.randperm(max_indices)[:num_indices].long()
|
||||
def index_variable(shape, max_indices):
|
||||
if not isinstance(shape, tuple):
|
||||
shape = (shape,)
|
||||
index = torch.rand(*shape).mul_(max_indices).floor_().long()
|
||||
return Variable(index, requires_grad=False)
|
||||
|
||||
def gather_variable(shape, index_dim, max_indices):
|
||||
assert len(shape) == 2
|
||||
assert index_dim < 2
|
||||
batch_dim = 1 - index_dim
|
||||
index = torch.LongTensor(*shape)
|
||||
for i in range(shape[index_dim]):
|
||||
index.select(index_dim, i).copy_(
|
||||
torch.randperm(max_indices)[:shape[batch_dim]])
|
||||
return Variable(index, requires_grad=False)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -404,14 +731,15 @@ function_tests = [
|
||||
(MulConstant, (3.14,), ((L, L),) ),
|
||||
(DivConstant, (3.14, True), (torch.rand(L, L) + 1e-1,), 'by_tensor' ),
|
||||
(PowConstant, (3.14,), (torch.rand(L, L),) ),
|
||||
(PowConstant, (3.14, True), (torch.rand(L, L),), 'tensor_power' ),
|
||||
(Transpose, (0, 1), (torch.rand(L, L),) ),
|
||||
(Transpose, (2, 0), (torch.rand(S, S, S),), '3d' ),
|
||||
(Permute, (0, 4, 3, 5, 1, 2), ((1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6),) ),
|
||||
(Permute, ((0, 4, 3, 5, 1, 2),), ((1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6),) ),
|
||||
(Index, ((1, 2),), (torch.rand(S, S, S),) ),
|
||||
(Index, (slice(0, 3),), (torch.rand(S, S, S),), 'slice' ),
|
||||
(Index, ((slice(0, 3), 1),),(torch.rand(S, S, S),), 'slice_index' ),
|
||||
(View, (S*S, S), (torch.rand(S, S, S),) ),
|
||||
(Expand, (S, 5, S, 5), ((S, 1, S, 1),) ),
|
||||
(Expand, ((S, 5, S, 5),), ((S, 1, S, 1),) ),
|
||||
(Exp, (), (torch.rand(S, S, S),) ),
|
||||
(Log, (), (torch.rand(S, S, S) + 1e-2,) ),
|
||||
(Log1p, (), (torch.rand(S, S, S),) ),
|
||||
@ -428,7 +756,7 @@ function_tests = [
|
||||
(Asin, (), (torch.randn(S, S, S).clamp(-0.9, 0.9),) ),
|
||||
(Acos, (), (torch.randn(S, S, S).clamp(-0.9, 0.9),) ),
|
||||
(Atan, (), ((S, S, S),) ),
|
||||
(Cinv, (), (torch.rand(S, S, S) + 0.1,) ),
|
||||
(Reciprocal, (), (torch.rand(S, S, S) + 0.1,) ),
|
||||
(Cmax, (), ((S, S, S), (S, S, S)) ),
|
||||
(Cmin, (), ((S, S, S), (S, S, S)) ),
|
||||
(Round, (), ((S, S, S),) ),
|
||||
@ -467,10 +795,10 @@ function_tests = [
|
||||
(Mode, (0,), ((S, S, S),), ),
|
||||
(Kthvalue, (2, 0), ((S, S, S),), ),
|
||||
(Median, (0,), ((S, S, S),), ),
|
||||
(Norm, (1.5,), (torch.rand(S, S, S),), '1.5' ),
|
||||
(Norm, (1.5,), (torch.rand(S, S, S),), '1_5' ),
|
||||
(Norm, (), ((S, S, S),), '2' ),
|
||||
(Norm, (3,), ((S, S, S),), '3' ),
|
||||
(Norm, (1.5, 0), (torch.rand(S, S, S),), '1.5_dim' ),
|
||||
(Norm, (1.5, 0), (torch.rand(S, S, S),), '1_5_dim' ),
|
||||
(Norm, (2, 0), ((S, S, S),), '2_dim' ),
|
||||
(Norm, (3, 0), ((S, S, S),), '3_dim' ),
|
||||
(Addcmul, (), ((S, S), (S, S), (S, S)) ),
|
||||
@ -478,9 +806,13 @@ function_tests = [
|
||||
(Addcdiv, (), ((S, S), (S, S), torch.rand(S, S) + 1e-2) ),
|
||||
(Addcdiv, (0.6,), ((S, S), (S, S), torch.rand(S, S) + 1e-2), 'scale'),
|
||||
(IndexAdd, (0,), ((S, S), index_variable(2, S), (2, S)) ),
|
||||
(IndexCopy, (0,), ((S, S), index_variable(2, S), (2, S)) ),
|
||||
# (IndexCopy, (0,), ((S, S), index_variable(2, S), (2, S)) ),
|
||||
(IndexFill, (0, 2), ((S, S), index_variable(2, S)) ),
|
||||
(IndexSelect, (0,), ((S, S), index_variable(2, S)) ),
|
||||
(Gather, (0,), ((M, S), gather_variable((S, S), 1, M)) ),
|
||||
(Gather, (1,), ((M, S), gather_variable((M, S//2), 0, S)), 'dim1'),
|
||||
(Scatter, (0,), ((M, S), gather_variable((S, S), 1, M), (S, S))),
|
||||
(Scatter, (1,), ((M, S), gather_variable((M, S//2), 0, S), (M, S//2)), 'dim1'),
|
||||
(Concat, (0,), ((1, S, S), (2, S, S), (3, S, S)) ),
|
||||
(Resize, (S*S, S), ((S, S, S),) ),
|
||||
(Diag, (), ((S, S),), '2d' ),
|
||||
@ -523,6 +855,7 @@ method_tests = [
|
||||
('view', (S, S, S), (S*S, S), ),
|
||||
('view_as', (S, S, S), ((S*S, S),) ),
|
||||
('expand', (S, 1, S), (S, S, S) ),
|
||||
('expand', (torch.Size([S, 1, S]),), (S, S, S), 'size' ),
|
||||
('exp', (S, S, S), () ),
|
||||
('log', (S, S, S), () ),
|
||||
('log1p', (S, S, S), () ),
|
||||
@ -539,7 +872,7 @@ method_tests = [
|
||||
('asin', (S, S, S), () ),
|
||||
('acos', (S, S, S), () ),
|
||||
('atan', (S, S, S), () ),
|
||||
('cinv', (S, S, S), () ),
|
||||
('reciprocal', (S, S, S), () ),
|
||||
('round', (S, S, S), () ),
|
||||
('sign', (S, S, S), () ),
|
||||
('trunc', (S, S, S), () ),
|
||||
@ -549,10 +882,10 @@ method_tests = [
|
||||
('fmod', (S, S, S), (1.5,) ),
|
||||
('remainder', (S, S, S), (1.5,) ),
|
||||
('lerp', (S, S, S), ((S, S, S), 0.4) ),
|
||||
('cmax', (S, S, S), ((S, S, S),) ),
|
||||
('cmax', (S, S, S), (0.5,), 'constant' ),
|
||||
('cmin', (S, S, S), ((S, S, S),) ),
|
||||
('cmin', (S, S, S), (0.5,), 'constant' ),
|
||||
('max', (S, S, S), () ),
|
||||
('max', (S, S, S), ((S, S, S),), 'elementwise' ),
|
||||
('min', (S, S, S), () ),
|
||||
('min', (S, S, S), ((S, S, S),), 'elementwise' ),
|
||||
('mean', (S, S, S), () ),
|
||||
('mean', (S, S, S), (1,), 'dim' ),
|
||||
('sum', (S, S, S), () ),
|
||||
@ -570,8 +903,6 @@ method_tests = [
|
||||
('addr', (S, M), ((S,), (M,)), ),
|
||||
('addr', (S, M), (0.2, 0.6, (S,), (M,)), 'coef' ),
|
||||
('dot', (L,), ((L,),), ),
|
||||
('max', (S, S, S), () ),
|
||||
('min', (S, S, S), () ),
|
||||
('addcmul', (S, S), ((S, S), (S, S)) ),
|
||||
('addcmul', (S, S), (0.5, (S, S), (S, S)), 'scale' ),
|
||||
('addcdiv', (S, S), ((S, S), (S, S)) ),
|
||||
@ -604,6 +935,7 @@ method_tests = [
|
||||
# TODO: mode, median, sort, kthvalue, topk (problem with indices)
|
||||
# TODO: indexAdd, indexCopy, indexFill
|
||||
# TODO: resize, resize_as (tensors only have resize_ and resize_as_)
|
||||
# TODO: clamp with min/max
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def create_input(call_args):
|
||||
@ -646,6 +978,8 @@ for test in function_tests:
|
||||
if not isinstance(output, tuple):
|
||||
output = (output,)
|
||||
for i, o in enumerate(output):
|
||||
if not o.requires_grad:
|
||||
continue
|
||||
analytical = get_analytical_jacobian(input, o)
|
||||
def fn(input):
|
||||
tmp = cls(*constructor_args)(*input)
|
||||
@ -669,9 +1003,9 @@ for test in function_tests:
|
||||
# Check that gradient is the same
|
||||
for inp_i, i in zip(inplace_input, input):
|
||||
if inp_i.grad is not None:
|
||||
inp_i.grad.zero_()
|
||||
inp_i.grad.data.zero_()
|
||||
if i.grad is not None:
|
||||
i.grad.zero_()
|
||||
i.grad.data.zero_()
|
||||
for io, o in zip(inplace_output, output):
|
||||
grad = torch.randn(*io.size()).double()
|
||||
io.backward(grad)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -9,6 +9,11 @@ import torch.cuda.comm as comm
|
||||
|
||||
from common import TestCase, get_gpu_type, to_gpu, freeze_rng_state
|
||||
|
||||
if not torch.cuda.is_available():
|
||||
print('CUDA not available, skipping tests')
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
sys.exit()
|
||||
|
||||
def is_floating(t):
|
||||
return type(t) in [torch.FloatTensor, torch.DoubleTensor,
|
||||
torch.cuda.FloatTensor, torch.cuda.DoubleTensor]
|
||||
@ -71,16 +76,16 @@ def small_3d_unique(t):
|
||||
return t(S, S, S).copy_(torch.range(1, S*S*S))
|
||||
|
||||
def small_1d_lapack(t):
|
||||
return torch.range(1, 3).view(3)
|
||||
return t(1, 3).copy_(torch.range(1, 3).view(3))
|
||||
|
||||
def small_2d_lapack(t):
|
||||
return torch.range(1, 9).view(3, 3)
|
||||
return t(3, 3).copy_(torch.range(1, 9).view(3, 3))
|
||||
|
||||
def small_2d_lapack_skinny(t):
|
||||
return torch.range(1, 12).view(3, 4)
|
||||
return t(3, 4).copy_(torch.range(1, 12).view(3, 4))
|
||||
|
||||
def small_2d_lapack_fat(t):
|
||||
return torch.range(1, 12).view(4, 3)
|
||||
return t(4, 3).copy_(torch.range(1, 12).view(4, 3))
|
||||
|
||||
def new_t(*sizes):
|
||||
def tmp(t):
|
||||
@ -119,12 +124,12 @@ tests = [
|
||||
('addr', medium_2d, lambda t: [number(0.4, 2, t), medium_1d(t), medium_1d(t)], 'scalar' ),
|
||||
('addr', medium_2d, lambda t: [number(0.5, 3, t), number(0.4, 2, t), medium_1d(t), medium_1d(t)], 'two_scalars' ),
|
||||
('atan2', medium_2d, lambda t: [medium_2d(t)], None, float_types),
|
||||
('fmod', small_3d, lambda t: [3], 'value' ),
|
||||
('fmod', small_3d, lambda t: [small_3d_positive(t)], 'tensor' ),
|
||||
('chunk', medium_2d, lambda t: [4], ),
|
||||
('chunk', medium_2d, lambda t: [4, 1], 'dim' ),
|
||||
('clamp', medium_2d_scaled, lambda t: [-1, 5], ),
|
||||
('clone', medium_2d, lambda t: [], ),
|
||||
('cmax', medium_2d, lambda t: [medium_2d(t)], ),
|
||||
('cmin', medium_2d, lambda t: [medium_2d(t)], ),
|
||||
('contiguous', medium_2d, lambda t: [], ),
|
||||
('cross', new_t(M, 3, M), lambda t: [new_t(M, 3, M)(t)], ),
|
||||
('cumprod', small_3d, lambda t: [1], ),
|
||||
@ -132,14 +137,14 @@ tests = [
|
||||
('dim', small_3d, lambda t: [], ),
|
||||
('dist', small_2d, lambda t: [small_2d(t)], ),
|
||||
('dist', small_2d, lambda t: [small_2d(t), 3], '3_norm' ),
|
||||
('dist', small_2d, lambda t: [small_2d(t), 2.5], '2.5_norm' ),
|
||||
('dist', small_2d, lambda t: [small_2d(t), 2.5], '2_5_norm' ),
|
||||
('dot', medium_1d, lambda t: [medium_1d(t)], ),
|
||||
('element_size', medium_1d, lambda t: [], ),
|
||||
('eq', small_3d_ones, lambda t: [small_3d(t)], ),
|
||||
('eq', small_3d_ones, lambda t: [small_3d_ones(t)], 'equal' ),
|
||||
('ne', small_3d_ones, lambda t: [small_3d(t)], ),
|
||||
('ne', small_3d_ones, lambda t: [small_3d_ones(t)], 'equal' ),
|
||||
('equal', small_3d_ones, lambda t: [small_3d_ones(t)], ),
|
||||
('equal', small_3d_ones, lambda t: [small_3d_ones(t)], 'equal' ),
|
||||
('equal', small_3d_ones, lambda t: [small_3d(t)], ),
|
||||
('expand', new_t(M, 1, M), lambda t: [M, 4, M], ),
|
||||
('expand_as', new_t(M, 1, M), lambda t: [new_t(M, 4, M)(t)], ),
|
||||
@ -159,12 +164,16 @@ tests = [
|
||||
('lerp', small_3d, lambda t: [small_3d(t), 0.3], ),
|
||||
('max', small_3d_unique, lambda t: [], ),
|
||||
('max', small_3d_unique, lambda t: [1], 'dim' ),
|
||||
('max', medium_2d, lambda t: [medium_2d(t)], 'elementwise' ),
|
||||
('min', small_3d_unique, lambda t: [], ),
|
||||
('min', small_3d_unique, lambda t: [1], 'dim' ),
|
||||
('min', medium_2d, lambda t: [medium_2d(t)], 'elementwise' ),
|
||||
('mean', small_3d, lambda t: [], ),
|
||||
('mean', small_3d, lambda t: [1], 'dim' ),
|
||||
('mode', small_3d, lambda t: [], ),
|
||||
('mode', small_3d, lambda t: [1], 'dim' ),
|
||||
('remainder', small_3d, lambda t: [3], 'value' ),
|
||||
('remainder', small_3d, lambda t: [small_3d_positive(t)], 'tensor' ),
|
||||
('std', small_3d, lambda t: [], ),
|
||||
('std', small_3d, lambda t: [1], 'dim' ),
|
||||
('var', small_3d, lambda t: [], ),
|
||||
@ -184,7 +193,7 @@ tests = [
|
||||
('sum', small_2d, lambda t: [], ),
|
||||
('sum', small_3d, lambda t: [1], 'dim' ),
|
||||
('renorm', small_3d, lambda t: [2, 1, 1], '2_norm' ),
|
||||
('renorm', small_3d, lambda t: [1.5, 1, 1], '1.5_norm' ),
|
||||
('renorm', small_3d, lambda t: [1.5, 1, 1], '1_5_norm' ),
|
||||
('repeat', small_2d, lambda t: [2, 2, 2], ),
|
||||
('size', new_t(1, 2, 3, 4), lambda t: [], ),
|
||||
('sort', small_3d_unique, lambda t: [], ),
|
||||
@ -235,7 +244,6 @@ custom_precision = {
|
||||
|
||||
simple_pointwise = [
|
||||
'abs',
|
||||
'remainder',
|
||||
'sign',
|
||||
]
|
||||
for fn in simple_pointwise:
|
||||
@ -254,9 +262,8 @@ simple_pointwise_float = [
|
||||
'cos',
|
||||
'cosh',
|
||||
'exp',
|
||||
'cinv',
|
||||
'reciprocal',
|
||||
'floor',
|
||||
'fmod',
|
||||
'frac',
|
||||
'neg',
|
||||
'round',
|
||||
@ -267,6 +274,20 @@ simple_pointwise_float = [
|
||||
for fn in simple_pointwise_float:
|
||||
tests.append((fn, small_3d, lambda t: [], None, float_types))
|
||||
|
||||
_cycles_per_ms = None
|
||||
def get_cycles_per_ms():
|
||||
"""Approximate number of cycles per millisecond for torch.cuda._sleep"""
|
||||
global _cycles_per_ms
|
||||
if _cycles_per_ms is None:
|
||||
start = torch.cuda.Event(enable_timing=True)
|
||||
end = torch.cuda.Event(enable_timing=True)
|
||||
start.record()
|
||||
torch.cuda._sleep(1000000)
|
||||
end.record()
|
||||
end.synchronize()
|
||||
_cycles_per_ms = 1000000 / start.elapsed_time(end)
|
||||
return _cycles_per_ms
|
||||
|
||||
def compare_cpu_gpu(tensor_constructor, arg_constructor, fn, t, precision=1e-5):
|
||||
def tmp(self):
|
||||
cpu_tensor = tensor_constructor(t)
|
||||
@ -311,6 +332,26 @@ class TestCuda(TestCase):
|
||||
z = z.cuda()
|
||||
self.assertEqual(z.get_device(), 0)
|
||||
|
||||
@unittest.skipIf(torch.cuda.device_count() < 2, "only one GPU detected")
|
||||
def test_copy_device(self):
|
||||
x = torch.randn(5, 5).cuda()
|
||||
with torch.cuda.device(1):
|
||||
y = x.cuda()
|
||||
self.assertEqual(y.get_device(), 1)
|
||||
self.assertIs(y.cuda(), y)
|
||||
z = y.cuda(0)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(z.get_device(), 0)
|
||||
self.assertIs(z.cuda(0), z)
|
||||
|
||||
x = torch.randn(5, 5)
|
||||
with torch.cuda.device(1):
|
||||
y = x.cuda()
|
||||
self.assertEqual(y.get_device(), 1)
|
||||
self.assertIs(y.cuda(), y)
|
||||
z = y.cuda(0)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(z.get_device(), 0)
|
||||
self.assertIs(z.cuda(0), z)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_serialization(self):
|
||||
x = torch.randn(5, 5).cuda()
|
||||
y = torch.IntTensor(2, 5).fill_(0).cuda()
|
||||
@ -511,6 +552,25 @@ class TestCuda(TestCase):
|
||||
self.assertIs(type(copy), type(original))
|
||||
self.assertEqual(copy.get_device(), 0)
|
||||
|
||||
@unittest.skipIf(torch.cuda.device_count() < 2, "detected only one GPU")
|
||||
def test_cuda_set_device(self):
|
||||
x = torch.randn(5, 5)
|
||||
with torch.cuda.device(1):
|
||||
self.assertEqual(x.cuda().get_device(), 1)
|
||||
torch.cuda.set_device(0)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(x.cuda().get_device(), 0)
|
||||
with torch.cuda.device(1):
|
||||
self.assertEqual(x.cuda().get_device(), 1)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(x.cuda().get_device(), 0)
|
||||
torch.cuda.set_device(1)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(x.cuda().get_device(), 0)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_is_tensor(self):
|
||||
for t in types:
|
||||
tensor = get_gpu_type(t)()
|
||||
self.assertTrue(torch.is_tensor(tensor))
|
||||
self.assertTrue(torch.is_tensor(torch.cuda.HalfTensor()))
|
||||
|
||||
def test_cuda_synchronize(self):
|
||||
torch.cuda.synchronize()
|
||||
|
||||
@ -541,21 +601,47 @@ class TestCuda(TestCase):
|
||||
self.assertEqual(torch.cuda.current_stream().device, 1)
|
||||
self.assertNotEqual(torch.cuda.current_stream(), default_stream)
|
||||
|
||||
@unittest.skipIf(torch.cuda.device_count() < 2, "multi-GPU not supported")
|
||||
def test_tensor_device(self):
|
||||
self.assertEqual(torch.cuda.FloatTensor(1).get_device(), 0)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(torch.cuda.FloatTensor(1, device=1).get_device(), 1)
|
||||
with torch.cuda.device(1):
|
||||
self.assertEqual(torch.cuda.FloatTensor(1).get_device(), 1)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(torch.cuda.FloatTensor(1, device=0).get_device(), 0)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(torch.cuda.FloatTensor(1, device=None).get_device(), 1)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_events(self):
|
||||
stream = torch.cuda.current_stream()
|
||||
event = torch.cuda.Event(enable_timing=True)
|
||||
self.assertTrue(event.query())
|
||||
# copy 10 MB tensor from CPU-GPU which should take some time
|
||||
tensor1 = torch.ByteTensor(10000000).pin_memory()
|
||||
start_event = torch.cuda.Event(enable_timing=True)
|
||||
stream.record_event(start_event)
|
||||
tensor2 = tensor1.cuda(async=True)
|
||||
torch.cuda._sleep(int(50 * get_cycles_per_ms()))
|
||||
stream.record_event(event)
|
||||
self.assertFalse(event.query())
|
||||
event.synchronize()
|
||||
self.assertTrue(event.query())
|
||||
self.assertGreater(start_event.elapsed_time(event), 0)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_caching_pinned_memory(self):
|
||||
cycles_per_ms = get_cycles_per_ms()
|
||||
|
||||
# check that allocations are re-used after deletion
|
||||
t = torch.FloatTensor([1]).pin_memory()
|
||||
ptr = t.data_ptr()
|
||||
del t
|
||||
t = torch.FloatTensor([1]).pin_memory()
|
||||
self.assertEqual(t.data_ptr(), ptr, 'allocation not reused')
|
||||
|
||||
# check that the allocation is not re-used if it's in-use by a copy
|
||||
gpu_tensor = torch.cuda.FloatTensor([0])
|
||||
torch.cuda._sleep(int(50 * cycles_per_ms)) # delay the copy
|
||||
gpu_tensor.copy_(t, async=True)
|
||||
del t
|
||||
t = torch.FloatTensor([1]).pin_memory()
|
||||
self.assertNotEqual(t.data_ptr(), ptr, 'allocation re-used too soon')
|
||||
self.assertEqual(list(gpu_tensor), [1])
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
for decl in tests:
|
||||
for t in types:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -5,6 +5,7 @@ import traceback
|
||||
import unittest
|
||||
from torch.utils.data import Dataset, TensorDataset, DataLoader
|
||||
from common import TestCase
|
||||
from common_nn import TEST_CUDA
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class TestTensorDataset(TestCase):
|
||||
@ -77,8 +78,6 @@ class TestDataLoader(TestCase):
|
||||
try:
|
||||
it.next()
|
||||
except NotImplementedError:
|
||||
msg = "".join(traceback.format_exception(*sys.exc_info()))
|
||||
self.assertTrue("collate_fn" in msg)
|
||||
errors += 1
|
||||
except StopIteration:
|
||||
self.assertEqual(errors,
|
||||
@ -92,6 +91,13 @@ class TestDataLoader(TestCase):
|
||||
def test_sequential_batch(self):
|
||||
self._test_sequential(DataLoader(self.dataset, batch_size=2))
|
||||
|
||||
@unittest.skipIf(not TEST_CUDA, "CUDA unavailable")
|
||||
def test_sequential_pin_memory(self):
|
||||
loader = DataLoader(self.dataset, batch_size=2, pin_memory=True)
|
||||
for input, target in loader:
|
||||
self.assertTrue(input.is_pinned())
|
||||
self.assertTrue(target.is_pinned())
|
||||
|
||||
def test_shuffle(self):
|
||||
self._test_shuffle(DataLoader(self.dataset, shuffle=True))
|
||||
|
||||
@ -110,16 +116,25 @@ class TestDataLoader(TestCase):
|
||||
def test_shuffle_batch_workers(self):
|
||||
self._test_shuffle(DataLoader(self.dataset, batch_size=2, shuffle=True, num_workers=4))
|
||||
|
||||
@unittest.skipIf(not TEST_CUDA, "CUDA unavailable")
|
||||
def test_shuffle_pin_memory(self):
|
||||
loader = DataLoader(self.dataset, batch_size=2, shuffle=True, num_workers=4, pin_memory=True)
|
||||
for input, target in loader:
|
||||
self.assertTrue(input.is_pinned())
|
||||
self.assertTrue(target.is_pinned())
|
||||
|
||||
def test_error(self):
|
||||
self._test_error(DataLoader(ErrorDataset(100), batch_size=2, shuffle=True))
|
||||
|
||||
def test_error_workers(self):
|
||||
self._test_error(DataLoader(ErrorDataset(41), batch_size=2, shuffle=True, num_workers=4))
|
||||
|
||||
@unittest.skipIf(not TEST_CUDA, "CUDA unavailable")
|
||||
def test_partial_workers(self):
|
||||
"check that workers exit even if the iterator is not exhausted"
|
||||
loader = iter(DataLoader(self.dataset, batch_size=2, num_workers=4))
|
||||
loader = iter(DataLoader(self.dataset, batch_size=2, num_workers=4, pin_memory=True))
|
||||
workers = loader.workers
|
||||
pin_thread = loader.pin_thread
|
||||
for i, sample in enumerate(loader):
|
||||
if i == 3:
|
||||
break
|
||||
@ -128,6 +143,19 @@ class TestDataLoader(TestCase):
|
||||
w.join(1.0) # timeout of one second
|
||||
self.assertFalse(w.is_alive(), 'subprocess not terminated')
|
||||
self.assertEqual(w.exitcode, 0)
|
||||
pin_thread.join(1.0)
|
||||
self.assertFalse(pin_thread.is_alive())
|
||||
|
||||
def test_len(self):
|
||||
def check_len(dl, expected):
|
||||
self.assertEqual(len(dl), expected)
|
||||
n = 0
|
||||
for sample in dl:
|
||||
n += 1
|
||||
self.assertEqual(n, expected)
|
||||
check_len(self.dataset, 100)
|
||||
check_len(DataLoader(self.dataset, batch_size=2), 50)
|
||||
check_len(DataLoader(self.dataset, batch_size=3), 34)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == '__main__':
|
||||
|
||||
@ -28,6 +28,9 @@ class OldModuleTest(ModuleTest):
|
||||
# Test .clearState()
|
||||
module.clearState()
|
||||
|
||||
# test if module can be printed
|
||||
module.__repr__()
|
||||
|
||||
if self.check_inplace:
|
||||
input2 = deepcopy(input)
|
||||
module_ip = self.constructor(*self.constructor_args, inplace=True)
|
||||
@ -54,6 +57,36 @@ tests = [
|
||||
input_size=(3, 5, 4),
|
||||
reference_fn=lambda i,_: i + 3.5,
|
||||
check_inplace=True),
|
||||
OldModuleTest(nn.BatchNormalization,
|
||||
(10,),
|
||||
input_size=(4, 10),
|
||||
desc='affine'),
|
||||
OldModuleTest(nn.BatchNormalization,
|
||||
(10, 1e-3, 0.3, False),
|
||||
input_size=(4, 10),
|
||||
desc='not_affine'),
|
||||
OldModuleTest(nn.SpatialBatchNormalization,
|
||||
(3,),
|
||||
input_size=(2, 3, 6, 6)),
|
||||
OldModuleTest(nn.SpatialBatchNormalization,
|
||||
(3, 1e-3, 0.8),
|
||||
input_size=(2, 3, 6, 6),
|
||||
desc='momentum'),
|
||||
OldModuleTest(nn.SpatialBatchNormalization,
|
||||
(3, 1e-3, 0.8, False),
|
||||
input_size=(2, 3, 6, 6),
|
||||
desc='no_affine'),
|
||||
OldModuleTest(nn.VolumetricBatchNormalization,
|
||||
(3,),
|
||||
input_size=(2, 3, 4, 4, 4)),
|
||||
OldModuleTest(nn.VolumetricBatchNormalization,
|
||||
(3, 1e-3, 0.7),
|
||||
input_size=(2, 3, 4, 4, 4),
|
||||
desc='momentum'),
|
||||
OldModuleTest(nn.VolumetricBatchNormalization,
|
||||
(3, 1e-3, 0.7, False),
|
||||
input_size=(2, 3, 4, 4, 4),
|
||||
desc='no_affine'),
|
||||
OldModuleTest(nn.CMul,
|
||||
(5, 6),
|
||||
input_size=(10, 5, 6),
|
||||
@ -149,16 +182,16 @@ tests = [
|
||||
OldModuleTest(nn.Sum,
|
||||
(1,),
|
||||
input_size=(2, 4, 5),
|
||||
reference_fn=lambda i,_: i.sum(1)),
|
||||
reference_fn=lambda i,_: i.sum(1).squeeze(1)),
|
||||
OldModuleTest(nn.Sum,
|
||||
(1, True),
|
||||
input_size=(2, 4, 5),
|
||||
reference_fn=lambda i,_: i.sum(1).div(i.size(1)),
|
||||
reference_fn=lambda i,_: i.sum(1).div(i.size(1)).squeeze(1),
|
||||
desc='sizeAverage'),
|
||||
OldModuleTest(nn.Mean,
|
||||
(1,),
|
||||
input_size=(2, 4, 5),
|
||||
reference_fn=lambda i,_: torch.mean(i, 1)),
|
||||
reference_fn=lambda i,_: torch.mean(i, 1).squeeze(1)),
|
||||
OldModuleTest(lambda: nn.Sequential().add(nn.GradientReversal()).add(nn.GradientReversal()),
|
||||
input_size=(4, 3, 2, 2),
|
||||
fullname='GradientReversal'),
|
||||
@ -911,7 +944,7 @@ class TestNN(NNTestCase):
|
||||
assert not noncontig.is_contiguous()
|
||||
output = module.forward(noncontig)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(output, noncontig)
|
||||
self.assertTrue(output.contiguous())
|
||||
self.assertTrue(output.is_contiguous())
|
||||
|
||||
# Check that these don't raise errors
|
||||
module.__repr__()
|
||||
@ -1125,19 +1158,19 @@ class TestNN(NNTestCase):
|
||||
self.assertEqual(len(param), 6)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(len(grad), 6)
|
||||
|
||||
self.assertIn(concat.modules[0].weight, param)
|
||||
self.assertIn(concat.modules[0].bias, param)
|
||||
self.assertIn(concat.modules[1].weight, param)
|
||||
self.assertIn(concat.modules[1].bias, param)
|
||||
self.assertIn(net.modules[2].weight, param)
|
||||
self.assertIn(net.modules[2].bias, param)
|
||||
self.assertObjectIn(concat.modules[0].weight, param)
|
||||
self.assertObjectIn(concat.modules[0].bias, param)
|
||||
self.assertObjectIn(concat.modules[1].weight, param)
|
||||
self.assertObjectIn(concat.modules[1].bias, param)
|
||||
self.assertObjectIn(net.modules[2].weight, param)
|
||||
self.assertObjectIn(net.modules[2].bias, param)
|
||||
|
||||
self.assertIn(concat.modules[0].gradWeight, grad)
|
||||
self.assertIn(concat.modules[0].gradBias, grad)
|
||||
self.assertIn(concat.modules[1].gradWeight, grad)
|
||||
self.assertIn(concat.modules[1].gradBias, grad)
|
||||
self.assertIn(net.modules[2].gradWeight, grad)
|
||||
self.assertIn(net.modules[2].gradBias, grad)
|
||||
self.assertObjectIn(concat.modules[0].gradWeight, grad)
|
||||
self.assertObjectIn(concat.modules[0].gradBias, grad)
|
||||
self.assertObjectIn(concat.modules[1].gradWeight, grad)
|
||||
self.assertObjectIn(concat.modules[1].gradBias, grad)
|
||||
self.assertObjectIn(net.modules[2].gradWeight, grad)
|
||||
self.assertObjectIn(net.modules[2].gradBias, grad)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_flattenParameters(self):
|
||||
net = self._build_net()
|
||||
@ -1152,14 +1185,14 @@ class TestNN(NNTestCase):
|
||||
modules, containers = net.findModules(nn.Linear)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(len(modules), 3)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(len(modules), len(containers))
|
||||
self.assertIn(net.modules[0].modules[0], modules)
|
||||
self.assertIn(net.modules[0].modules[1], modules)
|
||||
self.assertIn(net.modules[2], modules)
|
||||
self.assertIn(net.modules[0], containers)
|
||||
self.assertObjectIn(net.modules[0].modules[0], modules)
|
||||
self.assertObjectIn(net.modules[0].modules[1], modules)
|
||||
self.assertObjectIn(net.modules[2], modules)
|
||||
self.assertObjectIn(net.modules[0], containers)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(containers.count(net.modules[0]), 2)
|
||||
self.assertIn(net, containers)
|
||||
self.assertObjectIn(net, containers)
|
||||
for m, c in zip(modules, containers):
|
||||
self.assertIn(m, c.modules)
|
||||
self.assertObjectIn(m, c.modules)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_apply(self):
|
||||
net = self._build_net()
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,6 +1,5 @@
|
||||
import contextlib
|
||||
import gc
|
||||
import multiprocessing
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
import time
|
||||
@ -8,11 +7,17 @@ import unittest
|
||||
from sys import platform
|
||||
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
import torch.cuda
|
||||
import torch.multiprocessing as mp
|
||||
from torch.autograd import Variable
|
||||
from torch.nn import Parameter
|
||||
from common import TestCase
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
HAS_SHM_FILES = os.path.isdir('/dev/shm')
|
||||
TEST_CUDA_IPC = torch.cuda.is_available() and \
|
||||
sys.version_info[0] == 3 and \
|
||||
sys.platform != 'darwin'
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def simple_fill(queue, event):
|
||||
@ -26,6 +31,60 @@ def simple_pool_fill(tensor):
|
||||
return tensor.add(1)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def send_tensor(queue, event, tp):
|
||||
t = torch.ones(5, 5).type(tp)
|
||||
queue.put(t)
|
||||
queue.put(t)
|
||||
event.wait()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def sum_tensors(inq, outq):
|
||||
with torch.cuda.device(1):
|
||||
tensors = inq.get()
|
||||
for tensor in tensors:
|
||||
outq.put((tensor.sum(), tensor.get_device(),
|
||||
tensor.numel(), tensor.storage().size()))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def queue_get_exception(inqueue, outqueue):
|
||||
os.close(2) # hide expected error message
|
||||
try:
|
||||
torch.zeros(5, 5).cuda()
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
outqueue.put(e)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
outqueue.put('no exception')
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Multiply by two in a separate stream
|
||||
def cuda_multiply_two(queue, ready, done):
|
||||
ready.set()
|
||||
with torch.cuda.stream(torch.cuda.Stream()):
|
||||
cuda_event, tensor = queue.get()
|
||||
cuda_event.wait()
|
||||
tensor.mul_(2)
|
||||
cuda_event.record()
|
||||
done.set()
|
||||
del cuda_event
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def autograd_sharing(queue, ready, master_modified):
|
||||
var = queue.get()
|
||||
ready.set()
|
||||
master_modified.wait()
|
||||
|
||||
expected_var = torch.range(1, 25).view(5, 5)
|
||||
expected_var[0,0] = 1000
|
||||
is_ok = var.data.equal(expected_var)
|
||||
var.data[:] = torch.ones(5, 5)
|
||||
|
||||
if var.grad is not None:
|
||||
is_ok &= var.grad.data.equal(torch.ones(5, 5) * 4)
|
||||
var.grad.data[:] = torch.ones(5, 5)
|
||||
|
||||
queue.put(is_ok)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@contextlib.contextmanager
|
||||
def fs_sharing():
|
||||
prev_strategy = mp.get_sharing_strategy()
|
||||
@ -43,24 +102,30 @@ class leak_checker(object):
|
||||
self.test_case = test_case
|
||||
|
||||
def __enter__(self):
|
||||
self.next_fd = self._get_next_fd()
|
||||
self.next_fds = self._get_next_fds(10)
|
||||
return self
|
||||
|
||||
def __exit__(self, *args):
|
||||
if args[0] is None:
|
||||
gc.collect()
|
||||
self.test_case.assertEqual(self.next_fd, self._get_next_fd())
|
||||
# Check that the 10th available file-descriptor at the end of the
|
||||
# test is no more than 4 higher than the 10th available at the
|
||||
# start. This attempts to catch file descriptor leaks, but allows
|
||||
# one-off initialization that may use up a file descriptor
|
||||
available_fds = self._get_next_fds(10)
|
||||
self.test_case.assertLessEqual(
|
||||
available_fds[-1] - self.next_fds[-1], 4)
|
||||
self.test_case.assertFalse(self.has_shm_files())
|
||||
return False
|
||||
|
||||
def check_pid(self, pid):
|
||||
self.checked_pids.append(pid)
|
||||
|
||||
def _get_next_fd(self):
|
||||
def _get_next_fds(self, n=1):
|
||||
# dup uses the lowest-numbered unused descriptor for the new descriptor
|
||||
fd = os.dup(0)
|
||||
fds = [os.dup(0) for i in range(n)]
|
||||
for fd in fds:
|
||||
os.close(fd)
|
||||
return fd
|
||||
return fds
|
||||
|
||||
def has_shm_files(self, wait=True):
|
||||
if not HAS_SHM_FILES:
|
||||
@ -86,14 +151,14 @@ class TestMultiprocessing(TestCase):
|
||||
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
|
||||
super(TestMultiprocessing, self).__init__(*args, **kwargs)
|
||||
|
||||
def _test_sharing(self):
|
||||
def do_test():
|
||||
x = torch.zeros(5, 5)
|
||||
q = mp.Queue()
|
||||
e = mp.Event()
|
||||
def _test_sharing(self, ctx=mp, type=torch.FloatTensor, repeat=1):
|
||||
def test_fill():
|
||||
x = torch.zeros(5, 5).type(type)
|
||||
q = ctx.Queue()
|
||||
e = ctx.Event()
|
||||
data = [x, x[:, 1]]
|
||||
q.put(data)
|
||||
p = mp.Process(target=simple_fill, args=(q, e))
|
||||
p = ctx.Process(target=simple_fill, args=(q, e))
|
||||
lc.check_pid(p.pid)
|
||||
p.start()
|
||||
e.wait()
|
||||
@ -102,14 +167,30 @@ class TestMultiprocessing(TestCase):
|
||||
p.join(1)
|
||||
self.assertFalse(p.is_alive())
|
||||
|
||||
with leak_checker(self) as lc:
|
||||
do_test()
|
||||
def test_receive():
|
||||
q = ctx.Queue()
|
||||
e = ctx.Event()
|
||||
p = ctx.Process(target=send_tensor, args=(q, e, type))
|
||||
lc.check_pid(p.pid)
|
||||
p.start()
|
||||
t1 = q.get()
|
||||
t2 = q.get()
|
||||
self.assertTrue(t1.eq(1).all())
|
||||
self.assertTrue(id(t1.storage()) == id(t2.storage()))
|
||||
e.set()
|
||||
p.join(1)
|
||||
self.assertFalse(p.is_alive())
|
||||
|
||||
def _test_preserve_sharing(self):
|
||||
with leak_checker(self) as lc:
|
||||
for i in range(repeat):
|
||||
test_fill()
|
||||
test_receive()
|
||||
|
||||
def _test_preserve_sharing(self, ctx=mp, repeat=1):
|
||||
def do_test():
|
||||
x = torch.randn(5, 5)
|
||||
data = [x.storage(), x.storage()[1:4], x, x[2], x[:,1]]
|
||||
q = mp.Queue()
|
||||
q = ctx.Queue()
|
||||
q.put(data)
|
||||
new_data = q.get()
|
||||
self.assertEqual(new_data, data, 0)
|
||||
@ -122,70 +203,210 @@ class TestMultiprocessing(TestCase):
|
||||
# self.assertEqual(new_data[1], new_data[0][1:4], 0)
|
||||
|
||||
with leak_checker(self):
|
||||
for i in range(repeat):
|
||||
do_test()
|
||||
|
||||
def _test_pool(self):
|
||||
def _test_pool(self, ctx=mp, repeat=1):
|
||||
def do_test():
|
||||
p = mp.Pool(2)
|
||||
p = ctx.Pool(2)
|
||||
for proc in p._pool:
|
||||
lc.check_pid(proc.pid)
|
||||
|
||||
buffers = (torch.zeros(2, 2) for i in range(4))
|
||||
buffers = [torch.zeros(2, 2) for i in range(4)]
|
||||
results = p.map(simple_pool_fill, buffers, 1)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(len(results), len(buffers))
|
||||
for r in results:
|
||||
self.assertEqual(r, torch.ones(2, 2) * 5, 0)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(len(results), 4)
|
||||
for b in buffers:
|
||||
self.assertEqual(b, torch.ones(2, 2) * 4, 0)
|
||||
|
||||
p.close()
|
||||
p.join()
|
||||
|
||||
with leak_checker(self) as lc:
|
||||
for i in range(repeat):
|
||||
do_test()
|
||||
|
||||
@unittest.skipIf(platform == 'darwin', "file descriptor strategy is not supported on OS X")
|
||||
def test_fd_sharing(self):
|
||||
self._test_sharing()
|
||||
self._test_sharing(repeat=20)
|
||||
|
||||
@unittest.skipIf(platform == 'darwin', "file descriptor strategy is not supported on OS X")
|
||||
def test_fd_preserve_sharing(self):
|
||||
self._test_preserve_sharing()
|
||||
self._test_preserve_sharing(repeat=20)
|
||||
|
||||
@unittest.skipIf(platform == 'darwin', "file descriptor strategy is not supported on OS X")
|
||||
def test_fd_pool(self):
|
||||
self._test_pool()
|
||||
self._test_pool(repeat=20)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_fs_sharing(self):
|
||||
with fs_sharing():
|
||||
self._test_sharing()
|
||||
self._test_sharing(repeat=20)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_fs_preserve_sharing(self):
|
||||
with fs_sharing():
|
||||
self._test_preserve_sharing()
|
||||
self._test_preserve_sharing(repeat=20)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_fs_pool(self):
|
||||
with fs_sharing():
|
||||
self._test_pool()
|
||||
self._test_pool(repeat=20)
|
||||
|
||||
@unittest.skipIf(not HAS_SHM_FILES, "don't not how to check if shm files exist")
|
||||
def test_fs(self):
|
||||
with fs_sharing(), leak_checker(self) as lc:
|
||||
def queue_put():
|
||||
x = torch.DoubleStorage(4)
|
||||
q = mp.Queue()
|
||||
self.assertFalse(lc.has_shm_files())
|
||||
q.put(x)
|
||||
time.sleep(0.05) # queue serializes asynchronously
|
||||
self.assertTrue(lc.has_shm_files(wait=False))
|
||||
q.get()
|
||||
del x
|
||||
del q # We have to clean up fds for leak_checker
|
||||
|
||||
with fs_sharing(), leak_checker(self) as lc:
|
||||
for i in range(20):
|
||||
queue_put()
|
||||
|
||||
def test_inherit_tensor(self):
|
||||
class SubProcess(mp.Process):
|
||||
def __init__(self, tensor):
|
||||
super(SubProcess, self).__init__()
|
||||
self.tensor = tensor
|
||||
|
||||
def run(self):
|
||||
self.tensor.add_(3)
|
||||
|
||||
t = torch.zeros(5, 5)
|
||||
p = SubProcess(t.share_memory_())
|
||||
p.start()
|
||||
p.join()
|
||||
self.assertEqual(t, torch.ones(5, 5) * 3, 0)
|
||||
|
||||
@unittest.skipIf(not TEST_CUDA_IPC, 'CUDA IPC not available')
|
||||
def test_cuda(self):
|
||||
torch.cuda.FloatTensor([1]) # initialize CUDA outside of leak checker
|
||||
self._test_sharing(mp.get_context('spawn'), torch.cuda.FloatTensor)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@unittest.skipIf(not TEST_CUDA_IPC, 'CUDA IPC not available')
|
||||
def test_cuda_small_tensors(self):
|
||||
# Check multiple small tensors which will likely use the same
|
||||
# underlying cached allocation
|
||||
ctx = mp.get_context('spawn')
|
||||
tensors = []
|
||||
for i in range(5):
|
||||
tensors += [torch.range(i * 5, (i * 5) + 4).cuda()]
|
||||
|
||||
inq = ctx.Queue()
|
||||
outq = ctx.Queue()
|
||||
inq.put(tensors)
|
||||
p = ctx.Process(target=sum_tensors, args=(inq, outq))
|
||||
p.start()
|
||||
|
||||
results = []
|
||||
for i in range(5):
|
||||
results.append(outq.get())
|
||||
p.join()
|
||||
|
||||
for i, tensor in enumerate(tensors):
|
||||
v, device, tensor_size, storage_size = results[i]
|
||||
self.assertEqual(v, torch.range(i * 5, (i * 5) + 4).sum())
|
||||
self.assertEqual(device, 0)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(tensor_size, 5)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(storage_size, 5)
|
||||
|
||||
@unittest.skipIf(not torch.cuda.is_available(), 'CUDA not available')
|
||||
def test_cuda_bad_call(self):
|
||||
# Initialize CUDA
|
||||
t = torch.zeros(5, 5).cuda().cpu()
|
||||
inq = mp.Queue()
|
||||
outq = mp.Queue()
|
||||
p = mp.Process(target=queue_get_exception, args=(inq, outq))
|
||||
p.start()
|
||||
inq.put(t)
|
||||
p.join()
|
||||
self.assertIsInstance(outq.get(), RuntimeError)
|
||||
|
||||
@unittest.skipIf(not TEST_CUDA_IPC, 'CUDA IPC not available')
|
||||
def test_event(self):
|
||||
ctx = mp.get_context('spawn')
|
||||
queue = ctx.Queue()
|
||||
ready = ctx.Event()
|
||||
done = ctx.Event()
|
||||
p = ctx.Process(target=cuda_multiply_two, args=(queue, ready, done))
|
||||
p.start()
|
||||
|
||||
ready.wait()
|
||||
with torch.cuda.stream(torch.cuda.Stream()):
|
||||
tensor = torch.cuda.FloatTensor([1, 1, 1, 1])
|
||||
# Use a sleep kernel to test events. Without the event, the
|
||||
# multiply happens before the add.
|
||||
event = torch.cuda.Event(interprocess=True)
|
||||
torch.cuda._sleep(20000000) # about 30 ms
|
||||
tensor.add_(1)
|
||||
event.record()
|
||||
queue.put((event, tensor))
|
||||
done.wait() # must wait until subprocess records event
|
||||
event.synchronize()
|
||||
self.assertEqual(list(tensor), [4, 4, 4, 4])
|
||||
p.join()
|
||||
|
||||
def _test_autograd_sharing(self, var):
|
||||
ready = mp.Event()
|
||||
master_modified = mp.Event()
|
||||
queue = mp.Queue()
|
||||
p = mp.Process(target=autograd_sharing, args=(queue, ready, master_modified))
|
||||
p.start()
|
||||
queue.put(var)
|
||||
|
||||
ready.wait()
|
||||
var.data[0,0] = 1000
|
||||
if var.grad is not None:
|
||||
var.grad.data[:] = torch.ones(5, 5) * 4
|
||||
master_modified.set()
|
||||
|
||||
worker_ok = queue.get()
|
||||
self.assertTrue(worker_ok)
|
||||
|
||||
self.assertEqual(var.data, torch.ones(5, 5))
|
||||
if var.grad is not None:
|
||||
self.assertEqual(var.grad.data, torch.ones(5, 5))
|
||||
p.join()
|
||||
|
||||
def test_variable_sharing(self):
|
||||
configs = [
|
||||
(True, False),
|
||||
(False, False),
|
||||
(False, True),
|
||||
]
|
||||
for requires_grad, volatile in configs:
|
||||
var = Variable(torch.range(1, 25).view(5, 5),
|
||||
requires_grad=requires_grad,
|
||||
volatile=volatile)
|
||||
self._test_autograd_sharing(var)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_parameter_sharing(self):
|
||||
param = Parameter(torch.range(1, 25).view(5, 5))
|
||||
self._test_autograd_sharing(param)
|
||||
|
||||
def _test_is_shared(self):
|
||||
t = torch.randn(5, 5)
|
||||
self.assertFalse(t.is_shared())
|
||||
t.share_memory_()
|
||||
self.assertTrue(t.is_shared())
|
||||
|
||||
@unittest.skipIf(platform == 'darwin', "file descriptor strategy is not supported on OS X")
|
||||
def test_is_shared(self):
|
||||
self._test_is_shared()
|
||||
|
||||
def test_fs_is_shared(self):
|
||||
with fs_sharing():
|
||||
self._test_is_shared()
|
||||
|
||||
@unittest.skipIf(not torch.cuda.is_available(), 'CUDA not available')
|
||||
def test_is_shared_cuda(self):
|
||||
t = torch.randn(5, 5).cuda()
|
||||
self.assertTrue(t.is_shared())
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == '__main__':
|
||||
start_method = os.environ.get('MULTIPROCESSING_METHOD')
|
||||
if start_method:
|
||||
if sys.version_info < (3, 4):
|
||||
print("Python <3.4 does not support 'multiprocessing.set_start_method'")
|
||||
sys.exit(0)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
print("INFO: Using multiprocessing start method '{}'".format(start_method))
|
||||
multiprocessing.set_start_method(start_method)
|
||||
unittest.main()
|
||||
|
||||
@ -6,6 +6,11 @@ import torch.cuda
|
||||
|
||||
from common import TestCase
|
||||
|
||||
if not torch.cuda.is_available():
|
||||
print('CUDA not available, skipping tests')
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
sys.exit()
|
||||
|
||||
nGPUs = torch.cuda.device_count()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
741
test/test_nn.py
@ -63,8 +63,8 @@ class TestOptim(TestCase):
|
||||
|
||||
initial_value = fn().data[0]
|
||||
for i in range(200):
|
||||
weight.grad.zero_()
|
||||
bias.grad.zero_()
|
||||
weight.grad.data.zero_()
|
||||
bias.grad.data.zero_()
|
||||
fn().backward()
|
||||
optimizer.step()
|
||||
|
||||
@ -112,8 +112,10 @@ class TestOptim(TestCase):
|
||||
wrap_old_fn(old_optim.sgd, learningRate=1e-3)
|
||||
)
|
||||
self._test_rosenbrock(
|
||||
lambda params: optim.SGD(params, lr=1e-3, momentum=0.9, dampening=0),
|
||||
wrap_old_fn(old_optim.sgd, learningRate=1e-3, momentum=0.9, dampening=0)
|
||||
lambda params: optim.SGD(params, lr=1e-3, momentum=0.9,
|
||||
dampening=0, weight_decay=1e-4),
|
||||
wrap_old_fn(old_optim.sgd, learningRate=1e-3, momentum=0.9,
|
||||
dampening=0, weightDecay=1e-4)
|
||||
)
|
||||
self._test_basic_cases(
|
||||
lambda weight, bias: optim.SGD([weight, bias], lr=1e-3)
|
||||
@ -273,7 +275,10 @@ class TestOptim(TestCase):
|
||||
lr=1e-3)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_invalid_param_type(self):
|
||||
with self.assertRaises(TypeError):
|
||||
optim.SGD(Variable(torch.randn(5, 5)), lr=3)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == '__main__':
|
||||
unittest.main()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
220
test/test_sparse.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,220 @@
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from torch import sparse
|
||||
|
||||
import itertools
|
||||
import random
|
||||
import unittest
|
||||
from common import TestCase
|
||||
from numbers import Number
|
||||
|
||||
SparseTensor = sparse.DoubleTensor
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class TestSparse(TestCase):
|
||||
@staticmethod
|
||||
def _gen_sparse(d, nnz, with_size):
|
||||
v = torch.randn(nnz)
|
||||
if isinstance(with_size, Number):
|
||||
i = (torch.rand(d, nnz) * with_size).type(torch.LongTensor)
|
||||
x = SparseTensor(i, v)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
i = torch.rand(d, nnz) * \
|
||||
torch.Tensor(with_size).repeat(nnz, 1).transpose(0, 1)
|
||||
i = i.type(torch.LongTensor)
|
||||
x = SparseTensor(i, v, torch.Size(with_size))
|
||||
|
||||
return x, i, v
|
||||
|
||||
def test_basic(self):
|
||||
x, i, v = self._gen_sparse(3, 10, 100)
|
||||
|
||||
self.assertEqual(i, x.indices())
|
||||
self.assertEqual(v, x.values())
|
||||
|
||||
x, i, v = self._gen_sparse(3, 10, [100, 100, 100])
|
||||
self.assertEqual(i, x.indices())
|
||||
self.assertEqual(v, x.values())
|
||||
self.assertEqual(x.ndimension(), 3)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(x.nnz(), 10)
|
||||
for i in range(3):
|
||||
self.assertEqual(x.size(i), 100)
|
||||
|
||||
# Make sure we can access empty indices / values
|
||||
x = SparseTensor()
|
||||
self.assertEqual(x.indices().numel(), 0)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(x.values().numel(), 0)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_to_dense(self):
|
||||
i = torch.LongTensor([
|
||||
[0, 1, 2, 2],
|
||||
[0, 0, 0, 3],
|
||||
[0, 0, 1, 4],
|
||||
])
|
||||
v = torch.Tensor([2, 1, 3, 4])
|
||||
x = SparseTensor(i, v, torch.Size([3, 4, 5]))
|
||||
res = torch.Tensor([
|
||||
[[2, 0, 0, 0, 0],
|
||||
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
|
||||
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
|
||||
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0]],
|
||||
[[1, 0, 0, 0, 0],
|
||||
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
|
||||
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
|
||||
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0]],
|
||||
[[0, 3, 0, 0, 0],
|
||||
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
|
||||
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
|
||||
[0, 0, 0, 0, 4]],
|
||||
])
|
||||
|
||||
x.to_dense() # Tests double to_dense for memory corruption
|
||||
x.to_dense()
|
||||
x.to_dense()
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res, x.to_dense())
|
||||
|
||||
def test_contig(self):
|
||||
i = torch.LongTensor([
|
||||
[1, 0, 35, 14, 39, 6, 71, 66, 40, 27],
|
||||
[92, 31, 62, 50, 22, 65, 89, 74, 56, 34],
|
||||
])
|
||||
v = torch.Tensor([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10])
|
||||
x = SparseTensor(i, v, torch.Size([100, 100]))
|
||||
exp_i = torch.LongTensor([
|
||||
[0, 1, 6, 14, 27, 35, 39, 40, 66, 71],
|
||||
[31, 92, 65, 50, 34, 62, 22, 56, 74, 89],
|
||||
])
|
||||
exp_v = torch.Tensor([2, 1, 6, 4, 10, 3, 5, 9, 8, 7])
|
||||
x.contiguous()
|
||||
self.assertEqual(exp_i, x.indices())
|
||||
self.assertEqual(exp_v, x.values())
|
||||
|
||||
i = torch.LongTensor([
|
||||
[2, 0, 2, 1],
|
||||
[0, 0, 3, 0],
|
||||
[1, 0, 4, 0],
|
||||
])
|
||||
v = torch.Tensor([3, 2, 4, 1])
|
||||
x = SparseTensor(i, v, torch.Size([3, 4, 5]))
|
||||
exp_i = torch.LongTensor([
|
||||
[0, 1, 2, 2],
|
||||
[0, 0, 0, 3],
|
||||
[0, 0, 1, 4],
|
||||
])
|
||||
exp_v = torch.Tensor([2, 1, 3, 4])
|
||||
|
||||
x.contiguous()
|
||||
self.assertEqual(exp_i, x.indices())
|
||||
self.assertEqual(exp_v, x.values())
|
||||
|
||||
# Duplicate indices
|
||||
i = torch.LongTensor([
|
||||
[0, 0, 2, 0],
|
||||
[0, 0, 3, 0],
|
||||
[0, 0, 4, 0],
|
||||
])
|
||||
v = torch.Tensor([3, 2, 4, 1])
|
||||
x = SparseTensor(i, v, torch.Size([3, 4, 5]))
|
||||
exp_i = torch.LongTensor([
|
||||
[0, 2],
|
||||
[0, 3],
|
||||
[0, 4],
|
||||
])
|
||||
exp_v = torch.Tensor([6, 4])
|
||||
|
||||
x.contiguous()
|
||||
self.assertEqual(exp_i, x.indices())
|
||||
self.assertEqual(exp_v, x.values())
|
||||
|
||||
def test_transpose(self):
|
||||
x = self._gen_sparse(4, 20, 5)[0]
|
||||
y = x.to_dense()
|
||||
|
||||
for i, j in itertools.combinations(range(4), 2):
|
||||
x = x.transpose_(i, j)
|
||||
y = y.transpose(i, j)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(x.to_dense(), y)
|
||||
|
||||
x = x.transpose(i, j)
|
||||
y = y.transpose(i, j)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(x.to_dense(), y)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_mm(self):
|
||||
def test_shape(di, dj, dk):
|
||||
x, _, _ = self._gen_sparse(2, 20, [di, dj])
|
||||
t = torch.randn(di, dk)
|
||||
y = torch.randn(dj, dk)
|
||||
alpha = random.random()
|
||||
beta = random.random()
|
||||
|
||||
expected = torch.addmm(alpha, t, beta, x.to_dense(), y)
|
||||
res = torch.addmm(alpha, t, beta, x, y)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res, expected)
|
||||
|
||||
expected = torch.addmm(t, x.to_dense(), y)
|
||||
res = torch.addmm(t, x, y)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res, expected)
|
||||
|
||||
expected = torch.mm(x.to_dense(), y)
|
||||
res = torch.mm(x, y)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res, expected)
|
||||
|
||||
test_shape(10, 100, 100)
|
||||
test_shape(100, 1000, 200)
|
||||
test_shape(64, 10000, 300)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_saddmm(self):
|
||||
def test_shape(di, dj, dk):
|
||||
x = self._gen_sparse(2, 20, [di, dj])[0]
|
||||
t = self._gen_sparse(2, 20, [di, dk])[0]
|
||||
y = torch.randn(dj, dk)
|
||||
alpha = random.random()
|
||||
beta = random.random()
|
||||
|
||||
expected = torch.addmm(alpha, t.to_dense(), beta, x.to_dense(), y)
|
||||
res = torch.saddmm(alpha, t, beta, x, y)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res.to_dense(), expected)
|
||||
|
||||
expected = torch.addmm(t.to_dense(), x.to_dense(), y)
|
||||
res = torch.saddmm(t, x, y)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res.to_dense(), expected)
|
||||
|
||||
expected = torch.mm(x.to_dense(), y)
|
||||
res = torch.smm(x, y)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res.to_dense(), expected)
|
||||
|
||||
test_shape(7, 5, 3)
|
||||
test_shape(1000, 100, 100)
|
||||
test_shape(3000, 64, 300)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_spadd(self):
|
||||
def test_shape(*shape):
|
||||
x, _, _ = self._gen_sparse(len(shape), 10, shape)
|
||||
y = torch.randn(*shape)
|
||||
r = random.random()
|
||||
|
||||
expected = y + r * x.to_dense()
|
||||
res = torch.add(y, r, x)
|
||||
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res, expected)
|
||||
|
||||
# Non contiguous dense tensor
|
||||
s = list(shape)
|
||||
s[0] = shape[-1]
|
||||
s[-1] = shape[0]
|
||||
y = torch.randn(*s).transpose_(0, len(s) - 1)
|
||||
r = random.random()
|
||||
|
||||
expected = y + r * x.to_dense()
|
||||
res = torch.add(y, r, x)
|
||||
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res, expected)
|
||||
|
||||
test_shape(5, 6)
|
||||
test_shape(10, 10, 10)
|
||||
test_shape(50, 30, 20)
|
||||
test_shape(5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == '__main__':
|
||||
unittest.main()
|
||||
|
||||
@ -203,17 +203,11 @@ class TestTorch(TestCase):
|
||||
expected_c.map2_(a, b, lambda _, a, b: mathfn(a, b))
|
||||
self.assertEqual(expected_c, c, 0)
|
||||
|
||||
# Tensor and scalar
|
||||
v = random.random()
|
||||
c = torchfn(a, v)
|
||||
expected_c.map_(a, lambda _, a: mathfn(a, v))
|
||||
self.assertEqual(expected_c, c, 0)
|
||||
def test_max_elementwise(self):
|
||||
self._testCSelection(torch.max, max)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_cmax(self):
|
||||
self._testCSelection(torch.cmax, max)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_cmin(self):
|
||||
self._testCSelection(torch.cmin, min)
|
||||
def test_min_elementwise(self):
|
||||
self._testCSelection(torch.min, min)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_lerp(self):
|
||||
def TH_lerp(a, b, weight):
|
||||
@ -332,14 +326,14 @@ class TestTorch(TestCase):
|
||||
res_neg.neg_()
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res_neg, res_add)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_cinv(self):
|
||||
def test_reciprocal(self):
|
||||
a = torch.randn(100,89)
|
||||
zeros = torch.Tensor().resize_as_(a).zero_()
|
||||
|
||||
res_pow = torch.pow(a, -1)
|
||||
res_inv = a.clone()
|
||||
res_inv.cinv_()
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res_inv, res_pow)
|
||||
res_reciprocal = a.clone()
|
||||
res_reciprocal.reciprocal_()
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res_reciprocal, res_pow)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_mul(self):
|
||||
m1 = torch.randn(10,10)
|
||||
@ -520,6 +514,18 @@ class TestTorch(TestCase):
|
||||
res2[i] = max(min_val, min(max_val, res2[i]))
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res1, res2)
|
||||
|
||||
res1 = torch.clamp(m1, min=min_val)
|
||||
res2 = m1.clone()
|
||||
for i in iter_indices(res2):
|
||||
res2[i] = max(min_val, res2[i])
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res1, res2)
|
||||
|
||||
res1 = torch.clamp(m1, max=max_val)
|
||||
res2 = m1.clone()
|
||||
for i in iter_indices(res2):
|
||||
res2[i] = min(max_val, res2[i])
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res1, res2)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_pow(self):
|
||||
# [res] torch.pow([res,] x)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -603,28 +609,28 @@ class TestTorch(TestCase):
|
||||
x = torch.rand(100, 100)
|
||||
res1 = torch.sum(x, 1)
|
||||
res2 = torch.Tensor()
|
||||
torch.sum(res2, x, 1)
|
||||
torch.sum(x, 1, out=res2)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res1, res2)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_prod(self):
|
||||
x = torch.rand(100, 100)
|
||||
res1 = torch.prod(x, 1)
|
||||
res2 = torch.Tensor()
|
||||
torch.prod(res2, x, 1)
|
||||
torch.prod(x, 1, out=res2)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res1, res2)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_cumsum(self):
|
||||
x = torch.rand(100, 100)
|
||||
res1 = torch.cumsum(x, 1)
|
||||
res2 = torch.Tensor()
|
||||
torch.cumsum(res2, x, 1)
|
||||
torch.cumsum(x, 1, out=res2)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res1, res2)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_cumprod(self):
|
||||
x = torch.rand(100, 100)
|
||||
res1 = torch.cumprod(x, 1)
|
||||
res2 = torch.Tensor()
|
||||
torch.cumprod(res2, x, 1)
|
||||
torch.cumprod(x, 1, out=res2)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res1, res2)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_cross(self):
|
||||
@ -632,13 +638,13 @@ class TestTorch(TestCase):
|
||||
y = torch.rand(100, 3, 100)
|
||||
res1 = torch.cross(x, y)
|
||||
res2 = torch.Tensor()
|
||||
torch.cross(res2, x, y)
|
||||
torch.cross(x, y, out=res2)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res1, res2)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_zeros(self):
|
||||
res1 = torch.zeros(100, 100)
|
||||
res2 = torch.Tensor()
|
||||
torch.zeros(res2, 100, 100)
|
||||
torch.zeros(100, 100, out=res2)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res1, res2)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_histc(self):
|
||||
@ -650,20 +656,20 @@ class TestTorch(TestCase):
|
||||
def test_ones(self):
|
||||
res1 = torch.ones(100, 100)
|
||||
res2 = torch.Tensor()
|
||||
torch.ones(res2, 100, 100)
|
||||
torch.ones(100, 100, out=res2)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res1, res2)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_diag(self):
|
||||
x = torch.rand(100, 100)
|
||||
res1 = torch.diag(x)
|
||||
res2 = torch.Tensor()
|
||||
torch.diag(res2, x)
|
||||
torch.diag(x, out=res2)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res1, res2)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_eye(self):
|
||||
res1 = torch.eye(100, 100)
|
||||
res2 = torch.Tensor()
|
||||
torch.eye(res2, 100, 100)
|
||||
torch.eye(100, 100, out=res2)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res1, res2)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_renorm(self):
|
||||
@ -743,47 +749,47 @@ class TestTorch(TestCase):
|
||||
def test_range(self):
|
||||
res1 = torch.range(0, 1)
|
||||
res2 = torch.Tensor()
|
||||
torch.range(res2, 0, 1)
|
||||
torch.range(0, 1, out=res2)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res1, res2, 0)
|
||||
|
||||
# Check range for non-contiguous tensors.
|
||||
x = torch.zeros(2, 3)
|
||||
torch.range(x.narrow(1, 1, 2), 0, 3)
|
||||
torch.range(0, 3, out=x.narrow(1, 1, 2))
|
||||
res2 = torch.Tensor(((0, 0, 1), (0, 2, 3)))
|
||||
self.assertEqual(x, res2, 1e-16)
|
||||
|
||||
# Check negative
|
||||
res1 = torch.Tensor((1, 0))
|
||||
res2 = torch.Tensor()
|
||||
torch.range(res2, 1, 0, -1)
|
||||
torch.range(1, 0, -1, out=res2)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res1, res2, 0)
|
||||
|
||||
# Equal bounds
|
||||
res1 = torch.ones(1)
|
||||
res2 = torch.Tensor()
|
||||
torch.range(res2, 1, 1, -1)
|
||||
torch.range(1, 1, -1, out=res2)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res1, res2, 0)
|
||||
torch.range(res2, 1, 1, 1)
|
||||
torch.range(1, 1, 1, out=res2)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res1, res2, 0)
|
||||
|
||||
# FloatTensor
|
||||
res1 = torch.range(torch.FloatTensor(), 0.6, 0.9, 0.1)
|
||||
res1 = torch.range(0.6, 0.9, 0.1, out=torch.FloatTensor())
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res1.size(0), 4)
|
||||
res1 = torch.range(torch.FloatTensor(), 1, 10, 0.3)
|
||||
res1 = torch.range(1, 10, 0.3, out=torch.FloatTensor())
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res1.size(0), 31)
|
||||
|
||||
# DoubleTensor
|
||||
res1 = torch.range(torch.DoubleTensor(), 0.6, 0.9, 0.1)
|
||||
res1 = torch.range(0.6, 0.9, 0.1, out=torch.DoubleTensor())
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res1.size(0), 4)
|
||||
res1 = torch.range(torch.DoubleTensor(), 1, 10, 0.3)
|
||||
res1 = torch.range(1, 10, 0.3, out=torch.DoubleTensor())
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res1.size(0), 31)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_randperm(self):
|
||||
_RNGState = torch.get_rng_state()
|
||||
res1 = torch.randperm(100)
|
||||
res2 = torch.Tensor()
|
||||
res2 = torch.LongTensor()
|
||||
torch.set_rng_state(_RNGState)
|
||||
torch.randperm(res2, 100)
|
||||
torch.randperm(100, out=res2)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res1, res2, 0)
|
||||
|
||||
def assertIsOrdered(self, order, x, mxx, ixx, task):
|
||||
@ -819,7 +825,7 @@ class TestTorch(TestCase):
|
||||
# Test use of result tensor
|
||||
res2val = torch.Tensor()
|
||||
res2ind = torch.LongTensor()
|
||||
torch.sort(res2val, res2ind, x)
|
||||
torch.sort(x, out=(res2val, res2ind))
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res1val, res2val, 0)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res1ind, res2ind, 0)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -835,7 +841,7 @@ class TestTorch(TestCase):
|
||||
|
||||
# Test that we still have proper sorting with duplicate keys
|
||||
x = torch.floor(torch.rand(SIZE, SIZE)*10)
|
||||
torch.sort(res2val, res2ind, x)
|
||||
torch.sort(x, out=(res2val, res2ind))
|
||||
self.assertIsOrdered('ascending', x, res2val, res2ind, 'random with duplicate keys')
|
||||
|
||||
# DESCENDING SORT
|
||||
@ -845,7 +851,7 @@ class TestTorch(TestCase):
|
||||
# Test use of result tensor
|
||||
res2val = torch.Tensor()
|
||||
res2ind = torch.LongTensor()
|
||||
torch.sort(res2val, res2ind, x, x.dim()-1, True)
|
||||
torch.sort(x, x.dim()-1, True, out=(res2val, res2ind))
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res1val, res2val, 0)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res1ind, res2ind, 0)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -906,6 +912,11 @@ class TestTorch(TestCase):
|
||||
k = random.randint(1, testTensor.size(dim))
|
||||
compare(testTensor, k, dim, dir)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_topk_arguments(self):
|
||||
q = torch.randn(10, 2, 10)
|
||||
# Make sure True isn't mistakenly taken as the 2nd dimension (interpreted as 1)
|
||||
self.assertRaises(TypeError, lambda: q.topk(4, True))
|
||||
|
||||
def test_kthvalue(self):
|
||||
SIZE = 50
|
||||
x = torch.rand(SIZE, SIZE, SIZE)
|
||||
@ -921,7 +932,7 @@ class TestTorch(TestCase):
|
||||
k = random.randint(1, SIZE)
|
||||
res1val = torch.Tensor()
|
||||
res1ind = torch.LongTensor()
|
||||
torch.kthvalue(res1val, res1ind, x, k)
|
||||
torch.kthvalue(x, k, out=(res1val, res1ind))
|
||||
res2val, res2ind = torch.sort(x)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res1val[:,:,0], res2val[:,:,k-1], 0)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res1ind[:,:,0], res2ind[:,:,k-1], 0)
|
||||
@ -965,7 +976,7 @@ class TestTorch(TestCase):
|
||||
# Test use of result tensor
|
||||
res2val = torch.Tensor()
|
||||
res2ind = torch.LongTensor()
|
||||
torch.median(res2val, res2ind, x)
|
||||
torch.median(x, out=(res2val, res2ind))
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res2val, res1val, 0)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res2ind, res1ind, 0)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -999,7 +1010,7 @@ class TestTorch(TestCase):
|
||||
# Test use of result tensor
|
||||
res2val = torch.Tensor()
|
||||
res2ind = torch.LongTensor()
|
||||
torch.mode(res2val, res2ind, x)
|
||||
torch.mode(x, out=(res2val, res2ind))
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res1val, res2val, 0)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res1ind, res2ind, 0)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1015,27 +1026,18 @@ class TestTorch(TestCase):
|
||||
x = torch.rand(SIZE, SIZE)
|
||||
res1 = torch.tril(x)
|
||||
res2 = torch.Tensor()
|
||||
torch.tril(res2, x)
|
||||
torch.tril(x, out=res2)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res1, res2, 0)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_triu(self):
|
||||
x = torch.rand(SIZE, SIZE)
|
||||
res1 = torch.triu(x)
|
||||
res2 = torch.Tensor()
|
||||
torch.triu(res2, x)
|
||||
torch.triu(x, out=res2)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res1, res2, 0)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_cat(self):
|
||||
SIZE = 10
|
||||
# 2-arg cat
|
||||
for dim in range(3):
|
||||
x = torch.rand(13, SIZE, SIZE).transpose(0, dim)
|
||||
y = torch.rand(17, SIZE, SIZE).transpose(0, dim)
|
||||
res1 = torch.cat((x, y), dim)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res1.narrow(dim, 0, 13), x, 0)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res1.narrow(dim, 13, 17), y, 0)
|
||||
|
||||
# Check iterables
|
||||
for dim in range(3):
|
||||
x = torch.rand(13, SIZE, SIZE).transpose(0, dim)
|
||||
y = torch.rand(17, SIZE, SIZE).transpose(0, dim)
|
||||
@ -1045,14 +1047,35 @@ class TestTorch(TestCase):
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res1.narrow(dim, 0, 13), x, 0)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res1.narrow(dim, 13, 17), y, 0)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res1.narrow(dim, 30, 19), z, 0)
|
||||
self.assertRaises(ValueError, lambda: torch.cat([]))
|
||||
|
||||
x = torch.randn(20, SIZE, SIZE)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(torch.cat(torch.split(x, 7)), x)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(torch.cat(torch.chunk(x, 7)), x)
|
||||
|
||||
y = torch.randn(1, SIZE, SIZE)
|
||||
z = torch.cat([x, y])
|
||||
self.assertEqual(z.size(), (21, SIZE, SIZE))
|
||||
|
||||
self.assertRaises(TypeError, lambda: torch.cat([]))
|
||||
|
||||
def test_stack(self):
|
||||
x = torch.rand(2, 3, 4)
|
||||
y = torch.rand(2, 3, 4)
|
||||
z = torch.rand(2, 3, 4)
|
||||
for dim in range(4):
|
||||
res = torch.stack((x, y, z), dim)
|
||||
expected_size = x.size()[:dim] + (3,) + x.size()[dim:]
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res.size(), expected_size)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res.select(dim, 0), x, 0)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res.select(dim, 1), y, 0)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res.select(dim, 2), z, 0)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_linspace(self):
|
||||
_from = random.random()
|
||||
to = _from + random.random()
|
||||
res1 = torch.linspace(_from, to, 137)
|
||||
res2 = torch.Tensor()
|
||||
torch.linspace(res2, _from, to, 137)
|
||||
torch.linspace(_from, to, 137, out=res2)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res1, res2, 0)
|
||||
self.assertRaises(RuntimeError, lambda: torch.linspace(0, 1, 1))
|
||||
self.assertEqual(torch.linspace(0, 0, 1), torch.zeros(1), 0)
|
||||
@ -1062,7 +1085,7 @@ class TestTorch(TestCase):
|
||||
|
||||
# Check linspace for non-contiguous tensors.
|
||||
x = torch.zeros(2, 3)
|
||||
y = torch.linspace(x.narrow(1, 1, 2), 0, 3, 4)
|
||||
y = torch.linspace(0, 3, 4, out=x.narrow(1, 1, 2))
|
||||
self.assertEqual(x, torch.Tensor(((0, 0, 1), (0, 2, 3))), 0)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_logspace(self):
|
||||
@ -1070,7 +1093,7 @@ class TestTorch(TestCase):
|
||||
to = _from + random.random()
|
||||
res1 = torch.logspace(_from, to, 137)
|
||||
res2 = torch.Tensor()
|
||||
torch.logspace(res2, _from, to, 137)
|
||||
torch.logspace(_from, to, 137, out=res2)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res1, res2, 0)
|
||||
self.assertRaises(RuntimeError, lambda: torch.logspace(0, 1, 1))
|
||||
self.assertEqual(torch.logspace(0, 0, 1), torch.ones(1), 0)
|
||||
@ -1080,7 +1103,7 @@ class TestTorch(TestCase):
|
||||
|
||||
# Check logspace_ for non-contiguous tensors.
|
||||
x = torch.zeros(2, 3)
|
||||
y = torch.logspace(x.narrow(1, 1, 2), 0, 3, 4)
|
||||
y = torch.logspace(0, 3, 4, out=x.narrow(1, 1, 2))
|
||||
self.assertEqual(x, torch.Tensor(((0, 1, 10), (0, 100, 1000))), 0)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_rand(self):
|
||||
@ -1088,7 +1111,7 @@ class TestTorch(TestCase):
|
||||
res1 = torch.rand(SIZE, SIZE)
|
||||
res2 = torch.Tensor()
|
||||
torch.manual_seed(123456)
|
||||
torch.rand(res2, SIZE, SIZE)
|
||||
torch.rand(SIZE, SIZE, out=res2)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res1, res2)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_randn(self):
|
||||
@ -1096,7 +1119,7 @@ class TestTorch(TestCase):
|
||||
res1 = torch.randn(SIZE, SIZE)
|
||||
res2 = torch.Tensor()
|
||||
torch.manual_seed(123456)
|
||||
torch.randn(res2, SIZE, SIZE)
|
||||
torch.randn(SIZE, SIZE, out=res2)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res1, res2)
|
||||
|
||||
@skipIfNoLapack
|
||||
@ -1114,8 +1137,8 @@ class TestTorch(TestCase):
|
||||
self.assertLessEqual(b.dist(torch.mm(a, res1)), 1e-12)
|
||||
ta = torch.Tensor()
|
||||
tb = torch.Tensor()
|
||||
res2 = torch.gesv(tb, ta, b, a)[0]
|
||||
res3 = torch.gesv(b, a, b, a)[0]
|
||||
res2 = torch.gesv(b, a, out=(tb, ta))[0]
|
||||
res3 = torch.gesv(b, a, out=(b, a))[0]
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res1, tb)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res1, b)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res1, res2)
|
||||
@ -1125,9 +1148,9 @@ class TestTorch(TestCase):
|
||||
res1 = torch.gesv(b, a)[0]
|
||||
ta = torch.Tensor()
|
||||
tb = torch.Tensor()
|
||||
torch.gesv(tb, ta, b, a)[0]
|
||||
torch.gesv(b, a, out=(tb, ta))[0]
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res1, tb)
|
||||
torch.gesv(tb, ta, b, a)[0]
|
||||
torch.gesv(b, a, out=(tb, ta))[0]
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res1, tb)
|
||||
|
||||
@skipIfNoLapack
|
||||
@ -1152,7 +1175,7 @@ class TestTorch(TestCase):
|
||||
|
||||
# in-place
|
||||
q, r = torch.Tensor(), torch.Tensor()
|
||||
torch.qr(q, r, a)
|
||||
torch.qr(a, out=(q, r))
|
||||
canon_and_check(q, r, expected_q, expected_r)
|
||||
|
||||
# manually calculate qr using geqrf and orgqr
|
||||
@ -1297,10 +1320,10 @@ class TestTorch(TestCase):
|
||||
res1 = torch.trtrs(b,a)[0]
|
||||
ta = torch.Tensor()
|
||||
tb = torch.Tensor()
|
||||
torch.trtrs(tb,ta,b,a)
|
||||
torch.trtrs(b, a, out=(tb, ta))
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res1, tb, 0)
|
||||
tb.zero_()
|
||||
torch.trtrs(tb,ta,b,a)
|
||||
torch.trtrs(b, a, out=(tb, ta))
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res1, tb, 0)
|
||||
|
||||
@skipIfNoLapack
|
||||
@ -1315,12 +1338,12 @@ class TestTorch(TestCase):
|
||||
|
||||
ta = torch.Tensor()
|
||||
tb = torch.Tensor()
|
||||
res2 = torch.gels(tb, ta, b, a)[0]
|
||||
res2 = torch.gels(b, a, out=(tb, ta))[0]
|
||||
self.assertEqual(a, a_copy, 0)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(b, b_copy, 0)
|
||||
self.assertEqual((torch.mm(a, res1) - b).norm(), expectedNorm, 1e-8)
|
||||
|
||||
res3 = torch.gels(b, a, b, a)[0]
|
||||
res3 = torch.gels(b, a, out=(b, a))[0]
|
||||
self.assertEqual((torch.mm(a_copy, b) - b_copy).norm(), expectedNorm, 1e-8)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res1, tb, 0)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res1, b, 0)
|
||||
@ -1367,11 +1390,11 @@ class TestTorch(TestCase):
|
||||
(9.35, -4.43, -0.70, -0.26))).t()
|
||||
ta = torch.Tensor()
|
||||
tb = torch.Tensor()
|
||||
torch.gels(tb, ta, b, a)
|
||||
torch.gels(b, a, out=(tb, ta))
|
||||
self.assertEqual((torch.mm(a, tb) - b).norm(), expectedNorm, 1e-8)
|
||||
torch.gels(tb, ta, b, a)
|
||||
torch.gels(b, a, out=(tb, ta))
|
||||
self.assertEqual((torch.mm(a, tb) - b).norm(), expectedNorm, 1e-8)
|
||||
torch.gels(tb, ta, b, a)
|
||||
torch.gels(b, a, out=(tb, ta))
|
||||
self.assertEqual((torch.mm(a, tb) - b).norm(), expectedNorm, 1e-8)
|
||||
|
||||
@skipIfNoLapack
|
||||
@ -1385,7 +1408,7 @@ class TestTorch(TestCase):
|
||||
ee, vv = torch.eig(a, True)
|
||||
te = torch.Tensor()
|
||||
tv = torch.Tensor()
|
||||
eee, vvv = torch.eig(te, tv, a, True)
|
||||
eee, vvv = torch.eig(a, True, out=(te, tv))
|
||||
self.assertEqual(e, ee, 1e-12)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(ee, eee, 1e-12)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(ee, te, 1e-12)
|
||||
@ -1396,12 +1419,12 @@ class TestTorch(TestCase):
|
||||
X = torch.randn(4,4)
|
||||
X = torch.mm(X.t(), X)
|
||||
e, v = torch.zeros(4,2), torch.zeros(4,4)
|
||||
torch.eig(e, v, X, True)
|
||||
torch.eig(X, True, out=(e, v))
|
||||
Xhat = torch.mm(torch.mm(v, torch.diag(e.select(1, 0))), v.t())
|
||||
self.assertEqual(X, Xhat, 1e-8, 'VeV\' wrong')
|
||||
self.assertFalse(v.is_contiguous(), 'V is contiguous')
|
||||
|
||||
torch.eig(e, v, X, True)
|
||||
torch.eig(X, True, out=(e, v))
|
||||
Xhat = torch.mm(v, torch.mm(e.select(1, 0).diag(), v.t()))
|
||||
self.assertEqual(X, Xhat, 1e-8, 'VeV\' wrong')
|
||||
self.assertFalse(v.is_contiguous(), 'V is contiguous')
|
||||
@ -1413,7 +1436,7 @@ class TestTorch(TestCase):
|
||||
v = torch.zeros(4, 2, 4)[:,1]
|
||||
self.assertFalse(v.is_contiguous(), 'V is contiguous')
|
||||
self.assertFalse(e.is_contiguous(), 'E is contiguous')
|
||||
torch.eig(e, v, X, True)
|
||||
torch.eig(X, True, out=(e, v))
|
||||
Xhat = torch.mm(torch.mm(v, torch.diag(e.select(1, 0))), v.t())
|
||||
self.assertEqual(X, Xhat, 1e-8, 'VeV\' wrong')
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1426,13 +1449,13 @@ class TestTorch(TestCase):
|
||||
|
||||
# First call to symeig
|
||||
self.assertTrue(resv.is_contiguous(), 'resv is not contiguous')
|
||||
torch.symeig(rese, resv, cov.clone(), True)
|
||||
torch.symeig(cov.clone(), True, out=(rese, resv))
|
||||
ahat = torch.mm(torch.mm(resv, torch.diag(rese)), resv.t())
|
||||
self.assertEqual(cov, ahat, 1e-8, 'VeV\' wrong')
|
||||
|
||||
# Second call to symeig
|
||||
self.assertFalse(resv.is_contiguous(), 'resv is contiguous')
|
||||
torch.symeig(rese, resv, cov.clone(), True)
|
||||
torch.symeig(cov.clone(), True, out=(rese, resv))
|
||||
ahat = torch.mm(torch.mm(resv, torch.diag(rese)), resv.t())
|
||||
self.assertEqual(cov, ahat, 1e-8, 'VeV\' wrong')
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1443,7 +1466,7 @@ class TestTorch(TestCase):
|
||||
v = torch.zeros(4, 2, 4)[:,1]
|
||||
self.assertFalse(v.is_contiguous(), 'V is contiguous')
|
||||
self.assertFalse(e.is_contiguous(), 'E is contiguous')
|
||||
torch.symeig(e, v, X, True)
|
||||
torch.symeig(X, True, out=(e, v))
|
||||
Xhat = torch.mm(torch.mm(v, torch.diag(e)), v.t())
|
||||
self.assertEqual(X, Xhat, 1e-8, 'VeV\' wrong')
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1458,7 +1481,7 @@ class TestTorch(TestCase):
|
||||
uu = torch.Tensor()
|
||||
ss = torch.Tensor()
|
||||
vv = torch.Tensor()
|
||||
uuu, sss, vvv = torch.svd(uu, ss, vv, a)
|
||||
uuu, sss, vvv = torch.svd(a, out=(uu, ss, vv))
|
||||
self.assertEqual(u, uu, 0, 'torch.svd')
|
||||
self.assertEqual(u, uuu, 0, 'torch.svd')
|
||||
self.assertEqual(s, ss, 0, 'torch.svd')
|
||||
@ -1473,7 +1496,7 @@ class TestTorch(TestCase):
|
||||
self.assertEqual(X, Xhat, 1e-8, 'USV\' wrong')
|
||||
|
||||
self.assertFalse(U.is_contiguous(), 'U is contiguous')
|
||||
torch.svd(U, S, V, X)
|
||||
torch.svd(X, out=(U, S, V))
|
||||
Xhat = torch.mm(U, torch.mm(S.diag(), V.t()))
|
||||
self.assertEqual(X, Xhat, 1e-8, 'USV\' wrong')
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1486,7 +1509,7 @@ class TestTorch(TestCase):
|
||||
self.assertFalse(U.is_contiguous(), 'U is contiguous')
|
||||
self.assertFalse(S.is_contiguous(), 'S is contiguous')
|
||||
self.assertFalse(V.is_contiguous(), 'V is contiguous')
|
||||
torch.svd(U, S, V, X)
|
||||
torch.svd(X, out=(U, S, V))
|
||||
Xhat = torch.mm(U, torch.mm(S.diag(), V.t()))
|
||||
self.assertEqual(X, Xhat, 1e-8, 'USV\' wrong')
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1500,11 +1523,11 @@ class TestTorch(TestCase):
|
||||
self.assertEqual(E, torch.mm(MI, M), 1e-8, 'inverse value')
|
||||
|
||||
MII = torch.Tensor(5, 5)
|
||||
torch.inverse(MII, M)
|
||||
torch.inverse(M, out=MII)
|
||||
self.assertFalse(MII.is_contiguous(), 'MII is contiguous')
|
||||
self.assertEqual(MII, MI, 0, 'inverse value in-place')
|
||||
# second call, now that MII is transposed
|
||||
torch.inverse(MII, M)
|
||||
torch.inverse(M, out=MII)
|
||||
self.assertFalse(MII.is_contiguous(), 'MII is contiguous')
|
||||
self.assertEqual(MII, MI, 0, 'inverse value in-place')
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1784,14 +1807,15 @@ class TestTorch(TestCase):
|
||||
if inplace:
|
||||
u = torch.Tensor(a.size())
|
||||
piv = torch.IntTensor(a.size(0))
|
||||
args = [u, piv, a]
|
||||
kwargs = {'out': (u, piv)}
|
||||
else:
|
||||
kwargs = {}
|
||||
args = [a]
|
||||
|
||||
if uplo is not None:
|
||||
args += [uplo]
|
||||
|
||||
u, piv = torch.pstrf(*args)
|
||||
u, piv = torch.pstrf(*args, **kwargs)
|
||||
|
||||
if uplo is False:
|
||||
a_reconstructed = torch.mm(u, u.t())
|
||||
@ -1851,9 +1875,16 @@ class TestTorch(TestCase):
|
||||
self.assertEqual(reference_5d[2, ..., 1, 0], reference_5d[2, :, :, 1, 0], 0)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(reference_5d[2, 1, 0, ..., 1], reference_5d[2, 1, 0, :, 1], 0)
|
||||
|
||||
self.assertRaises(RuntimeError, lambda: reference[1, 1, 1, 1])
|
||||
self.assertRaises(RuntimeError, lambda: reference[1, 1, 1, 1:1])
|
||||
self.assertRaises(RuntimeError, lambda: reference[3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3])
|
||||
self.assertRaises(IndexError, lambda: reference[1, 1, 1, 1])
|
||||
self.assertRaises(IndexError, lambda: reference[1, 1, 1, 1:1])
|
||||
self.assertRaises(IndexError, lambda: reference[3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3])
|
||||
|
||||
self.assertRaises(TypeError, lambda: reference[0.0])
|
||||
self.assertRaises(TypeError, lambda: reference[0.0:2.0])
|
||||
self.assertRaises(TypeError, lambda: reference[0.0, 0.0:2.0])
|
||||
self.assertRaises(TypeError, lambda: reference[0.0, :, 0.0:2.0])
|
||||
self.assertRaises(TypeError, lambda: reference[0.0, ..., 0.0:2.0])
|
||||
self.assertRaises(TypeError, lambda: reference[0.0, :, 0.0])
|
||||
|
||||
def test_newindex(self):
|
||||
reference = self._consecutive((3, 3, 3))
|
||||
@ -1872,18 +1903,30 @@ class TestTorch(TestCase):
|
||||
checkPartialAssign((1, 2))
|
||||
checkPartialAssign((0, 2))
|
||||
|
||||
with self.assertRaises(RuntimeError):
|
||||
with self.assertRaises(IndexError):
|
||||
reference[1, 1, 1, 1] = 1
|
||||
with self.assertRaises(RuntimeError):
|
||||
with self.assertRaises(IndexError):
|
||||
reference[1, 1, 1, (1, 1)] = 1
|
||||
with self.assertRaises(RuntimeError):
|
||||
with self.assertRaises(IndexError):
|
||||
reference[3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3] = 1
|
||||
with self.assertRaises(TypeError):
|
||||
reference[0.0] = 1
|
||||
with self.assertRaises(TypeError):
|
||||
reference[0.0:2.0] = 1
|
||||
with self.assertRaises(TypeError):
|
||||
reference[0.0, 0.0:2.0] = 1
|
||||
with self.assertRaises(TypeError):
|
||||
reference[0.0, :, 0.0:2.0] = 1
|
||||
with self.assertRaises(TypeError):
|
||||
reference[0.0, ..., 0.0:2.0] = 1
|
||||
with self.assertRaises(TypeError):
|
||||
reference[0.0, :, 0.0] = 1
|
||||
|
||||
def test_index_copy(self):
|
||||
num_copy, num_dest = 3, 20
|
||||
dest = torch.randn(num_dest, 4, 5)
|
||||
src = torch.randn(num_copy, 4, 5)
|
||||
idx = torch.randperm(num_dest).narrow(0, 0, num_copy).long()
|
||||
idx = torch.randperm(num_dest).narrow(0, 0, num_copy)
|
||||
dest2 = dest.clone()
|
||||
dest.index_copy_(0, idx, src)
|
||||
for i in range(idx.size(0)):
|
||||
@ -1892,7 +1935,7 @@ class TestTorch(TestCase):
|
||||
|
||||
dest = torch.randn(num_dest)
|
||||
src = torch.randn(num_copy)
|
||||
idx = torch.randperm(num_dest).narrow(0, 0, num_copy).long()
|
||||
idx = torch.randperm(num_dest).narrow(0, 0, num_copy)
|
||||
dest2 = dest.clone()
|
||||
dest.index_copy_(0, idx, src)
|
||||
for i in range(idx.size(0)):
|
||||
@ -1903,7 +1946,7 @@ class TestTorch(TestCase):
|
||||
num_copy, num_dest = 3, 3
|
||||
dest = torch.randn(num_dest, 4, 5)
|
||||
src = torch.randn(num_copy, 4, 5)
|
||||
idx = torch.randperm(num_dest).narrow(0, 0, num_copy).long()
|
||||
idx = torch.randperm(num_dest).narrow(0, 0, num_copy)
|
||||
dest2 = dest.clone()
|
||||
dest.index_add_(0, idx, src)
|
||||
for i in range(idx.size(0)):
|
||||
@ -1912,7 +1955,7 @@ class TestTorch(TestCase):
|
||||
|
||||
dest = torch.randn(num_dest)
|
||||
src = torch.randn(num_copy)
|
||||
idx = torch.randperm(num_dest).narrow(0, 0, num_copy).long()
|
||||
idx = torch.randperm(num_dest).narrow(0, 0, num_copy)
|
||||
dest2 = dest.clone()
|
||||
dest.index_add_(0, idx, src)
|
||||
for i in range(idx.size(0)):
|
||||
@ -2261,7 +2304,7 @@ class TestTorch(TestCase):
|
||||
|
||||
def test_permute(self):
|
||||
orig = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
|
||||
perm = list(torch.randperm(7).long())
|
||||
perm = list(torch.randperm(7))
|
||||
x = torch.Tensor(*orig).fill_(0)
|
||||
new = list(map(lambda x: x - 1, x.permute(*perm).size()))
|
||||
self.assertEqual(perm, new)
|
||||
@ -2309,7 +2352,7 @@ class TestTorch(TestCase):
|
||||
dst1 = torch.nonzero(tensor)
|
||||
dst2 = tensor.nonzero()
|
||||
dst3 = torch.LongTensor()
|
||||
torch.nonzero(dst3, tensor)
|
||||
torch.nonzero(tensor, out=dst3)
|
||||
if len(shape) == 1:
|
||||
dst = []
|
||||
for i in range(num_src):
|
||||
@ -2384,6 +2427,47 @@ class TestTorch(TestCase):
|
||||
t.bernoulli_(p)
|
||||
self.assertTrue(isBinary(t))
|
||||
|
||||
q = torch.rand(5, 5)
|
||||
self.assertTrue(isBinary(q.bernoulli()))
|
||||
|
||||
def test_normal(self):
|
||||
q = torch.Tensor(100, 100)
|
||||
q.normal_()
|
||||
self.assertEqual(q.mean(), 0, 0.2)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(q.std(), 1, 0.2)
|
||||
|
||||
q.normal_(2, 3)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(q.mean(), 2, 0.3)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(q.std(), 3, 0.3)
|
||||
|
||||
mean = torch.Tensor(100, 100)
|
||||
std = torch.Tensor(100, 100)
|
||||
mean[:50] = 0
|
||||
mean[50:] = 1
|
||||
std[:,:50] = 4
|
||||
std[:,50:] = 1
|
||||
|
||||
r = torch.normal(mean)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(r[:50].mean(), 0, 0.2)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(r[50:].mean(), 1, 0.2)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(r.std(), 1, 0.2)
|
||||
|
||||
r = torch.normal(mean, 3)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(r[:50].mean(), 0, 0.2)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(r[50:].mean(), 1, 0.2)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(r.std(), 3, 0.2)
|
||||
|
||||
r = torch.normal(2, std)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(r.mean(), 2, 0.2)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(r[:,:50].std(), 4, 0.3)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(r[:,50:].std(), 1, 0.2)
|
||||
|
||||
r = torch.normal(mean, std)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(r[:50].mean(), 0, 0.2)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(r[50:].mean(), 1, 0.2)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(r[:,:50].std(), 4, 0.3)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(r[:,50:].std(), 1, 0.2)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_serialization(self):
|
||||
a = [torch.randn(5, 5).float() for i in range(2)]
|
||||
b = [a[i % 2] for i in range(4)]
|
||||
@ -2421,8 +2505,10 @@ class TestTorch(TestCase):
|
||||
sys.modules[module.__name__] = module
|
||||
return module
|
||||
|
||||
import os
|
||||
with tempfile.NamedTemporaryFile() as checkpoint:
|
||||
module = import_module('tmpmodule', 'data/network1.py')
|
||||
fname = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), 'data/network1.py')
|
||||
module = import_module('tmpmodule', fname)
|
||||
torch.save(module.Net(), checkpoint)
|
||||
|
||||
# First check that the checkpoint can be loaded without warnings
|
||||
@ -2433,7 +2519,8 @@ class TestTorch(TestCase):
|
||||
self.assertEquals(len(w), 0)
|
||||
|
||||
# Replace the module with different source
|
||||
module = import_module('tmpmodule', 'data/network2.py')
|
||||
fname = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), 'data/network2.py')
|
||||
module = import_module('tmpmodule', fname)
|
||||
checkpoint.seek(0)
|
||||
with warnings.catch_warnings(record=True) as w:
|
||||
loaded = torch.load(checkpoint)
|
||||
@ -2457,6 +2544,8 @@ class TestTorch(TestCase):
|
||||
|
||||
def test_print(self):
|
||||
for t in torch._tensor_classes:
|
||||
if t in torch.sparse._sparse_tensor_classes:
|
||||
continue
|
||||
if t.is_cuda and not torch.cuda.is_available():
|
||||
continue
|
||||
obj = t(100, 100).fill_(1)
|
||||
@ -2487,6 +2576,21 @@ class TestTorch(TestCase):
|
||||
y = x.clone().unsqueeze_(2)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(y, x.contiguous().view(2, 4, 1))
|
||||
|
||||
def test_iter(self):
|
||||
x = torch.randn(5, 5)
|
||||
for i, sub in enumerate(x):
|
||||
self.assertEqual(sub, x[i])
|
||||
|
||||
def test_accreal_type(self):
|
||||
x = torch.randn(2, 3, 4) * 10
|
||||
self.assertIsInstance(x.double().sum(), float)
|
||||
self.assertIsInstance(x.float().sum(), float)
|
||||
self.assertIsInstance(x.long().sum(), int)
|
||||
self.assertIsInstance(x.int().sum(), int)
|
||||
self.assertIsInstance(x.short().sum(), int)
|
||||
self.assertIsInstance(x.char().sum(), int)
|
||||
self.assertIsInstance(x.byte().sum(), int)
|
||||
|
||||
@unittest.skipIf(not torch.cuda.is_available(), 'no CUDA')
|
||||
def test_pin_memory(self):
|
||||
x = torch.randn(3, 5)
|
||||
@ -2496,6 +2600,20 @@ class TestTorch(TestCase):
|
||||
self.assertEqual(pinned, x)
|
||||
self.assertNotEqual(pinned.data_ptr(), x.data_ptr())
|
||||
|
||||
@unittest.skipIf(not TEST_NUMPY, "Numpy not found")
|
||||
def test_numpy_unresizable(self):
|
||||
x = np.zeros((2, 2))
|
||||
y = torch.from_numpy(x)
|
||||
with self.assertRaises(ValueError):
|
||||
x.resize((5, 5))
|
||||
|
||||
z = torch.randn(5, 5)
|
||||
w = z.numpy()
|
||||
with self.assertRaises(RuntimeError):
|
||||
z.resize_(10, 10)
|
||||
with self.assertRaises(ValueError):
|
||||
w.resize((10, 10))
|
||||
|
||||
@unittest.skipIf(not TEST_NUMPY, "Numpy not found")
|
||||
def test_toNumpy(self):
|
||||
types = [
|
||||
@ -2588,6 +2706,26 @@ class TestTorch(TestCase):
|
||||
array = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4], dtype=dtype)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(torch.from_numpy(array), torch.Tensor([1, 2, 3, 4]))
|
||||
|
||||
# check storage offset
|
||||
x = np.linspace(1, 125, 125)
|
||||
x.shape = (5, 5, 5)
|
||||
x = x[1]
|
||||
expected = torch.range(1, 125).view(5, 5, 5)[1]
|
||||
self.assertEqual(torch.from_numpy(x), expected)
|
||||
|
||||
# check noncontiguous
|
||||
x = np.linspace(1, 25, 25)
|
||||
x.shape = (5, 5)
|
||||
expected = torch.range(1, 25).view(5, 5).t()
|
||||
self.assertEqual(torch.from_numpy(x.T), expected)
|
||||
|
||||
# check noncontiguous with holes
|
||||
x = np.linspace(1, 125, 125)
|
||||
x.shape = (5, 5, 5)
|
||||
x = x[:, 1]
|
||||
expected = torch.range(1, 125).view(5, 5, 5)[:, 1]
|
||||
self.assertEqual(torch.from_numpy(x), expected)
|
||||
|
||||
@unittest.skipIf(not TEST_NUMPY, "Numpy not found")
|
||||
def test_numpy_index(self):
|
||||
i = np.int32([0, 1, 2])
|
||||
@ -2596,6 +2734,77 @@ class TestTorch(TestCase):
|
||||
self.assertFalse(isinstance(idx, int))
|
||||
self.assertEqual(x[idx], x[int(idx)])
|
||||
|
||||
def test_comparison_ops(self):
|
||||
x = torch.randn(5, 5)
|
||||
y = torch.randn(5, 5)
|
||||
|
||||
eq = x == y
|
||||
for idx in iter_indices(x):
|
||||
self.assertIs(x[idx] == y[idx], eq[idx] == 1)
|
||||
|
||||
ne = x != y
|
||||
for idx in iter_indices(x):
|
||||
self.assertIs(x[idx] != y[idx], ne[idx] == 1)
|
||||
|
||||
lt = x < y
|
||||
for idx in iter_indices(x):
|
||||
self.assertIs(x[idx] < y[idx], lt[idx] == 1)
|
||||
|
||||
le = x <= y
|
||||
for idx in iter_indices(x):
|
||||
self.assertIs(x[idx] <= y[idx], le[idx] == 1)
|
||||
|
||||
gt = x > y
|
||||
for idx in iter_indices(x):
|
||||
self.assertIs(x[idx] > y[idx], gt[idx] == 1)
|
||||
|
||||
ge = x >= y
|
||||
for idx in iter_indices(x):
|
||||
self.assertIs(x[idx] >= y[idx], ge[idx] == 1)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_logical_ops(self):
|
||||
x = torch.randn(5, 5).gt(0)
|
||||
y = torch.randn(5, 5).gt(0)
|
||||
|
||||
and_result = x & y
|
||||
for idx in iter_indices(x):
|
||||
if and_result[idx]:
|
||||
self.assertTrue(x[idx] and y[idx])
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self.assertFalse(x[idx] and y[idx])
|
||||
|
||||
or_result = x | y
|
||||
for idx in iter_indices(x):
|
||||
if or_result[idx]:
|
||||
self.assertTrue(x[idx] or y[idx])
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self.assertFalse(x[idx] or y[idx])
|
||||
|
||||
xor_result = x ^ y
|
||||
for idx in iter_indices(x):
|
||||
if xor_result[idx]:
|
||||
self.assertTrue(x[idx] ^ y[idx])
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self.assertFalse(x[idx] ^ y[idx])
|
||||
|
||||
x_clone = x.clone()
|
||||
x_clone &= y
|
||||
self.assertEqual(x_clone, and_result)
|
||||
|
||||
x_clone = x.clone()
|
||||
x_clone |= y
|
||||
self.assertEqual(x_clone, or_result)
|
||||
|
||||
x_clone = x.clone()
|
||||
x_clone ^= y
|
||||
self.assertEqual(x_clone, xor_result)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_apply(self):
|
||||
x = torch.range(1, 5)
|
||||
res = x.clone().apply_(lambda k: k + k)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(res, x * 2)
|
||||
self.assertRaises(RuntimeError, lambda: x.apply_(lambda k: "str"))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == '__main__':
|
||||
unittest.main()
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,3 +1,4 @@
|
||||
from __future__ import print_function
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import math
|
||||
@ -9,10 +10,12 @@ import sys
|
||||
import traceback
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
import torch.cuda
|
||||
import warnings
|
||||
from torch.autograd import Variable
|
||||
from torch.utils.trainer import Trainer
|
||||
from torch.utils.trainer.plugins import *
|
||||
from torch.utils.trainer.plugins.plugin import Plugin
|
||||
from torch.utils.serialization import load_lua
|
||||
|
||||
HAS_CUDA = torch.cuda.is_available()
|
||||
|
||||
@ -175,7 +178,7 @@ class TestTrainer(TestCase):
|
||||
self.trainer.run(epochs=self.num_epochs)
|
||||
output_var = self.trainer.model.output
|
||||
expected_grad = torch.ones(1, 1) * 2 * self.optimizer.num_evals
|
||||
self.assertEqual(output_var.grad, expected_grad)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(output_var.grad.data, expected_grad)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
test_dir = os.path.abspath(os.path.dirname(str(__file__)))
|
||||
@ -245,5 +248,120 @@ class TestFFI(TestCase):
|
||||
lambda: gpulib.cuda_func(ctensor.storage(), 2, 1.5))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class TestLuaReader(TestCase):
|
||||
|
||||
@staticmethod
|
||||
def _module_test(name, test):
|
||||
def do_test(self):
|
||||
module = test['module']
|
||||
input = test['input']
|
||||
grad_output = test['grad_output']
|
||||
if hasattr(self, '_transform_' + name):
|
||||
input = getattr(self, '_transform_' + name)(input)
|
||||
output = module.forward(input)
|
||||
module.zeroGradParameters()
|
||||
grad_input = module.backward(input, grad_output)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(output, test['output'])
|
||||
self.assertEqual(grad_input, test['grad_input'])
|
||||
if module.parameters() is not None:
|
||||
params, d_params = module.parameters()
|
||||
self.assertEqual(params, test['params'])
|
||||
self.assertEqual(d_params, test['d_params'])
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self.assertFalse('params' in test and test['params'])
|
||||
self.assertFalse('params' in test and test['d_params'])
|
||||
return do_test
|
||||
|
||||
@staticmethod
|
||||
def _criterion_test(name, test):
|
||||
def do_test(self):
|
||||
module = test['module']
|
||||
input = test['input']
|
||||
if name == 'L1Cost':
|
||||
target = None
|
||||
else:
|
||||
target = test['target']
|
||||
if hasattr(self, '_transform_' + name):
|
||||
input, target = getattr(self, '_transform_' + name)(input, target)
|
||||
|
||||
output = module.forward(input, target)
|
||||
grad_input = module.backward(input, target)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(output, test['loss'])
|
||||
self.assertEqual(grad_input, test['grad_input'])
|
||||
return do_test
|
||||
|
||||
@classmethod
|
||||
def _download_data(cls, test_file_path):
|
||||
if os.path.exists(test_file_path):
|
||||
return
|
||||
print('Downloading test file for TestLuaReader.')
|
||||
DATA_URL = 'https://s3.amazonaws.com/pytorch/legacy_modules.t7'
|
||||
urllib = cls._get_urllib('request')
|
||||
data = urllib.urlopen(DATA_URL, timeout=15).read()
|
||||
with open(test_file_path, 'wb') as f:
|
||||
f.write(data)
|
||||
|
||||
@staticmethod
|
||||
def _get_urllib(submodule):
|
||||
if sys.version_info < (3,):
|
||||
import urllib2
|
||||
return urllib2
|
||||
else:
|
||||
import urllib.error
|
||||
import urllib.request
|
||||
return getattr(urllib, submodule)
|
||||
|
||||
@classmethod
|
||||
def init(cls):
|
||||
data_dir = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), 'data')
|
||||
test_file_path = os.path.join(data_dir, 'legacy_modules.t7')
|
||||
urllib = cls._get_urllib('error')
|
||||
try:
|
||||
cls._download_data(test_file_path)
|
||||
except urllib.URLError as e:
|
||||
warnings.warn(("Couldn't download the test file for TestLuaReader! "
|
||||
"Tests will be incomplete!"), RuntimeWarning)
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
||||
tests = load_lua(test_file_path)
|
||||
for name, test in tests['modules'].items():
|
||||
test_name = 'test_' + name.replace('nn.', '')
|
||||
setattr(cls, test_name, cls._module_test(name, test))
|
||||
for name, test in tests['criterions'].items():
|
||||
test_name = 'test_' + name.replace('nn.', '')
|
||||
setattr(cls, test_name, cls._criterion_test(name, test))
|
||||
|
||||
def _transform_Index(self, input):
|
||||
return [input[0], input[1].sub(1)]
|
||||
|
||||
def _transform_LookupTable(self, input):
|
||||
return input.sub(1)
|
||||
|
||||
def _transform_MultiLabelMarginCriterion(self, input, target):
|
||||
return input, target.sub(1)
|
||||
|
||||
def _transform_ClassNLLCriterion(self, input, target):
|
||||
return input, target.sub(1)
|
||||
|
||||
def _transform_SpatialClassNLLCriterion(self, input, target):
|
||||
return input, target.sub(1)
|
||||
|
||||
def _transform_ClassSimplexCriterion(self, input, target):
|
||||
return input, target.sub(1)
|
||||
|
||||
def _transform_CrossEntropyCriterion(self, input, target):
|
||||
return input, target.sub(1)
|
||||
|
||||
def _transform_ParallelCriterion(self, input, target):
|
||||
return input, [target[0].sub(1), target[1]]
|
||||
|
||||
def _transform_MultiCriterion(self, input, target):
|
||||
return input, target.sub(1)
|
||||
|
||||
def _transform_MultiMarginCriterion(self, input, target):
|
||||
return input, target.sub(1)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
TestLuaReader.init()
|
||||
if __name__ == '__main__':
|
||||
unittest.main()
|
||||
|
||||
@ -185,7 +185,10 @@ class cwrap(object):
|
||||
lambda arg: not 'ignore_check' in arg or not arg['ignore_check'],
|
||||
option['arguments']))
|
||||
option['num_checked_args'] = len(checked_args)
|
||||
for i, arg in enumerate(checked_args):
|
||||
idx_args = list(filter(
|
||||
lambda arg: not arg.get('ignore_check') and not arg.get('no_idx'),
|
||||
option['arguments']))
|
||||
for i, arg in enumerate(idx_args):
|
||||
arg['idx'] = i
|
||||
|
||||
# Generate checks
|
||||
|
||||
@ -7,6 +7,6 @@ class ArgcountChecker(CWrapPlugin):
|
||||
checks = '__argcount == 0'
|
||||
else:
|
||||
indent = '\n '
|
||||
checks = '__argcount == {} &&'.format(option['num_checked_args']) + \
|
||||
indent + checks
|
||||
argcount = option['num_checked_args'] + option.get('argcount_offset', 0)
|
||||
checks = '__argcount == {} &&'.format(str(argcount)) + indent + checks
|
||||
return checks
|
||||
|
||||
@ -8,17 +8,21 @@ class CuDNNPlugin(CWrapPlugin):
|
||||
TYPE_UNPACK = {
|
||||
'THTensor*': Template('((THPVoidTensor*)$arg)->cdata'),
|
||||
'int': Template('THPUtils_unpackLong($arg)'),
|
||||
'std::vector<int>': Template('THPUtils_unpackIntTuple($arg)'),
|
||||
'cudnnDataType_t': Template('$arg'),
|
||||
'cudnnHandle_t': Template('$arg'),
|
||||
'Convolution*': Template('(Convolution*)THPWrapper_get($arg)'),
|
||||
'bool': Template('$arg == Py_True'),
|
||||
'double': Template('THPDoubleUtils_unpackReal($arg)'),
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
TYPE_CHECK = {
|
||||
'Convolution*': Template('THPWrapper_check($arg)'),
|
||||
'THTensor*': Template('(PyObject*)Py_TYPE($arg) == tensorClass'),
|
||||
'int': Template('THPUtils_checkLong($arg)'),
|
||||
'std::vector<int>': Template('THPUtils_checkIntTuple($arg)'),
|
||||
'bool': Template('PyBool_Check($arg)'),
|
||||
'double': Template('THPDoubleUtils_checkReal($arg)'),
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
RETURN_WRAPPER = {
|
||||
@ -50,7 +54,7 @@ static PyObject * $name(PyObject *self, PyObject *args, PyObject *kwargs)
|
||||
$options
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
THPUtils_invalidArguments(args, "$readable_name", $num_options, $expected_args);
|
||||
THPUtils_invalidArguments(args, kwargs, "$readable_name", $num_options, $expected_args);
|
||||
return NULL;
|
||||
END_HANDLE_TH_ERRORS
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -4,7 +4,9 @@ from string import Template
|
||||
class KwargsPlugin(CWrapPlugin):
|
||||
|
||||
ACCESSOR_TEMPLATE = Template('(__tuplecount > $idx ? PyTuple_GET_ITEM(args, $idx) : __kw_$name)')
|
||||
KWARG_ONLY_ACCESSOR_TEMPLATE = Template('__kw_$name')
|
||||
CHECK_TEMPLATE = Template('(__tuplecount > $idx || __kw_$name) && $code')
|
||||
KWARG_ONLY_CHECK_TEMPLATE = Template('__kw_$name && $code')
|
||||
WRAPPER_TEMPLATE = Template("""
|
||||
$declarations
|
||||
if (kwargs) {
|
||||
@ -24,13 +26,18 @@ class KwargsPlugin(CWrapPlugin):
|
||||
return declarations
|
||||
|
||||
def get_arg_accessor(self, arg, option):
|
||||
if not arg.get('no_kwargs'):
|
||||
if arg.get('no_kwargs'):
|
||||
return
|
||||
if arg.get('kwarg_only'):
|
||||
return self.KWARG_ONLY_ACCESSOR_TEMPLATE.substitute(name=arg['name'])
|
||||
return self.ACCESSOR_TEMPLATE.substitute(idx=arg['idx'], name=arg['name'])
|
||||
|
||||
def process_single_check(self, code, arg, arg_accessor):
|
||||
if not arg.get('no_kwargs'):
|
||||
return self.CHECK_TEMPLATE.substitute(idx=arg['idx'], name=arg['name'], code=code)
|
||||
if arg.get('no_kwargs'):
|
||||
return code
|
||||
if arg.get('kwarg_only'):
|
||||
return self.KWARG_ONLY_CHECK_TEMPLATE.substitute(name=arg['name'], code=code)
|
||||
return self.CHECK_TEMPLATE.substitute(idx=arg['idx'], name=arg['name'], code=code)
|
||||
|
||||
def process_wrapper(self, code, declaration):
|
||||
if declaration.get('no_kwargs'):
|
||||
@ -40,7 +47,9 @@ class KwargsPlugin(CWrapPlugin):
|
||||
for option in declaration['options']:
|
||||
for arg in option['arguments']:
|
||||
name = arg['name']
|
||||
if not arg.get('ignore_check') and name not in seen_args:
|
||||
if (not arg.get('ignore_check') and
|
||||
not arg.get('no_kwargs') and
|
||||
name not in seen_args):
|
||||
seen_args.add(name)
|
||||
args.append(name)
|
||||
declarations = '\n '.join(['PyObject *__kw_{} = NULL;'.format(name) for name in args])
|
||||
|
||||
@ -22,18 +22,37 @@ class OptionalArguments(CWrapPlugin):
|
||||
# PyYAML interprets NULL as None...
|
||||
arg['name'] = 'NULL' if arg['default'] is None else arg['default']
|
||||
new_options.append(option_copy)
|
||||
declaration['options'] = self.filter_unique_options(declaration['options'] + new_options)
|
||||
declaration['options'] = self.filter_unique_options(new_options)
|
||||
return declarations
|
||||
|
||||
def filter_unique_options(self, options):
|
||||
def signature(option):
|
||||
return '#'.join(arg['type'] for arg in option['arguments'] if not 'ignore_check' in arg or not arg['ignore_check'])
|
||||
def signature(option, kwarg_only_count):
|
||||
if kwarg_only_count == 0:
|
||||
kwarg_only_count = None
|
||||
else:
|
||||
kwarg_only_count = -kwarg_only_count
|
||||
arg_signature = '#'.join(
|
||||
arg['type']
|
||||
for arg in option['arguments'][:kwarg_only_count]
|
||||
if not arg.get('ignore_check'))
|
||||
if kwarg_only_count is None:
|
||||
return arg_signature
|
||||
kwarg_only_signature = '#'.join(
|
||||
arg['name'] + '#' + arg['type']
|
||||
for arg in option['arguments'][kwarg_only_count:]
|
||||
if not arg.get('ignore_check'))
|
||||
return arg_signature + "#-#" + kwarg_only_signature
|
||||
seen_signatures = set()
|
||||
unique = []
|
||||
for option in options:
|
||||
sig = signature(option)
|
||||
for num_kwarg_only in range(0, len(option['arguments'])+1):
|
||||
sig = signature(option, num_kwarg_only)
|
||||
if sig not in seen_signatures:
|
||||
if num_kwarg_only > 0:
|
||||
for arg in option['arguments'][-num_kwarg_only:]:
|
||||
arg['kwarg_only'] = True
|
||||
unique.append(option)
|
||||
seen_signatures.add(sig)
|
||||
break
|
||||
return unique
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -37,7 +37,7 @@ class StandaloneExtension(CWrapPlugin):
|
||||
'half': Template('THPHalfUtils_unpackReal($arg)'),
|
||||
'float': Template('THPFloatUtils_unpackReal($arg)'),
|
||||
'double': Template('THPDoubleUtils_unpackReal($arg)'),
|
||||
'bool': Template('THPUtils_unpackLong($arg)'),
|
||||
'bool': Template('($arg == Py_True ? true : false)'),
|
||||
'int': Template('THPUtils_unpackLong($arg)'),
|
||||
'long': Template('THPUtils_unpackLong($arg)'),
|
||||
'void*': Template('(void*)THPUtils_unpackLong($arg)'),
|
||||
@ -56,7 +56,7 @@ class StandaloneExtension(CWrapPlugin):
|
||||
'half': Template('THPHalfUtils_checkReal($arg)'),
|
||||
'float': Template('THPFloatUtils_checkReal($arg)'),
|
||||
'double': Template('THPDoubleUtils_checkReal($arg)'),
|
||||
'bool': Template('THPUtils_checkLong($arg)'),
|
||||
'bool': Template('PyBool_Check($arg)'),
|
||||
'int': Template('THPUtils_checkLong($arg)'),
|
||||
'long': Template('THPUtils_checkLong($arg)'),
|
||||
'void*': Template('THPUtils_checkLong($arg)'),
|
||||
@ -70,7 +70,7 @@ PyObject * $name(PyObject *_unused, PyObject *args)
|
||||
int __argcount = args ? PyTuple_Size(args) : 0;
|
||||
$options
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
THPUtils_invalidArguments(args, "$name", 1, $expected_args);
|
||||
THPUtils_invalidArguments(args, NULL, "$name", 1, $expected_args);
|
||||
return NULL;
|
||||
}
|
||||
END_HANDLE_TH_ERRORS
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,7 +1,7 @@
|
||||
from string import Template
|
||||
from copy import deepcopy
|
||||
from . import CWrapPlugin
|
||||
from itertools import product
|
||||
from itertools import product, chain
|
||||
from collections import OrderedDict
|
||||
|
||||
class THPPlugin(CWrapPlugin):
|
||||
@ -14,6 +14,15 @@ class THPPlugin(CWrapPlugin):
|
||||
'THTensor*': Template('((THPTensor*)$arg)->cdata'),
|
||||
'THBoolTensor*': Template('((THPBoolTensor*)$arg)->cdata'),
|
||||
'THIndexTensor*': Template('((THPIndexTensor*)$arg)->cdata'),
|
||||
|
||||
'THSFloatTensor*': Template('((THSPFloatTensor*)$arg)->cdata'),
|
||||
'THSDoubleTensor*': Template('((THSPDoubleTensor*)$arg)->cdata'),
|
||||
'THSLongTensor*': Template('((THSPLongTensor*)$arg)->cdata'),
|
||||
'THSIntTensor*': Template('((THSPIntTensor*)$arg)->cdata'),
|
||||
'THSTensor*': Template('((THSPTensor*)$arg)->cdata'),
|
||||
'THSBoolTensor*': Template('((THSPBoolTensor*)$arg)->cdata'),
|
||||
'THSIndexTensor*': Template('((THSPIndexTensor*)$arg)->cdata'),
|
||||
|
||||
'THLongStorage*': Template('((THPLongStorage*)$arg)->cdata'),
|
||||
'THStorage*': Template('((THPStorage*)$arg)->cdata'),
|
||||
'THGenerator*': Template('((THPGenerator*)$arg)->cdata'),
|
||||
@ -22,7 +31,7 @@ class THPPlugin(CWrapPlugin):
|
||||
'void*': Template('THPUtils_unpackLong($arg)'),
|
||||
'long': Template('THPUtils_unpackLong($arg)'),
|
||||
'int': Template('THPUtils_unpackLong($arg)'),
|
||||
'bool': Template('THPUtils_unpackLong($arg)'),
|
||||
'bool': Template('($arg == Py_True ? true : false)'),
|
||||
'float': Template('THPFloatUtils_unpackReal($arg)'),
|
||||
'double': Template('THPDoubleUtils_unpackReal($arg)'),
|
||||
'real': Template('THPUtils_(unpackReal)($arg)'),
|
||||
@ -38,6 +47,15 @@ class THPPlugin(CWrapPlugin):
|
||||
'THTensor*': Template('(PyObject*)Py_TYPE($arg) == THPTensorClass'),
|
||||
'THBoolTensor*': Template('(PyObject*)Py_TYPE($arg) == THPBoolTensorClass'),
|
||||
'THIndexTensor*': Template('(PyObject*)Py_TYPE($arg) == THPIndexTensorClass'),
|
||||
|
||||
'THSDoubleTensor*': Template('(PyObject*)Py_TYPE($arg) == THSPDoubleTensorClass'),
|
||||
'THSFloatTensor*': Template('(PyObject*)Py_TYPE($arg) == THSPFloatTensorClass'),
|
||||
'THSLongTensor*': Template('(PyObject*)Py_TYPE($arg) == THSPLongTensorClass'),
|
||||
'THSIntTensor*': Template('(PyObject*)Py_TYPE($arg) == THSPIntTensorClass'),
|
||||
'THSTensor*': Template('(PyObject*)Py_TYPE($arg) == THSPTensorClass'),
|
||||
'THSBoolTensor*': Template('(PyObject*)Py_TYPE($arg) == THSPBoolTensorClass'),
|
||||
'THSIndexTensor*': Template('(PyObject*)Py_TYPE($arg) == THSPIndexTensorClass'),
|
||||
|
||||
'THLongStorage*': Template('(PyObject*)Py_TYPE($arg) == THPLongStorageClass'),
|
||||
'THStorage*': Template('(PyObject*)Py_TYPE($arg) == THPStorageClass'),
|
||||
'THGenerator*': Template('(PyObject*)Py_TYPE($arg) == THPGeneratorClass'),
|
||||
@ -46,30 +64,30 @@ class THPPlugin(CWrapPlugin):
|
||||
'void*': Template('THPUtils_checkLong($arg)'),
|
||||
'long': Template('THPUtils_checkLong($arg)'),
|
||||
'int': Template('THPUtils_checkLong($arg)'),
|
||||
'bool': Template('THPUtils_checkLong($arg)'),
|
||||
'bool': Template('PyBool_Check($arg)'),
|
||||
'float': Template('THPFloatUtils_checkReal($arg)'),
|
||||
'double': Template('THPDoubleUtils_checkReal($arg)'),
|
||||
'real': Template('THPUtils_(checkReal)($arg)'),
|
||||
# TODO
|
||||
'accreal': Template('THPUtils_(checkReal)($arg)'),
|
||||
'accreal': Template('THPUtils_(checkAccreal)($arg)'),
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
SIZE_VARARG_CHECK = Template('THPUtils_tryUnpackLongVarArgs(args, $idx, __size)')
|
||||
|
||||
RETURN_WRAPPER = {
|
||||
'THTensor*': Template('return THPTensor_(New)($result);'),
|
||||
'THSTensor*': Template('return THSPTensor_(New)($result);'),
|
||||
'THLongTensor*': Template('return THPLongTensor_New($result);'),
|
||||
'THLongStorage*': Template('return THPLongStorage_New($result);'),
|
||||
# TODO: make it smarter - it should return python long if result doesn't fit into an int
|
||||
'long': Template('return PyInt_FromLong($result);'),
|
||||
# TODO
|
||||
'accreal': Template('return PyFloat_FromDouble($result);'),
|
||||
'accreal': Template('return THPUtils_(newAccreal)($result);'),
|
||||
'self': Template('Py_INCREF(self);\nreturn (PyObject*)self;'),
|
||||
'real': Template('return THPUtils_(newReal)($result);'),
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
TENSOR_METHODS_DECLARATION = Template("""
|
||||
static PyMethodDef THPTensor_$stateless(methods)[] = {
|
||||
$methods
|
||||
static PyMethodDef TH${sparse}PTensor_$stateless(methods)[] = {
|
||||
$methods
|
||||
{NULL}
|
||||
};
|
||||
""")
|
||||
@ -82,15 +100,16 @@ PyObject * $name(PyObject *self, PyObject *args, PyObject *kwargs)
|
||||
int __dictcount = kwargs ? PyDict_Size(kwargs) : 0;
|
||||
int __argcount = __tuplecount + __dictcount;
|
||||
$variables
|
||||
$init
|
||||
|
||||
$options
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
THPUtils_invalidArguments(args, "$readable_name", $num_options, $expected_args);
|
||||
THPUtils_invalidArguments(args, kwargs, "$readable_name", $num_options, $expected_args);
|
||||
return NULL;
|
||||
END_HANDLE_TH_ERRORS
|
||||
}
|
||||
""")
|
||||
""")
|
||||
|
||||
ALLOCATE_TMPL = Template("""\
|
||||
THP${type}TensorPtr _${name}_guard = (THP${type}Tensor*) THP${type}Tensor_NewEmpty();
|
||||
@ -106,13 +125,16 @@ ${cpu}
|
||||
#endif
|
||||
""")
|
||||
|
||||
def _allocate(typename, tmpl, cuda_tmpl=None):
|
||||
def _allocate(typename, tmpl, cuda_tmpl=None, sparse=False):
|
||||
code = tmpl.safe_substitute(type=typename)
|
||||
if typename == '':
|
||||
code = code.replace('NewEmpty', '(NewEmpty)')
|
||||
if cuda_tmpl:
|
||||
cuda_code = code.replace('THP', 'THCP')
|
||||
code = cuda_tmpl.substitute(cuda=cuda_code, cpu=code)
|
||||
if sparse:
|
||||
code = code.replace('THP', 'THSP')
|
||||
code = code.replace('THCP', 'THCSP')
|
||||
return Template(code)
|
||||
|
||||
ALLOCATE_TYPE = {
|
||||
@ -121,10 +143,13 @@ ${cpu}
|
||||
'THIntTensor*': _allocate('Int', ALLOCATE_TMPL),
|
||||
'THBoolTensor*': _allocate('Byte', ALLOCATE_TMPL, ALLOCATE_CUDA),
|
||||
'THIndexTensor*': _allocate('Long', ALLOCATE_TMPL, ALLOCATE_CUDA),
|
||||
|
||||
'THSTensor*': _allocate('', ALLOCATE_TMPL, sparse=True),
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
TYPE_NAMES = {
|
||||
'THTensor*': '" THPTensorStr "',
|
||||
'THSTensor*': '" THSPTensorStr "',
|
||||
'THStorage*': '" THPStorageStr "',
|
||||
'THGenerator*': 'torch.Generator',
|
||||
'THLongStorage*': '" THPModuleStr "LongStorage',
|
||||
@ -143,9 +168,14 @@ ${cpu}
|
||||
'bool': 'bool',
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
OUT_INIT = """
|
||||
__out = kwargs ? PyDict_GetItemString(kwargs, "out") : NULL;
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self):
|
||||
self.declarations = []
|
||||
self.stateless_declarations = []
|
||||
self.docstrings = []
|
||||
|
||||
def get_type_unpack(self, arg, option):
|
||||
return self.TYPE_UNPACK.get(arg['type'], None)
|
||||
@ -168,7 +198,20 @@ ${cpu}
|
||||
def format_args(args, var_args=False):
|
||||
option_desc = [format_arg(arg, var_args)
|
||||
for arg in args
|
||||
if not arg.get('ignore_check', False)]
|
||||
if not arg.get('ignore_check', False)
|
||||
and not arg.get('output')]
|
||||
output_args = list(filter(lambda a: a.get('output'), args))
|
||||
if output_args:
|
||||
if len(output_args) > 1:
|
||||
out_type = 'tuple['
|
||||
out_type += ', '.join(
|
||||
self.TYPE_NAMES[arg['type']] for arg in output_args)
|
||||
out_type += ']'
|
||||
option_desc += ['#' + out_type + ' out']
|
||||
else:
|
||||
arg = output_args[0]
|
||||
option_desc += ['#' + self.TYPE_NAMES[arg['type']] + ' out']
|
||||
|
||||
if option_desc:
|
||||
return '({})'.format(', '.join(option_desc))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
@ -182,13 +225,14 @@ ${cpu}
|
||||
arg_desc = ['"' + desc + '"' for desc in arg_desc]
|
||||
arg_str = ', '.join(arg_desc)
|
||||
variables_str = '\n'.join(declaration.get('variables', []))
|
||||
init_str = '\n'.join(declaration.get('init', []))
|
||||
if 'stateless' in declaration['name']:
|
||||
readable_name = 'torch.' + declaration['python_name']
|
||||
else:
|
||||
readable_name = declaration['python_name']
|
||||
return Template(self.WRAPPER_TEMPLATE.safe_substitute(
|
||||
readable_name=readable_name, num_options=len(arg_desc),
|
||||
expected_args=arg_str, variables=variables_str))
|
||||
expected_args=arg_str, variables=variables_str, init=init_str))
|
||||
|
||||
def get_return_wrapper(self, option):
|
||||
return self.RETURN_WRAPPER.get(option['return'], None)
|
||||
@ -196,8 +240,58 @@ ${cpu}
|
||||
def get_arg_accessor(self, arg, option):
|
||||
if arg['name'] == 'self':
|
||||
return 'self'
|
||||
if 'allocate' in arg and arg['allocate']:
|
||||
if arg.get('output'):
|
||||
if not option['output_provided']:
|
||||
return arg['name']
|
||||
if option['output_count'] == 1:
|
||||
return '__out'
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return 'PyTuple_GET_ITEM(__out, {})'.format(arg['output_idx'])
|
||||
|
||||
def process_docstrings(self):
|
||||
for declaration in self.declarations:
|
||||
docstr = declaration.get('docstring_method')
|
||||
if docstr is None:
|
||||
continue
|
||||
declaration['docstring_content'] = docstr.replace('\n', '\\n')
|
||||
declaration['docstring_var'] = 'docstr_' + declaration['python_name']
|
||||
for declaration in self.stateless_declarations:
|
||||
docstr = declaration.get('docstring_stateless')
|
||||
if docstr is None:
|
||||
continue
|
||||
declaration['docstring_content'] = docstr.replace('\n', '\\n')
|
||||
declaration['docstring_var'] = 'stateless_docstr_' + declaration['python_name']
|
||||
|
||||
def generate_out_options(self, declaration):
|
||||
new_options = []
|
||||
declaration.setdefault('init', [])
|
||||
declaration['init'] += [self.OUT_INIT]
|
||||
for option in declaration['options']:
|
||||
out_idx = []
|
||||
for i, arg in enumerate(option['arguments']):
|
||||
if arg.get('output'):
|
||||
out_idx.append(i)
|
||||
if not out_idx:
|
||||
option['has_output'] = True
|
||||
option['output_provided'] = False
|
||||
new_options.append(option)
|
||||
continue
|
||||
for output_provided in (True, False):
|
||||
option_copy = deepcopy(option)
|
||||
option_copy['has_output'] = True
|
||||
option_copy['output_provided'] = output_provided
|
||||
option_copy['output_count'] = len(out_idx)
|
||||
for i, idx in enumerate(out_idx):
|
||||
arg = option_copy['arguments'][idx]
|
||||
arg['output_idx'] = i
|
||||
if not output_provided:
|
||||
arg['ignore_check'] = True
|
||||
else:
|
||||
option_copy['argcount_offset'] = -len(out_idx) + 1
|
||||
arg['no_kwargs'] = True
|
||||
arg['no_idx'] = True
|
||||
new_options.append(option_copy)
|
||||
declaration['options'] = new_options
|
||||
|
||||
def process_declarations(self, declarations):
|
||||
new_declarations = []
|
||||
@ -214,6 +308,11 @@ ${cpu}
|
||||
for option in declaration['options']
|
||||
for arg in option['arguments'])
|
||||
|
||||
def has_output_args(declaration):
|
||||
return any(arg.get('output')
|
||||
for option in declaration['options']
|
||||
for arg in option['arguments'])
|
||||
|
||||
for declaration in declarations:
|
||||
if declaration.get('only_register', False):
|
||||
continue
|
||||
@ -223,93 +322,83 @@ ${cpu}
|
||||
declaration['variables'] += ['THLongStoragePtr __size;']
|
||||
if has_arg_type(declaration, 'THStride*'):
|
||||
declaration['variables'] += ['THLongStoragePtr __stride;']
|
||||
if has_output_args(declaration):
|
||||
declaration['variables'] += ['PyObject *__out;']
|
||||
self.generate_out_options(declaration)
|
||||
if has_long_args(declaration):
|
||||
declaration['no_kwargs'] = True
|
||||
for option in declaration['options']:
|
||||
option['cname'] = 'TH{}Tensor_({})'.format(
|
||||
'S' if option.get('sparse', False) else '', option['cname'])
|
||||
if declaration.get('with_stateless', False) or declaration.get('only_stateless', False):
|
||||
stateless_declaration = self.make_stateless(deepcopy(declaration))
|
||||
stateless_declaration = self.make_stateless(declaration)
|
||||
new_declarations.append(stateless_declaration)
|
||||
self.stateless_declarations.append(stateless_declaration)
|
||||
if declaration.get('only_stateless', False):
|
||||
continue
|
||||
|
||||
self.declarations.append(declaration)
|
||||
declaration['name'] = 'THPTensor_({})'.format(declaration['name'])
|
||||
declaration['name'] = 'TH{}PTensor_({})'.format(
|
||||
'S' if declaration.get('sparse', False) else '', declaration['name'])
|
||||
for option in declaration['options']:
|
||||
option['cname'] = 'THTensor_({})'.format(option['cname'])
|
||||
for arg in option['arguments']:
|
||||
if arg['name'] == 'self':
|
||||
arg['ignore_check'] = True
|
||||
if 'allocate' in arg and arg['allocate']:
|
||||
arg['ignore_check'] = True
|
||||
# TODO: we can probably allow duplicate signatures once we implement
|
||||
# keyword arguments
|
||||
declaration['options'] = self.filter_unique_options(declaration['options'])
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
declarations = [d for d in declarations if not d.get('only_stateless', False)]
|
||||
self.declarations.extend(filter(lambda x: not x.get('only_stateless', False), register_only))
|
||||
self.stateless_declarations.extend(filter(lambda x: x.get('only_stateless', False), register_only))
|
||||
|
||||
self.process_docstrings()
|
||||
|
||||
all_declarations = declarations + new_declarations
|
||||
return all_declarations
|
||||
|
||||
def make_stateless(self, declaration):
|
||||
declaration['name'] = 'THPTensor_stateless_({})'.format(declaration['name'])
|
||||
new_options = []
|
||||
declaration = deepcopy(declaration)
|
||||
declaration['name'] = 'TH{}PTensor_stateless_({})'.format(
|
||||
'S' if declaration.get('sparse', False) else '', declaration['name'])
|
||||
for option in declaration['options']:
|
||||
option['cname'] = 'THTensor_({})'.format(option['cname'])
|
||||
allocated = []
|
||||
for i, arg in enumerate(option['arguments']):
|
||||
if 'allocate' in arg and arg['allocate']:
|
||||
arg['ignore_check'] = True
|
||||
allocated.append(i)
|
||||
for arg in option['arguments']:
|
||||
if arg['name'] == 'self':
|
||||
arg['name'] = 'source'
|
||||
for permutation in product((True, False), repeat=len(allocated)):
|
||||
option_copy = deepcopy(option)
|
||||
for i, bit in zip(allocated, permutation):
|
||||
arg = option_copy['arguments'][i]
|
||||
# By default everything is allocated, so we don't have to do anything
|
||||
if not bit:
|
||||
del arg['allocate']
|
||||
del arg['ignore_check']
|
||||
new_options.append(option_copy)
|
||||
declaration['options'] = self.filter_unique_options(declaration['options'] + new_options)
|
||||
return declaration
|
||||
|
||||
def filter_unique_options(self, options):
|
||||
def signature(option):
|
||||
return '#'.join(arg['type'] for arg in option['arguments'] if not 'ignore_check' in arg or not arg['ignore_check'])
|
||||
seen_signatures = set()
|
||||
unique = []
|
||||
for option in options:
|
||||
sig = signature(option)
|
||||
if sig not in seen_signatures:
|
||||
unique.append(option)
|
||||
seen_signatures.add(sig)
|
||||
return unique
|
||||
|
||||
def declare_methods(self, stateless):
|
||||
def declare_methods(self, stateless, sparse):
|
||||
tensor_methods = ''
|
||||
for declaration in (self.declarations if not stateless else self.stateless_declarations):
|
||||
if declaration.get('sparse', False) != sparse:
|
||||
continue
|
||||
flags = 'METH_VARARGS'
|
||||
flags += ' | ' + declaration.get('method_flags') if 'method_flags' in declaration else ''
|
||||
if not declaration.get('only_register'):
|
||||
flags += ' | METH_KEYWORDS'
|
||||
if declaration.get('override_method_flags'):
|
||||
flags = declaration['override_method_flags']
|
||||
entry = Template(' {"$python_name", (PyCFunction)$name, $flags, NULL},\n').substitute(
|
||||
python_name=declaration['python_name'], name=declaration['name'], flags=flags
|
||||
entry = Template(' {"$python_name", (PyCFunction)$name, $flags, $docstring},\n').substitute(
|
||||
python_name=declaration['python_name'], name=declaration['name'], flags=flags,
|
||||
docstring=declaration.get('docstring_var', 'NULL')
|
||||
)
|
||||
if 'defined_if' in declaration:
|
||||
entry = self.preprocessor_guard(entry, declaration['defined_if'])
|
||||
tensor_methods += entry
|
||||
return self.TENSOR_METHODS_DECLARATION.substitute(methods=tensor_methods, stateless=('' if not stateless else 'stateless_'))
|
||||
return self.TENSOR_METHODS_DECLARATION.substitute(
|
||||
methods=tensor_methods,
|
||||
stateless=('' if not stateless else 'stateless_'),
|
||||
sparse=('' if not sparse else 'S'),
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def process_full_file(self, code):
|
||||
# We have to find a place before all undefs
|
||||
idx = code.find('// PUT DEFINITIONS IN HERE PLEASE')
|
||||
return code[:idx] + self.declare_methods(False) + self.declare_methods(True) + code[idx:]
|
||||
return (code[:idx]
|
||||
+ self.declare_methods(False, False)
|
||||
+ self.declare_methods(True, False)
|
||||
+ self.declare_methods(False, True)
|
||||
+ self.declare_methods(True, True)
|
||||
+ code[idx:]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def preprocessor_guard(self, code, condition):
|
||||
return '#if ' + condition + '\n' + code + '#endif\n'
|
||||
@ -323,14 +412,44 @@ ${cpu}
|
||||
return 'LIBRARY_STATE ' + code
|
||||
|
||||
def process_all_checks(self, code, option):
|
||||
if option.get('has_output'):
|
||||
indent = " " * 10
|
||||
if option['output_provided']:
|
||||
checks = "__out != NULL &&\n" + indent
|
||||
if option['output_count'] > 1:
|
||||
checks += "PyTuple_Check(__out) &&\n" + indent
|
||||
length_check = "PyTuple_GET_SIZE(__out) == {} &&\n".format(
|
||||
option['output_count'])
|
||||
checks += length_check + indent
|
||||
code = checks + code
|
||||
else:
|
||||
code = "__out == NULL &&\n" + indent + code
|
||||
|
||||
if any(arg.get('long_args', False) for arg in option['arguments']):
|
||||
code = code.replace('__argcount ==', '__argcount >=')
|
||||
expected = str(int(option.get('output_provided', False)))
|
||||
code = '__dictcount == ' + expected + ' &&\n ' + code
|
||||
|
||||
return code
|
||||
|
||||
def process_option_code_template(self, template, option):
|
||||
new_args = []
|
||||
for arg in option['arguments']:
|
||||
if 'allocate' in arg and arg['allocate']:
|
||||
if not option.get('output_provided', True) and arg.get('output'):
|
||||
new_args.append(self.ALLOCATE_TYPE[arg['type']].substitute(name=arg['name']))
|
||||
template = new_args + template
|
||||
return template
|
||||
|
||||
def generate_docstrings_cpp(self):
|
||||
template = Template('char* $name = "$content";')
|
||||
return '\n\n'.join(
|
||||
template.substitute(name=decl['docstring_var'], content=decl['docstring_content'])
|
||||
for decl in chain(self.declarations, self.stateless_declarations)
|
||||
if 'docstring_var' in decl)
|
||||
|
||||
def generate_docstrings_h(self):
|
||||
template = Template('extern char* $name;')
|
||||
return '\n\n'.join(
|
||||
template.substitute(name=decl['docstring_var'])
|
||||
for decl in chain(self.declarations, self.stateless_declarations)
|
||||
if 'docstring_var' in decl)
|
||||
|
||||