mirror of
https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate.git
synced 2025-11-14 14:14:32 +08:00
Compare commits
138 Commits
check-docs
...
v0.26.1
| Author | SHA1 | Date | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 6f05bbd41a | |||
| f823404f69 | |||
| ef2fe912c5 | |||
| e3e9b87592 | |||
| 456afd92ce | |||
| 0d2280dadc | |||
| 55d4a496dd | |||
| 2a8829d9a5 | |||
| 3969731ce8 | |||
| 411aa58a77 | |||
| 4420ec641d | |||
| 2241725ad6 | |||
| 5cac878984 | |||
| 5d31423308 | |||
| 2721387b98 | |||
| 2cfa88bdf1 | |||
| 102caf4fab | |||
| 07df5d268f | |||
| 68b3dbf666 | |||
| 403c0714d1 | |||
| 848ed800fa | |||
| ad957ce556 | |||
| 3db088f5d6 | |||
| d1abd59114 | |||
| ceb7c699bc | |||
| c5baa055c0 | |||
| 349be97ccb | |||
| b60061dfd2 | |||
| b565a6c58a | |||
| a03c361ffb | |||
| b0528392c8 | |||
| 060678415a | |||
| 6b2d968897 | |||
| ad3a5bc920 | |||
| eafcea07f6 | |||
| eff30e2130 | |||
| 694f2e2c12 | |||
| 9964f90fd7 | |||
| f86876d56d | |||
| 0a37e2042e | |||
| 54d670be41 | |||
| 339854a9a4 | |||
| 5296419df4 | |||
| 6a4857fec2 | |||
| 9569150174 | |||
| 8f871f41f1 | |||
| 47e6c36155 | |||
| 47c144570c | |||
| 6a54d0781b | |||
| 0482548363 | |||
| 0e48b2358d | |||
| 3499cf25aa | |||
| 68d63ee15f | |||
| 151637920d | |||
| 0ba3e9bb50 | |||
| b04d36c75f | |||
| 5fc1b230d3 | |||
| 244122c736 | |||
| d25efa71ce | |||
| 1aeb1e8997 | |||
| 0e51680994 | |||
| 7d430cf8de | |||
| b8ca803f98 | |||
| 1243191ecb | |||
| 2b25b8b3c5 | |||
| ca300c0a04 | |||
| 427ef8bd00 | |||
| 35b0206353 | |||
| fbe00d7897 | |||
| 62af737219 | |||
| cd51581248 | |||
| a5a7c039a0 | |||
| cf745c936d | |||
| 99877f56d6 | |||
| 0f2686c8d3 | |||
| a912b2ee09 | |||
| e9fd72a613 | |||
| 8dedb140ef | |||
| b55855a3d4 | |||
| 2b53a9089c | |||
| 39d255b3d0 | |||
| 99dff1a167 | |||
| a0a16e118a | |||
| 15458c5737 | |||
| fc0a43c3c1 | |||
| 8256a9c2d4 | |||
| 6727ac4394 | |||
| 9674b40580 | |||
| 0b0d9215a9 | |||
| e638b1e21a | |||
| 76de60dbdc | |||
| 217e1a248c | |||
| 5e0eb0d750 | |||
| 183c9dd3ce | |||
| 4f100318f4 | |||
| fa6f43033c | |||
| 820fc4ca7a | |||
| bd72a5f1a8 | |||
| 55088a2cf5 | |||
| c2d8e245e9 | |||
| d8e1285409 | |||
| 5b3f3b99d6 | |||
| 2935057606 | |||
| bb6759d634 | |||
| 55747318a0 | |||
| 217faafe08 | |||
| 5440387529 | |||
| e1fab05ce7 | |||
| c3ec7ff5a9 | |||
| d8535921ad | |||
| eb8c535c17 | |||
| b7686ccb44 | |||
| f3229872bc | |||
| 7843286f2e | |||
| 11e2e99cfc | |||
| 07e745f1c4 | |||
| c7c99a30ea | |||
| 8f45a2eae8 | |||
| 9fd64b7ea9 | |||
| 5be16ad90b | |||
| dab62832de | |||
| caa9f9bcbb | |||
| 943efedb88 | |||
| 50acb0c2ec | |||
| e6d96e5f70 | |||
| 1dfb6e9304 | |||
| 4bef6bc511 | |||
| 73640d0463 | |||
| 7a1159143e | |||
| cbb0b82fa2 | |||
| 5ae6111180 | |||
| 230a5f541b | |||
| 956114ac92 | |||
| 76ee7f211d | |||
| 420743af22 | |||
| 206ab491ed | |||
| 936d2f4f5c | |||
| da98d601b5 |
@ -15,13 +15,13 @@ jobs:
|
||||
outputs:
|
||||
version: ${{ steps.step1.outputs.version }}
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@v3
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@v3.1.0
|
||||
- id: step1
|
||||
run: echo "version=$(python setup.py --version)" >> $GITHUB_OUTPUT
|
||||
|
||||
version-cpu:
|
||||
name: "Latest Accelerate CPU [version]"
|
||||
runs-on: [self-hosted, docker-gpu, multi-gpu]
|
||||
runs-on: [self-hosted, intel-cpu, 8-cpu, ci]
|
||||
needs: get-version
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Set up Docker Buildx
|
||||
@ -41,7 +41,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
|
||||
version-cuda:
|
||||
name: "Latest Accelerate GPU [version]"
|
||||
runs-on: [self-hosted, docker-gpu, multi-gpu]
|
||||
runs-on: [self-hosted, single-gpu, nvidia-gpu, t4, ci]
|
||||
needs: get-version
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Set up Docker Buildx
|
||||
|
||||
4
.github/workflows/build_and_run_tests.yml
vendored
4
.github/workflows/build_and_run_tests.yml
vendored
@ -22,7 +22,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Get changed files
|
||||
id: changed-files
|
||||
uses: tj-actions/changed-files@v22.2
|
||||
uses: tj-actions/changed-files@v41
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Was setup changed
|
||||
id: was_changed
|
||||
@ -45,6 +45,6 @@ jobs:
|
||||
uses: ./.github/workflows/run_merge_tests.yml
|
||||
|
||||
run-integration-tests:
|
||||
needs: run-merge-tests
|
||||
needs: build-docker-containers
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
uses: ./.github/workflows/self_hosted_integration_tests.yml
|
||||
15
.github/workflows/build_docker_images.yml
vendored
15
.github/workflows/build_docker_images.yml
vendored
@ -11,19 +11,9 @@ concurrency:
|
||||
cancel-in-progress: false
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
clean-storage:
|
||||
name: "Clean docker image storage"
|
||||
runs-on: [self-hosted, docker-gpu, multi-gpu]
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Clean storage
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
docker image prune --all -f --filter "until=48h"
|
||||
docker system prune --all -f --filter "until=48h"
|
||||
|
||||
latest-cpu:
|
||||
name: "Latest Accelerate CPU [dev]"
|
||||
runs-on: [self-hosted, docker-gpu, multi-gpu]
|
||||
needs: clean-storage
|
||||
runs-on: [self-hosted, intel-cpu, 8-cpu, ci]
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Set up Docker Buildx
|
||||
uses: docker/setup-buildx-action@v2
|
||||
@ -41,8 +31,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
|
||||
latest-cuda:
|
||||
name: "Latest Accelerate GPU [dev]"
|
||||
runs-on: [self-hosted, docker-gpu, multi-gpu]
|
||||
needs: clean-storage
|
||||
runs-on: [self-hosted, nvidia-gpu, t4, ci]
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Set up Docker Buildx
|
||||
uses: docker/setup-buildx-action@v2
|
||||
|
||||
1
.github/workflows/build_documentation.yml
vendored
1
.github/workflows/build_documentation.yml
vendored
@ -14,5 +14,4 @@ jobs:
|
||||
commit_sha: ${{ github.sha }}
|
||||
package: accelerate
|
||||
secrets:
|
||||
token: ${{ secrets.HUGGINGFACE_PUSH }}
|
||||
hf_token: ${{ secrets.HF_DOC_BUILD_PUSH }}
|
||||
|
||||
14
.github/workflows/delete_doc_comment.yml
vendored
14
.github/workflows/delete_doc_comment.yml
vendored
@ -1,14 +0,0 @@
|
||||
name: Delete doc comment
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
workflow_run:
|
||||
workflows: ["Delete doc comment trigger"]
|
||||
types:
|
||||
- completed
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
delete:
|
||||
uses: huggingface/doc-builder/.github/workflows/delete_doc_comment.yml@main
|
||||
secrets:
|
||||
comment_bot_token: ${{ secrets.COMMENT_BOT_TOKEN }}
|
||||
12
.github/workflows/delete_doc_comment_trigger.yml
vendored
12
.github/workflows/delete_doc_comment_trigger.yml
vendored
@ -1,12 +0,0 @@
|
||||
name: Delete doc comment trigger
|
||||
|
||||
on:
|
||||
pull_request:
|
||||
types: [ closed ]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
delete:
|
||||
uses: huggingface/doc-builder/.github/workflows/delete_doc_comment_trigger.yml@main
|
||||
with:
|
||||
pr_number: ${{ github.event.number }}
|
||||
8
.github/workflows/integration_tests.yml
vendored
8
.github/workflows/integration_tests.yml
vendored
@ -25,11 +25,6 @@ jobs:
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
fail-fast: false
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
transformers-version: [
|
||||
pypi,
|
||||
github
|
||||
]
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@v3.1.0
|
||||
- name: Set up python 3.8
|
||||
@ -47,9 +42,6 @@ jobs:
|
||||
cd ..
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/huggingface/transformers
|
||||
cd transformers
|
||||
if [[ ${{ matrix.transformers-version }} = pypi ]]; then
|
||||
git checkout $(git describe --tags `git rev-list --tags --max-count=1`)
|
||||
fi
|
||||
pip install .[torch,testing]
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Show installed libraries
|
||||
|
||||
24
.github/workflows/nightly.yml
vendored
24
.github/workflows/nightly.yml
vendored
@ -13,7 +13,7 @@ env:
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
run_all_tests_single_gpu:
|
||||
runs-on: [self-hosted, docker-gpu, multi-gpu]
|
||||
runs-on: [self-hosted, single-gpu, nvidia-gpu, t4, ci]
|
||||
env:
|
||||
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES: "0"
|
||||
TEST_TYPE: "single_gpu"
|
||||
@ -22,23 +22,25 @@ jobs:
|
||||
options: --gpus all --shm-size "16gb"
|
||||
defaults:
|
||||
run:
|
||||
working-directory: accelerate/
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Update clone & pip install
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
source activate accelerate
|
||||
git config --global --add safe.directory '*'
|
||||
git fetch && git checkout ${{ github.sha }}
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate;
|
||||
cd accelerate;
|
||||
git checkout ${{ github.sha }};
|
||||
pip install -e . --no-deps
|
||||
pip install pytest-reportlog tabulate
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run test on GPUs
|
||||
working-directory: accelerate
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
source activate accelerate
|
||||
make test
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run examples on GPUs
|
||||
working-directory: accelerate
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
source activate accelerate
|
||||
@ -46,13 +48,14 @@ jobs:
|
||||
make test_examples
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Generate Report
|
||||
working-directory: accelerate
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
pip install slack_sdk tabulate
|
||||
python utils/log_reports.py >> $GITHUB_STEP_SUMMARY
|
||||
|
||||
run_all_tests_multi_gpu:
|
||||
runs-on: [self-hosted, docker-gpu, multi-gpu]
|
||||
runs-on: [self-hosted, multi-gpu, nvidia-gpu, t4, ci]
|
||||
env:
|
||||
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES: "0,1"
|
||||
TEST_TYPE: "multi_gpu"
|
||||
@ -61,18 +64,19 @@ jobs:
|
||||
options: --gpus all --shm-size "16gb"
|
||||
defaults:
|
||||
run:
|
||||
working-directory: accelerate/
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Update clone
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
source activate accelerate
|
||||
git config --global --add safe.directory '*'
|
||||
git fetch && git checkout ${{ github.sha }}
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate;
|
||||
cd accelerate;
|
||||
git checkout ${{ github.sha }};
|
||||
pip install -e . --no-deps
|
||||
pip install pytest-reportlog tabulate
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run core and big modeling tests on GPUs
|
||||
working-directory: accelerate
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
source activate accelerate
|
||||
make test_core
|
||||
@ -80,12 +84,14 @@ jobs:
|
||||
make test_cli
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run Integration tests on GPUs
|
||||
working-directory: accelerate
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
source activate accelerate
|
||||
make test_integrations
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run examples on GPUs
|
||||
working-directory: accelerate
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
source activate accelerate
|
||||
@ -93,6 +99,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
make test_examples
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Generate Report
|
||||
working-directory: accelerate
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
pip install slack_sdk tabulate
|
||||
@ -100,6 +107,5 @@ jobs:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
run-integration-tests:
|
||||
needs: [run_all_tests_single_gpu, run_all_tests_multi_gpu]
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
uses: ./.github/workflows/self_hosted_integration_tests.yml
|
||||
2
.github/workflows/quality.yml
vendored
2
.github/workflows/quality.yml
vendored
@ -6,7 +6,7 @@ jobs:
|
||||
quality:
|
||||
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@v2
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@v3.1.0
|
||||
- name: Set up Python 3.8
|
||||
uses: actions/setup-python@v3
|
||||
with:
|
||||
|
||||
59
.github/workflows/run_merge_tests.yml
vendored
59
.github/workflows/run_merge_tests.yml
vendored
@ -10,7 +10,7 @@ env:
|
||||
|
||||
jobs:
|
||||
run_all_tests_single_gpu:
|
||||
runs-on: [self-hosted, docker-gpu, multi-gpu]
|
||||
runs-on: [self-hosted, single-gpu, nvidia-gpu, t4, ci]
|
||||
env:
|
||||
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES: "0"
|
||||
container:
|
||||
@ -18,72 +18,81 @@ jobs:
|
||||
options: --gpus all --shm-size "16gb"
|
||||
defaults:
|
||||
run:
|
||||
working-directory: accelerate/
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Update clone & pip install
|
||||
- name: Install accelerate
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
source activate accelerate
|
||||
git config --global --add safe.directory '*'
|
||||
git fetch && git checkout ${{ github.sha }}
|
||||
pip install -e .[testing,test_trackers] -U
|
||||
pip install pytest-reportlog tabulate
|
||||
source activate accelerate;
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate;
|
||||
cd accelerate;
|
||||
git checkout ${{ github.sha }};
|
||||
pip install -e .[testing,test_trackers] -U;
|
||||
pip install pytest-reportlog tabulate ;
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run CLI tests
|
||||
- name: Run CLI tests (use make cli)
|
||||
working-directory: accelerate
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
source activate accelerate
|
||||
source activate accelerate;
|
||||
make test_cli
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run test on GPUs
|
||||
working-directory: accelerate
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
source activate accelerate
|
||||
source activate accelerate;
|
||||
make test
|
||||
- name: Run examples on GPUs
|
||||
working-directory: accelerate
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
source activate accelerate
|
||||
pip uninstall comet_ml -y
|
||||
source activate accelerate;
|
||||
pip uninstall comet_ml -y;
|
||||
make test_examples
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Generate Report
|
||||
working-directory: accelerate
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
pip install tabulate
|
||||
pip install tabulate;
|
||||
python utils/log_reports.py >> $GITHUB_STEP_SUMMARY
|
||||
|
||||
run_all_tests_multi_gpu:
|
||||
runs-on: [self-hosted, docker-gpu, multi-gpu]
|
||||
runs-on: [self-hosted, multi-gpu, nvidia-gpu, t4, ci]
|
||||
env:
|
||||
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES: 0,1
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: huggingface/accelerate-gpu:latest
|
||||
options: --gpus all --shm-size "16gb"
|
||||
defaults:
|
||||
run:
|
||||
working-directory: accelerate/
|
||||
shell: bash
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Update clone
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
source activate accelerate
|
||||
git config --global --add safe.directory '*'
|
||||
git fetch && git checkout ${{ github.sha }}
|
||||
pip install -e .[testing,test_trackers] -U
|
||||
source activate accelerate;
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate;
|
||||
cd accelerate;
|
||||
git checkout ${{ github.sha }};
|
||||
pip install -e .[testing,test_trackers] -U;
|
||||
pip install pytest-reportlog tabulate
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run test on GPUs
|
||||
working-directory: accelerate
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
source activate accelerate
|
||||
source activate accelerate;
|
||||
make test
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run examples on GPUs
|
||||
working-directory: accelerate
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
source activate accelerate
|
||||
pip uninstall comet_ml -y
|
||||
source activate accelerate;
|
||||
pip uninstall comet_ml -y;
|
||||
make test_examples
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Generate Report
|
||||
working-directory: accelerate
|
||||
if: always()
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
pip install tabulate
|
||||
python utils/log_reports.py >> $GITHUB_STEP_SUMMARY
|
||||
source activate accelerate;
|
||||
python utils/log_reports.py >> $GITHUB_STEP_SUMMARY
|
||||
|
||||
@ -25,37 +25,32 @@ jobs:
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: huggingface/accelerate-gpu:latest
|
||||
options: --gpus all --shm-size "16gb"
|
||||
runs-on: [self-hosted, docker-gpu, multi-gpu]
|
||||
runs-on: [self-hosted, multi-gpu, nvidia-gpu, t4, ci]
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
fail-fast: false
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
transformers-version: [
|
||||
pypi,
|
||||
github
|
||||
]
|
||||
cuda_visible_devices: [
|
||||
"0",
|
||||
"0,1"
|
||||
]
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Update accelerate clone and pip install
|
||||
working-directory: accelerate/
|
||||
run:
|
||||
source activate accelerate;
|
||||
git config --global --add safe.directory '*';
|
||||
git checkout main && git fetch && git checkout ${{ github.sha }};
|
||||
pip install -e .;
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Update transformers clone & pip install
|
||||
working-directory: transformers/
|
||||
- name: Install transformers
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
source activate accelerate
|
||||
git config --global --add safe.directory '*'
|
||||
git checkout main && git pull
|
||||
if [[ ${{ matrix.transformers-version }} = pypi ]]; then
|
||||
git checkout $(git describe --tags `git rev-list --tags --max-count=1`)
|
||||
fi
|
||||
pip install .[torch,deepspeed-testing]
|
||||
source activate accelerate;
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/huggingface/transformers --depth 1;
|
||||
cd transformers;
|
||||
pip install .[torch,deepspeed-testing];
|
||||
cd ..;
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Install accelerate
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
source activate accelerate;
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate;
|
||||
cd accelerate;
|
||||
git checkout ${{ github.sha }} ;
|
||||
pip install -e .[testing];
|
||||
pip uninstall comet_ml wandb dvclive -y
|
||||
cd ..;
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Show installed libraries
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
@ -81,36 +76,40 @@ jobs:
|
||||
source activate accelerate;
|
||||
pytest -sv tests/deepspeed
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Run transformers examples tests
|
||||
working-directory: transformers/
|
||||
env:
|
||||
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES: ${{ matrix.cuda_visible_devices }}
|
||||
WANDB_DISABLED: true
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
source activate accelerate
|
||||
pip install -r examples/pytorch/_tests_requirements.txt
|
||||
pytest -sv examples/pytorch/test_accelerate_examples.py examples/pytorch/test_pytorch_examples.py
|
||||
|
||||
run-skorch-tests:
|
||||
container:
|
||||
image: huggingface/accelerate-gpu:latest
|
||||
options: --gpus all --shm-size "16gb"
|
||||
runs-on: [self-hosted, docker-gpu, multi-gpu]
|
||||
runs-on: [self-hosted, multi-gpu, nvidia-gpu, t4, ci]
|
||||
strategy:
|
||||
fail-fast: false
|
||||
matrix:
|
||||
skorch-version: [
|
||||
pypi,
|
||||
github
|
||||
]
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- name: Update accelerate clone and pip install
|
||||
working-directory: accelerate/
|
||||
- name: Install accelerate
|
||||
run:
|
||||
source activate accelerate;
|
||||
git config --global --add safe.directory '*';
|
||||
git checkout main && git fetch && git checkout ${{ github.sha }};
|
||||
pip install -e .;
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate;
|
||||
cd accelerate;
|
||||
git checkout ${{ github.sha }};
|
||||
pip install -e .[testing];
|
||||
cd ..
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Update skorch clone & pip install
|
||||
working-directory: skorch/
|
||||
- name: Install skorch
|
||||
run: |
|
||||
source activate accelerate
|
||||
git clone https://github.com/skorch-dev/skorch;
|
||||
cd skorch;
|
||||
git config --global --add safe.directory '*'
|
||||
git checkout master && git pull
|
||||
if [[ ${{ matrix.skorch-version }} = pypi ]]; then
|
||||
git checkout $(git describe --tags `git rev-list --tags --max-count=1`)
|
||||
fi
|
||||
pip install .[testing]
|
||||
pip install flaky
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
4
.github/workflows/stale.yml
vendored
4
.github/workflows/stale.yml
vendored
@ -13,10 +13,10 @@ jobs:
|
||||
env:
|
||||
GITHUB_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
|
||||
steps:
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@v2
|
||||
- uses: actions/checkout@v3.1.0
|
||||
|
||||
- name: Setup Python
|
||||
uses: actions/setup-python@v1
|
||||
uses: actions/setup-python@v3
|
||||
with:
|
||||
python-version: 3.8
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -220,6 +220,7 @@ You shouldn't use 🤗 Accelerate if you don't want to write a training loop you
|
||||
|
||||
If you like the simplicity of 🤗 Accelerate but would prefer a higher-level abstraction around its capabilities, some frameworks and libraries that are built on top of 🤗 Accelerate are listed below:
|
||||
|
||||
* [Amphion](https://github.com/open-mmlab/Amphion) is a toolkit for Audio, Music, and Speech Generation. Its purpose is to support reproducible research and help junior researchers and engineers get started in the field of audio, music, and speech generation research and development.
|
||||
* [Animus](https://github.com/Scitator/animus) is a minimalistic framework to run machine learning experiments. Animus highlights common "breakpoints" in ML experiments and provides a unified interface for them within [IExperiment](https://github.com/Scitator/animus/blob/main/animus/core.py#L76).
|
||||
* [Catalyst](https://github.com/catalyst-team/catalyst#getting-started) is a PyTorch framework for Deep Learning Research and Development. It focuses on reproducibility, rapid experimentation, and codebase reuse so you can create something new rather than write yet another train loop. Catalyst provides a [Runner](https://catalyst-team.github.io/catalyst/api/core.html#runner) to connect all parts of the experiment: hardware backend, data transformations, model training, and inference logic.
|
||||
* [fastai](https://github.com/fastai/fastai#installing) is a PyTorch framework for Deep Learning that simplifies training fast and accurate neural nets using modern best practices. fastai provides a [Learner](https://docs.fast.ai/learner.html#Learner) to handle the training, fine-tuning, and inference of deep learning algorithms.
|
||||
@ -269,7 +270,7 @@ If you use 🤗 Accelerate in your publication, please cite it by using the foll
|
||||
```bibtex
|
||||
@Misc{accelerate,
|
||||
title = {Accelerate: Training and inference at scale made simple, efficient and adaptable.},
|
||||
author = {Sylvain Gugger, Lysandre Debut, Thomas Wolf, Philipp Schmid, Zachary Mueller, Sourab Mangrulkar, Marc Sun, Benjamin Bossan},
|
||||
author = {Sylvain Gugger and Lysandre Debut and Thomas Wolf and Philipp Schmid and Zachary Mueller and Sourab Mangrulkar and Marc Sun and Benjamin Bossan},
|
||||
howpublished = {\url{https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate}},
|
||||
year = {2022}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -28,7 +28,7 @@ RUN source activate accelerate && \
|
||||
RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir bitsandbytes
|
||||
|
||||
# Stage 2
|
||||
FROM nvidia/cuda:11.2.2-cudnn8-devel-ubuntu20.04 AS build-image
|
||||
FROM nvidia/cuda:12.1.0-cudnn8-devel-ubuntu20.04 AS build-image
|
||||
COPY --from=compile-image /opt/conda /opt/conda
|
||||
ENV PATH /opt/conda/bin:$PATH
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -15,6 +15,8 @@
|
||||
title: Launching distributed code
|
||||
- local: basic_tutorials/notebook
|
||||
title: Launching distributed training from Jupyter Notebooks
|
||||
- local: basic_tutorials/troubleshooting
|
||||
title: Troubleshooting guide
|
||||
title: Tutorials
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: usage_guides/explore
|
||||
@ -37,12 +39,10 @@
|
||||
title: Saving and loading training states
|
||||
- local: usage_guides/tracking
|
||||
title: Using experiment trackers
|
||||
- local: usage_guides/debug
|
||||
title: Debugging timeout errors
|
||||
- local: usage_guides/memory
|
||||
title: How to avoid CUDA Out-of-Memory
|
||||
- local: usage_guides/mps
|
||||
title: How to use Apple Silicon M1 GPUs
|
||||
- local: usage_guides/low_precision_training
|
||||
title: How to train in low precision (FP8)
|
||||
- local: usage_guides/deepspeed
|
||||
title: How to use DeepSpeed
|
||||
- local: usage_guides/fsdp
|
||||
@ -55,6 +55,8 @@
|
||||
title: How to use 🤗 Accelerate with Intel® Extension for PyTorch for cpu
|
||||
title: How-To Guides
|
||||
- sections:
|
||||
- local: concept_guides/internal_mechanism
|
||||
title: 🤗 Accelerate's internal mechanism
|
||||
- local: concept_guides/big_model_inference
|
||||
title: Loading big models into memory
|
||||
- local: concept_guides/performance
|
||||
@ -63,6 +65,8 @@
|
||||
title: Executing and deferring jobs
|
||||
- local: concept_guides/gradient_synchronization
|
||||
title: Gradient synchronization
|
||||
- local: concept_guides/low_precision_training
|
||||
title: How training in low-precision environments is possible (FP8)
|
||||
- local: concept_guides/training_tpu
|
||||
title: TPU best practices
|
||||
title: Concepts and fundamentals
|
||||
|
||||
@ -153,6 +153,15 @@ the below example enabling unbuffered stdout and stderr:
|
||||
python -u -m accelerate.commands.launch --num_processes=2 {script_name.py} {--arg1} {--arg2}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
You can run your code on CPU as well! This is helpful for debugging and testing purposes on toy models and datasets.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
accelerate launch --cpu {script_name.py} {--arg1} {--arg2}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## Why you should always use `accelerate config`
|
||||
|
||||
@ -200,3 +209,24 @@ Launching a script from the location of that custom yaml file looks like the fol
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
accelerate launch --config_file {path/to/config/my_config_file.yaml} {script_name.py} {--arg1} {--arg2} ...
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Multi-node training
|
||||
Multi-node training with 🤗Accelerate is similar to [multi-node training with torchrun](https://pytorch.org/tutorials/intermediate/ddp_series_multinode.html). The simplest way to launch a multi-node training run is to do the following:
|
||||
|
||||
- Copy your codebase and data to all nodes. (or place them on a shared filesystem)
|
||||
- Setup your python packages on all nodes.
|
||||
- Run `accelerate config` on the main single node first. After specifying the number of nodes, you will be asked to specify the rank of each node (this will be 0 for the main/master node), along with the IP address and port for the main process. This is required for the worker nodes to communicate with the main process. Afterwards, you can copy or send this config file across all of your nodes, changing the `machine_rank` to 1, 2,3, etc. to avoid having to run the command (or just follow their directions directly for launching with `torchrun` as well)
|
||||
|
||||
Once you have done this, you can start your multi-node training run by running `accelerate launch` (or `torchrun`) on all nodes.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
It is required that the command be ran on all nodes for everything to start, not just running it from the main node. You can use something like SLURM or a different process executor to wrap around this requirement and call everything from a single command.
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
It is recommended to use the intranet IP of your main node over the public IP for better latency. This is the `192.168.x.x` or the `172.x.x.x` address you see when you run `hostname -I` on the main node.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
To get a better idea about multi-node training, check out our example for [multi-node training with FSDP](https://huggingface.co/blog/ram-efficient-pytorch-fsdp).
|
||||
|
||||
222
docs/source/basic_tutorials/troubleshooting.md
Normal file
222
docs/source/basic_tutorials/troubleshooting.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,222 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Troubleshooting guide
|
||||
|
||||
This guide aims to provide you the tools and knowledge required to navigate some common issues. However,
|
||||
as 🤗 Accelerate continuously evolves and the use cases and setups are diverse, you might encounter an issue not covered in this
|
||||
guide. If the suggestions listed in this guide do not cover your such situation, please refer to the final section of
|
||||
the guide, [Asking for Help](#ask-for-help), to learn where to find help with your specific issue.
|
||||
|
||||
## Logging
|
||||
|
||||
When facing an error, logging can help narrow down where it is coming from. In a distributed setup with multiple processes,
|
||||
logging can be a challenge, but 🤗 Accelerate provides a utility that streamlines the logging process and ensures that
|
||||
logs are synchronized and managed effectively across the distributed setup.
|
||||
|
||||
To troubleshoot an issue, use `accelerate.logging` instead of the standard Python `logging` module:
|
||||
|
||||
```diff
|
||||
- import logging
|
||||
+ from accelerate.logging import get_logger
|
||||
- logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
|
||||
+ logger = get_logger(__name__)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To set the log level (`INFO`, `DEBUG`, `WARNING`, `ERROR`, `CRITICAL`), export it as the `ACCELERATE_LOG_LEVEL` environment,
|
||||
or pass as `log_level` to `get_logger`:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from accelerate.logging import get_logger
|
||||
|
||||
logger = get_logger(__name__, log_level="INFO")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
By default, the log is called on main processes only. To call it on all processes, pass `main_process_only=False`.
|
||||
If a log should be called on all processes and in order, also pass `in_order=True`.
|
||||
|
||||
## Hanging code and timeout errors
|
||||
|
||||
### Mismatched tensor shapes
|
||||
|
||||
If your code seems to be hanging for a significant amount time on a distributed setup, a common cause is mismatched shapes of tensors on different
|
||||
devices.
|
||||
|
||||
When running scripts in a distributed fashion, functions such as [`Accelerator.gather`] and [`Accelerator.reduce`] are
|
||||
necessary to grab tensors across devices to perform operations on them collectively. These (and other) functions rely on
|
||||
`torch.distributed` performing a `gather` operation, which requires that tensors have the **exact same shape** across all processes.
|
||||
When the tensor shapes don't match, you will experience handing code, and eventually hit a timeout exception.
|
||||
|
||||
If you suspect this to be the case, use Accelerate's operational debug mode to immediately catch the issue.
|
||||
|
||||
The recommended way to enable Accelerate's operational debug mode is during `accelerate config` setup.
|
||||
Alternative ways to enable debug mode are:
|
||||
|
||||
* From the CLI:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
accelerate launch --debug {my_script.py} --arg1 --arg2
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* As an environmental variable (which avoids the need for `accelerate launch`):
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
ACCELERATE_DEBUG_MODE="1" torchrun {my_script.py} --arg1 --arg2
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
* Manually changing the `config.yaml` file:
|
||||
|
||||
```diff
|
||||
compute_environment: LOCAL_MACHINE
|
||||
+debug: true
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Once you enable the debug mode, you should get a similar traceback that points to the tensor shape mismatch issue:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
Traceback (most recent call last):
|
||||
File "/home/zach_mueller_huggingface_co/test.py", line 18, in <module>
|
||||
main()
|
||||
File "/home/zach_mueller_huggingface_co/test.py", line 15, in main
|
||||
broadcast_tensor = broadcast(tensor)
|
||||
File "/home/zach_mueller_huggingface_co/accelerate/src/accelerate/utils/operations.py", line 303, in wrapper
|
||||
accelerate.utils.operations.DistributedOperationException:
|
||||
|
||||
Cannot apply desired operation due to shape mismatches. All shapes across devices must be valid.
|
||||
|
||||
Operation: `accelerate.utils.operations.broadcast`
|
||||
Input shapes:
|
||||
- Process 0: [1, 5]
|
||||
- Process 1: [1, 2, 5]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Early stopping leads to hanging
|
||||
|
||||
When doing early stopping in distributed training, if each process has a specific stopping condition (e.g. validation loss),
|
||||
it may not be synchronized across all of them. As a result, a break can happen on process 0 but not on process 1.
|
||||
This will cause the code to hang indefinitely until a timeout occurs.
|
||||
|
||||
If you have early stopping conditionals, use `set_breakpoint` and `check_breakpoint` methods to make sure all the processes
|
||||
are ended correctly:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
# Assume `should_do_breakpoint` is a custom defined function that returns a conditional,
|
||||
# and that conditional might be true only on process 1
|
||||
if should_do_breakpoint(loss):
|
||||
accelerator.set_breakpoint()
|
||||
|
||||
# Later in the training script when we need to check for the breakpoint
|
||||
if accelerator.check_breakpoint():
|
||||
break
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Hanging on low kernel versions on Linux
|
||||
|
||||
This is a known issue. On Linux with kernel version < 5.5, hanging processes have been reported. To avoid
|
||||
encountering this problem, we recommend upgrading your system to a later kernel version.
|
||||
|
||||
## CUDA out of memory
|
||||
|
||||
One of the most frustrating errors when it comes to running training scripts is hitting "CUDA Out-of-Memory",
|
||||
as the entire script needs to be restarted, progress is lost, and typically a developer would want to simply
|
||||
start their script and let it run.
|
||||
|
||||
To address this problem, `Accelerate` offers a utility `find_executable_batch_size` that is heavily based on [toma](https://github.com/BlackHC/toma).
|
||||
The utility retries code that fails due to OOM (out-of-memory) conditions and lowers batch sizes automatically.
|
||||
|
||||
### find_executable_batch_size
|
||||
|
||||
This algorithm operates with exponential decay, decreasing the batch size in half after each failed run on some
|
||||
training script. To use it, restructure your training function to include an inner function that includes this wrapper,
|
||||
and build your dataloaders inside it. At a minimum, this could look like 4 new lines of code.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
The inner function *must* take in the batch size as the first parameter, but we do not pass one to it when called. The wrapper handles this for us.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
It should also be noted that anything which will consume CUDA memory and passed to the `accelerator` **must** be declared inside the inner function,
|
||||
such as models and optimizers.
|
||||
|
||||
```diff
|
||||
def training_function(args):
|
||||
accelerator = Accelerator()
|
||||
|
||||
+ @find_executable_batch_size(starting_batch_size=args.batch_size)
|
||||
+ def inner_training_loop(batch_size):
|
||||
+ nonlocal accelerator # Ensure they can be used in our context
|
||||
+ accelerator.free_memory() # Free all lingering references
|
||||
model = get_model()
|
||||
model.to(accelerator.device)
|
||||
optimizer = get_optimizer()
|
||||
train_dataloader, eval_dataloader = get_dataloaders(accelerator, batch_size)
|
||||
lr_scheduler = get_scheduler(
|
||||
optimizer,
|
||||
num_training_steps=len(train_dataloader)*num_epochs
|
||||
)
|
||||
model, optimizer, train_dataloader, eval_dataloader, lr_scheduler = accelerator.prepare(
|
||||
model, optimizer, train_dataloader, eval_dataloader, lr_scheduler
|
||||
)
|
||||
train(model, optimizer, train_dataloader, lr_scheduler)
|
||||
validate(model, eval_dataloader)
|
||||
+ inner_training_loop()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To find out more, check the documentation [here](../package_reference/utilities#accelerate.find_executable_batch_size).
|
||||
|
||||
## Non-reproducible results between device setups
|
||||
|
||||
If you have changed the device setup and are observing different model performance, this is likely due to the fact that
|
||||
you have not updated your script when moving from one setup to another. The same script with the same batch size across TPU,
|
||||
multi-GPU, and single-GPU with Accelerate will have different results.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, if you were previously training on a single GPU with a batch size of 16, when moving to two GPU setup,
|
||||
you need to change the batch size to 8 to have the same effective batch size. This is because when training with Accelerate,
|
||||
the batch size passed to the dataloader is the **batch size per GPU**.
|
||||
|
||||
To make sure you can reproduce the results between the setups, make sure to use the same seed, adjust the batch size
|
||||
accordingly, consider scaling the learning rate.
|
||||
|
||||
For more details and a quick reference for batch sizes, check out the [Comparing performance between different device setups](../concept_guides/performance) guide.
|
||||
|
||||
## Performance issues on different GPUs
|
||||
|
||||
If your multi-GPU setup consists of different GPUs, you may hit some limitations:
|
||||
|
||||
- There may be an imbalance in GPU memory between the GPUs. In this case, the GPU with smaller memory will limit the batch size or the size of the model that can be loaded onto the GPUs.
|
||||
- If you are using GPUs with different performance profiles, the performance will be driven by the slowest GPU that you are using as the other GPUs will have to wait for it to complete its workload.
|
||||
|
||||
Vastly different GPUs within the same setup can lead to performance bottlenecks.
|
||||
|
||||
## Ask for help
|
||||
|
||||
If the above troubleshooting tools and advice did not help you resolve your issue, reach out for help to the community
|
||||
and the team.
|
||||
|
||||
### Forums
|
||||
|
||||
Ask for help on the Hugging Face forums - post your question in the [🤗Accelerate category](https://discuss.huggingface.co/c/accelerate/18)
|
||||
Make sure to write a descriptive post with relevant context about your setup and reproducible code to maximize the likelihood that your problem is solved!
|
||||
|
||||
### Discord
|
||||
|
||||
Post a question on [Discord](http://hf.co/join/discord), and let the team and the community help you.
|
||||
|
||||
### GitHub Issues
|
||||
|
||||
Create an Issue on the 🤗 Accelerate [GitHub repository](https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate/issues) if you suspect
|
||||
to have found a bug related to the library. Include context regarding the bug and details about your distributed setup
|
||||
to help us better figure out what's wrong and how we can fix it.
|
||||
@ -154,7 +154,7 @@ By passing `device_map="auto"`, we tell 🤗 Accelerate to determine automatical
|
||||
#### `no_split_module_classes`
|
||||
|
||||
This parameter will indicate that some of the modules with the name `"Block"` should not be split across different devices. You should set here all blocks that
|
||||
include a residutal connection of some kind.
|
||||
include a residual connection of some kind.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### The `device_map`
|
||||
@ -295,11 +295,44 @@ device_map = {"block1": 0, "block2.linear1": 1, "block2.linear2": 1}
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## CPU offload only
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to offload your model on CPU, you can use [`cpu_offload`]. As a result, all parameters of the model will be offloaded and only one copy of the state dict of the model will be kept. During the forward pass, parameters will be extracted from that state dict and put on the execution device and passed as they are needed, then offloaded again.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
cpu_offload(model, execution_device)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can also use [`cpu_offload_with_hook`]. This function will offloads a model on the CPU and puts it back to an execution device when executed. The difference with [`cpu_offload`] is that the model stays on the execution device after the forward and is only offloaded again when the `offload` method of the returned `hook` is called. Furthermore, [`cpu_offload_with_hook`] is more performant but less memory saving. It is useful for pipelines running a model in a loop:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
model_1, hook_1 = cpu_offload_with_hook(model_1, execution_device)
|
||||
model_2, hook_2 = cpu_offload_with_hook(model_2, execution_device, prev_module_hook=hook_1)
|
||||
model_3, hook_3 = cpu_offload_with_hook(model_3, execution_device, prev_module_hook=hook_2)
|
||||
|
||||
hid_1 = model_1(input)
|
||||
for i in range(50):
|
||||
# model1 is offloaded on the CPU at the first iteration, model 2 stays on the GPU for this whole loop.
|
||||
hid_2 = model_2(hid_1)
|
||||
# model2 is offloaded to the CPU just before this forward.
|
||||
hid_3 = model_3(hid_3)
|
||||
|
||||
# For model3, you need to manually call the hook offload method.
|
||||
hook_3.offload()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Disk offload only
|
||||
|
||||
To perform disk offload, you can use [`disk_offload`]. As a result, all parameters of the model will be offloaded as memory-mapped array in a given folder. During the forward pass, parameters will be accessed from that folder and put on the execution device passed as they are needed, then offloaded again.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
disk_offload(model, offload_dir, execution_device)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Limits and further development
|
||||
|
||||
We are aware of the current limitations in the API:
|
||||
|
||||
- While this could theoretically work on just one CPU with potential disk offload, you need at least one GPU to run this API. This will be fixed in further development.
|
||||
- [`infer_auto_device_map`] (or `device_map="auto"` in [`load_checkpoint_and_dispatch`]) tries to maximize GPU and CPU RAM it sees available when you execute it. While PyTorch is very good at managing GPU RAM efficiently (and giving it back when not needed), it's not entirely true with Python and CPU RAM. Therefore, an automatically computed device map might be too intense on the CPU. Move a few modules to the disk device if you get crashes due to a lack of RAM.
|
||||
- [`infer_auto_device_map`] (or `device_map="auto"` in [`load_checkpoint_and_dispatch`]) attributes devices sequentially (to avoid moving things back and forth) so if your first layer is bigger than the size of the GPU you have, it will end up with everything on the CPU/Disk.
|
||||
- [`load_checkpoint_and_dispatch`] and [`load_checkpoint_in_model`] do not perform any check on the correctness of your state dict compared to your model at the moment (this will be fixed in a future version), so you may get some weird errors if trying to load a checkpoint with mismatched or missing keys.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -55,8 +55,8 @@ their gradients computed, collated, and updated before moving on to the next
|
||||
batch of data.
|
||||
When performing gradient accumulation, you accumulate `n` loss gradients and
|
||||
skip `optimizer.step()` until `n` batches have been reached. As all training
|
||||
processes only need to sychronize by the time `optimizer.step()` is called,
|
||||
without any modification to your training step, this neededless inter-process
|
||||
processes only need to synchronize by the time `optimizer.step()` is called,
|
||||
without any modification to your training step, this needless inter-process
|
||||
communication can cause a significant slowdown.
|
||||
|
||||
How can you avoid this overhead?
|
||||
|
||||
72
docs/source/concept_guides/internal_mechanism.md
Normal file
72
docs/source/concept_guides/internal_mechanism.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,72 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2021 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# 🤗 Accelerate's internal mechanisms
|
||||
|
||||
Internally, 🤗 Accelerate works by first analyzing the environment in which the script is launched to determine which
|
||||
kind of distributed setup is used, how many different processes there are and which one the current script is in. All
|
||||
that information is stored in the [`~AcceleratorState`].
|
||||
|
||||
This class is initialized the first time you instantiate an [`~Accelerator`] as well as performing any
|
||||
specific initialization your distributed setup needs. Its state is then uniquely shared through all instances of
|
||||
[`~state.AcceleratorState`]. (The same can also be done with the [`PartialState`], a more barebones version it inherits)
|
||||
|
||||
Then, when calling [`~Accelerator.prepare`], the library:
|
||||
|
||||
- wraps your model(s) in the container adapted for the distributed setup,
|
||||
- wraps your optimizer(s) in an [`~optimizer.AcceleratedOptimizer`],
|
||||
- wraps your scheduler(s) in an [`~scheduler.AcceleratedScheduler`]
|
||||
- creates a new version of your dataloader(s) in a [`~data_loader.DataLoaderShard`] or [`~data_loader.DataLoaderDispatcher`]
|
||||
|
||||
While the model(s), optimizer(s), and scheduler(s) are just put in simple wrappers, the dataloader(s) are re-created. This is mostly
|
||||
because PyTorch does not let the user change the `batch_sampler` of a dataloader once it's been created and the
|
||||
library handles the sharding of your data between processes by changing that `batch_sampler` to yield every other
|
||||
`num_processes` batches (if enabled).
|
||||
|
||||
The [`~data_loader.DataLoaderShard`] subclasses `DataLoader` to add the following functionality:
|
||||
|
||||
- it synchronizes the appropriate random number generator of all processes at each new iteration, to ensure any
|
||||
randomization (like shuffling) is done the exact same way across processes.
|
||||
- it puts the batches on the proper device before yielding them (unless you have opted out of
|
||||
`device_placement=True`).
|
||||
|
||||
The [`~data_loader.DataLoaderDispatcher`] subclasses differs from the [`~data_loader.DataLoaderShard`] in that when iterating through the `DataLoader`, the data is all starting from process 0 and *then* split and sent off to each process rather than it happening at the dataset level.
|
||||
|
||||
The random number generator synchronization will by default synchronize:
|
||||
|
||||
- the `generator` attribute of a given sampler (like the PyTorch `RandomSampler`) for PyTorch >= 1.6
|
||||
- the main random number generator in PyTorch <=1.5.1
|
||||
|
||||
You can choose which random number generator(s) to synchronize with the `rng_types` argument of the main
|
||||
[`Accelerator`]. In PyTorch >= 1.6, it is recommended to rely on a local `generator` to avoid
|
||||
setting the same seed in the main random number generator in all processes.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
Synchronization of the main torch (or CUDA or XLA) random number generator will affect any other potential random
|
||||
artifacts you could have in your dataset (like random data augmentation) in the sense that all processes will get
|
||||
the same random numbers from the torch random modules (so will apply the same random data augmentation if it's
|
||||
controlled by torch).
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
The randomization part of your custom sampler, batch sampler or iterable dataset should be done using a local
|
||||
`torch.Generator` object (in PyTorch >= 1.6), see the traditional `RandomSampler`, as an example.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
For more details about the internals, see the [Internals page](package_reference/torch_wrappers).
|
||||
74
docs/source/concept_guides/low_precision_training.md
Normal file
74
docs/source/concept_guides/low_precision_training.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,74 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Low Precision Training Methods
|
||||
|
||||
The release of new kinds of hardware led to the emergence of new training paradigms that better utilize them. Currently, this is in the form of training
|
||||
in 8-bit precision using packages such as [TranformersEngine](https://github.com/NVIDIA/TransformerEngine) (TE) or [MS-AMP](https://github.com/Azure/MS-AMP/tree/main).
|
||||
|
||||
For an introduction to the topics discussed today, we recommend reviewing the [low-precision usage guide](../usage_guides/low_precision_training.md) as this documentation will reference it regularly.
|
||||
|
||||
## A Quick Chart
|
||||
|
||||
Below is a quick chart from the MS-AMP documentation showing the different bit-precisions for each solution during training:
|
||||
|
||||
Optimization Level | Computation(GEMM) | Comm | Weight | Master Weight | Weight Gradient | Optimizer States
|
||||
-- | -- | -- | -- | -- | -- | --
|
||||
FP16 AMP | FP16 | FP32 | FP32 | N/A | FP32 | FP32+FP32
|
||||
Nvidia TE | FP8 | FP32 | FP32 | N/A | FP32 | FP32+FP32
|
||||
MS-AMP O1 | FP8 | FP8 | FP16 | N/A | FP8 | FP32+FP32
|
||||
MS-AMP O2 | FP8 | FP8 | FP16 | N/A | FP8 | FP8+FP16
|
||||
MS-AMP O3 | FP8 | FP8 | FP8 | FP16 | FP8 | FP8+FP16
|
||||
|
||||
## `TransformersEngine`
|
||||
|
||||
`TranformersEngine` is the first solution to trying to train in 8-bit floating point. It works by using drop-in replacement layers for certain ones in a model that utilize their FP8-engine to reduce the number of bits (such as 32 to 8) without degrading the final accuracy of the model.
|
||||
|
||||
Specifically, 🤗 Accelerate will find and replace the following layers with `TranformersEngine` versions:
|
||||
|
||||
* `nn.LayerNorm` for `te.LayerNorm`
|
||||
* `nn.Linear` for `te.Linear`
|
||||
|
||||
As a result we wind up with a model that has most of its layers in BF16, while some layers are in FP8 reducing some of the memory.
|
||||
|
||||
Anecdotally, we have noticed that performance gains don't really start showing when using `TransformerEngine` until a large majority of the layers
|
||||
in the model are made up of those two layers to replace. As a result, only larger models have shown performance improvements when the number of parameters is around and upwards of a few billion.
|
||||
|
||||
The `TransformerEngine` can receive many different arguments that customize how it performs FP8 calculations and what they do. A full list of the arguments is available below:
|
||||
|
||||
* `margin`: The margin to use for the gradient scaling.
|
||||
* `interval`: The interval to use for how often the scaling factor is recomputed.
|
||||
* `fp8_format``: The format to use for the FP8 recipe. Must be one of `E4M3` or `HYBRID`.
|
||||
* `amax_history_len`: The length of the history to use for the scaling factor computation
|
||||
* `amax_compute_algo`: The algorithm to use for the scaling factor computation. Must be one of `max` or `most_recent`.
|
||||
* `override_linear_precision`: Whether or not to execute `fprop`, `dgrad`, and `wgrad` GEMMS in higher precision.
|
||||
|
||||
You can customize each of these as part of [`utils.FP8RecipeKwargs`] to help optimize performance of your models.
|
||||
|
||||
If we notice in the chart mentioned earlier, TE simply casts the computation layers into FP8, while everything else is in FP32. As a result this winds up utilizing the most memory but does so with the benefit of guaranteeing the least amount of loss in end accuracy during training.
|
||||
|
||||
## `MS-AMP`
|
||||
|
||||
MS-AMP takes a different approach to `TransformersEngine` by providing three different optimization levels to convert more operations in FP8 or FP16.
|
||||
|
||||
* The base optimization level (`O1`), passes communications of the weights (such as in DDP) in FP8, stores the weights of the model in FP16, and leaves the optimizer states in FP32. The main benefit of this optimization level is that we can reduce the communication bandwidth by essentially half. Additionally, more GPU memory is saved due to 1/2 of everything being cast in FP8, and the weights being cast to FP16. Notably, both the optimizer states remain in FP32.
|
||||
|
||||
* The second optimization level (`O2`) improves upon this by also reducing the precision of the optimizer states. One is in FP8 while the other is in FP16. Generally it's been shown that this will only provide a net-gain of no degredated end accuracy, increased training speed, and reduced memory as now every state is either in FP16 or FP8.
|
||||
|
||||
* Finally, MS-AMP has a third optimization level (`O3`) which helps during DDP scenarios such as DeepSpeed. The weights of the model in memory are fully cast to FP8, and the master weights are now stored in FP16. This fully reduces memory by the highest factor as now not only is almost everything in FP8, only two states are left in FP16. Currently, only DeepSpeed versions up through 0.9.2 are supported, so this capability is not included in the 🤗 Accelerate integration
|
||||
|
||||
## Combining the two
|
||||
|
||||
More experiments need to be performed but it's been noted that combining both MS-AMP and TransformersEngine can lead to the highest throughput by relying on NVIDIA's optimized FP8 operators and utilizing how MS-AMP reduces the memory overhead.
|
||||
@ -74,7 +74,7 @@ In this example, there are two GPUs for "Multi-GPU" and a TPU pod with 8 workers
|
||||
|
||||
## Learning Rates
|
||||
|
||||
As noted in multiple sources[[1](https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/machine-learning/scalable-multi-node-deep-learning-training-using-gpus-in-the-aws-cloud/)][[2](https://docs.nvidia.com/clara/tlt-mi_archive/clara-train-sdk-v2.0/nvmidl/appendix/training_with_multiple_gpus.html)], the learning rate should be scaled *linearly* based on the number of devices present. The below
|
||||
As noted in multiple sources[[1](https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/machine-learning/scalable-multi-node-deep-learning-training-using-gpus-in-the-aws-cloud/)][[2](https://docs.nvidia.com/clara/clara-train-sdk/pt/model.html#classification-models-multi-gpu-training)], the learning rate should be scaled *linearly* based on the number of devices present. The below
|
||||
snippet shows doing so with Accelerate:
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -36,7 +36,7 @@ Below is an example of a training function passed to the [`notebook_launcher`] i
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
This code snippet is based off the one from the `simple_nlp_example` notebook found [here](https://github.com/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/accelerate/simple_nlp_example.ipynb) with slight
|
||||
This code snippet is based off the one from the `simple_nlp_example` notebook found [here](https://github.com/huggingface/notebooks/blob/main/examples/accelerate_examples/simple_nlp_example.ipynb) with slight
|
||||
modifications for the sake of simplicity
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -19,6 +19,7 @@ rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] big_modeling.init_empty_weights
|
||||
[[autodoc]] big_modeling.cpu_offload
|
||||
[[autodoc]] big_modeling.cpu_offload_with_hook
|
||||
[[autodoc]] big_modeling.disk_offload
|
||||
[[autodoc]] big_modeling.dispatch_model
|
||||
[[autodoc]] big_modeling.load_checkpoint_and_dispatch
|
||||
|
||||
@ -199,7 +199,7 @@ The following arguments are only useful when `use_deepspeed` is passed or `deeps
|
||||
|
||||
**Fully Sharded Data Parallelism Arguments**:
|
||||
|
||||
The following arguments are only useful when `use_fdsp` is passed or Fully Sharded Data Parallelism is configured through `accelerate config`:
|
||||
The following arguments are only useful when `use_fsdp` is passed or Fully Sharded Data Parallelism is configured through `accelerate config`:
|
||||
|
||||
* `--fsdp_offload_params` (`str`) -- Decides Whether (true|false) to offload parameters and gradients to CPU.
|
||||
* `--fsdp_min_num_params` (`int`) -- FSDP's minimum number of parameters for Default Auto Wrapping.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -15,23 +15,7 @@ rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
# Logging with Accelerate
|
||||
|
||||
Accelerate has its own logging utility to handle logging while in a distributed system.
|
||||
To utilize this replace cases of `logging` with `accelerate.logging`:
|
||||
```diff
|
||||
- import logging
|
||||
+ from accelerate.logging import get_logger
|
||||
- logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
|
||||
+ logger = get_logger(__name__)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Setting the log level
|
||||
|
||||
The log level can be set with the `ACCELERATE_LOG_LEVEL` environment variable or by passing
|
||||
`log_level` to `get_logger`:
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from accelerate.logging import get_logger
|
||||
|
||||
logger = get_logger(__name__, log_level="INFO")
|
||||
```
|
||||
Refer to the [Troubleshooting guide](../usage_guides/troubleshooting#logging) or to the example below to learn
|
||||
how to use 🤗 Accelerate's logger.
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] logging.get_logger
|
||||
@ -31,3 +31,5 @@ rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
- __init__
|
||||
[[autodoc]] tracking.MLflowTracker
|
||||
- __init__
|
||||
[[autodoc]] tracking.ClearMLTracker
|
||||
- __init__
|
||||
|
||||
@ -40,6 +40,12 @@ The following are constants used when utilizing [`Accelerator.save_model`]
|
||||
|
||||
These are basic dataclasses used throughout 🤗 Accelerate and they can be passed in as parameters.
|
||||
|
||||
### Standalone
|
||||
|
||||
These are standalone dataclasses used for checks, such as the type of distributed system being used
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.ComputeEnvironment
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.DistributedType
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.DynamoBackend
|
||||
@ -48,7 +54,25 @@ These are basic dataclasses used throughout 🤗 Accelerate and they can be pass
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.PrecisionType
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.ProjectConfiguration
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.RNGType
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.SageMakerDistributedType
|
||||
|
||||
### Kwargs
|
||||
|
||||
These are configurable arguemnts for specific interactions throughout the PyTorch ecosystem that Accelerate handles under the hood.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.AutocastKwargs
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.DistributedDataParallelKwargs
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.FP8RecipeKwargs
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.GradScalerKwargs
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.InitProcessGroupKwargs
|
||||
|
||||
## Plugins
|
||||
|
||||
@ -65,6 +89,22 @@ for convience all of them are available to see here:
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.TorchDynamoPlugin
|
||||
|
||||
## Configurations
|
||||
|
||||
These are classes which can be configured and passed through to the appropriate integration
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.BnbQuantizationConfig
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.ProjectConfiguration
|
||||
|
||||
## Environmental Variables
|
||||
|
||||
These are environmental variables that can be enabled for different use cases
|
||||
|
||||
* `ACCELERATE_DEBUG_MODE` (`str`): Whether to run accelerate in debug mode. More info available [here](../usage_guides/debug.md).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Data Manipulation and Operations
|
||||
|
||||
@ -72,16 +112,30 @@ These include data operations that mimic the same `torch` ops but can be used on
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.broadcast
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.broadcast_object_list
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.concatenate
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.convert_outputs_to_fp32
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.convert_to_fp32
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.gather
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.gather_object
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.listify
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.pad_across_processes
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.recursively_apply
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.reduce
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.send_to_device
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.slice_tensors
|
||||
|
||||
## Environment Checks
|
||||
|
||||
These functionalities check the state of the current working environment including information about the operating system itself, what it can support, and if particular dependencies are installed.
|
||||
@ -112,20 +166,38 @@ When setting up 🤗 Accelerate for the first time, rather than running `acceler
|
||||
|
||||
## Memory
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.get_max_memory
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.find_executable_batch_size
|
||||
|
||||
## Modeling
|
||||
|
||||
These utilities relate to interacting with PyTorch models
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.calculate_maximum_sizes
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.compute_module_sizes
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.extract_model_from_parallel
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.get_balanced_memory
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.get_max_layer_size
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.infer_auto_device_map
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.load_checkpoint_in_model
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.load_offloaded_weights
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.load_state_dict
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.offload_state_dict
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.retie_parameters
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.set_module_tensor_to_device
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.shard_checkpoint
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Parallel
|
||||
|
||||
@ -166,5 +238,3 @@ These include utilities that are useful to load checkpoints.
|
||||
These include utilities that are useful to quantize model.
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.load_and_quantize_model
|
||||
|
||||
[[autodoc]] utils.BnbQuantizationConfig
|
||||
@ -15,13 +15,20 @@ rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
# Quick tour
|
||||
|
||||
Let's have a look at the 🤗 Accelerate main features and traps to avoid.
|
||||
This guide aims to help you get started with 🤗 Accelerate quickly. It covers the essential steps you need to take to
|
||||
enable distributed training, as well as the adjustments that you need to make in some common scenarios.
|
||||
|
||||
## Main use
|
||||
To help you navigate, the guide is split into two sections:
|
||||
* [Getting Started with 🤗 Accelerate](#getting-started-with--accelerate): start here to learn how to modify your script to enable distributed training with 🤗 Accelerate
|
||||
* [Common adaptations to the base case](#common-adaptations-to-the-base-case): check out this section for common deviations from the baseline scenario and what adjustments may need to be made to support them.
|
||||
|
||||
To use 🤗 Accelerate in your own script, you have to change four things:
|
||||
## Getting started with 🤗 Accelerate
|
||||
|
||||
1. Import the [`Accelerator`] main class and instantiate one in an `accelerator` object:
|
||||
### Enable distributed training in your script
|
||||
|
||||
To use 🤗 Accelerate in your own training script, you have to modify four things:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Import the [`Accelerator`] main class and instantiate one in an `accelerator` object.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from accelerate import Accelerator
|
||||
@ -29,27 +36,27 @@ from accelerate import Accelerator
|
||||
accelerator = Accelerator()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This should happen as early as possible in your training script as it will initialize everything necessary for
|
||||
distributed training. You don't need to indicate the kind of environment you are in (just one machine with a GPU, one
|
||||
machines with several GPUs, several machines with multiple GPUs or a TPU), the library will detect this automatically.
|
||||
Add this at the beginning of your training script as it will initialize everything necessary for distributed training.
|
||||
You don't need to indicate the kind of environment you are in (a single machine with a GPU, a machine with several GPUs,
|
||||
or several machines with multiple GPUs or a TPU), the library will detect this automatically.
|
||||
|
||||
2. Remove the call `.to(device)` or `.cuda()` for your model and input data. The `accelerator` object
|
||||
will handle this for you and place all those objects on the right device for you. If you know what you're doing, you
|
||||
can leave those `.to(device)` calls but you should use the device provided by the `accelerator` object:
|
||||
`accelerator.device`.
|
||||
2. Remove the `.to(device)` or `.cuda()` calls for your model and input data.
|
||||
|
||||
To fully deactivate the automatic device placement, pass along `device_placement=False` when initializing your
|
||||
[`Accelerator`].
|
||||
The `accelerator` object will handle placing these objects on the right device for you.
|
||||
If you choose to leave those `.to(device)` calls, make sure to use the device provided by the `accelerator` object: `accelerator.device`.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
If you place your objects manually on the proper device, be careful to create your optimizer after putting your
|
||||
You can fully deactivate the automatic device placement by passing along `device_placement=False` when
|
||||
initializing the [`Accelerator`].
|
||||
However, if you place your objects manually on the proper device, be careful to create your optimizer after putting your
|
||||
model on `accelerator.device` or your training will fail on TPU.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
3. Pass all objects relevant to training (optimizer, model, training dataloader, learning rate scheduler) to the
|
||||
[`~Accelerator.prepare`] method. This will make sure everything is ready for training.
|
||||
3. Pass all PyTorch objects relevant to training (optimizer, model, dataloader(s), learning rate scheduler) to the
|
||||
[`~Accelerator.prepare`] method as soon as these objects are created, before starting your actual
|
||||
training loop:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
model, optimizer, train_dataloader, lr_scheduler = accelerator.prepare(
|
||||
@ -57,60 +64,42 @@ model, optimizer, train_dataloader, lr_scheduler = accelerator.prepare(
|
||||
)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
In particular, your training dataloader will be sharded across all GPUs/TPU cores available so that each one sees a
|
||||
different portion of the training dataset. Also, the random states of all processes will be synchronized at the
|
||||
beginning of each iteration through your dataloader, to make sure the data is shuffled the same way (if you decided to
|
||||
use `shuffle=True` or any kind of random sampler).
|
||||
**Important notes**:
|
||||
|
||||
* You should always pass the the learning rate scheduler to [`~Accelerator.prepare`], however if the scheduler should *not* be stepped at each optimization step, pass `step_with_optimizer=False` to the [`Accelerator`] init.
|
||||
* While you can send your dataloader to [`~Accelerator.prepare`] on its own (and there are cases for doing so, such as distributed inference), it's best to send it to [`~Accelerator.prepare`] together with the model and optimizer.
|
||||
* If you wish to run distributed evaluation, send your validation dataloader to [`~Accelerator.prepare`] as well. There are some nuances to distributed validation, check the [Distributed evaluation](#add-distributed-evaluation) section of the guide.
|
||||
* Any instruction using your training dataloader length (for instance if you want to log the number of total training
|
||||
steps) should go after the call to [`~Accelerator.prepare`].
|
||||
|
||||
Passing `DataLoader` objects to the [`~Accelerator.prepare`] method ensures that your dataloader will be sharded across
|
||||
all GPUs/TPU cores available so that each one sees a different portion of the training dataset. In other words, if there are 8 processes and a dataset of 64 items, each process will see 8 of these items per iteration. Also, the random states
|
||||
of all processes will be synchronized at the beginning of each iteration through your dataloader, to make sure the data
|
||||
is shuffled the same way (if you decided to use `shuffle=True` or any kind of random sampler).
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
The actual batch size for your training will be the number of devices used multiplied by the batch size you set in
|
||||
your script: for instance training on 4 GPUs with a batch size of 16 set when creating the training dataloader will
|
||||
train at an actual batch size of 64.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Alternatively, you can use the option `split_batches=True` when creating and initializing your
|
||||
[`Accelerator`], in which case the batch size will always stay the same, whether you run your
|
||||
script on 1, 2, 4, or 64 GPUs.
|
||||
|
||||
You should execute this instruction as soon as all objects for training are created, before starting your actual
|
||||
training loop.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
You should only pass the learning rate scheduler to [`~Accelerator.prepare`] when the scheduler needs to be stepped
|
||||
at each optimizer step.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
your script. For instance, training on 4 GPUs with a batch size of 16 set when creating the training dataloader will
|
||||
train at an actual batch size of 64 (4 * 16).
|
||||
If you want the batch size remain the same regardless of how many GPUs the script is run on, you can use the
|
||||
option `split_batches=True` when creating and initializing [`Accelerator`].
|
||||
Your training dataloader may change length when going through this method: if you run on X GPUs, it will have its
|
||||
length divided by X (since your actual batch size will be multiplied by X), unless you set
|
||||
`split_batches=True`.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Any instruction using your training dataloader length (for instance if you want to log the number of total training
|
||||
steps) should go after the call to [`~Accelerator.prepare`].
|
||||
|
||||
You can perfectly send your dataloader to [`~Accelerator.prepare`] on its own, but it's best to send the
|
||||
model and optimizer to [`~Accelerator.prepare`] together.
|
||||
|
||||
You may or may not want to send your validation dataloader to [`~Accelerator.prepare`], depending on
|
||||
whether you want to run distributed evaluation or not (see below).
|
||||
|
||||
4. Replace the line `loss.backward()` by `accelerator.backward(loss)`.
|
||||
4. Replace the `loss.backward()` line with `accelerator.backward(loss)`.
|
||||
|
||||
And you're all set! With all these changes, your script will run on your local machine as well as on multiple GPUs or a
|
||||
TPU! You can either use your favorite tool to launch the distributed training, or you can use the 🤗 Accelerate
|
||||
launcher.
|
||||
|
||||
### Add distributed evaluation
|
||||
|
||||
## Distributed evaluation
|
||||
|
||||
You can perform regular evaluation in your training script, if you leave your validation dataloader out of the
|
||||
You can perform regular evaluation in your training script if you leave your validation dataloader out of the
|
||||
[`~Accelerator.prepare`] method. In this case, you will need to put the input data on the
|
||||
`accelerator.device` manually.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -121,9 +110,9 @@ method:
|
||||
validation_dataloader = accelerator.prepare(validation_dataloader)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
As for your training dataloader, it will mean that (should you run your script on multiple devices) each device will
|
||||
only see part of the evaluation data. This means you will need to group your predictions together. This is very easy to
|
||||
do with the [`~Accelerator.gather_for_metrics`] method.
|
||||
Same as with your training dataloader, each device will only see part of the evaluation data should you run your script
|
||||
on multiple devices. This means you will need to group your predictions together which you can do with
|
||||
the [`~Accelerator.gather_for_metrics`] method.
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
for inputs, targets in validation_dataloader:
|
||||
@ -142,11 +131,9 @@ for inputs, targets in validation_dataloader:
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Any instruction using your training dataloader length (for instance if you need the number of total training steps
|
||||
to create a learning rate scheduler) should go after the call to [`~Accelerator.prepare`].
|
||||
|
||||
Some data at the end of the dataset may be duplicated so the batch can be divided equally among all workers. As a result, metrics
|
||||
should be calculated through the [`~Accelerator.gather_for_metrics`] method to automatically remove the duplicated data while gathering.
|
||||
Some data at the end of the dataset may be duplicated so the batch can be divided equally among all workers. As a result,
|
||||
metrics should be calculated through the [`~Accelerator.gather_for_metrics`] method to automatically remove the duplicated
|
||||
data while gathering and provide a more accurate metric.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -165,36 +152,35 @@ should be calculated through the [`~Accelerator.gather_for_metrics`] method to a
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## Launching your distributed script
|
||||
### Launch your distributed script
|
||||
|
||||
You can use the regular commands to launch your distributed training (like `torch.distributed.run` for
|
||||
PyTorch), they are fully compatible with 🤗 Accelerate.
|
||||
PyTorch) - they are fully compatible with 🤗 Accelerate.
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 Accelerate also provides a CLI tool that unifies all launchers, so you only have to remember one command. To use it,
|
||||
just run:
|
||||
Alternatively, 🤗 Accelerate provides a CLI tool that unifies all launchers, so you only have to remember one command. \
|
||||
To use it, run a quick configuration setup first on your machine and answer the questions:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
accelerate config
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
on your machine and reply to the questions asked. This will save a *default_config.yaml* file in your cache folder for
|
||||
🤗 Accelerate. That cache folder is (with decreasing order of priority):
|
||||
At the end of the setup, a *default_config.yaml* file will be saved in your cache folder for 🤗 Accelerate. That cache
|
||||
folder is (with decreasing order of priority):
|
||||
|
||||
- The content of your environment variable `HF_HOME` suffixed with *accelerate*.
|
||||
- If it does not exist, the content of your environment variable `XDG_CACHE_HOME` suffixed with
|
||||
*huggingface/accelerate*.
|
||||
- If this does not exist either, the folder *~/.cache/huggingface/accelerate*
|
||||
- If this does not exist either, the folder *~/.cache/huggingface/accelerate*.
|
||||
|
||||
You can also specify with the flag `--config_file` the location of the file you want to save.
|
||||
|
||||
Once this is done, you can test everything is going well on your setup by running:
|
||||
By specifying the `--config_file` flag you can specify an alternative location of the configuration file.
|
||||
Once the configuration setup is complete, you can test your setup by running:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
accelerate test
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This will launch a short script that will test the distributed environment. If it runs fine, you are ready for the next
|
||||
step!
|
||||
This will launch a short script that will test the distributed environment. If it runs without issues, you are ready for
|
||||
the next step!
|
||||
|
||||
Note that if you specified a location for the config file in the previous step, you need to pass it here as well:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -214,19 +200,23 @@ If you stored the config file in a non-default location, you can indicate it to
|
||||
accelerate launch --config_file path_to_config.yaml path_to_script.py --args_for_the_script
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can also override any of the arguments determined by your config file.
|
||||
To see the complete list of parameters that you can pass in, run `accelerate launch -h`.
|
||||
You can override any of the arguments determined by your config file. To see the complete list of parameters that you
|
||||
can pass in, run `accelerate launch -h`. (And further niche argument help by passing in partial commands, such as `accelerate launch --multi_gpu -h` for all `multi_gpu` args)
|
||||
|
||||
Check out the [Launch tutorial](basic_tutorials/launch) for more information about launching your scripts.
|
||||
Check out the [Launch tutorial](basic_tutorials/launch) for more information about launching your scripts.
|
||||
|
||||
## Common modifications of the base case
|
||||
|
||||
## Launching training from a notebook
|
||||
The previous section covers the minimal essential steps to move a training script into a distributed setup with 🤗 Accelerate.
|
||||
Here we describe common modifications/deviations from the base case scenario and the adjustments you need to make to accommodate for them.
|
||||
|
||||
In Accelerate 0.3.0, a new [`notebook_launcher`] has been introduced to help you launch your training
|
||||
function from a notebook. This launcher supports launching a training with TPUs on Colab or Kaggle, as well as training
|
||||
on several GPUs (if the machine on which you are running your notebook has them).
|
||||
### Launch distributed training from a notebook
|
||||
|
||||
Just define a function responsible for your whole training and/or evaluation in a cell of the notebook, then execute a
|
||||
Accelerate has a [`notebook_launcher`] to help you launch your training function from a
|
||||
notebook. This launcher supports launching a training with TPUs on Colab or Kaggle, as well as training on several GPUs and machines
|
||||
(if the machine on which you are running your notebook has them).
|
||||
|
||||
Define a function responsible for your whole training and/or evaluation in a cell of the notebook, then execute a
|
||||
cell with the following code:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
@ -242,10 +232,9 @@ notebook_launcher(training_function)
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Check out the [Notebook Launcher tutorial](basic_tutorials/notebook) for more information about training on TPUs.
|
||||
Check out the [Notebook Launcher tutorial](basic_tutorials/notebook) for more information about training on TPUs.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Training on TPU
|
||||
### Specifics of training on TPU
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to launch your script on TPUs, there are a few caveats you should be aware of. Behind the scenes, the TPUs
|
||||
will create a graph of all the operations happening in your training step (forward pass, backward pass and optimizer
|
||||
@ -284,12 +273,7 @@ passed your model to [`~Accelerator.prepare`]) will break the tying. You will ne
|
||||
after. You can find an example of this in the [run_clm_no_trainer](https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/blob/master/examples/pytorch/language-modeling/run_clm.py) script in
|
||||
the Transformers repository.
|
||||
|
||||
Check out the [TPU tutorial](concept_guides/training_tpu) for more information about training on TPUs.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Other caveats
|
||||
|
||||
We list here all smaller issues you could have in your script conversion and how to resolve them.
|
||||
Check out the [TPU tutorial](concept_guides/training_tpu) for more information about training on TPUs.
|
||||
|
||||
### Execute a statement only on one processes
|
||||
|
||||
@ -323,14 +307,14 @@ For printing statements you only want executed once per machine, you can just re
|
||||
`accelerator.print`.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Defer execution
|
||||
### Defer execution on multiple GPUs
|
||||
|
||||
When you run your usual script, instructions are executed in order. Using 🤗 Accelerate to deploy your script on several
|
||||
GPUs at the same time introduces a complication: while each process executes all instructions in order, some may be
|
||||
faster than others.
|
||||
|
||||
You might need to wait for all processes to have reached a certain point before executing a given instruction. For
|
||||
instance, you shouldn't save a model before being sure every process is done with training. To do this, just write the
|
||||
instance, you shouldn't save a model before making sure every process is done with training. To do this, add the
|
||||
following line in your code:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -341,7 +325,7 @@ This instruction will block all the processes that arrive first until all the ot
|
||||
point (if you run your script on just one GPU or CPU, this won't do anything).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Saving/loading a model
|
||||
### Save/load a model in a distributed setup
|
||||
|
||||
Saving the model you trained might need a bit of adjustment: first you should wait for all processes to reach that
|
||||
point in the script as shown above, and then, you should unwrap your model before saving it. This is because when going
|
||||
@ -349,15 +333,16 @@ through the [`~Accelerator.prepare`] method, your model may have been placed ins
|
||||
which deals with the distributed training. This in turn means that saving your model state dictionary without taking
|
||||
any precaution will take that potential extra layer into account, and you will end up with weights you can't load back
|
||||
in your base model. The [`~Accelerator.save_model`] method will help you to achieve that. It will unwrap your model and save
|
||||
the model state dictionnary.
|
||||
the model state dictionary.
|
||||
|
||||
Here is an example:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
accelerator.wait_for_everyone()
|
||||
accelerator.save_model(model, save_directory)
|
||||
```
|
||||
The [`~Accelerator.save_model`] method can also save a model into sharded checkpoints or with safetensors format.
|
||||
Here is an example:
|
||||
|
||||
The [`~Accelerator.save_model`] method can also save a model into sharded checkpoints or with safetensors format:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
accelerator.wait_for_everyone()
|
||||
@ -376,15 +361,18 @@ unwrapped_model.load_state_dict(torch.load(path_to_checkpoint))
|
||||
|
||||
Note that since all the model parameters are references to tensors, this will load your weights inside `model`.
|
||||
|
||||
If you want to load a sharded checkpoint or a checkpoint with safetensors format into the model with a specific `device`, we recommend you to load it with [`~utils.load_checkpoint_in_model`] function. Here's an example:
|
||||
If you want to load a sharded checkpoint or a checkpoint with safetensors format into the model with a specific `device`,
|
||||
we recommend you to load it with [`~utils.load_checkpoint_in_model`] function. Here's an example:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
load_checkpoint_in_model(unwrapped_model, save_directory, device_map={"":device})
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Saving/loading entire states
|
||||
|
||||
When training your model, you may want to save the current state of the model, optimizer, random generators, and potentially LR schedulers to be restored in the _same script_.
|
||||
### Save/load entire states
|
||||
|
||||
When training your model, you may want to save the current state of the model, optimizer, random generators, and potentially
|
||||
learning rate schedulers to be restored in the _same script_.
|
||||
You can use [`~Accelerator.save_state`] and [`~Accelerator.load_state`] respectively to do so.
|
||||
|
||||
To further customize where and how states saved through [`~Accelerator.save_state`] the [`~utils.ProjectConfiguration`] class can be used. For example
|
||||
@ -399,19 +387,19 @@ If you have registered any other stateful items to be stored through [`~Accelera
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Gradient clipping
|
||||
### Use gradient clipping
|
||||
|
||||
If you are using gradient clipping in your script, you should replace the calls to
|
||||
`torch.nn.utils.clip_grad_norm_` or `torch.nn.utils.clip_grad_value_` with [`~Accelerator.clip_grad_norm_`]
|
||||
and [`~Accelerator.clip_grad_value_`] respectively.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Mixed Precision training
|
||||
### Train with mixed precision
|
||||
|
||||
If you are running your training in Mixed Precision with 🤗 Accelerate, you will get the best result with your loss being
|
||||
computed inside your model (like in Transformer models for instance). Every computation outside of the model will be
|
||||
executed in full precision (which is generally what you want for loss computation, especially if it involves a
|
||||
softmax). However you might want to put your loss computation inside the [`~Accelerator.autocast`] context manager:
|
||||
softmax). However, you might want to put your loss computation inside the [`~Accelerator.autocast`] context manager:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
with accelerator.autocast():
|
||||
@ -432,7 +420,7 @@ if not accelerator.optimizer_step_was_skipped:
|
||||
lr_scheduler.step()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Gradient Accumulation
|
||||
### Use gradient accumulation
|
||||
|
||||
To perform gradient accumulation use [`~Accelerator.accumulate`] and specify a `gradient_accumulation_steps`.
|
||||
This will also automatically ensure the gradients are synced or unsynced when on multi-device training, check if the step should
|
||||
@ -451,70 +439,3 @@ for input, label in training_dataloader:
|
||||
scheduler.step()
|
||||
optimizer.zero_grad()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### DeepSpeed
|
||||
|
||||
DeepSpeed support is experimental, so the underlying API will evolve in the near future and may have some slight
|
||||
breaking changes. In particular, 🤗 Accelerate does not support DeepSpeed config you have written yourself yet, this
|
||||
will be added in a next version.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
The [`notebook_launcher`] does not support the DeepSpeed integration yet.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## Internal mechanism
|
||||
|
||||
Internally, the library works by first analyzing the environment in which the script is launched to determine which
|
||||
kind of distributed setup is used, how many different processes there are and which one the current script is in. All
|
||||
that information is stored in the [`~AcceleratorState`].
|
||||
|
||||
This class is initialized the first time you instantiate an [`~Accelerator`] as well as performing any
|
||||
specific initialization your distributed setup needs. Its state is then uniquely shared through all instances of
|
||||
[`~state.AcceleratorState`].
|
||||
|
||||
Then, when calling [`~Accelerator.prepare`], the library:
|
||||
|
||||
- wraps your model(s) in the container adapted for the distributed setup,
|
||||
- wraps your optimizer(s) in a [`~optimizer.AcceleratedOptimizer`],
|
||||
- creates a new version of your dataloader(s) in a [`~data_loader.DataLoaderShard`].
|
||||
|
||||
While the model(s) and optimizer(s) are just put in simple wrappers, the dataloader(s) are re-created. This is mostly
|
||||
because PyTorch does not let the user change the `batch_sampler` of a dataloader once it's been created and the
|
||||
library handles the sharding of your data between processes by changing that `batch_sampler` to yield every other
|
||||
`num_processes` batches.
|
||||
|
||||
The [`~data_loader.DataLoaderShard`] subclasses `DataLoader` to add the following functionality:
|
||||
|
||||
- it synchronizes the appropriate random number generator of all processes at each new iteration, to ensure any
|
||||
randomization (like shuffling) is done the exact same way across processes.
|
||||
- it puts the batches on the proper device before yielding them (unless you have opted out of
|
||||
`device_placement=True`).
|
||||
|
||||
The random number generator synchronization will by default synchronize:
|
||||
|
||||
- the `generator` attribute of a given sampler (like the PyTorch `RandomSampler`) for PyTorch >= 1.6
|
||||
- the main random number generator in PyTorch <=1.5.1
|
||||
|
||||
You can choose which random number generator(s) to synchronize with the `rng_types` argument of the main
|
||||
[`Accelerator`]. In PyTorch >= 1.6, it is recommended to rely on a local `generator` to avoid
|
||||
setting the same seed in the main random number generator in all processes.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
Synchronization of the main torch (or CUDA or XLA) random number generator will affect any other potential random
|
||||
artifacts you could have in your dataset (like random data augmentation) in the sense that all processes will get
|
||||
the same random numbers from the torch random modules (so will apply the same random data augmentation if it's
|
||||
controlled by torch).
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
The randomization part of your custom sampler, batch sampler or iterable dataset should be done using a local
|
||||
`torch.Generator` object (in PyTorch >= 1.6), see the traditional `RandomSampler`, as an example.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
For more details about the internals, see the [Internals page](package_reference/torch_wrappers).
|
||||
|
||||
@ -52,7 +52,7 @@ will attempt to fill all the space in your GPU(s), then loading them to the CPU,
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
For more details on desigining your own device map, see this section of the [concept guide](../concept_guide/big_model_inference#desigining-a-device-map)
|
||||
For more details on desigining your own device map, see this section of the [concept guide](../concept_guide/big_model_inference#designing-a-device-map)
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,93 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Debugging Distributed Operations
|
||||
|
||||
When running scripts in a distributed fashion, often functions such as [`Accelerator.gather`] and [`Accelerator.reduce`] (and others) are neccessary to grab tensors across devices and perform certain operations on them. However, if the tensors which are being grabbed are not the proper shapes then this will result in your code hanging forever. The only sign that exists of this truly happening is hitting a timeout exception from `torch.distributed`, but this can get quite costly as usually the timeout is 10 minutes.
|
||||
|
||||
Accelerate now has a `debug` mode which adds a neglible amount of time to each operation, but allows it to verify that the inputs you are bringing in can *actually* perform the operation you want **without** hitting this timeout problem!
|
||||
|
||||
## Visualizing the problem
|
||||
|
||||
To have a tangible example of this issue, let's take the following setup (on 2 GPUs):
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from accelerate import PartialState
|
||||
|
||||
state = PartialState()
|
||||
if state.process_index == 0:
|
||||
tensor = torch.tensor([[0.0, 1, 2, 3, 4]]).to(state.device)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
tensor = torch.tensor([[[0.0, 1, 2, 3, 4], [5, 6, 7, 8, 9]]]).to(state.device)
|
||||
|
||||
broadcast_tensor = broadcast(tensor)
|
||||
print(broadcast_tensor)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
We've created a single tensor on each device, with two radically different shapes. With this setup if we want to perform an operation such as [`utils.broadcast`], we would forever hit a timeout because `torch.distributed` requires that these operations have the **exact same shape** across all processes for it to work.
|
||||
|
||||
If you run this yourself, you will find that `broadcast_tensor` can be printed on the main process, but its results won't quite be right, and then it will just hang never printing it on any of the other processes:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
>>> tensor([[0, 1, 2, 3, 4]], device='cuda:0')
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## The solution
|
||||
|
||||
By enabling Accelerate's operational debug mode, Accelerate will properly find and catch errors such as this and provide a very clear traceback immediatly:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Traceback (most recent call last):
|
||||
File "/home/zach_mueller_huggingface_co/test.py", line 18, in <module>
|
||||
main()
|
||||
File "/home/zach_mueller_huggingface_co/test.py", line 15, in main
|
||||
main()broadcast_tensor = broadcast(tensor)
|
||||
File "/home/zach_mueller_huggingface_co/accelerate/src/accelerate/utils/operations.py", line 303, in wrapper
|
||||
broadcast_tensor = broadcast(tensor)
|
||||
accelerate.utils.operations.DistributedOperationException: Cannot apply desired operation due to shape mismatches. All shapes across devices must be valid.
|
||||
|
||||
Operation: `accelerate.utils.operations.broadcast`
|
||||
Input shapes:
|
||||
- Process 0: [1, 5]
|
||||
- Process 1: [1, 2, 5]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
This explains that the shapes across our devices were *not* the same, and that we should ensure that they match properly to be compatible. Typically this means that there is either an extra dimension, or certain dimensions are incompatible with the operation.
|
||||
|
||||
To enable this please do one of the following:
|
||||
|
||||
Enable it through the questionarre during `accelerate config` (recommended)
|
||||
|
||||
From the CLI:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
accelerate launch --debug {my_script.py} --arg1 --arg2
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
As an environmental variable (which avoids the need for `accelerate launch`):
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
ACCELERATE_DEBUG_MODE="1" accelerate launch {my_script.py} --arg1 --arg2
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Manually changing the `config.yaml` file:
|
||||
|
||||
```diff
|
||||
compute_environment: LOCAL_MACHINE
|
||||
+debug: true
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -13,9 +13,9 @@ specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# DeepSpeed
|
||||
# DeepSpeed
|
||||
|
||||
[DeepSpeed](https://github.com/microsoft/DeepSpeed) implements everything described in the [ZeRO paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/1910.02054). Currently, it provides full support for:
|
||||
[DeepSpeed](https://github.com/microsoft/DeepSpeed) implements everything described in the [ZeRO paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/1910.02054). Some of the salient optimizations are:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Optimizer state partitioning (ZeRO stage 1)
|
||||
2. Gradient partitioning (ZeRO stage 2)
|
||||
@ -23,6 +23,7 @@ rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
4. Custom mixed precision training handling
|
||||
5. A range of fast CUDA-extension-based optimizers
|
||||
6. ZeRO-Offload to CPU and Disk/NVMe
|
||||
7. Heirarchical partitioning of model parameters (ZeRO++)
|
||||
|
||||
ZeRO-Offload has its own dedicated paper: [ZeRO-Offload: Democratizing Billion-Scale Model Training](https://arxiv.org/abs/2101.06840). And NVMe-support is described in the paper [ZeRO-Infinity: Breaking the GPU
|
||||
Memory Wall for Extreme Scale Deep Learning](https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.07857).
|
||||
@ -35,16 +36,16 @@ won't be possible on a single GPU.
|
||||
🤗 Accelerate integrates [DeepSpeed](https://github.com/microsoft/DeepSpeed) via 2 options:
|
||||
|
||||
1. Integration of the DeepSpeed features via `deepspeed config file` specification in `accelerate config` . You just supply your custom config file or use our template. Most of
|
||||
this document is focused on this feature. This supports all the core features of DeepSpeed and gives user a lot of flexibility.
|
||||
this document is focused on this feature. This supports all the core features of DeepSpeed and gives user a lot of flexibility.
|
||||
User may have to change a few lines of code depending on the config.
|
||||
2. Integration via `deepspeed_plugin`.This supports subset of the DeepSpeed features and uses default options for the rest of the configurations.
|
||||
2. Integration via `deepspeed_plugin`.This supports subset of the DeepSpeed features and uses default options for the rest of the configurations.
|
||||
User need not change any code and is good for those who are fine with most of the default settings of DeepSpeed.
|
||||
|
||||
## What is integrated?
|
||||
|
||||
Training:
|
||||
|
||||
1. DeepSpeed ZeRO training supports the full ZeRO stages 1, 2 and 3 as well as CPU/Disk offload of optimizer states, gradients and parameters.
|
||||
1. 🤗 Accelerate integrates all features of DeepSpeed ZeRO. This includes all the ZeRO stages 1, 2 and 3 as well as ZeRO-Offload, ZeRO-Infinity (which can offload to disk/NVMe) and ZeRO++.
|
||||
Below is a short description of Data Parallelism using ZeRO - Zero Redundancy Optimizer along with diagram from this [blog post](https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/blog/zero-deepspeed-new-system-optimizations-enable-training-models-with-over-100-billion-parameters/)
|
||||
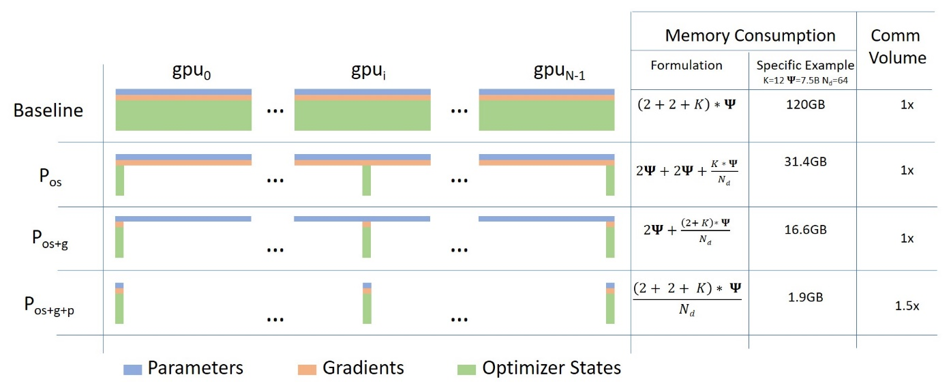
|
||||
|
||||
@ -60,6 +61,8 @@ Below is a short description of Data Parallelism using ZeRO - Zero Redundancy Op
|
||||
|
||||
e. **Param Offload**: Offloads the model parameters to CPU/Disk building on top of ZERO Stage 3
|
||||
|
||||
f. **Heirarchical Paritioning**: Enables efficient multi-node training with data-parallel training across nodes and ZeRO-3 sharding within a node, built on top of ZeRO Stage 3.
|
||||
|
||||
<u>Note</u>: With respect to Disk Offload, the disk should be an NVME for decent speed but it technically works on any Disk
|
||||
|
||||
Inference:
|
||||
@ -74,8 +77,8 @@ Inference:
|
||||
**Pre-Requisites**: Install DeepSpeed version >=0.6.5. Please refer to the [DeepSpeed Installation details](https://github.com/microsoft/DeepSpeed#installation)
|
||||
for more information.
|
||||
|
||||
We will first look at easy to use integration via `accelerate config`.
|
||||
Followed by more flexible and feature rich `deepspeed config file` integration.
|
||||
We will first look at easy to use integration via `accelerate config`.
|
||||
Followed by more flexible and feature rich `deepspeed config file` integration.
|
||||
|
||||
### Accelerate DeepSpeed Plugin
|
||||
On your machine(s) just run:
|
||||
@ -157,7 +160,7 @@ Currently, `Accelerate` supports following config through the CLI:
|
||||
`offload_param_device`: [none] Disable parameter offloading, [cpu] offload parameters to CPU, [nvme] offload parameters to NVMe SSD. Only applicable with ZeRO Stage-3.
|
||||
`zero3_init_flag`: Decides whether to enable `deepspeed.zero.Init` for constructing massive models. Only applicable with ZeRO Stage-3.
|
||||
`zero3_save_16bit_model`: Decides whether to save 16-bit model weights when using ZeRO Stage-3.
|
||||
`mixed_precision`: `no` for FP32 training, `fp16` for FP16 mixed-precision training and `bf16` for BF16 mixed-precision training.
|
||||
`mixed_precision`: `no` for FP32 training, `fp16` for FP16 mixed-precision training and `bf16` for BF16 mixed-precision training.
|
||||
```
|
||||
To be able to tweak more options, you will need to use a DeepSpeed config file.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -168,8 +171,8 @@ On your machine(s) just run:
|
||||
accelerate config
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
and answer the questions asked. It will ask whether you want to use a config file for deepspeed to which you answer yes
|
||||
and provide the path to the deepspeed config file.
|
||||
and answer the questions asked. It will ask whether you want to use a config file for deepspeed to which you answer yes
|
||||
and provide the path to the deepspeed config file.
|
||||
This will generate a config file that will be used automatically to properly set the
|
||||
default options when doing
|
||||
|
||||
@ -349,12 +352,33 @@ accelerate launch examples/by_feature/deepspeed_with_config_support.py \
|
||||
--report_to "wandb"\
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**ZeRO++ Config Example**
|
||||
You can use the the features of ZeRO++ by using the appropriate config parameters. Note that ZeRO++ is an extension for ZeRO Stage 3. Here is how the config file can be modified, from [DeepSpeed's ZeRO++ tutorial](https://www.deepspeed.ai/tutorials/zeropp/):
|
||||
|
||||
```json
|
||||
{
|
||||
"zero_optimization": {
|
||||
"stage": 3,
|
||||
"reduce_bucket_size": "auto",
|
||||
|
||||
"zero_quantized_weights": true,
|
||||
"zero_hpz_partition_size": 8,
|
||||
"zero_quantized_gradients": true,
|
||||
|
||||
"contiguous_gradients": true,
|
||||
"overlap_comm": true
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For heirarchical partitioning, the partition size `zero_hpz_partition_size` should ideally be set to the number of GPUs per node. (For example, the above config file assumes 8 GPUs per node)
|
||||
|
||||
**Important code changes when using DeepSpeed Config File**
|
||||
|
||||
1. DeepSpeed Optimizers and Schedulers. For more information on these,
|
||||
1. DeepSpeed Optimizers and Schedulers. For more information on these,
|
||||
see the [DeepSpeed Optimizers](https://deepspeed.readthedocs.io/en/latest/optimizers.html) and [DeepSpeed Schedulers](https://deepspeed.readthedocs.io/en/latest/schedulers.html) documentation.
|
||||
We will look at the changes needed in the code when using these.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
a. DS Optim + DS Scheduler: The case when both `optimizer` and `scheduler` keys are present in the DeepSpeed config file.
|
||||
In this situation, those will be used and the user has to use `accelerate.utils.DummyOptim` and `accelerate.utils.DummyScheduler` to replace the PyTorch/Custom optimizers and schedulers in their code.
|
||||
Below is the snippet from `examples/by_feature/deepspeed_with_config_support.py` showing this:
|
||||
@ -388,16 +412,25 @@ We will look at the changes needed in the code when using these.
|
||||
In this situation, no code changes are needed from the user and this is the case when using integration via DeepSpeed Plugin.
|
||||
In the above example we can see that the code remains unchanged if the `optimizer` and `scheduler` keys are absent in the DeepSpeed config file.
|
||||
|
||||
c. Custom Optim + DS Scheduler: The case when only `scheduler` key is present in the DeepSpeed config file.
|
||||
In this situation, the user has to use `accelerate.utils.DummyScheduler` to replace the PyTorch/Custom scheduler in their code.
|
||||
c. Custom Optim + DS Scheduler: The case when only `scheduler` key is present in the DeepSpeed config file.
|
||||
In this situation, the user has to use `accelerate.utils.DummyScheduler` to replace the PyTorch/Custom scheduler in their code.
|
||||
|
||||
d. DS Optim + Custom Scheduler: The case when only `optimizer` key is present in the DeepSpeed config file.
|
||||
d. DS Optim + Custom Scheduler: The case when only `optimizer` key is present in the DeepSpeed config file.
|
||||
This will result in an error because you can only use DS Scheduler when using DS Optim.
|
||||
|
||||
2. Notice the `auto` values in the above example DeepSpeed config files. These are automatically handled by `prepare` method
|
||||
based on model, dataloaders, dummy optimizer and dummy schedulers provided to `prepare` method.
|
||||
2. Notice the `auto` values in the above example DeepSpeed config files. These are automatically handled by `prepare` method
|
||||
based on model, dataloaders, dummy optimizer and dummy schedulers provided to `prepare` method.
|
||||
Only the `auto` fields specified in above examples are handled by `prepare` method and the rest have to be explicitly specified by the user.
|
||||
|
||||
The `auto` values are calculated as:
|
||||
|
||||
- `reduce_bucket_size`: `hidden_size * hidden_size`
|
||||
- `stage3_prefetch_bucket_size`: `0.9 * hidden_size * hidden_size`
|
||||
- `stage3_param_persistence_threshold`: `10 * hidden_size`
|
||||
|
||||
For the `auto` feature to work for these 3 config entries - Accelerate will use `model.config.hidden_size` or `max(model.config.hidden_sizes)` as `hidden_size`. If neither of these is available, the launching will fail and you will have to set these 3 config entries manually. Remember the first 2 config entries are the communication buffers - the larger they are the more efficient the comms will be, and the larger they are the more GPU memory they will consume, so it's a tunable performance trade-off.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
**Things to note when using DeepSpeed Config File**
|
||||
|
||||
Below is a sample script using `deepspeed_config_file` in different scenarios.
|
||||
@ -482,8 +515,8 @@ use_cpu: false
|
||||
3. Output of `accelerate launch test.py`:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
ValueError: When using `deepspeed_config_file`, the following accelerate config variables will be ignored:
|
||||
['gradient_accumulation_steps', 'gradient_clipping', 'zero_stage', 'offload_optimizer_device', 'offload_param_device',
|
||||
ValueError: When using `deepspeed_config_file`, the following accelerate config variables will be ignored:
|
||||
['gradient_accumulation_steps', 'gradient_clipping', 'zero_stage', 'offload_optimizer_device', 'offload_param_device',
|
||||
'zero3_save_16bit_model', 'mixed_precision'].
|
||||
Please specify them appropriately in the DeepSpeed config file.
|
||||
If you are using an accelerate config file, remove others config variables mentioned in the above specified list.
|
||||
@ -499,15 +532,15 @@ It will only ask for the necessary config variables when using `deepspeed_config
|
||||
$ accelerate config
|
||||
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
In which compute environment are you running?
|
||||
This machine
|
||||
This machine
|
||||
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
Which type of machine are you using?
|
||||
multi-GPU
|
||||
How many different machines will you use (use more than 1 for multi-node training)? [1]:
|
||||
Do you wish to optimize your script with torch dynamo?[yes/NO]:
|
||||
Do you want to use DeepSpeed? [yes/NO]: yes
|
||||
Do you want to specify a json file to a DeepSpeed config? [yes/NO]: yes
|
||||
Please enter the path to the json DeepSpeed config file: ds_config.json
|
||||
Which type of machine are you using?
|
||||
multi-GPU
|
||||
How many different machines will you use (use more than 1 for multi-node training)? [1]:
|
||||
Do you wish to optimize your script with torch dynamo?[yes/NO]:
|
||||
Do you want to use DeepSpeed? [yes/NO]: yes
|
||||
Do you want to specify a json file to a DeepSpeed config? [yes/NO]: yes
|
||||
Please enter the path to the json DeepSpeed config file: ds_config.json
|
||||
Do you want to enable `deepspeed.zero.Init` when using ZeRO Stage-3 for constructing massive models? [yes/NO]: yes
|
||||
How many GPU(s) should be used for distributed training? [1]:4
|
||||
accelerate configuration saved at ds_config_sample.yaml
|
||||
@ -585,10 +618,10 @@ Mixed precision type: fp16
|
||||
ds_config: {'bf16': {'enabled': False}, 'zero_optimization': {'stage': 3, 'stage3_gather_16bit_weights_on_model_save': True, 'offload_optimizer': {'device': 'nvme'}, 'offload_param': {'device': 'cpu'}}, 'gradient_clipping': 1.0, 'train_batch_size': 'auto', 'train_micro_batch_size_per_gpu': 'auto', 'gradient_accumulation_steps': 5, 'steps_per_print': inf, 'fp16': {'enabled': True, 'auto_cast': True}}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**Note**:
|
||||
1. Remaining `"auto"` values are handled in `accelerator.prepare()` call as explained in point 2 of
|
||||
**Note**:
|
||||
1. Remaining `"auto"` values are handled in `accelerator.prepare()` call as explained in point 2 of
|
||||
`Important code changes when using DeepSpeed Config File`.
|
||||
2. Only when `gradient_accumulation_steps` is `auto`, the value passed while creating `Accelerator` object via `Accelerator(gradient_accumulation_steps=k)` will be used. When using DeepSpeed Plugin, the value from it will be used and it will overwrite the value passed while creating Accelerator object.
|
||||
2. Only when `gradient_accumulation_steps` is `auto`, the value passed while creating `Accelerator` object via `Accelerator(gradient_accumulation_steps=k)` will be used. When using DeepSpeed Plugin, the value from it will be used and it will overwrite the value passed while creating Accelerator object.
|
||||
|
||||
## Saving and loading
|
||||
|
||||
@ -599,7 +632,7 @@ ZeRO Stage-3 has 2 options:
|
||||
|
||||
a. Saving the entire 16bit model weights to directly load later on using `model.load_state_dict(torch.load(pytorch_model.bin))`.
|
||||
For this, either set `zero_optimization.stage3_gather_16bit_weights_on_model_save` to True in DeepSpeed Config file or set
|
||||
`zero3_save_16bit_model` to True in DeepSpeed Plugin.
|
||||
`zero3_save_16bit_model` to True in DeepSpeed Plugin.
|
||||
**Note that this option requires consolidation of the weights on one GPU it can be slow and memory demanding, so only use this feature when needed.**
|
||||
Below is the snippet from `examples/by_feature/deepspeed_with_config_support.py` showing this:
|
||||
```python
|
||||
@ -628,10 +661,10 @@ ZeRO Stage-3 has 2 options:
|
||||
logging.info(f"Success {status_msg}")
|
||||
else:
|
||||
logging.warning(f"Failure {status_msg}")
|
||||
```
|
||||
```
|
||||
This will create ZeRO model and optimizer partitions along with `zero_to_fp32.py` script in checkpoint directory.
|
||||
You can use this script to do offline consolidation.
|
||||
It requires no configuration files or GPUs. Here is an example of its usage:
|
||||
You can use this script to do offline consolidation.
|
||||
It requires no configuration files or GPUs. Here is an example of its usage:
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
$ cd /path/to/checkpoint_dir
|
||||
$ ./zero_to_fp32.py . pytorch_model.bin
|
||||
@ -655,7 +688,7 @@ ZeRO Stage-3 has 2 options:
|
||||
Note that all these functions require ~2x memory (general RAM) of the size of the final checkpoint.
|
||||
|
||||
## ZeRO Inference
|
||||
DeepSpeed ZeRO Inference supports ZeRO stage 3 with ZeRO-Infinity.
|
||||
DeepSpeed ZeRO Inference supports ZeRO stage 3 with ZeRO-Infinity.
|
||||
It uses the same ZeRO protocol as training, but it doesn't use an optimizer and a lr scheduler and only stage 3 is relevant.
|
||||
With accelerate integration, you just need to prepare the model and dataloader as shown below:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -663,11 +696,11 @@ With accelerate integration, you just need to prepare the model and dataloader a
|
||||
model, eval_dataloader = accelerator.prepare(model, eval_dataloader)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Few caveats to be aware of
|
||||
## Few caveats to be aware of
|
||||
|
||||
1. Current integration doesn’t support Pipeline Parallelism of DeepSpeed.
|
||||
2. Current integration doesn’t support `mpu`, limiting the tensor parallelism which is supported in Megatron-LM.
|
||||
3. Current integration doesn’t support multiple models.
|
||||
2. Current integration doesn’t support `mpu`, limiting the tensor parallelism which is supported in Megatron-LM.
|
||||
3. Current integration doesn’t support multiple models.
|
||||
|
||||
## DeepSpeed Resources
|
||||
|
||||
@ -683,7 +716,8 @@ Papers:
|
||||
- [ZeRO: Memory Optimizations Toward Training Trillion Parameter Models](https://arxiv.org/abs/1910.02054)
|
||||
- [ZeRO-Offload: Democratizing Billion-Scale Model Training](https://arxiv.org/abs/2101.06840)
|
||||
- [ZeRO-Infinity: Breaking the GPU Memory Wall for Extreme Scale Deep Learning](https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.07857)
|
||||
- [ZeRO++: Extremely Efficient Collective Communication for Giant Model Training](https://arxiv.org/abs/2306.10209)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, please, remember that 🤗 `Accelerate` only integrates DeepSpeed, therefore if you
|
||||
have any problems or questions with regards to DeepSpeed usage, please, file an issue with [DeepSpeed GitHub](https://github.com/microsoft/DeepSpeed/issues).
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -51,7 +51,7 @@ def run_inference(rank, world_size):
|
||||
One will notice how we have to check the rank to know what prompt to send, which can be a bit tedious.
|
||||
|
||||
A user might then also think that with 🤗 Accelerate, using the `Accelerator` to prepare a dataloader for such a task might also be
|
||||
a simple way to manage this. (To learn more, check out the relvent section in the [Quick Tour](../quicktour#distributed-evaluation))
|
||||
a simple way to manage this. (To learn more, check out the relevant section in the [Quick Tour](../quicktour#distributed-evaluation))
|
||||
|
||||
Can it manage it? Yes. Does it add unneeded extra code however: also yes.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -16,7 +16,7 @@ rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
# Learning how to incorporate 🤗 Accelerate features quickly!
|
||||
|
||||
Please use the interactive tool below to help you get started with learning about a particular
|
||||
feature of 🤗 Accelerate and how to utilize it! It will provide you with a code diff, an explaination
|
||||
feature of 🤗 Accelerate and how to utilize it! It will provide you with a code diff, an explanation
|
||||
towards what is going on, as well as provide you with some useful links to explore more within
|
||||
the documentation!
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -36,27 +36,34 @@ default options when doing
|
||||
accelerate launch my_script.py --args_to_my_script
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For instance, here is how you would run the NLP example (from the root of the repo) with FSDP enabled:
|
||||
For instance, here is how you would run `examples/nlp_example.py` (from the root of the repo) with FSDP enabled:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
compute_environment: LOCAL_MACHINE
|
||||
deepspeed_config: {}
|
||||
debug: false
|
||||
distributed_type: FSDP
|
||||
downcast_bf16: 'no'
|
||||
fsdp_config:
|
||||
fsdp_auto_wrap_policy: TRANSFORMER_BASED_WRAP
|
||||
fsdp_backward_prefetch_policy: BACKWARD_PRE
|
||||
fsdp_forward_prefetch: false
|
||||
fsdp_cpu_ram_efficient_loading: true
|
||||
fsdp_offload_params: false
|
||||
fsdp_sharding_strategy: 1
|
||||
fsdp_state_dict_type: FULL_STATE_DICT
|
||||
fsdp_sharding_strategy: FULL_SHARD
|
||||
fsdp_state_dict_type: SHARDED_STATE_DICT
|
||||
fsdp_sync_module_states: true
|
||||
fsdp_transformer_layer_cls_to_wrap: BertLayer
|
||||
fsdp_use_orig_params: true
|
||||
machine_rank: 0
|
||||
main_process_ip: null
|
||||
main_process_port: null
|
||||
main_training_function: main
|
||||
mixed_precision: 'no'
|
||||
mixed_precision: bf16
|
||||
num_machines: 1
|
||||
num_processes: 2
|
||||
rdzv_backend: static
|
||||
same_network: true
|
||||
tpu_env: []
|
||||
tpu_use_cluster: false
|
||||
tpu_use_sudo: false
|
||||
use_cpu: false
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
@ -66,40 +73,30 @@ accelerate launch examples/nlp_example.py
|
||||
|
||||
Currently, `Accelerate` supports the following config through the CLI:
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
`Sharding Strategy`: [1] FULL_SHARD (shards optimizer states, gradients and parameters), [2] SHARD_GRAD_OP (shards optimizer states and gradients), [3] NO_SHARD (DDP), [4] HYBRID_SHARD (shards optimizer states, gradients and parameters within each node while each node has full copy), [5] HYBRID_SHARD_ZERO2 (shards optimizer states and gradients within each node while each node has full copy)
|
||||
`fsdp_sharding_strategy`: [1] FULL_SHARD (shards optimizer states, gradients and parameters), [2] SHARD_GRAD_OP (shards optimizer states and gradients), [3] NO_SHARD (DDP), [4] HYBRID_SHARD (shards optimizer states, gradients and parameters within each node while each node has full copy), [5] HYBRID_SHARD_ZERO2 (shards optimizer states and gradients within each node while each node has full copy)
|
||||
|
||||
`Offload Params`: Decides Whether to offload parameters and gradients to CPU
|
||||
`fsdp_offload_params` : Decides Whether to offload parameters and gradients to CPU
|
||||
|
||||
`Auto Wrap Policy`: [1] TRANSFORMER_BASED_WRAP, [2] SIZE_BASED_WRAP, [3] NO_WRAP
|
||||
`fsdp_auto_wrap_policy`: [1] TRANSFORMER_BASED_WRAP, [2] SIZE_BASED_WRAP, [3] NO_WRAP
|
||||
|
||||
`Transformer Layer Class to Wrap`: When using `TRANSFORMER_BASED_WRAP`, user specifies comma-separated string of transformer layer class names (case-sensitive) to wrap ,e.g,
|
||||
`BertLayer`, `GPTJBlock`, `T5Block`, `BertLayer,BertEmbeddings,BertSelfOutput`...
|
||||
This is important because submodules that share weights (e.g., embedding layer) should not end up in different FSDP wrapped units.
|
||||
Using this policy, wrapping happens for each block containing Multi-Head Attention followed by couple of MLP layers.
|
||||
Remaining layers including the shared embeddings are conveniently wrapped in same outermost FSDP unit.
|
||||
Therefore, use this for transformer based models.
|
||||
You can use the `model._no_split_modules` for 🤗 Transformer models by answering `yes` to
|
||||
`Do you want to use the model's `_no_split_modules` to wrap. Only applicable for 🤗 Transformers`.
|
||||
It will try to use `model._no_split_modules` when available.
|
||||
`fsdp_transformer_layer_cls_to_wrap`: Only applicable for 🤗 Transformers. When using `fsdp_auto_wrap_policy=TRANSFORMER_BASED_WRAP`, a user may provide a comma-separated string of transformer layer class names (case-sensitive) to wrap, e.g., `BertLayer`, `GPTJBlock`, `T5Block`, `BertLayer,BertEmbeddings,BertSelfOutput`. This is important because submodules that share weights (e.g., embedding layers) should not end up in different FSDP wrapped units. Using this policy, wrapping happens for each block containing Multi-Head Attention followed by a couple of MLP layers. Remaining layers including the shared embeddings are conveniently wrapped in same outermost FSDP unit. Therefore, use this for transformer-based models. You can use the `model._no_split_modules` for 🤗 Transformer models by answering `yes` to `Do you want to use the model's `_no_split_modules` to wrap. It will try to use `model._no_split_modules` when possible.
|
||||
|
||||
`Min Num Params`: minimum number of parameters when using `SIZE_BASED_WRAP`
|
||||
`fsdp_min_num_params`: minimum number of parameters when using `fsdp_auto_wrap_policy=SIZE_BASED_WRAP`.
|
||||
|
||||
`Backward Prefetch`: [1] BACKWARD_PRE, [2] BACKWARD_POST, [3] NO_PREFETCH
|
||||
`fsdp_backward_prefetch_policy`: [1] BACKWARD_PRE, [2] BACKWARD_POST, [3] NO_PREFETCH
|
||||
|
||||
`State Dict Type`: [1] FULL_STATE_DICT, [2] LOCAL_STATE_DICT, [3] SHARDED_STATE_DICT
|
||||
`fsdp_forward_prefetch`: if True, then FSDP explicitly prefetches the next upcoming all-gather while executing in the forward pass. Should only be used for static-graph models since the prefetching follows the first iteration’s execution order. i.e., if the sub-modules' order changes dynamically during the model's executation do not enable this feature.
|
||||
|
||||
`Forward Prefetch`: if True, then FSDP explicitly prefetches the next upcoming
|
||||
all-gather while executing in the forward pass. only use with Static graphs.
|
||||
`fsdp_state_dict_type`: [1] FULL_STATE_DICT, [2] LOCAL_STATE_DICT, [3] SHARDED_STATE_DICT
|
||||
|
||||
`Use Orig Params`: If True, allows non-uniform `requires_grad` during init, which means support for interspersed frozen and trainable paramteres.
|
||||
Useful in cases such as parameter-efficient fine-tuning.
|
||||
Please refer this [blog](https://dev-discuss.pytorch.org/t/rethinking-pytorch-fully-sharded-data-parallel-fsdp-from-first-principles/1019)
|
||||
`fsdp_use_orig_params`: If True, allows non-uniform `requires_grad` during init, which means support for interspersed frozen and trainable paramteres. This setting is useful in cases such as parameter-efficient fine-tuning as discussed in [this post](https://dev-discuss.pytorch.org/t/rethinking-pytorch-fully-sharded-data-parallel-fsdp-from-first-principles/1019). This option also allows one to have multiple optimizer param groups. This should be `True` when creating an optimizer before preparing/wrapping the model with FSDP.
|
||||
|
||||
`Sync Module States`: If True, each individually wrapped FSDP unit will broadcast module parameters from rank 0
|
||||
```
|
||||
`fsdp_cpu_ram_efficient_loading`: Only applicable for 🤗 Transformers models. If True, only the first process loads the pretrained model checkpoint while all other processes have empty weights. This should be set to False if you experience errors when loading the pretrained 🤗 Transformers model via `from_pretrained` method. When this setting is True `fsdp_sync_module_states` also must to be True, otherwise all the processes except the main process would have random weights leading to unexpected behaviour during training.
|
||||
|
||||
For additional and more nuanced control, you can specify other FSDP parameters via `FullyShardedDataParallelPlugin`.
|
||||
`fsdp_sync_module_states`: If True, each individually wrapped FSDP unit will broadcast module parameters from rank 0.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
For additional and more nuanced control, you can specify other FSDP parameters via `FullyShardedDataParallelPlugin`.
|
||||
When creating `FullyShardedDataParallelPlugin` object, pass it the parameters that weren't part of the accelerate config or if you want to override them.
|
||||
The FSDP parameters will be picked based on the accelerate config file or launch command arguments and other parameters that you will pass directly through the `FullyShardedDataParallelPlugin` object will set/override that.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -128,7 +125,7 @@ accelerator.save_state("ckpt")
|
||||
|
||||
Inspect the ckeckpoint folder to see model and optimizer as shards per process:
|
||||
```
|
||||
ls ckpt
|
||||
ls ckpt
|
||||
# optimizer_0 pytorch_model_0 random_states_0.pkl random_states_1.pkl scheduler.bin
|
||||
|
||||
cd ckpt
|
||||
@ -146,7 +143,7 @@ To load them back for resuming the training, use the `load_state` utility of acc
|
||||
accelerator.load_state("ckpt")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
When using transformers `save_pretrained`, pass `state_dict=accelerator.get_state_dict(model)` to save the model state dict.
|
||||
When using transformers `save_pretrained`, pass `state_dict=accelerator.get_state_dict(model)` to save the model state dict.
|
||||
Below is an example:
|
||||
|
||||
```diff
|
||||
@ -160,66 +157,13 @@ When using transformers `save_pretrained`, pass `state_dict=accelerator.get_stat
|
||||
|
||||
### State Dict
|
||||
|
||||
`accelerator.get_state_dict` will call the underlying `model.state_dict` implementation. With a model wrapped by FSDP, the default behavior of `state_dict` is to gather all of the state in the rank 0 device. This can cause CUDA out of memory errors if the parameters don't fit on a single GPU.
|
||||
|
||||
To avoid this, PyTorch provides a context manager that adjusts the behavior of `state_dict`. To offload some of the state dict onto CPU, you can use the following code:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
from torch.distributed.fsdp import FullyShardedDataParallel as FSDP, StateDictType, FullStateDictConfig
|
||||
|
||||
full_state_dict_config = FullStateDictConfig(offload_to_cpu=True, rank0_only=True)
|
||||
with FSDP.state_dict_type(unwrapped_model, StateDictType.FULL_STATE_DICT, full_state_dict_config):
|
||||
state = accelerator.get_state_dict(unwrapped_model)
|
||||
```
|
||||
`accelerator.get_state_dict` will call the underlying `model.state_dict` implementation using `FullStateDictConfig(offload_to_cpu=True, rank0_only=True)` context manager to get the state dict only for rank 0 and it will be offloaded to CPU.
|
||||
|
||||
You can then pass `state` into the `save_pretrained` method. There are several modes for `StateDictType` and `FullStateDictConfig` that you can use to control the behavior of `state_dict`. For more information, see the [PyTorch documentation](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/fsdp.html).
|
||||
|
||||
## A few caveats to be aware of
|
||||
|
||||
- PyTorch FSDP auto wraps sub-modules, flattens the parameters and shards the parameters in place.
|
||||
Due to this, any optimizer created before model wrapping gets broken and occupies more memory.
|
||||
Hence, it is highly recommended and efficient to prepare the model before creating the optimizer.
|
||||
`Accelerate` will automatically wrap the model and create an optimizer for you in case of single model with a warning message.
|
||||
> FSDP Warning: When using FSDP, it is efficient and recommended to call prepare for the model before creating the optimizer
|
||||
|
||||
However, below is the recommended way to prepare model and optimizer while using FSDP:
|
||||
|
||||
```diff
|
||||
model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained("bert-base-cased", return_dict=True)
|
||||
+ model = accelerator.prepare(model)
|
||||
|
||||
optimizer = torch.optim.AdamW(params=model.parameters(), lr=lr)
|
||||
|
||||
- model, optimizer, train_dataloader, eval_dataloader, lr_scheduler = accelerator.prepare(
|
||||
- model, optimizer, train_dataloader, eval_dataloader, lr_scheduler
|
||||
- )
|
||||
|
||||
+ optimizer, train_dataloader, eval_dataloader, lr_scheduler = accelerator.prepare(
|
||||
+ optimizer, train_dataloader, eval_dataloader, lr_scheduler
|
||||
+ )
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
- In case of a single model, if you have created the optimizer with multiple parameter groups and called prepare with them together,
|
||||
then the parameter groups will be lost and the following warning is displayed:
|
||||
> FSDP Warning: When using FSDP, several parameter groups will be conflated into
|
||||
> a single one due to nested module wrapping and parameter flattening.
|
||||
|
||||
This is because parameter groups created before wrapping will have no meaning post wrapping due to parameter flattening of nested FSDP modules into 1D arrays (which can consume many layers).
|
||||
For instance, below are the named parameters of an FSDP model on GPU 0 (When using 2 GPUs. Around 55M (110M/2) params in 1D arrays as this will have the 1st shard of the parameters).
|
||||
Here, if one has applied no weight decay for [bias, LayerNorm.weight] the named parameters of an unwrapped BERT model,
|
||||
it can't be applied to the below FSDP wrapped model as there are no named parameters with either of those strings and
|
||||
the parameters of those layers are concatenated with parameters of various other layers.
|
||||
```
|
||||
{
|
||||
'_fsdp_wrapped_module.flat_param': torch.Size([494209]),
|
||||
'_fsdp_wrapped_module._fpw_module.bert.embeddings.word_embeddings._fsdp_wrapped_module.flat_param': torch.Size([11720448]),
|
||||
'_fsdp_wrapped_module._fpw_module.bert.encoder._fsdp_wrapped_module.flat_param': torch.Size([42527232])
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- In case of multiple models, it is necessary to prepare the models before creating optimizers or else it will throw an error.
|
||||
Then pass the optimizers to the prepare call in the same order as corresponding models else `accelerator.save_state()` and `accelerator.load_state()` will result in wrong/unexpected behaviour.
|
||||
- In case of multiple models, pass the optimizers to the prepare call in the same order as corresponding models else `accelerator.save_state()` and `accelerator.load_state()` will result in wrong/unexpected behaviour.
|
||||
- This feature is incompatible with `--predict_with_generate` in the `run_translation.py` script of 🤗 `Transformers` library.
|
||||
|
||||
For more control, users can leverage the `FullyShardedDataParallelPlugin`. After creating an instance of this class, users can pass it to the Accelerator class instantiation.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -118,8 +118,24 @@ You can remove all the special checks for the step number and the loss adjustmen
|
||||
As you can see the [`Accelerator`] is able to keep track of the batch number you are on and it will automatically know whether to step through the prepared optimizer and how to adjust the loss.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Typically with gradient accumulation, you would need to adjust the number of steps to reflect the change in total batches you are
|
||||
training on. 🤗 Accelerate automagically does this for you by default. Behind the scenes we instantiate a GradientAccumulationPlugin configured to do this.
|
||||
training on. 🤗 Accelerate automagically does this for you by default. Behind the scenes we instantiate a [`GradientAccumulationPlugin`] configured to do this.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip warning={true}>
|
||||
|
||||
The [`state.GradientState`] is sync'd with the active dataloader being iterated upon. As such it assumes naively that when we have reached the end of the dataloader everything will sync and a step will be performed. To disable this, set `sync_with_dataloader` to be `False` in the [`GradientAccumulationPlugin`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```{python}
|
||||
from accelerate import Accelerator
|
||||
from accelerate.utils import GradientAccumulationPlugin
|
||||
|
||||
plugin = GradientAccumulationPlugin(sync_with_dataloader=False)
|
||||
accelerator = Accelerator(..., gradient_accumulation_plugin=plugin)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## The finished code
|
||||
|
||||
92
docs/source/usage_guides/low_precision_training.md
Normal file
92
docs/source/usage_guides/low_precision_training.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,92 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2023 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Low Precision Training Methods
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 Accelerate provides integrations to train on lower precision methods using specified supported hardware through the `TransformersEngine` and `MS-AMP` packages. This documentation will help guide you through what hardware is supported, how to configure your [`Accelerator`] to leverage the low precision methods, and what you can expect when training.
|
||||
|
||||
## What training on FP8 means
|
||||
|
||||
To explore more of the nitty-gritty in traninig in FP8 with PyTorch and 🤗 Accelerate, check out the [concept_guide](../concept_guides/low_precision_training.md) on why this can be difficult. But essentially rather than training in BF16, some (or all) aspects of training a model can be performed using 8 bits instead of 16. The challenge is doing so without degrading final performance.
|
||||
|
||||
This is only enabled on specific NVIDIA hardware, namely:
|
||||
|
||||
* Anything after the 3000 series consumer graphics cards (such as the 4090)
|
||||
* Hopper-based GPU architectures (such as the `H100` and `H200`)
|
||||
|
||||
What this will result in is some gain in the memory used (as we've cut the needed memory in half for some parts of training) and an increase in throughput *should* be seen as well for larger models that can replace certain layers with FP8-enabled ones.
|
||||
|
||||
## Configuring the Accelerator
|
||||
|
||||
Currently two different backends for FP8 are supported (`TransformersEngine` and `MS-AMP`), each with different capabilities and configurations.
|
||||
|
||||
To use either, the same core API is used. Just pass `mixed_precision="fp8"` to either the [`Accelerator`], during `accelerate config` when prompted about mixed precision, or as part of your `config.yaml` file in the `mixed_precision` key:
|
||||
|
||||
```{python}
|
||||
from accelerate import Accelerator
|
||||
accelerator = Accelerator(mixed_precision="fp8")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
By default, if `MS-AMP` is available in your environment, 🤗 Accelerate will automatically utilize it as a backend. To specify it yourself (and customize other parts of the FP8 mixed precision setup), you can utilize the [`utils.FP8RecipeKwargs`]:
|
||||
|
||||
```{python}
|
||||
from accelerate import Accelerator
|
||||
from accelerate.utils import FP8RecipeKwargs
|
||||
kwargs = [FP8RecipeKwargs(backend="msamp")]
|
||||
# Or to specify the backend as `TransformersEngine` even if MS-AMP is installed
|
||||
# kwargs = [FP8RecipeKwargs(backend="te")]
|
||||
accelerator = Accelerator(mixed_precision="fp8", kwarg_handlers=kwargs)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Configuring MS-AMP
|
||||
|
||||
Of the two, `MS-AMP` is traditionally the easier one to configure as there is only a single argument: the optimization level.
|
||||
|
||||
Currently two levels of optimization are supported in the 🤗 Accelerate integration, `"O1"` and `"O2"` (using the letter 'o', not zero).
|
||||
|
||||
* `"O1"` will cast the weight gradients and `all_reduce` communications to happen in 8-bit, while the rest are done in 16 bit. This reduces the general GPU memory usage and speeds up communication bandwidths.
|
||||
* `"O2"` will also cast first-order optimizer states into 8 bit, while the second order states are in FP16. (Currently just the `Adam` optimizer is supported). This tries it's best to minimize final accuracy degredation and will save the highest potential memory.
|
||||
|
||||
To specify an optimization level, pass it to the `FP8KwargsHandler` by setting the `optimization_level` argument:
|
||||
|
||||
```{python}
|
||||
from accelerate import Accelerator
|
||||
from accelerate.utils import FP8RecipeKwargs
|
||||
kwargs = [FP8RecipeKwargs(backend="msamp", optimization_level="O2")]
|
||||
accelerator = Accelerator(mixed_precision="fp8", kwarg_handlers=kwargs)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Configuring TransformersEngine
|
||||
|
||||
TransformersEngine has much more available for customizing how and what FP8 calculations are performed. A full list of supported arguments and what they mean are available in [NVIDIA's documentation](https://docs.nvidia.com/deeplearning/transformer-engine/user-guide/api/common.html), however they are restated as part of [`FP8KwargsHandler`]'s docstring for your convience.
|
||||
|
||||
🤗 Accelerate tries to set sensible defaults, but exploring and tweaking the various parameters yourself can lead to better performance potentially.
|
||||
|
||||
To use it, specify `backend="te"` and modify any of the arguments you want as part of your kwarg handler:
|
||||
|
||||
```{python}
|
||||
from accelerate import Accelerator
|
||||
from accelerate.utils import FP8RecipeKwargs
|
||||
kwargs = [FP8RecipeKwargs(backend="te", ...)]
|
||||
accelerator = Accelerator(mixed_precision="fp8", kwarg_handlers=kwargs)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Futher Reading
|
||||
|
||||
To learn more about training in FP8 please check out the following resources:
|
||||
|
||||
* [Our concept guide](../concept_guides/low_precision_training.md) detailing into more about both TransformersEngine and MS-AMP
|
||||
* [The `transformers-engine` documentation](https://docs.nvidia.com/deeplearning/transformer-engine/user-guide/api/common.html)
|
||||
* [The `MS-AMP` documentation](https://azure.github.io/MS-AMP/docs/)
|
||||
@ -128,7 +128,7 @@ Do you want to enable Sequence Parallelism? [YES/no]:
|
||||
What is the Pipeline Parallelism degree/size? [1]:2
|
||||
What is the number of micro-batches? [1]:2
|
||||
Do you want to enable selective activation recomputation? [YES/no]:
|
||||
Do you want to use distributed optimizer which shards optimizer state and gradients across data pralellel ranks? [YES/no]:
|
||||
Do you want to use distributed optimizer which shards optimizer state and gradients across data parallel ranks? [YES/no]:
|
||||
What is the gradient clipping value based on global L2 Norm (0 to disable)? [1.0]:
|
||||
How many GPU(s) should be used for distributed training? [1]:4
|
||||
Do you wish to use FP16 or BF16 (mixed precision)? [NO/fp16/bf16]: bf16
|
||||
@ -355,8 +355,8 @@ def main():
|
||||
|
||||
2. For using the Megatron-LM datasets, a few more changes are required. Dataloaders for these datasets
|
||||
are available only on rank 0 of each tensor parallel group. As such, there are rank where dataloader won't be
|
||||
avaiable and this requires tweaks to the training loop. Being able to do all this shows how
|
||||
felixble and extensible 🤗 Accelerate is. The changes required are as follows.
|
||||
available and this requires tweaks to the training loop. Being able to do all this shows how
|
||||
flexible and extensible 🤗 Accelerate is. The changes required are as follows.
|
||||
|
||||
a. For Megatron-LM indexed datasets, we need to use `MegatronLMDummyDataLoader`
|
||||
and pass the required dataset args to it such as `data_path`, `seq_length` etc.
|
||||
@ -547,7 +547,7 @@ The `model(**batch_data)` call return loss(es) averaged across the data parallel
|
||||
This is fine for most cases wherein pre-training jobs are run using Megatron-LM features and
|
||||
you can easily compute the `perplexity` using the loss.
|
||||
For GPT model, returning logits in addition to loss(es) is supported.
|
||||
These logits aren't gathered across data prallel ranks. Use `accelerator.utils.gather_across_data_parallel_groups`
|
||||
These logits aren't gathered across data parallel ranks. Use `accelerator.utils.gather_across_data_parallel_groups`
|
||||
to gather logits across data parallel ranks. These logits along with labels can be used for computing various
|
||||
performance metrics.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,58 +0,0 @@
|
||||
<!--Copyright 2022 The HuggingFace Team. All rights reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
|
||||
the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on
|
||||
an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the
|
||||
specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
⚠️ Note that this file is in Markdown but contain specific syntax for our doc-builder (similar to MDX) that may not be
|
||||
rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
-->
|
||||
|
||||
# Memory Utilities
|
||||
|
||||
One of the most frustrating errors when it comes to running training scripts is hitting "CUDA Out-of-Memory",
|
||||
as the entire script needs to be restarted, progress is lost, and typically a developer would want to simply
|
||||
start their script and let it run.
|
||||
|
||||
`Accelerate` provides a utility heavily based on [toma](https://github.com/BlackHC/toma) to give this capability.
|
||||
|
||||
## find_executable_batch_size
|
||||
|
||||
This algorithm operates with exponential decay, decreasing the batch size in half after each failed run on some
|
||||
training script. To use it, restructure your training function to include an inner function that includes this wrapper,
|
||||
and build your dataloaders inside it. At a minimum, this could look like 4 new lines of code.
|
||||
> Note: The inner function *must* take in the batch size as the first parameter, but we do not pass one to it when called. The wrapper handles this for us
|
||||
|
||||
It should also be noted that anything which will consume CUDA memory and passed to the `accelerator` **must** be declared inside the inner function,
|
||||
such as models and optimizers.
|
||||
|
||||
```diff
|
||||
def training_function(args):
|
||||
accelerator = Accelerator()
|
||||
|
||||
+ @find_executable_batch_size(starting_batch_size=args.batch_size)
|
||||
+ def inner_training_loop(batch_size):
|
||||
+ nonlocal accelerator # Ensure they can be used in our context
|
||||
+ accelerator.free_memory() # Free all lingering references
|
||||
model = get_model()
|
||||
model.to(accelerator.device)
|
||||
optimizer = get_optimizer()
|
||||
train_dataloader, eval_dataloader = get_dataloaders(accelerator, batch_size)
|
||||
lr_scheduler = get_scheduler(
|
||||
optimizer,
|
||||
num_training_steps=len(train_dataloader)*num_epochs
|
||||
)
|
||||
model, optimizer, train_dataloader, eval_dataloader, lr_scheduler = accelerator.prepare(
|
||||
model, optimizer, train_dataloader, eval_dataloader, lr_scheduler
|
||||
)
|
||||
train(model, optimizer, train_dataloader, lr_scheduler)
|
||||
validate(model, eval_dataloader)
|
||||
+ inner_training_loop()
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To find out more, check the documentation [here](../package_reference/utilities#accelerate.find_executable_batch_size).
|
||||
@ -32,6 +32,27 @@ Currently we support searching for models that can be used in `timm` and `transf
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
## Gradio Demos
|
||||
|
||||
Below are a few gradio demos related to what was described above. The first is the official Hugging Face memory estimation space, utilizing Accelerate directly:
|
||||
|
||||
<div class="block dark:hidden">
|
||||
<iframe
|
||||
src="https://hf-accelerate-model-memory-usage.hf.space?__theme=light"
|
||||
width="850"
|
||||
height="1600"
|
||||
></iframe>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
<div class="hidden dark:block">
|
||||
<iframe
|
||||
src="https://hf-accelerate-model-memory-usage.hf.space?__theme=dark"
|
||||
width="850"
|
||||
height="1600"
|
||||
></iframe>
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
A community member has taken the idea and expended it further, allowing you to filter models directly and see if you can run a particular LLM given GPU constraints and LoRA configurations. To play with it, see [here](https://huggingface.co/spaces/Vokturz/can-it-run-llm) for more details.
|
||||
|
||||
## The Command
|
||||
|
||||
When using `accelerate estimate-memory`, you need to pass in the name of the model you want to use, potentially the framework
|
||||
@ -113,9 +134,4 @@ This calculator will tell you how much memory is needed to purely load the model
|
||||
This calculation is accurate within a few % of the actual value, so it is a very good view of just how much memory it will take. For instance loading `bert-base-cased` actually takes `413.68 MB` when loaded on CUDA in full precision, and the calculator estimates `413.18 MB`.
|
||||
|
||||
When performing inference you can expect to add up to an additional 20% as found by [EleutherAI](https://blog.eleuther.ai/transformer-math/). We'll be conducting research into finding a more accurate estimate to these values, and will update
|
||||
this calculator once done.
|
||||
|
||||
## Live Gradio Demo
|
||||
|
||||
Lastly, we invite you to try the [live Gradio demo](https://huggingface.co/spaces/hf-accelerate/model-memory-usage) of this utility,
|
||||
which includes an option to post a discussion thread on a models repository with this data. Doing so will help provide access to these numbers in the community faster and help users know what you've learned!
|
||||
this calculator once done.
|
||||
@ -20,12 +20,15 @@ There are a large number of experiment tracking API's available, however getting
|
||||
|
||||
## Integrated Trackers
|
||||
|
||||
Currently `Accelerate` supports four trackers out-of-the-box:
|
||||
Currently `Accelerate` supports seven trackers out-of-the-box:
|
||||
|
||||
- TensorBoard
|
||||
- WandB
|
||||
- CometML
|
||||
- Aim
|
||||
- MLFlow
|
||||
- ClearML
|
||||
- DVCLive
|
||||
|
||||
To use any of them, pass in the selected type(s) to the `log_with` parameter in [`Accelerate`]:
|
||||
```python
|
||||
|
||||
@ -15,7 +15,7 @@ rendered properly in your Markdown viewer.
|
||||
|
||||
# Example Zoo
|
||||
|
||||
Below contains a non-exhuastive list of tutorials and scripts showcasing 🤗 Accelerate
|
||||
Below contains a non-exhaustive list of tutorials and scripts showcasing 🤗 Accelerate
|
||||
|
||||
## Official Accelerate Examples:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -72,6 +72,11 @@ These are tutorials from libraries that integrate with 🤗 Accelerate:
|
||||
|
||||
> Don't find your integration here? Make a PR to include it!
|
||||
|
||||
### Amphion
|
||||
- [Training Text-to-Speech Models with Amphion](https://github.com/open-mmlab/Amphion/blob/main/egs/tts/README.md)
|
||||
- [Training Singing Voice Conversion Models with Amphion](https://github.com/open-mmlab/Amphion/blob/main/egs/svc/README.md)
|
||||
- [Training Vocoders with Amphion](https://github.com/open-mmlab/Amphion/blob/main/egs/vocoder/README.md)
|
||||
|
||||
### Catalyst
|
||||
|
||||
- [Distributed training tutorial with Catalyst](https://catalyst-team.github.io/catalyst/tutorials/ddp.html)
|
||||
@ -154,12 +159,12 @@ Below contains a non-exhaustive list of papers utilizing 🤗 Accelerate.
|
||||
* Puijin Cheng, Li Lin, Yijin Huang, Huaqing He, Wenhan Luo, Xiaoying Tang: “Learning Enhancement From Degradation: A Diffusion Model For Fundus Image Enhancement”, 2023; [arXiv:2303.04603](http://arxiv.org/abs/2303.04603).
|
||||
* Shun Shao, Yftah Ziser, Shay Cohen: “Erasure of Unaligned Attributes from Neural Representations”, 2023; [arXiv:2302.02997](http://arxiv.org/abs/2302.02997).
|
||||
* Seonghyeon Ye, Hyeonbin Hwang, Sohee Yang, Hyeongu Yun, Yireun Kim, Minjoon Seo: “In-Context Instruction Learning”, 2023; [arXiv:2302.14691](http://arxiv.org/abs/2302.14691).
|
||||
* Shikun Liu, Linxi Fan, Edward Johns, Zhiding Yu, Chaowei Xiao, Anima Anandkumar: “Prismer: A Vision-Language Model with An Ensemble of Experts”, 2023; [arXiv:2303.02506](http://arxiv.org/abs/2303.02506 ).
|
||||
* Shikun Liu, Linxi Fan, Edward Johns, Zhiding Yu, Chaowei Xiao, Anima Anandkumar: “Prismer: A Vision-Language Model with An Ensemble of Experts”, 2023; [arXiv:2303.02506](http://arxiv.org/abs/2303.02506).
|
||||
* Haoyu Chen, Zhihua Wang, Yang Yang, Qilin Sun, Kede Ma: “Learning a Deep Color Difference Metric for Photographic Images”, 2023; [arXiv:2303.14964](http://arxiv.org/abs/2303.14964).
|
||||
* Van-Hoang Le, Hongyu Zhang: “Log Parsing with Prompt-based Few-shot Learning”, 2023; [arXiv:2302.07435](http://arxiv.org/abs/2302.07435).
|
||||
* Keito Kudo, Yoichi Aoki, Tatsuki Kuribayashi, Ana Brassard, Masashi Yoshikawa, Keisuke Sakaguchi, Kentaro Inui: “Do Deep Neural Networks Capture Compositionality in Arithmetic Reasoning?”, 2023; [arXiv:2302.07866](http://arxiv.org/abs/2302.07866).
|
||||
* Ruoyao Wang, Peter Jansen, Marc-Alexandre Côté, Prithviraj Ammanabrolu: “Behavior Cloned Transformers are Neurosymbolic Reasoners”, 2022; [arXiv:2210.07382](http://arxiv.org/abs/2210.07382).
|
||||
* Martin Wessel, Tomáš Horych, Terry Ruas, Akiko Aizawa, Bela Gipp, Timo Spinde: “Introducing MBIB -- the first Media Bias Identification Benchmark Task and Dataset Collection”, 2023; [arXiv:2304.13148](http://arxiv.org/abs/2304.13148 ). DOI: [https://dx.doi.org/10.1145/3539618.3591882 10.1145/3539618.3591882].
|
||||
* Martin Wessel, Tomáš Horych, Terry Ruas, Akiko Aizawa, Bela Gipp, Timo Spinde: “Introducing MBIB -- the first Media Bias Identification Benchmark Task and Dataset Collection”, 2023; [arXiv:2304.13148](http://arxiv.org/abs/2304.13148). DOI: [https://dx.doi.org/10.1145/3539618.3591882 10.1145/3539618.3591882].
|
||||
* Hila Chefer, Yuval Alaluf, Yael Vinker, Lior Wolf, Daniel Cohen-Or: “Attend-and-Excite: Attention-Based Semantic Guidance for Text-to-Image Diffusion Models”, 2023; [arXiv:2301.13826](http://arxiv.org/abs/2301.13826).
|
||||
* Marcio Fonseca, Yftah Ziser, Shay B. Cohen: “Factorizing Content and Budget Decisions in Abstractive Summarization of Long Documents”, 2022; [arXiv:2205.12486](http://arxiv.org/abs/2205.12486).
|
||||
* Elad Richardson, Gal Metzer, Yuval Alaluf, Raja Giryes, Daniel Cohen-Or: “TEXTure: Text-Guided Texturing of 3D Shapes”, 2023; [arXiv:2302.01721](http://arxiv.org/abs/2302.01721).
|
||||
@ -172,4 +177,4 @@ Below contains a non-exhaustive list of papers utilizing 🤗 Accelerate.
|
||||
* Zhiruo Wang, Shuyan Zhou, Daniel Fried, Graham Neubig: “Execution-Based Evaluation for Open-Domain Code Generation”, 2022; [arXiv:2212.10481](http://arxiv.org/abs/2212.10481).
|
||||
* Minh-Long Luu, Zeyi Huang, Eric P. Xing, Yong Jae Lee, Haohan Wang: “Expeditious Saliency-guided Mix-up through Random Gradient Thresholding”, 2022; [arXiv:2212.04875](http://arxiv.org/abs/2212.04875).
|
||||
* Jun Hao Liew, Hanshu Yan, Daquan Zhou, Jiashi Feng: “MagicMix: Semantic Mixing with Diffusion Models”, 2022; [arXiv:2210.16056](http://arxiv.org/abs/2210.16056).
|
||||
* Yaqing Wang, Subhabrata Mukherjee, Xiaodong Liu, Jing Gao, Ahmed Hassan Awadallah, Jianfeng Gao: “LiST: Lite Prompted Self-training Makes Parameter-Efficient Few-shot Learners”, 2021; [arXiv:2110.06274](http://arxiv.org/abs/2110.06274).
|
||||
* Yaqing Wang, Subhabrata Mukherjee, Xiaodong Liu, Jing Gao, Ahmed Hassan Awadallah, Jianfeng Gao: “LiST: Lite Prompted Self-training Makes Parameter-Efficient Few-shot Learners”, 2021; [arXiv:2110.06274](http://arxiv.org/abs/2110.06274).
|
||||
|
||||
@ -64,9 +64,9 @@ To run it in each of these various modes, use the following commands:
|
||||
accelerate config # This will create a config file on your server
|
||||
accelerate launch ./nlp_example.py # This will run the script on your server
|
||||
```
|
||||
* With traditional PyTorch launcher (`torch.distributed.launch` can be used with older versions of PyTorch)
|
||||
* With traditional PyTorch launcher (`python -m torch.distributed.run` can be used instead of `torchrun`)
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python -m torchrun --nproc_per_node 2 --use_env ./nlp_example.py
|
||||
torchrun --nproc_per_node 2 ./nlp_example.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
- multi GPUs, multi node (several machines, using PyTorch distributed mode)
|
||||
* With Accelerate config and launcher, on each machine:
|
||||
@ -74,18 +74,15 @@ To run it in each of these various modes, use the following commands:
|
||||
accelerate config # This will create a config file on each server
|
||||
accelerate launch ./nlp_example.py # This will run the script on each server
|
||||
```
|
||||
* With PyTorch launcher only (`torch.distributed.launch` can be used in older versions of PyTorch)
|
||||
* With PyTorch launcher only (`python -m torch.distributed.run` can be used instead of `torchrun`). Run this command on each node:
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python -m torchrun --nproc_per_node 2 \
|
||||
--use_env \
|
||||
--node_rank 0 \
|
||||
--master_addr master_node_ip_address \
|
||||
./nlp_example.py # On the first server
|
||||
python -m torchrun --nproc_per_node 2 \
|
||||
--use_env \
|
||||
--node_rank 1 \
|
||||
--master_addr master_node_ip_address \
|
||||
./nlp_example.py # On the second server
|
||||
torchrun \ # python -m torch.distributed.run
|
||||
--nproc_per_node 2 \
|
||||
--nnodes 2 \
|
||||
--rdzv_id 2299 \ # A unique job id
|
||||
--rdzv_backend c10d \
|
||||
--rdzv_endpoint master_node_ip_address:29500 \
|
||||
./nlp_example.py
|
||||
```
|
||||
- (multi) TPUs
|
||||
* With Accelerate config and launcher
|
||||
@ -149,37 +146,34 @@ To run it in each of these various modes, use the following commands:
|
||||
- multi GPUs (using PyTorch distributed mode)
|
||||
* With Accelerate config and launcher
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
accelerate config # This will create a config file on your server
|
||||
accelerate launch ./cv_example.py --data_dir path_to_data # This will run the script on your server
|
||||
accelerate config --config_file config.yaml # This will create a config file on your server to `config.yaml`
|
||||
accelerate launch --config_file config.yaml ./cv_example.py --data_dir path_to_data # This will run the script on your server
|
||||
```
|
||||
* With traditional PyTorch launcher (`torch.distributed.launch` can be used with older versions of PyTorch)
|
||||
* With traditional PyTorch launcher (`python -m torch.distributed.run` can be used instead of `torchrun`)
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python -m torchrun --nproc_per_node 2 --use_env ./cv_example.py --data_dir path_to_data
|
||||
torchrun --nproc_per_node 2 ./cv_example.py --data_dir path_to_data
|
||||
```
|
||||
- multi GPUs, multi node (several machines, using PyTorch distributed mode)
|
||||
* With Accelerate config and launcher, on each machine:
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
accelerate config # This will create a config file on each server
|
||||
accelerate launch ./cv_example.py --data_dir path_to_data # This will run the script on each server
|
||||
accelerate config --config_file config.yaml # This will create a config file on your server to `config.yaml`
|
||||
accelerate launch --config_file config.yaml ./cv_example.py --data_dir path_to_data # This will run the script on each server
|
||||
```
|
||||
* With PyTorch launcher only (`torch.distributed.launch` can be used with older versions of PyTorch)
|
||||
* With PyTorch launcher only (`python -m torch.distributed.run` can be used instead of `torchrun`). Run this command on each node:
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python -m torchrun --nproc_per_node 2 \
|
||||
--use_env \
|
||||
--node_rank 0 \
|
||||
--master_addr master_node_ip_address \
|
||||
./cv_example.py --data_dir path_to_data # On the first server
|
||||
python -m torchrun --nproc_per_node 2 \
|
||||
--use_env \
|
||||
--node_rank 1 \
|
||||
--master_addr master_node_ip_address \
|
||||
./cv_example.py --data_dir path_to_data # On the second server
|
||||
torchrun \ # python -m torch.distributed.run
|
||||
--nproc_per_node 2 \
|
||||
--nnodes 2 \
|
||||
--rdzv_id 2299 \ # A unique job id
|
||||
--rdzv_backend c10d \
|
||||
--rdzv_endpoint master_node_ip_address:29500 \
|
||||
./cv_example.py --data_dir path_to_data
|
||||
```
|
||||
- (multi) TPUs
|
||||
* With Accelerate config and launcher
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
accelerate config # This will create a config file on your TPU server
|
||||
accelerate launch ./cv_example.py --data_dir path_to_data # This will run the script on each server
|
||||
accelerate config --config_file config.yaml # This will create a config file on your server to `config.yaml`
|
||||
accelerate launch --config_file config.yaml ./cv_example.py --data_dir path_to_data # This will run the script on each server
|
||||
```
|
||||
* In PyTorch:
|
||||
Add an `xmp.spawn` line in your script as you usually do.
|
||||
@ -206,6 +200,13 @@ with `pip install runhouse`, and you can refer to
|
||||
for hardware setup instructions, or this
|
||||
[Colab tutorial](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1qVwYyLTCPYPSdz9ZX7BZl9Qm0A3j7RJe) for a more in-depth walkthrough.
|
||||
|
||||
## SLURM Scripts
|
||||
In [/slurm/submit_multigpu.sh](./slurm/submit_multigpu.sh) and [/slurm/submit_multinode.sh](./slurm/submit_multinode.sh) we present two scripts for running the examples on a machine with [SLURM](https://slurm.schedmd.com/documentation.html) workload manager.
|
||||
|
||||
In [/slurm/submit_multigpu.sh](./slurm/submit_multigpu.sh) the only parameter in the launcher that needs to be modified is `--num_processes`, which determines the number of GPUs we will use. In this case, using the environment variable `$SLURM_GPUS`, we indicate that we want to utilize all the GPUs available on the node we have requested.
|
||||
|
||||
In [/slurm/submit_multinode.sh](./slurm/submit_multinode.sh) we must specify the number of nodes that will be part of the training (`--num_machines`), how many GPUs we will use in total (`--num_processes`), the [`backend`](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/elastic/run.html#note-on-rendezvous-backend), `--main_process_ip` which will be the address the master node and the `--main_process_port`.
|
||||
|
||||
## Finer Examples
|
||||
|
||||
While the first two scripts are extremely barebones when it comes to what you can do with accelerate, more advanced features are documented in two other locations.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -220,7 +220,7 @@ def parse_args():
|
||||
default="all",
|
||||
help=(
|
||||
'The integration to report the results and logs to. Supported platforms are `"tensorboard"`,'
|
||||
' `"wandb"` and `"comet_ml"`. Use `"all"` (default) to report to all integrations.'
|
||||
' `"wandb"`, `"comet_ml"`, and `"dvclive"`. Use `"all"` (default) to report to all integrations.'
|
||||
"Only applicable when `--with_tracking` is passed."
|
||||
),
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -247,16 +247,19 @@ def training_function(config, args):
|
||||
args.model_name_or_path, return_dict=True, low_cpu_mem_usage=True
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# New Code #
|
||||
# For FSDP feature, it is highly recommended and efficient to prepare the model before creating optimizer
|
||||
model = accelerator.prepare(model)
|
||||
accelerator.print(model)
|
||||
no_decay = ["bias", "LayerNorm.weight"]
|
||||
optimizer_grouped_parameters = [
|
||||
{
|
||||
"params": [p for n, p in model.named_parameters() if not any(nd in n for nd in no_decay)],
|
||||
"weight_decay": 0.003,
|
||||
},
|
||||
{
|
||||
"params": [p for n, p in model.named_parameters() if any(nd in n for nd in no_decay)],
|
||||
"weight_decay": 0.0,
|
||||
},
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
# Instantiate optimizer
|
||||
# New Code #
|
||||
# For FSDP feature, at present it doesn't support multiple parameter groups,
|
||||
# so we need to create a single parameter group for the whole model
|
||||
optimizer = torch.optim.AdamW(params=model.parameters(), lr=lr, weight_decay=2e-4)
|
||||
optimizer = torch.optim.AdamW(params=optimizer_grouped_parameters, lr=lr, weight_decay=2e-4)
|
||||
|
||||
# Instantiate scheduler
|
||||
lr_scheduler = get_linear_schedule_with_warmup(
|
||||
@ -265,13 +268,8 @@ def training_function(config, args):
|
||||
num_training_steps=(len(train_dataloader) * num_epochs) // gradient_accumulation_steps,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# New Code #
|
||||
# For FSDP feature, prepare everything except the model as we have already prepared the model
|
||||
# before creating the optimizer
|
||||
# There is no specific order to remember, we just need to unpack the objects in the same order we gave them to the
|
||||
# prepare method.
|
||||
optimizer, train_dataloader, eval_dataloader, lr_scheduler = accelerator.prepare(
|
||||
optimizer, train_dataloader, eval_dataloader, lr_scheduler
|
||||
model, optimizer, train_dataloader, eval_dataloader, lr_scheduler = accelerator.prepare(
|
||||
model, optimizer, train_dataloader, eval_dataloader, lr_scheduler
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
overall_step = 0
|
||||
|
||||
@ -216,7 +216,7 @@ def parse_args():
|
||||
default="all",
|
||||
help=(
|
||||
'The integration to report the results and logs to. Supported platforms are `"tensorboard"`,'
|
||||
' `"wandb"` and `"comet_ml"`. Use `"all"` (default) to report to all integrations.'
|
||||
' `"wandb"`, `"comet_ml"`, and `"dvclive"`. Use `"all"` (default) to report to all integrations.'
|
||||
"Only applicable when `--with_tracking` is passed."
|
||||
),
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -11,7 +11,7 @@ def launch_train(*args):
|
||||
num_processes = torch.cuda.device_count()
|
||||
print(f"Device count: {num_processes}")
|
||||
with patch_environment(
|
||||
world_size=num_processes, master_addr="127.0.01", master_port="29500", mixed_precision=args[1].mixed_precision
|
||||
world_size=num_processes, master_addr="127.0.0.1", master_port="29500", mixed_precision=args[1].mixed_precision
|
||||
):
|
||||
launcher = PrepareForLaunch(training_function, distributed_type="MULTI_GPU")
|
||||
torch.multiprocessing.start_processes(launcher, args=args, nprocs=num_processes, start_method="spawn")
|
||||
|
||||
27
examples/slurm/submit_multigpu.sh
Normal file
27
examples/slurm/submit_multigpu.sh
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,27 @@
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
|
||||
#SBATCH --job-name=multigpu
|
||||
#SBATCH -D .
|
||||
#SBATCH --output=O-%x.%j
|
||||
#SBATCH --error=E-%x.%j
|
||||
#SBATCH --nodes=1
|
||||
#SBATCH --ntasks-per-node=1 # number of MP tasks
|
||||
#SBATCH --gres=gpu:4 # number of GPUs per node
|
||||
#SBATCH --cpus-per-task=160 # number of cores per tasks
|
||||
#SBATCH --time=01:59:00 # maximum execution time (HH:MM:SS)
|
||||
|
||||
######################
|
||||
### Set enviroment ###
|
||||
######################
|
||||
source activateEnviroment.sh
|
||||
export GPUS_PER_NODE=4
|
||||
######################
|
||||
|
||||
export SCRIPT=/accelerate/examples/complete_nlp_example.py
|
||||
export SCRIPT_ARGS=" \
|
||||
--mixed_precision fp16 \
|
||||
--output_dir /accelerate/examples/output \
|
||||
--with_tracking \
|
||||
"
|
||||
|
||||
accelerate launch --num_processes $GPUS_PER_NODE $SCRIPT $SCRIPT_ARGS
|
||||
41
examples/slurm/submit_multinode.sh
Normal file
41
examples/slurm/submit_multinode.sh
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,41 @@
|
||||
#!/bin/bash
|
||||
|
||||
#SBATCH --job-name=multinode
|
||||
#SBATCH -D .
|
||||
#SBATCH --output=O-%x.%j
|
||||
#SBATCH --error=E-%x.%j
|
||||
#SBATCH --nodes=4 # number of nodes
|
||||
#SBATCH --ntasks-per-node=1 # number of MP tasks
|
||||
#SBATCH --gres=gpu:4 # number of GPUs per node
|
||||
#SBATCH --cpus-per-task=160 # number of cores per tasks
|
||||
#SBATCH --time=01:59:00 # maximum execution time (HH:MM:SS)
|
||||
|
||||
######################
|
||||
### Set enviroment ###
|
||||
######################
|
||||
source activateEnviroment.sh
|
||||
export GPUS_PER_NODE=4
|
||||
######################
|
||||
|
||||
######################
|
||||
#### Set network #####
|
||||
######################
|
||||
head_node_ip=$(scontrol show hostnames $SLURM_JOB_NODELIST | head -n 1)
|
||||
######################
|
||||
|
||||
export LAUNCHER="accelerate launch \
|
||||
--num_processes $((SLURM_NNODES * GPUS_PER_NODE)) \
|
||||
--num_machines $SLURM_NNODES \
|
||||
--rdzv_backend c10d \
|
||||
--main_process_ip $head_node_ip \
|
||||
--main_process_port 29500 \
|
||||
"
|
||||
export SCRIPT="/accelerate/examples/complete_nlp_example.py"
|
||||
export SCRIPT_ARGS=" \
|
||||
--mixed_precision fp16 \
|
||||
--output_dir /accelerate/examples/output \
|
||||
"
|
||||
|
||||
# This step is necessary because accelerate launch does not handle multiline arguments properly
|
||||
export CMD="$LAUNCHER $PYTHON_FILE $ARGS"
|
||||
srun $CMD
|
||||
10
setup.py
10
setup.py
@ -19,11 +19,13 @@ extras = {}
|
||||
extras["quality"] = ["black ~= 23.1", "ruff >= 0.0.241", "hf-doc-builder >= 0.3.0", "urllib3 < 2.0.0"]
|
||||
extras["docs"] = []
|
||||
extras["test_prod"] = ["pytest", "pytest-xdist", "pytest-subtests", "parameterized"]
|
||||
extras["test_dev"] = ["datasets", "evaluate", "transformers", "scipy", "scikit-learn", "deepspeed", "tqdm", "bitsandbytes", "timm"]
|
||||
extras["test_dev"] = [
|
||||
"datasets", "evaluate", "transformers", "scipy", "scikit-learn", "deepspeed", "tqdm", "bitsandbytes", "timm"
|
||||
]
|
||||
extras["testing"] = extras["test_prod"] + extras["test_dev"]
|
||||
extras["rich"] = ["rich"]
|
||||
|
||||
extras["test_trackers"] = ["wandb", "comet-ml", "tensorboard"]
|
||||
extras["test_trackers"] = ["wandb", "comet-ml", "tensorboard", "dvclive"]
|
||||
extras["dev"] = extras["quality"] + extras["testing"] + extras["rich"]
|
||||
|
||||
extras["sagemaker"] = [
|
||||
@ -32,7 +34,7 @@ extras["sagemaker"] = [
|
||||
|
||||
setup(
|
||||
name="accelerate",
|
||||
version="0.24.0.dev0",
|
||||
version="0.26.1",
|
||||
description="Accelerate",
|
||||
long_description=open("README.md", "r", encoding="utf-8").read(),
|
||||
long_description_content_type="text/markdown",
|
||||
@ -52,7 +54,7 @@ setup(
|
||||
]
|
||||
},
|
||||
python_requires=">=3.8.0",
|
||||
install_requires=["numpy>=1.17", "packaging>=20.0", "psutil", "pyyaml", "torch>=1.10.0", "huggingface_hub"],
|
||||
install_requires=["numpy>=1.17", "packaging>=20.0", "psutil", "pyyaml", "torch>=1.10.0", "huggingface_hub", "safetensors>=0.3.1"],
|
||||
extras_require=extras,
|
||||
classifiers=[
|
||||
"Development Status :: 5 - Production/Stable",
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
|
||||
__version__ = "0.24.0.dev0"
|
||||
__version__ = "0.26.1"
|
||||
|
||||
from .accelerator import Accelerator
|
||||
from .big_modeling import (
|
||||
|
||||
@ -14,7 +14,6 @@
|
||||
|
||||
from __future__ import annotations
|
||||
|
||||
import collections
|
||||
import contextlib
|
||||
import functools
|
||||
import json
|
||||
@ -35,6 +34,7 @@ import torch.utils.hooks as hooks
|
||||
|
||||
from .checkpointing import load_accelerator_state, load_custom_state, save_accelerator_state, save_custom_state
|
||||
from .data_loader import DataLoaderDispatcher, prepare_data_loader, skip_first_batches
|
||||
from .hooks import AlignDevicesHook
|
||||
from .logging import get_logger
|
||||
from .optimizer import AcceleratedOptimizer
|
||||
from .scheduler import AcceleratedScheduler
|
||||
@ -63,6 +63,8 @@ from .utils import (
|
||||
ProjectConfiguration,
|
||||
RNGType,
|
||||
TorchDynamoPlugin,
|
||||
check_os_kernel,
|
||||
clean_state_dict_for_safetensors,
|
||||
compare_versions,
|
||||
convert_model,
|
||||
convert_outputs_to_fp32,
|
||||
@ -72,14 +74,13 @@ from .utils import (
|
||||
get_mixed_precision_context_manager,
|
||||
get_pretty_name,
|
||||
has_transformer_engine_layers,
|
||||
id_tensor_storage,
|
||||
is_bf16_available,
|
||||
is_deepspeed_available,
|
||||
is_fp8_available,
|
||||
is_ipex_available,
|
||||
is_megatron_lm_available,
|
||||
is_msamp_available,
|
||||
is_npu_available,
|
||||
is_safetensors_available,
|
||||
is_torch_version,
|
||||
is_tpu_available,
|
||||
is_xpu_available,
|
||||
@ -97,6 +98,7 @@ from .utils import (
|
||||
wait_for_everyone,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from .utils.constants import FSDP_PYTORCH_VERSION
|
||||
from .utils.modeling import get_state_dict_offloaded_model
|
||||
from .utils.other import is_compiled_module
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -215,6 +217,11 @@ class Accelerator:
|
||||
If set to `True`, in cases where the total batch size across all processes does not exactly divide the
|
||||
dataset, samples at the start of the dataset will be duplicated so the batch can be divided equally among
|
||||
all workers.
|
||||
use_seedable_sampler (`bool`, *optional*, defaults to `False`):
|
||||
Whether or not use a fully seedable random sampler ([`~data_loader.SeedableRandomSampler`]). Ensures
|
||||
training results are fully reproducable using a different sampling technique. While seed-to-seed results
|
||||
may differ, on average the differences are neglible when using multiple different seeds to compare. Should
|
||||
also be ran with [`~utils.set_seed`] for the best results.
|
||||
step_scheduler_with_optimizer (`bool`, *optional`, defaults to `True`):
|
||||
Set `True` if the learning rate scheduler is stepped at the same time as the optimizer, `False` if only
|
||||
done under certain circumstances (at the end of each epoch, for instance).
|
||||
@ -260,10 +267,12 @@ class Accelerator:
|
||||
gradient_accumulation_plugin: GradientAccumulationPlugin | None = None,
|
||||
dispatch_batches: bool | None = None,
|
||||
even_batches: bool = True,
|
||||
use_seedable_sampler: bool = False,
|
||||
step_scheduler_with_optimizer: bool = True,
|
||||
kwargs_handlers: list[KwargsHandler] | None = None,
|
||||
dynamo_backend: DynamoBackend | str | None = None,
|
||||
):
|
||||
self.trackers = []
|
||||
if project_config is not None:
|
||||
self.project_configuration = project_config
|
||||
else:
|
||||
@ -364,6 +373,8 @@ class Accelerator:
|
||||
raise ValueError("You can only pass one `AutocastKwargs` in `kwargs_handler`.")
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self.autocast_handler = handler
|
||||
if self.fp8_recipe_handler is None and mixed_precision == "fp8":
|
||||
self.fp8_recipe_handler = FP8RecipeKwargs()
|
||||
|
||||
kwargs = self.init_handler.to_kwargs() if self.init_handler is not None else {}
|
||||
self.state = AcceleratorState(
|
||||
@ -412,6 +423,7 @@ class Accelerator:
|
||||
self.split_batches = split_batches
|
||||
self.dispatch_batches = dispatch_batches
|
||||
self.even_batches = even_batches
|
||||
self.use_seedable_sampler = use_seedable_sampler
|
||||
self.step_scheduler_with_optimizer = step_scheduler_with_optimizer
|
||||
|
||||
# Mixed precision attributes
|
||||
@ -469,6 +481,8 @@ class Accelerator:
|
||||
# Set a flag tensor for early stopping and other breakpoints
|
||||
self.flag_tensor = None
|
||||
|
||||
check_os_kernel()
|
||||
|
||||
@property
|
||||
def use_distributed(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
@ -956,8 +970,8 @@ class Accelerator:
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
*models (list of `torch.nn.Module`):
|
||||
PyTorch Modules that was prepared with `Accelerator.prepare`. Models passed to `accumulate()` will skip
|
||||
gradient syncing during backward pass in distributed training
|
||||
PyTorch Modules that were prepared with `Accelerator.prepare`. Models passed to `accumulate()` will
|
||||
skip gradient syncing during backward pass in distributed training
|
||||
|
||||
Example:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1098,52 +1112,6 @@ class Accelerator:
|
||||
# Return the unprocessed object if previous criteria was not met
|
||||
return obj
|
||||
|
||||
def _prepare_fsdp(self, *args):
|
||||
result = []
|
||||
for obj in args:
|
||||
if isinstance(obj, torch.nn.Module):
|
||||
model = obj
|
||||
break
|
||||
optimizers = []
|
||||
|
||||
self._schedulers = []
|
||||
self._models = []
|
||||
intermediate_result = []
|
||||
for obj in args:
|
||||
if isinstance(obj, torch.optim.Optimizer):
|
||||
if len(obj.param_groups) > 1:
|
||||
logger.warning(
|
||||
"FSDP Warning: When using FSDP, several parameter groups will be conflated into "
|
||||
"a single one due to nested module wrapping and parameter flattening."
|
||||
)
|
||||
try:
|
||||
optimizer = obj.optimizer.__class__(model.parameters(), **obj.optimizer.defaults)
|
||||
except TypeError:
|
||||
if "differentiable" in obj.optimizer.defaults:
|
||||
# https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate/issues/801
|
||||
defaults = {k: v for k, v in obj.optimizer.defaults.items() if k != "differentiable"}
|
||||
optimizer = obj.optimizer.__class__(model.parameters(), **defaults)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
raise
|
||||
obj = self.prepare_optimizer(optimizer)
|
||||
optimizers.append(obj)
|
||||
elif isinstance(obj, torch.nn.Module):
|
||||
self._models.append(obj)
|
||||
intermediate_result.append(obj)
|
||||
|
||||
for obj in intermediate_result:
|
||||
if isinstance(obj, AcceleratedScheduler):
|
||||
obj.optimizer = optimizers
|
||||
for i, opt in enumerate(self._optimizers):
|
||||
if getattr(obj.scheduler, "optimizer", None) == opt.optimizer:
|
||||
obj.scheduler.optimizer = optimizers[i]
|
||||
obj.optimizers = [optimizers[i]]
|
||||
break
|
||||
self._schedulers.append(obj)
|
||||
result.append(obj)
|
||||
self._optimizers = optimizers
|
||||
return tuple(result)
|
||||
|
||||
def prepare(self, *args, device_placement=None):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Prepare all objects passed in `args` for distributed training and mixed precision, then return them in the same
|
||||
@ -1212,35 +1180,6 @@ class Accelerator:
|
||||
" Please rerun your script specifying `--num_processes=1` or by launching with `python {{myscript.py}}`."
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if self.distributed_type == DistributedType.FSDP:
|
||||
from torch.distributed.fsdp.fully_sharded_data_parallel import FullyShardedDataParallel as FSDP
|
||||
|
||||
model_count = 0
|
||||
optimizer_present = False
|
||||
is_type_fsdp = False
|
||||
for obj in args:
|
||||
if isinstance(obj, torch.nn.Module):
|
||||
model_count += 1
|
||||
# if the model is compiled using PyTorch 2.0,
|
||||
# check that the wrapped model is FSDP or not;
|
||||
# else check if it is FSDP or not;
|
||||
is_type_fsdp = isinstance(obj, FSDP) or (
|
||||
is_compiled_module(obj) and isinstance(obj._orig_mod, FSDP)
|
||||
)
|
||||
if isinstance(obj, torch.optim.Optimizer):
|
||||
optimizer_present = True
|
||||
if model_count > 1 and optimizer_present:
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
"For FSDP to work with multiple models (>1), "
|
||||
"prepare must be called for all the models before optimizers are created. "
|
||||
"Then pass the optimizers to the prepare call in the same order as corresponding models."
|
||||
)
|
||||
elif model_count == 1 and not is_type_fsdp and optimizer_present:
|
||||
logger.warning(
|
||||
"FSDP Warning: When using FSDP, "
|
||||
"it is efficient and recommended to call prepare for the model before creating the optimizer"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if self.distributed_type == DistributedType.DEEPSPEED:
|
||||
model_count = 0
|
||||
for obj in args:
|
||||
@ -1267,7 +1206,7 @@ class Accelerator:
|
||||
|
||||
# If we're dealing with device placement, this deals with that by...
|
||||
tpu_should_fix_optimizer = self.device_placement and self.distributed_type == DistributedType.TPU
|
||||
if tpu_should_fix_optimizer or self.mixed_precision == "fp8":
|
||||
if tpu_should_fix_optimizer or (self.mixed_precision == "fp8" and self.fp8_recipe_handler.backend == "TE"):
|
||||
# 1. grabbing old model parameters
|
||||
old_named_params = self._get_named_parameters(*args)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1281,12 +1220,16 @@ class Accelerator:
|
||||
elif self.distributed_type == DistributedType.MEGATRON_LM:
|
||||
result = self._prepare_megatron_lm(*args)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
if self.mixed_precision == "fp8" and self.fp8_recipe_handler.backend == "MSAMP":
|
||||
args = self._prepare_msamp(*args)
|
||||
# MS-AMP will handle the device placement
|
||||
device_placement = [False for _ in args]
|
||||
result = tuple(
|
||||
self._prepare_one(obj, first_pass=True, device_placement=d) for obj, d in zip(args, device_placement)
|
||||
)
|
||||
result = tuple(self._prepare_one(obj, device_placement=d) for obj, d in zip(result, device_placement))
|
||||
|
||||
if tpu_should_fix_optimizer or self.mixed_precision == "fp8":
|
||||
if tpu_should_fix_optimizer or (self.mixed_precision == "fp8" and self.fp8_recipe_handler.backend == "TE"):
|
||||
# 2. grabbing new model parameters
|
||||
new_named_params = self._get_named_parameters(*result)
|
||||
# 3. building a map from the first to the second
|
||||
@ -1296,14 +1239,6 @@ class Accelerator:
|
||||
if isinstance(obj, torch.optim.Optimizer):
|
||||
obj._switch_parameters(mapping)
|
||||
|
||||
if (
|
||||
self.distributed_type == DistributedType.FSDP
|
||||
and model_count == 1
|
||||
and not is_type_fsdp
|
||||
and optimizer_present
|
||||
):
|
||||
result = self._prepare_fsdp(*result)
|
||||
|
||||
for item in result:
|
||||
if any(
|
||||
item in container
|
||||
@ -1353,6 +1288,29 @@ class Accelerator:
|
||||
" Please rerun your script specifying `--num_processes=1` or by launching with `python {{myscript.py}}`."
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if self.native_amp:
|
||||
model._original_forward = model.forward
|
||||
model_forward_func = model.forward.__func__ if hasattr(model.forward, "__func__") else model.forward
|
||||
autocast_context = get_mixed_precision_context_manager(self.native_amp, self.autocast_handler)
|
||||
new_forward = autocast_context(model_forward_func)
|
||||
if hasattr(model.forward, "__func__"):
|
||||
model.forward = MethodType(new_forward, model)
|
||||
model.forward = MethodType(convert_outputs_to_fp32(model.forward.__func__), model)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
model.forward = convert_outputs_to_fp32(new_forward)
|
||||
elif self.mixed_precision == "fp8" and self.fp8_recipe_handler.backend == "TE":
|
||||
if not has_transformer_engine_layers(model):
|
||||
with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
convert_model(model)
|
||||
model._converted_to_transformer_engine = True
|
||||
model._original_forward = model.forward
|
||||
|
||||
kwargs = self.fp8_recipe_handler.to_kwargs() if self.fp8_recipe_handler is not None else {}
|
||||
if "fp8_format" in kwargs:
|
||||
kwargs["fp8_format"] = getattr(te_recipe.Format, kwargs["fp8_format"])
|
||||
fp8_recipe = te_recipe.DelayedScaling(**kwargs)
|
||||
model.forward = fp8_autocast(enabled=True, fp8_recipe=fp8_recipe)(model.forward)
|
||||
|
||||
if (getattr(model, "is_loaded_in_8bit", False) or getattr(model, "is_loaded_in_4bit", False)) and getattr(
|
||||
model, "hf_device_map", False
|
||||
):
|
||||
@ -1371,7 +1329,6 @@ class Accelerator:
|
||||
if (self.device.index is not None) or (current_device_index != 0):
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
"You can't train a model that has been loaded in 8-bit precision on a different device than the one "
|
||||
"you're training on. Make sure you loaded the model on the correct device using for example `device_map={'':torch.cuda.current_device()}"
|
||||
"you're training on. Make sure you loaded the model on the correct device using for example `device_map={'':torch.cuda.current_device() or device_map={'':torch.xpu.current_device()}"
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1381,37 +1338,6 @@ class Accelerator:
|
||||
)
|
||||
elif device_placement and not self.verify_device_map(model):
|
||||
model = model.to(self.device)
|
||||
|
||||
if self.native_amp:
|
||||
model._original_forward = model.forward
|
||||
model_forward_func = model.forward.__func__ if hasattr(model.forward, "__func__") else model.forward
|
||||
autocast_context = get_mixed_precision_context_manager(self.native_amp, self.autocast_handler)
|
||||
new_forward = autocast_context(model_forward_func)
|
||||
if hasattr(model.forward, "__func__"):
|
||||
model.forward = MethodType(new_forward, model)
|
||||
model.forward = MethodType(convert_outputs_to_fp32(model.forward.__func__), model)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
model.forward = convert_outputs_to_fp32(new_forward)
|
||||
elif self.mixed_precision == "fp8":
|
||||
if not has_transformer_engine_layers(model):
|
||||
with torch.no_grad():
|
||||
convert_model(model)
|
||||
model._converted_to_transformer_engine = True
|
||||
model._original_forward = model.forward
|
||||
|
||||
kwargs = self.fp8_recipe_handler.to_kwargs() if self.fp8_recipe_handler is not None else {}
|
||||
if "fp8_format" in kwargs:
|
||||
kwargs["fp8_format"] = getattr(te_recipe.Format, kwargs["fp8_format"])
|
||||
fp8_recipe = te_recipe.DelayedScaling(**kwargs)
|
||||
cuda_device_capacity = torch.cuda.get_device_capability()
|
||||
fp8_enabled = cuda_device_capacity >= (8, 9)
|
||||
if not fp8_enabled:
|
||||
logger.warn(
|
||||
f"The current device has compute capability of {cuda_device_capacity} which is "
|
||||
"insufficient for FP8 mixed precision training (requires a GPU Hopper/Ada Lovelace "
|
||||
"or higher, compute capability of 8.9 or higher). Will use FP16 instead."
|
||||
)
|
||||
model.forward = fp8_autocast(enabled=fp8_enabled, fp8_recipe=fp8_recipe)(model.forward)
|
||||
if not evaluation_mode:
|
||||
if self.distributed_type in (
|
||||
DistributedType.MULTI_GPU,
|
||||
@ -1495,38 +1421,38 @@ class Accelerator:
|
||||
deepspeed_plugin = self.state.deepspeed_plugin
|
||||
|
||||
is_dataloader_present = any(isinstance(obj, torch.utils.data.DataLoader) for obj in args)
|
||||
if deepspeed_plugin.deepspeed_config["train_micro_batch_size_per_gpu"] == "auto" or is_dataloader_present:
|
||||
result = [
|
||||
self._prepare_one(obj, first_pass=True) if isinstance(obj, torch.utils.data.DataLoader) else obj
|
||||
for obj in args
|
||||
]
|
||||
result = [
|
||||
self._prepare_one(obj, first_pass=True) if isinstance(obj, torch.utils.data.DataLoader) else obj
|
||||
for obj in args
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
batch_sizes = [obj.batch_size for obj in args if hasattr(obj, "batch_size")]
|
||||
if self.split_batches:
|
||||
batch_sizes = [batch_size // self.num_processes for batch_size in batch_sizes]
|
||||
if deepspeed_plugin.is_auto("train_micro_batch_size_per_gpu"):
|
||||
if is_dataloader_present:
|
||||
batch_sizes = [obj.batch_size for obj in args if hasattr(obj, "batch_size")]
|
||||
if any(bs is None for bs in batch_sizes):
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
"At least one of the dataloaders passed to `accelerate.prepare()` has `None` as batch size. "
|
||||
"Please set an integer value in `train_micro_batch_size_per_gpu` in the deepspeed config file "
|
||||
"or assign integer value to `AcceleratorState().deepspeed_plugin.deepspeed_config['train_micro_batch_size_per_gpu']`."
|
||||
)
|
||||
if self.split_batches:
|
||||
batch_sizes = [batch_size // self.num_processes for batch_size in batch_sizes]
|
||||
|
||||
if any(bs is None for bs in batch_sizes):
|
||||
batch_size_per_device = min(batch_sizes) if deepspeed_plugin.is_train_batch_min else max(batch_sizes)
|
||||
if len(batch_sizes) > 1:
|
||||
logger.info(
|
||||
"Since you passed both train and evaluation dataloader, `is_train_batch_min` (here "
|
||||
f"{deepspeed_plugin.is_train_batch_min} will decide the `train_batch_size` ({batch_size_per_device})."
|
||||
)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
"At least one of the dataloaders passed to `accelerate.prepare()` has `None` as batch size."
|
||||
"Please set an integer value in `train_micro_batch_size_per_gpu` in the deepspeed config file"
|
||||
"When using DeepSpeed, `accelerate.prepare()` requires you to pass at least one of training or evaluation dataloaders "
|
||||
"with `batch_size` attribute returning an integer value "
|
||||
"or alternatively set an integer value in `train_micro_batch_size_per_gpu` in the deepspeed config file "
|
||||
"or assign integer value to `AcceleratorState().deepspeed_plugin.deepspeed_config['train_micro_batch_size_per_gpu']`."
|
||||
)
|
||||
if len(batch_sizes) == 0:
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
"When using DeepSpeed `accelerate.prepare()` requires you to pass at least one of training or evaluation dataloaders "
|
||||
"or alternatively set an integer value in `train_micro_batch_size_per_gpu` in the deepspeed config file"
|
||||
"or assign integer value to `AcceleratorState().deepspeed_plugin.deepspeed_config['train_micro_batch_size_per_gpu']`."
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
batch_size_per_device = min(batch_sizes) if deepspeed_plugin.is_train_batch_min else max(batch_sizes)
|
||||
if len(batch_sizes) > 1:
|
||||
logger.info(
|
||||
"Since you passed both train and evaluation dataloader, `is_train_batch_min` (here "
|
||||
f"{deepspeed_plugin.is_train_batch_min} will decide the `train_batch_size` ({batch_size_per_device})."
|
||||
)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
batch_size_per_device = deepspeed_plugin.deepspeed_config["train_micro_batch_size_per_gpu"]
|
||||
result = [obj for obj in args]
|
||||
batch_size_per_device = deepspeed_plugin.get_value("train_micro_batch_size_per_gpu")
|
||||
|
||||
# handle `gradient_accumulation_steps` when the value is `auto`
|
||||
deepspeed_plugin.fill_match(
|
||||
@ -1538,7 +1464,7 @@ class Accelerator:
|
||||
config_kwargs = {
|
||||
"train_micro_batch_size_per_gpu": batch_size_per_device,
|
||||
"train_batch_size": batch_size_per_device
|
||||
* deepspeed_plugin.deepspeed_config["gradient_accumulation_steps"]
|
||||
* deepspeed_plugin.get_value("gradient_accumulation_steps")
|
||||
* self.num_processes,
|
||||
"gradient_clipping": 1.0,
|
||||
"zero_optimization.stage3_gather_16bit_weights_on_model_save": False,
|
||||
@ -1597,21 +1523,40 @@ class Accelerator:
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if model is not None:
|
||||
if hasattr(model, "config"):
|
||||
hidden_size = (
|
||||
max(model.config.hidden_sizes)
|
||||
if getattr(model.config, "hidden_sizes", None)
|
||||
else getattr(model.config, "hidden_size", None)
|
||||
# deal with config keys that use `auto` value and rely on model's hidden_size
|
||||
hidden_size_based_keys = [
|
||||
"zero_optimization.reduce_bucket_size",
|
||||
"zero_optimization.stage3_prefetch_bucket_size",
|
||||
"zero_optimization.stage3_param_persistence_threshold",
|
||||
]
|
||||
hidden_size_auto_keys = [x for x in hidden_size_based_keys if deepspeed_plugin.is_auto(x)]
|
||||
if len(hidden_size_auto_keys) > 0:
|
||||
reasoning = (
|
||||
"therefore it's not possible to automatically fill out the following `auto` entries "
|
||||
+ f"in the DeepSpeed config file: {hidden_size_auto_keys}. You can fix that by replacing "
|
||||
+ "`auto` values for these keys with an integer value of your choice."
|
||||
)
|
||||
if hidden_size is not None:
|
||||
config_kwargs.update(
|
||||
{
|
||||
"zero_optimization.reduce_bucket_size": hidden_size * hidden_size,
|
||||
"zero_optimization.stage3_prefetch_bucket_size": 0.9 * hidden_size * hidden_size,
|
||||
"zero_optimization.stage3_param_persistence_threshold": 10 * hidden_size,
|
||||
}
|
||||
if not hasattr(model, "config"):
|
||||
raise ValueError("Can't find `model.config` entry, " + reasoning)
|
||||
|
||||
if hasattr(model.config, "hidden_size"):
|
||||
hidden_size = model.config.hidden_size
|
||||
elif hasattr(model.config, "hidden_sizes"):
|
||||
# if there are many hidden sizes pick the largest one
|
||||
hidden_size = max(model.config.hidden_sizes)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
"Can find neither `model.config.hidden_size` nor `model.config.hidden_sizes`, " + reasoning
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
config_kwargs.update(
|
||||
{
|
||||
"zero_optimization.reduce_bucket_size": hidden_size * hidden_size,
|
||||
"zero_optimization.stage3_prefetch_bucket_size": 0.9 * hidden_size * hidden_size,
|
||||
"zero_optimization.stage3_param_persistence_threshold": 10 * hidden_size,
|
||||
}
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if isinstance(optimizer, (DummyOptim)):
|
||||
config_kwargs.update(
|
||||
{"optimizer.params.lr": optimizer.lr, "optimizer.params.weight_decay": optimizer.weight_decay}
|
||||
@ -1653,10 +1598,7 @@ class Accelerator:
|
||||
optimizer = DeepSpeedCPUAdam(optimizer.param_groups, **defaults)
|
||||
kwargs["optimizer"] = optimizer
|
||||
if scheduler is not None:
|
||||
if (
|
||||
isinstance(scheduler, LRScheduler)
|
||||
or type(scheduler).__name__ in deepspeed.runtime.lr_schedules.VALID_LR_SCHEDULES
|
||||
):
|
||||
if type(scheduler).__name__ in deepspeed.runtime.lr_schedules.VALID_LR_SCHEDULES:
|
||||
kwargs["lr_scheduler"] = scheduler
|
||||
|
||||
engine, optimizer, _, lr_scheduler = deepspeed.initialize(**kwargs)
|
||||
@ -1829,6 +1771,42 @@ class Accelerator:
|
||||
result[i] = optimizer
|
||||
return tuple(result)
|
||||
|
||||
def _prepare_msamp(self, *args):
|
||||
if not is_msamp_available():
|
||||
raise ImportError(
|
||||
"MS-AMP was not found on your system. Please ensure that MS-AMP is available "
|
||||
" or choose `'te'` as the backend for FP8 mixed precision training."
|
||||
)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
import msamp
|
||||
|
||||
model, optimizer = None, None
|
||||
num_models, num_optimizers = 0, 0
|
||||
result = [obj for obj in args]
|
||||
for obj in result:
|
||||
if isinstance(obj, torch.nn.Module):
|
||||
model = obj
|
||||
num_models += 1
|
||||
elif isinstance(obj, (torch.optim.Optimizer)):
|
||||
optimizer = obj
|
||||
num_optimizers += 1
|
||||
if optimizer is None or model is None:
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
"You must pass a model and an optimizer together to `accelerate.prepare()` when using MS-AMP."
|
||||
)
|
||||
elif num_models > 1 or num_optimizers > 1:
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
f"You can't use multiple models ({num_models}) or optimizers {num_optimizers} with MS-AMP."
|
||||
)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
model, optimizer = msamp.initialize(model, optimizer, opt_level=self.fp8_recipe_handler.opt_level)
|
||||
for i in range(len(result)):
|
||||
if isinstance(result[i], torch.nn.Module):
|
||||
result[i] = model
|
||||
elif isinstance(result[i], (torch.optim.Optimizer)):
|
||||
result[i] = optimizer
|
||||
return tuple(result)
|
||||
|
||||
def prepare_data_loader(
|
||||
self, data_loader: torch.utils.data.DataLoader, device_placement=None, slice_fn_for_dispatch=None
|
||||
):
|
||||
@ -1876,6 +1854,7 @@ class Accelerator:
|
||||
dispatch_batches=self.dispatch_batches,
|
||||
even_batches=self.even_batches,
|
||||
slice_fn_for_dispatch=slice_fn_for_dispatch,
|
||||
use_seedable_sampler=self.use_seedable_sampler,
|
||||
)
|
||||
self._dataloaders.append(prepared_data_loader)
|
||||
return prepared_data_loader
|
||||
@ -2399,7 +2378,6 @@ class Accelerator:
|
||||
... )
|
||||
```
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self.trackers = []
|
||||
for tracker in self.log_with:
|
||||
if issubclass(type(tracker), GeneralTracker):
|
||||
# Custom trackers are already initialized
|
||||
@ -2441,7 +2419,7 @@ class Accelerator:
|
||||
>>> tensorboard_tracker = accelerator.get_tracker("tensorboard")
|
||||
```
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if len(getattr(self, "trackers", [])) > 0:
|
||||
if len(self.trackers) > 0:
|
||||
for tracker in self.trackers:
|
||||
if tracker.name == name:
|
||||
return tracker.tracker if unwrap else tracker
|
||||
@ -2508,6 +2486,10 @@ class Accelerator:
|
||||
f (`str` or `os.PathLike`): Where to save the content of `obj`.
|
||||
safe_serialization (`bool`, *optional*, defaults to `False`): Whether to save `obj` using `safetensors`
|
||||
|
||||
Note:
|
||||
If `save_on_each_node` was passed in as a `ProjectConfiguration`, will save the object once per node,
|
||||
rather than only once on the main node.
|
||||
|
||||
Example:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
@ -2518,14 +2500,19 @@ class Accelerator:
|
||||
>>> accelerator.save(arr, "array.pkl")
|
||||
```
|
||||
"""
|
||||
save(obj, f, safe_serialization=safe_serialization)
|
||||
save(
|
||||
obj,
|
||||
f,
|
||||
save_on_each_node=self.project_configuration.save_on_each_node,
|
||||
safe_serialization=safe_serialization,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def save_model(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
model: torch.nn.Module,
|
||||
save_directory: Union[str, os.PathLike],
|
||||
max_shard_size: Union[int, str] = "10GB",
|
||||
safe_serialization: bool = False,
|
||||
safe_serialization: bool = True,
|
||||
):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Save a model so that it can be re-loaded using load_checkpoint_in_model
|
||||
@ -2546,7 +2533,7 @@ class Accelerator:
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
safe_serialization (`bool`, *optional*, defaults to `False`):
|
||||
safe_serialization (`bool`, *optional*, defaults to `True`):
|
||||
Whether to save the model using `safetensors` or the traditional PyTorch way (that uses `pickle`).
|
||||
|
||||
Example:
|
||||
@ -2560,9 +2547,6 @@ class Accelerator:
|
||||
```
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
if safe_serialization and not is_safetensors_available():
|
||||
raise ImportError("`safe_serialization` requires the `safetensors library: `pip install safetensors`.")
|
||||
|
||||
if os.path.isfile(save_directory):
|
||||
logger.error(f"Provided path ({save_directory}) should be a directory, not a file")
|
||||
return
|
||||
@ -2570,38 +2554,21 @@ class Accelerator:
|
||||
os.makedirs(save_directory, exist_ok=True)
|
||||
|
||||
# get the state_dict of the model
|
||||
state_dict = self.get_state_dict(model)
|
||||
if any(
|
||||
[
|
||||
module._hf_hook.offload
|
||||
for module in model.modules()
|
||||
if hasattr(module, "_hf_hook") and isinstance(module._hf_hook, AlignDevicesHook)
|
||||
]
|
||||
):
|
||||
state_dict = get_state_dict_offloaded_model(model)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
if any(param.device == torch.device("meta") for param in model.parameters()):
|
||||
raise RuntimeError("You can't save the model since some parameters are on the meta device.")
|
||||
state_dict = self.get_state_dict(model)
|
||||
|
||||
if safe_serialization:
|
||||
# Safetensors does not allow tensor aliasing.
|
||||
# We're going to remove aliases before saving
|
||||
ptrs = collections.defaultdict(list)
|
||||
# when bnb serialization is used the weights in the state dict can be strings
|
||||
for name, tensor in state_dict.items():
|
||||
if not isinstance(tensor, str):
|
||||
ptrs[id_tensor_storage(tensor)].append(name)
|
||||
|
||||
# These are all the pointers of shared tensors.
|
||||
shared_ptrs = {ptr: names for ptr, names in ptrs.items() if len(names) > 1}
|
||||
warn_names = set()
|
||||
for names in shared_ptrs.values():
|
||||
# When not all duplicates have been cleaned, still remove those keys, but put a clear warning.
|
||||
# If the link between tensors was done at runtime then `from_pretrained` will not get
|
||||
# the key back leading to random tensor. A proper warning will be shown
|
||||
# during reload (if applicable), but since the file is not necessarily compatible with
|
||||
# the config, better show a proper warning.
|
||||
found = 0
|
||||
for name in names:
|
||||
if name in state_dict:
|
||||
found += 1
|
||||
if found > 1:
|
||||
del state_dict[name]
|
||||
warn_names.add(name)
|
||||
if len(warn_names) > 0:
|
||||
logger.warning(
|
||||
f"Removed shared tensor {warn_names} while saving. This should be OK, but check by verifying that you don't receive any warning while reloading",
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
state_dict = clean_state_dict_for_safetensors(state_dict)
|
||||
weights_name = SAFE_WEIGHTS_NAME if safe_serialization else WEIGHTS_NAME
|
||||
|
||||
# Shard the model if it is too big.
|
||||
@ -2679,7 +2646,7 @@ class Accelerator:
|
||||
self._save_model_state_pre_hook[handle.id] = hook
|
||||
return handle
|
||||
|
||||
def save_state(self, output_dir: str = None, **save_model_func_kwargs):
|
||||
def save_state(self, output_dir: str = None, safe_serialization: bool = True, **save_model_func_kwargs):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Saves the current states of the model, optimizer, scaler, RNG generators, and registered objects to a folder.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -2700,6 +2667,8 @@ class Accelerator:
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
output_dir (`str` or `os.PathLike`):
|
||||
The name of the folder to save all relevant weights and states.
|
||||
safe_serialization (`bool`, *optional*, defaults to `True`):
|
||||
Whether to save the model using `safetensors` or the traditional PyTorch way (that uses `pickle`).
|
||||
save_model_func_kwargs (`dict`, *optional*):
|
||||
Additional keyword arguments for saving model which can be passed to the underlying save function, such
|
||||
as optional arguments for DeepSpeed's `save_checkpoint` function.
|
||||
@ -2770,7 +2739,7 @@ class Accelerator:
|
||||
# Save the optimizers taking care of FSDP and DeepSpeed nuances
|
||||
optimizers = []
|
||||
if self.distributed_type == DistributedType.FSDP:
|
||||
for opt in self._optimizers:
|
||||
for i, opt in enumerate(self._optimizers):
|
||||
logger.info("Saving FSDP Optimizer")
|
||||
save_fsdp_optimizer(self.state.fsdp_plugin, self, opt, self._models[i], output_dir, i)
|
||||
logger.info(f"FSDP Optimizer saved to output dir {output_dir}")
|
||||
@ -2787,16 +2756,27 @@ class Accelerator:
|
||||
elif self.distributed_type not in [DistributedType.MEGATRON_LM]:
|
||||
schedulers = self._schedulers
|
||||
|
||||
# Save the samplers of the dataloaders
|
||||
dataloaders = self._dataloaders
|
||||
|
||||
# Call model loading hooks that might have been registered with
|
||||
# accelerator.register_model_state_hook
|
||||
for hook in self._save_model_state_pre_hook.values():
|
||||
hook(self._models, weights, output_dir)
|
||||
|
||||
save_location = save_accelerator_state(
|
||||
output_dir, weights, optimizers, schedulers, self.state.process_index, self.scaler
|
||||
output_dir,
|
||||
weights,
|
||||
optimizers,
|
||||
schedulers,
|
||||
dataloaders,
|
||||
self.state.process_index,
|
||||
self.scaler,
|
||||
save_on_each_node=self.project_configuration.save_on_each_node,
|
||||
safe_serialization=safe_serialization,
|
||||
)
|
||||
for i, obj in enumerate(self._custom_objects):
|
||||
save_custom_state(obj, output_dir, i)
|
||||
save_custom_state(obj, output_dir, i, save_on_each_node=self.project_configuration.save_on_each_node)
|
||||
self.project_configuration.iteration += 1
|
||||
return save_location
|
||||
|
||||
@ -2920,6 +2900,8 @@ class Accelerator:
|
||||
elif self.distributed_type not in [DistributedType.MEGATRON_LM]:
|
||||
schedulers = self._schedulers
|
||||
|
||||
dataloaders = self._dataloaders
|
||||
|
||||
# Call model loading hooks that might have been registered with
|
||||
# accelerator.register_model_state_hook
|
||||
for hook in self._load_model_state_pre_hook.values():
|
||||
@ -2940,6 +2922,7 @@ class Accelerator:
|
||||
models,
|
||||
optimizers,
|
||||
schedulers,
|
||||
dataloaders,
|
||||
self.state.process_index,
|
||||
self.scaler,
|
||||
map_location,
|
||||
@ -3071,6 +3054,13 @@ class Accelerator:
|
||||
from deepspeed.checkpoint.utils import clone_tensors_for_torch_save
|
||||
|
||||
state_dict = clone_tensors_for_torch_save(self.unwrap_model(model).state_dict())
|
||||
elif self.distributed_type == DistributedType.FSDP:
|
||||
from torch.distributed.fsdp import FullStateDictConfig, StateDictType
|
||||
from torch.distributed.fsdp import FullyShardedDataParallel as FSDP
|
||||
|
||||
full_state_dict_config = FullStateDictConfig(offload_to_cpu=True, rank0_only=True)
|
||||
with FSDP.state_dict_type(model, StateDictType.FULL_STATE_DICT, full_state_dict_config):
|
||||
state_dict = model.state_dict()
|
||||
else:
|
||||
if unwrap:
|
||||
model = self.unwrap_model(model)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -36,6 +36,7 @@ from .utils import (
|
||||
find_tied_parameters,
|
||||
get_balanced_memory,
|
||||
infer_auto_device_map,
|
||||
is_npu_available,
|
||||
is_torch_version,
|
||||
load_checkpoint_in_model,
|
||||
offload_state_dict,
|
||||
@ -72,6 +73,8 @@ def init_empty_weights(include_buffers: bool = None):
|
||||
|
||||
Any model created under this context manager has no weights. As such you can't do something like
|
||||
`model.to(some_device)` with it. To load weights inside your empty model, see [`load_checkpoint_and_dispatch`].
|
||||
Make sure to overwrite the default device_map param for [`load_checkpoint_and_dispatch`], otherwise dispatch is not
|
||||
called.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
"""
|
||||
@ -402,6 +405,16 @@ def dispatch_model(
|
||||
skip_keys=skip_keys,
|
||||
preload_module_classes=preload_module_classes,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# warn if there is any params on the meta device
|
||||
offloaded_devices_str = " and ".join(
|
||||
[device for device in set(device_map.values()) if device in ("cpu", "disk")]
|
||||
)
|
||||
if len(offloaded_devices_str) > 0:
|
||||
logging.warning(
|
||||
f"Some parameters are on the meta device device because they were offloaded to the {offloaded_devices_str}."
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Attaching the hook may break tied weights, so we retie them
|
||||
retie_parameters(model, tied_params)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -418,10 +431,16 @@ def dispatch_model(
|
||||
return wrapper
|
||||
|
||||
model.to = add_warning(model.to, model)
|
||||
model.cuda = add_warning(model.cuda, model)
|
||||
if is_npu_available():
|
||||
model.npu = add_warning(model.npu, model)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
model.cuda = add_warning(model.cuda, model)
|
||||
|
||||
else:
|
||||
device = list(device_map.values())[0]
|
||||
# `torch.Tensor.to(<int num>)` is not supported by `torch_npu` (see this [issue](https://github.com/Ascend/pytorch/issues/16)).
|
||||
if is_npu_available() and isinstance(device, int):
|
||||
device = f"npu:{device}"
|
||||
if device != "disk":
|
||||
model.to(device)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
@ -462,7 +481,8 @@ def load_checkpoint_and_dispatch(
|
||||
name, once a given module name is inside, every submodule of it will be sent to the same device.
|
||||
|
||||
To have Accelerate compute the most optimized `device_map` automatically, set `device_map="auto"`. For more
|
||||
information about each option see [here](big_modeling#designing-a-device-map).
|
||||
information about each option see [here](../concept_guides/big_model_inference#designing-a-device-map).
|
||||
Defaults to None, which means [`dispatch_model`] will not be called.
|
||||
max_memory (`Dict`, *optional*):
|
||||
A dictionary device identifier to maximum memory. Will default to the maximum memory available for each GPU
|
||||
and the available CPU RAM if unset.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -12,21 +12,25 @@
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import random
|
||||
from pathlib import Path
|
||||
from typing import List
|
||||
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from safetensors.torch import load_file
|
||||
from torch.cuda.amp import GradScaler
|
||||
|
||||
from .utils import (
|
||||
MODEL_NAME,
|
||||
OPTIMIZER_NAME,
|
||||
RNG_STATE_NAME,
|
||||
SAFE_MODEL_NAME,
|
||||
SAFE_WEIGHTS_NAME,
|
||||
SAMPLER_NAME,
|
||||
SCALER_NAME,
|
||||
SCHEDULER_NAME,
|
||||
WEIGHTS_NAME,
|
||||
get_pretty_name,
|
||||
is_tpu_available,
|
||||
is_xpu_available,
|
||||
@ -49,12 +53,22 @@ def save_accelerator_state(
|
||||
model_states: List[dict],
|
||||
optimizers: list,
|
||||
schedulers: list,
|
||||
dataloaders: list,
|
||||
process_index: int,
|
||||
scaler: GradScaler = None,
|
||||
save_on_each_node: bool = False,
|
||||
safe_serialization: bool = True,
|
||||
):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Saves the current states of the models, optimizers, scaler, and RNG generators to a given directory.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
If `safe_serialization` is `True`, models will be saved with `safetensors` while the rest are saved using native
|
||||
`pickle`.
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
output_dir (`str` or `os.PathLike`):
|
||||
The name of the folder to save all relevant weights and states.
|
||||
@ -64,35 +78,58 @@ def save_accelerator_state(
|
||||
A list of optimizer instances
|
||||
schedulers (`List[torch.optim.lr_scheduler._LRScheduler]`):
|
||||
A list of learning rate schedulers
|
||||
dataloaders (`List[torch.utils.data.DataLoader]`):
|
||||
A list of dataloader instances to save their sampler states
|
||||
process_index (`int`):
|
||||
The current process index in the Accelerator state
|
||||
scaler (`torch.cuda.amp.GradScaler`, *optional*):
|
||||
An optional gradient scaler instance to save
|
||||
save_on_each_node (`bool`, *optional*):
|
||||
Whether to save on every node, or only the main node.
|
||||
safe_serialization (`bool`, *optional*, defaults to `True`):
|
||||
Whether to save the model using `safetensors` or the traditional PyTorch way (that uses `pickle`).
|
||||
"""
|
||||
output_dir = Path(output_dir)
|
||||
# Model states
|
||||
for i, state in enumerate(model_states):
|
||||
weights_name = f"{MODEL_NAME}.bin" if i == 0 else f"{MODEL_NAME}_{i}.bin"
|
||||
output_model_file = os.path.join(output_dir, weights_name)
|
||||
save(state, output_model_file)
|
||||
weights_name = WEIGHTS_NAME if not safe_serialization else SAFE_WEIGHTS_NAME
|
||||
if i > 0:
|
||||
weights_name = weights_name.replace(".", f"_{i}.")
|
||||
output_model_file = output_dir.joinpath(weights_name)
|
||||
save(state, output_model_file, save_on_each_node=save_on_each_node, safe_serialization=safe_serialization)
|
||||
logger.info(f"Model weights saved in {output_model_file}")
|
||||
# Optimizer states
|
||||
for i, opt in enumerate(optimizers):
|
||||
state = opt.state_dict()
|
||||
optimizer_name = f"{OPTIMIZER_NAME}.bin" if i == 0 else f"{OPTIMIZER_NAME}_{i}.bin"
|
||||
output_optimizer_file = os.path.join(output_dir, optimizer_name)
|
||||
save(state, output_optimizer_file)
|
||||
output_optimizer_file = output_dir.joinpath(optimizer_name)
|
||||
save(state, output_optimizer_file, save_on_each_node=save_on_each_node, safe_serialization=False)
|
||||
logger.info(f"Optimizer state saved in {output_optimizer_file}")
|
||||
# Scheduler states
|
||||
for i, scheduler in enumerate(schedulers):
|
||||
state = scheduler.state_dict()
|
||||
scheduler_name = f"{SCHEDULER_NAME}.bin" if i == 0 else f"{SCHEDULER_NAME}_{i}.bin"
|
||||
output_scheduler_file = os.path.join(output_dir, scheduler_name)
|
||||
save(state, output_scheduler_file)
|
||||
output_scheduler_file = output_dir.joinpath(scheduler_name)
|
||||
save(state, output_scheduler_file, save_on_each_node=save_on_each_node, safe_serialization=False)
|
||||
logger.info(f"Scheduler state saved in {output_scheduler_file}")
|
||||
# DataLoader states
|
||||
for i, dataloader in enumerate(dataloaders):
|
||||
sampler_name = f"{SAMPLER_NAME}.bin" if i == 0 else f"{SAMPLER_NAME}_{i}.bin"
|
||||
output_sampler_file = output_dir.joinpath(sampler_name)
|
||||
# Only save if we have our custom sampler
|
||||
from .data_loader import IterableDatasetShard, SeedableRandomSampler
|
||||
|
||||
if isinstance(dataloader.dataset, IterableDatasetShard):
|
||||
sampler = dataloader.sampler.sampler
|
||||
|
||||
if isinstance(sampler, SeedableRandomSampler):
|
||||
save(sampler, output_sampler_file, save_on_each_node=save_on_each_node, safe_serialization=False)
|
||||
logger.info(f"Sampler state for dataloader {i} saved in {output_sampler_file}")
|
||||
|
||||
# GradScaler state
|
||||
if scaler is not None:
|
||||
state = scaler.state_dict()
|
||||
output_scaler_file = os.path.join(output_dir, SCALER_NAME)
|
||||
output_scaler_file = output_dir.joinpath(SCALER_NAME)
|
||||
torch.save(state, output_scaler_file)
|
||||
logger.info(f"Gradient scaler state saved in {output_scaler_file}")
|
||||
# Random number generator states
|
||||
@ -107,7 +144,7 @@ def save_accelerator_state(
|
||||
states["torch_cuda_manual_seed"] = torch.cuda.get_rng_state_all()
|
||||
if is_tpu_available():
|
||||
states["xm_seed"] = xm.get_rng_state()
|
||||
output_states_file = os.path.join(output_dir, states_name)
|
||||
output_states_file = output_dir.joinpath(states_name)
|
||||
torch.save(states, output_states_file)
|
||||
logger.info(f"Random states saved in {output_states_file}")
|
||||
return output_dir
|
||||
@ -118,6 +155,7 @@ def load_accelerator_state(
|
||||
models,
|
||||
optimizers,
|
||||
schedulers,
|
||||
dataloaders,
|
||||
process_index,
|
||||
scaler=None,
|
||||
map_location=None,
|
||||
@ -152,17 +190,25 @@ def load_accelerator_state(
|
||||
map_location = "cpu"
|
||||
elif map_location == "on_device":
|
||||
map_location = PartialState().device
|
||||
|
||||
input_dir = Path(input_dir)
|
||||
# Model states
|
||||
for i, model in enumerate(models):
|
||||
weights_name = f"{MODEL_NAME}.bin" if i == 0 else f"{MODEL_NAME}_{i}.bin"
|
||||
input_model_file = os.path.join(input_dir, weights_name)
|
||||
models[i].load_state_dict(torch.load(input_model_file, map_location=map_location), **load_model_func_kwargs)
|
||||
ending = f"_{i}" if i > 0 else ""
|
||||
input_model_file = input_dir.joinpath(f"{SAFE_MODEL_NAME}{ending}.safetensors")
|
||||
if input_model_file.exists():
|
||||
state_dict = load_file(input_model_file, device=str(map_location))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
# Load with torch
|
||||
input_model_file = input_dir.joinpath(f"{MODEL_NAME}{ending}.bin")
|
||||
state_dict = torch.load(input_model_file, map_location=map_location)
|
||||
models[i].load_state_dict(state_dict, **load_model_func_kwargs)
|
||||
logger.info("All model weights loaded successfully")
|
||||
|
||||
# Optimizer states
|
||||
for i, opt in enumerate(optimizers):
|
||||
optimizer_name = f"{OPTIMIZER_NAME}.bin" if i == 0 else f"{OPTIMIZER_NAME}_{i}.bin"
|
||||
input_optimizer_file = os.path.join(input_dir, optimizer_name)
|
||||
input_optimizer_file = input_dir.joinpath(optimizer_name)
|
||||
optimizer_state = torch.load(input_optimizer_file, map_location=map_location)
|
||||
optimizers[i].load_state_dict(optimizer_state)
|
||||
logger.info("All optimizer states loaded successfully")
|
||||
@ -170,19 +216,32 @@ def load_accelerator_state(
|
||||
# Scheduler states
|
||||
for i, scheduler in enumerate(schedulers):
|
||||
scheduler_name = f"{SCHEDULER_NAME}.bin" if i == 0 else f"{SCHEDULER_NAME}_{i}.bin"
|
||||
input_scheduler_file = os.path.join(input_dir, scheduler_name)
|
||||
input_scheduler_file = input_dir.joinpath(scheduler_name)
|
||||
scheduler.load_state_dict(torch.load(input_scheduler_file))
|
||||
logger.info("All scheduler states loaded successfully")
|
||||
|
||||
for i, dataloader in enumerate(dataloaders):
|
||||
sampler_name = f"{SAMPLER_NAME}.bin" if i == 0 else f"{SAMPLER_NAME}_{i}.bin"
|
||||
input_sampler_file = input_dir.joinpath(sampler_name)
|
||||
# Only load if we have our custom sampler
|
||||
from .data_loader import IterableDatasetShard, SeedableRandomSampler
|
||||
|
||||
if isinstance(dataloader.dataset, IterableDatasetShard):
|
||||
sampler = dataloader.sampler.sampler
|
||||
|
||||
if isinstance(sampler, SeedableRandomSampler):
|
||||
dataloader.sampler.sampler = torch.load(input_sampler_file)
|
||||
logger.info("All dataloader sampler states loaded successfully")
|
||||
|
||||
# GradScaler state
|
||||
if scaler is not None:
|
||||
input_scaler_file = os.path.join(input_dir, SCALER_NAME)
|
||||
input_scaler_file = input_dir.joinpath(SCALER_NAME)
|
||||
scaler.load_state_dict(torch.load(input_scaler_file))
|
||||
logger.info("GradScaler state loaded successfully")
|
||||
|
||||
# Random states
|
||||
try:
|
||||
states = torch.load(os.path.join(input_dir, f"{RNG_STATE_NAME}_{process_index}.pkl"))
|
||||
states = torch.load(input_dir.joinpath(f"{RNG_STATE_NAME}_{process_index}.pkl"))
|
||||
random.setstate(states["random_state"])
|
||||
np.random.set_state(states["numpy_random_seed"])
|
||||
torch.set_rng_state(states["torch_manual_seed"])
|
||||
@ -197,14 +256,14 @@ def load_accelerator_state(
|
||||
logger.info("Could not load random states")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def save_custom_state(obj, path, index: int = 0):
|
||||
def save_custom_state(obj, path, index: int = 0, save_on_each_node: bool = False):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Saves the state of `obj` to `{path}/custom_checkpoint_{index}.pkl`
|
||||
"""
|
||||
# Should this be the right way to get a qual_name type value from `obj`?
|
||||
save_location = Path(path) / f"custom_checkpoint_{index}.pkl"
|
||||
logger.info(f"Saving the state of {get_pretty_name(obj)} to {save_location}")
|
||||
torch.save(obj.state_dict(), save_location)
|
||||
save(obj.state_dict(), save_location, save_on_each_node=save_on_each_node)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def load_custom_state(obj, path, index: int = 0):
|
||||
|
||||
@ -179,7 +179,7 @@ def get_cluster_input():
|
||||
|
||||
use_mps = not use_cpu and is_mps_available()
|
||||
deepspeed_config = {}
|
||||
if distributed_type in [DistributedType.MULTI_GPU, DistributedType.NO] and not use_mps:
|
||||
if distributed_type in [DistributedType.MULTI_GPU, DistributedType.MULTI_NPU, DistributedType.NO] and not use_mps:
|
||||
use_deepspeed = _ask_field(
|
||||
"Do you want to use DeepSpeed? [yes/NO]: ",
|
||||
_convert_yes_no_to_bool,
|
||||
@ -327,8 +327,7 @@ def get_cluster_input():
|
||||
fsdp_config["fsdp_sharding_strategy"] = _ask_options(
|
||||
sharding_strategy_query,
|
||||
FSDP_SHARDING_STRATEGY,
|
||||
lambda x: int(x) + 1,
|
||||
default=1,
|
||||
lambda x: FSDP_SHARDING_STRATEGY[int(x)],
|
||||
)
|
||||
fsdp_config["fsdp_offload_params"] = _ask_field(
|
||||
"Do you want to offload parameters and gradients to CPU? [yes/NO]: ",
|
||||
@ -362,7 +361,7 @@ def get_cluster_input():
|
||||
default=100000000,
|
||||
)
|
||||
fsdp_backward_prefetch_query = "What should be your FSDP's backward prefetch policy?"
|
||||
fsdp_config["fsdp_backward_prefetch_policy"] = _ask_options(
|
||||
fsdp_config["fsdp_backward_prefetch"] = _ask_options(
|
||||
fsdp_backward_prefetch_query,
|
||||
FSDP_BACKWARD_PREFETCH,
|
||||
lambda x: FSDP_BACKWARD_PREFETCH[int(x)],
|
||||
@ -381,17 +380,26 @@ def get_cluster_input():
|
||||
error_message="Please enter yes or no.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
fsdp_config["fsdp_use_orig_params"] = _ask_field(
|
||||
"Do you want to enable FSDP's `use_orig_params` feature? [yes/NO]: ",
|
||||
_convert_yes_no_to_bool,
|
||||
default=False,
|
||||
error_message="Please enter yes or no.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
fsdp_config["fsdp_sync_module_states"] = _ask_field(
|
||||
"Do you want each individually wrapped FSDP unit to broadcast module parameters from rank 0 at the start? [YES/no]: ",
|
||||
"Do you want to enable FSDP's `use_orig_params` feature? [YES/no]: ",
|
||||
_convert_yes_no_to_bool,
|
||||
default=True,
|
||||
error_message="Please enter yes or no.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
fsdp_config["fsdp_cpu_ram_efficient_loading"] = _ask_field(
|
||||
"Do you want to enable CPU RAM efficient model loading? Only applicable for 🤗 Transformers models. [YES/no]: ",
|
||||
_convert_yes_no_to_bool,
|
||||
default=True,
|
||||
error_message="Please enter yes or no.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
if fsdp_config["fsdp_cpu_ram_efficient_loading"]:
|
||||
fsdp_config["fsdp_sync_module_states"] = True
|
||||
else:
|
||||
fsdp_config["fsdp_sync_module_states"] = _ask_field(
|
||||
"Do you want each individually wrapped FSDP unit to broadcast module parameters from rank 0 at the start? [YES/no]: ",
|
||||
_convert_yes_no_to_bool,
|
||||
default=True,
|
||||
error_message="Please enter yes or no.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
megatron_lm_config = {}
|
||||
if distributed_type in [DistributedType.MULTI_GPU]:
|
||||
@ -442,7 +450,7 @@ def get_cluster_input():
|
||||
|
||||
megatron_lm_config[prefix + "use_distributed_optimizer"] = _ask_field(
|
||||
"Do you want to use distributed optimizer "
|
||||
"which shards optimizer state and gradients across data pralellel ranks? [YES/no]: ",
|
||||
"which shards optimizer state and gradients across data parallel ranks? [YES/no]: ",
|
||||
_convert_yes_no_to_bool,
|
||||
default=True,
|
||||
error_message="Please enter yes or no.",
|
||||
|
||||
@ -30,13 +30,15 @@ DYNAMO_BACKENDS = [
|
||||
"EAGER",
|
||||
"AOT_EAGER",
|
||||
"INDUCTOR",
|
||||
"NVFUSER",
|
||||
"AOT_NVFUSER",
|
||||
"AOT_CUDAGRAPHS",
|
||||
"AOT_TS_NVFUSER",
|
||||
"NVPRIMS_NVFUSER",
|
||||
"CUDAGRAPHS",
|
||||
"OFI",
|
||||
"FX2TRT",
|
||||
"ONNXRT",
|
||||
"TENSORRT",
|
||||
"IPEX",
|
||||
"TVM",
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -34,6 +34,7 @@ from accelerate.utils import (
|
||||
DistributedType,
|
||||
PrepareForLaunch,
|
||||
_filter_args,
|
||||
check_cuda_p2p_ib_support,
|
||||
is_bf16_available,
|
||||
is_deepspeed_available,
|
||||
is_npu_available,
|
||||
@ -481,8 +482,8 @@ def launch_command_parser(subparsers=None):
|
||||
)
|
||||
fsdp_args.add_argument(
|
||||
"--fsdp_sharding_strategy",
|
||||
type=int,
|
||||
default=1,
|
||||
type=str,
|
||||
default="FULL_SHARD",
|
||||
help="FSDP's Sharding Strategy. (useful only when `use_fsdp` flag is passed).",
|
||||
)
|
||||
fsdp_args.add_argument(
|
||||
@ -502,6 +503,12 @@ def launch_command_parser(subparsers=None):
|
||||
"--fsdp_backward_prefetch_policy",
|
||||
default=None,
|
||||
type=str,
|
||||
help="This argument is deprecated and will be removed in version 0.27.0 of 🤗 Accelerate. Use `fsdp_backward_prefetch` instead.",
|
||||
)
|
||||
fsdp_args.add_argument(
|
||||
"--fsdp_backward_prefetch",
|
||||
default=None,
|
||||
type=str,
|
||||
help="FSDP's backward prefetch policy. (useful only when `use_fsdp` flag is passed).",
|
||||
)
|
||||
fsdp_args.add_argument(
|
||||
@ -519,11 +526,19 @@ def launch_command_parser(subparsers=None):
|
||||
)
|
||||
fsdp_args.add_argument(
|
||||
"--fsdp_use_orig_params",
|
||||
default="false",
|
||||
default="true",
|
||||
type=str,
|
||||
help="If True, allows non-uniform `requires_grad` during init, which means support for interspersed frozen and trainable paramteres."
|
||||
" (useful only when `use_fsdp` flag is passed).",
|
||||
)
|
||||
fsdp_args.add_argument(
|
||||
"--fsdp_cpu_ram_efficient_loading",
|
||||
default="true",
|
||||
type=str,
|
||||
help="If True, only the first process loads the pretrained model checkoint while all other processes have empty weights. "
|
||||
"Only applicable for 🤗 Transformers. When using this, `--fsdp_sync_module_states` needs to True. "
|
||||
"(useful only when `use_fsdp` flag is passed).",
|
||||
)
|
||||
fsdp_args.add_argument(
|
||||
"--fsdp_sync_module_states",
|
||||
default="true",
|
||||
@ -634,6 +649,17 @@ def multi_gpu_launcher(args):
|
||||
import torch.distributed.run as distrib_run
|
||||
|
||||
current_env = prepare_multi_gpu_env(args)
|
||||
if not check_cuda_p2p_ib_support():
|
||||
message = "Using RTX 3090 or 4000 series which doesn't support faster communication speedups. Ensuring P2P and IB communications are disabled."
|
||||
warn = False
|
||||
if "NCCL_P2P_DISABLE" not in current_env:
|
||||
current_env["NCCL_P2P_DISABLE"] = "1"
|
||||
warn = True
|
||||
if "NCCL_IB_DISABLE" not in current_env:
|
||||
current_env["NCCL_IB_DISABLE"] = "1"
|
||||
warn = True
|
||||
if warn:
|
||||
logger.warning(message)
|
||||
|
||||
debug = getattr(args, "debug", False)
|
||||
args = _filter_args(
|
||||
@ -660,6 +686,17 @@ def deepspeed_launcher(args):
|
||||
raise ImportError("DeepSpeed is not installed => run `pip3 install deepspeed` or build it from source.")
|
||||
|
||||
cmd, current_env = prepare_deepspeed_cmd_env(args)
|
||||
if not check_cuda_p2p_ib_support():
|
||||
message = "Using RTX 3090 or 4000 series which doesn't support faster communication speedups. Ensuring P2P and IB communications are disabled."
|
||||
warn = False
|
||||
if "NCCL_P2P_DISABLE" not in current_env:
|
||||
current_env["NCCL_P2P_DISABLE"] = "1"
|
||||
warn = True
|
||||
if "NCCL_IB_DISABLE" not in current_env:
|
||||
current_env["NCCL_IB_DISABLE"] = "1"
|
||||
warn = True
|
||||
if warn:
|
||||
logger.warning(message)
|
||||
|
||||
if args.num_machines > 1 and args.deepspeed_multinode_launcher != DEEPSPEED_MULTINODE_LAUNCHERS[1]:
|
||||
with open(".deepspeed_env", "a") as f:
|
||||
@ -748,7 +785,7 @@ def tpu_pod_launcher(args):
|
||||
"--tpu",
|
||||
"--no_tpu_cluster",
|
||||
"--num_machines",
|
||||
str(1),
|
||||
"1",
|
||||
"--mixed_precision",
|
||||
"no",
|
||||
"--dynamo_backend",
|
||||
|
||||
@ -17,7 +17,7 @@ from contextlib import suppress
|
||||
from typing import Callable, List, Optional, Union
|
||||
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from torch.utils.data import BatchSampler, DataLoader, IterableDataset
|
||||
from torch.utils.data import BatchSampler, DataLoader, IterableDataset, RandomSampler
|
||||
|
||||
from .logging import get_logger
|
||||
from .state import AcceleratorState, DistributedType, GradientState, is_tpu_available
|
||||
@ -64,6 +64,38 @@ for v, additional_kwargs in _PYTORCH_DATALOADER_ADDITIONAL_KWARGS.items():
|
||||
_PYTORCH_DATALOADER_KWARGS.update(additional_kwargs)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class SeedableRandomSampler(RandomSampler):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Same as a random sampler, except that in `__iter__` a seed can be used.
|
||||
|
||||
Needed specifically in distributed cases, when the random generator for each GPU needs to start from the same seed
|
||||
and be fully reproducable on multiple iterations.
|
||||
|
||||
If a custom `generator` is passed, it will rely on its initial seed as well as the current iteration it is on
|
||||
(stored in `self.epoch`).
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
|
||||
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
|
||||
self.epoch = 0
|
||||
self.seed = torch.random.initial_seed()
|
||||
|
||||
def __iter__(self):
|
||||
if self.generator is None:
|
||||
self.generator = torch.Generator()
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self.seed = self.generator.initial_seed()
|
||||
# Allow `self.epoch` to modify the seed of the generator
|
||||
seed = self.epoch + self.seed
|
||||
self.generator.manual_seed(seed)
|
||||
yield from super().__iter__()
|
||||
self.set_epoch(self.epoch + 1)
|
||||
|
||||
def set_epoch(self, epoch: int):
|
||||
"Sets the current iteration of the sampler."
|
||||
self.epoch = epoch
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class BatchSamplerShard(BatchSampler):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Wraps a PyTorch `BatchSampler` to generate batches for one of the processes only. Instances of this class will
|
||||
@ -120,7 +152,10 @@ class BatchSamplerShard(BatchSampler):
|
||||
self.batch_size = getattr(batch_sampler, "batch_size", None)
|
||||
self.drop_last = getattr(batch_sampler, "drop_last", False)
|
||||
if self.batch_size is None and self.even_batches:
|
||||
raise ValueError("You need to use `even_batches=False` when the batch sampler has no batch size.")
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
"You need to use `even_batches=False` when the batch sampler has no batch size. If you "
|
||||
"are not calling this method directly, set `accelerator.even_batches=False` instead."
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@property
|
||||
def total_length(self):
|
||||
@ -271,7 +306,25 @@ class IterableDatasetShard(IterableDataset):
|
||||
self.process_index = process_index
|
||||
self.split_batches = split_batches
|
||||
|
||||
def set_epoch(self, epoch):
|
||||
self.epoch = epoch
|
||||
if hasattr(self.dataset, "set_epoch"):
|
||||
self.dataset.set_epoch(epoch)
|
||||
|
||||
def __len__(self):
|
||||
# We will just raise the downstream error if the underlying dataset is not sized
|
||||
if self.drop_last:
|
||||
return (len(self.dataset) // (self.batch_size * self.num_processes)) * self.batch_size
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return math.ceil(len(self.dataset) / (self.batch_size * self.num_processes)) * self.batch_size
|
||||
|
||||
def __iter__(self):
|
||||
if (
|
||||
not hasattr(self.dataset, "set_epoch")
|
||||
and hasattr(self.dataset, "generator")
|
||||
and isinstance(self.dataset.generator, torch.Generator)
|
||||
):
|
||||
self.dataset.generator.manual_seed(self.epoch)
|
||||
real_batch_size = self.batch_size if self.split_batches else (self.batch_size * self.num_processes)
|
||||
process_batch_size = (self.batch_size // self.num_processes) if self.split_batches else self.batch_size
|
||||
process_slice = range(self.process_index * process_batch_size, (self.process_index + 1) * process_batch_size)
|
||||
@ -324,8 +377,9 @@ class DataLoaderStateMixin:
|
||||
"Prepares the gradient state for the current dataloader"
|
||||
self.reset()
|
||||
with suppress(Exception):
|
||||
length = getattr(self.dataset, "total_dataset_length", len(self.dataset))
|
||||
self.remainder = length % self.total_batch_size
|
||||
if not self._drop_last:
|
||||
length = getattr(self.dataset, "total_dataset_length", len(self.dataset))
|
||||
self.remainder = length % self.total_batch_size
|
||||
self.gradient_state._add_dataloader(self)
|
||||
|
||||
def end(self):
|
||||
@ -352,7 +406,7 @@ class DataLoaderShard(DataLoader, DataLoaderStateMixin):
|
||||
- `"generator"`: an optional `torch.Generator`
|
||||
synchronized_generator (`torch.Generator`, *optional*):
|
||||
A random number generator to keep synchronized across processes.
|
||||
split_batches (`int`, *optional*, defaults to 0):
|
||||
skip_batches (`int`, *optional*, defaults to 0):
|
||||
The number of batches to skip at the beginning.
|
||||
kwargs:
|
||||
All other keyword arguments to pass to the regular `DataLoader` initialization.
|
||||
@ -366,18 +420,31 @@ class DataLoaderShard(DataLoader, DataLoaderStateMixin):
|
||||
- **total_dataset_length** (`int`) -- Total length of the inner dataset across all processes.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, dataset, device=None, rng_types=None, synchronized_generator=None, skip_batches=0, **kwargs):
|
||||
def __init__(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
dataset,
|
||||
device=None,
|
||||
rng_types=None,
|
||||
synchronized_generator=None,
|
||||
skip_batches=0,
|
||||
_drop_last: bool = False,
|
||||
**kwargs,
|
||||
):
|
||||
super().__init__(dataset, **kwargs)
|
||||
self.device = device
|
||||
self.rng_types = rng_types
|
||||
self.synchronized_generator = synchronized_generator
|
||||
self.skip_batches = skip_batches
|
||||
self.gradient_state = GradientState()
|
||||
self._drop_last = _drop_last
|
||||
self.iteration = 0
|
||||
|
||||
def __iter__(self):
|
||||
if self.rng_types is not None:
|
||||
synchronize_rng_states(self.rng_types, self.synchronized_generator)
|
||||
self.begin()
|
||||
|
||||
self.set_epoch(self.iteration)
|
||||
dataloader_iter = super().__iter__()
|
||||
# We iterate one batch ahead to check when we are at the end
|
||||
try:
|
||||
@ -401,8 +468,21 @@ class DataLoaderShard(DataLoader, DataLoaderStateMixin):
|
||||
if batch_index >= self.skip_batches:
|
||||
yield current_batch
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
self.iteration += 1
|
||||
self.end()
|
||||
|
||||
def set_epoch(self, epoch: int):
|
||||
# In case it is manually passed in, the user can set it to what they like
|
||||
if self.iteration != epoch:
|
||||
self.iteration = epoch
|
||||
if hasattr(self.batch_sampler, "sampler") and hasattr(self.batch_sampler.sampler, "set_epoch"):
|
||||
self.batch_sampler.sampler.set_epoch(epoch)
|
||||
# We support if a custom `Dataset` implementation has `set_epoch`
|
||||
# or in general HF datasets `Datasets`
|
||||
elif hasattr(self.dataset, "set_epoch"):
|
||||
self.dataset.set_epoch(epoch)
|
||||
|
||||
@property
|
||||
def total_batch_size(self):
|
||||
batch_sampler = self.sampler if isinstance(self.sampler, BatchSampler) else self.batch_sampler
|
||||
@ -459,6 +539,10 @@ if is_tpu_available(check_device=False):
|
||||
def total_dataset_length(self):
|
||||
return self._loader.total_dataset_length
|
||||
|
||||
@property
|
||||
def batch_sampler(self):
|
||||
return self._loader.batch_sampler
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class DataLoaderDispatcher(DataLoader, DataLoaderStateMixin):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
@ -506,6 +590,7 @@ class DataLoaderDispatcher(DataLoader, DataLoaderStateMixin):
|
||||
self.skip_batches = skip_batches
|
||||
|
||||
self.slice_fn = slice_tensors if slice_fn is None else slice_fn
|
||||
self.iteration = 0
|
||||
|
||||
def _fetch_batches(self, iterator):
|
||||
batches, batch = None, None
|
||||
@ -521,7 +606,15 @@ class DataLoaderDispatcher(DataLoader, DataLoaderStateMixin):
|
||||
batches = []
|
||||
for _ in range(self.state.num_processes):
|
||||
batches.append(next(iterator))
|
||||
batch = concatenate(batches, dim=0)
|
||||
try:
|
||||
batch = concatenate(batches, dim=0)
|
||||
except RuntimeError as e:
|
||||
raise RuntimeError(
|
||||
"You can't use batches of different size with `dispatch_batches=True` or when using an `IterableDataset`."
|
||||
"either pass `dispatch_batches=False` and have each process fetch its own batch "
|
||||
" or pass `split_batches=True`. By doing so, the main process will fetch a full batch and "
|
||||
"slice it into `num_processes` batches for each process."
|
||||
) from e
|
||||
# In both cases, we need to get the structure of the batch that we will broadcast on other
|
||||
# processes to initialize the tensors with the right shape.
|
||||
# data_structure, stop_iteration
|
||||
@ -546,6 +639,7 @@ class DataLoaderDispatcher(DataLoader, DataLoaderStateMixin):
|
||||
|
||||
def __iter__(self):
|
||||
self.begin()
|
||||
self.set_epoch(self.iteration)
|
||||
main_iterator = None
|
||||
if is_torch_version(">=", "2.0.1"):
|
||||
# NOTE PyTorch DataLoader adds forward compatibilities for DataPipes, which broadcasts
|
||||
@ -615,8 +709,18 @@ class DataLoaderDispatcher(DataLoader, DataLoaderStateMixin):
|
||||
if batch_index >= self.skip_batches:
|
||||
yield batch
|
||||
batch_index += 1
|
||||
self.iteration += 1
|
||||
self.end()
|
||||
|
||||
def set_epoch(self, epoch: int):
|
||||
# In case it is manually passed in, the user can set it to what they like
|
||||
if self.iteration != epoch:
|
||||
self.iteration = epoch
|
||||
if hasattr(self.batch_sampler.sampler, "set_epoch"):
|
||||
self.batch_sampler.sampler.set_epoch(epoch)
|
||||
elif hasattr(self.dataset, "set_epoch"):
|
||||
self.dataset.set_epoch(epoch)
|
||||
|
||||
def __len__(self):
|
||||
whole_length = super().__len__()
|
||||
if self.split_batches:
|
||||
@ -648,6 +752,7 @@ def prepare_data_loader(
|
||||
dispatch_batches: Optional[bool] = None,
|
||||
even_batches: bool = True,
|
||||
slice_fn_for_dispatch: Optional[Callable] = None,
|
||||
use_seedable_sampler: bool = False,
|
||||
) -> DataLoader:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Wraps a PyTorch `DataLoader` to generate batches for one of the processes only.
|
||||
@ -701,6 +806,10 @@ def prepare_data_loader(
|
||||
If passed, this function will be used to slice tensors across `num_processes`. Will default to
|
||||
[`~utils.slice_tensors`]. This argument is used only when `dispatch_batches` is set to `True` and will be
|
||||
ignored otherwise.
|
||||
use_seedable_sampler (`bool`, *optional*, defaults to `False`):
|
||||
Whether to use the [`~data_loader.SeedableRandomSampler`] instead of a `RandomSampler` for better
|
||||
reproducability. Comes at a cost of potentially different performances due to different shuffling
|
||||
algorithms but ensures results will be the *exact* same.
|
||||
|
||||
Returns:
|
||||
`torch.utils.data.dataloader.DataLoader`: A new data loader that will yield the portion of the batches
|
||||
@ -728,7 +837,8 @@ def prepare_data_loader(
|
||||
process_index = state.process_index
|
||||
|
||||
# Sanity check
|
||||
if split_batches and dataloader.batch_size > 1 and dataloader.batch_size % num_processes != 0:
|
||||
batch_size = dataloader.batch_size if dataloader.batch_size is not None else dataloader.batch_sampler.batch_size
|
||||
if split_batches and batch_size > 1 and batch_size % num_processes != 0:
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
f"To use a `DataLoader` in `split_batches` mode, the batch size ({dataloader.batch_size}) "
|
||||
f"needs to be a round multiple of the number of processes ({num_processes})."
|
||||
@ -739,6 +849,23 @@ def prepare_data_loader(
|
||||
new_batch_sampler = dataloader.batch_sampler if not isinstance(new_dataset, IterableDataset) else None
|
||||
sampler_is_batch_sampler = False
|
||||
synchronized_generator = None
|
||||
sampler_is_batch_sampler = isinstance(dataloader.sampler, BatchSampler)
|
||||
if sampler_is_batch_sampler:
|
||||
sampler = getattr(dataloader.sampler, "sampler", None)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
sampler = getattr(dataloader.batch_sampler, "sampler", None)
|
||||
if isinstance(sampler, RandomSampler) and use_seedable_sampler:
|
||||
# When iterating through the dataloader during distributed processes
|
||||
# we want to ensure that on each process we are iterating through the same
|
||||
# samples in the same order if a seed is set. This requires a tweak
|
||||
# to the `torch.utils.data.RandomSampler` class (if used).
|
||||
sampler = SeedableRandomSampler(
|
||||
data_source=sampler.data_source,
|
||||
replacement=sampler.replacement,
|
||||
num_samples=sampler._num_samples,
|
||||
generator=getattr(sampler, "generator", torch.Generator()),
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# No change if no multiprocess
|
||||
if (num_processes != 1 or state.distributed_type == DistributedType.MEGATRON_LM) and not dispatch_batches:
|
||||
if isinstance(new_dataset, IterableDataset):
|
||||
@ -753,17 +880,6 @@ def prepare_data_loader(
|
||||
split_batches=split_batches,
|
||||
)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
# New batch sampler for the current process.
|
||||
sampler_is_batch_sampler = isinstance(dataloader.sampler, BatchSampler)
|
||||
if sampler_is_batch_sampler:
|
||||
sampler = dataloader.sampler.sampler
|
||||
else:
|
||||
sampler = dataloader.batch_sampler.sampler
|
||||
if hasattr(sampler, "generator"):
|
||||
if sampler.generator is None:
|
||||
sampler.generator = torch.Generator()
|
||||
synchronized_generator = sampler.generator
|
||||
|
||||
batch_sampler = dataloader.sampler if sampler_is_batch_sampler else dataloader.batch_sampler
|
||||
new_batch_sampler = BatchSamplerShard(
|
||||
batch_sampler,
|
||||
@ -797,7 +913,11 @@ def prepare_data_loader(
|
||||
kwargs["batch_size"] = (
|
||||
dataloader.batch_size // num_processes if split_batches and not dispatch_batches else dataloader.batch_size
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if isinstance(sampler, SeedableRandomSampler) and use_seedable_sampler:
|
||||
if sampler_is_batch_sampler:
|
||||
dataloader.sampler.sampler = sampler
|
||||
else:
|
||||
dataloader.batch_sampler.sampler = sampler
|
||||
if dispatch_batches:
|
||||
kwargs.pop("generator")
|
||||
dataloader = DataLoaderDispatcher(
|
||||
@ -815,6 +935,7 @@ def prepare_data_loader(
|
||||
sampler=new_batch_sampler,
|
||||
batch_size=dataloader.batch_size,
|
||||
rng_types=rng_types,
|
||||
_drop_last=dataloader.drop_last,
|
||||
synchronized_generator=synchronized_generator,
|
||||
**kwargs,
|
||||
)
|
||||
@ -825,6 +946,7 @@ def prepare_data_loader(
|
||||
batch_sampler=new_batch_sampler,
|
||||
rng_types=rng_types,
|
||||
synchronized_generator=synchronized_generator,
|
||||
_drop_last=dataloader.drop_last,
|
||||
**kwargs,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -26,6 +26,7 @@ from .utils import (
|
||||
send_to_device,
|
||||
set_module_tensor_to_device,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from .utils.modeling import get_non_persistent_buffers
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class ModelHook:
|
||||
@ -262,14 +263,17 @@ class AlignDevicesHook(ModelHook):
|
||||
module, include_buffers=self.offload_buffers, recurse=self.place_submodules
|
||||
)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
for name, _ in named_module_tensors(
|
||||
module, include_buffers=self.offload_buffers, recurse=self.place_submodules
|
||||
module, include_buffers=self.offload_buffers, recurse=self.place_submodules, remove_non_persistent=True
|
||||
):
|
||||
set_module_tensor_to_device(module, name, "meta")
|
||||
if not self.offload_buffers and self.execution_device is not None:
|
||||
for name, _ in module.named_buffers(recurse=self.place_submodules):
|
||||
set_module_tensor_to_device(module, name, self.execution_device)
|
||||
elif self.offload_buffers and self.execution_device is not None:
|
||||
for name in get_non_persistent_buffers(module, recurse=self.place_submodules):
|
||||
set_module_tensor_to_device(module, name, self.execution_device)
|
||||
|
||||
return module
|
||||
|
||||
def pre_forward(self, module, *args, **kwargs):
|
||||
@ -277,7 +281,10 @@ class AlignDevicesHook(ModelHook):
|
||||
self.input_device = find_device([args, kwargs])
|
||||
if self.offload:
|
||||
for name, _ in named_module_tensors(
|
||||
module, include_buffers=self.offload_buffers, recurse=self.place_submodules
|
||||
module,
|
||||
include_buffers=self.offload_buffers,
|
||||
recurse=self.place_submodules,
|
||||
remove_non_persistent=True,
|
||||
):
|
||||
fp16_statistics = None
|
||||
if "weight" in name and name.replace("weight", "SCB") in self.weights_map.keys():
|
||||
@ -294,7 +301,10 @@ class AlignDevicesHook(ModelHook):
|
||||
def post_forward(self, module, output):
|
||||
if self.offload:
|
||||
for name, _ in named_module_tensors(
|
||||
module, include_buffers=self.offload_buffers, recurse=self.place_submodules
|
||||
module,
|
||||
include_buffers=self.offload_buffers,
|
||||
recurse=self.place_submodules,
|
||||
remove_non_persistent=True,
|
||||
):
|
||||
set_module_tensor_to_device(module, name, "meta")
|
||||
if type(module).__name__ == "Linear8bitLt":
|
||||
|
||||
@ -19,7 +19,14 @@ import tempfile
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
from .state import AcceleratorState, PartialState
|
||||
from .utils import PrecisionType, PrepareForLaunch, is_mps_available, patch_environment
|
||||
from .utils import (
|
||||
PrecisionType,
|
||||
PrepareForLaunch,
|
||||
are_libraries_initialized,
|
||||
check_cuda_p2p_ib_support,
|
||||
is_mps_available,
|
||||
patch_environment,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def test_launch():
|
||||
@ -142,16 +149,34 @@ def notebook_launcher(
|
||||
"inside your training function. Restart your notebook and make sure no cells initializes an "
|
||||
"`Accelerator`."
|
||||
)
|
||||
# torch.distributed will expect a few environment variable to be here. We set the ones common to each
|
||||
# process here (the other ones will be set be the launcher).
|
||||
with patch_environment(
|
||||
# Check for specific libraries known to initialize CUDA that users constantly use
|
||||
problematic_imports = are_libraries_initialized("bitsandbytes")
|
||||
if len(problematic_imports) > 0:
|
||||
err = (
|
||||
"Could not start distributed process. Libraries known to initialize CUDA upon import have been "
|
||||
"imported already. Please keep these imports inside your training function to try and help with this:"
|
||||
)
|
||||
for lib_name in problematic_imports:
|
||||
err += f"\n\t* `{lib_name}`"
|
||||
raise RuntimeError(err)
|
||||
|
||||
patched_env = dict(
|
||||
nproc=num_processes,
|
||||
node_rank=node_rank,
|
||||
world_size=num_nodes * num_processes,
|
||||
master_addr=master_addr,
|
||||
master_port=use_port,
|
||||
mixed_precision=mixed_precision,
|
||||
):
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Check for CUDA P2P and IB issues
|
||||
if not check_cuda_p2p_ib_support():
|
||||
patched_env["nccl_p2p_disable"] = "1"
|
||||
patched_env["nccl_ib_disable"] = "1"
|
||||
|
||||
# torch.distributed will expect a few environment variable to be here. We set the ones common to each
|
||||
# process here (the other ones will be set be the launcher).
|
||||
with patch_environment(**patched_env):
|
||||
# First dummy launch
|
||||
if os.environ.get("ACCELERATE_DEBUG_MODE", "false").lower() == "true":
|
||||
launcher = PrepareForLaunch(test_launch, distributed_type="MULTI_GPU")
|
||||
@ -222,7 +247,7 @@ def debug_launcher(function, args=(), num_processes=2):
|
||||
# process here (the other ones will be set be the launcher).
|
||||
with patch_environment(
|
||||
world_size=num_processes,
|
||||
master_addr="127.0.01",
|
||||
master_addr="127.0.0.1",
|
||||
master_port="29500",
|
||||
accelerate_mixed_precision="no",
|
||||
accelerate_debug_rdv_file=tmp_file.name,
|
||||
|
||||
@ -12,6 +12,7 @@
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
import functools
|
||||
import logging
|
||||
import os
|
||||
|
||||
@ -67,6 +68,17 @@ class MultiProcessAdapter(logging.LoggerAdapter):
|
||||
self.logger.log(level, msg, *args, **kwargs)
|
||||
state.wait_for_everyone()
|
||||
|
||||
@functools.lru_cache(None)
|
||||
def warning_once(self, *args, **kwargs):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
This method is identical to `logger.warning()`, but will emit the warning with the same message only once
|
||||
|
||||
Note: The cache is for the function arguments, so 2 different callers using the same arguments will hit the
|
||||
cache. The assumption here is that all warning messages are unique across the code. If they aren't then need to
|
||||
switch to another type of cache that includes the caller frame information in the hashing function.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self.warning(*args, **kwargs)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def get_logger(name: str, log_level: str = None):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
@ -85,9 +97,11 @@ def get_logger(name: str, log_level: str = None):
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
>>> from accelerate.logging import get_logger
|
||||
>>> from accelerate import Accelerator
|
||||
|
||||
>>> logger = get_logger(__name__)
|
||||
|
||||
>>> accelerator = Accelerator()
|
||||
>>> logger.info("My log", main_process_only=False)
|
||||
>>> logger.debug("My log", main_process_only=True)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -95,9 +109,6 @@ def get_logger(name: str, log_level: str = None):
|
||||
>>> logger.info("My log")
|
||||
>>> logger.debug("My second log")
|
||||
|
||||
>>> from accelerate import Accelerator
|
||||
|
||||
>>> accelerator = Accelerator()
|
||||
>>> array = ["a", "b", "c", "d"]
|
||||
>>> letter_at_rank = array[accelerator.process_index]
|
||||
>>> logger.info(letter_at_rank, in_order=True)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -14,6 +14,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
from __future__ import annotations
|
||||
|
||||
import logging
|
||||
import math
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import threading
|
||||
@ -28,6 +29,8 @@ from .utils import (
|
||||
DistributedType,
|
||||
DynamoBackend,
|
||||
GradientAccumulationPlugin,
|
||||
check_cuda_p2p_ib_support,
|
||||
check_fp8_capability,
|
||||
get_ccl_version,
|
||||
get_int_from_env,
|
||||
is_ccl_available,
|
||||
@ -51,6 +54,8 @@ if is_tpu_available(check_device=False):
|
||||
if is_npu_available(check_device=False):
|
||||
import torch_npu # noqa: F401
|
||||
|
||||
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def is_initialized() -> bool:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
@ -175,6 +180,8 @@ class PartialState:
|
||||
if is_xpu_available and is_ccl_available():
|
||||
# Set DeepSpeed backend to ccl for xpu
|
||||
self.backend = "ccl"
|
||||
elif is_npu_available():
|
||||
self.backend = "hccl"
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self.backend = "nccl"
|
||||
dist.init_distributed(dist_backend=self.backend, auto_mpi_discovery=False, **kwargs)
|
||||
@ -187,10 +194,21 @@ class PartialState:
|
||||
self.device = torch.device("xpu", self.local_process_index)
|
||||
if self.device is not None:
|
||||
torch.xpu.set_device(self.device)
|
||||
elif is_npu_available():
|
||||
self.device = torch.device("npu", self.local_process_index)
|
||||
if self.device is not None:
|
||||
torch.npu.set_device(self.device)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self.device = torch.device("cuda", self.local_process_index)
|
||||
if self.device is not None:
|
||||
torch.cuda.set_device(self.device)
|
||||
if self.device.type == "cuda" and not check_cuda_p2p_ib_support():
|
||||
if "NCCL_P2P_DISABLE" not in os.environ or "NCCL_IB_DISABLE" not in os.environ:
|
||||
raise NotImplementedError(
|
||||
"Using RTX 3090 or 4000 series doesn't support faster communication broadband via P2P or IB. "
|
||||
'Please set `NCCL_P2P_DISABLE="1"` and `NCCL_IB_DISABLE="1" or use `accelerate launch` which '
|
||||
"will do this automatically."
|
||||
)
|
||||
self._mixed_precision = "no" # deepspeed handles mixed_precision using deepspeed_config
|
||||
elif int(os.environ.get("LOCAL_RANK", -1)) != -1 and not cpu and torch.cuda.is_available():
|
||||
self.distributed_type = DistributedType.MULTI_GPU
|
||||
@ -200,6 +218,13 @@ class PartialState:
|
||||
if self.backend is None:
|
||||
self.backend = "nccl"
|
||||
torch.distributed.init_process_group(backend=self.backend, **kwargs)
|
||||
if not check_cuda_p2p_ib_support():
|
||||
if "NCCL_P2P_DISABLE" not in os.environ or "NCCL_IB_DISABLE" not in os.environ:
|
||||
raise NotImplementedError(
|
||||
"Using RTX 3090 or 4000 series doesn't support faster communication broadband via P2P or IB. "
|
||||
'Please set `NCCL_P2P_DISABLE="1"` and `NCCL_IB_DISABLE="1" or use `accelerate launch` which '
|
||||
"will do this automatically."
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.num_processes = torch.distributed.get_world_size()
|
||||
self.process_index = torch.distributed.get_rank()
|
||||
self.local_process_index = int(os.environ.get("LOCAL_RANK", -1))
|
||||
@ -287,7 +312,11 @@ class PartialState:
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self.device = self.default_device
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self.distributed_type = DistributedType.NO
|
||||
self.distributed_type = (
|
||||
DistributedType.NO
|
||||
if os.environ.get("ACCELERATE_USE_DEEPSPEED", "false") == "false"
|
||||
else DistributedType.DEEPSPEED
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.num_processes = 1
|
||||
self.process_index = self.local_process_index = 0
|
||||
|
||||
@ -740,8 +769,19 @@ class AcceleratorState:
|
||||
if mixed_precision is None
|
||||
else mixed_precision.lower()
|
||||
)
|
||||
if mixed_precision == "fp8" and not is_fp8_available():
|
||||
raise ValueError("Using `fp8` precision requires `transformer_engine` to be installed.")
|
||||
if mixed_precision == "fp8":
|
||||
if not is_fp8_available():
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
"Using `fp8` precision requires `transformer_engine` or `MS-AMP` to be installed."
|
||||
)
|
||||
elif not check_fp8_capability():
|
||||
logger.warning(
|
||||
f"The current device has compute capability of {torch.cuda.get_device_capability()} which is "
|
||||
"insufficient for FP8 mixed precision training (requires a GPU Hopper/Ada Lovelace "
|
||||
"or higher, compute capability of 8.9 or higher). Will use FP16 instead."
|
||||
)
|
||||
mixed_precision = "fp16"
|
||||
|
||||
self.dynamo_plugin = dynamo_plugin
|
||||
if not _from_accelerator:
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,15 +1,18 @@
|
||||
from .testing import (
|
||||
are_the_same_tensors,
|
||||
assert_exception,
|
||||
device_count,
|
||||
execute_subprocess_async,
|
||||
require_bnb,
|
||||
require_cpu,
|
||||
require_cuda,
|
||||
require_huggingface_suite,
|
||||
require_mps,
|
||||
require_multi_device,
|
||||
require_multi_gpu,
|
||||
require_multi_xpu,
|
||||
require_safetensors,
|
||||
require_non_cpu,
|
||||
require_single_device,
|
||||
require_single_gpu,
|
||||
require_single_xpu,
|
||||
require_torch_min_version,
|
||||
@ -17,6 +20,7 @@ from .testing import (
|
||||
require_xpu,
|
||||
skip,
|
||||
slow,
|
||||
torch_device,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from .training import RegressionDataset, RegressionModel, RegressionModel4XPU
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -27,8 +27,8 @@ from transformers import AutoModelForSequenceClassification, AutoTokenizer
|
||||
|
||||
from accelerate import Accelerator
|
||||
from accelerate.data_loader import DataLoaderDispatcher
|
||||
from accelerate.test_utils import RegressionDataset, RegressionModel
|
||||
from accelerate.utils import is_tpu_available, set_seed
|
||||
from accelerate.test_utils import RegressionDataset, RegressionModel, torch_device
|
||||
from accelerate.utils import set_seed
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
os.environ["TRANSFORMERS_NO_ADVISORY_WARNINGS"] = "true"
|
||||
@ -87,7 +87,10 @@ def get_mrpc_setup(dispatch_batches, split_batches):
|
||||
"hf-internal-testing/mrpc-bert-base-cased", return_dict=True
|
||||
)
|
||||
ddp_model, ddp_dataloader = accelerator.prepare(model, dataloader)
|
||||
return {"ddp": [ddp_model, ddp_dataloader, "cuda:0"], "no": [model, dataloader, accelerator.device]}, accelerator
|
||||
return {
|
||||
"ddp": [ddp_model, ddp_dataloader, torch_device],
|
||||
"no": [model, dataloader, accelerator.device],
|
||||
}, accelerator
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def generate_predictions(model, dataloader, accelerator):
|
||||
@ -219,6 +222,25 @@ def test_gather_for_metrics_with_iterable_dataset():
|
||||
logger.removeHandler(list_handler)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def test_gather_for_metrics_drop_last():
|
||||
accelerator = Accelerator()
|
||||
per_device_batch_size = 5
|
||||
num_items = (10 * accelerator.num_processes) + 1
|
||||
dataloader = DataLoader(range(num_items), batch_size=per_device_batch_size, drop_last=True)
|
||||
dataloader = accelerator.prepare(dataloader)
|
||||
|
||||
iterator = iter(dataloader)
|
||||
next(iterator) # Skip first batch tensor([0, 1, 2, 3, 4], device='cuda:0')
|
||||
batch = next(iterator)
|
||||
gathered_items = accelerator.gather_for_metrics(batch)
|
||||
|
||||
# Should return a full set of complete batches from each GPU
|
||||
num_expected_items = per_device_batch_size * accelerator.num_processes
|
||||
assert gathered_items.size(0) == (
|
||||
num_expected_items
|
||||
), f"Expected number of items: {num_expected_items}, Actual: {gathered_items.size(0)}"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def main():
|
||||
accelerator = Accelerator(split_batches=False, dispatch_batches=False)
|
||||
if accelerator.is_local_main_process:
|
||||
@ -228,7 +250,7 @@ def main():
|
||||
datasets.utils.logging.set_verbosity_error()
|
||||
transformers.utils.logging.set_verbosity_error()
|
||||
# These are a bit slower so they should only be ran on the GPU or TPU
|
||||
if torch.cuda.is_available() or is_tpu_available():
|
||||
if accelerator.device.type != "cpu":
|
||||
if accelerator.is_local_main_process:
|
||||
print("**Testing gather_for_metrics**")
|
||||
for split_batches in [True, False]:
|
||||
@ -255,6 +277,10 @@ def main():
|
||||
accelerator = Accelerator()
|
||||
test_torch_metrics(accelerator, 512)
|
||||
accelerator.state._reset_state()
|
||||
if accelerator.is_local_main_process:
|
||||
print("**Test that `drop_last` is taken into account**")
|
||||
test_gather_for_metrics_drop_last()
|
||||
accelerator.state._reset_state()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _mp_fn(index):
|
||||
|
||||
@ -102,15 +102,10 @@ def training_function(config, args):
|
||||
)
|
||||
optimizer = optimizer_cls(params=model.parameters(), lr=lr)
|
||||
|
||||
if accelerator.state.deepspeed_plugin is not None:
|
||||
gradient_accumulation_steps = accelerator.state.deepspeed_plugin.deepspeed_config[
|
||||
"gradient_accumulation_steps"
|
||||
]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
gradient_accumulation_steps = 1
|
||||
max_training_steps = (len(train_dataloader) * num_epochs) // gradient_accumulation_steps
|
||||
max_training_steps = len(train_dataloader) * num_epochs
|
||||
|
||||
# Instantiate scheduler
|
||||
linear_decay_scheduler = False
|
||||
if (
|
||||
accelerator.state.deepspeed_plugin is None
|
||||
or "scheduler" not in accelerator.state.deepspeed_plugin.deepspeed_config
|
||||
@ -120,6 +115,7 @@ def training_function(config, args):
|
||||
num_warmup_steps=0,
|
||||
num_training_steps=max_training_steps,
|
||||
)
|
||||
linear_decay_scheduler = True
|
||||
else:
|
||||
lr_scheduler = DummyScheduler(optimizer, total_num_steps=max_training_steps, warmup_num_steps=0)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -130,8 +126,6 @@ def training_function(config, args):
|
||||
model, optimizer, train_dataloader, eval_dataloader, lr_scheduler
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# We need to keep track of how many total steps we have iterated over
|
||||
overall_step = 0
|
||||
# We also need to keep track of the stating epoch so files are named properly
|
||||
starting_epoch = 0
|
||||
|
||||
@ -139,19 +133,32 @@ def training_function(config, args):
|
||||
metric = evaluate.load("glue", "mrpc")
|
||||
best_performance = 0
|
||||
performance_metric = {}
|
||||
expected_lr_after_first_optim_step = lr * (
|
||||
1 - 1 / (max_training_steps / accelerator.num_processes / accelerator.gradient_accumulation_steps)
|
||||
)
|
||||
lr_scheduler_check_completed = False
|
||||
for epoch in range(starting_epoch, num_epochs):
|
||||
model.train()
|
||||
for step, batch in enumerate(train_dataloader):
|
||||
outputs = model(**batch)
|
||||
loss = outputs.loss
|
||||
loss = loss / gradient_accumulation_steps
|
||||
accelerator.backward(loss)
|
||||
if step % gradient_accumulation_steps == 0:
|
||||
with accelerator.accumulate(model):
|
||||
outputs = model(**batch)
|
||||
loss = outputs.loss
|
||||
accelerator.backward(loss)
|
||||
optimizer.step()
|
||||
lr_scheduler.step()
|
||||
optimizer.zero_grad()
|
||||
|
||||
overall_step += 1
|
||||
# assert the learning rate after first optimizer step
|
||||
if (
|
||||
accelerator.sync_gradients
|
||||
and not lr_scheduler_check_completed
|
||||
and linear_decay_scheduler
|
||||
and accelerator.state.mixed_precision == "no"
|
||||
):
|
||||
assert (
|
||||
lr_scheduler.get_last_lr()[0] == expected_lr_after_first_optim_step
|
||||
), f"Wrong lr found at second step, expected {expected_lr_after_first_optim_step}, got {lr_scheduler.get_last_lr()[0]}"
|
||||
lr_scheduler_check_completed = True
|
||||
|
||||
model.eval()
|
||||
samples_seen = 0
|
||||
@ -184,6 +191,12 @@ def training_function(config, args):
|
||||
if best_performance < eval_metric["accuracy"]:
|
||||
best_performance = eval_metric["accuracy"]
|
||||
|
||||
# check that the LR is 0
|
||||
if linear_decay_scheduler and accelerator.state.mixed_precision == "no":
|
||||
assert (
|
||||
lr_scheduler.get_last_lr()[0] == 0
|
||||
), f"Wrong lr found at last step, expected 0, got {lr_scheduler.get_last_lr()[0]}"
|
||||
|
||||
if args.performance_lower_bound is not None:
|
||||
assert (
|
||||
args.performance_lower_bound <= best_performance
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,17 +1,40 @@
|
||||
# Test file to ensure that in general certain situational setups for notebooks work.
|
||||
import argparse
|
||||
import os
|
||||
|
||||
from pytest import raises
|
||||
|
||||
from accelerate import PartialState, notebook_launcher
|
||||
from accelerate.test_utils import require_bnb
|
||||
from accelerate.utils import is_bnb_available
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
|
||||
parser.add_argument("--num_processes", type=int, default=1)
|
||||
args = parser.parse_args()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def function():
|
||||
def basic_function():
|
||||
# Just prints the PartialState
|
||||
print(f"PartialState:\n{PartialState()}")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
NUM_PROCESSES = int(os.environ.get("ACCELERATE_NUM_PROCESSES", 1))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def test_can_initialize():
|
||||
notebook_launcher(basic_function, (), num_processes=NUM_PROCESSES)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@require_bnb
|
||||
def test_problematic_imports():
|
||||
with raises(RuntimeError, match="Please keep these imports"):
|
||||
import bitsandbytes as bnb # noqa: F401
|
||||
|
||||
notebook_launcher(basic_function, (), num_processes=NUM_PROCESSES)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def main():
|
||||
print("Test basic notebook can be ran")
|
||||
test_can_initialize()
|
||||
if is_bnb_available():
|
||||
print("Test problematic imports (bnb)")
|
||||
test_problematic_imports()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
notebook_launcher(function, num_processes=int(args.num_processes))
|
||||
main()
|
||||
|
||||
@ -21,11 +21,12 @@ import time
|
||||
from copy import deepcopy
|
||||
from pathlib import Path
|
||||
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
|
||||
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader, Dataset
|
||||
|
||||
from accelerate import Accelerator
|
||||
from accelerate.data_loader import prepare_data_loader
|
||||
from accelerate.data_loader import SeedableRandomSampler, prepare_data_loader
|
||||
from accelerate.state import AcceleratorState
|
||||
from accelerate.test_utils import RegressionDataset, are_the_same_tensors
|
||||
from accelerate.utils import (
|
||||
@ -288,11 +289,68 @@ def central_dl_preparation_check():
|
||||
print("Shuffled central dataloader passing.")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def mock_training(length, batch_size, generator):
|
||||
def custom_sampler_check():
|
||||
state = AcceleratorState()
|
||||
|
||||
class CustomDataset(Dataset):
|
||||
def __init__(self, data):
|
||||
self.data = data
|
||||
|
||||
def __len__(self):
|
||||
return len(self.data)
|
||||
|
||||
def __getitem__(self, index):
|
||||
return self.data[index]
|
||||
|
||||
class CustomBatchSampler:
|
||||
def __init__(self, dataset_length: int, batch_size: int, shuffle: bool = True):
|
||||
self.batch_size = batch_size
|
||||
self.data_index = np.arange(dataset_length)
|
||||
self.shuffle = shuffle
|
||||
|
||||
def __iter__(self):
|
||||
num_batches = len(self)
|
||||
if self.shuffle:
|
||||
index = np.random.permutation(self.data_index)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
index = self.data_index
|
||||
output = np.array_split(index, num_batches)
|
||||
yield from output
|
||||
|
||||
def __len__(self):
|
||||
return math.ceil(len(self.data_index) / self.batch_size)
|
||||
|
||||
dataset = CustomDataset(range(32 * state.num_processes))
|
||||
sampler = CustomBatchSampler(len(dataset), batch_size=8)
|
||||
dl = DataLoader(dataset, batch_sampler=sampler)
|
||||
dl = prepare_data_loader(dl, state.device, state.num_processes, state.process_index)
|
||||
# We need just ensure that `dl.batch_sampler` (or `dl.batch_sampler.batch_sampler` is indeed the old batch sampler
|
||||
if hasattr(dl.batch_sampler, "batch_sampler"):
|
||||
assert isinstance(
|
||||
dl.batch_sampler.batch_sampler, CustomBatchSampler
|
||||
), "Custom sampler was changed after calling `prepare_data_loader`"
|
||||
else:
|
||||
assert isinstance(
|
||||
dl.batch_sampler, CustomBatchSampler
|
||||
), "Custom sampler was changed after calling `prepare_data_loader`"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def mock_training(length, batch_size, generator, use_seedable_sampler=False):
|
||||
set_seed(42)
|
||||
generator.manual_seed(42)
|
||||
train_set = RegressionDataset(length=length, seed=42)
|
||||
train_dl = DataLoader(train_set, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True, generator=generator)
|
||||
|
||||
if use_seedable_sampler:
|
||||
# The SeedableRandomSampler is needed during distributed setups
|
||||
# for full reproducability across processes with the `DataLoader`
|
||||
sampler = SeedableRandomSampler(
|
||||
generator=generator,
|
||||
data_source=train_set,
|
||||
num_samples=len(train_set),
|
||||
)
|
||||
train_dl = DataLoader(train_set, batch_size=batch_size, sampler=sampler)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
train_dl = DataLoader(train_set, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True, generator=generator)
|
||||
model = RegressionModel()
|
||||
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.1)
|
||||
for epoch in range(3):
|
||||
@ -305,18 +363,28 @@ def mock_training(length, batch_size, generator):
|
||||
return train_set, model
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def training_check():
|
||||
def training_check(use_seedable_sampler=False):
|
||||
state = AcceleratorState()
|
||||
generator = torch.Generator()
|
||||
batch_size = 8
|
||||
length = batch_size * 4 * state.num_processes
|
||||
|
||||
train_set, old_model = mock_training(length, batch_size * state.num_processes, generator)
|
||||
train_set, old_model = mock_training(length, batch_size * state.num_processes, generator, use_seedable_sampler)
|
||||
assert are_the_same_tensors(old_model.a), "Did not obtain the same model on both processes."
|
||||
assert are_the_same_tensors(old_model.b), "Did not obtain the same model on both processes."
|
||||
|
||||
accelerator = Accelerator()
|
||||
train_dl = DataLoader(train_set, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True, generator=generator)
|
||||
if use_seedable_sampler:
|
||||
# The SeedableRandomSampler is needed during distributed setups
|
||||
# for full reproducability across processes with the `DataLoader`
|
||||
sampler = SeedableRandomSampler(
|
||||
generator=generator,
|
||||
data_source=train_set,
|
||||
num_samples=len(train_set),
|
||||
)
|
||||
train_dl = DataLoader(train_set, batch_size=batch_size, sampler=sampler)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
train_dl = DataLoader(train_set, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True, generator=generator)
|
||||
model = RegressionModel()
|
||||
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.1)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -337,7 +405,7 @@ def training_check():
|
||||
|
||||
accelerator.print("Training yielded the same results on one CPU or distributed setup with no batch split.")
|
||||
|
||||
accelerator = Accelerator(split_batches=True)
|
||||
accelerator = Accelerator(split_batches=True, use_seedable_sampler=use_seedable_sampler)
|
||||
train_dl = DataLoader(train_set, batch_size=batch_size * state.num_processes, shuffle=True, generator=generator)
|
||||
model = RegressionModel()
|
||||
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.1)
|
||||
@ -363,7 +431,7 @@ def training_check():
|
||||
# Mostly a test that FP16 doesn't crash as the operation inside the model is not converted to FP16
|
||||
print("FP16 training check.")
|
||||
AcceleratorState._reset_state()
|
||||
accelerator = Accelerator(mixed_precision="fp16")
|
||||
accelerator = Accelerator(mixed_precision="fp16", use_seedable_sampler=use_seedable_sampler)
|
||||
train_dl = DataLoader(train_set, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True, generator=generator)
|
||||
model = RegressionModel()
|
||||
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.1)
|
||||
@ -403,7 +471,7 @@ def training_check():
|
||||
# Mostly a test that BF16 doesn't crash as the operation inside the model is not converted to BF16
|
||||
print("BF16 training check.")
|
||||
AcceleratorState._reset_state()
|
||||
accelerator = Accelerator(mixed_precision="bf16")
|
||||
accelerator = Accelerator(mixed_precision="bf16", use_seedable_sampler=use_seedable_sampler)
|
||||
train_dl = DataLoader(train_set, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True, generator=generator)
|
||||
model = RegressionModel()
|
||||
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.1)
|
||||
@ -427,7 +495,7 @@ def training_check():
|
||||
if is_ipex_available():
|
||||
print("ipex BF16 training check.")
|
||||
AcceleratorState._reset_state()
|
||||
accelerator = Accelerator(mixed_precision="bf16", cpu=True)
|
||||
accelerator = Accelerator(mixed_precision="bf16", cpu=True, use_seedable_sampler=use_seedable_sampler)
|
||||
train_dl = DataLoader(train_set, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True, generator=generator)
|
||||
model = RegressionModel()
|
||||
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.1)
|
||||
@ -451,7 +519,7 @@ def training_check():
|
||||
if is_xpu_available():
|
||||
print("xpu BF16 training check.")
|
||||
AcceleratorState._reset_state()
|
||||
accelerator = Accelerator(mixed_precision="bf16", cpu=False)
|
||||
accelerator = Accelerator(mixed_precision="bf16", cpu=False, use_seedable_sampler=use_seedable_sampler)
|
||||
train_dl = DataLoader(train_set, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True, generator=generator)
|
||||
model = RegressionModel()
|
||||
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.1)
|
||||
@ -598,6 +666,7 @@ def main():
|
||||
dl_preparation_check()
|
||||
if state.distributed_type != DistributedType.TPU:
|
||||
central_dl_preparation_check()
|
||||
custom_sampler_check()
|
||||
|
||||
# Trainings are not exactly the same in DeepSpeed and CPU mode
|
||||
if state.distributed_type == DistributedType.DEEPSPEED:
|
||||
@ -605,7 +674,8 @@ def main():
|
||||
|
||||
if state.local_process_index == 0:
|
||||
print("\n**Training integration test**")
|
||||
training_check()
|
||||
training_check(use_seedable_sampler=False)
|
||||
training_check(use_seedable_sampler=True)
|
||||
|
||||
if state.local_process_index == 0:
|
||||
print("\n**Breakpoint trigger test**")
|
||||
|
||||
@ -31,11 +31,15 @@ from ..state import AcceleratorState, PartialState
|
||||
from ..utils import (
|
||||
gather,
|
||||
is_bnb_available,
|
||||
is_clearml_available,
|
||||
is_comet_ml_available,
|
||||
is_cuda_available,
|
||||
is_datasets_available,
|
||||
is_deepspeed_available,
|
||||
is_dvclive_available,
|
||||
is_mps_available,
|
||||
is_safetensors_available,
|
||||
is_npu_available,
|
||||
is_pandas_available,
|
||||
is_tensorboard_available,
|
||||
is_timm_available,
|
||||
is_torch_version,
|
||||
@ -47,6 +51,22 @@ from ..utils import (
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def get_backend():
|
||||
if is_cuda_available():
|
||||
return "cuda", torch.cuda.device_count()
|
||||
elif is_mps_available():
|
||||
return "mps", 1
|
||||
elif is_npu_available():
|
||||
return "npu", torch.npu.device_count()
|
||||
elif is_xpu_available():
|
||||
return "xpu", torch.xpu.device_count()
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return "cpu", 1
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
torch_device, device_count = get_backend()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def parse_flag_from_env(key, default=False):
|
||||
try:
|
||||
value = os.environ[key]
|
||||
@ -83,14 +103,22 @@ def require_cpu(test_case):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Decorator marking a test that must be only ran on the CPU. These tests are skipped when a GPU is available.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return unittest.skipUnless(not torch.cuda.is_available(), "test requires only a CPU")(test_case)
|
||||
return unittest.skipUnless(torch_device == "cpu", "test requires only a CPU")(test_case)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def require_non_cpu(test_case):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Decorator marking a test that requires a hardware accelerator backend. These tests are skipped when there are no
|
||||
hardware accelerator available.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return unittest.skipUnless(torch_device != "cpu", "test requires a GPU")(test_case)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def require_cuda(test_case):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Decorator marking a test that requires CUDA. These tests are skipped when there are no GPU available.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return unittest.skipUnless(torch.cuda.is_available(), "test requires a GPU")(test_case)
|
||||
return unittest.skipUnless(is_cuda_available(), "test requires a GPU")(test_case)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def require_xpu(test_case):
|
||||
@ -145,6 +173,16 @@ def require_tpu(test_case):
|
||||
return unittest.skipUnless(is_tpu_available(), "test requires TPU")(test_case)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def require_single_device(test_case):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Decorator marking a test that requires a single device. These tests are skipped when there is no hardware
|
||||
accelerator available or number of devices is more than one.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return unittest.skipUnless(torch_device != "cpu" and device_count == 1, "test requires a hardware accelerator")(
|
||||
test_case
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def require_single_gpu(test_case):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Decorator marking a test that requires CUDA on a single GPU. These tests are skipped when there are no GPU
|
||||
@ -161,6 +199,14 @@ def require_single_xpu(test_case):
|
||||
return unittest.skipUnless(torch.xpu.device_count() == 1, "test requires a XPU")(test_case)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def require_multi_device(test_case):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Decorator marking a test that requires a multi-device setup. These tests are skipped on a machine without multiple
|
||||
devices.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return unittest.skipUnless(device_count > 1, "test requires multiple hardware accelerators")(test_case)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def require_multi_gpu(test_case):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Decorator marking a test that requires a multi-GPU setup. These tests are skipped on a machine without multiple
|
||||
@ -177,14 +223,6 @@ def require_multi_xpu(test_case):
|
||||
return unittest.skipUnless(torch.xpu.device_count() > 1, "test requires multiple XPUs")(test_case)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def require_safetensors(test_case):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Decorator marking a test that requires safetensors installed. These tests are skipped when safetensors isn't
|
||||
installed
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return unittest.skipUnless(is_safetensors_available(), "test requires safetensors")(test_case)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def require_deepspeed(test_case):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Decorator marking a test that requires DeepSpeed installed. These tests are skipped when DeepSpeed isn't installed
|
||||
@ -231,6 +269,27 @@ def require_comet_ml(test_case):
|
||||
return unittest.skipUnless(is_comet_ml_available(), "test requires comet_ml")(test_case)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def require_clearml(test_case):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Decorator marking a test that requires clearml installed. These tests are skipped when clearml isn't installed
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return unittest.skipUnless(is_clearml_available(), "test requires clearml")(test_case)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def require_dvclive(test_case):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Decorator marking a test that requires dvclive installed. These tests are skipped when dvclive isn't installed
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return unittest.skipUnless(is_dvclive_available(), "test requires dvclive")(test_case)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def require_pandas(test_case):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Decorator marking a test that requires pandas installed. These tests are skipped when pandas isn't installed
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return unittest.skipUnless(is_pandas_available(), "test requires pandas")(test_case)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
_atleast_one_tracker_available = (
|
||||
any([is_wandb_available(), is_tensorboard_available()]) and not is_comet_ml_available()
|
||||
)
|
||||
@ -416,13 +475,15 @@ class SubprocessCallException(Exception):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def run_command(command: List[str], return_stdout=False):
|
||||
def run_command(command: List[str], return_stdout=False, env=None):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Runs `command` with `subprocess.check_output` and will potentially return the `stdout`. Will also properly capture
|
||||
if an error occured while running `command`
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if env is None:
|
||||
env = os.environ.copy()
|
||||
try:
|
||||
output = subprocess.check_output(command, stderr=subprocess.STDOUT)
|
||||
output = subprocess.check_output(command, stderr=subprocess.STDOUT, env=env)
|
||||
if return_stdout:
|
||||
if hasattr(output, "decode"):
|
||||
output = output.decode("utf-8")
|
||||
|
||||
@ -28,7 +28,9 @@ from .state import PartialState
|
||||
from .utils import (
|
||||
LoggerType,
|
||||
is_aim_available,
|
||||
is_clearml_available,
|
||||
is_comet_ml_available,
|
||||
is_dvclive_available,
|
||||
is_mlflow_available,
|
||||
is_tensorboard_available,
|
||||
is_wandb_available,
|
||||
@ -53,6 +55,12 @@ if is_aim_available():
|
||||
if is_mlflow_available():
|
||||
_available_trackers.append(LoggerType.MLFLOW)
|
||||
|
||||
if is_clearml_available():
|
||||
_available_trackers.append(LoggerType.CLEARML)
|
||||
|
||||
if is_dvclive_available():
|
||||
_available_trackers.append(LoggerType.DVCLIVE)
|
||||
|
||||
logger = get_logger(__name__)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -365,11 +373,11 @@ class WandBTracker(GeneralTracker):
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
table_name (`str`):
|
||||
The name to give to the logged table on the wandb workspace
|
||||
columns (List of `str`'s *optional*):
|
||||
columns (list of `str`, *optional*):
|
||||
The name of the columns on the table
|
||||
data (List of List of Any data type *optional*):
|
||||
data (List of List of Any data type, *optional*):
|
||||
The data to be logged in the table
|
||||
dataframe (Any data type *optional*):
|
||||
dataframe (Any data type, *optional*):
|
||||
The data to be logged in the table
|
||||
step (`int`, *optional*):
|
||||
The run step. If included, the log will be affiliated with this step.
|
||||
@ -528,6 +536,38 @@ class AimTracker(GeneralTracker):
|
||||
for key, value in values.items():
|
||||
self.writer.track(value, name=key, step=step, **kwargs)
|
||||
|
||||
@on_main_process
|
||||
def log_images(self, values: dict, step: Optional[int] = None, kwargs: Optional[Dict[str, dict]] = None):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Logs `images` to the current run.
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
values (`Dict[str, Union[np.ndarray, PIL.Image, Tuple[np.ndarray, str], Tuple[PIL.Image, str]]]`):
|
||||
Values to be logged as key-value pairs. The values need to have type `np.ndarray` or PIL.Image. If a
|
||||
tuple is provided, the first element should be the image and the second element should be the caption.
|
||||
step (`int`, *optional*):
|
||||
The run step. If included, the log will be affiliated with this step.
|
||||
kwargs (`Dict[str, dict]`):
|
||||
Additional key word arguments passed along to the `Run.Image` and `Run.track` method specified by the
|
||||
keys `aim_image` and `track`, respectively.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
import aim
|
||||
|
||||
aim_image_kw = {}
|
||||
track_kw = {}
|
||||
|
||||
if kwargs is not None:
|
||||
aim_image_kw = kwargs.get("aim_image", {})
|
||||
track_kw = kwargs.get("track", {})
|
||||
|
||||
for key, value in values.items():
|
||||
if isinstance(value, tuple):
|
||||
img, caption = value
|
||||
else:
|
||||
img, caption = value, ""
|
||||
aim_image = aim.Image(img, caption=caption, **aim_image_kw)
|
||||
self.writer.track(aim_image, name=key, step=step, **track_kw)
|
||||
|
||||
@on_main_process
|
||||
def finish(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
@ -632,8 +672,8 @@ class MLflowTracker(GeneralTracker):
|
||||
for name, value in list(values.items()):
|
||||
# internally, all values are converted to str in MLflow
|
||||
if len(str(value)) > mlflow.utils.validation.MAX_PARAM_VAL_LENGTH:
|
||||
logger.warning(
|
||||
f'Trainer is attempting to log a value of "{value}" for key "{name}" as a parameter. MLflow\'s'
|
||||
logger.warning_once(
|
||||
f'Accelerate is attempting to log a value of "{value}" for key "{name}" as a parameter. MLflow\'s'
|
||||
f" log_param() only accepts values no longer than {mlflow.utils.validation.MAX_PARAM_VAL_LENGTH} characters so we dropped this attribute."
|
||||
)
|
||||
del values[name]
|
||||
@ -662,7 +702,7 @@ class MLflowTracker(GeneralTracker):
|
||||
if isinstance(v, (int, float)):
|
||||
metrics[k] = v
|
||||
else:
|
||||
logger.warning(
|
||||
logger.warning_once(
|
||||
f'MLflowTracker is attempting to log a value of "{v}" of type {type(v)} for key "{k}" as a metric. '
|
||||
"MLflow's log_metric() only accepts float and int types so we dropped this attribute."
|
||||
)
|
||||
@ -681,17 +721,256 @@ class MLflowTracker(GeneralTracker):
|
||||
mlflow.end_run()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class ClearMLTracker(GeneralTracker):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
A `Tracker` class that supports `clearml`. Should be initialized at the start of your script.
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
run_name (`str`, *optional*):
|
||||
Name of the experiment. Environment variables `CLEARML_PROJECT` and `CLEARML_TASK` have priority over this
|
||||
argument.
|
||||
kwargs:
|
||||
Kwargs passed along to the `Task.__init__` method.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
name = "clearml"
|
||||
requires_logging_directory = False
|
||||
|
||||
@on_main_process
|
||||
def __init__(self, run_name: str = None, **kwargs):
|
||||
from clearml import Task
|
||||
|
||||
current_task = Task.current_task()
|
||||
self._initialized_externally = False
|
||||
if current_task:
|
||||
self._initialized_externally = True
|
||||
self.task = current_task
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
||||
kwargs.setdefault("project_name", os.environ.get("CLEARML_PROJECT", run_name))
|
||||
kwargs.setdefault("task_name", os.environ.get("CLEARML_TASK", run_name))
|
||||
self.task = Task.init(**kwargs)
|
||||
|
||||
@property
|
||||
def tracker(self):
|
||||
return self.task
|
||||
|
||||
@on_main_process
|
||||
def store_init_configuration(self, values: dict):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Connect configuration dictionary to the Task object. Should be run at the beginning of your experiment.
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
values (`dict`):
|
||||
Values to be stored as initial hyperparameters as key-value pairs.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return self.task.connect_configuration(values)
|
||||
|
||||
@on_main_process
|
||||
def log(self, values: Dict[str, Union[int, float]], step: Optional[int] = None, **kwargs):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Logs `values` dictionary to the current run. The dictionary keys must be strings. The dictionary values must be
|
||||
ints or floats
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
values (`Dict[str, Union[int, float]]`):
|
||||
Values to be logged as key-value pairs. If the key starts with 'eval_'/'test_'/'train_', the value will
|
||||
be reported under the 'eval'/'test'/'train' series and the respective prefix will be removed.
|
||||
Otherwise, the value will be reported under the 'train' series, and no prefix will be removed.
|
||||
step (`int`, *optional*):
|
||||
If specified, the values will be reported as scalars, with the iteration number equal to `step`.
|
||||
Otherwise they will be reported as single values.
|
||||
kwargs:
|
||||
Additional key word arguments passed along to the `clearml.Logger.report_single_value` or
|
||||
`clearml.Logger.report_scalar` methods.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
clearml_logger = self.task.get_logger()
|
||||
for k, v in values.items():
|
||||
if not isinstance(v, (int, float)):
|
||||
logger.warning_once(
|
||||
"Accelerator is attempting to log a value of "
|
||||
f'"{v}" of type {type(v)} for key "{k}" as a scalar. '
|
||||
"This invocation of ClearML logger's report_scalar() "
|
||||
"is incorrect so we dropped this attribute."
|
||||
)
|
||||
continue
|
||||
if step is None:
|
||||
clearml_logger.report_single_value(name=k, value=v, **kwargs)
|
||||
continue
|
||||
title, series = ClearMLTracker._get_title_series(k)
|
||||
clearml_logger.report_scalar(title=title, series=series, value=v, iteration=step, **kwargs)
|
||||
|
||||
@on_main_process
|
||||
def log_images(self, values: dict, step: Optional[int] = None, **kwargs):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Logs `images` to the current run.
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
values (`Dict[str, List[Union[np.ndarray, PIL.Image]]`):
|
||||
Values to be logged as key-value pairs. The values need to have type `List` of `np.ndarray` or
|
||||
step (`int`, *optional*):
|
||||
The run step. If included, the log will be affiliated with this step.
|
||||
kwargs:
|
||||
Additional key word arguments passed along to the `clearml.Logger.report_image` method.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
clearml_logger = self.task.get_logger()
|
||||
for k, v in values.items():
|
||||
title, series = ClearMLTracker._get_title_series(k)
|
||||
clearml_logger.report_image(title=title, series=series, iteration=step, image=v, **kwargs)
|
||||
|
||||
@on_main_process
|
||||
def log_table(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
table_name: str,
|
||||
columns: List[str] = None,
|
||||
data: List[List[Any]] = None,
|
||||
dataframe: Any = None,
|
||||
step: Optional[int] = None,
|
||||
**kwargs,
|
||||
):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Log a Table to the task. Can be defined eitherwith `columns` and `data` or with `dataframe`.
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
table_name (`str`):
|
||||
The name of the table
|
||||
columns (list of `str`, *optional*):
|
||||
The name of the columns on the table
|
||||
data (List of List of Any data type, *optional*):
|
||||
The data to be logged in the table. If `columns` is not specified, then the first entry in data will be
|
||||
the name of the columns of the table
|
||||
dataframe (Any data type, *optional*):
|
||||
The data to be logged in the table
|
||||
step (`int`, *optional*):
|
||||
The run step. If included, the log will be affiliated with this step.
|
||||
kwargs:
|
||||
Additional key word arguments passed along to the `clearml.Logger.report_table` method.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
to_report = dataframe
|
||||
if dataframe is None:
|
||||
if data is None:
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
"`ClearMLTracker.log_table` requires that `data` to be supplied if `dataframe` is `None`"
|
||||
)
|
||||
to_report = [columns] + data if columns else data
|
||||
title, series = ClearMLTracker._get_title_series(table_name)
|
||||
self.task.get_logger().report_table(title=title, series=series, table_plot=to_report, iteration=step, **kwargs)
|
||||
|
||||
@on_main_process
|
||||
def finish(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Close the ClearML task. If the task was initialized externally (e.g. by manually calling `Task.init`), this
|
||||
function is a noop
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if self.task and not self._initialized_externally:
|
||||
self.task.close()
|
||||
|
||||
@staticmethod
|
||||
def _get_title_series(name):
|
||||
for prefix in ["eval", "test", "train"]:
|
||||
if name.startswith(prefix + "_"):
|
||||
return name[len(prefix) + 1 :], prefix
|
||||
return name, "train"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class DVCLiveTracker(GeneralTracker):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
A `Tracker` class that supports `dvclive`. Should be initialized at the start of your script.
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
run_name (`str`, *optional*):
|
||||
Ignored for dvclive. See `kwargs` instead.
|
||||
kwargs:
|
||||
Additional key word arguments passed along to [`dvclive.Live()`](https://dvc.org/doc/dvclive/live).
|
||||
|
||||
Example:
|
||||
|
||||
```py
|
||||
from accelerate import Accelerator
|
||||
|
||||
accelerator = Accelerator(log_with="dvclive")
|
||||
accelerator.init_trackers(project_name="my_project", init_kwargs={"dvclive": {"dir": "my_directory"}})
|
||||
```
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
name = "dvclive"
|
||||
requires_logging_directory = False
|
||||
|
||||
@on_main_process
|
||||
def __init__(self, run_name: Optional[str] = None, live: Optional[Any] = None, **kwargs):
|
||||
from dvclive import Live
|
||||
|
||||
super().__init__()
|
||||
self.live = live if live is not None else Live(**kwargs)
|
||||
|
||||
@property
|
||||
def tracker(self):
|
||||
return self.live
|
||||
|
||||
@on_main_process
|
||||
def store_init_configuration(self, values: dict):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Logs `values` as hyperparameters for the run. Should be run at the beginning of your experiment. Stores the
|
||||
hyperparameters in a yaml file for future use.
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
values (Dictionary `str` to `bool`, `str`, `float`, `int`, or a List or Dict of those types):
|
||||
Values to be stored as initial hyperparameters as key-value pairs. The values need to have type `bool`,
|
||||
`str`, `float`, or `int`.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self.live.log_params(values)
|
||||
|
||||
@on_main_process
|
||||
def log(self, values: dict, step: Optional[int] = None, **kwargs):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Logs `values` to the current run.
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
values (Dictionary `str` to `str`, `float`, or `int`):
|
||||
Values to be logged as key-value pairs. The values need to have type `str`, `float`, or `int`.
|
||||
step (`int`, *optional*):
|
||||
The run step. If included, the log will be affiliated with this step.
|
||||
kwargs:
|
||||
Additional key word arguments passed along to `dvclive.Live.log_metric()`.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
from dvclive.plots import Metric
|
||||
|
||||
if step is not None:
|
||||
self.live.step = step
|
||||
for k, v in values.items():
|
||||
if Metric.could_log(v):
|
||||
self.live.log_metric(k, v, **kwargs)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
logger.warning_once(
|
||||
"Accelerator attempted to log a value of "
|
||||
f'"{v}" of type {type(v)} for key "{k}" as a scalar. '
|
||||
"This invocation of DVCLive's Live.log_metric() "
|
||||
"is incorrect so we dropped this attribute."
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.live.next_step()
|
||||
|
||||
@on_main_process
|
||||
def finish(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Closes `dvclive.Live()`.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self.live.end()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
LOGGER_TYPE_TO_CLASS = {
|
||||
"aim": AimTracker,
|
||||
"comet_ml": CometMLTracker,
|
||||
"mlflow": MLflowTracker,
|
||||
"tensorboard": TensorBoardTracker,
|
||||
"wandb": WandBTracker,
|
||||
"clearml": ClearMLTracker,
|
||||
"dvclive": DVCLiveTracker,
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def filter_trackers(
|
||||
log_with: List[Union[str, LoggerType, GeneralTracker]], logging_dir: Union[str, os.PathLike] = None
|
||||
log_with: List[Union[str, LoggerType, GeneralTracker]],
|
||||
logging_dir: Union[str, os.PathLike] = None,
|
||||
):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Takes in a list of potential tracker types and checks that:
|
||||
@ -709,6 +988,7 @@ def filter_trackers(
|
||||
- `"wandb"`
|
||||
- `"comet_ml"`
|
||||
- `"mlflow"`
|
||||
- `"dvclive"`
|
||||
If `"all"` is selected, will pick up all available trackers in the environment and initialize them. Can
|
||||
also accept implementations of `GeneralTracker` for custom trackers, and can be combined with `"all"`.
|
||||
logging_dir (`str`, `os.PathLike`, *optional*):
|
||||
|
||||
@ -2,8 +2,10 @@ from .constants import (
|
||||
MODEL_NAME,
|
||||
OPTIMIZER_NAME,
|
||||
RNG_STATE_NAME,
|
||||
SAFE_MODEL_NAME,
|
||||
SAFE_WEIGHTS_INDEX_NAME,
|
||||
SAFE_WEIGHTS_NAME,
|
||||
SAMPLER_NAME,
|
||||
SCALER_NAME,
|
||||
SCHEDULER_NAME,
|
||||
TORCH_DISTRIBUTED_OPERATION_TYPES,
|
||||
@ -35,7 +37,15 @@ from .dataclasses import (
|
||||
TensorInformation,
|
||||
TorchDynamoPlugin,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from .environment import get_int_from_env, parse_choice_from_env, parse_flag_from_env, str_to_bool
|
||||
from .environment import (
|
||||
are_libraries_initialized,
|
||||
check_cuda_p2p_ib_support,
|
||||
check_fp8_capability,
|
||||
get_int_from_env,
|
||||
parse_choice_from_env,
|
||||
parse_flag_from_env,
|
||||
str_to_bool,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from .imports import (
|
||||
get_ccl_version,
|
||||
is_4bit_bnb_available,
|
||||
@ -45,22 +55,26 @@ from .imports import (
|
||||
is_bnb_available,
|
||||
is_boto3_available,
|
||||
is_ccl_available,
|
||||
is_clearml_available,
|
||||
is_comet_ml_available,
|
||||
is_cuda_available,
|
||||
is_datasets_available,
|
||||
is_deepspeed_available,
|
||||
is_dvclive_available,
|
||||
is_fp8_available,
|
||||
is_ipex_available,
|
||||
is_megatron_lm_available,
|
||||
is_mlflow_available,
|
||||
is_mps_available,
|
||||
is_msamp_available,
|
||||
is_npu_available,
|
||||
is_pandas_available,
|
||||
is_rich_available,
|
||||
is_safetensors_available,
|
||||
is_sagemaker_available,
|
||||
is_tensorboard_available,
|
||||
is_timm_available,
|
||||
is_tpu_available,
|
||||
is_transformer_engine_available,
|
||||
is_transformers_available,
|
||||
is_wandb_available,
|
||||
is_xpu_available,
|
||||
@ -98,6 +112,7 @@ from .offload import (
|
||||
save_offload_index,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from .operations import (
|
||||
CannotPadNestedTensorWarning,
|
||||
broadcast,
|
||||
broadcast_object_list,
|
||||
concatenate,
|
||||
@ -164,6 +179,8 @@ from .megatron_lm import prepare_optimizer as megatron_lm_prepare_optimizer
|
||||
from .megatron_lm import prepare_scheduler as megatron_lm_prepare_scheduler
|
||||
from .memory import find_executable_batch_size, release_memory
|
||||
from .other import (
|
||||
check_os_kernel,
|
||||
clean_state_dict_for_safetensors,
|
||||
clear_environment,
|
||||
convert_bytes,
|
||||
extract_model_from_parallel,
|
||||
|
||||
@ -17,13 +17,15 @@ import operator as op
|
||||
|
||||
SCALER_NAME = "scaler.pt"
|
||||
MODEL_NAME = "pytorch_model"
|
||||
SAFE_MODEL_NAME = "model"
|
||||
RNG_STATE_NAME = "random_states"
|
||||
OPTIMIZER_NAME = "optimizer"
|
||||
SCHEDULER_NAME = "scheduler"
|
||||
WEIGHTS_NAME = "pytorch_model.bin"
|
||||
WEIGHTS_INDEX_NAME = "pytorch_model.bin.index.json"
|
||||
SAFE_WEIGHTS_NAME = "model.safetensors"
|
||||
SAFE_WEIGHTS_INDEX_NAME = "model.safetensors.index.json"
|
||||
SAMPLER_NAME = "sampler"
|
||||
WEIGHTS_NAME = f"{MODEL_NAME}.bin"
|
||||
WEIGHTS_INDEX_NAME = f"{WEIGHTS_NAME}.index.json"
|
||||
SAFE_WEIGHTS_NAME = f"{SAFE_MODEL_NAME}.safetensors"
|
||||
SAFE_WEIGHTS_INDEX_NAME = f"{SAFE_WEIGHTS_NAME}.index.json"
|
||||
SAGEMAKER_PYTORCH_VERSION = "1.10.2"
|
||||
SAGEMAKER_PYTHON_VERSION = "py38"
|
||||
SAGEMAKER_TRANSFORMERS_VERSION = "4.17.0"
|
||||
@ -32,7 +34,8 @@ FSDP_SHARDING_STRATEGY = ["FULL_SHARD", "SHARD_GRAD_OP", "NO_SHARD", "HYBRID_SHA
|
||||
FSDP_AUTO_WRAP_POLICY = ["TRANSFORMER_BASED_WRAP", "SIZE_BASED_WRAP", "NO_WRAP"]
|
||||
FSDP_BACKWARD_PREFETCH = ["BACKWARD_PRE", "BACKWARD_POST", "NO_PREFETCH"]
|
||||
FSDP_STATE_DICT_TYPE = ["FULL_STATE_DICT", "LOCAL_STATE_DICT", "SHARDED_STATE_DICT"]
|
||||
FSDP_PYTORCH_VERSION = "2.0.1"
|
||||
FSDP_PYTORCH_VERSION = "2.1.0"
|
||||
FSDP_MODEL_NAME = "pytorch_model_fsdp"
|
||||
DEEPSPEED_MULTINODE_LAUNCHERS = ["pdsh", "standard", "openmpi", "mvapich", "mpich"]
|
||||
TORCH_DYNAMO_MODES = ["default", "reduce-overhead", "max-autotune"]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -26,12 +26,13 @@ import warnings
|
||||
from contextlib import contextmanager
|
||||
from dataclasses import dataclass, field
|
||||
from datetime import timedelta
|
||||
from typing import Any, Callable, Dict, Iterable, List, Optional, Tuple
|
||||
from typing import Any, Callable, Dict, Iterable, List, Literal, Optional, Tuple, get_args
|
||||
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
from .constants import FSDP_AUTO_WRAP_POLICY, FSDP_BACKWARD_PREFETCH, FSDP_STATE_DICT_TYPE
|
||||
from .constants import FSDP_AUTO_WRAP_POLICY, FSDP_BACKWARD_PREFETCH, FSDP_SHARDING_STRATEGY, FSDP_STATE_DICT_TYPE
|
||||
from .environment import str_to_bool
|
||||
from .imports import is_cuda_available, is_npu_available, is_xpu_available
|
||||
from .versions import compare_versions
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -168,36 +169,116 @@ class InitProcessGroupKwargs(KwargsHandler):
|
||||
timeout: timedelta = timedelta(seconds=1800)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# Literals
|
||||
Backend = Literal["msamp", "te"]
|
||||
OptLevel = Literal["O1", "O2"]
|
||||
FP8Format = Literal["E4M3", "HYBRID"]
|
||||
AmaxComputeAlgorithm = Literal["max", "most_recent"]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@dataclass
|
||||
class FP8RecipeKwargs(KwargsHandler):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Use this object in your [`Accelerator`] to customize the initialization of the recipe for FP8 mixed precision
|
||||
training. Please refer to the documentation of this
|
||||
[class](https://docs.nvidia.com/deeplearning/transformer-engine/user-guide/api/common.html#transformer_engine.common.recipe.DelayedScaling)
|
||||
for more information on each argument.
|
||||
training with `transformer-engine` or `ms-amp`.
|
||||
|
||||
<Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
For more information on `transformer-engine` args, please refer to the API
|
||||
[documentation](https://docs.nvidia.com/deeplearning/transformer-engine/user-guide/api/common.html).
|
||||
|
||||
For more information on the `ms-amp` args, please refer to the Optimization Level
|
||||
[documentation](https://azure.github.io/MS-AMP/docs/user-tutorial/optimization-level).
|
||||
|
||||
</Tip>
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from accelerate import Accelerator
|
||||
from accelerate.utils import FP8RecipeKwargs
|
||||
|
||||
kwargs = FP8RecipeKwargs(fp8_format="HYBRID")
|
||||
kwargs = FP8RecipeKwargs(backend="te", fp8_format="HYBRID")
|
||||
accelerator = Accelerator(mixed_precision="fp8", kwargs_handlers=[kwargs])
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To use MS-AMP as an engine, pass `backend="msamp"` and the `optimization_level`:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
kwargs = FP8RecipeKwargs(backend="msamp", optimization_level="02")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
backend (`str`, *optional*, defaults to "msamp"):
|
||||
Which FP8 engine to use. Must be one of `"msamp"` (MS-AMP) or `"te"` (TransformerEngine).
|
||||
margin (`int`, *optional*, default to 0):
|
||||
The margin to use for the gradient scaling.
|
||||
interval (`int`, *optional*, default to 1):
|
||||
The interval to use for how often the scaling factor is recomputed.
|
||||
fp8_format (`str`, *optional*, default to "E4M3"):
|
||||
The format to use for the FP8 recipe. Must be one of `E4M3` or `HYBRID`.
|
||||
amax_history_len (`int`, *optional*, default to 1024):
|
||||
The length of the history to use for the scaling factor computation
|
||||
amax_compute_algo (`str`, *optional*, default to "most_recent"):
|
||||
The algorithm to use for the scaling factor computation. Must be one of `max` or `most_recent`.
|
||||
override_linear_precision (`tuple` of three `bool`, *optional*, default to `(False, False, False)`):
|
||||
Whether or not to execute `fprop`, `dgrad`, and `wgrad` GEMMS in higher precision.
|
||||
optimization_level (`str`), one of `O1`, `O2`. (default is `O2`):
|
||||
What level of 8-bit collective communication should be used with MS-AMP. In general:
|
||||
* O1: Weight gradients and `all_reduce` communications are done in fp8, reducing GPU
|
||||
memory usage and communication bandwidth
|
||||
* O2: First-order optimizer states are in 8-bit, and second order states are in FP16.
|
||||
Only available when using Adam or AdamW. This maintains accuracy and can potentially save the
|
||||
highest memory.
|
||||
* 03: Specifically for DeepSpeed, implements capabilities so weights and master weights of models
|
||||
are stored in FP8. If `fp8` is selected and deepspeed is enabled, will be used by default. (Not
|
||||
available currently).
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
backend: Backend = "msamp"
|
||||
opt_level: OptLevel = "O2"
|
||||
margin: int = 0
|
||||
interval: int = 1
|
||||
fp8_format: str = "E4M3"
|
||||
fp8_format: FP8Format = "E4M3"
|
||||
amax_history_len: int = 1
|
||||
amax_compute_algo: str = "most_recent"
|
||||
amax_compute_algo: AmaxComputeAlgorithm = "most_recent"
|
||||
override_linear_precision: Tuple[bool, bool, bool] = (False, False, False)
|
||||
|
||||
def __post_init__(self):
|
||||
self.fp8_format = self.fp8_format.upper()
|
||||
if self.fp8_format not in ["E4M3", "HYBRID"]:
|
||||
raise ValueError("`fp8_format` must be 'E4M3' or 'HYBRID'.")
|
||||
if self.amax_compute_algo not in ["max", "most_recent"]:
|
||||
raise ValueError("`amax_compute_algo` must be 'max' or 'most_recent'")
|
||||
self.backend = self.backend.upper()
|
||||
if self.backend not in get_args(Backend):
|
||||
raise ValueError("`backend` must be 'MSAMP' or 'TE' (TransformerEngine).")
|
||||
# Check TE args
|
||||
if self.backend == "TE":
|
||||
self.fp8_format = self.fp8_format.upper()
|
||||
if self.fp8_format not in get_args(FP8Format):
|
||||
raise ValueError(f"`fp8_format` must be one of {' or '.join(get_args(FP8Format))}.")
|
||||
if self.amax_compute_algo not in get_args(AmaxComputeAlgorithm):
|
||||
raise ValueError(f"`amax_compute_algo` must be one of {' or '.join(get_args(AmaxComputeAlgorithm))}")
|
||||
elif self.backend == "MSAMP":
|
||||
if self.opt_level not in get_args(OptLevel):
|
||||
raise ValueError(f"`optimization_level` must be one of {' or '.join(get_args(OptLevel))}")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class EnumWithContains(enum.EnumMeta):
|
||||
"A metaclass that adds the ability to check if `self` contains an item with the `in` operator"
|
||||
|
||||
def __contains__(cls, item):
|
||||
try:
|
||||
cls(item)
|
||||
except ValueError:
|
||||
return False
|
||||
return True
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class BaseEnum(enum.Enum, metaclass=EnumWithContains):
|
||||
"An enum class that can get the value of an item with `str(Enum.key)`"
|
||||
|
||||
def __str__(self):
|
||||
return self.value
|
||||
|
||||
@classmethod
|
||||
def list(cls):
|
||||
"Method to list all the possible items in `cls`"
|
||||
return list(map(str, cls))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class DistributedType(str, enum.Enum):
|
||||
@ -259,7 +340,7 @@ class ComputeEnvironment(str, enum.Enum):
|
||||
AMAZON_SAGEMAKER = "AMAZON_SAGEMAKER"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class DynamoBackend(str, enum.Enum):
|
||||
class DynamoBackend(str, BaseEnum):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Represents a dynamo backend (see https://github.com/pytorch/torchdynamo).
|
||||
|
||||
@ -273,19 +354,21 @@ class DynamoBackend(str, enum.Enum):
|
||||
- **INDUCTOR** -- Uses TorchInductor backend with AotAutograd and cudagraphs by leveraging codegened Triton
|
||||
kernels. [Read
|
||||
more](https://dev-discuss.pytorch.org/t/torchinductor-a-pytorch-native-compiler-with-define-by-run-ir-and-symbolic-shapes/747)
|
||||
- **NVFUSER** -- nvFuser with TorchScript. [Read
|
||||
- **AOT_TS_NVFUSER** -- nvFuser with AotAutograd/TorchScript. [Read
|
||||
more](https://dev-discuss.pytorch.org/t/tracing-with-primitives-update-1-nvfuser-and-its-primitives/593)
|
||||
- **AOT_NVFUSER** -- nvFuser with AotAutograd. [Read
|
||||
- **NVPRIMS_NVFUSER** -- nvFuser with PrimTorch. [Read
|
||||
more](https://dev-discuss.pytorch.org/t/tracing-with-primitives-update-1-nvfuser-and-its-primitives/593)
|
||||
- **AOT_CUDAGRAPHS** -- cudagraphs with AotAutograd. [Read
|
||||
more](https://github.com/pytorch/torchdynamo/pull/757)
|
||||
- **CUDAGRAPHS** -- cudagraphs with AotAutograd. [Read more](https://github.com/pytorch/torchdynamo/pull/757)
|
||||
- **OFI** -- Uses Torchscript optimize_for_inference. Inference only. [Read
|
||||
more](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.jit.optimize_for_inference.html)
|
||||
- **FX2TRT** -- Uses Nvidia TensorRT for inference optimizations. Inference only. [Read
|
||||
more](https://github.com/pytorch/TensorRT/blob/master/docsrc/tutorials/getting_started_with_fx_path.rst)
|
||||
- **ONNXRT** -- Uses ONNXRT for inference on CPU/GPU. Inference only. [Read more](https://onnxruntime.ai/)
|
||||
- **TENSORRT** -- Uses ONNXRT to run TensorRT for inference optimizations. [Read
|
||||
more](https://github.com/onnx/onnx-tensorrt)
|
||||
- **IPEX** -- Uses IPEX for inference on CPU. Inference only. [Read
|
||||
more](https://github.com/intel/intel-extension-for-pytorch).
|
||||
- **TVM** -- Uses Apach TVM for inference optimizations. [Read more](https://tvm.apache.org/)
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
@ -294,36 +377,15 @@ class DynamoBackend(str, enum.Enum):
|
||||
EAGER = "EAGER"
|
||||
AOT_EAGER = "AOT_EAGER"
|
||||
INDUCTOR = "INDUCTOR"
|
||||
NVFUSER = "NVFUSER"
|
||||
AOT_NVFUSER = "AOT_NVFUSER"
|
||||
AOT_CUDAGRAPHS = "AOT_CUDAGRAPHS"
|
||||
AOT_TS_NVFUSER = "AOT_TS_NVFUSER"
|
||||
NVPRIMS_NVFUSER = "NVPRIMS_NVFUSER"
|
||||
CUDAGRAPHS = "CUDAGRAPHS"
|
||||
OFI = "OFI"
|
||||
FX2TRT = "FX2TRT"
|
||||
ONNXRT = "ONNXRT"
|
||||
TENSORRT = "TENSORRT"
|
||||
IPEX = "IPEX"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class EnumWithContains(enum.EnumMeta):
|
||||
"A metaclass that adds the ability to check if `self` contains an item with the `in` operator"
|
||||
|
||||
def __contains__(cls, item):
|
||||
try:
|
||||
cls(item)
|
||||
except ValueError:
|
||||
return False
|
||||
return True
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class BaseEnum(enum.Enum, metaclass=EnumWithContains):
|
||||
"An enum class that can get the value of an item with `str(Enum.key)`"
|
||||
|
||||
def __str__(self):
|
||||
return self.value
|
||||
|
||||
@classmethod
|
||||
def list(cls):
|
||||
"Method to list all the possible items in `cls`"
|
||||
return list(map(str, cls))
|
||||
TVM = "TVM"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class LoggerType(BaseEnum):
|
||||
@ -335,6 +397,7 @@ class LoggerType(BaseEnum):
|
||||
- **TENSORBOARD** -- TensorBoard as an experiment tracker
|
||||
- **WANDB** -- wandb as an experiment tracker
|
||||
- **COMETML** -- comet_ml as an experiment tracker
|
||||
- **DVCLIVE** -- dvclive as an experiment tracker
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
ALL = "all"
|
||||
@ -343,6 +406,8 @@ class LoggerType(BaseEnum):
|
||||
WANDB = "wandb"
|
||||
COMETML = "comet_ml"
|
||||
MLFLOW = "mlflow"
|
||||
CLEARML = "clearml"
|
||||
DVCLIVE = "dvclive"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class PrecisionType(BaseEnum):
|
||||
@ -374,6 +439,7 @@ class CustomDtype(enum.Enum):
|
||||
r"""
|
||||
An enum that contains multiple custom dtypes that can be used for `infer_auto_device_map`.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
FP8 = "fp8"
|
||||
INT4 = "int4"
|
||||
|
||||
@ -415,6 +481,16 @@ class ProjectConfiguration:
|
||||
metadata={"help": "The current save iteration."},
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
save_on_each_node: bool = field(
|
||||
default=False,
|
||||
metadata={
|
||||
"help": (
|
||||
"When doing multi-node distributed training, whether to save models and checkpoints on each node, or"
|
||||
" only on the main one"
|
||||
)
|
||||
},
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def set_directories(self, project_dir: str = None):
|
||||
"Sets `self.project_dir` and `self.logging_dir` to the appropriate values."
|
||||
self.project_dir = project_dir
|
||||
@ -654,7 +730,7 @@ class DeepSpeedPlugin:
|
||||
else:
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
f"`{ds_key_long}` not found in kwargs. "
|
||||
f"Please specify `{ds_key_long}` without `auto`(set to correct value) in the DeepSpeed config file or "
|
||||
f"Please specify `{ds_key_long}` without `auto` (set to correct value) in the DeepSpeed config file or "
|
||||
"pass it in kwargs."
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -666,6 +742,16 @@ class DeepSpeedPlugin:
|
||||
if ds_val != kwargs[ds_key_long]:
|
||||
mismatches.append(f"- ds {ds_key_long}={ds_val} vs arg {ds_key_long}={kwargs[ds_key_long]}")
|
||||
|
||||
def is_auto(self, ds_key_long):
|
||||
val = self.hf_ds_config.get_value(ds_key_long)
|
||||
if val is None:
|
||||
return False
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return val == "auto"
|
||||
|
||||
def get_value(self, ds_key_long, default=None):
|
||||
return self.hf_ds_config.get_value(ds_key_long, default)
|
||||
|
||||
def deepspeed_config_process(self, prefix="", mismatches=None, config=None, must_match=True, **kwargs):
|
||||
"""Process the DeepSpeed config with the values from the kwargs."""
|
||||
mismatches = [] if mismatches is None else mismatches
|
||||
@ -727,7 +813,7 @@ class DeepSpeedPlugin:
|
||||
or ds_config["train_micro_batch_size_per_gpu"] == "auto"
|
||||
):
|
||||
ds_config["train_micro_batch_size_per_gpu"] = 1
|
||||
if ds_config["train_batch_size"] == "auto":
|
||||
if ds_config.get("train_batch_size", None) == "auto":
|
||||
del ds_config["train_batch_size"]
|
||||
|
||||
if compare_versions("transformers", "<", "4.33"):
|
||||
@ -843,7 +929,7 @@ class FullyShardedDataParallelPlugin:
|
||||
},
|
||||
)
|
||||
limit_all_gathers: bool = field(
|
||||
default=False,
|
||||
default=True,
|
||||
metadata={
|
||||
"help": "If False, then FSDP allows the CPU thread to schedule all-gathers "
|
||||
"without any extra synchronization. If True, then FSDP explicitly synchronizes the CPU thread to prevent "
|
||||
@ -852,11 +938,12 @@ class FullyShardedDataParallelPlugin:
|
||||
},
|
||||
)
|
||||
use_orig_params: bool = field(
|
||||
default=False,
|
||||
default=True,
|
||||
metadata={
|
||||
"help": "If True, allows non-uniform `requires_grad` during init, which means support for interspersed frozen and trainable paramteres. "
|
||||
"help": "If `True`, allows non-uniform `requires_grad` during init, which means support for interspersed frozen and trainable parameters. "
|
||||
"Useful in cases such as parameter-efficient fine-tuning. "
|
||||
"Please refer this [blog](https://dev-discuss.pytorch.org/t/rethinking-pytorch-fully-sharded-data-parallel-fsdp-from-first-principles/1019)"
|
||||
"Please refer this [blog](https://dev-discuss.pytorch.org/t/rethinking-pytorch-fully-sharded-data-parallel-fsdp-from-first-principles/1019). "
|
||||
"This also enables multiple optimizer param groups. This should be `True` when creating an optimizer object before preparing/wrapping the model with FSDP."
|
||||
},
|
||||
)
|
||||
param_init_fn: Optional[Callable[[torch.nn.Module], None]] = field(
|
||||
@ -894,7 +981,13 @@ class FullyShardedDataParallelPlugin:
|
||||
|
||||
prefix = "FSDP_"
|
||||
if self.sharding_strategy is None:
|
||||
self.sharding_strategy = ShardingStrategy(int(os.environ.get(prefix + "SHARDING_STRATEGY", 1)))
|
||||
sharding_strategy = os.environ.get(prefix + "SHARDING_STRATEGY", "FULL_SHARD")
|
||||
sharding_strategy = (
|
||||
FSDP_SHARDING_STRATEGY.index(sharding_strategy) + 1
|
||||
if not sharding_strategy.isdigit()
|
||||
else int(sharding_strategy)
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.sharding_strategy = ShardingStrategy(sharding_strategy)
|
||||
|
||||
if self.cpu_offload is None:
|
||||
if str_to_bool(os.environ.get(prefix + "OFFLOAD_PARAMS", "False")) == 1:
|
||||
@ -916,7 +1009,17 @@ class FullyShardedDataParallelPlugin:
|
||||
self.activation_checkpointing = str_to_bool(os.environ.get(prefix + "ACTIVATION_CHECKPOINTING", "False")) == 1
|
||||
|
||||
if self.sync_module_states:
|
||||
self.param_init_fn = lambda x: x.to_empty(device=torch.cuda.current_device(), recurse=False)
|
||||
if is_npu_available():
|
||||
device = torch.npu.current_device()
|
||||
elif is_cuda_available():
|
||||
device = torch.cuda.current_device()
|
||||
elif is_xpu_available():
|
||||
device = torch.xpu.current_device()
|
||||
else:
|
||||
raise RuntimeError(
|
||||
"There are currently no available devices found, must be one of 'XPU', 'CUDA', or 'NPU'."
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.param_init_fn = lambda x: x.to_empty(device=device, recurse=False)
|
||||
|
||||
@staticmethod
|
||||
def get_module_class_from_name(module, name):
|
||||
@ -1015,7 +1118,7 @@ class MegatronLMPlugin:
|
||||
default=None,
|
||||
metadata={"help": "enable sequence parallelism"},
|
||||
)
|
||||
recompute_activation: bool = field(
|
||||
recompute_activations: bool = field(
|
||||
default=None,
|
||||
metadata={"help": "enable selective activation recomputation"},
|
||||
)
|
||||
@ -1168,8 +1271,8 @@ class MegatronLMPlugin:
|
||||
self.num_micro_batches = int(os.environ.get(prefix + "NUM_MICRO_BATCHES", 1))
|
||||
if self.gradient_clipping is None:
|
||||
self.gradient_clipping = float(os.environ.get(prefix + "GRADIENT_CLIPPING", 1.0))
|
||||
if self.recompute_activation is None:
|
||||
self.recompute_activation = str_to_bool(os.environ.get(prefix + "RECOMPUTE_ACTIVATION", "False")) == 1
|
||||
if self.recompute_activations is None:
|
||||
self.recompute_activations = str_to_bool(os.environ.get(prefix + "RECOMPUTE_ACTIVATIONS", "False")) == 1
|
||||
if self.use_distributed_optimizer is None:
|
||||
self.use_distributed_optimizer = (
|
||||
str_to_bool(os.environ.get(prefix + "USE_DISTRIBUTED_OPTIMIZER", "False")) == 1
|
||||
@ -1206,7 +1309,7 @@ class MegatronLMPlugin:
|
||||
"eval_iters": self.eval_iters,
|
||||
"eval_interval": self.eval_interval,
|
||||
}
|
||||
if self.recompute_activation:
|
||||
if self.recompute_activations:
|
||||
self.megatron_lm_default_args["recompute_granularity"] = "selective"
|
||||
if self.tensorboard_dir is not None:
|
||||
self.megatron_lm_default_args["tensorboard_dir"] = self.tensorboard_dir
|
||||
|
||||
@ -13,6 +13,13 @@
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import platform
|
||||
import subprocess
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
from distutils import spawn
|
||||
from typing import Dict
|
||||
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def str_to_bool(value) -> int:
|
||||
@ -48,3 +55,68 @@ def parse_flag_from_env(key, default=False):
|
||||
def parse_choice_from_env(key, default="no"):
|
||||
value = os.environ.get(key, str(default))
|
||||
return value
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def are_libraries_initialized(*library_names: str) -> Dict[str, bool]:
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Checks if any of `library_names` are imported in the environment. Will return results as a `key:bool` pair.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
return [lib_name for lib_name in library_names if lib_name in sys.modules.keys()]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def get_gpu_info():
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Gets GPU count and names using `nvidia-smi` instead of torch to not initialize CUDA.
|
||||
|
||||
Largely based on the `gputil` library.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if platform.system() == "Windows":
|
||||
# If platform is Windows and nvidia-smi can't be found in path
|
||||
# try from systemd rive with default installation path
|
||||
command = spawn.find_executable("nvidia-smi")
|
||||
if command is None:
|
||||
command = "%s\\Program Files\\NVIDIA Corporation\\NVSMI\\nvidia-smi.exe" % os.environ["systemdrive"]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
command = "nvidia-smi"
|
||||
# Returns as list of `n` GPUs and their names
|
||||
output = subprocess.check_output(
|
||||
[command, "--query-gpu=count,name", "--format=csv,noheader"], universal_newlines=True
|
||||
)
|
||||
output = output.strip()
|
||||
gpus = output.split(os.linesep)
|
||||
# Get names from output
|
||||
gpu_count = len(gpus)
|
||||
gpu_names = [gpu.split(",")[1].strip() for gpu in gpus]
|
||||
return gpu_names, gpu_count
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def check_cuda_p2p_ib_support():
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Checks if the devices being used have issues with P2P and IB communications, namely any consumer GPU hardware after
|
||||
the 3090.
|
||||
|
||||
Noteably uses `nvidia-smi` instead of torch to not initialize CUDA.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
try:
|
||||
device_names, device_count = get_gpu_info()
|
||||
unsupported_devices = {"RTX 3090", "RTX 40"}
|
||||
if device_count > 1:
|
||||
if any(
|
||||
unsupported_device in device_name
|
||||
for device_name in device_names
|
||||
for unsupported_device in unsupported_devices
|
||||
):
|
||||
return False
|
||||
except Exception:
|
||||
pass
|
||||
return True
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def check_fp8_capability():
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Checks if all the current GPUs available support FP8.
|
||||
|
||||
Notably must initialize `torch.cuda` to check.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
cuda_device_capacity = torch.cuda.get_device_capability()
|
||||
return cuda_device_capacity >= (8, 9)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -16,7 +16,7 @@ import os
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
from ..logging import get_logger
|
||||
from .constants import FSDP_PYTORCH_VERSION, MODEL_NAME, OPTIMIZER_NAME
|
||||
from .constants import FSDP_MODEL_NAME, FSDP_PYTORCH_VERSION, OPTIMIZER_NAME
|
||||
from .imports import is_torch_distributed_available
|
||||
from .versions import is_torch_version
|
||||
|
||||
@ -47,7 +47,7 @@ def save_fsdp_model(fsdp_plugin, accelerator, model, output_dir, model_index=0):
|
||||
):
|
||||
state_dict = model.state_dict()
|
||||
if fsdp_plugin.state_dict_type == StateDictType.FULL_STATE_DICT:
|
||||
weights_name = f"{MODEL_NAME}.bin" if model_index == 0 else f"{MODEL_NAME}_{model_index}.bin"
|
||||
weights_name = f"{FSDP_MODEL_NAME}.bin" if model_index == 0 else f"{FSDP_MODEL_NAME}_{model_index}.bin"
|
||||
output_model_file = os.path.join(output_dir, weights_name)
|
||||
if accelerator.process_index == 0:
|
||||
logger.info(f"Saving model to {output_model_file}")
|
||||
@ -55,16 +55,16 @@ def save_fsdp_model(fsdp_plugin, accelerator, model, output_dir, model_index=0):
|
||||
logger.info(f"Model saved to {output_model_file}")
|
||||
elif fsdp_plugin.state_dict_type == StateDictType.LOCAL_STATE_DICT:
|
||||
weights_name = (
|
||||
f"{MODEL_NAME}_rank{accelerator.process_index}.bin"
|
||||
f"{FSDP_MODEL_NAME}_rank{accelerator.process_index}.bin"
|
||||
if model_index == 0
|
||||
else f"{MODEL_NAME}_{model_index}_rank{accelerator.process_index}.bin"
|
||||
else f"{FSDP_MODEL_NAME}_{model_index}_rank{accelerator.process_index}.bin"
|
||||
)
|
||||
output_model_file = os.path.join(output_dir, weights_name)
|
||||
logger.info(f"Saving model to {output_model_file}")
|
||||
torch.save(state_dict, output_model_file)
|
||||
logger.info(f"Model saved to {output_model_file}")
|
||||
elif fsdp_plugin.state_dict_type == StateDictType.SHARDED_STATE_DICT:
|
||||
ckpt_dir = os.path.join(output_dir, f"{MODEL_NAME}_{model_index}")
|
||||
ckpt_dir = os.path.join(output_dir, f"{FSDP_MODEL_NAME}_{model_index}")
|
||||
os.makedirs(ckpt_dir, exist_ok=True)
|
||||
logger.info(f"Saving model to {ckpt_dir}")
|
||||
state_dict = {"model": state_dict}
|
||||
@ -96,16 +96,16 @@ def load_fsdp_model(fsdp_plugin, accelerator, model, input_dir, model_index=0):
|
||||
"initializing FSDP object"
|
||||
)
|
||||
return
|
||||
weights_name = f"{MODEL_NAME}.bin" if model_index == 0 else f"{MODEL_NAME}_{model_index}.bin"
|
||||
weights_name = f"{FSDP_MODEL_NAME}.bin" if model_index == 0 else f"{FSDP_MODEL_NAME}_{model_index}.bin"
|
||||
input_model_file = os.path.join(input_dir, weights_name)
|
||||
logger.info(f"Loading model from {input_model_file}")
|
||||
state_dict = torch.load(input_model_file)
|
||||
logger.info(f"Model loaded from {input_model_file}")
|
||||
elif fsdp_plugin.state_dict_type == StateDictType.LOCAL_STATE_DICT:
|
||||
weights_name = (
|
||||
f"{MODEL_NAME}_rank{accelerator.process_index}.bin"
|
||||
f"{FSDP_MODEL_NAME}_rank{accelerator.process_index}.bin"
|
||||
if model_index == 0
|
||||
else f"{MODEL_NAME}_{model_index}_rank{accelerator.process_index}.bin"
|
||||
else f"{FSDP_MODEL_NAME}_{model_index}_rank{accelerator.process_index}.bin"
|
||||
)
|
||||
input_model_file = os.path.join(input_dir, weights_name)
|
||||
logger.info(f"Loading model from {input_model_file}")
|
||||
@ -113,8 +113,8 @@ def load_fsdp_model(fsdp_plugin, accelerator, model, input_dir, model_index=0):
|
||||
logger.info(f"Model loaded from {input_model_file}")
|
||||
elif fsdp_plugin.state_dict_type == StateDictType.SHARDED_STATE_DICT:
|
||||
ckpt_dir = (
|
||||
os.path.join(input_dir, f"{MODEL_NAME}_{model_index}")
|
||||
if f"{MODEL_NAME}" not in input_dir
|
||||
os.path.join(input_dir, f"{FSDP_MODEL_NAME}_{model_index}")
|
||||
if f"{FSDP_MODEL_NAME}" not in input_dir
|
||||
else input_dir
|
||||
)
|
||||
logger.info(f"Loading model from {ckpt_dir}")
|
||||
@ -164,16 +164,14 @@ def load_fsdp_optimizer(fsdp_plugin, accelerator, optimizer, model, input_dir, o
|
||||
):
|
||||
if fsdp_plugin.state_dict_type == StateDictType.FULL_STATE_DICT:
|
||||
optim_state = None
|
||||
# below check should work but currently it isn't working (mostly opytorch issue),
|
||||
# in the meantime disabling it at the cost of excess memory usage
|
||||
# if accelerator.process_index == 0 or not fsdp_plugin.optim_state_dict_config.rank0_only:
|
||||
optimizer_name = (
|
||||
f"{OPTIMIZER_NAME}.bin" if optimizer_index == 0 else f"{OPTIMIZER_NAME}_{optimizer_index}.bin"
|
||||
)
|
||||
input_optimizer_file = os.path.join(input_dir, optimizer_name)
|
||||
logger.info(f"Loading Optimizer state from {input_optimizer_file}")
|
||||
optim_state = torch.load(input_optimizer_file)
|
||||
logger.info(f"Optimizer state loaded from {input_optimizer_file}")
|
||||
if accelerator.process_index == 0 or not fsdp_plugin.optim_state_dict_config.rank0_only:
|
||||
optimizer_name = (
|
||||
f"{OPTIMIZER_NAME}.bin" if optimizer_index == 0 else f"{OPTIMIZER_NAME}_{optimizer_index}.bin"
|
||||
)
|
||||
input_optimizer_file = os.path.join(input_dir, optimizer_name)
|
||||
logger.info(f"Loading Optimizer state from {input_optimizer_file}")
|
||||
optim_state = torch.load(input_optimizer_file)
|
||||
logger.info(f"Optimizer state loaded from {input_optimizer_file}")
|
||||
else:
|
||||
ckpt_dir = (
|
||||
os.path.join(input_dir, f"{OPTIMIZER_NAME}_{optimizer_index}")
|
||||
|
||||
@ -72,10 +72,26 @@ def get_ccl_version():
|
||||
return importlib.metadata.version("oneccl_bind_pt")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def is_fp8_available():
|
||||
def is_msamp_available():
|
||||
package_exists = importlib.util.find_spec("msamp") is not None
|
||||
if package_exists:
|
||||
try:
|
||||
# MS-AMP has a different metadata name
|
||||
_ = importlib.metadata.metadata("ms-amp")
|
||||
return True
|
||||
except importlib.metadata.PackageNotFoundError:
|
||||
return False
|
||||
return False
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def is_transformer_engine_available():
|
||||
return _is_package_available("transformer_engine")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def is_fp8_available():
|
||||
return is_msamp_available() or is_transformer_engine_available()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def is_cuda_available():
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Checks if `cuda` is available via an `nvml-based` check which won't trigger the drivers and leave cuda
|
||||
@ -114,7 +130,7 @@ def is_bf16_available(ignore_tpu=False):
|
||||
"Checks if bf16 is supported, optionally ignoring the TPU"
|
||||
if is_tpu_available():
|
||||
return not ignore_tpu
|
||||
if torch.cuda.is_available():
|
||||
if is_cuda_available():
|
||||
return torch.cuda.is_bf16_supported()
|
||||
return True
|
||||
|
||||
@ -151,10 +167,6 @@ def is_megatron_lm_available():
|
||||
return False
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def is_safetensors_available():
|
||||
return _is_package_available("safetensors")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def is_transformers_available():
|
||||
return _is_package_available("transformers")
|
||||
|
||||
@ -210,6 +222,14 @@ def is_tqdm_available():
|
||||
return _is_package_available("tqdm")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def is_clearml_available():
|
||||
return _is_package_available("clearml")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def is_pandas_available():
|
||||
return _is_package_available("pandas")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def is_mlflow_available():
|
||||
if _is_package_available("mlflow"):
|
||||
return True
|
||||
@ -293,3 +313,7 @@ def is_xpu_available(check_device=False):
|
||||
except RuntimeError:
|
||||
return False
|
||||
return hasattr(torch, "xpu") and torch.xpu.is_available()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def is_dvclive_available():
|
||||
return _is_package_available("dvclive")
|
||||
|
||||
@ -15,13 +15,13 @@
|
||||
import argparse
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import sys
|
||||
import warnings
|
||||
from ast import literal_eval
|
||||
from typing import Any, Dict, List, Tuple
|
||||
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
from ..commands.config.config_args import SageMakerConfig
|
||||
from ..commands.config.config_utils import DYNAMO_BACKENDS
|
||||
from ..utils import (
|
||||
DynamoBackend,
|
||||
PrecisionType,
|
||||
@ -89,7 +89,9 @@ def prepare_simple_launcher_cmd_env(args: argparse.Namespace) -> Tuple[List[str]
|
||||
try:
|
||||
dynamo_backend = DynamoBackend(args.dynamo_backend.upper())
|
||||
except ValueError:
|
||||
raise ValueError(f"Unknown dynamo backend: {args.dynamo_backend.upper()}. Choose between {DYNAMO_BACKENDS}.")
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
f"Unknown dynamo backend: {args.dynamo_backend.upper()}. Choose between {DynamoBackend.list()}."
|
||||
)
|
||||
current_env["ACCELERATE_DYNAMO_BACKEND"] = dynamo_backend.value
|
||||
current_env["ACCELERATE_DYNAMO_MODE"] = args.dynamo_mode
|
||||
current_env["ACCELERATE_DYNAMO_USE_FULLGRAPH"] = str(args.dynamo_use_fullgraph)
|
||||
@ -127,7 +129,10 @@ def prepare_multi_gpu_env(args: argparse.Namespace) -> Dict[str, str]:
|
||||
if main_process_port is None:
|
||||
main_process_port = 29500
|
||||
|
||||
if is_port_in_use(main_process_port):
|
||||
# only need to check port availability in main process, in case we have to start multiple launchers on the same machine
|
||||
# for some reasons like splitting log files.
|
||||
need_port_check = num_machines <= 1 or int(args.machine_rank) == 0
|
||||
if need_port_check and is_port_in_use(main_process_port):
|
||||
raise ConnectionError(
|
||||
f"Tried to launch distributed communication on port `{main_process_port}`, but another process is utilizing it. "
|
||||
"Please specify a different port (such as using the `----main_process_port` flag or specifying a different `main_process_port` in your config file)"
|
||||
@ -163,7 +168,9 @@ def prepare_multi_gpu_env(args: argparse.Namespace) -> Dict[str, str]:
|
||||
try:
|
||||
dynamo_backend = DynamoBackend(args.dynamo_backend.upper())
|
||||
except ValueError:
|
||||
raise ValueError(f"Unknown dynamo backend: {args.dynamo_backend.upper()}. Choose between {DYNAMO_BACKENDS}.")
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
f"Unknown dynamo backend: {args.dynamo_backend.upper()}. Choose between {DynamoBackend.list()}."
|
||||
)
|
||||
current_env["ACCELERATE_DYNAMO_BACKEND"] = dynamo_backend.value
|
||||
current_env["ACCELERATE_DYNAMO_MODE"] = args.dynamo_mode
|
||||
current_env["ACCELERATE_DYNAMO_USE_FULLGRAPH"] = str(args.dynamo_use_fullgraph)
|
||||
@ -171,6 +178,9 @@ def prepare_multi_gpu_env(args: argparse.Namespace) -> Dict[str, str]:
|
||||
|
||||
if args.use_fsdp:
|
||||
current_env["ACCELERATE_USE_FSDP"] = "true"
|
||||
if args.fsdp_cpu_ram_efficient_loading and not args.fsdp_sync_module_states:
|
||||
raise ValueError("When using `--fsdp_cpu_ram_efficient_loading` set `--fsdp_sync_module_states` to `True`")
|
||||
|
||||
current_env["FSDP_SHARDING_STRATEGY"] = str(args.fsdp_sharding_strategy)
|
||||
current_env["FSDP_OFFLOAD_PARAMS"] = str(args.fsdp_offload_params).lower()
|
||||
current_env["FSDP_MIN_NUM_PARAMS"] = str(args.fsdp_min_num_params)
|
||||
@ -179,11 +189,19 @@ def prepare_multi_gpu_env(args: argparse.Namespace) -> Dict[str, str]:
|
||||
if args.fsdp_transformer_layer_cls_to_wrap is not None:
|
||||
current_env["FSDP_TRANSFORMER_CLS_TO_WRAP"] = str(args.fsdp_transformer_layer_cls_to_wrap)
|
||||
if args.fsdp_backward_prefetch_policy is not None:
|
||||
current_env["FSDP_BACKWARD_PREFETCH"] = str(args.fsdp_backward_prefetch_policy)
|
||||
warnings.warn(
|
||||
"`fsdp_backward_prefetch_policy` is deprecated and will be removed in version 0.27.0 of 🤗 Accelerate. Use"
|
||||
" `fsdp_backward_prefetch` instead",
|
||||
FutureWarning,
|
||||
)
|
||||
args.fsdp_backward_prefetch = args.fsdp_backward_prefetch_policy
|
||||
if args.fsdp_backward_prefetch is not None:
|
||||
current_env["FSDP_BACKWARD_PREFETCH"] = str(args.fsdp_backward_prefetch)
|
||||
if args.fsdp_state_dict_type is not None:
|
||||
current_env["FSDP_STATE_DICT_TYPE"] = str(args.fsdp_state_dict_type)
|
||||
current_env["FSDP_FORWARD_PREFETCH"] = str(args.fsdp_forward_prefetch).lower()
|
||||
current_env["FSDP_USE_ORIG_PARAMS"] = str(args.fsdp_use_orig_params).lower()
|
||||
current_env["FSDP_CPU_RAM_EFFICIENT_LOADING"] = str(args.fsdp_cpu_ram_efficient_loading).lower()
|
||||
current_env["FSDP_SYNC_MODULE_STATES"] = str(args.fsdp_sync_module_states).lower()
|
||||
|
||||
if args.use_megatron_lm:
|
||||
@ -265,7 +283,10 @@ def prepare_deepspeed_cmd_env(args: argparse.Namespace) -> Tuple[List[str], Dict
|
||||
if main_process_port is None:
|
||||
main_process_port = 29500
|
||||
|
||||
if is_port_in_use(main_process_port):
|
||||
# only need to check port availability in main process, in case we have to start multiple launchers on the same machine
|
||||
# for some reasons like splitting log files.
|
||||
need_port_check = num_machines <= 1 or int(args.machine_rank) == 0
|
||||
if need_port_check and is_port_in_use(main_process_port):
|
||||
raise ConnectionError(
|
||||
f"Tried to launch distributed communication on port `{main_process_port}`, but another process is utilizing it. "
|
||||
"Please specify a different port (such as using the `----main_process_port` flag or specifying a different `main_process_port` in your config file)"
|
||||
@ -284,10 +305,12 @@ def prepare_deepspeed_cmd_env(args: argparse.Namespace) -> Tuple[List[str], Dict
|
||||
current_env["ACCELERATE_DEBUG_MODE"] = "true"
|
||||
gpu_ids = getattr(args, "gpu_ids", "all")
|
||||
if gpu_ids != "all" and args.gpu_ids is not None:
|
||||
if not is_xpu_available():
|
||||
current_env["CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES"] = gpu_ids
|
||||
else:
|
||||
if is_xpu_available():
|
||||
current_env["ZE_AFFINITY_MASK"] = gpu_ids
|
||||
elif is_npu_available():
|
||||
current_env["ASCEND_RT_VISIBLE_DEVICES"] = gpu_ids
|
||||
else:
|
||||
current_env["CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES"] = gpu_ids
|
||||
try:
|
||||
mixed_precision = PrecisionType(args.mixed_precision.lower())
|
||||
except ValueError:
|
||||
@ -419,7 +442,9 @@ def prepare_sagemager_args_inputs(
|
||||
try:
|
||||
dynamo_backend = DynamoBackend(args.dynamo_backend.upper())
|
||||
except ValueError:
|
||||
raise ValueError(f"Unknown dynamo backend: {args.dynamo_backend.upper()}. Choose between {DYNAMO_BACKENDS}.")
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
f"Unknown dynamo backend: {args.dynamo_backend.upper()}. Choose between {DynamoBackend.list()}."
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Environment variables to be set for use during training job
|
||||
environment = {
|
||||
|
||||
@ -21,7 +21,7 @@ import os
|
||||
import re
|
||||
import shutil
|
||||
import tempfile
|
||||
from collections import defaultdict
|
||||
from collections import OrderedDict, defaultdict
|
||||
from typing import Dict, List, Optional, Tuple, Union
|
||||
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
@ -30,7 +30,7 @@ import torch.nn as nn
|
||||
from ..state import AcceleratorState
|
||||
from .constants import SAFE_WEIGHTS_NAME, WEIGHTS_NAME
|
||||
from .dataclasses import AutocastKwargs, CustomDtype, DistributedType
|
||||
from .imports import is_mps_available, is_npu_available, is_safetensors_available, is_xpu_available
|
||||
from .imports import is_mps_available, is_npu_available, is_xpu_available
|
||||
from .offload import load_offloaded_weight, offload_weight, save_offload_index
|
||||
from .tqdm import is_tqdm_available, tqdm
|
||||
|
||||
@ -38,17 +38,42 @@ from .tqdm import is_tqdm_available, tqdm
|
||||
if is_npu_available(check_device=False):
|
||||
import torch_npu # noqa: F401
|
||||
|
||||
from safetensors import safe_open
|
||||
from safetensors.torch import load_file as safe_load_file
|
||||
|
||||
if is_safetensors_available():
|
||||
from safetensors import safe_open
|
||||
from safetensors.torch import load_file as safe_load_file
|
||||
|
||||
WEIGHTS_INDEX_NAME = "pytorch_model.bin.index.json"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def check_device_same(first_device, second_device):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Utility method to check if two `torch` devices are similar. When dealing with CUDA devices, torch throws `False`
|
||||
for `torch.device("cuda") == torch.device("cuda:0")` whereas they should be the same
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
first_device (`torch.device`):
|
||||
First device to check
|
||||
second_device (`torch.device`):
|
||||
Second device to check
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if first_device.type != second_device.type:
|
||||
return False
|
||||
|
||||
if first_device.type == "cuda" and first_device.index is None:
|
||||
# In case the first_device is a cuda device and have
|
||||
# the index attribute set to `None`, default it to `0`
|
||||
first_device = torch.device("cuda", index=0)
|
||||
|
||||
if second_device.type == "cuda" and second_device.index is None:
|
||||
# In case the second_device is a cuda device and have
|
||||
# the index attribute set to `None`, default it to `0`
|
||||
second_device = torch.device("cuda", index=0)
|
||||
|
||||
return first_device == second_device
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def convert_file_size_to_int(size: Union[int, str]):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Converts a size expressed as a string with digits an unit (like `"5MB"`) to an integer (in bytes).
|
||||
@ -221,7 +246,7 @@ def shard_checkpoint(
|
||||
weight_map = {}
|
||||
shards = {}
|
||||
for idx, shard in enumerate(sharded_state_dicts):
|
||||
shard_file = weights_name.replace(".bin", f"-{idx+1:05d}-of-{len(sharded_state_dicts):05d}.bin")
|
||||
shard_file = weights_name.replace(".bin", f"-{idx + 1:05d}-of-{len(sharded_state_dicts):05d}.bin")
|
||||
shard_file = shard_file.replace(
|
||||
".safetensors", f"-{idx + 1:05d}-of-{len(sharded_state_dicts):05d}.safetensors"
|
||||
)
|
||||
@ -250,7 +275,7 @@ def set_module_tensor_to_device(
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
module (`torch.nn.Module`):
|
||||
The module in which the tensor we want to move lives.
|
||||
param_name (`str`):
|
||||
tensor_name (`str`):
|
||||
The full name of the parameter/buffer.
|
||||
device (`int`, `str` or `torch.device`):
|
||||
The device on which to set the tensor.
|
||||
@ -303,14 +328,19 @@ def set_module_tensor_to_device(
|
||||
param is not None
|
||||
and param.device.type != "cuda"
|
||||
and torch.device(device).type == "cuda"
|
||||
and param_cls.__name__ in ["Int8Params", "FP4Params"]
|
||||
and param_cls.__name__ in ["Int8Params", "FP4Params", "Params4bit"]
|
||||
):
|
||||
device_quantization = device
|
||||
device = "cpu"
|
||||
# `torch.Tensor.to(<int num>)` is not supported by `torch_npu` (see this [issue](https://github.com/Ascend/pytorch/issues/16)).
|
||||
if is_npu_available() and isinstance(device, int):
|
||||
device = f"npu:{device}"
|
||||
if value is None:
|
||||
new_value = old_value.to(device)
|
||||
if dtype is not None and device in ["meta", torch.device("meta")]:
|
||||
new_value = new_value.to(dtype)
|
||||
if not str(old_value.dtype).startswith(("torch.uint", "torch.int", "torch.bool")):
|
||||
new_value = new_value.to(dtype)
|
||||
|
||||
if not is_buffer:
|
||||
module._parameters[tensor_name] = param_cls(new_value, requires_grad=old_value.requires_grad)
|
||||
elif isinstance(value, torch.Tensor):
|
||||
@ -321,7 +351,7 @@ def set_module_tensor_to_device(
|
||||
device = device_quantization
|
||||
if is_buffer:
|
||||
module._buffers[tensor_name] = new_value
|
||||
elif value is not None or torch.device(device) != module._parameters[tensor_name].device:
|
||||
elif value is not None or not check_device_same(torch.device(device), module._parameters[tensor_name].device):
|
||||
param_cls = type(module._parameters[tensor_name])
|
||||
kwargs = module._parameters[tensor_name].__dict__
|
||||
if param_cls.__name__ in ["Int8Params", "FP4Params"]:
|
||||
@ -362,10 +392,15 @@ def set_module_tensor_to_device(
|
||||
if not getattr(module.weight, "quant_state", None) and device_index is not None:
|
||||
module.weight = module.weight.cuda(device_index)
|
||||
# clean pre and post foward hook
|
||||
torch.cuda.empty_cache()
|
||||
if is_npu_available():
|
||||
torch.npu.empty_cache()
|
||||
else:
|
||||
torch.cuda.empty_cache()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def named_module_tensors(module: nn.Module, include_buffers: bool = True, recurse: bool = False):
|
||||
def named_module_tensors(
|
||||
module: nn.Module, include_buffers: bool = True, recurse: bool = False, remove_non_persistent: bool = False
|
||||
):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
A helper function that gathers all the tensors (parameters + buffers) of a given module. If `include_buffers=True`
|
||||
it's the same as doing `module.named_parameters(recurse=recurse) + module.named_buffers(recurse=recurse)`.
|
||||
@ -377,13 +412,40 @@ def named_module_tensors(module: nn.Module, include_buffers: bool = True, recurs
|
||||
Whether or not to include the buffers in the result.
|
||||
recurse (`bool`, *optional`, defaults to `False`):
|
||||
Whether or not to go look in every submodule or just return the direct parameters and buffers.
|
||||
remove_non_persistent (`bool`, *optional*, defaults to `False`):
|
||||
Whether or not to remove the non persistent buffer from the buffers. Useful only when include_buffers =
|
||||
True
|
||||
"""
|
||||
for named_parameter in module.named_parameters(recurse=recurse):
|
||||
yield named_parameter
|
||||
|
||||
if include_buffers:
|
||||
non_persistent_buffers = set()
|
||||
if remove_non_persistent:
|
||||
non_persistent_buffers = get_non_persistent_buffers(module, recurse=recurse)
|
||||
for named_buffer in module.named_buffers(recurse=recurse):
|
||||
yield named_buffer
|
||||
name, _ = named_buffer
|
||||
if name not in non_persistent_buffers:
|
||||
yield named_buffer
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def get_non_persistent_buffers(module: nn.Module, recurse: bool = False):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Gather all non persistent buffers of a given modules into a set
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
module (`nn.Module`):
|
||||
The module we want the non persistent buffers on.
|
||||
recurse (`bool`, *optional*, defaults to `False`):
|
||||
Whether or not to go look in every submodule or just return the direct non persistent buffers.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
non_persistent_buffers_set = module._non_persistent_buffers_set
|
||||
if recurse:
|
||||
for _, m in module.named_modules():
|
||||
non_persistent_buffers_set |= m._non_persistent_buffers_set
|
||||
|
||||
return non_persistent_buffers_set
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class FindTiedParametersResult(list):
|
||||
@ -535,15 +597,22 @@ def retie_parameters(model, tied_params):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
for tied_group in tied_params:
|
||||
param_to_tie = None
|
||||
# First iteration of the loop will set param_to_tie, next ones will tie it to the others
|
||||
# two loops : the first one to set param_to_tie , the second one to change the values of tied_group
|
||||
for param_name in tied_group:
|
||||
module = model
|
||||
splits = param_name.split(".")
|
||||
for split in splits[:-1]:
|
||||
module = getattr(module, split)
|
||||
if param_to_tie is None:
|
||||
param_to_tie = getattr(module, splits[-1])
|
||||
else:
|
||||
param = getattr(module, splits[-1])
|
||||
if param_to_tie is None and param.device != torch.device("meta"):
|
||||
param_to_tie = param
|
||||
break
|
||||
if param_to_tie is not None:
|
||||
for param_name in tied_group:
|
||||
module = model
|
||||
splits = param_name.split(".")
|
||||
for split in splits[:-1]:
|
||||
module = getattr(module, split)
|
||||
setattr(module, splits[-1], param_to_tie)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -633,19 +702,23 @@ def get_max_memory(max_memory: Optional[Dict[Union[int, str], Union[int, str]]]
|
||||
import psutil
|
||||
|
||||
if max_memory is None:
|
||||
if not (torch.cuda.is_available() or is_xpu_available()):
|
||||
if not (torch.cuda.is_available() or is_npu_available() or is_xpu_available()):
|
||||
max_memory = {}
|
||||
|
||||
else:
|
||||
# Make sure CUDA is initialized on each GPU to have the right memory info.
|
||||
if not is_xpu_available():
|
||||
for i in range(torch.cuda.device_count()):
|
||||
_ = torch.tensor([0], device=i)
|
||||
max_memory = {i: torch.cuda.mem_get_info(i)[0] for i in range(torch.cuda.device_count())}
|
||||
else:
|
||||
if is_npu_available():
|
||||
for i in range(torch.npu.device_count()):
|
||||
_ = torch.tensor(0, device=torch.device("npu", i))
|
||||
max_memory = {i: torch.npu.mem_get_info(i)[0] for i in range(torch.npu.device_count())}
|
||||
elif is_xpu_available():
|
||||
for i in range(torch.xpu.device_count()):
|
||||
_ = torch.tensor(0, device=torch.device("xpu", i))
|
||||
max_memory = {i: torch.xpu.max_memory_allocated(i) for i in range(torch.xpu.device_count())}
|
||||
else:
|
||||
for i in range(torch.cuda.device_count()):
|
||||
_ = torch.tensor([0], device=i)
|
||||
max_memory = {i: torch.cuda.mem_get_info(i)[0] for i in range(torch.cuda.device_count())}
|
||||
# allocate everything in the mps device as the RAM is shared
|
||||
if is_mps_available():
|
||||
max_memory["mps"] = psutil.virtual_memory().available
|
||||
@ -658,11 +731,16 @@ def get_max_memory(max_memory: Optional[Dict[Union[int, str], Union[int, str]]]
|
||||
max_memory[key] = convert_file_size_to_int(max_memory[key])
|
||||
|
||||
# Need to sort the device by type to make sure that we allocate the gpu first.
|
||||
# As gpu/xpu are represented by int, we need to sort them first.
|
||||
# As gpu/npu/xpu are represented by int, we need to sort them first.
|
||||
gpu_devices = [k for k in max_memory.keys() if isinstance(k, int)]
|
||||
gpu_devices.sort()
|
||||
# check if gpu/xgpu devices are available and if not, throw a warning
|
||||
num_devices = torch.xpu.device_count() if is_xpu_available() else torch.cuda.device_count()
|
||||
# check if gpu/npu/xpu devices are available and if not, throw a warning
|
||||
if is_npu_available():
|
||||
num_devices = torch.npu.device_count()
|
||||
elif is_xpu_available():
|
||||
num_devices = torch.xpu.device_count()
|
||||
else:
|
||||
num_devices = torch.cuda.device_count()
|
||||
for device in gpu_devices:
|
||||
if device >= num_devices or device < 0:
|
||||
logger.warning(f"Device {device} is not available, available devices are {list(range(num_devices))}")
|
||||
@ -770,9 +848,9 @@ def get_balanced_memory(
|
||||
user_not_set_max_memory = max_memory is None
|
||||
max_memory = get_max_memory(max_memory)
|
||||
|
||||
if not is_xpu_available():
|
||||
num_devices = len([d for d in max_memory if torch.device(d).type == "cuda" and max_memory[d] > 0])
|
||||
else:
|
||||
if is_npu_available():
|
||||
num_devices = len([d for d in max_memory if torch.device(d).type == "npu" and max_memory[d] > 0])
|
||||
elif is_xpu_available():
|
||||
num_devices = len(
|
||||
[
|
||||
d
|
||||
@ -784,6 +862,8 @@ def get_balanced_memory(
|
||||
and max_memory[d] > 0
|
||||
]
|
||||
)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
num_devices = len([d for d in max_memory if torch.device(d).type == "cuda" and max_memory[d] > 0])
|
||||
|
||||
if num_devices == 0:
|
||||
return max_memory
|
||||
@ -885,6 +965,7 @@ def infer_auto_device_map(
|
||||
dtype: Optional[Union[str, torch.dtype]] = None,
|
||||
special_dtypes: Optional[Dict[str, Union[str, torch.dtype]]] = None,
|
||||
verbose: bool = False,
|
||||
clean_result: bool = True,
|
||||
):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Compute a device map for a given model giving priority to GPUs, then offload on CPU and finally offload to disk,
|
||||
@ -918,6 +999,8 @@ def infer_auto_device_map(
|
||||
all weights).
|
||||
verbose (`bool`, *optional*, defaults to `False`):
|
||||
Whether or not to provide debugging statements as the function builds the device_map.
|
||||
clean_result (`bool`, *optional*, defaults to `True`):
|
||||
Clean the resulting device_map by grouping all submodules that go on the same device together.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
# Get default / clean up max_memory
|
||||
max_memory = get_max_memory(max_memory)
|
||||
@ -947,7 +1030,7 @@ def infer_auto_device_map(
|
||||
"The model weights are not tied. Please use the `tie_weights` method before using the `infer_auto_device` function."
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
device_map = {}
|
||||
device_map = OrderedDict()
|
||||
current_device = 0
|
||||
current_memory_used = 0
|
||||
|
||||
@ -978,15 +1061,22 @@ def infer_auto_device_map(
|
||||
|
||||
# We keep relevant tied parameters only: one of the tied parameters in the group is inside the current module
|
||||
# and the other is not.
|
||||
# Note: If we are currently processing the name `compute.weight`, an other parameter named e.g. `compute.weight_submodule.parameter`
|
||||
# needs to be considered outside the current module, hence the check with additional dots.
|
||||
tied_param_goups = [
|
||||
tied_group
|
||||
for tied_group in tied_parameters
|
||||
if any(name in k for k in tied_group) and not all(name in k for k in tied_group)
|
||||
if any(name + "." in k + "." for k in tied_group) and not all(name + "." in k + "." for k in tied_group)
|
||||
]
|
||||
|
||||
if verbose and len(tied_param_goups) > 0:
|
||||
print(f" Found the relevant tied param groups {tied_param_goups}")
|
||||
|
||||
# Then we keep track of all the parameters that are tied to the current module, but not in the current module
|
||||
tied_params = sum([[p for p in tied_group if name not in p] for tied_group in tied_param_goups], [])
|
||||
tied_params = sum(
|
||||
[[p for p in tied_group if name + "." not in p + "."] for tied_group in tied_param_goups], []
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if verbose and len(tied_params) > 0:
|
||||
print(f" So those parameters need to be taken into account {tied_params}")
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1002,7 +1092,7 @@ def infer_auto_device_map(
|
||||
if verbose:
|
||||
print(
|
||||
f"Not enough space on {devices[current_device]} to put {name} (space available "
|
||||
f"{current_max_size-current_memory_used}, module size {module_size})."
|
||||
f"{current_max_size - current_memory_used}, module size {module_size})."
|
||||
)
|
||||
if len(modules_children) == 0 or module.__class__.__name__ in no_split_module_classes:
|
||||
# -> no split, we go to the next device
|
||||
@ -1065,7 +1155,7 @@ def infer_auto_device_map(
|
||||
if verbose:
|
||||
print(
|
||||
f"Not enough space on {devices[current_device]} to put {name} and {tied_module_names} (space "
|
||||
f"available {current_max_size-current_memory_used}, needed size {module_size_with_ties})."
|
||||
f"available {current_max_size - current_memory_used}, needed size {module_size_with_ties})."
|
||||
)
|
||||
split_happened = False
|
||||
for tied_module_name, tied_module in zip(tied_module_names, tied_modules):
|
||||
@ -1110,12 +1200,14 @@ def infer_auto_device_map(
|
||||
else:
|
||||
print(
|
||||
f"Putting {name} (size={module_size}) on {devices[current_device]} "
|
||||
f"(available={current_max_size-current_memory_used})."
|
||||
f"(available={current_max_size - current_memory_used})."
|
||||
)
|
||||
current_memory_used += module_size
|
||||
device_map[name] = devices[current_device]
|
||||
|
||||
return clean_device_map(device_map)
|
||||
if clean_result:
|
||||
device_map = clean_device_map(device_map)
|
||||
return device_map
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def check_device_map(model: nn.Module, device_map: Dict[str, Union[int, str, torch.device]]):
|
||||
@ -1156,10 +1248,6 @@ def load_state_dict(checkpoint_file, device_map=None):
|
||||
name, once a given module name is inside, every submodule of it will be sent to the same device.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if checkpoint_file.endswith(".safetensors"):
|
||||
if not is_safetensors_available():
|
||||
raise ImportError(
|
||||
f"To load {checkpoint_file}, the `safetensors` library is necessary `pip install safetensors`."
|
||||
)
|
||||
with safe_open(checkpoint_file, framework="pt") as f:
|
||||
metadata = f.metadata()
|
||||
weight_names = f.keys()
|
||||
@ -1228,6 +1316,54 @@ def load_state_dict(checkpoint_file, device_map=None):
|
||||
return torch.load(checkpoint_file, map_location=torch.device("cpu"))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def get_state_dict_offloaded_model(model: nn.Module):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Returns the state dictionary for an offloaded model via iterative onloading
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
model (`torch.nn.Module`):
|
||||
The offloaded model we want to save
|
||||
"""
|
||||
from ..hooks import AlignDevicesHook
|
||||
|
||||
state_dict = {}
|
||||
placeholders = set()
|
||||
for name, module in model.named_modules():
|
||||
if name == "":
|
||||
continue
|
||||
if hasattr(module, "_hf_hook") and isinstance(module._hf_hook, AlignDevicesHook) and module._hf_hook.offload:
|
||||
original_device = module._hf_hook.execution_device
|
||||
# assign hook execution device to cpu
|
||||
module._hf_hook.execution_device = "cpu"
|
||||
# onload meta tensors to execution device
|
||||
try:
|
||||
module._hf_hook.pre_forward(module)
|
||||
except MemoryError:
|
||||
raise MemoryError("Offloaded module must fit in CPU memory to call save_model!") from None
|
||||
module_state_dict = module.state_dict()
|
||||
# offload meta tensors from cpu
|
||||
module._hf_hook.post_forward(module, torch.tensor([]))
|
||||
# re-assign hook to original execution device
|
||||
module._hf_hook.execution_device = original_device
|
||||
else:
|
||||
module_state_dict = module.state_dict()
|
||||
|
||||
for key in module_state_dict:
|
||||
# ignore placeholder parameters that are still on the meta device
|
||||
if module_state_dict[key].device == torch.device("meta"):
|
||||
placeholders.add(name + f".{key}")
|
||||
continue
|
||||
params = module_state_dict[key]
|
||||
state_dict[name + f".{key}"] = params
|
||||
for key in placeholders.copy():
|
||||
if key in state_dict:
|
||||
placeholders.remove(key)
|
||||
if placeholders:
|
||||
logger.warning(f"The following tensors were not saved because they were still on meta device: {placeholders}")
|
||||
|
||||
return state_dict
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def load_checkpoint_in_model(
|
||||
model: nn.Module,
|
||||
checkpoint: Union[str, os.PathLike],
|
||||
@ -1286,8 +1422,8 @@ def load_checkpoint_in_model(
|
||||
logger.warn(
|
||||
"The model weights are not tied. Please use the `tie_weights` method before using the `infer_auto_device` function."
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
check_tied_parameters_on_same_device(tied_params, device_map)
|
||||
if device_map is not None:
|
||||
check_tied_parameters_on_same_device(tied_params, device_map)
|
||||
|
||||
if offload_folder is None and device_map is not None and "disk" in device_map.values():
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
@ -1458,6 +1594,7 @@ def get_mixed_precision_context_manager(native_amp: bool = False, autocast_kwarg
|
||||
DistributedType.MULTI_GPU,
|
||||
DistributedType.MULTI_NPU,
|
||||
DistributedType.MULTI_XPU,
|
||||
DistributedType.FSDP,
|
||||
]:
|
||||
return torch.autocast(device_type=state.device.type, dtype=torch.bfloat16, **autocast_kwargs)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -19,8 +19,7 @@ from typing import Dict, List, Optional, Union
|
||||
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
from .imports import is_safetensors_available
|
||||
from safetensors import safe_open
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def offload_weight(weight, weight_name, offload_folder, index=None):
|
||||
@ -165,19 +164,22 @@ class OffloadedWeightsLoader(Mapping):
|
||||
return self.state_dict[key]
|
||||
weight_info = self.index[key]
|
||||
if weight_info.get("safetensors_file") is not None:
|
||||
if not is_safetensors_available():
|
||||
raise ImportError("These offloaded weights require the use of safetensors: `pip install safetensors`.")
|
||||
|
||||
from safetensors import safe_open
|
||||
|
||||
device = "cpu" if self.device is None else self.device
|
||||
with safe_open(weight_info["safetensors_file"], framework="pt", device=device) as f:
|
||||
tensor = f.get_tensor(weight_info.get("weight_name", key))
|
||||
tensor = None
|
||||
try:
|
||||
with safe_open(weight_info["safetensors_file"], framework="pt", device=device) as f:
|
||||
tensor = f.get_tensor(weight_info.get("weight_name", key))
|
||||
except TypeError:
|
||||
# if failed to get_tensor on the device, such as bf16 on mps, try to load it on CPU first
|
||||
with safe_open(weight_info["safetensors_file"], framework="pt", device="cpu") as f:
|
||||
tensor = f.get_tensor(weight_info.get("weight_name", key))
|
||||
|
||||
if "dtype" in weight_info:
|
||||
return tensor.to(getattr(torch, weight_info["dtype"]))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
return tensor
|
||||
tensor = tensor.to(getattr(torch, weight_info["dtype"]))
|
||||
|
||||
if tensor.device != torch.device(device):
|
||||
tensor = tensor.to(device)
|
||||
return tensor
|
||||
|
||||
weight_file = os.path.join(self.save_folder, f"{key}.dat")
|
||||
return load_offloaded_weight(weight_file, weight_info)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -17,6 +17,7 @@ A set of basic tensor ops compatible with tpu, gpu, and multigpu
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
import pickle
|
||||
import warnings
|
||||
from functools import update_wrapper, wraps
|
||||
from typing import Any, Mapping
|
||||
|
||||
@ -25,7 +26,7 @@ import torch
|
||||
from ..state import PartialState
|
||||
from .constants import TORCH_DISTRIBUTED_OPERATION_TYPES
|
||||
from .dataclasses import DistributedType, TensorInformation
|
||||
from .imports import is_torch_distributed_available, is_tpu_available
|
||||
from .imports import is_npu_available, is_torch_distributed_available, is_torch_version, is_tpu_available
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if is_tpu_available(check_device=False):
|
||||
@ -163,6 +164,9 @@ def send_to_device(tensor, device, non_blocking=False, skip_keys=None):
|
||||
}
|
||||
)
|
||||
elif hasattr(tensor, "to"):
|
||||
# `torch.Tensor.to(<int num>)` is not supported by `torch_npu` (see this [issue](https://github.com/Ascend/pytorch/issues/16)).
|
||||
if is_npu_available() and isinstance(device, int):
|
||||
device = f"npu:{device}"
|
||||
try:
|
||||
return tensor.to(device, non_blocking=non_blocking)
|
||||
except TypeError: # .to() doesn't accept non_blocking as kwarg
|
||||
@ -231,6 +235,9 @@ def find_batch_size(data):
|
||||
Returns:
|
||||
`int`: The batch size.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if isinstance(data, (tuple, list, Mapping)) and (len(data) == 0):
|
||||
raise ValueError(f"Cannot find the batch size from empty {type(data)}.")
|
||||
|
||||
if isinstance(data, (tuple, list)):
|
||||
return find_batch_size(data[0])
|
||||
elif isinstance(data, Mapping):
|
||||
@ -280,6 +287,12 @@ def _tpu_gather(tensor):
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _gpu_gather(tensor):
|
||||
state = PartialState()
|
||||
if is_torch_version(">=", "1.13"):
|
||||
gather_op = torch.distributed.all_gather_into_tensor
|
||||
else:
|
||||
gather_op = torch.distributed._all_gather_base
|
||||
|
||||
def _gpu_gather_one(tensor):
|
||||
if tensor.ndim == 0:
|
||||
tensor = tensor.clone()[None]
|
||||
@ -287,9 +300,26 @@ def _gpu_gather(tensor):
|
||||
# Can only gather contiguous tensors
|
||||
if not tensor.is_contiguous():
|
||||
tensor = tensor.contiguous()
|
||||
output_tensors = [torch.empty_like(tensor) for _ in range(torch.distributed.get_world_size())]
|
||||
torch.distributed.all_gather(output_tensors, tensor)
|
||||
return torch.cat(output_tensors, dim=0)
|
||||
|
||||
if state.backend is not None and state.backend != "gloo":
|
||||
# We use `empty` as `all_gather_into_tensor` slightly
|
||||
# differs from `all_gather` for better efficiency,
|
||||
# and we rely on the number of items in the tensor
|
||||
# rather than its direct shape
|
||||
output_tensors = torch.empty(
|
||||
state.num_processes * tensor.numel(),
|
||||
dtype=tensor.dtype,
|
||||
device=state.device,
|
||||
)
|
||||
gather_op(output_tensors, tensor)
|
||||
return output_tensors.view(-1, *tensor.size()[1:])
|
||||
else:
|
||||
# a backend of `None` is always CPU
|
||||
# also gloo does not support `all_gather_into_tensor`,
|
||||
# which will result in a larger memory overhead for the op
|
||||
output_tensors = [torch.empty_like(tensor) for _ in range(state.num_processes)]
|
||||
torch.distributed.all_gather(output_tensors, tensor)
|
||||
return torch.cat(output_tensors, dim=0)
|
||||
|
||||
return recursively_apply(_gpu_gather_one, tensor, error_on_other_type=True)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -317,6 +347,11 @@ def verify_operation(function):
|
||||
tensor = kwargs["tensor"]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
tensor = args[0]
|
||||
if PartialState().device.type != find_device(tensor).type:
|
||||
raise DistributedOperationException(
|
||||
f"One or more of the tensors passed to {operation} were not on the {tensor.device.type} while the `Accelerator` is configured for {PartialState().device.type}. "
|
||||
f"Please move it to the {PartialState().device.type} before calling {operation}."
|
||||
)
|
||||
shapes = get_shape(tensor)
|
||||
output = gather_object([shapes])
|
||||
if output[0] is not None:
|
||||
@ -499,6 +534,10 @@ def concatenate(data, dim=0):
|
||||
return torch.cat(data, dim=dim)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class CannotPadNestedTensorWarning(UserWarning):
|
||||
pass
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@chained_operation
|
||||
def pad_across_processes(tensor, dim=0, pad_index=0, pad_first=False):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
@ -517,6 +556,12 @@ def pad_across_processes(tensor, dim=0, pad_index=0, pad_first=False):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
def _pad_across_processes(tensor, dim=0, pad_index=0, pad_first=False):
|
||||
if getattr(tensor, "is_nested", False):
|
||||
warnings.warn(
|
||||
"Cannot pad nested tensors without more information. Leaving unprocessed.",
|
||||
CannotPadNestedTensorWarning,
|
||||
)
|
||||
return tensor
|
||||
if dim >= len(tensor.shape):
|
||||
return tensor
|
||||
|
||||
@ -570,7 +615,13 @@ def reduce(tensor, reduction="mean", scale=1.0):
|
||||
if state.distributed_type == DistributedType.NO:
|
||||
return cloned_tensor
|
||||
if state.distributed_type == DistributedType.TPU:
|
||||
xm.all_reduce("sum", cloned_tensor, scale)
|
||||
# Some processes may have different HLO graphs than other
|
||||
# processes, for example in the breakpoint API
|
||||
# accelerator.set_trigger(). Use mark_step to make HLOs
|
||||
# the same on all processes.
|
||||
xm.mark_step()
|
||||
xm.all_reduce(xm.REDUCE_SUM, [cloned_tensor], scale)
|
||||
xm.mark_step()
|
||||
elif state.distributed_type.value in TORCH_DISTRIBUTED_OPERATION_TYPES:
|
||||
torch.distributed.all_reduce(cloned_tensor, ReduceOp.SUM)
|
||||
if reduction == "mean":
|
||||
|
||||
@ -12,28 +12,37 @@
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
import collections
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import platform
|
||||
import re
|
||||
import socket
|
||||
from contextlib import contextmanager
|
||||
from functools import partial
|
||||
from types import MethodType
|
||||
from typing import OrderedDict
|
||||
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from packaging.version import Version
|
||||
from safetensors.torch import save_file as safe_save_file
|
||||
|
||||
from ..commands.config.default import write_basic_config # noqa: F401
|
||||
from ..logging import get_logger
|
||||
from ..state import PartialState
|
||||
from .constants import FSDP_PYTORCH_VERSION
|
||||
from .dataclasses import DistributedType
|
||||
from .imports import is_deepspeed_available, is_safetensors_available, is_tpu_available
|
||||
from .imports import is_deepspeed_available, is_torch_distributed_available, is_tpu_available
|
||||
from .modeling import id_tensor_storage
|
||||
from .transformer_engine import convert_model
|
||||
from .versions import is_torch_version
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
logger = get_logger(__name__)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if is_tpu_available(check_device=False):
|
||||
import torch_xla.core.xla_model as xm
|
||||
|
||||
if is_safetensors_available():
|
||||
from safetensors.torch import save_file as safe_save_file
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def is_compiled_module(module):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
@ -69,7 +78,7 @@ def extract_model_from_parallel(model, keep_fp32_wrapper: bool = True):
|
||||
|
||||
options += (DeepSpeedEngine,)
|
||||
|
||||
if is_torch_version(">=", FSDP_PYTORCH_VERSION):
|
||||
if is_torch_version(">=", FSDP_PYTORCH_VERSION) and is_torch_distributed_available():
|
||||
from torch.distributed.fsdp.fully_sharded_data_parallel import FullyShardedDataParallel as FSDP
|
||||
|
||||
options += (FSDP,)
|
||||
@ -109,22 +118,69 @@ def wait_for_everyone():
|
||||
PartialState().wait_for_everyone()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def save(obj, f, safe_serialization=False):
|
||||
def clean_state_dict_for_safetensors(state_dict: dict):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Cleans the state dictionary from a model and removes tensor aliasing if present.
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
state_dict (`dict`):
|
||||
The state dictionary from a model
|
||||
"""
|
||||
ptrs = collections.defaultdict(list)
|
||||
# When bnb serialization is used, weights in state dict can be strings
|
||||
for name, tensor in state_dict.items():
|
||||
if not isinstance(tensor, str):
|
||||
ptrs[id_tensor_storage(tensor)].append(name)
|
||||
|
||||
# These are all pointers of tensors with shared memory
|
||||
shared_ptrs = {ptr: names for ptr, names in ptrs.items() if len(names) > 1}
|
||||
warn_names = set()
|
||||
for names in shared_ptrs.values():
|
||||
# When not all duplicates have been cleaned, we still remove those keys but put a clear warning.
|
||||
# If the link between tensors was done at runtime then `from_pretrained` will not get
|
||||
# the key back leading to random tensor. A proper warning will be shown
|
||||
# during reload (if applicable), but since the file is not necessarily compatible with
|
||||
# the config, better show a proper warning.
|
||||
found_names = [name for name in names if name in state_dict]
|
||||
warn_names.update(found_names[1:])
|
||||
for name in found_names[1:]:
|
||||
del state_dict[name]
|
||||
if len(warn_names) > 0:
|
||||
logger.warning(
|
||||
f"Removed shared tensor {warn_names} while saving. This should be OK, but check by verifying that you don't receive any warning while reloading",
|
||||
)
|
||||
state_dict = {k: v.contiguous() if isinstance(v, torch.Tensor) else v for k, v in state_dict.items()}
|
||||
return state_dict
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def save(obj, f, save_on_each_node: bool = False, safe_serialization: bool = False):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
Save the data to disk. Use in place of `torch.save()`.
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
obj: The data to save
|
||||
f: The file (or file-like object) to use to save the data
|
||||
safe_serialization (`bool`, *optional*, defaults to `False`): Whether to save `obj` using `safetensors`
|
||||
obj:
|
||||
The data to save
|
||||
f:
|
||||
The file (or file-like object) to use to save the data
|
||||
save_on_each_node (`bool`, *optional*, defaults to `False`):
|
||||
Whether to only save on the global main process
|
||||
safe_serialization (`bool`, *optional*, defaults to `False`):
|
||||
Whether to save `obj` using `safetensors` or the traditional PyTorch way (that uses `pickle`).
|
||||
"""
|
||||
# Check if it's a model and remove duplicates
|
||||
if safe_serialization:
|
||||
save_func = partial(safe_save_file, metadata={"format": "pt"})
|
||||
if isinstance(obj, OrderedDict):
|
||||
obj = clean_state_dict_for_safetensors(obj)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
save_func = torch.save
|
||||
|
||||
if PartialState().distributed_type == DistributedType.TPU:
|
||||
xm.save(obj, f)
|
||||
elif PartialState().local_process_index == 0:
|
||||
if safe_serialization:
|
||||
safe_save_file(obj, f, metadata={"format": "pt"})
|
||||
else:
|
||||
torch.save(obj, f)
|
||||
elif PartialState().is_main_process and not save_on_each_node:
|
||||
save_func(obj, f)
|
||||
elif PartialState().is_local_main_process and save_on_each_node:
|
||||
save_func(obj, f)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@contextmanager
|
||||
@ -246,3 +302,21 @@ def convert_bytes(size):
|
||||
size /= 1024.0
|
||||
|
||||
return f"{round(size, 2)} PB"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def check_os_kernel():
|
||||
"""Warns if the kernel version is below the recommended minimum on Linux."""
|
||||
# see issue #1929
|
||||
info = platform.uname()
|
||||
system = info.system
|
||||
if system != "Linux":
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
||||
_, version, *_ = re.split(r"(\d+\.\d+\.\d+)", info.release)
|
||||
min_version = "5.5.0"
|
||||
if Version(version) < Version(min_version):
|
||||
msg = (
|
||||
f"Detected kernel version {version}, which is below the recommended minimum of {min_version}; this can "
|
||||
"cause the process to hang. It is recommended to upgrade the kernel to the minimum version or higher."
|
||||
)
|
||||
logger.warning(msg, main_process_only=True)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -33,5 +33,5 @@ def tqdm(main_process_only: bool = True, *args, **kwargs):
|
||||
raise ImportError("Accelerate's `tqdm` module requires `tqdm` to be installed. Please run `pip install tqdm`.")
|
||||
disable = False
|
||||
if main_process_only:
|
||||
disable = PartialState().local_process_index == 0
|
||||
disable = PartialState().local_process_index != 0
|
||||
return _tqdm(*args, **kwargs, disable=disable)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -36,15 +36,15 @@ def convert_model(model, to_transformer_engine=True, _convert_linear=True, _conv
|
||||
te_module = te.Linear(
|
||||
module.in_features, module.out_features, bias=has_bias, params_dtype=module.weight.dtype
|
||||
)
|
||||
te_module.weight.data = module.weight.data.clone()
|
||||
te_module.weight.copy_(module.weight)
|
||||
if has_bias:
|
||||
te_module.bias.data = module.bias.data.clone()
|
||||
te_module.bias.copy_(module.bias)
|
||||
|
||||
setattr(model, name, te_module)
|
||||
elif isinstance(module, nn.LayerNorm) and to_transformer_engine and _convert_ln:
|
||||
te_module = te.LayerNorm(module.normalized_shape[0], eps=module.eps, params_dtype=module.weight.dtype)
|
||||
te_module.weight.data = module.weight.data.clone()
|
||||
te_module.bias.data = module.bias.data.clone()
|
||||
te_module.weight.copy_(module.weight)
|
||||
te_module.bias.copy_(module.bias)
|
||||
|
||||
setattr(model, name, te_module)
|
||||
elif isinstance(module, te.Linear) and not to_transformer_engine and _convert_linear:
|
||||
@ -52,15 +52,15 @@ def convert_model(model, to_transformer_engine=True, _convert_linear=True, _conv
|
||||
new_module = nn.Linear(
|
||||
module.in_features, module.out_features, bias=has_bias, params_dtype=module.weight.dtype
|
||||
)
|
||||
new_module.weight.data = module.weight.data.clone()
|
||||
new_module.weight.copy_(module.weight)
|
||||
if has_bias:
|
||||
new_module.bias.data = module.bias.data.clone()
|
||||
new_module.bias.copy_(module.bias)
|
||||
|
||||
setattr(model, name, new_module)
|
||||
elif isinstance(module, te.LayerNorm) and not to_transformer_engine and _convert_ln:
|
||||
new_module = nn.LayerNorm(module.normalized_shape[0], eps=module.eps, params_dtype=module.weight.dtype)
|
||||
new_module.weight.data = module.weight.data.clone()
|
||||
new_module.bias.data = module.bias.data.clone()
|
||||
new_module.weight.copy_(module.weight)
|
||||
new_module.bias.copy_(module.bias)
|
||||
|
||||
setattr(model, name, new_module)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
@ -79,6 +79,6 @@ def has_transformer_engine_layers(model):
|
||||
if not is_fp8_available():
|
||||
raise ImportError("Using `has_transformer_engine_layers` requires transformer_engine to be installed.")
|
||||
for m in model.modules():
|
||||
if isinstance(m, (te.LayerNorm, te.Linear)):
|
||||
if isinstance(m, (te.LayerNorm, te.Linear, te.TransformerLayer)):
|
||||
return True
|
||||
return False
|
||||
|
||||
@ -23,25 +23,26 @@ from pathlib import Path
|
||||
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from parameterized import parameterized
|
||||
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
|
||||
from transformers import AutoModel, AutoModelForCausalLM, get_scheduler
|
||||
from torch.utils.data import BatchSampler, DataLoader, RandomSampler, SequentialSampler
|
||||
from transformers import AutoConfig, AutoModel, AutoModelForCausalLM, get_scheduler
|
||||
from transformers.testing_utils import mockenv_context
|
||||
from transformers.trainer_utils import set_seed
|
||||
from transformers.utils import is_torch_bf16_available
|
||||
|
||||
import accelerate
|
||||
from accelerate.accelerator import Accelerator
|
||||
from accelerate.scheduler import AcceleratedScheduler
|
||||
from accelerate.state import AcceleratorState
|
||||
from accelerate.test_utils.testing import (
|
||||
AccelerateTestCase,
|
||||
TempDirTestCase,
|
||||
execute_subprocess_async,
|
||||
require_cuda,
|
||||
require_deepspeed,
|
||||
require_multi_gpu,
|
||||
require_multi_device,
|
||||
require_non_cpu,
|
||||
slow,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from accelerate.test_utils.training import RegressionDataset
|
||||
from accelerate.test_utils.training import RegressionDataset, RegressionModel
|
||||
from accelerate.utils.dataclasses import DeepSpeedPlugin
|
||||
from accelerate.utils.deepspeed import (
|
||||
DeepSpeedEngineWrapper,
|
||||
@ -55,9 +56,8 @@ from accelerate.utils.other import patch_environment
|
||||
|
||||
set_seed(42)
|
||||
|
||||
T5_SMALL = "t5-small"
|
||||
T5_TINY = "patrickvonplaten/t5-tiny-random"
|
||||
GPT2_TINY = "sshleifer/tiny-gpt2"
|
||||
MOBILEVIT = "apple/mobilevit-xx-small"
|
||||
|
||||
ZERO2 = "zero2"
|
||||
ZERO3 = "zero3"
|
||||
@ -70,9 +70,15 @@ CUSTOM_SCHEDULER = "custom_scheduler"
|
||||
DS_OPTIMIZER = "deepspeed_optimizer"
|
||||
DS_SCHEDULER = "deepspeed_scheduler"
|
||||
|
||||
NO_CONFIG = "no_config"
|
||||
CONFIG_WITH_NO_HIDDEN_SIZE = "config_with_no_hidden_size"
|
||||
CONFIG_WITH_HIDDEN_SIZE = "config_with_hidden_size"
|
||||
CONFIG_WITH_HIDDEN_SIZES = "config_with_hidden_sizes"
|
||||
|
||||
stages = [ZERO2, ZERO3]
|
||||
optims = [CUSTOM_OPTIMIZER, DS_OPTIMIZER]
|
||||
schedulers = [CUSTOM_SCHEDULER, DS_SCHEDULER]
|
||||
model_types = [NO_CONFIG, CONFIG_WITH_NO_HIDDEN_SIZE, CONFIG_WITH_HIDDEN_SIZE, CONFIG_WITH_HIDDEN_SIZES]
|
||||
if is_torch_bf16_available():
|
||||
dtypes = [FP16, BF16]
|
||||
else:
|
||||
@ -91,8 +97,13 @@ params = list(itertools.product(stages, dtypes))
|
||||
optim_scheduler_params = list(itertools.product(optims, schedulers))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class DummyConfig:
|
||||
def __init__(self):
|
||||
self._name_or_path = "dummy"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@require_deepspeed
|
||||
@require_cuda
|
||||
@require_non_cpu
|
||||
class DeepSpeedConfigIntegration(AccelerateTestCase):
|
||||
def setUp(self):
|
||||
super().setUp()
|
||||
@ -339,8 +350,9 @@ class DeepSpeedConfigIntegration(AccelerateTestCase):
|
||||
with self.assertRaises(ValueError) as cm:
|
||||
model, optimizer, lr_scheduler = accelerator.prepare(model, optimizer, lr_scheduler)
|
||||
self.assertTrue(
|
||||
"When using DeepSpeed `accelerate.prepare()` requires you to pass at least one of training or evaluation dataloaders "
|
||||
"or alternatively set an integer value in `train_micro_batch_size_per_gpu` in the deepspeed config file"
|
||||
"When using DeepSpeed, `accelerate.prepare()` requires you to pass at least one of training or evaluation dataloaders "
|
||||
"with `batch_size` attribute returning an integer value "
|
||||
"or alternatively set an integer value in `train_micro_batch_size_per_gpu` in the deepspeed config file "
|
||||
"or assign integer value to `AcceleratorState().deepspeed_plugin.deepspeed_config['train_micro_batch_size_per_gpu']`."
|
||||
in str(cm.exception)
|
||||
)
|
||||
@ -352,7 +364,7 @@ class DeepSpeedConfigIntegration(AccelerateTestCase):
|
||||
self.assertTrue(accelerator.deepspeed_config["train_batch_size"], 16)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(type(model), DeepSpeedEngine)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(type(optimizer), DeepSpeedOptimizerWrapper)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(type(lr_scheduler), DeepSpeedSchedulerWrapper)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(type(lr_scheduler), AcceleratedScheduler)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(type(accelerator.deepspeed_engine_wrapped), DeepSpeedEngineWrapper)
|
||||
|
||||
elif optim_type == DS_OPTIMIZER and scheduler_type == DS_SCHEDULER:
|
||||
@ -508,6 +520,47 @@ class DeepSpeedConfigIntegration(AccelerateTestCase):
|
||||
model, dummy_optimizer, train_dataloader, eval_dataloader, dummy_lr_scheduler
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_dataloader_with_batch_sampler(self):
|
||||
deepspeed_plugin = DeepSpeedPlugin(
|
||||
gradient_accumulation_steps=1,
|
||||
gradient_clipping=1.0,
|
||||
zero_stage=2,
|
||||
offload_optimizer_device="cpu",
|
||||
offload_param_device="cpu",
|
||||
zero3_save_16bit_model=False,
|
||||
zero3_init_flag=False,
|
||||
)
|
||||
with mockenv_context(**self.dist_env):
|
||||
accelerator = Accelerator(mixed_precision="fp16", deepspeed_plugin=deepspeed_plugin)
|
||||
|
||||
train_set = RegressionDataset(length=80)
|
||||
eval_set = RegressionDataset(length=20)
|
||||
train_dataloader = DataLoader(
|
||||
train_set, batch_sampler=BatchSampler(RandomSampler(train_set), batch_size=10, drop_last=False)
|
||||
)
|
||||
eval_dataloader = DataLoader(
|
||||
eval_set, batch_sampler=BatchSampler(SequentialSampler(eval_set), batch_size=10, drop_last=False)
|
||||
)
|
||||
model = AutoModel.from_pretrained(GPT2_TINY)
|
||||
optimizer = torch.optim.AdamW(model.parameters(), lr=5e-5)
|
||||
lr_scheduler = get_scheduler(
|
||||
name="linear",
|
||||
optimizer=optimizer,
|
||||
num_warmup_steps=0,
|
||||
num_training_steps=1000,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
with self.assertRaises(ValueError) as cm:
|
||||
model, optimizer, train_dataloader, eval_dataloader, lr_scheduler = accelerator.prepare(
|
||||
model, optimizer, train_dataloader, eval_dataloader, lr_scheduler
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.assertTrue(
|
||||
"At least one of the dataloaders passed to `accelerate.prepare()` has `None` as batch size. "
|
||||
"Please set an integer value in `train_micro_batch_size_per_gpu` in the deepspeed config file "
|
||||
"or assign integer value to `AcceleratorState().deepspeed_plugin.deepspeed_config['train_micro_batch_size_per_gpu']`."
|
||||
in str(cm.exception)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_save_checkpoints(self):
|
||||
deepspeed_plugin = DeepSpeedPlugin(
|
||||
hf_ds_config=self.ds_config_file[ZERO3],
|
||||
@ -606,6 +659,70 @@ class DeepSpeedConfigIntegration(AccelerateTestCase):
|
||||
accelerator.deepspeed_config["zero_optimization"]["stage3_gather_16bit_weights_on_model_save"]
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@parameterized.expand(model_types, name_func=parameterized_custom_name_func)
|
||||
def test_autofill_comm_buffers_dsconfig(self, model_type):
|
||||
deepspeed_plugin = DeepSpeedPlugin(
|
||||
hf_ds_config=self.ds_config_file[ZERO3],
|
||||
zero3_init_flag=True,
|
||||
)
|
||||
del deepspeed_plugin.deepspeed_config["bf16"]
|
||||
del deepspeed_plugin.deepspeed_config["fp16"]
|
||||
del deepspeed_plugin.deepspeed_config["optimizer"]
|
||||
del deepspeed_plugin.deepspeed_config["scheduler"]
|
||||
with mockenv_context(**self.dist_env):
|
||||
accelerator = Accelerator(mixed_precision="fp16", deepspeed_plugin=deepspeed_plugin)
|
||||
|
||||
train_set = RegressionDataset(length=80)
|
||||
eval_set = RegressionDataset(length=20)
|
||||
train_dataloader = DataLoader(train_set, batch_size=16, shuffle=True)
|
||||
eval_dataloader = DataLoader(eval_set, batch_size=32, shuffle=False)
|
||||
model = RegressionModel()
|
||||
if model_type == CONFIG_WITH_NO_HIDDEN_SIZE:
|
||||
model.config = DummyConfig()
|
||||
elif model_type == CONFIG_WITH_HIDDEN_SIZE:
|
||||
model.config = AutoConfig.from_pretrained(GPT2_TINY)
|
||||
hidden_size = model.config.hidden_size
|
||||
elif model_type == CONFIG_WITH_HIDDEN_SIZES:
|
||||
model.config = AutoConfig.from_pretrained(MOBILEVIT)
|
||||
hidden_size = max(model.config.hidden_sizes)
|
||||
optimizer = torch.optim.AdamW(model.parameters(), lr=5e-5)
|
||||
lr_scheduler = get_scheduler(
|
||||
name="linear",
|
||||
optimizer=optimizer,
|
||||
num_warmup_steps=0,
|
||||
num_training_steps=1000,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
if model_type == NO_CONFIG:
|
||||
with self.assertRaises(ValueError) as cm:
|
||||
model, optimizer, train_dataloader, eval_dataloader, lr_scheduler = accelerator.prepare(
|
||||
model, optimizer, train_dataloader, eval_dataloader, lr_scheduler
|
||||
)
|
||||
msg = "Can't find `model.config` entry"
|
||||
self.assertTrue(msg in str(cm.exception))
|
||||
elif model_type == CONFIG_WITH_NO_HIDDEN_SIZE:
|
||||
with self.assertRaises(ValueError) as cm:
|
||||
model, optimizer, train_dataloader, eval_dataloader, lr_scheduler = accelerator.prepare(
|
||||
model, optimizer, train_dataloader, eval_dataloader, lr_scheduler
|
||||
)
|
||||
msg = "Can find neither `model.config.hidden_size` nor `model.config.hidden_sizes`"
|
||||
self.assertTrue(msg in str(cm.exception))
|
||||
else:
|
||||
model, optimizer, train_dataloader, eval_dataloader, lr_scheduler = accelerator.prepare(
|
||||
model, optimizer, train_dataloader, eval_dataloader, lr_scheduler
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(
|
||||
accelerator.deepspeed_config["zero_optimization"]["reduce_bucket_size"], hidden_size * hidden_size
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(
|
||||
accelerator.deepspeed_config["zero_optimization"]["stage3_prefetch_bucket_size"],
|
||||
0.9 * hidden_size * hidden_size,
|
||||
)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(
|
||||
accelerator.deepspeed_config["zero_optimization"]["stage3_param_persistence_threshold"],
|
||||
10 * hidden_size,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@parameterized.expand([FP16, BF16], name_func=parameterized_custom_name_func)
|
||||
def test_autofill_dsconfig_from_ds_plugin(self, dtype):
|
||||
ds_config = self.ds_config_dict["zero3"]
|
||||
@ -753,7 +870,7 @@ class DeepSpeedConfigIntegration(AccelerateTestCase):
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@require_deepspeed
|
||||
@require_multi_gpu
|
||||
@require_multi_device
|
||||
@slow
|
||||
class DeepSpeedIntegrationTest(TempDirTestCase):
|
||||
def setUp(self):
|
||||
@ -945,3 +1062,27 @@ class DeepSpeedIntegrationTest(TempDirTestCase):
|
||||
)
|
||||
with patch_environment(omp_num_threads=1):
|
||||
execute_subprocess_async(cmd_stage, env=os.environ.copy())
|
||||
|
||||
def test_lr_scheduler(self):
|
||||
self.test_file_path = os.path.join(self.test_scripts_folder, "test_performance.py")
|
||||
cmd = [
|
||||
"accelerate",
|
||||
"launch",
|
||||
"--num_processes=2",
|
||||
"--num_machines=1",
|
||||
"--machine_rank=0",
|
||||
"--mixed_precision=no",
|
||||
"--use_deepspeed",
|
||||
"--gradient_accumulation_steps=1",
|
||||
"--gradient_clipping=1",
|
||||
"--zero3_init_flag=True",
|
||||
"--zero3_save_16bit_model=True",
|
||||
"--zero_stage=3",
|
||||
"--offload_optimizer_device=none",
|
||||
"--offload_param_device=none",
|
||||
self.test_file_path,
|
||||
f"--output_dir={self.tmpdir}",
|
||||
f"--performance_lower_bound={self.performance_lower_bound}",
|
||||
]
|
||||
with patch_environment(omp_num_threads=1):
|
||||
execute_subprocess_async(cmd, env=os.environ.copy())
|
||||
|
||||
@ -28,9 +28,9 @@ from accelerate.test_utils.testing import (
|
||||
AccelerateTestCase,
|
||||
TempDirTestCase,
|
||||
execute_subprocess_async,
|
||||
require_cuda,
|
||||
require_fsdp,
|
||||
require_multi_gpu,
|
||||
require_multi_device,
|
||||
require_non_cpu,
|
||||
slow,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from accelerate.utils.constants import (
|
||||
@ -52,7 +52,7 @@ dtypes = [FP16, BF16]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@require_fsdp
|
||||
@require_cuda
|
||||
@require_non_cpu
|
||||
class FSDPPluginIntegration(AccelerateTestCase):
|
||||
def setUp(self):
|
||||
super().setUp()
|
||||
@ -69,10 +69,18 @@ class FSDPPluginIntegration(AccelerateTestCase):
|
||||
def test_sharding_strategy(self):
|
||||
from torch.distributed.fsdp.fully_sharded_data_parallel import ShardingStrategy
|
||||
|
||||
# check that giving enums works fine
|
||||
for i, strategy in enumerate(FSDP_SHARDING_STRATEGY):
|
||||
env = self.dist_env.copy()
|
||||
env["FSDP_SHARDING_STRATEGY"] = f"{i + 1}"
|
||||
env["FSDP_SHARDING_STRATEGY_NAME"] = strategy
|
||||
with mockenv_context(**env):
|
||||
fsdp_plugin = FullyShardedDataParallelPlugin()
|
||||
self.assertEqual(fsdp_plugin.sharding_strategy, ShardingStrategy(i + 1))
|
||||
|
||||
# check that giving names works fine
|
||||
for i, strategy in enumerate(FSDP_SHARDING_STRATEGY):
|
||||
env = self.dist_env.copy()
|
||||
env["FSDP_SHARDING_STRATEGY"] = strategy
|
||||
with mockenv_context(**env):
|
||||
fsdp_plugin = FullyShardedDataParallelPlugin()
|
||||
self.assertEqual(fsdp_plugin.sharding_strategy, ShardingStrategy(i + 1))
|
||||
@ -170,7 +178,7 @@ class FSDPPluginIntegration(AccelerateTestCase):
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@require_fsdp
|
||||
@require_multi_gpu
|
||||
@require_multi_device
|
||||
@slow
|
||||
class FSDPIntegrationTest(TempDirTestCase):
|
||||
def setUp(self):
|
||||
@ -201,7 +209,7 @@ class FSDPIntegrationTest(TempDirTestCase):
|
||||
cmd_config = cmd.copy()
|
||||
for i, strategy in enumerate(FSDP_SHARDING_STRATEGY):
|
||||
if strategy.lower() in config:
|
||||
cmd_config.append(f"--fsdp_sharding_strategy={i+1}")
|
||||
cmd_config.append(f"--fsdp_sharding_strategy={strategy}")
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
if "fp32" in config:
|
||||
@ -247,11 +255,16 @@ class FSDPIntegrationTest(TempDirTestCase):
|
||||
|
||||
for i, strategy in enumerate(FSDP_SHARDING_STRATEGY):
|
||||
cmd_config = cmd.copy()
|
||||
cmd_config.append(f"--fsdp_sharding_strategy={i+1}")
|
||||
cmd_config.append(f"--fsdp_sharding_strategy={strategy}")
|
||||
if strategy != "FULL_SHARD":
|
||||
continue
|
||||
state_dict_config_index = len(cmd_config)
|
||||
for state_dict_type in FSDP_STATE_DICT_TYPE:
|
||||
# Todo: Currently failing for `LOCAL_STATE_DICT` with error
|
||||
# Unexpected key(s) in state_dict: "_fsdp_wrapped_module._flat_param".
|
||||
if state_dict_type == "LOCAL_STATE_DICT":
|
||||
continue
|
||||
|
||||
cmd_config = cmd_config[:state_dict_config_index]
|
||||
cmd_config.append(f"--fsdp_state_dict_type={state_dict_type}")
|
||||
cmd_config.extend(
|
||||
@ -296,7 +309,7 @@ class FSDPIntegrationTest(TempDirTestCase):
|
||||
cmd_config.extend(["--use_fsdp"])
|
||||
for i, strategy in enumerate(FSDP_SHARDING_STRATEGY):
|
||||
if strategy.lower() in spec:
|
||||
cmd_config.append(f"--fsdp_sharding_strategy={i+1}")
|
||||
cmd_config.append(f"--fsdp_sharding_strategy={strategy}")
|
||||
break
|
||||
|
||||
if "cpu_offload" in spec:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -5,12 +5,13 @@ import tempfile
|
||||
from unittest.mock import patch
|
||||
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from parameterized import parameterized
|
||||
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader, TensorDataset
|
||||
|
||||
from accelerate import DistributedType, infer_auto_device_map, init_empty_weights
|
||||
from accelerate import DistributedType, infer_auto_device_map, init_empty_weights, load_checkpoint_and_dispatch
|
||||
from accelerate.accelerator import Accelerator
|
||||
from accelerate.state import GradientState, PartialState
|
||||
from accelerate.test_utils import require_bnb, require_multi_gpu, require_safetensors, slow
|
||||
from accelerate.test_utils import require_bnb, require_multi_gpu, slow
|
||||
from accelerate.test_utils.testing import AccelerateTestCase, require_cuda
|
||||
from accelerate.utils import patch_environment
|
||||
from accelerate.utils.modeling import load_checkpoint_in_model
|
||||
@ -26,6 +27,17 @@ def create_components():
|
||||
return model, optimizer, scheduler, train_dl, valid_dl
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class ModelForTest(torch.nn.Module):
|
||||
def __init__(self):
|
||||
super().__init__()
|
||||
self.linear1 = torch.nn.Linear(3, 4)
|
||||
self.batchnorm = torch.nn.BatchNorm1d(4)
|
||||
self.linear2 = torch.nn.Linear(4, 5)
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, x):
|
||||
return self.linear2(self.batchnorm(self.linear1(x)))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def get_signature(model):
|
||||
return (model.weight.abs().sum() + model.bias.abs().sum()).item()
|
||||
|
||||
@ -35,6 +47,13 @@ def load_random_weights(model):
|
||||
model.load_state_dict(state)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def parameterized_custom_name_func(func, param_num, param):
|
||||
# customize the test name generator function as we want both params to appear in the sub-test
|
||||
# name, as by default it shows only the first param
|
||||
param_based_name = "use_safetensors" if param.args[0] is True else "use_pytorch"
|
||||
return f"{func.__name__}_{param_based_name}"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class AcceleratorTester(AccelerateTestCase):
|
||||
@require_cuda
|
||||
def test_accelerator_can_be_reinstantiated(self):
|
||||
@ -97,7 +116,8 @@ class AcceleratorTester(AccelerateTestCase):
|
||||
accelerator = Accelerator()
|
||||
self.assertEqual(str(accelerator.state.device), "cuda:64")
|
||||
|
||||
def test_save_load_model(self):
|
||||
@parameterized.expand((True, False), name_func=parameterized_custom_name_func)
|
||||
def test_save_load_model(self, use_safetensors):
|
||||
accelerator = Accelerator()
|
||||
model, optimizer, scheduler, train_dl, valid_dl = create_components()
|
||||
accelerator.prepare(model, optimizer, scheduler, train_dl, valid_dl)
|
||||
@ -105,7 +125,7 @@ class AcceleratorTester(AccelerateTestCase):
|
||||
model_signature = get_signature(model)
|
||||
|
||||
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmpdirname:
|
||||
accelerator.save_state(tmpdirname)
|
||||
accelerator.save_state(tmpdirname, safe_serialization=use_safetensors)
|
||||
|
||||
# make sure random weights don't match
|
||||
load_random_weights(model)
|
||||
@ -115,31 +135,40 @@ class AcceleratorTester(AccelerateTestCase):
|
||||
accelerator.load_state(tmpdirname)
|
||||
self.assertTrue(abs(model_signature - get_signature(model)) < 1e-3)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_save_model_pytorch(self):
|
||||
@parameterized.expand([True, False], name_func=parameterized_custom_name_func)
|
||||
def test_save_model(self, use_safetensors):
|
||||
accelerator = Accelerator()
|
||||
model = torch.nn.Linear(10, 10)
|
||||
|
||||
model_signature = get_signature(model)
|
||||
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmpdirname:
|
||||
accelerator.save_model(model, tmpdirname, safe_serialization=False)
|
||||
accelerator.save_model(model, tmpdirname, safe_serialization=use_safetensors)
|
||||
# make sure loaded weights match
|
||||
load_checkpoint_in_model(model, tmpdirname)
|
||||
self.assertTrue(abs(model_signature - get_signature(model)) < 1e-3)
|
||||
|
||||
@require_safetensors
|
||||
def test_save_model_safetensors(self):
|
||||
@parameterized.expand([True, False], name_func=parameterized_custom_name_func)
|
||||
def test_save_model_offload(self, use_safetensors):
|
||||
accelerator = Accelerator()
|
||||
model = torch.nn.Linear(10, 10)
|
||||
|
||||
model_signature = get_signature(model)
|
||||
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmpdirname:
|
||||
accelerator.save_model(model, tmpdirname, safe_serialization=True)
|
||||
device_map = {"linear1": "cpu", "batchnorm": "disk", "linear2": "cpu"}
|
||||
|
||||
# make sure loaded weights match
|
||||
load_checkpoint_in_model(model, tmpdirname)
|
||||
self.assertTrue(abs(model_signature - get_signature(model)) < 1e-3)
|
||||
inputs = torch.randn(3, 3)
|
||||
model = ModelForTest()
|
||||
expected = model(inputs)
|
||||
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmp_dir:
|
||||
accelerator.save_model(model, tmp_dir, safe_serialization=use_safetensors)
|
||||
# load and save offloaded model
|
||||
load_checkpoint_and_dispatch(model, tmp_dir, device_map=device_map, offload_folder=tmp_dir)
|
||||
accelerator.save_model(model, tmp_dir, safe_serialization=use_safetensors)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_save_load_model_with_hooks(self):
|
||||
# load weights that were saved from the offloaded model
|
||||
load_checkpoint_and_dispatch(model, tmp_dir)
|
||||
output = model(inputs)
|
||||
self.assertTrue(torch.allclose(expected, output, atol=1e-5))
|
||||
|
||||
@parameterized.expand([True, False], name_func=parameterized_custom_name_func)
|
||||
def test_save_load_model_with_hooks(self, use_safetensors):
|
||||
accelerator = Accelerator()
|
||||
model, optimizer, scheduler, train_dl, valid_dl = create_components()
|
||||
accelerator.prepare(model, optimizer, scheduler, train_dl, valid_dl)
|
||||
@ -164,7 +193,7 @@ class AcceleratorTester(AccelerateTestCase):
|
||||
load_hook = accelerator.register_load_state_pre_hook(load_config)
|
||||
|
||||
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmpdirname:
|
||||
accelerator.save_state(tmpdirname)
|
||||
accelerator.save_state(tmpdirname, safe_serialization=use_safetensors)
|
||||
|
||||
# make sure random weights don't match with hooks
|
||||
load_random_weights(model)
|
||||
@ -185,7 +214,7 @@ class AcceleratorTester(AccelerateTestCase):
|
||||
load_hook.remove()
|
||||
|
||||
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmpdirname:
|
||||
accelerator.save_state(tmpdirname)
|
||||
accelerator.save_state(tmpdirname, safe_serialization=use_safetensors)
|
||||
|
||||
# make sure random weights don't match with hooks removed
|
||||
load_random_weights(model)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -45,6 +45,33 @@ class ModelForTest(nn.Module):
|
||||
return self.linear2(self.batchnorm(self.linear1(x)))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class LinearWithNonPersistentBuffers(nn.Module):
|
||||
def __init__(self, in_features: int, out_features: int, bias: bool = True, device=None, dtype=None) -> None:
|
||||
factory_kwargs = {"device": device, "dtype": dtype}
|
||||
super().__init__()
|
||||
self.in_features = in_features
|
||||
self.out_features = out_features
|
||||
self.register_buffer("weight", torch.ones((out_features, in_features), **factory_kwargs))
|
||||
if bias:
|
||||
self.register_buffer("bias", torch.ones(out_features, **factory_kwargs), persistent=False)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self.register_buffer("bias", None)
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, input: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
|
||||
return torch.nn.functional.linear(input, self.weight, self.bias)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class ModelForTestNonPersistentBuffers(nn.Module):
|
||||
def __init__(self):
|
||||
super().__init__()
|
||||
self.linear1 = LinearWithNonPersistentBuffers(3, 4)
|
||||
self.batchnorm = nn.BatchNorm1d(4)
|
||||
self.linear2 = LinearWithNonPersistentBuffers(4, 5)
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, x):
|
||||
return self.linear2(self.batchnorm(self.linear1(x)))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class ModelForTestCopy(nn.Module):
|
||||
def __init__(self, id: int):
|
||||
super().__init__()
|
||||
@ -302,6 +329,18 @@ class BigModelingTester(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
output = model(x)
|
||||
self.assertTrue(torch.allclose(expected, output.cpu(), atol=1e-5))
|
||||
|
||||
@require_cuda
|
||||
def test_dispatch_model_with_non_persistent_buffers(self):
|
||||
model = ModelForTestNonPersistentBuffers()
|
||||
device_map = {"linear1": 0, "batchnorm": "cpu", "linear2": "disk"}
|
||||
x = torch.randn(2, 3)
|
||||
expected = model(x)
|
||||
|
||||
with TemporaryDirectory() as tmp_dir:
|
||||
dispatch_model(model, device_map, offload_dir=tmp_dir, offload_buffers=True)
|
||||
output = model(x)
|
||||
self.assertTrue(torch.allclose(expected, output.cpu(), atol=1e-5))
|
||||
|
||||
@require_mps
|
||||
def test_dispatch_model_mps(self):
|
||||
model = ModelForTest()
|
||||
|
||||
@ -24,6 +24,7 @@ import accelerate
|
||||
from accelerate.commands.estimate import estimate_command, estimate_command_parser, gather_data
|
||||
from accelerate.test_utils import execute_subprocess_async
|
||||
from accelerate.test_utils.testing import (
|
||||
require_multi_gpu,
|
||||
require_timm,
|
||||
require_transformers,
|
||||
run_command,
|
||||
@ -40,6 +41,7 @@ class AccelerateLauncherTester(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
|
||||
mod_file = inspect.getfile(accelerate.test_utils)
|
||||
test_file_path = os.path.sep.join(mod_file.split(os.path.sep)[:-1] + ["scripts", "test_cli.py"])
|
||||
notebook_launcher_path = os.path.sep.join(mod_file.split(os.path.sep)[:-1] + ["scripts", "test_notebook.py"])
|
||||
|
||||
base_cmd = ["accelerate", "launch"]
|
||||
config_folder = Path.home() / ".cache/huggingface/accelerate"
|
||||
@ -87,6 +89,16 @@ class AccelerateLauncherTester(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
def test_accelerate_test(self):
|
||||
execute_subprocess_async(["accelerate", "test"], env=os.environ.copy())
|
||||
|
||||
@require_multi_gpu
|
||||
def test_notebook_launcher(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
This test checks a variety of situations and scenarios
|
||||
with the `notebook_launcher`
|
||||
"""
|
||||
cmd = ["python", self.notebook_launcher_path]
|
||||
with patch_environment(omp_num_threads=1, accelerate_num_processes=2):
|
||||
run_command(cmd, env=os.environ.copy())
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class TpuConfigTester(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
@ -269,8 +281,8 @@ class ModelEstimatorTester(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
estimate_command(args)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_gated(self):
|
||||
with self.assertRaises(GatedRepoError, msg="Repo for model `meta-llama/Llama-2-7b` is gated"):
|
||||
args = self.parser.parse_args(["meta-llama/Llama-2-7b"])
|
||||
with self.assertRaises(GatedRepoError, msg="Repo for model `meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-hf` is gated"):
|
||||
args = self.parser.parse_args(["meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-hf"])
|
||||
with patch_environment(hf_hub_disable_implicit_token="1"):
|
||||
estimate_command(args)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -205,7 +205,7 @@ class FeatureExamplesTests(TempDirTestCase):
|
||||
run_command(self._launch_args + testargs)
|
||||
|
||||
@require_trackers
|
||||
@mock.patch.dict(os.environ, {"WANDB_MODE": "offline"})
|
||||
@mock.patch.dict(os.environ, {"WANDB_MODE": "offline", "DVCLIVE_TEST": "true"})
|
||||
def test_tracking(self):
|
||||
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmpdir:
|
||||
testargs = f"""
|
||||
|
||||
@ -92,11 +92,11 @@ class KwargsHandlerTester(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
prefix = "ACCELERATE_DYNAMO_"
|
||||
# nvfuser's dynamo backend name is "nvprims_nvfuser"
|
||||
# use "nvfuser" here to cause exception if this test causes os.environ changed permanently
|
||||
os.environ[prefix + "BACKEND"] = "nvfuser"
|
||||
os.environ[prefix + "BACKEND"] = "aot_ts_nvfuser"
|
||||
os.environ[prefix + "MODE"] = "reduce-overhead"
|
||||
|
||||
dynamo_plugin_kwargs = TorchDynamoPlugin().to_kwargs()
|
||||
self.assertEqual(dynamo_plugin_kwargs, {"backend": "nvfuser", "mode": "reduce-overhead"})
|
||||
self.assertEqual(dynamo_plugin_kwargs, {"backend": "aot_ts_nvfuser", "mode": "reduce-overhead"})
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
|
||||
@ -16,16 +16,15 @@ import inspect
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import unittest
|
||||
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
import accelerate
|
||||
from accelerate import debug_launcher
|
||||
from accelerate.test_utils import (
|
||||
device_count,
|
||||
execute_subprocess_async,
|
||||
require_cpu,
|
||||
require_huggingface_suite,
|
||||
require_multi_gpu,
|
||||
require_single_gpu,
|
||||
require_multi_device,
|
||||
require_single_device,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from accelerate.utils import patch_environment
|
||||
|
||||
@ -50,13 +49,13 @@ class MetricTester(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
def test_metric_cpu_multi(self):
|
||||
debug_launcher(self.test_metrics.main)
|
||||
|
||||
@require_single_gpu
|
||||
def test_metric_gpu(self):
|
||||
@require_single_device
|
||||
def test_metric_accelerator(self):
|
||||
self.test_metrics.main()
|
||||
|
||||
@require_multi_gpu
|
||||
def test_metric_gpu_multi(self):
|
||||
print(f"Found {torch.cuda.device_count()} devices.")
|
||||
cmd = ["torchrun", f"--nproc_per_node={torch.cuda.device_count()}", self.test_file_path]
|
||||
@require_multi_device
|
||||
def test_metric_accelerator_multi(self):
|
||||
print(f"Found {device_count} devices.")
|
||||
cmd = ["torchrun", f"--nproc_per_node={device_count}", self.test_file_path]
|
||||
with patch_environment(omp_num_threads=1, ACCELERATE_LOG_LEVEL="INFO"):
|
||||
execute_subprocess_async(cmd, env=os.environ.copy())
|
||||
|
||||
@ -20,9 +20,10 @@ from collections import OrderedDict
|
||||
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
import torch.nn as nn
|
||||
from safetensors.torch import save_file
|
||||
|
||||
from accelerate import init_empty_weights
|
||||
from accelerate.test_utils import require_cuda, require_huggingface_suite, require_multi_gpu, require_safetensors
|
||||
from accelerate.test_utils import require_cuda, require_huggingface_suite, require_multi_gpu
|
||||
from accelerate.utils.modeling import (
|
||||
check_device_map,
|
||||
clean_device_map,
|
||||
@ -50,6 +51,32 @@ class ModelForTest(nn.Module):
|
||||
return self.linear2(self.batchnorm(self.linear1(x)))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class LinearWithNonPersistentBuffers(nn.Module):
|
||||
def __init__(self, in_features: int, out_features: int, bias: bool = True, device=None, dtype=None) -> None:
|
||||
factory_kwargs = {"device": device, "dtype": dtype}
|
||||
super().__init__()
|
||||
self.in_features = in_features
|
||||
self.out_features = out_features
|
||||
self.register_buffer("weight", torch.empty((out_features, in_features), **factory_kwargs))
|
||||
if bias:
|
||||
self.register_buffer("bias", torch.empty(out_features, **factory_kwargs), persistent=False)
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self.register_buffer("bias", None)
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, input: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
|
||||
return torch.nn.functional.linear(input, self.weight, self.bias)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class ModelSeveralDtypes(nn.Module):
|
||||
def __init__(self):
|
||||
super().__init__()
|
||||
self.register_buffer("int_param", torch.randint(high=10, size=(15, 30)))
|
||||
self.register_parameter("float_param", torch.nn.Parameter(torch.rand(10, 5)))
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, x):
|
||||
return x + 2
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def sequential_model(num_layers):
|
||||
layers = OrderedDict([(f"linear{i}", nn.Linear(1000, 1000)) for i in range(1, num_layers + 1)])
|
||||
return nn.Sequential(layers)
|
||||
@ -186,6 +213,14 @@ class ModelingUtilsTester(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
["linear1.weight", "linear1.bias", "batchnorm.weight", "batchnorm.bias", "linear2.weight", "linear2.bias"],
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
model = LinearWithNonPersistentBuffers(10, 10)
|
||||
|
||||
named_tensors = named_module_tensors(model, include_buffers=True, remove_non_persistent=False)
|
||||
self.assertListEqual([name for name, _ in named_tensors], ["weight", "bias"])
|
||||
|
||||
named_tensors = named_module_tensors(model, include_buffers=True, remove_non_persistent=True)
|
||||
self.assertListEqual([name for name, _ in named_tensors], ["weight"])
|
||||
|
||||
def test_find_tied_parameters(self):
|
||||
model = sequential_model(4)
|
||||
self.assertListEqual(find_tied_parameters(model), [])
|
||||
@ -400,6 +435,19 @@ class ModelingUtilsTester(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
self.assertEqual(model.batchnorm.weight.device, torch.device("cpu"))
|
||||
self.assertEqual(model.linear2.weight.device, torch.device(1))
|
||||
|
||||
def test_load_checkpoint_in_model_dtype(self):
|
||||
with tempfile.NamedTemporaryFile(suffix=".pt") as tmpfile:
|
||||
model = ModelSeveralDtypes()
|
||||
torch.save(model.state_dict(), tmpfile.name)
|
||||
|
||||
new_model = ModelSeveralDtypes()
|
||||
load_checkpoint_in_model(
|
||||
new_model, tmpfile.name, offload_state_dict=True, dtype=torch.float16, device_map={"": "cpu"}
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
self.assertEqual(new_model.int_param.dtype, torch.int64)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(new_model.float_param.dtype, torch.float16)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_clean_device_map(self):
|
||||
# Regroup everything if all is on the same device
|
||||
self.assertDictEqual(clean_device_map({"a": 0, "b": 0, "c": 0}), {"": 0})
|
||||
@ -497,6 +545,36 @@ class ModelingUtilsTester(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
expected = {"linear1": 0, "linear2": 1, "linear3": 0, "linear4": 1}
|
||||
self.assertDictEqual(device_map, expected)
|
||||
|
||||
# With tied weights sharing a same prefix name (`compute.weight` vs `compute.weight_submodule.parameter`)
|
||||
class SubModule(torch.nn.Module):
|
||||
def __init__(self, ref_to_parameter):
|
||||
super().__init__()
|
||||
self.parameter = ref_to_parameter
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, x):
|
||||
return self.x + torch.max(self.parameter)
|
||||
|
||||
class LinearModuleAndSubModule(torch.nn.Linear):
|
||||
def __init__(self, in_features, out_features):
|
||||
super().__init__(in_features, out_features)
|
||||
self.weight_submodule = SubModule(self.weight)
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, x):
|
||||
return torch.nn.functional.linear(self.weight_submodule(x), self.weight)
|
||||
|
||||
class Model(torch.nn.Module):
|
||||
def __init__(self):
|
||||
super().__init__()
|
||||
self.compute = LinearModuleAndSubModule(3, 8)
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, x):
|
||||
return self.compute(x)
|
||||
|
||||
model = Model()
|
||||
|
||||
device_memory = {0: 4, "cpu": 96000} # Low memory device, just to force splitting and trigger the error
|
||||
infer_auto_device_map(model, device_memory)
|
||||
|
||||
@require_huggingface_suite
|
||||
def test_infer_auto_device_map_on_t0pp(self):
|
||||
from transformers import AutoConfig, AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM
|
||||
@ -552,10 +630,7 @@ class ModelingUtilsTester(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
self.assertDictEqual({0: 0, "cpu": 100}, max_memory)
|
||||
|
||||
@require_cuda
|
||||
@require_safetensors
|
||||
def test_load_state_dict(self):
|
||||
from safetensors.torch import save_file
|
||||
|
||||
state_dict = {k: torch.randn(4, 5) for k in ["a", "b", "c"]}
|
||||
device_maps = [{"a": "cpu", "b": 0, "c": "disk"}, {"a": 0, "b": 0, "c": "disk"}, {"a": 0, "b": 0, "c": 0}]
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -21,7 +21,7 @@ import torch
|
||||
import accelerate
|
||||
from accelerate import Accelerator
|
||||
from accelerate.big_modeling import dispatch_model
|
||||
from accelerate.test_utils import assert_exception, execute_subprocess_async, require_multi_gpu, skip
|
||||
from accelerate.test_utils import assert_exception, execute_subprocess_async, require_multi_gpu
|
||||
from accelerate.utils import patch_environment
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -66,24 +66,6 @@ class MultiGPUTester(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
with patch_environment(omp_num_threads=1, cuda_visible_devices="0,1"):
|
||||
execute_subprocess_async(cmd, env=os.environ.copy())
|
||||
|
||||
# Need to see why this test raises forking issues when ran as a suite
|
||||
@skip
|
||||
@require_multi_gpu
|
||||
def test_notebook_launcher(self):
|
||||
"""
|
||||
This test checks that the `notebook_launcher` will be able to intialize
|
||||
a `PartialState` without issue
|
||||
"""
|
||||
cmd = [
|
||||
"python",
|
||||
"-m",
|
||||
"accelerate.test_utils.scripts.test_notebook",
|
||||
"--num_processes",
|
||||
str(torch.cuda.device_count()),
|
||||
]
|
||||
with patch_environment(omp_num_threads=1):
|
||||
execute_subprocess_async(cmd, env=os.environ.copy())
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
accelerator = Accelerator()
|
||||
|
||||
@ -444,7 +444,7 @@ class MixedInt8EmptyModelTest(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
model_8bit_from_saved = load_and_quantize_model(
|
||||
model_8bit_from_saved,
|
||||
bnb_quantization_config,
|
||||
weights_location=tmpdirname + "/pytorch_model.bin",
|
||||
weights_location=tmpdirname,
|
||||
device_map=device_map,
|
||||
no_split_module_classes=["BloomBlock"],
|
||||
offload_folder=tmpdirname + "/tmp",
|
||||
|
||||
@ -24,11 +24,12 @@ from contextlib import contextmanager
|
||||
|
||||
import pytest
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from parameterized import parameterized_class
|
||||
from torch import nn
|
||||
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader, TensorDataset
|
||||
|
||||
from accelerate import Accelerator
|
||||
from accelerate.test_utils import execute_subprocess_async, require_cuda
|
||||
from accelerate.test_utils import device_count, execute_subprocess_async, require_non_cpu
|
||||
from accelerate.utils import ProjectConfiguration, set_seed
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -80,6 +81,14 @@ class DummyModel(nn.Module):
|
||||
return x * self.a + self.b
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def parameterized_custom_name_func(func, param_num, param):
|
||||
# customize the test name generator function as we want both params to appear in the sub-test
|
||||
# name, as by default it shows only the first param
|
||||
param_based_name = "use_safetensors" if param["use_safetensors"] is True else "use_pytorch"
|
||||
return f"{func.__name__}_{param_based_name}"
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@parameterized_class(("use_safetensors",), [[True], [False]], class_name_func=parameterized_custom_name_func)
|
||||
class CheckpointTest(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
def test_with_save_limit(self):
|
||||
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmpdir:
|
||||
@ -94,10 +103,10 @@ class CheckpointTest(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
model, optimizer, train_dataloader, valid_dataloader
|
||||
)
|
||||
# Save initial
|
||||
accelerator.save_state()
|
||||
accelerator.save_state(safe_serialization=self.use_safetensors)
|
||||
|
||||
# Save second state
|
||||
accelerator.save_state()
|
||||
accelerator.save_state(safe_serialization=self.use_safetensors)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(len(os.listdir(accelerator.project_dir)), 1)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_can_resume_training_with_folder(self):
|
||||
@ -113,7 +122,7 @@ class CheckpointTest(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
)
|
||||
# Save initial
|
||||
initial = os.path.join(tmpdir, "initial")
|
||||
accelerator.save_state(initial)
|
||||
accelerator.save_state(initial, safe_serialization=self.use_safetensors)
|
||||
(a, b) = model.a.item(), model.b.item()
|
||||
opt_state = optimizer.state_dict()
|
||||
ground_truth_rands = train(3, model, train_dataloader, optimizer, accelerator)
|
||||
@ -139,7 +148,7 @@ class CheckpointTest(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
test_rands = train(2, model, train_dataloader, optimizer, accelerator)
|
||||
# Save everything
|
||||
checkpoint = os.path.join(tmpdir, "checkpoint")
|
||||
accelerator.save_state(checkpoint)
|
||||
accelerator.save_state(checkpoint, safe_serialization=self.use_safetensors)
|
||||
|
||||
# Load everything back in and make sure all states work
|
||||
accelerator.load_state(checkpoint)
|
||||
@ -165,7 +174,7 @@ class CheckpointTest(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
model, optimizer, train_dataloader, valid_dataloader
|
||||
)
|
||||
# Save initial
|
||||
accelerator.save_state()
|
||||
accelerator.save_state(safe_serialization=self.use_safetensors)
|
||||
(a, b) = model.a.item(), model.b.item()
|
||||
opt_state = optimizer.state_dict()
|
||||
ground_truth_rands = train(3, model, train_dataloader, optimizer, accelerator)
|
||||
@ -191,7 +200,7 @@ class CheckpointTest(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
|
||||
test_rands = train(2, model, train_dataloader, optimizer, accelerator)
|
||||
# Save everything
|
||||
accelerator.save_state()
|
||||
accelerator.save_state(safe_serialization=self.use_safetensors)
|
||||
|
||||
# Load everything back in and make sure all states work
|
||||
accelerator.load_state(os.path.join(tmpdir, "checkpoints", "checkpoint_1"))
|
||||
@ -230,7 +239,7 @@ class CheckpointTest(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
model, optimizer, train_dataloader, valid_dataloader
|
||||
)
|
||||
# Save initial
|
||||
accelerator.save_state()
|
||||
accelerator.save_state(safe_serialization=self.use_safetensors)
|
||||
(a, b) = model.a.item(), model.b.item()
|
||||
opt_state = optimizer.state_dict()
|
||||
ground_truth_rands = train(3, model, train_dataloader, optimizer, accelerator)
|
||||
@ -256,7 +265,7 @@ class CheckpointTest(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
|
||||
test_rands = train(2, model, train_dataloader, optimizer, accelerator)
|
||||
# Save everything
|
||||
accelerator.save_state()
|
||||
accelerator.save_state(safe_serialization=self.use_safetensors)
|
||||
|
||||
# Load everything back in and make sure all states work
|
||||
accelerator.load_state(os.path.join(tmpdir, "checkpoints", "checkpoint_1"))
|
||||
@ -296,7 +305,7 @@ class CheckpointTest(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
model, optimizer, train_dataloader, valid_dataloader, scheduler
|
||||
)
|
||||
# Save initial
|
||||
accelerator.save_state()
|
||||
accelerator.save_state(safe_serialization=self.use_safetensors)
|
||||
scheduler_state = scheduler.state_dict()
|
||||
train(3, model, train_dataloader, optimizer, accelerator, scheduler)
|
||||
self.assertNotEqual(scheduler_state, scheduler.state_dict())
|
||||
@ -319,11 +328,11 @@ class CheckpointTest(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
model, optimizer, train_dataloader, valid_dataloader, scheduler
|
||||
)
|
||||
# Save initial
|
||||
accelerator.save_state()
|
||||
accelerator.save_state(safe_serialization=self.use_safetensors)
|
||||
train(2, model, train_dataloader, optimizer, accelerator, scheduler)
|
||||
(a2, b2) = model.a.item(), model.b.item()
|
||||
# Save a first time
|
||||
accelerator.save_state()
|
||||
accelerator.save_state(safe_serialization=self.use_safetensors)
|
||||
train(1, model, train_dataloader, optimizer, accelerator, scheduler)
|
||||
(a3, b3) = model.a.item(), model.b.item()
|
||||
|
||||
@ -344,18 +353,22 @@ class CheckpointTest(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
model = accelerator.prepare(model)
|
||||
# Save 3 states:
|
||||
for _ in range(11):
|
||||
accelerator.save_state()
|
||||
accelerator.save_state(safe_serialization=self.use_safetensors)
|
||||
self.assertTrue(not os.path.exists(os.path.join(tmpdir, "checkpoints", "checkpoint_0")))
|
||||
self.assertTrue(os.path.exists(os.path.join(tmpdir, "checkpoints", "checkpoint_9")))
|
||||
self.assertTrue(os.path.exists(os.path.join(tmpdir, "checkpoints", "checkpoint_10")))
|
||||
|
||||
@require_cuda
|
||||
@require_non_cpu
|
||||
def test_map_location(self):
|
||||
cmd = ["torchrun", f"--nproc_per_node={torch.cuda.device_count()}", inspect.getfile(self.__class__)]
|
||||
execute_subprocess_async(cmd, env=os.environ.copy())
|
||||
cmd = ["torchrun", f"--nproc_per_node={device_count}", inspect.getfile(self.__class__)]
|
||||
env = os.environ.copy()
|
||||
env["USE_SAFETENSORS"] = str(self.use_safetensors)
|
||||
env["OMP_NUM_THREADS"] = "1"
|
||||
execute_subprocess_async(cmd, env=env)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
use_safetensors = os.environ.get("USE_SAFETENSORS", "False") == "True"
|
||||
savedir = "/tmp/accelerate/state_checkpointing"
|
||||
model = DummyModel()
|
||||
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(params=model.parameters(), lr=1e-3)
|
||||
@ -380,7 +393,7 @@ if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
assert param_device.type == accelerator.device.type
|
||||
model = model.cpu()
|
||||
accelerator.wait_for_everyone()
|
||||
accelerator.save_state()
|
||||
accelerator.save_state(safe_serialization=use_safetensors)
|
||||
accelerator.wait_for_everyone()
|
||||
|
||||
# Check CPU state
|
||||
|
||||
@ -25,6 +25,7 @@ from pathlib import Path
|
||||
from typing import Optional
|
||||
from unittest import mock
|
||||
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
|
||||
# We use TF to parse the logs
|
||||
@ -32,13 +33,21 @@ from accelerate import Accelerator
|
||||
from accelerate.test_utils.testing import (
|
||||
MockingTestCase,
|
||||
TempDirTestCase,
|
||||
require_clearml,
|
||||
require_comet_ml,
|
||||
require_dvclive,
|
||||
require_pandas,
|
||||
require_tensorboard,
|
||||
require_wandb,
|
||||
skip,
|
||||
)
|
||||
from accelerate.tracking import CometMLTracker, GeneralTracker
|
||||
from accelerate.utils import ProjectConfiguration, is_comet_ml_available, is_tensorboard_available
|
||||
from accelerate.utils import (
|
||||
ProjectConfiguration,
|
||||
is_comet_ml_available,
|
||||
is_dvclive_available,
|
||||
is_tensorboard_available,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if is_comet_ml_available():
|
||||
@ -49,6 +58,11 @@ if is_tensorboard_available():
|
||||
|
||||
import tensorboard.compat.proto.event_pb2 as event_pb2
|
||||
|
||||
if is_dvclive_available():
|
||||
from dvclive.plots.metric import Metric
|
||||
from dvclive.serialize import load_yaml
|
||||
from dvclive.utils import parse_metrics
|
||||
|
||||
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -250,6 +264,147 @@ class CometMLTest(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
self.assertEqual(self.get_value_from_key(list_of_json, "my_text"), "some_value")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@require_clearml
|
||||
class ClearMLTest(TempDirTestCase, MockingTestCase):
|
||||
def setUp(self):
|
||||
super().setUp()
|
||||
# ClearML offline session location is stored in CLEARML_CACHE_DIR
|
||||
self.add_mocks(mock.patch.dict(os.environ, {"CLEARML_CACHE_DIR": self.tmpdir}))
|
||||
|
||||
@staticmethod
|
||||
def _get_offline_dir(accelerator):
|
||||
from clearml.config import get_offline_dir
|
||||
|
||||
return get_offline_dir(task_id=accelerator.get_tracker("clearml", unwrap=True).id)
|
||||
|
||||
@staticmethod
|
||||
def _get_metrics(offline_dir):
|
||||
metrics = []
|
||||
with open(os.path.join(offline_dir, "metrics.jsonl")) as f:
|
||||
json_lines = f.readlines()
|
||||
for json_line in json_lines:
|
||||
metrics.extend(json.loads(json_line))
|
||||
return metrics
|
||||
|
||||
def test_init_trackers(self):
|
||||
from clearml import Task
|
||||
from clearml.utilities.config import text_to_config_dict
|
||||
|
||||
Task.set_offline(True)
|
||||
accelerator = Accelerator(log_with="clearml")
|
||||
config = {"num_iterations": 12, "learning_rate": 1e-2, "some_boolean": False, "some_string": "some_value"}
|
||||
accelerator.init_trackers("test_project_with_config", config)
|
||||
|
||||
offline_dir = ClearMLTest._get_offline_dir(accelerator)
|
||||
accelerator.end_training()
|
||||
|
||||
with open(os.path.join(offline_dir, "task.json")) as f:
|
||||
offline_session = json.load(f)
|
||||
clearml_offline_config = text_to_config_dict(offline_session["configuration"]["General"]["value"])
|
||||
self.assertDictEqual(config, clearml_offline_config)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_log(self):
|
||||
from clearml import Task
|
||||
|
||||
Task.set_offline(True)
|
||||
accelerator = Accelerator(log_with="clearml")
|
||||
accelerator.init_trackers("test_project_with_log")
|
||||
values_with_iteration = {"should_be_under_train": 1, "eval_value": 2, "test_value": 3.1, "train_value": 4.1}
|
||||
accelerator.log(values_with_iteration, step=1)
|
||||
single_values = {"single_value_1": 1.1, "single_value_2": 2.2}
|
||||
accelerator.log(single_values)
|
||||
|
||||
offline_dir = ClearMLTest._get_offline_dir(accelerator)
|
||||
accelerator.end_training()
|
||||
|
||||
metrics = ClearMLTest._get_metrics(offline_dir)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(len(values_with_iteration) + len(single_values), len(metrics))
|
||||
for metric in metrics:
|
||||
if metric["metric"] == "Summary":
|
||||
self.assertIn(metric["variant"], single_values)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(metric["value"], single_values[metric["variant"]])
|
||||
elif metric["metric"] == "should_be_under_train":
|
||||
self.assertEqual(metric["variant"], "train")
|
||||
self.assertEqual(metric["iter"], 1)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(metric["value"], values_with_iteration["should_be_under_train"])
|
||||
else:
|
||||
values_with_iteration_key = metric["variant"] + "_" + metric["metric"]
|
||||
self.assertIn(values_with_iteration_key, values_with_iteration)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(metric["iter"], 1)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(metric["value"], values_with_iteration[values_with_iteration_key])
|
||||
|
||||
def test_log_images(self):
|
||||
from clearml import Task
|
||||
|
||||
Task.set_offline(True)
|
||||
accelerator = Accelerator(log_with="clearml")
|
||||
accelerator.init_trackers("test_project_with_log_images")
|
||||
|
||||
base_image = np.eye(256, 256, dtype=np.uint8) * 255
|
||||
base_image_3d = np.concatenate((np.atleast_3d(base_image), np.zeros((256, 256, 2), dtype=np.uint8)), axis=2)
|
||||
images = {
|
||||
"base_image": base_image,
|
||||
"base_image_3d": base_image_3d,
|
||||
}
|
||||
accelerator.get_tracker("clearml").log_images(images, step=1)
|
||||
|
||||
offline_dir = ClearMLTest._get_offline_dir(accelerator)
|
||||
accelerator.end_training()
|
||||
|
||||
images_saved = Path(os.path.join(offline_dir, "data")).rglob("*.jpeg")
|
||||
self.assertEqual(len(list(images_saved)), len(images))
|
||||
|
||||
def test_log_table(self):
|
||||
from clearml import Task
|
||||
|
||||
Task.set_offline(True)
|
||||
accelerator = Accelerator(log_with="clearml")
|
||||
accelerator.init_trackers("test_project_with_log_table")
|
||||
|
||||
accelerator.get_tracker("clearml").log_table(
|
||||
"from lists with columns", columns=["A", "B", "C"], data=[[1, 3, 5], [2, 4, 6]]
|
||||
)
|
||||
accelerator.get_tracker("clearml").log_table("from lists", data=[["A2", "B2", "C2"], [7, 9, 11], [8, 10, 12]])
|
||||
offline_dir = ClearMLTest._get_offline_dir(accelerator)
|
||||
accelerator.end_training()
|
||||
|
||||
metrics = ClearMLTest._get_metrics(offline_dir)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(len(metrics), 2)
|
||||
for metric in metrics:
|
||||
self.assertIn(metric["metric"], ["from lists", "from lists with columns"])
|
||||
plot = json.loads(metric["plot_str"])
|
||||
if metric["metric"] == "from lists with columns":
|
||||
print(plot["data"][0])
|
||||
self.assertCountEqual(plot["data"][0]["header"]["values"], ["A", "B", "C"])
|
||||
self.assertCountEqual(plot["data"][0]["cells"]["values"], [[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]])
|
||||
else:
|
||||
self.assertCountEqual(plot["data"][0]["header"]["values"], ["A2", "B2", "C2"])
|
||||
self.assertCountEqual(plot["data"][0]["cells"]["values"], [[7, 8], [9, 10], [11, 12]])
|
||||
|
||||
@require_pandas
|
||||
def test_log_table_pandas(self):
|
||||
import pandas as pd
|
||||
from clearml import Task
|
||||
|
||||
Task.set_offline(True)
|
||||
accelerator = Accelerator(log_with="clearml")
|
||||
accelerator.init_trackers("test_project_with_log_table_pandas")
|
||||
|
||||
accelerator.get_tracker("clearml").log_table(
|
||||
"from df", dataframe=pd.DataFrame({"A": [1, 2], "B": [3, 4], "C": [5, 6]}), step=1
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
offline_dir = ClearMLTest._get_offline_dir(accelerator)
|
||||
accelerator.end_training()
|
||||
|
||||
metrics = ClearMLTest._get_metrics(offline_dir)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(len(metrics), 1)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(metrics[0]["metric"], "from df")
|
||||
plot = json.loads(metrics[0]["plot_str"])
|
||||
self.assertCountEqual(plot["data"][0]["header"]["values"], [["A"], ["B"], ["C"]])
|
||||
self.assertCountEqual(plot["data"][0]["cells"]["values"], [[1, 2], [3, 4], [5, 6]])
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class MyCustomTracker(GeneralTracker):
|
||||
"Basic tracker that writes to a csv for testing"
|
||||
_col_names = [
|
||||
@ -329,3 +484,48 @@ class CustomTrackerTestCase(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
"some_string": "",
|
||||
}
|
||||
self.assertDictEqual(data, truth)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@require_dvclive
|
||||
@mock.patch("dvclive.live.get_dvc_repo", return_value=None)
|
||||
class DVCLiveTrackingTest(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
def test_init_trackers(self, mock_repo):
|
||||
project_name = "test_project_with_config"
|
||||
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as dirpath:
|
||||
accelerator = Accelerator(log_with="dvclive")
|
||||
config = {
|
||||
"num_iterations": 12,
|
||||
"learning_rate": 1e-2,
|
||||
"some_boolean": False,
|
||||
"some_string": "some_value",
|
||||
}
|
||||
init_kwargs = {"dvclive": {"dir": dirpath, "save_dvc_exp": False, "dvcyaml": None}}
|
||||
accelerator.init_trackers(project_name, config, init_kwargs)
|
||||
accelerator.end_training()
|
||||
live = accelerator.trackers[0].live
|
||||
params = load_yaml(live.params_file)
|
||||
assert params == config
|
||||
|
||||
def test_log(self, mock_repo):
|
||||
project_name = "test_project_with_log"
|
||||
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as dirpath:
|
||||
accelerator = Accelerator(log_with="dvclive", project_dir=dirpath)
|
||||
init_kwargs = {"dvclive": {"dir": dirpath, "save_dvc_exp": False, "dvcyaml": None}}
|
||||
accelerator.init_trackers(project_name, init_kwargs=init_kwargs)
|
||||
values = {"total_loss": 0.1, "iteration": 1, "my_text": "some_value"}
|
||||
# Log step 0
|
||||
accelerator.log(values)
|
||||
# Log step 1
|
||||
accelerator.log(values)
|
||||
# Log step 3 (skip step 2)
|
||||
accelerator.log(values, step=3)
|
||||
accelerator.end_training()
|
||||
live = accelerator.trackers[0].live
|
||||
logs, latest = parse_metrics(live)
|
||||
assert latest.pop("step") == 3
|
||||
assert latest == values
|
||||
scalars = os.path.join(live.plots_dir, Metric.subfolder)
|
||||
for val in values.keys():
|
||||
val_path = os.path.join(scalars, f"{val}.tsv")
|
||||
steps = [int(row["step"]) for row in logs[val_path]]
|
||||
assert steps == [0, 1, 3]
|
||||
|
||||
@ -14,20 +14,29 @@
|
||||
|
||||
import os
|
||||
import pickle
|
||||
import tempfile
|
||||
import unittest
|
||||
import warnings
|
||||
from collections import UserDict, namedtuple
|
||||
from unittest.mock import Mock, patch
|
||||
|
||||
import torch
|
||||
from torch import nn
|
||||
|
||||
from accelerate.state import PartialState
|
||||
from accelerate.test_utils.testing import require_cuda, require_torch_min_version
|
||||
from accelerate.test_utils.training import RegressionModel
|
||||
from accelerate.utils import (
|
||||
CannotPadNestedTensorWarning,
|
||||
check_os_kernel,
|
||||
convert_outputs_to_fp32,
|
||||
extract_model_from_parallel,
|
||||
find_device,
|
||||
listify,
|
||||
pad_across_processes,
|
||||
patch_environment,
|
||||
recursively_apply,
|
||||
save,
|
||||
send_to_device,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -36,6 +45,10 @@ ExampleNamedTuple = namedtuple("ExampleNamedTuple", "a b c")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class UtilsTester(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
def setUp(self):
|
||||
# logging requires initialized state
|
||||
PartialState()
|
||||
|
||||
def test_send_to_device(self):
|
||||
tensor = torch.randn(5, 2)
|
||||
device = torch.device("cuda") if torch.cuda.is_available() else torch.device("cpu")
|
||||
@ -173,3 +186,54 @@ class UtilsTester(unittest.TestCase):
|
||||
self.assertEqual(find_device([1, "a", torch.tensor([1, 2, 3])]), torch.device("cpu"))
|
||||
self.assertEqual(find_device({"a": 1, "b": torch.tensor([1, 2, 3])}), torch.device("cpu"))
|
||||
self.assertIsNone(find_device([1, "a"]))
|
||||
|
||||
def test_check_os_kernel_no_warning_when_release_gt_min(self):
|
||||
# min version is 5.5
|
||||
with patch("platform.uname", return_value=Mock(release="5.15.0-35-generic", system="Linux")):
|
||||
with warnings.catch_warnings(record=True) as w:
|
||||
check_os_kernel()
|
||||
self.assertEqual(len(w), 0)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_check_os_kernel_no_warning_when_not_linux(self):
|
||||
# system must be Linux
|
||||
with patch("platform.uname", return_value=Mock(release="5.4.0-35-generic", system="Darwin")):
|
||||
with warnings.catch_warnings(record=True) as w:
|
||||
check_os_kernel()
|
||||
self.assertEqual(len(w), 0)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_check_os_kernel_warning_when_release_lt_min(self):
|
||||
# min version is 5.5
|
||||
with patch("platform.uname", return_value=Mock(release="5.4.0-35-generic", system="Linux")):
|
||||
with self.assertLogs() as ctx:
|
||||
check_os_kernel()
|
||||
self.assertEqual(len(ctx.records), 1)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(ctx.records[0].levelname, "WARNING")
|
||||
self.assertIn("5.4.0", ctx.records[0].msg)
|
||||
self.assertIn("5.5.0", ctx.records[0].msg)
|
||||
|
||||
def test_save_safetensor_shared_memory(self):
|
||||
class Model(nn.Module):
|
||||
def __init__(self):
|
||||
super().__init__()
|
||||
self.a = nn.Linear(100, 100)
|
||||
self.b = self.a
|
||||
|
||||
def forward(self, x):
|
||||
return self.b(self.a(x))
|
||||
|
||||
model = Model()
|
||||
with tempfile.TemporaryDirectory() as tmp_dir:
|
||||
save_path = os.path.join(tmp_dir, "model.safetensors")
|
||||
with self.assertLogs(level="WARNING") as log:
|
||||
save(model.state_dict(), save_path, safe_serialization=True)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(len(log.records), 1)
|
||||
self.assertIn("Removed shared tensor", log.output[0])
|
||||
|
||||
@require_torch_min_version(version="1.12")
|
||||
def test_pad_across_processes(self):
|
||||
from torch.nested import nested_tensor
|
||||
|
||||
nt = nested_tensor([[1, 2, 3], [1], [1, 2]])
|
||||
with self.assertWarns(CannotPadNestedTensorWarning):
|
||||
nt2 = pad_across_processes(nt)
|
||||
self.assertIs(nt, nt2)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -17,6 +17,7 @@ https://github.com/allenai/allennlp.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
import os
|
||||
from datetime import datetime as dt
|
||||
from datetime import timezone
|
||||
|
||||
from github import Github
|
||||
|
||||
@ -36,7 +37,7 @@ def main():
|
||||
for issue in open_issues:
|
||||
comments = sorted([comment for comment in issue.get_comments()], key=lambda i: i.created_at, reverse=True)
|
||||
last_comment = comments[0] if len(comments) > 0 else None
|
||||
current_time = dt.utcnow()
|
||||
current_time = dt.now(timezone.utc)
|
||||
days_since_updated = (current_time - issue.updated_at).days
|
||||
days_since_creation = (current_time - issue.created_at).days
|
||||
if (
|
||||
|
||||
Reference in New Issue
Block a user