mirror of
https://github.com/huggingface/peft.git
synced 2025-10-27 20:28:07 +08:00
Compare commits
848 Commits
v0.0.1
...
remove-dep
| Author | SHA1 | Date | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 70532bfb6d | |||
| 500c97fe63 | |||
| 31c884e934 | |||
| 88875f1cf5 | |||
| 0d283ae0e6 | |||
| e07095a654 | |||
| 5b60ec0204 | |||
| dfac641c63 | |||
| 26726bf1dd | |||
| 16ec3f995a | |||
| ca6bbb594f | |||
| 2e821c1dc8 | |||
| 8452d71e14 | |||
| 02b5aeddf9 | |||
| c4c826c0c0 | |||
| d582b68c7f | |||
| 4537317961 | |||
| ffb8512396 | |||
| 78daa4cf76 | |||
| 65b75a6798 | |||
| a62b337940 | |||
| 8221246f2f | |||
| 8e979fc732 | |||
| a86b29a217 | |||
| 8dd45b75d7 | |||
| 91e4b0879d | |||
| a18734d87a | |||
| 6008f272a5 | |||
| a9425d1409 | |||
| 3b63996964 | |||
| 3eb6bbacee | |||
| 5471c9a1be | |||
| d28fffb917 | |||
| 6dca6d2292 | |||
| a1fe368bfc | |||
| 234bbabd9b | |||
| e3840c249e | |||
| 7e84dec20b | |||
| e7e95c004b | |||
| e597388305 | |||
| 7662f342e0 | |||
| b58b13b528 | |||
| 98f4db2c79 | |||
| c43cc5028e | |||
| 84abf5a5ab | |||
| 34f3fba2b3 | |||
| 9119b780eb | |||
| 7e5335d093 | |||
| 096fe53737 | |||
| 90aa2c1e05 | |||
| 01732176e0 | |||
| aa2ca83ca7 | |||
| 1b3b7b5b2a | |||
| bc9426f10b | |||
| 3967fcc8ea | |||
| 23213cad8d | |||
| 2efc36ccdf | |||
| cc27cfd478 | |||
| b74c2f644d | |||
| 470b66c639 | |||
| f81147268e | |||
| 37dd675f91 | |||
| 7b7e4b2194 | |||
| 043d5c0bd6 | |||
| 8a0dce2fb9 | |||
| ede3c7df22 | |||
| cf467d8aa0 | |||
| 47c4d9578c | |||
| 65513e5db4 | |||
| f5a95930c2 | |||
| 963e3128ed | |||
| 8db74d42c4 | |||
| a564779b67 | |||
| cde8f1af2b | |||
| 25dec602f3 | |||
| 83de1af281 | |||
| 5f2084698b | |||
| e95dc1360b | |||
| 234774345b | |||
| 7d0c0a33d3 | |||
| 7716dd86e9 | |||
| 60ec4d8502 | |||
| 6e953810af | |||
| a1c472f08f | |||
| 055e4dbe1e | |||
| c1a83fd692 | |||
| 7da7f85188 | |||
| eba459553c | |||
| 9bb83ed1a5 | |||
| b5492db514 | |||
| ddf90a8b2f | |||
| 97f3ed577e | |||
| 17273aa4bf | |||
| fc78a2491e | |||
| 497bbeafbd | |||
| 21d8d467dc | |||
| e805a3173a | |||
| 9350ab8a9d | |||
| 912ad41e96 | |||
| ce925d844a | |||
| d1be2696fd | |||
| 4da2876a10 | |||
| a30e006bb2 | |||
| fff24008eb | |||
| dffde4537f | |||
| 9d943672c0 | |||
| 1a7f3e3478 | |||
| 68b90a14d7 | |||
| 75e4ef3536 | |||
| 5e4aa7eb92 | |||
| 5eb5b492af | |||
| a2d96d097a | |||
| 30889ef260 | |||
| 67918efb49 | |||
| 189a9a666d | |||
| bfc102c0c0 | |||
| 1c1c7fdaa6 | |||
| 4a15595822 | |||
| bb2471d926 | |||
| 54ca31153d | |||
| ebbff4023a | |||
| 62237dc9b1 | |||
| eaa5eef28e | |||
| bf54136a79 | |||
| a43ec59762 | |||
| 0089ebd272 | |||
| fe01d6de85 | |||
| f9b673ea37 | |||
| dc28a61e82 | |||
| 71585d611f | |||
| c6bcf91ca1 | |||
| 4354a7d496 | |||
| f36f50acb4 | |||
| 777c0b6ad7 | |||
| 6451cbd70c | |||
| 7d28536b18 | |||
| eb2c12d99a | |||
| c6b28a22b8 | |||
| e96eef9ea1 | |||
| 54ee2fb1af | |||
| cbd783b4df | |||
| 26504a0119 | |||
| 4186c9b104 | |||
| 8665e2b571 | |||
| cbf346d962 | |||
| 2a0fb71f4f | |||
| c4cf9e7d3b | |||
| cf04d0353f | |||
| 4023da904f | |||
| 6fe1aac65d | |||
| 799420aef1 | |||
| 993836ff90 | |||
| 1c9679ac71 | |||
| e745ffd7d0 | |||
| 029dcd5a1c | |||
| 482a2a6d9a | |||
| 119de1715c | |||
| a0a46c06db | |||
| 3708793ba9 | |||
| 46a84bd395 | |||
| bd544bb2ce | |||
| 55c37e9c0b | |||
| 997e6ec5ab | |||
| ddb114af0a | |||
| 4b02148af2 | |||
| 0f1e9091cc | |||
| 88e2e75cc3 | |||
| c9df262d69 | |||
| 67a08009ff | |||
| 971dd6e815 | |||
| ee6f6dcee7 | |||
| 21c304f6f6 | |||
| e73967edea | |||
| b08e6faf2b | |||
| 5c13ea3b12 | |||
| 00b820061e | |||
| 504d3c8329 | |||
| fc9f4b3176 | |||
| 895513c465 | |||
| c893394808 | |||
| 86562eec49 | |||
| b467e3de5c | |||
| 2ab005f3ab | |||
| b482391b80 | |||
| d56df7fc64 | |||
| a87ff4c744 | |||
| 2665f80a17 | |||
| 9fd788bedb | |||
| 2336780f9e | |||
| c22a8e5d47 | |||
| 1a7433b136 | |||
| 70d559d029 | |||
| bffbbbf76a | |||
| 9c70468a3c | |||
| f7cf460f7c | |||
| 1b1091c158 | |||
| c456d55216 | |||
| e05b2670c5 | |||
| 5ed46e4f04 | |||
| 5bad88ba04 | |||
| 6a57472665 | |||
| da17ac0f48 | |||
| 2674f5ea66 | |||
| 2b901ee572 | |||
| 8298f1a366 | |||
| f0fb9516d8 | |||
| 04c411010b | |||
| da29ae62d4 | |||
| 64c8d1da85 | |||
| e586f96740 | |||
| e35d46de19 | |||
| b4faffea8a | |||
| 19145bba8a | |||
| c0dd27bc97 | |||
| fb607d00ad | |||
| a634f6a13e | |||
| dd4771b2f4 | |||
| 043238578f | |||
| b4ac2d840b | |||
| 0ae52fece1 | |||
| 8351331d78 | |||
| f1ecfa6ae6 | |||
| b5a8a294ed | |||
| 9cdaed2769 | |||
| 18a0910113 | |||
| 99e1a55f54 | |||
| 21df968fd1 | |||
| 5a3a5acff2 | |||
| 70302d7b4f | |||
| 3ff90626b6 | |||
| 1877329093 | |||
| 98429b8184 | |||
| d350a00ece | |||
| ad756173f1 | |||
| 94877b5008 | |||
| f020404ee6 | |||
| 79298c7c24 | |||
| b25ce8a0cd | |||
| 5d84484079 | |||
| 49ddefa834 | |||
| 3af469eeea | |||
| 5e7e5ad836 | |||
| 9d8287f3e3 | |||
| 2efd02769b | |||
| 669dd4edeb | |||
| b5641cc744 | |||
| c5d94855cd | |||
| face67dfeb | |||
| d9094cebea | |||
| 493ae58beb | |||
| ed4ce9fc94 | |||
| 4c48970cb0 | |||
| 46e03602ed | |||
| 45343a4ccc | |||
| 276c91b143 | |||
| cfe35a7878 | |||
| d47d23aa0e | |||
| 02f0a4ca59 | |||
| 23cfbf22eb | |||
| 9da72d25ed | |||
| 0ad95fa361 | |||
| 6960076699 | |||
| bdeb06b16c | |||
| 884b1ac3a8 | |||
| 207229ad5e | |||
| 2464c572eb | |||
| 8b21a4e5ab | |||
| 894e68a408 | |||
| 7594903444 | |||
| 1d0535e255 | |||
| 56556faa17 | |||
| 15a013af5f | |||
| 45565f4357 | |||
| aaa7e9f44a | |||
| 07f2b82dae | |||
| eced2edff8 | |||
| e98df91906 | |||
| 0c16918c34 | |||
| c2c544dc9f | |||
| d7f520a320 | |||
| d17266d599 | |||
| dfd99f61f8 | |||
| dbd40d96a1 | |||
| 99f792e8a3 | |||
| a7fb9fb090 | |||
| a977ce69a5 | |||
| 3d0edccc4a | |||
| 763511dc28 | |||
| 1367bc6f0d | |||
| 88dfc5d2a8 | |||
| 7a5f17f39e | |||
| 52ff0cde9f | |||
| cacee957e6 | |||
| bedcaa4f82 | |||
| f66c3859b0 | |||
| 69665f24e9 | |||
| 08b6665167 | |||
| d54a23d30e | |||
| 9856f79cf9 | |||
| 634bd197f2 | |||
| 1af8ca484b | |||
| 1c0654b9a5 | |||
| 1dc4a6761e | |||
| f3d4fef6e6 | |||
| 39264a0141 | |||
| ba0477f298 | |||
| 139624750a | |||
| 1bbde1bfe0 | |||
| 6b4554e643 | |||
| c8c936eddf | |||
| 93d0c03d5b | |||
| 5bdbf2bcd6 | |||
| 4c611f40b4 | |||
| 8bdd4848f4 | |||
| b786b884f6 | |||
| 0fa63fb4a2 | |||
| f5aae1b47d | |||
| 6d140bad39 | |||
| 1f55957402 | |||
| 08368a1fba | |||
| 20d9c175e2 | |||
| d4dbf684e0 | |||
| 0c9354bda9 | |||
| f113af0b9e | |||
| 43381008d6 | |||
| 7d99466446 | |||
| ecaaae8719 | |||
| 0b2f950cc2 | |||
| 85013987aa | |||
| a23b9213f4 | |||
| 140a69bb90 | |||
| 8c17d556a8 | |||
| 0e37b85609 | |||
| 6e783780ca | |||
| fd1c0f66eb | |||
| a4ca8fa3b6 | |||
| 3d9ceb5162 | |||
| bbaafc2fef | |||
| 573cb35036 | |||
| 6c44096c7b | |||
| 4b371b489b | |||
| 87c1d2410e | |||
| 2439203eff | |||
| 312d294fdd | |||
| 369a0fba85 | |||
| 438b16b8c9 | |||
| dbe7e644f1 | |||
| a916465ad0 | |||
| 412d7bc985 | |||
| 7d44026dea | |||
| ba90047d70 | |||
| 10cf3a4fa3 | |||
| aac7722b9e | |||
| ed396a69ed | |||
| ec267c644a | |||
| 9b5808938f | |||
| b10a8cedf6 | |||
| bfb264ad96 | |||
| 702f9377e3 | |||
| 0e33ac1efe | |||
| e27e883443 | |||
| ffbb6bcf9c | |||
| 8541b60acb | |||
| 96c0277a1b | |||
| b15c185939 | |||
| a955ef1088 | |||
| e06d94ddeb | |||
| 1681cebf60 | |||
| a09f66c8cd | |||
| 1869fe6e05 | |||
| 1c27e24d50 | |||
| 30fd5a4c88 | |||
| 3040782e04 | |||
| 1b8b17de86 | |||
| 029f416fce | |||
| a1953baef6 | |||
| e90dcc4be4 | |||
| 71b326db68 | |||
| 42ab10699b | |||
| 5a0e19dda1 | |||
| 86ad5ce55c | |||
| 61a8e3a3bd | |||
| 0675541154 | |||
| fa5957f7ca | |||
| 5265eb7ebd | |||
| 878a8bc990 | |||
| b1bafca333 | |||
| 92d38b50af | |||
| 5de5c24a8a | |||
| 062d95a09e | |||
| c33c42f158 | |||
| c46d76ae3a | |||
| 4f542e319f | |||
| b5e341bb8a | |||
| 06fd06a4d2 | |||
| 7d1d959879 | |||
| 39ef2546d5 | |||
| 9f7492577f | |||
| bef8e3584c | |||
| 032fff92fb | |||
| 6c8659f8f9 | |||
| 5884bdbea4 | |||
| 86290e9660 | |||
| 563acf0832 | |||
| f4526d57fc | |||
| d9b0a118af | |||
| f5352f08c5 | |||
| 48ffd07276 | |||
| eb01b5ee1d | |||
| a7ea02a709 | |||
| 66fd087205 | |||
| 0e8932f1cb | |||
| e2b8e3260d | |||
| c476c1e348 | |||
| 18544647ac | |||
| 8af8dbd2ec | |||
| 39fc09ec1b | |||
| 016722addd | |||
| fd10faedfa | |||
| 702d06098e | |||
| 0b62b4378b | |||
| b8b84cb6ce | |||
| 08cb3dde57 | |||
| 03eb378eb9 | |||
| 6b81d7179f | |||
| 0270b7c780 | |||
| 38e9c650ba | |||
| 9320373c12 | |||
| 019b7ff9d6 | |||
| b519e3f9e1 | |||
| e48dfc331c | |||
| 4d51464045 | |||
| 8563a63af2 | |||
| eb75374fb1 | |||
| 1cbc985018 | |||
| 58f4dee67a | |||
| a8d11b36a3 | |||
| 189a6b8e35 | |||
| e45529b149 | |||
| ba7b1011b8 | |||
| c23be52881 | |||
| 7fb5f90a38 | |||
| fcff23f005 | |||
| 42a184f742 | |||
| 7add756923 | |||
| 9914e76d5b | |||
| 668f045972 | |||
| 38f48dd769 | |||
| db55fb34b8 | |||
| 76d4ecd40d | |||
| 27f956a73b | |||
| dd1c0d87fe | |||
| 207d290865 | |||
| 5e8ee44091 | |||
| 662ebe593e | |||
| c42968617b | |||
| 3714aa2fff | |||
| 0fcc30dd43 | |||
| d6015bc11f | |||
| 4fd374e80d | |||
| 3d7770bfd5 | |||
| f173f97e9d | |||
| ef8523b5a4 | |||
| 63c5c9a2c0 | |||
| 5ed95f49d0 | |||
| 8a3fcd060d | |||
| b1059b73aa | |||
| 1a1cfe3479 | |||
| 8e53e16005 | |||
| 6a18585f25 | |||
| e509b8207d | |||
| a37156c2c7 | |||
| 632997d1fb | |||
| 0c1e3b470a | |||
| e8f66b8a42 | |||
| 2c2bbb4064 | |||
| 3890665e60 | |||
| 49a20c16dc | |||
| af1849e805 | |||
| 2822398fbe | |||
| 1ef4b61425 | |||
| f703cb2414 | |||
| 9413b555c4 | |||
| 8818740bef | |||
| 34027fe813 | |||
| 0bdb54f03f | |||
| 4ee024846b | |||
| 26577aba84 | |||
| b21559e042 | |||
| c0209c35ab | |||
| 070e3f75f3 | |||
| 4ca286c333 | |||
| 59778af504 | |||
| 10a2a6db5d | |||
| 70af02a2bc | |||
| cc82b674b5 | |||
| 6ba67723df | |||
| 202f1d7c3d | |||
| e1c41d7183 | |||
| 053573e0df | |||
| 1117d47721 | |||
| f982d75fa0 | |||
| fdebf8ac4f | |||
| ff282c2a8f | |||
| 7b7038273a | |||
| 0422df466e | |||
| f35b20a845 | |||
| c22a57420c | |||
| 04689b6535 | |||
| bd1b4b5aa9 | |||
| 445940fb7b | |||
| e8b0085d2b | |||
| 31560c67fb | |||
| d5feb8b787 | |||
| 3258b709a3 | |||
| a591b4b905 | |||
| 3aaf482704 | |||
| 07a4b8aacc | |||
| b6c751455e | |||
| dee2a96fea | |||
| b728f5f559 | |||
| 74e2a3da50 | |||
| 1a6151b91f | |||
| 7397160435 | |||
| 75808eb2a6 | |||
| 382b178911 | |||
| a7d5e518c3 | |||
| 072da6d9d6 | |||
| 4f8c134102 | |||
| b8a57a3649 | |||
| d892beb0e7 | |||
| 9a534d047c | |||
| c240a9693c | |||
| b3e6ef6224 | |||
| 3e6a88a8f9 | |||
| 37e1f9ba34 | |||
| d936aa9349 | |||
| 7888f699f5 | |||
| deff03f2c2 | |||
| 405f68f54a | |||
| 44f3e86b62 | |||
| 75131959d1 | |||
| b9433a8208 | |||
| 6f1f26f426 | |||
| dbdb8f3757 | |||
| 41b2fd770f | |||
| d4c2bc60e4 | |||
| 122f708ae8 | |||
| 18ccde8e86 | |||
| d4b64c8280 | |||
| 96ca100e34 | |||
| bd80d61b2a | |||
| 6e0f124df3 | |||
| 7ed9ad04bf | |||
| 8266e2ee4f | |||
| 8c83386ef4 | |||
| 4cbd6cfd43 | |||
| 96cd039036 | |||
| 46ab59628c | |||
| f569bc682b | |||
| af6794e424 | |||
| c7e22ccd75 | |||
| 3d1e87cb78 | |||
| c2ef46f145 | |||
| e29d6511f5 | |||
| 4d3b4ab206 | |||
| 127a74baa2 | |||
| 93f1d35cc7 | |||
| 697b6a3fe1 | |||
| 9299c88a43 | |||
| 2fe22da3a2 | |||
| 50191cd1ec | |||
| c2e9a6681a | |||
| 2b8c4b0416 | |||
| 519c07fb00 | |||
| ff9a1edbfd | |||
| 8058709d5a | |||
| f413e3bdaf | |||
| 45d7aab39a | |||
| 4ddb85ce1e | |||
| dd30335ffd | |||
| 39cbd7d8ed | |||
| 7ef47be5f5 | |||
| e536616888 | |||
| 11edb618c3 | |||
| cfe992f0f9 | |||
| f948a9b4ae | |||
| 86f4e45dcc | |||
| 8e61e26370 | |||
| 622a5a231e | |||
| 7c31f51567 | |||
| 47f05fe7b5 | |||
| 8fd53e0045 | |||
| 39fb96316f | |||
| 165ee0b5ff | |||
| 221b39256d | |||
| de2a46a2f9 | |||
| 8a6004232b | |||
| 1d01a70d92 | |||
| 4d27c0c467 | |||
| 9ced552e65 | |||
| d49cde41a7 | |||
| e4dcfaf1b3 | |||
| 8f63f565c6 | |||
| f15548ebeb | |||
| d4292300a0 | |||
| e3b4cd4671 | |||
| 300abd1439 | |||
| ccf53ad489 | |||
| 542f2470e7 | |||
| 98f51e0876 | |||
| c7b5280d3c | |||
| d3a48a891e | |||
| ce61e2452a | |||
| d6ae6650b2 | |||
| 1141b125d0 | |||
| d6c68ae1a5 | |||
| df71b84341 | |||
| d8d1007732 | |||
| 51f49a5fe4 | |||
| 4626b36e27 | |||
| d242dc0e72 | |||
| 2c84a5ecdd | |||
| 002da1b450 | |||
| 7c8ee5814a | |||
| 090d074399 | |||
| 8ec7cb8435 | |||
| e9d45da4c5 | |||
| 64cae2aab2 | |||
| 7d7c598647 | |||
| af252b709b | |||
| 891584c8d9 | |||
| c21afbe868 | |||
| 13476a807c | |||
| 3d00af4799 | |||
| 098962fa65 | |||
| d8c3b6bca4 | |||
| 2632e7eba7 | |||
| b5b3ae3cbe | |||
| 13e53fc7ee | |||
| 54b6ce2c0e | |||
| 64f63a7df2 | |||
| df0e1fb592 | |||
| 1c11bc067f | |||
| 3b3fc47f84 | |||
| 321cbd6829 | |||
| 43cb7040c6 | |||
| 644d68ee6f | |||
| 354bea8719 | |||
| e85c18f019 | |||
| 50aaf99da7 | |||
| 80c96de277 | |||
| eb07373477 | |||
| f1980e9be2 | |||
| 8777b5606d | |||
| 4497d6438c | |||
| 3d898adb26 | |||
| 842b09a280 | |||
| 91c69a80ab | |||
| c1199931de | |||
| 5e788b329d | |||
| 48dc4c624e | |||
| d2b99c0b62 | |||
| baa2a4d53f | |||
| 27c2701555 | |||
| a43ef6ec72 | |||
| c81b6680e7 | |||
| 8358b27445 | |||
| b9451ab458 | |||
| ce4e6f3dd9 | |||
| 53eb209387 | |||
| a84414f6de | |||
| 2c532713ad | |||
| fa65b95b9e | |||
| 0a0c6ea6ea | |||
| 7471035885 | |||
| 35cd771c97 | |||
| 1a3680d8a7 | |||
| 510f172c58 | |||
| 6a03e43cbc | |||
| 4acd811429 | |||
| be86f90490 | |||
| 26b84e6fd9 | |||
| 94f00b7d27 | |||
| 7820a539dd | |||
| 81eec9ba70 | |||
| 47601bab7c | |||
| 99901896cc | |||
| 5c7fe97753 | |||
| aa18556c56 | |||
| e6bf09db80 | |||
| 681ce93cc1 | |||
| 85ad682530 | |||
| e19ee681ac | |||
| 83d6d55d4b | |||
| 7dfb472424 | |||
| a78f8a0495 | |||
| 6175ee2c4c | |||
| a3537160dc | |||
| 75925b1aae | |||
| 1ef0f89a0c | |||
| e6ef85a711 | |||
| 6f2803e8a7 | |||
| 1c9d197693 | |||
| 592b1dd99f | |||
| 3240c0bb36 | |||
| e8fbcfcac3 | |||
| 1a8928c5a4 | |||
| 173dc3dedf | |||
| dbf44fe316 | |||
| 648fcb397c | |||
| 7aadb6d9ec | |||
| 49842e1961 | |||
| 44d0ac3f25 | |||
| 43a9a42991 | |||
| 145b13c238 | |||
| 8ace5532b2 | |||
| c1281b96ff | |||
| ca7b46209a | |||
| 81285f30a5 | |||
| c9b225d257 | |||
| af7414a67d | |||
| 6d6149cf81 | |||
| a31dfa3001 | |||
| afa7739131 | |||
| f1ee1e4c0f | |||
| ed5a7bff6b | |||
| 42a793e2f5 | |||
| eb8362bbe1 | |||
| 5733ea9f64 | |||
| 36c7e3b441 | |||
| 0e80648010 | |||
| be0e79c271 | |||
| 5acd392880 | |||
| 951119fcfa | |||
| 29d608f481 | |||
| 15de814bb4 | |||
| a29a12701e | |||
| 3bd50315a6 | |||
| 45186ee04e | |||
| c8e215b989 | |||
| d1735e098c | |||
| c53ea2c9f4 | |||
| f8e737648a | |||
| b1af297707 | |||
| 85c7b98307 | |||
| e41152e5f1 | |||
| 9f19ce6729 | |||
| ae85e185ad | |||
| 93762cc658 | |||
| ed608025eb | |||
| 14a293a6b3 | |||
| c7b744db79 | |||
| 250edccdda | |||
| 1daf087682 | |||
| d3d601d5c3 | |||
| 8083c9515f | |||
| 73cd16b7b5 | |||
| 65112b75bb | |||
| 3cf0b7a2d4 | |||
| afb171eefb | |||
| b07ea17f49 | |||
| 83ded43ee7 | |||
| 537c971a47 | |||
| ed0c962ff5 | |||
| eec0b9329d | |||
| 1929a84e1e | |||
| 522a6b6c17 | |||
| 462b65fe45 | |||
| 2b89fbf963 | |||
| b5c97f2039 | |||
| 64d2d19598 | |||
| a7dd034710 | |||
| ed0bcdac4f | |||
| bdeb3778d0 | |||
| 185c852088 | |||
| a1b7e42783 | |||
| 3c4b64785f | |||
| ab43d6aa5c | |||
| 3cf7034e9c | |||
| ddb37c353c | |||
| dbe3b9b99e | |||
| 5bc815e2e2 | |||
| 5a43a3a321 | |||
| 7ae63299a8 | |||
| 57de1d2677 | |||
| 383b5abb33 | |||
| d8ccd7d84c | |||
| df5b201c6b | |||
| 44d8e72ca8 | |||
| c37ee25be7 | |||
| c884daf96a | |||
| fcd213708d | |||
| 915a5db0c6 | |||
| d53a631608 | |||
| b4d0885203 | |||
| d04f6661ee | |||
| 80e1b262e5 | |||
| dd518985ff | |||
| a17cea104e | |||
| 3f9b310c6a | |||
| 06e49c0a87 | |||
| 6cf2cf5dae | |||
| 3faaf0916a | |||
| 6c9534e660 | |||
| 22295c4278 | |||
| 16182ea972 | |||
| ad69958e52 | |||
| f8a2829318 | |||
| 634f3692d8 | |||
| 2cc7f2cbac | |||
| 2896cf05fb | |||
| 776a28f053 | |||
| d75746be70 | |||
| 1dbe7fc0db | |||
| ff8a5b9a69 | |||
| 36267af51b | |||
| fef162cff8 | |||
| a8587916c8 | |||
| 77670ead76 | |||
| 360fb2f816 | |||
| a40f20ad6c | |||
| 407482eb37 | |||
| d9e7d6cd22 | |||
| dbf438f99d | |||
| ebff758b1c | |||
| c1ab732ffe | |||
| a0644fce88 | |||
| 7eb0d4cd94 | |||
| 5de79b29e9 | |||
| f930518cb2 | |||
| 2362bd1b60 | |||
| f0177067c0 | |||
| 6b6177a716 | |||
| 9d997c59d7 | |||
| e66e27afc0 | |||
| 8a09e7c31a | |||
| 590bfa0f09 | |||
| e919c605f7 | |||
| c46230ca8a | |||
| 0a7bae06f9 | |||
| 866891c6c4 | |||
| 89675315cb | |||
| 013e4c759b | |||
| 12fda61d73 | |||
| 187a8001c4 | |||
| 3b75299f53 | |||
| fcf0e42ce8 |
70
.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/bug-report.yml
vendored
Normal file
70
.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/bug-report.yml
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,70 @@
|
||||
name: "\U0001F41B Bug Report"
|
||||
description: Submit a bug report to help us improve the library
|
||||
body:
|
||||
- type: textarea
|
||||
id: system-info
|
||||
attributes:
|
||||
label: System Info
|
||||
description: Please share your relevant system information with us
|
||||
placeholder: peft & accelerate & transformers version, platform, python version, ...
|
||||
validations:
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
|
||||
- type: textarea
|
||||
id: who-can-help
|
||||
attributes:
|
||||
label: Who can help?
|
||||
description: |
|
||||
Your issue will be replied to more quickly if you can figure out the right person to tag with @.
|
||||
If you know how to use git blame, that is the easiest way, otherwise, here is a rough guide of **who to tag**.
|
||||
|
||||
All issues are read by one of the core maintainers, so if you don't know who to tag, just leave this blank and
|
||||
a core maintainer will ping the right person.
|
||||
|
||||
Please tag fewer than 3 people.
|
||||
|
||||
Library: @pacman100 @younesbelkada @benjaminbossan @sayakpaul
|
||||
|
||||
Documentation: @stevhliu
|
||||
|
||||
placeholder: "@Username ..."
|
||||
|
||||
- type: checkboxes
|
||||
id: information-scripts-examples
|
||||
attributes:
|
||||
label: Information
|
||||
description: 'The problem arises when using:'
|
||||
options:
|
||||
- label: "The official example scripts"
|
||||
- label: "My own modified scripts"
|
||||
|
||||
- type: checkboxes
|
||||
id: information-tasks
|
||||
attributes:
|
||||
label: Tasks
|
||||
description: "The tasks I am working on are:"
|
||||
options:
|
||||
- label: "An officially supported task in the `examples` folder"
|
||||
- label: "My own task or dataset (give details below)"
|
||||
|
||||
- type: textarea
|
||||
id: reproduction
|
||||
validations:
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
attributes:
|
||||
label: Reproduction
|
||||
description: |
|
||||
Please provide a code sample that reproduces the problem you ran into. It can be a Colab link or just a code snippet.
|
||||
Please provide the simplest reproducer as possible so that we can quickly fix the issue. When you paste
|
||||
the error message, please include the full traceback.
|
||||
|
||||
placeholder: |
|
||||
Reproducer:
|
||||
|
||||
- type: textarea
|
||||
id: expected-behavior
|
||||
validations:
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
attributes:
|
||||
label: Expected behavior
|
||||
description: "A clear and concise description of what you would expect to happen."
|
||||
30
.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/feature-request.yml
vendored
Normal file
30
.github/ISSUE_TEMPLATE/feature-request.yml
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,30 @@
|
||||
name: "\U0001F680 Feature request"
|
||||
description: Submit a proposal/request for a new feature
|
||||
labels: [ "feature" ]
|
||||
body:
|
||||
- type: textarea
|
||||
id: feature-request
|
||||
validations:
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
attributes:
|
||||
label: Feature request
|
||||
description: |
|
||||
A clear and concise description of the feature proposal. Please provide a link to the paper and code in case they exist.
|
||||
|
||||
- type: textarea
|
||||
id: motivation
|
||||
validations:
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
attributes:
|
||||
label: Motivation
|
||||
description: |
|
||||
Please outline the motivation for the proposal. Is your feature request related to a problem?
|
||||
|
||||
- type: textarea
|
||||
id: contribution
|
||||
validations:
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
attributes:
|
||||
label: Your contribution
|
||||
description: |
|
||||
Is there any way that you could help, e.g. by submitting a PR?
|
||||
241
.github/workflows/build_docker_images.yml
vendored
Normal file
241
.github/workflows/build_docker_images.yml
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,241 @@
|
||||
name: Build Docker images (scheduled)
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
workflow_dispatch:
|
||||
workflow_call:
|
||||
schedule:
|
||||
- cron: "0 1 * * *"
|
||||
|
||||
concurrency:
|
||||
group: docker-image-builds
|
||||
cancel-in-progress: false
|
||||
|
||||
env:
|
||||
CI_SLACK_CHANNEL: ${{ secrets.CI_DOCKER_CHANNEL }}
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
latest-cpu:
|
||||
name: "Latest Peft CPU [dev]"
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Cleanup disk
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
sudo ls -l /usr/local/lib/
|
||||
sudo ls -l /usr/share/
|
||||
sudo du -sh /usr/local/lib/
|
||||
sudo du -sh /usr/share/
|
||||
sudo rm -rf /usr/local/lib/android
|
||||
sudo rm -rf /usr/share/dotnet
|
||||
sudo du -sh /usr/local/lib/
|
||||
sudo du -sh /usr/share/
|
||||
- name: Set up Docker Buildx
|
||||
uses: docker/setup-buildx-action@v1
|
||||
- name: Check out code
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v3
|
||||
- name: Login to DockerHub
|
||||
uses: docker/login-action@v2
|
||||
with:
|
||||
username: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME }}
|
||||
password: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_PASSWORD }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Build and Push CPU
|
||||
uses: docker/build-push-action@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
context: ./docker/peft-cpu
|
||||
push: true
|
||||
tags: huggingface/peft-cpu
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Post to a Slack channel
|
||||
id: slack
|
||||
#uses: slackapi/slack-github-action@v1.25.0
|
||||
uses: slackapi/slack-github-action@6c661ce58804a1a20f6dc5fbee7f0381b469e001
|
||||
with:
|
||||
# Slack channel id, channel name, or user id to post message.
|
||||
# See also: https://api.slack.com/methods/chat.postMessage#channels
|
||||
channel-id: ${{ env.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL }}
|
||||
# For posting a rich message using Block Kit
|
||||
payload: |
|
||||
{
|
||||
"text": "peft-cpu Docker Image build result: ${{ job.status }}\n${{ github.event.pull_request.html_url || github.event.head_commit.url }}",
|
||||
"blocks": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "section",
|
||||
"text": {
|
||||
"type": "mrkdwn",
|
||||
"text": "peft-cpu Docker Image build result: ${{ job.status }}\n${{ github.event.pull_request.html_url || github.event.head_commit.url }}"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
env:
|
||||
SLACK_BOT_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
|
||||
latest-cuda:
|
||||
name: "Latest Peft GPU [dev]"
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Cleanup disk
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
sudo ls -l /usr/local/lib/
|
||||
sudo ls -l /usr/share/
|
||||
sudo du -sh /usr/local/lib/
|
||||
sudo du -sh /usr/share/
|
||||
sudo rm -rf /usr/local/lib/android
|
||||
sudo rm -rf /usr/share/dotnet
|
||||
sudo du -sh /usr/local/lib/
|
||||
sudo du -sh /usr/share/
|
||||
- name: Set up Docker Buildx
|
||||
uses: docker/setup-buildx-action@v1
|
||||
- name: Check out code
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v3
|
||||
- name: Login to DockerHub
|
||||
uses: docker/login-action@v1
|
||||
with:
|
||||
username: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME }}
|
||||
password: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_PASSWORD }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Build and Push GPU
|
||||
uses: docker/build-push-action@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
context: ./docker/peft-gpu
|
||||
push: true
|
||||
tags: huggingface/peft-gpu
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Post to a Slack channel
|
||||
id: slack
|
||||
#uses: slackapi/slack-github-action@v1.25.0
|
||||
uses: slackapi/slack-github-action@6c661ce58804a1a20f6dc5fbee7f0381b469e001
|
||||
with:
|
||||
# Slack channel id, channel name, or user id to post message.
|
||||
# See also: https://api.slack.com/methods/chat.postMessage#channels
|
||||
channel-id: ${{ env.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL }}
|
||||
# For posting a rich message using Block Kit
|
||||
payload: |
|
||||
{
|
||||
"text": "peft-gpu Docker Image build result: ${{ job.status }}\n${{ github.event.pull_request.html_url || github.event.head_commit.url }}",
|
||||
"blocks": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "section",
|
||||
"text": {
|
||||
"type": "mrkdwn",
|
||||
"text": "peft-gpu Docker Image build result: ${{ job.status }}\n${{ github.event.pull_request.html_url || github.event.head_commit.url }}"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
env:
|
||||
SLACK_BOT_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
|
||||
latest-cuda-bnb-source:
|
||||
name: "Latest Peft GPU + bnb source [dev]"
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Cleanup disk
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
sudo ls -l /usr/local/lib/
|
||||
sudo ls -l /usr/share/
|
||||
sudo du -sh /usr/local/lib/
|
||||
sudo du -sh /usr/share/
|
||||
sudo rm -rf /usr/local/lib/android
|
||||
sudo rm -rf /usr/share/dotnet
|
||||
sudo du -sh /usr/local/lib/
|
||||
sudo du -sh /usr/share/
|
||||
- name: Set up Docker Buildx
|
||||
uses: docker/setup-buildx-action@v1
|
||||
- name: Check out code
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v3
|
||||
- name: Login to DockerHub
|
||||
uses: docker/login-action@v1
|
||||
with:
|
||||
username: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME }}
|
||||
password: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_PASSWORD }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Build and Push GPU
|
||||
uses: docker/build-push-action@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
context: ./docker/peft-gpu-bnb-source
|
||||
push: true
|
||||
tags: huggingface/peft-gpu-bnb-source
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Post to a Slack channel
|
||||
id: slack
|
||||
#uses: slackapi/slack-github-action@v1.25.0
|
||||
uses: slackapi/slack-github-action@6c661ce58804a1a20f6dc5fbee7f0381b469e001
|
||||
with:
|
||||
# Slack channel id, channel name, or user id to post message.
|
||||
# See also: https://api.slack.com/methods/chat.postMessage#channels
|
||||
channel-id: ${{ env.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL }}
|
||||
# For posting a rich message using Block Kit
|
||||
payload: |
|
||||
{
|
||||
"text": "peft-gpu + bnb-source (source) Docker Image build result: ${{ job.status }}\n${{ github.event.pull_request.html_url || github.event.head_commit.url }}",
|
||||
"blocks": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "section",
|
||||
"text": {
|
||||
"type": "mrkdwn",
|
||||
"text": "peft-gpu + bnb-source (source) Docker Image build result: ${{ job.status }}\n${{ github.event.pull_request.html_url || github.event.head_commit.url }}"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
env:
|
||||
SLACK_BOT_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
latest-cuda-bnb-source-latest:
|
||||
name: "Latest Peft GPU + bnb source [accelerate / peft / transformers latest]"
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Cleanup disk
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
sudo ls -l /usr/local/lib/
|
||||
sudo ls -l /usr/share/
|
||||
sudo du -sh /usr/local/lib/
|
||||
sudo du -sh /usr/share/
|
||||
sudo rm -rf /usr/local/lib/android
|
||||
sudo rm -rf /usr/share/dotnet
|
||||
sudo du -sh /usr/local/lib/
|
||||
sudo du -sh /usr/share/
|
||||
- name: Set up Docker Buildx
|
||||
uses: docker/setup-buildx-action@v1
|
||||
- name: Check out code
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v3
|
||||
- name: Login to DockerHub
|
||||
uses: docker/login-action@v1
|
||||
with:
|
||||
username: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_USERNAME }}
|
||||
password: ${{ secrets.DOCKERHUB_PASSWORD }}
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Build and Push GPU
|
||||
uses: docker/build-push-action@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
context: ./docker/peft-gpu-bnb-latest
|
||||
push: true
|
||||
tags: huggingface/peft-gpu-bnb-latest
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Post to a Slack channel
|
||||
id: slack
|
||||
#uses: slackapi/slack-github-action@v1.25.0
|
||||
uses: slackapi/slack-github-action@6c661ce58804a1a20f6dc5fbee7f0381b469e001
|
||||
with:
|
||||
# Slack channel id, channel name, or user id to post message.
|
||||
# See also: https://api.slack.com/methods/chat.postMessage#channels
|
||||
channel-id: ${{ env.CI_SLACK_CHANNEL }}
|
||||
# For posting a rich message using Block Kit
|
||||
payload: |
|
||||
{
|
||||
"text": "peft-gpu + bnb-source (latest) Docker Image build result: ${{ job.status }}\n${{ github.event.pull_request.html_url || github.event.head_commit.url }}",
|
||||
"blocks": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"type": "section",
|
||||
"text": {
|
||||
"type": "mrkdwn",
|
||||
"text": "peft-gpu + bnb-source (latest) Docker Image build result: ${{ job.status }}\n${{ github.event.pull_request.html_url || github.event.head_commit.url }}"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
env:
|
||||
SLACK_BOT_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.SLACK_CIFEEDBACK_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
19
.github/workflows/build_documentation.yml
vendored
Normal file
19
.github/workflows/build_documentation.yml
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,19 @@
|
||||
name: Build documentation
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
push:
|
||||
branches:
|
||||
- main
|
||||
- doc-builder*
|
||||
- v*-release
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
build:
|
||||
uses: huggingface/doc-builder/.github/workflows/build_main_documentation.yml@main
|
||||
with:
|
||||
commit_sha: ${{ github.sha }}
|
||||
package: peft
|
||||
notebook_folder: peft_docs
|
||||
secrets:
|
||||
token: ${{ secrets.HUGGINGFACE_PUSH }}
|
||||
hf_token: ${{ secrets.HF_DOC_BUILD_PUSH }}
|
||||
16
.github/workflows/build_pr_documentation.yml
vendored
Normal file
16
.github/workflows/build_pr_documentation.yml
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,16 @@
|
||||
name: Build PR Documentation
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
pull_request:
|
||||
|
||||
concurrency:
|
||||
group: ${{ github.workflow }}-${{ github.head_ref || github.run_id }}
|
||||
cancel-in-progress: true
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
build:
|
||||
uses: huggingface/doc-builder/.github/workflows/build_pr_documentation.yml@main
|
||||
with:
|
||||
commit_sha: ${{ github.event.pull_request.head.sha }}
|
||||
pr_number: ${{ github.event.number }}
|
||||
package: peft
|
||||
82
.github/workflows/integrations_tests.yml
vendored
Normal file
82
.github/workflows/integrations_tests.yml
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,82 @@
|
||||
name: integration tests
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
workflow_dispatch:
|
||||
inputs:
|
||||
branch:
|
||||
description: 'Branch to test on'
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
run_transformers_integration_tests:
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
fail-fast: false
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
transformers-version: ['main', 'latest']
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
ref: ${{ github.event.inputs.branch }}
|
||||
repository: ${{ github.event.pull_request.head.repo.full_name }}
|
||||
- name: Set up Python
|
||||
uses: actions/setup-python@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
python-version: "3.10"
|
||||
cache: "pip"
|
||||
cache-dependency-path: "setup.py"
|
||||
- name: print environment variables
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "env.CI_BRANCH = ${{ env.CI_BRANCH }}"
|
||||
echo "env.CI_SHA = ${{ env.CI_SHA }}"
|
||||
- name: Install dependencies
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m pip install --upgrade pip
|
||||
python -m pip install .[test]
|
||||
if [ "${{ matrix.transformers-version }}" == "main" ]; then
|
||||
pip install -U git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git
|
||||
else
|
||||
echo "Nothing to do as transformers latest already installed"
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Test transformers integration
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
cd .. && git clone https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git && cd transformers/ && git rev-parse HEAD
|
||||
RUN_SLOW=1 pytest tests/peft_integration/test_peft_integration.py
|
||||
run_diffusers_integration_tests:
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
fail-fast: false
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
# For now diffusers integration is not on PyPI
|
||||
diffusers-version: ['main']
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
ref: ${{ github.event.inputs.branch }}
|
||||
repository: ${{ github.event.pull_request.head.repo.full_name }}
|
||||
- name: Set up Python
|
||||
uses: actions/setup-python@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
python-version: "3.10"
|
||||
cache: "pip"
|
||||
cache-dependency-path: "setup.py"
|
||||
- name: print environment variables
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "env.CI_BRANCH = ${{ env.CI_BRANCH }}"
|
||||
echo "env.CI_SHA = ${{ env.CI_SHA }}"
|
||||
- name: Install dependencies
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m pip install --upgrade pip
|
||||
python -m pip install .[test]
|
||||
|
||||
if [ "${{ matrix.diffusers-version }}" == "main" ]; then
|
||||
pip install -U git+https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers.git
|
||||
else
|
||||
echo "Nothing to do as diffusers latest already installed"
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Test diffusers integration
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
cd .. && git clone https://github.com/huggingface/diffusers.git && cd diffusers/ && git rev-parse HEAD
|
||||
pytest tests/lora/test_lora_layers_peft.py
|
||||
133
.github/workflows/nightly-bnb.yml
vendored
Normal file
133
.github/workflows/nightly-bnb.yml
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,133 @@
|
||||
name: BNB from source self-hosted runner with slow tests (scheduled)
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
workflow_dispatch:
|
||||
schedule:
|
||||
- cron: "0 2 * * *"
|
||||
|
||||
env:
|
||||
RUN_SLOW: "yes"
|
||||
IS_GITHUB_CI: "1"
|
||||
# To be able to run tests on CUDA 12.2
|
||||
NVIDIA_DISABLE_REQUIRE: "1"
|
||||
SLACK_API_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.SLACK_API_TOKEN }}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
run_all_tests_single_gpu:
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
fail-fast: false
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
docker-image-name: ["huggingface/peft-gpu-bnb-source:latest", "huggingface/peft-gpu-bnb-latest:latest"]
|
||||
runs-on: [self-hosted, single-gpu, nvidia-gpu, t4, ci]
|
||||
env:
|
||||
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES: "0"
|
||||
TEST_TYPE: "single_gpu_${{ matrix.docker-image-name }}"
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: ${{ matrix.docker-image-name }}
|
||||
options: --gpus all --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
defaults:
|
||||
run:
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@v3
|
||||
- name: Pip install
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
source activate peft
|
||||
pip install -e . --no-deps
|
||||
pip install pytest-reportlog pytest-cov parameterized datasets scipy einops
|
||||
pip install "pytest>=7.2.0,<8.0.0" # see: https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/ce4fff0be7f6464d713f7ac3e0bbaafbc6959ae5/setup.py#L148C6-L148C26
|
||||
mkdir transformers-clone && git clone https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git transformers-clone # rename to transformers clone to avoid modules conflict
|
||||
if [ "${{ matrix.docker-image-name }}" == "huggingface/peft-gpu-bnb-latest:latest" ]; then
|
||||
cd transformers-clone
|
||||
transformers_version=$(pip show transformers | grep '^Version:' | cut -d ' ' -f2 | sed 's/\.dev0//')
|
||||
echo "Checking out tag for Transformers version: v$transformers_version"
|
||||
git fetch --tags
|
||||
git checkout tags/v$transformers_version
|
||||
cd ..
|
||||
fi
|
||||
- name: Run examples on single GPU
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
source activate peft
|
||||
make tests_examples_single_gpu_bnb
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run core tests on single GPU
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
source activate peft
|
||||
make tests_core_single_gpu_bnb
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run transformers tests on single GPU
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
source activate peft
|
||||
make transformers_tests
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Generate Report
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
pip install slack_sdk tabulate
|
||||
python scripts/log_reports.py --slack_channel_name bnb-daily-ci-collab >> $GITHUB_STEP_SUMMARY
|
||||
|
||||
run_all_tests_multi_gpu:
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
fail-fast: false
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
docker-image-name: ["huggingface/peft-gpu-bnb-source:latest", "huggingface/peft-gpu-bnb-latest:latest"]
|
||||
runs-on: [self-hosted, multi-gpu, nvidia-gpu, t4, ci]
|
||||
env:
|
||||
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES: "0,1"
|
||||
TEST_TYPE: "multi_gpu_${{ matrix.docker-image-name }}"
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: ${{ matrix.docker-image-name }}
|
||||
options: --gpus all --shm-size "16gb" --ipc host -v /mnt/cache/.cache/huggingface:/mnt/cache/
|
||||
defaults:
|
||||
run:
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@v3
|
||||
- name: Pip install
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
source activate peft
|
||||
pip install -e . --no-deps
|
||||
pip install pytest-reportlog pytest-cov parameterized datasets scipy einops
|
||||
pip install "pytest>=7.2.0,<8.0.0" # see: https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/ce4fff0be7f6464d713f7ac3e0bbaafbc6959ae5/setup.py#L148C6-L148C26
|
||||
mkdir transformers-clone && git clone https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git transformers-clone
|
||||
if [ "${{ matrix.docker-image-name }}" == "huggingface/peft-gpu-bnb-latest:latest" ]; then
|
||||
cd transformers-clone
|
||||
transformers_version=$(pip show transformers | grep '^Version:' | cut -d ' ' -f2 | sed 's/\.dev0//')
|
||||
echo "Checking out tag for Transformers version: v$transformers_version"
|
||||
git fetch --tags
|
||||
git checkout tags/v$transformers_version
|
||||
cd ..
|
||||
fi
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run core GPU tests on multi-gpu
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
source activate peft
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run examples on multi GPU
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
source activate peft
|
||||
make tests_examples_multi_gpu_bnb
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run core tests on multi GPU
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
source activate peft
|
||||
make tests_core_multi_gpu_bnb
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run transformers tests on multi GPU
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
source activate peft
|
||||
make transformers_tests
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Generate Report
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
pip install slack_sdk tabulate
|
||||
python scripts/log_reports.py --slack_channel_name bnb-daily-ci-collab >> $GITHUB_STEP_SUMMARY
|
||||
108
.github/workflows/nightly.yml
vendored
Normal file
108
.github/workflows/nightly.yml
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,108 @@
|
||||
name: Self-hosted runner with slow tests (scheduled)
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
workflow_dispatch:
|
||||
schedule:
|
||||
- cron: "0 2 * * *"
|
||||
|
||||
env:
|
||||
RUN_SLOW: "yes"
|
||||
IS_GITHUB_CI: "1"
|
||||
# To be able to run tests on CUDA 12.2
|
||||
NVIDIA_DISABLE_REQUIRE: "1"
|
||||
SLACK_API_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.SLACK_API_TOKEN }}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
run_all_tests_single_gpu:
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
fail-fast: false
|
||||
runs-on: [self-hosted, single-gpu, nvidia-gpu, t4, ci]
|
||||
env:
|
||||
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES: "0"
|
||||
TEST_TYPE: "single_gpu"
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: huggingface/peft-gpu:latest
|
||||
options: --gpus all --shm-size "16gb" -e NVIDIA_DISABLE_REQUIRE=true
|
||||
defaults:
|
||||
run:
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@v3
|
||||
- name: Pip install
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
source activate peft
|
||||
pip install -e . --no-deps
|
||||
pip install pytest-reportlog
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run common tests on single GPU
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
source activate peft
|
||||
make tests_common_gpu
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run examples on single GPU
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
source activate peft
|
||||
make tests_examples_single_gpu
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run core tests on single GPU
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
source activate peft
|
||||
make tests_core_single_gpu
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run regression tests on single GPU
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
source activate peft
|
||||
make tests_regression
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Generate Report
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
pip install slack_sdk tabulate
|
||||
python scripts/log_reports.py >> $GITHUB_STEP_SUMMARY
|
||||
|
||||
run_all_tests_multi_gpu:
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
fail-fast: false
|
||||
runs-on: [self-hosted, multi-gpu, nvidia-gpu, t4, ci]
|
||||
env:
|
||||
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES: "0,1"
|
||||
TEST_TYPE: "multi_gpu"
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: huggingface/peft-gpu:latest
|
||||
options: --gpus all --shm-size "16gb" -e NVIDIA_DISABLE_REQUIRE=true
|
||||
defaults:
|
||||
run:
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@v3
|
||||
- name: Pip install
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
source activate peft
|
||||
pip install -e . --no-deps
|
||||
pip install pytest-reportlog
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run core GPU tests on multi-gpu
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
source activate peft
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run common tests on multi GPU
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
source activate peft
|
||||
make tests_common_gpu
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run examples on multi GPU
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
source activate peft
|
||||
make tests_examples_multi_gpu
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run core tests on multi GPU
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
source activate peft
|
||||
make tests_core_multi_gpu
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Generate Report
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
pip install slack_sdk tabulate
|
||||
python scripts/log_reports.py >> $GITHUB_STEP_SUMMARY
|
||||
27
.github/workflows/stale.yml
vendored
Normal file
27
.github/workflows/stale.yml
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
|
||||
name: Stale Bot
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
schedule:
|
||||
- cron: "0 15 * * *"
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
close_stale_issues:
|
||||
name: Close Stale Issues
|
||||
if: github.repository == 'huggingface/peft'
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
env:
|
||||
GITHUB_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@v3
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Setup Python
|
||||
uses: actions/setup-python@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
python-version: 3.8
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Install requirements
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
pip install PyGithub
|
||||
- name: Close stale issues
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python scripts/stale.py
|
||||
59
.github/workflows/test-docker-build.yml
vendored
Normal file
59
.github/workflows/test-docker-build.yml
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,59 @@
|
||||
name: Test Docker images (on PR)
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
pull_request:
|
||||
paths:
|
||||
# Run only when DockerFile files are modified
|
||||
- "docker/**"
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
get_changed_files:
|
||||
name: "Build all modified docker images"
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
outputs:
|
||||
matrix: ${{ steps.set-matrix.outputs.matrix }}
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Check out code
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v3
|
||||
- name: Get changed files
|
||||
id: changed-files
|
||||
uses: tj-actions/changed-files@1c8e6069583811afb28f97afeaf8e7da80c6be5c #v42
|
||||
with:
|
||||
files: docker/**
|
||||
json: "true"
|
||||
- name: Run step if only the files listed above change
|
||||
if: steps.changed-files.outputs.any_changed == 'true'
|
||||
id: set-matrix
|
||||
env:
|
||||
ALL_CHANGED_FILES: ${{ steps.changed-files.outputs.all_changed_files }}
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "matrix=${{ steps.changed-files.outputs.all_changed_files}}" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
|
||||
build_modified_files:
|
||||
needs: get_changed_files
|
||||
name: Build Docker images on modified files
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
if: ${{ needs.get_changed_files.outputs.matrix }} != ''
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
fail-fast: false
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
docker-file: ${{ fromJson(needs.get_changed_files.outputs.matrix) }}
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Cleanup disk
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
sudo ls -l /usr/local/lib/
|
||||
sudo ls -l /usr/share/
|
||||
sudo du -sh /usr/local/lib/
|
||||
sudo du -sh /usr/share/
|
||||
sudo rm -rf /usr/local/lib/android
|
||||
sudo rm -rf /usr/share/dotnet
|
||||
sudo du -sh /usr/local/lib/
|
||||
sudo du -sh /usr/share/
|
||||
- name: Set up Docker Buildx
|
||||
uses: docker/setup-buildx-action@v1
|
||||
- name: Check out code
|
||||
uses: actions/checkout@v3
|
||||
- name: Build Docker image
|
||||
uses: docker/build-push-action@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
file: ${{ matrix.docker-file }}
|
||||
context: .
|
||||
push: False
|
||||
28
.github/workflows/tests-main.yml
vendored
Normal file
28
.github/workflows/tests-main.yml
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,28 @@
|
||||
name: tests on transformers main
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
push:
|
||||
branches: [main]
|
||||
paths-ignore:
|
||||
- 'docs/**'
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
tests:
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@v3
|
||||
- name: Set up Python 3.11
|
||||
uses: actions/setup-python@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
python-version: 3.11
|
||||
cache: "pip"
|
||||
cache-dependency-path: "setup.py"
|
||||
- name: Install dependencies
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m pip install --upgrade pip
|
||||
# cpu version of pytorch
|
||||
pip install -U git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers.git
|
||||
pip install -e .[test]
|
||||
- name: Test with pytest
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
make test
|
||||
53
.github/workflows/tests.yml
vendored
Normal file
53
.github/workflows/tests.yml
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,53 @@
|
||||
name: tests
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
push:
|
||||
branches: [main]
|
||||
paths-ignore:
|
||||
- 'docs/**'
|
||||
pull_request:
|
||||
paths-ignore:
|
||||
- 'docs/**'
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
check_code_quality:
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@v3
|
||||
- name: Set up Python
|
||||
uses: actions/setup-python@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
python-version: "3.8"
|
||||
cache: "pip"
|
||||
cache-dependency-path: "setup.py"
|
||||
- name: Install dependencies
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m pip install --upgrade pip
|
||||
pip install .[dev]
|
||||
- name: Check quality
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
make quality
|
||||
|
||||
tests:
|
||||
needs: check_code_quality
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
python-version: ["3.8", "3.9", "3.10", "3.11"]
|
||||
os: ["ubuntu-latest", "macos-latest", "windows-latest"]
|
||||
runs-on: ${{ matrix.os }}
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@v3
|
||||
- name: Set up Python ${{ matrix.python-version }}
|
||||
uses: actions/setup-python@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
python-version: ${{ matrix.python-version }}
|
||||
cache: "pip"
|
||||
cache-dependency-path: "setup.py"
|
||||
- name: Install dependencies
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m pip install --upgrade pip
|
||||
# cpu version of pytorch
|
||||
pip install -e .[test]
|
||||
- name: Test with pytest
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
make test
|
||||
43
.github/workflows/torch_compile_tests.yml
vendored
Normal file
43
.github/workflows/torch_compile_tests.yml
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
|
||||
name: torch compile tests
|
||||
|
||||
# see peft/tests/__init__.py
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
workflow_dispatch:
|
||||
inputs:
|
||||
branch:
|
||||
description: 'Branch to test on'
|
||||
required: true
|
||||
pytorch_nightly:
|
||||
description: 'Whether to use PyTorch nightly (true/false)'
|
||||
required: false
|
||||
default: false
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
run_tests_with_compile:
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
env:
|
||||
PEFT_DEBUG_WITH_TORCH_COMPILE: 1
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
ref: ${{ github.event.inputs.branch }}
|
||||
repository: ${{ github.event.pull_request.head.repo.full_name }}
|
||||
- name: Set up Python
|
||||
uses: actions/setup-python@v4
|
||||
with:
|
||||
python-version: "3.10"
|
||||
cache: "pip"
|
||||
cache-dependency-path: "setup.py"
|
||||
- name: Install dependencies
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
python -m pip install --upgrade pip
|
||||
python -m pip install .[test]
|
||||
if [ "${{ github.event.inputs.pytorch_nightly }}" = "true" ]; then
|
||||
python -m pip install --upgrade --pre torch --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/nightly/cpu
|
||||
fi
|
||||
- name: Test compile with pytest
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
echo "PEFT_DEBUG_WITH_TORCH_COMPILE=$PEFT_DEBUG_WITH_TORCH_COMPILE"
|
||||
git status
|
||||
make test
|
||||
16
.github/workflows/upload_pr_documentation.yml
vendored
Normal file
16
.github/workflows/upload_pr_documentation.yml
vendored
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,16 @@
|
||||
name: Upload PR Documentation
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
workflow_run:
|
||||
workflows: ["Build PR Documentation"]
|
||||
types:
|
||||
- completed
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
build:
|
||||
uses: huggingface/doc-builder/.github/workflows/upload_pr_documentation.yml@main
|
||||
with:
|
||||
package_name: peft
|
||||
secrets:
|
||||
hf_token: ${{ secrets.HF_DOC_BUILD_PUSH }}
|
||||
comment_bot_token: ${{ secrets.COMMENT_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
13
.pre-commit-config.yaml
Normal file
13
.pre-commit-config.yaml
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,13 @@
|
||||
repos:
|
||||
- repo: https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff-pre-commit
|
||||
rev: v0.2.1
|
||||
hooks:
|
||||
- id: ruff
|
||||
args:
|
||||
- --fix
|
||||
- id: ruff-format
|
||||
- repo: https://github.com/pre-commit/pre-commit-hooks
|
||||
rev: v4.5.0
|
||||
hooks:
|
||||
- id: check-merge-conflict
|
||||
- id: check-yaml
|
||||
@ -1 +0,0 @@
|
||||
include LICENSE
|
||||
54
Makefile
54
Makefile
@ -1,19 +1,55 @@
|
||||
.PHONY: quality style test docs
|
||||
|
||||
check_dirs := src examples
|
||||
check_dirs := src tests examples docs scripts docker
|
||||
|
||||
# Check that source code meets quality standards
|
||||
|
||||
# this target runs checks on all files
|
||||
quality:
|
||||
black --check $(check_dirs)
|
||||
isort --check-only $(check_dirs)
|
||||
flake8 $(check_dirs)
|
||||
doc-builder style src --max_len 119 --check_only
|
||||
ruff $(check_dirs)
|
||||
ruff format --check $(check_dirs)
|
||||
doc-builder style src/peft tests docs/source --max_len 119 --check_only
|
||||
|
||||
# Format source code automatically and check is there are any problems left that need manual fixing
|
||||
style:
|
||||
black $(check_dirs)
|
||||
isort $(check_dirs)
|
||||
doc-builder style src --max_len 119
|
||||
|
||||
ruff $(check_dirs) --fix
|
||||
ruff format $(check_dirs)
|
||||
doc-builder style src/peft tests docs/source --max_len 119
|
||||
|
||||
test:
|
||||
python -m pytest -n 3 tests/ $(if $(IS_GITHUB_CI),--report-log "ci_tests.log",)
|
||||
|
||||
tests_examples_multi_gpu:
|
||||
python -m pytest -m multi_gpu_tests tests/test_gpu_examples.py $(if $(IS_GITHUB_CI),--report-log "multi_gpu_examples.log",)
|
||||
|
||||
tests_examples_single_gpu:
|
||||
python -m pytest -m single_gpu_tests tests/test_gpu_examples.py $(if $(IS_GITHUB_CI),--report-log "single_gpu_examples.log",)
|
||||
|
||||
tests_core_multi_gpu:
|
||||
python -m pytest -m multi_gpu_tests tests/test_common_gpu.py $(if $(IS_GITHUB_CI),--report-log "core_multi_gpu.log",)
|
||||
|
||||
tests_core_single_gpu:
|
||||
python -m pytest -m single_gpu_tests tests/test_common_gpu.py $(if $(IS_GITHUB_CI),--report-log "core_single_gpu.log",)
|
||||
|
||||
tests_common_gpu:
|
||||
python -m pytest tests/test_decoder_models.py $(if $(IS_GITHUB_CI),--report-log "common_decoder.log",)
|
||||
python -m pytest tests/test_encoder_decoder_models.py $(if $(IS_GITHUB_CI),--report-log "common_encoder_decoder.log",)
|
||||
|
||||
tests_examples_multi_gpu_bnb:
|
||||
python -m pytest -m "multi_gpu_tests and bitsandbytes" tests/test_gpu_examples.py $(if $(IS_GITHUB_CI),--report-log "multi_gpu_examples.log",)
|
||||
|
||||
tests_examples_single_gpu_bnb:
|
||||
python -m pytest -m "single_gpu_tests and bitsandbytes" tests/test_gpu_examples.py $(if $(IS_GITHUB_CI),--report-log "single_gpu_examples.log",)
|
||||
|
||||
tests_core_multi_gpu_bnb:
|
||||
python -m pytest -m "multi_gpu_tests and bitsandbytes" tests/test_common_gpu.py $(if $(IS_GITHUB_CI),--report-log "core_multi_gpu.log",)
|
||||
|
||||
tests_core_single_gpu_bnb:
|
||||
python -m pytest -m "single_gpu_tests and bitsandbytes" tests/test_common_gpu.py $(if $(IS_GITHUB_CI),--report-log "core_single_gpu.log",)
|
||||
|
||||
# For testing transformers tests for bnb runners
|
||||
transformers_tests:
|
||||
RUN_SLOW=1 python -m pytest transformers-clone/tests/quantization/bnb $(if $(IS_GITHUB_CI),--report-log "transformers_tests.log",)
|
||||
|
||||
tests_regression:
|
||||
python -m pytest -s --regression tests/regression/ $(if $(IS_GITHUB_CI),--report-log "regression_tests.log",)
|
||||
|
||||
322
README.md
322
README.md
@ -19,43 +19,67 @@ limitations under the License.
|
||||
<p>State-of-the-art Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT) methods</p>
|
||||
</h3>
|
||||
|
||||
Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT) methods enable efficient adaptation of pre-trained language models (PLMs) to various downstream applications without fine-tuning all the model's parameters. Fine-tuning large-scale PLMs is often prohibitively costly. In this regard, PEFT methods only fine-tune a small number of (extra) model parameters, thereby greatly decreasing the computational and storage costs. Recent State-of-the-Art PEFT techniques achieve performance comparable to that of full fine-tuning.
|
||||
Fine-tuning large pretrained models is often prohibitively costly due to their scale. Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT) methods enable efficient adaptation of large pretrained models to various downstream applications by only fine-tuning a small number of (extra) model parameters instead of all the model's parameters. This significantly decreases the computational and storage costs. Recent state-of-the-art PEFT techniques achieve performance comparable to fully fine-tuned models.
|
||||
|
||||
Seamlessly integrated with 🤗 Accelerate for large scale models leveraging PyTorch FSDP.
|
||||
PEFT is integrated with Transformers for easy model training and inference, Diffusers for conveniently managing different adapters, and Accelerate for distributed training and inference for really big models.
|
||||
|
||||
Supported methods:
|
||||
> [!TIP]
|
||||
> Visit the [PEFT](https://huggingface.co/PEFT) organization to read about the PEFT methods implemented in the library and to see notebooks demonstrating how to apply these methods to a variety of downstream tasks. Click the "Watch repos" button on the organization page to be notified of newly implemented methods and notebooks!
|
||||
|
||||
1. LoRA: [LORA: LOW-RANK ADAPTATION OF LARGE LANGUAGE MODELS](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2106.09685.pdf)
|
||||
2. Prefix Tuning: [P-Tuning v2: Prompt Tuning Can Be Comparable to Fine-tuning Universally Across Scales and Tasks](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2110.07602.pdf)
|
||||
3. P-Tuning: [GPT Understands, Too](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2103.10385.pdf)
|
||||
4. Prompt Tuning: [The Power of Scale for Parameter-Efficient Prompt Tuning](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2104.08691.pdf)
|
||||
Check the PEFT Adapters API Reference section for a list of supported PEFT methods, and read the [Adapters](https://huggingface.co/docs/peft/en/conceptual_guides/adapter), [Soft prompts](https://huggingface.co/docs/peft/en/conceptual_guides/prompting), and [IA3](https://huggingface.co/docs/peft/en/conceptual_guides/ia3) conceptual guides to learn more about how these methods work.
|
||||
|
||||
## Getting started
|
||||
## Quickstart
|
||||
|
||||
Install PEFT from pip:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install peft
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Prepare a model for training with a PEFT method such as LoRA by wrapping the base model and PEFT configuration with `get_peft_model`. For the bigscience/mt0-large model, you're only training 0.19% of the parameters!
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM
|
||||
from peft import get_peft_config, get_peft_model, LoRAConfig, TaskType
|
||||
from peft import get_peft_config, get_peft_model, LoraConfig, TaskType
|
||||
model_name_or_path = "bigscience/mt0-large"
|
||||
tokenizer_name_or_path = "bigscience/mt0-large"
|
||||
|
||||
peft_config = LoRAConfig(
|
||||
peft_config = LoraConfig(
|
||||
task_type=TaskType.SEQ_2_SEQ_LM, inference_mode=False, r=8, lora_alpha=32, lora_dropout=0.1
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained(model_name_or_path)
|
||||
model = get_peft_model(model, peft_config)
|
||||
model.print_trainable_parameters()
|
||||
# output: trainable params: 2359296 || all params: 1231940608 || trainable%: 0.19151053100118282
|
||||
"trainable params: 2359296 || all params: 1231940608 || trainable%: 0.19151053100118282"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Use Cases
|
||||
To load a PEFT model for inference:
|
||||
|
||||
### Get comparable performance to full finetuning by adapting LLMs to downstream tasks using consumer hardware
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from peft import AutoPeftModelForCausalLM
|
||||
from transformers import AutoTokenizer
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
GPU memory required for adapting LLMs on the few-shot dataset `ought/raft/twitter_complaints`. Here, settings considered
|
||||
are full finetuning, PEFT-LoRA using plain PyTorch and PEFT-LoRA using DeepSpeed with CPU Offloading.
|
||||
model = AutoPeftModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("ybelkada/opt-350m-lora").to("cuda")
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("facebook/opt-350m")
|
||||
|
||||
Hardware: Single A100 80GB GPU with CPU RAM above 64GB
|
||||
model.eval()
|
||||
inputs = tokenizer("Preheat the oven to 350 degrees and place the cookie dough", return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
|
||||
outputs = model.generate(input_ids=inputs["input_ids"].to("cuda"), max_new_tokens=50)
|
||||
print(tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs, skip_special_tokens=True)[0])
|
||||
|
||||
"Preheat the oven to 350 degrees and place the cookie dough in the center of the oven. In a large bowl, combine the flour, baking powder, baking soda, salt, and cinnamon. In a separate bowl, combine the egg yolks, sugar, and vanilla."
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Why you should use PEFT
|
||||
|
||||
There are many benefits of using PEFT but the main one is the huge savings in compute and storage, making PEFT applicable to many different use cases.
|
||||
|
||||
### High performance on consumer hardware
|
||||
|
||||
Consider the memory requirements for training the following models on the [ought/raft/twitter_complaints](https://huggingface.co/datasets/ought/raft/viewer/twitter_complaints) dataset with an A100 80GB GPU with more than 64GB of CPU RAM.
|
||||
|
||||
| Model | Full Finetuning | PEFT-LoRA PyTorch | PEFT-LoRA DeepSpeed with CPU Offloading |
|
||||
| --------- | ---- | ---- | ---- |
|
||||
@ -63,9 +87,7 @@ Hardware: Single A100 80GB GPU with CPU RAM above 64GB
|
||||
| bigscience/mt0-xxl (12B params) | OOM GPU | 56GB GPU / 3GB CPU | 22GB GPU / 52GB CPU |
|
||||
| bigscience/bloomz-7b1 (7B params) | OOM GPU | 32GB GPU / 3.8GB CPU | 18.1GB GPU / 35GB CPU |
|
||||
|
||||
Performance of PEFT-LoRA tuned `bigscience/T0_3B` on `ought/raft/twitter_complaints` leaderboard.
|
||||
A point to note is that we didn't try to sequeeze performance by playing around with input instruction templates, LoRA hyperparams and other training related hyperparams. Also, we didn't use the larger 13B mt0-xxl model.
|
||||
So, we are already seeing comparable performance to SoTA with parameter effcient tuning. Also, the final checkpoint size is just `19MB` in comparison to `11GB` size of the backbone `bigscience/T0_3B` model.
|
||||
With LoRA you can fully finetune a 12B parameter model that would've otherwise run out of memory on the 80GB GPU, and comfortably fit and train a 3B parameter model. When you look at the 3B parameter model's performance, it is comparable to a fully finetuned model at a fraction of the GPU memory.
|
||||
|
||||
| Submission Name | Accuracy |
|
||||
| --------- | ---- |
|
||||
@ -73,257 +95,63 @@ So, we are already seeing comparable performance to SoTA with parameter effcient
|
||||
| Flan-T5 | 0.892 |
|
||||
| lora-t0-3b | 0.863 |
|
||||
|
||||
**Therefore, we can see that performance comparable to SoTA is achievable by PEFT methods with consumer hardware such as 16GB and 24GB GPUs.**
|
||||
> [!TIP]
|
||||
> The bigscience/T0_3B model performance isn't optimized in the table above. You can squeeze even more performance out of it by playing around with the input instruction templates, LoRA hyperparameters, and other training related hyperparameters. The final checkpoint size of this model is just 19MB compared to 11GB of the full bigscience/T0_3B model. Learn more about the advantages of finetuning with PEFT in this [blog post](https://www.philschmid.de/fine-tune-flan-t5-peft).
|
||||
|
||||
### Parameter Efficient Tuning of Diffusion Models
|
||||
### Quantization
|
||||
|
||||
GPU memory required by different settings during training are given below. The final checkpoint size being `8.8 MB`.
|
||||
Quantization is another method for reducing the memory requirements of a model by representing the data in a lower precision. It can be combined with PEFT methods to make it even easier to train and load LLMs for inference.
|
||||
|
||||
Hardware: Single A100 80GB GPU with CPU RAM above 64G
|
||||
* Learn how to finetune [meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-hf](https://huggingface.co/meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-hf) with QLoRA and the [TRL](https://huggingface.co/docs/trl/index) library on a 16GB GPU in the [Finetune LLMs on your own consumer hardware using tools from PyTorch and Hugging Face ecosystem](https://pytorch.org/blog/finetune-llms/) blog post.
|
||||
* Learn how to finetune a [openai/whisper-large-v2](https://huggingface.co/openai/whisper-large-v2) model for multilingual automatic speech recognition with LoRA and 8-bit quantization in this [notebook](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1DOkD_5OUjFa0r5Ik3SgywJLJtEo2qLxO?usp=sharing) (see this [notebook](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1vhF8yueFqha3Y3CpTHN6q9EVcII9EYzs?usp=sharing) instead for an example of streaming a dataset).
|
||||
|
||||
| Model | Full Finetuning | PEFT-LoRA | PEFT-LoRA with Gradient Checkpoitning |
|
||||
### Save compute and storage
|
||||
|
||||
PEFT can help you save storage by avoiding full finetuning of models on each of downstream task or dataset. In many cases, you're only finetuning a very small fraction of a model's parameters and each checkpoint is only a few MBs in size (instead of GBs). These smaller PEFT adapters demonstrate performance comparable to a fully finetuned model. If you have many datasets, you can save a lot of storage with a PEFT model and not have to worry about catastrophic forgetting or overfitting the backbone or base model.
|
||||
|
||||
## PEFT integrations
|
||||
|
||||
PEFT is widely supported across the Hugging Face ecosystem because of the massive efficiency it brings to training and inference.
|
||||
|
||||
### Diffusers
|
||||
|
||||
The iterative diffusion process consumes a lot of memory which can make it difficult to train. PEFT can help reduce the memory requirements and reduce the storage size of the final model checkpoint. For example, consider the memory required for training a Stable Diffusion model with LoRA on an A100 80GB GPU with more than 64GB of CPU RAM. The final model checkpoint size is only 8.8MB!
|
||||
|
||||
| Model | Full Finetuning | PEFT-LoRA | PEFT-LoRA with Gradient Checkpointing |
|
||||
| --------- | ---- | ---- | ---- |
|
||||
| CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4 | 27.5GB GPU / 3.97GB CPU | 15.5GB GPU / 3.84GB CPU | 8.12GB GPU / 3.77GB CPU |
|
||||
|
||||
> [!TIP]
|
||||
> Take a look at the [examples/lora_dreambooth/train_dreambooth.py](examples/lora_dreambooth/train_dreambooth.py) training script to try training your own Stable Diffusion model with LoRA, and play around with the [smangrul/peft-lora-sd-dreambooth](https://huggingface.co/spaces/smangrul/peft-lora-sd-dreambooth) Space which is running on a T4 instance. Learn more about the PEFT integration in Diffusers in this [tutorial](https://huggingface.co/docs/peft/main/en/tutorial/peft_integrations#diffusers).
|
||||
|
||||
**Training**
|
||||
An example of using LoRA for parameter efficient dreambooth training is given in `~examples/lora_dreambooth/train_dreambooth.py`
|
||||
### Accelerate
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
export MODEL_NAME= "CompVis/stable-diffusion-v1-4" #"stabilityai/stable-diffusion-2-1"
|
||||
export INSTANCE_DIR="path-to-instance-images"
|
||||
export CLASS_DIR="path-to-class-images"
|
||||
export OUTPUT_DIR="path-to-save-model"
|
||||
[Accelerate](https://huggingface.co/docs/accelerate/index) is a library for distributed training and inference on various training setups and hardware (GPUs, TPUs, Apple Silicon, etc.). PEFT models work with Accelerate out of the box, making it really convenient to train really large models or use them for inference on consumer hardware with limited resources.
|
||||
|
||||
accelerate launch train_dreambooth.py \
|
||||
--pretrained_model_name_or_path=$MODEL_NAME \
|
||||
--instance_data_dir=$INSTANCE_DIR \
|
||||
--class_data_dir=$CLASS_DIR \
|
||||
--output_dir=$OUTPUT_DIR \
|
||||
--train_text_encoder \
|
||||
--with_prior_preservation --prior_loss_weight=1.0 \
|
||||
--instance_prompt="a photo of sks dog" \
|
||||
--class_prompt="a photo of dog" \
|
||||
--resolution=512 \
|
||||
--train_batch_size=1 \
|
||||
--lr_scheduler="constant" \
|
||||
--lr_warmup_steps=0 \
|
||||
--num_class_images=200 \
|
||||
--use_lora \
|
||||
--lora_r 16 \
|
||||
--lora_alpha 27 \
|
||||
--lora_text_encoder_r 16 \
|
||||
--lora_text_encoder_alpha 17 \
|
||||
--learning_rate=1e-4 \
|
||||
--gradient_accumulation_steps=1 \
|
||||
--gradient_checkpointing \
|
||||
--max_train_steps=800
|
||||
```
|
||||
### TRL
|
||||
|
||||
Try out the 🤗 Gradio Space which should run seamlessly on a T4 instance:
|
||||
[smangrul/peft-lora-sd-dreambooth](https://huggingface.co/spaces/smangrul/peft-lora-sd-dreambooth).
|
||||
PEFT can also be applied to training LLMs with RLHF components such as the ranker and policy. Get started by reading:
|
||||
|
||||
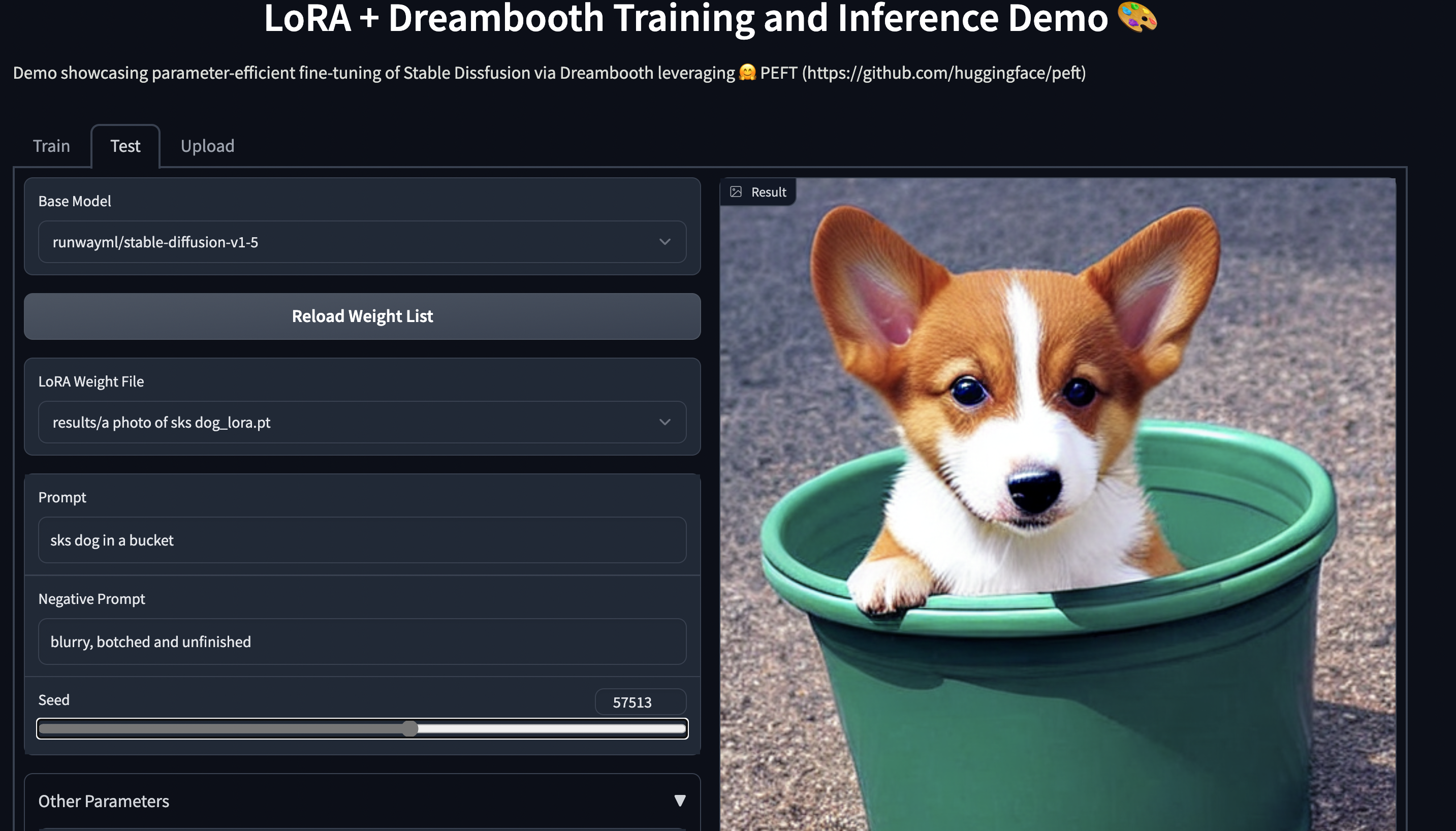
|
||||
* [Fine-tune a Mistral-7b model with Direct Preference Optimization](https://towardsdatascience.com/fine-tune-a-mistral-7b-model-with-direct-preference-optimization-708042745aac) with PEFT and the [TRL](https://huggingface.co/docs/trl/index) library to learn more about the Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) method and how to apply it to a LLM.
|
||||
* [Fine-tuning 20B LLMs with RLHF on a 24GB consumer GPU](https://huggingface.co/blog/trl-peft) with PEFT and the [TRL](https://huggingface.co/docs/trl/index) library, and then try out the [gpt2-sentiment_peft.ipynb](https://github.com/huggingface/trl/blob/main/examples/notebooks/gpt2-sentiment.ipynb) notebook to optimize GPT2 to generate positive movie reviews.
|
||||
* [StackLLaMA: A hands-on guide to train LLaMA with RLHF](https://huggingface.co/blog/stackllama) with PEFT, and then try out the [stack_llama/scripts](https://github.com/huggingface/trl/tree/main/examples/research_projects/stack_llama/scripts) for supervised finetuning, reward modeling, and RL finetuning.
|
||||
|
||||
### Parameter Efficient Tuning of LLMs for RLHF components such as Ranker and Policy [ToDo]
|
||||
## Model support
|
||||
|
||||
### Save compute and storage even for medium and small models
|
||||
Use this [Space](https://stevhliu-peft-methods.hf.space) or check out the [docs](https://huggingface.co/docs/peft/main/en/index) to find which models officially support a PEFT method out of the box. Even if you don't see a model listed below, you can manually configure the model config to enable PEFT for a model. Read the [New transformers architecture](https://huggingface.co/docs/peft/main/en/developer_guides/custom_models#new-transformers-architectures) guide to learn how.
|
||||
|
||||
Save storage by avoiding full finetuning of models on each of the downstream tasks/datasets,
|
||||
With PEFT methods, users only need to store tiny checkpoints in the order of `MBs` all the while retaining
|
||||
performance comparable to full finetuning.
|
||||
## Contribute
|
||||
|
||||
An example of using LoRA for the task of adaping `LayoutLMForTokenClassification` on `FUNSD` dataset is given in `~examples/token_classification/PEFT_LoRA_LayoutLMForTokenClassification_on_FUNSD.py`. We can observe that with only `0.62 %` of parameters being trainable, we achieve performance (F1 0.777) comparable to full finetuning (F1 0.786) (without any hyerparam tuning runs for extracting more performance), and the checkpoint of this is only `2.8MB`. Now, if there are `N` such datasets, just have these PEFT models one for each dataset and save a lot of storage without having to worry about the problem of catastrophic forgetting or overfitting of backbone/base model.
|
||||
|
||||
Another example is fine-tuning `roberta-large` on `MRPC` GLUE dataset suing differenct PEFT methods. The notebooks are given in `~examples/sequence_classification`.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## PEFT + 🤗 Accelerate
|
||||
|
||||
PEFT models work with 🤗 Accelerate out of the box. Use 🤗 Accelerate for Distributed training on various hardware such as GPUs, Apple Silicon devices etc during training.
|
||||
Use 🤗 Accelerate for inferencing on consumer hardware with small resources.
|
||||
|
||||
### Example of PEFT model training using 🤗 Accelerate's DeepSpeed integation
|
||||
|
||||
Currently DeepSpeed requires PR [ZeRO3 handling frozen weights](https://github.com/microsoft/DeepSpeed/pull/2653) to fix [[REQUEST] efficiently deal with frozen weights during training](https://github.com/microsoft/DeepSpeed/issues/2615) issue. Example is provided in `~examples/conditional_generation/peft_lora_seq2seq_accelerate_ds_zero3_offload.py`.
|
||||
a. First run `accelerate config --config_file ds_zero3_cpu.yaml` and answer the questionaire.
|
||||
Below are the contents of the config file.
|
||||
```
|
||||
compute_environment: LOCAL_MACHINE
|
||||
deepspeed_config:
|
||||
gradient_accumulation_steps: 1
|
||||
gradient_clipping: 1.0
|
||||
offload_optimizer_device: cpu
|
||||
offload_param_device: cpu
|
||||
zero3_init_flag: true
|
||||
zero3_save_16bit_model: true
|
||||
zero_stage: 3
|
||||
distributed_type: DEEPSPEED
|
||||
downcast_bf16: 'no'
|
||||
dynamo_backend: 'NO'
|
||||
fsdp_config: {}
|
||||
machine_rank: 0
|
||||
main_training_function: main
|
||||
megatron_lm_config: {}
|
||||
mixed_precision: 'no'
|
||||
num_machines: 1
|
||||
num_processes: 1
|
||||
rdzv_backend: static
|
||||
same_network: true
|
||||
use_cpu: false
|
||||
```
|
||||
b. run the below command to launch example script
|
||||
```
|
||||
accelerate launch --config_file ds_zero3_cpu.yaml examples/peft_lora_seq2seq_accelerate_ds_zero3_offload.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
c. output logs:
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
GPU Memory before entering the train : 1916
|
||||
GPU Memory consumed at the end of the train (end-begin): 66
|
||||
GPU Peak Memory consumed during the train (max-begin): 7488
|
||||
GPU Total Peak Memory consumed during the train (max): 9404
|
||||
CPU Memory before entering the train : 19411
|
||||
CPU Memory consumed at the end of the train (end-begin): 0
|
||||
CPU Peak Memory consumed during the train (max-begin): 0
|
||||
CPU Total Peak Memory consumed during the train (max): 19411
|
||||
epoch=4: train_ppl=tensor(1.0705, device='cuda:0') train_epoch_loss=tensor(0.0681, device='cuda:0')
|
||||
100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 7/7 [00:27<00:00, 3.92s/it]
|
||||
GPU Memory before entering the eval : 1982
|
||||
GPU Memory consumed at the end of the eval (end-begin): -66
|
||||
GPU Peak Memory consumed during the eval (max-begin): 672
|
||||
GPU Total Peak Memory consumed during the eval (max): 2654
|
||||
CPU Memory before entering the eval : 19411
|
||||
CPU Memory consumed at the end of the eval (end-begin): 0
|
||||
CPU Peak Memory consumed during the eval (max-begin): 0
|
||||
CPU Total Peak Memory consumed during the eval (max): 19411
|
||||
accuracy=100.0
|
||||
eval_preds[:10]=['no complaint', 'no complaint', 'complaint', 'complaint', 'no complaint', 'no complaint', 'no complaint', 'complaint', 'complaint', 'no complaint']
|
||||
dataset['train'][label_column][:10]=['no complaint', 'no complaint', 'complaint', 'complaint', 'no complaint', 'no complaint', 'no complaint', 'complaint', 'complaint', 'no complaint']
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Example of PEFT model inference using 🤗 Accelerate's Big Model Inferencing capabilities
|
||||
|
||||
Example is provided in `~examples/causal_language_modeling/peft_lora_clm_accelerate_big_model_inference.ipynb`.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Models support matrix
|
||||
|
||||
### Causal Language Modeling
|
||||
| Model | LoRA | Prefix Tuning | P-Tuning | Prompt Tuning |
|
||||
| --------- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- |
|
||||
| GPT-2 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| Bloom | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| OPT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| GPT-Neo | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| GPT-J | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
|
||||
### Conditional Generation
|
||||
| Model | LoRA | Prefix Tuning | P-Tuning | Prompt Tuning |
|
||||
| --------- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- |
|
||||
| T5 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| BART | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
|
||||
### Sequence Classification
|
||||
| Model | LoRA | Prefix Tuning | P-Tuning | Prompt Tuning |
|
||||
| --------- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- |
|
||||
| BERT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| RoBERTa | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| GPT-2 | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| Bloom | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| OPT | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| GPT-Neo | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| GPT-J | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| Deberta | ✅ | | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
| Deberta-v2 | ✅ | | ✅ | ✅ |
|
||||
|
||||
### Token Classification
|
||||
| Model | LoRA | Prefix Tuning | P-Tuning | Prompt Tuning |
|
||||
| --------- | ---- | ---- | ---- | ---- |
|
||||
| BERT | ✅ | ✅ | | |
|
||||
| RoBERTa | ✅ | ✅ | | |
|
||||
| GPT-2 | ✅ | ✅ | | |
|
||||
| Bloom | ✅ | ✅ | | |
|
||||
| OPT | ✅ | ✅ | | |
|
||||
| GPT-Neo | ✅ | ✅ | | |
|
||||
| GPT-J | ✅ | ✅ | | |
|
||||
| Deberta | ✅ | | | |
|
||||
| Deberta-v2 | ✅ | | | |
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Caveats:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Below is an example of using PyTorch FSDP for training. However, it doesn't lead to
|
||||
any GPU memory savings. Please refer issue [[FSDP] FSDP with CPU offload consumes 1.65X more GPU memory when training models with most of the params frozen](https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/issues/91165).
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from peft.utils.other import fsdp_auto_wrap_policy
|
||||
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
if os.environ.get("ACCELERATE_USE_FSDP", None) is not None:
|
||||
accelerator.state.fsdp_plugin.auto_wrap_policy = fsdp_auto_wrap_policy(model)
|
||||
|
||||
model = accelerator.prepare(model)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Example of parameter efficient tuning with `mt0-xxl` base model using 🤗 Accelerate is provided in `~examples/conditional_generation/peft_lora_seq2seq_accelerate_fsdp.py`.
|
||||
a. First run `accelerate config --config_file fsdp_config.yaml` and answer the questionaire.
|
||||
Below are the contents of the config file.
|
||||
```
|
||||
command_file: null
|
||||
commands: null
|
||||
compute_environment: LOCAL_MACHINE
|
||||
deepspeed_config: {}
|
||||
distributed_type: FSDP
|
||||
downcast_bf16: 'no'
|
||||
dynamo_backend: 'NO'
|
||||
fsdp_config:
|
||||
fsdp_auto_wrap_policy: TRANSFORMER_BASED_WRAP
|
||||
fsdp_backward_prefetch_policy: BACKWARD_PRE
|
||||
fsdp_offload_params: true
|
||||
fsdp_sharding_strategy: 1
|
||||
fsdp_state_dict_type: FULL_STATE_DICT
|
||||
fsdp_transformer_layer_cls_to_wrap: T5Block
|
||||
gpu_ids: null
|
||||
machine_rank: 0
|
||||
main_process_ip: null
|
||||
main_process_port: null
|
||||
main_training_function: main
|
||||
megatron_lm_config: {}
|
||||
mixed_precision: 'no'
|
||||
num_machines: 1
|
||||
num_processes: 2
|
||||
rdzv_backend: static
|
||||
same_network: true
|
||||
tpu_name: null
|
||||
tpu_zone: null
|
||||
use_cpu: false
|
||||
```
|
||||
b. run the below command to launch example script
|
||||
```
|
||||
accelerate launch --config_file fsdp_config.yaml examples/peft_lora_seq2seq_accelerate_fsdp.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. When using `P_TUNING` or `PROMPT_TUNING` with `SEQ_2_SEQ` task, remember to remove the `num_virtual_token` virtual prompt predictions from the left side of the model outputs during evaluations.
|
||||
|
||||
3. `P_TUNING` or `PROMPT_TUNING` doesn't support `generate` functionality of transformers bcause `generate` strictly requires `input_ids`/`decoder_input_ids` but
|
||||
`P_TUNING`/`PROMPT_TUNING` appends soft prompt embeddings to `input_embeds` to create
|
||||
new `input_embeds` to be given to the model. Therefore, `generate` doesn't support this yet.
|
||||
|
||||
## Backlog:
|
||||
1. Explore and possibly integrate `(IA)^3` and `UniPELT`
|
||||
2. Add tests
|
||||
3. Add more use cases and examples
|
||||
If you would like to contribute to PEFT, please check out our [contribution guide](https://huggingface.co/docs/peft/developer_guides/contributing).
|
||||
|
||||
## Citing 🤗 PEFT
|
||||
|
||||
If you use 🤗 PEFT in your publication, please cite it by using the following BibTeX entry.
|
||||
To use 🤗 PEFT in your publication, please cite it by using the following BibTeX entry.
|
||||
|
||||
```bibtex
|
||||
@Misc{peft,
|
||||
title = {PEFT: State-of-the-art Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning methods},
|
||||
author = {Sourab Mangrulkar, Sylvain Gugger},
|
||||
author = {Sourab Mangrulkar and Sylvain Gugger and Lysandre Debut and Younes Belkada and Sayak Paul and Benjamin Bossan},
|
||||
howpublished = {\url{https://github.com/huggingface/peft}},
|
||||
year = {2022}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
52
docker/peft-cpu/Dockerfile
Normal file
52
docker/peft-cpu/Dockerfile
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,52 @@
|
||||
# Builds GPU docker image of PyTorch
|
||||
# Uses multi-staged approach to reduce size
|
||||
# Stage 1
|
||||
# Use base conda image to reduce time
|
||||
FROM continuumio/miniconda3:latest AS compile-image
|
||||
# Specify py version
|
||||
ENV PYTHON_VERSION=3.8
|
||||
# Install apt libs - copied from https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate/blob/main/docker/accelerate-gpu/Dockerfile
|
||||
RUN apt-get update && \
|
||||
apt-get install -y curl git wget software-properties-common git-lfs && \
|
||||
apt-get clean && \
|
||||
rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists*
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Install audio-related libraries
|
||||
RUN apt-get update && \
|
||||
apt install -y ffmpeg
|
||||
|
||||
RUN apt install -y libsndfile1-dev
|
||||
RUN git lfs install
|
||||
|
||||
# Create our conda env - copied from https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate/blob/main/docker/accelerate-gpu/Dockerfile
|
||||
RUN conda create --name peft python=${PYTHON_VERSION} ipython jupyter pip
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir --upgrade pip
|
||||
|
||||
# Below is copied from https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate/blob/main/docker/accelerate-gpu/Dockerfile
|
||||
# We don't install pytorch here yet since CUDA isn't available
|
||||
# instead we use the direct torch wheel
|
||||
ENV PATH /opt/conda/envs/peft/bin:$PATH
|
||||
# Activate our bash shell
|
||||
RUN chsh -s /bin/bash
|
||||
SHELL ["/bin/bash", "-c"]
|
||||
# Activate the conda env and install transformers + accelerate from source
|
||||
RUN source activate peft && \
|
||||
python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir \
|
||||
librosa \
|
||||
"soundfile>=0.12.1" \
|
||||
scipy \
|
||||
git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers \
|
||||
git+https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate \
|
||||
peft[test]@git+https://github.com/huggingface/peft
|
||||
|
||||
# Install apt libs
|
||||
RUN apt-get update && \
|
||||
apt-get install -y curl git wget && \
|
||||
apt-get clean && \
|
||||
rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists*
|
||||
|
||||
RUN echo "source activate peft" >> ~/.profile
|
||||
|
||||
# Activate the virtualenv
|
||||
CMD ["/bin/bash"]
|
||||
68
docker/peft-gpu-bnb-latest/Dockerfile
Normal file
68
docker/peft-gpu-bnb-latest/Dockerfile
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,68 @@
|
||||
# Builds GPU docker image of PyTorch
|
||||
# Uses multi-staged approach to reduce size
|
||||
# Stage 1
|
||||
# Use base conda image to reduce time
|
||||
FROM continuumio/miniconda3:latest AS compile-image
|
||||
# Specify py version
|
||||
ENV PYTHON_VERSION=3.8
|
||||
# Install apt libs - copied from https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate/blob/main/docker/accelerate-gpu/Dockerfile
|
||||
RUN apt-get update && \
|
||||
apt-get install -y curl git wget software-properties-common git-lfs && \
|
||||
apt-get clean && \
|
||||
rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists*
|
||||
|
||||
# Install audio-related libraries
|
||||
RUN apt-get update && \
|
||||
apt install -y ffmpeg
|
||||
|
||||
RUN apt install -y libsndfile1-dev
|
||||
RUN git lfs install
|
||||
|
||||
# Create our conda env - copied from https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate/blob/main/docker/accelerate-gpu/Dockerfile
|
||||
RUN conda create --name peft python=${PYTHON_VERSION} ipython jupyter pip
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir --upgrade pip
|
||||
|
||||
# Below is copied from https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate/blob/main/docker/accelerate-gpu/Dockerfile
|
||||
# We don't install pytorch here yet since CUDA isn't available
|
||||
# instead we use the direct torch wheel
|
||||
ENV PATH /opt/conda/envs/peft/bin:$PATH
|
||||
# Activate our bash shell
|
||||
RUN chsh -s /bin/bash
|
||||
SHELL ["/bin/bash", "-c"]
|
||||
|
||||
# Stage 2
|
||||
FROM nvidia/cuda:12.1.0-devel-ubuntu22.04 AS build-image
|
||||
COPY --from=compile-image /opt/conda /opt/conda
|
||||
ENV PATH /opt/conda/bin:$PATH
|
||||
|
||||
RUN chsh -s /bin/bash
|
||||
SHELL ["/bin/bash", "-c"]
|
||||
|
||||
# Install apt libs
|
||||
RUN apt-get update && \
|
||||
apt-get install -y curl git wget cmake && \
|
||||
apt-get clean && \
|
||||
rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists*
|
||||
|
||||
# Activate the conda env and install transformers + accelerate from latest pypi
|
||||
# Also clone BNB and build it from source.
|
||||
RUN source activate peft && \
|
||||
python3 -m pip install -U --no-cache-dir \
|
||||
librosa \
|
||||
"soundfile>=0.12.1" \
|
||||
scipy \
|
||||
transformers \
|
||||
accelerate \
|
||||
peft \
|
||||
optimum \
|
||||
auto-gptq && \
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/TimDettmers/bitsandbytes && cd bitsandbytes && \
|
||||
cmake -B . -DCOMPUTE_BACKEND=cuda -S . && \
|
||||
cmake --build . && \
|
||||
pip install -e . && \
|
||||
pip freeze | grep bitsandbytes
|
||||
|
||||
RUN echo "source activate peft" >> ~/.profile
|
||||
|
||||
# Activate the virtualenv
|
||||
CMD ["/bin/bash"]
|
||||
68
docker/peft-gpu-bnb-source/Dockerfile
Normal file
68
docker/peft-gpu-bnb-source/Dockerfile
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,68 @@
|
||||
# Builds GPU docker image of PyTorch
|
||||
# Uses multi-staged approach to reduce size
|
||||
# Stage 1
|
||||
# Use base conda image to reduce time
|
||||
FROM continuumio/miniconda3:latest AS compile-image
|
||||
# Specify py version
|
||||
ENV PYTHON_VERSION=3.8
|
||||
# Install apt libs - copied from https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate/blob/main/docker/accelerate-gpu/Dockerfile
|
||||
RUN apt-get update && \
|
||||
apt-get install -y curl git wget software-properties-common git-lfs && \
|
||||
apt-get clean && \
|
||||
rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists*
|
||||
|
||||
# Install audio-related libraries
|
||||
RUN apt-get update && \
|
||||
apt install -y ffmpeg
|
||||
|
||||
RUN apt install -y libsndfile1-dev
|
||||
RUN git lfs install
|
||||
|
||||
# Create our conda env - copied from https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate/blob/main/docker/accelerate-gpu/Dockerfile
|
||||
RUN conda create --name peft python=${PYTHON_VERSION} ipython jupyter pip
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir --upgrade pip
|
||||
|
||||
# Below is copied from https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate/blob/main/docker/accelerate-gpu/Dockerfile
|
||||
# We don't install pytorch here yet since CUDA isn't available
|
||||
# instead we use the direct torch wheel
|
||||
ENV PATH /opt/conda/envs/peft/bin:$PATH
|
||||
# Activate our bash shell
|
||||
RUN chsh -s /bin/bash
|
||||
SHELL ["/bin/bash", "-c"]
|
||||
|
||||
# Stage 2
|
||||
FROM nvidia/cuda:12.1.0-devel-ubuntu22.04 AS build-image
|
||||
COPY --from=compile-image /opt/conda /opt/conda
|
||||
ENV PATH /opt/conda/bin:$PATH
|
||||
|
||||
RUN chsh -s /bin/bash
|
||||
SHELL ["/bin/bash", "-c"]
|
||||
|
||||
# Install apt libs
|
||||
RUN apt-get update && \
|
||||
apt-get install -y curl git wget cmake && \
|
||||
apt-get clean && \
|
||||
rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists*
|
||||
|
||||
# Activate the conda env and install transformers + accelerate from source
|
||||
# Also clone BNB and build it from source.
|
||||
RUN source activate peft && \
|
||||
python3 -m pip install -U --no-cache-dir \
|
||||
librosa \
|
||||
"soundfile>=0.12.1" \
|
||||
scipy \
|
||||
git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers \
|
||||
git+https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate \
|
||||
peft[test]@git+https://github.com/huggingface/peft \
|
||||
optimum \
|
||||
auto-gptq && \
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/TimDettmers/bitsandbytes && cd bitsandbytes && \
|
||||
cmake -B . -DCOMPUTE_BACKEND=cuda -S . && \
|
||||
cmake --build . && \
|
||||
pip install -e . && \
|
||||
pip freeze | grep bitsandbytes
|
||||
|
||||
RUN echo "source activate peft" >> ~/.profile
|
||||
|
||||
# Activate the virtualenv
|
||||
CMD ["/bin/bash"]
|
||||
75
docker/peft-gpu/Dockerfile
Normal file
75
docker/peft-gpu/Dockerfile
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,75 @@
|
||||
# Builds GPU docker image of PyTorch
|
||||
# Uses multi-staged approach to reduce size
|
||||
# Stage 1
|
||||
# Use base conda image to reduce time
|
||||
FROM continuumio/miniconda3:latest AS compile-image
|
||||
# Specify py version
|
||||
ENV PYTHON_VERSION=3.8
|
||||
# Install apt libs - copied from https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate/blob/main/docker/accelerate-gpu/Dockerfile
|
||||
RUN apt-get update && \
|
||||
apt-get install -y curl git wget software-properties-common git-lfs && \
|
||||
apt-get clean && \
|
||||
rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists*
|
||||
|
||||
# Install audio-related libraries
|
||||
RUN apt-get update && \
|
||||
apt install -y ffmpeg
|
||||
|
||||
RUN apt install -y libsndfile1-dev
|
||||
RUN git lfs install
|
||||
|
||||
# Create our conda env - copied from https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate/blob/main/docker/accelerate-gpu/Dockerfile
|
||||
RUN conda create --name peft python=${PYTHON_VERSION} ipython jupyter pip
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir --upgrade pip
|
||||
|
||||
# Below is copied from https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate/blob/main/docker/accelerate-gpu/Dockerfile
|
||||
# We don't install pytorch here yet since CUDA isn't available
|
||||
# instead we use the direct torch wheel
|
||||
ENV PATH /opt/conda/envs/peft/bin:$PATH
|
||||
# Activate our bash shell
|
||||
RUN chsh -s /bin/bash
|
||||
SHELL ["/bin/bash", "-c"]
|
||||
|
||||
# Stage 2
|
||||
FROM nvidia/cuda:12.2.2-devel-ubuntu22.04 AS build-image
|
||||
COPY --from=compile-image /opt/conda /opt/conda
|
||||
ENV PATH /opt/conda/bin:$PATH
|
||||
|
||||
RUN chsh -s /bin/bash
|
||||
SHELL ["/bin/bash", "-c"]
|
||||
RUN source activate peft && \
|
||||
python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir bitsandbytes optimum auto-gptq
|
||||
|
||||
# Add autoawq for quantization testing
|
||||
RUN source activate peft && \
|
||||
python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir https://github.com/casper-hansen/AutoAWQ/releases/download/v0.2.1/autoawq-0.2.1-cp38-cp38-linux_x86_64.whl
|
||||
RUN source activate peft && \
|
||||
python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir https://github.com/casper-hansen/AutoAWQ_kernels/releases/download/v0.0.4/autoawq_kernels-0.0.4-cp38-cp38-linux_x86_64.whl
|
||||
|
||||
# Install apt libs
|
||||
RUN apt-get update && \
|
||||
apt-get install -y curl git wget && \
|
||||
apt-get clean && \
|
||||
rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists*
|
||||
|
||||
# Activate the conda env and install transformers + accelerate from source
|
||||
RUN source activate peft && \
|
||||
python3 -m pip install -U --no-cache-dir \
|
||||
librosa \
|
||||
"soundfile>=0.12.1" \
|
||||
scipy \
|
||||
git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers \
|
||||
git+https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate \
|
||||
peft[test]@git+https://github.com/huggingface/peft
|
||||
|
||||
# Add aqlm for quantization testing
|
||||
RUN source activate peft && \
|
||||
pip install aqlm[gpu]>=1.0.2
|
||||
|
||||
RUN source activate peft && \
|
||||
pip freeze | grep transformers
|
||||
|
||||
RUN echo "source activate peft" >> ~/.profile
|
||||
|
||||
# Activate the virtualenv
|
||||
CMD ["/bin/bash"]
|
||||
19
docs/Makefile
Normal file
19
docs/Makefile
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,19 @@
|
||||
# Minimal makefile for Sphinx documentation
|
||||
#
|
||||
|
||||
# You can set these variables from the command line.
|
||||
SPHINXOPTS =
|
||||
SPHINXBUILD = sphinx-build
|
||||
SOURCEDIR = source
|
||||
BUILDDIR = _build
|
||||
|
||||
# Put it first so that "make" without argument is like "make help".
|
||||
help:
|
||||
@$(SPHINXBUILD) -M help "$(SOURCEDIR)" "$(BUILDDIR)" $(SPHINXOPTS) $(O)
|
||||
|
||||
.PHONY: help Makefile
|
||||
|
||||
# Catch-all target: route all unknown targets to Sphinx using the new
|
||||
# "make mode" option. $(O) is meant as a shortcut for $(SPHINXOPTS).
|
||||
%: Makefile
|
||||
@$(SPHINXBUILD) -M $@ "$(SOURCEDIR)" "$(BUILDDIR)" $(SPHINXOPTS) $(O)
|
||||
267
docs/README.md
Normal file
267
docs/README.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,267 @@
|
||||
<!---
|
||||
Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Generating the documentation
|
||||
|
||||
To generate the documentation, you first have to build it. Several packages are necessary to build the doc,
|
||||
you can install them with the following command, at the root of the code repository:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install -e ".[docs]"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then you need to install our special tool that builds the documentation:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/doc-builder
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
**NOTE**
|
||||
|
||||
You only need to generate the documentation to inspect it locally (if you're planning changes and want to
|
||||
check how they look before committing for instance). You don't have to commit to the built documentation.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Building the documentation
|
||||
|
||||
Once you have setup the `doc-builder` and additional packages, you can generate the documentation by
|
||||
typing the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
doc-builder build peft docs/source/ --build_dir ~/tmp/test-build
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can adapt the `--build_dir` to set any temporary folder you prefer. This command will create it and generate
|
||||
the MDX files that will be rendered as the documentation on the main website. You can inspect them in your favorite
|
||||
Markdown editor.
|
||||
|
||||
## Previewing the documentation
|
||||
|
||||
To preview the docs, first install the `watchdog` module with:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install watchdog
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then run the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
doc-builder preview {package_name} {path_to_docs}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For example:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
doc-builder preview peft docs/source
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The docs will be viewable at [http://localhost:3000](http://localhost:3000). You can also preview the docs once you have opened a PR. You will see a bot add a comment to a link where the documentation with your changes lives.
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
**NOTE**
|
||||
|
||||
The `preview` command only works with existing doc files. When you add a completely new file, you need to update `_toctree.yml` & restart `preview` command (`ctrl-c` to stop it & call `doc-builder preview ...` again).
|
||||
|
||||
---
|
||||
|
||||
## Adding a new element to the navigation bar
|
||||
|
||||
Accepted files are Markdown (.md or .mdx).
|
||||
|
||||
Create a file with its extension and put it in the source directory. You can then link it to the toc-tree by putting
|
||||
the filename without the extension in the [`_toctree.yml`](https://github.com/huggingface/peft/blob/main/docs/source/_toctree.yml) file.
|
||||
|
||||
## Renaming section headers and moving sections
|
||||
|
||||
It helps to keep the old links working when renaming the section header and/or moving sections from one document to another. This is because the old links are likely to be used in Issues, Forums, and Social media and it'd make for a much more superior user experience if users reading those months later could still easily navigate to the originally intended information.
|
||||
|
||||
Therefore, we simply keep a little map of moved sections at the end of the document where the original section was. The key is to preserve the original anchor.
|
||||
|
||||
So if you renamed a section from: "Section A" to "Section B", then you can add at the end of the file:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Sections that were moved:
|
||||
|
||||
[ <a href="#section-b">Section A</a><a id="section-a"></a> ]
|
||||
```
|
||||
and of course, if you moved it to another file, then:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Sections that were moved:
|
||||
|
||||
[ <a href="../new-file#section-b">Section A</a><a id="section-a"></a> ]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Use the relative style to link to the new file so that the versioned docs continue to work.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Writing Documentation - Specification
|
||||
|
||||
The `huggingface/peft` documentation follows the
|
||||
[Google documentation](https://sphinxcontrib-napoleon.readthedocs.io/en/latest/example_google.html) style for docstrings,
|
||||
although we can write them directly in Markdown.
|
||||
|
||||
### Adding a new tutorial
|
||||
|
||||
Adding a new tutorial or section is done in two steps:
|
||||
|
||||
- Add a new file under `./source`. This file can either be ReStructuredText (.rst) or Markdown (.md).
|
||||
- Link that file in `./source/_toctree.yml` on the correct toc-tree.
|
||||
|
||||
Make sure to put your new file under the proper section. It's unlikely to go in the first section (*Get Started*), so
|
||||
depending on the intended targets (beginners, more advanced users, or researchers) it should go into sections two, three, or
|
||||
four.
|
||||
|
||||
### Writing source documentation
|
||||
|
||||
Values that should be put in `code` should either be surrounded by backticks: \`like so\`. Note that argument names
|
||||
and objects like True, None, or any strings should usually be put in `code`.
|
||||
|
||||
When mentioning a class, function, or method, it is recommended to use our syntax for internal links so that our tool
|
||||
adds a link to its documentation with this syntax: \[\`XXXClass\`\] or \[\`function\`\]. This requires the class or
|
||||
function to be in the main package.
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to create a link to some internal class or function, you need to
|
||||
provide its path. For instance: \[\`utils.gather\`\]. This will be converted into a link with
|
||||
`utils.gather` in the description. To get rid of the path and only keep the name of the object you are
|
||||
linking to in the description, add a ~: \[\`~utils.gather\`\] will generate a link with `gather` in the description.
|
||||
|
||||
The same works for methods so you can either use \[\`XXXClass.method\`\] or \[~\`XXXClass.method\`\].
|
||||
|
||||
#### Defining arguments in a method
|
||||
|
||||
Arguments should be defined with the `Args:` (or `Arguments:` or `Parameters:`) prefix, followed by a line return and
|
||||
an indentation. The argument should be followed by its type, with its shape if it is a tensor, a colon, and its
|
||||
description:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
n_layers (`int`): The number of layers of the model.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If the description is too long to fit in one line (more than 119 characters in total), another indentation is necessary
|
||||
before writing the description after the argument.
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, to maintain uniformity if any *one* description is too long to fit on one line, the
|
||||
rest of the parameters should follow suit and have an indention before their description.
|
||||
|
||||
Here's an example showcasing everything so far:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
gradient_accumulation_steps (`int`, *optional*, default to 1):
|
||||
The number of steps that should pass before gradients are accumulated. A number > 1 should be combined with `Accelerator.accumulate`.
|
||||
cpu (`bool`, *optional*):
|
||||
Whether or not to force the script to execute on CPU. Will ignore GPU available if set to `True` and force the execution on one process only.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For optional arguments or arguments with defaults we follow the following syntax: imagine we have a function with the
|
||||
following signature:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
def my_function(x: str = None, a: float = 1):
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
then its documentation should look like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
x (`str`, *optional*):
|
||||
This argument controls ... and has a description longer than 119 chars.
|
||||
a (`float`, *optional*, defaults to 1):
|
||||
This argument is used to ... and has a description longer than 119 chars.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Note that we always omit the "defaults to \`None\`" when None is the default for any argument. Also note that even
|
||||
if the first line describing your argument type and its default gets long, you can't break it into several lines. You can
|
||||
however write as many lines as you want in the indented description (see the example above with `input_ids`).
|
||||
|
||||
#### Writing a multi-line code block
|
||||
|
||||
Multi-line code blocks can be useful for displaying examples. They are done between two lines of three backticks as usual in Markdown:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
````
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# first line of code
|
||||
# second line
|
||||
# etc
|
||||
```
|
||||
````
|
||||
|
||||
#### Writing a return block
|
||||
|
||||
The return block should be introduced with the `Returns:` prefix, followed by a line return and an indentation.
|
||||
The first line should be the type of the return, followed by a line return. No need to indent further for the elements
|
||||
building the return.
|
||||
|
||||
Here's an example of a single value return:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Returns:
|
||||
`List[int]`: A list of integers in the range [0, 1] --- 1 for a special token, 0 for a sequence token.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Here's an example of a tuple return, comprising several objects:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Returns:
|
||||
`tuple(torch.FloatTensor)` comprising various elements depending on the configuration ([`BertConfig`]) and inputs:
|
||||
- ** loss** (*optional*, returned when `masked_lm_labels` is provided) `torch.FloatTensor` of shape `(1,)` --
|
||||
Total loss is the sum of the masked language modeling loss and the next sequence prediction (classification) loss.
|
||||
- **prediction_scores** (`torch.FloatTensor` of shape `(batch_size, sequence_length, config.vocab_size)`) --
|
||||
Prediction scores of the language modeling head (scores for each vocabulary token before SoftMax).
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Styling the docstring
|
||||
|
||||
We have an automatic script running with the `make style` comment that will make sure that:
|
||||
- the docstrings fully take advantage of the line width
|
||||
- all code examples are formatted using black, like the code of the Transformers library
|
||||
|
||||
This script may have some weird failures if you make a syntax mistake or if you uncover a bug. Therefore, it's
|
||||
recommended to commit your changes before running `make style`, so you can revert the changes done by that script
|
||||
easily.
|
||||
|
||||
## Writing documentation examples
|
||||
|
||||
The syntax, for example, docstrings can look as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Example:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> import time
|
||||
>>> from accelerate import Accelerator
|
||||
>>> accelerator = Accelerator()
|
||||
>>> if accelerator.is_main_process:
|
||||
... time.sleep(2)
|
||||
>>> else:
|
||||
... print("I'm waiting for the main process to finish its sleep...")
|
||||
>>> accelerator.wait_for_everyone()
|
||||
>>> # Should print on every process at the same time
|
||||
>>> print("Everyone is here")
|
||||
```
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The docstring should give a minimal, clear example of how the respective function
|
||||
is to be used in inference and also include the expected (ideally sensible)
|
||||
output.
|
||||
Often, readers will try out the example before even going through the function
|
||||
or class definitions. Therefore, it is of utmost importance that the example
|
||||
works as expected.
|
||||
7
docs/source/_config.py
Normal file
7
docs/source/_config.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,7 @@
|
||||
# docstyle-ignore
|
||||
INSTALL_CONTENT = """
|
||||
# PEFT installation
|
||||
! pip install peft accelerate transformers
|
||||
# To install from source instead of the last release, comment the command above and uncomment the following one.
|
||||
# ! pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/peft.git
|
||||
"""
|
||||
107
docs/source/_toctree.yml
Normal file
107
docs/source/_toctree.yml
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,107 @@
|
||||
- title: Get started
|
||||
sections:
|
||||
- local: index
|
||||
title: 🤗 PEFT
|
||||
- local: quicktour
|
||||
title: Quicktour
|
||||
- local: install
|
||||
title: Installation
|
||||
|
||||
- title: Tutorial
|
||||
sections:
|
||||
- local: tutorial/peft_model_config
|
||||
title: Configurations and models
|
||||
- local: tutorial/peft_integrations
|
||||
title: Integrations
|
||||
|
||||
- title: PEFT method guides
|
||||
sections:
|
||||
- local: task_guides/prompt_based_methods
|
||||
title: Prompt-based methods
|
||||
- local: task_guides/lora_based_methods
|
||||
title: LoRA methods
|
||||
- local: task_guides/ia3
|
||||
title: IA3
|
||||
|
||||
- title: Developer guides
|
||||
sections:
|
||||
- local: developer_guides/model_merging
|
||||
title: Model merging
|
||||
- local: developer_guides/quantization
|
||||
title: Quantization
|
||||
- local: developer_guides/lora
|
||||
title: LoRA
|
||||
- local: developer_guides/custom_models
|
||||
title: Custom models
|
||||
- local: developer_guides/low_level_api
|
||||
title: Adapter injection
|
||||
- local: developer_guides/mixed_models
|
||||
title: Mixed adapter types
|
||||
- local: developer_guides/contributing
|
||||
title: Contribute to PEFT
|
||||
- local: developer_guides/troubleshooting
|
||||
title: Troubleshooting
|
||||
|
||||
- title: 🤗 Accelerate integrations
|
||||
sections:
|
||||
- local: accelerate/deepspeed
|
||||
title: DeepSpeed
|
||||
- local: accelerate/fsdp
|
||||
title: Fully Sharded Data Parallel
|
||||
|
||||
- title: Conceptual guides
|
||||
sections:
|
||||
- local: conceptual_guides/adapter
|
||||
title: Adapters
|
||||
- local: conceptual_guides/prompting
|
||||
title: Soft prompts
|
||||
- local: conceptual_guides/ia3
|
||||
title: IA3
|
||||
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: package_reference/auto_class
|
||||
title: AutoPeftModel
|
||||
- local: package_reference/peft_model
|
||||
title: PEFT model
|
||||
- local: package_reference/peft_types
|
||||
title: PEFT types
|
||||
- local: package_reference/config
|
||||
title: Configuration
|
||||
- local: package_reference/tuners
|
||||
title: Tuner
|
||||
title: Main classes
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: package_reference/adalora
|
||||
title: AdaLoRA
|
||||
- local: package_reference/ia3
|
||||
title: IA3
|
||||
- local: package_reference/llama_adapter
|
||||
title: Llama-Adapter
|
||||
- local: package_reference/loha
|
||||
title: LoHa
|
||||
- local: package_reference/lokr
|
||||
title: LoKr
|
||||
- local: package_reference/lora
|
||||
title: LoRA
|
||||
- local: package_reference/adapter_utils
|
||||
title: LyCORIS
|
||||
- local: package_reference/multitask_prompt_tuning
|
||||
title: Multitask Prompt Tuning
|
||||
- local: package_reference/oft
|
||||
title: OFT
|
||||
- local: package_reference/poly
|
||||
title: Polytropon
|
||||
- local: package_reference/p_tuning
|
||||
title: P-tuning
|
||||
- local: package_reference/prefix_tuning
|
||||
title: Prefix tuning
|
||||
- local: package_reference/prompt_tuning
|
||||
title: Prompt tuning
|
||||
title: Adapters
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: package_reference/merge_utils
|
||||
title: Model merge
|
||||
title: Utilities
|
||||
title: API reference
|
||||
|
||||
449
docs/source/accelerate/deepspeed.md
Normal file
449
docs/source/accelerate/deepspeed.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,449 @@
|
||||
<!--⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# DeepSpeed
|
||||
|
||||
[DeepSpeed](https://www.deepspeed.ai/) is a library designed for speed and scale for distributed training of large models with billions of parameters. At its core is the Zero Redundancy Optimizer (ZeRO) that shards optimizer states (ZeRO-1), gradients (ZeRO-2), and parameters (ZeRO-3) across data parallel processes. This drastically reduces memory usage, allowing you to scale your training to billion parameter models. To unlock even more memory efficiency, ZeRO-Offload reduces GPU compute and memory by leveraging CPU resources during optimization.
|
||||
|
||||
Both of these features are supported in 🤗 Accelerate, and you can use them with 🤗 PEFT.
|
||||
|
||||
## Compatibility with `bitsandbytes` quantization + LoRA
|
||||
|
||||
Below is a table that summarizes the compatibility between PEFT's LoRA, [`bitsandbytes`](https://github.com/TimDettmers/bitsandbytes) library and DeepSpeed Zero stages with respect to fine-tuning. DeepSpeed Zero-1 and 2 will have no effect at inference as stage 1 shards the optimizer states and stage 2 shards the optimizer states and gradients:
|
||||
|
||||
| DeepSpeed stage | Is compatible? |
|
||||
|---|---|
|
||||
| Zero-1 | 🟢 |
|
||||
| Zero-2 | 🟢 |
|
||||
| Zero-3 | 🟢 |
|
||||
|
||||
For DeepSpeed Stage 3 + QLoRA, please refer to the section [Use PEFT QLoRA and DeepSpeed with ZeRO3 for finetuning large models on multiple GPUs](#use-peft-qlora-and-deepspeed-with-zero3-for-finetuning-large-models-on-multiple-gpus) below.
|
||||
|
||||
For confirming these observations, we ran the SFT (Supervised Fine-tuning) [offical example scripts](https://github.com/huggingface/trl/tree/main/examples) of the [Transformers Reinforcement Learning (TRL) library](https://github.com/huggingface/trl) using QLoRA + PEFT and the accelerate configs available [here](https://github.com/huggingface/trl/tree/main/examples/accelerate_configs). We ran these experiments on a 2x NVIDIA T4 GPU.
|
||||
|
||||
Note DeepSpeed-Zero3 and `bitsandbytes` are currently **not** compatible.
|
||||
|
||||
# Use PEFT and DeepSpeed with ZeRO3 for finetuning large models on multiple devices and multiple nodes
|
||||
|
||||
This section of guide will help you learn how to use our DeepSpeed [training script](https://github.com/huggingface/peft/blob/main/examples/sft/train.py) for performing SFT. You'll configure the script to do SFT (supervised fine-tuning) of Llama-70B model with LoRA and ZeRO-3 on 8xH100 80GB GPUs on a single machine. You can configure it to scale to multiple machines by changing the accelerate config.
|
||||
|
||||
## Configuration
|
||||
|
||||
Start by running the following command to [create a DeepSpeed configuration file](https://huggingface.co/docs/accelerate/quicktour#launching-your-distributed-script) with 🤗 Accelerate. The `--config_file` flag allows you to save the configuration file to a specific location, otherwise it is saved as a `default_config.yaml` file in the 🤗 Accelerate cache.
|
||||
|
||||
The configuration file is used to set the default options when you launch the training script.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
accelerate config --config_file deepspeed_config.yaml
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You'll be asked a few questions about your setup, and configure the following arguments. In this example, you'll use ZeRO-3 so make sure you pick those options.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
`zero_stage`: [0] Disabled, [1] optimizer state partitioning, [2] optimizer+gradient state partitioning and [3] optimizer+gradient+parameter partitioning
|
||||
`gradient_accumulation_steps`: Number of training steps to accumulate gradients before averaging and applying them. Pass the same value as you would pass via cmd argument else you will encounter mismatch error.
|
||||
`gradient_clipping`: Enable gradient clipping with value. Don't set this as you will be passing it via cmd arguments.
|
||||
`offload_optimizer_device`: [none] Disable optimizer offloading, [cpu] offload optimizer to CPU, [nvme] offload optimizer to NVMe SSD. Only applicable with ZeRO >= Stage-2. Set this as `none` as don't want to enable offloading.
|
||||
`offload_param_device`: [none] Disable parameter offloading, [cpu] offload parameters to CPU, [nvme] offload parameters to NVMe SSD. Only applicable with ZeRO Stage-3. Set this as `none` as don't want to enable offloading.
|
||||
`zero3_init_flag`: Decides whether to enable `deepspeed.zero.Init` for constructing massive models. Only applicable with ZeRO Stage-3. Set this to `True`.
|
||||
`zero3_save_16bit_model`: Decides whether to save 16-bit model weights when using ZeRO Stage-3. Set this to `True`.
|
||||
`mixed_precision`: `no` for FP32 training, `fp16` for FP16 mixed-precision training and `bf16` for BF16 mixed-precision training. Set this to `True`.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Once this is done, the corresponding config should look like below and you can find it in config folder at [deepspeed_config.yaml](https://github.com/huggingface/peft/blob/main/examples/sft/configs/deepspeed_config.yaml):
|
||||
|
||||
```yml
|
||||
compute_environment: LOCAL_MACHINE
|
||||
debug: false
|
||||
deepspeed_config:
|
||||
deepspeed_multinode_launcher: standard
|
||||
gradient_accumulation_steps: 4
|
||||
offload_optimizer_device: none
|
||||
offload_param_device: none
|
||||
zero3_init_flag: true
|
||||
zero3_save_16bit_model: true
|
||||
zero_stage: 3
|
||||
distributed_type: DEEPSPEED
|
||||
downcast_bf16: 'no'
|
||||
machine_rank: 0
|
||||
main_training_function: main
|
||||
mixed_precision: bf16
|
||||
num_machines: 1
|
||||
num_processes: 8
|
||||
rdzv_backend: static
|
||||
same_network: true
|
||||
tpu_env: []
|
||||
tpu_use_cluster: false
|
||||
tpu_use_sudo: false
|
||||
use_cpu: false
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Launch command
|
||||
|
||||
The launch command is available at [run_peft_deepspeed.sh](https://github.com/huggingface/peft/blob/main/examples/sft/run_peft_deepspeed.sh) and it is also shown below:
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
accelerate launch --config_file "configs/deepspeed_config.yaml" train.py \
|
||||
--seed 100 \
|
||||
--model_name_or_path "meta-llama/Llama-2-70b-hf" \
|
||||
--dataset_name "smangrul/ultrachat-10k-chatml" \
|
||||
--chat_template_format "chatml" \
|
||||
--add_special_tokens False \
|
||||
--append_concat_token False \
|
||||
--splits "train,test" \
|
||||
--max_seq_len 2048 \
|
||||
--num_train_epochs 1 \
|
||||
--logging_steps 5 \
|
||||
--log_level "info" \
|
||||
--logging_strategy "steps" \
|
||||
--evaluation_strategy "epoch" \
|
||||
--save_strategy "epoch" \
|
||||
--push_to_hub \
|
||||
--hub_private_repo True \
|
||||
--hub_strategy "every_save" \
|
||||
--bf16 True \
|
||||
--packing True \
|
||||
--learning_rate 1e-4 \
|
||||
--lr_scheduler_type "cosine" \
|
||||
--weight_decay 1e-4 \
|
||||
--warmup_ratio 0.0 \
|
||||
--max_grad_norm 1.0 \
|
||||
--output_dir "llama-sft-lora-deepspeed" \
|
||||
--per_device_train_batch_size 8 \
|
||||
--per_device_eval_batch_size 8 \
|
||||
--gradient_accumulation_steps 4 \
|
||||
--gradient_checkpointing True \
|
||||
--use_reentrant False \
|
||||
--dataset_text_field "content" \
|
||||
--use_flash_attn True \
|
||||
--use_peft_lora True \
|
||||
--lora_r 8 \
|
||||
--lora_alpha 16 \
|
||||
--lora_dropout 0.1 \
|
||||
--lora_target_modules "all-linear" \
|
||||
--use_4bit_quantization False
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Notice that we are using LoRA with rank=8, alpha=16 and targeting all linear layers. We are passing the deepspeed config file and finetuning 70B Llama model on a subset of the ultrachat dataset.
|
||||
|
||||
## The important parts
|
||||
|
||||
Let's dive a little deeper into the script so you can see what's going on, and understand how it works.
|
||||
|
||||
The first thing to know is that the script uses DeepSpeed for distributed training as the DeepSpeed config has been passed. The `SFTTrainer` class handles all the heavy lifting of creating the PEFT model using the peft config that is passed. After that, when you call `trainer.train()`, `SFTTrainer` internally uses 🤗 Accelerate to prepare the model, optimizer and trainer using the DeepSpeed config to create DeepSpeed engine which is then trained. The main code snippet is below:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# trainer
|
||||
trainer = SFTTrainer(
|
||||
model=model,
|
||||
tokenizer=tokenizer,
|
||||
args=training_args,
|
||||
train_dataset=train_dataset,
|
||||
eval_dataset=eval_dataset,
|
||||
peft_config=peft_config,
|
||||
packing=data_args.packing,
|
||||
dataset_kwargs={
|
||||
"append_concat_token": data_args.append_concat_token,
|
||||
"add_special_tokens": data_args.add_special_tokens,
|
||||
},
|
||||
dataset_text_field=data_args.dataset_text_field,
|
||||
max_seq_length=data_args.max_seq_length,
|
||||
)
|
||||
trainer.accelerator.print(f"{trainer.model}")
|
||||
|
||||
# train
|
||||
checkpoint = None
|
||||
if training_args.resume_from_checkpoint is not None:
|
||||
checkpoint = training_args.resume_from_checkpoint
|
||||
trainer.train(resume_from_checkpoint=checkpoint)
|
||||
|
||||
# saving final model
|
||||
trainer.save_model()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Memory usage
|
||||
|
||||
In the above example, the memory consumed per GPU is 64 GB (80%) as seen in the screenshot below:
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/peft/peft_deepspeed_mem_usage.png"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<small>GPU memory usage for the training run</small>
|
||||
|
||||
## More resources
|
||||
You can also refer this blog post [Falcon 180B Finetuning using 🤗 PEFT and DeepSpeed](https://medium.com/@sourabmangrulkar/falcon-180b-finetuning-using-peft-and-deepspeed-b92643091d99) on how to finetune 180B Falcon model on 16 A100 GPUs on 2 machines.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Use PEFT QLoRA and DeepSpeed with ZeRO3 for finetuning large models on multiple GPUs
|
||||
|
||||
In this section, we will look at how to use QLoRA and DeepSpeed Stage-3 for finetuning 70B llama model on 2X40GB GPUs.
|
||||
For this, we first need `bitsandbytes>=0.43.0`, `accelerate>=0.28.0`, `transformers>4.38.2`, `trl>0.7.11` and `peft>0.9.0`. We need to set `zero3_init_flag` to true when using Accelerate config. Below is the config which can be found at [deepspeed_config_z3_qlora.yaml](https://github.com/huggingface/peft/blob/main/examples/sft/configs/deepspeed_config_z3_qlora.yaml):
|
||||
|
||||
```yml
|
||||
compute_environment: LOCAL_MACHINE
|
||||
debug: false
|
||||
deepspeed_config:
|
||||
deepspeed_multinode_launcher: standard
|
||||
offload_optimizer_device: none
|
||||
offload_param_device: none
|
||||
zero3_init_flag: true
|
||||
zero3_save_16bit_model: true
|
||||
zero_stage: 3
|
||||
distributed_type: DEEPSPEED
|
||||
downcast_bf16: 'no'
|
||||
machine_rank: 0
|
||||
main_training_function: main
|
||||
mixed_precision: bf16
|
||||
num_machines: 1
|
||||
num_processes: 2
|
||||
rdzv_backend: static
|
||||
same_network: true
|
||||
tpu_env: []
|
||||
tpu_use_cluster: false
|
||||
tpu_use_sudo: false
|
||||
use_cpu: false
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Launch command is given below which is available at [run_peft_qlora_deepspeed_stage3.sh](https://github.com/huggingface/peft/blob/main/examples/sft/run_peft_deepspeed.sh):
|
||||
```
|
||||
accelerate launch --config_file "configs/deepspeed_config_z3_qlora.yaml" train.py \
|
||||
--seed 100 \
|
||||
--model_name_or_path "meta-llama/Llama-2-70b-hf" \
|
||||
--dataset_name "smangrul/ultrachat-10k-chatml" \
|
||||
--chat_template_format "chatml" \
|
||||
--add_special_tokens False \
|
||||
--append_concat_token False \
|
||||
--splits "train,test" \
|
||||
--max_seq_len 2048 \
|
||||
--num_train_epochs 1 \
|
||||
--logging_steps 5 \
|
||||
--log_level "info" \
|
||||
--logging_strategy "steps" \
|
||||
--evaluation_strategy "epoch" \
|
||||
--save_strategy "epoch" \
|
||||
--push_to_hub \
|
||||
--hub_private_repo True \
|
||||
--hub_strategy "every_save" \
|
||||
--bf16 True \
|
||||
--packing True \
|
||||
--learning_rate 1e-4 \
|
||||
--lr_scheduler_type "cosine" \
|
||||
--weight_decay 1e-4 \
|
||||
--warmup_ratio 0.0 \
|
||||
--max_grad_norm 1.0 \
|
||||
--output_dir "llama-sft-qlora-dsz3" \
|
||||
--per_device_train_batch_size 2 \
|
||||
--per_device_eval_batch_size 2 \
|
||||
--gradient_accumulation_steps 2 \
|
||||
--gradient_checkpointing True \
|
||||
--use_reentrant True \
|
||||
--dataset_text_field "content" \
|
||||
--use_flash_attn True \
|
||||
--use_peft_lora True \
|
||||
--lora_r 8 \
|
||||
--lora_alpha 16 \
|
||||
--lora_dropout 0.1 \
|
||||
--lora_target_modules "all-linear" \
|
||||
--use_4bit_quantization True \
|
||||
--use_nested_quant True \
|
||||
--bnb_4bit_compute_dtype "bfloat16" \
|
||||
--bnb_4bit_quant_storage_dtype "bfloat16"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Notice the new argument being passed `bnb_4bit_quant_storage_dtype` which denotes the data type for packing the 4-bit parameters. For example, when it is set to `bfloat16`, **32/4 = 8** 4-bit params are packed together post quantization.
|
||||
|
||||
In terms of training code, the important code changes are:
|
||||
|
||||
```diff
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
bnb_config = BitsAndBytesConfig(
|
||||
load_in_4bit=args.use_4bit_quantization,
|
||||
bnb_4bit_quant_type=args.bnb_4bit_quant_type,
|
||||
bnb_4bit_compute_dtype=compute_dtype,
|
||||
bnb_4bit_use_double_quant=args.use_nested_quant,
|
||||
+ bnb_4bit_quant_storage=quant_storage_dtype,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
|
||||
args.model_name_or_path,
|
||||
quantization_config=bnb_config,
|
||||
trust_remote_code=True,
|
||||
attn_implementation="flash_attention_2" if args.use_flash_attn else "eager",
|
||||
+ torch_dtype=quant_storage_dtype or torch.float32,
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Notice that `torch_dtype` for `AutoModelForCausalLM` is same as the `bnb_4bit_quant_storage` data type. That's it. Everything else is handled by Trainer and TRL.
|
||||
|
||||
## Memory usage
|
||||
|
||||
In the above example, the memory consumed per GPU is **36.6 GB**. Therefore, what took 8X80GB GPUs with DeepSpeed Stage 3+LoRA and a couple of 80GB GPUs with DDP+QLoRA now requires 2X40GB GPUs. This makes finetuning of large models more accessible.
|
||||
|
||||
# Use PEFT and DeepSpeed with ZeRO3 and CPU Offloading for finetuning large models on a single GPU
|
||||
This section of guide will help you learn how to use our DeepSpeed [training script](https://github.com/huggingface/peft/blob/main/examples/conditional_generation/peft_lora_seq2seq_accelerate_ds_zero3_offload.py). You'll configure the script to train a large model for conditional generation with ZeRO-3 and CPU Offload.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
💡 To help you get started, check out our example training scripts for [causal language modeling](https://github.com/huggingface/peft/blob/main/examples/causal_language_modeling/peft_lora_clm_accelerate_ds_zero3_offload.py) and [conditional generation](https://github.com/huggingface/peft/blob/main/examples/conditional_generation/peft_lora_seq2seq_accelerate_ds_zero3_offload.py). You can adapt these scripts for your own applications or even use them out of the box if your task is similar to the one in the scripts.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## Configuration
|
||||
|
||||
Start by running the following command to [create a DeepSpeed configuration file](https://huggingface.co/docs/accelerate/quicktour#launching-your-distributed-script) with 🤗 Accelerate. The `--config_file` flag allows you to save the configuration file to a specific location, otherwise it is saved as a `default_config.yaml` file in the 🤗 Accelerate cache.
|
||||
|
||||
The configuration file is used to set the default options when you launch the training script.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
accelerate config --config_file ds_zero3_cpu.yaml
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You'll be asked a few questions about your setup, and configure the following arguments. In this example, you'll use ZeRO-3 along with CPU-Offload so make sure you pick those options.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
`zero_stage`: [0] Disabled, [1] optimizer state partitioning, [2] optimizer+gradient state partitioning and [3] optimizer+gradient+parameter partitioning
|
||||
`gradient_accumulation_steps`: Number of training steps to accumulate gradients before averaging and applying them.
|
||||
`gradient_clipping`: Enable gradient clipping with value.
|
||||
`offload_optimizer_device`: [none] Disable optimizer offloading, [cpu] offload optimizer to CPU, [nvme] offload optimizer to NVMe SSD. Only applicable with ZeRO >= Stage-2.
|
||||
`offload_param_device`: [none] Disable parameter offloading, [cpu] offload parameters to CPU, [nvme] offload parameters to NVMe SSD. Only applicable with ZeRO Stage-3.
|
||||
`zero3_init_flag`: Decides whether to enable `deepspeed.zero.Init` for constructing massive models. Only applicable with ZeRO Stage-3.
|
||||
`zero3_save_16bit_model`: Decides whether to save 16-bit model weights when using ZeRO Stage-3.
|
||||
`mixed_precision`: `no` for FP32 training, `fp16` for FP16 mixed-precision training and `bf16` for BF16 mixed-precision training.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
An example [configuration file](https://github.com/huggingface/peft/blob/main/examples/conditional_generation/accelerate_ds_zero3_cpu_offload_config.yaml) might look like the following. The most important thing to notice is that `zero_stage` is set to `3`, and `offload_optimizer_device` and `offload_param_device` are set to the `cpu`.
|
||||
|
||||
```yml
|
||||
compute_environment: LOCAL_MACHINE
|
||||
deepspeed_config:
|
||||
gradient_accumulation_steps: 1
|
||||
gradient_clipping: 1.0
|
||||
offload_optimizer_device: cpu
|
||||
offload_param_device: cpu
|
||||
zero3_init_flag: true
|
||||
zero3_save_16bit_model: true
|
||||
zero_stage: 3
|
||||
distributed_type: DEEPSPEED
|
||||
downcast_bf16: 'no'
|
||||
dynamo_backend: 'NO'
|
||||
fsdp_config: {}
|
||||
machine_rank: 0
|
||||
main_training_function: main
|
||||
megatron_lm_config: {}
|
||||
mixed_precision: 'no'
|
||||
num_machines: 1
|
||||
num_processes: 1
|
||||
rdzv_backend: static
|
||||
same_network: true
|
||||
use_cpu: false
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## The important parts
|
||||
|
||||
Let's dive a little deeper into the script so you can see what's going on, and understand how it works.
|
||||
|
||||
Within the [`main`](https://github.com/huggingface/peft/blob/2822398fbe896f25d4dac5e468624dc5fd65a51b/examples/conditional_generation/peft_lora_seq2seq_accelerate_ds_zero3_offload.py#L103) function, the script creates an [`~accelerate.Accelerator`] class to initialize all the necessary requirements for distributed training.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
💡 Feel free to change the model and dataset inside the `main` function. If your dataset format is different from the one in the script, you may also need to write your own preprocessing function.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
The script also creates a configuration for the 🤗 PEFT method you're using, which in this case, is LoRA. The [`LoraConfig`] specifies the task type and important parameters such as the dimension of the low-rank matrices, the matrices scaling factor, and the dropout probability of the LoRA layers. If you want to use a different 🤗 PEFT method, make sure you replace `LoraConfig` with the appropriate [class](../package_reference/tuners).
|
||||
|
||||
```diff
|
||||
def main():
|
||||
+ accelerator = Accelerator()
|
||||
model_name_or_path = "facebook/bart-large"
|
||||
dataset_name = "twitter_complaints"
|
||||
+ peft_config = LoraConfig(
|
||||
task_type=TaskType.SEQ_2_SEQ_LM, inference_mode=False, r=8, lora_alpha=32, lora_dropout=0.1
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Throughout the script, you'll see the [`~accelerate.Accelerator.main_process_first`] and [`~accelerate.Accelerator.wait_for_everyone`] functions which help control and synchronize when processes are executed.
|
||||
|
||||
The [`get_peft_model`] function takes a base model and the [`peft_config`] you prepared earlier to create a [`PeftModel`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```diff
|
||||
model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained(model_name_or_path)
|
||||
+ model = get_peft_model(model, peft_config)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Pass all the relevant training objects to 🤗 Accelerate's [`~accelerate.Accelerator.prepare`] which makes sure everything is ready for training:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
model, train_dataloader, eval_dataloader, test_dataloader, optimizer, lr_scheduler = accelerator.prepare(
|
||||
model, train_dataloader, eval_dataloader, test_dataloader, optimizer, lr_scheduler
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The next bit of code checks whether the DeepSpeed plugin is used in the `Accelerator`, and if the plugin exists, then we check if we are using ZeRO-3. This conditional flag is used when calling `generate` function call during inference for syncing GPUs when the model parameters are sharded:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
is_ds_zero_3 = False
|
||||
if getattr(accelerator.state, "deepspeed_plugin", None):
|
||||
is_ds_zero_3 = accelerator.state.deepspeed_plugin.zero_stage == 3
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Inside the training loop, the usual `loss.backward()` is replaced by 🤗 Accelerate's [`~accelerate.Accelerator.backward`] which uses the correct `backward()` method based on your configuration:
|
||||
|
||||
```diff
|
||||
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
|
||||
with TorchTracemalloc() as tracemalloc:
|
||||
model.train()
|
||||
total_loss = 0
|
||||
for step, batch in enumerate(tqdm(train_dataloader)):
|
||||
outputs = model(**batch)
|
||||
loss = outputs.loss
|
||||
total_loss += loss.detach().float()
|
||||
+ accelerator.backward(loss)
|
||||
optimizer.step()
|
||||
lr_scheduler.step()
|
||||
optimizer.zero_grad()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
That is all! The rest of the script handles the training loop, evaluation, and even pushes it to the Hub for you.
|
||||
|
||||
## Train
|
||||
|
||||
Run the following command to launch the training script. Earlier, you saved the configuration file to `ds_zero3_cpu.yaml`, so you'll need to pass the path to the launcher with the `--config_file` argument like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
accelerate launch --config_file ds_zero3_cpu.yaml examples/peft_lora_seq2seq_accelerate_ds_zero3_offload.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You'll see some output logs that track memory usage during training, and once it's completed, the script returns the accuracy and compares the predictions to the labels:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
GPU Memory before entering the train : 1916
|
||||
GPU Memory consumed at the end of the train (end-begin): 66
|
||||
GPU Peak Memory consumed during the train (max-begin): 7488
|
||||
GPU Total Peak Memory consumed during the train (max): 9404
|
||||
CPU Memory before entering the train : 19411
|
||||
CPU Memory consumed at the end of the train (end-begin): 0
|
||||
CPU Peak Memory consumed during the train (max-begin): 0
|
||||
CPU Total Peak Memory consumed during the train (max): 19411
|
||||
epoch=4: train_ppl=tensor(1.0705, device='cuda:0') train_epoch_loss=tensor(0.0681, device='cuda:0')
|
||||
100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 7/7 [00:27<00:00, 3.92s/it]
|
||||
GPU Memory before entering the eval : 1982
|
||||
GPU Memory consumed at the end of the eval (end-begin): -66
|
||||
GPU Peak Memory consumed during the eval (max-begin): 672
|
||||
GPU Total Peak Memory consumed during the eval (max): 2654
|
||||
CPU Memory before entering the eval : 19411
|
||||
CPU Memory consumed at the end of the eval (end-begin): 0
|
||||
CPU Peak Memory consumed during the eval (max-begin): 0
|
||||
CPU Total Peak Memory consumed during the eval (max): 19411
|
||||
accuracy=100.0
|
||||
eval_preds[:10]=['no complaint', 'no complaint', 'complaint', 'complaint', 'no complaint', 'no complaint', 'no complaint', 'complaint', 'complaint', 'no complaint']
|
||||
dataset['train'][label_column][:10]=['no complaint', 'no complaint', 'complaint', 'complaint', 'no complaint', 'no complaint', 'no complaint', 'complaint', 'complaint', 'no complaint']
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
# Caveats
|
||||
1. Merging when using PEFT and DeepSpeed is currently unsupported and will raise error.
|
||||
2. When using CPU offloading, the major gains from using PEFT to shrink the optimizer states and gradients to that of the adapter weights would be realized on CPU RAM and there won't be savings with respect to GPU memory.
|
||||
3. DeepSpeed Stage 3 and qlora when used with CPU offloading leads to more GPU memory usage when compared to disabling CPU offloading.
|
||||
291
docs/source/accelerate/fsdp.md
Normal file
291
docs/source/accelerate/fsdp.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,291 @@
|
||||
<!--⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Fully Sharded Data Parallel
|
||||
|
||||
[Fully sharded data parallel](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/fsdp.html) (FSDP) is developed for distributed training of large pretrained models up to 1T parameters. FSDP achieves this by sharding the model parameters, gradients, and optimizer states across data parallel processes and it can also offload sharded model parameters to a CPU. The memory efficiency afforded by FSDP allows you to scale training to larger batch or model sizes.
|
||||
|
||||
Both of these features are supported in 🤗 Accelerate, and you can use them with 🤗 PEFT.
|
||||
|
||||
# Use PEFT and FSDP
|
||||
This section of guide will help you learn how to use our DeepSpeed [training script](https://github.com/huggingface/peft/blob/main/examples/sft/train.py) for performing SFT. You'll configure the script to do SFT (supervised fine-tuning) of Llama-70B model with LoRA and FSDP on 8xH100 80GB GPUs on a single machine. You can configure it to scale to multiple machines by changing the accelerate config.
|
||||
|
||||
## Configuration
|
||||
|
||||
Start by running the following command to [create a FSDP configuration file](https://huggingface.co/docs/accelerate/quicktour#launching-your-distributed-script) with 🤗 Accelerate. The `--config_file` flag allows you to save the configuration file to a specific location, otherwise it is saved as a `default_config.yaml` file in the 🤗 Accelerate cache.
|
||||
|
||||
The configuration file is used to set the default options when you launch the training script.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
accelerate config --config_file fsdp_config.yaml
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You'll be asked a few questions about your setup, and configure the following arguments. In this example, you'll answer the questionnaire as shown in the image below.
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/peft/fsdp-peft-config.png"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<small>Creating Accelerate's config to use FSDP</small>
|
||||
|
||||
Once this is done, the corresponding config should look like below and you can find it in config folder at [fsdp_config.yaml](https://github.com/huggingface/peft/blob/main/examples/sft/configs/fsdp_config.yaml):
|
||||
|
||||
```yml
|
||||
compute_environment: LOCAL_MACHINE
|
||||
debug: false
|
||||
distributed_type: FSDP
|
||||
downcast_bf16: 'no'
|
||||
fsdp_config:
|
||||
fsdp_auto_wrap_policy: TRANSFORMER_BASED_WRAP
|
||||
fsdp_backward_prefetch: BACKWARD_PRE
|
||||
fsdp_cpu_ram_efficient_loading: true
|
||||
fsdp_forward_prefetch: false
|
||||
fsdp_offload_params: false
|
||||
fsdp_sharding_strategy: FULL_SHARD
|
||||
fsdp_state_dict_type: SHARDED_STATE_DICT
|
||||
fsdp_sync_module_states: true
|
||||
fsdp_use_orig_params: false
|
||||
machine_rank: 0
|
||||
main_training_function: main
|
||||
mixed_precision: bf16
|
||||
num_machines: 1
|
||||
num_processes: 8
|
||||
rdzv_backend: static
|
||||
same_network: true
|
||||
tpu_env: []
|
||||
tpu_use_cluster: false
|
||||
tpu_use_sudo: false
|
||||
use_cpu: false
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Launch command
|
||||
|
||||
The launch command is available at [run_peft_fsdp.sh](https://github.com/huggingface/peft/blob/main/examples/sft/run_peft_fsdp.sh) and it is also shown below:
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
accelerate launch --config_file "configs/fsdp_config.yaml" train.py \
|
||||
--seed 100 \
|
||||
--model_name_or_path "meta-llama/Llama-2-70b-hf" \
|
||||
--dataset_name "smangrul/ultrachat-10k-chatml" \
|
||||
--chat_template_format "chatml" \
|
||||
--add_special_tokens False \
|
||||
--append_concat_token False \
|
||||
--splits "train,test" \
|
||||
--max_seq_len 2048 \
|
||||
--num_train_epochs 1 \
|
||||
--logging_steps 5 \
|
||||
--log_level "info" \
|
||||
--logging_strategy "steps" \
|
||||
--evaluation_strategy "epoch" \
|
||||
--save_strategy "epoch" \
|
||||
--push_to_hub \
|
||||
--hub_private_repo True \
|
||||
--hub_strategy "every_save" \
|
||||
--bf16 True \
|
||||
--packing True \
|
||||
--learning_rate 1e-4 \
|
||||
--lr_scheduler_type "cosine" \
|
||||
--weight_decay 1e-4 \
|
||||
--warmup_ratio 0.0 \
|
||||
--max_grad_norm 1.0 \
|
||||
--output_dir "llama-sft-lora-fsdp" \
|
||||
--per_device_train_batch_size 8 \
|
||||
--per_device_eval_batch_size 8 \
|
||||
--gradient_accumulation_steps 4 \
|
||||
--gradient_checkpointing True \
|
||||
--use_reentrant False \
|
||||
--dataset_text_field "content" \
|
||||
--use_flash_attn True \
|
||||
--use_peft_lora True \
|
||||
--lora_r 8 \
|
||||
--lora_alpha 16 \
|
||||
--lora_dropout 0.1 \
|
||||
--lora_target_modules "all-linear" \
|
||||
--use_4bit_quantization False
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Notice that we are using LoRA with rank=8, alpha=16 and targeting all linear layers. We are passing the FSDP config file and finetuning the 70B Llama model on a subset of the [ultrachat dataset](https://huggingface.co/datasets/HuggingFaceH4/ultrachat_200k).
|
||||
|
||||
## The important parts
|
||||
|
||||
Let's dive a little deeper into the script so you can see what's going on, and understand how it works.
|
||||
|
||||
The first thing to know is that the script uses FSDP for distributed training as the FSDP config has been passed. The `SFTTrainer` class handles all the heavy lifting of creating PEFT model using the peft config that is passed. After that when you call `trainer.train()`, Trainer internally uses 🤗 Accelerate to prepare model, optimizer and trainer using the FSDP config to create FSDP wrapped model which is then trained. The main code snippet is below:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
# trainer
|
||||
trainer = SFTTrainer(
|
||||
model=model,
|
||||
tokenizer=tokenizer,
|
||||
args=training_args,
|
||||
train_dataset=train_dataset,
|
||||
eval_dataset=eval_dataset,
|
||||
peft_config=peft_config,
|
||||
packing=data_args.packing,
|
||||
dataset_kwargs={
|
||||
"append_concat_token": data_args.append_concat_token,
|
||||
"add_special_tokens": data_args.add_special_tokens,
|
||||
},
|
||||
dataset_text_field=data_args.dataset_text_field,
|
||||
max_seq_length=data_args.max_seq_length,
|
||||
)
|
||||
trainer.accelerator.print(f"{trainer.model}")
|
||||
if model_args.use_peft_lora:
|
||||
# handle PEFT+FSDP case
|
||||
trainer.model.print_trainable_parameters()
|
||||
if getattr(trainer.accelerator.state, "fsdp_plugin", None):
|
||||
from peft.utils.other import fsdp_auto_wrap_policy
|
||||
|
||||
fsdp_plugin = trainer.accelerator.state.fsdp_plugin
|
||||
fsdp_plugin.auto_wrap_policy = fsdp_auto_wrap_policy(trainer.model)
|
||||
|
||||
# train
|
||||
checkpoint = None
|
||||
if training_args.resume_from_checkpoint is not None:
|
||||
checkpoint = training_args.resume_from_checkpoint
|
||||
trainer.train(resume_from_checkpoint=checkpoint)
|
||||
|
||||
# saving final model
|
||||
if trainer.is_fsdp_enabled:
|
||||
trainer.accelerator.state.fsdp_plugin.set_state_dict_type("FULL_STATE_DICT")
|
||||
trainer.save_model()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Here, one main thing to note currently when using FSDP with PEFT is that `use_orig_params` needs to be `False` to realize GPU memory savings. Due to `use_orig_params=False`, the auto wrap policy for FSDP needs to change so that trainable and non-trainable parameters are wrapped separately. This is done by the code snippt below which uses the util function `fsdp_auto_wrap_policy` from PEFT:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
if getattr(trainer.accelerator.state, "fsdp_plugin", None):
|
||||
from peft.utils.other import fsdp_auto_wrap_policy
|
||||
|
||||
fsdp_plugin = trainer.accelerator.state.fsdp_plugin
|
||||
fsdp_plugin.auto_wrap_policy = fsdp_auto_wrap_policy(trainer.model)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Memory usage
|
||||
|
||||
In the above example, the memory consumed per GPU is 72-80 GB (90-98%) as seen in the screenshot below. The slight increase in GPU memory at the end is when saving the model using `FULL_STATE_DICT` state dict type instead of the `SHARDED_STATE_DICT` so that the model has adapter weights that can be loaded normally with `from_pretrained` method during inference:
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/peft/peft_fsdp_mem_usage.png"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<small>GPU memory usage for the training run</small>
|
||||
|
||||
# Use PEFT QLoRA and FSDP for finetuning large models on multiple GPUs
|
||||
|
||||
In this section, we will look at how to use QLoRA and FSDP for finetuning 70B llama model on 2X24GB GPUs. [Answer.AI](https://www.answer.ai/) in collaboration with bitsandbytes and Hugging Face 🤗 open sourced code enabling the usage of FSDP+QLoRA and explained the whole process in their insightful blogpost [You can now train a 70b language model at home](https://www.answer.ai/posts/2024-03-06-fsdp-qlora.html). This is now integrated in Hugging Face ecosystem.
|
||||
|
||||
For this, we first need `bitsandbytes>=0.43.0`, `accelerate>=0.28.0`, `transformers>4.38.2`, `trl>0.7.11` and `peft>0.9.0`. We need to set `fsdp_cpu_ram_efficient_loading=true`, `fsdp_use_orig_params=false` and `fsdp_offload_params=true`(cpu offloading) when using Accelerate config. When not using accelerate launcher, you can alternately set the environment variable `export FSDP_CPU_RAM_EFFICIENT_LOADING=true`. Here, we will be using accelerate config and below is the config which can be found at [fsdp_config_qlora.yaml](https://github.com/huggingface/peft/blob/main/examples/sft/configs/fsdp_config_qlora.yaml):
|
||||
|
||||
```yml
|
||||
compute_environment: LOCAL_MACHINE
|
||||
debug: false
|
||||
distributed_type: FSDP
|
||||
downcast_bf16: 'no'
|
||||
fsdp_config:
|
||||
fsdp_auto_wrap_policy: TRANSFORMER_BASED_WRAP
|
||||
fsdp_backward_prefetch: BACKWARD_PRE
|
||||
fsdp_cpu_ram_efficient_loading: true
|
||||
fsdp_forward_prefetch: false
|
||||
fsdp_offload_params: true
|
||||
fsdp_sharding_strategy: FULL_SHARD
|
||||
fsdp_state_dict_type: SHARDED_STATE_DICT
|
||||
fsdp_sync_module_states: true
|
||||
fsdp_use_orig_params: false
|
||||
machine_rank: 0
|
||||
main_training_function: main
|
||||
mixed_precision: 'no'
|
||||
num_machines: 1
|
||||
num_processes: 2
|
||||
rdzv_backend: static
|
||||
same_network: true
|
||||
tpu_env: []
|
||||
tpu_use_cluster: false
|
||||
tpu_use_sudo: false
|
||||
use_cpu: false
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Launch command is given below which is available at [run_peft_qlora_fsdp.sh](https://github.com/huggingface/peft/blob/main/examples/sft/run_peft_qlora_fsdp.sh):
|
||||
```
|
||||
accelerate launch --config_file "configs/fsdp_config_qlora.yaml" train.py \
|
||||
--seed 100 \
|
||||
--model_name_or_path "meta-llama/Llama-2-70b-hf" \
|
||||
--dataset_name "smangrul/ultrachat-10k-chatml" \
|
||||
--chat_template_format "chatml" \
|
||||
--add_special_tokens False \
|
||||
--append_concat_token False \
|
||||
--splits "train,test" \
|
||||
--max_seq_len 2048 \
|
||||
--num_train_epochs 1 \
|
||||
--logging_steps 5 \
|
||||
--log_level "info" \
|
||||
--logging_strategy "steps" \
|
||||
--evaluation_strategy "epoch" \
|
||||
--save_strategy "epoch" \
|
||||
--push_to_hub \
|
||||
--hub_private_repo True \
|
||||
--hub_strategy "every_save" \
|
||||
--bf16 True \
|
||||
--packing True \
|
||||
--learning_rate 1e-4 \
|
||||
--lr_scheduler_type "cosine" \
|
||||
--weight_decay 1e-4 \
|
||||
--warmup_ratio 0.0 \
|
||||
--max_grad_norm 1.0 \
|
||||
--output_dir "llama-sft-qlora-fsdp" \
|
||||
--per_device_train_batch_size 2 \
|
||||
--per_device_eval_batch_size 2 \
|
||||
--gradient_accumulation_steps 2 \
|
||||
--gradient_checkpointing True \
|
||||
--use_reentrant True \
|
||||
--dataset_text_field "content" \
|
||||
--use_flash_attn True \
|
||||
--use_peft_lora True \
|
||||
--lora_r 8 \
|
||||
--lora_alpha 16 \
|
||||
--lora_dropout 0.1 \
|
||||
--lora_target_modules "all-linear" \
|
||||
--use_4bit_quantization True \
|
||||
--use_nested_quant True \
|
||||
--bnb_4bit_compute_dtype "bfloat16" \
|
||||
--bnb_4bit_quant_storage_dtype "bfloat16"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Notice the new argument being passed, `bnb_4bit_quant_storage_dtype`, which denotes the data type for packing the 4-bit parameters. For example, when it is set to `bfloat16`, **32/4 = 8** 4-bit params are packed together post quantization. When using mixed precision training with `bfloat16`, `bnb_4bit_quant_storage_dtype` can be either `bfloat16` for pure `bfloat16` finetuning, or `float32` for automatic mixed precision (this consumes more GPU memory). When using mixed precision training with `float16`, `bnb_4bit_quant_storage_dtype` should be set to `float32` for stable automatic mixed precision training.
|
||||
|
||||
In terms of training code, the important code changes are:
|
||||
|
||||
```diff
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
bnb_config = BitsAndBytesConfig(
|
||||
load_in_4bit=args.use_4bit_quantization,
|
||||
bnb_4bit_quant_type=args.bnb_4bit_quant_type,
|
||||
bnb_4bit_compute_dtype=compute_dtype,
|
||||
bnb_4bit_use_double_quant=args.use_nested_quant,
|
||||
+ bnb_4bit_quant_storage=quant_storage_dtype,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
|
||||
args.model_name_or_path,
|
||||
quantization_config=bnb_config,
|
||||
trust_remote_code=True,
|
||||
attn_implementation="flash_attention_2" if args.use_flash_attn else "eager",
|
||||
+ torch_dtype=quant_storage_dtype or torch.float32,
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Notice that `torch_dtype` for `AutoModelForCausalLM` is same as the `bnb_4bit_quant_storage` data type. That's it. Everything else is handled by Trainer and TRL.
|
||||
|
||||
## Memory usage
|
||||
|
||||
In the above example, the memory consumed per GPU is **19.6 GB** while CPU RAM usage is around **107 GB**. When disabling CPU offloading, the GPU memory usage is **35.6 GB/ GPU**. Therefore, what took 16X80GB GPUs for full finetuning, 8X80GB GPUs with FSDP+LoRA, and a couple of 80GB GPUs with DDP+QLoRA, now requires 2X24GB GPUs. This makes finetuning of large models more accessible.
|
||||
|
||||
## More resources
|
||||
You can also refer the [llama-recipes](https://github.com/facebookresearch/llama-recipes/?tab=readme-ov-file#fine-tuning) repo and [Getting started with Llama](https://llama.meta.com/get-started/#fine-tuning) guide on how to finetune using FSDP and PEFT.
|
||||
|
||||
## Caveats
|
||||
1. Merging when using PEFT and FSDP is currently unsupported and will raise error.
|
||||
2. Passing `modules_to_save` config parameter to is untested at present.
|
||||
3. GPU Memory saving when using CPU Offloading is untested at present.
|
||||
4. When using FSDP+QLoRA, `paged_adamw_8bit` currently results in an error when saving a checkpoint.
|
||||
89
docs/source/conceptual_guides/adapter.md
Normal file
89
docs/source/conceptual_guides/adapter.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,89 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Adapters
|
||||
|
||||
Adapter-based methods add extra trainable parameters after the attention and fully-connected layers of a frozen pretrained model to reduce memory-usage and speed up training. The method varies depending on the adapter, it could simply be an extra added layer or it could be expressing the weight updates ∆W as a low-rank decomposition of the weight matrix. Either way, the adapters are typically small but demonstrate comparable performance to a fully finetuned model and enable training larger models with fewer resources.
|
||||
|
||||
This guide will give you a brief overview of the adapter methods supported by PEFT (if you're interested in learning more details about a specific method, take a look at the linked paper).
|
||||
|
||||
## Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA)
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
LoRA is one of the most popular PEFT methods and a good starting point if you're just getting started with PEFT. It was originally developed for large language models but it is a tremendously popular training method for diffusion models because of its efficiency and effectiveness.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
As mentioned briefly earlier, [LoRA](https://hf.co/papers/2106.09685) is a technique that accelerates finetuning large models while consuming less memory.
|
||||
|
||||
LoRA represents the weight updates ∆W with two smaller matrices (called *update matrices*) through low-rank decomposition. These new matrices can be trained to adapt to the new data while keeping the overall number of parameters low. The original weight matrix remains frozen and doesn't receive any further updates. To produce the final results, the original and extra adapted weights are combined. You could also merge the adapter weights with the base model to eliminate inference latency.
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/peft/lora_animated.gif"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
This approach has a number of advantages:
|
||||
|
||||
* LoRA makes finetuning more efficient by drastically reducing the number of trainable parameters.
|
||||
* The original pretrained weights are kept frozen, which means you can have multiple lightweight and portable LoRA models for various downstream tasks built on top of them.
|
||||
* LoRA is orthogonal to other parameter-efficient methods and can be combined with many of them.
|
||||
* Performance of models finetuned using LoRA is comparable to the performance of fully finetuned models.
|
||||
|
||||
In principle, LoRA can be applied to any subset of weight matrices in a neural network to reduce the number of trainable parameters. However, for simplicity and further parameter efficiency, LoRA is typically only applied to the attention blocks in Transformer models. The resulting number of trainable parameters in a LoRA model depends on the size of the update matrices, which is determined mainly by the rank `r` and the shape of the original weight matrix.
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/peft/lora.png"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<small><a href="https://hf.co/papers/2103.10385">Navigating Text-To-Image Customization: From LyCORIS Fine-Tuning to Model Evaluation</a></small>
|
||||
|
||||
## Low-Rank Hadamard Product (LoHa)
|
||||
|
||||
Low-rank decomposition can impact performance because the weight updates are limited to the low-rank space, which can constrain a model's expressiveness. However, you don't necessarily want to use a larger rank because it increases the number of trainable parameters. To address this, [LoHa](https://huggingface.co/papers/2108.06098) (a method originally developed for computer vision) was applied to diffusion models where the ability to generate diverse images is an important consideration. LoHa should also work with general model types, but the embedding layers aren't currently implemented in PEFT.
|
||||
|
||||
LoHa uses the [Hadamard product](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hadamard_product_(matrices)) (element-wise product) instead of the matrix product. ∆W is represented by four smaller matrices instead of two - like in LoRA - and each pair of these low-rank matrices are combined with the Hadamard product. As a result, ∆W can have the same number of trainable parameters but a higher rank and expressivity.
|
||||
|
||||
## Low-Rank Kronecker Product (LoKr)
|
||||
|
||||
[LoKr](https://hf.co/papers/2309.14859) is very similar to LoRA and LoHa, and it is also mainly applied to diffusion models, though you could also use it with other model types. LoKr replaces the matrix product with the [Kronecker product](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kronecker_product) instead. The Kronecker product decomposition creates a block matrix which preserves the rank of the original weight matrix. Another benefit of the Kronecker product is that it can be vectorized by stacking the matrix columns. This can speed up the process because you're avoiding fully reconstructing ∆W.
|
||||
|
||||
## Orthogonal Finetuning (OFT)
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/peft/oft.png"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<small><a href="https://hf.co/papers/2306.07280">Controlling Text-to-Image Diffusion by Orthogonal Finetuning</a></small>
|
||||
|
||||
[OFT](https://hf.co/papers/2306.07280) is a method that primarily focuses on preserving a pretrained model's generative performance in the finetuned model. It tries to maintain the same cosine similarity (hyperspherical energy) between all pairwise neurons in a layer because this better captures the semantic information among neurons. This means OFT is more capable at preserving the subject and it is better for controllable generation (similar to [ControlNet](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/using-diffusers/controlnet)).
|
||||
|
||||
OFT preserves the hyperspherical energy by learning an orthogonal transformation for neurons to keep the cosine similarity between them unchanged. In practice, this means taking the matrix product of an orthogonal matrix with the pretrained weight matrix. However, to be parameter-efficient, the orthogonal matrix is represented as a block-diagonal matrix with rank `r` blocks. Whereas LoRA reduces the number of trainable parameters with low-rank structures, OFT reduces the number of trainable parameters with a sparse block-diagonal matrix structure.
|
||||
|
||||
## Adaptive Low-Rank Adaptation (AdaLoRA)
|
||||
|
||||
[AdaLoRA](https://hf.co/papers/2303.10512) manages the parameter budget introduced from LoRA by allocating more parameters - in other words, a higher rank `r` - for important weight matrices that are better adapted for a task and pruning less important ones. The rank is controlled by a method similar to singular value decomposition (SVD). The ∆W is parameterized with two orthogonal matrices and a diagonal matrix which contains singular values. This parametrization method avoids iteratively applying SVD which is computationally expensive. Based on this method, the rank of ∆W is adjusted according to an importance score. ∆W is divided into triplets and each triplet is scored according to its contribution to model performance. Triplets with low importance scores are pruned and triplets with high importance scores are kept for finetuning.
|
||||
|
||||
## Llama-Adapter
|
||||
|
||||
[Llama-Adapter](https://hf.co/papers/2303.16199) is a method for adapting Llama into a instruction-following model. To help adapt the model for instruction-following, the adapter is trained with a 52K instruction-output dataset.
|
||||
|
||||
A set of of learnable adaption prompts are prefixed to the input instruction tokens. These are inserted into the upper layers of the model because it is better to learn with the higher-level semantics of the pretrained model. The instruction-output tokens prefixed to the input guide the adaption prompt to generate a contextual response.
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/peft/llama-adapter.png"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<small><a href="https://hf.co/papers/2303.16199">LLaMA-Adapter: Efficient Fine-tuning of Language Models with Zero-init Attention</a></small>
|
||||
|
||||
To avoid adding noise to the tokens, the adapter uses zero-initialized attention. On top of this, the adapter adds a learnable gating factor (initialized with zeros) to progressively add information to the model during training. This prevents overwhelming the model's pretrained knowledge with the newly learned instructions.
|
||||
68
docs/source/conceptual_guides/ia3.md
Normal file
68
docs/source/conceptual_guides/ia3.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,68 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# IA3
|
||||
|
||||
This conceptual guide gives a brief overview of [IA3](https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.05638), a parameter-efficient fine tuning technique that is
|
||||
intended to improve over [LoRA](./lora).
|
||||
|
||||
To make fine-tuning more efficient, IA3 (Infused Adapter by Inhibiting and Amplifying Inner Activations)
|
||||
rescales inner activations with learned vectors. These learned vectors are injected in the attention and feedforward modules
|
||||
in a typical transformer-based architecture. These learned vectors are the only trainable parameters during fine-tuning, and thus the original
|
||||
weights remain frozen. Dealing with learned vectors (as opposed to learned low-rank updates to a weight matrix like LoRA)
|
||||
keeps the number of trainable parameters much smaller.
|
||||
|
||||
Being similar to LoRA, IA3 carries many of the same advantages:
|
||||
|
||||
* IA3 makes fine-tuning more efficient by drastically reducing the number of trainable parameters. (For T0, an IA3 model only has about 0.01% trainable parameters, while even LoRA has > 0.1%)
|
||||
* The original pre-trained weights are kept frozen, which means you can have multiple lightweight and portable IA3 models for various downstream tasks built on top of them.
|
||||
* Performance of models fine-tuned using IA3 is comparable to the performance of fully fine-tuned models.
|
||||
* IA3 does not add any inference latency because adapter weights can be merged with the base model.
|
||||
|
||||
In principle, IA3 can be applied to any subset of weight matrices in a neural network to reduce the number of trainable
|
||||
parameters. Following the authors' implementation, IA3 weights are added to the key, value and feedforward layers
|
||||
of a Transformer model. To be specific, for transformer models, IA3 weights are added to the outputs of key and value layers, and to the input of the second feedforward layer
|
||||
in each transformer block.
|
||||
|
||||
Given the target layers for injecting IA3 parameters, the number of trainable parameters
|
||||
can be determined based on the size of the weight matrices.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Common IA3 parameters in PEFT
|
||||
|
||||
As with other methods supported by PEFT, to fine-tune a model using IA3, you need to:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Instantiate a base model.
|
||||
2. Create a configuration (`IA3Config`) where you define IA3-specific parameters.
|
||||
3. Wrap the base model with `get_peft_model()` to get a trainable `PeftModel`.
|
||||
4. Train the `PeftModel` as you normally would train the base model.
|
||||
|
||||
`IA3Config` allows you to control how IA3 is applied to the base model through the following parameters:
|
||||
|
||||
- `target_modules`: The modules (for example, attention blocks) to apply the IA3 vectors.
|
||||
- `feedforward_modules`: The list of modules to be treated as feedforward layers in `target_modules`. While learned vectors are multiplied with
|
||||
the output activation for attention blocks, the vectors are multiplied with the input for classic feedforward layers. Note that `feedforward_modules` must be a subset of `target_modules`.
|
||||
- `modules_to_save`: List of modules apart from IA3 layers to be set as trainable and saved in the final checkpoint. These typically include model's custom head that is randomly initialized for the fine-tuning task.
|
||||
|
||||
## Example Usage
|
||||
|
||||
For the task of sequence classification, one can initialize the IA3 config for a Llama model as follows:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
peft_config = IA3Config(
|
||||
task_type=TaskType.SEQ_CLS, target_modules=["k_proj", "v_proj", "down_proj"], feedforward_modules=["down_proj"]
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
77
docs/source/conceptual_guides/prompting.md
Normal file
77
docs/source/conceptual_guides/prompting.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,77 @@
|
||||
<!--⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Soft prompts
|
||||
|
||||
Training large pretrained language models is very time-consuming and compute-intensive. As they continue to grow in size, there is increasing interest in more efficient training methods such as *prompting*. Prompting primes a frozen pretrained model for a specific downstream task by including a text prompt that describes the task or even demonstrates an example of the task. With prompting, you can avoid fully training a separate model for each downstream task, and use the same frozen pretrained model instead. This is a lot easier because you can use the same model for several different tasks, and it is significantly more efficient to train and store a smaller set of prompt parameters than to train all the model's parameters.
|
||||
|
||||
There are two categories of prompting methods:
|
||||
|
||||
- hard prompts are manually handcrafted text prompts with discrete input tokens; the downside is that it requires a lot of effort to create a good prompt
|
||||
- soft prompts are learnable tensors concatenated with the input embeddings that can be optimized to a dataset; the downside is that they aren't human readable because you aren't matching these "virtual tokens" to the embeddings of a real word
|
||||
|
||||
This conceptual guide provides a brief overview of the soft prompt methods included in 🤗 PEFT: prompt tuning, prefix tuning, P-tuning, and multitask prompt tuning.
|
||||
|
||||
## Prompt tuning
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/peft/prompt-tuning.png"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<small>Only train and store a significantly smaller set of task-specific prompt parameters <a href="https://hf.co/papers/2104.08691">(image source)</a>.</small>
|
||||
|
||||
[Prompt tuning](https://hf.co/papers/2104.08691) was developed for text classification tasks on T5 models, and all downstream tasks are cast as a text generation task. For example, sequence classification usually assigns a single class label to a sequence of text. By casting it as a text generation task, the tokens that make up the class label are *generated*. Prompts are added to the input as a series of tokens. Typically, the model parameters are fixed which means the prompt tokens are also fixed by the model parameters.
|
||||
|
||||
The key idea behind prompt tuning is that prompt tokens have their own parameters that are updated independently. This means you can keep the pretrained model's parameters frozen, and only update the gradients of the prompt token embeddings. The results are comparable to the traditional method of training the entire model, and prompt tuning performance scales as model size increases.
|
||||
|
||||
Take a look at [Prompt tuning for causal language modeling](../task_guides/clm-prompt-tuning) for a step-by-step guide on how to train a model with prompt tuning.
|
||||
|
||||
## Prefix tuning
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/peft/prefix-tuning.png"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<small>Optimize the prefix parameters for each task <a href="https://hf.co/papers/2101.00190">(image source)</a>.</small>
|
||||
|
||||
[Prefix tuning](https://hf.co/papers/2101.00190) was designed for natural language generation (NLG) tasks on GPT models. It is very similar to prompt tuning; prefix tuning also prepends a sequence of task-specific vectors to the input that can be trained and updated while keeping the rest of the pretrained model's parameters frozen.
|
||||
|
||||
The main difference is that the prefix parameters are inserted in **all** of the model layers, whereas prompt tuning only adds the prompt parameters to the model input embeddings. The prefix parameters are also optimized by a separate feed-forward network (FFN) instead of training directly on the soft prompts because it causes instability and hurts performance. The FFN is discarded after updating the soft prompts.
|
||||
|
||||
As a result, the authors found that prefix tuning demonstrates comparable performance to fully finetuning a model, despite having 1000x fewer parameters, and it performs even better in low-data settings.
|
||||
|
||||
Take a look at [Prefix tuning for conditional generation](../task_guides/seq2seq-prefix-tuning) for a step-by-step guide on how to train a model with prefix tuning.
|
||||
|
||||
## P-tuning
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/peft/p-tuning.png"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<small>Prompt tokens can be inserted anywhere in the input sequence, and they are optimized by a prompt encoder <a href="https://hf.co/papers/2103.10385">(image source)</a>.</small>
|
||||
|
||||
[P-tuning](https://hf.co/papers/2103.10385) is designed for natural language understanding (NLU) tasks and all language models.
|
||||
It is another variation of a soft prompt method; P-tuning also adds a trainable embedding tensor that can be optimized to find better prompts, and it uses a prompt encoder (a bidirectional long-short term memory network or LSTM) to optimize the prompt parameters. Unlike prefix tuning though:
|
||||
|
||||
- the prompt tokens can be inserted anywhere in the input sequence, and it isn't restricted to only the beginning
|
||||
- the prompt tokens are only added to the input instead of adding them to every layer of the model
|
||||
- introducing *anchor* tokens can improve performance because they indicate characteristics of a component in the input sequence
|
||||
|
||||
The results suggest that P-tuning is more efficient than manually crafting prompts, and it enables GPT-like models to compete with BERT-like models on NLU tasks.
|
||||
|
||||
Take a look at [P-tuning for sequence classification](../task_guides/ptuning-seq-classification) for a step-by-step guide on how to train a model with P-tuning.
|
||||
|
||||
## Multitask prompt tuning
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/peft/mpt.png"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<small><a href="https://hf.co/papers/2103.10385">Multitask prompt tuning enables parameter-efficient transfer learning</a>.</small>
|
||||
|
||||
[Multitask prompt tuning (MPT)](https://hf.co/papers/2103.10385) learns a single prompt from data for multiple task types that can be shared for different target tasks. Other existing approaches learn a separate soft prompt for each task that need to be retrieved or aggregated for adaptation to target tasks. MPT consists of two stages:
|
||||
|
||||
1. source training - for each task, its soft prompt is decomposed into task-specific vectors. The task-specific vectors are multiplied together to form another matrix W, and the Hadamard product is used between W and a shared prompt matrix P to generate a task-specific prompt matrix. The task-specific prompts are distilled into a single prompt matrix that is shared across all tasks. This prompt is trained with multitask training.
|
||||
2. target adaptation - to adapt the single prompt for a target task, a target prompt is initialized and expressed as the Hadamard product of the shared prompt matrix and the task-specific low-rank prompt matrix.
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/peft/mpt-decomposition.png"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<small><a href="https://hf.co/papers/2103.10385">Prompt decomposition</a>.</small>
|
||||
92
docs/source/developer_guides/contributing.md
Normal file
92
docs/source/developer_guides/contributing.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,92 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Contribute to PEFT
|
||||
|
||||
We are happy to accept contributions to PEFT. If you plan to contribute, please read this to make the process as smooth as possible.
|
||||
|
||||
## Installation
|
||||
|
||||
For code contributions to PEFT, you should choose the ["source"](../install#source) installation method.
|
||||
|
||||
If you are new to creating a pull request, follow the [Creating a pull request](https://docs.github.com/en/pull-requests/collaborating-with-pull-requests/proposing-changes-to-your-work-with-pull-requests/creating-a-pull-request) guide by GitHub.
|
||||
|
||||
## Tests and code quality checks
|
||||
|
||||
Regardless of the contribution type (unless it’s only about the docs), you should run tests and code quality checks before creating a PR to ensure your contribution doesn’t break anything and follows the project standards.
|
||||
|
||||
We provide a Makefile to execute the necessary tests. Run the code below for the unit test:
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
make test
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Run one of the following to either only check or check and fix code quality and style:
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
make quality # just check
|
||||
make style # check and fix
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can also set up [`pre-commit`](https://pre-commit.com/) to run these fixes
|
||||
automatically as Git commit hooks.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ pip install pre-commit
|
||||
$ pre-commit install
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Running all the tests can take a couple of minutes, so during development it can be more efficient to only run tests specific to your change:
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
pytest tests/ -k <name-of-test>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This should finish much quicker and allow for faster iteration. However, you should still run the whole test suite before creating a PR because your change can inadvertently break tests that at first glance are unrelated.
|
||||
|
||||
If your change is specific to a hardware setting (e.g., it requires CUDA), take a look at [tests/test_gpu_examples.py](https://github.com/huggingface/peft/blob/1c1c7fdaa6e6abaa53939b865dee1eded82ad032/tests/test_gpu_examples.py) and [tests/test_common_gpu.py](https://github.com/huggingface/peft/blob/1c1c7fdaa6e6abaa53939b865dee1eded82ad032/tests/test_common_gpu.py) to see if it makes sense to add tests there. If your change could have an effect on saving and loading models, please run the tests with the `--regression` flag to trigger regression tests.
|
||||
|
||||
It can happen that while you’re working on your PR, the underlying code base changes due to other changes being merged. If that happens – especially when there is a merge conflict – please update your branch with the latest changes. This can be a merge or a rebase, and we'll squash and merge the PR once it’s ready.
|
||||
|
||||
## PR description
|
||||
|
||||
When opening a PR, please provide a nice description of the change you're proposing. If it relates to other issues or PRs, please reference them. Providing a good description not only helps the reviewers review your code better and faster, it can also be used later (as a basis) for the commit message which helps with long term maintenance of the project.
|
||||
|
||||
If your code makes some non-trivial changes, it may also be a good idea to add comments to the code to explain those changes. For example, if you had to iterate on your implementation multiple times because the most obvious way didn’t work, it’s a good indication that a code comment is needed.
|
||||
|
||||
## Bugfixes
|
||||
|
||||
Please give a description of the circumstances that led to the bug. If there is an existing issue, please link to it (e.g., “Resolves #12345”).
|
||||
|
||||
Ideally when a bugfix is provided, it should be accompanied by a test for the bug. The test should fail with the current code and pass with the bugfix. Add a comment to the test that references the issue or PR. Without a test, it is more difficult to prevent regressions in the future.
|
||||
|
||||
## Add a new fine-tuning method
|
||||
|
||||
New parameter-efficient fine-tuning methods are developed all the time. If you would like to add a new and promising method to PEFT, please follow these steps.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Before you start to implement the new method, please open a GitHub issue with your proposal. This way, the maintainers can give you some early feedback.
|
||||
2. Please add a link to the source (usually a paper) of the method. Some evidence should be provided there is general interest in using the method. We will not add new methods that are freshly published, but there is no evidence of demand for it.
|
||||
3. When implementing the method, it makes sense to look for existing implementations that already exist as a guide. Moreover, when you structure your code, please take inspiration from the other PEFT methods. For example, if your method is similar to LoRA, it makes sense to structure your code similarly or even reuse some functions or classes where it makes sense (some code duplication is okay, but don’t overdo it).
|
||||
4. Ideally, in addition to the implementation of the new method, there should also be examples (notebooks, scripts), documentation, and an extensive test suite that proves the method works with a variety of tasks. However, this can be more challenging so it is acceptable to only provide the implementation and at least one working example. Documentation and tests can be added in follow up PRs.
|
||||
5. Once you have something that seems to be working, don’t hesitate to create a draft PR even if it’s not in a mergeable state yet. The maintainers are happy to give you feedback and guidance along the way.
|
||||
|
||||
## Add other features
|
||||
|
||||
It is best if you first open an issue on GitHub with a proposal to add the new feature. This way, you can discuss with the maintainers if it makes sense to add the feature before spending too much time on implementing it.
|
||||
|
||||
New features should generally be accompanied by tests and documentation or examples. Without the latter, users will have a hard time discovering your cool new feature.
|
||||
|
||||
Changes to the code should be implemented in a backward-compatible way. For example, existing code should continue to work the same way after the feature is merged.
|
||||
240
docs/source/developer_guides/custom_models.md
Normal file
240
docs/source/developer_guides/custom_models.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,240 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Custom models
|
||||
|
||||
Some fine-tuning techniques, such as prompt tuning, are specific to language models. That means in 🤗 PEFT, it is
|
||||
assumed a 🤗 Transformers model is being used. However, other fine-tuning techniques - like
|
||||
[LoRA](../conceptual_guides/lora) - are not restricted to specific model types.
|
||||
|
||||
In this guide, we will see how LoRA can be applied to a multilayer perceptron, a computer vision model from the [timm](https://huggingface.co/docs/timm/index) library, or a new 🤗 Transformers architecture.
|
||||
|
||||
## Multilayer perceptron
|
||||
|
||||
Let's assume that we want to fine-tune a multilayer perceptron with LoRA. Here is the definition:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from torch import nn
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class MLP(nn.Module):
|
||||
def __init__(self, num_units_hidden=2000):
|
||||
super().__init__()
|
||||
self.seq = nn.Sequential(
|
||||
nn.Linear(20, num_units_hidden),
|
||||
nn.ReLU(),
|
||||
nn.Linear(num_units_hidden, num_units_hidden),
|
||||
nn.ReLU(),
|
||||
nn.Linear(num_units_hidden, 2),
|
||||
nn.LogSoftmax(dim=-1),
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, X):
|
||||
return self.seq(X)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This is a straightforward multilayer perceptron with an input layer, a hidden layer, and an output layer.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
For this toy example, we choose an exceedingly large number of hidden units to highlight the efficiency gains
|
||||
from PEFT, but those gains are in line with more realistic examples.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
There are a few linear layers in this model that could be tuned with LoRA. When working with common 🤗 Transformers
|
||||
models, PEFT will know which layers to apply LoRA to, but in this case, it is up to us as a user to choose the layers.
|
||||
To determine the names of the layers to tune:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
print([(n, type(m)) for n, m in MLP().named_modules()])
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This should print:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[('', __main__.MLP),
|
||||
('seq', torch.nn.modules.container.Sequential),
|
||||
('seq.0', torch.nn.modules.linear.Linear),
|
||||
('seq.1', torch.nn.modules.activation.ReLU),
|
||||
('seq.2', torch.nn.modules.linear.Linear),
|
||||
('seq.3', torch.nn.modules.activation.ReLU),
|
||||
('seq.4', torch.nn.modules.linear.Linear),
|
||||
('seq.5', torch.nn.modules.activation.LogSoftmax)]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Let's say we want to apply LoRA to the input layer and to the hidden layer, those are `'seq.0'` and `'seq.2'`. Moreover,
|
||||
let's assume we want to update the output layer without LoRA, that would be `'seq.4'`. The corresponding config would
|
||||
be:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from peft import LoraConfig
|
||||
|
||||
config = LoraConfig(
|
||||
target_modules=["seq.0", "seq.2"],
|
||||
modules_to_save=["seq.4"],
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
With that, we can create our PEFT model and check the fraction of parameters trained:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from peft import get_peft_model
|
||||
|
||||
model = MLP()
|
||||
peft_model = get_peft_model(model, config)
|
||||
peft_model.print_trainable_parameters()
|
||||
# prints trainable params: 56,164 || all params: 4,100,164 || trainable%: 1.369798866581922
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, we can use any training framework we like, or write our own fit loop, to train the `peft_model`.
|
||||
|
||||
For a complete example, check out [this notebook](https://github.com/huggingface/peft/blob/main/examples/multilayer_perceptron/multilayer_perceptron_lora.ipynb).
|
||||
|
||||
## timm models
|
||||
|
||||
The [timm](https://huggingface.co/docs/timm/index) library contains a large number of pretrained computer vision models.
|
||||
Those can also be fine-tuned with PEFT. Let's check out how this works in practice.
|
||||
|
||||
To start, ensure that timm is installed in the Python environment:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python -m pip install -U timm
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Next we load a timm model for an image classification task:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import timm
|
||||
|
||||
num_classes = ...
|
||||
model_id = "timm/poolformer_m36.sail_in1k"
|
||||
model = timm.create_model(model_id, pretrained=True, num_classes=num_classes)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Again, we need to make a decision about what layers to apply LoRA to. Since LoRA supports 2D conv layers, and since
|
||||
those are a major building block of this model, we should apply LoRA to the 2D conv layers. To identify the names of
|
||||
those layers, let's look at all the layer names:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
print([(n, type(m)) for n, m in model.named_modules()])
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This will print a very long list, we'll only show the first few:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
[('', timm.models.metaformer.MetaFormer),
|
||||
('stem', timm.models.metaformer.Stem),
|
||||
('stem.conv', torch.nn.modules.conv.Conv2d),
|
||||
('stem.norm', torch.nn.modules.linear.Identity),
|
||||
('stages', torch.nn.modules.container.Sequential),
|
||||
('stages.0', timm.models.metaformer.MetaFormerStage),
|
||||
('stages.0.downsample', torch.nn.modules.linear.Identity),
|
||||
('stages.0.blocks', torch.nn.modules.container.Sequential),
|
||||
('stages.0.blocks.0', timm.models.metaformer.MetaFormerBlock),
|
||||
('stages.0.blocks.0.norm1', timm.layers.norm.GroupNorm1),
|
||||
('stages.0.blocks.0.token_mixer', timm.models.metaformer.Pooling),
|
||||
('stages.0.blocks.0.token_mixer.pool', torch.nn.modules.pooling.AvgPool2d),
|
||||
('stages.0.blocks.0.drop_path1', torch.nn.modules.linear.Identity),
|
||||
('stages.0.blocks.0.layer_scale1', timm.models.metaformer.Scale),
|
||||
('stages.0.blocks.0.res_scale1', torch.nn.modules.linear.Identity),
|
||||
('stages.0.blocks.0.norm2', timm.layers.norm.GroupNorm1),
|
||||
('stages.0.blocks.0.mlp', timm.layers.mlp.Mlp),
|
||||
('stages.0.blocks.0.mlp.fc1', torch.nn.modules.conv.Conv2d),
|
||||
('stages.0.blocks.0.mlp.act', torch.nn.modules.activation.GELU),
|
||||
('stages.0.blocks.0.mlp.drop1', torch.nn.modules.dropout.Dropout),
|
||||
('stages.0.blocks.0.mlp.norm', torch.nn.modules.linear.Identity),
|
||||
('stages.0.blocks.0.mlp.fc2', torch.nn.modules.conv.Conv2d),
|
||||
('stages.0.blocks.0.mlp.drop2', torch.nn.modules.dropout.Dropout),
|
||||
('stages.0.blocks.0.drop_path2', torch.nn.modules.linear.Identity),
|
||||
('stages.0.blocks.0.layer_scale2', timm.models.metaformer.Scale),
|
||||
('stages.0.blocks.0.res_scale2', torch.nn.modules.linear.Identity),
|
||||
('stages.0.blocks.1', timm.models.metaformer.MetaFormerBlock),
|
||||
('stages.0.blocks.1.norm1', timm.layers.norm.GroupNorm1),
|
||||
('stages.0.blocks.1.token_mixer', timm.models.metaformer.Pooling),
|
||||
('stages.0.blocks.1.token_mixer.pool', torch.nn.modules.pooling.AvgPool2d),
|
||||
...
|
||||
('head.global_pool.flatten', torch.nn.modules.linear.Identity),
|
||||
('head.norm', timm.layers.norm.LayerNorm2d),
|
||||
('head.flatten', torch.nn.modules.flatten.Flatten),
|
||||
('head.drop', torch.nn.modules.linear.Identity),
|
||||
('head.fc', torch.nn.modules.linear.Linear)]
|
||||
]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Upon closer inspection, we see that the 2D conv layers have names such as `"stages.0.blocks.0.mlp.fc1"` and
|
||||
`"stages.0.blocks.0.mlp.fc2"`. How can we match those layer names specifically? You can write a [regular
|
||||
expressions](https://docs.python.org/3/library/re.html) to match the layer names. For our case, the regex
|
||||
`r".*\.mlp\.fc\d"` should do the job.
|
||||
|
||||
Furthermore, as in the first example, we should ensure that the output layer, in this case the classification head, is
|
||||
also updated. Looking at the end of the list printed above, we can see that it's named `'head.fc'`. With that in mind,
|
||||
here is our LoRA config:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
config = LoraConfig(target_modules=r".*\.mlp\.fc\d", modules_to_save=["head.fc"])
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then we only need to create the PEFT model by passing our base model and the config to `get_peft_model`:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
peft_model = get_peft_model(model, config)
|
||||
peft_model.print_trainable_parameters()
|
||||
# prints trainable params: 1,064,454 || all params: 56,467,974 || trainable%: 1.88505789139876
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This shows us that we only need to train less than 2% of all parameters, which is a huge efficiency gain.
|
||||
|
||||
For a complete example, check out [this notebook](https://github.com/huggingface/peft/blob/main/examples/image_classification/image_classification_timm_peft_lora.ipynb).
|
||||
|
||||
## New transformers architectures
|
||||
|
||||
When new popular transformers architectures are released, we do our best to quickly add them to PEFT. If you come across a transformers model that is not supported out of the box, don't worry, it will most likely still work if the config is set correctly. Specifically, you have to identify the layers that should be adapted and set them correctly when initializing the corresponding config class, e.g. `LoraConfig`. Here are some tips to help with this.
|
||||
|
||||
As a first step, it is a good idea is to check the existing models for inspiration. You can find them inside of [constants.py](https://github.com/huggingface/peft/blob/main/src/peft/utils/constants.py) in the PEFT repository. Often, you'll find a similar architecture that uses the same names. For example, if the new model architecture is a variation of the "mistral" model and you want to apply LoRA, you can see that the entry for "mistral" in `TRANSFORMERS_MODELS_TO_LORA_TARGET_MODULES_MAPPING` contains `["q_proj", "v_proj"]`. This tells you that for "mistral" models, the `target_modules` for LoRA should be `["q_proj", "v_proj"]`:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from peft import LoraConfig, get_peft_model
|
||||
|
||||
my_mistral_model = ...
|
||||
config = LoraConfig(
|
||||
target_modules=["q_proj", "v_proj"],
|
||||
..., # other LoRA arguments
|
||||
)
|
||||
peft_model = get_peft_model(my_mistral_model, config)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If that doesn't help, check the existing modules in your model architecture with the `named_modules` method and try to identify the attention layers, especially the key, query, and value layers. Those will often have names such as `c_attn`, `query`, `q_proj`, etc. The key layer is not always adapted, and ideally, you should check whether including it results in better performance.
|
||||
|
||||
Additionally, linear layers are common targets to be adapted (e.g. in [QLoRA paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2305.14314), authors suggest to adapt them as well). Their names will often contain the strings `fc` or `dense`.
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to add a new model to PEFT, please create an entry in [constants.py](https://github.com/huggingface/peft/blob/main/src/peft/utils/constants.py) and open a pull request on the [repository](https://github.com/huggingface/peft/pulls). Don't forget to update the [README](https://github.com/huggingface/peft#models-support-matrix) as well.
|
||||
|
||||
## Verify parameters and layers
|
||||
|
||||
You can verify whether you've correctly applied a PEFT method to your model in a few ways.
|
||||
|
||||
* Check the fraction of parameters that are trainable with the [`~PeftModel.print_trainable_parameters`] method. If this number is lower or higher than expected, check the model `repr` by printing the model. This shows the names of all the layer types in the model. Ensure that only the intended target layers are replaced by the adapter layers. For example, if LoRA is applied to `nn.Linear` layers, then you should only see `lora.Linear` layers being used.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
peft_model.print_trainable_parameters()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* Another way you can view the adapted layers is to use the `targeted_module_names` attribute to list the name of each module that was adapted.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
print(peft_model.targeted_module_names)
|
||||
```
|
||||
304
docs/source/developer_guides/lora.md
Normal file
304
docs/source/developer_guides/lora.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,304 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# LoRA
|
||||
|
||||
LoRA is low-rank decomposition method to reduce the number of trainable parameters which speeds up finetuning large models and uses less memory. In PEFT, using LoRA is as easy as setting up a [`LoraConfig`] and wrapping it with [`get_peft_model`] to create a trainable [`PeftModel`].
|
||||
|
||||
This guide explores in more detail other options and features for using LoRA.
|
||||
|
||||
## Initialization
|
||||
|
||||
The initialization of LoRA weights is controlled by the parameter `init_lora_weights` in [`LoraConfig`]. By default, PEFT initializes LoRA weights with Kaiming-uniform for weight A and zeros for weight B resulting in an identity transform (same as the reference [implementation](https://github.com/microsoft/LoRA)).
|
||||
|
||||
It is also possible to pass `init_lora_weights="gaussian"`. As the name suggests, this initializes weight A with a Gaussian distribution and zeros for weight B (this is how [Diffusers](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/index) initializes LoRA weights).
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from peft import LoraConfig
|
||||
|
||||
config = LoraConfig(init_lora_weights="gaussian", ...)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
There is also an option to set `init_lora_weights=False` which is useful for debugging and testing. This should be the only time you use this option. When choosing this option, the LoRA weights are initialized such that they do *not* result in an identity transform.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from peft import LoraConfig
|
||||
|
||||
config = LoraConfig(init_lora_weights=False, ...)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### LoftQ
|
||||
|
||||
#### Standard approach
|
||||
|
||||
When quantizing the base model for QLoRA training, consider using the [LoftQ initialization](https://arxiv.org/abs/2310.08659), which has been shown to improve performance when training quantized models. The idea is that the LoRA weights are initialized such that the quantization error is minimized. To use LoftQ, follow [these instructions](https://github.com/huggingface/peft/tree/main/examples/loftq_finetuning).
|
||||
|
||||
In general, for LoftQ to work best, it is recommended to target as many layers with LoRA as possible, since those not targeted cannot have LoftQ applied. This means that passing `LoraConfig(..., target_modules="all-linear")` will most likely give the best results. Also, you should use `nf4` as quant type in your quantization config when using 4bit quantization, i.e. `BitsAndBytesConfig(load_in_4bit=True, bnb_4bit_quant_type="nf4")`.
|
||||
|
||||
#### A more convienient way
|
||||
|
||||
An easier but more limited way to apply LoftQ initialization is to use the convenience function `replace_lora_weights_loftq`. This takes the quantized PEFT model as input and replaces the LoRA weights in-place with their LoftQ-initialized counterparts.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from peft import replace_lora_weights_loftq
|
||||
from transformers import BitsAndBytesConfig
|
||||
|
||||
bnb_config = BitsAndBytesConfig(load_in_4bit=True, ...)
|
||||
base_model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(..., quantization_config=bnb_config)
|
||||
# note: don't pass init_lora_weights="loftq" or loftq_config!
|
||||
lora_config = LoraConfig(task_type="CAUSAL_LM")
|
||||
peft_model = get_peft_model(base_model, lora_config)
|
||||
replace_lora_weights_loftq(peft_model)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
`replace_lora_weights_loftq` also allows you to pass a `callback` argument to give you more control over which layers should be modified or not, which empirically can improve the results quite a lot. To see a more elaborate example of this, check out [this notebook](https://github.com/huggingface/peft/blob/main/examples/loftq_finetuning/LoftQ_weight_replacement.ipynb).
|
||||
|
||||
`replace_lora_weights_loftq` implements only one iteration step of LoftQ. This means that only the LoRA weights are updated, instead of iteratevily updating LoRA weights and quantized base model weights. This may lead to lower performance but has the advantage that we can use the original quantized weights derived from the base model, instead of having to keep an extra copy of modified quantized weights. Whether this tradeoff is worthwhile depends on the use case.
|
||||
|
||||
At the moment, `replace_lora_weights_loftq` has these additional limitations:
|
||||
|
||||
- Model files must be stored as a `safetensors` file.
|
||||
- Only bitsandbytes 4bit quantization is supported.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Learn more about how PEFT works with quantization in the [Quantization](quantization) guide.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
### Rank-stabilized LoRA
|
||||
|
||||
Another way to initialize [`LoraConfig`] is with the [rank-stabilized LoRA (rsLoRA)](https://huggingface.co/papers/2312.03732) method. The LoRA architecture scales each adapter during every forward pass by a fixed scalar which is set at initialization and depends on the rank `r`. The scalar is given by `lora_alpha/r` in the original implementation, but rsLoRA uses `lora_alpha/math.sqrt(r)` which stabilizes the adapters and increases the performance potential from using a higher `r`.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from peft import LoraConfig
|
||||
|
||||
config = LoraConfig(use_rslora=True, ...)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Weight-Decomposed Low-Rank Adaptation (DoRA)
|
||||
|
||||
This technique decomposes the updates of the weights into two parts, magnitude and direction. Direction is handled by normal LoRA, whereas the magnitude is handled by a separate learnable parameter. This can improve the performance of LoRA, especially at low ranks. For more information on DoRA, see https://arxiv.org/abs/2402.09353.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from peft import LoraConfig
|
||||
|
||||
config = LoraConfig(use_dora=True, ...)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Caveats
|
||||
|
||||
- DoRA only supports linear and Conv2d layers at the momement.
|
||||
- DoRA introduces a bigger overhead than pure LoRA, so it is recommended to merge weights for inference, see [`LoraModel.merge_and_unload`].
|
||||
- DoRA should work with weights quantized with bitsandbytes ("QDoRA"). However, issues have been reported when using QDoRA with DeepSpeed Zero2.
|
||||
|
||||
### QLoRA-style training
|
||||
|
||||
The default LoRA settings in PEFT add trainable weights to the query and value layers of each attention block. But [QLoRA](https://hf.co/papers/2305.14314), which adds trainable weights to all the linear layers of a transformer model, can provide performance equal to a fully finetuned model. To apply LoRA to all the linear layers, like in QLoRA, set `target_modules="all-linear"` (easier than specifying individual modules by name which can vary depending on the architecture).
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
config = LoraConfig(target_modules="all-linear", ...)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Memory efficient Layer Replication with LoRA
|
||||
|
||||
An approach used to improve the performance of models is to expand a model by duplicating layers in the model to build a larger model from a pretrained model of a given size. For example increasing a 7B model to a 10B model as described in the [SOLAR](https://arxiv.org/abs/2312.15166) paper. PEFT LoRA supports this kind of expansion in a memory efficient manner that supports further fine-tuning using LoRA adapters attached to the layers post replication of the layers. The replicated layers do not take additional memory as they share the underlying weights so the only additional memory required is the memory for the adapter weights. To use this feature you would create a config with the `layer_replication` argument.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
config = LoraConfig(layer_replication=[[0,4], [2,5]], ...)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Assuming the original model had 5 layers `[0, 1, 2 ,3, 4]`, this would create a model with 7 layers arranged as `[0, 1, 2, 3, 2, 3, 4]`. This follows the [mergekit](https://github.com/arcee-ai/mergekit) pass through merge convention where sequences of layers specified as start inclusive and end exclusive tuples are stacked to build the final model. Each layer in the final model gets its own distinct set of LoRA adpaters.
|
||||
|
||||
[Fewshot-Metamath-OrcaVicuna-Mistral-10B](https://huggingface.co/abacusai/Fewshot-Metamath-OrcaVicuna-Mistral-10B) is an example of a model trained using this method on Mistral-7B expanded to 10B. The
|
||||
[adapter_config.json](https://huggingface.co/abacusai/Fewshot-Metamath-OrcaVicuna-Mistral-10B/blob/main/adapter_config.json) shows a sample LoRA adapter config applying this method for fine-tuning.
|
||||
|
||||
## Merge adapters
|
||||
|
||||
While LoRA is significantly smaller and faster to train, you may encounter latency issues during inference due to separately loading the base model and the LoRA adapter. To eliminate latency, use the [`~LoraModel.merge_and_unload`] function to merge the adapter weights with the base model. This allows you to use the newly merged model as a standalone model. The [`~LoraModel.merge_and_unload`] function doesn't keep the adapter weights in memory.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM
|
||||
from peft import PeftModel
|
||||
|
||||
base_model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("mistralai/Mistral-7B-v0.1")
|
||||
peft_model_id = "alignment-handbook/zephyr-7b-sft-lora"
|
||||
model = PeftModel.from_pretrained(base_model, peft_model_id)
|
||||
model.merge_and_unload()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you need to keep a copy of the weights so you can unmerge the adapter later or delete and load different ones, you should use the [`~LoraModel.merge_adapter`] function instead. Now you have the option to use [`~LoraModel.unmerge_adapter`] to return the base model.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM
|
||||
from peft import PeftModel
|
||||
|
||||
base_model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("mistralai/Mistral-7B-v0.1")
|
||||
peft_model_id = "alignment-handbook/zephyr-7b-sft-lora"
|
||||
model = PeftModel.from_pretrained(base_model, peft_model_id)
|
||||
model.merge_adapter()
|
||||
|
||||
# unmerge the LoRA layers from the base model
|
||||
model.unmerge_adapter()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The [`~LoraModel.add_weighted_adapter`] function is useful for merging multiple LoRAs into a new adapter based on a user provided weighting scheme in the `weights` parameter. Below is an end-to-end example.
|
||||
|
||||
First load the base model:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM
|
||||
from peft import PeftModel
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
base_model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"mistralai/Mistral-7B-v0.1", torch_dtype=torch.float16, device_map="auto"
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then we load the first adapter:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
peft_model_id = "alignment-handbook/zephyr-7b-sft-lora"
|
||||
model = PeftModel.from_pretrained(base_model, peft_model_id, adapter_name="sft")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then load a different adapter and merge it with the first one:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
weighted_adapter_name = "sft-dpo"
|
||||
model.load_adapter("alignment-handbook/zephyr-7b-dpo-lora", adapter_name="dpo")
|
||||
model.add_weighted_adapter(
|
||||
adapters=["sft", "dpo"],
|
||||
weights=[0.7, 0.3],
|
||||
adapter_name=weighted_adapter_name,
|
||||
combination_type="linear"
|
||||
)
|
||||
model.set_adapter(weighted_adapter_name)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
There are several supported methods for `combination_type`. Refer to the [documentation](../package_reference/lora#peft.LoraModel.add_weighted_adapter) for more details. Note that "svd" as the `combination_type` is not supported when using `torch.float16` or `torch.bfloat16` as the datatype.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Now, perform inference:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("mistralai/Mistral-7B-v0.1")
|
||||
|
||||
prompt = "Hey, are you conscious? Can you talk to me?"
|
||||
inputs = tokenizer(prompt, return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
inputs = {k: v.to("cuda") for k, v in inputs.items()}
|
||||
|
||||
with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
generate_ids = model.generate(**inputs, max_length=30)
|
||||
outputs = tokenizer.batch_decode(generate_ids, skip_special_tokens=True, clean_up_tokenization_spaces=False)[0]
|
||||
print(outputs)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Load adapters
|
||||
|
||||
Adapters can be loaded onto a pretrained model with [`~PeftModel.load_adapter`], which is useful for trying out different adapters whose weights aren't merged. Set the active adapter weights with the [`~LoraModel.set_adapter`] function.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM
|
||||
from peft import PeftModel
|
||||
|
||||
base_model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("mistralai/Mistral-7B-v0.1")
|
||||
peft_model_id = "alignment-handbook/zephyr-7b-sft-lora"
|
||||
model = PeftModel.from_pretrained(base_model, peft_model_id)
|
||||
|
||||
# load different adapter
|
||||
model.load_adapter("alignment-handbook/zephyr-7b-dpo-lora", adapter_name="dpo")
|
||||
|
||||
# set adapter as active
|
||||
model.set_adapter("dpo")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To return the base model, you could use [`~LoraModel.unload`] to unload all of the LoRA modules or [`~LoraModel.delete_adapter`] to delete the adapter entirely.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
# unload adapter
|
||||
model.unload()
|
||||
|
||||
# delete adapter
|
||||
model.delete_adapter("dpo")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Inference with different LoRA adapters in the same batch
|
||||
|
||||
Normally, each inference batch has to use the same adapter(s) in PEFT. This can sometimes be annoying, because we may have batches that contain samples intended to be used with different LoRA adapters. For example, we could have a base model that works well in English and two more LoRA adapters, one for French and one for German. Usually, we would have to split our batches such that each batch only contains samples of one of the languages, we cannot combine different languages in the same batch.
|
||||
|
||||
Thankfully, it is possible to mix different LoRA adapters in the same batch using the `adapter_name` argument. Below, we show an examle of how this works in practice. First, let's load the base model, English, and the two adapters, French and German, like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLM
|
||||
from peft import PeftModel
|
||||
|
||||
model_id = ...
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_id)
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_id)
|
||||
# load the LoRA adapter for French
|
||||
peft_model = PeftModel.from_pretrained(model, <path>, adapter_name="adapter_fr")
|
||||
# next, load the LoRA adapter for German
|
||||
peft_model.load_adapter(<path>, adapter_name="adapter_de")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now, we want to generate text on a sample that contains all three languages: The first three samples are in English, the next three are in French, and the last three are in German. We can use the `adapter_names` argument to specify which adapter to use for each sample. Since our base model is used for English, we use the special string `"__base__"` for these samples. For the next three samples, we indicate the adapter name of the French LoRA fine-tune, in this case `"adapter_fr"`. For the last three samples, we indicate the adapter name of the German LoRA fine-tune, in this case `"adapter_de"`. This way, we can use the base model and the two adapters in a single batch.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
inputs = tokenizer(
|
||||
[
|
||||
"Hello, my dog is cute",
|
||||
"Hello, my cat is awesome",
|
||||
"Hello, my fish is great",
|
||||
"Salut, mon chien est mignon",
|
||||
"Salut, mon chat est génial",
|
||||
"Salut, mon poisson est super",
|
||||
"Hallo, mein Hund ist süß",
|
||||
"Hallo, meine Katze ist toll",
|
||||
"Hallo, mein Fisch ist großartig",
|
||||
],
|
||||
return_tensors="pt",
|
||||
padding=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
adapter_names = [
|
||||
"__base__", "__base__", "__base__",
|
||||
"adapter_fr", "adapter_fr", "adapter_fr",
|
||||
"adapter_de", "adapter_de", "adapter_de",
|
||||
]
|
||||
output = peft_model.generate(**inputs, adapter_names=adapter_names, max_new_tokens=20)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Note that the order does not matter here, i.e. the samples in the batch don't need to be grouped by adapter as in the example above. We just need to ensure that the `adapter_names` argument is aligned correctly with the samples.
|
||||
|
||||
### Caveats
|
||||
|
||||
Using this features has some drawbacks, namely:
|
||||
|
||||
- It only works for inference, not for training.
|
||||
- Disabling adapters using the `with model.disable_adapter()` context takes precedence over `adapter_names`.
|
||||
- You cannot pass `adapter_names` when some adapter weights where merged with base weight using the `merge_adapter` method. Please unmerge all adapters first by calling `model.unmerge_adapter()`.
|
||||
- For obvious reasons, this cannot be used after calling `merge_and_unload()`, since all the LoRA adapters will be merged into the base weights in this case.
|
||||
- This feature does not currently work with DoRA, so set `use_dora=False` in your `LoraConfig` if you want to use it.
|
||||
- There is an expected overhead for inference with `adapter_names`, especially if the amount of different adapters in the batch is high. This is because the batch size is effectively reduced to the number of samples per adapter. If runtime performance is your top priority, try the following:
|
||||
- Increase the batch size.
|
||||
- Try to avoid having a large number of different adapters in the same batch, prefer homogeneous batches. This can be achieved by buffering samples with the same adapter and only perform inference with a small handfull of different adapters.
|
||||
- Take a look at alternative implementations such as [LoRAX](https://github.com/predibase/lorax), [punica](https://github.com/punica-ai/punica), or [S-LoRA](https://github.com/S-LoRA/S-LoRA), which are specialized to work with a large number of different adapters.
|
||||
97
docs/source/developer_guides/low_level_api.md
Normal file
97
docs/source/developer_guides/low_level_api.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,97 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Adapter injection
|
||||
|
||||
With PEFT, you can inject trainable adapters into any `torch` module which allows you to use adapter methods without relying on the modeling classes in PEFT. Currently, PEFT supports injecting [LoRA](../conceptual_guides/adapter#low-rank-adaptation-lora), [AdaLoRA](../conceptual_guides/adapter#adaptive-low-rank-adaptation-adalora), and [IA3](../conceptual_guides/ia3) into models because for these adapters, inplace modification of the model is sufficient for finetuning it.
|
||||
|
||||
Check the table below to see when you should inject adapters.
|
||||
|
||||
| Pros | Cons |
|
||||
|---|---|
|
||||
| the model is modified inplace, keeping all the original attributes and methods | manually write the `from_pretrained` and `save_pretrained` utility functions from Hugging Face to save and load adapters |
|
||||
| works for any `torch` module and modality | doesn't work with any of the utility methods provided by `PeftModel` such as disabling and merging adapters |
|
||||
|
||||
To perform the adapter injection, use the [`inject_adapter_in_model`] method. This method takes 3 arguments, the PEFT config, the model, and an optional adapter name. You can also attach multiple adapters to the model if you call [`inject_adapter_in_model`] multiple times with different adapter names.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, to inject LoRA adapters into the `linear` submodule of the `DummyModel` module:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from peft import inject_adapter_in_model, LoraConfig
|
||||
|
||||
class DummyModel(torch.nn.Module):
|
||||
def __init__(self):
|
||||
super().__init__()
|
||||
self.embedding = torch.nn.Embedding(10, 10)
|
||||
self.linear = torch.nn.Linear(10, 10)
|
||||
self.lm_head = torch.nn.Linear(10, 10)
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, input_ids):
|
||||
x = self.embedding(input_ids)
|
||||
x = self.linear(x)
|
||||
x = self.lm_head(x)
|
||||
return x
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
lora_config = LoraConfig(
|
||||
lora_alpha=16,
|
||||
lora_dropout=0.1,
|
||||
r=64,
|
||||
bias="none",
|
||||
target_modules=["linear"],
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
model = DummyModel()
|
||||
model = inject_adapter_in_model(lora_config, model)
|
||||
|
||||
dummy_inputs = torch.LongTensor([[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]])
|
||||
dummy_outputs = model(dummy_inputs)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Print the model to see that the adapters have been correctly injected.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
DummyModel(
|
||||
(embedding): Embedding(10, 10)
|
||||
(linear): Linear(
|
||||
in_features=10, out_features=10, bias=True
|
||||
(lora_dropout): ModuleDict(
|
||||
(default): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)
|
||||
)
|
||||
(lora_A): ModuleDict(
|
||||
(default): Linear(in_features=10, out_features=64, bias=False)
|
||||
)
|
||||
(lora_B): ModuleDict(
|
||||
(default): Linear(in_features=64, out_features=10, bias=False)
|
||||
)
|
||||
(lora_embedding_A): ParameterDict()
|
||||
(lora_embedding_B): ParameterDict()
|
||||
)
|
||||
(lm_head): Linear(in_features=10, out_features=10, bias=True)
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To only save the adapter, use the [`get_peft_model_state_dict`] function:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from peft import get_peft_model_state_dict
|
||||
|
||||
peft_state_dict = get_peft_model_state_dict(model)
|
||||
print(peft_state_dict)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Otherwise, `model.state_dict()` returns the full state dict of the model.
|
||||
37
docs/source/developer_guides/mixed_models.md
Normal file
37
docs/source/developer_guides/mixed_models.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Mixed adapter types
|
||||
|
||||
Normally, it isn't possible to mix different adapter types in 🤗 PEFT. You can create a PEFT model with two different LoRA adapters (which can have different config options), but it is not possible to combine a LoRA and LoHa adapter. With [`PeftMixedModel`] however, this works as long as the adapter types are compatible. The main purpose of allowing mixed adapter types is to combine trained adapters for inference. While it is possible to train a mixed adapter model, this has not been tested and is not recommended.
|
||||
|
||||
To load different adapter types into a PEFT model, use [`PeftMixedModel`] instead of [`PeftModel`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from peft import PeftMixedModel
|
||||
|
||||
base_model = ... # load the base model, e.g. from transformers
|
||||
# load first adapter, which will be called "default"
|
||||
peft_model = PeftMixedModel.from_pretrained(base_model, <path_to_adapter1>)
|
||||
peft_model.load_adapter(<path_to_adapter2>, adapter_name="other")
|
||||
peft_model.set_adapter(["default", "other"])
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The [`~PeftMixedModel.set_adapter`] method is necessary to activate both adapters, otherwise only the first adapter would be active. You can keep adding more adapters by calling [`~PeftModel.add_adapter`] repeatedly.
|
||||
|
||||
[`PeftMixedModel`] does not support saving and loading mixed adapters. The adapters should already be trained, and loading the model requires a script to be run each time.
|
||||
|
||||
## Tips
|
||||
|
||||
- Not all adapter types can be combined. See [`peft.tuners.mixed.COMPATIBLE_TUNER_TYPES`](https://github.com/huggingface/peft/blob/1c1c7fdaa6e6abaa53939b865dee1eded82ad032/src/peft/tuners/mixed/model.py#L35) for a list of compatible types. An error will be raised if you try to combine incompatible adapter types.
|
||||
- It is possible to mix multiple adapters of the same type which can be useful for combining adapters with very different configs.
|
||||
- If you want to combine a lot of different adapters, the most performant way to do it is to consecutively add the same adapter types. For example, add LoRA1, LoRA2, LoHa1, LoHa2 in this order, instead of LoRA1, LoHa1, LoRA2, and LoHa2. While the order can affect the output, there is no inherently *best* order, so it is best to choose the fastest one.
|
||||
140
docs/source/developer_guides/model_merging.md
Normal file
140
docs/source/developer_guides/model_merging.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,140 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Model merging
|
||||
|
||||
Training a model for each task can be costly, take up storage space, and the models aren't able to learn new information to improve their performance. Multitask learning can overcome some of these limitations by training a model to learn several tasks, but it is expensive to train and designing a dataset for it is challenging. *Model merging* offers a solution to these challenges by combining multiple pretrained models into one model, giving it the combined abilities of each individual model without any additional training.
|
||||
|
||||
PEFT provides several methods for merging models like a linear or SVD combination. This guide focuses on two methods that are more efficient for merging LoRA adapters by eliminating redundant parameters:
|
||||
|
||||
* [TIES](https://hf.co/papers/2306.01708) - TrIm, Elect, and Merge (TIES) is a three-step method for merging models. First, redundant parameters are trimmed, then conflicting signs are resolved into an aggregated vector, and finally the parameters whose signs are the same as the aggregate sign are averaged. This method takes into account that some values (redundant and sign disagreement) can degrade performance in the merged model.
|
||||
* [DARE](https://hf.co/papers/2311.03099) - Drop And REscale is a method that can be used to prepare for other model merging methods like TIES. It works by randomly dropping parameters according to a drop rate and rescaling the remaining parameters. This helps to reduce the number of redundant and potentially interfering parameters among multiple models.
|
||||
|
||||
Models are merged with the [`~LoraModel.add_weighted_adapter`] method, and the specific model merging method is specified in the `combination_type` parameter.
|
||||
|
||||
## Merge method
|
||||
|
||||
With TIES and DARE, merging is enabled by setting `combination_type` and `density` to a value of the weights to keep from the individual models. For example, let's merge three finetuned [TinyLlama/TinyLlama-1.1B-intermediate-step-1431k-3T](https://huggingface.co/TinyLlama/TinyLlama-1.1B-intermediate-step-1431k-3T) models: [tinyllama_lora_nobots](https://huggingface.co/smangrul/tinyllama_lora_norobots), [tinyllama_lora_sql](https://huggingface.co/smangrul/tinyllama_lora_sql), and [tinyllama_lora_adcopy](https://huggingface.co/smangrul/tinyllama_lora_adcopy).
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warninig={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
When you're attempting to merge fully trained models with TIES, you should be aware of any special tokens each model may have added to the embedding layer which are not a part of the original checkpoint's vocabulary. This may cause an issue because each model may have added a special token to the same embedding position. If this is the case, you should use the [`~transformers.PreTrainedModel.resize_token_embeddings`] method to avoid merging the special tokens at the same embedding index.
|
||||
|
||||
<br>
|
||||
|
||||
This shouldn't be an issue if you're only merging LoRA adapters trained from the same base model.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Load a base model and can use the [`~PeftModel.load_adapter`] method to load and assign each adapter a name:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from peft import PeftConfig, PeftModel
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
config = PeftConfig.from_pretrained("smangrul/tinyllama_lora_norobots")
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(config.base_model_name_or_path, load_in_4bit=True, device_map="auto").eval()
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("smangrul/tinyllama_lora_norobots")
|
||||
|
||||
model = PeftModel.from_pretrained(model, "smangrul/tinyllama_lora_norobots", adapter_name="norobots")
|
||||
_ = model.load_adapter("smangrul/tinyllama_lora_sql", adapter_name="sql")
|
||||
_ = model.load_adapter("smangrul/tinyllama_lora_adcopy", adapter_name="adcopy")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Set the adapters, weights, `adapter_name`, `combination_type`, and `density` with the [`~LoraModel.add_weighted_adapter`] method.
|
||||
|
||||
<hfoptions id="merge-method">
|
||||
<hfoption id="TIES">
|
||||
|
||||
Weight values greater than `1.0` typically produce better results because they preserve the correct scale. A good default starting value for the weights is to set all values to `1.0`.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
adapters = ["norobots", "adcopy", "sql"]
|
||||
weights = [2.0, 1.0, 1.0]
|
||||
adapter_name = "merge"
|
||||
density = 0.2
|
||||
model.add_weighted_adapter(adapters, weights, adapter_name, combination_type="ties", density=density)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="DARE">
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
adapters = ["norobots", "adcopy", "sql"]
|
||||
weights = [2.0, 0.3, 0.7]
|
||||
adapter_name = "merge"
|
||||
density = 0.2
|
||||
model.add_weighted_adapter(adapters, weights, adapter_name, combination_type="dare_ties", density=density)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
</hfoptions>
|
||||
|
||||
Set the newly merged model as the active model with the [`~LoraModel.set_adapter`] method.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
model.set_adapter("merge")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can use the merged model as an instruction-tuned model to write ad copy or SQL queries!
|
||||
|
||||
<hfoptions id="ties">
|
||||
<hfoption id="instruct">
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
messages = [
|
||||
{"role": "user", "content": "Write an essay about Generative AI."},
|
||||
]
|
||||
text = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(messages, add_generation_prompt=True, tokenize=False)
|
||||
inputs = tokenizer(text, return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
inputs = {k: v.to("cuda") for k, v in inputs.items()}
|
||||
outputs = model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=256, do_sample=True, top_p=0.95, temperature=0.2, repetition_penalty=1.2, eos_token_id=tokenizer.eos_token_id)
|
||||
print(tokenizer.decode(outputs[0]))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="ad copy">
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
messages = [
|
||||
{"role": "system", "content": "Create a text ad given the following product and description."},
|
||||
{"role": "user", "content": "Product: Sony PS5 PlayStation Console\nDescription: The PS5 console unleashes new gaming possibilities that you never anticipated."},
|
||||
]
|
||||
text = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(messages, add_generation_prompt=True, tokenize=False)
|
||||
inputs = tokenizer(text, return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
inputs = {k: v.to("cuda") for k, v in inputs.items()}
|
||||
outputs = model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=128, do_sample=True, top_p=0.95, temperature=0.2, repetition_penalty=1.2, eos_token_id=tokenizer.eos_token_id)
|
||||
print(tokenizer.decode(outputs[0]))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="SQL">
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
text = """Table: 2-11365528-2
|
||||
Columns: ['Team', 'Head Coach', 'President', 'Home Ground', 'Location']
|
||||
Natural Query: Who is the Head Coach of the team whose President is Mario Volarevic?
|
||||
SQL Query:"""
|
||||
|
||||
inputs = tokenizer(text, return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
inputs = {k: v.to("cuda") for k, v in inputs.items()}
|
||||
outputs = model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=64, repetition_penalty=1.1, eos_token_id=tokenizer("</s>").input_ids[-1])
|
||||
print(tokenizer.decode(outputs[0]))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
</hfoptions>
|
||||
136
docs/source/developer_guides/quantization.md
Normal file
136
docs/source/developer_guides/quantization.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,136 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Quantization
|
||||
|
||||
Quantization represents data with fewer bits, making it a useful technique for reducing memory-usage and accelerating inference especially when it comes to large language models (LLMs). There are several ways to quantize a model including:
|
||||
|
||||
* optimizing which model weights are quantized with the [AWQ](https://hf.co/papers/2306.00978) algorithm
|
||||
* independently quantizing each row of a weight matrix with the [GPTQ](https://hf.co/papers/2210.17323) algorithm
|
||||
* quantizing to 8-bit and 4-bit precision with the [bitsandbytes](https://github.com/TimDettmers/bitsandbytes) library
|
||||
* quantizing to as low as 2-bit precision with the [AQLM](https://arxiv.org/abs/2401.06118) algorithm
|
||||
|
||||
However, after a model is quantized it isn't typically further trained for downstream tasks because training can be unstable due to the lower precision of the weights and activations. But since PEFT methods only add *extra* trainable parameters, this allows you to train a quantized model with a PEFT adapter on top! Combining quantization with PEFT can be a good strategy for training even the largest models on a single GPU. For example, [QLoRA](https://hf.co/papers/2305.14314) is a method that quantizes a model to 4-bits and then trains it with LoRA. This method allows you to finetune a 65B parameter model on a single 48GB GPU!
|
||||
|
||||
In this guide, you'll see how to quantize a model to 4-bits and train it with LoRA.
|
||||
|
||||
## Quantize a model
|
||||
|
||||
[bitsandbytes](https://github.com/TimDettmers/bitsandbytes) is a quantization library with a Transformers integration. With this integration, you can quantize a model to 8 or 4-bits and enable many other options by configuring the [`~transformers.BitsAndBytesConfig`] class. For example, you can:
|
||||
|
||||
* set `load_in_4bit=True` to quantize the model to 4-bits when you load it
|
||||
* set `bnb_4bit_quant_type="nf4"` to use a special 4-bit data type for weights initialized from a normal distribution
|
||||
* set `bnb_4bit_use_double_quant=True` to use a nested quantization scheme to quantize the already quantized weights
|
||||
* set `bnb_4bit_compute_dtype=torch.bfloat16` to use bfloat16 for faster computation
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from transformers import BitsAndBytesConfig
|
||||
|
||||
config = BitsAndBytesConfig(
|
||||
load_in_4bit=True,
|
||||
bnb_4bit_quant_type="nf4",
|
||||
bnb_4bit_use_double_quant=True,
|
||||
bnb_4bit_compute_dtype=torch.bfloat16,
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Pass the `config` to the [`~transformers.AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained`] method.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("mistralai/Mistral-7B-v0.1", quantization_config=config)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Next, you should call the [`~peft.utils.prepare_model_for_kbit_training`] function to preprocess the quantized model for training.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from peft import prepare_model_for_kbit_training
|
||||
|
||||
model = prepare_model_for_kbit_training(model)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now that the quantized model is ready, let's set up a configuration.
|
||||
|
||||
## LoraConfig
|
||||
|
||||
Create a [`LoraConfig`] with the following parameters (or choose your own):
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from peft import LoraConfig
|
||||
|
||||
config = LoraConfig(
|
||||
r=16,
|
||||
lora_alpha=8,
|
||||
target_modules=["q_proj", "k_proj", "v_proj", "o_proj"],
|
||||
lora_dropout=0.05,
|
||||
bias="none",
|
||||
task_type="CAUSAL_LM"
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then use the [`get_peft_model`] function to create a [`PeftModel`] from the quantized model and configuration.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from peft import get_peft_model
|
||||
|
||||
model = get_peft_model(model, config)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You're all set for training with whichever training method you prefer!
|
||||
|
||||
### LoftQ initialization
|
||||
|
||||
[LoftQ](https://hf.co/papers/2310.08659) initializes LoRA weights such that the quantization error is minimized, and it can improve performance when training quantized models. To get started, follow [these instructions](https://github.com/huggingface/peft/tree/main/examples/loftq_finetuning).
|
||||
|
||||
In general, for LoftQ to work best, it is recommended to target as many layers with LoRA as possible, since those not targeted cannot have LoftQ applied. This means that passing `LoraConfig(..., target_modules="all-linear")` will most likely give the best results. Also, you should use `nf4` as quant type in your quantization config when using 4bit quantization, i.e. `BitsAndBytesConfig(load_in_4bit=True, bnb_4bit_quant_type="nf4")`.
|
||||
|
||||
### QLoRA-style training
|
||||
|
||||
QLoRA adds trainable weights to all the linear layers in the transformer architecture. Since the attribute names for these linear layers can vary across architectures, set `target_modules` to `"all-linear"` to add LoRA to all the linear layers:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
config = LoraConfig(target_modules="all-linear", ...)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## AQLM quantization
|
||||
|
||||
Additive Quantization of Language Models ([AQLM](https://arxiv.org/abs/2401.06118)) is a Large Language Models compression method. It quantizes multiple weights together and takes advantage of interdependencies between them. AQLM represents groups of 8-16 weights as a sum of multiple vector codes. This allows it to compress models down to as low as 2-bit with considerably low accuracy losses.
|
||||
|
||||
Since the AQLM quantization process is computationally expensive, a use of prequantized models is recommended. A partial list of available models can be found in the official aqlm [repository](https://github.com/Vahe1994/AQLM).
|
||||
|
||||
The models support LoRA adapter tuning. To tune the quantized model you'll need to install the `aqlm` inference library: `pip install aqlm>=1.0.2`. Finetuned LoRA adapters shall be saved separately, as merging them with AQLM quantized weights is not possible.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
quantized_model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"BlackSamorez/Mixtral-8x7b-AQLM-2Bit-1x16-hf-test-dispatch",
|
||||
torch_dtype="auto", device_map="auto", low_cpu_mem_usage=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
peft_config = LoraConfig(...)
|
||||
|
||||
quantized_model = get_peft_model(quantized_model, peft_config)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can refer to the [Google Colab](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/12GTp1FCj5_0SnnNQH18h_2XFh9vS_guX?usp=sharing) example for an overview of AQLM+LoRA finetuning.
|
||||
|
||||
## Next steps
|
||||
|
||||
If you're interested in learning more about quantization, the following may be helpful:
|
||||
|
||||
* Learn more about details about QLoRA and check out some benchmarks on its impact in the [Making LLMs even more accessible with bitsandbytes, 4-bit quantization and QLoRA](https://huggingface.co/blog/4bit-transformers-bitsandbytes) blog post.
|
||||
* Read more about different quantization schemes in the Transformers [Quantization](https://hf.co/docs/transformers/main/quantization) guide.
|
||||
137
docs/source/developer_guides/troubleshooting.md
Normal file
137
docs/source/developer_guides/troubleshooting.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,137 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Troubleshooting
|
||||
|
||||
If you encounter any issue when using PEFT, please check the following list of common issues and their solutions.
|
||||
|
||||
## Examples don't work
|
||||
|
||||
Examples often rely on the most recent package versions, so please ensure they're up-to-date. In particular, check the following package versions:
|
||||
|
||||
- `peft`
|
||||
- `transformers`
|
||||
- `accelerate`
|
||||
- `torch`
|
||||
|
||||
In general, you can update the package version by running this command inside your Python environment:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python -m pip install -U <package_name>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Installing PEFT from source is useful for keeping up with the latest developments:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python -m pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/peft
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## ValueError: Attempting to unscale FP16 gradients
|
||||
|
||||
This error probably occurred because the model was loaded with `torch_dtype=torch.float16` and then used in an automatic mixed precision (AMP) context, e.g. by setting `fp16=True` in the [`~transformers.Trainer`] class from 🤗 Transformers. The reason is that when using AMP, trainable weights should never use fp16. To make this work without loading the whole model in fp32, add the following to your code:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
peft_model = get_peft_model(...)
|
||||
|
||||
# add this:
|
||||
for param in model.parameters():
|
||||
if param.requires_grad:
|
||||
param.data = param.data.float()
|
||||
|
||||
# proceed as usual
|
||||
trainer = Trainer(model=peft_model, fp16=True, ...)
|
||||
trainer.train()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Alternatively, you can use the [`~utils.cast_mixed_precision_params`] function to correctly cast the weights:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from peft import cast_mixed_precision_params
|
||||
|
||||
peft_model = get_peft_model(...)
|
||||
cast_mixed_precision_params(peft_model, dtype=torch.float16)
|
||||
|
||||
# proceed as usual
|
||||
trainer = Trainer(model=peft_model, fp16=True, ...)
|
||||
trainer.train()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Bad results from a loaded PEFT model
|
||||
|
||||
There can be several reasons for getting a poor result from a loaded PEFT model which are listed below. If you're still unable to troubleshoot the problem, see if anyone else had a similar [issue](https://github.com/huggingface/peft/issues) on GitHub, and if you can't find any, open a new issue.
|
||||
|
||||
When opening an issue, it helps a lot if you provide a minimal code example that reproduces the issue. Also, please report if the loaded model performs at the same level as the model did before fine-tuning, if it performs at a random level, or if it is only slightly worse than expected. This information helps us identify the problem more quickly.
|
||||
|
||||
### Random deviations
|
||||
|
||||
If your model outputs are not exactly the same as previous runs, there could be an issue with random elements. For example:
|
||||
|
||||
1. please ensure it is in `.eval()` mode, which is important, for instance, if the model uses dropout
|
||||
2. if you use [`~transformers.GenerationMixin.generate`] on a language model, there could be random sampling, so obtaining the same result requires setting a random seed
|
||||
3. if you used quantization and merged the weights, small deviations are expected due to rounding errors
|
||||
|
||||
### Incorrectly loaded model
|
||||
|
||||
Please ensure that you load the model correctly. A common error is trying to load a _trained_ model with [`get_peft_model`] which is incorrect. Instead, the loading code should look like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from peft import PeftModel, PeftConfig
|
||||
|
||||
base_model = ... # to load the base model, use the same code as when you trained it
|
||||
config = PeftConfig.from_pretrained(peft_model_id)
|
||||
peft_model = PeftModel.from_pretrained(base_model, peft_model_id)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Randomly initialized layers
|
||||
|
||||
For some tasks, it is important to correctly configure `modules_to_save` in the config to account for randomly initialized layers.
|
||||
|
||||
As an example, this is necessary if you use LoRA to fine-tune a language model for sequence classification because 🤗 Transformers adds a randomly initialized classification head on top of the model. If you do not add this layer to `modules_to_save`, the classification head won't be saved. The next time you load the model, you'll get a _different_ randomly initialized classification head, resulting in completely different results.
|
||||
|
||||
PEFT tries to correctly guess the `modules_to_save` if you provide the `task_type` argument in the config. This should work for transformers models that follow the standard naming scheme. It is always a good idea to double check though because we can't guarantee all models follow the naming scheme.
|
||||
|
||||
When you load a transformers model that has randomly initialized layers, you should see a warning along the lines of:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Some weights of <MODEL> were not initialized from the model checkpoint at <ID> and are newly initialized: [<LAYER_NAMES>].
|
||||
You should probably TRAIN this model on a down-stream task to be able to use it for predictions and inference.
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The mentioned layers should be added to `modules_to_save` in the config to avoid the described problem.
|
||||
|
||||
### Extending the vocabulary
|
||||
|
||||
For many language fine-tuning tasks, extending the model's vocabulary is necessary since new tokens are being introduced. This requires extending the embedding layer to account for the new tokens and also storing the embedding layer in addition to the adapter weights when saving the adapter.
|
||||
|
||||
Save the embedding layer by adding it to the `target_modules` of the config. The embedding layer name must follow the standard naming scheme from Transformers. For example, the Mistral config could look like this:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
config = LoraConfig(..., target_modules=["embed_tokens", "lm_head", "q_proj", "v_proj"])
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Once added to `target_modules`, PEFT automatically stores the embedding layer when saving the adapter if the model has the [`~transformers.PreTrainedModel.get_input_embeddings`] and [`~transformers.PreTrainedModel.get_output_embeddings`]. This is generally the case for Transformers models.
|
||||
|
||||
If the model's embedding layer doesn't follow the Transformer's naming scheme, you can still save it by manually passing `save_embedding_layers=True` when saving the adapter:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
model = get_peft_model(...)
|
||||
# train the model
|
||||
model.save_adapter("my_adapter", save_embedding_layers=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For inference, load the base model first and resize it the same way you did before you trained the model. After you've resized the base model, you can load the PEFT checkpoint.
|
||||
|
||||
For a complete example, please check out [this notebook](https://github.com/huggingface/peft/blob/main/examples/causal_language_modeling/peft_lora_clm_with_additional_tokens.ipynb).
|
||||
49
docs/source/index.md
Normal file
49
docs/source/index.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,49 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# PEFT
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 PEFT (Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning) is a library for efficiently adapting large pretrained models to various downstream applications without fine-tuning all of a model's parameters because it is prohibitively costly. PEFT methods only fine-tune a small number of (extra) model parameters - significantly decreasing computational and storage costs - while yielding performance comparable to a fully fine-tuned model. This makes it more accessible to train and store large language models (LLMs) on consumer hardware.
|
||||
|
||||
PEFT is integrated with the Transformers, Diffusers, and Accelerate libraries to provide a faster and easier way to load, train, and use large models for inference.
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="mt-10">
|
||||
<div class="w-full flex flex-col space-y-4 md:space-y-0 md:grid md:grid-cols-2 md:gap-y-4 md:gap-x-5">
|
||||
<a class="!no-underline border dark:border-gray-700 p-5 rounded-lg shadow hover:shadow-lg" href="quicktour"
|
||||
><div class="w-full text-center bg-gradient-to-br from-blue-400 to-blue-500 rounded-lg py-1.5 font-semibold mb-5 text-white text-lg leading-relaxed">Get started</div>
|
||||
<p class="text-gray-700">Start here if you're new to 🤗 PEFT to get an overview of the library's main features, and how to train a model with a PEFT method.</p>
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a class="!no-underline border dark:border-gray-700 p-5 rounded-lg shadow hover:shadow-lg" href="./task_guides/image_classification_lora"
|
||||
><div class="w-full text-center bg-gradient-to-br from-indigo-400 to-indigo-500 rounded-lg py-1.5 font-semibold mb-5 text-white text-lg leading-relaxed">How-to guides</div>
|
||||
<p class="text-gray-700">Practical guides demonstrating how to apply various PEFT methods across different types of tasks like image classification, causal language modeling, automatic speech recognition, and more. Learn how to use 🤗 PEFT with the DeepSpeed and Fully Sharded Data Parallel scripts.</p>
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a class="!no-underline border dark:border-gray-700 p-5 rounded-lg shadow hover:shadow-lg" href="./conceptual_guides/lora"
|
||||
><div class="w-full text-center bg-gradient-to-br from-pink-400 to-pink-500 rounded-lg py-1.5 font-semibold mb-5 text-white text-lg leading-relaxed">Conceptual guides</div>
|
||||
<p class="text-gray-700">Get a better theoretical understanding of how LoRA and various soft prompting methods help reduce the number of trainable parameters to make training more efficient.</p>
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
<a class="!no-underline border dark:border-gray-700 p-5 rounded-lg shadow hover:shadow-lg" href="./package_reference/config"
|
||||
><div class="w-full text-center bg-gradient-to-br from-purple-400 to-purple-500 rounded-lg py-1.5 font-semibold mb-5 text-white text-lg leading-relaxed">Reference</div>
|
||||
<p class="text-gray-700">Technical descriptions of how 🤗 PEFT classes and methods work.</p>
|
||||
</a>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<iframe
|
||||
src="https://stevhliu-peft-methods.hf.space"
|
||||
frameborder="0"
|
||||
width="850"
|
||||
height="620"
|
||||
></iframe>
|
||||
47
docs/source/install.md
Normal file
47
docs/source/install.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,47 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Installation
|
||||
|
||||
Before you start, you will need to setup your environment, install the appropriate packages, and configure 🤗 PEFT. 🤗 PEFT is tested on **Python 3.8+**.
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 PEFT is available on PyPI, as well as GitHub:
|
||||
|
||||
## PyPI
|
||||
|
||||
To install 🤗 PEFT from PyPI:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install peft
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Source
|
||||
|
||||
New features that haven't been released yet are added every day, which also means there may be some bugs. To try them out, install from the GitHub repository:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/peft
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you're working on contributing to the library or wish to play with the source code and see live
|
||||
results as you run the code, an editable version can be installed from a locally-cloned version of the
|
||||
repository:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/huggingface/peft
|
||||
cd peft
|
||||
pip install -e .
|
||||
```
|
||||
31
docs/source/package_reference/adalora.md
Normal file
31
docs/source/package_reference/adalora.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# AdaLoRA
|
||||
|
||||
[AdaLoRA](https://hf.co/papers/2303.10512) is a method for optimizing the number of trainable parameters to assign to weight matrices and layers, unlike LoRA, which distributes parameters evenly across all modules. More parameters are budgeted for important weight matrices and layers while less important ones receive fewer parameters.
|
||||
|
||||
The abstract from the paper is:
|
||||
|
||||
*Fine-tuning large pre-trained language models on downstream tasks has become an important paradigm in NLP. However, common practice fine-tunes all of the parameters in a pre-trained model, which becomes prohibitive when a large number of downstream tasks are present. Therefore, many fine-tuning methods are proposed to learn incremental updates of pre-trained weights in a parameter efficient way, e.g., low-rank increments. These methods often evenly distribute the budget of incremental updates across all pre-trained weight matrices, and overlook the varying importance of different weight parameters. As a consequence, the fine-tuning performance is suboptimal. To bridge this gap, we propose AdaLoRA, which adaptively allocates the parameter budget among weight matrices according to their importance score. In particular, AdaLoRA parameterizes the incremental updates in the form of singular value decomposition. Such a novel approach allows us to effectively prune the singular values of unimportant updates, which is essentially to reduce their parameter budget but circumvent intensive exact SVD computations. We conduct extensive experiments with several pre-trained models on natural language processing, question answering, and natural language generation to validate the effectiveness of AdaLoRA. Results demonstrate that AdaLoRA manifests notable improvement over baselines, especially in the low budget settings. Our code is publicly available at https://github.com/QingruZhang/AdaLoRA*.
|
||||
|
||||
## AdaLoraConfig
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] tuners.adalora.config.AdaLoraConfig
|
||||
|
||||
## AdaLoraModel
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] tuners.adalora.model.AdaLoraModel
|
||||
31
docs/source/package_reference/adapter_utils.md
Normal file
31
docs/source/package_reference/adapter_utils.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# LyCORIS
|
||||
|
||||
[LyCORIS](https://hf.co/papers/2309.14859) (Lora beYond Conventional methods, Other Rank adaptation Implementations for Stable diffusion) are LoRA-like matrix decomposition adapters that modify the cross-attention layer of the UNet. The [LoHa](loha) and [LoKr](lokr) methods inherit from the `Lycoris` classes here.
|
||||
|
||||
## LycorisConfig
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] tuners.lycoris_utils.LycorisConfig
|
||||
|
||||
## LycorisLayer
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] tuners.lycoris_utils.LycorisLayer
|
||||
|
||||
## LycorisTuner
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] tuners.lycoris_utils.LycorisTuner
|
||||
48
docs/source/package_reference/auto_class.md
Normal file
48
docs/source/package_reference/auto_class.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,48 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# AutoPeftModels
|
||||
|
||||
The `AutoPeftModel` classes loads the appropriate PEFT model for the task type by automatically inferring it from the configuration file. They are designed to quickly and easily load a PEFT model in a single line of code without having to worry about which exact model class you need or manually loading a [`PeftConfig`].
|
||||
|
||||
## AutoPeftModel
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] auto.AutoPeftModel
|
||||
- from_pretrained
|
||||
|
||||
## AutoPeftModelForCausalLM
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] auto.AutoPeftModelForCausalLM
|
||||
|
||||
## AutoPeftModelForSeq2SeqLM
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] auto.AutoPeftModelForSeq2SeqLM
|
||||
|
||||
## AutoPeftModelForSequenceClassification
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] auto.AutoPeftModelForSequenceClassification
|
||||
|
||||
## AutoPeftModelForTokenClassification
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] auto.AutoPeftModelForTokenClassification
|
||||
|
||||
## AutoPeftModelForQuestionAnswering
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] auto.AutoPeftModelForQuestionAnswering
|
||||
|
||||
## AutoPeftModelForFeatureExtraction
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] auto.AutoPeftModelForFeatureExtraction
|
||||
22
docs/source/package_reference/config.md
Normal file
22
docs/source/package_reference/config.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,22 @@
|
||||
<!--⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Configuration
|
||||
|
||||
[`PeftConfigMixin`] is the base configuration class for storing the adapter configuration of a [`PeftModel`], and [`PromptLearningConfig`] is the base configuration class for soft prompt methods (p-tuning, prefix tuning, and prompt tuning). These base classes contain methods for saving and loading model configurations from the Hub, specifying the PEFT method to use, type of task to perform, and model configurations like number of layers and number of attention heads.
|
||||
|
||||
## PeftConfigMixin
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] config.PeftConfigMixin
|
||||
- all
|
||||
|
||||
## PeftConfig
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] PeftConfig
|
||||
- all
|
||||
|
||||
## PromptLearningConfig
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] PromptLearningConfig
|
||||
- all
|
||||
31
docs/source/package_reference/ia3.md
Normal file
31
docs/source/package_reference/ia3.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# IA3
|
||||
|
||||
Infused Adapter by Inhibiting and Amplifying Inner Activations, or [IA3](https://hf.co/papers/2205.05638), is a method that adds three learned vectors to rescale the keys and values of the self-attention and encoder-decoder attention layers, and the intermediate activation of the position-wise feed-forward network.
|
||||
|
||||
The abstract from the paper is:
|
||||
|
||||
*Few-shot in-context learning (ICL) enables pre-trained language models to perform a previously-unseen task without any gradient-based training by feeding a small number of training examples as part of the input. ICL incurs substantial computational, memory, and storage costs because it involves processing all of the training examples every time a prediction is made. Parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) (e.g. adapter modules, prompt tuning, sparse update methods, etc.) offers an alternative paradigm where a small set of parameters are trained to enable a model to perform the new task. In this paper, we rigorously compare few-shot ICL and PEFT and demonstrate that the latter offers better accuracy as well as dramatically lower computational costs. Along the way, we introduce a new PEFT method called (IA)^3 that scales activations by learned vectors, attaining stronger performance while only introducing a relatively tiny amount of new parameters. We also propose a simple recipe based on the T0 model called T-Few that can be applied to new tasks without task-specific tuning or modifications. We validate the effectiveness of T-Few on completely unseen tasks by applying it to the RAFT benchmark, attaining super-human performance for the first time and outperforming the state-of-the-art by 6% absolute. All of the code used in our experiments is publicly available*.
|
||||
|
||||
## IA3Config
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] tuners.ia3.config.IA3Config
|
||||
|
||||
## IA3Model
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] tuners.ia3.model.IA3Model
|
||||
31
docs/source/package_reference/llama_adapter.md
Normal file
31
docs/source/package_reference/llama_adapter.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Llama-Adapter
|
||||
|
||||
[Llama-Adapter](https://hf.co/papers/2303.16199) is a PEFT method specifically designed for turning Llama into an instruction-following model. The Llama model is frozen and only a set of adaptation prompts prefixed to the input instruction tokens are learned. Since randomly initialized modules inserted into the model can cause the model to lose some of its existing knowledge, Llama-Adapter uses zero-initialized attention with zero gating to progressively add the instructional prompts to the model.
|
||||
|
||||
The abstract from the paper is:
|
||||
|
||||
*We present LLaMA-Adapter, a lightweight adaption method to efficiently fine-tune LLaMA into an instruction-following model. Using 52K self-instruct demonstrations, LLaMA-Adapter only introduces 1.2M learnable parameters upon the frozen LLaMA 7B model, and costs less than one hour for fine-tuning on 8 A100 GPUs. Specifically, we adopt a set of learnable adaption prompts, and prepend them to the input text tokens at higher transformer layers. Then, a zero-init attention mechanism with zero gating is proposed, which adaptively injects the new instructional cues into LLaMA, while effectively preserves its pre-trained knowledge. With efficient training, LLaMA-Adapter generates high-quality responses, comparable to Alpaca with fully fine-tuned 7B parameters. Furthermore, our approach can be simply extended to multi-modal input, e.g., images, for image-conditioned LLaMA, which achieves superior reasoning capacity on ScienceQA. We release our code at https://github.com/ZrrSkywalker/LLaMA-Adapter*.
|
||||
|
||||
## AdaptionPromptConfig
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] tuners.adaption_prompt.config.AdaptionPromptConfig
|
||||
|
||||
## AdaptionPromptModel
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] tuners.adaption_prompt.model.AdaptionPromptModel
|
||||
31
docs/source/package_reference/loha.md
Normal file
31
docs/source/package_reference/loha.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# LoHa
|
||||
|
||||
Low-Rank Hadamard Product ([LoHa](https://huggingface.co/papers/2108.06098)), is similar to LoRA except it approximates the large weight matrix with more low-rank matrices and combines them with the Hadamard product. This method is even more parameter-efficient than LoRA and achieves comparable performance.
|
||||
|
||||
The abstract from the paper is:
|
||||
|
||||
*In this work, we propose a communication-efficient parameterization, FedPara, for federated learning (FL) to overcome the burdens on frequent model uploads and downloads. Our method re-parameterizes weight parameters of layers using low-rank weights followed by the Hadamard product. Compared to the conventional low-rank parameterization, our FedPara method is not restricted to low-rank constraints, and thereby it has a far larger capacity. This property enables to achieve comparable performance while requiring 3 to 10 times lower communication costs than the model with the original layers, which is not achievable by the traditional low-rank methods. The efficiency of our method can be further improved by combining with other efficient FL optimizers. In addition, we extend our method to a personalized FL application, pFedPara, which separates parameters into global and local ones. We show that pFedPara outperforms competing personalized FL methods with more than three times fewer parameters*.
|
||||
|
||||
## LoHaConfig
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] tuners.loha.config.LoHaConfig
|
||||
|
||||
## LoHaModel
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] tuners.loha.model.LoHaModel
|
||||
27
docs/source/package_reference/lokr.md
Normal file
27
docs/source/package_reference/lokr.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# LoKr
|
||||
|
||||
Low-Rank Kronecker Product ([LoKr](https://hf.co/papers/2309.14859)), is a LoRA-variant method that approximates the large weight matrix with two low-rank matrices and combines them with the Kronecker product. LoKr also provides an optional third low-rank matrix to provide better control during fine-tuning.
|
||||
|
||||
## LoKrConfig
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] tuners.lokr.config.LoKrConfig
|
||||
|
||||
## LoKrModel
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] tuners.lokr.model.LoKrModel
|
||||
35
docs/source/package_reference/lora.md
Normal file
35
docs/source/package_reference/lora.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# LoRA
|
||||
|
||||
Low-Rank Adaptation ([LoRA](https://huggingface.co/papers/2309.15223)) is a PEFT method that decomposes a large matrix into two smaller low-rank matrices in the attention layers. This drastically reduces the number of parameters that need to be fine-tuned.
|
||||
|
||||
The abstract from the paper is:
|
||||
|
||||
*We propose a neural language modeling system based on low-rank adaptation (LoRA) for speech recognition output rescoring. Although pretrained language models (LMs) like BERT have shown superior performance in second-pass rescoring, the high computational cost of scaling up the pretraining stage and adapting the pretrained models to specific domains limit their practical use in rescoring. Here we present a method based on low-rank decomposition to train a rescoring BERT model and adapt it to new domains using only a fraction (0.08%) of the pretrained parameters. These inserted matrices are optimized through a discriminative training objective along with a correlation-based regularization loss. The proposed low-rank adaptation Rescore-BERT (LoRB) architecture is evaluated on LibriSpeech and internal datasets with decreased training times by factors between 5.4 and 3.6.*.
|
||||
|
||||
## LoraConfig
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] tuners.lora.config.LoraConfig
|
||||
|
||||
## LoraModel
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] tuners.lora.model.LoraModel
|
||||
|
||||
## Utility
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.loftq_utils.replace_lora_weights_loftq
|
||||
33
docs/source/package_reference/merge_utils.md
Normal file
33
docs/source/package_reference/merge_utils.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Model merge
|
||||
|
||||
PEFT provides several internal utilities for [merging LoRA adapters](../developer_guides/model_merging) with the TIES and DARE methods.
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.merge_utils.prune
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.merge_utils.calculate_majority_sign_mask
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.merge_utils.disjoint_merge
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.merge_utils.task_arithmetic
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.merge_utils.ties
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.merge_utils.dare_linear
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.merge_utils.dare_ties
|
||||
31
docs/source/package_reference/multitask_prompt_tuning.md
Normal file
31
docs/source/package_reference/multitask_prompt_tuning.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Multitask prompt tuning
|
||||
|
||||
[Multitask prompt tuning](https://huggingface.co/papers/2303.02861) decomposes the soft prompts of each task into a single learned transferable prompt instead of a separate prompt for each task. The single learned prompt can be adapted for each task by multiplicative low rank updates.
|
||||
|
||||
The abstract from the paper is:
|
||||
|
||||
*Prompt tuning, in which a base pretrained model is adapted to each task via conditioning on learned prompt vectors, has emerged as a promising approach for efficiently adapting large language models to multiple downstream tasks. However, existing methods typically learn soft prompt vectors from scratch, and it has not been clear how to exploit the rich cross-task knowledge with prompt vectors in a multitask learning setting. We propose multitask prompt tuning (MPT), which first learns a single transferable prompt by distilling knowledge from multiple task-specific source prompts. We then learn multiplicative low rank updates to this shared prompt to efficiently adapt it to each downstream target task. Extensive experiments on 23 NLP datasets demonstrate that our proposed approach outperforms the state-of-the-art methods, including the full finetuning baseline in some cases, despite only tuning 0.035% as many task-specific parameters*.
|
||||
|
||||
## MultitaskPromptTuningConfig
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] tuners.multitask_prompt_tuning.config.MultitaskPromptTuningConfig
|
||||
|
||||
## MultitaskPromptEmbedding
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] tuners.multitask_prompt_tuning.model.MultitaskPromptEmbedding
|
||||
31
docs/source/package_reference/oft.md
Normal file
31
docs/source/package_reference/oft.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# OFT
|
||||
|
||||
[Orthogonal Finetuning (OFT)](https://hf.co/papers/2306.07280) is a method developed for adapting text-to-image diffusion models. It works by reparameterizing the pretrained weight matrices with it's orthogonal matrix to preserve information in the pretrained model. To reduce the number of parameters, OFT introduces a block-diagonal structure in the orthogonal matrix.
|
||||
|
||||
The abstract from the paper is:
|
||||
|
||||
*Large text-to-image diffusion models have impressive capabilities in generating photorealistic images from text prompts. How to effectively guide or control these powerful models to perform different downstream tasks becomes an important open problem. To tackle this challenge, we introduce a principled finetuning method -- Orthogonal Finetuning (OFT), for adapting text-to-image diffusion models to downstream tasks. Unlike existing methods, OFT can provably preserve hyperspherical energy which characterizes the pairwise neuron relationship on the unit hypersphere. We find that this property is crucial for preserving the semantic generation ability of text-to-image diffusion models. To improve finetuning stability, we further propose Constrained Orthogonal Finetuning (COFT) which imposes an additional radius constraint to the hypersphere. Specifically, we consider two important finetuning text-to-image tasks: subject-driven generation where the goal is to generate subject-specific images given a few images of a subject and a text prompt, and controllable generation where the goal is to enable the model to take in additional control signals. We empirically show that our OFT framework outperforms existing methods in generation quality and convergence speed*.
|
||||
|
||||
## OFTConfig
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] tuners.oft.config.OFTConfig
|
||||
|
||||
## OFTModel
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] tuners.oft.model.OFTModel
|
||||
31
docs/source/package_reference/p_tuning.md
Normal file
31
docs/source/package_reference/p_tuning.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# P-tuning
|
||||
|
||||
[P-tuning](https://hf.co/papers/2103.10385) adds trainable prompt embeddings to the input that is optimized by a prompt encoder to find a better prompt, eliminating the need to manually design prompts. The prompt tokens can be added anywhere in the input sequence, and p-tuning also introduces anchor tokens for improving performance.
|
||||
|
||||
The abstract from the paper is:
|
||||
|
||||
*While GPTs with traditional fine-tuning fail to achieve strong results on natural language understanding (NLU), we show that GPTs can be better than or comparable to similar-sized BERTs on NLU tasks with a novel method P-tuning -- which employs trainable continuous prompt embeddings. On the knowledge probing (LAMA) benchmark, the best GPT recovers 64\% (P@1) of world knowledge without any additional text provided during test time, which substantially improves the previous best by 20+ percentage points. On the SuperGlue benchmark, GPTs achieve comparable and sometimes better performance to similar-sized BERTs in supervised learning. Importantly, we find that P-tuning also improves BERTs' performance in both few-shot and supervised settings while largely reducing the need for prompt engineering. Consequently, P-tuning outperforms the state-of-the-art approaches on the few-shot SuperGlue benchmark.*.
|
||||
|
||||
## PromptEncoderConfig
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] tuners.p_tuning.config.PromptEncoderConfig
|
||||
|
||||
## PromptEncoder
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] tuners.p_tuning.model.PromptEncoder
|
||||
73
docs/source/package_reference/peft_model.md
Normal file
73
docs/source/package_reference/peft_model.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,73 @@
|
||||
<!--⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Models
|
||||
|
||||
[`PeftModel`] is the base model class for specifying the base Transformer model and configuration to apply a PEFT method to. The base `PeftModel` contains methods for loading and saving models from the Hub.
|
||||
|
||||
## PeftModel
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] PeftModel
|
||||
- all
|
||||
|
||||
## PeftModelForSequenceClassification
|
||||
|
||||
A `PeftModel` for sequence classification tasks.
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] PeftModelForSequenceClassification
|
||||
- all
|
||||
|
||||
## PeftModelForTokenClassification
|
||||
|
||||
A `PeftModel` for token classification tasks.
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] PeftModelForTokenClassification
|
||||
- all
|
||||
|
||||
## PeftModelForCausalLM
|
||||
|
||||
A `PeftModel` for causal language modeling.
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] PeftModelForCausalLM
|
||||
- all
|
||||
|
||||
## PeftModelForSeq2SeqLM
|
||||
|
||||
A `PeftModel` for sequence-to-sequence language modeling.
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] PeftModelForSeq2SeqLM
|
||||
- all
|
||||
|
||||
## PeftModelForQuestionAnswering
|
||||
|
||||
A `PeftModel` for question answering.
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] PeftModelForQuestionAnswering
|
||||
- all
|
||||
|
||||
## PeftModelForFeatureExtraction
|
||||
|
||||
A `PeftModel` for getting extracting features/embeddings from transformer models.
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] PeftModelForFeatureExtraction
|
||||
- all
|
||||
|
||||
## PeftMixedModel
|
||||
|
||||
A `PeftModel` for mixing different adapter types (e.g. LoRA and LoHa).
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] PeftMixedModel
|
||||
- all
|
||||
|
||||
## Utilities
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.cast_mixed_precision_params
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] get_peft_model
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] inject_adapter_in_model
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.get_peft_model_state_dict
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.prepare_model_for_kbit_training
|
||||
27
docs/source/package_reference/peft_types.md
Normal file
27
docs/source/package_reference/peft_types.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# PEFT types
|
||||
|
||||
[`PeftType`] includes the supported adapters in PEFT, and [`TaskType`] includes PEFT-supported tasks.
|
||||
|
||||
## PeftType
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.peft_types.PeftType
|
||||
|
||||
## TaskType
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.peft_types.TaskType
|
||||
44
docs/source/package_reference/poly.md
Normal file
44
docs/source/package_reference/poly.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,44 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Polytropon
|
||||
|
||||
[Polytropon](https://hf.co/papers/2202.13914) is a multitask model with a number of different LoRA adapters in it's "inventory". The model learns the correct combination of adapters from the inventory with a routing function to choose the best subset of modules for a specific task. PEFT also supports [Multi-Head Adapter Routing (MHR)](https://hf.co/papers/2211.03831) for Polytropon which builds on and improves the routing function by combining the adapter heads more granularly. The adapter heads are separated into disjoint blocks and a different routing function is learned for each one, allowing for more expressivity.
|
||||
|
||||
<hfoptions id="paper">
|
||||
<hfoption id="Combining Modular Skills in Multitask Learning">
|
||||
|
||||
The abstract from the paper is:
|
||||
|
||||
*A modular design encourages neural models to disentangle and recombine different facets of knowledge to generalise more systematically to new tasks. In this work, we assume that each task is associated with a subset of latent discrete skills from a (potentially small) inventory. In turn, skills correspond to parameter-efficient (sparse / low-rank) model parameterisations. By jointly learning these and a task-skill allocation matrix, the network for each task is instantiated as the average of the parameters of active skills. To favour non-trivial soft partitions of skills across tasks, we experiment with a series of inductive biases, such as an Indian Buffet Process prior and a two-speed learning rate. We evaluate our latent-skill model on two main settings: 1) multitask reinforcement learning for grounded instruction following on 8 levels of the BabyAI platform; and 2) few-shot adaptation of pre-trained text-to-text generative models on CrossFit, a benchmark comprising 160 NLP tasks. We find that the modular design of a network significantly increases sample efficiency in reinforcement learning and few-shot generalisation in supervised learning, compared to baselines with fully shared, task-specific, or conditionally generated parameters where knowledge is entangled across tasks. In addition, we show how discrete skills help interpretability, as they yield an explicit hierarchy of tasks.*
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="Multi-Head Adapter Routing for Cross-Task Generalization">
|
||||
|
||||
The abstract from the paper is:
|
||||
|
||||
*Parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) for cross-task generalization consists in pre-training adapters on a multi-task training set before few-shot adaptation to test tasks. Polytropon [Ponti et al., 2023] (Poly) jointly learns an inventory of adapters and a routing function that selects a (variable-size) subset of adapters for each task during both pre-training and few-shot adaptation. In this paper, we investigate the role that adapter routing plays in its success and design new variants based on our findings. First, we build on the intuition that finer-grained routing provides more expressivity. Hence, we propose MHR (Multi-Head Routing), which combines subsets of adapter parameters and outperforms Poly under a comparable parameter budget; by only fine-tuning the routing function and not the adapters (MHR-z), we achieve competitive performance with extreme parameter efficiency. Second, we find that Poly/MHR performance is a result of better multi-task optimization, rather than modular inductive biases that facilitate adapter recombination and local adaptation, as previously hypothesized. In fact, we find that MHR exhibits higher gradient alignment between tasks than any other method. Since this implies that routing is only crucial during multi-task pre-training, we propose MHR-mu, which discards routing and fine-tunes the average of the pre-trained adapters during few-shot adaptation. This establishes MHR-mu as an effective method for single-adapter fine-tuning.*.
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
</hfoptions>
|
||||
|
||||
## PolyConfig
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] tuners.poly.config.PolyConfig
|
||||
|
||||
## PolyModel
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] tuners.poly.model.PolyModel
|
||||
31
docs/source/package_reference/prefix_tuning.md
Normal file
31
docs/source/package_reference/prefix_tuning.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Prefix tuning
|
||||
|
||||
[Prefix tuning](https://hf.co/papers/2101.00190) prefixes a series of task-specific vectors to the input sequence that can be learned while keeping the pretrained model frozen. The prefix parameters are inserted in all of the model layers.
|
||||
|
||||
The abstract from the paper is:
|
||||
|
||||
*Fine-tuning is the de facto way to leverage large pretrained language models to perform downstream tasks. However, it modifies all the language model parameters and therefore necessitates storing a full copy for each task. In this paper, we propose prefix-tuning, a lightweight alternative to fine-tuning for natural language generation tasks, which keeps language model parameters frozen, but optimizes a small continuous task-specific vector (called the prefix). Prefix-tuning draws inspiration from prompting, allowing subsequent tokens to attend to this prefix as if it were "virtual tokens". We apply prefix-tuning to GPT-2 for table-to-text generation and to BART for summarization. We find that by learning only 0.1\% of the parameters, prefix-tuning obtains comparable performance in the full data setting, outperforms fine-tuning in low-data settings, and extrapolates better to examples with topics unseen during training*.
|
||||
|
||||
## PrefixTuningConfig
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] tuners.prefix_tuning.config.PrefixTuningConfig
|
||||
|
||||
## PrefixEncoder
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] tuners.prefix_tuning.model.PrefixEncoder
|
||||
31
docs/source/package_reference/prompt_tuning.md
Normal file
31
docs/source/package_reference/prompt_tuning.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Prompt tuning
|
||||
|
||||
[Prompt tuning](https://hf.co/papers/2104.08691) adds task-specific prompts to the input, and these prompt parameters are updated independently of the pretrained model parameters which are frozen.
|
||||
|
||||
The abstract from the paper is:
|
||||
|
||||
*In this work, we explore "prompt tuning", a simple yet effective mechanism for learning "soft prompts" to condition frozen language models to perform specific downstream tasks. Unlike the discrete text prompts used by GPT-3, soft prompts are learned through backpropagation and can be tuned to incorporate signal from any number of labeled examples. Our end-to-end learned approach outperforms GPT-3's "few-shot" learning by a large margin. More remarkably, through ablations on model size using T5, we show that prompt tuning becomes more competitive with scale: as models exceed billions of parameters, our method "closes the gap" and matches the strong performance of model tuning (where all model weights are tuned). This finding is especially relevant in that large models are costly to share and serve, and the ability to reuse one frozen model for multiple downstream tasks can ease this burden. Our method can be seen as a simplification of the recently proposed "prefix tuning" of Li and Liang (2021), and we provide a comparison to this and other similar approaches. Finally, we show that conditioning a frozen model with soft prompts confers benefits in robustness to domain transfer, as compared to full model tuning*.
|
||||
|
||||
## PromptTuningConfig
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] tuners.prompt_tuning.config.PromptTuningConfig
|
||||
|
||||
## PromptEmbedding
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] tuners.prompt_tuning.model.PromptEmbedding
|
||||
27
docs/source/package_reference/tuners.md
Normal file
27
docs/source/package_reference/tuners.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Tuners
|
||||
|
||||
A tuner (or adapter) is a module that can be plugged into a `torch.nn.Module`. [`BaseTuner`] base class for other tuners and provides shared methods and attributes for preparing an adapter configuration and replacing a target module with the adapter module. [`BaseTunerLayer`] is a base class for adapter layers. It offers methods and attributes for managing adapters such as activating and disabling adapters.
|
||||
|
||||
## BaseTuner
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] tuners.tuners_utils.BaseTuner
|
||||
|
||||
## BaseTunerLayer
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] tuners.tuners_utils.BaseTunerLayer
|
||||
170
docs/source/quicktour.md
Normal file
170
docs/source/quicktour.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,170 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Quicktour
|
||||
|
||||
PEFT offers parameter-efficient methods for finetuning large pretrained models. The traditional paradigm is to finetune all of a model's parameters for each downstream task, but this is becoming exceedingly costly and impractical because of the enormous number of parameters in models today. Instead, it is more efficient to train a smaller number of prompt parameters or use a reparametrization method like low-rank adaptation (LoRA) to reduce the number of trainable parameters.
|
||||
|
||||
This quicktour will show you PEFT's main features and how you can train or run inference on large models that would typically be inaccessible on consumer devices.
|
||||
|
||||
## Train
|
||||
|
||||
Each PEFT method is defined by a [`PeftConfig`] class that stores all the important parameters for building a [`PeftModel`]. For example, to train with LoRA, load and create a [`LoraConfig`] class and specify the following parameters:
|
||||
|
||||
- `task_type`: the task to train for (sequence-to-sequence language modeling in this case)
|
||||
- `inference_mode`: whether you're using the model for inference or not
|
||||
- `r`: the dimension of the low-rank matrices
|
||||
- `lora_alpha`: the scaling factor for the low-rank matrices
|
||||
- `lora_dropout`: the dropout probability of the LoRA layers
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from peft import LoraConfig, TaskType
|
||||
|
||||
peft_config = LoraConfig(task_type=TaskType.SEQ_2_SEQ_LM, inference_mode=False, r=8, lora_alpha=32, lora_dropout=0.1)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
See the [`LoraConfig`] reference for more details about other parameters you can adjust, such as the modules to target or the bias type.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Once the [`LoraConfig`] is setup, create a [`PeftModel`] with the [`get_peft_model`] function. It takes a base model - which you can load from the Transformers library - and the [`LoraConfig`] containing the parameters for how to configure a model for training with LoRA.
|
||||
|
||||
Load the base model you want to finetune.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained("bigscience/mt0-large")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Wrap the base model and `peft_config` with the [`get_peft_model`] function to create a [`PeftModel`]. To get a sense of the number of trainable parameters in your model, use the [`print_trainable_parameters`] method.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from peft import get_peft_model
|
||||
|
||||
model = get_peft_model(model, peft_config)
|
||||
model.print_trainable_parameters()
|
||||
"output: trainable params: 2359296 || all params: 1231940608 || trainable%: 0.19151053100118282"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Out of [bigscience/mt0-large's](https://huggingface.co/bigscience/mt0-large) 1.2B parameters, you're only training 0.19% of them!
|
||||
|
||||
That is it 🎉! Now you can train the model with the Transformers [`~transformers.Trainer`], Accelerate, or any custom PyTorch training loop.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, to train with the [`~transformers.Trainer`] class, setup a [`~transformers.TrainingArguments`] class with some training hyperparameters.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
training_args = TrainingArguments(
|
||||
output_dir="your-name/bigscience/mt0-large-lora",
|
||||
learning_rate=1e-3,
|
||||
per_device_train_batch_size=32,
|
||||
per_device_eval_batch_size=32,
|
||||
num_train_epochs=2,
|
||||
weight_decay=0.01,
|
||||
evaluation_strategy="epoch",
|
||||
save_strategy="epoch",
|
||||
load_best_model_at_end=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Pass the model, training arguments, dataset, tokenizer, and any other necessary component to the [`~transformers.Trainer`], and call [`~transformers.Trainer.train`] to start training.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
trainer = Trainer(
|
||||
model=model,
|
||||
args=training_args,
|
||||
train_dataset=tokenized_datasets["train"],
|
||||
eval_dataset=tokenized_datasets["test"],
|
||||
tokenizer=tokenizer,
|
||||
data_collator=data_collator,
|
||||
compute_metrics=compute_metrics,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
trainer.train()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Save model
|
||||
|
||||
After your model is finished training, you can save your model to a directory using the [`~transformers.PreTrainedModel.save_pretrained`] function.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
model.save_pretrained("output_dir")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can also save your model to the Hub (make sure you're logged in to your Hugging Face account first) with the [`~transformers.PreTrainedModel.push_to_hub`] function.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from huggingface_hub import notebook_login
|
||||
|
||||
notebook_login()
|
||||
model.push_to_hub("your-name/bigscience/mt0-large-lora")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Both methods only save the extra PEFT weights that were trained, meaning it is super efficient to store, transfer, and load. For example, this [facebook/opt-350m](https://huggingface.co/ybelkada/opt-350m-lora) model trained with LoRA only contains two files: `adapter_config.json` and `adapter_model.safetensors`. The `adapter_model.safetensors` file is just 6.3MB!
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex flex-col justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/peft/PEFT-hub-screenshot.png"/>
|
||||
<figcaption class="text-center">The adapter weights for a opt-350m model stored on the Hub are only ~6MB compared to the full size of the model weights, which can be ~700MB.</figcaption>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
## Inference
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Take a look at the [AutoPeftModel](package_reference/auto_class) API reference for a complete list of available `AutoPeftModel` classes.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Easily load any PEFT-trained model for inference with the [`AutoPeftModel`] class and the [`~transformers.PreTrainedModel.from_pretrained`] method:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from peft import AutoPeftModelForCausalLM
|
||||
from transformers import AutoTokenizer
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoPeftModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("ybelkada/opt-350m-lora")
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("facebook/opt-350m")
|
||||
|
||||
model = model.to("cuda")
|
||||
model.eval()
|
||||
inputs = tokenizer("Preheat the oven to 350 degrees and place the cookie dough", return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
|
||||
outputs = model.generate(input_ids=inputs["input_ids"].to("cuda"), max_new_tokens=50)
|
||||
print(tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs.detach().cpu().numpy(), skip_special_tokens=True)[0])
|
||||
|
||||
"Preheat the oven to 350 degrees and place the cookie dough in the center of the oven. In a large bowl, combine the flour, baking powder, baking soda, salt, and cinnamon. In a separate bowl, combine the egg yolks, sugar, and vanilla."
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For other tasks that aren't explicitly supported with an `AutoPeftModelFor` class - such as automatic speech recognition - you can still use the base [`AutoPeftModel`] class to load a model for the task.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from peft import AutoPeftModel
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoPeftModel.from_pretrained("smangrul/openai-whisper-large-v2-LORA-colab")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Next steps
|
||||
|
||||
Now that you've seen how to train a model with one of the PEFT methods, we encourage you to try out some of the other methods like prompt tuning. The steps are very similar to the ones shown in the quicktour:
|
||||
|
||||
1. prepare a [`PeftConfig`] for a PEFT method
|
||||
2. use the [`get_peft_model`] method to create a [`PeftModel`] from the configuration and base model
|
||||
|
||||
Then you can train it however you like! To load a PEFT model for inference, you can use the [`AutoPeftModel`] class.
|
||||
|
||||
Feel free to also take a look at the task guides if you're interested in training a model with another PEFT method for a specific task such as semantic segmentation, multilingual automatic speech recognition, DreamBooth, token classification, and more.
|
||||
239
docs/source/task_guides/ia3.md
Normal file
239
docs/source/task_guides/ia3.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,239 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# IA3
|
||||
|
||||
[IA3](../conceptual_guides/ia3) multiplies the model's activations (the keys and values in the self-attention and encoder-decoder attention blocks, and the intermediate activation of the position-wise feedforward network) by three learned vectors. This PEFT method introduces an even smaller number of trainable parameters than LoRA which introduces weight matrices instead of vectors. The original model's parameters are kept frozen and only these vectors are updated. As a result, it is faster, cheaper and more efficient to finetune for a new downstream task.
|
||||
|
||||
This guide will show you how to train a sequence-to-sequence model with IA3 to *generate a sentiment* given some financial news.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Some familiarity with the general process of training a sequence-to-sequence would be really helpful and allow you to focus on how to apply IA3. If you’re new, we recommend taking a look at the [Translation](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/tasks/translation) and [Summarization](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/tasks/summarization) guides first from the Transformers documentation. When you’re ready, come back and see how easy it is to drop PEFT in to your training!
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## Dataset
|
||||
|
||||
You'll use the sentences_allagree subset of the [financial_phrasebank](https://huggingface.co/datasets/financial_phrasebank) dataset. This subset contains financial news with 100% annotator agreement on the sentiment label. Take a look at the [dataset viewer](https://huggingface.co/datasets/financial_phrasebank/viewer/sentences_allagree) for a better idea of the data and sentences you'll be working with.
|
||||
|
||||
Load the dataset with the [`~datasets.load_dataset`] function. This subset of the dataset only contains a train split, so use the [`~datasets.train_test_split`] function to create a train and validation split. Create a new `text_label` column so it is easier to understand what the `label` values `0`, `1`, and `2` mean.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
|
||||
ds = load_dataset("financial_phrasebank", "sentences_allagree")
|
||||
ds = ds["train"].train_test_split(test_size=0.1)
|
||||
ds["validation"] = ds["test"]
|
||||
del ds["test"]
|
||||
|
||||
classes = ds["train"].features["label"].names
|
||||
ds = ds.map(
|
||||
lambda x: {"text_label": [classes[label] for label in x["label"]]},
|
||||
batched=True,
|
||||
num_proc=1,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
ds["train"][0]
|
||||
{'sentence': 'It will be operated by Nokia , and supported by its Nokia NetAct network and service management system .',
|
||||
'label': 1,
|
||||
'text_label': 'neutral'}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Load a tokenizer and create a preprocessing function that:
|
||||
|
||||
1. tokenizes the inputs, pads and truncates the sequence to the `max_length`
|
||||
2. apply the same tokenizer to the labels but with a shorter `max_length` that corresponds to the label
|
||||
3. mask the padding tokens
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import AutoTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
text_column = "sentence"
|
||||
label_column = "text_label"
|
||||
max_length = 128
|
||||
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("bigscience/mt0-large")
|
||||
|
||||
def preprocess_function(examples):
|
||||
inputs = examples[text_column]
|
||||
targets = examples[label_column]
|
||||
model_inputs = tokenizer(inputs, max_length=max_length, padding="max_length", truncation=True, return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
labels = tokenizer(targets, max_length=3, padding="max_length", truncation=True, return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
labels = labels["input_ids"]
|
||||
labels[labels == tokenizer.pad_token_id] = -100
|
||||
model_inputs["labels"] = labels
|
||||
return model_inputs
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Use the [`~datasets.Dataset.map`] function to apply the preprocessing function to the entire dataset.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
processed_ds = ds.map(
|
||||
preprocess_function,
|
||||
batched=True,
|
||||
num_proc=1,
|
||||
remove_columns=ds["train"].column_names,
|
||||
load_from_cache_file=False,
|
||||
desc="Running tokenizer on dataset",
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Create a training and evaluation [`DataLoader`](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/data.html#torch.utils.data.DataLoader), and set `pin_memory=True` to speed up data transfer to the GPU during training if your dataset samples are on a CPU.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
|
||||
from transformers import default_data_collator
|
||||
|
||||
train_ds = processed_ds["train"]
|
||||
eval_ds = processed_ds["validation"]
|
||||
|
||||
batch_size = 8
|
||||
|
||||
train_dataloader = DataLoader(
|
||||
train_ds, shuffle=True, collate_fn=default_data_collator, batch_size=batch_size, pin_memory=True
|
||||
)
|
||||
eval_dataloader = DataLoader(eval_ds, collate_fn=default_data_collator, batch_size=batch_size, pin_memory=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Model
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can load a pretrained model to use as the base model for IA3. This guide uses the [bigscience/mt0-large](https://huggingface.co/bigscience/mt0-large) model, but you can use any sequence-to-sequence model you like.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained("bigscience/mt0-large")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### PEFT configuration and model
|
||||
|
||||
All PEFT methods need a configuration that contains and specifies all the parameters for how the PEFT method should be applied. Create an [`IA3Config`] with the task type and set the inference mode to `False`. You can find additional parameters for this configuration in the [API reference](../package_reference/ia3#ia3config).
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Call the [`~PeftModel.print_trainable_parameters`] method to compare the number of trainable parameters of [`PeftModel`] versus the number of parameters in the base model!
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Once the configuration is setup, pass it to the [`get_peft_model`] function along with the base model to create a trainable [`PeftModel`].
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from peft import IA3Config, get_peft_model
|
||||
|
||||
peft_config = IA3Config(task_type="SEQ_2_SEQ_LM")
|
||||
model = get_peft_model(model, peft_config)
|
||||
model.print_trainable_parameters()
|
||||
"trainable params: 282,624 || all params: 1,229,863,936 || trainable%: 0.022980103060766553"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Training
|
||||
|
||||
Set up an optimizer and learning rate scheduler.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from transformers import get_linear_schedule_with_warmup
|
||||
|
||||
lr = 8e-3
|
||||
num_epochs = 3
|
||||
|
||||
optimizer = torch.optim.AdamW(model.parameters(), lr=lr)
|
||||
lr_scheduler = get_linear_schedule_with_warmup(
|
||||
optimizer=optimizer,
|
||||
num_warmup_steps=0,
|
||||
num_training_steps=(len(train_dataloader) * num_epochs),
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Move the model to the GPU and create a training loop that reports the loss and perplexity for each epoch.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from tqdm import tqdm
|
||||
|
||||
device = "cuda"
|
||||
model = model.to(device)
|
||||
|
||||
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
|
||||
model.train()
|
||||
total_loss = 0
|
||||
for step, batch in enumerate(tqdm(train_dataloader)):
|
||||
batch = {k: v.to(device) for k, v in batch.items()}
|
||||
outputs = model(**batch)
|
||||
loss = outputs.loss
|
||||
total_loss += loss.detach().float()
|
||||
loss.backward()
|
||||
optimizer.step()
|
||||
lr_scheduler.step()
|
||||
optimizer.zero_grad()
|
||||
|
||||
model.eval()
|
||||
eval_loss = 0
|
||||
eval_preds = []
|
||||
for step, batch in enumerate(tqdm(eval_dataloader)):
|
||||
batch = {k: v.to(device) for k, v in batch.items()}
|
||||
with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
outputs = model(**batch)
|
||||
loss = outputs.loss
|
||||
eval_loss += loss.detach().float()
|
||||
eval_preds.extend(
|
||||
tokenizer.batch_decode(torch.argmax(outputs.logits, -1).detach().cpu().numpy(), skip_special_tokens=True)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
eval_epoch_loss = eval_loss / len(eval_dataloader)
|
||||
eval_ppl = torch.exp(eval_epoch_loss)
|
||||
train_epoch_loss = total_loss / len(train_dataloader)
|
||||
train_ppl = torch.exp(train_epoch_loss)
|
||||
print(f"{epoch=}: {train_ppl=} {train_epoch_loss=} {eval_ppl=} {eval_epoch_loss=}")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Share your model
|
||||
|
||||
After training is complete, you can upload your model to the Hub with the [`~transformers.PreTrainedModel.push_to_hub`] method. You'll need to login to your Hugging Face account first and enter your token when prompted.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from huggingface_hub import notebook_login
|
||||
|
||||
account = <your-hf-account-name>
|
||||
peft_model_id = f"{account}/mt0-large-ia3"
|
||||
model.push_to_hub(peft_model_id)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Inference
|
||||
|
||||
To load the model for inference, use the [`~AutoPeftModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained`] method. Let's also load a sentence of financial news from the dataset to generate a sentiment for.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from peft import AutoPeftModelForSeq2SeqLM
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoPeftModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained("<your-hf-account-name>/mt0-large-ia3").to("cuda")
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("bigscience/mt0-large")
|
||||
|
||||
i = 15
|
||||
inputs = tokenizer(ds["validation"][text_column][i], return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
print(ds["validation"][text_column][i])
|
||||
"The robust growth was the result of the inclusion of clothing chain Lindex in the Group in December 2007 ."
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Call the [`~transformers.GenerationMixin.generate`] method to generate the predicted sentiment label.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
inputs = {k: v.to(device) for k, v in inputs.items()}
|
||||
outputs = model.generate(input_ids=inputs["input_ids"], max_new_tokens=10)
|
||||
print(tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs.detach().cpu().numpy(), skip_special_tokens=True))
|
||||
['positive']
|
||||
```
|
||||
348
docs/source/task_guides/lora_based_methods.md
Normal file
348
docs/source/task_guides/lora_based_methods.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,348 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# LoRA methods
|
||||
|
||||
A popular way to efficiently train large models is to insert (typically in the attention blocks) smaller trainable matrices that are a low-rank decomposition of the delta weight matrix to be learnt during finetuning. The pretrained model's original weight matrix is frozen and only the smaller matrices are updated during training. This reduces the number of trainable parameters, reducing memory usage and training time which can be very expensive for large models.
|
||||
|
||||
There are several different ways to express the weight matrix as a low-rank decomposition, but [Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA)](../conceptual_guides/adapter#low-rank-adaptation-lora) is the most common method. The PEFT library supports several other LoRA variants, such as [Low-Rank Hadamard Product (LoHa)](../conceptual_guides/adapter#low-rank-hadamard-product-loha), [Low-Rank Kronecker Product (LoKr)](../conceptual_guides/adapter#low-rank-kronecker-product-lokr), and [Adaptive Low-Rank Adaptation (AdaLoRA)](../conceptual_guides/adapter#adaptive-low-rank-adaptation-adalora). You can learn more about how these methods work conceptually in the [Adapters](../conceptual_guides/adapter) guide. If you're interested in applying these methods to other tasks and use cases like semantic segmentation, token classification, take a look at our [notebook collection](https://huggingface.co/collections/PEFT/notebooks-6573b28b33e5a4bf5b157fc1)!
|
||||
|
||||
This guide will show you how to quickly train an image classification model - with a low-rank decomposition method - to identify the class of food shown in an image.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Some familiarity with the general process of training an image classification model would be really helpful and allow you to focus on the low-rank decomposition methods. If you're new, we recommend taking a look at the [Image classification](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/tasks/image_classification) guide first from the Transformers documentation. When you're ready, come back and see how easy it is to drop PEFT in to your training!
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Before you begin, make sure you have all the necessary libraries installed.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install -q peft transformers datasets
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Dataset
|
||||
|
||||
In this guide, you'll use the [Food-101](https://huggingface.co/datasets/food101) dataset which contains images of 101 food classes (take a look at the [dataset viewer](https://huggingface.co/datasets/food101/viewer/default/train) to get a better idea of what the dataset looks like).
|
||||
|
||||
Load the dataset with the [`~datasets.load_dataset`] function.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
|
||||
ds = load_dataset("food101")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Each food class is labeled with an integer, so to make it easier to understand what these integers represent, you'll create a `label2id` and `id2label` dictionary to map the integer to its class label.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
labels = ds["train"].features["label"].names
|
||||
label2id, id2label = dict(), dict()
|
||||
for i, label in enumerate(labels):
|
||||
label2id[label] = i
|
||||
id2label[i] = label
|
||||
|
||||
id2label[2]
|
||||
"baklava"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Load an image processor to properly resize and normalize the pixel values of the training and evaluation images.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import AutoImageProcessor
|
||||
|
||||
image_processor = AutoImageProcessor.from_pretrained("google/vit-base-patch16-224-in21k")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can also use the image processor to prepare some transformation functions for data augmentation and pixel scaling.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from torchvision.transforms import (
|
||||
CenterCrop,
|
||||
Compose,
|
||||
Normalize,
|
||||
RandomHorizontalFlip,
|
||||
RandomResizedCrop,
|
||||
Resize,
|
||||
ToTensor,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
normalize = Normalize(mean=image_processor.image_mean, std=image_processor.image_std)
|
||||
train_transforms = Compose(
|
||||
[
|
||||
RandomResizedCrop(image_processor.size["height"]),
|
||||
RandomHorizontalFlip(),
|
||||
ToTensor(),
|
||||
normalize,
|
||||
]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
val_transforms = Compose(
|
||||
[
|
||||
Resize(image_processor.size["height"]),
|
||||
CenterCrop(image_processor.size["height"]),
|
||||
ToTensor(),
|
||||
normalize,
|
||||
]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def preprocess_train(example_batch):
|
||||
example_batch["pixel_values"] = [train_transforms(image.convert("RGB")) for image in example_batch["image"]]
|
||||
return example_batch
|
||||
|
||||
def preprocess_val(example_batch):
|
||||
example_batch["pixel_values"] = [val_transforms(image.convert("RGB")) for image in example_batch["image"]]
|
||||
return example_batch
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Define the training and validation datasets, and use the [`~datasets.Dataset.set_transform`] function to apply the transformations on-the-fly.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
train_ds = ds["train"]
|
||||
val_ds = ds["validation"]
|
||||
|
||||
train_ds.set_transform(preprocess_train)
|
||||
val_ds.set_transform(preprocess_val)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, you'll need a data collator to create a batch of training and evaluation data and convert the labels to `torch.tensor` objects.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
def collate_fn(examples):
|
||||
pixel_values = torch.stack([example["pixel_values"] for example in examples])
|
||||
labels = torch.tensor([example["label"] for example in examples])
|
||||
return {"pixel_values": pixel_values, "labels": labels}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Model
|
||||
|
||||
Now let's load a pretrained model to use as the base model. This guide uses the [google/vit-base-patch16-224-in21k](https://huggingface.co/google/vit-base-patch16-224-in21k) model, but you can use any image classification model you want. Pass the `label2id` and `id2label` dictionaries to the model so it knows how to map the integer labels to their class labels, and you can optionally pass the `ignore_mismatched_sizes=True` parameter if you're finetuning a checkpoint that has already been finetuned.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForImageClassification, TrainingArguments, Trainer
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModelForImageClassification.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"google/vit-base-patch16-224-in21k",
|
||||
label2id=label2id,
|
||||
id2label=id2label,
|
||||
ignore_mismatched_sizes=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### PEFT configuration and model
|
||||
|
||||
Every PEFT method requires a configuration that holds all the parameters specifying how the PEFT method should be applied. Once the configuration is setup, pass it to the [`~peft.get_peft_model`] function along with the base model to create a trainable [`PeftModel`].
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Call the [`~PeftModel.print_trainable_parameters`] method to compare the number of parameters of [`PeftModel`] versus the number of parameters in the base model!
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
<hfoptions id="loras">
|
||||
<hfoption id="LoRA">
|
||||
|
||||
[LoRA](../conceptual_guides/adapter#low-rank-adaptation-lora) decomposes the weight update matrix into *two* smaller matrices. The size of these low-rank matrices is determined by its *rank* or `r`. A higher rank means the model has more parameters to train, but it also means the model has more learning capacity. You'll also want to specify the `target_modules` which determine where the smaller matrices are inserted. For this guide, you'll target the *query* and *value* matrices of the attention blocks. Other important parameters to set are `lora_alpha` (scaling factor), `bias` (whether `none`, `all` or only the LoRA bias parameters should be trained), and `modules_to_save` (the modules apart from the LoRA layers to be trained and saved). All of these parameters - and more - are found in the [`LoraConfig`].
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from peft import LoraConfig, get_peft_model
|
||||
|
||||
config = LoraConfig(
|
||||
r=16,
|
||||
lora_alpha=16,
|
||||
target_modules=["query", "value"],
|
||||
lora_dropout=0.1,
|
||||
bias="none",
|
||||
modules_to_save=["classifier"],
|
||||
)
|
||||
model = get_peft_model(model, config)
|
||||
model.print_trainable_parameters()
|
||||
"trainable params: 667,493 || all params: 86,543,818 || trainable%: 0.7712775047664294"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="LoHa">
|
||||
|
||||
[LoHa](../conceptual_guides/adapter#low-rank-hadamard-product-loha) decomposes the weight update matrix into *four* smaller matrices and each pair of smaller matrices is combined with the Hadamard product. This allows the weight update matrix to keep the same number of trainable parameters when compared to LoRA, but with a higher rank (`r^2` for LoHA when compared to `2*r` for LoRA). The size of the smaller matrices is determined by its *rank* or `r`. You'll also want to specify the `target_modules` which determines where the smaller matrices are inserted. For this guide, you'll target the *query* and *value* matrices of the attention blocks. Other important parameters to set are `alpha` (scaling factor), and `modules_to_save` (the modules apart from the LoHa layers to be trained and saved). All of these parameters - and more - are found in the [`LoHaConfig`].
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from peft import LoHaConfig, get_peft_model
|
||||
|
||||
config = LoHaConfig(
|
||||
r=16,
|
||||
alpha=16,
|
||||
target_modules=["query", "value"],
|
||||
module_dropout=0.1,
|
||||
modules_to_save=["classifier"],
|
||||
)
|
||||
model = get_peft_model(model, config)
|
||||
model.print_trainable_parameters()
|
||||
"trainable params: 1,257,317 || all params: 87,133,642 || trainable%: 1.4429753779831676"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="LoKr">
|
||||
|
||||
[LoKr](../conceptual_guides/adapter#low-rank-kronecker-product-lokr) expresses the weight update matrix as a decomposition of a Kronecker product, creating a block matrix that is able to preserve the rank of the original weight matrix. The size of the smaller matrices are determined by its *rank* or `r`. You'll also want to specify the `target_modules` which determines where the smaller matrices are inserted. For this guide, you'll target the *query* and *value* matrices of the attention blocks. Other important parameters to set are `alpha` (scaling factor), and `modules_to_save` (the modules apart from the LoKr layers to be trained and saved). All of these parameters - and more - are found in the [`LoKrConfig`].
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from peft import LoKrConfig, get_peft_model
|
||||
|
||||
config = LoKrConfig(
|
||||
r=16,
|
||||
alpha=16,
|
||||
target_modules=["query", "value"],
|
||||
module_dropout=0.1,
|
||||
modules_to_save=["classifier"],
|
||||
)
|
||||
model = get_peft_model(model, config)
|
||||
model.print_trainable_parameters()
|
||||
"trainable params: 116,069 || all params: 87,172,042 || trainable%: 0.13314934162033282"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="AdaLoRA">
|
||||
|
||||
[AdaLoRA](../conceptual_guides/adapter#adaptive-low-rank-adaptation-adalora) efficiently manages the LoRA parameter budget by assigning important weight matrices more parameters and pruning less important ones. In contrast, LoRA evenly distributes parameters across all modules. You can control the average desired *rank* or `r` of the matrices, and which modules to apply AdaLoRA to with `target_modules`. Other important parameters to set are `lora_alpha` (scaling factor), and `modules_to_save` (the modules apart from the AdaLoRA layers to be trained and saved). All of these parameters - and more - are found in the [`AdaLoraConfig`].
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from peft import AdaLoraConfig, get_peft_model
|
||||
|
||||
config = AdaLoraConfig(
|
||||
r=8,
|
||||
init_r=12,
|
||||
tinit=200,
|
||||
tfinal=1000,
|
||||
deltaT=10,
|
||||
target_modules=["query", "value"],
|
||||
modules_to_save=["classifier"],
|
||||
)
|
||||
model = get_peft_model(model, config)
|
||||
model.print_trainable_parameters()
|
||||
"trainable params: 520,325 || all params: 87,614,722 || trainable%: 0.5938785036606062"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
</hfoptions>
|
||||
|
||||
### Training
|
||||
|
||||
For training, let's use the [`~transformers.Trainer`] class from Transformers. The [`Trainer`] contains a PyTorch training loop, and when you're ready, call [`~transformers.Trainer.train`] to start training. To customize the training run, configure the training hyperparameters in the [`~transformers.TrainingArguments`] class. With LoRA-like methods, you can afford to use a higher batch size and learning rate.
|
||||
|
||||
> [!WARNING]
|
||||
> AdaLoRA has an [`~AdaLoraModel.update_and_allocate`] method that should be called at each training step to update the parameter budget and mask, otherwise the adaptation step is not performed. This requires writing a custom training loop or subclassing the [`~transformers.Trainer`] to incorporate this method. As an example, take a look at this [custom training loop](https://github.com/huggingface/peft/blob/912ad41e96e03652cabf47522cd876076f7a0c4f/examples/conditional_generation/peft_adalora_seq2seq.py#L120).
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import TrainingArguments, Trainer
|
||||
|
||||
account = "stevhliu"
|
||||
peft_model_id = f"{account}/google/vit-base-patch16-224-in21k-lora"
|
||||
batch_size = 128
|
||||
|
||||
args = TrainingArguments(
|
||||
peft_model_id,
|
||||
remove_unused_columns=False,
|
||||
evaluation_strategy="epoch",
|
||||
save_strategy="epoch",
|
||||
learning_rate=5e-3,
|
||||
per_device_train_batch_size=batch_size,
|
||||
gradient_accumulation_steps=4,
|
||||
per_device_eval_batch_size=batch_size,
|
||||
fp16=True,
|
||||
num_train_epochs=5,
|
||||
logging_steps=10,
|
||||
load_best_model_at_end=True,
|
||||
label_names=["labels"],
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Begin training with [`~transformers.Trainer.train`].
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
trainer = Trainer(
|
||||
model,
|
||||
args,
|
||||
train_dataset=train_ds,
|
||||
eval_dataset=val_ds,
|
||||
tokenizer=image_processor,
|
||||
data_collator=collate_fn,
|
||||
)
|
||||
trainer.train()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Share your model
|
||||
|
||||
Once training is complete, you can upload your model to the Hub with the [`~transformers.PreTrainedModel.push_to_hub`] method. You’ll need to login to your Hugging Face account first and enter your token when prompted.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from huggingface_hub import notebook_login
|
||||
|
||||
notebook_login()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Call [`~transformers.PreTrainedModel.push_to_hub`] to save your model to your repositoy.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
model.push_to_hub(peft_model_id)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Inference
|
||||
|
||||
Let's load the model from the Hub and test it out on a food image.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from peft import PeftConfig, PeftModel
|
||||
from transfomers import AutoImageProcessor
|
||||
from PIL import Image
|
||||
import requests
|
||||
|
||||
config = PeftConfig.from_pretrained("stevhliu/vit-base-patch16-224-in21k-lora")
|
||||
model = AutoModelForImageClassification.from_pretrained(
|
||||
config.base_model_name_or_path,
|
||||
label2id=label2id,
|
||||
id2label=id2label,
|
||||
ignore_mismatched_sizes=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
model = PeftModel.from_pretrained(model, "stevhliu/vit-base-patch16-224-in21k-lora")
|
||||
|
||||
url = "https://huggingface.co/datasets/sayakpaul/sample-datasets/resolve/main/beignets.jpeg"
|
||||
image = Image.open(requests.get(url, stream=True).raw)
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/sayakpaul/sample-datasets/resolve/main/beignets.jpeg">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
Convert the image to RGB and return the underlying PyTorch tensors.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
encoding = image_processor(image.convert("RGB"), return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now run the model and return the predicted class!
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
outputs = model(**encoding)
|
||||
logits = outputs.logits
|
||||
|
||||
predicted_class_idx = logits.argmax(-1).item()
|
||||
print("Predicted class:", model.config.id2label[predicted_class_idx])
|
||||
"Predicted class: beignets"
|
||||
```
|
||||
305
docs/source/task_guides/prompt_based_methods.md
Normal file
305
docs/source/task_guides/prompt_based_methods.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,305 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Prompt-based methods
|
||||
|
||||
A prompt can describe a task or provide an example of a task you want the model to learn. Instead of manually creating these prompts, soft prompting methods add learnable parameters to the input embeddings that can be optimized for a specific task while keeping the pretrained model's parameters frozen. This makes it both faster and easier to finetune large language models (LLMs) for new downstream tasks.
|
||||
|
||||
The PEFT library supports several types of prompting methods (p-tuning, prefix tuning, prompt tuning) and you can learn more about how these methods work conceptually in the [Soft prompts](../conceptual_guides/prompting) guide. If you're interested in applying these methods to other tasks and use cases, take a look at our [notebook collection](https://huggingface.co/spaces/PEFT/soft-prompting)!
|
||||
|
||||
This guide will show you how to train a causal language model - with a soft prompting method - to *generate a classification* for whether a tweet is a complaint or not.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Some familiarity with the general process of training a causal language model would be really helpful and allow you to focus on the soft prompting methods. If you're new, we recommend taking a look at the [Causal language modeling](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/tasks/language_modeling) guide first from the Transformers documentation. When you're ready, come back and see how easy it is to drop PEFT in to your training!
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Before you begin, make sure you have all the necessary libraries installed.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install -q peft transformers datasets
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Dataset
|
||||
|
||||
For this guide, you'll use the `twitter_complaints` subset of the [RAFT](https://huggingface.co/datasets/ought/raft) dataset. The `twitter_complaints` subset contains tweets labeled as `complaint` and `no complaint` and you can check out the [dataset viewer](https://huggingface.co/datasets/ought/raft/viewer/twitter_complaints) for a better idea of what the data looks like.
|
||||
|
||||
Use the [`~datasets.load_dataset`] function to load the dataset and create a new `text_label` column so it is easier to understand what the `Label` values, `1` and `2` mean.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
|
||||
ds = load_dataset("ought/raft", "twitter_complaints")
|
||||
|
||||
classes = [k.replace("_", " ") for k in ds["train"].features["Label"].names]
|
||||
ds = ds.map(
|
||||
lambda x: {"text_label": [classes[label] for label in x["Label"]]},
|
||||
batched=True,
|
||||
num_proc=1,
|
||||
)
|
||||
ds["train"][0]
|
||||
{"Tweet text": "@HMRCcustomers No this is my first job", "ID": 0, "Label": 2, "text_label": "no complaint"}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Load a tokenizer, define the padding token to use, and determine the maximum length of the tokenized label.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import AutoTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("bigscience/bloomz-560m")
|
||||
if tokenizer.pad_token_id is None:
|
||||
tokenizer.pad_token_id = tokenizer.eos_token_id
|
||||
target_max_length = max([len(tokenizer(class_label)["input_ids"]) for class_label in classes])
|
||||
print(target_max_length)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Create a preprocessing function that tokenizes the tweet text and labels, pad the inputs and labels in each batch, create an attention mask, and truncate sequences to the `max_length`. Then convert the `input_ids`, `attention_mask`, and `labels` to PyTorch tensors.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
max_length = 64
|
||||
|
||||
def preprocess_function(examples, text_column="Tweet text", label_column="text_label"):
|
||||
batch_size = len(examples[text_column])
|
||||
inputs = [f"{text_column} : {x} Label : " for x in examples[text_column]]
|
||||
targets = [str(x) for x in examples[label_column]]
|
||||
model_inputs = tokenizer(inputs)
|
||||
labels = tokenizer(targets)
|
||||
classes = [k.replace("_", " ") for k in ds["train"].features["Label"].names]
|
||||
for i in range(batch_size):
|
||||
sample_input_ids = model_inputs["input_ids"][i]
|
||||
label_input_ids = labels["input_ids"][i]
|
||||
model_inputs["input_ids"][i] = [tokenizer.pad_token_id] * (
|
||||
max_length - len(sample_input_ids)
|
||||
) + sample_input_ids
|
||||
model_inputs["attention_mask"][i] = [0] * (max_length - len(sample_input_ids)) + model_inputs[
|
||||
"attention_mask"
|
||||
][i]
|
||||
labels["input_ids"][i] = [-100] * (max_length - len(sample_input_ids)) + label_input_ids
|
||||
model_inputs["input_ids"][i] = torch.tensor(model_inputs["input_ids"][i][:max_length])
|
||||
model_inputs["attention_mask"][i] = torch.tensor(model_inputs["attention_mask"][i][:max_length])
|
||||
labels["input_ids"][i] = torch.tensor(labels["input_ids"][i][:max_length])
|
||||
model_inputs["labels"] = labels["input_ids"]
|
||||
return model_inputs
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Apply the preprocessing function to the entire dataset with the [`~datasets.Dataset.map`] function, and remove the unprocessed columns because the model won't need them.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
processed_ds = ds.map(
|
||||
preprocess_function,
|
||||
batched=True,
|
||||
num_proc=1,
|
||||
remove_columns=ds["train"].column_names,
|
||||
load_from_cache_file=False,
|
||||
desc="Running tokenizer on dataset",
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, create a training and evaluation [`DataLoader`](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/data.html#torch.utils.data.DataLoader). You can set `pin_memory=True` to speed up the data transfer to the GPU during training if the samples in your dataset are on a CPU.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
|
||||
from transformers import default_data_collator
|
||||
|
||||
train_ds = processed_ds["train"]
|
||||
eval_ds = processed_ds["test"]
|
||||
|
||||
batch_size = 16
|
||||
|
||||
train_dataloader = DataLoader(train_ds, shuffle=True, collate_fn=default_data_collator, batch_size=batch_size, pin_memory=True)
|
||||
eval_dataloader = DataLoader(eval_ds, collate_fn=default_data_collator, batch_size=batch_size, pin_memory=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Model
|
||||
|
||||
Now let's load a pretrained model to use as the base model for the soft prompt method. This guide uses the [bigscience/bloomz-560m](https://huggingface.co/bigscience/bloomz-560m) model, but you can use any causal language model you want.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("bigscience/bloomz-560m")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### PEFT configuration and model
|
||||
|
||||
For any PEFT method, you'll need to create a configuration which contains all the parameters that specify how the PEFT method should be applied. Once the configuration is setup, pass it to the [`~peft.get_peft_model`] function along with the base model to create a trainable [`PeftModel`].
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Call the [`~PeftModel.print_trainable_parameters`] method to compare the number of trainable parameters of [`PeftModel`] versus the number of parameters in the base model!
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
<hfoptions id="configurations">
|
||||
<hfoption id="p-tuning">
|
||||
|
||||
[P-tuning](../conceptual_guides/prompting#p-tuning) adds a trainable embedding tensor where the prompt tokens can be added anywhere in the input sequence. Create a [`PromptEncoderConfig`] with the task type, the number of virtual tokens to add and learn, and the hidden size of the encoder for learning the prompt parameters.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from peft import PromptEncoderConfig, get_peft_model
|
||||
|
||||
peft_config = PromptEncoderConfig(task_type="CAUSAL_LM", num_virtual_tokens=20, encoder_hidden_size=128)
|
||||
model = get_peft_model(model, peft_config)
|
||||
model.print_trainable_parameters()
|
||||
"trainable params: 300,288 || all params: 559,514,880 || trainable%: 0.05366935013417338"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="prefix tuning">
|
||||
|
||||
[Prefix tuning](../conceptual_guides/prompting#prefix-tuning) adds task-specific parameters in all of the model layers, which are optimized by a separate feed-forward network. Create a [`PrefixTuningConfig`] with the task type and number of virtual tokens to add and learn.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from peft import PrefixTuningConfig, get_peft_model
|
||||
|
||||
peft_config = PrefixTuningConfig(task_type="CAUSAL_LM", num_virtual_tokens=20)
|
||||
model = get_peft_model(model, peft_config)
|
||||
model.print_trainable_parameters()
|
||||
"trainable params: 983,040 || all params: 560,197,632 || trainable%: 0.1754809274167014"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="prompt tuning">
|
||||
|
||||
[Prompt tuning](../conceptual_guides/prompting#prompt-tuning) formulates all tasks as a *generation* task and it adds a task-specific prompt to the input which is updated independently. The `prompt_tuning_init_text` parameter specifies how to finetune the model (in this case, it is classifying whether tweets are complaints or not). For the best results, the `prompt_tuning_init_text` should have the same number of tokens that should be predicted. To do this, you can set `num_virtual_tokens` to the number of tokens of the `prompt_tuning_init_text`.
|
||||
|
||||
Create a [`PromptTuningConfig`] with the task type, the initial prompt tuning text to train the model with, the number of virtual tokens to add and learn, and a tokenizer.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from peft import PromptTuningConfig, PromptTuningInit, get_peft_model
|
||||
|
||||
prompt_tuning_init_text = "Classify if the tweet is a complaint or no complaint.\n"
|
||||
peft_config = PromptTuningConfig(
|
||||
task_type="CAUSAL_LM",
|
||||
prompt_tuning_init=PromptTuningInit.TEXT,
|
||||
num_virtual_tokens=len(tokenizer(prompt_tuning_init_text)["input_ids"]),
|
||||
prompt_tuning_init_text=prompt_tuning_init_text,
|
||||
tokenizer_name_or_path="bigscience/bloomz-560m",
|
||||
)
|
||||
model = get_peft_model(model, peft_config)
|
||||
model.print_trainable_parameters()
|
||||
"trainable params: 8,192 || all params: 559,222,784 || trainable%: 0.0014648902430985358"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
</hfoptions>
|
||||
|
||||
### Training
|
||||
|
||||
Set up an optimizer and learning rate scheduler.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import get_linear_schedule_with_warmup
|
||||
|
||||
lr = 3e-2
|
||||
num_epochs = 50
|
||||
|
||||
optimizer = torch.optim.AdamW(model.parameters(), lr=lr)
|
||||
lr_scheduler = get_linear_schedule_with_warmup(
|
||||
optimizer=optimizer,
|
||||
num_warmup_steps=0,
|
||||
num_training_steps=(len(train_dataloader) * num_epochs),
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Move the model to the GPU and create a training loop that reports the loss and perplexity for each epoch.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from tqdm import tqdm
|
||||
|
||||
device = "cuda"
|
||||
model = model.to(device)
|
||||
|
||||
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
|
||||
model.train()
|
||||
total_loss = 0
|
||||
for step, batch in enumerate(tqdm(train_dataloader)):
|
||||
batch = {k: v.to(device) for k, v in batch.items()}
|
||||
outputs = model(**batch)
|
||||
loss = outputs.loss
|
||||
total_loss += loss.detach().float()
|
||||
loss.backward()
|
||||
optimizer.step()
|
||||
lr_scheduler.step()
|
||||
optimizer.zero_grad()
|
||||
|
||||
model.eval()
|
||||
eval_loss = 0
|
||||
eval_preds = []
|
||||
for step, batch in enumerate(tqdm(eval_dataloader)):
|
||||
batch = {k: v.to(device) for k, v in batch.items()}
|
||||
with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
outputs = model(**batch)
|
||||
loss = outputs.loss
|
||||
eval_loss += loss.detach().float()
|
||||
eval_preds.extend(
|
||||
tokenizer.batch_decode(torch.argmax(outputs.logits, -1).detach().cpu().numpy(), skip_special_tokens=True)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
eval_epoch_loss = eval_loss / len(eval_dataloader)
|
||||
eval_ppl = torch.exp(eval_epoch_loss)
|
||||
train_epoch_loss = total_loss / len(train_dataloader)
|
||||
train_ppl = torch.exp(train_epoch_loss)
|
||||
print(f"{epoch=}: {train_ppl=} {train_epoch_loss=} {eval_ppl=} {eval_epoch_loss=}")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Share your model
|
||||
|
||||
Once training is complete, you can upload your model to the Hub with the [`~transformers.PreTrainedModel.push_to_hub`] method. You'll need to login to your Hugging Face account first and enter your token when prompted.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from huggingface_hub import notebook_login
|
||||
|
||||
account = <your-hf-account-name>
|
||||
peft_model_id = f"{account}/bloomz-560-m-peft-method"
|
||||
model.push_to_hub(peft_model_id)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you check the model file size in the repository, you’ll see that it is a lot smaller than a full sized model!
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex flex-col justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/huggingface/documentation-images/resolve/main/peft/PEFT-hub-screenshot.png"/>
|
||||
<figcaption class="text-center">For example, the adapter weights for a opt-350m model stored on the Hub are only ~6MB compared to the full model size which can be ~700MB.</figcaption>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
## Inference
|
||||
|
||||
Let's load the model for inference and test it out on a tweet!
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from peft import AutoPeftModelForCausalLM
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoPeftModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("peft_model_id").to("cuda")
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("bigscience/bloomz-560m")
|
||||
|
||||
i = 15
|
||||
inputs = tokenizer(f'{text_column} : {ds["test"][i]["Tweet text"]} Label : ', return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
print(ds["test"][i]["Tweet text"])
|
||||
"@NYTsupport i have complained a dozen times & yet my papers are still thrown FAR from my door. Why is this so hard to resolve?"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Call the [`~transformers.GenerationMixin.generate`] method to generate the predicted classification label.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
inputs = {k: v.to(device) for k, v in inputs.items()}
|
||||
outputs = model.generate(input_ids=inputs["input_ids"], max_new_tokens=10)
|
||||
print(tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs.detach().cpu().numpy(), skip_special_tokens=True))
|
||||
"['Tweet text : @NYTsupport i have complained a dozen times & yet my papers are still thrown FAR from my door. Why is this so hard to resolve? Label : complaint']"
|
||||
```
|
||||
150
docs/source/tutorial/peft_integrations.md
Normal file
150
docs/source/tutorial/peft_integrations.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,150 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# PEFT integrations
|
||||
|
||||
PEFT's practical benefits extends to other Hugging Face libraries like [Diffusers](https://hf.co/docs/diffusers) and [Transformers](https://hf.co/docs/transformers). One of the main benefits of PEFT is that an adapter file generated by a PEFT method is a lot smaller than the original model, which makes it super easy to manage and use multiple adapters. You can use one pretrained base model for multiple tasks by simply loading a new adapter finetuned for the task you're solving. Or you can combine multiple adapters with a text-to-image diffusion model to create new effects.
|
||||
|
||||
This tutorial will show you how PEFT can help you manage adapters in Diffusers and Transformers.
|
||||
|
||||
## Diffusers
|
||||
|
||||
Diffusers is a generative AI library for creating images and videos from text or images with diffusion models. LoRA is an especially popular training method for diffusion models because you can very quickly train and share diffusion models to generate images in new styles. To make it easier to use and try multiple LoRA models, Diffusers uses the PEFT library to help manage different adapters for inference.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, load a base model and then load the [artificialguybr/3DRedmond-V1](https://huggingface.co/artificialguybr/3DRedmond-V1) adapter for inference with the [`load_lora_weights`](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/v0.24.0/en/api/loaders/lora#diffusers.loaders.LoraLoaderMixin.load_lora_weights) method. The `adapter_name` argument in the loading method is enabled by PEFT and allows you to set a name for the adapter so it is easier to reference.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from diffusers import DiffusionPipeline
|
||||
|
||||
pipeline = DiffusionPipeline.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"stabilityai/stable-diffusion-xl-base-1.0", torch_dtype=torch.float16
|
||||
).to("cuda")
|
||||
pipeline.load_lora_weights(
|
||||
"peft-internal-testing/artificialguybr__3DRedmond-V1",
|
||||
weight_name="3DRedmond-3DRenderStyle-3DRenderAF.safetensors",
|
||||
adapter_name="3d"
|
||||
)
|
||||
image = pipeline("sushi rolls shaped like kawaii cat faces").images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/ybelkada/documentation-images/resolve/main/test-lora-diffusers.png"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
Now let's try another cool LoRA model, [ostris/super-cereal-sdxl-lora](https://huggingface.co/ostris/super-cereal-sdxl-lora). All you need to do is load and name this new adapter with `adapter_name`, and use the [`set_adapters`](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/api/loaders/unet#diffusers.loaders.UNet2DConditionLoadersMixin.set_adapters) method to set it as the currently active adapter.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
pipeline.load_lora_weights(
|
||||
"ostris/super-cereal-sdxl-lora",
|
||||
weight_name="cereal_box_sdxl_v1.safetensors",
|
||||
adapter_name="cereal"
|
||||
)
|
||||
pipeline.set_adapters("cereal")
|
||||
image = pipeline("sushi rolls shaped like kawaii cat faces").images[0]
|
||||
image
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="flex justify-center">
|
||||
<img src="https://huggingface.co/datasets/ybelkada/documentation-images/resolve/main/test-lora-diffusers-2.png"/>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, you can call the [`disable_lora`](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/api/loaders/unet#diffusers.loaders.UNet2DConditionLoadersMixin.disable_lora) method to restore the base model.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
pipeline.disable_lora()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Learn more about how PEFT supports Diffusers in the [Inference with PEFT](https://huggingface.co/docs/diffusers/tutorials/using_peft_for_inference) tutorial.
|
||||
|
||||
## Transformers
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 [Transformers](https://hf.co/docs/transformers) is a collection of pretrained models for all types of tasks in all modalities. You can load these models for training or inference. Many of the models are large language models (LLMs), so it makes sense to integrate PEFT with Transformers to manage and train adapters.
|
||||
|
||||
Load a base pretrained model to train.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("facebook/opt-350m")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Next, add an adapter configuration to specify how to adapt the model parameters. Call the [`~PeftModel.add_adapter`] method to add the configuration to the base model.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from peft import LoraConfig
|
||||
|
||||
config = LoraConfig(
|
||||
lora_alpha=16,
|
||||
lora_dropout=0.1,
|
||||
r=64,
|
||||
bias="none",
|
||||
task_type="CAUSAL_LM"
|
||||
)
|
||||
model.add_adapter(peft_config)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can train the model with Transformer's [`~transformers.Trainer`] class or whichever training framework you prefer.
|
||||
|
||||
To use the newly trained model for inference, the [`~transformers.AutoModel`] class uses PEFT on the backend to load the adapter weights and configuration file into a base pretrained model.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("peft-internal-testing/opt-350m-lora")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Alternatively, you can use transformers [Pipelines](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/en/main_classes/pipelines) to load the model for conveniently running inference:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
model = pipeline("text-generation", "peft-internal-testing/opt-350m-lora")
|
||||
print(model("Hello World"))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you're interested in comparing or using more than one adapter, you can call the [`~PeftModel.add_adapter`] method to add the adapter configuration to the base model. The only requirement is the adapter type must be the same (you can't mix a LoRA and LoHa adapter).
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM
|
||||
from peft import LoraConfig
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("facebook/opt-350m")
|
||||
model.add_adapter(lora_config_1, adapter_name="adapter_1")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Call [`~PeftModel.add_adapter`] again to attach a new adapter to the base model.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
model.add_adapter(lora_config_2, adapter_name="adapter_2")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Then you can use [`~PeftModel.set_adapter`] to set the currently active adapter.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
model.set_adapter("adapter_1")
|
||||
output = model.generate(**inputs)
|
||||
print(tokenizer.decode(output_disabled[0], skip_special_tokens=True))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To disable the adapter, call the [`~PeftModel.disable_adapter`] method.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
model.disable_adapter()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you're curious, check out the [Load and train adapters with PEFT](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/main/peft) tutorial to learn more.
|
||||
182
docs/source/tutorial/peft_model_config.md
Normal file
182
docs/source/tutorial/peft_model_config.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,182 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# PEFT configurations and models
|
||||
|
||||
The sheer size of today's large pretrained models - which commonly have billions of parameters - present a significant training challenge because they require more storage space and more computational power to crunch all those calculations. You'll need access to powerful GPUs or TPUs to train these large pretrained models which is expensive, not widely accessible to everyone, not environmentally friendly, and not very practical. PEFT methods address many of these challenges. There are several types of PEFT methods (soft prompting, matrix decomposition, adapters), but they all focus on the same thing, reduce the number of trainable parameters. This makes it more accessible to train and store large models on consumer hardware.
|
||||
|
||||
The PEFT library is designed to help you quickly train large models on free or low-cost GPUs, and in this tutorial, you'll learn how to setup a configuration to apply a PEFT method to a pretrained base model for training. Once the PEFT configuration is setup, you can use any training framework you like (Transformer's [`~transformers.Trainer`] class, [Accelerate](https://hf.co/docs/accelerate), a custom PyTorch training loop).
|
||||
|
||||
## PEFT configurations
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Learn more about the parameters you can configure for each PEFT method in their respective API reference page.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
A configuration stores important parameters that specify how a particular PEFT method should be applied.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, take a look at the following [`LoraConfig`](https://huggingface.co/ybelkada/opt-350m-lora/blob/main/adapter_config.json) for applying LoRA and [`PromptEncoderConfig`](https://huggingface.co/smangrul/roberta-large-peft-p-tuning/blob/main/adapter_config.json) for applying p-tuning (these configuration files are already JSON-serialized). Whenever you load a PEFT adapter, it is a good idea to check whether it has an associated adapter_config.json file which is required.
|
||||
|
||||
<hfoptions id="config">
|
||||
<hfoption id="LoraConfig">
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"base_model_name_or_path": "facebook/opt-350m", #base model to apply LoRA to
|
||||
"bias": "none",
|
||||
"fan_in_fan_out": false,
|
||||
"inference_mode": true,
|
||||
"init_lora_weights": true,
|
||||
"layers_pattern": null,
|
||||
"layers_to_transform": null,
|
||||
"lora_alpha": 32,
|
||||
"lora_dropout": 0.05,
|
||||
"modules_to_save": null,
|
||||
"peft_type": "LORA", #PEFT method type
|
||||
"r": 16,
|
||||
"revision": null,
|
||||
"target_modules": [
|
||||
"q_proj", #model modules to apply LoRA to (query and value projection layers)
|
||||
"v_proj"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"task_type": "CAUSAL_LM" #type of task to train model on
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can create your own configuration for training by initializing a [`LoraConfig`].
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from peft import LoraConfig, TaskType
|
||||
|
||||
lora_config = LoraConfig(
|
||||
r=16,
|
||||
target_modules=["q_proj", "v_proj"],
|
||||
task_type=TaskType.CAUSAL_LM,
|
||||
lora_alpha=32,
|
||||
lora_dropout=0.05
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
<hfoption id="PromptEncoderConfig">
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"base_model_name_or_path": "roberta-large", #base model to apply p-tuning to
|
||||
"encoder_dropout": 0.0,
|
||||
"encoder_hidden_size": 128,
|
||||
"encoder_num_layers": 2,
|
||||
"encoder_reparameterization_type": "MLP",
|
||||
"inference_mode": true,
|
||||
"num_attention_heads": 16,
|
||||
"num_layers": 24,
|
||||
"num_transformer_submodules": 1,
|
||||
"num_virtual_tokens": 20,
|
||||
"peft_type": "P_TUNING", #PEFT method type
|
||||
"task_type": "SEQ_CLS", #type of task to train model on
|
||||
"token_dim": 1024
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can create your own configuration for training by initializing a [`PromptEncoderConfig`].
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from peft import PromptEncoderConfig, TaskType
|
||||
|
||||
p_tuning_config = PromptEncoderConfig(
|
||||
encoder_reprameterization_type="MLP",
|
||||
encoder_hidden_size=128,
|
||||
num_attention_heads=16,
|
||||
num_layers=24,
|
||||
num_transformer_submodules=1,
|
||||
num_virtual_tokens=20,
|
||||
token_dim=1024,
|
||||
task_type=TaskType.SEQ_CLS
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</hfoption>
|
||||
</hfoptions>
|
||||
|
||||
## PEFT models
|
||||
|
||||
With a PEFT configuration in hand, you can now apply it to any pretrained model to create a [`PeftModel`]. Choose from any of the state-of-the-art models from the [Transformers](https://hf.co/docs/transformers) library, a custom model, and even new and unsupported transformer architectures.
|
||||
|
||||
For this tutorial, load a base [facebook/opt-350m](https://huggingface.co/facebook/opt-350m) model to finetune.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("facebook/opt-350m")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Use the [`get_peft_model`] function to create a [`PeftModel`] from the base facebook/opt-350m model and the `lora_config` you created earlier.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from peft import get_peft_model
|
||||
|
||||
lora_model = get_peft_model(model, lora_config)
|
||||
lora_model.print_trainable_parameters()
|
||||
"trainable params: 1,572,864 || all params: 332,769,280 || trainable%: 0.472659014678278"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Now you can train the [`PeftModel`] with your preferred training framework! After training, you can save your model locally with [`~PeftModel.save_pretrained`] or upload it to the Hub with the [`~transformers.PreTrainedModel.push_to_hub`] method.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
# save locally
|
||||
lora_model.save_pretrained("your-name/opt-350m-lora")
|
||||
|
||||
# push to Hub
|
||||
lora_model.push_to_hub("your-name/opt-350m-lora")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To load a [`PeftModel`] for inference, you'll need to provide the [`PeftConfig`] used to create it and the base model it was trained from.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from peft import PeftModel, PeftConfig
|
||||
|
||||
config = PeftConfig.from_pretrained("ybelkada/opt-350m-lora")
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(config.base_model_name_or_path)
|
||||
lora_model = PeftModel.from_pretrained(model, "ybelkada/opt-350m-lora")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
By default, the [`PeftModel`] is set for inference, but if you'd like to train the adapter some more you can set `is_trainable=True`.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
lora_model = PeftModel.from_pretrained(model, "ybelkada/opt-350m-lora", is_trainable=True)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
The [`PeftModel.from_pretrained`] method is the most flexible way to load a [`PeftModel`] because it doesn't matter what model framework was used (Transformers, timm, a generic PyTorch model). Other classes, like [`AutoPeftModel`], are just a convenient wrapper around the base [`PeftModel`], and makes it easier to load PEFT models directly from the Hub or locally where the PEFT weights are stored.
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from peft import AutoPeftModelForCausalLM
|
||||
|
||||
lora_model = AutoPeftModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained("ybelkada/opt-350m-lora")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Take a look at the [AutoPeftModel](package_reference/auto_class) API reference to learn more about the [`AutoPeftModel`] classes.
|
||||
|
||||
## Next steps
|
||||
|
||||
With the appropriate [`PeftConfig`], you can apply it to any pretrained model to create a [`PeftModel`] and train large powerful models faster on freely available GPUs! To learn more about PEFT configurations and models, the following guide may be helpful:
|
||||
|
||||
* Learn how to configure a PEFT method for models that aren't from Transformers in the [Working with custom models](../developer_guides/custom_models) guide.
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,22 @@
|
||||
compute_environment: LOCAL_MACHINE
|
||||
deepspeed_config:
|
||||
gradient_accumulation_steps: 1
|
||||
gradient_clipping: 1.0
|
||||
offload_optimizer_device: none
|
||||
offload_param_device: none
|
||||
zero3_init_flag: true
|
||||
zero3_save_16bit_model: true
|
||||
zero_stage: 3
|
||||
distributed_type: DEEPSPEED
|
||||
downcast_bf16: 'no'
|
||||
dynamo_backend: 'NO'
|
||||
fsdp_config: {}
|
||||
machine_rank: 0
|
||||
main_training_function: main
|
||||
megatron_lm_config: {}
|
||||
mixed_precision: 'no'
|
||||
num_machines: 1
|
||||
num_processes: 1
|
||||
rdzv_backend: static
|
||||
same_network: true
|
||||
use_cpu: false
|
||||
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
@ -3,10 +3,12 @@ import os
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
import threading
|
||||
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
import psutil
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from accelerate import Accelerator
|
||||
from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
|
||||
from tqdm import tqdm
|
||||
from transformers import (
|
||||
AutoModelForCausalLM,
|
||||
AutoTokenizer,
|
||||
@ -15,31 +17,28 @@ from transformers import (
|
||||
set_seed,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
import psutil
|
||||
from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
from peft import LoraConfig, TaskType, get_peft_model, get_peft_model_state_dict
|
||||
from tqdm import tqdm
|
||||
from peft import LoraConfig, TaskType, get_peft_model
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def levenshtein_distance(str1, str2):
|
||||
# TC: O(N^2)
|
||||
# SC: O(N^2)
|
||||
# SC: O(N)
|
||||
if str1 == str2:
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
num_rows = len(str1) + 1
|
||||
num_cols = len(str2) + 1
|
||||
dp_matrix = np.empty((num_rows, num_cols))
|
||||
dp_matrix[0, :] = range(num_cols)
|
||||
dp_matrix[:, 0] = range(num_rows)
|
||||
|
||||
dp_matrix = list(range(num_cols))
|
||||
for i in range(1, num_rows):
|
||||
prev = dp_matrix[0]
|
||||
dp_matrix[0] = i
|
||||
for j in range(1, num_cols):
|
||||
temp = dp_matrix[j]
|
||||
if str1[i - 1] == str2[j - 1]:
|
||||
dp_matrix[i, j] = dp_matrix[i - 1, j - 1]
|
||||
dp_matrix[j] = prev
|
||||
else:
|
||||
dp_matrix[i, j] = min(dp_matrix[i - 1, j - 1], dp_matrix[i - 1, j], dp_matrix[i, j - 1]) + 1
|
||||
|
||||
return dp_matrix[num_rows - 1, num_cols - 1]
|
||||
dp_matrix[j] = min(prev, dp_matrix[j], dp_matrix[j - 1]) + 1
|
||||
prev = temp
|
||||
return dp_matrix[num_cols - 1]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def get_closest_label(eval_pred, classes):
|
||||
@ -111,9 +110,6 @@ def main():
|
||||
model_name_or_path = "bigscience/bloomz-7b1"
|
||||
dataset_name = "twitter_complaints"
|
||||
peft_config = LoraConfig(task_type=TaskType.CAUSAL_LM, inference_mode=False, r=8, lora_alpha=32, lora_dropout=0.1)
|
||||
checkpoint_name = (
|
||||
f"{dataset_name}_{model_name_or_path}_{peft_config.peft_type}_{peft_config.task_type}_v1.pt".replace("/", "_")
|
||||
)
|
||||
text_column = "Tweet text"
|
||||
label_column = "text_label"
|
||||
lr = 3e-3
|
||||
@ -121,6 +117,7 @@ def main():
|
||||
batch_size = 8
|
||||
seed = 42
|
||||
max_length = 64
|
||||
do_test = False
|
||||
set_seed(seed)
|
||||
|
||||
dataset = load_dataset("ought/raft", dataset_name)
|
||||
@ -138,10 +135,10 @@ def main():
|
||||
inputs = [f"{text_column} : {x} Label : " for x in examples[text_column]]
|
||||
targets = [str(x) for x in examples[label_column]]
|
||||
model_inputs = tokenizer(inputs)
|
||||
labels = tokenizer(targets)
|
||||
labels = tokenizer(targets, add_special_tokens=False) # don't add bos token because we concatenate with inputs
|
||||
for i in range(batch_size):
|
||||
sample_input_ids = model_inputs["input_ids"][i]
|
||||
label_input_ids = labels["input_ids"][i] + [tokenizer.pad_token_id]
|
||||
label_input_ids = labels["input_ids"][i] + [tokenizer.eos_token_id]
|
||||
model_inputs["input_ids"][i] = sample_input_ids + label_input_ids
|
||||
labels["input_ids"][i] = [-100] * len(sample_input_ids) + label_input_ids
|
||||
model_inputs["attention_mask"][i] = [1] * len(model_inputs["input_ids"][i])
|
||||
@ -252,24 +249,20 @@ def main():
|
||||
lr_scheduler.step()
|
||||
optimizer.zero_grad()
|
||||
# Printing the GPU memory usage details such as allocated memory, peak memory, and total memory usage
|
||||
accelerator.print("GPU Memory before entering the train : {}".format(b2mb(tracemalloc.begin)))
|
||||
accelerator.print("GPU Memory consumed at the end of the train (end-begin): {}".format(tracemalloc.used))
|
||||
accelerator.print("GPU Peak Memory consumed during the train (max-begin): {}".format(tracemalloc.peaked))
|
||||
accelerator.print(f"GPU Memory before entering the train : {b2mb(tracemalloc.begin)}")
|
||||
accelerator.print(f"GPU Memory consumed at the end of the train (end-begin): {tracemalloc.used}")
|
||||
accelerator.print(f"GPU Peak Memory consumed during the train (max-begin): {tracemalloc.peaked}")
|
||||
accelerator.print(
|
||||
"GPU Total Peak Memory consumed during the train (max): {}".format(
|
||||
tracemalloc.peaked + b2mb(tracemalloc.begin)
|
||||
)
|
||||
f"GPU Total Peak Memory consumed during the train (max): {tracemalloc.peaked + b2mb(tracemalloc.begin)}"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
accelerator.print("CPU Memory before entering the train : {}".format(b2mb(tracemalloc.cpu_begin)))
|
||||
accelerator.print("CPU Memory consumed at the end of the train (end-begin): {}".format(tracemalloc.cpu_used))
|
||||
accelerator.print("CPU Peak Memory consumed during the train (max-begin): {}".format(tracemalloc.cpu_peaked))
|
||||
accelerator.print(f"CPU Memory before entering the train : {b2mb(tracemalloc.cpu_begin)}")
|
||||
accelerator.print(f"CPU Memory consumed at the end of the train (end-begin): {tracemalloc.cpu_used}")
|
||||
accelerator.print(f"CPU Peak Memory consumed during the train (max-begin): {tracemalloc.cpu_peaked}")
|
||||
accelerator.print(
|
||||
"CPU Total Peak Memory consumed during the train (max): {}".format(
|
||||
tracemalloc.cpu_peaked + b2mb(tracemalloc.cpu_begin)
|
||||
)
|
||||
f"CPU Total Peak Memory consumed during the train (max): {tracemalloc.cpu_peaked + b2mb(tracemalloc.cpu_begin)}"
|
||||
)
|
||||
train_epoch_loss = total_loss / len(eval_dataloader)
|
||||
train_epoch_loss = total_loss / len(train_dataloader)
|
||||
train_ppl = torch.exp(train_epoch_loss)
|
||||
accelerator.print(f"{epoch=}: {train_ppl=} {train_epoch_loss=}")
|
||||
|
||||
@ -282,30 +275,31 @@ def main():
|
||||
outputs = accelerator.unwrap_model(model).generate(
|
||||
**batch, synced_gpus=is_ds_zero_3, max_new_tokens=10
|
||||
) # synced_gpus=True for DS-stage 3
|
||||
preds = outputs[:, max_length:].detach().cpu().numpy()
|
||||
outputs = accelerator.pad_across_processes(outputs, dim=1, pad_index=tokenizer.pad_token_id)
|
||||
preds = accelerator.gather_for_metrics(outputs)
|
||||
preds = preds[:, max_length:].detach().cpu().numpy()
|
||||
eval_preds.extend(tokenizer.batch_decode(preds, skip_special_tokens=True))
|
||||
|
||||
# Printing the GPU memory usage details such as allocated memory, peak memory, and total memory usage
|
||||
accelerator.print("GPU Memory before entering the eval : {}".format(b2mb(tracemalloc.begin)))
|
||||
accelerator.print("GPU Memory consumed at the end of the eval (end-begin): {}".format(tracemalloc.used))
|
||||
accelerator.print("GPU Peak Memory consumed during the eval (max-begin): {}".format(tracemalloc.peaked))
|
||||
accelerator.print(f"GPU Memory before entering the eval : {b2mb(tracemalloc.begin)}")
|
||||
accelerator.print(f"GPU Memory consumed at the end of the eval (end-begin): {tracemalloc.used}")
|
||||
accelerator.print(f"GPU Peak Memory consumed during the eval (max-begin): {tracemalloc.peaked}")
|
||||
accelerator.print(
|
||||
"GPU Total Peak Memory consumed during the eval (max): {}".format(
|
||||
tracemalloc.peaked + b2mb(tracemalloc.begin)
|
||||
)
|
||||
f"GPU Total Peak Memory consumed during the eval (max): {tracemalloc.peaked + b2mb(tracemalloc.begin)}"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
accelerator.print("CPU Memory before entering the eval : {}".format(b2mb(tracemalloc.cpu_begin)))
|
||||
accelerator.print("CPU Memory consumed at the end of the eval (end-begin): {}".format(tracemalloc.cpu_used))
|
||||
accelerator.print("CPU Peak Memory consumed during the eval (max-begin): {}".format(tracemalloc.cpu_peaked))
|
||||
accelerator.print(f"CPU Memory before entering the eval : {b2mb(tracemalloc.cpu_begin)}")
|
||||
accelerator.print(f"CPU Memory consumed at the end of the eval (end-begin): {tracemalloc.cpu_used}")
|
||||
accelerator.print(f"CPU Peak Memory consumed during the eval (max-begin): {tracemalloc.cpu_peaked}")
|
||||
accelerator.print(
|
||||
"CPU Total Peak Memory consumed during the eval (max): {}".format(
|
||||
tracemalloc.cpu_peaked + b2mb(tracemalloc.cpu_begin)
|
||||
)
|
||||
f"CPU Total Peak Memory consumed during the eval (max): {tracemalloc.cpu_peaked + b2mb(tracemalloc.cpu_begin)}"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
correct = 0
|
||||
total = 0
|
||||
assert len(eval_preds) == len(
|
||||
dataset["train"][label_column]
|
||||
), f"{len(eval_preds)} != {len(dataset['train'][label_column])}"
|
||||
for pred, true in zip(eval_preds, dataset["train"][label_column]):
|
||||
if pred.strip() == true.strip():
|
||||
correct += 1
|
||||
@ -315,35 +309,52 @@ def main():
|
||||
accelerator.print(f"{eval_preds[:10]=}")
|
||||
accelerator.print(f"{dataset['train'][label_column][:10]=}")
|
||||
|
||||
model.eval()
|
||||
test_preds = []
|
||||
for _, batch in enumerate(tqdm(test_dataloader)):
|
||||
batch = {k: v for k, v in batch.items() if k != "labels"}
|
||||
with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
outputs = accelerator.unwrap_model(model).generate(
|
||||
**batch, synced_gpus=is_ds_zero_3, max_new_tokens=10
|
||||
) # synced_gpus=True for DS-stage 3
|
||||
test_preds.extend(
|
||||
tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs[:, max_length:].detach().cpu().numpy(), skip_special_tokens=True)
|
||||
)
|
||||
if do_test:
|
||||
model.eval()
|
||||
test_preds = []
|
||||
for _, batch in enumerate(tqdm(test_dataloader)):
|
||||
batch = {k: v for k, v in batch.items() if k != "labels"}
|
||||
with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
outputs = accelerator.unwrap_model(model).generate(
|
||||
**batch, synced_gpus=is_ds_zero_3, max_new_tokens=10
|
||||
) # synced_gpus=True for DS-stage 3
|
||||
outputs = accelerator.pad_across_processes(outputs, dim=1, pad_index=tokenizer.pad_token_id)
|
||||
preds = accelerator.gather(outputs)
|
||||
preds = preds[:, max_length:].detach().cpu().numpy()
|
||||
test_preds.extend(tokenizer.batch_decode(preds, skip_special_tokens=True))
|
||||
|
||||
test_preds_cleaned = []
|
||||
for _, pred in enumerate(test_preds):
|
||||
test_preds_cleaned.append(get_closest_label(pred, classes))
|
||||
test_preds_cleaned = []
|
||||
for _, pred in enumerate(test_preds):
|
||||
test_preds_cleaned.append(get_closest_label(pred, classes))
|
||||
|
||||
test_df = dataset["test"].to_pandas()
|
||||
test_df[label_column] = test_preds_cleaned
|
||||
test_df["text_labels_orig"] = test_preds
|
||||
accelerator.print(test_df[[text_column, label_column]].sample(20))
|
||||
test_df = dataset["test"].to_pandas()
|
||||
assert len(test_preds_cleaned) == len(test_df), f"{len(test_preds_cleaned)} != {len(test_df)}"
|
||||
test_df[label_column] = test_preds_cleaned
|
||||
test_df["text_labels_orig"] = test_preds
|
||||
accelerator.print(test_df[[text_column, label_column]].sample(20))
|
||||
|
||||
pred_df = test_df[["ID", label_column]]
|
||||
pred_df.columns = ["ID", "Label"]
|
||||
pred_df = test_df[["ID", label_column]]
|
||||
pred_df.columns = ["ID", "Label"]
|
||||
|
||||
os.makedirs(f"data/{dataset_name}", exist_ok=True)
|
||||
pred_df.to_csv(f"data/{dataset_name}/predictions.csv", index=False)
|
||||
os.makedirs(f"data/{dataset_name}", exist_ok=True)
|
||||
pred_df.to_csv(f"data/{dataset_name}/predictions.csv", index=False)
|
||||
|
||||
accelerator.wait_for_everyone()
|
||||
accelerator.save(get_peft_model_state_dict(model, state_dict=accelerator.get_state_dict(model)), checkpoint_name)
|
||||
# Option1: Pushing the model to Hugging Face Hub
|
||||
# model.push_to_hub(
|
||||
# f"{dataset_name}_{model_name_or_path}_{peft_config.peft_type}_{peft_config.task_type}".replace("/", "_"),
|
||||
# token = "hf_..."
|
||||
# )
|
||||
# token (`bool` or `str`, *optional*):
|
||||
# `token` is to be used for HTTP Bearer authorization when accessing remote files. If `True`, will use the token generated
|
||||
# when running `huggingface-cli login` (stored in `~/.huggingface`). Will default to `True` if `repo_url`
|
||||
# is not specified.
|
||||
# Or you can get your token from https://huggingface.co/settings/token
|
||||
# Option2: Saving the model locally
|
||||
peft_model_id = f"{dataset_name}_{model_name_or_path}_{peft_config.peft_type}_{peft_config.task_type}".replace(
|
||||
"/", "_"
|
||||
)
|
||||
model.save_pretrained(peft_model_id)
|
||||
accelerator.wait_for_everyone()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
1229
examples/causal_language_modeling/peft_prompt_tuning_clm.ipynb
Normal file
1229
examples/causal_language_modeling/peft_prompt_tuning_clm.ipynb
Normal file
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
@ -1,6 +1,5 @@
|
||||
transformers
|
||||
accelerate
|
||||
loralib
|
||||
evaluate
|
||||
deepspeed
|
||||
tqdm
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,22 @@
|
||||
compute_environment: LOCAL_MACHINE
|
||||
deepspeed_config:
|
||||
gradient_accumulation_steps: 1
|
||||
gradient_clipping: 1.0
|
||||
offload_optimizer_device: none
|
||||
offload_param_device: none
|
||||
zero3_init_flag: true
|
||||
zero3_save_16bit_model: true
|
||||
zero_stage: 3
|
||||
distributed_type: DEEPSPEED
|
||||
downcast_bf16: 'no'
|
||||
dynamo_backend: 'NO'
|
||||
fsdp_config: {}
|
||||
machine_rank: 0
|
||||
main_training_function: main
|
||||
megatron_lm_config: {}
|
||||
mixed_precision: 'no'
|
||||
num_machines: 1
|
||||
num_processes: 1
|
||||
rdzv_backend: static
|
||||
same_network: true
|
||||
use_cpu: false
|
||||
408
examples/conditional_generation/multitask_prompt_tuning.ipynb
Normal file
408
examples/conditional_generation/multitask_prompt_tuning.ipynb
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,408 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cells": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"id": "58ff91ca-ce92-43d0-ae8b-4e9e89e193f6",
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"tags": []
|
||||
},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from datasets import load_dataset\n",
|
||||
"from transformers import set_seed, AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM, AutoTokenizer\n",
|
||||
"from peft import get_peft_model, MultitaskPromptTuningConfig, TaskType, MultitaskPromptTuningInit\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"set_seed(42)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"model_name = \"google/flan-t5-base\"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"peft_config = MultitaskPromptTuningConfig(\n",
|
||||
" tokenizer_name_or_path=model_name,\n",
|
||||
" num_tasks=2,\n",
|
||||
" task_type=TaskType.SEQ_2_SEQ_LM,\n",
|
||||
" prompt_tuning_init=MultitaskPromptTuningInit.TEXT,\n",
|
||||
" num_virtual_tokens=50,\n",
|
||||
" num_transformer_submodules=1,\n",
|
||||
" prompt_tuning_init_text=\"classify the following into either positive or negative, or entailment, neutral or contradiction:\",\n",
|
||||
")\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)\n",
|
||||
"model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained(model_name)\n",
|
||||
"model = get_peft_model(model, peft_config)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"model = model.cuda()\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"def send_to_device(batch):\n",
|
||||
" for i in batch:\n",
|
||||
" batch[i] = batch[i].cuda()\n",
|
||||
" return batch"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"id": "eb112bc1-ffaf-49fa-a216-0d601ec304ee",
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"tags": []
|
||||
},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"def get_sst2(split: str):\n",
|
||||
" examples = load_dataset(\"sst2\")[split]\n",
|
||||
" result_examples = []\n",
|
||||
" for example in examples:\n",
|
||||
" result_examples.append({})\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" result_examples[-1][\"input\"] = example[\"sentence\"].strip() + \"</s>\"\n",
|
||||
" result_examples[-1][\"output\"] = (\n",
|
||||
" f\"positive{tokenizer.eos_token}\" if example[\"label\"] == 1 else f\"negative{tokenizer.eos_token}\"\n",
|
||||
" )\n",
|
||||
" result_examples[-1][\"task_id\"] = 0\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" return result_examples\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"def get_mnli(split: str):\n",
|
||||
" examples = load_dataset(\"multi_nli\")[split]\n",
|
||||
" result_examples = []\n",
|
||||
" for example in examples:\n",
|
||||
" result_examples.append({})\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" result_examples[-1][\"input\"] = example[\"premise\"].strip() + \" \" + example[\"hypothesis\"].strip() + \"</s>\"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" if example[\"label\"] == 0:\n",
|
||||
" result_examples[-1][\"output\"] = f\"entailment{tokenizer.eos_token}\"\n",
|
||||
" elif example[\"label\"] == 1:\n",
|
||||
" result_examples[-1][\"output\"] = f\"neutral{tokenizer.eos_token}\"\n",
|
||||
" else:\n",
|
||||
" result_examples[-1][\"output\"] = f\"contradiction{tokenizer.eos_token}\"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" result_examples[-1][\"task_id\"] = 1\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" return result_examples"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"id": "e5a16ec4-8fef-4ba9-95b6-a661eb51e50c",
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"tags": []
|
||||
},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from typing import Tuple\n",
|
||||
"from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader\n",
|
||||
"import torch\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"class MyDataset(Dataset):\n",
|
||||
" def __init__(self, split: str, mode: str = \"source\") -> None:\n",
|
||||
" super().__init__()\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" if split == \"train\":\n",
|
||||
" if mode == \"source\":\n",
|
||||
" self.examples = get_sst2(split) + get_mnli(split)\n",
|
||||
" elif mode == \"target\":\n",
|
||||
" self.examples = get_sst2(split)\n",
|
||||
" if split == \"val\":\n",
|
||||
" self.examples = get_sst2(\"validation\")\n",
|
||||
" if split == \"test\":\n",
|
||||
" self.examples = get_sst2(\"validation\")\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" def __getitem__(self, index) -> dict:\n",
|
||||
" return self.examples[index]\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" def __len__(self) -> int:\n",
|
||||
" return len(self.examples)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" def __getitem__(self, index) -> dict:\n",
|
||||
" return self.examples[index]\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" def __len__(self) -> int:\n",
|
||||
" return len(self.examples)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"def collate_fn(batch: dict) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]:\n",
|
||||
" input = [i[\"input\"] for i in batch]\n",
|
||||
" input = tokenizer(input, add_special_tokens=False, return_tensors=\"pt\", padding=True)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" output = [i[\"output\"] for i in batch]\n",
|
||||
" output = tokenizer(output, add_special_tokens=False, return_tensors=\"pt\", padding=True).input_ids\n",
|
||||
" output[output == tokenizer.pad_token_id] = -100\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" task_ids = [i[\"task_id\"] for i in batch]\n",
|
||||
" task_ids = torch.tensor(task_ids)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" return {\n",
|
||||
" \"input_ids\": input.input_ids,\n",
|
||||
" \"attention_mask\": input.attention_mask,\n",
|
||||
" \"labels\": output,\n",
|
||||
" \"task_ids\": task_ids,\n",
|
||||
" }\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"train = DataLoader(MyDataset(\"train\"), shuffle=True, batch_size=8, collate_fn=collate_fn)\n",
|
||||
"val = DataLoader(MyDataset(\"val\"), shuffle=False, batch_size=8, collate_fn=collate_fn)\n",
|
||||
"test = DataLoader(MyDataset(\"test\"), shuffle=False, batch_size=8, collate_fn=collate_fn)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"id": "fe0aec7b-f61e-4b00-a90e-c1201dc1f84c",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## source training"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"id": "cceecc94-f43a-4f62-8d45-926f2f02f36d",
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"tags": []
|
||||
},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from torch.optim.adamw import AdamW\n",
|
||||
"from transformers import get_cosine_schedule_with_warmup\n",
|
||||
"from tqdm import tqdm\n",
|
||||
"from sklearn.metrics import f1_score"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"id": "eae5516b-73ab-44a8-a083-4e8de6127f30",
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"tags": []
|
||||
},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"POSITIVE_TOKEN_ID = tokenizer(\" positive\", add_special_tokens=False)[\"input_ids\"][0]\n",
|
||||
"NEGATIVE_TOKEN_ID = tokenizer(\" negative\", add_special_tokens=False)[\"input_ids\"][0]\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"def classify(batch):\n",
|
||||
" batch = send_to_device(batch)\n",
|
||||
" # we pass labels here since we need to generate and peft doesn't support generation yet.\n",
|
||||
" # No clue how to get around this\n",
|
||||
" scores = model(**batch).logits\n",
|
||||
" preds = []\n",
|
||||
" for i in range(scores.shape[0]):\n",
|
||||
" if scores[i, 0, POSITIVE_TOKEN_ID] > scores[i, 0, NEGATIVE_TOKEN_ID]:\n",
|
||||
" preds.append(POSITIVE_TOKEN_ID)\n",
|
||||
" else:\n",
|
||||
" preds.append(NEGATIVE_TOKEN_ID)\n",
|
||||
" return preds\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"@torch.inference_mode()\n",
|
||||
"def evaluate(model, data):\n",
|
||||
" loss = 0\n",
|
||||
" preds = []\n",
|
||||
" golds = []\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" for batch in tqdm(data):\n",
|
||||
" batch = send_to_device(batch)\n",
|
||||
" loss += model(**batch).loss\n",
|
||||
" golds.extend(batch[\"labels\"][:, 0].tolist())\n",
|
||||
" preds.extend(classify(batch))\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" return loss / len(val), f1_score(golds, preds, pos_label=POSITIVE_TOKEN_ID)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"optimizer = AdamW(model.parameters(), lr=1e-4)\n",
|
||||
"scheduler = get_cosine_schedule_with_warmup(optimizer, 200, len(train))\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"n = 1000\n",
|
||||
"step = 0\n",
|
||||
"train_ = tqdm(train)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"val_loss, f1 = evaluate(model, val)\n",
|
||||
"print(\n",
|
||||
" f\"\"\"\n",
|
||||
"before source training\n",
|
||||
"val loss = {val_loss}\n",
|
||||
"f1 = {f1}\"\"\"\n",
|
||||
")\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"for batch in train_:\n",
|
||||
" if step % n == 0:\n",
|
||||
" val_loss, f1 = evaluate(model, val)\n",
|
||||
" print(\n",
|
||||
" f\"\"\"\n",
|
||||
"step = {step}\n",
|
||||
"val loss = {val_loss}\n",
|
||||
"f1 = {f1}\"\"\"\n",
|
||||
" )\n",
|
||||
" model.save_pretrained(f\"checkpoints_source/{step}\")\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" step += 1\n",
|
||||
" batch = send_to_device(batch)\n",
|
||||
" loss = model(**batch).loss\n",
|
||||
" loss.backward()\n",
|
||||
" optimizer.step()\n",
|
||||
" scheduler.step()\n",
|
||||
" train_.set_postfix(train_loss=loss)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"id": "74168ef3-66f3-41a7-a40b-7840b103fbf9",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## target training"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"id": "b09fd456-163e-4dc1-b24d-f2d0d349036c",
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"tags": []
|
||||
},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"train = DataLoader(MyDataset(\"train\", \"target\"), shuffle=True, batch_size=8, collate_fn=collate_fn)\n",
|
||||
"val = DataLoader(MyDataset(\"val\", \"target\"), shuffle=False, batch_size=8, collate_fn=collate_fn)\n",
|
||||
"test = DataLoader(MyDataset(\"test\", \"target\"), shuffle=False, batch_size=8, collate_fn=collate_fn)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"id": "4a539944-f16c-4c3f-bb4a-7b5d9a6042e2",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"#### create a fresh model"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"id": "5520d904-aa6c-4654-9335-ed4e7d76cba2",
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"tags": []
|
||||
},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"peft_config = MultitaskPromptTuningConfig(\n",
|
||||
" tokenizer_name_or_path=model_name,\n",
|
||||
" num_tasks=1,\n",
|
||||
" task_type=TaskType.SEQ_2_SEQ_LM,\n",
|
||||
" prompt_tuning_init=MultitaskPromptTuningInit.EXACT_SOURCE_TASK,\n",
|
||||
" prompt_tuning_init_state_dict_path=\"checkpoints_source/50000/adapter_model.bin\",\n",
|
||||
" num_virtual_tokens=50,\n",
|
||||
" num_transformer_submodules=1,\n",
|
||||
")\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)\n",
|
||||
"model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained(model_name)\n",
|
||||
"model = get_peft_model(model, peft_config)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"model = model.cuda()"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"id": "dfa39c2d-d1c5-4ed4-90f8-26e8e324371c",
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"tags": []
|
||||
},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"optimizer = AdamW(model.parameters(), lr=1e-4)\n",
|
||||
"scheduler = get_cosine_schedule_with_warmup(optimizer, 200, len(train))\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"n = 1000\n",
|
||||
"step = 0\n",
|
||||
"train_ = tqdm(train)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"val_loss, f1 = evaluate(model, val)\n",
|
||||
"print(\n",
|
||||
" f\"\"\"\n",
|
||||
"before target training\n",
|
||||
"val loss = {val_loss}\n",
|
||||
"f1 = {f1}\"\"\"\n",
|
||||
")\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"for batch in train_:\n",
|
||||
" if step % n == 0:\n",
|
||||
" val_loss, f1 = evaluate(model, val)\n",
|
||||
" print(\n",
|
||||
" f\"\"\"\n",
|
||||
"step = {step}\n",
|
||||
"val loss = {val_loss}\n",
|
||||
"f1 = {f1}\"\"\"\n",
|
||||
" )\n",
|
||||
" model.save_pretrained(f\"checkpoints_target/{step}\")\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" step += 1\n",
|
||||
" batch = send_to_device(batch)\n",
|
||||
" loss = model(**batch).loss\n",
|
||||
" loss.backward()\n",
|
||||
" optimizer.step()\n",
|
||||
" scheduler.step()\n",
|
||||
" train_.set_postfix(train_loss=loss)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"id": "b6a6eeda-1e09-49a6-8845-cd96c8573145",
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"tags": []
|
||||
},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# load last checkpoint for now\n",
|
||||
"from peft import set_peft_model_state_dict\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"sd_6000 = torch.load(\"checkpoints_target/6000/adapter_model.bin\")\n",
|
||||
"set_peft_model_state_dict(model, sd_6000)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# evaluate val\n",
|
||||
"val_loss, f1 = evaluate(model, val)\n",
|
||||
"print(\n",
|
||||
" f\"\"\"\n",
|
||||
"final\n",
|
||||
"val loss = {val_loss}\n",
|
||||
"f1 = {f1}\"\"\"\n",
|
||||
")\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"# evaluate test\n",
|
||||
"test_loss, f1 = evaluate(model, test)\n",
|
||||
"print(\n",
|
||||
" f\"\"\"\n",
|
||||
"final\n",
|
||||
"test loss = {test_loss}\n",
|
||||
"f1 = {f1}\"\"\"\n",
|
||||
")"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"kernelspec": {
|
||||
"display_name": "Python 3 (ipykernel)",
|
||||
"language": "python",
|
||||
"name": "python3"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"language_info": {
|
||||
"codemirror_mode": {
|
||||
"name": "ipython",
|
||||
"version": 3
|
||||
},
|
||||
"file_extension": ".py",
|
||||
"mimetype": "text/x-python",
|
||||
"name": "python",
|
||||
"nbconvert_exporter": "python",
|
||||
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
|
||||
"version": "3.9.13"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"nbformat": 4,
|
||||
"nbformat_minor": 5
|
||||
}
|
||||
182
examples/conditional_generation/peft_adalora_seq2seq.py
Normal file
182
examples/conditional_generation/peft_adalora_seq2seq.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,182 @@
|
||||
import os
|
||||
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
|
||||
from tqdm import tqdm
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM, AutoTokenizer, default_data_collator, get_linear_schedule_with_warmup
|
||||
|
||||
from peft import AdaLoraConfig, PeftConfig, PeftModel, TaskType, get_peft_model
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
os.environ["TOKENIZERS_PARALLELISM"] = "false"
|
||||
|
||||
device = "cuda"
|
||||
model_name_or_path = "facebook/bart-base"
|
||||
tokenizer_name_or_path = "facebook/bart-base"
|
||||
|
||||
checkpoint_name = "financial_sentiment_analysis_lora_v1.pt"
|
||||
text_column = "sentence"
|
||||
label_column = "text_label"
|
||||
max_length = 128
|
||||
lr = 1e-3
|
||||
num_epochs = 8
|
||||
batch_size = 8
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# creating model
|
||||
peft_config = AdaLoraConfig(
|
||||
init_r=12,
|
||||
target_r=8,
|
||||
beta1=0.85,
|
||||
beta2=0.85,
|
||||
tinit=200,
|
||||
tfinal=1000,
|
||||
deltaT=10,
|
||||
lora_alpha=32,
|
||||
lora_dropout=0.1,
|
||||
task_type=TaskType.SEQ_2_SEQ_LM,
|
||||
inference_mode=False,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained(model_name_or_path)
|
||||
model = get_peft_model(model, peft_config)
|
||||
model.print_trainable_parameters()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# loading dataset
|
||||
dataset = load_dataset("financial_phrasebank", "sentences_allagree")
|
||||
dataset = dataset["train"].train_test_split(test_size=0.1)
|
||||
dataset["validation"] = dataset["test"]
|
||||
del dataset["test"]
|
||||
|
||||
classes = dataset["train"].features["label"].names
|
||||
dataset = dataset.map(
|
||||
lambda x: {"text_label": [classes[label] for label in x["label"]]},
|
||||
batched=True,
|
||||
num_proc=1,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# data preprocessing
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name_or_path)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def preprocess_function(examples):
|
||||
inputs = examples[text_column]
|
||||
targets = examples[label_column]
|
||||
model_inputs = tokenizer(inputs, max_length=max_length, padding="max_length", truncation=True, return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
labels = tokenizer(targets, max_length=3, padding="max_length", truncation=True, return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
labels = labels["input_ids"]
|
||||
labels[labels == tokenizer.pad_token_id] = -100
|
||||
model_inputs["labels"] = labels
|
||||
return model_inputs
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
processed_datasets = dataset.map(
|
||||
preprocess_function,
|
||||
batched=True,
|
||||
num_proc=1,
|
||||
remove_columns=dataset["train"].column_names,
|
||||
load_from_cache_file=False,
|
||||
desc="Running tokenizer on dataset",
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
train_dataset = processed_datasets["train"]
|
||||
eval_dataset = processed_datasets["validation"]
|
||||
|
||||
train_dataloader = DataLoader(
|
||||
train_dataset, shuffle=True, collate_fn=default_data_collator, batch_size=batch_size, pin_memory=True
|
||||
)
|
||||
eval_dataloader = DataLoader(eval_dataset, collate_fn=default_data_collator, batch_size=batch_size, pin_memory=True)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# optimizer and lr scheduler
|
||||
optimizer = torch.optim.AdamW(model.parameters(), lr=lr)
|
||||
lr_scheduler = get_linear_schedule_with_warmup(
|
||||
optimizer=optimizer,
|
||||
num_warmup_steps=0,
|
||||
num_training_steps=(len(train_dataloader) * num_epochs),
|
||||
)
|
||||
model.base_model.peft_config["default"].total_step = len(train_dataloader) * num_epochs
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# training and evaluation
|
||||
model = model.to(device)
|
||||
global_step = 0
|
||||
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
|
||||
model.train()
|
||||
total_loss = 0
|
||||
for step, batch in enumerate(tqdm(train_dataloader)):
|
||||
batch = {k: v.to(device) for k, v in batch.items()}
|
||||
outputs = model(**batch)
|
||||
loss = outputs.loss
|
||||
total_loss += loss.detach().float()
|
||||
loss.backward()
|
||||
optimizer.step()
|
||||
lr_scheduler.step()
|
||||
# Update the importance of low-rank matrices
|
||||
# and allocate the budget accordingly.
|
||||
model.base_model.update_and_allocate(global_step)
|
||||
optimizer.zero_grad()
|
||||
global_step += 1
|
||||
|
||||
model.eval()
|
||||
eval_loss = 0
|
||||
eval_preds = []
|
||||
for step, batch in enumerate(tqdm(eval_dataloader)):
|
||||
batch = {k: v.to(device) for k, v in batch.items()}
|
||||
with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
outputs = model(**batch)
|
||||
loss = outputs.loss
|
||||
eval_loss += loss.detach().float()
|
||||
eval_preds.extend(
|
||||
tokenizer.batch_decode(torch.argmax(outputs.logits, -1).detach().cpu().numpy(), skip_special_tokens=True)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
eval_epoch_loss = eval_loss / len(train_dataloader)
|
||||
eval_ppl = torch.exp(eval_epoch_loss)
|
||||
train_epoch_loss = total_loss / len(eval_dataloader)
|
||||
train_ppl = torch.exp(train_epoch_loss)
|
||||
print(f"{epoch=}: {train_ppl=} {train_epoch_loss=} {eval_ppl=} {eval_epoch_loss=}")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# print accuracy
|
||||
correct = 0
|
||||
total = 0
|
||||
for pred, true in zip(eval_preds, dataset["validation"]["text_label"]):
|
||||
if pred.strip() == true.strip():
|
||||
correct += 1
|
||||
total += 1
|
||||
accuracy = correct / total * 100
|
||||
print(f"{accuracy=} % on the evaluation dataset")
|
||||
print(f"{eval_preds[:10]=}")
|
||||
print(f"{dataset['validation']['text_label'][:10]=}")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# saving model
|
||||
peft_model_id = f"{model_name_or_path}_{peft_config.peft_type}_{peft_config.task_type}"
|
||||
model.save_pretrained(peft_model_id)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
ckpt = f"{peft_model_id}/adapter_model.bin"
|
||||
# get_ipython().system('du -h $ckpt')
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
peft_model_id = f"{model_name_or_path}_{peft_config.peft_type}_{peft_config.task_type}"
|
||||
|
||||
config = PeftConfig.from_pretrained(peft_model_id)
|
||||
model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained(config.base_model_name_or_path)
|
||||
model = PeftModel.from_pretrained(model, peft_model_id)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
model.eval()
|
||||
i = 13
|
||||
inputs = tokenizer(dataset["validation"][text_column][i], return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
print(dataset["validation"][text_column][i])
|
||||
print(inputs)
|
||||
|
||||
with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
outputs = model.generate(input_ids=inputs["input_ids"], max_new_tokens=10)
|
||||
print(outputs)
|
||||
print(tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs.detach().cpu().numpy(), skip_special_tokens=True))
|
||||
2711
examples/conditional_generation/peft_ia3_seq2seq.ipynb
Normal file
2711
examples/conditional_generation/peft_ia3_seq2seq.ipynb
Normal file
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
@ -2,20 +2,37 @@
|
||||
"cells": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 17,
|
||||
"execution_count": 1,
|
||||
"id": "5f93b7d1",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"outputs": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "stdout",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"===================================BUG REPORT===================================\n",
|
||||
"Welcome to bitsandbytes. For bug reports, please submit your error trace to: https://github.com/TimDettmers/bitsandbytes/issues\n",
|
||||
"For effortless bug reporting copy-paste your error into this form: https://docs.google.com/forms/d/e/1FAIpQLScPB8emS3Thkp66nvqwmjTEgxp8Y9ufuWTzFyr9kJ5AoI47dQ/viewform?usp=sf_link\n",
|
||||
"================================================================================\n",
|
||||
"CUDA SETUP: CUDA runtime path found: /home/sourab/miniconda3/envs/ml/lib/libcudart.so\n",
|
||||
"CUDA SETUP: Highest compute capability among GPUs detected: 7.5\n",
|
||||
"CUDA SETUP: Detected CUDA version 117\n",
|
||||
"CUDA SETUP: Loading binary /home/sourab/miniconda3/envs/ml/lib/python3.10/site-packages/bitsandbytes/libbitsandbytes_cuda117.so...\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from transformers import AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM\n",
|
||||
"from peft import get_peft_config,get_peft_model, get_peft_model_state_dict, LoraConfig, TaskType\n",
|
||||
"from peft import get_peft_config, get_peft_model, get_peft_model_state_dict, LoraConfig, TaskType\n",
|
||||
"import torch\n",
|
||||
"from datasets import load_dataset\n",
|
||||
"import os\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"os.environ[\"TOKENIZERS_PARALLELISM\"] = \"false\"\n",
|
||||
"from transformers import AutoTokenizer\n",
|
||||
"from torch.utils.data import DataLoader\n",
|
||||
"from transformers import default_data_collator,get_linear_schedule_with_warmup\n",
|
||||
"from transformers import default_data_collator, get_linear_schedule_with_warmup\n",
|
||||
"from tqdm import tqdm\n",
|
||||
"from datasets import load_dataset\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
@ -26,10 +43,10 @@
|
||||
"checkpoint_name = \"financial_sentiment_analysis_lora_v1.pt\"\n",
|
||||
"text_column = \"sentence\"\n",
|
||||
"label_column = \"text_label\"\n",
|
||||
"max_length=128\n",
|
||||
"max_length = 128\n",
|
||||
"lr = 1e-3\n",
|
||||
"num_epochs = 3\n",
|
||||
"batch_size=8\n"
|
||||
"batch_size = 8"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
@ -40,9 +57,7 @@
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# creating model\n",
|
||||
"peft_config = LoraConfig(\n",
|
||||
" task_type=TaskType.SEQ_2_SEQ_LM, inference_mode=False, r=8, lora_alpha=32, lora_dropout=0.1\n",
|
||||
")\n",
|
||||
"peft_config = LoraConfig(task_type=TaskType.SEQ_2_SEQ_LM, inference_mode=False, r=8, lora_alpha=32, lora_dropout=0.1)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained(model_name_or_path)\n",
|
||||
"model = get_peft_model(model, peft_config)\n",
|
||||
@ -60,15 +75,13 @@
|
||||
"name": "stderr",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"/home/sourab/miniconda3/envs/ml/lib/python3.10/site-packages/huggingface_hub/utils/_deprecation.py:97: FutureWarning: Deprecated argument(s) used in 'dataset_info': token. Will not be supported from version '0.12'.\n",
|
||||
" warnings.warn(message, FutureWarning)\n",
|
||||
"Found cached dataset financial_phrasebank (/home/sourab/.cache/huggingface/datasets/financial_phrasebank/sentences_allagree/1.0.0/550bde12e6c30e2674da973a55f57edde5181d53f5a5a34c1531c53f93b7e141)\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"data": {
|
||||
"application/vnd.jupyter.widget-view+json": {
|
||||
"model_id": "6de075f8208349108291ac5ab7f5c980",
|
||||
"model_id": "3403bf3d718042018b0531848cc30209",
|
||||
"version_major": 2,
|
||||
"version_minor": 0
|
||||
},
|
||||
@ -82,7 +95,7 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"data": {
|
||||
"application/vnd.jupyter.widget-view+json": {
|
||||
"model_id": "4b0e67b6d93f43e4b0f6a2f8978e4b0c",
|
||||
"model_id": "d3d5c45e3776469f9560b6eaa9346f8f",
|
||||
"version_major": 2,
|
||||
"version_minor": 0
|
||||
},
|
||||
@ -96,7 +109,7 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"data": {
|
||||
"application/vnd.jupyter.widget-view+json": {
|
||||
"model_id": "a9551029c9884529bda7421a99170b51",
|
||||
"model_id": "e9736f26e9aa450b8d65f95c0b9c81cc",
|
||||
"version_major": 2,
|
||||
"version_minor": 0
|
||||
},
|
||||
@ -110,7 +123,7 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"data": {
|
||||
"text/plain": [
|
||||
"{'sentence': 'The order was valued at USD12 .2 m.',\n",
|
||||
"{'sentence': \"The 10,000-odd square metre plot that Stockmann has bought for the Nevsky Center shopping center is located on Nevsky Prospect , St Petersburg 's high street , next to the Vosstaniya Square underground station , in the immediate vicinity of Moscow Station .\",\n",
|
||||
" 'label': 1,\n",
|
||||
" 'text_label': 'neutral'}"
|
||||
]
|
||||
@ -122,17 +135,16 @@
|
||||
],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# loading dataset\n",
|
||||
"dataset = load_dataset(\"financial_phrasebank\", 'sentences_allagree')\n",
|
||||
"dataset = load_dataset(\"financial_phrasebank\", \"sentences_allagree\")\n",
|
||||
"dataset = dataset[\"train\"].train_test_split(test_size=0.1)\n",
|
||||
"dataset[\"validation\"] = dataset[\"test\"]\n",
|
||||
"del(dataset[\"test\"])\n",
|
||||
"del dataset[\"test\"]\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"classes = dataset[\"train\"].features[\"label\"].names\n",
|
||||
"dataset = dataset.map(\n",
|
||||
" lambda x: {\"text_label\": [classes[label] for label in x[\"label\"]]},\n",
|
||||
" batched=True,\n",
|
||||
" num_proc=1,\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
")\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"dataset[\"train\"][0]"
|
||||
@ -147,7 +159,7 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"data": {
|
||||
"application/vnd.jupyter.widget-view+json": {
|
||||
"model_id": "4421971232434db1b6141e91fda2f6d7",
|
||||
"model_id": "c460989d4ab24e3f97d81ef040b1d1b4",
|
||||
"version_major": 2,
|
||||
"version_minor": 0
|
||||
},
|
||||
@ -161,7 +173,7 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"data": {
|
||||
"application/vnd.jupyter.widget-view+json": {
|
||||
"model_id": "9b2ef793d93443949f4a5d5874d4bc05",
|
||||
"model_id": "1acc389b08b94f8a87900b9fbdbccce4",
|
||||
"version_major": 2,
|
||||
"version_minor": 0
|
||||
},
|
||||
@ -176,36 +188,35 @@
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# data preprocessing\n",
|
||||
"tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name_or_path)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"def preprocess_function(examples):\n",
|
||||
" inputs = examples[text_column]\n",
|
||||
" targets = examples[label_column]\n",
|
||||
" model_inputs = tokenizer(inputs, max_length=max_length, padding=\"max_length\", truncation=True, return_tensors=\"pt\")\n",
|
||||
" labels = tokenizer(targets, max_length=3, padding=\"max_length\", truncation=True, return_tensors=\"pt\")\n",
|
||||
" labels = labels[\"input_ids\"]\n",
|
||||
" labels[labels==tokenizer.pad_token_id] = -100\n",
|
||||
" labels[labels == tokenizer.pad_token_id] = -100\n",
|
||||
" model_inputs[\"labels\"] = labels\n",
|
||||
" return model_inputs\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"processed_datasets = dataset.map(\n",
|
||||
" preprocess_function,\n",
|
||||
" batched=True,\n",
|
||||
" num_proc=1,\n",
|
||||
" remove_columns=dataset[\"train\"].column_names,\n",
|
||||
" load_from_cache_file=False,\n",
|
||||
" desc=\"Running tokenizer on dataset\",\n",
|
||||
" )\n",
|
||||
" preprocess_function,\n",
|
||||
" batched=True,\n",
|
||||
" num_proc=1,\n",
|
||||
" remove_columns=dataset[\"train\"].column_names,\n",
|
||||
" load_from_cache_file=False,\n",
|
||||
" desc=\"Running tokenizer on dataset\",\n",
|
||||
")\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"train_dataset = processed_datasets[\"train\"]\n",
|
||||
"eval_dataset = processed_datasets[\"validation\"]\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"train_dataloader = DataLoader(\n",
|
||||
" train_dataset, shuffle=True, collate_fn=default_data_collator, batch_size=batch_size, pin_memory=True\n",
|
||||
" )\n",
|
||||
"eval_dataloader = DataLoader(eval_dataset, collate_fn=default_data_collator, batch_size=batch_size, pin_memory=True)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" "
|
||||
" train_dataset, shuffle=True, collate_fn=default_data_collator, batch_size=batch_size, pin_memory=True\n",
|
||||
")\n",
|
||||
"eval_dataloader = DataLoader(eval_dataset, collate_fn=default_data_collator, batch_size=batch_size, pin_memory=True)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
@ -221,7 +232,7 @@
|
||||
" optimizer=optimizer,\n",
|
||||
" num_warmup_steps=0,\n",
|
||||
" num_training_steps=(len(train_dataloader) * num_epochs),\n",
|
||||
")\n"
|
||||
")"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
@ -234,45 +245,52 @@
|
||||
"name": "stderr",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"100%|█████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 255/255 [00:53<00:00, 4.80it/s]\n",
|
||||
"100%|███████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 29/29 [00:02<00:00, 14.16it/s]\n"
|
||||
"100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 255/255 [02:21<00:00, 1.81it/s]\n",
|
||||
"100%|██████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 29/29 [00:07<00:00, 4.13it/s]\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "stdout",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"epoch=0: train_ppl=tensor(13.6966, device='cuda:0') train_epoch_loss=tensor(2.6171, device='cuda:0') eval_ppl=tensor(1.0046, device='cuda:0') eval_epoch_loss=tensor(0.0046, device='cuda:0')\n"
|
||||
"epoch=0: train_ppl=tensor(14.6341, device='cuda:0') train_epoch_loss=tensor(2.6834, device='cuda:0') eval_ppl=tensor(1.0057, device='cuda:0') eval_epoch_loss=tensor(0.0057, device='cuda:0')\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "stderr",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"100%|█████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 255/255 [00:52<00:00, 4.88it/s]\n",
|
||||
"100%|███████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 29/29 [00:02<00:00, 14.20it/s]\n"
|
||||
"100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 255/255 [02:00<00:00, 2.11it/s]\n",
|
||||
"100%|██████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 29/29 [00:05<00:00, 5.66it/s]\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "stdout",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"epoch=1: train_ppl=tensor(1.5893, device='cuda:0') train_epoch_loss=tensor(0.4633, device='cuda:0') eval_ppl=tensor(1.0020, device='cuda:0') eval_epoch_loss=tensor(0.0020, device='cuda:0')\n"
|
||||
"epoch=1: train_ppl=tensor(1.7576, device='cuda:0') train_epoch_loss=tensor(0.5640, device='cuda:0') eval_ppl=tensor(1.0052, device='cuda:0') eval_epoch_loss=tensor(0.0052, device='cuda:0')\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "stderr",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"100%|█████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 255/255 [00:52<00:00, 4.87it/s]\n",
|
||||
"100%|███████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 29/29 [00:02<00:00, 14.18it/s]\n"
|
||||
"100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 255/255 [01:33<00:00, 2.74it/s]\n",
|
||||
"100%|██████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 29/29 [00:04<00:00, 6.23it/s]"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "stdout",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"epoch=2: train_ppl=tensor(1.3210, device='cuda:0') train_epoch_loss=tensor(0.2784, device='cuda:0') eval_ppl=tensor(1.0026, device='cuda:0') eval_epoch_loss=tensor(0.0026, device='cuda:0')\n"
|
||||
"epoch=2: train_ppl=tensor(1.3830, device='cuda:0') train_epoch_loss=tensor(0.3243, device='cuda:0') eval_ppl=tensor(1.0035, device='cuda:0') eval_epoch_loss=tensor(0.0035, device='cuda:0')\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "stderr",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
@ -302,18 +320,20 @@
|
||||
" outputs = model(**batch)\n",
|
||||
" loss = outputs.loss\n",
|
||||
" eval_loss += loss.detach().float()\n",
|
||||
" eval_preds.extend(tokenizer.batch_decode(torch.argmax(outputs.logits, -1).detach().cpu().numpy(), skip_special_tokens=True))\n",
|
||||
" eval_preds.extend(\n",
|
||||
" tokenizer.batch_decode(torch.argmax(outputs.logits, -1).detach().cpu().numpy(), skip_special_tokens=True)\n",
|
||||
" )\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" eval_epoch_loss = eval_loss/len(train_dataloader)\n",
|
||||
" eval_epoch_loss = eval_loss / len(eval_dataloader)\n",
|
||||
" eval_ppl = torch.exp(eval_epoch_loss)\n",
|
||||
" train_epoch_loss = total_loss/len(eval_dataloader)\n",
|
||||
" train_epoch_loss = total_loss / len(train_dataloader)\n",
|
||||
" train_ppl = torch.exp(train_epoch_loss)\n",
|
||||
" print(f\"{epoch=}: {train_ppl=} {train_epoch_loss=} {eval_ppl=} {eval_epoch_loss=}\")\n"
|
||||
" print(f\"{epoch=}: {train_ppl=} {train_epoch_loss=} {eval_ppl=} {eval_epoch_loss=}\")"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 20,
|
||||
"execution_count": 7,
|
||||
"id": "6cafa67b",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [
|
||||
@ -321,21 +341,21 @@
|
||||
"name": "stdout",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"accuracy=98.23788546255507 % on the evaluation dataset\n",
|
||||
"eval_preds[:10]=['neutral', 'neutral', 'positive', 'positive', 'neutral', 'neutral', 'neutral', 'neutral', 'neutral', 'neutral']\n",
|
||||
"dataset['validation']['text_label'][:10]=['neutral', 'neutral', 'positive', 'positive', 'neutral', 'neutral', 'neutral', 'neutral', 'neutral', 'neutral']\n"
|
||||
"accuracy=97.3568281938326 % on the evaluation dataset\n",
|
||||
"eval_preds[:10]=['neutral', 'neutral', 'neutral', 'positive', 'neutral', 'positive', 'positive', 'neutral', 'neutral', 'neutral']\n",
|
||||
"dataset['validation']['text_label'][:10]=['neutral', 'neutral', 'neutral', 'positive', 'neutral', 'positive', 'positive', 'neutral', 'neutral', 'neutral']\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# print accuracy\n",
|
||||
"correct =0\n",
|
||||
"correct = 0\n",
|
||||
"total = 0\n",
|
||||
"for pred,true in zip(eval_preds, dataset[\"validation\"][\"text_label\"]):\n",
|
||||
" if pred.strip()==true.strip():\n",
|
||||
" correct+=1\n",
|
||||
" total+=1 \n",
|
||||
"accuracy = correct/total*100\n",
|
||||
"for pred, true in zip(eval_preds, dataset[\"validation\"][\"text_label\"]):\n",
|
||||
" if pred.strip() == true.strip():\n",
|
||||
" correct += 1\n",
|
||||
" total += 1\n",
|
||||
"accuracy = correct / total * 100\n",
|
||||
"print(f\"{accuracy=} % on the evaluation dataset\")\n",
|
||||
"print(f\"{eval_preds[:10]=}\")\n",
|
||||
"print(f\"{dataset['validation']['text_label'][:10]=}\")"
|
||||
@ -343,20 +363,19 @@
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"execution_count": 8,
|
||||
"id": "a8de6005",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# saving model\n",
|
||||
"state_dict = get_peft_model_state_dict(model)\n",
|
||||
"torch.save(state_dict, checkpoint_name)\n",
|
||||
"print(state_dict)"
|
||||
"peft_model_id = f\"{model_name_or_path}_{peft_config.peft_type}_{peft_config.task_type}\"\n",
|
||||
"model.save_pretrained(peft_model_id)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 18,
|
||||
"execution_count": 9,
|
||||
"id": "bd20cd4c",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [
|
||||
@ -364,18 +383,75 @@
|
||||
"name": "stdout",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"19M\tfinancial_sentiment_analysis_lora_v1.pt\r\n"
|
||||
"9,2M\tbigscience/mt0-large_LORA_SEQ_2_SEQ_LM/adapter_model.bin\r\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"!du -h $checkpoint_name"
|
||||
"ckpt = f\"{peft_model_id}/adapter_model.bin\"\n",
|
||||
"!du -h $ckpt"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 11,
|
||||
"id": "76c2fc29",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from peft import PeftModel, PeftConfig\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"peft_model_id = f\"{model_name_or_path}_{peft_config.peft_type}_{peft_config.task_type}\"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"config = PeftConfig.from_pretrained(peft_model_id)\n",
|
||||
"model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained(config.base_model_name_or_path)\n",
|
||||
"model = PeftModel.from_pretrained(model, peft_model_id)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 15,
|
||||
"id": "37d712ce",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "stdout",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"- Demand for fireplace products was lower than expected , especially in Germany .\n",
|
||||
"{'input_ids': tensor([[ 259, 264, 259, 82903, 332, 1090, 10040, 10371, 639, 259,\n",
|
||||
" 19540, 2421, 259, 25505, 259, 261, 259, 21230, 281, 17052,\n",
|
||||
" 259, 260, 1]]), 'attention_mask': tensor([[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]])}\n",
|
||||
"tensor([[ 0, 259, 32588, 1]])\n",
|
||||
"['negative']\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"model.eval()\n",
|
||||
"i = 13\n",
|
||||
"inputs = tokenizer(dataset[\"validation\"][text_column][i], return_tensors=\"pt\")\n",
|
||||
"print(dataset[\"validation\"][text_column][i])\n",
|
||||
"print(inputs)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"with torch.no_grad():\n",
|
||||
" outputs = model.generate(input_ids=inputs[\"input_ids\"], max_new_tokens=10)\n",
|
||||
" print(outputs)\n",
|
||||
" print(tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs.detach().cpu().numpy(), skip_special_tokens=True))"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"id": "76c2fc29",
|
||||
"id": "66c65ea4",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": []
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"id": "65e71f78",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": []
|
||||
@ -383,7 +459,7 @@
|
||||
],
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"kernelspec": {
|
||||
"display_name": "Python 3.10.5 64-bit",
|
||||
"display_name": "Python 3 (ipykernel)",
|
||||
"language": "python",
|
||||
"name": "python3"
|
||||
},
|
||||
@ -397,7 +473,7 @@
|
||||
"name": "python",
|
||||
"nbconvert_exporter": "python",
|
||||
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
|
||||
"version": "3.10.5 (v3.10.5:f377153967, Jun 6 2022, 12:36:10) [Clang 13.0.0 (clang-1300.0.29.30)]"
|
||||
"version": "3.10.5"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"vscode": {
|
||||
"interpreter": {
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,253 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cells": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"id": "71fbfca2",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from transformers import AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM\n",
|
||||
"from peft import PeftModel, PeftConfig\n",
|
||||
"import torch\n",
|
||||
"from datasets import load_dataset\n",
|
||||
"import os\n",
|
||||
"from transformers import AutoTokenizer\n",
|
||||
"from torch.utils.data import DataLoader\n",
|
||||
"from transformers import default_data_collator, get_linear_schedule_with_warmup\n",
|
||||
"from tqdm import tqdm\n",
|
||||
"from datasets import load_dataset\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"dataset_name = \"twitter_complaints\"\n",
|
||||
"text_column = \"Tweet text\"\n",
|
||||
"label_column = \"text_label\"\n",
|
||||
"batch_size = 8\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"peft_model_id = \"smangrul/twitter_complaints_bigscience_T0_3B_LORA_SEQ_2_SEQ_LM\"\n",
|
||||
"config = PeftConfig.from_pretrained(peft_model_id)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 2,
|
||||
"id": "cc55820a",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"peft_model_id = \"smangrul/twitter_complaints_bigscience_T0_3B_LORA_SEQ_2_SEQ_LM\"\n",
|
||||
"max_memory = {0: \"6GIB\", 1: \"0GIB\", 2: \"0GIB\", 3: \"0GIB\", 4: \"0GIB\", \"cpu\": \"30GB\"}\n",
|
||||
"config = PeftConfig.from_pretrained(peft_model_id)\n",
|
||||
"model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained(config.base_model_name_or_path, device_map=\"auto\", max_memory=max_memory)\n",
|
||||
"model = PeftModel.from_pretrained(model, peft_model_id, device_map=\"auto\", max_memory=max_memory)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"id": "e1a3648b",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from datasets import load_dataset\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"dataset = load_dataset(\"ought/raft\", dataset_name)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"classes = [k.replace(\"_\", \" \") for k in dataset[\"train\"].features[\"Label\"].names]\n",
|
||||
"print(classes)\n",
|
||||
"dataset = dataset.map(\n",
|
||||
" lambda x: {\"text_label\": [classes[label] for label in x[\"Label\"]]},\n",
|
||||
" batched=True,\n",
|
||||
" num_proc=1,\n",
|
||||
")\n",
|
||||
"print(dataset)\n",
|
||||
"dataset[\"train\"][0]"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"id": "fe12d4d3",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(config.base_model_name_or_path)\n",
|
||||
"target_max_length = max([len(tokenizer(class_label)[\"input_ids\"]) for class_label in classes])\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"def preprocess_function(examples):\n",
|
||||
" inputs = examples[text_column]\n",
|
||||
" targets = examples[label_column]\n",
|
||||
" model_inputs = tokenizer(inputs, truncation=True)\n",
|
||||
" labels = tokenizer(\n",
|
||||
" targets, max_length=target_max_length, padding=\"max_length\", truncation=True, return_tensors=\"pt\"\n",
|
||||
" )\n",
|
||||
" labels = labels[\"input_ids\"]\n",
|
||||
" labels[labels == tokenizer.pad_token_id] = -100\n",
|
||||
" model_inputs[\"labels\"] = labels\n",
|
||||
" return model_inputs\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"processed_datasets = dataset.map(\n",
|
||||
" preprocess_function,\n",
|
||||
" batched=True,\n",
|
||||
" num_proc=1,\n",
|
||||
" remove_columns=dataset[\"train\"].column_names,\n",
|
||||
" load_from_cache_file=True,\n",
|
||||
" desc=\"Running tokenizer on dataset\",\n",
|
||||
")\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"train_dataset = processed_datasets[\"train\"]\n",
|
||||
"eval_dataset = processed_datasets[\"train\"]\n",
|
||||
"test_dataset = processed_datasets[\"test\"]\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"def collate_fn(examples):\n",
|
||||
" return tokenizer.pad(examples, padding=\"longest\", return_tensors=\"pt\")\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"train_dataloader = DataLoader(\n",
|
||||
" train_dataset, shuffle=True, collate_fn=collate_fn, batch_size=batch_size, pin_memory=True\n",
|
||||
")\n",
|
||||
"eval_dataloader = DataLoader(eval_dataset, collate_fn=collate_fn, batch_size=batch_size, pin_memory=True)\n",
|
||||
"test_dataloader = DataLoader(test_dataset, collate_fn=collate_fn, batch_size=batch_size, pin_memory=True)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 5,
|
||||
"id": "b33be5e6",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "stdout",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"@NYTsupport i have complained a dozen times & yet my papers are still thrown FAR from my door. Why is this so hard to resolve?\n",
|
||||
"{'input_ids': tensor([[25335, 1499, 3, 10, 3320, 12056, 382, 20390, 3, 23,\n",
|
||||
" 43, 25932, 3, 9, 9611, 648, 3, 184, 4624, 117,\n",
|
||||
" 780, 82, 5778, 33, 341, 3, 12618, 377, 4280, 45,\n",
|
||||
" 82, 1365, 5, 1615, 19, 48, 78, 614, 12, 7785,\n",
|
||||
" 58, 16229, 3, 10, 3, 1]]), 'attention_mask': tensor([[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,\n",
|
||||
" 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]])}\n",
|
||||
"tensor([[ 0, 10394, 1]], device='cuda:0')\n",
|
||||
"['complaint']\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"model.eval()\n",
|
||||
"i = 15\n",
|
||||
"inputs = tokenizer(f'{text_column} : {dataset[\"test\"][i][\"Tweet text\"]} Label : ', return_tensors=\"pt\")\n",
|
||||
"print(dataset[\"test\"][i][\"Tweet text\"])\n",
|
||||
"print(inputs)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"with torch.no_grad():\n",
|
||||
" outputs = model.generate(input_ids=inputs[\"input_ids\"].to(\"cuda\"), max_new_tokens=10)\n",
|
||||
" print(outputs)\n",
|
||||
" print(tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs.detach().cpu().numpy(), skip_special_tokens=True))"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 6,
|
||||
"id": "b6d6cd5b",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "stderr",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
" 0%| | 0/7 [00:00<?, ?it/s]You're using a T5TokenizerFast tokenizer. Please note that with a fast tokenizer, using the `__call__` method is faster than using a method to encode the text followed by a call to the `pad` method to get a padded encoding.\n",
|
||||
"100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 7/7 [00:10<00:00, 1.48s/it]\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"model.eval()\n",
|
||||
"eval_preds = []\n",
|
||||
"for _, batch in enumerate(tqdm(eval_dataloader)):\n",
|
||||
" batch = {k: v.to(\"cuda\") for k, v in batch.items() if k != \"labels\"}\n",
|
||||
" with torch.no_grad():\n",
|
||||
" outputs = model.generate(**batch, max_new_tokens=10)\n",
|
||||
" preds = outputs.detach().cpu().numpy()\n",
|
||||
" eval_preds.extend(tokenizer.batch_decode(preds, skip_special_tokens=True))"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 7,
|
||||
"id": "61264abe",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "stdout",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"accuracy=100.0\n",
|
||||
"eval_preds[:10]=['no complaint', 'no complaint', 'complaint', 'complaint', 'no complaint', 'no complaint', 'no complaint', 'complaint', 'complaint', 'no complaint']\n",
|
||||
"dataset['train'][label_column][:10]=['no complaint', 'no complaint', 'complaint', 'complaint', 'no complaint', 'no complaint', 'no complaint', 'complaint', 'complaint', 'no complaint']\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"correct = 0\n",
|
||||
"total = 0\n",
|
||||
"for pred, true in zip(eval_preds, dataset[\"train\"][label_column]):\n",
|
||||
" if pred.strip() == true.strip():\n",
|
||||
" correct += 1\n",
|
||||
" total += 1\n",
|
||||
"accuracy = correct / total * 100\n",
|
||||
"print(f\"{accuracy=}\")\n",
|
||||
"print(f\"{eval_preds[:10]=}\")\n",
|
||||
"print(f\"{dataset['train'][label_column][:10]=}\")"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"id": "a70802a3",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"model.eval()\n",
|
||||
"test_preds = []\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"for _, batch in enumerate(tqdm(test_dataloader)):\n",
|
||||
" batch = {k: v for k, v in batch.items() if k != \"labels\"}\n",
|
||||
" with torch.no_grad():\n",
|
||||
" outputs = model.generate(**batch, max_new_tokens=10)\n",
|
||||
" preds = outputs.detach().cpu().numpy()\n",
|
||||
" test_preds.extend(tokenizer.batch_decode(preds, skip_special_tokens=True))\n",
|
||||
" if len(test_preds) > 100:\n",
|
||||
" break\n",
|
||||
"test_preds"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"kernelspec": {
|
||||
"display_name": "Python 3 (ipykernel)",
|
||||
"language": "python",
|
||||
"name": "python3"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"language_info": {
|
||||
"codemirror_mode": {
|
||||
"name": "ipython",
|
||||
"version": 3
|
||||
},
|
||||
"file_extension": ".py",
|
||||
"mimetype": "text/x-python",
|
||||
"name": "python",
|
||||
"nbconvert_exporter": "python",
|
||||
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
|
||||
"version": "3.10.5 (v3.10.5:f377153967, Jun 6 2022, 12:36:10) [Clang 13.0.0 (clang-1300.0.29.30)]"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"vscode": {
|
||||
"interpreter": {
|
||||
"hash": "aee8b7b246df8f9039afb4144a1f6fd8d2ca17a180786b69acc140d282b71a49"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"nbformat": 4,
|
||||
"nbformat_minor": 5
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -3,37 +3,36 @@ import os
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
import threading
|
||||
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
import psutil
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from accelerate import Accelerator
|
||||
from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
|
||||
from tqdm import tqdm
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM, AutoTokenizer, get_linear_schedule_with_warmup, set_seed
|
||||
|
||||
import psutil
|
||||
from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
from peft import LoraConfig, TaskType, get_peft_model, get_peft_model_state_dict
|
||||
from tqdm import tqdm
|
||||
from peft import LoraConfig, TaskType, get_peft_model
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def levenshtein_distance(str1, str2):
|
||||
# TC: O(N^2)
|
||||
# SC: O(N^2)
|
||||
# SC: O(N)
|
||||
if str1 == str2:
|
||||
return 0
|
||||
num_rows = len(str1) + 1
|
||||
num_cols = len(str2) + 1
|
||||
dp_matrix = np.empty((num_rows, num_cols))
|
||||
dp_matrix[0, :] = range(num_cols)
|
||||
dp_matrix[:, 0] = range(num_rows)
|
||||
|
||||
dp_matrix = list(range(num_cols))
|
||||
for i in range(1, num_rows):
|
||||
prev = dp_matrix[0]
|
||||
dp_matrix[0] = i
|
||||
for j in range(1, num_cols):
|
||||
temp = dp_matrix[j]
|
||||
if str1[i - 1] == str2[j - 1]:
|
||||
dp_matrix[i, j] = dp_matrix[i - 1, j - 1]
|
||||
dp_matrix[j] = prev
|
||||
else:
|
||||
dp_matrix[i, j] = min(dp_matrix[i - 1, j - 1], dp_matrix[i - 1, j], dp_matrix[i, j - 1]) + 1
|
||||
|
||||
return dp_matrix[num_rows - 1, num_cols - 1]
|
||||
dp_matrix[j] = min(prev, dp_matrix[j], dp_matrix[j - 1]) + 1
|
||||
prev = temp
|
||||
return dp_matrix[num_cols - 1]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def get_closest_label(eval_pred, classes):
|
||||
@ -102,20 +101,19 @@ class TorchTracemalloc:
|
||||
|
||||
def main():
|
||||
accelerator = Accelerator()
|
||||
model_name_or_path = "bigscience/T0_3B"
|
||||
# model_name_or_path = "bigscience/T0_3B"
|
||||
model_name_or_path = "facebook/bart-large"
|
||||
dataset_name = "twitter_complaints"
|
||||
peft_config = LoraConfig(
|
||||
task_type=TaskType.SEQ_2_SEQ_LM, inference_mode=False, r=8, lora_alpha=32, lora_dropout=0.1
|
||||
)
|
||||
checkpoint_name = (
|
||||
f"{dataset_name}_{model_name_or_path}_{peft_config.peft_type}_{peft_config.task_type}_v1.pt".replace("/", "_")
|
||||
)
|
||||
text_column = "Tweet text"
|
||||
label_column = "text_label"
|
||||
lr = 3e-3
|
||||
num_epochs = 5
|
||||
batch_size = 8
|
||||
seed = 42
|
||||
do_test = False
|
||||
set_seed(seed)
|
||||
|
||||
dataset = load_dataset("ought/raft", dataset_name)
|
||||
@ -202,24 +200,20 @@ def main():
|
||||
lr_scheduler.step()
|
||||
optimizer.zero_grad()
|
||||
# Printing the GPU memory usage details such as allocated memory, peak memory, and total memory usage
|
||||
accelerator.print("GPU Memory before entering the train : {}".format(b2mb(tracemalloc.begin)))
|
||||
accelerator.print("GPU Memory consumed at the end of the train (end-begin): {}".format(tracemalloc.used))
|
||||
accelerator.print("GPU Peak Memory consumed during the train (max-begin): {}".format(tracemalloc.peaked))
|
||||
accelerator.print(f"GPU Memory before entering the train : {b2mb(tracemalloc.begin)}")
|
||||
accelerator.print(f"GPU Memory consumed at the end of the train (end-begin): {tracemalloc.used}")
|
||||
accelerator.print(f"GPU Peak Memory consumed during the train (max-begin): {tracemalloc.peaked}")
|
||||
accelerator.print(
|
||||
"GPU Total Peak Memory consumed during the train (max): {}".format(
|
||||
tracemalloc.peaked + b2mb(tracemalloc.begin)
|
||||
)
|
||||
f"GPU Total Peak Memory consumed during the train (max): {tracemalloc.peaked + b2mb(tracemalloc.begin)}"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
accelerator.print("CPU Memory before entering the train : {}".format(b2mb(tracemalloc.cpu_begin)))
|
||||
accelerator.print("CPU Memory consumed at the end of the train (end-begin): {}".format(tracemalloc.cpu_used))
|
||||
accelerator.print("CPU Peak Memory consumed during the train (max-begin): {}".format(tracemalloc.cpu_peaked))
|
||||
accelerator.print(f"CPU Memory before entering the train : {b2mb(tracemalloc.cpu_begin)}")
|
||||
accelerator.print(f"CPU Memory consumed at the end of the train (end-begin): {tracemalloc.cpu_used}")
|
||||
accelerator.print(f"CPU Peak Memory consumed during the train (max-begin): {tracemalloc.cpu_peaked}")
|
||||
accelerator.print(
|
||||
"CPU Total Peak Memory consumed during the train (max): {}".format(
|
||||
tracemalloc.cpu_peaked + b2mb(tracemalloc.cpu_begin)
|
||||
)
|
||||
f"CPU Total Peak Memory consumed during the train (max): {tracemalloc.cpu_peaked + b2mb(tracemalloc.cpu_begin)}"
|
||||
)
|
||||
train_epoch_loss = total_loss / len(eval_dataloader)
|
||||
train_epoch_loss = total_loss / len(train_dataloader)
|
||||
train_ppl = torch.exp(train_epoch_loss)
|
||||
accelerator.print(f"{epoch=}: {train_ppl=} {train_epoch_loss=}")
|
||||
|
||||
@ -232,30 +226,30 @@ def main():
|
||||
outputs = accelerator.unwrap_model(model).generate(
|
||||
**batch, synced_gpus=is_ds_zero_3
|
||||
) # synced_gpus=True for DS-stage 3
|
||||
preds = outputs.detach().cpu().numpy()
|
||||
outputs = accelerator.pad_across_processes(outputs, dim=1, pad_index=tokenizer.pad_token_id)
|
||||
preds = accelerator.gather_for_metrics(outputs).detach().cpu().numpy()
|
||||
eval_preds.extend(tokenizer.batch_decode(preds, skip_special_tokens=True))
|
||||
|
||||
# Printing the GPU memory usage details such as allocated memory, peak memory, and total memory usage
|
||||
accelerator.print("GPU Memory before entering the eval : {}".format(b2mb(tracemalloc.begin)))
|
||||
accelerator.print("GPU Memory consumed at the end of the eval (end-begin): {}".format(tracemalloc.used))
|
||||
accelerator.print("GPU Peak Memory consumed during the eval (max-begin): {}".format(tracemalloc.peaked))
|
||||
accelerator.print(f"GPU Memory before entering the eval : {b2mb(tracemalloc.begin)}")
|
||||
accelerator.print(f"GPU Memory consumed at the end of the eval (end-begin): {tracemalloc.used}")
|
||||
accelerator.print(f"GPU Peak Memory consumed during the eval (max-begin): {tracemalloc.peaked}")
|
||||
accelerator.print(
|
||||
"GPU Total Peak Memory consumed during the eval (max): {}".format(
|
||||
tracemalloc.peaked + b2mb(tracemalloc.begin)
|
||||
)
|
||||
f"GPU Total Peak Memory consumed during the eval (max): {tracemalloc.peaked + b2mb(tracemalloc.begin)}"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
accelerator.print("CPU Memory before entering the eval : {}".format(b2mb(tracemalloc.cpu_begin)))
|
||||
accelerator.print("CPU Memory consumed at the end of the eval (end-begin): {}".format(tracemalloc.cpu_used))
|
||||
accelerator.print("CPU Peak Memory consumed during the eval (max-begin): {}".format(tracemalloc.cpu_peaked))
|
||||
accelerator.print(f"CPU Memory before entering the eval : {b2mb(tracemalloc.cpu_begin)}")
|
||||
accelerator.print(f"CPU Memory consumed at the end of the eval (end-begin): {tracemalloc.cpu_used}")
|
||||
accelerator.print(f"CPU Peak Memory consumed during the eval (max-begin): {tracemalloc.cpu_peaked}")
|
||||
accelerator.print(
|
||||
"CPU Total Peak Memory consumed during the eval (max): {}".format(
|
||||
tracemalloc.cpu_peaked + b2mb(tracemalloc.cpu_begin)
|
||||
)
|
||||
f"CPU Total Peak Memory consumed during the eval (max): {tracemalloc.cpu_peaked + b2mb(tracemalloc.cpu_begin)}"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
correct = 0
|
||||
total = 0
|
||||
assert len(eval_preds) == len(
|
||||
dataset["train"][label_column]
|
||||
), f"{len(eval_preds)} != {len(dataset['train'][label_column])}"
|
||||
for pred, true in zip(eval_preds, dataset["train"][label_column]):
|
||||
if pred.strip() == true.strip():
|
||||
correct += 1
|
||||
@ -265,33 +259,52 @@ def main():
|
||||
accelerator.print(f"{eval_preds[:10]=}")
|
||||
accelerator.print(f"{dataset['train'][label_column][:10]=}")
|
||||
|
||||
model.eval()
|
||||
test_preds = []
|
||||
for _, batch in enumerate(tqdm(test_dataloader)):
|
||||
batch = {k: v for k, v in batch.items() if k != "labels"}
|
||||
with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
outputs = accelerator.unwrap_model(model).generate(
|
||||
**batch, synced_gpus=is_ds_zero_3
|
||||
) # synced_gpus=True for DS-stage 3
|
||||
test_preds.extend(tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs.detach().cpu().numpy(), skip_special_tokens=True))
|
||||
if do_test:
|
||||
model.eval()
|
||||
test_preds = []
|
||||
for _, batch in enumerate(tqdm(test_dataloader)):
|
||||
batch = {k: v for k, v in batch.items() if k != "labels"}
|
||||
with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
outputs = accelerator.unwrap_model(model).generate(
|
||||
**batch, synced_gpus=is_ds_zero_3
|
||||
) # synced_gpus=True for DS-stage 3
|
||||
outputs = accelerator.pad_across_processes(outputs, dim=1, pad_index=tokenizer.pad_token_id)
|
||||
preds = accelerator.gather(outputs).detach().cpu().numpy()
|
||||
test_preds.extend(tokenizer.batch_decode(preds, skip_special_tokens=True))
|
||||
|
||||
test_preds_cleaned = []
|
||||
for _, pred in enumerate(test_preds):
|
||||
test_preds_cleaned.append(get_closest_label(pred, classes))
|
||||
test_preds_cleaned = []
|
||||
for _, pred in enumerate(test_preds):
|
||||
test_preds_cleaned.append(get_closest_label(pred, classes))
|
||||
|
||||
test_df = dataset["test"].to_pandas()
|
||||
test_df[label_column] = test_preds_cleaned
|
||||
test_df["text_labels_orig"] = test_preds
|
||||
accelerator.print(test_df[[text_column, label_column]].sample(20))
|
||||
test_df = dataset["test"].to_pandas()
|
||||
assert len(test_preds_cleaned) == len(test_df), f"{len(test_preds_cleaned)} != {len(test_df)}"
|
||||
test_df[label_column] = test_preds_cleaned
|
||||
test_df["text_labels_orig"] = test_preds
|
||||
accelerator.print(test_df[[text_column, label_column]].sample(20))
|
||||
|
||||
pred_df = test_df[["ID", label_column]]
|
||||
pred_df.columns = ["ID", "Label"]
|
||||
pred_df = test_df[["ID", label_column]]
|
||||
pred_df.columns = ["ID", "Label"]
|
||||
|
||||
os.makedirs(f"data/{dataset_name}", exist_ok=True)
|
||||
pred_df.to_csv(f"data/{dataset_name}/predictions.csv", index=False)
|
||||
os.makedirs(f"data/{dataset_name}", exist_ok=True)
|
||||
pred_df.to_csv(f"data/{dataset_name}/predictions.csv", index=False)
|
||||
|
||||
accelerator.wait_for_everyone()
|
||||
accelerator.save(get_peft_model_state_dict(model, state_dict=accelerator.get_state_dict(model)), checkpoint_name)
|
||||
# Option1: Pushing the model to Hugging Face Hub
|
||||
# model.push_to_hub(
|
||||
# f"{dataset_name}_{model_name_or_path}_{peft_config.peft_type}_{peft_config.task_type}".replace("/", "_"),
|
||||
# token = "hf_..."
|
||||
# )
|
||||
# token (`bool` or `str`, *optional*):
|
||||
# `token` is to be used for HTTP Bearer authorization when accessing remote files. If `True`, will use the token generated
|
||||
# when running `huggingface-cli login` (stored in `~/.huggingface`). Will default to `True` if `repo_url`
|
||||
# is not specified.
|
||||
# Or you can get your token from https://huggingface.co/settings/token
|
||||
|
||||
# Option2: Saving the model locally
|
||||
peft_model_id = f"{dataset_name}_{model_name_or_path}_{peft_config.peft_type}_{peft_config.task_type}".replace(
|
||||
"/", "_"
|
||||
)
|
||||
model.save_pretrained(peft_model_id)
|
||||
accelerator.wait_for_everyone()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -2,13 +2,13 @@ import os
|
||||
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from accelerate import Accelerator
|
||||
from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
|
||||
from tqdm import tqdm
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM, AutoTokenizer, default_data_collator, get_linear_schedule_with_warmup
|
||||
|
||||
from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
from peft import LoraConfig, TaskType, get_peft_model, get_peft_model_state_dict
|
||||
from peft import LoraConfig, TaskType, get_peft_model
|
||||
from peft.utils.other import fsdp_auto_wrap_policy
|
||||
from tqdm import tqdm
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def main():
|
||||
@ -25,7 +25,6 @@ def main():
|
||||
peft_config = LoraConfig(
|
||||
task_type=TaskType.SEQ_2_SEQ_LM, inference_mode=False, r=8, lora_alpha=32, lora_dropout=0.1
|
||||
)
|
||||
checkpoint_name = "financial_sentiment_analysis_lora_fsdp_v1.pt"
|
||||
model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained(model_name_or_path)
|
||||
model = get_peft_model(model, peft_config)
|
||||
accelerator.print(model.print_trainable_parameters())
|
||||
@ -109,9 +108,9 @@ def main():
|
||||
eval_loss += loss.detach().float()
|
||||
preds = accelerator.gather_for_metrics(torch.argmax(outputs.logits, -1)).detach().cpu().numpy()
|
||||
eval_preds.extend(tokenizer.batch_decode(preds, skip_special_tokens=True))
|
||||
eval_epoch_loss = eval_loss / len(train_dataloader)
|
||||
eval_epoch_loss = eval_loss / len(eval_dataloader)
|
||||
eval_ppl = torch.exp(eval_epoch_loss)
|
||||
train_epoch_loss = total_loss / len(eval_dataloader)
|
||||
train_epoch_loss = total_loss / len(train_dataloader)
|
||||
train_ppl = torch.exp(train_epoch_loss)
|
||||
accelerator.print(f"{epoch=}: {train_ppl=} {train_epoch_loss=} {eval_ppl=} {eval_epoch_loss=}")
|
||||
|
||||
@ -126,9 +125,19 @@ def main():
|
||||
accelerator.print(f"{eval_preds[:10]=}")
|
||||
accelerator.print(f"{dataset['validation'][label_column][:10]=}")
|
||||
accelerator.wait_for_everyone()
|
||||
accelerator.save(
|
||||
get_peft_model_state_dict(model, state_dict=accelerator.get_state_dict(model)), checkpoint_name
|
||||
)
|
||||
# Option1: Pushing the model to Hugging Face Hub
|
||||
# model.push_to_hub(
|
||||
# f"{dataset_name}_{model_name_or_path}_{peft_config.peft_type}_{peft_config.task_type}".replace("/", "_"),
|
||||
# token = "hf_..."
|
||||
# )
|
||||
# token (`bool` or `str`, *optional*):
|
||||
# `token` is to be used for HTTP Bearer authorization when accessing remote files. If `True`, will use the token generated
|
||||
# when running `huggingface-cli login` (stored in `~/.huggingface`). Will default to `True` if `repo_url`
|
||||
# is not specified.
|
||||
# Or you can get your token from https://huggingface.co/settings/token
|
||||
# Option2: Saving the model locally
|
||||
peft_model_id = f"{model_name_or_path}_{peft_config.peft_type}_{peft_config.task_type}".replace("/", "_")
|
||||
model.save_pretrained(peft_model_id)
|
||||
accelerator.wait_for_everyone()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -5,18 +5,35 @@
|
||||
"execution_count": 1,
|
||||
"id": "5f93b7d1",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"outputs": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "stdout",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"===================================BUG REPORT===================================\n",
|
||||
"Welcome to bitsandbytes. For bug reports, please submit your error trace to: https://github.com/TimDettmers/bitsandbytes/issues\n",
|
||||
"For effortless bug reporting copy-paste your error into this form: https://docs.google.com/forms/d/e/1FAIpQLScPB8emS3Thkp66nvqwmjTEgxp8Y9ufuWTzFyr9kJ5AoI47dQ/viewform?usp=sf_link\n",
|
||||
"================================================================================\n",
|
||||
"CUDA SETUP: CUDA runtime path found: /home/sourab/miniconda3/envs/ml/lib/libcudart.so\n",
|
||||
"CUDA SETUP: Highest compute capability among GPUs detected: 7.5\n",
|
||||
"CUDA SETUP: Detected CUDA version 117\n",
|
||||
"CUDA SETUP: Loading binary /home/sourab/miniconda3/envs/ml/lib/python3.10/site-packages/bitsandbytes/libbitsandbytes_cuda117.so...\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from transformers import AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM\n",
|
||||
"from peft import get_peft_config,get_peft_model, get_peft_model_state_dict, PrefixTuningConfig, TaskType\n",
|
||||
"from peft import get_peft_config, get_peft_model, get_peft_model_state_dict, PrefixTuningConfig, TaskType\n",
|
||||
"import torch\n",
|
||||
"from datasets import load_dataset\n",
|
||||
"import os\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"os.environ[\"TOKENIZERS_PARALLELISM\"] = \"false\"\n",
|
||||
"os.environ[\"CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES\"] = \"3\"\n",
|
||||
"from transformers import AutoTokenizer\n",
|
||||
"from torch.utils.data import DataLoader\n",
|
||||
"from transformers import default_data_collator,get_linear_schedule_with_warmup\n",
|
||||
"from transformers import default_data_collator, get_linear_schedule_with_warmup\n",
|
||||
"from tqdm import tqdm\n",
|
||||
"from datasets import load_dataset\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
@ -27,10 +44,10 @@
|
||||
"checkpoint_name = \"financial_sentiment_analysis_prefix_tuning_v1.pt\"\n",
|
||||
"text_column = \"sentence\"\n",
|
||||
"label_column = \"text_label\"\n",
|
||||
"max_length=128\n",
|
||||
"max_length = 128\n",
|
||||
"lr = 1e-2\n",
|
||||
"num_epochs = 5\n",
|
||||
"batch_size=8\n"
|
||||
"batch_size = 8"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
@ -41,9 +58,7 @@
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# creating model\n",
|
||||
"peft_config = PrefixTuningConfig(\n",
|
||||
" task_type=TaskType.SEQ_2_SEQ_LM, inference_mode=False, num_virtual_tokens=20\n",
|
||||
")\n",
|
||||
"peft_config = PrefixTuningConfig(task_type=TaskType.SEQ_2_SEQ_LM, inference_mode=False, num_virtual_tokens=20)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained(model_name_or_path)\n",
|
||||
"model = get_peft_model(model, peft_config)\n",
|
||||
@ -61,15 +76,13 @@
|
||||
"name": "stderr",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"/home/sourab/miniconda3/envs/ml/lib/python3.10/site-packages/huggingface_hub/utils/_deprecation.py:97: FutureWarning: Deprecated argument(s) used in 'dataset_info': token. Will not be supported from version '0.12'.\n",
|
||||
" warnings.warn(message, FutureWarning)\n",
|
||||
"Found cached dataset financial_phrasebank (/home/sourab/.cache/huggingface/datasets/financial_phrasebank/sentences_allagree/1.0.0/550bde12e6c30e2674da973a55f57edde5181d53f5a5a34c1531c53f93b7e141)\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"data": {
|
||||
"application/vnd.jupyter.widget-view+json": {
|
||||
"model_id": "e3f8b8faca0a4112b2c3499faee9544b",
|
||||
"model_id": "ec4be98991b84181bfa75f8846422b8b",
|
||||
"version_major": 2,
|
||||
"version_minor": 0
|
||||
},
|
||||
@ -83,7 +96,7 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"data": {
|
||||
"application/vnd.jupyter.widget-view+json": {
|
||||
"model_id": "935c8aebde284a5784348588e0bb013a",
|
||||
"model_id": "82a6bd694c4f4751a23c370ab51f01a4",
|
||||
"version_major": 2,
|
||||
"version_minor": 0
|
||||
},
|
||||
@ -97,7 +110,7 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"data": {
|
||||
"application/vnd.jupyter.widget-view+json": {
|
||||
"model_id": "e3487cd55f6847588492bf7fa51348ca",
|
||||
"model_id": "3844878631534468a1495e435563e4b0",
|
||||
"version_major": 2,
|
||||
"version_minor": 0
|
||||
},
|
||||
@ -111,9 +124,9 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"data": {
|
||||
"text/plain": [
|
||||
"{'sentence': 'ADPnews - Feb 5 , 2010 - Finnish real estate investor Sponda Oyj HEL : SDA1V said today that it slipped to a net loss of EUR 81.5 million USD 11.8 m in 2009 from a profit of EUR 29.3 million in 2008 .',\n",
|
||||
" 'label': 0,\n",
|
||||
" 'text_label': 'negative'}"
|
||||
"{'sentence': 'Finnish elevators and escalators maker KONE Corporation said on Tuesday ( 18 March ) that it has received a major order from Sir Robert McAlpine to supply all elevators and escalators for the Watermark Place project in the City of London .',\n",
|
||||
" 'label': 2,\n",
|
||||
" 'text_label': 'positive'}"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
"execution_count": 3,
|
||||
@ -123,17 +136,16 @@
|
||||
],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# loading dataset\n",
|
||||
"dataset = load_dataset(\"financial_phrasebank\", 'sentences_allagree')\n",
|
||||
"dataset = load_dataset(\"financial_phrasebank\", \"sentences_allagree\")\n",
|
||||
"dataset = dataset[\"train\"].train_test_split(test_size=0.1)\n",
|
||||
"dataset[\"validation\"] = dataset[\"test\"]\n",
|
||||
"del(dataset[\"test\"])\n",
|
||||
"del dataset[\"test\"]\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"classes = dataset[\"train\"].features[\"label\"].names\n",
|
||||
"dataset = dataset.map(\n",
|
||||
" lambda x: {\"text_label\": [classes[label] for label in x[\"label\"]]},\n",
|
||||
" batched=True,\n",
|
||||
" num_proc=1,\n",
|
||||
" \n",
|
||||
")\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"dataset[\"train\"][0]"
|
||||
@ -145,39 +157,11 @@
|
||||
"id": "adf9608c",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"data": {
|
||||
"application/vnd.jupyter.widget-view+json": {
|
||||
"model_id": "2ce088f4437d4e2c80c267332a5b84e5",
|
||||
"version_major": 2,
|
||||
"version_minor": 0
|
||||
},
|
||||
"text/plain": [
|
||||
"Downloading: 0%| | 0.00/792k [00:00<?, ?B/s]"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"output_type": "display_data"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"data": {
|
||||
"application/vnd.jupyter.widget-view+json": {
|
||||
"model_id": "4e5f69b61f194220b39336e48edd2f9e",
|
||||
"version_major": 2,
|
||||
"version_minor": 0
|
||||
},
|
||||
"text/plain": [
|
||||
"Downloading: 0%| | 0.00/1.39M [00:00<?, ?B/s]"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"output_type": "display_data"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "stderr",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"/home/sourab/transformers/src/transformers/models/t5/tokenization_t5_fast.py:156: FutureWarning: This tokenizer was incorrectly instantiated with a model max length of 512 which will be corrected in Transformers v5.\n",
|
||||
"/home/sourab/transformers/src/transformers/models/t5/tokenization_t5_fast.py:155: FutureWarning: This tokenizer was incorrectly instantiated with a model max length of 512 which will be corrected in Transformers v5.\n",
|
||||
"For now, this behavior is kept to avoid breaking backwards compatibility when padding/encoding with `truncation is True`.\n",
|
||||
"- Be aware that you SHOULD NOT rely on t5-large automatically truncating your input to 512 when padding/encoding.\n",
|
||||
"- If you want to encode/pad to sequences longer than 512 you can either instantiate this tokenizer with `model_max_length` or pass `max_length` when encoding/padding.\n",
|
||||
@ -188,7 +172,7 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"data": {
|
||||
"application/vnd.jupyter.widget-view+json": {
|
||||
"model_id": "230c5631891e4ea8ac7a1b39f315a4f0",
|
||||
"model_id": "4af8c12efb5643659573347509079f3a",
|
||||
"version_major": 2,
|
||||
"version_minor": 0
|
||||
},
|
||||
@ -202,7 +186,7 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"data": {
|
||||
"application/vnd.jupyter.widget-view+json": {
|
||||
"model_id": "b581e5677d2a45459ceb725534ed0891",
|
||||
"model_id": "86033b6257384584afd034075af808cb",
|
||||
"version_major": 2,
|
||||
"version_minor": 0
|
||||
},
|
||||
@ -217,36 +201,35 @@
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# data preprocessing\n",
|
||||
"tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name_or_path)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"def preprocess_function(examples):\n",
|
||||
" inputs = examples[text_column]\n",
|
||||
" targets = examples[label_column]\n",
|
||||
" model_inputs = tokenizer(inputs, max_length=max_length, padding=\"max_length\", truncation=True, return_tensors=\"pt\")\n",
|
||||
" labels = tokenizer(targets, max_length=2, padding=\"max_length\", truncation=True, return_tensors=\"pt\")\n",
|
||||
" labels = labels[\"input_ids\"]\n",
|
||||
" labels[labels==tokenizer.pad_token_id] = -100\n",
|
||||
" labels[labels == tokenizer.pad_token_id] = -100\n",
|
||||
" model_inputs[\"labels\"] = labels\n",
|
||||
" return model_inputs\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"processed_datasets = dataset.map(\n",
|
||||
" preprocess_function,\n",
|
||||
" batched=True,\n",
|
||||
" num_proc=1,\n",
|
||||
" remove_columns=dataset[\"train\"].column_names,\n",
|
||||
" load_from_cache_file=False,\n",
|
||||
" desc=\"Running tokenizer on dataset\",\n",
|
||||
" )\n",
|
||||
" preprocess_function,\n",
|
||||
" batched=True,\n",
|
||||
" num_proc=1,\n",
|
||||
" remove_columns=dataset[\"train\"].column_names,\n",
|
||||
" load_from_cache_file=False,\n",
|
||||
" desc=\"Running tokenizer on dataset\",\n",
|
||||
")\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"train_dataset = processed_datasets[\"train\"]\n",
|
||||
"eval_dataset = processed_datasets[\"validation\"]\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"train_dataloader = DataLoader(\n",
|
||||
" train_dataset, shuffle=True, collate_fn=default_data_collator, batch_size=batch_size, pin_memory=True\n",
|
||||
" )\n",
|
||||
"eval_dataloader = DataLoader(eval_dataset, collate_fn=default_data_collator, batch_size=batch_size, pin_memory=True)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" "
|
||||
" train_dataset, shuffle=True, collate_fn=default_data_collator, batch_size=batch_size, pin_memory=True\n",
|
||||
")\n",
|
||||
"eval_dataloader = DataLoader(eval_dataset, collate_fn=default_data_collator, batch_size=batch_size, pin_memory=True)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
@ -262,7 +245,7 @@
|
||||
" optimizer=optimizer,\n",
|
||||
" num_warmup_steps=0,\n",
|
||||
" num_training_steps=(len(train_dataloader) * num_epochs),\n",
|
||||
")\n"
|
||||
")"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
@ -275,82 +258,75 @@
|
||||
"name": "stderr",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"100%|█████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 255/255 [00:20<00:00, 12.27it/s]\n",
|
||||
"100%|███████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 29/29 [00:01<00:00, 17.32it/s]\n"
|
||||
"100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 255/255 [00:49<00:00, 5.15it/s]\n",
|
||||
"100%|██████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 29/29 [00:03<00:00, 7.56it/s]\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "stdout",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"epoch=0: train_ppl=tensor(2697769., device='cuda:0') train_epoch_loss=tensor(14.8079, device='cuda:0') eval_ppl=tensor(1.0089, device='cuda:0') eval_epoch_loss=tensor(0.0089, device='cuda:0')\n"
|
||||
"epoch=0: train_ppl=tensor(2760654.5000, device='cuda:0') train_epoch_loss=tensor(14.8310, device='cuda:0') eval_ppl=tensor(1.0124, device='cuda:0') eval_epoch_loss=tensor(0.0124, device='cuda:0')\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "stderr",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"100%|█████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 255/255 [00:19<00:00, 12.75it/s]\n",
|
||||
"100%|███████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 29/29 [00:01<00:00, 17.33it/s]\n"
|
||||
"100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 255/255 [00:40<00:00, 6.22it/s]\n",
|
||||
"100%|██████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 29/29 [00:05<00:00, 5.05it/s]\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "stdout",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"epoch=1: train_ppl=tensor(2.9475, device='cuda:0') train_epoch_loss=tensor(1.0809, device='cuda:0') eval_ppl=tensor(1.0072, device='cuda:0') eval_epoch_loss=tensor(0.0072, device='cuda:0')\n"
|
||||
"epoch=1: train_ppl=tensor(2.7329, device='cuda:0') train_epoch_loss=tensor(1.0054, device='cuda:0') eval_ppl=tensor(1.0081, device='cuda:0') eval_epoch_loss=tensor(0.0080, device='cuda:0')\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "stderr",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"100%|█████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 255/255 [00:20<00:00, 12.71it/s]\n",
|
||||
"100%|███████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 29/29 [00:01<00:00, 17.31it/s]\n"
|
||||
"100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 255/255 [00:58<00:00, 4.36it/s]\n",
|
||||
"100%|██████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 29/29 [00:05<00:00, 5.05it/s]\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "stdout",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"epoch=2: train_ppl=tensor(2.0588, device='cuda:0') train_epoch_loss=tensor(0.7221, device='cuda:0') eval_ppl=tensor(1.0055, device='cuda:0') eval_epoch_loss=tensor(0.0054, device='cuda:0')\n"
|
||||
"epoch=2: train_ppl=tensor(2.1698, device='cuda:0') train_epoch_loss=tensor(0.7747, device='cuda:0') eval_ppl=tensor(1.0057, device='cuda:0') eval_epoch_loss=tensor(0.0057, device='cuda:0')\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "stderr",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"100%|█████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 255/255 [00:20<00:00, 12.70it/s]\n",
|
||||
"100%|███████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 29/29 [00:01<00:00, 17.32it/s]\n"
|
||||
"100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 255/255 [00:58<00:00, 4.35it/s]\n",
|
||||
"100%|██████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 29/29 [00:05<00:00, 5.06it/s]\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "stdout",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"epoch=3: train_ppl=tensor(1.7939, device='cuda:0') train_epoch_loss=tensor(0.5844, device='cuda:0') eval_ppl=tensor(1.0063, device='cuda:0') eval_epoch_loss=tensor(0.0063, device='cuda:0')\n"
|
||||
"epoch=3: train_ppl=tensor(2.0724, device='cuda:0') train_epoch_loss=tensor(0.7287, device='cuda:0') eval_ppl=tensor(1.0051, device='cuda:0') eval_epoch_loss=tensor(0.0051, device='cuda:0')\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "stderr",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"100%|█████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 255/255 [00:19<00:00, 13.01it/s]\n",
|
||||
"100%|███████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 29/29 [00:01<00:00, 17.33it/s]"
|
||||
"100%|████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 255/255 [01:02<00:00, 4.10it/s]\n",
|
||||
"100%|██████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 29/29 [00:06<00:00, 4.74it/s]\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "stdout",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"epoch=4: train_ppl=tensor(1.7740, device='cuda:0') train_epoch_loss=tensor(0.5732, device='cuda:0') eval_ppl=tensor(1.0062, device='cuda:0') eval_epoch_loss=tensor(0.0061, device='cuda:0')\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "stderr",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"\n"
|
||||
"epoch=4: train_ppl=tensor(1.7598, device='cuda:0') train_epoch_loss=tensor(0.5652, device='cuda:0') eval_ppl=tensor(1.0047, device='cuda:0') eval_epoch_loss=tensor(0.0047, device='cuda:0')\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
@ -380,13 +356,15 @@
|
||||
" outputs = model(**batch)\n",
|
||||
" loss = outputs.loss\n",
|
||||
" eval_loss += loss.detach().float()\n",
|
||||
" eval_preds.extend(tokenizer.batch_decode(torch.argmax(outputs.logits, -1).detach().cpu().numpy(), skip_special_tokens=True))\n",
|
||||
" eval_preds.extend(\n",
|
||||
" tokenizer.batch_decode(torch.argmax(outputs.logits, -1).detach().cpu().numpy(), skip_special_tokens=True)\n",
|
||||
" )\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" eval_epoch_loss = eval_loss/len(train_dataloader)\n",
|
||||
" eval_epoch_loss = eval_loss / len(eval_dataloader)\n",
|
||||
" eval_ppl = torch.exp(eval_epoch_loss)\n",
|
||||
" train_epoch_loss = total_loss/len(eval_dataloader)\n",
|
||||
" train_epoch_loss = total_loss / len(train_dataloader)\n",
|
||||
" train_ppl = torch.exp(train_epoch_loss)\n",
|
||||
" print(f\"{epoch=}: {train_ppl=} {train_epoch_loss=} {eval_ppl=} {eval_epoch_loss=}\")\n"
|
||||
" print(f\"{epoch=}: {train_ppl=} {train_epoch_loss=} {eval_ppl=} {eval_epoch_loss=}\")"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
@ -399,21 +377,21 @@
|
||||
"name": "stdout",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"accuracy=96.47577092511013 % on the evaluation dataset\n",
|
||||
"eval_preds[:10]=['neutral', 'neutral', 'neutral', 'negative', 'neutral', 'neutral', 'neutral', 'neutral', 'positive', 'positive']\n",
|
||||
"dataset['validation']['text_label'][:10]=['neutral', 'neutral', 'neutral', 'negative', 'neutral', 'neutral', 'neutral', 'neutral', 'positive', 'positive']\n"
|
||||
"accuracy=96.91629955947137 % on the evaluation dataset\n",
|
||||
"eval_preds[:10]=['negative', 'positive', 'neutral', 'neutral', 'neutral', 'neutral', 'neutral', 'neutral', 'neutral', 'neutral']\n",
|
||||
"dataset['validation']['text_label'][:10]=['negative', 'neutral', 'neutral', 'neutral', 'neutral', 'neutral', 'neutral', 'neutral', 'neutral', 'neutral']\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# print accuracy\n",
|
||||
"correct =0\n",
|
||||
"correct = 0\n",
|
||||
"total = 0\n",
|
||||
"for pred,true in zip(eval_preds, dataset[\"validation\"][\"text_label\"]):\n",
|
||||
" if pred.strip()==true.strip():\n",
|
||||
" correct+=1\n",
|
||||
" total+=1 \n",
|
||||
"accuracy = correct/total*100\n",
|
||||
"for pred, true in zip(eval_preds, dataset[\"validation\"][\"text_label\"]):\n",
|
||||
" if pred.strip() == true.strip():\n",
|
||||
" correct += 1\n",
|
||||
" total += 1\n",
|
||||
"accuracy = correct / total * 100\n",
|
||||
"print(f\"{accuracy=} % on the evaluation dataset\")\n",
|
||||
"print(f\"{eval_preds[:10]=}\")\n",
|
||||
"print(f\"{dataset['validation']['text_label'][:10]=}\")"
|
||||
@ -424,26 +402,11 @@
|
||||
"execution_count": 8,
|
||||
"id": "a8de6005",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "stdout",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"{'prompt_embeddings': tensor([[-0.3165, -0.8389, 0.3262, ..., -1.5049, -1.6963, 0.3444],\n",
|
||||
" [-1.8359, 1.1936, 1.0483, ..., 0.6197, -0.4452, 0.5844],\n",
|
||||
" [-0.6027, 0.3246, -1.5601, ..., -0.3645, 0.2329, 0.3402],\n",
|
||||
" ...,\n",
|
||||
" [-1.9525, -0.5035, 0.8474, ..., 0.4793, -0.0789, -0.9305],\n",
|
||||
" [-1.9741, 0.5242, -2.0594, ..., -0.7970, -0.4889, 2.7323],\n",
|
||||
" [ 0.9355, -0.2714, 0.4610, ..., 0.2692, -1.5801, -1.6405]])}\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# saving model\n",
|
||||
"state_dict = get_peft_model_state_dict(model)\n",
|
||||
"torch.save(state_dict, checkpoint_name)\n",
|
||||
"print(state_dict)"
|
||||
"peft_model_id = f\"{model_name_or_path}_{peft_config.peft_type}_{peft_config.task_type}\"\n",
|
||||
"model.save_pretrained(peft_model_id)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
@ -456,18 +419,69 @@
|
||||
"name": "stdout",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"3,8M\tfinancial_sentiment_analysis_prefix_tuning_v1.pt\r\n"
|
||||
"3,8M\tt5-large_PREFIX_TUNING_SEQ_2_SEQ_LM/adapter_model.bin\r\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"!du -h $checkpoint_name"
|
||||
"ckpt = f\"{peft_model_id}/adapter_model.bin\"\n",
|
||||
"!du -h $ckpt"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 11,
|
||||
"id": "76c2fc29",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from peft import PeftModel, PeftConfig\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"peft_model_id = f\"{model_name_or_path}_{peft_config.peft_type}_{peft_config.task_type}\"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"config = PeftConfig.from_pretrained(peft_model_id)\n",
|
||||
"model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained(config.base_model_name_or_path)\n",
|
||||
"model = PeftModel.from_pretrained(model, peft_model_id)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 27,
|
||||
"id": "d997f1cc",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "stdout",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"Acando AB ( ACANB SS ) fell 8.9 percent to 13.35 kronor , the lowest close since Dec. 11 .\n",
|
||||
"{'input_ids': tensor([[ 4292, 232, 32, 3, 5359, 41, 3, 22029, 14972, 3,\n",
|
||||
" 4256, 3, 61, 4728, 4848, 1298, 1093, 12, 8808, 2469,\n",
|
||||
" 3, 22318, 29, 127, 3, 6, 8, 7402, 885, 437,\n",
|
||||
" 4451, 5, 850, 3, 5, 1]]), 'attention_mask': tensor([[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,\n",
|
||||
" 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1]])}\n",
|
||||
"tensor([[ 0, 2841, 1]])\n",
|
||||
"['negative']\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"model.eval()\n",
|
||||
"i = 107\n",
|
||||
"inputs = tokenizer(dataset[\"validation\"][text_column][i], return_tensors=\"pt\")\n",
|
||||
"print(dataset[\"validation\"][text_column][i])\n",
|
||||
"print(inputs)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"with torch.no_grad():\n",
|
||||
" outputs = model.generate(input_ids=inputs[\"input_ids\"], max_new_tokens=10)\n",
|
||||
" print(outputs)\n",
|
||||
" print(tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs.detach().cpu().numpy(), skip_special_tokens=True))"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": null,
|
||||
"id": "76c2fc29",
|
||||
"id": "fb746c1e",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": []
|
||||
@ -475,7 +489,7 @@
|
||||
],
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"kernelspec": {
|
||||
"display_name": "Python 3.10.5 64-bit",
|
||||
"display_name": "Python 3 (ipykernel)",
|
||||
"language": "python",
|
||||
"name": "python3"
|
||||
},
|
||||
@ -489,7 +503,7 @@
|
||||
"name": "python",
|
||||
"nbconvert_exporter": "python",
|
||||
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
|
||||
"version": "3.10.5 (v3.10.5:f377153967, Jun 6 2022, 12:36:10) [Clang 13.0.0 (clang-1300.0.29.30)]"
|
||||
"version": "3.10.5"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"vscode": {
|
||||
"interpreter": {
|
||||
|
||||
804
examples/conditional_generation/peft_prompt_tuning_seq2seq.ipynb
Normal file
804
examples/conditional_generation/peft_prompt_tuning_seq2seq.ipynb
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,804 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cells": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 1,
|
||||
"id": "5f93b7d1",
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"ExecuteTime": {
|
||||
"end_time": "2023-05-30T08:37:58.711225Z",
|
||||
"start_time": "2023-05-30T08:37:56.881307Z"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"outputs": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "stdout",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"===================================BUG REPORT===================================\n",
|
||||
"Welcome to bitsandbytes. For bug reports, please run\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"python -m bitsandbytes\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" and submit this information together with your error trace to: https://github.com/TimDettmers/bitsandbytes/issues\n",
|
||||
"================================================================================\n",
|
||||
"bin /udir/tschilla/anaconda3/envs/peft/lib/python3.9/site-packages/bitsandbytes/libbitsandbytes_cuda117.so\n",
|
||||
"CUDA_SETUP: WARNING! libcudart.so not found in any environmental path. Searching in backup paths...\n",
|
||||
"CUDA SETUP: CUDA runtime path found: /usr/local/cuda/lib64/libcudart.so.11.0\n",
|
||||
"CUDA SETUP: Highest compute capability among GPUs detected: 8.0\n",
|
||||
"CUDA SETUP: Detected CUDA version 117\n",
|
||||
"CUDA SETUP: Loading binary /udir/tschilla/anaconda3/envs/peft/lib/python3.9/site-packages/bitsandbytes/libbitsandbytes_cuda117.so...\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "stderr",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"/udir/tschilla/anaconda3/envs/peft/lib/python3.9/site-packages/bitsandbytes/cuda_setup/main.py:149: UserWarning: /udir/tschilla/anaconda3 did not contain ['libcudart.so', 'libcudart.so.11.0', 'libcudart.so.12.0'] as expected! Searching further paths...\n",
|
||||
" warn(msg)\n",
|
||||
"/udir/tschilla/anaconda3/envs/peft/lib/python3.9/site-packages/bitsandbytes/cuda_setup/main.py:149: UserWarning: WARNING: The following directories listed in your path were found to be non-existent: {PosixPath('Europe/Paris')}\n",
|
||||
" warn(msg)\n",
|
||||
"/udir/tschilla/anaconda3/envs/peft/lib/python3.9/site-packages/bitsandbytes/cuda_setup/main.py:149: UserWarning: WARNING: The following directories listed in your path were found to be non-existent: {PosixPath('/udir/tschilla/.cache/dotnet_bundle_extract')}\n",
|
||||
" warn(msg)\n",
|
||||
"/udir/tschilla/anaconda3/envs/peft/lib/python3.9/site-packages/bitsandbytes/cuda_setup/main.py:149: UserWarning: WARNING: The following directories listed in your path were found to be non-existent: {PosixPath('5002'), PosixPath('http'), PosixPath('//127.0.0.1')}\n",
|
||||
" warn(msg)\n",
|
||||
"/udir/tschilla/anaconda3/envs/peft/lib/python3.9/site-packages/bitsandbytes/cuda_setup/main.py:149: UserWarning: WARNING: The following directories listed in your path were found to be non-existent: {PosixPath('() { ( alias;\\n eval ${which_declare} ) | /usr/bin/which --tty-only --read-alias --read-functions --show-tilde --show-dot $@\\n}')}\n",
|
||||
" warn(msg)\n",
|
||||
"/udir/tschilla/anaconda3/envs/peft/lib/python3.9/site-packages/bitsandbytes/cuda_setup/main.py:149: UserWarning: WARNING: The following directories listed in your path were found to be non-existent: {PosixPath('module'), PosixPath('//matplotlib_inline.backend_inline')}\n",
|
||||
" warn(msg)\n",
|
||||
"/udir/tschilla/anaconda3/envs/peft/lib/python3.9/site-packages/bitsandbytes/cuda_setup/main.py:149: UserWarning: Found duplicate ['libcudart.so', 'libcudart.so.11.0', 'libcudart.so.12.0'] files: {PosixPath('/usr/local/cuda/lib64/libcudart.so.11.0'), PosixPath('/usr/local/cuda/lib64/libcudart.so')}.. We'll flip a coin and try one of these, in order to fail forward.\n",
|
||||
"Either way, this might cause trouble in the future:\n",
|
||||
"If you get `CUDA error: invalid device function` errors, the above might be the cause and the solution is to make sure only one ['libcudart.so', 'libcudart.so.11.0', 'libcudart.so.12.0'] in the paths that we search based on your env.\n",
|
||||
" warn(msg)\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"import os\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"import torch\n",
|
||||
"from transformers import AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM, AutoTokenizer, default_data_collator, get_linear_schedule_with_warmup\n",
|
||||
"from peft import get_peft_model, PromptTuningConfig, TaskType, PromptTuningInit\n",
|
||||
"from torch.utils.data import DataLoader\n",
|
||||
"from tqdm import tqdm\n",
|
||||
"from datasets import load_dataset\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"os.environ[\"TOKENIZERS_PARALLELISM\"] = \"false\"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"device = \"cuda\"\n",
|
||||
"model_name_or_path = \"t5-large\"\n",
|
||||
"tokenizer_name_or_path = \"t5-large\"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"checkpoint_name = \"financial_sentiment_analysis_prompt_tuning_v1.pt\"\n",
|
||||
"text_column = \"sentence\"\n",
|
||||
"label_column = \"text_label\"\n",
|
||||
"max_length = 128\n",
|
||||
"lr = 1\n",
|
||||
"num_epochs = 5\n",
|
||||
"batch_size = 8"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 2,
|
||||
"id": "8d0850ac",
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"ExecuteTime": {
|
||||
"end_time": "2023-05-30T08:38:12.413984Z",
|
||||
"start_time": "2023-05-30T08:38:04.601042Z"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"outputs": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "stdout",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"trainable params: 40960 || all params: 737709056 || trainable%: 0.005552324411210698\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "stderr",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"/udir/tschilla/anaconda3/envs/peft/lib/python3.9/site-packages/transformers/models/t5/tokenization_t5_fast.py:155: FutureWarning: This tokenizer was incorrectly instantiated with a model max length of 512 which will be corrected in Transformers v5.\n",
|
||||
"For now, this behavior is kept to avoid breaking backwards compatibility when padding/encoding with `truncation is True`.\n",
|
||||
"- Be aware that you SHOULD NOT rely on t5-large automatically truncating your input to 512 when padding/encoding.\n",
|
||||
"- If you want to encode/pad to sequences longer than 512 you can either instantiate this tokenizer with `model_max_length` or pass `max_length` when encoding/padding.\n",
|
||||
"- To avoid this warning, please instantiate this tokenizer with `model_max_length` set to your preferred value.\n",
|
||||
" warnings.warn(\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"data": {
|
||||
"text/plain": [
|
||||
"PeftModelForSeq2SeqLM(\n",
|
||||
" (base_model): T5ForConditionalGeneration(\n",
|
||||
" (shared): Embedding(32128, 1024)\n",
|
||||
" (encoder): T5Stack(\n",
|
||||
" (embed_tokens): Embedding(32128, 1024)\n",
|
||||
" (block): ModuleList(\n",
|
||||
" (0): T5Block(\n",
|
||||
" (layer): ModuleList(\n",
|
||||
" (0): T5LayerSelfAttention(\n",
|
||||
" (SelfAttention): T5Attention(\n",
|
||||
" (q): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=1024, bias=False)\n",
|
||||
" (k): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=1024, bias=False)\n",
|
||||
" (v): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=1024, bias=False)\n",
|
||||
" (o): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=1024, bias=False)\n",
|
||||
" (relative_attention_bias): Embedding(32, 16)\n",
|
||||
" )\n",
|
||||
" (layer_norm): T5LayerNorm()\n",
|
||||
" (dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)\n",
|
||||
" )\n",
|
||||
" (1): T5LayerFF(\n",
|
||||
" (DenseReluDense): T5DenseActDense(\n",
|
||||
" (wi): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=4096, bias=False)\n",
|
||||
" (wo): Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=1024, bias=False)\n",
|
||||
" (dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)\n",
|
||||
" (act): ReLU()\n",
|
||||
" )\n",
|
||||
" (layer_norm): T5LayerNorm()\n",
|
||||
" (dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)\n",
|
||||
" )\n",
|
||||
" )\n",
|
||||
" )\n",
|
||||
" (1-23): 23 x T5Block(\n",
|
||||
" (layer): ModuleList(\n",
|
||||
" (0): T5LayerSelfAttention(\n",
|
||||
" (SelfAttention): T5Attention(\n",
|
||||
" (q): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=1024, bias=False)\n",
|
||||
" (k): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=1024, bias=False)\n",
|
||||
" (v): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=1024, bias=False)\n",
|
||||
" (o): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=1024, bias=False)\n",
|
||||
" )\n",
|
||||
" (layer_norm): T5LayerNorm()\n",
|
||||
" (dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)\n",
|
||||
" )\n",
|
||||
" (1): T5LayerFF(\n",
|
||||
" (DenseReluDense): T5DenseActDense(\n",
|
||||
" (wi): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=4096, bias=False)\n",
|
||||
" (wo): Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=1024, bias=False)\n",
|
||||
" (dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)\n",
|
||||
" (act): ReLU()\n",
|
||||
" )\n",
|
||||
" (layer_norm): T5LayerNorm()\n",
|
||||
" (dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)\n",
|
||||
" )\n",
|
||||
" )\n",
|
||||
" )\n",
|
||||
" )\n",
|
||||
" (final_layer_norm): T5LayerNorm()\n",
|
||||
" (dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)\n",
|
||||
" )\n",
|
||||
" (decoder): T5Stack(\n",
|
||||
" (embed_tokens): Embedding(32128, 1024)\n",
|
||||
" (block): ModuleList(\n",
|
||||
" (0): T5Block(\n",
|
||||
" (layer): ModuleList(\n",
|
||||
" (0): T5LayerSelfAttention(\n",
|
||||
" (SelfAttention): T5Attention(\n",
|
||||
" (q): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=1024, bias=False)\n",
|
||||
" (k): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=1024, bias=False)\n",
|
||||
" (v): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=1024, bias=False)\n",
|
||||
" (o): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=1024, bias=False)\n",
|
||||
" (relative_attention_bias): Embedding(32, 16)\n",
|
||||
" )\n",
|
||||
" (layer_norm): T5LayerNorm()\n",
|
||||
" (dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)\n",
|
||||
" )\n",
|
||||
" (1): T5LayerCrossAttention(\n",
|
||||
" (EncDecAttention): T5Attention(\n",
|
||||
" (q): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=1024, bias=False)\n",
|
||||
" (k): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=1024, bias=False)\n",
|
||||
" (v): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=1024, bias=False)\n",
|
||||
" (o): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=1024, bias=False)\n",
|
||||
" )\n",
|
||||
" (layer_norm): T5LayerNorm()\n",
|
||||
" (dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)\n",
|
||||
" )\n",
|
||||
" (2): T5LayerFF(\n",
|
||||
" (DenseReluDense): T5DenseActDense(\n",
|
||||
" (wi): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=4096, bias=False)\n",
|
||||
" (wo): Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=1024, bias=False)\n",
|
||||
" (dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)\n",
|
||||
" (act): ReLU()\n",
|
||||
" )\n",
|
||||
" (layer_norm): T5LayerNorm()\n",
|
||||
" (dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)\n",
|
||||
" )\n",
|
||||
" )\n",
|
||||
" )\n",
|
||||
" (1-23): 23 x T5Block(\n",
|
||||
" (layer): ModuleList(\n",
|
||||
" (0): T5LayerSelfAttention(\n",
|
||||
" (SelfAttention): T5Attention(\n",
|
||||
" (q): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=1024, bias=False)\n",
|
||||
" (k): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=1024, bias=False)\n",
|
||||
" (v): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=1024, bias=False)\n",
|
||||
" (o): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=1024, bias=False)\n",
|
||||
" )\n",
|
||||
" (layer_norm): T5LayerNorm()\n",
|
||||
" (dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)\n",
|
||||
" )\n",
|
||||
" (1): T5LayerCrossAttention(\n",
|
||||
" (EncDecAttention): T5Attention(\n",
|
||||
" (q): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=1024, bias=False)\n",
|
||||
" (k): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=1024, bias=False)\n",
|
||||
" (v): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=1024, bias=False)\n",
|
||||
" (o): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=1024, bias=False)\n",
|
||||
" )\n",
|
||||
" (layer_norm): T5LayerNorm()\n",
|
||||
" (dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)\n",
|
||||
" )\n",
|
||||
" (2): T5LayerFF(\n",
|
||||
" (DenseReluDense): T5DenseActDense(\n",
|
||||
" (wi): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=4096, bias=False)\n",
|
||||
" (wo): Linear(in_features=4096, out_features=1024, bias=False)\n",
|
||||
" (dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)\n",
|
||||
" (act): ReLU()\n",
|
||||
" )\n",
|
||||
" (layer_norm): T5LayerNorm()\n",
|
||||
" (dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)\n",
|
||||
" )\n",
|
||||
" )\n",
|
||||
" )\n",
|
||||
" )\n",
|
||||
" (final_layer_norm): T5LayerNorm()\n",
|
||||
" (dropout): Dropout(p=0.1, inplace=False)\n",
|
||||
" )\n",
|
||||
" (lm_head): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=32128, bias=False)\n",
|
||||
" )\n",
|
||||
" (prompt_encoder): ModuleDict(\n",
|
||||
" (default): PromptEmbedding(\n",
|
||||
" (embedding): Embedding(40, 1024)\n",
|
||||
" )\n",
|
||||
" )\n",
|
||||
" (word_embeddings): Embedding(32128, 1024)\n",
|
||||
")"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
"execution_count": 2,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"output_type": "execute_result"
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# creating model\n",
|
||||
"peft_config = PromptTuningConfig(\n",
|
||||
" task_type=TaskType.SEQ_2_SEQ_LM,\n",
|
||||
" prompt_tuning_init=PromptTuningInit.TEXT,\n",
|
||||
" num_virtual_tokens=20,\n",
|
||||
" prompt_tuning_init_text=\"What is the sentiment of this article?\\n\",\n",
|
||||
" inference_mode=False,\n",
|
||||
" tokenizer_name_or_path=model_name_or_path,\n",
|
||||
")\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained(model_name_or_path)\n",
|
||||
"model = get_peft_model(model, peft_config)\n",
|
||||
"model.print_trainable_parameters()\n",
|
||||
"model"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 3,
|
||||
"id": "4ee2babf",
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"ExecuteTime": {
|
||||
"end_time": "2023-05-30T08:38:18.759143Z",
|
||||
"start_time": "2023-05-30T08:38:17.881621Z"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"outputs": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "stderr",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"Found cached dataset financial_phrasebank (/data/proxem/huggingface/datasets/financial_phrasebank/sentences_allagree/1.0.0/550bde12e6c30e2674da973a55f57edde5181d53f5a5a34c1531c53f93b7e141)\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"data": {
|
||||
"application/vnd.jupyter.widget-view+json": {
|
||||
"model_id": "fb63f50cb7cb4f5aae10648ba74d6c4e",
|
||||
"version_major": 2,
|
||||
"version_minor": 0
|
||||
},
|
||||
"text/plain": [
|
||||
" 0%| | 0/1 [00:00<?, ?it/s]"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"output_type": "display_data"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"data": {
|
||||
"application/vnd.jupyter.widget-view+json": {
|
||||
"model_id": "",
|
||||
"version_major": 2,
|
||||
"version_minor": 0
|
||||
},
|
||||
"text/plain": [
|
||||
"Map: 0%| | 0/2037 [00:00<?, ? examples/s]"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"output_type": "display_data"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"data": {
|
||||
"application/vnd.jupyter.widget-view+json": {
|
||||
"model_id": "",
|
||||
"version_major": 2,
|
||||
"version_minor": 0
|
||||
},
|
||||
"text/plain": [
|
||||
"Map: 0%| | 0/227 [00:00<?, ? examples/s]"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"output_type": "display_data"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"data": {
|
||||
"text/plain": [
|
||||
"{'sentence': '`` Lining stone sales were also good in the early autumn , and order books are strong to the end of the year .',\n",
|
||||
" 'label': 2,\n",
|
||||
" 'text_label': 'positive'}"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
"execution_count": 3,
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"output_type": "execute_result"
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# loading dataset\n",
|
||||
"dataset = load_dataset(\"financial_phrasebank\", \"sentences_allagree\")\n",
|
||||
"dataset = dataset[\"train\"].train_test_split(test_size=0.1)\n",
|
||||
"dataset[\"validation\"] = dataset[\"test\"]\n",
|
||||
"del dataset[\"test\"]\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"classes = dataset[\"train\"].features[\"label\"].names\n",
|
||||
"dataset = dataset.map(\n",
|
||||
" lambda x: {\"text_label\": [classes[label] for label in x[\"label\"]]},\n",
|
||||
" batched=True,\n",
|
||||
" num_proc=1,\n",
|
||||
")\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"dataset[\"train\"][0]"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 4,
|
||||
"id": "adf9608c",
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"ExecuteTime": {
|
||||
"end_time": "2023-05-30T08:38:21.132266Z",
|
||||
"start_time": "2023-05-30T08:38:20.340722Z"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"outputs": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"data": {
|
||||
"application/vnd.jupyter.widget-view+json": {
|
||||
"model_id": "",
|
||||
"version_major": 2,
|
||||
"version_minor": 0
|
||||
},
|
||||
"text/plain": [
|
||||
"Running tokenizer on dataset: 0%| | 0/2037 [00:00<?, ? examples/s]"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"output_type": "display_data"
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"data": {
|
||||
"application/vnd.jupyter.widget-view+json": {
|
||||
"model_id": "",
|
||||
"version_major": 2,
|
||||
"version_minor": 0
|
||||
},
|
||||
"text/plain": [
|
||||
"Running tokenizer on dataset: 0%| | 0/227 [00:00<?, ? examples/s]"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"output_type": "display_data"
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# data preprocessing\n",
|
||||
"tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name_or_path)\n",
|
||||
"target_max_length = max([len(tokenizer(class_label)[\"input_ids\"]) for class_label in classes])\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"def preprocess_function(examples):\n",
|
||||
" inputs = examples[text_column]\n",
|
||||
" targets = examples[label_column]\n",
|
||||
" model_inputs = tokenizer(inputs, max_length=max_length, padding=\"max_length\", truncation=True, return_tensors=\"pt\")\n",
|
||||
" labels = tokenizer(\n",
|
||||
" targets, max_length=target_max_length, padding=\"max_length\", truncation=True, return_tensors=\"pt\"\n",
|
||||
" )\n",
|
||||
" labels = labels[\"input_ids\"]\n",
|
||||
" labels[labels == tokenizer.pad_token_id] = -100\n",
|
||||
" model_inputs[\"labels\"] = labels\n",
|
||||
" return model_inputs\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"processed_datasets = dataset.map(\n",
|
||||
" preprocess_function,\n",
|
||||
" batched=True,\n",
|
||||
" num_proc=1,\n",
|
||||
" remove_columns=dataset[\"train\"].column_names,\n",
|
||||
" load_from_cache_file=False,\n",
|
||||
" desc=\"Running tokenizer on dataset\",\n",
|
||||
")\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"train_dataset = processed_datasets[\"train\"]\n",
|
||||
"eval_dataset = processed_datasets[\"validation\"]\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"train_dataloader = DataLoader(\n",
|
||||
" train_dataset, shuffle=True, collate_fn=default_data_collator, batch_size=batch_size, pin_memory=True\n",
|
||||
")\n",
|
||||
"eval_dataloader = DataLoader(eval_dataset, collate_fn=default_data_collator, batch_size=batch_size, pin_memory=True)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 5,
|
||||
"id": "f733a3c6",
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"ExecuteTime": {
|
||||
"end_time": "2023-05-30T08:38:22.907922Z",
|
||||
"start_time": "2023-05-30T08:38:22.901057Z"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# optimizer and lr scheduler\n",
|
||||
"optimizer = torch.optim.AdamW(model.parameters(), lr=lr)\n",
|
||||
"lr_scheduler = get_linear_schedule_with_warmup(\n",
|
||||
" optimizer=optimizer,\n",
|
||||
" num_warmup_steps=0,\n",
|
||||
" num_training_steps=(len(train_dataloader) * num_epochs),\n",
|
||||
")"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 7,
|
||||
"id": "6b3a4090",
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"ExecuteTime": {
|
||||
"end_time": "2023-05-30T08:42:29.409070Z",
|
||||
"start_time": "2023-05-30T08:38:50.102263Z"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"outputs": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "stderr",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"100%|█████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 255/255 [00:42<00:00, 6.05it/s]\n",
|
||||
"100%|███████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 29/29 [00:02<00:00, 14.40it/s]\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "stdout",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"epoch=0: train_ppl=tensor(8.0846, device='cuda:0') train_epoch_loss=tensor(2.0900, device='cuda:0') eval_ppl=tensor(1.3542, device='cuda:0') eval_epoch_loss=tensor(0.3032, device='cuda:0')\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "stderr",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"100%|█████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 255/255 [00:41<00:00, 6.15it/s]\n",
|
||||
"100%|███████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 29/29 [00:02<00:00, 14.42it/s]\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "stdout",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"epoch=1: train_ppl=tensor(1.5088, device='cuda:0') train_epoch_loss=tensor(0.4113, device='cuda:0') eval_ppl=tensor(1.2692, device='cuda:0') eval_epoch_loss=tensor(0.2384, device='cuda:0')\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "stderr",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"100%|█████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 255/255 [00:41<00:00, 6.18it/s]\n",
|
||||
"100%|███████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 29/29 [00:02<00:00, 14.45it/s]\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "stdout",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"epoch=2: train_ppl=tensor(1.5322, device='cuda:0') train_epoch_loss=tensor(0.4267, device='cuda:0') eval_ppl=tensor(1.2065, device='cuda:0') eval_epoch_loss=tensor(0.1877, device='cuda:0')\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "stderr",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"100%|█████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 255/255 [00:41<00:00, 6.17it/s]\n",
|
||||
"100%|███████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 29/29 [00:02<00:00, 14.38it/s]\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "stdout",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"epoch=3: train_ppl=tensor(1.4475, device='cuda:0') train_epoch_loss=tensor(0.3699, device='cuda:0') eval_ppl=tensor(1.2346, device='cuda:0') eval_epoch_loss=tensor(0.2107, device='cuda:0')\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "stderr",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"100%|█████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 255/255 [00:42<00:00, 5.94it/s]\n",
|
||||
"100%|███████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 29/29 [00:02<00:00, 14.42it/s]"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "stdout",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"epoch=4: train_ppl=tensor(1.3428, device='cuda:0') train_epoch_loss=tensor(0.2948, device='cuda:0') eval_ppl=tensor(1.2041, device='cuda:0') eval_epoch_loss=tensor(0.1857, device='cuda:0')\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "stderr",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# training and evaluation\n",
|
||||
"model = model.to(device)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"for epoch in range(num_epochs):\n",
|
||||
" model.train()\n",
|
||||
" total_loss = 0\n",
|
||||
" for step, batch in enumerate(tqdm(train_dataloader)):\n",
|
||||
" batch = {k: v.to(device) for k, v in batch.items()}\n",
|
||||
" outputs = model(**batch)\n",
|
||||
" loss = outputs.loss\n",
|
||||
" total_loss += loss.detach().float()\n",
|
||||
" loss.backward()\n",
|
||||
" optimizer.step()\n",
|
||||
" lr_scheduler.step()\n",
|
||||
" optimizer.zero_grad()\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" model.eval()\n",
|
||||
" eval_loss = 0\n",
|
||||
" eval_preds = []\n",
|
||||
" for step, batch in enumerate(tqdm(eval_dataloader)):\n",
|
||||
" batch = {k: v.to(device) for k, v in batch.items()}\n",
|
||||
" with torch.no_grad():\n",
|
||||
" outputs = model(**batch)\n",
|
||||
" loss = outputs.loss\n",
|
||||
" eval_loss += loss.detach().float()\n",
|
||||
" eval_preds.extend(\n",
|
||||
" tokenizer.batch_decode(torch.argmax(outputs.logits, -1).detach().cpu().numpy(), skip_special_tokens=True)\n",
|
||||
" )\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" eval_epoch_loss = eval_loss / len(eval_dataloader)\n",
|
||||
" eval_ppl = torch.exp(eval_epoch_loss)\n",
|
||||
" train_epoch_loss = total_loss / len(train_dataloader)\n",
|
||||
" train_ppl = torch.exp(train_epoch_loss)\n",
|
||||
" print(f\"{epoch=}: {train_ppl=} {train_epoch_loss=} {eval_ppl=} {eval_epoch_loss=}\")"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 8,
|
||||
"id": "6cafa67b",
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"ExecuteTime": {
|
||||
"end_time": "2023-05-30T08:42:42.844671Z",
|
||||
"start_time": "2023-05-30T08:42:42.840447Z"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"outputs": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "stdout",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"accuracy=85.46255506607929 % on the evaluation dataset\n",
|
||||
"eval_preds[:10]=['neutral', 'neutral', 'neutral', 'neutral', 'neutral', 'positive', 'neutral', 'negative', 'neutral', 'positive']\n",
|
||||
"dataset['validation']['text_label'][:10]=['neutral', 'neutral', 'neutral', 'neutral', 'neutral', 'positive', 'neutral', 'negative', 'positive', 'neutral']\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# print accuracy\n",
|
||||
"correct = 0\n",
|
||||
"total = 0\n",
|
||||
"for pred, true in zip(eval_preds, dataset[\"validation\"][\"text_label\"]):\n",
|
||||
" if pred.strip() == true.strip():\n",
|
||||
" correct += 1\n",
|
||||
" total += 1\n",
|
||||
"accuracy = correct / total * 100\n",
|
||||
"print(f\"{accuracy=} % on the evaluation dataset\")\n",
|
||||
"print(f\"{eval_preds[:10]=}\")\n",
|
||||
"print(f\"{dataset['validation']['text_label'][:10]=}\")"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 9,
|
||||
"id": "a8de6005",
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"ExecuteTime": {
|
||||
"end_time": "2023-05-30T08:42:45.752765Z",
|
||||
"start_time": "2023-05-30T08:42:45.742397Z"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# saving model\n",
|
||||
"peft_model_id = f\"{model_name_or_path}_{peft_config.peft_type}_{peft_config.task_type}\"\n",
|
||||
"model.save_pretrained(peft_model_id)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 10,
|
||||
"id": "bd20cd4c",
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"ExecuteTime": {
|
||||
"end_time": "2023-05-30T08:42:47.660873Z",
|
||||
"start_time": "2023-05-30T08:42:47.488293Z"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"outputs": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "stdout",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"164K\tt5-large_PROMPT_TUNING_SEQ_2_SEQ_LM/adapter_model.bin\r\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"ckpt = f\"{peft_model_id}/adapter_model.bin\"\n",
|
||||
"!du -h $ckpt"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 11,
|
||||
"id": "76c2fc29",
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"ExecuteTime": {
|
||||
"end_time": "2023-05-30T08:42:56.721990Z",
|
||||
"start_time": "2023-05-30T08:42:49.060700Z"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from peft import PeftModel, PeftConfig\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"peft_model_id = f\"{model_name_or_path}_{peft_config.peft_type}_{peft_config.task_type}\"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"config = PeftConfig.from_pretrained(peft_model_id)\n",
|
||||
"model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained(config.base_model_name_or_path)\n",
|
||||
"model = PeftModel.from_pretrained(model, peft_model_id)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 12,
|
||||
"id": "d997f1cc",
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"ExecuteTime": {
|
||||
"end_time": "2023-05-30T08:42:59.600916Z",
|
||||
"start_time": "2023-05-30T08:42:58.961468Z"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"outputs": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "stdout",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"Danske Bank is Denmark 's largest bank with 3.5 million customers .\n",
|
||||
"tensor([[ 3039, 1050, 1925, 19, 18001, 3, 31, 7, 2015, 2137,\n",
|
||||
" 28, 3, 9285, 770, 722, 3, 5, 1]])\n",
|
||||
"tensor([[ 0, 7163, 1]])\n",
|
||||
"['neutral']\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"model.eval()\n",
|
||||
"i = 107\n",
|
||||
"input_ids = tokenizer(dataset[\"validation\"][text_column][i], return_tensors=\"pt\").input_ids\n",
|
||||
"print(dataset[\"validation\"][text_column][i])\n",
|
||||
"print(input_ids)\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"with torch.no_grad():\n",
|
||||
" outputs = model.generate(input_ids=input_ids, max_new_tokens=10)\n",
|
||||
" print(outputs)\n",
|
||||
" print(tokenizer.batch_decode(outputs.detach().cpu().numpy(), skip_special_tokens=True))"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"kernelspec": {
|
||||
"display_name": "peft",
|
||||
"language": "python",
|
||||
"name": "peft"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"language_info": {
|
||||
"codemirror_mode": {
|
||||
"name": "ipython",
|
||||
"version": 3
|
||||
},
|
||||
"file_extension": ".py",
|
||||
"mimetype": "text/x-python",
|
||||
"name": "python",
|
||||
"nbconvert_exporter": "python",
|
||||
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
|
||||
"version": "3.9.16"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"toc": {
|
||||
"base_numbering": 1,
|
||||
"nav_menu": {},
|
||||
"number_sections": true,
|
||||
"sideBar": true,
|
||||
"skip_h1_title": false,
|
||||
"title_cell": "Table of Contents",
|
||||
"title_sidebar": "Contents",
|
||||
"toc_cell": false,
|
||||
"toc_position": {},
|
||||
"toc_section_display": true,
|
||||
"toc_window_display": false
|
||||
},
|
||||
"varInspector": {
|
||||
"cols": {
|
||||
"lenName": 16,
|
||||
"lenType": 16,
|
||||
"lenVar": 40
|
||||
},
|
||||
"kernels_config": {
|
||||
"python": {
|
||||
"delete_cmd_postfix": "",
|
||||
"delete_cmd_prefix": "del ",
|
||||
"library": "var_list.py",
|
||||
"varRefreshCmd": "print(var_dic_list())"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"r": {
|
||||
"delete_cmd_postfix": ") ",
|
||||
"delete_cmd_prefix": "rm(",
|
||||
"library": "var_list.r",
|
||||
"varRefreshCmd": "cat(var_dic_list()) "
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"types_to_exclude": [
|
||||
"module",
|
||||
"function",
|
||||
"builtin_function_or_method",
|
||||
"instance",
|
||||
"_Feature"
|
||||
],
|
||||
"window_display": false
|
||||
},
|
||||
"vscode": {
|
||||
"interpreter": {
|
||||
"hash": "aee8b7b246df8f9039afb4144a1f6fd8d2ca17a180786b69acc140d282b71a49"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"nbformat": 4,
|
||||
"nbformat_minor": 5
|
||||
}
|
||||
File diff suppressed because one or more lines are too long
@ -1,6 +1,5 @@
|
||||
transformers
|
||||
accelerate
|
||||
loralib
|
||||
evaluate
|
||||
deepspeed
|
||||
tqdm
|
||||
|
||||
@ -0,0 +1,501 @@
|
||||
# Copyright 2023-present the HuggingFace Inc. team.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
import argparse
|
||||
import logging
|
||||
import math
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import random
|
||||
from pathlib import Path
|
||||
|
||||
import datasets
|
||||
import evaluate
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
import transformers
|
||||
from accelerate import Accelerator
|
||||
from accelerate.logging import get_logger
|
||||
from accelerate.utils import set_seed
|
||||
from datasets import DatasetDict, load_dataset
|
||||
from huggingface_hub import HfApi
|
||||
from torch import nn
|
||||
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
|
||||
from tqdm import tqdm
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModel, AutoTokenizer, SchedulerType, default_data_collator, get_scheduler
|
||||
|
||||
from peft import LoraConfig, TaskType, get_peft_model
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
logger = get_logger(__name__)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def parse_args():
|
||||
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="Training a PEFT model for Semantic Search task")
|
||||
parser.add_argument("--dataset_name", type=str, default=None, help="dataset name on HF hub")
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--max_length",
|
||||
type=int,
|
||||
default=128,
|
||||
help=(
|
||||
"The maximum total input sequence length after tokenization. Sequences longer than this will be truncated,"
|
||||
" sequences shorter will be padded if `--pad_to_max_length` is passed."
|
||||
),
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--model_name_or_path",
|
||||
type=str,
|
||||
help="Path to pretrained model or model identifier from huggingface.co/models.",
|
||||
required=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--per_device_train_batch_size",
|
||||
type=int,
|
||||
default=8,
|
||||
help="Batch size (per device) for the training dataloader.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--per_device_eval_batch_size",
|
||||
type=int,
|
||||
default=8,
|
||||
help="Batch size (per device) for the evaluation dataloader.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--learning_rate",
|
||||
type=float,
|
||||
default=5e-5,
|
||||
help="Initial learning rate (after the potential warmup period) to use.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument("--weight_decay", type=float, default=0.0, help="Weight decay to use.")
|
||||
parser.add_argument("--num_train_epochs", type=int, default=3, help="Total number of training epochs to perform.")
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--max_train_steps",
|
||||
type=int,
|
||||
default=None,
|
||||
help="Total number of training steps to perform. If provided, overrides num_train_epochs.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--gradient_accumulation_steps",
|
||||
type=int,
|
||||
default=1,
|
||||
help="Number of updates steps to accumulate before performing a backward/update pass.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--lr_scheduler_type",
|
||||
type=SchedulerType,
|
||||
default="linear",
|
||||
help="The scheduler type to use.",
|
||||
choices=["linear", "cosine", "cosine_with_restarts", "polynomial", "constant", "constant_with_warmup"],
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--num_warmup_steps", type=int, default=0, help="Number of steps for the warmup in the lr scheduler."
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument("--output_dir", type=str, default=None, help="Where to store the final model.")
|
||||
parser.add_argument("--seed", type=int, default=None, help="A seed for reproducible training.")
|
||||
parser.add_argument("--push_to_hub", action="store_true", help="Whether or not to push the model to the Hub.")
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--hub_model_id", type=str, help="The name of the repository to keep in sync with the local `output_dir`."
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument("--hub_token", type=str, help="The token to use to push to the Model Hub.")
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--checkpointing_steps",
|
||||
type=str,
|
||||
default=None,
|
||||
help="Whether the various states should be saved at the end of every n steps, or 'epoch' for each epoch.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--resume_from_checkpoint",
|
||||
type=str,
|
||||
default=None,
|
||||
help="If the training should continue from a checkpoint folder.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--with_tracking",
|
||||
action="store_true",
|
||||
help="Whether to enable experiment trackers for logging.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--report_to",
|
||||
type=str,
|
||||
default="all",
|
||||
help=(
|
||||
'The integration to report the results and logs to. Supported platforms are `"tensorboard"`,'
|
||||
' `"wandb"`, `"comet_ml"` and `"clearml"`. Use `"all"` (default) to report to all integrations.'
|
||||
"Only applicable when `--with_tracking` is passed."
|
||||
),
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--sanity_test",
|
||||
action="store_true",
|
||||
help="Whether to enable sanity test.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--use_peft",
|
||||
action="store_true",
|
||||
help="Whether to use PEFT.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
args = parser.parse_args()
|
||||
|
||||
if args.push_to_hub:
|
||||
assert args.output_dir is not None, "Need an `output_dir` to create a repo when `--push_to_hub` is passed."
|
||||
|
||||
return args
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def save_model_hook(models, weights, output_dir):
|
||||
for i, model in enumerate(models):
|
||||
model.save_pretrained(output_dir, state_dict=weights[i])
|
||||
# make sure to pop weight so that corresponding model is not saved again
|
||||
weights.pop()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def load_model_hook(models, input_dir):
|
||||
while len(models) > 0:
|
||||
model = models.pop()
|
||||
# pop models so that they are not loaded again
|
||||
if hasattr(model, "active_adapter") and hasattr(model, "load_adapter"):
|
||||
model.load_adapter(input_dir, model.active_adapter, is_trainable=True)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class AutoModelForSentenceEmbedding(nn.Module):
|
||||
def __init__(self, model_name, tokenizer, normalize=True):
|
||||
super().__init__()
|
||||
|
||||
self.model = AutoModel.from_pretrained(
|
||||
model_name
|
||||
) # , quantizaton_config=BitsAndBytesConfig(load_in_8bit=True), device_map={"":0})
|
||||
self.normalize = normalize
|
||||
self.tokenizer = tokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, **kwargs):
|
||||
model_output = self.model(**kwargs)
|
||||
embeddings = self.mean_pooling(model_output, kwargs["attention_mask"])
|
||||
if self.normalize:
|
||||
embeddings = torch.nn.functional.normalize(embeddings, p=2, dim=1)
|
||||
|
||||
return embeddings
|
||||
|
||||
def mean_pooling(self, model_output, attention_mask):
|
||||
token_embeddings = model_output[0] # First element of model_output contains all token embeddings
|
||||
input_mask_expanded = attention_mask.unsqueeze(-1).expand(token_embeddings.size()).float()
|
||||
return torch.sum(token_embeddings * input_mask_expanded, 1) / torch.clamp(input_mask_expanded.sum(1), min=1e-9)
|
||||
|
||||
def __getattr__(self, name: str):
|
||||
"""Forward missing attributes to the wrapped module."""
|
||||
try:
|
||||
return super().__getattr__(name) # defer to nn.Module's logic
|
||||
except AttributeError:
|
||||
return getattr(self.model, name)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def get_cosing_embeddings(query_embs, product_embs):
|
||||
return torch.sum(query_embs * product_embs, axis=1)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def get_loss(cosine_score, labels):
|
||||
return torch.mean(torch.square(labels * (1 - cosine_score) + torch.clamp((1 - labels) * cosine_score, min=0.0)))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def main():
|
||||
args = parse_args()
|
||||
|
||||
accelerator_kwargs = {"gradient_accumulation_steps": args.gradient_accumulation_steps}
|
||||
if args.with_tracking:
|
||||
accelerator_kwargs["log_with"] = args.report_to
|
||||
accelerator_kwargs["project_dir"] = args.output_dir
|
||||
accelerator = Accelerator(**accelerator_kwargs)
|
||||
|
||||
# Make one log on every process with the configuration for debugging.
|
||||
logging.basicConfig(
|
||||
format="%(asctime)s - %(levelname)s - %(name)s - %(message)s",
|
||||
datefmt="%m/%d/%Y %H:%M:%S",
|
||||
level=logging.INFO,
|
||||
)
|
||||
logger.info(accelerator.state, main_process_only=False)
|
||||
if accelerator.is_local_main_process:
|
||||
datasets.utils.logging.set_verbosity_warning()
|
||||
transformers.utils.logging.set_verbosity_info()
|
||||
else:
|
||||
datasets.utils.logging.set_verbosity_error()
|
||||
transformers.utils.logging.set_verbosity_error()
|
||||
|
||||
# If passed along, set the training seed now.
|
||||
if args.seed is not None:
|
||||
set_seed(args.seed)
|
||||
|
||||
# Handle the repository creation
|
||||
if accelerator.is_main_process:
|
||||
if args.push_to_hub:
|
||||
api = HfApi(token=args.hub_token)
|
||||
|
||||
# Create repo (repo_name from args or inferred)
|
||||
repo_name = args.hub_model_id
|
||||
if repo_name is None:
|
||||
repo_name = Path(args.output_dir).absolute().name
|
||||
repo_id = api.create_repo(repo_name, exist_ok=True).repo_id
|
||||
|
||||
with open(os.path.join(args.output_dir, ".gitignore"), "w+") as gitignore:
|
||||
if "step_*" not in gitignore:
|
||||
gitignore.write("step_*\n")
|
||||
if "epoch_*" not in gitignore:
|
||||
gitignore.write("epoch_*\n")
|
||||
elif args.output_dir is not None:
|
||||
os.makedirs(args.output_dir, exist_ok=True)
|
||||
accelerator.wait_for_everyone()
|
||||
|
||||
# get the tokenizer
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(args.model_name_or_path)
|
||||
|
||||
# dataset download and preprocessing
|
||||
if args.sanity_test:
|
||||
train_dataset = load_dataset("smangrul/amazon_esci", split="train[:1024]")
|
||||
val_dataset = load_dataset("smangrul/amazon_esci", split="validation[:1024]")
|
||||
|
||||
dataset = DatasetDict({"train": train_dataset, "validation": val_dataset})
|
||||
else:
|
||||
dataset = load_dataset(args.dataset_name)
|
||||
|
||||
def preprocess_function(examples):
|
||||
queries = examples["query"]
|
||||
result = tokenizer(queries, padding="max_length", max_length=70, truncation=True)
|
||||
result = {f"query_{k}": v for k, v in result.items()}
|
||||
|
||||
products = examples["product_title"]
|
||||
result_products = tokenizer(products, padding="max_length", max_length=70, truncation=True)
|
||||
for k, v in result_products.items():
|
||||
result[f"product_{k}"] = v
|
||||
|
||||
result["labels"] = examples["relevance_label"]
|
||||
return result
|
||||
|
||||
processed_datasets = dataset.map(
|
||||
preprocess_function,
|
||||
batched=True,
|
||||
remove_columns=dataset["train"].column_names,
|
||||
desc="Running tokenizer on dataset",
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Log a few random samples from the training set:
|
||||
for index in random.sample(range(len(processed_datasets["train"])), 3):
|
||||
logger.info(f"Sample {index} of the training set: {processed_datasets['train'][index]}.")
|
||||
|
||||
# base model
|
||||
model = AutoModelForSentenceEmbedding(args.model_name_or_path, tokenizer)
|
||||
|
||||
if args.use_peft:
|
||||
# peft config and wrapping
|
||||
peft_config = LoraConfig(
|
||||
r=8,
|
||||
lora_alpha=16,
|
||||
bias="none",
|
||||
task_type=TaskType.FEATURE_EXTRACTION,
|
||||
target_modules=["key", "query", "value"],
|
||||
)
|
||||
model = get_peft_model(model, peft_config)
|
||||
model.print_trainable_parameters()
|
||||
|
||||
accelerator.print(model)
|
||||
|
||||
# get dataloaders
|
||||
train_dataloader = DataLoader(
|
||||
processed_datasets["train"],
|
||||
shuffle=True,
|
||||
collate_fn=default_data_collator,
|
||||
batch_size=args.per_device_train_batch_size,
|
||||
pin_memory=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
eval_dataloader = DataLoader(
|
||||
processed_datasets["validation"],
|
||||
shuffle=False,
|
||||
collate_fn=default_data_collator,
|
||||
batch_size=args.per_device_eval_batch_size,
|
||||
pin_memory=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=args.learning_rate)
|
||||
|
||||
# Scheduler and math around the number of training steps.
|
||||
overrode_max_train_steps = False
|
||||
num_update_steps_per_epoch = math.ceil(len(train_dataloader) / args.gradient_accumulation_steps)
|
||||
if args.max_train_steps is None:
|
||||
args.max_train_steps = args.num_train_epochs * num_update_steps_per_epoch
|
||||
overrode_max_train_steps = True
|
||||
|
||||
lr_scheduler = get_scheduler(
|
||||
name=args.lr_scheduler_type,
|
||||
optimizer=optimizer,
|
||||
num_warmup_steps=args.num_warmup_steps,
|
||||
num_training_steps=args.max_train_steps,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Prepare everything with our `accelerator`.
|
||||
model, optimizer, train_dataloader, eval_dataloader, lr_scheduler = accelerator.prepare(
|
||||
model, optimizer, train_dataloader, eval_dataloader, lr_scheduler
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# We need to recalculate our total training steps as the size of the training dataloader may have changed
|
||||
num_update_steps_per_epoch = math.ceil(len(train_dataloader) / args.gradient_accumulation_steps)
|
||||
if overrode_max_train_steps:
|
||||
args.max_train_steps = args.num_train_epochs * num_update_steps_per_epoch
|
||||
# Afterwards we recalculate our number of training epochs
|
||||
args.num_train_epochs = math.ceil(args.max_train_steps / num_update_steps_per_epoch)
|
||||
|
||||
# Figure out how many steps we should save the Accelerator states
|
||||
checkpointing_steps = args.checkpointing_steps
|
||||
if checkpointing_steps is not None and checkpointing_steps.isdigit():
|
||||
checkpointing_steps = int(checkpointing_steps)
|
||||
|
||||
# We need to initialize the trackers we use, and also store our configuration.
|
||||
# The trackers initializes automatically on the main process.
|
||||
if args.with_tracking:
|
||||
experiment_config = vars(args)
|
||||
# TensorBoard cannot log Enums, need the raw value
|
||||
experiment_config["lr_scheduler_type"] = experiment_config["lr_scheduler_type"].value
|
||||
accelerator.init_trackers("peft_semantic_search", experiment_config)
|
||||
|
||||
metric = evaluate.load("roc_auc")
|
||||
|
||||
total_batch_size = args.per_device_train_batch_size * accelerator.num_processes * args.gradient_accumulation_steps
|
||||
|
||||
if args.use_peft:
|
||||
# saving and loading checkpoints for resuming training
|
||||
accelerator.register_save_state_pre_hook(save_model_hook)
|
||||
accelerator.register_load_state_pre_hook(load_model_hook)
|
||||
|
||||
logger.info("***** Running training *****")
|
||||
logger.info(f" Num examples = {len(processed_datasets['train'])}")
|
||||
logger.info(f" Num Epochs = {args.num_train_epochs}")
|
||||
logger.info(f" Instantaneous batch size per device = {args.per_device_train_batch_size}")
|
||||
logger.info(f" Total train batch size (w. parallel, distributed & accumulation) = {total_batch_size}")
|
||||
logger.info(f" Gradient Accumulation steps = {args.gradient_accumulation_steps}")
|
||||
logger.info(f" Total optimization steps = {args.max_train_steps}")
|
||||
|
||||
# Only show the progress bar once on each machine.
|
||||
progress_bar = tqdm(range(args.max_train_steps), disable=not accelerator.is_local_main_process)
|
||||
completed_steps = 0
|
||||
starting_epoch = 0
|
||||
# Potentially load in the weights and states from a previous save
|
||||
if args.resume_from_checkpoint:
|
||||
if args.resume_from_checkpoint is not None or args.resume_from_checkpoint != "":
|
||||
accelerator.print(f"Resumed from checkpoint: {args.resume_from_checkpoint}")
|
||||
accelerator.load_state(args.resume_from_checkpoint)
|
||||
path = os.path.basename(args.resume_from_checkpoint)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
# Get the most recent checkpoint
|
||||
dirs = [f.name for f in os.scandir(os.getcwd()) if f.is_dir()]
|
||||
dirs.sort(key=os.path.getctime)
|
||||
path = dirs[-1] # Sorts folders by date modified, most recent checkpoint is the last
|
||||
# Extract `epoch_{i}` or `step_{i}`
|
||||
training_difference = os.path.splitext(path)[0]
|
||||
|
||||
if "epoch" in training_difference:
|
||||
starting_epoch = int(training_difference.replace("epoch_", "")) + 1
|
||||
resume_step = None
|
||||
completed_steps = starting_epoch * num_update_steps_per_epoch
|
||||
else:
|
||||
# need to multiply `gradient_accumulation_steps` to reflect real steps
|
||||
resume_step = int(training_difference.replace("step_", "")) * args.gradient_accumulation_steps
|
||||
starting_epoch = resume_step // len(train_dataloader)
|
||||
resume_step -= starting_epoch * len(train_dataloader)
|
||||
completed_steps = resume_step // args.gradient_accumulation_steps
|
||||
|
||||
# update the progress_bar if load from checkpoint
|
||||
progress_bar.update(completed_steps)
|
||||
|
||||
for epoch in range(starting_epoch, args.num_train_epochs):
|
||||
model.train()
|
||||
if args.with_tracking:
|
||||
total_loss = 0
|
||||
if args.resume_from_checkpoint and epoch == starting_epoch and resume_step is not None:
|
||||
# We skip the first `n` batches in the dataloader when resuming from a checkpoint
|
||||
active_dataloader = accelerator.skip_first_batches(train_dataloader, resume_step)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
active_dataloader = train_dataloader
|
||||
for step, batch in enumerate(active_dataloader):
|
||||
with accelerator.accumulate(model):
|
||||
query_embs = model(**{k.replace("query_", ""): v for k, v in batch.items() if "query" in k})
|
||||
product_embs = model(**{k.replace("product_", ""): v for k, v in batch.items() if "product" in k})
|
||||
loss = get_loss(get_cosing_embeddings(query_embs, product_embs), batch["labels"])
|
||||
total_loss += accelerator.reduce(loss.detach().float(), reduction="sum")
|
||||
accelerator.backward(loss)
|
||||
optimizer.step()
|
||||
lr_scheduler.step()
|
||||
model.zero_grad()
|
||||
|
||||
# Checks if the accelerator has performed an optimization step behind the scenes
|
||||
if accelerator.sync_gradients:
|
||||
progress_bar.update(1)
|
||||
completed_steps += 1
|
||||
|
||||
if (step + 1) % 100 == 0:
|
||||
logger.info(f"Step: {step+1}, Loss: {total_loss/(step+1)}")
|
||||
if args.with_tracking:
|
||||
accelerator.log({"train/loss": total_loss / (step + 1)}, step=completed_steps)
|
||||
|
||||
if isinstance(checkpointing_steps, int):
|
||||
if completed_steps % checkpointing_steps == 0:
|
||||
output_dir = f"step_{completed_steps }"
|
||||
if args.output_dir is not None:
|
||||
output_dir = os.path.join(args.output_dir, output_dir)
|
||||
accelerator.save_state(output_dir)
|
||||
|
||||
if completed_steps >= args.max_train_steps:
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
model.eval()
|
||||
for step, batch in enumerate(eval_dataloader):
|
||||
with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
query_embs = model(**{k.replace("query_", ""): v for k, v in batch.items() if "query" in k})
|
||||
product_embs = model(**{k.replace("product_", ""): v for k, v in batch.items() if "product" in k})
|
||||
prediction_scores = get_cosing_embeddings(query_embs, product_embs)
|
||||
prediction_scores, references = accelerator.gather_for_metrics((prediction_scores, batch["labels"]))
|
||||
metric.add_batch(
|
||||
prediction_scores=prediction_scores,
|
||||
references=references,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
result = metric.compute()
|
||||
result = {f"eval/{k}": v for k, v in result.items()}
|
||||
# Use accelerator.print to print only on the main process.
|
||||
accelerator.print(f"epoch {epoch}:", result)
|
||||
if args.with_tracking:
|
||||
result["train/epoch_loss"] = total_loss.item() / len(train_dataloader)
|
||||
accelerator.log(result, step=completed_steps)
|
||||
|
||||
if args.output_dir is not None:
|
||||
accelerator.wait_for_everyone()
|
||||
if accelerator.is_main_process:
|
||||
if isinstance(checkpointing_steps, str):
|
||||
accelerator.save_state(os.path.join(args.output_dir, f"epoch_{epoch}"))
|
||||
accelerator.unwrap_model(model).save_pretrained(
|
||||
args.output_dir, state_dict=accelerator.get_state_dict(accelerator.unwrap_model(model))
|
||||
)
|
||||
tokenizer.save_pretrained(args.output_dir)
|
||||
if args.push_to_hub:
|
||||
commit_message = (
|
||||
f"Training in progress epoch {epoch}"
|
||||
if epoch < args.num_train_epochs - 1
|
||||
else "End of training"
|
||||
)
|
||||
api.upload_folder(
|
||||
repo_id=repo_id,
|
||||
folder_path=args.output_dir,
|
||||
commit_message=commit_message,
|
||||
run_as_future=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
accelerator.wait_for_everyone()
|
||||
accelerator.end_training()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
main()
|
||||
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
10
examples/feature_extraction/requirements.txt
Normal file
10
examples/feature_extraction/requirements.txt
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,10 @@
|
||||
git+https://github.com/huggingface/peft
|
||||
git+https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate
|
||||
git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers
|
||||
datasets
|
||||
evaluate
|
||||
hnswlib
|
||||
pandas
|
||||
tqdm
|
||||
huggingface_hub
|
||||
wandb
|
||||
193
examples/fp4_finetuning/finetune_fp4_opt_bnb_peft.py
Executable file
193
examples/fp4_finetuning/finetune_fp4_opt_bnb_peft.py
Executable file
@ -0,0 +1,193 @@
|
||||
import os
|
||||
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
import torch.nn as nn
|
||||
import transformers
|
||||
from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer, BitsAndBytesConfig
|
||||
|
||||
from peft import LoraConfig, get_peft_model
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
os.environ["CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES"] = "0"
|
||||
|
||||
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
|
||||
"""Finetune-opt-bnb-peft.ipynb
|
||||
|
||||
Automatically generated by Colaboratory.
|
||||
|
||||
Original file is located at
|
||||
https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1jCkpikz0J2o20FBQmYmAGdiKmJGOMo-o
|
||||
|
||||
## Fine-tune large models using 🤗 `peft` adapters, `transformers` & `bitsandbytes`
|
||||
|
||||
In this tutorial we will cover how we can fine-tune large language models using the very recent `peft` library and `bitsandbytes` for loading large models in 8-bit.
|
||||
The fine-tuning method will rely on a recent method called "Low Rank Adapters" (LoRA), instead of fine-tuning the entire model you just have to fine-tune these adapters and load them properly inside the model.
|
||||
After fine-tuning the model you can also share your adapters on the 🤗 Hub and load them very easily. Let's get started!
|
||||
|
||||
### Install requirements
|
||||
|
||||
First, run the cells below to install the requirements:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
"""### Model loading
|
||||
|
||||
Here let's load the `opt-6.7b` model, its weights in half-precision (float16) are about 13GB on the Hub! If we load them in 8-bit we would require around 7GB of memory instead.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
free_in_GB = int(torch.cuda.mem_get_info()[0] / 1024**3)
|
||||
max_memory = f"{free_in_GB-2}GB"
|
||||
|
||||
n_gpus = torch.cuda.device_count()
|
||||
max_memory = {i: max_memory for i in range(n_gpus)}
|
||||
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"facebook/opt-350m",
|
||||
max_memory=max_memory,
|
||||
quantization_config=BitsAndBytesConfig(
|
||||
load_in_4bit=True,
|
||||
llm_int8_threshold=6.0,
|
||||
llm_int8_has_fp16_weight=False,
|
||||
bnb_4bit_compute_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
bnb_4bit_use_double_quant=True,
|
||||
bnb_4bit_quant_type="nf4",
|
||||
),
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("facebook/opt-350m")
|
||||
|
||||
"""### Post-processing on the model
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, we need to apply some post-processing on the 8-bit model to enable training, let's freeze all our layers, and cast the layer-norm in `float32` for stability. We also cast the output of the last layer in `float32` for the same reasons.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
print(model)
|
||||
|
||||
for param in model.parameters():
|
||||
param.requires_grad = False # freeze the model - train adapters later
|
||||
if param.ndim == 1:
|
||||
# cast the small parameters (e.g. layernorm) to fp32 for stability
|
||||
param.data = param.data.to(torch.float32)
|
||||
|
||||
# model.gradient_checkpointing_enable() # reduce number of stored activations
|
||||
# model.model.decoder.project_in = lambda x: x.requires_grad_(True)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class CastOutputToFloat(nn.Sequential):
|
||||
def forward(self, x):
|
||||
return super().forward(x).to(torch.float32)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
model.lm_head = CastOutputToFloat(model.lm_head)
|
||||
|
||||
"""### Apply LoRA
|
||||
|
||||
Here comes the magic with `peft`! Let's load a `PeftModel` and specify that we are going to use low-rank adapters (LoRA) using `get_peft_model` utility function from `peft`.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def print_trainable_parameters(model):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Prints the number of trainable parameters in the model.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
trainable_params = 0
|
||||
all_param = 0
|
||||
for _, param in model.named_parameters():
|
||||
all_param += param.numel()
|
||||
if param.requires_grad:
|
||||
trainable_params += param.numel()
|
||||
print(
|
||||
f"trainable params: {trainable_params} || all params: {all_param} || trainable%: {100 * trainable_params / all_param}"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
config = LoraConfig(
|
||||
r=64,
|
||||
lora_alpha=32,
|
||||
target_modules=["q_proj", "v_proj", "out_proj", "fc1", "fc2"],
|
||||
lora_dropout=0.01,
|
||||
bias="none",
|
||||
task_type="CAUSAL_LM",
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
model = get_peft_model(model, config)
|
||||
print_trainable_parameters(model)
|
||||
|
||||
# Verifying the datatypes.
|
||||
dtypes = {}
|
||||
for _, p in model.named_parameters():
|
||||
dtype = p.dtype
|
||||
if dtype not in dtypes:
|
||||
dtypes[dtype] = 0
|
||||
dtypes[dtype] += p.numel()
|
||||
total = 0
|
||||
for k, v in dtypes.items():
|
||||
total += v
|
||||
for k, v in dtypes.items():
|
||||
print(k, v, v / total)
|
||||
|
||||
"""### Training"""
|
||||
|
||||
data = load_dataset("Abirate/english_quotes")
|
||||
data = data.map(lambda samples: tokenizer(samples["quote"]), batched=True)
|
||||
|
||||
trainer = transformers.Trainer(
|
||||
model=model,
|
||||
train_dataset=data["train"],
|
||||
args=transformers.TrainingArguments(
|
||||
per_device_train_batch_size=4,
|
||||
gradient_accumulation_steps=4,
|
||||
warmup_steps=10,
|
||||
max_steps=20,
|
||||
learning_rate=3e-4,
|
||||
fp16=True,
|
||||
logging_steps=1,
|
||||
output_dir="outputs",
|
||||
),
|
||||
data_collator=transformers.DataCollatorForLanguageModeling(tokenizer, mlm=False),
|
||||
)
|
||||
model.config.use_cache = False # silence the warnings. Please re-enable for inference!
|
||||
trainer.train()
|
||||
|
||||
# from huggingface_hub import notebook_login
|
||||
|
||||
# notebook_login()
|
||||
|
||||
# model.push_to_hub("ybelkada/opt-6.7b-lora", use_auth_token=True)
|
||||
|
||||
"""## Load adapters from the Hub
|
||||
|
||||
You can also directly load adapters from the Hub using the commands below:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
# import torch
|
||||
# from peft import PeftModel, PeftConfig
|
||||
# from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer, BitsAndBytesConfig
|
||||
#
|
||||
# peft_model_id = "ybelkada/opt-6.7b-lora"
|
||||
# config = PeftConfig.from_pretrained(peft_model_id)
|
||||
# model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(config.base_model_name_or_path, return_dict=True, quantization_config=BitsAndBytesConfig(load_in_8bit=True), device_map='auto')
|
||||
# tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(config.base_model_name_or_path)
|
||||
#
|
||||
## Load the Lora model
|
||||
# model = PeftModel.from_pretrained(model, peft_model_id)
|
||||
#
|
||||
# """## Inference
|
||||
#
|
||||
# You can then directly use the trained model or the model that you have loaded from the 🤗 Hub for inference as you would do it usually in `transformers`.
|
||||
# """
|
||||
#
|
||||
batch = tokenizer("Two things are infinite: ", return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
|
||||
model.config.use_cache = False # silence the warnings. Please re-enable for inference!
|
||||
model.eval()
|
||||
with torch.cuda.amp.autocast():
|
||||
output_tokens = model.generate(**batch, max_new_tokens=50)
|
||||
|
||||
print("\n\n", tokenizer.decode(output_tokens[0], skip_special_tokens=True))
|
||||
# model.save('./test.pt')
|
||||
|
||||
# """As you can see by fine-tuning for few steps we have almost recovered the quote from Albert Einstein that is present in the [training data](https://huggingface.co/datasets/Abirate/english_quotes)."""
|
||||
15
examples/image_classification/README.md
Normal file
15
examples/image_classification/README.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,15 @@
|
||||
# Fine-tuning for image classification using LoRA and 🤗 PEFT
|
||||
|
||||
## Vision Transformer model from transformers
|
||||
|
||||
[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/peft/blob/main/examples/image_classification/image_classification_peft_lora.ipynb)
|
||||
|
||||
We provide a notebook (`image_classification_peft_lora.ipynb`) where we learn how to use [LoRA](https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.09685) from 🤗 PEFT to fine-tune an image classification model by ONLY using **0.7%** of the original trainable parameters of the model.
|
||||
|
||||
LoRA adds low-rank "update matrices" to certain blocks in the underlying model (in this case the attention blocks) and ONLY trains those matrices during fine-tuning. During inference, these update matrices are _merged_ with the original model parameters. For more details, check out the [original LoRA paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.09685).
|
||||
|
||||
## PoolFormer model from timm
|
||||
|
||||
[](https://colab.research.google.com/github/huggingface/peft/blob/main/examples/image_classification/image_classification_timm_peft_lora.ipynb)
|
||||
|
||||
The notebook `image_classification_timm_peft_lora.ipynb` showcases fine-tuning an image classification model using from the [timm](https://huggingface.co/docs/timm/index) library. Again, LoRA is used to reduce the numberof trainable parameters to a fraction of the total.
|
||||
14951
examples/image_classification/image_classification_peft_lora.ipynb
Normal file
14951
examples/image_classification/image_classification_peft_lora.ipynb
Normal file
File diff suppressed because one or more lines are too long
File diff suppressed because one or more lines are too long
8314
examples/int8_training/Finetune_flan_t5_large_bnb_peft.ipynb
Normal file
8314
examples/int8_training/Finetune_flan_t5_large_bnb_peft.ipynb
Normal file
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
9274
examples/int8_training/Finetune_opt_bnb_peft.ipynb
Normal file
9274
examples/int8_training/Finetune_opt_bnb_peft.ipynb
Normal file
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
104
examples/int8_training/fine_tune_blip2_int8.py
Normal file
104
examples/int8_training/fine_tune_blip2_int8.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,104 @@
|
||||
# Copyright 2023-present the HuggingFace Inc. team.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from datasets import load_dataset
|
||||
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader, Dataset
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForVision2Seq, AutoProcessor, BitsAndBytesConfig
|
||||
|
||||
from peft import LoraConfig, get_peft_model
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Let's define the LoraConfig
|
||||
config = LoraConfig(
|
||||
r=16,
|
||||
lora_alpha=32,
|
||||
lora_dropout=0.05,
|
||||
bias="none",
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# We load our model and processor using `transformers`
|
||||
model = AutoModelForVision2Seq.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"Salesforce/blip2-opt-2.7b", quantization_config=BitsAndBytesConfig(load_in_8bit=True)
|
||||
)
|
||||
processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained("Salesforce/blip2-opt-2.7b")
|
||||
|
||||
# Get our peft model and print the number of trainable parameters
|
||||
model = get_peft_model(model, config)
|
||||
model.print_trainable_parameters()
|
||||
|
||||
# Let's load the dataset here!
|
||||
dataset = load_dataset("ybelkada/football-dataset", split="train")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class ImageCaptioningDataset(Dataset):
|
||||
def __init__(self, dataset, processor):
|
||||
self.dataset = dataset
|
||||
self.processor = processor
|
||||
|
||||
def __len__(self):
|
||||
return len(self.dataset)
|
||||
|
||||
def __getitem__(self, idx):
|
||||
item = self.dataset[idx]
|
||||
encoding = self.processor(images=item["image"], padding="max_length", return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
# remove batch dimension
|
||||
encoding = {k: v.squeeze() for k, v in encoding.items()}
|
||||
encoding["text"] = item["text"]
|
||||
return encoding
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def collator(batch):
|
||||
# pad the input_ids and attention_mask
|
||||
processed_batch = {}
|
||||
for key in batch[0].keys():
|
||||
if key != "text":
|
||||
processed_batch[key] = torch.stack([example[key] for example in batch])
|
||||
else:
|
||||
text_inputs = processor.tokenizer(
|
||||
[example["text"] for example in batch], padding=True, return_tensors="pt"
|
||||
)
|
||||
processed_batch["input_ids"] = text_inputs["input_ids"]
|
||||
processed_batch["attention_mask"] = text_inputs["attention_mask"]
|
||||
return processed_batch
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
train_dataset = ImageCaptioningDataset(dataset, processor)
|
||||
train_dataloader = DataLoader(train_dataset, shuffle=True, batch_size=2, collate_fn=collator)
|
||||
|
||||
optimizer = torch.optim.AdamW(model.parameters(), lr=5e-5)
|
||||
|
||||
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
|
||||
|
||||
model.train()
|
||||
|
||||
for epoch in range(50):
|
||||
print("Epoch:", epoch)
|
||||
for idx, batch in enumerate(train_dataloader):
|
||||
input_ids = batch.pop("input_ids").to(device)
|
||||
pixel_values = batch.pop("pixel_values").to(device, torch.float16)
|
||||
|
||||
outputs = model(input_ids=input_ids, pixel_values=pixel_values, labels=input_ids)
|
||||
|
||||
loss = outputs.loss
|
||||
|
||||
print("Loss:", loss.item())
|
||||
|
||||
loss.backward()
|
||||
|
||||
optimizer.step()
|
||||
optimizer.zero_grad()
|
||||
|
||||
if idx % 10 == 0:
|
||||
generated_output = model.generate(pixel_values=pixel_values)
|
||||
print(processor.batch_decode(generated_output, skip_special_tokens=True))
|
||||
779
examples/int8_training/peft_adalora_whisper_large_training.py
Normal file
779
examples/int8_training/peft_adalora_whisper_large_training.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,779 @@
|
||||
import argparse
|
||||
import gc
|
||||
import json
|
||||
import logging
|
||||
import math
|
||||
import os
|
||||
from dataclasses import dataclass
|
||||
from datetime import datetime
|
||||
from pathlib import Path
|
||||
from random import randint
|
||||
from typing import Any, Dict, List, Union
|
||||
|
||||
# datasets imports
|
||||
import datasets
|
||||
|
||||
# metric imports
|
||||
import evaluate
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
import transformers
|
||||
import wandb
|
||||
|
||||
# accelerate imports
|
||||
from accelerate import Accelerator, dispatch_model
|
||||
from accelerate.logging import get_logger
|
||||
from datasets import Audio, DatasetDict, IterableDatasetDict, interleave_datasets, load_dataset
|
||||
|
||||
# hf imports
|
||||
from huggingface_hub import HfApi
|
||||
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
|
||||
from tqdm import tqdm
|
||||
from transformers import (
|
||||
BitsAndBytesConfig,
|
||||
SchedulerType,
|
||||
WhisperForConditionalGeneration,
|
||||
WhisperProcessor,
|
||||
get_scheduler,
|
||||
set_seed,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from transformers.models.whisper.english_normalizer import BasicTextNormalizer
|
||||
|
||||
# peft imports
|
||||
from peft import AdaLoraConfig, LoraConfig, PeftModel, get_peft_model
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
logger = get_logger(__name__, log_level="INFO")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def parse_args():
|
||||
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="Whisper Fine-Tuning with AdaLora")
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--model_name_or_path",
|
||||
type=str,
|
||||
help="Path to pretrained model or model identifier from huggingface.co/models.",
|
||||
required=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument("--language", type=str, help="Language to use for training; e.g., 'Hindi' ", required=True)
|
||||
parser.add_argument("--language_abbr", type=str, help="Language to use for training; e.g., 'hi' ", required=True)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--task", type=str, default="transcribe", help="Task to use for training; e.g., 'transcribe' ", required=False
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--dataset_name",
|
||||
type=str,
|
||||
default="mozilla-foundation/common_voice_11_0",
|
||||
help="Dataset to use for training; e.g., 'whisper' ",
|
||||
required=False,
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--dataset_in_streaming_mode",
|
||||
action="store_true",
|
||||
help="Whether to use streaming mode for the dataset.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--do_lower_case", action="store_true", help="lowercase the transcribed text before tokenizing"
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--do_remove_punctuation", action="store_true", help="remove punctuation from the transcribed text"
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument("--push_to_hub", action="store_true", help="Whether or not to push the model to the Hub.")
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--overwrite_cache", type=bool, default=False, help="Overwrite the cached training and evaluation sets"
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument("--max_audio_input_length", type=float, default=30.0, help="Maximum audio length in seconds.")
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--preprocessing_num_workers",
|
||||
type=int,
|
||||
default=None,
|
||||
help="The number of processes to use for the preprocessing.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--per_device_train_batch_size",
|
||||
type=int,
|
||||
default=8,
|
||||
help="Batch size (per device) for the training dataloader.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--per_device_eval_batch_size",
|
||||
type=int,
|
||||
default=8,
|
||||
help="Batch size (per device) for the evaluation dataloader.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--buffer_size",
|
||||
type=int,
|
||||
default=5000,
|
||||
help="Number of samples to prefetch in the streaming mode.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--dataloader_pin_memory",
|
||||
action="store_true",
|
||||
help="Whether or not to pin memory for the DataLoader.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--dataloader_num_workers",
|
||||
type=int,
|
||||
default=0,
|
||||
help="Number of subprocesses to use for data loading.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--learning_rate",
|
||||
type=float,
|
||||
default=5e-5,
|
||||
help="Initial learning rate (after the potential warmup period) to use.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument("--weight_decay", type=float, default=0.0, help="Weight decay to use.")
|
||||
parser.add_argument("--num_train_epochs", type=int, default=3, help="Total number of training epochs to perform.")
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--max_train_steps",
|
||||
type=int,
|
||||
default=None,
|
||||
help="Total number of training steps to perform. If provided, overrides num_train_epochs.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--gradient_accumulation_steps",
|
||||
type=int,
|
||||
default=1,
|
||||
help="Number of updates steps to accumulate before performing a backward/update pass.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--lr_scheduler_type",
|
||||
type=SchedulerType,
|
||||
default="linear",
|
||||
help="The scheduler type to use.",
|
||||
choices=["linear", "cosine", "cosine_with_restarts", "polynomial", "constant", "constant_with_warmup"],
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--num_warmup_steps", type=int, default=0, help="Number of steps for the warmup in the lr scheduler."
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument("--output_dir", type=str, default=None, help="Where to store the final model.")
|
||||
parser.add_argument("--seed", type=int, default=None, help="A seed for reproducible training.")
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--load_best_model",
|
||||
action="store_true",
|
||||
help="Whether to load the best model at the end of training",
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--with_tracking",
|
||||
action="store_true",
|
||||
help="Whether to enable experiment trackers for logging.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--report_to",
|
||||
type=str,
|
||||
default="all",
|
||||
help=(
|
||||
'The integration to report the results and logs to. Supported platforms are `"tensorboard"`,'
|
||||
' `"wandb"` and `"comet_ml"`. Use `"all"` (default) to report to all integrations.'
|
||||
"Only applicable when `--with_tracking` is passed."
|
||||
),
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument("--hub_token", type=str, help="The token to use to push to the Model Hub.")
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--hub_model_id", type=str, help="The name of the repository to keep in sync with the local `output_dir`."
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--checkpointing_steps",
|
||||
type=int,
|
||||
default=500,
|
||||
help="Whether the various states should be saved at the end of every n steps, or 'epoch' for each epoch.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--logging_steps",
|
||||
type=int,
|
||||
default=100,
|
||||
help="Whether the various states should be saved at the end of every n steps, or 'epoch' for each epoch.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--evaluation_steps",
|
||||
type=int,
|
||||
default=500,
|
||||
help="Whether the various states should be saved at the end of every n steps, or 'epoch' for each epoch.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--resume_from_checkpoint",
|
||||
type=str,
|
||||
default=None,
|
||||
help="If the training should continue from a checkpoint folder.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# lora/adalora specific args
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--use_peft",
|
||||
action="store_true",
|
||||
help="Whether to use PEFT",
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--use_adalora",
|
||||
action="store_true",
|
||||
help="Whether to use AdaLoRA or LoRA. If set, uses AdaLoRA instead of the default LoRA.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--init_r",
|
||||
type=int,
|
||||
default=12,
|
||||
help="Initial AdaLoRA rank",
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--target_r",
|
||||
type=int,
|
||||
default=4,
|
||||
help="Target AdaLoRA rank",
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--tinit",
|
||||
type=int,
|
||||
default=200,
|
||||
help="number of warmup steps for AdaLoRA wherein no pruning is performed",
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--tfinal",
|
||||
type=int,
|
||||
default=1000,
|
||||
help=" fix the resulting budget distribution and fine-tune the model for tfinal steps when using AdaLoRA ",
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--delta_t",
|
||||
type=int,
|
||||
default=10,
|
||||
help="interval of steps for AdaLoRA to update rank",
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--lora_alpha",
|
||||
type=int,
|
||||
default=32,
|
||||
help="LORA alpha",
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--r",
|
||||
type=int,
|
||||
default=8,
|
||||
help="LORA rank",
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--lora_dropout",
|
||||
type=float,
|
||||
default=0.1,
|
||||
help="LORA dropout",
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--orth_reg_weight",
|
||||
type=float,
|
||||
default=0.5,
|
||||
help="Orthogonal regularization weight",
|
||||
)
|
||||
parser.add_argument(
|
||||
"--debug_mode",
|
||||
action="store_true",
|
||||
help="Whether to use debug mode",
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
args = parser.parse_args()
|
||||
|
||||
if args.push_to_hub:
|
||||
assert args.output_dir is not None, "Need an `output_dir` to create a repo when `--push_to_hub` is passed."
|
||||
|
||||
return args
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def load_streaming_dataset(dataset_name, dataset_config_name, split, **kwargs):
|
||||
if "+" in split:
|
||||
# load multiple splits separated by the `+` symbol *with* streaming mode
|
||||
dataset_splits = [
|
||||
load_dataset(dataset_name, dataset_config_name, split=split_name, streaming=True, **kwargs)
|
||||
for split_name in split.split("+")
|
||||
]
|
||||
# interleave multiple splits to form one dataset
|
||||
interleaved_dataset = interleave_datasets(dataset_splits)
|
||||
return interleaved_dataset
|
||||
else:
|
||||
# load a single split *with* streaming mode
|
||||
dataset = load_dataset(dataset_name, dataset_config_name, split=split, streaming=True, **kwargs)
|
||||
return dataset
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def prepare_dataset_wrapper(do_lower_case, do_remove_punctuation, processor, normalizer):
|
||||
def prepare_dataset(batch):
|
||||
# load and (possibly) resample audio data to 16kHz
|
||||
audio = batch["audio"]
|
||||
|
||||
# compute log-Mel input features from input audio array
|
||||
batch["input_features"] = processor.feature_extractor(
|
||||
audio["array"], sampling_rate=audio["sampling_rate"]
|
||||
).input_features[0]
|
||||
# compute input length of audio sample in seconds
|
||||
batch["input_length"] = len(audio["array"]) / audio["sampling_rate"]
|
||||
|
||||
# optional pre-processing steps
|
||||
transcription = batch["sentence"]
|
||||
if do_lower_case:
|
||||
transcription = transcription.lower()
|
||||
if do_remove_punctuation:
|
||||
transcription = normalizer(transcription).strip()
|
||||
|
||||
# encode target text to label ids
|
||||
batch["labels"] = processor.tokenizer(transcription).input_ids
|
||||
return batch
|
||||
|
||||
return prepare_dataset
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def save_model_hook(models, weights, output_dir):
|
||||
for model in models:
|
||||
model.save_pretrained(output_dir)
|
||||
# make sure to pop weight so that corresponding model is not saved again
|
||||
weights.pop()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def load_model_hook(models, input_dir):
|
||||
while len(models) > 0:
|
||||
model = models.pop()
|
||||
# pop models so that they are not loaded again
|
||||
PeftModel.from_pretrained(model.base_model.model, input_dir)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@dataclass
|
||||
class DataCollatorSpeechSeq2SeqWithPadding:
|
||||
processor: Any
|
||||
|
||||
def __call__(self, features: List[Dict[str, Union[List[int], torch.Tensor]]]) -> Dict[str, torch.Tensor]:
|
||||
# split inputs and labels since they have to be of different lengths and need different padding methods
|
||||
# first treat the audio inputs by simply returning torch tensors
|
||||
input_features = [{"input_features": feature["input_features"]} for feature in features]
|
||||
batch = self.processor.feature_extractor.pad(input_features, return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
|
||||
# get the tokenized label sequences
|
||||
label_features = [{"input_ids": feature["labels"]} for feature in features]
|
||||
# pad the labels to max length
|
||||
labels_batch = self.processor.tokenizer.pad(label_features, return_tensors="pt")
|
||||
|
||||
# replace padding with -100 to ignore loss correctly
|
||||
labels = labels_batch["input_ids"].masked_fill(labels_batch.attention_mask.ne(1), -100)
|
||||
|
||||
# if bos token is appended in previous tokenization step,
|
||||
# cut bos token here as it's append later anyways
|
||||
if (labels[:, 0] == self.processor.tokenizer.bos_token_id).all().cpu().item():
|
||||
labels = labels[:, 1:]
|
||||
|
||||
batch["labels"] = labels
|
||||
|
||||
return batch
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def get_audio_length_processor(max_input_length):
|
||||
def is_audio_in_length_range(length):
|
||||
return length < max_input_length
|
||||
|
||||
return is_audio_in_length_range
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def evaluation_loop(model, eval_dataloader, processor, normalizer, metric, forced_decoder_ids, accelerator):
|
||||
model.eval()
|
||||
predictions = []
|
||||
references = []
|
||||
normalized_predictions = []
|
||||
normalized_references = []
|
||||
for _, batch in enumerate(tqdm(eval_dataloader)):
|
||||
with torch.cuda.amp.autocast():
|
||||
with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
generated_tokens = (
|
||||
model.generate(
|
||||
input_features=batch["input_features"],
|
||||
forced_decoder_ids=forced_decoder_ids,
|
||||
max_new_tokens=255,
|
||||
)
|
||||
.cpu()
|
||||
.numpy()
|
||||
)
|
||||
labels = batch["labels"].cpu().numpy()
|
||||
labels = np.where(labels != -100, labels, processor.tokenizer.pad_token_id)
|
||||
decoded_preds = processor.tokenizer.batch_decode(generated_tokens, skip_special_tokens=True)
|
||||
decoded_labels = processor.tokenizer.batch_decode(labels, skip_special_tokens=True)
|
||||
predictions.extend(decoded_preds)
|
||||
references.extend(decoded_labels)
|
||||
normalized_predictions.extend([normalizer(pred).strip() for pred in decoded_preds])
|
||||
normalized_references.extend([normalizer(label).strip() for label in decoded_labels])
|
||||
del generated_tokens, labels, batch
|
||||
gc.collect()
|
||||
wer = 100 * metric.compute(predictions=predictions, references=references)
|
||||
normalized_wer = 100 * metric.compute(predictions=normalized_predictions, references=normalized_references)
|
||||
eval_metrics = {"eval/wer": wer, "eval/normalized_wer": normalized_wer}
|
||||
if accelerator.get_tracker("wandb"):
|
||||
sample_size = min(len(predictions), 256)
|
||||
ids = [randint(0, len(predictions) - 1) for p in range(0, sample_size)]
|
||||
sample_predictions = [predictions[i] for i in ids]
|
||||
sample_references = [references[i] for i in ids]
|
||||
sample_normalized_predictions = [normalized_predictions[i] for i in ids]
|
||||
sample_normalized_references = [normalized_references[i] for i in ids]
|
||||
table_rows = [
|
||||
list(r)
|
||||
for r in zip(
|
||||
sample_predictions, sample_references, sample_normalized_predictions, sample_normalized_references
|
||||
)
|
||||
]
|
||||
eval_metrics["eval_samples"] = wandb.Table(
|
||||
columns=["predictions", "references", "normalized_predictions", "normalized_references"],
|
||||
rows=table_rows,
|
||||
)
|
||||
return eval_metrics
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def main():
|
||||
args = parse_args()
|
||||
|
||||
accelerator_kwargs = {"gradient_accumulation_steps": args.gradient_accumulation_steps}
|
||||
if args.with_tracking:
|
||||
accelerator_kwargs["log_with"] = args.report_to
|
||||
accelerator_kwargs["project_dir"] = args.output_dir
|
||||
accelerator = Accelerator(**accelerator_kwargs)
|
||||
|
||||
# Make one log on every process with the configuration for debugging.
|
||||
logging.basicConfig(
|
||||
format="%(asctime)s - %(levelname)s - %(name)s - %(message)s",
|
||||
datefmt="%m/%d/%Y %H:%M:%S",
|
||||
level=logging.INFO,
|
||||
)
|
||||
logger.info(accelerator.state, main_process_only=False)
|
||||
if accelerator.is_local_main_process:
|
||||
datasets.utils.logging.set_verbosity_warning()
|
||||
transformers.utils.logging.set_verbosity_info()
|
||||
else:
|
||||
datasets.utils.logging.set_verbosity_error()
|
||||
transformers.utils.logging.set_verbosity_error()
|
||||
|
||||
# If passed along, set the training seed now.
|
||||
if args.seed is not None:
|
||||
set_seed(args.seed)
|
||||
|
||||
# Handle the repository creation
|
||||
if accelerator.is_main_process:
|
||||
if args.push_to_hub:
|
||||
api = HfApi(token=args.hub_token)
|
||||
|
||||
# Create repo (repo_name from args or inferred)
|
||||
repo_name = args.hub_model_id
|
||||
if repo_name is None:
|
||||
repo_name = Path(args.output_dir).absolute().name
|
||||
repo_id = api.create_repo(repo_name, exist_ok=True).repo_id
|
||||
|
||||
with open(os.path.join(args.output_dir, ".gitignore"), "w+") as gitignore:
|
||||
if "step_*" not in gitignore:
|
||||
gitignore.write("step_*\n")
|
||||
if "epoch_*" not in gitignore:
|
||||
gitignore.write("epoch_*\n")
|
||||
elif args.output_dir is not None:
|
||||
os.makedirs(args.output_dir, exist_ok=True)
|
||||
accelerator.wait_for_everyone()
|
||||
|
||||
# load dataset either in streaming mode or not
|
||||
processor = WhisperProcessor.from_pretrained(args.model_name_or_path, language=args.language, task=args.task)
|
||||
normalizer = BasicTextNormalizer()
|
||||
prepare_dataset = prepare_dataset_wrapper(args.do_lower_case, args.do_remove_punctuation, processor, normalizer)
|
||||
is_audio_in_length_range = get_audio_length_processor(args.max_audio_input_length)
|
||||
data_collator = DataCollatorSpeechSeq2SeqWithPadding(processor=processor)
|
||||
|
||||
if args.dataset_in_streaming_mode:
|
||||
raw_datasets = IterableDatasetDict()
|
||||
loading_method = load_streaming_dataset
|
||||
else:
|
||||
raw_datasets = DatasetDict()
|
||||
loading_method = load_dataset
|
||||
|
||||
if args.debug_mode:
|
||||
train_split = "train[:100]"
|
||||
test_split = "test[:10]"
|
||||
else:
|
||||
train_split = "train+validation"
|
||||
test_split = "test"
|
||||
|
||||
raw_datasets["train"] = loading_method(
|
||||
args.dataset_name, args.language_abbr, split=train_split, use_auth_token=True
|
||||
)
|
||||
raw_datasets["test"] = loading_method(args.dataset_name, args.language_abbr, split=test_split, use_auth_token=True)
|
||||
raw_datasets = raw_datasets.cast_column("audio", Audio(sampling_rate=16000))
|
||||
|
||||
logger.info("Dataset loaded: %s", raw_datasets)
|
||||
logger.info(f'{raw_datasets["train"][0]}')
|
||||
|
||||
vectorized_datasets = raw_datasets.map(
|
||||
prepare_dataset,
|
||||
remove_columns=list(next(iter(raw_datasets.values())).features),
|
||||
num_proc=args.preprocessing_num_workers,
|
||||
).with_format("torch")
|
||||
|
||||
if args.dataset_in_streaming_mode:
|
||||
vectorized_datasets["train"] = vectorized_datasets["train"].shuffle(
|
||||
buffer_size=args.buffer_size,
|
||||
seed=args.seed,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# filter out audio files that are too long from the training set
|
||||
is_audio_in_length_range = get_audio_length_processor(args.max_audio_input_length)
|
||||
vectorized_datasets["train"] = vectorized_datasets["train"].filter(
|
||||
is_audio_in_length_range, input_columns=["input_length"]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# get dataloaders
|
||||
train_dataloader = DataLoader(
|
||||
vectorized_datasets["train"],
|
||||
batch_size=args.per_device_train_batch_size,
|
||||
shuffle=True,
|
||||
collate_fn=data_collator,
|
||||
num_workers=args.dataloader_num_workers,
|
||||
pin_memory=args.dataloader_pin_memory,
|
||||
)
|
||||
eval_dataloader = DataLoader(
|
||||
vectorized_datasets["test"],
|
||||
batch_size=args.per_device_eval_batch_size,
|
||||
collate_fn=data_collator,
|
||||
num_workers=args.dataloader_num_workers,
|
||||
pin_memory=args.dataloader_pin_memory,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# metric
|
||||
metric = evaluate.load("wer")
|
||||
|
||||
# model
|
||||
model = WhisperForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained(
|
||||
args.model_name_or_path, quantization_config=BitsAndBytesConfig(load_in_8bit=True)
|
||||
)
|
||||
model.config.forced_decoder_ids = None
|
||||
model.config.suppress_tokens = []
|
||||
if len(set(model.hf_device_map.values()).intersection({"cpu", "disk"})) > 0:
|
||||
raise ValueError("Training on CPU or disk is not supported.")
|
||||
if len(set(model.hf_device_map.values())) > 1:
|
||||
device_map = model.hf_device_map.copy()
|
||||
# required because `labels` are on main execution device (0) while the output of `proj_out` is on other device.
|
||||
# So, this leads to device mismatch error when calculation cross-entropy between logits and labels.
|
||||
# Won't arise during inference as `labels` aren't supplied during that time
|
||||
# instead of changing device of one of the tied modules, I have to do this for all tied modules
|
||||
# else the execution device of remaining tied modules isn't changed
|
||||
device_map["model.decoder.embed_tokens"] = model._hf_hook.execution_device
|
||||
device_map["model.decoder.embed_positions"] = model._hf_hook.execution_device
|
||||
device_map["proj_out"] = model._hf_hook.execution_device
|
||||
dispatch_model(model, device_map=device_map)
|
||||
|
||||
# preparing peft model
|
||||
if args.use_peft:
|
||||
from peft import prepare_model_for_kbit_training
|
||||
|
||||
model = prepare_model_for_kbit_training(model)
|
||||
|
||||
# as Whisper model uses Conv layer in encoder, checkpointing disables grad computation
|
||||
# to avoid this, make the inputs trainable
|
||||
def make_inputs_require_grad(module, input, output):
|
||||
output.requires_grad_(True)
|
||||
|
||||
model.model.encoder.conv1.register_forward_hook(make_inputs_require_grad)
|
||||
|
||||
# wrapping model with adalora tuner
|
||||
if args.use_adalora:
|
||||
config = AdaLoraConfig(
|
||||
init_r=args.init_r,
|
||||
target_r=args.target_r,
|
||||
beta1=0.85,
|
||||
beta2=0.85,
|
||||
tinit=args.tinit,
|
||||
tfinal=args.tfinal,
|
||||
deltaT=args.delta_t,
|
||||
lora_alpha=args.lora_alpha,
|
||||
lora_dropout=args.lora_dropout,
|
||||
target_modules=["k_proj", "q_proj", "v_proj", "out_proj", "fc1", "fc2"],
|
||||
orth_reg_weight=args.orth_reg_weight,
|
||||
)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
config = LoraConfig(
|
||||
r=args.r,
|
||||
lora_alpha=args.lora_alpha,
|
||||
target_modules=["q_proj", "v_proj"],
|
||||
lora_dropout=args.lora_dropout,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
model = get_peft_model(model, config)
|
||||
model.print_trainable_parameters()
|
||||
|
||||
# optimizer
|
||||
optimizer = torch.optim.AdamW(model.parameters(), lr=args.learning_rate, weight_decay=args.weight_decay)
|
||||
|
||||
if args.max_train_steps is None:
|
||||
num_update_steps_per_epoch = math.ceil(len(train_dataloader) / args.gradient_accumulation_steps)
|
||||
args.max_train_steps = args.num_train_epochs * num_update_steps_per_epoch
|
||||
else:
|
||||
args.num_train_epochs = math.ceil(args.max_train_steps / num_update_steps_per_epoch)
|
||||
|
||||
# scheduler
|
||||
lr_scheduler = get_scheduler(
|
||||
name=args.lr_scheduler_type,
|
||||
optimizer=optimizer,
|
||||
num_warmup_steps=args.num_warmup_steps,
|
||||
num_training_steps=args.max_train_steps,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Prepare everything with our `accelerator`.
|
||||
model, optimizer, train_dataloader, eval_dataloader, lr_scheduler = accelerator.prepare(
|
||||
model, optimizer, train_dataloader, eval_dataloader, lr_scheduler
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
accelerator.print(model)
|
||||
|
||||
# Note here that the max steps is adjusted by the accelerator's num_processes
|
||||
args.max_train_steps = math.ceil(args.max_train_steps / accelerator.num_processes)
|
||||
if args.use_peft and args.use_adalora:
|
||||
model.base_model.peft_config["default"].total_step = args.max_train_steps
|
||||
# model.base_model.peft_config.total_step = args.max_train_steps
|
||||
|
||||
# We need to initialize the trackers we use, and also store our configuration.
|
||||
# The trackers initializes automatically on the main process.
|
||||
if args.with_tracking:
|
||||
run_name = f"run-{datetime.now().strftime('%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M-%S')}"
|
||||
experiment_config = vars(args)
|
||||
# TensorBoard cannot log Enums, need the raw value
|
||||
experiment_config["lr_scheduler_type"] = experiment_config["lr_scheduler_type"].value
|
||||
accelerator.init_trackers(
|
||||
"Whisper PEFT Fine-Tuning", config=experiment_config, init_kwargs={"wandb": {"name": run_name}}
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# saving and loading checkpoints for resuming training
|
||||
accelerator.register_save_state_pre_hook(save_model_hook)
|
||||
accelerator.register_load_state_pre_hook(load_model_hook)
|
||||
|
||||
total_batch_size = args.per_device_train_batch_size * accelerator.num_processes * args.gradient_accumulation_steps
|
||||
logger.info("***** Running training *****")
|
||||
logger.info(f" Num Epochs = {args.num_train_epochs}")
|
||||
logger.info(f" Instantaneous batch size per device = {args.per_device_train_batch_size}")
|
||||
logger.info(f" Total train batch size (w. parallel, distributed & accumulation) = {total_batch_size}")
|
||||
logger.info(f" Gradient Accumulation steps = {args.gradient_accumulation_steps}")
|
||||
logger.info(f" Total optimization steps = {args.max_train_steps}")
|
||||
# Only show the progress bar once on each machine.
|
||||
progress_bar = tqdm(range(args.max_train_steps), disable=not accelerator.is_local_main_process)
|
||||
global_step = 0
|
||||
starting_epoch = 0
|
||||
best_metric = None
|
||||
resume_step = 0
|
||||
forced_decoder_ids = processor.get_decoder_prompt_ids(language=args.language, task=args.task)
|
||||
|
||||
# Potentially load in the weights and states from a previous save
|
||||
if args.resume_from_checkpoint:
|
||||
accelerator.load_state(args.resume_from_checkpoint)
|
||||
path = os.path.basename(args.resume_from_checkpoint)
|
||||
training_difference = os.path.splitext(path)[0]
|
||||
global_step = resume_step = int(training_difference.replace("step_", ""))
|
||||
starting_epoch = resume_step // len(train_dataloader)
|
||||
resume_step -= starting_epoch * len(train_dataloader)
|
||||
|
||||
# We need to adjust the progress bar to the current step
|
||||
progress_bar.update(resume_step)
|
||||
for epoch in range(starting_epoch, args.num_train_epochs):
|
||||
model.train()
|
||||
if args.with_tracking:
|
||||
total_loss = 0
|
||||
running_loss = 0
|
||||
for step, batch in enumerate(accelerator.skip_first_batches(train_dataloader, num_batches=resume_step)):
|
||||
with accelerator.accumulate(model):
|
||||
outputs = model(**batch)
|
||||
loss = outputs.loss
|
||||
accelerator.backward(loss)
|
||||
optimizer.step()
|
||||
lr_scheduler.step()
|
||||
|
||||
# Update the importance of low-rank matrices
|
||||
# and allocate the budget accordingly.
|
||||
# This is only needed for AdaLora.
|
||||
# Note that this requires parameter gradients.
|
||||
# Hence being called before optimizer.zero_grad().
|
||||
if args.use_peft and args.use_adalora:
|
||||
model.update_and_allocate(global_step)
|
||||
|
||||
optimizer.zero_grad()
|
||||
global_step += 1
|
||||
progress_bar.update(1)
|
||||
|
||||
if args.with_tracking:
|
||||
step_loss = accelerator.reduce(loss.detach().clone()).item()
|
||||
total_loss += step_loss
|
||||
running_loss += step_loss
|
||||
|
||||
if global_step % args.checkpointing_steps == 0:
|
||||
output_dir = os.path.join(args.output_dir, f"step_{global_step}")
|
||||
accelerator.save_state(output_dir)
|
||||
|
||||
if global_step % args.logging_steps == 0:
|
||||
if args.with_tracking:
|
||||
accelerator.log({"train/running_loss": running_loss / args.logging_steps}, step=global_step)
|
||||
running_loss = 0
|
||||
|
||||
if global_step % args.evaluation_steps == 0:
|
||||
eval_metrics = evaluation_loop(
|
||||
model, eval_dataloader, processor, normalizer, metric, forced_decoder_ids, accelerator
|
||||
)
|
||||
if args.with_tracking:
|
||||
logger.info(f"Step {global_step} eval metrics: {eval_metrics}")
|
||||
accelerator.log(eval_metrics, step=global_step)
|
||||
if best_metric is None or eval_metrics["eval/wer"] < best_metric:
|
||||
best_metric = eval_metrics["eval/wer"]
|
||||
accelerator.save_state(os.path.join(args.output_dir, "best_checkpoint"))
|
||||
model.train()
|
||||
|
||||
if global_step >= args.max_train_steps:
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
if args.with_tracking:
|
||||
train_epoch_loss = total_loss / (step + 1)
|
||||
logger.info(f"Epoch {epoch} train loss: {train_epoch_loss}")
|
||||
accelerator.log({"epoch/train_loss": train_epoch_loss}, step=epoch)
|
||||
|
||||
if args.push_to_hub and epoch <= args.num_train_epochs - 1:
|
||||
accelerator.wait_for_everyone()
|
||||
unwrapped_model = accelerator.unwrap_model(model)
|
||||
unwrapped_model.save_pretrained(args.output_dir, is_main_process=accelerator.is_main_process)
|
||||
# evaluate the model at the end of training
|
||||
eval_metrics = evaluation_loop(
|
||||
model, eval_dataloader, processor, normalizer, metric, forced_decoder_ids, accelerator
|
||||
)
|
||||
if args.with_tracking:
|
||||
logger.info(f"Step {global_step} eval metrics: {eval_metrics}")
|
||||
accelerator.log(eval_metrics, step=global_step)
|
||||
if best_metric is None or eval_metrics["eval/wer"] < best_metric:
|
||||
best_metric = eval_metrics["eval/wer"]
|
||||
accelerator.save_state(os.path.join(args.output_dir, "best_checkpoint"))
|
||||
|
||||
if accelerator.is_main_process:
|
||||
processor.tokenizer.save_pretrained(args.output_dir)
|
||||
api.upload_folder(
|
||||
repo_id=repo_id,
|
||||
folder_path=args.output_dir,
|
||||
commit_message=f"Training in progress epoch {epoch}",
|
||||
run_as_future=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if args.load_best_model:
|
||||
# load the best model
|
||||
accelerator.load_state(os.path.join(args.output_dir, "best_checkpoint"))
|
||||
model.resize_modules_by_rank_pattern(model.peft_config["default"].rank_pattern, "default")
|
||||
eval_metrics = evaluation_loop(
|
||||
model, eval_dataloader, processor, normalizer, metric, forced_decoder_ids, accelerator
|
||||
)
|
||||
if args.with_tracking:
|
||||
best_metrics = {"best_" + k: v for k, v in eval_metrics.items()}
|
||||
accelerator.log(best_metrics, step=global_step)
|
||||
|
||||
accelerator.wait_for_everyone()
|
||||
unwrapped_model = accelerator.unwrap_model(model)
|
||||
unwrapped_model.save_pretrained(args.output_dir, is_main_process=accelerator.is_main_process)
|
||||
if accelerator.is_main_process:
|
||||
processor.tokenizer.save_pretrained(args.output_dir)
|
||||
if args.push_to_hub:
|
||||
api.upload_folder(
|
||||
repo_id=repo_id,
|
||||
folder_path=args.output_dir,
|
||||
commit_message="End of training",
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
with open(os.path.join(args.output_dir, "all_results.json"), "w") as f:
|
||||
eval_metrics.pop("eval_samples")
|
||||
json.dump(eval_metrics, f)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
main()
|
||||
20608
examples/int8_training/peft_bnb_whisper_large_v2_training.ipynb
Normal file
20608
examples/int8_training/peft_bnb_whisper_large_v2_training.ipynb
Normal file
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
37
examples/int8_training/run_adalora_whisper_int8.sh
Normal file
37
examples/int8_training/run_adalora_whisper_int8.sh
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
|
||||
accelerate launch --config_file config.yaml peft_adalora_whisper_large_training.py \
|
||||
--model_name_or_path "openai/whisper-large-v2" \
|
||||
--language "Marathi" \
|
||||
--language_abbr "mr" \
|
||||
--task "transcribe" \
|
||||
--dataset_name "mozilla-foundation/common_voice_11_0" \
|
||||
--push_to_hub \
|
||||
--preprocessing_num_workers 2 \
|
||||
--per_device_train_batch_size 8 \
|
||||
--per_device_eval_batch_size 8 \
|
||||
--dataloader_pin_memory \
|
||||
--dataloader_num_workers 2 \
|
||||
--learning_rate 1e-3 \
|
||||
--weight_decay 1e-4 \
|
||||
--num_train_epochs 3 \
|
||||
--gradient_accumulation_steps 1 \
|
||||
--lr_scheduler_type "linear" \
|
||||
--num_warmup_steps 50 \
|
||||
--output_dir "adalora_whisper_large_marathi_multi_adapter" \
|
||||
--seed 42 \
|
||||
--load_best_model \
|
||||
--with_tracking \
|
||||
--report_to "wandb" \
|
||||
--hub_token $HUB_TOKEN \
|
||||
--checkpointing_steps 2000 \
|
||||
--evaluation_steps 2000 \
|
||||
--logging_steps 25 \
|
||||
--use_peft \
|
||||
--use_adalora \
|
||||
--init_r 12 \
|
||||
--target_r 8 \
|
||||
--tinit 100 \
|
||||
--tfinal 800 \
|
||||
--delta_t 10 \
|
||||
--lora_alpha 32 \
|
||||
--lora_dropout 0.1 \
|
||||
--orth_reg_weight 0.5
|
||||
801
examples/loftq_finetuning/LoftQ_weight_replacement.ipynb
Normal file
801
examples/loftq_finetuning/LoftQ_weight_replacement.ipynb
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,801 @@
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cells": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"id": "546b6c6d-f949-4387-9c41-6989223911f8",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Initializing weights with LoftQ by replacing LoRA weights in-place"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"id": "d041ecb4-6957-467e-8f3e-d4a12c674e9f",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"This notebook shows how to apply [LoftQ](https://arxiv.org/abs/2310.08659) initialization on our QLoRA model.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"In short, the idea behind LoftQ is the following. When we use QLoRA, i.e. we quantize the base model with bitsandbytes to save memory, and then train LoRA weights on top of this base model, we expect a certain performance gap. This is partly due to the fact that quantization is onyl an approximation of the \"real\" weights and thus introduces a quantization error. By default, LoRA weights are initialized such that they are a no-op at the start of the training. However, we can instead initialize them so that they minimize the quantization error. This is the idea behind LoftQ.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"Note that this only influences the initialization of the model. Everything that follows stays the same as always."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"id": "90d5420f-de32-42fa-8792-247f60e3647d",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Imports"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 1,
|
||||
"id": "a2c69b7c-c922-405f-aae1-ccc4f6911155",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"import os\n",
|
||||
"import torch"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 2,
|
||||
"id": "22be0432-8798-44a2-9014-d929525e3059",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer, BitsAndBytesConfig"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 3,
|
||||
"id": "f087ce0f-71b4-45ec-b2f9-197677bbc1ee",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"from peft import get_peft_model, LoraConfig, replace_lora_weights_loftq"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"id": "63fdf18e-4ac4-409e-8475-88147cf85067",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Functions"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 4,
|
||||
"id": "af14bd0a-597e-446c-800b-619fc0599ee0",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"def get_mae(x, y):\n",
|
||||
" return (x - y).abs().mean()\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"def get_mse(x, y):\n",
|
||||
" return torch.pow(x - y, 2).mean()\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"def error_report(x, y):\n",
|
||||
" mae = get_mae(x, y)\n",
|
||||
" mse = get_mse(x, y)\n",
|
||||
" print(\n",
|
||||
" f\"Mean absolute error: {mae:>8.5f}\\n\"\n",
|
||||
" f\"Mean squared error: {mse:>8.5f}\"\n",
|
||||
" )"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"id": "1bc01a5f-7ee8-400f-8e80-3f2b7df29882",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Base model"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"id": "fdc447d9-2f4f-4d0f-afdb-1cf5c4237321",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"First, let's load a base model and calculate some logits. These logits are the baseline, i.e. we try to match their values as best as possible. We only need these logits for demonstration purposes. In practice, it is not necessary to load the non-quantized weights to apply LoftQ initialization.\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
"**Note**: We have to choose a model with a `model.safetensors` file. As PyTorch checkpoints (pickle) cannot be loaded lazily, we have to use [safetensors](https://huggingface.co/docs/safetensors/index). If those don't exist for your model, save the pretrained model as a safetensors file using `safe_pretrained` and pass the model path to `replace_lora_weights_loftq`."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 5,
|
||||
"id": "0cb29074-d180-4fdc-8a47-27d2b9857264",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"model_id = \"bigscience/bloomz-560m\""
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 6,
|
||||
"id": "e7ddd6a2-04dd-42ec-9f48-100a3946ae04",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_id)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 7,
|
||||
"id": "1f5b27db-51cc-41da-a21d-049ff747a149",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_id)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 8,
|
||||
"id": "51548b6a-945c-4797-b02a-0e3fc77d1242",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"s = \"\"\"Beautiful is better than ugly.\n",
|
||||
"Explicit is better than implicit.\n",
|
||||
"Simple is better than complex.\n",
|
||||
"Complex is better than complicated.\n",
|
||||
"Flat is better than nested.\n",
|
||||
"Sparse is better than dense.\n",
|
||||
"Readability counts.\n",
|
||||
"Special cases aren't special enough to break the rules.\n",
|
||||
"Although practicality beats purity.\n",
|
||||
"Errors should never pass silently.\n",
|
||||
"Unless explicitly silenced.\n",
|
||||
"In the face of ambiguity, refuse the temptation to guess.\n",
|
||||
"There should be one-- and preferably only one --obvious way to do it.\n",
|
||||
"Although that way may not be obvious at first unless you're Dutch.\n",
|
||||
"Now is better than never.\n",
|
||||
"Although never is often better than *right* now.\n",
|
||||
"If the implementation is hard to explain, it's a bad idea.\n",
|
||||
"If the implementation is easy to explain, it may be a good idea.\n",
|
||||
"Namespaces are one honking great idea -- let's do more of those!\"\"\""
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 9,
|
||||
"id": "ce72d923-5283-48ba-96ef-7f859309ad84",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"inputs = tokenizer(s.splitlines(), return_tensors=\"pt\", padding=True)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"id": "3bfe54cb-76ef-4981-ba25-3e544d264c62",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"Our baseline logits:"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 10,
|
||||
"id": "04bebcaa-3a05-4621-9a03-e25de72fa27c",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"logits_base = model(**inputs).logits"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"id": "fa9c9001-8ade-422d-92f8-bcafa50917c7",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Normal LoRA model"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"id": "8024390b-736a-4b21-848b-aa4f30951d51",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"Now we load the model quantized with bitsandbytes. For now, only 4bit is supported."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 11,
|
||||
"id": "01d1912a-646e-42d2-8292-6702b77d1948",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"bnb_config = BitsAndBytesConfig(\n",
|
||||
" load_in_4bit=True,\n",
|
||||
" bnb_4bit_use_double_quant=True,\n",
|
||||
" bnb_4bit_compute_dtype=torch.float16,\n",
|
||||
")"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 12,
|
||||
"id": "b1218717-4db4-48ce-978d-c05dc190fa91",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "stderr",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"`low_cpu_mem_usage` was None, now set to True since model is quantized.\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_id, quantization_config=bnb_config)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"id": "a0b4e4c5-3932-4d9a-9457-41a05f24d556",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"Next we create a LoRA model using PEFT and compute the logits of that model."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 13,
|
||||
"id": "4741bce0-cd2b-4f05-a50c-4f9e56b43e72",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"lora_config = LoraConfig(task_type=\"CAUSAL_LM\", target_modules=\"all-linear\")"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 14,
|
||||
"id": "cf55cc48-b55d-4806-b6ab-e9b8035ed526",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"peft_model = get_peft_model(model, lora_config)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 15,
|
||||
"id": "f2f11e25-4a1e-485b-be4c-65aec62ac207",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "stderr",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
".../bitsandbytes/nn/modules.py:391: UserWarning: Input type into Linear4bit is torch.float16, but bnb_4bit_compute_dtype=torch.float32 (default). This will lead to slow inference or training speed.\n",
|
||||
" warnings.warn('Input type into Linear4bit is torch.float16, but bnb_4bit_compute_dtype=torch.float32 (default). This will lead to slow inference or training speed.')\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"logits_lora = peft_model(**inputs).logits"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"id": "5bc0cde7-0b9f-4305-ac0e-e3a6d2cfa401",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"Let's check the influence of the quantization error on our logits:"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 16,
|
||||
"id": "6f404c0d-f428-4923-9122-7b830410f089",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "stdout",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"Mean absolute error: 3.61113\n",
|
||||
"Mean squared error: 36.53259\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"error_report(logits_base, logits_lora)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"id": "58c437e1-4fae-4a2f-9c42-ada6bedb9a4d",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## LoftQ"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"id": "1af05376-c8b0-48ec-8d80-7d7f4d32bbd7",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"Next, let's use LoftQ initialization and see if it helps reduce the error."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 17,
|
||||
"id": "890e6108-3f02-469c-9e7d-f2144448227c",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"replace_lora_weights_loftq(peft_model)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 18,
|
||||
"id": "b452db0e-a510-42d3-bef5-f567186e26c2",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"logits_loftq = peft_model(**inputs).logits"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 19,
|
||||
"id": "456dc564-f268-4cf3-9d59-a6942d3733ad",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "stdout",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"Mean absolute error: 3.24111\n",
|
||||
"Mean squared error: 31.13725\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"error_report(logits_base, logits_loftq)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"id": "1ddf9e0f-3f78-426c-be59-77c6481674ec",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"We can see that LoftQ initialization helped a little bit, but the difference is not huge."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"id": "0dd344f2-249c-4fe9-8357-7fe3bcd1e82f",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## LoftQ with callback"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"id": "e2fd7dd5-88b3-40b8-95c2-3f3895d8093d",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"To help with this, let's write a small callback function and pass it to `replace_lora_weights_loftq`. What this function does is that each time one weight is being replaced with LoftQ-initialized weights, we perform a test if the quantization error is actually reduced. If it it is not, we roll back the replacement. This way, we keep only those replacements that improve the results."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 20,
|
||||
"id": "1f882802-22b7-4969-919e-120b1f2893d2",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "stderr",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"`low_cpu_mem_usage` was None, now set to True since model is quantized.\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"# Since PEFT has modified the base model, we should reload it\n",
|
||||
"model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_id, quantization_config=bnb_config)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 21,
|
||||
"id": "c6438363-b66e-4507-8667-5a6df379a03f",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"peft_model = get_peft_model(model, lora_config)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 22,
|
||||
"id": "7b93d082-0fcb-4b20-982e-c1aaf0c71d13",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"current_mse = float(\"inf\")"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 23,
|
||||
"id": "e22eb18d-b06e-47fe-91ba-ff34cbf62f60",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"def my_callback(model, module_name):\n",
|
||||
" \"\"\"Callable to replace weights with LoFTQ if the mse is lower than the current best one.\"\"\"\n",
|
||||
" global current_mse\n",
|
||||
"\n",
|
||||
" logits = model(**inputs).logits\n",
|
||||
" mse = get_mse(logits_base, logits)\n",
|
||||
" if mse < current_mse:\n",
|
||||
" current_mse = mse\n",
|
||||
" print(f\"MSE improved for module {module_name}\")\n",
|
||||
" return True\n",
|
||||
" print(f\"MSE did not improve for module {module_name}\")\n",
|
||||
" return False"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 24,
|
||||
"id": "44ee90d1-e15a-4740-a39d-ebf9e7adb79c",
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"scrolled": true
|
||||
},
|
||||
"outputs": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "stdout",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"MSE improved for module transformer.h.0.self_attention.query_key_value\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.0.self_attention.dense\n",
|
||||
"MSE improved for module transformer.h.0.mlp.dense_h_to_4h\n",
|
||||
"MSE improved for module transformer.h.0.mlp.dense_4h_to_h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.1.self_attention.query_key_value\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.1.self_attention.dense\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.1.mlp.dense_h_to_4h\n",
|
||||
"MSE improved for module transformer.h.1.mlp.dense_4h_to_h\n",
|
||||
"MSE improved for module transformer.h.2.self_attention.query_key_value\n",
|
||||
"MSE improved for module transformer.h.2.self_attention.dense\n",
|
||||
"MSE improved for module transformer.h.2.mlp.dense_h_to_4h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.2.mlp.dense_4h_to_h\n",
|
||||
"MSE improved for module transformer.h.3.self_attention.query_key_value\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.3.self_attention.dense\n",
|
||||
"MSE improved for module transformer.h.3.mlp.dense_h_to_4h\n",
|
||||
"MSE improved for module transformer.h.3.mlp.dense_4h_to_h\n",
|
||||
"MSE improved for module transformer.h.4.self_attention.query_key_value\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.4.self_attention.dense\n",
|
||||
"MSE improved for module transformer.h.4.mlp.dense_h_to_4h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.4.mlp.dense_4h_to_h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.5.self_attention.query_key_value\n",
|
||||
"MSE improved for module transformer.h.5.self_attention.dense\n",
|
||||
"MSE improved for module transformer.h.5.mlp.dense_h_to_4h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.5.mlp.dense_4h_to_h\n",
|
||||
"MSE improved for module transformer.h.6.self_attention.query_key_value\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.6.self_attention.dense\n",
|
||||
"MSE improved for module transformer.h.6.mlp.dense_h_to_4h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.6.mlp.dense_4h_to_h\n",
|
||||
"MSE improved for module transformer.h.7.self_attention.query_key_value\n",
|
||||
"MSE improved for module transformer.h.7.self_attention.dense\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.7.mlp.dense_h_to_4h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.7.mlp.dense_4h_to_h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.8.self_attention.query_key_value\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.8.self_attention.dense\n",
|
||||
"MSE improved for module transformer.h.8.mlp.dense_h_to_4h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.8.mlp.dense_4h_to_h\n",
|
||||
"MSE improved for module transformer.h.9.self_attention.query_key_value\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.9.self_attention.dense\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.9.mlp.dense_h_to_4h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.9.mlp.dense_4h_to_h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.10.self_attention.query_key_value\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.10.self_attention.dense\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.10.mlp.dense_h_to_4h\n",
|
||||
"MSE improved for module transformer.h.10.mlp.dense_4h_to_h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.11.self_attention.query_key_value\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.11.self_attention.dense\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.11.mlp.dense_h_to_4h\n",
|
||||
"MSE improved for module transformer.h.11.mlp.dense_4h_to_h\n",
|
||||
"MSE improved for module transformer.h.12.self_attention.query_key_value\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.12.self_attention.dense\n",
|
||||
"MSE improved for module transformer.h.12.mlp.dense_h_to_4h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.12.mlp.dense_4h_to_h\n",
|
||||
"MSE improved for module transformer.h.13.self_attention.query_key_value\n",
|
||||
"MSE improved for module transformer.h.13.self_attention.dense\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.13.mlp.dense_h_to_4h\n",
|
||||
"MSE improved for module transformer.h.13.mlp.dense_4h_to_h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.14.self_attention.query_key_value\n",
|
||||
"MSE improved for module transformer.h.14.self_attention.dense\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.14.mlp.dense_h_to_4h\n",
|
||||
"MSE improved for module transformer.h.14.mlp.dense_4h_to_h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.15.self_attention.query_key_value\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.15.self_attention.dense\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.15.mlp.dense_h_to_4h\n",
|
||||
"MSE improved for module transformer.h.15.mlp.dense_4h_to_h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.16.self_attention.query_key_value\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.16.self_attention.dense\n",
|
||||
"MSE improved for module transformer.h.16.mlp.dense_h_to_4h\n",
|
||||
"MSE improved for module transformer.h.16.mlp.dense_4h_to_h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.17.self_attention.query_key_value\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.17.self_attention.dense\n",
|
||||
"MSE improved for module transformer.h.17.mlp.dense_h_to_4h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.17.mlp.dense_4h_to_h\n",
|
||||
"MSE improved for module transformer.h.18.self_attention.query_key_value\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.18.self_attention.dense\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.18.mlp.dense_h_to_4h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.18.mlp.dense_4h_to_h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.19.self_attention.query_key_value\n",
|
||||
"MSE improved for module transformer.h.19.self_attention.dense\n",
|
||||
"MSE improved for module transformer.h.19.mlp.dense_h_to_4h\n",
|
||||
"MSE improved for module transformer.h.19.mlp.dense_4h_to_h\n",
|
||||
"MSE improved for module transformer.h.20.self_attention.query_key_value\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.20.self_attention.dense\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.20.mlp.dense_h_to_4h\n",
|
||||
"MSE improved for module transformer.h.20.mlp.dense_4h_to_h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.21.self_attention.query_key_value\n",
|
||||
"MSE improved for module transformer.h.21.self_attention.dense\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.21.mlp.dense_h_to_4h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.21.mlp.dense_4h_to_h\n",
|
||||
"MSE improved for module transformer.h.22.self_attention.query_key_value\n",
|
||||
"MSE improved for module transformer.h.22.self_attention.dense\n",
|
||||
"MSE improved for module transformer.h.22.mlp.dense_h_to_4h\n",
|
||||
"MSE improved for module transformer.h.22.mlp.dense_4h_to_h\n",
|
||||
"MSE improved for module transformer.h.23.self_attention.query_key_value\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.23.self_attention.dense\n",
|
||||
"MSE improved for module transformer.h.23.mlp.dense_h_to_4h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.23.mlp.dense_4h_to_h\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"replace_lora_weights_loftq(peft_model, callback=my_callback)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 25,
|
||||
"id": "e31adc81-a090-49b2-90f6-9906743c76ae",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"logits_loftq_callback = peft_model(**inputs).logits"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 26,
|
||||
"id": "7c640092-1f26-48be-bea4-487511205440",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "stdout",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"Mean absolute error: 1.79576\n",
|
||||
"Mean squared error: 8.47075\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"error_report(logits_base, logits_loftq_callback)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"id": "1896857e-3d87-44a9-887f-90c765bc8d91",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"We can see that applying LoftQ with the help of the callback reduced the error quite significantly."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"id": "8eaf86cf-4fb4-455d-ab07-892591564303",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"## Applying LoftQ multiple times"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"id": "70836a75-5c6d-4b7b-9175-f395aef8383b",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"It is possible to run `replace_lora_weights_loftq` multiple times on the same model when using the callback."
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 27,
|
||||
"id": "8e5ee38c-007c-4c75-9248-005d94b19445",
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"scrolled": true
|
||||
},
|
||||
"outputs": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "stdout",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.0.self_attention.query_key_value\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.0.self_attention.dense\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.0.mlp.dense_h_to_4h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.0.mlp.dense_4h_to_h\n",
|
||||
"MSE improved for module transformer.h.1.self_attention.query_key_value\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.1.self_attention.dense\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.1.mlp.dense_h_to_4h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.1.mlp.dense_4h_to_h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.2.self_attention.query_key_value\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.2.self_attention.dense\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.2.mlp.dense_h_to_4h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.2.mlp.dense_4h_to_h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.3.self_attention.query_key_value\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.3.self_attention.dense\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.3.mlp.dense_h_to_4h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.3.mlp.dense_4h_to_h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.4.self_attention.query_key_value\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.4.self_attention.dense\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.4.mlp.dense_h_to_4h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.4.mlp.dense_4h_to_h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.5.self_attention.query_key_value\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.5.self_attention.dense\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.5.mlp.dense_h_to_4h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.5.mlp.dense_4h_to_h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.6.self_attention.query_key_value\n",
|
||||
"MSE improved for module transformer.h.6.self_attention.dense\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.6.mlp.dense_h_to_4h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.6.mlp.dense_4h_to_h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.7.self_attention.query_key_value\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.7.self_attention.dense\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.7.mlp.dense_h_to_4h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.7.mlp.dense_4h_to_h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.8.self_attention.query_key_value\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.8.self_attention.dense\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.8.mlp.dense_h_to_4h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.8.mlp.dense_4h_to_h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.9.self_attention.query_key_value\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.9.self_attention.dense\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.9.mlp.dense_h_to_4h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.9.mlp.dense_4h_to_h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.10.self_attention.query_key_value\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.10.self_attention.dense\n",
|
||||
"MSE improved for module transformer.h.10.mlp.dense_h_to_4h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.10.mlp.dense_4h_to_h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.11.self_attention.query_key_value\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.11.self_attention.dense\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.11.mlp.dense_h_to_4h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.11.mlp.dense_4h_to_h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.12.self_attention.query_key_value\n",
|
||||
"MSE improved for module transformer.h.12.self_attention.dense\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.12.mlp.dense_h_to_4h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.12.mlp.dense_4h_to_h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.13.self_attention.query_key_value\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.13.self_attention.dense\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.13.mlp.dense_h_to_4h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.13.mlp.dense_4h_to_h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.14.self_attention.query_key_value\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.14.self_attention.dense\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.14.mlp.dense_h_to_4h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.14.mlp.dense_4h_to_h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.15.self_attention.query_key_value\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.15.self_attention.dense\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.15.mlp.dense_h_to_4h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.15.mlp.dense_4h_to_h\n",
|
||||
"MSE improved for module transformer.h.16.self_attention.query_key_value\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.16.self_attention.dense\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.16.mlp.dense_h_to_4h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.16.mlp.dense_4h_to_h\n",
|
||||
"MSE improved for module transformer.h.17.self_attention.query_key_value\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.17.self_attention.dense\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.17.mlp.dense_h_to_4h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.17.mlp.dense_4h_to_h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.18.self_attention.query_key_value\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.18.self_attention.dense\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.18.mlp.dense_h_to_4h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.18.mlp.dense_4h_to_h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.19.self_attention.query_key_value\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.19.self_attention.dense\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.19.mlp.dense_h_to_4h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.19.mlp.dense_4h_to_h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.20.self_attention.query_key_value\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.20.self_attention.dense\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.20.mlp.dense_h_to_4h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.20.mlp.dense_4h_to_h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.21.self_attention.query_key_value\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.21.self_attention.dense\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.21.mlp.dense_h_to_4h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.21.mlp.dense_4h_to_h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.22.self_attention.query_key_value\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.22.self_attention.dense\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.22.mlp.dense_h_to_4h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.22.mlp.dense_4h_to_h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.23.self_attention.query_key_value\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.23.self_attention.dense\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.23.mlp.dense_h_to_4h\n",
|
||||
"MSE did not improve for module transformer.h.23.mlp.dense_4h_to_h\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"replace_lora_weights_loftq(peft_model, callback=my_callback)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 28,
|
||||
"id": "2abe2702-9510-4814-b5f2-63140a102c17",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"logits_loftq_callback_twice = peft_model(**inputs).logits"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "code",
|
||||
"execution_count": 29,
|
||||
"id": "e908de14-01f9-4fdc-91b5-61118a3ce6cb",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"outputs": [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"name": "stdout",
|
||||
"output_type": "stream",
|
||||
"text": [
|
||||
"Mean absolute error: 1.76357\n",
|
||||
"Mean squared error: 8.33938\n"
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"error_report(logits_base, logits_loftq_callback_twice)"
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"cell_type": "markdown",
|
||||
"id": "5b8b09fe-d369-4444-b6e2-cd514e775637",
|
||||
"metadata": {},
|
||||
"source": [
|
||||
"There are further gains, but they are not very big."
|
||||
]
|
||||
}
|
||||
],
|
||||
"metadata": {
|
||||
"kernelspec": {
|
||||
"display_name": "Python 3 (ipykernel)",
|
||||
"language": "python",
|
||||
"name": "python3"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"language_info": {
|
||||
"codemirror_mode": {
|
||||
"name": "ipython",
|
||||
"version": 3
|
||||
},
|
||||
"file_extension": ".py",
|
||||
"mimetype": "text/x-python",
|
||||
"name": "python",
|
||||
"nbconvert_exporter": "python",
|
||||
"pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
|
||||
"version": "3.10.11"
|
||||
}
|
||||
},
|
||||
"nbformat": 4,
|
||||
"nbformat_minor": 5
|
||||
}
|
||||
144
examples/loftq_finetuning/README.md
Normal file
144
examples/loftq_finetuning/README.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,144 @@
|
||||
# LoftQ: LoRA-fine-tuning-aware Quantization
|
||||
|
||||
## Introduction
|
||||
|
||||
LoftQ finds quantized LoRA initialization: quantized backbone Q and LoRA adapters A and B, given a pre-trained weight W.
|
||||
|
||||
## Quick Start
|
||||
Steps:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Apply LoftQ to a full-precision pre-trained weight and save.
|
||||
2. Load LoftQ initialization and train.
|
||||
|
||||
For step 1, we have provided off-the-shelf LoftQ initializations (see [supported model list](#appendix-off-the-shelf-model-table))
|
||||
in [Huggingface Hub LoftQ](https://huggingface.co/LoftQ).
|
||||
If you want to do it yourself, jump to [LoftQ DIY](#loftq-diy).
|
||||
|
||||
For step 2, below is an example of loading 4bit Mistral-7B with 64rank LoRA adapters from Huggingface Hub.
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, BitsAndBytesConfig
|
||||
from peft import PeftModel
|
||||
|
||||
MODEL_ID = "LoftQ/Mistral-7B-v0.1-4bit-64rank"
|
||||
|
||||
base_model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
|
||||
MODEL_ID,
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16, # you may change it with different models
|
||||
quantization_config=BitsAndBytesConfig(
|
||||
load_in_4bit=True,
|
||||
bnb_4bit_compute_dtype=torch.bfloat16, # bfloat16 is recommended
|
||||
bnb_4bit_use_double_quant=False,
|
||||
bnb_4bit_quant_type='nf4',
|
||||
),
|
||||
)
|
||||
peft_model = PeftModel.from_pretrained(
|
||||
base_model,
|
||||
MODEL_ID,
|
||||
subfolder="loftq_init",
|
||||
is_trainable=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Do training with peft_model ...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## LoftQ DIY
|
||||
|
||||
### Apply LoftQ and save
|
||||
We provide [quantize_save_load.py](quantize_save_load.py) as an example to apply LoftQ with
|
||||
different bits(`--bits`), ranks(`--rank`), and alternating steps (`--iter`, a hyper-parameter in LoftQ, see Algorithm 1 in [LoftQ paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/2310.08659)). Currently, this example supports
|
||||
`llama-2`, `falcon`, `mistral`, `bart`, `t5`, `deberta`, `bert`, `roberta`.
|
||||
|
||||
Below is an example of obtaining 4bit LLAMA-2-7b with 16-rank LoRA adapters by 5 alternating steps.
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
SAVE_DIR="model_zoo/loftq/"
|
||||
python quantize_save_load.py \
|
||||
--model_name_or_path meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-hf \ # high-precision model id in HF
|
||||
--token HF_TOKEN \ # your HF token if the model is private, e.g., llama-2
|
||||
--bits 4 \
|
||||
--iter 5 \
|
||||
--rank 16 \
|
||||
--save_dir $SAVE_DIR
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
The above commands end up with creating the model directory under `$SAVE_DIR`.
|
||||
Specifically, the model directory is named as
|
||||
|
||||
`MODEL_DIR = SAVE_DIR + f"{args.model_name_or_path.split('/')[-1]}-{args.bits}bits-{args.rank}rank"`
|
||||
|
||||
In this example, `MODEL_DIR="model_zoo/loftq/Llama-2-7b-hf-4bit-16rank"`, where the backbone is stored in `$MODEL_DIR`
|
||||
and the LoRA adapters are at the sub-folder `$MODEL_DIR/loftq_init`.
|
||||
|
||||
### Load and train
|
||||
Similar to loading from Huggingface Hub, we only need to change the `MODEL_ID` to the `MODEL_DIR`.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, BitsAndBytesConfig
|
||||
from peft import PeftModel
|
||||
|
||||
MODEL_DIR = "model_zoo/loftq/Llama-2-7b-hf-4bit-16rank"
|
||||
|
||||
base_model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
|
||||
MODEL_DIR,
|
||||
torch_dtype=torch.bfloat16,
|
||||
quantization_config=BitsAndBytesConfig(
|
||||
load_in_4bit=True,
|
||||
bnb_4bit_compute_dtype=torch.bfloat16,
|
||||
bnb_4bit_use_double_quant=False,
|
||||
bnb_4bit_quant_type='nf4',
|
||||
),
|
||||
)
|
||||
peft_model = PeftModel.from_pretrained(
|
||||
base_model,
|
||||
MODEL_DIR,
|
||||
subfolder="loftq_init",
|
||||
is_trainable=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
# Do training with peft_model ...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## LoftQ Fine-tuning
|
||||
|
||||
We also provide an example to fine-tune LoftQ on GSM8K.
|
||||
We load the quantized backbone and LoRA adapters from the [LoftQ Huggingface hub](https://huggingface.co/LoftQ).
|
||||
|
||||
```sh
|
||||
python train_gsm8k_llama.py \
|
||||
--model_name_or_path LoftQ/Llama-2-13b-hf-4bit-64rank \
|
||||
--output_dir exp_results/gsm8k/llama-2-13b/bit4-rank64/lr1e-4 \
|
||||
--learning_rate 1e-4 \
|
||||
--weight_decay 0.1 \
|
||||
--lr_scheduler_type cosine \
|
||||
--num_warmup_steps 100 \
|
||||
--seed 202 \
|
||||
--dataset_name gsm8k \
|
||||
--dataset_config main \
|
||||
--pad_to_max_length \
|
||||
--max_source_length 128 \
|
||||
--max_target_length 256 \
|
||||
--num_train_epochs 5 \
|
||||
--per_device_train_batch_size 4 \
|
||||
--per_device_eval_batch_size 4 \
|
||||
--gradient_accumulation_steps 4 \
|
||||
--with_tracking \
|
||||
--report_to tensorboard
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Appendix: Off-the-shelf Model List
|
||||
| Model Name | Bits | Ranks |
|
||||
| ----------- | ---- | ----- |
|
||||
| LLAMA-2-7b | 4 | 64 |
|
||||
| LLAMA-2-13b | 4 | 64 |
|
||||
| LLAMA-2-70b | 4 | 64 |
|
||||
| Mistral | 4 | 64 |
|
||||
| Mistral | 4 | 32 |
|
||||
| BART-large | 4 | 8 |
|
||||
| BART-large | 4 | 16 |
|
||||
| BART-large | 4 | 32 |
|
||||
| BART-large | 2 | 8 |
|
||||
|
||||
## In-place application of LoftQ initialization
|
||||
|
||||
PEFT provides a convenience function `replace_lora_weights_loftq` to apply LoftQ initialization in-place to the quantized model. Check out [this notebook](https://github.com/huggingface/peft/blob/main/examples/loftq_finetuning/LoftQ_weight_replacement.ipynb) for an example.
|
||||
Some files were not shown because too many files have changed in this diff Show More
Reference in New Issue
Block a user