mirror of
https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate.git
synced 2025-11-16 15:24:34 +08:00
Compare commits
37 Commits
fix-genera
...
v0.27.0
| Author | SHA1 | Date | |
|---|---|---|---|
| b7087be5f6 | |||
| f75c6245ba | |||
| 9c1d5bac15 | |||
| b0b867da85 | |||
| 433d693b70 | |||
| c3aec59b12 | |||
| 9467a62744 | |||
| 86228e321d | |||
| 06b138d845 | |||
| 0867c09318 | |||
| 0e1ee4b92d | |||
| d8a64cb79d | |||
| b703efdcc3 | |||
| 68f54720dc | |||
| 46f1391b79 | |||
| cd7ff5e137 | |||
| f4b411f84b | |||
| 7ba64e632c | |||
| 8b770a7dab | |||
| 3d8b998fbb | |||
| 03365a3d17 | |||
| 7aafa25673 | |||
| f88661b5d9 | |||
| 581fabba48 | |||
| e909eb34e2 | |||
| 7644a02e6b | |||
| 162a82164e | |||
| 0d6a5fa8ee | |||
| 53845d2596 | |||
| 5ec00da2be | |||
| 649e65b542 | |||
| 14d7c3fca6 | |||
| c7d11d7e40 | |||
| ec4f01a099 | |||
| f5c01eeb63 | |||
| 20ff458d80 | |||
| 6719cb6db3 |
@ -152,7 +152,7 @@ Follow these steps to start contributing:
|
||||
$ make test
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
`accelerate` relies on `black` and `ruff` to format its source code
|
||||
`accelerate` relies on `ruff` to format its source code
|
||||
consistently. After you make changes, apply automatic style corrections and code verifications
|
||||
that can't be automated in one go with:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -235,4 +235,4 @@ $ python -m pytest -sv ./tests
|
||||
In fact, that's how `make test` is implemented (sans the `pip install` line)!
|
||||
|
||||
You can specify a smaller set of tests in order to test only the feature
|
||||
you're working on.
|
||||
you're working on.
|
||||
|
||||
18
Makefile
18
Makefile
@ -1,6 +1,6 @@
|
||||
.PHONY: quality style test docs utils
|
||||
|
||||
check_dirs := tests src examples benchmarks utils
|
||||
check_dirs := .
|
||||
|
||||
# Check that source code meets quality standards
|
||||
|
||||
@ -12,20 +12,17 @@ extra_quality_checks:
|
||||
|
||||
# this target runs checks on all files
|
||||
quality:
|
||||
black --required-version 23 --check $(check_dirs)
|
||||
ruff $(check_dirs)
|
||||
ruff format --check $(check_dirs)
|
||||
doc-builder style src/accelerate docs/source --max_len 119 --check_only
|
||||
|
||||
# Format source code automatically and check is there are any problems left that need manual fixing
|
||||
style:
|
||||
black --required-version 23 $(check_dirs)
|
||||
ruff $(check_dirs) --fix
|
||||
ruff format $(check_dirs)
|
||||
doc-builder style src/accelerate docs/source --max_len 119
|
||||
|
||||
# Run tests for the library
|
||||
test:
|
||||
python -m pytest -s -v ./tests/ --ignore=./tests/test_examples.py $(if $(IS_GITHUB_CI),--report-log "$(PYTORCH_VERSION)_all.log",)
|
||||
|
||||
test_big_modeling:
|
||||
python -m pytest -s -v ./tests/test_big_modeling.py ./tests/test_modeling_utils.py $(if $(IS_GITHUB_CI),--report-log "$(PYTORCH_VERSION)_big_modeling.log",)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -42,6 +39,15 @@ test_deepspeed:
|
||||
test_fsdp:
|
||||
python -m pytest -s -v ./tests/fsdp $(if $(IS_GITHUB_CI),--report-log "$(PYTORCH_VERSION)_fsdp.log",)
|
||||
|
||||
# Since the new version of pytest will *change* how things are collected, we need `deepspeed` to
|
||||
# run after test_core and test_cli
|
||||
test:
|
||||
$(MAKE) test_core
|
||||
$(MAKE) test_cli
|
||||
$(MAKE) test_big_modeling
|
||||
$(MAKE) test_deepspeed
|
||||
$(MAKE) test_fsdp
|
||||
|
||||
test_examples:
|
||||
python -m pytest -s -v ./tests/test_examples.py $(if $(IS_GITHUB_CI),--report-log "$(PYTORCH_VERSION)_examples.log",)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
|
||||
# Builds GPU docker image of PyTorch
|
||||
# Builds GPU docker image of PyTorch specifically
|
||||
# Uses multi-staged approach to reduce size
|
||||
# Stage 1
|
||||
# Use base conda image to reduce time
|
||||
@ -19,7 +19,8 @@ ENV PATH /opt/conda/envs/accelerate/bin:$PATH
|
||||
# Activate our bash shell
|
||||
RUN chsh -s /bin/bash
|
||||
SHELL ["/bin/bash", "-c"]
|
||||
# Activate the conda env and install torch + accelerate
|
||||
# Activate the conda env, install mpy4pi, and install torch + accelerate
|
||||
RUN source activate accelerate && conda install -c conda-forge mpi4py
|
||||
RUN source activate accelerate && \
|
||||
python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir \
|
||||
git+https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate#egg=accelerate[testing,test_trackers] \
|
||||
|
||||
@ -89,6 +89,8 @@
|
||||
title: Logging
|
||||
- local: package_reference/big_modeling
|
||||
title: Working with large models
|
||||
- local: package_reference/inference
|
||||
title: Distributed inference with big models
|
||||
- local: package_reference/kwargs
|
||||
title: Kwargs handlers
|
||||
- local: package_reference/utilities
|
||||
|
||||
20
docs/source/package_reference/inference.md
Normal file
20
docs/source/package_reference/inference.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,20 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# The inference API
|
||||
|
||||
These docs refer to the [PiPPy](https://github.com/PyTorch/PiPPy) integration.
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] inference.prepare_pippy
|
||||
@ -15,12 +15,18 @@ rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
# Distributed Inference with 🤗 Accelerate
|
||||
|
||||
Distributed inference is a common use case, especially with natural language processing (NLP) models. Users often want to
|
||||
send a number of different prompts, each to a different GPU, and then get the results back. This also has other cases
|
||||
outside of just NLP, however for this tutorial we will focus on just this idea of each GPU receiving a different prompt,
|
||||
and then returning the results.
|
||||
Distributed inference can fall into three brackets:
|
||||
|
||||
## The Problem
|
||||
1. Loading an entire model onto each GPU and sending chunks of a batch through each GPU's model copy at a time
|
||||
2. Loading parts of a model onto each GPU and processing a single input at one time
|
||||
3. Loading parts of a model onto each GPU and using what is called scheduled Pipeline Parallelism to combine the two prior techniques.
|
||||
|
||||
We're going to go through the first and the last bracket, showcasing how to do each as they are more realistic scenarios.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Sending chunks of a batch automatically to each loaded model
|
||||
|
||||
This is the most memory-intensive solution, as it requires each GPU to keep a full copy of the model in memory at a given time.
|
||||
|
||||
Normally when doing this, users send the model to a specific device to load it from the CPU, and then move each prompt to a different device.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -55,7 +61,6 @@ a simple way to manage this. (To learn more, check out the relevant section in t
|
||||
|
||||
Can it manage it? Yes. Does it add unneeded extra code however: also yes.
|
||||
|
||||
## The Solution
|
||||
|
||||
With 🤗 Accelerate, we can simplify this process by using the [`Accelerator.split_between_processes`] context manager (which also exists in `PartialState` and `AcceleratorState`).
|
||||
This function will automatically split whatever data you pass to it (be it a prompt, a set of tensors, a dictionary of the prior data, etc.) across all the processes (with a potential
|
||||
@ -134,3 +139,97 @@ with distributed_state.split_between_processes(["a dog", "a cat", "a chicken"],
|
||||
|
||||
On the first GPU, the prompts will be `["a dog", "a cat"]`, and on the second GPU it will be `["a chicken", "a chicken"]`.
|
||||
Make sure to drop the final sample, as it will be a duplicate of the previous one.
|
||||
|
||||
## Memory-efficient pipeline parallelism (experimental)
|
||||
|
||||
This next part will discuss using *pipeline parallelism*. This is an **experimental** API utilizing the [PiPPy library by PyTorch](https://github.com/pytorch/PiPPy/) as a native solution.
|
||||
|
||||
The general idea with pipeline parallelism is: say you have 4 GPUs and a model big enough it can be *split* on four GPUs using `device_map="auto"`. With this method you can send in 4 inputs at a time (for example here, any amount works) and each model chunk will work on an input, then receive the next input once the prior chunk finished, making it *much* more efficient **and faster** than the method described earlier. Here's a visual taken from the PyTorch repository:
|
||||
|
||||
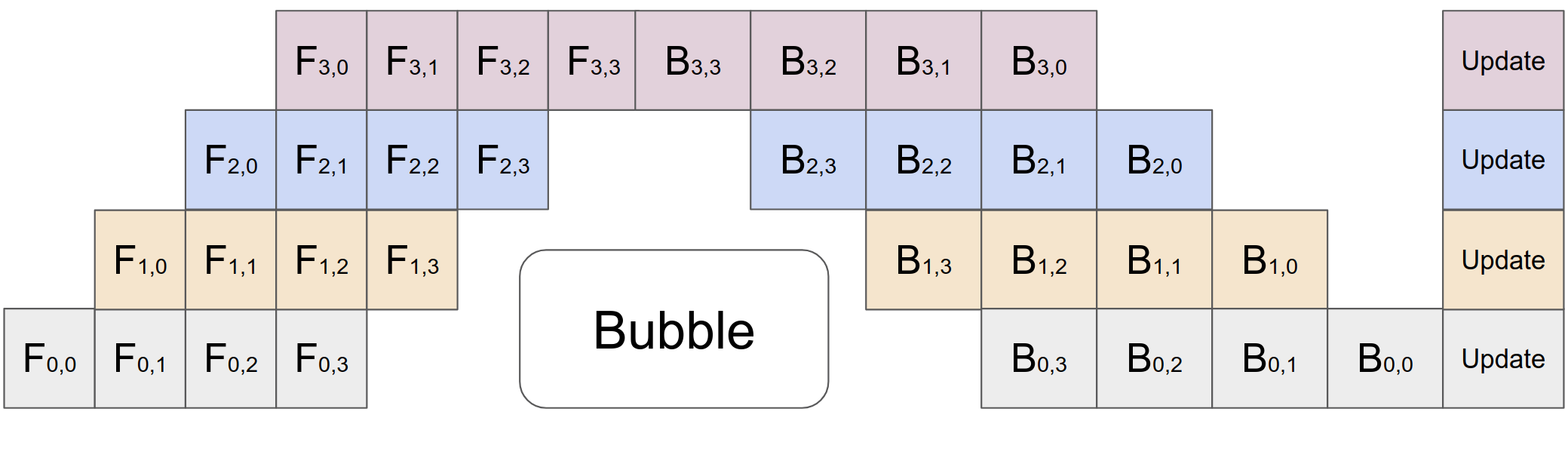
|
||||
|
||||
To illustrate how you can use this with Accelerate, we have created an [example zoo](https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate/tree/main/examples/inference) showcasing a number of different models and situations. In this tutorial, we'll show this method for GPT2 across two GPUs.
|
||||
|
||||
Before you proceed, please make sure you have the latest pippy installed by running the following:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install torchpippy
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We require at least version 0.2.0. To confirm that you have the correct version, run `pip show torchpippy`.
|
||||
|
||||
Start by creating the model on the CPU:
|
||||
|
||||
```{python}
|
||||
from transformers import GPT2ForSequenceClassification, GPT2Config
|
||||
|
||||
config = GPT2Config()
|
||||
model = GPT2ForSequenceClassification(config)
|
||||
model.eval()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Next you'll need to create some example inputs to use. These help PiPPy trace the model.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
However you make this example will determine the relative batch size that will be used/passed
|
||||
through the model at a given time, so make sure to remember how many items there are!
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
```{python}
|
||||
input = torch.randint(
|
||||
low=0,
|
||||
high=config.vocab_size,
|
||||
size=(2, 1024), # bs x seq_len
|
||||
device="cpu",
|
||||
dtype=torch.int64,
|
||||
requires_grad=False,
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
Next we need to actually perform the tracing and get the model ready. To do so, use the [`inference.prepare_pippy`] function and it will fully wrap the model for pipeline parallelism automatically:
|
||||
|
||||
```{python}
|
||||
from accelerate.inference import prepare_pippy
|
||||
example_inputs = {"input_ids": input}
|
||||
model = prepare_pippy(model, example_args=(input,))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
There are a variety of parameters you can pass through to `prepare_pippy`:
|
||||
|
||||
* `split_points` lets you determine what layers to split the model at. By default we use wherever `device_map="auto" declares, such as `fc` or `conv1`.
|
||||
|
||||
* `num_chunks` determines how the batch will be split and sent to the model itself (so `num_chunks=1` with four split points/four GPUs will have a naive MP where a single input gets passed between the four layer split points)
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
From here, all that's left is to actually perform the distributed inference!
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
When passing inputs, we highly recommend to pass them in as a tuple of arguments. Using `kwargs` is supported, however, this approach is experimental.
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
```{python}
|
||||
args = some_more_arguments
|
||||
with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
output = model(*args)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
When finished all the data will be on the last process only:
|
||||
|
||||
```{python}
|
||||
from accelerate import PartialState
|
||||
if PartialState().is_last_process:
|
||||
print(output)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
If you pass in `gather_output=True` to [`inference.prepare_pippy`], the output will be sent
|
||||
across to all the GPUs afterwards without needing the `is_last_process` check. This is
|
||||
`False` by default as it incurs a communication call.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
And that's it! To explore more, please check out the inference examples in the [Accelerate repo](https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate/tree/main/examples/inference) and our [documentation](../package_reference/inference) as we work to improving this integration.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -73,7 +73,7 @@ accelerate launch examples/nlp_example.py
|
||||
|
||||
Currently, `Accelerate` supports the following config through the CLI:
|
||||
|
||||
`fsdp_sharding_strategy`: [1] FULL_SHARD (shards optimizer states, gradients and parameters), [2] SHARD_GRAD_OP (shards optimizer states and gradients), [3] NO_SHARD (DDP), [4] HYBRID_SHARD (shards optimizer states, gradients and parameters within each node while each node has full copy), [5] HYBRID_SHARD_ZERO2 (shards optimizer states and gradients within each node while each node has full copy)
|
||||
`fsdp_sharding_strategy`: [1] FULL_SHARD (shards optimizer states, gradients and parameters), [2] SHARD_GRAD_OP (shards optimizer states and gradients), [3] NO_SHARD (DDP), [4] HYBRID_SHARD (shards optimizer states, gradients and parameters within each node while each node has full copy), [5] HYBRID_SHARD_ZERO2 (shards optimizer states and gradients within each node while each node has full copy). For more information, please refer the official [PyTorch docs](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/fsdp.html#torch.distributed.fsdp.ShardingStrategy).
|
||||
|
||||
`fsdp_offload_params` : Decides Whether to offload parameters and gradients to CPU
|
||||
|
||||
@ -91,7 +91,7 @@ Currently, `Accelerate` supports the following config through the CLI:
|
||||
|
||||
`fsdp_use_orig_params`: If True, allows non-uniform `requires_grad` during init, which means support for interspersed frozen and trainable parameters. This setting is useful in cases such as parameter-efficient fine-tuning as discussed in [this post](https://dev-discuss.pytorch.org/t/rethinking-pytorch-fully-sharded-data-parallel-fsdp-from-first-principles/1019). This option also allows one to have multiple optimizer param groups. This should be `True` when creating an optimizer before preparing/wrapping the model with FSDP.
|
||||
|
||||
`fsdp_cpu_ram_efficient_loading`: Only applicable for 🤗 Transformers models. If True, only the first process loads the pretrained model checkpoint while all other processes have empty weights. This should be set to False if you experience errors when loading the pretrained 🤗 Transformers model via `from_pretrained` method. When this setting is True `fsdp_sync_module_states` also must to be True, otherwise all the processes except the main process would have random weights leading to unexpected behaviour during training.
|
||||
`fsdp_cpu_ram_efficient_loading`: Only applicable for 🤗 Transformers models. If True, only the first process loads the pretrained model checkpoint while all other processes have empty weights. This should be set to False if you experience errors when loading the pretrained 🤗 Transformers model via `from_pretrained` method. When this setting is True `fsdp_sync_module_states` also must to be True, otherwise all the processes except the main process would have random weights leading to unexpected behaviour during training. For this to work, make sure the distributed process group is initialized before calling Transformers `from_pretrained` method. When using 🤗 Trainer API, the distributed process group is initialized when you create an instance of `TrainingArguments` class.
|
||||
|
||||
`fsdp_sync_module_states`: If True, each individually wrapped FSDP unit will broadcast module parameters from rank 0.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -161,6 +161,13 @@ When using transformers `save_pretrained`, pass `state_dict=accelerator.get_stat
|
||||
|
||||
You can then pass `state` into the `save_pretrained` method. There are several modes for `StateDictType` and `FullStateDictConfig` that you can use to control the behavior of `state_dict`. For more information, see the [PyTorch documentation](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/fsdp.html).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Mapping between FSDP sharding strategies and DeepSpeed ZeRO Stages
|
||||
* `FULL_SHARD` maps to the DeepSpeed `ZeRO Stage-3`. Shards optimizer states, gradients and parameters.
|
||||
* `SHARD_GRAD_OP` maps to the DeepSpeed `ZeRO Stage-2`. Shards optimizer states and gradients.
|
||||
* `NO_SHARD` maps to `ZeRO Stage-0`. No sharding wherein each GPU has full copy of model, optimizer states and gradients.
|
||||
* `HYBRID_SHARD` maps to `ZeRO++ Stage-3` wherein `zero_hpz_partition_size=<num_gpus_per_node>`. Here, this will shard optimizer states, gradients and parameters within each node while each node has full copy.
|
||||
|
||||
## A few caveats to be aware of
|
||||
|
||||
- In case of multiple models, pass the optimizers to the prepare call in the same order as corresponding models else `accelerator.save_state()` and `accelerator.load_state()` will result in wrong/unexpected behaviour.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -207,6 +207,22 @@ In [/slurm/submit_multigpu.sh](./slurm/submit_multigpu.sh) the only parameter in
|
||||
|
||||
In [/slurm/submit_multinode.sh](./slurm/submit_multinode.sh) we must specify the number of nodes that will be part of the training (`--num_machines`), how many GPUs we will use in total (`--num_processes`), the [`backend`](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/elastic/run.html#note-on-rendezvous-backend), `--main_process_ip` which will be the address the master node and the `--main_process_port`.
|
||||
|
||||
In both scripts, we run `activateEnviroment.sh` at the beginning. This script should contain the necessary instructions to initialize the environment for execution. Below, we show an example that loads the necessary libraries ([Environment modules](https://github.com/cea-hpc/modules)), activates the Python environment, and sets up various environment variables, most of them to run the scripts in offline mode in case we don't have internet connection from the cluster.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# activateEnvironment.sh
|
||||
module purge
|
||||
module load anaconda3/2020.02 cuda/10.2 cudnn/8.0.5 nccl/2.9.9 arrow/7.0.0 openmpi
|
||||
source activate /home/nct01/nct01328/pytorch_antoni_local
|
||||
|
||||
export HF_HOME=/gpfs/projects/nct01/nct01328/
|
||||
export HF_LOCAL_HOME=/gpfs/projects/nct01/nct01328/HF_LOCAL
|
||||
export HF_DATASETS_OFFLINE=1
|
||||
export TRANSFORMERS_OFFLINE=1
|
||||
export PYTHONPATH=/home/nct01/nct01328/transformers-in-supercomputers:$PYTHONPATH
|
||||
export GPUS_PER_NODE=4
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Finer Examples
|
||||
|
||||
While the first two scripts are extremely barebones when it comes to what you can do with accelerate, more advanced features are documented in two other locations.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -130,8 +130,6 @@ def training_function(config, args):
|
||||
accelerator = Accelerator(
|
||||
cpu=args.cpu, mixed_precision=args.mixed_precision, gradient_accumulation_steps=gradient_accumulation_steps
|
||||
)
|
||||
if accelerator.distributed_type not in [DistributedType.NO, DistributedType.MULTI_CPU, DistributedType.MULTI_GPU]:
|
||||
raise NotImplementedError("LocalSGD is supported only for CPUs and GPUs (no DeepSpeed or MegatronLM)")
|
||||
# Sample hyper-parameters for learning rate, batch size, seed and a few other HPs
|
||||
lr = config["lr"]
|
||||
num_epochs = int(config["num_epochs"])
|
||||
|
||||
@ -405,7 +405,7 @@ def main():
|
||||
f"The tokenizer picked seems to have a very large `model_max_length` ({tokenizer.model_max_length}). "
|
||||
"Picking 1024 instead. You can change that default value by passing --block_size xxx."
|
||||
)
|
||||
block_size = 1024
|
||||
block_size = 1024
|
||||
else:
|
||||
if args.block_size > tokenizer.model_max_length:
|
||||
logger.warning(
|
||||
|
||||
62
examples/inference/README.md
Normal file
62
examples/inference/README.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,62 @@
|
||||
# Distributed inference examples with PiPPy
|
||||
|
||||
This repo contains a variety of tutorials for using the [PiPPy](https://github.com/PyTorch/PiPPy) pipeline parallelism library with accelerate. You will find examples covering:
|
||||
|
||||
1. How to trace the model using `accelerate.prepare_pippy`
|
||||
2. How to specify inputs based on what the model expects (when to use `kwargs`, `args`, and such)
|
||||
3. How to gather the results at the end.
|
||||
|
||||
## Installation
|
||||
|
||||
This requires the `main` branch of accelerate (or a version at least 0.27.0), `pippy` version of 0.2.0 or greater, and at least python 3.9. Please install using `pip install .` to pull from the `setup.py` in this repo, or run manually:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
pip install 'accelerate>=0.27.0' 'torchpippy>=0.2.0'
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Running code
|
||||
|
||||
You can either use `torchrun` or the recommended way of `accelerate launch` (without needing to run `accelerate config`) on each script:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
accelerate launch bert.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Or:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
accelerate launch --num_processes {NUM_GPUS} bert.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Or:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
torchrun --nproc-per-node {NUM_GPUS} bert.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## General speedups
|
||||
|
||||
One can expect that PiPPy will outperform native model parallism by a multiplicative factor since all GPUs are running at all times with inputs, rather than one input being passed through a GPU at a time waiting for the prior to finish.
|
||||
|
||||
Below are some benchmarks we have found when using the accelerate-pippy integration for a few models when running on 2x4090's:
|
||||
|
||||
### Bert
|
||||
|
||||
| | Accelerate/Sequential | PiPPy + Accelerate |
|
||||
|---|---|---|
|
||||
| First batch | 0.2137s | 0.3119s |
|
||||
| Average of 5 batches | 0.0099s | **0.0062s** |
|
||||
|
||||
### GPT2
|
||||
|
||||
| | Accelerate/Sequential | PiPPy + Accelerate |
|
||||
|---|---|---|
|
||||
| First batch | 0.1959s | 0.4189s |
|
||||
| Average of 5 batches | 0.0205s | **0.0126s** |
|
||||
|
||||
### T5
|
||||
|
||||
| | Accelerate/Sequential | PiPPy + Accelerate |
|
||||
|---|---|---|
|
||||
| First batch | 0.2789s | 0.3809s |
|
||||
| Average of 5 batches | 0.0198s | **0.0166s** |
|
||||
79
examples/inference/bert.py
Normal file
79
examples/inference/bert.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,79 @@
|
||||
# coding=utf-8
|
||||
# Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Inc. team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
import time
|
||||
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForMaskedLM
|
||||
|
||||
from accelerate import PartialState, prepare_pippy
|
||||
from accelerate.utils import set_seed
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Set the random seed to have reproducable outputs
|
||||
set_seed(42)
|
||||
|
||||
# Create an example model
|
||||
model = AutoModelForMaskedLM.from_pretrained("bert-base-uncased")
|
||||
model.eval()
|
||||
|
||||
# Input configs
|
||||
# Create example inputs for the model
|
||||
input = torch.randint(
|
||||
low=0,
|
||||
high=model.config.vocab_size,
|
||||
size=(2, 512), # bs x seq_len
|
||||
device="cpu",
|
||||
dtype=torch.int64,
|
||||
requires_grad=False,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Create a pipeline stage from the model
|
||||
# Using `auto` is equivalent to letting `device_map="auto"` figure
|
||||
# out device mapping and will also split the model according to the
|
||||
# number of total GPUs available if it fits on one GPU
|
||||
model = prepare_pippy(model, split_points="auto", example_args=(input,))
|
||||
|
||||
# You can pass `gather_output=True` to have the output from the model
|
||||
# available on all GPUs
|
||||
# model = prepare_pippy(model, split_points="auto", example_args=(input,), gather_output=True)
|
||||
|
||||
# Move the inputs to the first device
|
||||
input = input.to("cuda:0")
|
||||
|
||||
# Take an average of 5 times
|
||||
# Measure first batch
|
||||
torch.cuda.synchronize()
|
||||
start_time = time.time()
|
||||
with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
output = model(input)
|
||||
torch.cuda.synchronize()
|
||||
end_time = time.time()
|
||||
first_batch = end_time - start_time
|
||||
|
||||
# Now that CUDA is init, measure after
|
||||
torch.cuda.synchronize()
|
||||
start_time = time.time()
|
||||
for i in range(5):
|
||||
with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
output = model(input)
|
||||
torch.cuda.synchronize()
|
||||
end_time = time.time()
|
||||
|
||||
# The outputs are only on the final process by default
|
||||
if PartialState().is_last_process:
|
||||
output = torch.stack(tuple(output[0]))
|
||||
print(f"Time of first pass: {first_batch}")
|
||||
print(f"Average time per batch: {(end_time - start_time)/5}")
|
||||
78
examples/inference/gpt2.py
Normal file
78
examples/inference/gpt2.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,78 @@
|
||||
# coding=utf-8
|
||||
# Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Inc. team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
import time
|
||||
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForSequenceClassification
|
||||
|
||||
from accelerate import PartialState, prepare_pippy
|
||||
from accelerate.utils import set_seed
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Set the random seed to have reproducable outputs
|
||||
set_seed(42)
|
||||
|
||||
# Create an example model
|
||||
model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained("gpt2")
|
||||
model.eval()
|
||||
|
||||
# Input configs
|
||||
# Create example inputs for the model
|
||||
input = torch.randint(
|
||||
low=0,
|
||||
high=model.config.vocab_size,
|
||||
size=(2, 1024), # bs x seq_len
|
||||
device="cpu",
|
||||
dtype=torch.int64,
|
||||
requires_grad=False,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Create a pipeline stage from the model
|
||||
# Using `auto` is equivalent to letting `device_map="auto"` figure
|
||||
# out device mapping and will also split the model according to the
|
||||
# number of total GPUs available if it fits on one GPU
|
||||
model = prepare_pippy(model, split_points="auto", example_args=(input,))
|
||||
|
||||
# You can pass `gather_output=True` to have the output from the model
|
||||
# available on all GPUs
|
||||
# model = prepare_pippy(model, split_points="auto", example_args=(input,), gather_output=True)
|
||||
|
||||
# Move the inputs to the first device
|
||||
input = input.to("cuda:0")
|
||||
|
||||
# Take an average of 5 times
|
||||
# Measure first batch
|
||||
torch.cuda.synchronize()
|
||||
start_time = time.time()
|
||||
with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
output = model(input)
|
||||
torch.cuda.synchronize()
|
||||
end_time = time.time()
|
||||
first_batch = end_time - start_time
|
||||
|
||||
# Now that CUDA is init, measure after
|
||||
torch.cuda.synchronize()
|
||||
start_time = time.time()
|
||||
for i in range(5):
|
||||
with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
output = model(input)
|
||||
torch.cuda.synchronize()
|
||||
end_time = time.time()
|
||||
|
||||
# The outputs are only on the final process by default
|
||||
if PartialState().is_last_process:
|
||||
output = torch.stack(tuple(output[0]))
|
||||
print(f"Time of first pass: {first_batch}")
|
||||
print(f"Average time per batch: {(end_time - start_time)/5}")
|
||||
55
examples/inference/llama.py
Normal file
55
examples/inference/llama.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,55 @@
|
||||
# coding=utf-8
|
||||
# Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Inc. team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
from accelerate import PartialState, prepare_pippy
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# sdpa implementation which is the default torch>2.1.2 fails with the tracing + attention mask kwarg
|
||||
# with attn_implementation="eager" mode, the forward is very slow for some reason
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
|
||||
"meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-chat-hf", low_cpu_mem_usage=True, attn_implementation="sdpa"
|
||||
)
|
||||
model.eval()
|
||||
|
||||
# Input configs
|
||||
# Create example inputs for the model
|
||||
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained("meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-chat-hf")
|
||||
prompts = ("I would like to", "I really like to", "The weather is") # bs = 3
|
||||
tokenizer.pad_token = tokenizer.eos_token
|
||||
inputs = tokenizer(prompts, return_tensors="pt", padding=True)
|
||||
|
||||
# Create a pipeline stage from the model
|
||||
# Using `auto` is equivalent to letting `device_map="auto"` figure
|
||||
# out device mapping and will also split the model according to the
|
||||
# number of total GPUs available if it fits on one GPU
|
||||
model = prepare_pippy(model, split_points="auto", example_args=inputs)
|
||||
|
||||
# You can pass `gather_output=True` to have the output from the model
|
||||
# available on all GPUs
|
||||
# model = prepare_pippy(model, split_points="auto", example_args=(input,), gather_output=True)
|
||||
|
||||
# currently we don't support `model.generate`
|
||||
# output = model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=1)
|
||||
|
||||
with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
output = model(**inputs)
|
||||
|
||||
# The outputs are only on the final process by default
|
||||
if PartialState().is_last_process:
|
||||
next_token_logits = output[0][:, -1, :]
|
||||
next_token = torch.argmax(next_token_logits, dim=-1)
|
||||
print(tokenizer.batch_decode(next_token))
|
||||
2
examples/inference/requirements.txt
Normal file
2
examples/inference/requirements.txt
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,2 @@
|
||||
accelerate
|
||||
pippy>=0.2.0
|
||||
90
examples/inference/t5.py
Normal file
90
examples/inference/t5.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,90 @@
|
||||
# coding=utf-8
|
||||
# Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Inc. team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
import time
|
||||
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM
|
||||
|
||||
from accelerate import PartialState, prepare_pippy
|
||||
from accelerate.utils import set_seed
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Set the random seed to have reproducable outputs
|
||||
set_seed(42)
|
||||
|
||||
# Create an example model
|
||||
model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained("t5-small")
|
||||
model.eval()
|
||||
|
||||
# Input configs
|
||||
# Create example inputs for the model
|
||||
input = torch.randint(
|
||||
low=0,
|
||||
high=model.config.vocab_size,
|
||||
size=(2, 1024), # bs x seq_len
|
||||
device="cpu",
|
||||
dtype=torch.int64,
|
||||
requires_grad=False,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
example_inputs = {"input_ids": input, "decoder_input_ids": input}
|
||||
|
||||
# Create a pipeline stage from the model
|
||||
# Using `auto` is equivalent to letting `device_map="auto"` figure
|
||||
# out device mapping and will also split the model according to the
|
||||
# number of total GPUs available if it fits on one GPU
|
||||
model = prepare_pippy(
|
||||
model,
|
||||
no_split_module_classes=["T5Block"],
|
||||
example_kwargs=example_inputs,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# You can pass `gather_output=True` to have the output from the model
|
||||
# available on all GPUs
|
||||
# model = prepare_pippy(
|
||||
# model,
|
||||
# no_split_module_classes=["T5Block"],
|
||||
# example_kwargs=example_inputs,
|
||||
# gather_outputs=True
|
||||
# )
|
||||
|
||||
# The model expects a tuple during real inference
|
||||
# with the data on the first device
|
||||
args = (example_inputs["input_ids"].to("cuda:0"), example_inputs["decoder_input_ids"].to("cuda:0"))
|
||||
|
||||
# Take an average of 5 times
|
||||
# Measure first batch
|
||||
torch.cuda.synchronize()
|
||||
start_time = time.time()
|
||||
with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
output = model(*args)
|
||||
torch.cuda.synchronize()
|
||||
end_time = time.time()
|
||||
first_batch = end_time - start_time
|
||||
|
||||
# Now that CUDA is init, measure after
|
||||
torch.cuda.synchronize()
|
||||
start_time = time.time()
|
||||
for i in range(5):
|
||||
with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
output = model(*args)
|
||||
torch.cuda.synchronize()
|
||||
end_time = time.time()
|
||||
|
||||
# The outputs are only on the final process by default
|
||||
if PartialState().is_last_process:
|
||||
output = torch.stack(tuple(output[0]))
|
||||
print(f"Time of first pass: {first_batch}")
|
||||
print(f"Average time per batch: {(end_time - start_time)/5}")
|
||||
@ -1,7 +1,3 @@
|
||||
[tool.black]
|
||||
line-length = 119
|
||||
target-version = ['py37']
|
||||
|
||||
[tool.ruff]
|
||||
# Never enforce `E501` (line length violations).
|
||||
ignore = ["E501", "E741", "W605"]
|
||||
@ -11,7 +7,13 @@ line-length = 119
|
||||
# Ignore import violations in all `__init__.py` files.
|
||||
[tool.ruff.per-file-ignores]
|
||||
"__init__.py" = ["E402", "F401", "F403", "F811"]
|
||||
"manim_animations/*" = ["ALL"]
|
||||
|
||||
[tool.ruff.isort]
|
||||
lines-after-imports = 2
|
||||
known-first-party = ["accelerate"]
|
||||
|
||||
[tool.ruff.format]
|
||||
exclude = [
|
||||
"manim_animations/*"
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
33
setup.py
33
setup.py
@ -12,15 +12,28 @@
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
from setuptools import setup
|
||||
from setuptools import find_packages
|
||||
from setuptools import find_packages, setup
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
extras = {}
|
||||
extras["quality"] = ["black ~= 23.1", "ruff >= 0.0.241", "hf-doc-builder >= 0.3.0", "urllib3 < 2.0.0"]
|
||||
extras["quality"] = [
|
||||
"black ~= 23.1", # hf-doc-builder has a hidden dependency on `black`
|
||||
"hf-doc-builder >= 0.3.0",
|
||||
"ruff ~= 0.1.15",
|
||||
]
|
||||
extras["docs"] = []
|
||||
extras["test_prod"] = ["pytest", "pytest-xdist", "pytest-subtests", "parameterized"]
|
||||
extras["test_dev"] = [
|
||||
"datasets", "evaluate", "transformers", "scipy", "scikit-learn", "deepspeed", "tqdm", "bitsandbytes", "timm"
|
||||
"datasets",
|
||||
"evaluate",
|
||||
"torchpippy>=0.2.0",
|
||||
"transformers",
|
||||
"scipy",
|
||||
"scikit-learn",
|
||||
"deepspeed<0.13.0",
|
||||
"tqdm",
|
||||
"bitsandbytes",
|
||||
"timm",
|
||||
]
|
||||
extras["testing"] = extras["test_prod"] + extras["test_dev"]
|
||||
extras["rich"] = ["rich"]
|
||||
@ -34,7 +47,7 @@ extras["sagemaker"] = [
|
||||
|
||||
setup(
|
||||
name="accelerate",
|
||||
version="0.27.0.dev0",
|
||||
version="0.27.0",
|
||||
description="Accelerate",
|
||||
long_description=open("README.md", "r", encoding="utf-8").read(),
|
||||
long_description_content_type="text/markdown",
|
||||
@ -54,7 +67,15 @@ setup(
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
python_requires=">=3.8.0",
|
||||
install_requires=["numpy>=1.17", "packaging>=20.0", "psutil", "pyyaml", "torch>=1.10.0", "huggingface_hub", "safetensors>=0.3.1"],
|
||||
install_requires=[
|
||||
"numpy>=1.17",
|
||||
"packaging>=20.0",
|
||||
"psutil",
|
||||
"pyyaml",
|
||||
"torch>=1.10.0",
|
||||
"huggingface_hub",
|
||||
"safetensors>=0.3.1",
|
||||
],
|
||||
extras_require=extras,
|
||||
classifiers=[
|
||||
"Development Status :: 5 - Production/Stable",
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
|
||||
__version__ = "0.27.0.dev0"
|
||||
__version__ = "0.27.0"
|
||||
|
||||
from .accelerator import Accelerator
|
||||
from .big_modeling import (
|
||||
@ -11,6 +11,7 @@ from .big_modeling import (
|
||||
load_checkpoint_and_dispatch,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from .data_loader import skip_first_batches
|
||||
from .inference import prepare_pippy
|
||||
from .launchers import debug_launcher, notebook_launcher
|
||||
from .state import PartialState
|
||||
from .utils import (
|
||||
|
||||
@ -373,8 +373,6 @@ class Accelerator:
|
||||
raise ValueError("You can only pass one `AutocastKwargs` in `kwargs_handler`.")
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self.autocast_handler = handler
|
||||
if self.fp8_recipe_handler is None and mixed_precision == "fp8":
|
||||
self.fp8_recipe_handler = FP8RecipeKwargs()
|
||||
|
||||
kwargs = self.init_handler.to_kwargs() if self.init_handler is not None else {}
|
||||
self.state = AcceleratorState(
|
||||
@ -388,6 +386,9 @@ class Accelerator:
|
||||
**kwargs,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if self.fp8_recipe_handler is None and self.state.mixed_precision == "fp8":
|
||||
self.fp8_recipe_handler = FP8RecipeKwargs(backend="MSAMP" if is_msamp_available() else "TE")
|
||||
|
||||
trackers = filter_trackers(log_with, self.logging_dir)
|
||||
if len(trackers) < 1 and log_with is not None:
|
||||
warnings.warn(f"`log_with={log_with}` was passed but no supported trackers are currently installed.")
|
||||
@ -1753,10 +1754,11 @@ class Accelerator:
|
||||
for obj in result:
|
||||
if isinstance(obj, torch.nn.Module):
|
||||
model = obj
|
||||
model.train()
|
||||
elif isinstance(obj, (torch.optim.Optimizer)):
|
||||
optimizer = obj
|
||||
if optimizer is not None and model is not None:
|
||||
dtype = torch.bfloat16 if self.state.mixed_precision == "bf16" else torch.float32
|
||||
dtype = torch.bfloat16 if self.state.mixed_precision == "bf16" else None
|
||||
if self.device.type == "xpu" and is_xpu_available():
|
||||
model = model.to(self.device)
|
||||
model, optimizer = torch.xpu.optimize(
|
||||
|
||||
@ -38,11 +38,13 @@ from .utils import (
|
||||
infer_auto_device_map,
|
||||
is_npu_available,
|
||||
is_torch_version,
|
||||
is_xpu_available,
|
||||
load_checkpoint_in_model,
|
||||
offload_state_dict,
|
||||
parse_flag_from_env,
|
||||
retie_parameters,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from .utils.other import recursive_getattr
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
|
||||
@ -123,6 +125,7 @@ def init_on_device(device: torch.device, include_buffers: bool = None):
|
||||
if param is not None:
|
||||
param_cls = type(module._parameters[name])
|
||||
kwargs = module._parameters[name].__dict__
|
||||
kwargs["requires_grad"] = param.requires_grad
|
||||
module._parameters[name] = param_cls(module._parameters[name].to(device), **kwargs)
|
||||
|
||||
def register_empty_buffer(module, name, buffer, persistent=True):
|
||||
@ -395,7 +398,22 @@ def dispatch_model(
|
||||
else:
|
||||
weights_map = None
|
||||
|
||||
# When dispatching the model's parameters to the devices specified in device_map, we want to avoid allocating memory several times for the
|
||||
# tied parameters. The dictionary tied_params_map keeps track of the already allocated data for a given tied parameter (represented by its
|
||||
# original pointer) on each devices.
|
||||
tied_params = find_tied_parameters(model)
|
||||
|
||||
tied_params_map = {}
|
||||
for group in tied_params:
|
||||
for param_name in group:
|
||||
# data_ptr() is enough here, as `find_tied_parameters` finds tied params simply by comparing `param1 is param2`, so we don't need
|
||||
# to care about views of tensors through storage_offset.
|
||||
data_ptr = recursive_getattr(model, param_name).data_ptr()
|
||||
tied_params_map[data_ptr] = {}
|
||||
|
||||
# Note: To handle the disk offloading case, we can not simply use weights_map[param_name].data_ptr() as the reference pointer,
|
||||
# as we have no guarantee that safetensors' `file.get_tensor()` will always give the same pointer.
|
||||
|
||||
attach_align_device_hook_on_blocks(
|
||||
model,
|
||||
execution_device=execution_device,
|
||||
@ -404,6 +422,7 @@ def dispatch_model(
|
||||
weights_map=weights_map,
|
||||
skip_keys=skip_keys,
|
||||
preload_module_classes=preload_module_classes,
|
||||
tied_params_map=tied_params_map,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# warn if there is any params on the meta device
|
||||
@ -433,6 +452,8 @@ def dispatch_model(
|
||||
model.to = add_warning(model.to, model)
|
||||
if is_npu_available():
|
||||
model.npu = add_warning(model.npu, model)
|
||||
elif is_xpu_available():
|
||||
model.xpu = add_warning(model.xpu, model)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
model.cuda = add_warning(model.cuda, model)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -441,6 +462,8 @@ def dispatch_model(
|
||||
# `torch.Tensor.to(<int num>)` is not supported by `torch_npu` (see this [issue](https://github.com/Ascend/pytorch/issues/16)).
|
||||
if is_npu_available() and isinstance(device, int):
|
||||
device = f"npu:{device}"
|
||||
elif is_xpu_available() and isinstance(device, int):
|
||||
device = f"xpu:{device}"
|
||||
if device != "disk":
|
||||
model.to(device)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -179,7 +179,11 @@ def get_cluster_input():
|
||||
|
||||
use_mps = not use_cpu and is_mps_available()
|
||||
deepspeed_config = {}
|
||||
if distributed_type in [DistributedType.MULTI_GPU, DistributedType.MULTI_NPU, DistributedType.NO] and not use_mps:
|
||||
if (
|
||||
distributed_type
|
||||
in [DistributedType.MULTI_GPU, DistributedType.MULTI_XPU, DistributedType.MULTI_NPU, DistributedType.NO]
|
||||
and not use_mps
|
||||
):
|
||||
use_deepspeed = _ask_field(
|
||||
"Do you want to use DeepSpeed? [yes/NO]: ",
|
||||
_convert_yes_no_to_bool,
|
||||
|
||||
@ -837,12 +837,26 @@ def prepare_data_loader(
|
||||
process_index = state.process_index
|
||||
|
||||
# Sanity check
|
||||
batch_size = dataloader.batch_size if dataloader.batch_size is not None else dataloader.batch_sampler.batch_size
|
||||
if split_batches and batch_size > 1 and batch_size % num_processes != 0:
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
f"To use a `DataLoader` in `split_batches` mode, the batch size ({dataloader.batch_size}) "
|
||||
f"needs to be a round multiple of the number of processes ({num_processes})."
|
||||
)
|
||||
if split_batches:
|
||||
if dataloader.batch_size is not None:
|
||||
batch_size_for_check = dataloader.batch_size
|
||||
else:
|
||||
# For custom batch_sampler
|
||||
if hasattr(dataloader.batch_sampler, "batch_size"):
|
||||
batch_size_for_check = dataloader.batch_sampler.batch_size
|
||||
else:
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
"In order to use `split_batches==True` you must have a `batch_size` attribute either in the passed "
|
||||
"`dataloader` or `dataloader.batch_sampler` objects, and it has to return a natural number. "
|
||||
"Your `dataloader.batch_size` is None and `dataloader.batch_sampler` "
|
||||
f"(`{type(dataloader.batch_sampler)}`) does not have the `batch_size` attribute set."
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if batch_size_for_check > 1 and batch_size_for_check % num_processes != 0:
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
f"To use a `DataLoader` in `split_batches` mode, the batch size ({dataloader.batch_size}) "
|
||||
f"needs to be a round multiple of the number of processes ({num_processes})."
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
new_dataset = dataloader.dataset
|
||||
# Iterable dataset doesn't like batch_sampler, but data_loader creates a default one for it
|
||||
|
||||
@ -27,6 +27,7 @@ from .utils import (
|
||||
set_module_tensor_to_device,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from .utils.modeling import get_non_persistent_buffers
|
||||
from .utils.other import recursive_getattr
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class ModelHook:
|
||||
@ -165,7 +166,12 @@ def add_hook_to_module(module: nn.Module, hook: ModelHook, append: bool = False)
|
||||
output = module._old_forward(*args, **kwargs)
|
||||
return module._hf_hook.post_forward(module, output)
|
||||
|
||||
module.forward = functools.update_wrapper(functools.partial(new_forward, module), old_forward)
|
||||
# Overriding a GraphModuleImpl forward freezes the forward call and later modifications on the graph will fail.
|
||||
# Reference: https://pytorch.slack.com/archives/C3PDTEV8E/p1705929610405409
|
||||
if "GraphModuleImpl" in str(type(module)):
|
||||
module.__class__.forward = functools.update_wrapper(functools.partial(new_forward, module), old_forward)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
module.forward = functools.update_wrapper(functools.partial(new_forward, module), old_forward)
|
||||
|
||||
return module
|
||||
|
||||
@ -188,7 +194,12 @@ def remove_hook_from_module(module: nn.Module, recurse=False):
|
||||
delattr(module, "_hf_hook")
|
||||
|
||||
if hasattr(module, "_old_forward"):
|
||||
module.forward = module._old_forward
|
||||
# Overriding a GraphModuleImpl forward freezes the forward call and later modifications on the graph will fail.
|
||||
# Reference: https://pytorch.slack.com/archives/C3PDTEV8E/p1705929610405409
|
||||
if "GraphModuleImpl" in str(type(module)):
|
||||
module.__class__.forward = module._old_forward
|
||||
else:
|
||||
module.forward = module._old_forward
|
||||
delattr(module, "_old_forward")
|
||||
|
||||
if recurse:
|
||||
@ -227,6 +238,7 @@ class AlignDevicesHook(ModelHook):
|
||||
offload_buffers: bool = False,
|
||||
place_submodules: bool = False,
|
||||
skip_keys: Optional[Union[str, List[str]]] = None,
|
||||
tied_params_map: Optional[Dict[int, Dict[torch.device, torch.Tensor]]] = None,
|
||||
):
|
||||
self.execution_device = execution_device
|
||||
self.offload = offload
|
||||
@ -240,6 +252,11 @@ class AlignDevicesHook(ModelHook):
|
||||
self.input_device = None
|
||||
self.param_original_devices = {}
|
||||
self.buffer_original_devices = {}
|
||||
self.tied_params_names = set()
|
||||
|
||||
# The hook pre_forward/post_forward need to have knowledge of this dictionary, as with offloading we want to avoid duplicating memory
|
||||
# for tied weights already loaded on the target execution device.
|
||||
self.tied_params_map = tied_params_map
|
||||
|
||||
def __repr__(self):
|
||||
return (
|
||||
@ -249,9 +266,13 @@ class AlignDevicesHook(ModelHook):
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def init_hook(self, module):
|
||||
# In case the AlignDevicesHook is on meta device, ignore tied weights as data_ptr() is then always zero.
|
||||
if self.execution_device == "meta" or self.execution_device == torch.device("meta"):
|
||||
self.tied_params_map = None
|
||||
|
||||
if not self.offload and self.execution_device is not None:
|
||||
for name, _ in named_module_tensors(module, recurse=self.place_submodules):
|
||||
set_module_tensor_to_device(module, name, self.execution_device)
|
||||
set_module_tensor_to_device(module, name, self.execution_device, tied_params_map=self.tied_params_map)
|
||||
elif self.offload:
|
||||
self.original_devices = {
|
||||
name: param.device for name, param in named_module_tensors(module, recurse=self.place_submodules)
|
||||
@ -266,13 +287,28 @@ class AlignDevicesHook(ModelHook):
|
||||
for name, _ in named_module_tensors(
|
||||
module, include_buffers=self.offload_buffers, recurse=self.place_submodules, remove_non_persistent=True
|
||||
):
|
||||
# When using disk offloading, we can not rely on `weights_map[name].data_ptr()` as the reference pointer,
|
||||
# as we have no guarantee that safetensors' `file.get_tensor()` will always give the same pointer.
|
||||
# As we have no reliable way to track the shared data pointer of tied weights in this case, we use tied_params_names: List[str]
|
||||
# to add on the fly pointers to `tied_params_map` in the pre_forward call.
|
||||
if (
|
||||
self.tied_params_map is not None
|
||||
and recursive_getattr(module, name).data_ptr() in self.tied_params_map
|
||||
):
|
||||
self.tied_params_names.add(name)
|
||||
|
||||
set_module_tensor_to_device(module, name, "meta")
|
||||
|
||||
if not self.offload_buffers and self.execution_device is not None:
|
||||
for name, _ in module.named_buffers(recurse=self.place_submodules):
|
||||
set_module_tensor_to_device(module, name, self.execution_device)
|
||||
set_module_tensor_to_device(
|
||||
module, name, self.execution_device, tied_params_map=self.tied_params_map
|
||||
)
|
||||
elif self.offload_buffers and self.execution_device is not None:
|
||||
for name in get_non_persistent_buffers(module, recurse=self.place_submodules):
|
||||
set_module_tensor_to_device(module, name, self.execution_device)
|
||||
set_module_tensor_to_device(
|
||||
module, name, self.execution_device, tied_params_map=self.tied_params_map
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
return module
|
||||
|
||||
@ -280,6 +316,8 @@ class AlignDevicesHook(ModelHook):
|
||||
if self.io_same_device:
|
||||
self.input_device = find_device([args, kwargs])
|
||||
if self.offload:
|
||||
self.tied_pointers_to_remove = set()
|
||||
|
||||
for name, _ in named_module_tensors(
|
||||
module,
|
||||
include_buffers=self.offload_buffers,
|
||||
@ -287,11 +325,32 @@ class AlignDevicesHook(ModelHook):
|
||||
remove_non_persistent=True,
|
||||
):
|
||||
fp16_statistics = None
|
||||
value = self.weights_map[name]
|
||||
if "weight" in name and name.replace("weight", "SCB") in self.weights_map.keys():
|
||||
if self.weights_map[name].dtype == torch.int8:
|
||||
if value.dtype == torch.int8:
|
||||
fp16_statistics = self.weights_map[name.replace("weight", "SCB")]
|
||||
|
||||
# In case we are using offloading with tied weights, we need to keep track of the offloaded weights
|
||||
# that are loaded on device at this point, as we will need to remove them as well from the dictionary
|
||||
# self.tied_params_map in order to allow to free memory.
|
||||
if name in self.tied_params_names and value.data_ptr() not in self.tied_params_map:
|
||||
self.tied_params_map[value.data_ptr()] = {}
|
||||
|
||||
if (
|
||||
value is not None
|
||||
and self.tied_params_map is not None
|
||||
and value.data_ptr() in self.tied_params_map
|
||||
and self.execution_device not in self.tied_params_map[value.data_ptr()]
|
||||
):
|
||||
self.tied_pointers_to_remove.add((value.data_ptr(), self.execution_device))
|
||||
|
||||
set_module_tensor_to_device(
|
||||
module, name, self.execution_device, value=self.weights_map[name], fp16_statistics=fp16_statistics
|
||||
module,
|
||||
name,
|
||||
self.execution_device,
|
||||
value=value,
|
||||
fp16_statistics=fp16_statistics,
|
||||
tied_params_map=self.tied_params_map,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
return send_to_device(args, self.execution_device), send_to_device(
|
||||
@ -311,6 +370,12 @@ class AlignDevicesHook(ModelHook):
|
||||
module.state.SCB = None
|
||||
module.state.CxB = None
|
||||
|
||||
# We may have loaded tied weights into self.tied_params_map (avoiding to load them several times in e.g. submodules): remove them from
|
||||
# this dictionary to allow the garbage collector to do its job.
|
||||
for value_pointer, device in self.tied_pointers_to_remove:
|
||||
del self.tied_params_map[value_pointer][device]
|
||||
self.tied_pointers_to_remove = None
|
||||
|
||||
if self.io_same_device and self.input_device is not None:
|
||||
output = send_to_device(output, self.input_device, skip_keys=self.skip_keys)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -329,6 +394,7 @@ def attach_execution_device_hook(
|
||||
execution_device: Union[int, str, torch.device],
|
||||
skip_keys: Optional[Union[str, List[str]]] = None,
|
||||
preload_module_classes: Optional[List[str]] = None,
|
||||
tied_params_map: Optional[Dict[int, Dict[torch.device, torch.Tensor]]] = None,
|
||||
):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Recursively attaches `AlignDevicesHook` to all submodules of a given model to make sure they have the right
|
||||
@ -346,16 +412,23 @@ def attach_execution_device_hook(
|
||||
of the forward. This should only be used for classes that have submodules which are registered but not
|
||||
called directly during the forward, for instance if a `dense` linear layer is registered, but at forward,
|
||||
`dense.weight` and `dense.bias` are used in some operations instead of calling `dense` directly.
|
||||
tied_params_map (Optional[Dict[int, Dict[torch.device, torch.Tensor]]], *optional*, defaults to `None`):
|
||||
A map of data pointers to dictionaries of devices to already dispatched tied weights. For a given execution
|
||||
device, this parameter is useful to reuse the first available pointer of a shared weight for all others,
|
||||
instead of duplicating memory.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if not hasattr(module, "_hf_hook") and len(module.state_dict()) > 0:
|
||||
add_hook_to_module(module, AlignDevicesHook(execution_device, skip_keys=skip_keys))
|
||||
add_hook_to_module(
|
||||
module,
|
||||
AlignDevicesHook(execution_device, skip_keys=skip_keys, tied_params_map=tied_params_map),
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Break the recursion if we get to a preload module.
|
||||
if preload_module_classes is not None and module.__class__.__name__ in preload_module_classes:
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
||||
for child in module.children():
|
||||
attach_execution_device_hook(child, execution_device)
|
||||
attach_execution_device_hook(child, execution_device, tied_params_map=tied_params_map)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def attach_align_device_hook(
|
||||
@ -367,6 +440,7 @@ def attach_align_device_hook(
|
||||
module_name: str = "",
|
||||
skip_keys: Optional[Union[str, List[str]]] = None,
|
||||
preload_module_classes: Optional[List[str]] = None,
|
||||
tied_params_map: Optional[Dict[int, Dict[torch.device, torch.Tensor]]] = None,
|
||||
):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Recursively attaches `AlignDevicesHook` to all submodules of a given model that have direct parameters and/or
|
||||
@ -392,6 +466,10 @@ def attach_align_device_hook(
|
||||
of the forward. This should only be used for classes that have submodules which are registered but not
|
||||
called directly during the forward, for instance if a `dense` linear layer is registered, but at forward,
|
||||
`dense.weight` and `dense.bias` are used in some operations instead of calling `dense` directly.
|
||||
tied_params_map (Optional[Dict[int, Dict[torch.device, torch.Tensor]]], *optional*, defaults to `None`):
|
||||
A map of data pointers to dictionaries of devices to already dispatched tied weights. For a given execution
|
||||
device, this parameter is useful to reuse the first available pointer of a shared weight for all others,
|
||||
instead of duplicating memory.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
# Attach the hook on this module if it has any direct tensor.
|
||||
directs = named_module_tensors(module)
|
||||
@ -412,6 +490,7 @@ def attach_align_device_hook(
|
||||
offload_buffers=offload_buffers,
|
||||
place_submodules=full_offload,
|
||||
skip_keys=skip_keys,
|
||||
tied_params_map=tied_params_map,
|
||||
)
|
||||
add_hook_to_module(module, hook, append=True)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -431,6 +510,7 @@ def attach_align_device_hook(
|
||||
module_name=child_name,
|
||||
preload_module_classes=preload_module_classes,
|
||||
skip_keys=skip_keys,
|
||||
tied_params_map=tied_params_map,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -455,6 +535,7 @@ def attach_align_device_hook_on_blocks(
|
||||
module_name: str = "",
|
||||
skip_keys: Optional[Union[str, List[str]]] = None,
|
||||
preload_module_classes: Optional[List[str]] = None,
|
||||
tied_params_map: Optional[Dict[int, Dict[torch.device, torch.Tensor]]] = None,
|
||||
):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Attaches `AlignDevicesHook` to all blocks of a given model as needed.
|
||||
@ -481,12 +562,20 @@ def attach_align_device_hook_on_blocks(
|
||||
of the forward. This should only be used for classes that have submodules which are registered but not
|
||||
called directly during the forward, for instance if a `dense` linear layer is registered, but at forward,
|
||||
`dense.weight` and `dense.bias` are used in some operations instead of calling `dense` directly.
|
||||
tied_params_map (Optional[Dict[int, Dict[torch.device, torch.Tensor]]], *optional*, defaults to `None`):
|
||||
A map of data pointers to dictionaries of devices to already dispatched tied weights. For a given execution
|
||||
device, this parameter is useful to reuse the first available pointer of a shared weight for all others,
|
||||
instead of duplicating memory.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
# If one device and one offload, we've got one hook.
|
||||
if not isinstance(execution_device, Mapping) and not isinstance(offload, dict):
|
||||
if not offload:
|
||||
hook = AlignDevicesHook(
|
||||
execution_device=execution_device, io_same_device=True, skip_keys=skip_keys, place_submodules=True
|
||||
execution_device=execution_device,
|
||||
io_same_device=True,
|
||||
skip_keys=skip_keys,
|
||||
place_submodules=True,
|
||||
tied_params_map=tied_params_map,
|
||||
)
|
||||
add_hook_to_module(module, hook)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
@ -498,6 +587,7 @@ def attach_align_device_hook_on_blocks(
|
||||
offload_buffers=offload_buffers,
|
||||
module_name=module_name,
|
||||
skip_keys=skip_keys,
|
||||
tied_params_map=tied_params_map,
|
||||
)
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
||||
@ -513,9 +603,10 @@ def attach_align_device_hook_on_blocks(
|
||||
io_same_device=(module_name == ""),
|
||||
place_submodules=True,
|
||||
skip_keys=skip_keys,
|
||||
tied_params_map=tied_params_map,
|
||||
)
|
||||
add_hook_to_module(module, hook)
|
||||
attach_execution_device_hook(module, execution_device[module_name])
|
||||
attach_execution_device_hook(module, execution_device[module_name], tied_params_map=tied_params_map)
|
||||
elif module_name in execution_device and module_name in offload:
|
||||
attach_align_device_hook(
|
||||
module,
|
||||
@ -526,10 +617,14 @@ def attach_align_device_hook_on_blocks(
|
||||
module_name=module_name,
|
||||
skip_keys=skip_keys,
|
||||
preload_module_classes=preload_module_classes,
|
||||
tied_params_map=tied_params_map,
|
||||
)
|
||||
if not hasattr(module, "_hf_hook"):
|
||||
hook = AlignDevicesHook(
|
||||
execution_device=execution_device[module_name], io_same_device=(module_name == ""), skip_keys=skip_keys
|
||||
execution_device=execution_device[module_name],
|
||||
io_same_device=(module_name == ""),
|
||||
skip_keys=skip_keys,
|
||||
tied_params_map=tied_params_map,
|
||||
)
|
||||
add_hook_to_module(module, hook)
|
||||
attach_execution_device_hook(
|
||||
@ -537,9 +632,15 @@ def attach_align_device_hook_on_blocks(
|
||||
execution_device[module_name],
|
||||
preload_module_classes=preload_module_classes,
|
||||
skip_keys=skip_keys,
|
||||
tied_params_map=tied_params_map,
|
||||
)
|
||||
elif module_name == "":
|
||||
hook = AlignDevicesHook(execution_device=execution_device.get(""), io_same_device=True, skip_keys=skip_keys)
|
||||
hook = AlignDevicesHook(
|
||||
execution_device=execution_device.get(""),
|
||||
io_same_device=True,
|
||||
skip_keys=skip_keys,
|
||||
tied_params_map=tied_params_map,
|
||||
)
|
||||
add_hook_to_module(module, hook)
|
||||
|
||||
for child_name, child in module.named_children():
|
||||
@ -553,6 +654,7 @@ def attach_align_device_hook_on_blocks(
|
||||
module_name=child_name,
|
||||
preload_module_classes=preload_module_classes,
|
||||
skip_keys=skip_keys,
|
||||
tied_params_map=tied_params_map,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
173
src/accelerate/inference.py
Normal file
173
src/accelerate/inference.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,173 @@
|
||||
import math
|
||||
from types import MethodType
|
||||
from typing import Any, Dict, List, Optional, Tuple, Union
|
||||
|
||||
from .state import PartialState
|
||||
from .utils import (
|
||||
calculate_maximum_sizes,
|
||||
convert_bytes,
|
||||
copy_tensor_to_devices,
|
||||
ignorant_find_batch_size,
|
||||
infer_auto_device_map,
|
||||
is_pippy_available,
|
||||
pad_input_tensors,
|
||||
send_to_device,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if is_pippy_available():
|
||||
from pippy.IR import Pipe, PipeSplitWrapper, annotate_split_points
|
||||
from pippy.PipelineStage import PipelineStage
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def generate_device_map(model, num_processes: int = 1, no_split_module_classes=None, max_memory: dict = None):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Calculates the device map for `model` with an offset for PiPPy
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if num_processes == 1:
|
||||
return infer_auto_device_map(model, no_split_module_classes=no_split_module_classes, clean_result=False)
|
||||
if max_memory is None:
|
||||
model_size, shared = calculate_maximum_sizes(model)
|
||||
|
||||
# Split into `n` chunks for each GPU
|
||||
memory = (model_size + shared[0]) / num_processes
|
||||
memory = convert_bytes(memory)
|
||||
value, ending = memory.split(" ")
|
||||
|
||||
# Add a chunk to deal with potential extra shared memory instances
|
||||
memory = math.ceil(float(value)) * 1.1
|
||||
memory = f"{memory} {ending}"
|
||||
max_memory = {i: memory for i in range(num_processes)}
|
||||
device_map = infer_auto_device_map(
|
||||
model,
|
||||
max_memory=max_memory,
|
||||
no_split_module_classes=no_split_module_classes,
|
||||
clean_result=False,
|
||||
)
|
||||
return device_map
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def find_pippy_batch_size(args, kwargs):
|
||||
found_batch_size = None
|
||||
if args is not None:
|
||||
for arg in args:
|
||||
found_batch_size = ignorant_find_batch_size(arg)
|
||||
if found_batch_size is not None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
if kwargs is not None and found_batch_size is None:
|
||||
for kwarg in kwargs.values():
|
||||
found_batch_size = ignorant_find_batch_size(kwarg)
|
||||
if found_batch_size is not None:
|
||||
break
|
||||
return found_batch_size
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def build_pipeline(model, split_points, args, kwargs, num_chunks):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Attaches the split points to the model based on `self.device_map` and generates a `PipelineStage`. Requires passing
|
||||
in needed `args` and `kwargs` as the model needs on the CPU.
|
||||
|
||||
Users can pass in custom `num_chunks` as an optional hyper-parameter. By default will use
|
||||
`AcceleratorState.num_processes`
|
||||
"""
|
||||
# We need to annotate the split points in the model for PiPPy
|
||||
state = PartialState()
|
||||
annotate_split_points(model, {split_point: PipeSplitWrapper.SplitPoint.BEGINNING for split_point in split_points})
|
||||
found_batch_size = find_pippy_batch_size(args, kwargs)
|
||||
if found_batch_size != num_chunks:
|
||||
args = pad_input_tensors(args, found_batch_size, num_chunks)
|
||||
kwargs = pad_input_tensors(kwargs, found_batch_size, num_chunks)
|
||||
pipe = Pipe.from_tracing(model, num_chunks=num_chunks, example_args=args, example_kwargs=kwargs)
|
||||
stage = PipelineStage(pipe, state.local_process_index, device=state.device)
|
||||
|
||||
return stage
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def pippy_forward(forward, num_chunks, gather_output, *args, **kwargs):
|
||||
state = PartialState()
|
||||
output = None
|
||||
|
||||
if state.num_processes == 1:
|
||||
output = forward(*args, **kwargs)
|
||||
elif state.is_local_main_process:
|
||||
found_batch_size = find_pippy_batch_size(args, kwargs)
|
||||
if found_batch_size is None:
|
||||
raise ValueError("Could not find batch size from args or kwargs")
|
||||
else:
|
||||
if found_batch_size != num_chunks:
|
||||
args = pad_input_tensors(args, found_batch_size, num_chunks)
|
||||
kwargs = pad_input_tensors(kwargs, found_batch_size, num_chunks)
|
||||
forward(*args, **kwargs)
|
||||
elif state.is_last_process:
|
||||
output = forward()
|
||||
else:
|
||||
forward()
|
||||
if gather_output:
|
||||
# Each node will get a copy of the full output which is only on the last GPU
|
||||
output = copy_tensor_to_devices(output)
|
||||
return output
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def prepare_pippy(
|
||||
model,
|
||||
split_points: Optional[Union[str, List[str]]] = "auto",
|
||||
no_split_module_classes: Optional[List[str]] = None,
|
||||
example_args: Optional[Tuple[Any]] = (),
|
||||
example_kwargs: Optional[Dict[str, Any]] = None,
|
||||
num_chunks: Optional[int] = None,
|
||||
gather_output: Optional[bool] = False,
|
||||
):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Wraps `model` for pipeline parallel inference.
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
model (`torch.nn.Module`):
|
||||
A model we want to split for pipeline-parallel inference
|
||||
split_points (`str` or `List[str]`, defaults to 'auto'):
|
||||
How to generate the split points and chunk the model across each GPU. 'auto' will find the best balanced
|
||||
split given any model. Should be a list of layer names in the model to split by otherwise.
|
||||
no_split_module_classes (`List[str]`):
|
||||
A list of class names for layers we don't want to be split.
|
||||
example_args (tuple of model inputs):
|
||||
The expected inputs for the model that uses order-based inputs. Recommended to use this method if possible.
|
||||
example_kwargs (dict of model inputs)
|
||||
The expected inputs for the model that uses dictionary-based inputs. This is a *highly* limiting structure
|
||||
that requires the same keys be present at *all* inference calls. Not recommended unless the prior condition
|
||||
is true for all cases.
|
||||
num_chunks (`int`, defaults to the number of available GPUs):
|
||||
The number of different stages the Pipeline will have. By default it will assign one chunk per GPU, but
|
||||
this can be tuned and played with. In general one should have num_chunks >= num_gpus.
|
||||
gather_output (`bool`, defaults to `False`):
|
||||
If `True`, the output from the last GPU (which holds the true outputs) is sent across to all GPUs.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if not is_pippy_available():
|
||||
raise ImportError(
|
||||
"`pippy` was not found to be installed on your system. Please "
|
||||
"install using `pip install torchpippy` or ensure you have at least version 0.2.0"
|
||||
)
|
||||
state = PartialState()
|
||||
example_args = send_to_device(example_args, "cpu")
|
||||
example_kwargs = send_to_device(example_kwargs, "cpu")
|
||||
if num_chunks is None:
|
||||
num_chunks = state.num_processes
|
||||
if split_points == "auto":
|
||||
device_map = generate_device_map(model, num_chunks, no_split_module_classes=no_split_module_classes)
|
||||
split_points = []
|
||||
for i in range(1, num_chunks):
|
||||
split_points.append(next(k for k, v in device_map.items() if v == i))
|
||||
model.hf_split_points = split_points
|
||||
stage = build_pipeline(model, split_points, example_args, example_kwargs, num_chunks)
|
||||
model._original_forward = model.forward
|
||||
model._original_call = model.__call__
|
||||
model.pippy_stage = stage
|
||||
model.hf_split_points = split_points
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(*args, **kwargs):
|
||||
return pippy_forward(stage.forward, num_chunks, gather_output, *args, **kwargs)
|
||||
|
||||
# To act like a decorator so that it can be popped when doing `extract_model_from_parallel`
|
||||
# Note: creates an infinite recursion loop with `generate`
|
||||
model_forward = MethodType(forward, model)
|
||||
forward.__wrapped__ = model_forward
|
||||
model.forward = forward
|
||||
return model
|
||||
@ -69,6 +69,7 @@ class LocalSGD:
|
||||
DistributedType.NO,
|
||||
DistributedType.MULTI_CPU,
|
||||
DistributedType.MULTI_GPU,
|
||||
DistributedType.MULTI_NPU,
|
||||
]:
|
||||
raise NotImplementedError("LocalSGD is supported only for CPUs and GPUs (no DeepSpeed or MegatronLM)")
|
||||
self.enabled = enabled and accelerator.distributed_type != DistributedType.NO
|
||||
|
||||
@ -180,6 +180,9 @@ class PartialState:
|
||||
if is_xpu_available and is_ccl_available():
|
||||
# Set DeepSpeed backend to ccl for xpu
|
||||
self.backend = "ccl"
|
||||
os.environ["CCL_PROCESS_LAUNCHER"] = "none"
|
||||
os.environ["CCL_LOCAL_SIZE"] = os.environ.get("LOCAL_WORLD_SIZE", "1")
|
||||
os.environ["CCL_LOCAL_RANK"] = os.environ.get("LOCAL_RANK", "0")
|
||||
elif is_npu_available():
|
||||
self.backend = "hccl"
|
||||
else:
|
||||
@ -269,12 +272,19 @@ class PartialState:
|
||||
["LOCAL_RANK", "MPI_LOCALRANKID", "OMPI_COMM_WORLD_LOCAL_RANK", "MV2_COMM_WORLD_LOCAL_RANK"], 0
|
||||
)
|
||||
local_size = get_int_from_env(
|
||||
["MPI_LOCALNRANKS", "OMPI_COMM_WORLD_LOCAL_SIZE", "MV2_COMM_WORLD_LOCAL_SIZE"], 1
|
||||
["LOCAL_WORLD_SIZE", "MPI_LOCALNRANKS", "OMPI_COMM_WORLD_LOCAL_SIZE", "MV2_COMM_WORLD_LOCAL_SIZE"],
|
||||
1,
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.local_process_index = local_rank
|
||||
os.environ["RANK"] = str(rank)
|
||||
os.environ["WORLD_SIZE"] = str(size)
|
||||
os.environ["LOCAL_RANK"] = str(local_rank)
|
||||
os.environ["LOCAL_WORLD_SIZE"] = str(local_size)
|
||||
|
||||
if backend == "ccl" and self.distributed_type == DistributedType.MULTI_XPU:
|
||||
os.environ["CCL_PROCESS_LAUNCHER"] = "none"
|
||||
os.environ["CCL_LOCAL_SIZE"] = str(local_size)
|
||||
os.environ["CCL_LOCAL_RANK"] = str(local_rank)
|
||||
if not os.environ.get("MASTER_PORT", None):
|
||||
os.environ["MASTER_PORT"] = "29500"
|
||||
if not os.environ.get("MASTER_ADDR", None):
|
||||
|
||||
@ -3,6 +3,7 @@ from .testing import (
|
||||
assert_exception,
|
||||
device_count,
|
||||
execute_subprocess_async,
|
||||
memory_allocated_func,
|
||||
require_bnb,
|
||||
require_cpu,
|
||||
require_cuda,
|
||||
@ -12,6 +13,9 @@ from .testing import (
|
||||
require_multi_gpu,
|
||||
require_multi_xpu,
|
||||
require_non_cpu,
|
||||
require_non_xpu,
|
||||
require_npu,
|
||||
require_pippy,
|
||||
require_single_device,
|
||||
require_single_gpu,
|
||||
require_single_xpu,
|
||||
|
||||
130
src/accelerate/test_utils/scripts/external_deps/test_pippy.py
Normal file
130
src/accelerate/test_utils/scripts/external_deps/test_pippy.py
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,130 @@
|
||||
# coding=utf-8
|
||||
# Copyright 2024 The HuggingFace Inc. team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
#
|
||||
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
#
|
||||
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from torchvision.models import resnet34
|
||||
from transformers import (
|
||||
BertConfig,
|
||||
BertForMaskedLM,
|
||||
GPT2Config,
|
||||
GPT2ForSequenceClassification,
|
||||
T5Config,
|
||||
T5ForConditionalGeneration,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
from accelerate import PartialState
|
||||
from accelerate.inference import prepare_pippy
|
||||
from accelerate.utils import DistributedType, send_to_device, set_seed
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
model_to_config = {
|
||||
"t5": (T5ForConditionalGeneration, T5Config, 1024),
|
||||
"bert": (BertForMaskedLM, BertConfig, 512),
|
||||
"gpt2": (GPT2ForSequenceClassification, GPT2Config, 1024),
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def get_model_and_data_for_text(model_name, device, num_processes: int = 2):
|
||||
initializer, config, seq_len = model_to_config[model_name]
|
||||
config_args = {}
|
||||
# Eventually needed for batch inference tests on gpt-2 when bs != 1
|
||||
# if model_name == "gpt2":
|
||||
# config_args["pad_token_id"] = 0
|
||||
model_config = config(**config_args)
|
||||
model = initializer(model_config)
|
||||
return model, torch.randint(
|
||||
low=0,
|
||||
high=model_config.vocab_size,
|
||||
size=(num_processes, seq_len),
|
||||
device=device,
|
||||
dtype=torch.int64,
|
||||
requires_grad=False,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def test_gpt2(batch_size: int = 2):
|
||||
set_seed(42)
|
||||
state = PartialState()
|
||||
model, inputs = get_model_and_data_for_text("gpt2", "cpu", batch_size)
|
||||
model = prepare_pippy(model, example_args=(inputs,), no_split_module_classes=model._no_split_modules)
|
||||
# For inference args need to be a tuple
|
||||
inputs = inputs.to("cuda")
|
||||
with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
output = model(inputs)
|
||||
# Zach: Check that we just grab the real outputs we need at the end
|
||||
if not state.is_last_process:
|
||||
assert output is None, "Output was not generated on just the last process!"
|
||||
else:
|
||||
assert output is not None, "Output was not generated in the last process!"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def test_t5(batch_size: int = 2):
|
||||
set_seed(42)
|
||||
state = PartialState()
|
||||
model, inputs = get_model_and_data_for_text("t5", "cpu", batch_size)
|
||||
example_inputs = {"input_ids": inputs, "decoder_input_ids": inputs}
|
||||
model = prepare_pippy(
|
||||
model,
|
||||
no_split_module_classes=model._no_split_modules,
|
||||
example_kwargs=example_inputs,
|
||||
)
|
||||
# For inference args need to be a tuple
|
||||
inputs = send_to_device(example_inputs, "cuda:0")
|
||||
with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
output = model(*inputs.values())
|
||||
# Zach: Check that we just grab the real outputs we need at the end
|
||||
if not state.is_last_process:
|
||||
assert output is None, "Output was not generated on just the last process!"
|
||||
else:
|
||||
assert output is not None, "Output was not generated in the last process!"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def test_resnet(batch_size: int = 2):
|
||||
set_seed(42)
|
||||
state = PartialState()
|
||||
model = resnet34()
|
||||
input_tensor = torch.rand(batch_size, 3, 224, 224)
|
||||
model = prepare_pippy(
|
||||
model,
|
||||
example_args=(input_tensor,),
|
||||
)
|
||||
inputs = send_to_device(input_tensor, "cuda:0")
|
||||
with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
output = model(inputs)
|
||||
# Zach: Check that we just grab the real outputs we need at the end
|
||||
if not state.is_last_process:
|
||||
assert output is None, "Output was not generated on just the last process!"
|
||||
else:
|
||||
assert output is not None, "Output was not generated in the last process!"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
state = PartialState()
|
||||
state.print("Testing pippy integration...")
|
||||
if state.distributed_type == DistributedType.MULTI_GPU:
|
||||
state.print("Testing GPT2...")
|
||||
test_gpt2()
|
||||
# Issue: When modifying the tokenizer for batch GPT2 inference, there's an issue
|
||||
# due to references
|
||||
# NameError: cannot access free variable 'chunk_args_list' where it is not associated with a value in enclosing scope
|
||||
# test_gpt2(3)
|
||||
state.print("Testing T5...")
|
||||
test_t5()
|
||||
test_t5(1)
|
||||
test_t5(3)
|
||||
state.print("Testing CV model...")
|
||||
test_resnet()
|
||||
test_resnet(3)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
print("Less than two GPUs found, not running tests!")
|
||||
@ -22,6 +22,7 @@ from accelerate.utils.dataclasses import DistributedType
|
||||
from accelerate.utils.operations import (
|
||||
DistributedOperationException,
|
||||
broadcast,
|
||||
copy_tensor_to_devices,
|
||||
gather,
|
||||
gather_object,
|
||||
pad_across_processes,
|
||||
@ -129,6 +130,17 @@ def test_op_checker(state):
|
||||
state.debug = False
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def test_copy_tensor_to_devices(state):
|
||||
if state.distributed_type not in [DistributedType.MULTI_GPU, DistributedType.TPU]:
|
||||
return
|
||||
if state.is_main_process:
|
||||
tensor = torch.tensor([1, 2, 3], dtype=torch.int).to(state.device)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
tensor = None
|
||||
tensor = copy_tensor_to_devices(tensor)
|
||||
assert torch.allclose(tensor, torch.tensor([1, 2, 3], dtype=torch.int, device="cuda"))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _mp_fn(index):
|
||||
# For xla_spawn (TPUs)
|
||||
main()
|
||||
@ -153,6 +165,8 @@ def main():
|
||||
test_reduce_mean(state)
|
||||
state.print("testing op_checker")
|
||||
test_op_checker(state)
|
||||
state.print("testing sending tensors across devices")
|
||||
test_copy_tensor_to_devices(state)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
|
||||
@ -40,6 +40,7 @@ from ..utils import (
|
||||
is_mps_available,
|
||||
is_npu_available,
|
||||
is_pandas_available,
|
||||
is_pippy_available,
|
||||
is_tensorboard_available,
|
||||
is_timm_available,
|
||||
is_torch_version,
|
||||
@ -53,18 +54,18 @@ from ..utils import (
|
||||
|
||||
def get_backend():
|
||||
if is_cuda_available():
|
||||
return "cuda", torch.cuda.device_count()
|
||||
return "cuda", torch.cuda.device_count(), torch.cuda.memory_allocated
|
||||
elif is_mps_available():
|
||||
return "mps", 1
|
||||
return "mps", 1, torch.mps.current_allocated_memory()
|
||||
elif is_npu_available():
|
||||
return "npu", torch.npu.device_count()
|
||||
return "npu", torch.npu.device_count(), torch.npu.memory_allocated
|
||||
elif is_xpu_available():
|
||||
return "xpu", torch.xpu.device_count()
|
||||
return "xpu", torch.xpu.device_count(), torch.xpu.memory_allocated
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return "cpu", 1
|
||||
return "cpu", 1, 0
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
torch_device, device_count = get_backend()
|
||||
torch_device, device_count, memory_allocated_func = get_backend()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def parse_flag_from_env(key, default=False):
|
||||
@ -128,6 +129,20 @@ def require_xpu(test_case):
|
||||
return unittest.skipUnless(is_xpu_available(), "test requires a XPU")(test_case)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def require_non_xpu(test_case):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Decorator marking a test that should be skipped for XPU.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return unittest.skipUnless(torch_device != "xpu", "test requires a non-XPU")(test_case)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def require_npu(test_case):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Decorator marking a test that requires NPU. These tests are skipped when there are no NPU available.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return unittest.skipUnless(is_npu_available(), "test require a NPU")(test_case)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def require_mps(test_case):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Decorator marking a test that requires MPS backend. These tests are skipped when torch doesn't support `mps`
|
||||
@ -290,6 +305,13 @@ def require_pandas(test_case):
|
||||
return unittest.skipUnless(is_pandas_available(), "test requires pandas")(test_case)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def require_pippy(test_case):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Decorator marking a test that requires pippy installed. These tests are skipped when pippy isn't installed
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return unittest.skipUnless(is_pippy_available(), "test requires pippy")(test_case)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
_atleast_one_tracker_available = (
|
||||
any([is_wandb_available(), is_tensorboard_available()]) and not is_comet_ml_available()
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -69,6 +69,8 @@ from .imports import (
|
||||
is_msamp_available,
|
||||
is_npu_available,
|
||||
is_pandas_available,
|
||||
is_peft_available,
|
||||
is_pippy_available,
|
||||
is_rich_available,
|
||||
is_sagemaker_available,
|
||||
is_tensorboard_available,
|
||||
@ -94,6 +96,7 @@ from .modeling import (
|
||||
get_mixed_precision_context_manager,
|
||||
id_tensor_storage,
|
||||
infer_auto_device_map,
|
||||
is_peft_model,
|
||||
load_checkpoint_in_model,
|
||||
load_offloaded_weights,
|
||||
load_state_dict,
|
||||
@ -118,18 +121,21 @@ from .operations import (
|
||||
concatenate,
|
||||
convert_outputs_to_fp32,
|
||||
convert_to_fp32,
|
||||
copy_tensor_to_devices,
|
||||
find_batch_size,
|
||||
find_device,
|
||||
gather,
|
||||
gather_object,
|
||||
get_data_structure,
|
||||
honor_type,
|
||||
ignorant_find_batch_size,
|
||||
initialize_tensors,
|
||||
is_namedtuple,
|
||||
is_tensor_information,
|
||||
is_torch_tensor,
|
||||
listify,
|
||||
pad_across_processes,
|
||||
pad_input_tensors,
|
||||
recursively_apply,
|
||||
reduce,
|
||||
send_to_device,
|
||||
@ -188,6 +194,7 @@ from .other import (
|
||||
is_port_in_use,
|
||||
merge_dicts,
|
||||
patch_environment,
|
||||
recursive_getattr,
|
||||
save,
|
||||
wait_for_everyone,
|
||||
write_basic_config,
|
||||
|
||||
@ -170,7 +170,7 @@ class InitProcessGroupKwargs(KwargsHandler):
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Literals
|
||||
Backend = Literal["msamp", "te"]
|
||||
Backend = Literal["MSAMP", "TE"]
|
||||
OptLevel = Literal["O1", "O2"]
|
||||
FP8Format = Literal["E4M3", "HYBRID"]
|
||||
AmaxComputeAlgorithm = Literal["max", "most_recent"]
|
||||
@ -233,7 +233,7 @@ class FP8RecipeKwargs(KwargsHandler):
|
||||
available currently).
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
backend: Backend = "msamp"
|
||||
backend: Backend = "MSAMP"
|
||||
opt_level: OptLevel = "O2"
|
||||
margin: int = 0
|
||||
interval: int = 1
|
||||
@ -243,9 +243,10 @@ class FP8RecipeKwargs(KwargsHandler):
|
||||
override_linear_precision: Tuple[bool, bool, bool] = (False, False, False)
|
||||
|
||||
def __post_init__(self):
|
||||
self.backend = self.backend.upper()
|
||||
if self.backend not in get_args(Backend):
|
||||
if self.backend.upper() not in get_args(Backend):
|
||||
raise ValueError("`backend` must be 'MSAMP' or 'TE' (TransformerEngine).")
|
||||
|
||||
self.backend = self.backend.upper()
|
||||
# Check TE args
|
||||
if self.backend == "TE":
|
||||
self.fp8_format = self.fp8_format.upper()
|
||||
|
||||
@ -16,7 +16,7 @@ import os
|
||||
import platform
|
||||
import subprocess
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
from distutils import spawn
|
||||
from shutil import which
|
||||
from typing import Dict
|
||||
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
@ -72,8 +72,8 @@ def get_gpu_info():
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if platform.system() == "Windows":
|
||||
# If platform is Windows and nvidia-smi can't be found in path
|
||||
# try from systemd rive with default installation path
|
||||
command = spawn.find_executable("nvidia-smi")
|
||||
# try from systemd drive with default installation path
|
||||
command = which("nvidia-smi")
|
||||
if command is None:
|
||||
command = "%s\\Program Files\\NVIDIA Corporation\\NVSMI\\nvidia-smi.exe" % os.environ["systemdrive"]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -18,6 +18,7 @@ import torch
|
||||
from ..logging import get_logger
|
||||
from .constants import FSDP_MODEL_NAME, FSDP_PYTORCH_VERSION, OPTIMIZER_NAME
|
||||
from .imports import is_torch_distributed_available
|
||||
from .modeling import is_peft_model
|
||||
from .versions import is_torch_version
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -32,7 +33,25 @@ if is_torch_version(">=", FSDP_PYTORCH_VERSION) and is_torch_distributed_availab
|
||||
logger = get_logger(__name__)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def save_fsdp_model(fsdp_plugin, accelerator, model, output_dir, model_index=0):
|
||||
def _get_model_state_dict(model, adapter_only=False):
|
||||
if adapter_only and is_peft_model(model):
|
||||
from peft import get_peft_model_state_dict
|
||||
|
||||
return get_peft_model_state_dict(model, adapter_name=model.active_adapter)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return model.state_dict()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _set_model_state_dict(model, state_dict, adapter_only=False):
|
||||
if adapter_only and is_peft_model(model):
|
||||
from peft import set_peft_model_state_dict
|
||||
|
||||
return set_peft_model_state_dict(model, state_dict, adapter_name=model.active_adapter)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return model.load_state_dict(state_dict)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def save_fsdp_model(fsdp_plugin, accelerator, model, output_dir, model_index=0, adapter_only=False):
|
||||
os.makedirs(output_dir, exist_ok=True)
|
||||
|
||||
if fsdp_plugin.state_dict_type == StateDictType.FULL_STATE_DICT:
|
||||
@ -45,7 +64,7 @@ def save_fsdp_model(fsdp_plugin, accelerator, model, output_dir, model_index=0):
|
||||
with FSDP.state_dict_type(
|
||||
model, fsdp_plugin.state_dict_type, fsdp_plugin.state_dict_config, fsdp_plugin.optim_state_dict_config
|
||||
):
|
||||
state_dict = model.state_dict()
|
||||
state_dict = _get_model_state_dict(model, adapter_only=adapter_only)
|
||||
if fsdp_plugin.state_dict_type == StateDictType.FULL_STATE_DICT:
|
||||
weights_name = f"{FSDP_MODEL_NAME}.bin" if model_index == 0 else f"{FSDP_MODEL_NAME}_{model_index}.bin"
|
||||
output_model_file = os.path.join(output_dir, weights_name)
|
||||
@ -77,7 +96,7 @@ def save_fsdp_model(fsdp_plugin, accelerator, model, output_dir, model_index=0):
|
||||
logger.info(f"Model saved to {ckpt_dir}")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def load_fsdp_model(fsdp_plugin, accelerator, model, input_dir, model_index=0):
|
||||
def load_fsdp_model(fsdp_plugin, accelerator, model, input_dir, model_index=0, adapter_only=False):
|
||||
accelerator.wait_for_everyone()
|
||||
if fsdp_plugin.state_dict_type == StateDictType.FULL_STATE_DICT:
|
||||
# FSDP raises error when single GPU is used with `offload_to_cpu=True` for FULL_STATE_DICT
|
||||
@ -118,7 +137,7 @@ def load_fsdp_model(fsdp_plugin, accelerator, model, input_dir, model_index=0):
|
||||
else input_dir
|
||||
)
|
||||
logger.info(f"Loading model from {ckpt_dir}")
|
||||
state_dict = {"model": model.state_dict()}
|
||||
state_dict = {"model": _get_model_state_dict(model, adapter_only=adapter_only)}
|
||||
dist_cp.load_state_dict(
|
||||
state_dict=state_dict,
|
||||
storage_reader=dist_cp.FileSystemReader(ckpt_dir),
|
||||
@ -126,7 +145,7 @@ def load_fsdp_model(fsdp_plugin, accelerator, model, input_dir, model_index=0):
|
||||
)
|
||||
state_dict = state_dict["model"]
|
||||
logger.info(f"Model loaded from {ckpt_dir}")
|
||||
load_result = model.load_state_dict(state_dict)
|
||||
load_result = _set_model_state_dict(model, state_dict, adapter_only=adapter_only)
|
||||
return load_result
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -157,7 +176,7 @@ def save_fsdp_optimizer(fsdp_plugin, accelerator, optimizer, model, output_dir,
|
||||
logger.info(f"Optimizer state saved in {ckpt_dir}")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def load_fsdp_optimizer(fsdp_plugin, accelerator, optimizer, model, input_dir, optimizer_index=0):
|
||||
def load_fsdp_optimizer(fsdp_plugin, accelerator, optimizer, model, input_dir, optimizer_index=0, adapter_only=False):
|
||||
accelerator.wait_for_everyone()
|
||||
with FSDP.state_dict_type(
|
||||
model, fsdp_plugin.state_dict_type, fsdp_plugin.state_dict_config, fsdp_plugin.optim_state_dict_config
|
||||
@ -180,7 +199,7 @@ def load_fsdp_optimizer(fsdp_plugin, accelerator, optimizer, model, input_dir, o
|
||||
)
|
||||
logger.info(f"Loading Optimizer from {ckpt_dir}")
|
||||
optim_state = load_sharded_optimizer_state_dict(
|
||||
model_state_dict=model.state_dict(),
|
||||
model_state_dict=_get_model_state_dict(model, adapter_only=adapter_only),
|
||||
optimizer_key="optimizer",
|
||||
storage_reader=dist_cp.FileSystemReader(ckpt_dir),
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -38,12 +38,13 @@ except ImportError:
|
||||
_torch_distributed_available = torch.distributed.is_available()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _is_package_available(pkg_name):
|
||||
def _is_package_available(pkg_name, metadata_name=None):
|
||||
# Check we're not importing a "pkg_name" directory somewhere but the actual library by trying to grab the version
|
||||
package_exists = importlib.util.find_spec(pkg_name) is not None
|
||||
if package_exists:
|
||||
try:
|
||||
_ = importlib.metadata.metadata(pkg_name)
|
||||
# Some libraries have different names in the metadata
|
||||
_ = importlib.metadata.metadata(pkg_name if metadata_name is None else metadata_name)
|
||||
return True
|
||||
except importlib.metadata.PackageNotFoundError:
|
||||
return False
|
||||
@ -73,15 +74,7 @@ def get_ccl_version():
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def is_msamp_available():
|
||||
package_exists = importlib.util.find_spec("msamp") is not None
|
||||
if package_exists:
|
||||
try:
|
||||
# MS-AMP has a different metadata name
|
||||
_ = importlib.metadata.metadata("ms-amp")
|
||||
return True
|
||||
except importlib.metadata.PackageNotFoundError:
|
||||
return False
|
||||
return False
|
||||
return _is_package_available("msamp", "ms-amp")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def is_transformer_engine_available():
|
||||
@ -126,6 +119,14 @@ def is_deepspeed_available():
|
||||
return _is_package_available("deepspeed")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def is_pippy_available():
|
||||
package_exists = _is_package_available("pippy", "torchpippy")
|
||||
if package_exists:
|
||||
pippy_version = version.parse(importlib.metadata.version("torchpippy"))
|
||||
return compare_versions(pippy_version, ">", "0.1.1")
|
||||
return False
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def is_bf16_available(ignore_tpu=False):
|
||||
"Checks if bf16 is supported, optionally ignoring the TPU"
|
||||
if is_tpu_available():
|
||||
@ -175,6 +176,10 @@ def is_datasets_available():
|
||||
return _is_package_available("datasets")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def is_peft_available():
|
||||
return _is_package_available("peft")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def is_timm_available():
|
||||
return _is_package_available("timm")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -846,9 +846,7 @@ def initialize(accelerator, extra_args_provider=None, args_defaults={}):
|
||||
if args.rank == 0:
|
||||
print(
|
||||
"WARNING: overriding default arguments for {key}:{v} \
|
||||
with {key}:{v2}".format(
|
||||
key=key, v=getattr(args, key), v2=value
|
||||
),
|
||||
with {key}:{v2}".format(key=key, v=getattr(args, key), v2=value),
|
||||
flush=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
setattr(args, key, value)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -14,6 +14,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
import contextlib
|
||||
import gc
|
||||
import importlib
|
||||
import inspect
|
||||
import json
|
||||
import logging
|
||||
@ -24,15 +25,17 @@ import tempfile
|
||||
from collections import OrderedDict, defaultdict
|
||||
from typing import Dict, List, Optional, Tuple, Union
|
||||
|
||||
import packaging
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
import torch.nn as nn
|
||||
|
||||
from ..state import AcceleratorState
|
||||
from .constants import SAFE_WEIGHTS_NAME, WEIGHTS_NAME
|
||||
from .dataclasses import AutocastKwargs, CustomDtype, DistributedType
|
||||
from .imports import is_mps_available, is_npu_available, is_xpu_available
|
||||
from .imports import is_mps_available, is_npu_available, is_peft_available, is_xpu_available
|
||||
from .offload import load_offloaded_weight, offload_weight, save_offload_index
|
||||
from .tqdm import is_tqdm_available, tqdm
|
||||
from .versions import compare_versions
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if is_npu_available(check_device=False):
|
||||
@ -47,6 +50,15 @@ WEIGHTS_INDEX_NAME = "pytorch_model.bin.index.json"
|
||||
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def is_peft_model(model):
|
||||
from .other import extract_model_from_parallel
|
||||
|
||||
if is_peft_available():
|
||||
from peft import PeftModel
|
||||
|
||||
return is_peft_available() and isinstance(extract_model_from_parallel(model), PeftModel)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def check_device_same(first_device, second_device):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Utility method to check if two `torch` devices are similar. When dealing with CUDA devices, torch throws `False`
|
||||
@ -267,6 +279,7 @@ def set_module_tensor_to_device(
|
||||
value: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
|
||||
dtype: Optional[Union[str, torch.dtype]] = None,
|
||||
fp16_statistics: Optional[torch.HalfTensor] = None,
|
||||
tied_params_map: Optional[Dict[int, Dict[torch.device, torch.Tensor]]] = None,
|
||||
):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
A helper function to set a given tensor (parameter of buffer) of a module on a specific device (note that doing
|
||||
@ -286,6 +299,10 @@ def set_module_tensor_to_device(
|
||||
the dtype of the existing parameter in the model.
|
||||
fp16_statistics (`torch.HalfTensor`, *optional*):
|
||||
The list of fp16 statistics to set on the module, used for 8 bit model serialization.
|
||||
tied_params_map (Dict[int, Dict[torch.device, torch.Tensor]], *optional*, defaults to `None`):
|
||||
A map of current data pointers to dictionaries of devices to already dispatched tied weights. For a given
|
||||
execution device, this parameter is useful to reuse the first available pointer of a shared weight on the
|
||||
device for all others, instead of duplicating memory.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
# Recurse if needed
|
||||
if "." in tensor_name:
|
||||
@ -302,6 +319,24 @@ def set_module_tensor_to_device(
|
||||
is_buffer = tensor_name in module._buffers
|
||||
old_value = getattr(module, tensor_name)
|
||||
|
||||
# Treat the case where old_value (or a custom `value`, typically offloaded to RAM/disk) belongs to a tied group, and one of the weight
|
||||
# in the tied group has already been dispatched to the device, by avoiding reallocating memory on the device and just copying the pointer.
|
||||
if (
|
||||
value is not None
|
||||
and tied_params_map is not None
|
||||
and value.data_ptr() in tied_params_map
|
||||
and device in tied_params_map[value.data_ptr()]
|
||||
):
|
||||
module._parameters[tensor_name] = tied_params_map[value.data_ptr()][device]
|
||||
return
|
||||
elif (
|
||||
tied_params_map is not None
|
||||
and old_value.data_ptr() in tied_params_map
|
||||
and device in tied_params_map[old_value.data_ptr()]
|
||||
):
|
||||
module._parameters[tensor_name] = tied_params_map[old_value.data_ptr()][device]
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
||||
if old_value.device == torch.device("meta") and device not in ["meta", torch.device("meta")] and value is None:
|
||||
raise ValueError(f"{tensor_name} is on the meta device, we need a `value` to put in on {device}.")
|
||||
|
||||
@ -335,6 +370,8 @@ def set_module_tensor_to_device(
|
||||
# `torch.Tensor.to(<int num>)` is not supported by `torch_npu` (see this [issue](https://github.com/Ascend/pytorch/issues/16)).
|
||||
if is_npu_available() and isinstance(device, int):
|
||||
device = f"npu:{device}"
|
||||
if is_xpu_available() and isinstance(device, int):
|
||||
device = f"xpu:{device}"
|
||||
if value is None:
|
||||
new_value = old_value.to(device)
|
||||
if dtype is not None and device in ["meta", torch.device("meta")]:
|
||||
@ -367,6 +404,7 @@ def set_module_tensor_to_device(
|
||||
new_value = param_cls(new_value, requires_grad=old_value.requires_grad, **kwargs).to(device)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
new_value = param_cls(new_value, requires_grad=old_value.requires_grad).to(device)
|
||||
|
||||
module._parameters[tensor_name] = new_value
|
||||
if fp16_statistics is not None:
|
||||
setattr(module._parameters[tensor_name], "SCB", fp16_statistics.to(device))
|
||||
@ -394,9 +432,27 @@ def set_module_tensor_to_device(
|
||||
# clean pre and post foward hook
|
||||
if is_npu_available():
|
||||
torch.npu.empty_cache()
|
||||
elif is_xpu_available():
|
||||
torch.xpu.empty_cache()
|
||||
else:
|
||||
torch.cuda.empty_cache()
|
||||
|
||||
# When handling tied weights, we update tied_params_map to keep track of the tied weights that have already been allocated on the device in
|
||||
# order to avoid duplicating memory, see above.
|
||||
if (
|
||||
tied_params_map is not None
|
||||
and old_value.data_ptr() in tied_params_map
|
||||
and device not in tied_params_map[old_value.data_ptr()]
|
||||
):
|
||||
tied_params_map[old_value.data_ptr()][device] = new_value
|
||||
elif (
|
||||
value is not None
|
||||
and tied_params_map is not None
|
||||
and value.data_ptr() in tied_params_map
|
||||
and device not in tied_params_map[value.data_ptr()]
|
||||
):
|
||||
tied_params_map[value.data_ptr()][device] = new_value
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def named_module_tensors(
|
||||
module: nn.Module, include_buffers: bool = True, recurse: bool = False, remove_non_persistent: bool = False
|
||||
@ -647,6 +703,10 @@ def compute_module_sizes(
|
||||
size = tensor.numel() * special_dtypes_size[name]
|
||||
elif dtype is None:
|
||||
size = tensor.numel() * dtype_byte_size(tensor.dtype)
|
||||
elif str(tensor.dtype).startswith(("torch.uint", "torch.int", "torch.bool")):
|
||||
# According to the code in set_module_tensor_to_device, these types won't be converted
|
||||
# so use their original size here
|
||||
size = tensor.numel() * dtype_byte_size(tensor.dtype)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
size = tensor.numel() * min(dtype_size, dtype_byte_size(tensor.dtype))
|
||||
name_parts = name.split(".")
|
||||
@ -832,6 +892,7 @@ def get_balanced_memory(
|
||||
The model to analyze.
|
||||
max_memory (`Dict`, *optional*):
|
||||
A dictionary device identifier to maximum memory. Will default to the maximum memory available if unset.
|
||||
Example: `max_memory={0: "1GB"}`.
|
||||
no_split_module_classes (`List[str]`, *optional*):
|
||||
A list of layer class names that should never be split across device (for instance any layer that has a
|
||||
residual connection).
|
||||
@ -989,6 +1050,7 @@ def infer_auto_device_map(
|
||||
The model to analyze.
|
||||
max_memory (`Dict`, *optional*):
|
||||
A dictionary device identifier to maximum memory. Will default to the maximum memory available if unset.
|
||||
Example: `max_memory={0: "1GB"}`.
|
||||
no_split_module_classes (`List[str]`, *optional*):
|
||||
A list of layer class names that should never be split across device (for instance any layer that has a
|
||||
residual connection).
|
||||
@ -1300,7 +1362,20 @@ def load_state_dict(checkpoint_file, device_map=None):
|
||||
else:
|
||||
progress_bar = None
|
||||
for device in devices:
|
||||
with safe_open(checkpoint_file, framework="pt", device=device) as f:
|
||||
target_device = device
|
||||
|
||||
if is_xpu_available():
|
||||
current_safetensors_version = packaging.version.parse(importlib.metadata.version("safetensors"))
|
||||
|
||||
if compare_versions(current_safetensors_version, "<", "0.4.2"):
|
||||
raise ModuleNotFoundError(
|
||||
f"You need at least safetensors 0.4.2 for Intel GPU, while you have {current_safetensors_version}"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if isinstance(device, int):
|
||||
target_device = f"xpu:{device}"
|
||||
|
||||
with safe_open(checkpoint_file, framework="pt", device=target_device) as f:
|
||||
for key in device_weights[device]:
|
||||
if progress_bar is not None:
|
||||
progress_bar.set_postfix(dev=device, refresh=False)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -26,7 +26,13 @@ import torch
|
||||
from ..state import PartialState
|
||||
from .constants import TORCH_DISTRIBUTED_OPERATION_TYPES
|
||||
from .dataclasses import DistributedType, TensorInformation
|
||||
from .imports import is_npu_available, is_torch_distributed_available, is_torch_version, is_tpu_available
|
||||
from .imports import (
|
||||
is_npu_available,
|
||||
is_torch_distributed_available,
|
||||
is_torch_version,
|
||||
is_tpu_available,
|
||||
is_xpu_available,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if is_tpu_available(check_device=False):
|
||||
@ -164,9 +170,18 @@ def send_to_device(tensor, device, non_blocking=False, skip_keys=None):
|
||||
}
|
||||
)
|
||||
elif hasattr(tensor, "to"):
|
||||
# `torch.Tensor.to(<int num>)` is not supported by `torch_npu` (see this [issue](https://github.com/Ascend/pytorch/issues/16)).
|
||||
if is_npu_available() and isinstance(device, int):
|
||||
device = f"npu:{device}"
|
||||
if is_npu_available():
|
||||
# `torch.Tensor.to(<int num>)` is not supported by `torch_npu` (see this [issue](https://github.com/Ascend/pytorch/issues/16)).
|
||||
if isinstance(device, int):
|
||||
device = f"npu:{device}"
|
||||
# `torch.Tensor.to("npu")` could not find context when called for the first time (see this [issue](https://gitee.com/ascend/pytorch/issues/I8KECW?from=project-issue)).
|
||||
elif device == torch.device("npu"):
|
||||
device = "npu:0"
|
||||
elif is_xpu_available():
|
||||
if isinstance(device, int):
|
||||
device = f"xpu:{device}"
|
||||
elif device == torch.device("xpu"):
|
||||
device = "xpu:0"
|
||||
try:
|
||||
return tensor.to(device, non_blocking=non_blocking)
|
||||
except TypeError: # .to() doesn't accept non_blocking as kwarg
|
||||
@ -248,6 +263,23 @@ def find_batch_size(data):
|
||||
return data.shape[0]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def ignorant_find_batch_size(data):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Same as [`utils.operations.find_batch_size`] except will ignore if `ValueError` and `TypeErrors` are raised
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
data (nested list/tuple/dictionary of `torch.Tensor`): The data from which to find the batch size.
|
||||
|
||||
Returns:
|
||||
`int`: The batch size.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
try:
|
||||
return find_batch_size(data)
|
||||
except (ValueError, TypeError):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
return None
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def listify(data):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Recursively finds tensors in a nested list/tuple/dictionary and converts them to a list of numbers.
|
||||
@ -449,6 +481,64 @@ def _tpu_broadcast(tensor, src=0, name="broadcast tensor"):
|
||||
return xm.mesh_reduce(name, tensor, lambda x: x[src])
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
TENSOR_TYPE_TO_INT = {
|
||||
torch.float: 1,
|
||||
torch.double: 2,
|
||||
torch.half: 3,
|
||||
torch.bfloat16: 4,
|
||||
torch.uint8: 5,
|
||||
torch.int8: 6,
|
||||
torch.int16: 7,
|
||||
torch.int32: 8,
|
||||
torch.int64: 9,
|
||||
torch.bool: 10,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
TENSOR_INT_TO_DTYPE = {v: k for k, v in TENSOR_TYPE_TO_INT.items()}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def gather_tensor_shape(tensor):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Grabs the shape of `tensor` only available on one process and returns a tensor of its shape
|
||||
"""
|
||||
# Allocate 80 bytes to store the shape
|
||||
max_tensor_dimension = 2**20
|
||||
state = PartialState()
|
||||
base_tensor = torch.empty(max_tensor_dimension, dtype=torch.int, device=state.device)
|
||||
|
||||
# Since PyTorch can't just send a tensor to another GPU without
|
||||
# knowing its size, we store the size of the tensor with data
|
||||
# in an allocation
|
||||
if tensor is not None:
|
||||
shape = tensor.shape
|
||||
tensor_dtype = TENSOR_TYPE_TO_INT[tensor.dtype]
|
||||
base_tensor[: len(shape) + 1] = torch.tensor(list(shape) + [tensor_dtype], dtype=int)
|
||||
# Perform a reduction to copy the size data onto all GPUs
|
||||
base_tensor = reduce(base_tensor, reduction="sum")
|
||||
base_tensor = base_tensor[base_tensor.nonzero()]
|
||||
# The last non-zero data contains the coded dtype the source tensor is
|
||||
dtype = int(base_tensor[-1:][0])
|
||||
base_tensor = base_tensor[:-1]
|
||||
return base_tensor, dtype
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def copy_tensor_to_devices(tensor=None) -> torch.Tensor:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Copys a tensor that only exists on a single device and broadcasts it to other devices. Differs from `broadcast` as
|
||||
each worker doesn't need to know its shape when used (and tensor can be `None`)
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
tensor (`torch.tensor`):
|
||||
The tensor that should be sent to all devices. Must only have it be defined on a single device, the rest
|
||||
should be `None`.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
state = PartialState()
|
||||
shape, dtype = gather_tensor_shape(tensor)
|
||||
if tensor is None:
|
||||
tensor = torch.zeros(shape, dtype=TENSOR_INT_TO_DTYPE[dtype]).to(state.device)
|
||||
return reduce(tensor, reduction="sum")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@verify_operation
|
||||
def broadcast(tensor, from_process: int = 0):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
@ -591,6 +681,46 @@ def pad_across_processes(tensor, dim=0, pad_index=0, pad_first=False):
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def pad_input_tensors(tensor, batch_size, num_processes, dim=0):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Takes a `tensor` of arbitrary size and pads it so that it can work given `num_processes` needed dimensions.
|
||||
|
||||
New tensors are just the last input repeated.
|
||||
|
||||
E.g.:
|
||||
Tensor: ([3,4,4]) Num processes: 4 Expected result shape: ([4,4,4])
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
def _pad_input_tensors(tensor, batch_size, num_processes, dim=0):
|
||||
remainder = batch_size // num_processes
|
||||
last_inputs = batch_size - (remainder * num_processes)
|
||||
if batch_size // num_processes == 0:
|
||||
to_pad = num_processes - batch_size
|
||||
else:
|
||||
to_pad = num_processes - (batch_size // num_processes)
|
||||
# In the rare case that `to_pad` is negative,
|
||||
# we need to pad the last inputs - the found `to_pad`
|
||||
if last_inputs > to_pad & to_pad < 1:
|
||||
to_pad = last_inputs - to_pad
|
||||
old_size = tensor.shape
|
||||
new_size = list(old_size)
|
||||
new_size[0] = batch_size + to_pad
|
||||
new_tensor = tensor.new_zeros(tuple(new_size))
|
||||
indices = tuple(slice(0, old_size[dim]) if i == dim else slice(None) for i in range(len(new_size)))
|
||||
new_tensor[indices] = tensor
|
||||
return new_tensor
|
||||
|
||||
return recursively_apply(
|
||||
_pad_input_tensors,
|
||||
tensor,
|
||||
error_on_other_type=True,
|
||||
batch_size=batch_size,
|
||||
num_processes=num_processes,
|
||||
dim=dim,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@verify_operation
|
||||
def reduce(tensor, reduction="mean", scale=1.0):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
@ -18,7 +18,7 @@ import platform
|
||||
import re
|
||||
import socket
|
||||
from contextlib import contextmanager
|
||||
from functools import partial
|
||||
from functools import partial, reduce
|
||||
from types import MethodType
|
||||
from typing import OrderedDict
|
||||
|
||||
@ -320,3 +320,20 @@ def check_os_kernel():
|
||||
"cause the process to hang. It is recommended to upgrade the kernel to the minimum version or higher."
|
||||
)
|
||||
logger.warning(msg, main_process_only=True)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def recursive_getattr(obj, attr: str):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Recursive `getattr`.
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
obj:
|
||||
A class instance holding the attribute.
|
||||
attr (`str`):
|
||||
The attribute that is to be retrieved, e.g. 'attribute1.attribute2'.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
def _getattr(obj, attr):
|
||||
return getattr(obj, attr)
|
||||
|
||||
return reduce(_getattr, [obj] + attr.split("."))
|
||||
|
||||
@ -11,8 +11,8 @@ from torch.utils.data import DataLoader, TensorDataset
|
||||
from accelerate import DistributedType, infer_auto_device_map, init_empty_weights, load_checkpoint_and_dispatch
|
||||
from accelerate.accelerator import Accelerator
|
||||
from accelerate.state import GradientState, PartialState
|
||||
from accelerate.test_utils import require_bnb, require_multi_gpu, slow
|
||||
from accelerate.test_utils.testing import AccelerateTestCase, require_cuda
|
||||
from accelerate.test_utils import require_bnb, require_multi_device, require_non_cpu, slow, torch_device
|
||||
from accelerate.test_utils.testing import AccelerateTestCase
|
||||
from accelerate.utils import patch_environment
|
||||
from accelerate.utils.modeling import load_checkpoint_in_model
|
||||
|
||||
@ -55,11 +55,11 @@ def parameterized_custom_name_func(func, param_num, param):
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class AcceleratorTester(AccelerateTestCase):
|
||||
@require_cuda
|
||||
@require_non_cpu
|
||||
def test_accelerator_can_be_reinstantiated(self):
|
||||
_ = Accelerator()
|
||||
assert PartialState._shared_state["_cpu"] is False
|
||||
assert PartialState._shared_state["device"].type == "cuda"
|
||||
assert PartialState._shared_state["device"].type in ["cuda", "mps", "npu", "xpu"]
|
||||
with self.assertRaises(ValueError):
|
||||
_ = Accelerator(cpu=True)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -326,12 +326,17 @@ class AcceleratorTester(AccelerateTestCase):
|
||||
|
||||
@slow
|
||||
@require_bnb
|
||||
@require_multi_gpu
|
||||
def test_accelerator_bnb_multi_gpu(self):
|
||||
@require_multi_device
|
||||
def test_accelerator_bnb_multi_device(self):
|
||||
"""Tests that the accelerator can be used with the BNB library."""
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM
|
||||
|
||||
PartialState._shared_state = {"distributed_type": DistributedType.MULTI_GPU}
|
||||
if torch_device == "cuda":
|
||||
PartialState._shared_state = {"distributed_type": DistributedType.MULTI_GPU}
|
||||
elif torch_device == "npu":
|
||||
PartialState._shared_state = {"distributed_type": DistributedType.MULTI_NPU}
|
||||
else:
|
||||
raise ValueError(f"{torch_device} is not supported in test_accelerator_bnb_multi_device.")
|
||||
|
||||
with init_empty_weights():
|
||||
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
|
||||
@ -356,8 +361,8 @@ class AcceleratorTester(AccelerateTestCase):
|
||||
|
||||
@slow
|
||||
@require_bnb
|
||||
@require_multi_gpu
|
||||
def test_accelerator_bnb_multi_gpu_no_distributed(self):
|
||||
@require_multi_device
|
||||
def test_accelerator_bnb_multi_device_no_distributed(self):
|
||||
"""Tests that the accelerator can be used with the BNB library."""
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM
|
||||
|
||||
@ -378,21 +383,21 @@ class AcceleratorTester(AccelerateTestCase):
|
||||
# This should work
|
||||
_ = accelerator.prepare(model)
|
||||
|
||||
@require_cuda
|
||||
@require_non_cpu
|
||||
def test_accelerator_cpu_flag_prepare(self):
|
||||
model = torch.nn.Linear(10, 10)
|
||||
sgd = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.01)
|
||||
accelerator = Accelerator(cpu=True)
|
||||
_ = accelerator.prepare(sgd)
|
||||
|
||||
@require_cuda
|
||||
@require_non_cpu
|
||||
def test_can_unwrap_model_fp16(self):
|
||||
# test for a regression introduced in #872
|
||||
# before the fix, after unwrapping with keep_fp32_wrapper=False, there would be the following error:
|
||||
# Linear.forward() missing 1 required positional argument: 'input'
|
||||
model = create_components()[0]
|
||||
accelerator = Accelerator(mixed_precision="fp16")
|
||||
inputs = torch.randn(10, 2).cuda()
|
||||
inputs = torch.randn(10, 2).to(torch_device)
|
||||
model = accelerator.prepare(model)
|
||||
model(inputs) # sanity check that this works
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -12,8 +12,10 @@
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
import copy
|
||||
import gc
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import unittest
|
||||
from collections import OrderedDict
|
||||
from tempfile import TemporaryDirectory
|
||||
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
@ -363,6 +365,247 @@ class BigModelingTester(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
dispatch_model(model, device_map)
|
||||
self.assertIs(model.linear2.weight, model.linear1.weight)
|
||||
|
||||
@require_multi_gpu
|
||||
def test_dispatch_model_tied_weights_memory(self):
|
||||
# Test that we do not duplicate tied weights at any point during dispatch_model call.
|
||||
|
||||
torch.cuda.empty_cache() # Needed in case we run several tests in a row.
|
||||
|
||||
model = nn.Sequential(
|
||||
OrderedDict(
|
||||
[
|
||||
("linear0", nn.Linear(5000, 5000, bias=False)),
|
||||
("linear1", nn.Linear(5000, 5000, bias=False)),
|
||||
("linear2", nn.Linear(5000, 5000, bias=False)),
|
||||
("linear3", nn.Linear(5000, 5000, bias=False)),
|
||||
("linear4", nn.Linear(5000, 5000, bias=False)),
|
||||
]
|
||||
)
|
||||
)
|
||||
model.linear2.weight = model.linear0.weight
|
||||
model.linear3.weight = model.linear0.weight
|
||||
model.linear4.weight = model.linear0.weight
|
||||
|
||||
x = torch.randn(5, 5000)
|
||||
with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
expected = model(x)
|
||||
|
||||
# We should need only 5000 * 5000 * 32 // 8 * 1e-6 = 100 MB on the device 0 for the four linear weights.
|
||||
device_map = {"linear0": 0, "linear1": 1, "linear2": 0, "linear3": 0, "linear4": 0}
|
||||
|
||||
# Just to intialize CUDA context.
|
||||
a = torch.rand(5).to("cuda:0") # noqa: F841
|
||||
|
||||
free_memory_bytes = torch.cuda.mem_get_info("cuda:0")[0]
|
||||
required_memory_bytes = 5000 * 5000 * (32 // 8)
|
||||
|
||||
# Leaving 50 MB of free memory for possible buffers, etc.
|
||||
n_vals = (free_memory_bytes - required_memory_bytes - int(50e6)) // (32 // 8)
|
||||
foo = torch.rand(n_vals, device="cuda:0") # noqa: F841
|
||||
|
||||
# If this does OOM: there is an issue in somewhere in dispatch_model, memory of tied weights is duplicated.
|
||||
try:
|
||||
dispatch_model(model, device_map)
|
||||
except torch.cuda.OutOfMemoryError as e:
|
||||
raise torch.cuda.OutOfMemoryError(
|
||||
f"OOM error in dispatch_model. This is a bug and should not happen, see test_dispatch_model_tied_weights_memory. {e}"
|
||||
)
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
raise e
|
||||
|
||||
with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
output = model(x)
|
||||
self.assertTrue(torch.allclose(expected, output.cpu(), atol=1e-5))
|
||||
|
||||
@require_cuda
|
||||
def test_dispatch_model_tied_weights_memory_with_nested_offload_cpu(self):
|
||||
# Test that we do not duplicate tied weights at any point during dispatch_model call.
|
||||
|
||||
torch.cuda.empty_cache() # Needed in case we run several tests in a row.
|
||||
|
||||
class SubModule(torch.nn.Module):
|
||||
def __init__(self, ref_to_parameter):
|
||||
super().__init__()
|
||||
self.parameter = ref_to_parameter
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, x):
|
||||
return x + torch.max(self.parameter)
|
||||
|
||||
class LinearModuleAndSubModule(torch.nn.Linear):
|
||||
def __init__(self, in_features, out_features):
|
||||
super().__init__(in_features, out_features, bias=False)
|
||||
self.weight_submodule = SubModule(self.weight)
|
||||
self.weight_submodule2 = SubModule(self.weight)
|
||||
self.weight_submodule3 = SubModule(self.weight)
|
||||
self.weight_submodule4 = SubModule(self.weight)
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, x):
|
||||
a = torch.nn.functional.linear(self.weight_submodule(x), self.weight)
|
||||
b = torch.nn.functional.linear(self.weight_submodule2(x), self.weight)
|
||||
c = torch.nn.functional.linear(self.weight_submodule3(x), self.weight)
|
||||
d = torch.nn.functional.linear(self.weight_submodule4(x), self.weight)
|
||||
return a + b + c + d
|
||||
|
||||
class ModelWithSubmodules(torch.nn.Module):
|
||||
def __init__(self):
|
||||
super().__init__()
|
||||
self.compute = LinearModuleAndSubModule(5000, 5000)
|
||||
self.compute1 = LinearModuleAndSubModule(5000, 5000)
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, x):
|
||||
a = self.compute(x)
|
||||
b = self.compute1(x)
|
||||
return a + b
|
||||
|
||||
# We should need only 2 * 5000 * 5000 * 32 // 8 * 1e-6 = 200 MB on the device 0 for the whole model forward, and not 600 MB.
|
||||
device_map = {"compute": 0, "compute1": "cpu"}
|
||||
|
||||
model = ModelWithSubmodules()
|
||||
|
||||
x = torch.randn(1, 5000)
|
||||
with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
expected = model(x)
|
||||
|
||||
# Just to intialize CUDA context.
|
||||
a = torch.rand(5).to("cuda:0") # noqa: F841
|
||||
|
||||
free_memory_bytes = torch.cuda.mem_get_info("cuda:0")[0]
|
||||
required_memory_bytes = 2 * 5000 * 5000 * (32 // 8) # 200 MB
|
||||
|
||||
# Leaving 150 MB of free memory for possible buffers, etc.
|
||||
n_vals = (free_memory_bytes - required_memory_bytes - int(150e6)) // (32 // 8)
|
||||
foo = torch.rand(n_vals, device="cuda:0") # noqa: F841
|
||||
|
||||
free_memory_bytes_before_dispatch = torch.cuda.mem_get_info("cuda:0")[0]
|
||||
dispatch_model(model, device_map)
|
||||
free_memory_bytes_after_dispatch = torch.cuda.mem_get_info("cuda:0")[0]
|
||||
|
||||
self.assertTrue((free_memory_bytes_after_dispatch - free_memory_bytes_before_dispatch) * 1e-6 < 130)
|
||||
|
||||
original_pointer = model.compute1._hf_hook.weights_map["weight"].data_ptr()
|
||||
|
||||
with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
try:
|
||||
output = model(x)
|
||||
except torch.cuda.OutOfMemoryError as e:
|
||||
raise torch.cuda.OutOfMemoryError(
|
||||
f"OOM error in dispatch_model. This is a bug and should not happen, see test_dispatch_model_tied_weights_memory_with_nested_offload_cpu. {e}"
|
||||
)
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
raise e
|
||||
|
||||
self.assertTrue(torch.allclose(expected, output.cpu(), atol=1e-5))
|
||||
|
||||
torch.cuda.empty_cache()
|
||||
|
||||
free_memory_bytes_after_infer = torch.cuda.mem_get_info("cuda:0")[0]
|
||||
|
||||
# Check that we have no more references on GPU for the offloaded tied weight.
|
||||
self.assertTrue(len(model.compute1.weight_submodule._hf_hook.tied_params_map[original_pointer]) == 0)
|
||||
self.assertTrue(len(model.compute1._hf_hook.tied_params_map[original_pointer]) == 0)
|
||||
self.assertTrue((free_memory_bytes_after_infer - free_memory_bytes_after_dispatch) * 1e-6 < 130)
|
||||
|
||||
# Test is flacky otherwise.
|
||||
del model
|
||||
gc.collect()
|
||||
|
||||
@require_cuda
|
||||
def test_dispatch_model_tied_weights_memory_with_nested_offload_disk(self):
|
||||
# Test that we do not duplicate tied weights at any point during dispatch_model call.
|
||||
|
||||
torch.cuda.empty_cache() # Needed in case we run several tests in a row.
|
||||
|
||||
class SubModule(torch.nn.Module):
|
||||
def __init__(self, ref_to_parameter):
|
||||
super().__init__()
|
||||
self.parameter = ref_to_parameter
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, x):
|
||||
return x + torch.max(self.parameter)
|
||||
|
||||
class LinearModuleAndSubModule(torch.nn.Linear):
|
||||
def __init__(self, in_features, out_features):
|
||||
super().__init__(in_features, out_features, bias=False)
|
||||
self.weight_submodule = SubModule(self.weight)
|
||||
self.weight_submodule2 = SubModule(self.weight)
|
||||
self.weight_submodule3 = SubModule(self.weight)
|
||||
self.weight_submodule4 = SubModule(self.weight)
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, x):
|
||||
a = torch.nn.functional.linear(self.weight_submodule(x), self.weight)
|
||||
b = torch.nn.functional.linear(self.weight_submodule2(x), self.weight)
|
||||
c = torch.nn.functional.linear(self.weight_submodule3(x), self.weight)
|
||||
d = torch.nn.functional.linear(self.weight_submodule4(x), self.weight)
|
||||
return a + b + c + d
|
||||
|
||||
class ModelWithSubmodules(torch.nn.Module):
|
||||
def __init__(self):
|
||||
super().__init__()
|
||||
self.compute = LinearModuleAndSubModule(5000, 5000)
|
||||
self.compute1 = LinearModuleAndSubModule(5000, 5000)
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, x):
|
||||
a = self.compute(x)
|
||||
b = self.compute1(x)
|
||||
return a + b
|
||||
|
||||
# We should need only 2 * 5000 * 5000 * 32 // 8 * 1e-6 = 200 MB on the device 0 for the whole model forward, and not 600 MB.
|
||||
device_map = {"compute": 0, "compute1": "disk"}
|
||||
|
||||
model = ModelWithSubmodules()
|
||||
|
||||
x = torch.randn(1, 5000)
|
||||
with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
expected = model(x)
|
||||
|
||||
# Just to intialize CUDA context.
|
||||
a = torch.rand(5).to("cuda:0") # noqa: F841
|
||||
|
||||
free_memory_bytes = torch.cuda.mem_get_info("cuda:0")[0]
|
||||
required_memory_bytes = 2 * 5000 * 5000 * (32 // 8) # 200 MB
|
||||
|
||||
# Leaving 150 MB of free memory for possible buffers, etc.
|
||||
n_vals = (free_memory_bytes - required_memory_bytes - int(200e6)) // (32 // 8)
|
||||
foo = torch.rand(n_vals, device="cuda:0") # noqa: F841
|
||||
|
||||
free_memory_bytes_before_dispatch = torch.cuda.mem_get_info("cuda:0")[0]
|
||||
with TemporaryDirectory() as tmp_dir:
|
||||
dispatch_model(model, device_map, offload_dir=tmp_dir)
|
||||
free_memory_bytes_after_dispatch = torch.cuda.mem_get_info("cuda:0")[0]
|
||||
|
||||
self.assertTrue((free_memory_bytes_after_dispatch - free_memory_bytes_before_dispatch) * 1e-6 < 130)
|
||||
|
||||
with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
try:
|
||||
output = model(x)
|
||||
except torch.cuda.OutOfMemoryError as e:
|
||||
raise torch.cuda.OutOfMemoryError(
|
||||
f"OOM error in dispatch_model. This is a bug and should not happen, see test_dispatch_model_tied_weights_memory_with_nested_offload_disk. {e}"
|
||||
)
|
||||
except Exception as e:
|
||||
raise e
|
||||
|
||||
self.assertTrue(torch.allclose(expected, output.cpu(), atol=1e-5))
|
||||
|
||||
torch.cuda.empty_cache()
|
||||
|
||||
free_memory_bytes_after_infer = torch.cuda.mem_get_info("cuda:0")[0]
|
||||
|
||||
# Check that we have no more references on GPU for the offloaded tied weight.
|
||||
n_non_empty = 0
|
||||
for pointer, pointer_dict in model.compute1.weight_submodule._hf_hook.tied_params_map.items():
|
||||
if len(pointer_dict) > 0:
|
||||
n_non_empty += 1
|
||||
self.assertTrue(n_non_empty == 1) # `compute` layer one.
|
||||
|
||||
n_non_empty = 0
|
||||
for pointer, pointer_dict in model.compute1._hf_hook.tied_params_map.items():
|
||||
if len(pointer_dict) > 0:
|
||||
n_non_empty += 1
|
||||
self.assertTrue(n_non_empty == 1) # `compute` layer one.
|
||||
|
||||
self.assertTrue((free_memory_bytes_after_infer - free_memory_bytes_after_dispatch) * 1e-6 < 130)
|
||||
|
||||
@require_multi_gpu
|
||||
def test_dispatch_model_multi_gpu(self):
|
||||
model = BiggerModelForTest()
|
||||
|
||||
@ -24,7 +24,7 @@ import accelerate
|
||||
from accelerate.commands.estimate import estimate_command, estimate_command_parser, gather_data
|
||||
from accelerate.test_utils import execute_subprocess_async
|
||||
from accelerate.test_utils.testing import (
|
||||
require_multi_gpu,
|
||||
require_multi_device,
|
||||
require_timm,
|
||||
require_transformers,
|
||||
run_command,
|
||||
@ -89,7 +89,7 @@ class AccelerateLauncherTester(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
def test_accelerate_test(self):
|
||||
execute_subprocess_async(["accelerate", "test"], env=os.environ.copy())
|
||||
|
||||
@require_multi_gpu
|
||||
@require_multi_device
|
||||
def test_notebook_launcher(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
This test checks a variety of situations and scenarios
|
||||
|
||||
@ -23,7 +23,14 @@ from unittest import mock
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
from accelerate.test_utils.examples import compare_against_test
|
||||
from accelerate.test_utils.testing import TempDirTestCase, require_trackers, run_command, slow
|
||||
from accelerate.test_utils.testing import (
|
||||
TempDirTestCase,
|
||||
require_multi_gpu,
|
||||
require_pippy,
|
||||
require_trackers,
|
||||
run_command,
|
||||
slow,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from accelerate.utils import write_basic_config
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -227,3 +234,28 @@ class FeatureExamplesTests(TempDirTestCase):
|
||||
def test_early_stopping(self):
|
||||
testargs = ["examples/by_feature/early_stopping.py"]
|
||||
run_command(self._launch_args + testargs)
|
||||
|
||||
@require_pippy
|
||||
@require_multi_gpu
|
||||
def test_pippy_examples_bert(self):
|
||||
testargs = ["examples/inference/bert.py"]
|
||||
run_command(self._launch_args + testargs)
|
||||
|
||||
@require_pippy
|
||||
@require_multi_gpu
|
||||
def test_pippy_examples_gpt2(self):
|
||||
testargs = ["examples/inference/gpt2.py"]
|
||||
run_command(self._launch_args + testargs)
|
||||
|
||||
@require_pippy
|
||||
@require_multi_gpu
|
||||
def test_pippy_examples_t5(self):
|
||||
testargs = ["examples/inference/t5.py"]
|
||||
run_command(self._launch_args + testargs)
|
||||
|
||||
@slow
|
||||
@require_pippy
|
||||
@require_multi_gpu
|
||||
def test_pippy_examples_llama(self):
|
||||
testargs = ["examples/inference/llama.py"]
|
||||
run_command(self._launch_args + testargs)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -16,15 +16,14 @@ import inspect
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import unittest
|
||||
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
import accelerate
|
||||
from accelerate import debug_launcher
|
||||
from accelerate.test_utils import (
|
||||
device_count,
|
||||
execute_subprocess_async,
|
||||
require_cpu,
|
||||
require_multi_gpu,
|
||||
require_single_gpu,
|
||||
require_multi_device,
|
||||
require_non_cpu,
|
||||
test_sync,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from accelerate.utils import patch_environment
|
||||
@ -43,13 +42,13 @@ class SyncScheduler(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
def test_gradient_sync_cpu_multi(self):
|
||||
debug_launcher(test_sync.main)
|
||||
|
||||
@require_single_gpu
|
||||
@require_non_cpu
|
||||
def test_gradient_sync_gpu(self):
|
||||
test_sync.main()
|
||||
|
||||
@require_multi_gpu
|
||||
@require_multi_device
|
||||
def test_gradient_sync_gpu_multi(self):
|
||||
print(f"Found {torch.cuda.device_count()} devices.")
|
||||
cmd = ["torchrun", f"--nproc_per_node={torch.cuda.device_count()}", self.test_file_path]
|
||||
print(f"Found {device_count} devices.")
|
||||
cmd = ["torchrun", f"--nproc_per_node={device_count}", self.test_file_path]
|
||||
with patch_environment(omp_num_threads=1):
|
||||
execute_subprocess_async(cmd, env=os.environ.copy())
|
||||
|
||||
@ -17,6 +17,7 @@ import unittest
|
||||
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
import torch.nn as nn
|
||||
from torch.fx import symbolic_trace
|
||||
|
||||
from accelerate.hooks import (
|
||||
AlignDevicesHook,
|
||||
@ -347,3 +348,51 @@ class HooksModelTester(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
self.assertEqual(model.linear1.weight.device, torch.device("cpu"))
|
||||
self.assertEqual(model.batchnorm.weight.device, torch.device("cpu"))
|
||||
self.assertEqual(model.linear2.weight.device, torch.device("cpu"))
|
||||
|
||||
def test_add_remove_hook_fx_graph_module(self):
|
||||
with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
test_model = ModelForTest()
|
||||
test_hook = ModelHook()
|
||||
|
||||
x = torch.randn(2, 3)
|
||||
output1 = test_model(x)
|
||||
|
||||
graph_model = symbolic_trace(test_model)
|
||||
|
||||
output2 = graph_model(x)
|
||||
|
||||
self.assertTrue(torch.allclose(output1, output2))
|
||||
|
||||
add_hook_to_module(graph_model, test_hook)
|
||||
remove_hook_from_module(graph_model, recurse=True)
|
||||
|
||||
# We want to make sure that `add_hook_to_module` and `remove_hook_from_module` yields back an fx.GraphModule
|
||||
# that behaves correctly (for example that is not frozen, see https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate/pull/2369).
|
||||
# For that, we add a sigmoid node to the FX graph and make sure that the new output (output3 below) is different than
|
||||
# the original model's output.
|
||||
linear2_node = None
|
||||
for node in graph_model.graph.nodes:
|
||||
if node.name == "linear2":
|
||||
linear2_node = node
|
||||
self.assertTrue(linear2_node is not None)
|
||||
|
||||
graph_model.graph.inserting_after(linear2_node)
|
||||
new_node = graph_model.graph.create_node(
|
||||
op="call_function", target=torch.sigmoid, args=(linear2_node,), name="relu"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
output_node = None
|
||||
for node in graph_model.graph.nodes:
|
||||
if node.name == "output":
|
||||
output_node = node
|
||||
self.assertTrue(output_node is not None)
|
||||
|
||||
output_node.replace_input_with(linear2_node, new_node)
|
||||
|
||||
graph_model.graph.lint()
|
||||
graph_model.recompile()
|
||||
|
||||
output3 = graph_model(x)
|
||||
|
||||
# Now the output is expected to be different since we modified the graph.
|
||||
self.assertFalse(torch.allclose(output1, output3))
|
||||
|
||||
@ -21,7 +21,13 @@ import torch
|
||||
|
||||
from accelerate import Accelerator, DistributedDataParallelKwargs, GradScalerKwargs
|
||||
from accelerate.state import AcceleratorState
|
||||
from accelerate.test_utils import execute_subprocess_async, require_cuda, require_multi_gpu
|
||||
from accelerate.test_utils import (
|
||||
device_count,
|
||||
execute_subprocess_async,
|
||||
require_multi_device,
|
||||
require_non_cpu,
|
||||
require_non_xpu,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from accelerate.utils import AutocastKwargs, KwargsHandler, TorchDynamoPlugin, clear_environment
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -40,7 +46,8 @@ class KwargsHandlerTester(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
self.assertDictEqual(MockClass(a=2, b=True).to_kwargs(), {"a": 2, "b": True})
|
||||
self.assertDictEqual(MockClass(a=2, c=2.25).to_kwargs(), {"a": 2, "c": 2.25})
|
||||
|
||||
@require_cuda
|
||||
@require_non_cpu
|
||||
@require_non_xpu
|
||||
def test_grad_scaler_kwargs(self):
|
||||
# If no defaults are changed, `to_kwargs` returns an empty dict.
|
||||
scaler_handler = GradScalerKwargs(init_scale=1024, growth_factor=2)
|
||||
@ -58,12 +65,12 @@ class KwargsHandlerTester(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
self.assertEqual(scaler._growth_interval, 2000)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(scaler._enabled, True)
|
||||
|
||||
@require_multi_gpu
|
||||
@require_multi_device
|
||||
def test_ddp_kwargs(self):
|
||||
cmd = ["torchrun", f"--nproc_per_node={torch.cuda.device_count()}", inspect.getfile(self.__class__)]
|
||||
cmd = ["torchrun", f"--nproc_per_node={device_count}", inspect.getfile(self.__class__)]
|
||||
execute_subprocess_async(cmd, env=os.environ.copy())
|
||||
|
||||
@require_cuda
|
||||
@require_non_cpu
|
||||
def test_autocast_kwargs(self):
|
||||
kwargs = AutocastKwargs(enabled=False)
|
||||
AcceleratorState._reset_state()
|
||||
|
||||
@ -14,10 +14,9 @@
|
||||
|
||||
import unittest
|
||||
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from torch import nn
|
||||
|
||||
from accelerate.test_utils import require_cuda
|
||||
from accelerate.test_utils import memory_allocated_func, require_non_cpu, torch_device
|
||||
from accelerate.utils.memory import find_executable_batch_size, release_memory
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -105,11 +104,11 @@ class MemoryTest(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
mock_training_loop_function()
|
||||
self.assertIn("Oops, we had an error!", cm.exception.args[0])
|
||||
|
||||
@require_cuda
|
||||
@require_non_cpu
|
||||
def test_release_memory(self):
|
||||
starting_memory = torch.cuda.memory_allocated()
|
||||
starting_memory = memory_allocated_func()
|
||||
model = ModelForTest()
|
||||
model.cuda()
|
||||
self.assertGreater(torch.cuda.memory_allocated(), starting_memory)
|
||||
model.to(torch_device)
|
||||
self.assertGreater(memory_allocated_func(), starting_memory)
|
||||
model = release_memory(model)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(torch.cuda.memory_allocated(), starting_memory)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(memory_allocated_func(), starting_memory)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -21,11 +21,18 @@ import torch
|
||||
import accelerate
|
||||
from accelerate import Accelerator
|
||||
from accelerate.big_modeling import dispatch_model
|
||||
from accelerate.test_utils import assert_exception, execute_subprocess_async, require_multi_gpu
|
||||
from accelerate.test_utils import (
|
||||
assert_exception,
|
||||
device_count,
|
||||
execute_subprocess_async,
|
||||
require_multi_device,
|
||||
require_multi_gpu,
|
||||
require_pippy,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from accelerate.utils import patch_environment
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class MultiGPUTester(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
class MultiDeviceTester(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
def setUp(self):
|
||||
mod_file = inspect.getfile(accelerate.test_utils)
|
||||
self.test_file_path = os.path.sep.join(mod_file.split(os.path.sep)[:-1] + ["scripts", "test_script.py"])
|
||||
@ -34,24 +41,24 @@ class MultiGPUTester(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.operation_file_path = os.path.sep.join(mod_file.split(os.path.sep)[:-1] + ["scripts", "test_ops.py"])
|
||||
|
||||
@require_multi_gpu
|
||||
def test_multi_gpu(self):
|
||||
print(f"Found {torch.cuda.device_count()} devices.")
|
||||
cmd = ["torchrun", f"--nproc_per_node={torch.cuda.device_count()}", self.test_file_path]
|
||||
@require_multi_device
|
||||
def test_multi_device(self):
|
||||
print(f"Found {device_count} devices.")
|
||||
cmd = ["torchrun", f"--nproc_per_node={device_count}", self.test_file_path]
|
||||
with patch_environment(omp_num_threads=1):
|
||||
execute_subprocess_async(cmd, env=os.environ.copy())
|
||||
|
||||
@require_multi_gpu
|
||||
def test_multi_gpu_ops(self):
|
||||
print(f"Found {torch.cuda.device_count()} devices.")
|
||||
cmd = ["torchrun", f"--nproc_per_node={torch.cuda.device_count()}", self.operation_file_path]
|
||||
@require_multi_device
|
||||
def test_multi_device_ops(self):
|
||||
print(f"Found {device_count} devices.")
|
||||
cmd = ["torchrun", f"--nproc_per_node={device_count}", self.operation_file_path]
|
||||
print(f"Command: {cmd}")
|
||||
with patch_environment(omp_num_threads=1):
|
||||
execute_subprocess_async(cmd, env=os.environ.copy())
|
||||
|
||||
@require_multi_gpu
|
||||
@require_multi_device
|
||||
def test_pad_across_processes(self):
|
||||
cmd = ["torchrun", f"--nproc_per_node={torch.cuda.device_count()}", inspect.getfile(self.__class__)]
|
||||
cmd = ["torchrun", f"--nproc_per_node={device_count}", inspect.getfile(self.__class__)]
|
||||
with patch_environment(omp_num_threads=1):
|
||||
execute_subprocess_async(cmd, env=os.environ.copy())
|
||||
|
||||
@ -61,11 +68,28 @@ class MultiGPUTester(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
This TestCase checks the behaviour that occurs during distributed training or evaluation,
|
||||
when the batch size does not evenly divide the dataset size.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
print(f"Found {torch.cuda.device_count()} devices, using 2 devices only")
|
||||
cmd = ["torchrun", f"--nproc_per_node={torch.cuda.device_count()}", self.data_loop_file_path]
|
||||
print(f"Found {device_count} devices, using 2 devices only")
|
||||
cmd = ["torchrun", "--nproc_per_node=2", self.data_loop_file_path]
|
||||
with patch_environment(omp_num_threads=1, cuda_visible_devices="0,1"):
|
||||
execute_subprocess_async(cmd, env=os.environ.copy())
|
||||
|
||||
@require_multi_gpu
|
||||
@require_pippy
|
||||
def test_pippy(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Checks the integration with the pippy framework
|
||||
"""
|
||||
print(f"Found {torch.cuda.device_count()} devices")
|
||||
cmd = [
|
||||
"accelerate",
|
||||
"launch",
|
||||
"--multi_gpu",
|
||||
f"--num_processes={torch.cuda.device_count()}",
|
||||
self.pippy_file_path,
|
||||
]
|
||||
with patch_environment(omp_num_threads=1):
|
||||
execute_subprocess_async(cmd, env=os.environ.copy())
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
accelerator = Accelerator()
|
||||
|
||||
@ -19,11 +19,11 @@ import torch
|
||||
|
||||
from accelerate import Accelerator
|
||||
from accelerate.state import AcceleratorState
|
||||
from accelerate.test_utils import require_cpu, require_cuda
|
||||
from accelerate.test_utils import require_cpu, require_non_cpu, require_non_xpu
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@require_cpu
|
||||
class OptimizerTester(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
class CPUOptimizerTester(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
def test_accelerated_optimizer_pickling(self):
|
||||
model = torch.nn.Linear(10, 10)
|
||||
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), 0.1)
|
||||
@ -36,8 +36,9 @@ class OptimizerTester(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
AcceleratorState._reset_state()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@require_cuda
|
||||
class CudaOptimizerTester(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
@require_non_cpu
|
||||
@require_non_xpu
|
||||
class OptimizerTester(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
def test_accelerated_optimizer_step_was_skipped(self):
|
||||
model = torch.nn.Linear(5, 5)
|
||||
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), 0.1)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -407,6 +407,7 @@ class ClearMLTest(TempDirTestCase, MockingTestCase):
|
||||
|
||||
class MyCustomTracker(GeneralTracker):
|
||||
"Basic tracker that writes to a csv for testing"
|
||||
|
||||
_col_names = [
|
||||
"total_loss",
|
||||
"iteration",
|
||||
|
||||
@ -11,7 +11,6 @@
|
||||
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import pickle
|
||||
import tempfile
|
||||
@ -34,6 +33,7 @@ from accelerate.utils import (
|
||||
find_device,
|
||||
listify,
|
||||
pad_across_processes,
|
||||
pad_input_tensors,
|
||||
patch_environment,
|
||||
recursively_apply,
|
||||
save,
|
||||
@ -237,3 +237,68 @@ class UtilsTester(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
with self.assertWarns(CannotPadNestedTensorWarning):
|
||||
nt2 = pad_across_processes(nt)
|
||||
self.assertIs(nt, nt2)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_slice_and_concatenate(self):
|
||||
# First base case: 2 processes, batch size of 1
|
||||
num_processes = 2
|
||||
batch_size = 1
|
||||
batch = torch.rand(batch_size, 4)
|
||||
result = pad_input_tensors(batch, batch_size, num_processes)
|
||||
# We should expect there to be 2 items now
|
||||
assert result.shape == torch.Size([2, 4])
|
||||
|
||||
# Second base case: 2 processes, batch size of 3
|
||||
num_processes = 2
|
||||
batch_size = 3
|
||||
batch = torch.rand(batch_size, 4)
|
||||
result = pad_input_tensors(batch, batch_size, num_processes)
|
||||
# We should expect there to be 4 items now
|
||||
assert result.shape == torch.Size([4, 4])
|
||||
|
||||
# Third base case: 3 processes, batch size of 4
|
||||
num_processes = 3
|
||||
batch_size = 4
|
||||
batch = torch.rand(batch_size, 4, 4)
|
||||
result = pad_input_tensors(batch, batch_size, num_processes)
|
||||
# We should expect there to be 6 items now
|
||||
assert result.shape == torch.Size([6, 4, 4])
|
||||
|
||||
# Fourth base case: 4 processes, batch size of 3
|
||||
num_processes = 4
|
||||
batch_size = 3
|
||||
batch = torch.rand(batch_size, 4, 4)
|
||||
result = pad_input_tensors(batch, batch_size, num_processes)
|
||||
# We should expect there to be 4 items now
|
||||
assert result.shape == torch.Size([4, 4, 4])
|
||||
|
||||
# Fifth base case: 6 processes, batch size of 4
|
||||
num_processes = 6
|
||||
batch_size = 4
|
||||
batch = torch.rand(batch_size, 4, 4)
|
||||
result = pad_input_tensors(batch, batch_size, num_processes)
|
||||
# We should expect there to be 6 items now
|
||||
assert result.shape == torch.Size([6, 4, 4])
|
||||
|
||||
# Sixth base case: 6 processes, batch size of 1
|
||||
num_processes = 6
|
||||
batch_size = 1
|
||||
batch = torch.rand(batch_size, 4, 4)
|
||||
result = pad_input_tensors(batch, batch_size, num_processes)
|
||||
# We should expect there to be 6 items now
|
||||
assert result.shape == torch.Size([6, 4, 4])
|
||||
|
||||
# Seventh base case: 6 processes, batch size of 2
|
||||
num_processes = 6
|
||||
batch_size = 2
|
||||
batch = torch.rand(batch_size, 4, 4)
|
||||
result = pad_input_tensors(batch, batch_size, num_processes)
|
||||
# We should expect there to be 6 items now
|
||||
assert result.shape == torch.Size([6, 4, 4])
|
||||
|
||||
# Eighth base case: 6 processes, batch size of 61
|
||||
num_processes = 6
|
||||
batch_size = 61
|
||||
batch = torch.rand(batch_size, 4, 4)
|
||||
result = pad_input_tensors(batch, batch_size, num_processes)
|
||||
# We should expect there to be 66 items now
|
||||
assert result.shape == torch.Size([66, 4, 4])
|
||||
|
||||
Reference in New Issue
Block a user